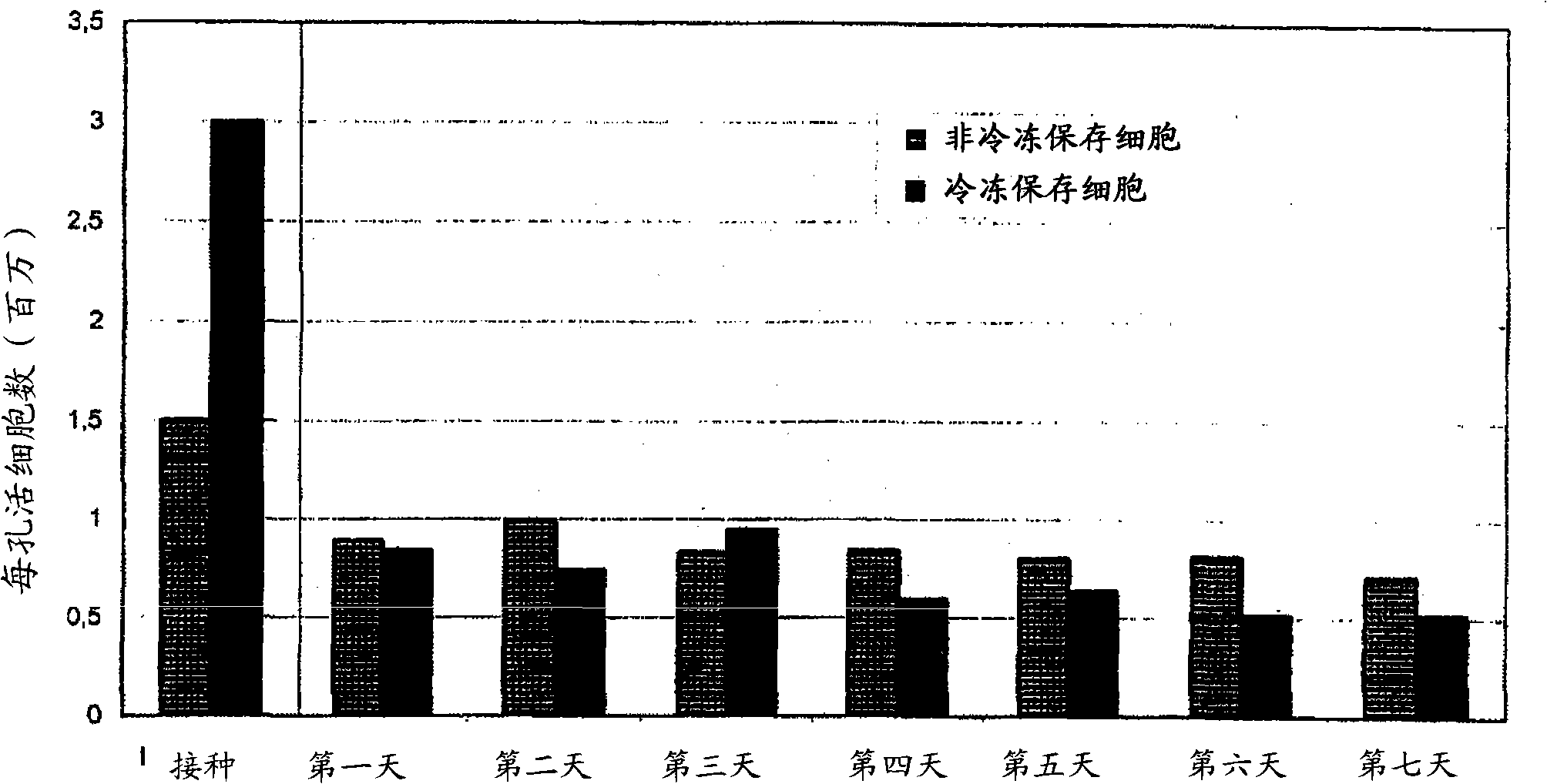
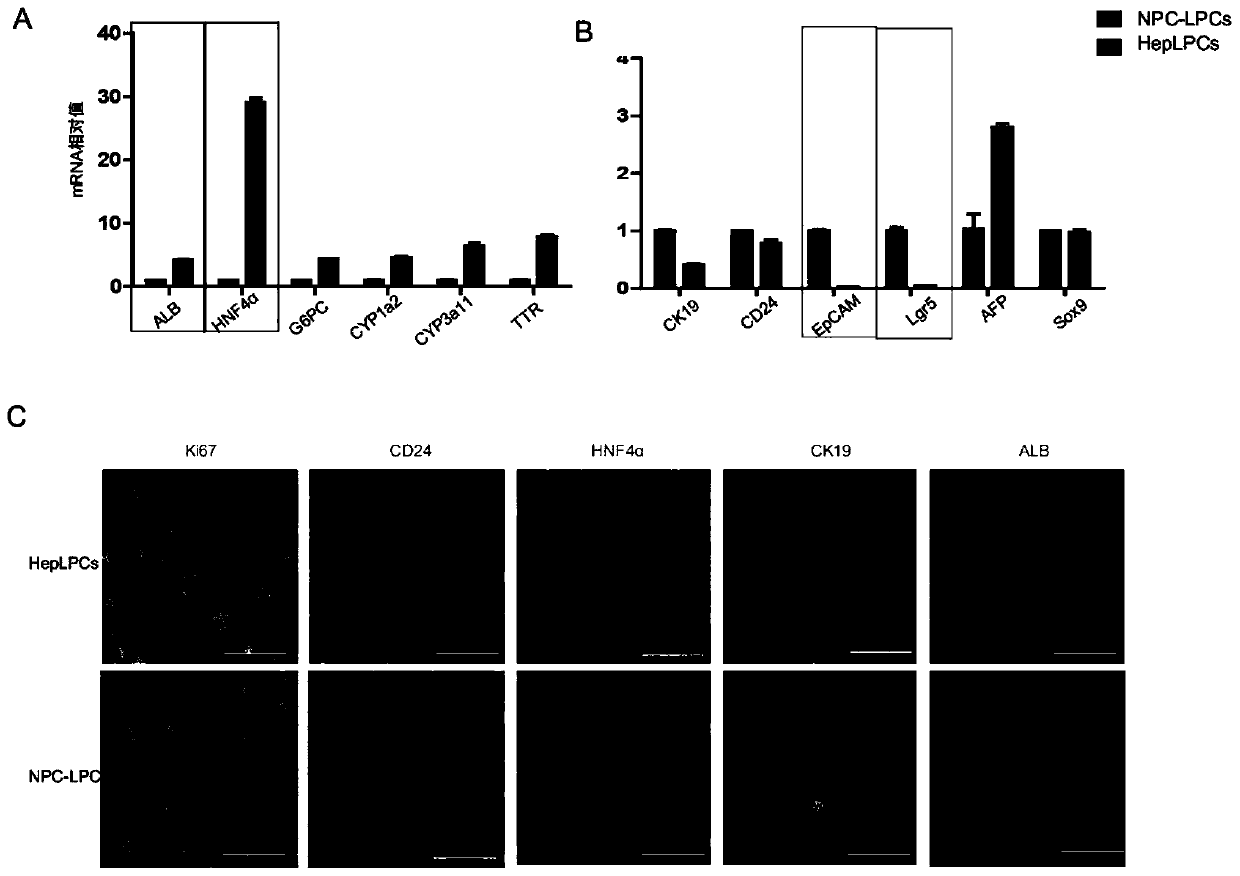
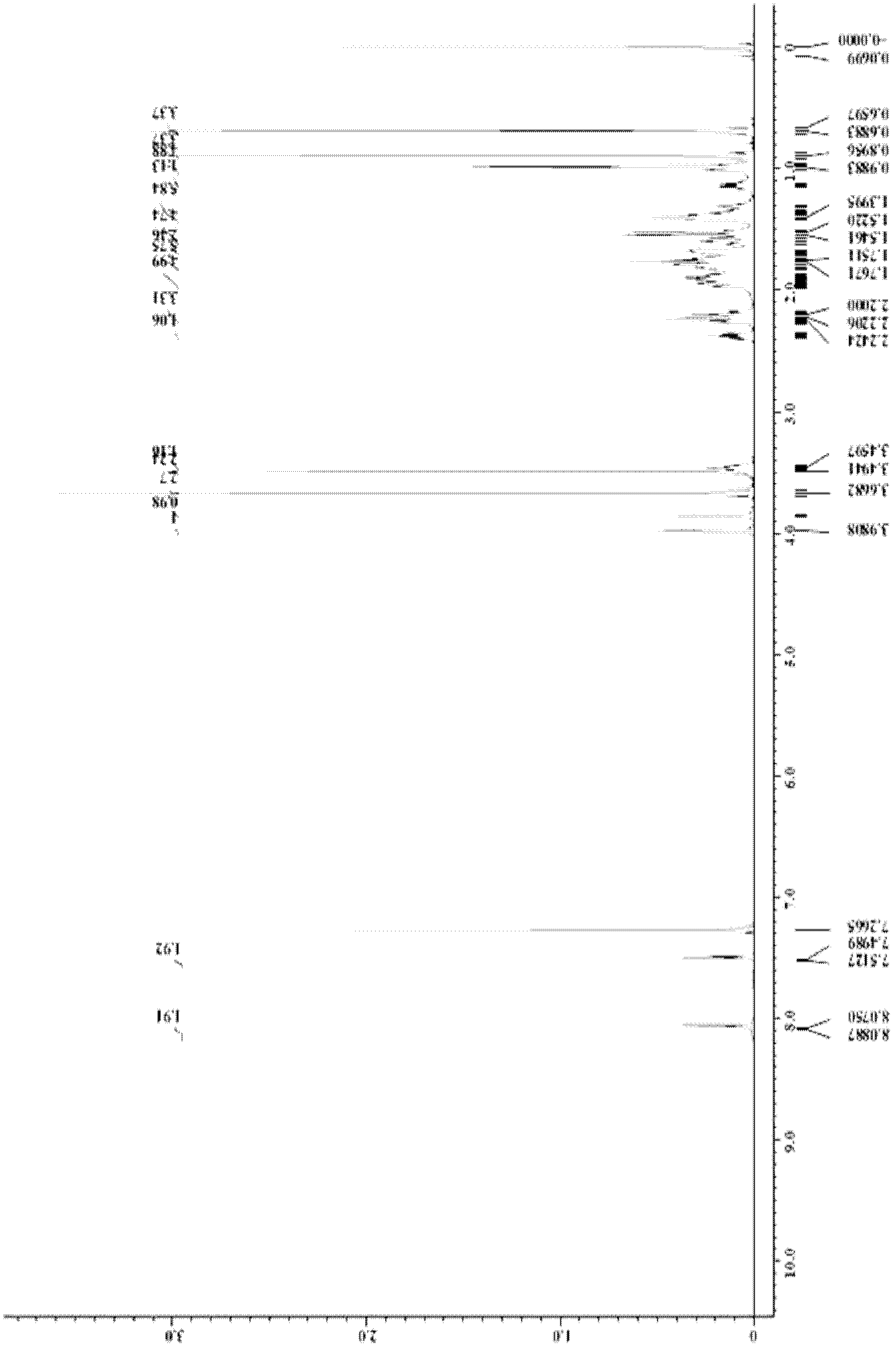
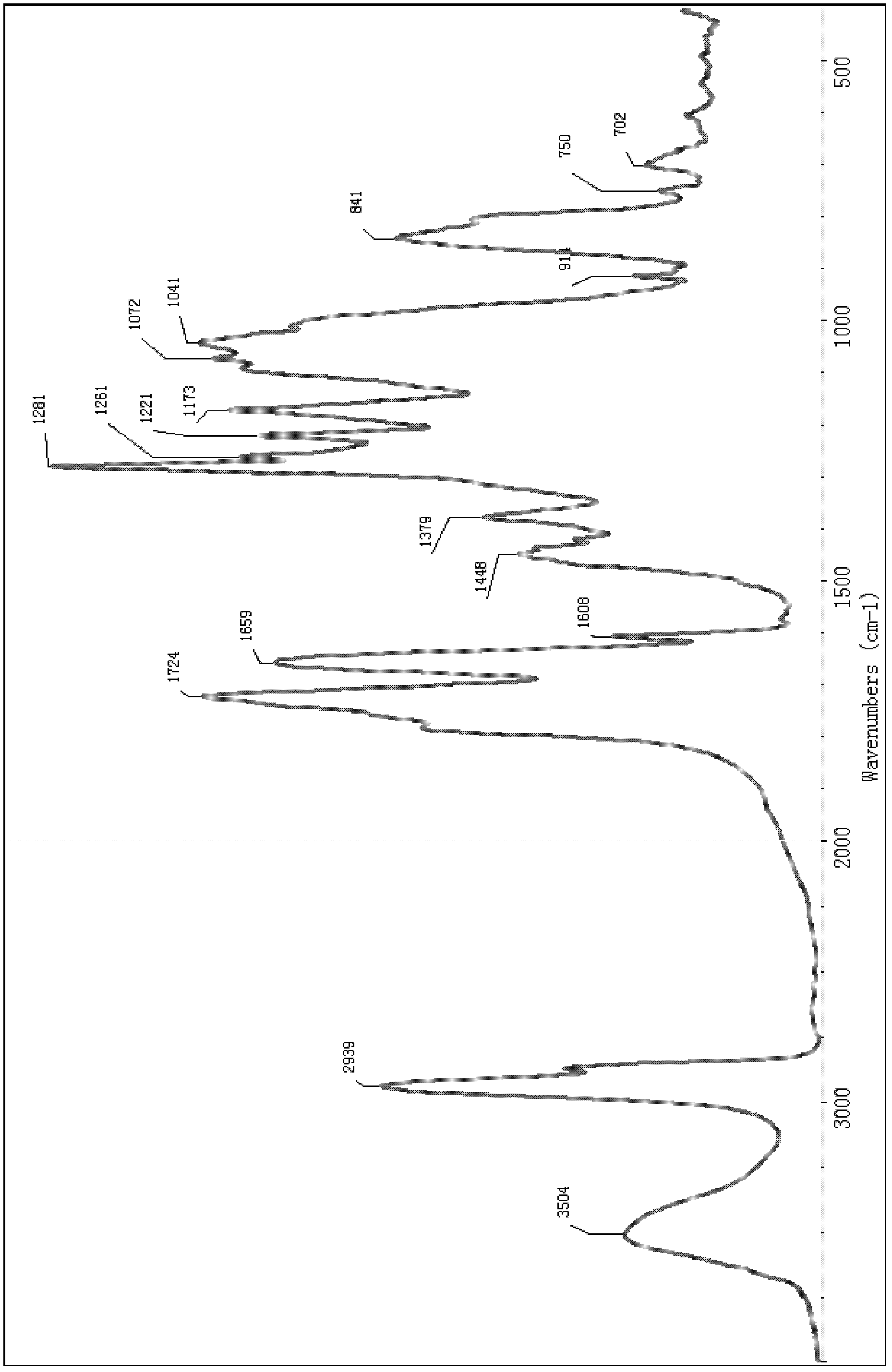
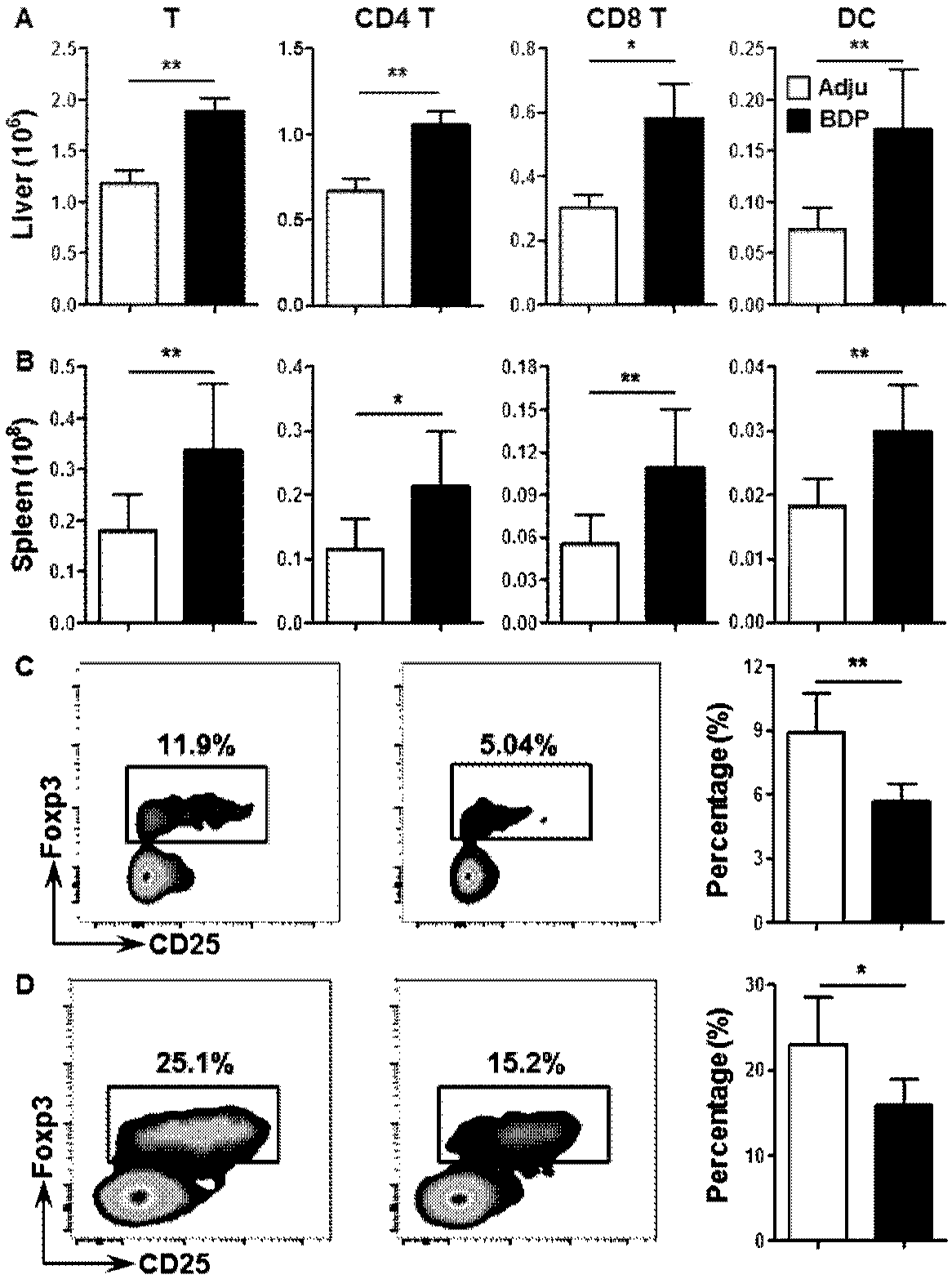
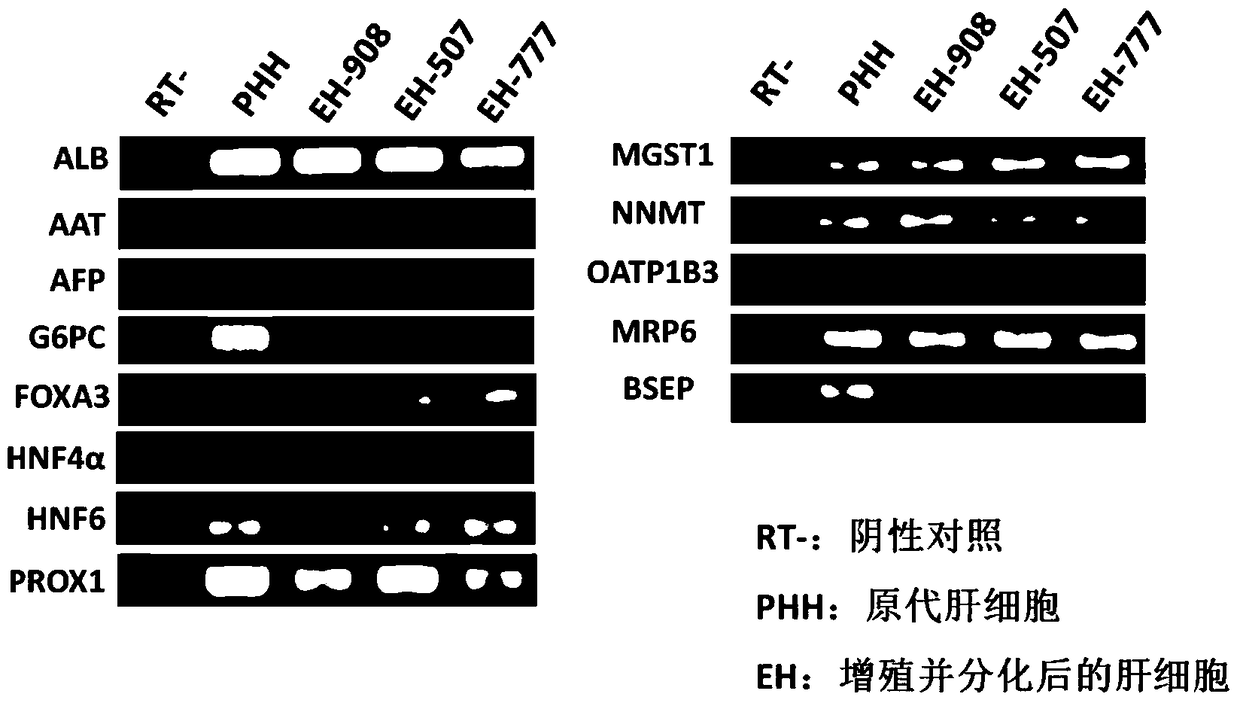
Patents
Literature
59 results about "Hepatic parenchymal cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Quick Answer. Hepatic parenchymal disease is damage to the functional cells of the liver, according to HealthTap. Liver diseases can be divided into those affecting the biliary ducts and those affecting the functional cells of the organ, known as the parenchyma.
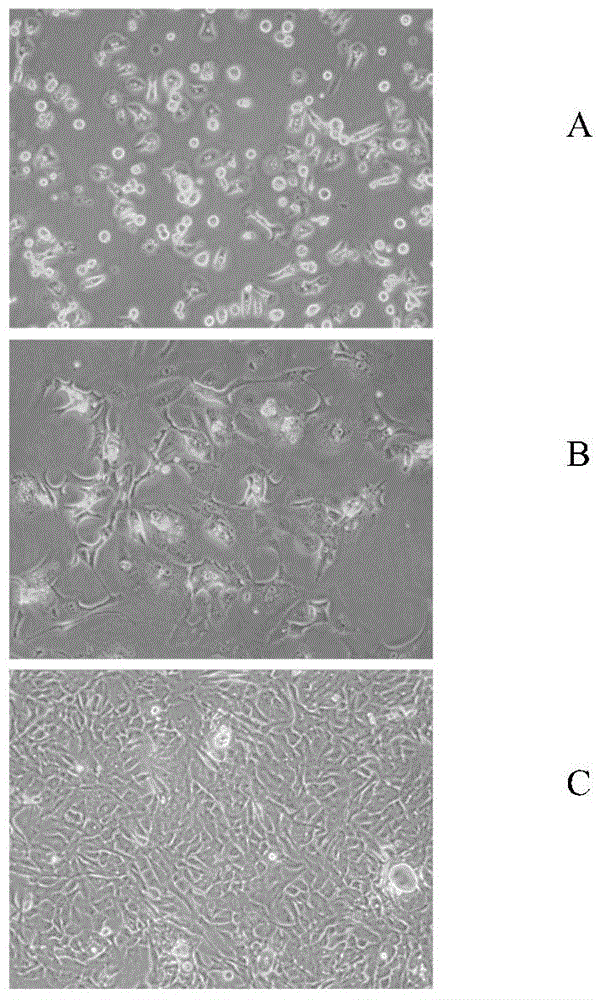
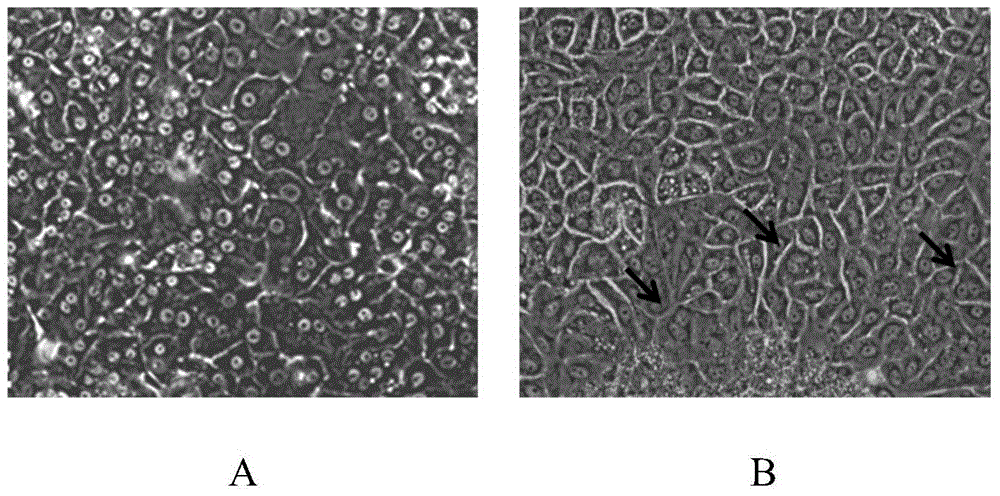
Method for long-time in-vitro culturing and proliferating hepatic cells and application of method
ActiveCN105296418AEasy to storeEasy to transportMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsOrganismCells transplantation
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology and provides a method for long-time in-vitro culturing and proliferating hepatic cells. The method includes that mature hepatic parenchymal cells are induced to be hepatic cells with infinite proliferation capability in vitro. The hepatic cells obtained by the method can be used for toxicological and pharmacological evaluation of compounds and drug, study and diagnosis as well as treatment of hepatitis virus, hepatic cell transplantation therapy and preparation of bioartificial liver.
