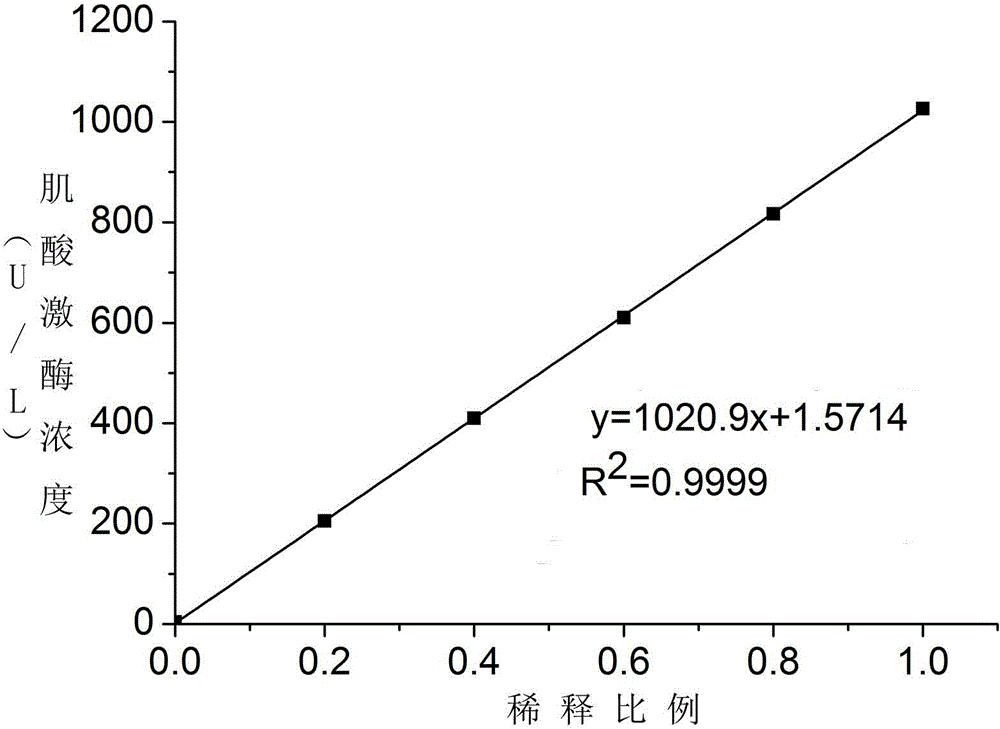
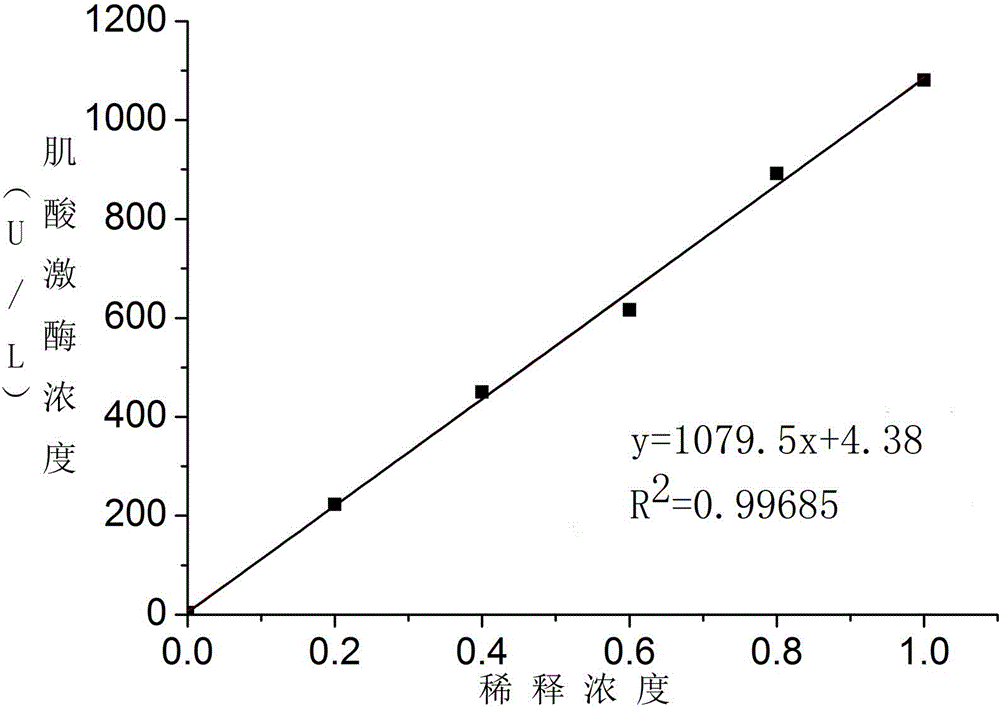
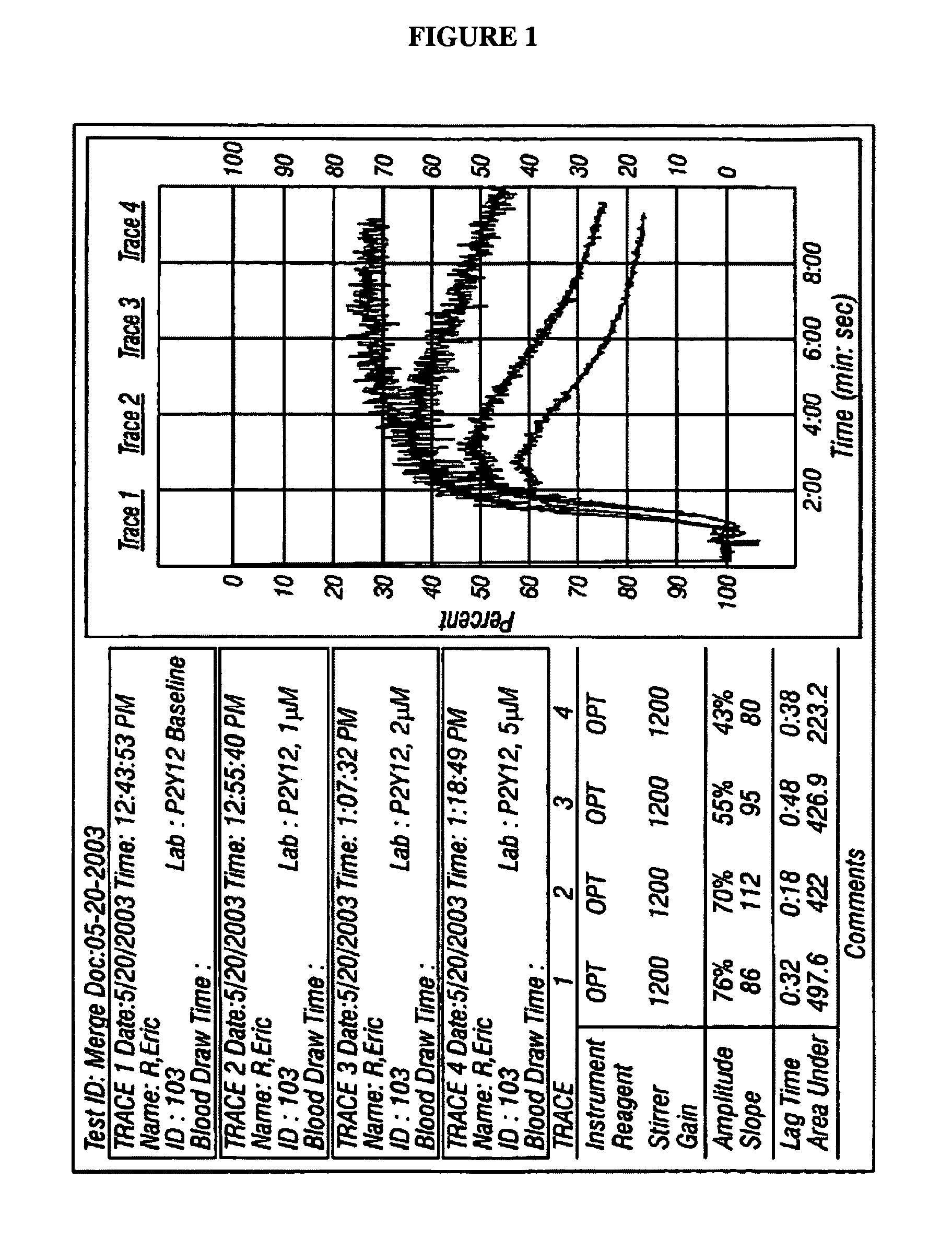
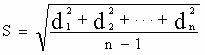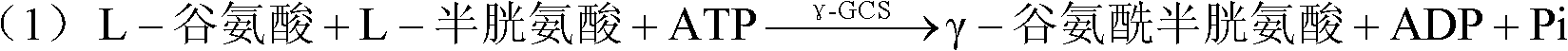Patents
Literature
