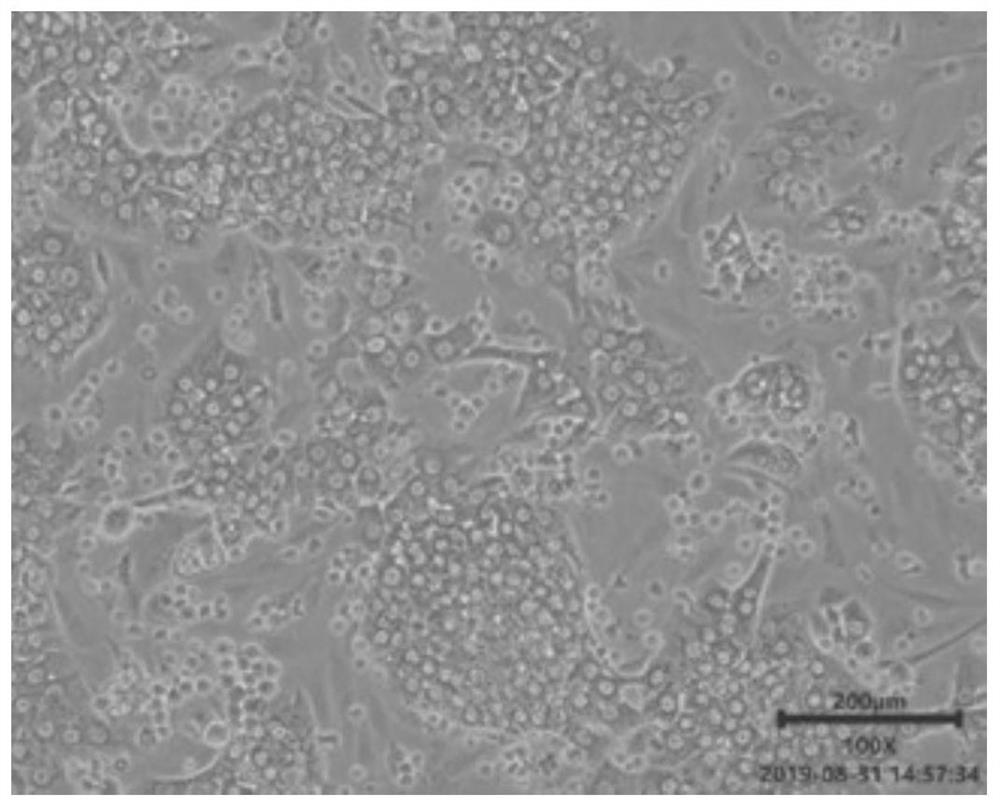
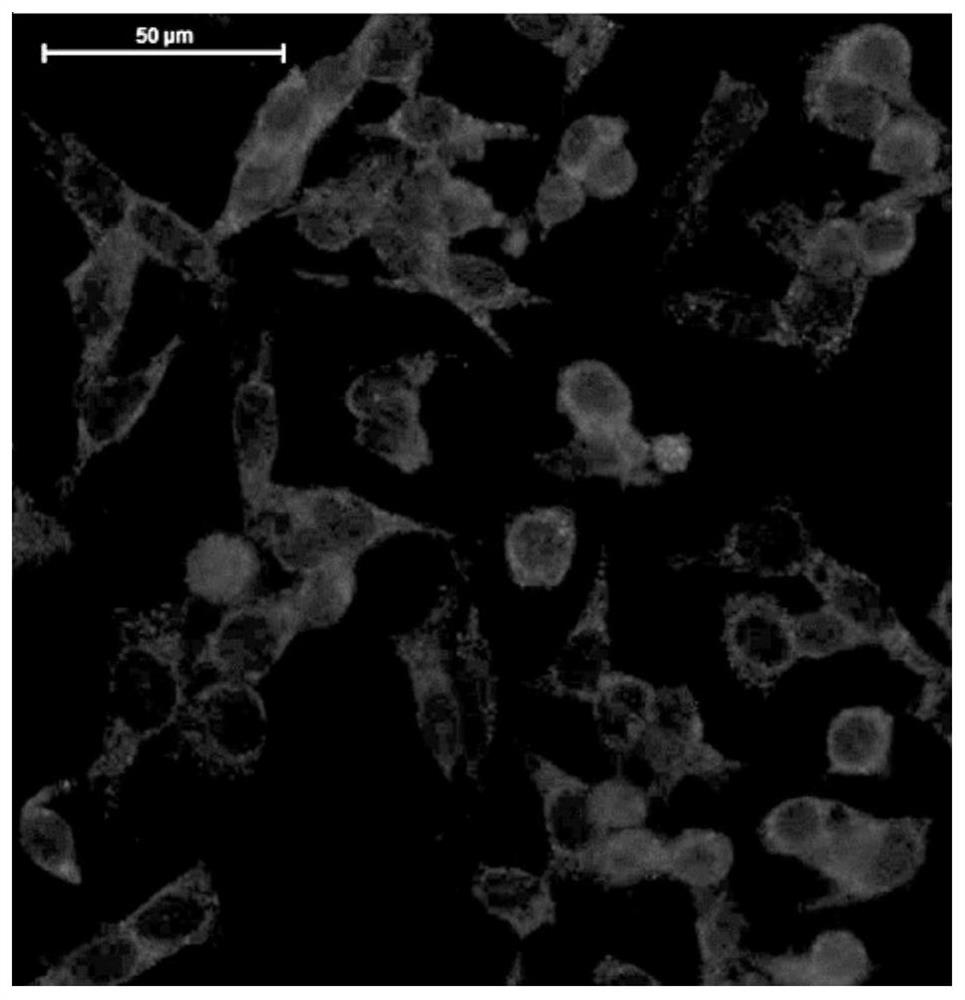
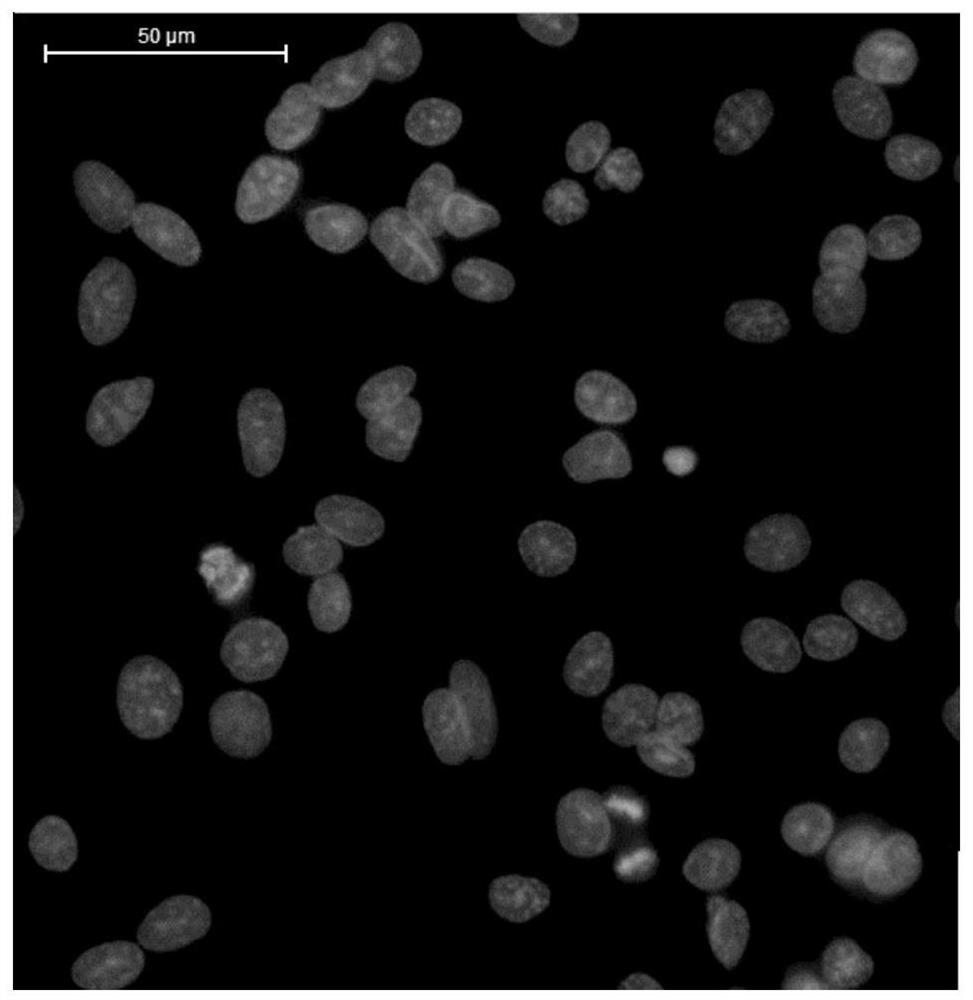
Separating and extracting method for primary liver parenchyma cells and application of primary liver parenchyma cells
A technology of hepatic parenchymal cells and extraction method, which is applied in the field of separation and extraction of primary hepatic parenchymal cells, can solve the problems that liver tissue is difficult to meet the requirements of the two-step perfusion method, reduce the cell yield, etc., and achieve the benefit of adherence and later growth , Good repeatability, and the effect of reducing operation time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] This example provides a method for separating and extracting sheep liver parenchymal cells. details as follows:
[0049] 1) Select a piece of fresh sheep liver tissue with a weight of about 7.5g, and wash the surface of the sheep liver tissue block with 4°C pre-cooled PBS; use a 10mL syringe to puncture the cut surface of the sheep liver tissue with a complete upper surface and a section of blood vessels, The needle was perpendicular to the cut surface, to avoid the needle passing through the tissue block, and the syringe was slowly advanced, and the perfusate Ia (25 mL) preheated at 38°C was injected into the center of the liver tissue, a large amount of blood flowed out, and the liver tissue block in the central area was darkened. The red color gradually turns brownish yellow, and the surrounding tissue blocks are still red in color. Then, at the same angle, inject preheated 38°C perfusate Ib (75mL) into the surrounding tissue area, blood can be seen flowing out, and...
Embodiment 2
[0064] This example provides a method for separating and extracting sheep liver parenchymal cells. The specific method is the same as in Example 1, except that the weight of the liver tissue block is about 15 g, the dosage of perfusate I is 200 mL (50 mL of perfusate Ia, 150 mL of perfusate Ib), and the perfusion time is 15 minutes; the perfusion solution II contains 5.5 mmol / L CaCl 2 and 1.2mg / mL type IV collagenase HBSS solution, the dosage is 300mL, and the perfusion time is 20min.
[0065] Experimental results: the cell survival rate reached 95.2%, and the number of living cells was 2.55×10 8 , the cell purity was 96.3%.
Embodiment 3
[0067] This example provides a method for separating and extracting sheep liver parenchymal cells. The specific method is the same as in Example 1, except that the weight of the liver tissue block is about 2.5 g, the amount of perfusate I is 40 mL (7 mL of perfusate Ia, and 33 mL of perfusate Ib), and the perfusion time is 8 minutes; the amount of perfusate II is 50 mL, and the perfusion The time is 6 minutes.
[0068] Experimental results: the cell survival rate reached 94.9%, and the number of living cells was 4.3×10 7 , the cell purity was 95.6%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com