Owner:SHANGHAI CELLIVER BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +1
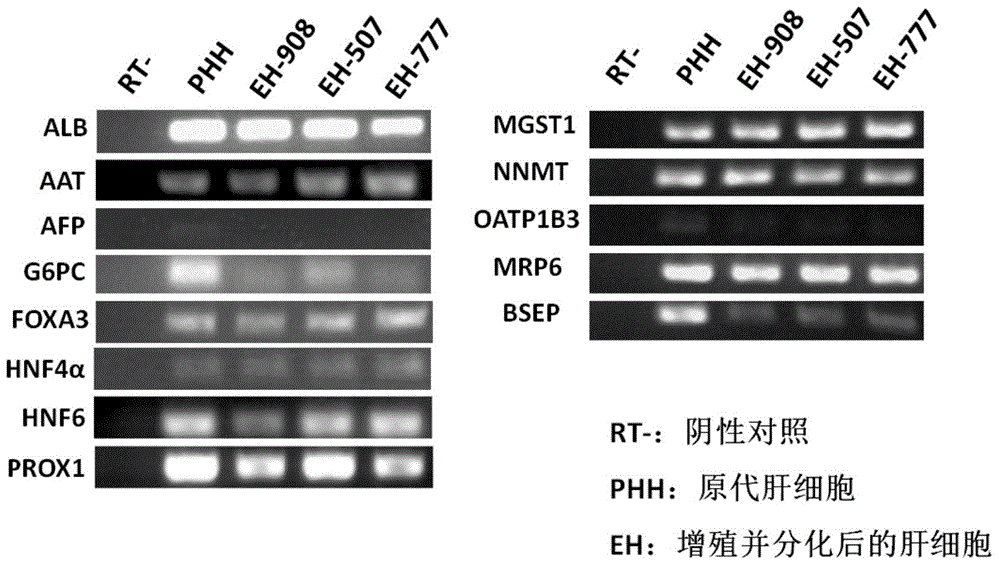
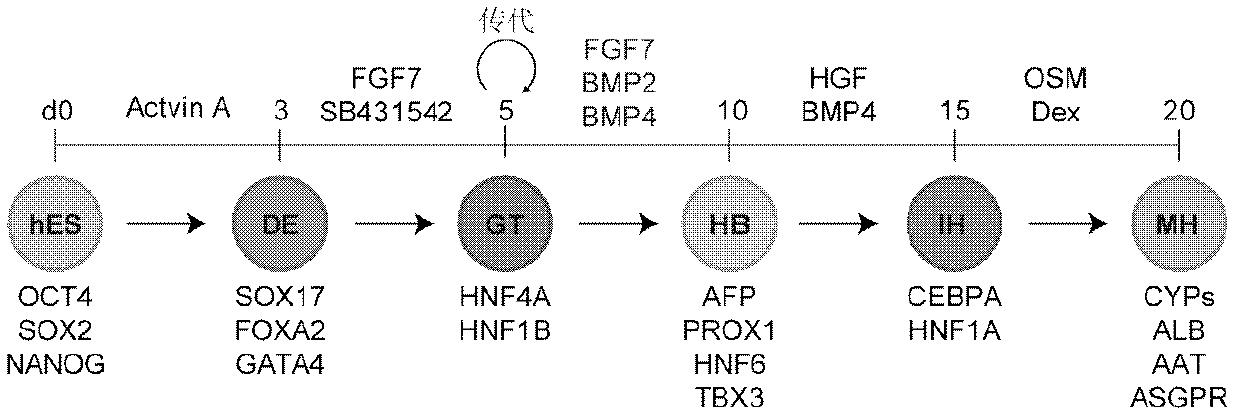
Parenchymal hepatic cell and preparation, identification and application methods thereof
ActiveCN103374546ACytochrome P450 enzyme activity is goodFunctionalMicrobiological testing/measurementVertebrate cellsGerm layerBiology
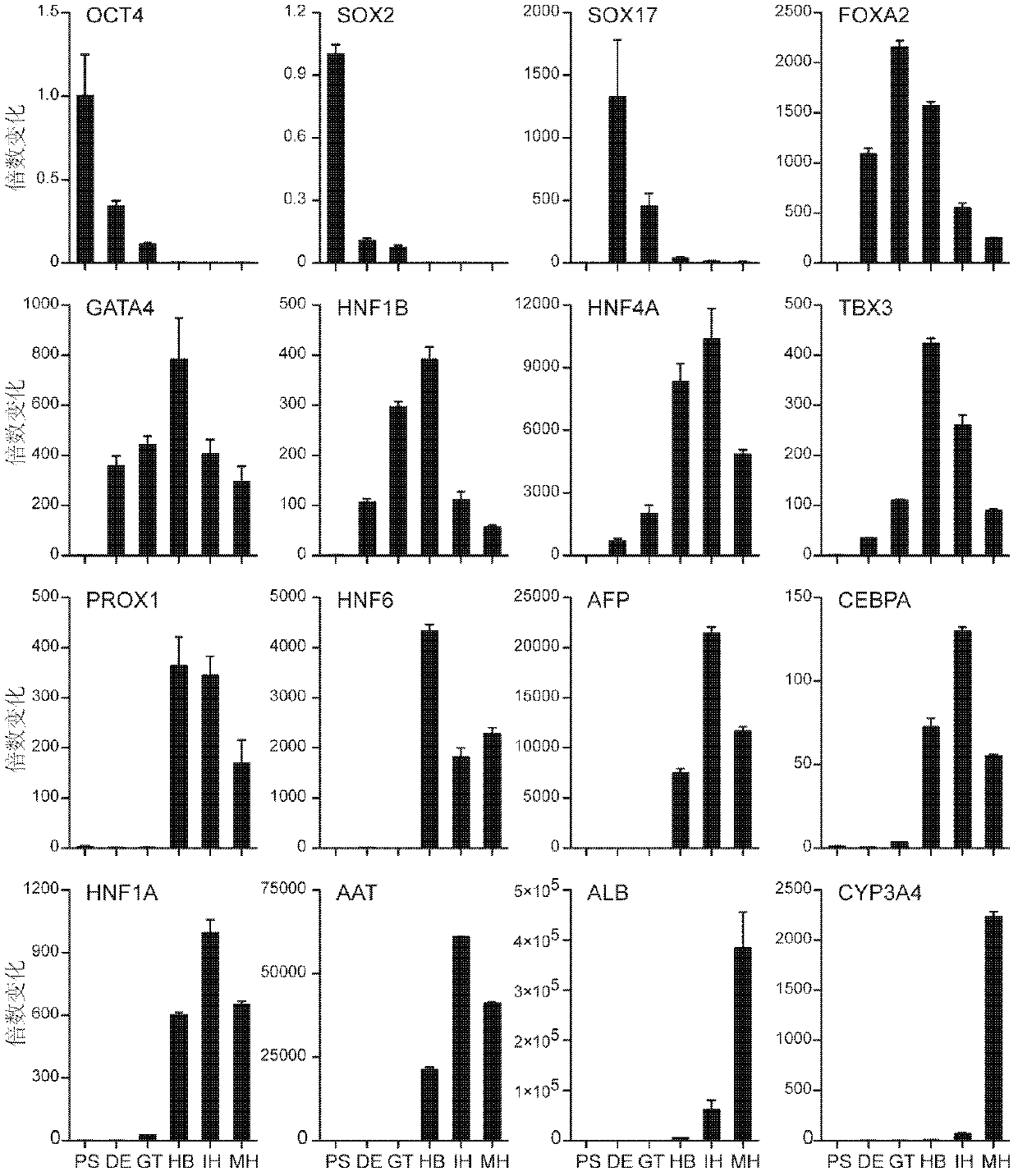
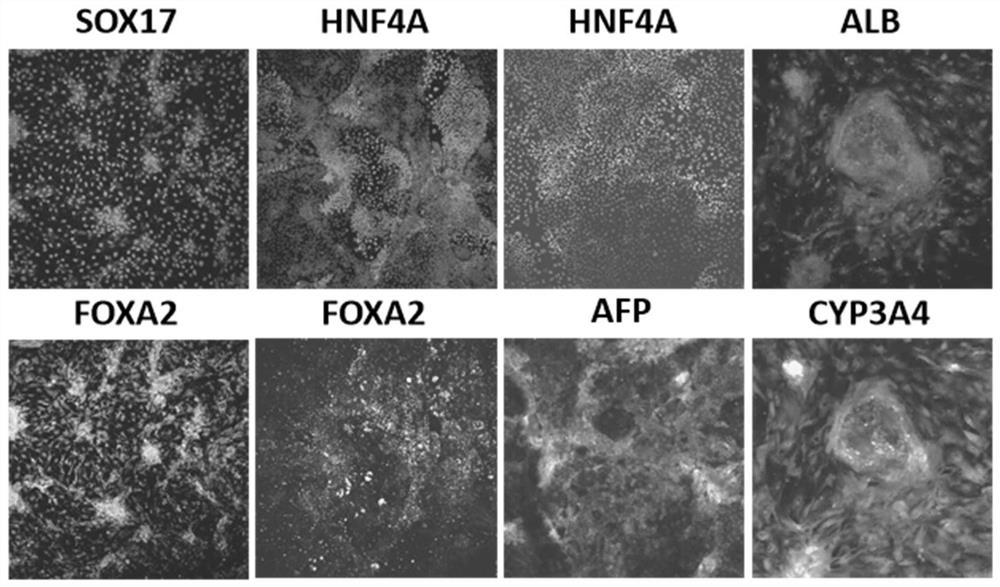
The invention discloses a parenchymal hepatic cell and preparation, identification and application methods thereof. The invention provides the method for preparing the parenchymal hepatic cell. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) culturing a pluripotent stem cell to obtain an endoderm cell; (2) culturing the endoderm cell obtained in the step (1) to obtain an original intestinal canal cell; (3) culturing the original intestinal canal cell obtained in the step (2) to obtain an adult hepatic cell; and (4) culturing the adult hepatic cell obtained in the step (3) to obtain a mature parenchymal hepatic cell, wherein the step (3) is characterized in that the cell obtained in the step (2) is subjected to passage and then transferred to a hepatic cell induction medium I containing fibroblast growth factors (FGF) and bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) for culturing to obtain the adult hepatic cell. The invention also relates to the parenchymal hepatic cell prepared by the method. The parenchymal hepatic cell prepared by the method has higher metabolic activity, high preparation efficiency and a wide application prospect than before.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Artificial liver tissue and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106581761AAccurate Pathological ResearchAccurate Drug Toxicity Test ScreeningHepatocytesArtificial cell constructsArtificial liverCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention provides an artificial liver tissue and a preparation method thereof. The artificial liver tissue comprises a lower chip, a first microporous membrane, a middle chip, a second microporous membrane and an upper chip from the top to the bottom in sequence in a laminated manner. Three layers of cavities of a lower cavity, a middle cavity and an upper cavity are formed in the lower chip, middle chip and upper chip respectively. Three cavities are all grouted with culture solution containing growth factor, extracellular matrix containing hepatic parenchymal cells and suspension liquid containing endothelial cells. Adjacent cavities are separated by the microporous membrane. The microporous membrane can separate the matrix flow outside of the cell, and cause no influence to the cell migration. The culture solution and is fed through an inlet and an outlet of the upper cavity and lower cavity. Under the guidance of the growth factor, endothelial cells pass through the extracellular matrix of the middle cavity to form a lumen, and form the artificial liver tissue containing capillaries. The artificial liver tissue can simulate the human body liver tissue in a good way, and simulate the intrahepatic capillary functions of mass transfer, selective permeability, toxic reaction and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Scylla paramamosain antibacterial peptide Scyreprocin and application thereof
ActiveCN111205359AImprove antibacterial propertiesBroad spectrum antibacterialAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsScylla paramamosainCytotoxicity
The invention discloses a scylla paramamosain antibacterial peptide Scyreprocin and an application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the scylla paramamosain antibacterial peptide Scyreprocin comprises a sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO 01. The scylla paramamosain antibacterial peptide Scyreprocin is obtained through expression and purification with a genetic engineering technique. The antibacterial peptide disclosed by the invention is broad in antimicrobial spectrum, good in antibacterial effects and high in sterilizing rate, shows enormous application value, and has favorable application inthe respect of preparation of antibacterial agents. The antibacterial peptide disclosed by the invention does not have cytotoxicity on hepatic parenchymal cells AML12 of mice, human normal liver cellsL02 and the like, and can be safely used for medication or can be used as a feed composition.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
All-small molecular culture medium for culturing liver organoid and application of all-small molecular culture medium
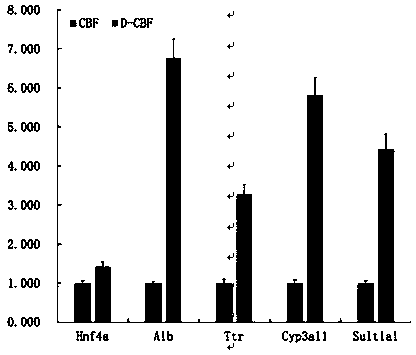
The invention discloses an all-small molecular culture medium for culturing a liver organoid and an application of the all-small molecular culture medium. The culture medium comprises a basic culturemedium and a combination of small molecules, and the maintained combination of the small molecules is CBF, wherein C is CHIR-99021, B is Blebbistatin, C is Forskolin. The small molecules CHIR, Blebbistatin and Forskolin are added into the basic culture medium, so that the addition of a growth factor is replaced, a hpatic bile duct organoid can be cultured in vitro for a long time, and differentiation can be further induced to form a parenchymal hepatic cell. The method is beneficial to the in-vitro mass amplification of the liver organoid and provides the basis for researches and therapy of liver related diseases.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Vesicle preparation
ActiveCN102292069AHeavy metal active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsSerum igeExocytic vesicle
It is found that a biologically active substance contained in an endoplasmic reticulum can be delivered to a hepatocyte efficiently and specifically by adsorbing or chemically binding vitamin E to the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum. This can be achieved by utilizing a serum component's property to deliver vitamin E to a hepatocyte.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD +1
Separation and culture method for dog hepatocytes
InactiveCN106978388AIncrease the degree of differentiationCell dissociation methodsCulture processMicrobiologyCell separation