234 results about "Adenosine diphosphate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
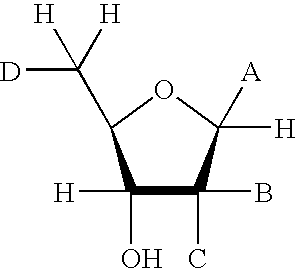
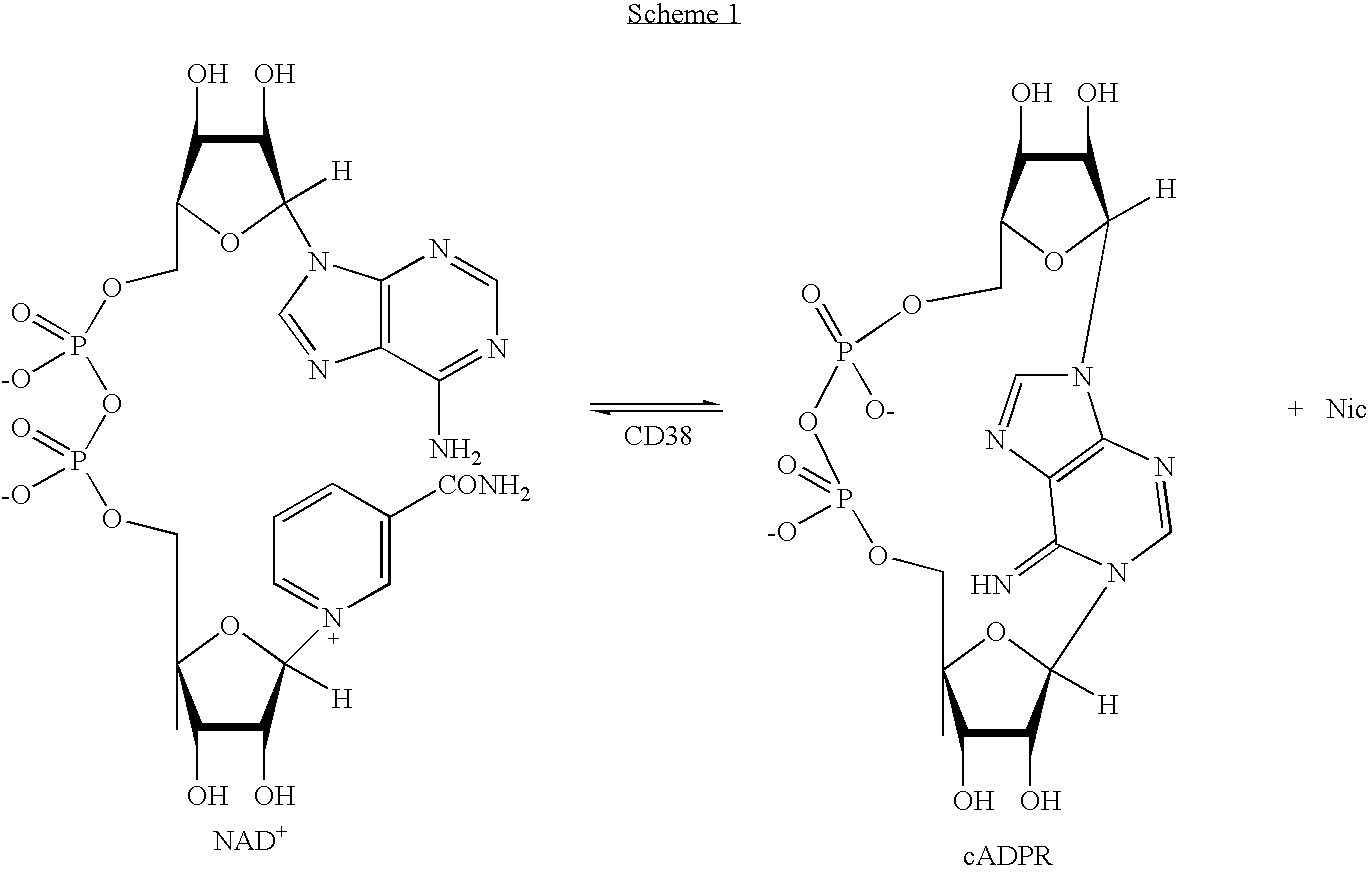
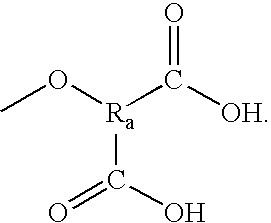
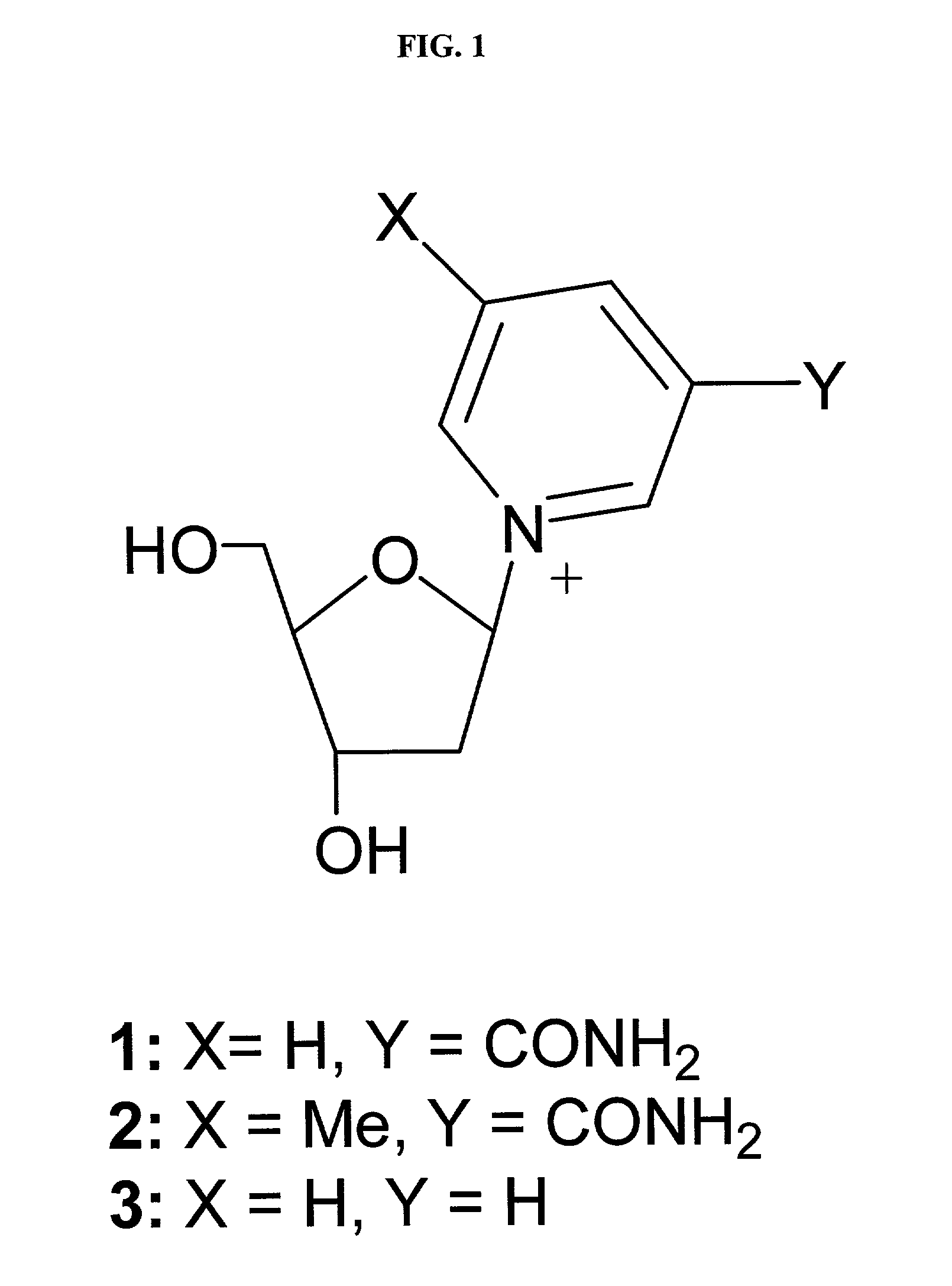
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP), also known as adenosine pyrophosphate (APP), is an important organic compound in metabolism and is essential to the flow of energy in living cells. ADP consists of three important structural components: a sugar backbone attached to adenine and two phosphate groups bonded to the 5 carbon atom of ribose. The diphosphate group of ADP is attached to the 5’ carbon of the sugar backbone, while the adenosine attaches to the 1’ carbon.
