Artificial liver organ and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of organoids and livers, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, artificial cell constructs, 3D culture, etc., can solve the problems of scarcity of liver disse gap organoids, low production efficiency of organoids, affecting nutrient and oxygen supply, etc., to achieve The manufacturing process can be standardized, the microstructure efficiency and repeatability are high, and the effect of imitation repeatability can be satisfied
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] Example 1 Using electrostatic bioprinting technology to engineer and prepare hydrogel 3D structures containing various cells
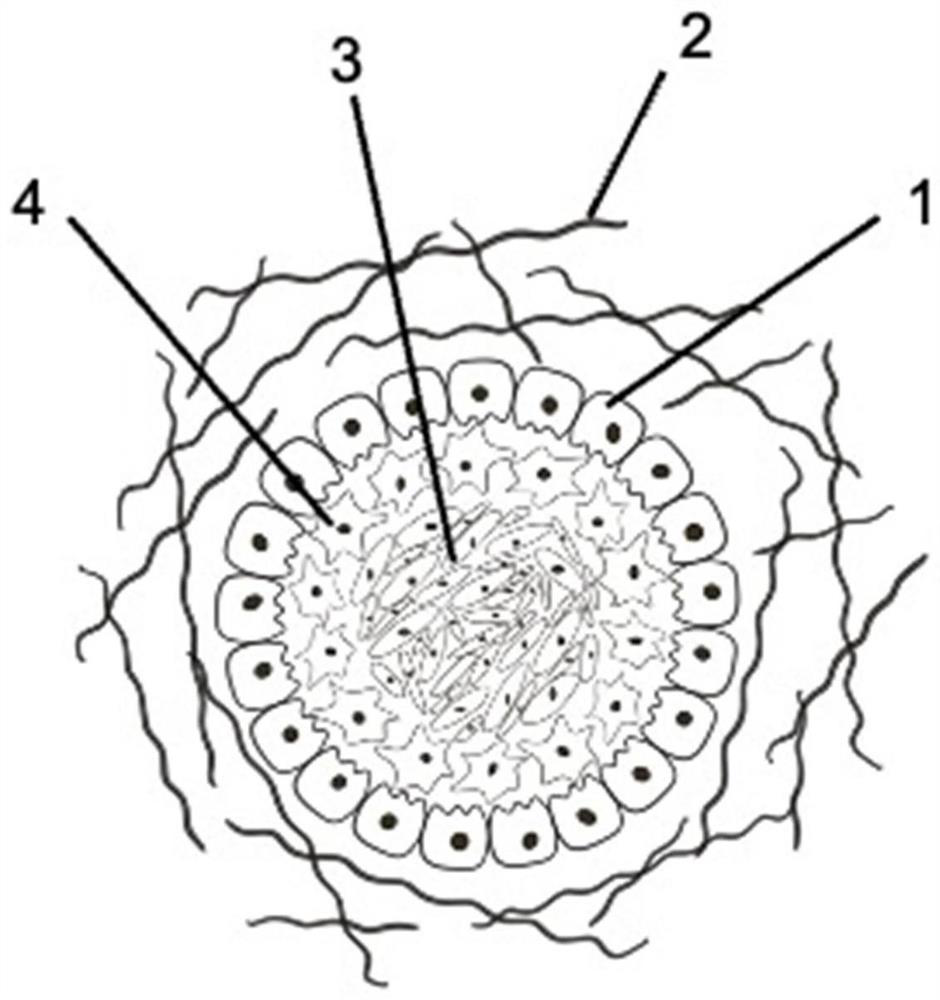
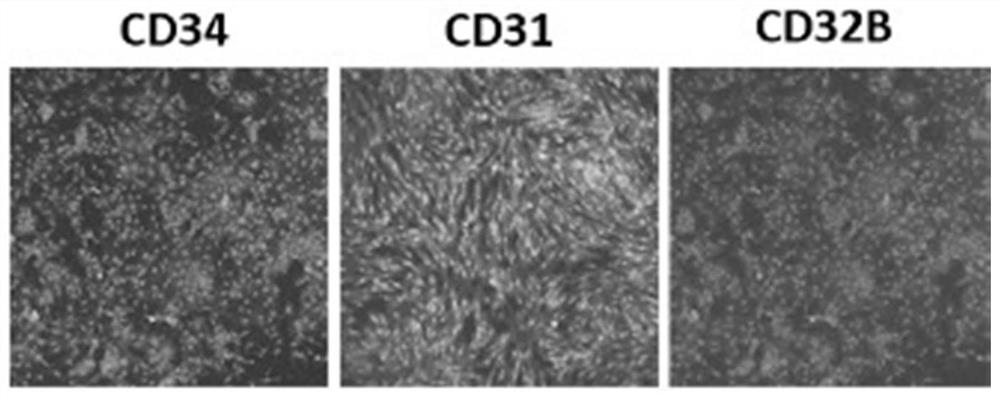
[0071] This embodiment provides a method for preparing artificial liver organoids (such as figure 1 As shown, wherein 1 is a hepatic parenchymal cell, 2 is a hydrogel material, 3 is an endothelial cell, and 4 is a process of a hepatic stellate cell), as follows:
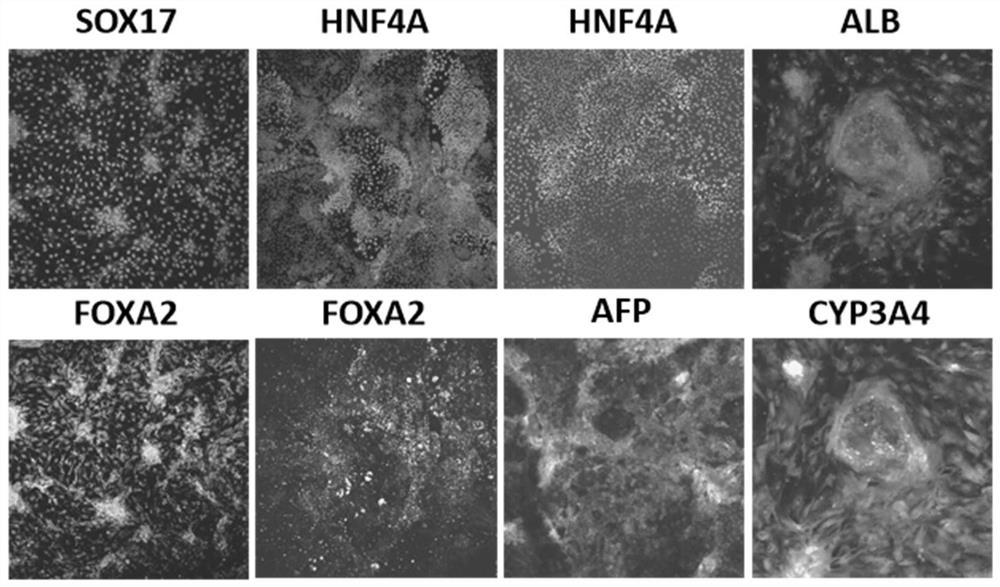
[0072] 1. Directed differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) into hepatic parenchymal cells
[0073] (1) Cell differentiation:
[0074] Culture iPSC (ATCC) to induce differentiation when the cell confluency reaches 80%;
[0075] First use induction medium 1 to culture for 3-5 days, the components include DMEM-F12 (Thermo Fisher), 1×B27 (Gibco), 50ng / mL Activin A (R&D, 338-AC), and restricted endoderm can be obtained at this stage cell.
[0076] Next, use induction medium 2 to culture for 4-8 days. The components include DMEM-F12 (Thermo Fisher), B27 (Gibco), 200ng / m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com