The invention belongs to the field of separation and culture of cells and in particular relates to a separation and culture method for dog hepatocytes. The separation and culture method comprises the following steps: S1, taking liver from a living body; S2, perfusing; S3, separating the hepatocytes; S4, culturing the hepatocytes. The perfusion is realized by the following steps: firstly, perfusing perfusate A preheated at the temperature of 37DEG C into a flushed liver at the flow speed of 50ml / min for 15 to 20 minutes; secondly, continuously perfusing perfusate B preheated at the temperature of 37DEG C at the flow speed of 50ml / min for 3 to 5 minutes; thirdly, perfusing perfusate C preheated at the temperature of 37DEG C at the flow speed of 20ml / min for 4 to 6 minutes; finally, pouring a basal culture medium which contains three antibodies and is precooled at the temperature of 4DEG C on the surface of the liver, wherein the volumetric ratio of the three antibodies to the basal culture medium is 1 to 99. The hepatocytes obtained by separating through the method are nearly pure parenchymal hepatic cells; various functions of the hepatocytes are retained; the hepatocytes have the advantages of high quantity, morphological integrity, good adherence and high activity.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method of separating pork liver stem cell
InactiveCN1233821CHigh purityConducive to survivalArtificially induced pluripotent cellsNon-embryonic pluripotent stem cellsPork LiverLiver tissue
The invention relates to a separating pork liver stem cell method, comprising steps of : cutting off a majority of liver to promote liver regeneration, adding collagenase to digest liver tissue into single cell, centrifuging to remove fibroblast of liver, using prolease E specificly digesting liver parenchymall cell , keeping the liver nonparenchymall cell, Percoll purifying using density gradient centrifugation method. The inventive method can provide highly purified, large amount and viable pork liver stem cell, which provide large amount of cells for stem cell fundamental research and clinical uses.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
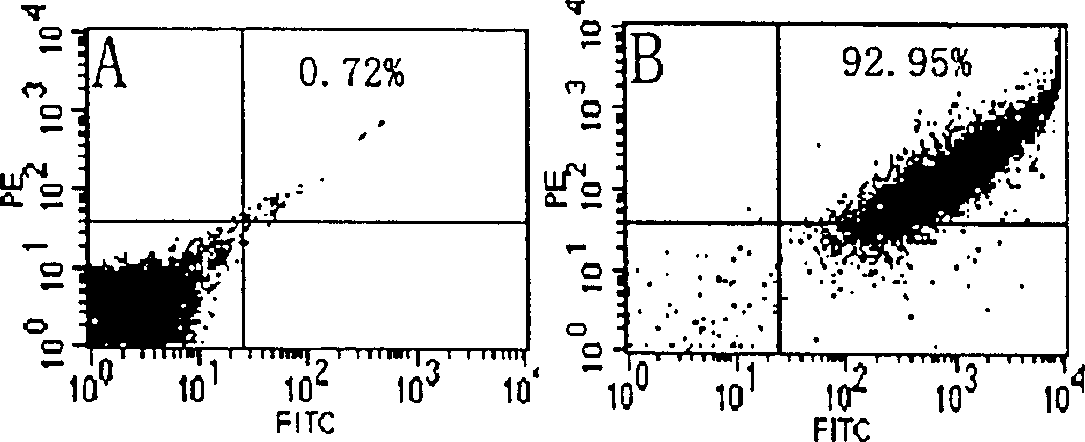
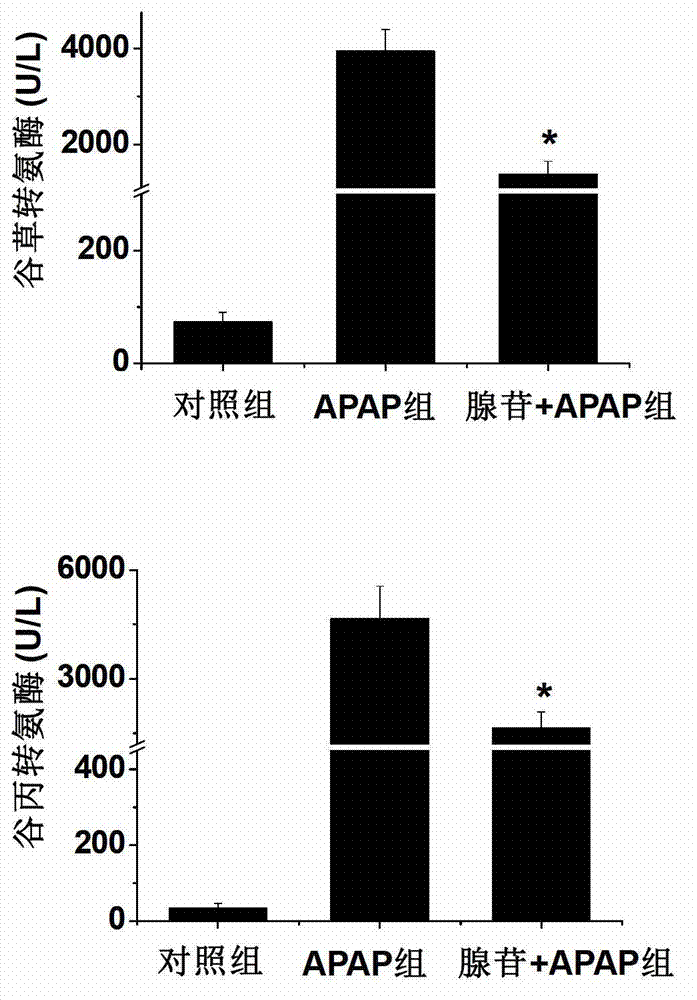
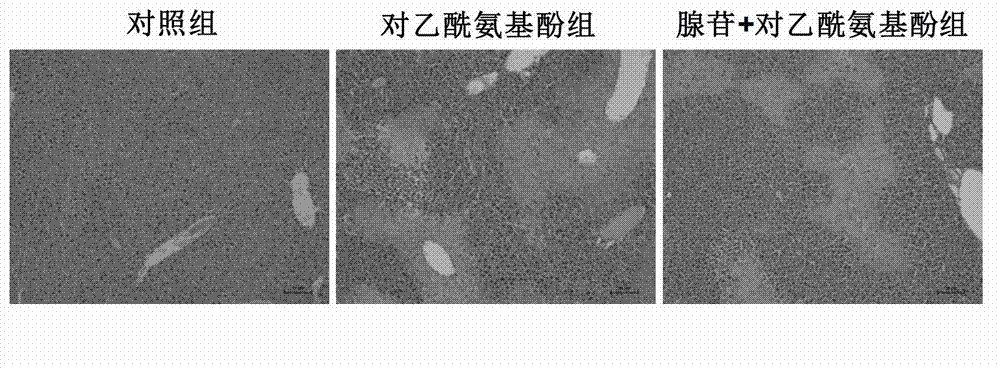
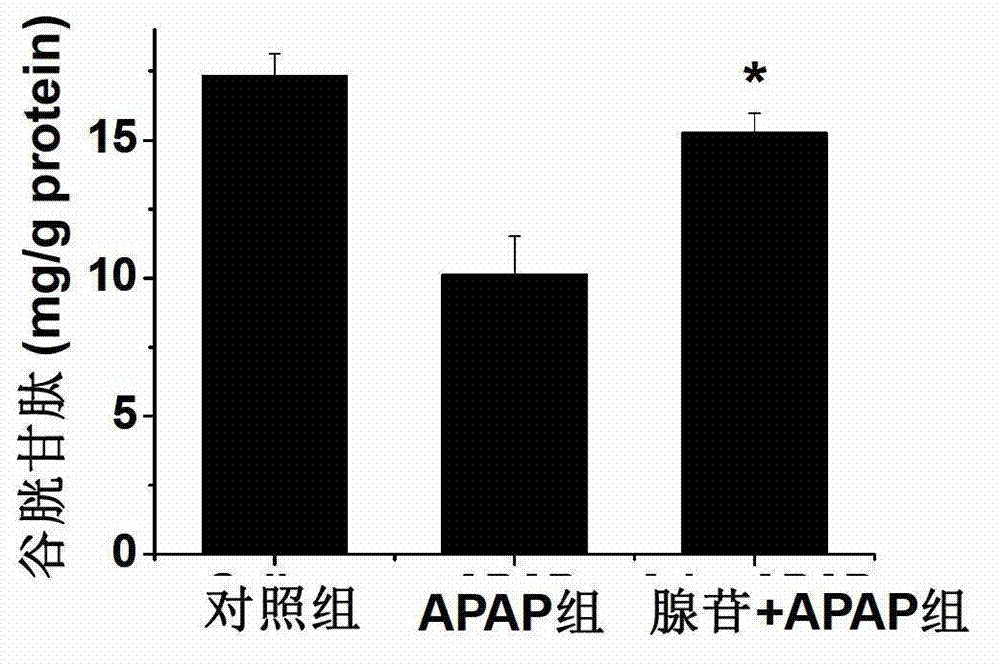
Application of adenosine and derivatives thereof in prevention and treatment of medicament-induced liver injury
InactiveCN103191145ANo side effectsQuickly Stops Liver DamageOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminaseAcute hepatic failure
The invention discloses application of adenosine and derivatives thereof in prevention and treatment of medicament-induced liver injury, relating to application of adenosine and derivatives thereof such as adenosine monophosphate, adenosine diphosphate and adenosine triphosphate in protection of acetaminophen-induced liver injury. A mouse model adopted in the application is an acetaminophen-induced mouse acute hepatic failure model, the dosage of the adenosine or derivatives thereof is 0.1 to 5mmol / kg, and the adenosine and derivatives thereof can reduce the activities of aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT) in the medicament-induced liver injury, reduce the substantial cell necrosis area and improve the glutathione level so as to prevent and treat the acetaminophen-induced liver injury caused by liver toxic medicaments. Animal experiments prove that the adenosine and derivatives thereof have a significant effect on preventing and treating the medicament-induced liver injury, so the adenosine and derivatives thereof can be used for the preventing and treating processes of the medicament-induced liver injury, and a new method and means are provided for clinically treating the medicament-induced liver injury.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Application of activin receptor-interacting protein 2 (ARIP2) gene to preparation of medicament
InactiveCN102343102AHas preventive effectPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention provides application of an activin receptor-interacting protein 2 (ARIP2) gene to preparation of a medicament, relating to the field of liver disease gene therapy medicaments. The application of the ARIP2 gene as a gene therapy medicament for treating liver diseases is characterized in that: a eukaryotic cell expression vector of a recombinant ARIP2 gene is transfected with liver cells, and ARIP2 proteins expressed by the ARIP2 gene in the liver cells can be used for maintaining liver cell survival and reducing inflammatory mediators and extracellular matrixes, so that the regeneration of liver parenchyma cells is facilitated, and liver inflammation and fibration are suppressed. The ARIP2 gene can be used for treating acute liver diseases and chronic liver diseases, including liver diseases such as hepatofibrosis, hepatocirrhosis and the like.
Owner:柳忠辉
Separating and extracting method for primary liver parenchyma cells and application of primary liver parenchyma cells
ActiveCN112251398APromote growthImprove survival rateCell dissociation methodsArtificial cell constructsCellular DebrisLiver parenchyma
The invention relates to the technical field of cell separation and particularly discloses a separating and extracting method for primary liver parenchyma cells and application of the primary liver parenchyma cells. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the steps: injecting perfusate I and perfusate II into a hepatic tissue mass to digest and separate the liver parenchyma cells so as toobtain a cell suspension, then, subjecting filter liquor, obtained after filtering the cell suspension, to normal-temperature centrifugation for 5 times sequentially, wherein centrifugation conditionssequentially are 1000-1580rpm / min*3-5min, 500-650rpm / min*3-5min, 200-300rpm / min*4min, 200-300rpm / min*4min and 200-300rpm / min*4min. According to the method, the operation is simple, consumed time is short, low-temperature centrifugation equipment is not required, red blood cells and cell debris can be efficiently removed, and obtained liver parenchyma cells are relatively high in survival rate andpurity.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Cryopreservation of hepatocytes
InactiveCN101312648AArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsCryopreservationHepatic parenchymal cell
The invention relates to methods for preparing hepatic cells for cryopreservation, to methods for the cryopreservation of isolated hepatic cells, and to methods for producing a culture of cryopreserved isolated hepatic cells.