Medical prosthetic devices and implants having improved biocompatibility
Disclosed are medical prosthetic devices or medical implants which exhibit improved biocompatitibly. The devices or implants include a metal material, e.g. titanium, in which the metal surface parts are coated with a corresponding hydride material that contains one or more biomolecule substance. This biomolecule substance may contain one or more biologically active molecules, e.g. bio-adhesives, biopolymers, blood proteins, enzymes, extra cellular matrix proteins, extra cellular matrix biomolecules, growth factors and hormones, peptide hormones, deoxyribonucleic acids, ribonucleic acids, receptors, enzyme inhibitors, drugs, biologically active anions and cations, vitamins, adenosine monophosphate (AMP), adenosine diphosphate (ADP), adenosine triphosphate (ATP), marker biomuolecules, amino acids, fatty acids, nucleotides (RNA and DNA bases), or sugars.
Owner:STRAUMANN HLDG AG
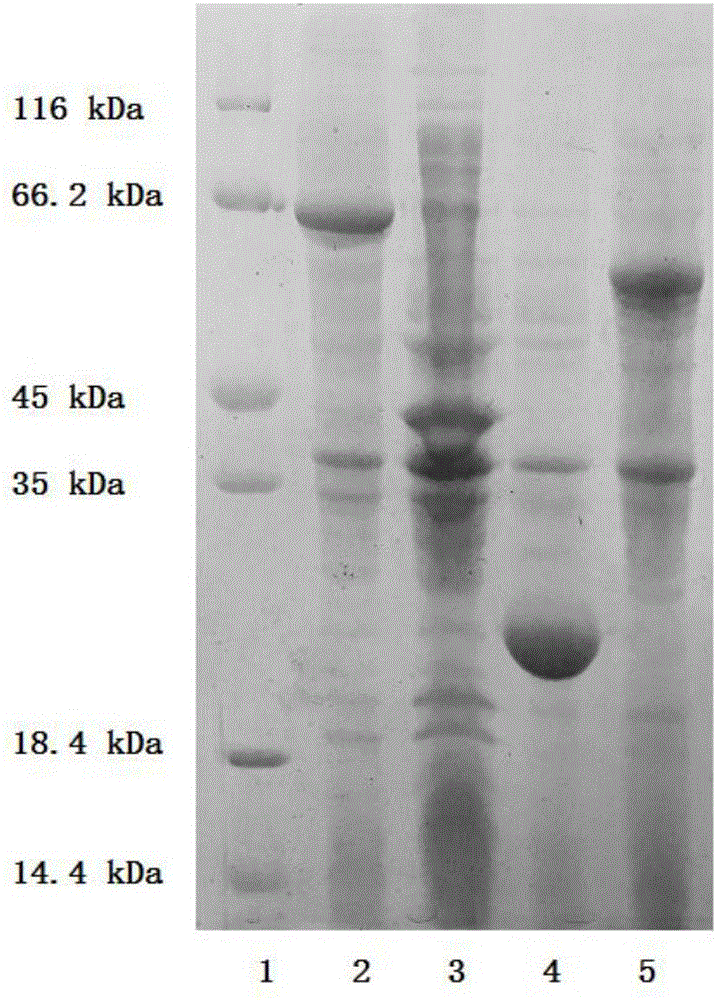
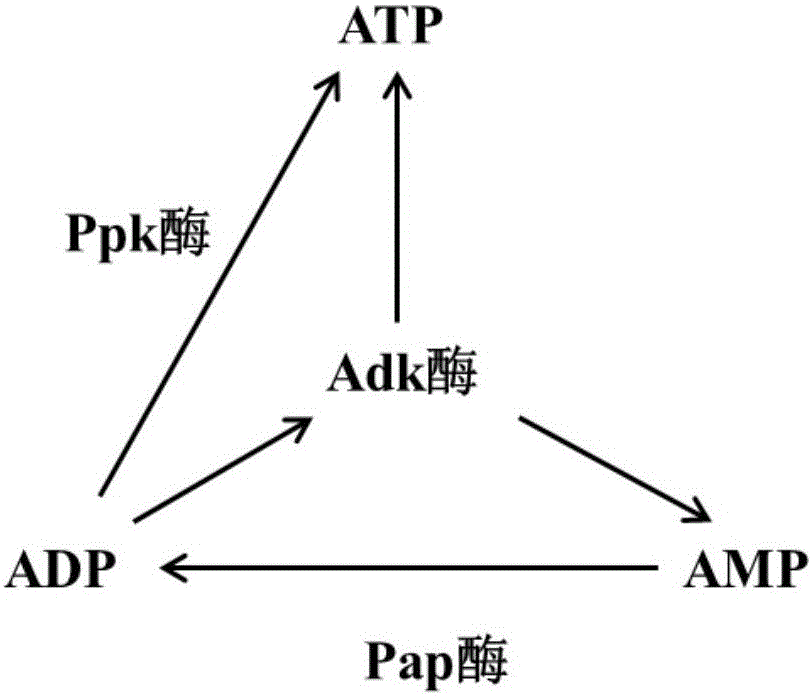
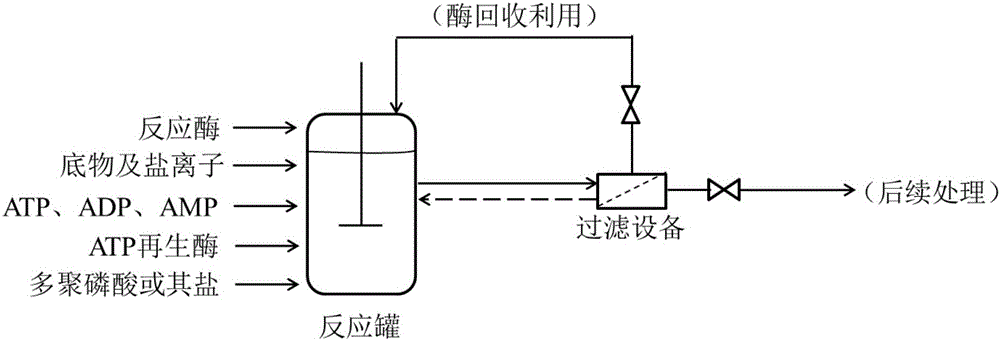
Method for regenerating ATP (adenosine triphosphate) by enzyme process and application thereof
InactiveCN105861598AReduce usagePromote regenerationTransferasesFermentationPhosphoric acidEnzyme catalysis