Owner:PROMETHERA BIOSCIENCES SA
Method of separating pork liver stem cell
InactiveCN1594553AHigh purityConducive to survivalArtificially induced pluripotent cellsNon-embryonic pluripotent stem cellsLiver tissuePork Liver
The invention relates to a separating pork liver stem cell method, comprising steps of : cutting off a majority of liver to promote liver regeneration, adding collagenase to digest liver tissue into single cell, centrifuging to remove fibroblast of liver, using prolease E specificly digesting liver parenchymall cell , keeping the liver nonparenchymall cell, Percoll purifying using density gradient centrifugation method. The inventive method can provide highly purified, large amount and viable pork liver stem cell, which provide large amount of cells for stem cell fundamental research and clinical uses.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method for hepatic progenitor cells from different sources and application of hepatic progenitor cells
ActiveCN110904026AMaintain cell-derived propertiesStudy biological morphological propertiesCell dissociation methodsHepatocytesPrecursor cellSomatic cell
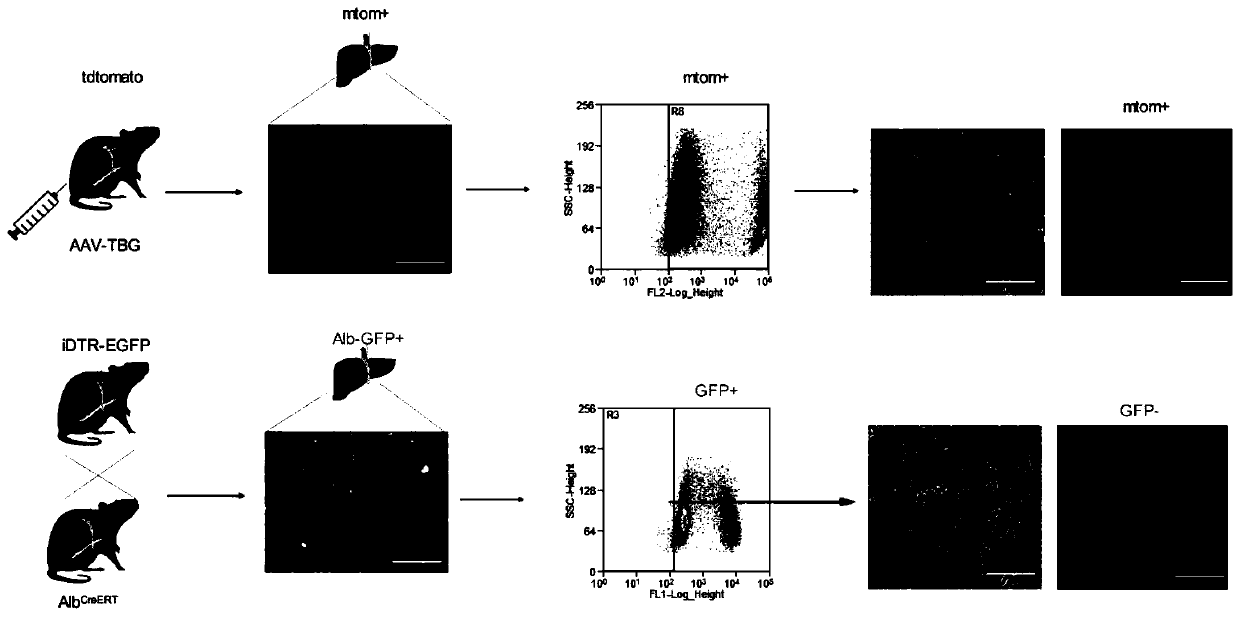
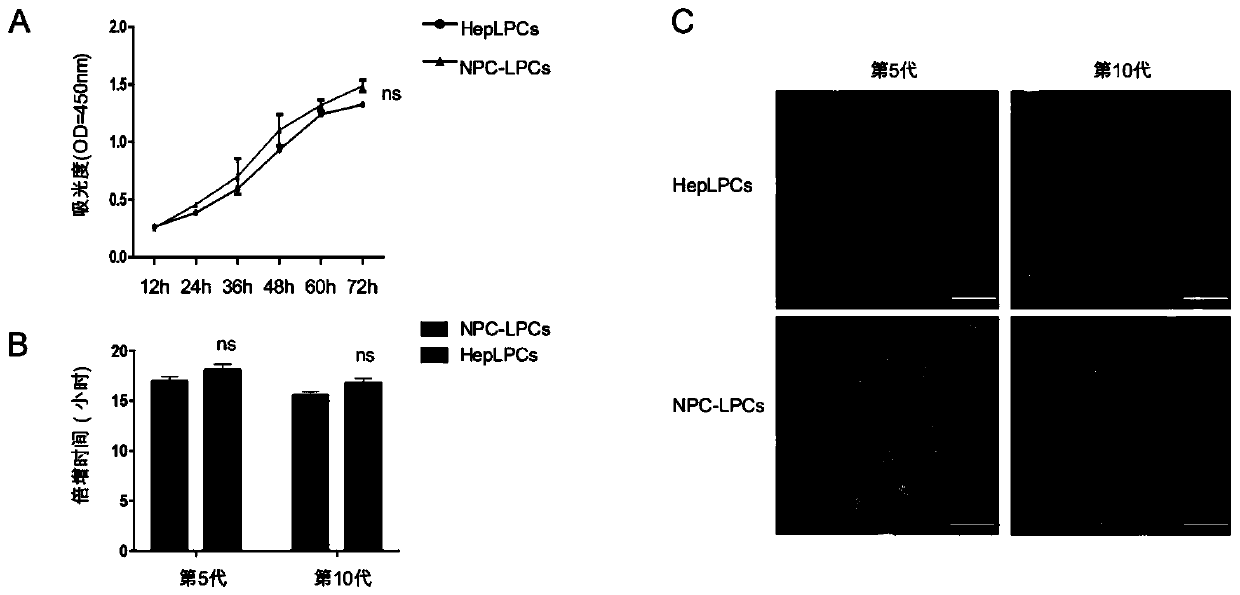
The invention relates to the technical field of cell models, in particular to a preparation method for hepatic progenitor cells from different sources. After induced culture is performed on hepatocytes and / or non-parenchymal cells with a hepatocyte transition and expansion medium, the induced-cultured hepatocytes and / or non-parenchymal cells transition into the hepatic progenitor cells which can expand and passage in vitro. According to the preparation method, by applying a lineage tracing method, the hepatocytes and the non-parenchymal cells in a mouse liver are isolated; by micromolecule assembly induced culture in vitro, the hepatocytes and the non-parenchymal cells successfully transition into the respective hepatic progenitor cells having an expansion and regeneration function; and meanwhile, proved by three-dimensional culture and organoid culture, the hepatocytes and the non-parenchymal cells both keep the characteristics of the cell sources thereof. The preparation method is conducive to further researching biological and morphologic characteristics of the hepatic progenitor cells from different sources, and further explores the application prospect of the hepatic progenitor cells as new transplanted cell sources.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
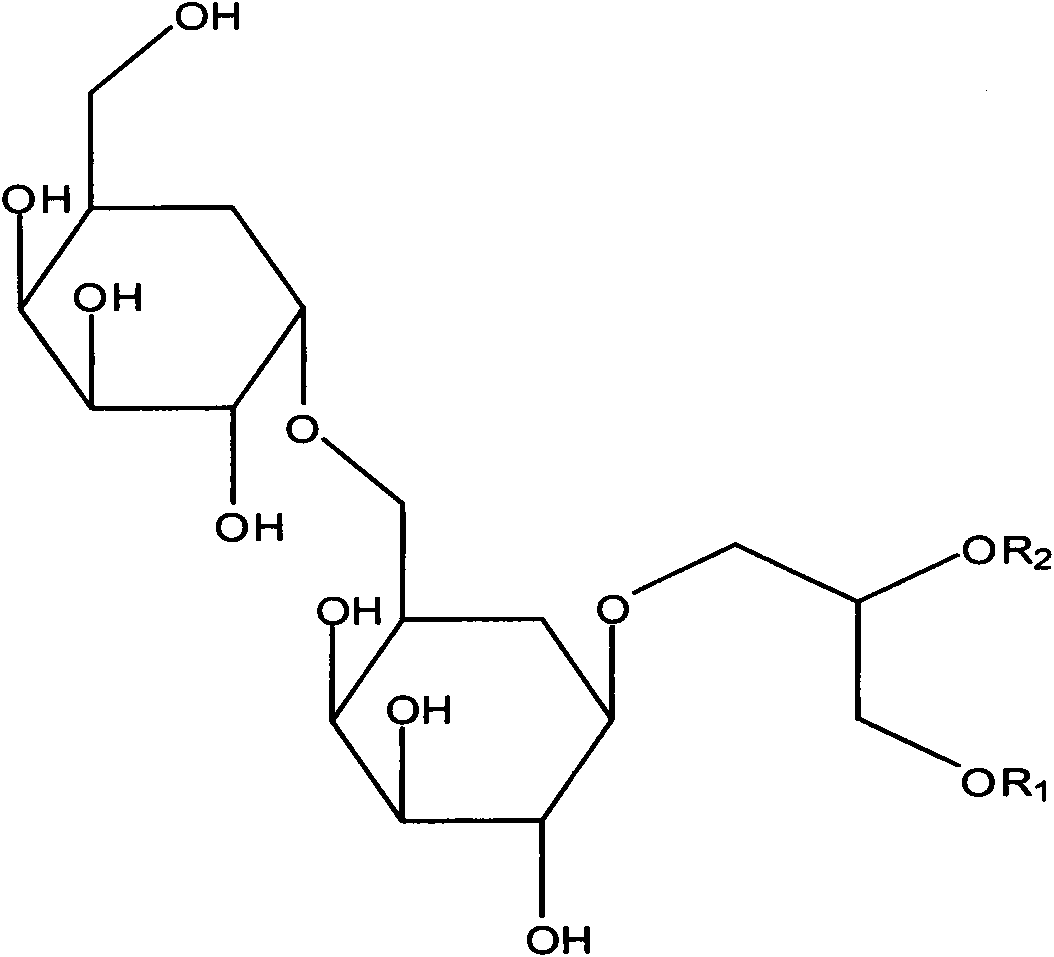
High-molecular material containing cholic acid and liver-targeting drug delivery nanoparticle modified by same
ActiveCN102351967BDoes not affect recognitionGood biocompatibilityPowder deliveryDigestive systemStructural formulaPharmaceutical Substances
The invention discloses a high-molecular material containing cholic acid and a drug-loaded nanoparticle modified by the same. The material has a structural formula as represented by formula III, and n in the formula is equal to 25 to 40. Monomers of the material are obtained by reacting hydroxy groups at C3 position of cholic acid methylester with 4-vinylbenzyl chloride and are initiated by an initiator so as to obtain a polymer precursor; ester groups at C24 position of the polymer precursor are hydrolyzed and turn into carboxyl groups so as to obtain the material in the invention. The material has amphipathy and is capable of assembling and of modifying the surface of the nanoparticles in the process of preparing the nanoparticles by using the method of emulsification-solvent evaporation. The molecular structure of cholic acid in the material can specifically bind to bile acid transporters on the surface of parenchymal hepatic cells; under the mediation of the bile acid transporters, the nanoparticles are absorbed by the parenchymal hepatic cells, and therefore, a drug is targetedly delivered to the parenchymal hepatic cells. Thus, the material provided in the invention can be used as an ideal surface modification material for development of a liver-targeting nanometer drug loading system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for separating, culturing and identifying primary hepatocytes of HBV transgenic mouse
InactiveCN109055302AImprove survival rateNormal hepatic parenchymal cell functionCell dissociation methodsMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh cellTwo step
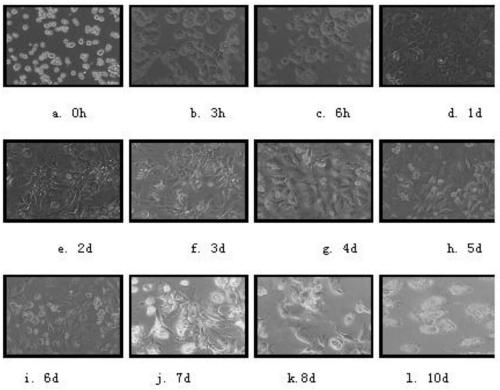
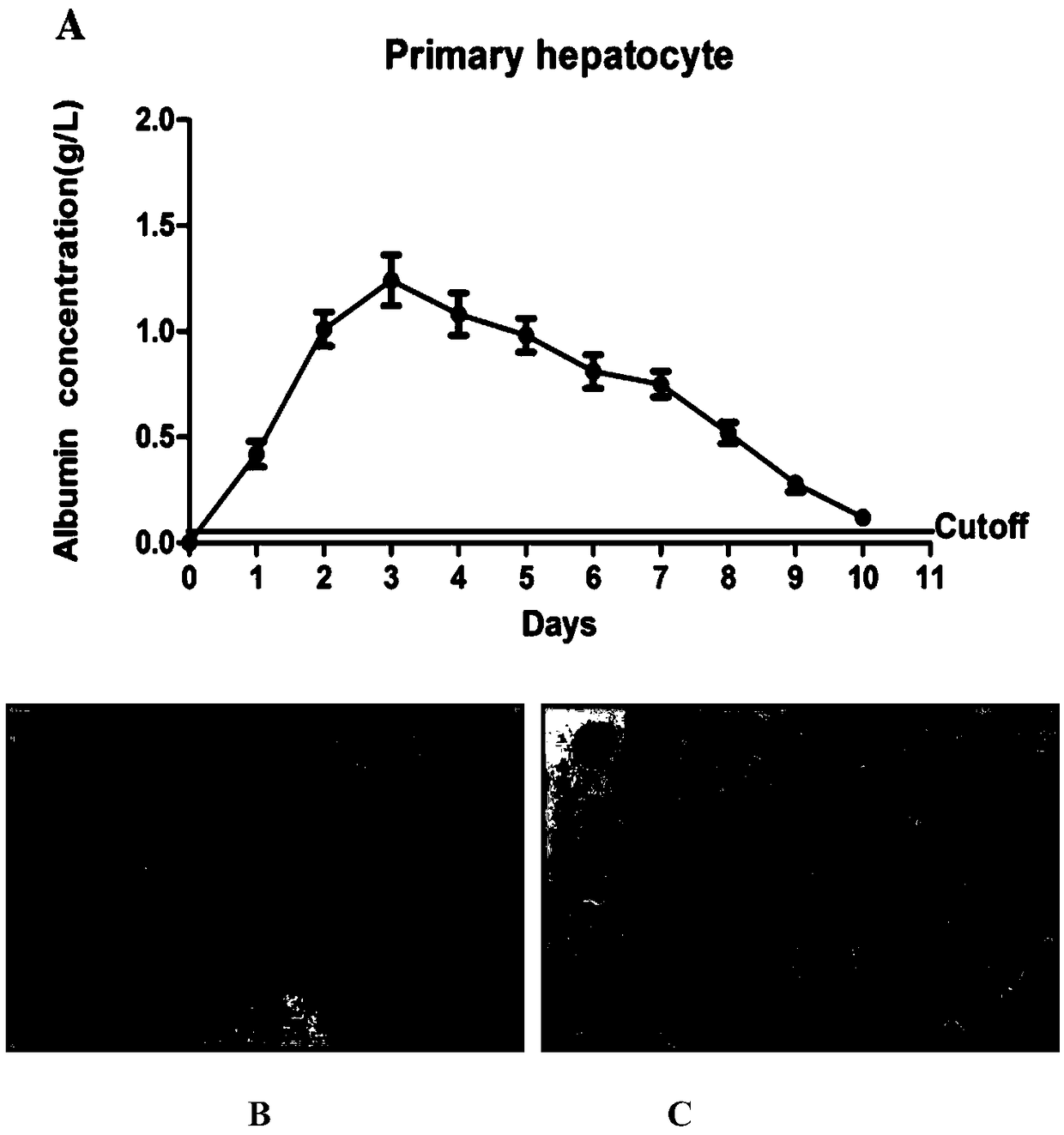
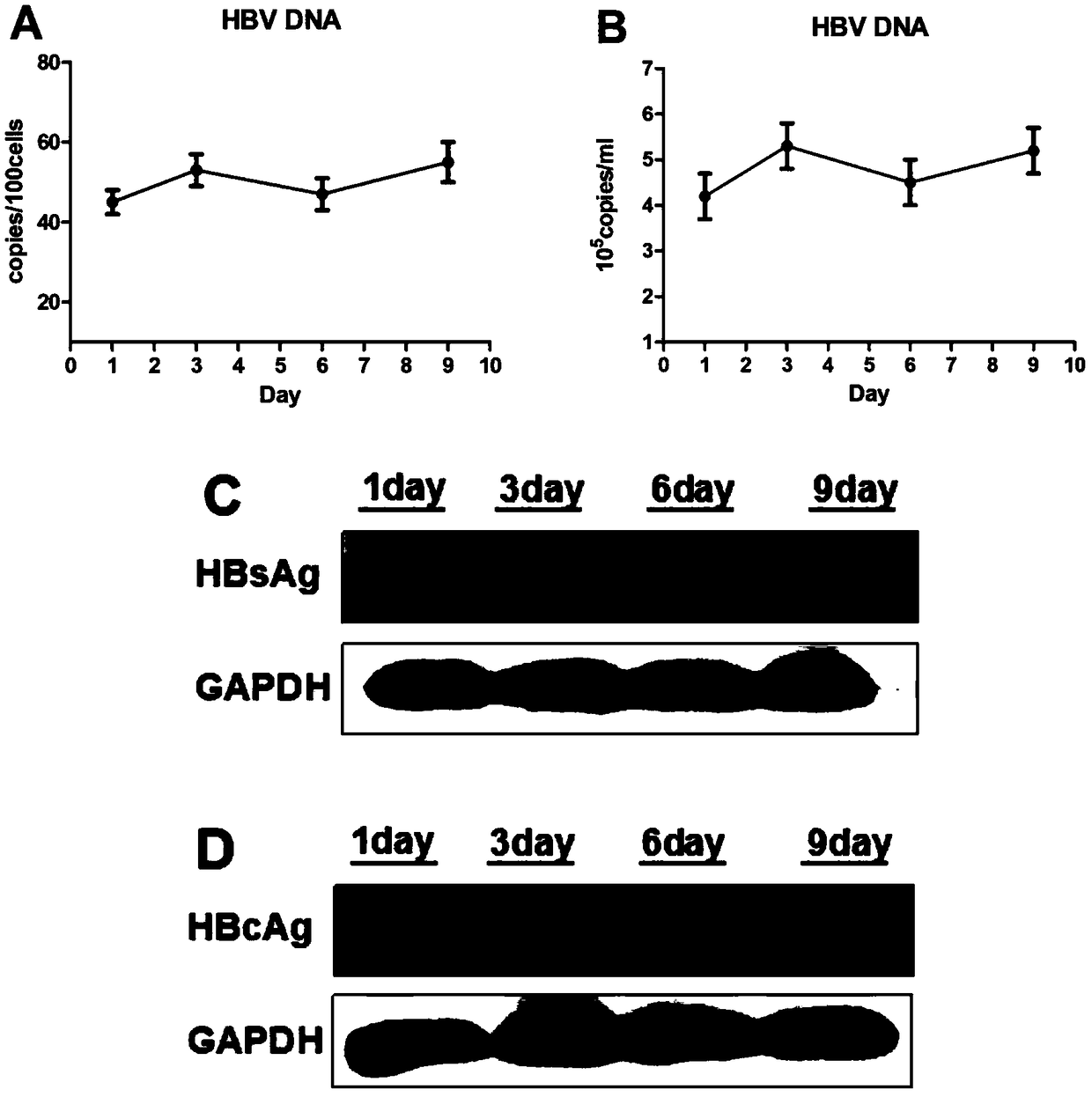
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and specifically relates to a method for separating, culturing and identifying primary hepatocytes of HBV transgenic mouse. The method comprises the following steps: performing separating and collecting primary hepatocytes by an improved collagenase two-step perfusion method; filtering the collected hepatocytes by a sterile cell filter; centrifuging and adding a culture medium for resuspension; performing cell counting and inoculated culture; the identification includes mouse primary hepatocyte albumin detection, mouse primary hepatocyte glycogen detection and expression analysis of HBV in the mouse primary hepatocyte. According to the method provided by the invention, the obtained HBV transgenic mouse primary hepatocyte has high cell viability as well as the functions of parenchymal hepatic cells, and the functions can be maintained for 8 days so as to more truly reflect the physiological metabolic activity of the hepatocytes in a HBV infection state, which is of great significance to in-vitro study of the physiological metabolic function of the hepatocytes as well as to the study of antiviral drugs.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
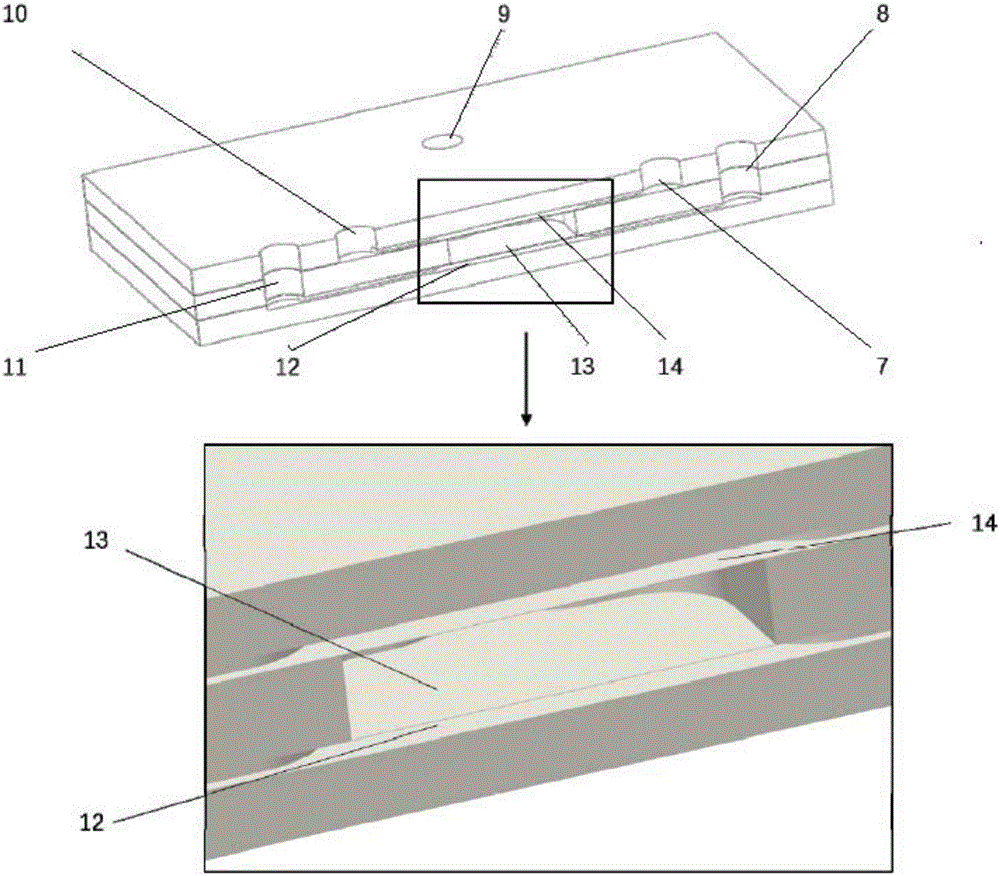
Constructing device and constructing method of artificial liver lobule functional unit
InactiveCN108504571AGood biocompatibilityThe result is accurateHepatocytesArtificial cell constructsArtificial liverLiver parenchyma
The invention discloses a constructing device and a constructing method of an artificial liver lobule functional unit. The constructing device comprises a liver plate basal layer, a liver parenchyma cell zone and a fluid passageway layer, wherein a liver plate patterning groove is formed in the liver plate basal layer through processing; the fluid passageway layer comprises a fluid inlet passageway, an endothelial cell oriented growth zone and a fluid outlet passageway. The constructing method corresponding to the constructing device comprises the following steps: paving collagen containing liver parenchyma cells to the inner part of the liver plate patterning groove, bonding the liver plate basal layer with the fluid passageway layer after solidifying the collagen, pouring an endothelialcell suspension solution to the endothelial cell oriented growth zone, and enabling a cell culture medium solution to unidirectionally flow in the fluid inlet passageway, the endothelial cell orientedgrowth zone and the fluid outlet passageway after increasing endothelial cells to a certain amount. According to the constructing device and the constructing method, disclosed by the invention, reallayer-to-layer position relationship between endodermis and liver parenchyma cells is realized under dynamic culturing, the response of the liver parenchyma cells to physicochemical and biochemical irritation under the protection of the endodermis of blood vessels more tends to reality, and a more accurate result can be obtained when the artificial liver lobule functional unit is applied to drug screening, case research and therapy detection.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Construction method of liver unit stent, liver unit stent and application of liver unit stent in field of drug testing
InactiveCN110511905ASuitable for proliferationSuitable for migrationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCross-linkInsertion stent
The invention relates to the field of biomedicine, in particular to a construction method of a liver unit stent, a liver unit stent and application of the liver unit stent in the field of drug testing. The invention aims to provide a construction method of a liver unit stent, a liver unit stent and application of the liver unit stent in the field of drug testing. The construction method of the liver unit stent comprises the following steps: a gelled first composition, which includes hepatic parenchymatous cells and a biodegradable material, is loaded into a biological 3D printer, and an intermediate is printed according to a preset path; a cross-linking agent is dropwise added to the intermediate such that the biodegradable material in the intermediate is cross-linked to form a liver unitstent, wherein a channel is formed in the liver unit stent. In the liver unit stent, cell variety, quantity and position are controllable and the channel is controllable, thus providing a microenvironment for different cells. In addition, the liver unit stent can be used for researching the drug hepatotoxicity of new drugs and is used for detecting drug metabolites, gene expression, protein expression, cell apoptosis and cell proliferation.
Owner:REGENOVO BIOTECH
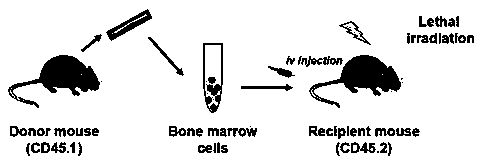
Separation method for hepatic inherent and infiltrating macrophages
PendingCN110669731AAccurate and efficient separationCell dissociation methodsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsHepatic macrophageSurface marker
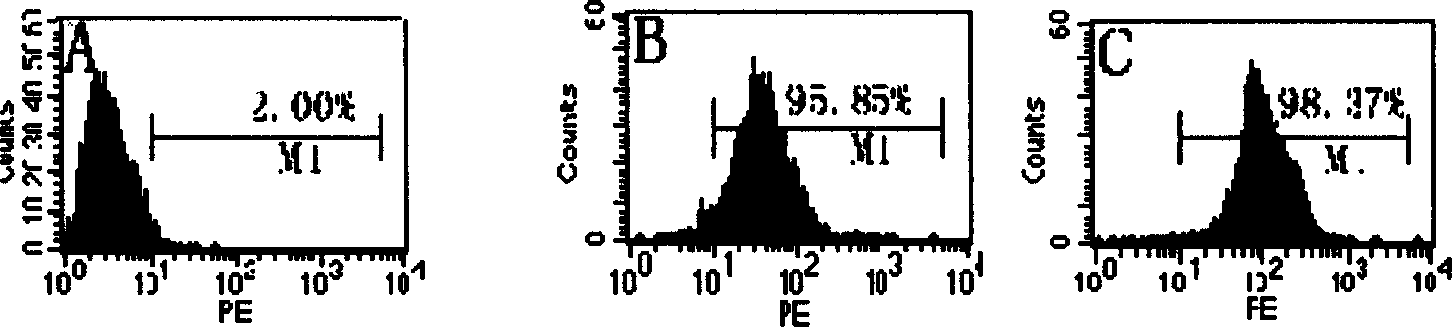
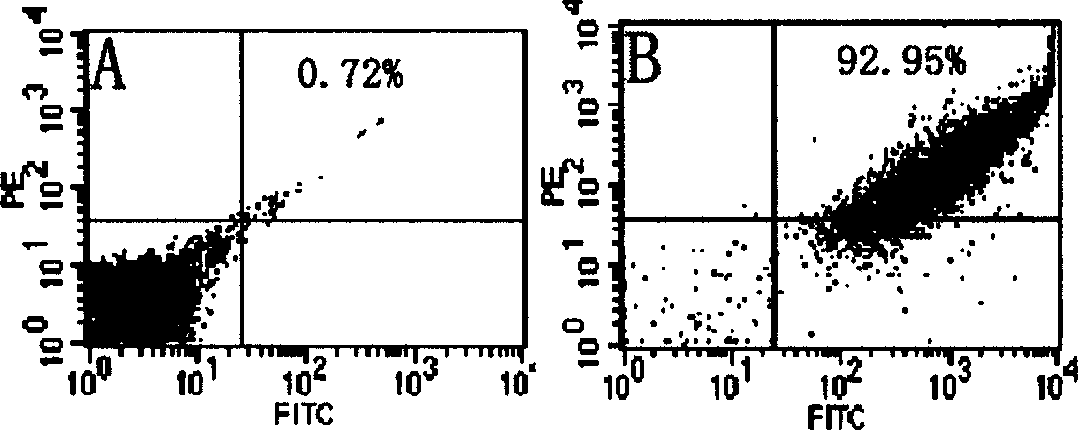
The invention provides a separation method for hepatic inherent and infiltrating macrophages. The separation method comprises the following steps of (1) establishing and identifying mouse allogeneicbone marrow transplantation model, wherein a surface marker of a mononuclear macrophage of a recipient mouse is CD45.2, and a surface marker of a mononuclear macrophage of a donor mouse is CD45.1; (2)observing and irradiating the influence on hepatic parenchymal cells and inherent macrophages with an IHC method and a flow cytometry; and (3) irradiating a mononuclear cell of a mouse liver in a transplantation group with primary isolation, and sorting the hepatic inherent and infiltrating macrophages with the flow cytometry according to the surface marker of the mononuclear macrophage of the donor mouse, and describing the quantities, distribution and phenotypes of the hepatic inherent and infiltrating macrophages. In the separation method provided by the invention, by removing the CD45.2 recipient mouse bone marrow derived macrophages by irradiation and supplementing and replacing bone marrow cells of the recipient mouse with CD45.1 donor mouse bone marrows, the bone marrow derived infiltrating macrophages and the bone marrow derived inherent macrophages have different molecular phenotypes and achieves the effect of accurately and efficiently separating different hepatic macrophages.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Establishment method of turbot hepatic parenchymal cell line and turbot hepatic parenchymal cell line
ActiveCN113215083AStable and sustainable useNo variationCell dissociation methodsGenetically modified cellsDigestion TreatmentNutrition
The invention relates to an establishment method of turbot hepatic parenchymal cell line and the turbot hepatic parenchymal cell line. The establishment method of the turbot hepatic parenchymal cell line comprises the following steps: obtaining turbot liver tissue; cutting the liver tissue into tissue blocks, and carrying out washing; carrying out digestion treatment by adopting type 4 collagenase, and carrying out washing again; carrying out digestion treatment on the tissue blocks obtained after the digestion treatment by adopting trypsin again; adding a primary complete medium to terminate digestion to obtain treated tissue blocks; uniformly attaching the treated tissue blocks into a culture bottle, placing the attached culture bottle into an incubator at 23 DEG C for 6 hours; inverting the culture bottle for 6 hours; adding 4 ml of a primary complete culture medium after the culture bottle is upright; performing primary culture; and then, performing subculture. The turbot hepatic parenchymal cell line established by the method can realize continuous passage so as to provide a large number of turbot hepatic cells; and the established stable and sustainable turbot hepatocyte line can be applied to the molecular cell biology research of turbot nutrition metabolism, thereby overcoming defects in the prior art at the cellular level.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Preparation method for digalactosyl diacylglycerol (DGDG) and application thereof
The invention relates to a preparation method for medicinal natural surfactant, namely, digalactosyl diacylglycerol (DGDG) and applications thereof as a pharmaceutical carrier. The preparation process is as follows: oat bran is extracted by acetone; leaching liquor is absorbed by silicon gel after being concentrated; eluent with different polarities are used for eluting; and refined DGDG is obtained from the final eluent. Or the oat bran can be degreased by supercritical carbon dioxide, and then extracted by acetone; leaching liquor is absorbed by silicon gel after being concentrated; and refined DGDG can be obtained after being eluted by eluent with different polarities. The hydrophile-lipophile balance value of the DGDG is 7.00 to 8.15, and the critical micelle concentration (CMC) thereof is 2*10 g / L. The raw materials of the method are easy to be obtained, and the obtained DGDG is thin-layer chromatographically pure without haemolysis and acrimony. The DGDG can be taken as a pharmaceutical carrier as two amphipathic properties thereof can self-assemble to form the property of bilayer vesicles. Galactose residues in DGDG molecules can be taken as ligands which can specifically distinguish galactose accepters on parenchymal hepatic cells so as to realize active hepatic targeting mediated by ligands.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Pharmaceutical composition containing adenosine or derivative of adenosine
InactiveCN103386131ANo side effectsImprove protectionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAdenosine diphosphateAdenosine 5 monophosphate
The invention discloses a pharmaceutical composition containing adenosine or derivatives of adenosine. The pharmaceutical composition comprises a composition of adenosine or the derivatives of adenosine and clinically compounds which lead to liver injury. The derivatives of adenosine are adenosine monophosphate, adenosine diphosphate or adenosine triphosphate. The clinically compounds which lead to liver injury comprise compounds for treating tuberculosis, antipyretic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory compounds, compounds for treating mental diseases, antibacterial compounds, hormonic compounds or anti-tumor compounds. The mouse model adopted by the invention is a mouse acute liver injury model induced by the compounds which lead to liver injury. The mass ratio of adenosine or the derivatives of adenosine and the compounds in the composition is (1:9)-(9:1). The pharmaceutical composition containing adenosine or the derivatives of adenosine and the compounds can reduce activity of AST (Aspartate Amino Transferase) and ALT (Alanine Amino Transferase) in liver injury and reduce necrosis area of parenchyma cells of liver, so that liver injury caused by the compounds is alleviated. The pharmaceutical composition disclosed by the invention shows that adenosine or the derivative of adenosine has protective effect on liver injury caused by the compounds.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
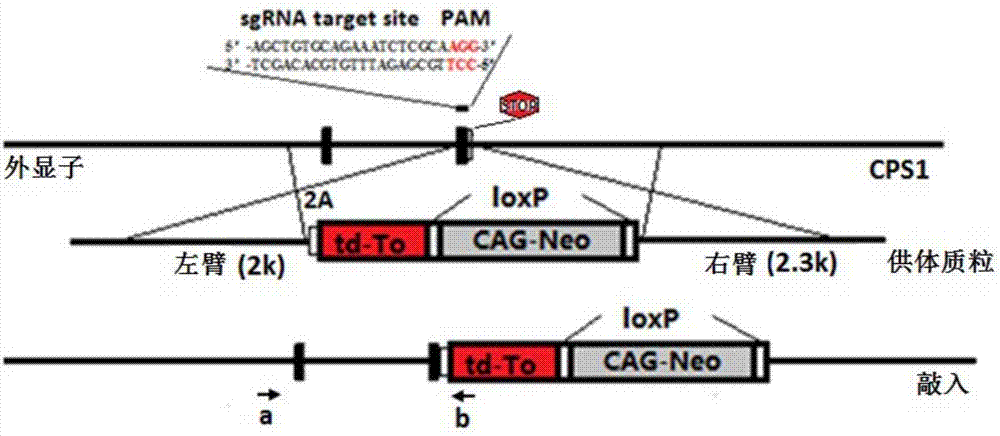
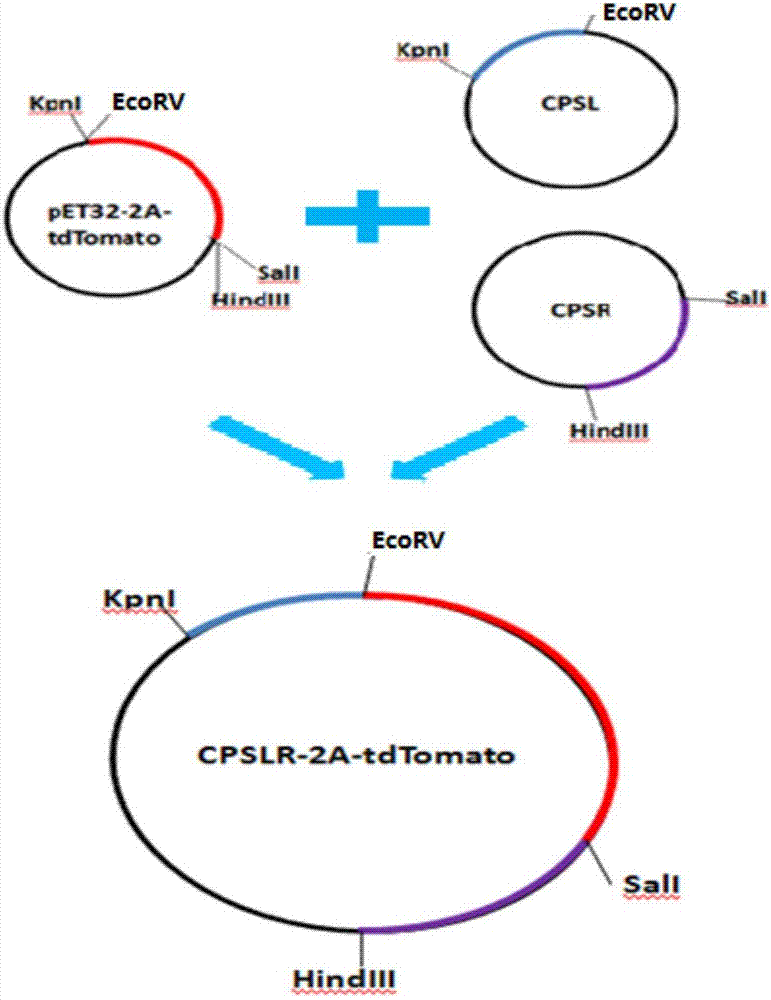
CPS1 reporter gene human liver cell line, construction method hereof and applications thereof
InactiveCN106947740AHigh purityHigh ammonia metabolism capacityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesArtificial liverAdult liver
The invention discloses a CPS1 reporter gene human liver cell line and its construction method and application. Aminoacylphosphate synthase 1 (CPS1) and a reporter gene are used to construct a human liver cell line. The obtained CPS1 reporter gene human liver cell has the characteristics of human primary adult The functions of liver parenchymal cells, including albumin secretion, cytochrome P450 enzyme metabolism and ammonia metabolism, can be used in artificial livers, drug metabolism research, drug toxicity evaluation or drug screening, and have broad application prospects.
Owner:FIELD OPERATION BLOOD TRANSFUSION INST OF PLA SCI ACAD OF MILITARY
Hepatoma targeting carbon nano tube loaded with doxorubicin hydrochloride and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104689334AGood biocompatibilitySmall side effectsOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSolubilityLiver parenchyma
The invention discloses a hepatoma targeting carbon nano tube loaded with doxorubicin hydrochloride and a preparation method thereof. Amidation reaction of amino in a chitosan structure and carboxyl in lactobionic acid is carried out; galactosyl is coupled to chitosan so as to obtain galactosylated chitosan; the galactosylated chitosan is modified onto the carbon nano tube; therefore, the water solubility and the biocompatibility of the carbon nano tube are increased; simultaneously, the specificity of non-reductive galactose or N-acetyl-galactose is identified and taken by utilizing an asialoglycoprotein acceptor on a liver parenchyma cell membrane, so that the active hepatoma targeting effect is realized; simultaneously, doxorubicin hydrochloride is combined with a vector in a non-covalent manner through phi-phi accumulation acting force; and therefore, the hepatoma targeting carbon nano tube loaded with doxorubicin hydrochloride is prepared. The hepatoma targeting carbon nano tube disclosed by the invention is simple in preparation process, moderate in experimental condition and easy to operate; release of the medicine loaded targeting carbon nano tube has pH dependency, good biocompatibility and obvious in-vivo tumour inhibition effect; and thus, the hepatoma targeting carbon nano tube has good practical value.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Animal experiment substitution method for toxicological evaluation of exogenous compounds
InactiveCN101735974AIncreased sensitivityHigh simulationMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue cultureLiver parenchymaMetabolic enzymes
The invention relates to a cell separation culture method of biological tissues and use thereof, in particular to a method for separating and culturing hepatic cells of a newborn rat (or mouse) and using the hepatic cells as a substitutional animal experiment model for toxicological evaluation of exogenous compounds. The method for separating and culturing the hepatic cells of the newborn rat (or mouse) of the invention has simple operation, does not need a liver perfusion process and expensive instruments, equipment and reagents, and can obtain more than 90% of liver parenchyma cells which have good uniformity and stability and high sensitivity and are easy for manual control. The hepatic cells separated and cultured by the invention are very sensitive to the toxicity of the exogenous compounds, have some functions and activity of in vivo hepatic cells, especially reserve the activity of drug metabolic enzyme, can well simulate the physiological environment of the in vivo liver, have the advantage of combining in vitro and integral animal toxicity tests, and can be expected to be used in high flux rapid detection of the toxicity of the exogenous compounds.
Owner:伍义行
Functional liver parenchyma cells and preparation method therefor
PendingCN113151147AStrong chimerismHigh proliferation rateMicrobiological testing/measurementCulture processLiver parenchymaDirected differentiation
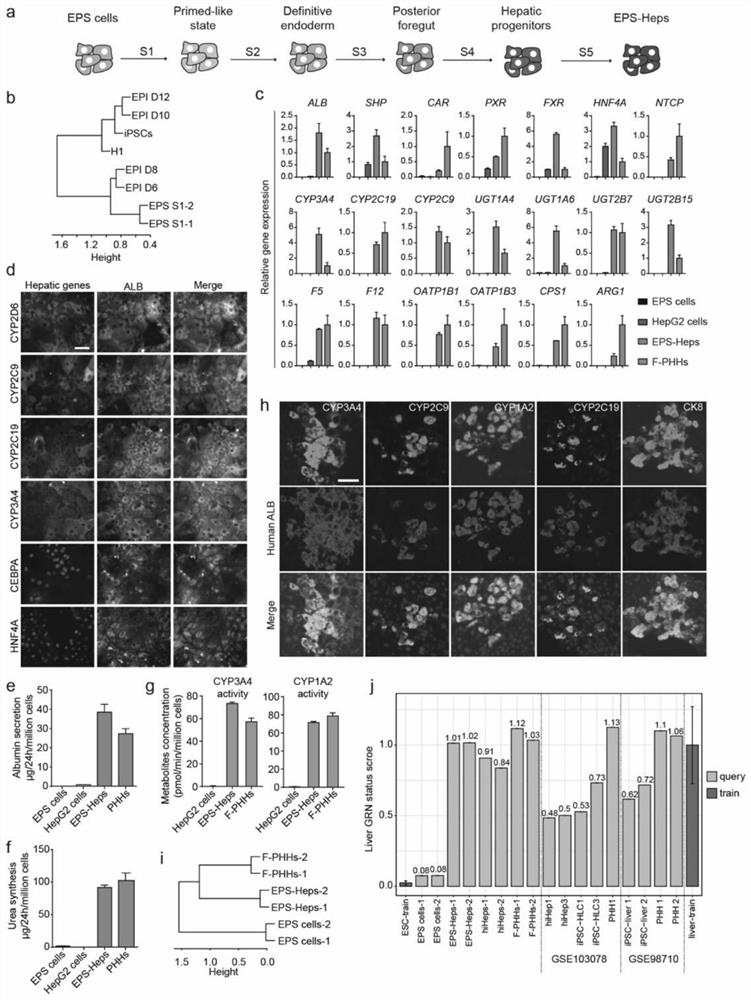
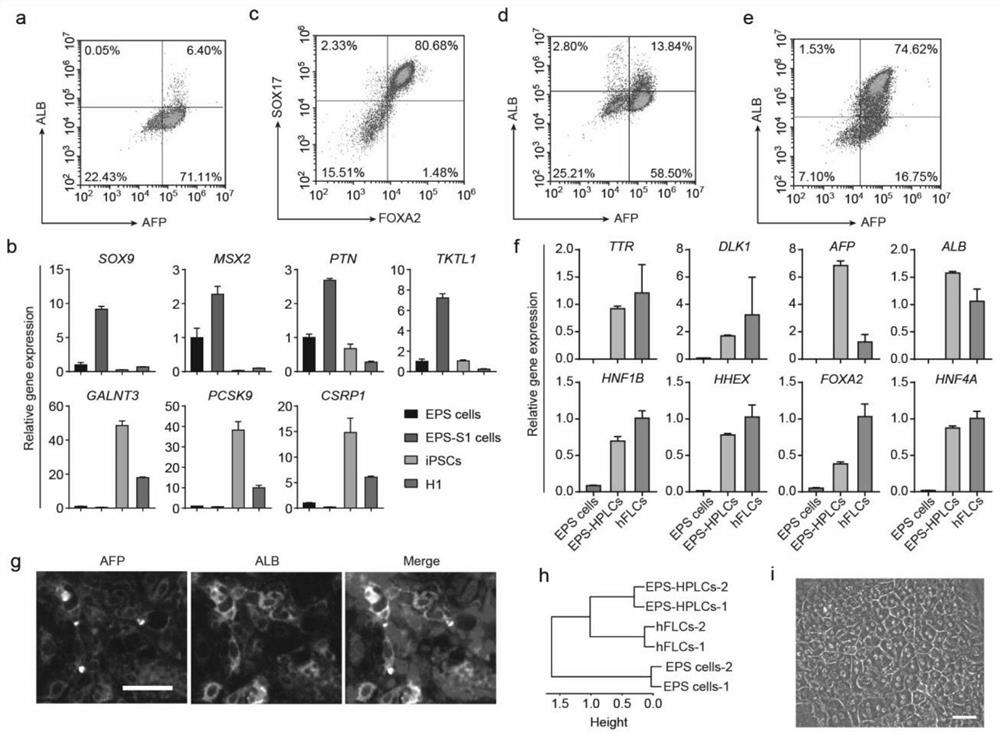
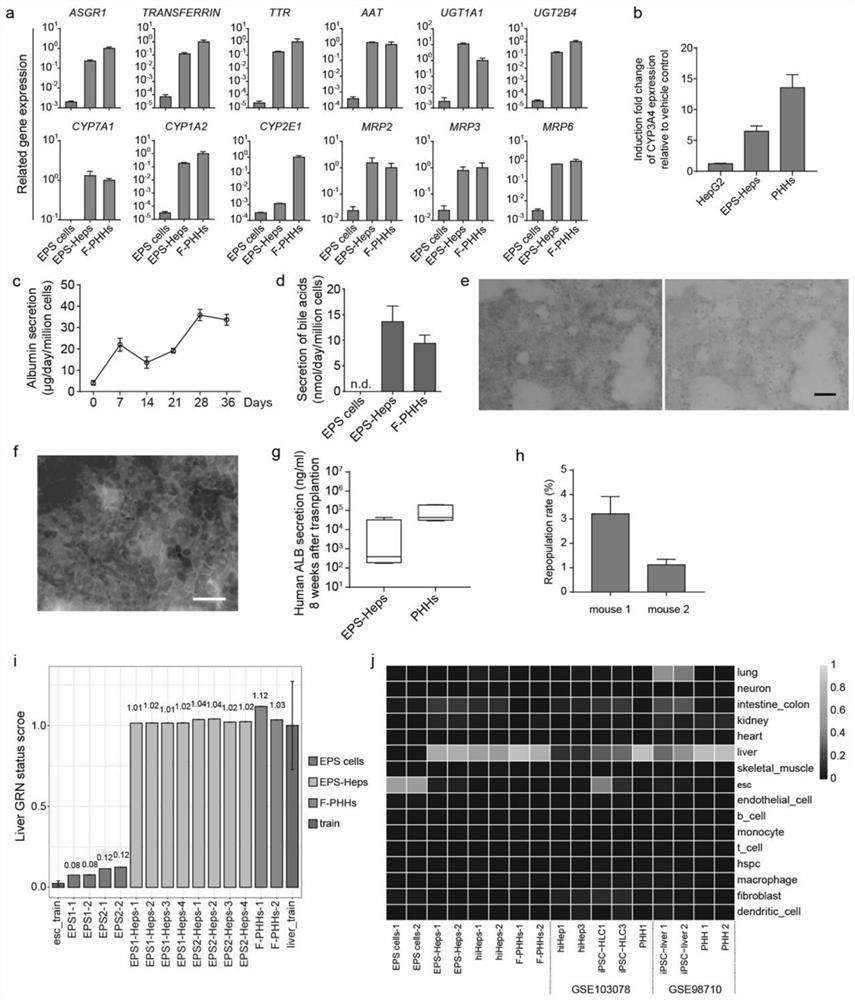
The invention discloses functional liver parenchyma cells and a preparation method therefor. According to the preparation method, potential-extended multipotential stem cells, i.e., EPS cells are subjected to directed differentiation, so as to prepare the functional liver parenchyma cells (or called liver cells). Furthermore, before directed differentiation of the EPS cells, the EPS cells is firstly pretreated in an iPSCs / ESCs culture medium. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, human EPS cells can be more efficiently differentiated into the functional liver parenchyma cells, and the functional liver parenchyma cells EPS-Heps obtained through EPS differentiation are more similar to fresh-separated primary liver cells in a full-gene transcription level.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Artificial liver organ and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN113717925ALong-term stable survivalOptimize space layoutArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsDiseaseArtificial liver
The invention relates to the field of biological materials and biomedical engineering, and particularly relates to an artificial liver organ and a preparation method and application thereof. The artificial liver organ comprises an endothelial cell layer, a hepatic stellate cell layer and a hepatic parenchyma cell layer; the different cell layers are arranged in a bionic and close mode, and the distance between different kinds of adjacent cells is smaller than 30 micrometers; the mechanical property of the artificial liver organ is 500Pa-1MPa; and the characteristic length of the artificial liver organ is 50-1000 micrometers. The constructed liver organ comprises liver cells, endothelial cells and hepatic stellate cells, the structure and physiological function of the liver Disse gap can be simulated, and the requirements of in-vitro liver physiological / pathological research, drug testing and drug development, tissue engineering and regenerative medicine are met. The artificial liver organ can be induced into various liver disease models at the same time, and corresponding pathological models can be constructed according to requirements.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Cryopreservation method of primary-generation mouse parenchymal liver cells
InactiveCN108260586AHigh purityA large amountDead animal preservationMouse Hepatic Parenchymal CellTwo step
The invention provides a cryopreservation method of primary-generation mouse parenchymal liver cells. The method includes the steps of firstly, preparing mouse parenchymal liver cell cryopreservationliquid; secondly, using a two-step perfusion method to separate the mouse parenchymal liver cells; thirdly, using the cryopreservation liquid to resuspend the mouse parenchymal liver cells, and then adding the mouse parenchymal liver cells into a cryopreservation tube; fourthly, using a step-by-step temperature reduction method to cryopreserve the mouse parenchymal liver cells; fifthly, resuscitating the mouse parenchymal liver cells; sixthly, using a dye exclusion method to measure the survival rate of the mouse parenchymal liver cells; seventhly, determining enzyme index activity; eighthly,observing the morphology of the mouse parenchymal liver cells; ninthly, performing ELISA method detection; tenthly, performing RT-PCR detection. The cryopreservation method has the advantages that themethod is simple to operate, many cells can be obtained after cryopreservation resuscitating, high survival rate is achieved, and the method is an ideal primary-generation mouse parenchymal liver cell cryopreservation method and capable of providing reliable cell resources for experiments.
Owner:JIANGYIN CHI SCI
Breeding method for establishing primary biliary cholangitis model mouse through bile duct antigen immunity
The invention provides a method for cultivating a mouse model of primary biliary cholangitis, the method comprising: (1) perfusing the mouse liver with collagenase IV for 10 minutes through the hepatic portal vein, removing hepatic parenchymal cells, and obtaining Complete bile ducts; (2) shredding the bile ducts obtained in step (1), further using ultrasonic waves for homogenization, and quantifying the protein concentration of the obtained bile duct protein homogenate; (3) using the obtained bile duct proteins to The source mice were subcutaneously immunized to establish primary biliary cholangitis model mice induced by bile duct antigen immunization. The mouse obtained by the method of the invention can be used as a new animal model for screening drugs for primary biliary cholangitis.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A method for long-term in vitro culture and expansion of hepatocytes and its application
ActiveCN105296418BAchieve unlimited supplyMicrobiological testing/measurementAntiviralsOrganismCells transplantation
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology and provides a method for long-time in-vitro culturing and proliferating hepatic cells. The method includes that mature hepatic parenchymal cells are induced to be hepatic cells with infinite proliferation capability in vitro. The hepatic cells obtained by the method can be used for toxicological and pharmacological evaluation of compounds and drug, study and diagnosis as well as treatment of hepatitis virus, hepatic cell transplantation therapy and preparation of bioartificial liver.
Owner:SHANGHAI CELLIVER BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com