The invention discloses a method for regenerating ATP by enzymatic method, which comprises the following steps: (1) preparing and obtaining ATP regenerating enzyme; (2) regenerating ATP in reaction liquid; (3) separating products and ATP regenerating enzyme. According to the method for regenerating ATP of the present invention, it has the following beneficial effects: (1) adopt three kinds of ATP regenerating enzymes of novel Ppk, Adk and Pap, the ATP consumed in the enzymatic reaction can be recycled and regenerated, greatly reducing the amount of ATP used, regenerated The process is simple and efficient, the reaction is easy to control, and the stability is high. (2) The substrate polyphosphoric acid or its salt to be added to the reaction is cheap and less polluting. (3) The enzymatic reaction does not need to add expensive ATP to start the reaction, add ADP or cheap AMP. (4) ATP regenerating enzyme recovery system was established, which is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:SHENZHEN GSH BIO TECH CO LTD
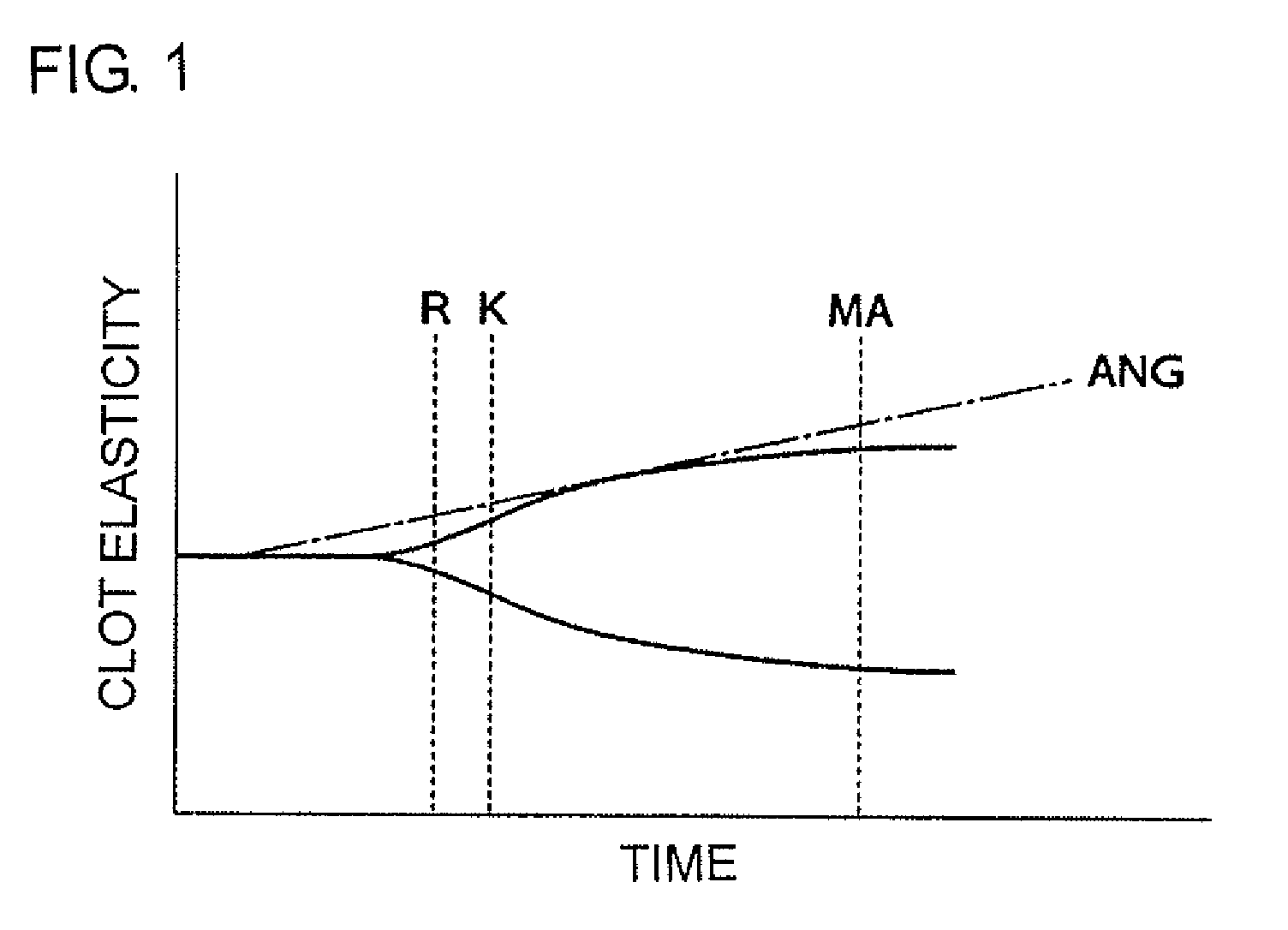
Method for testing efficacy of antithrombotic agent
InactiveUS7947505B2Quick and easy testingMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisAntithrombotic AgentAnticoagulant
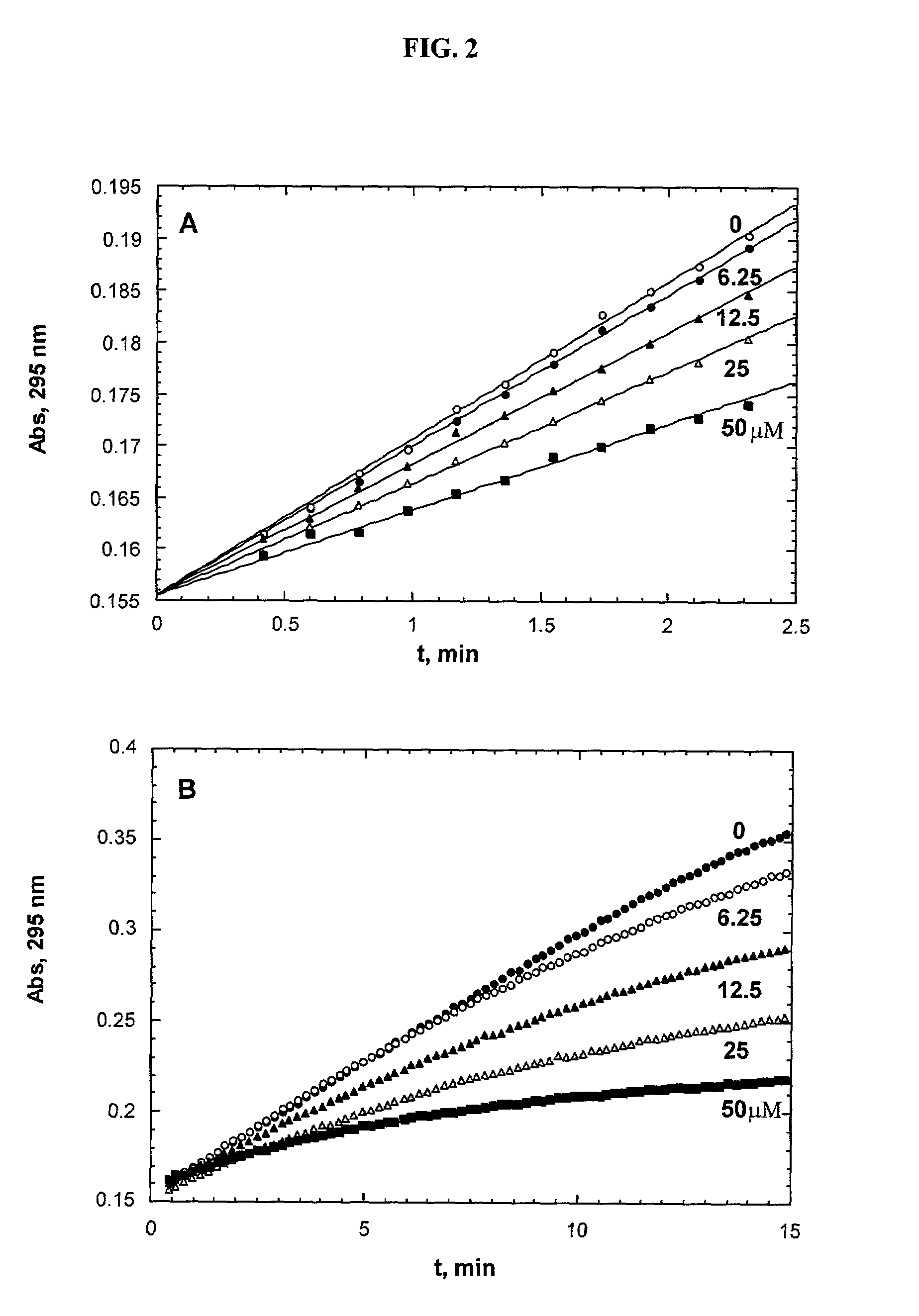
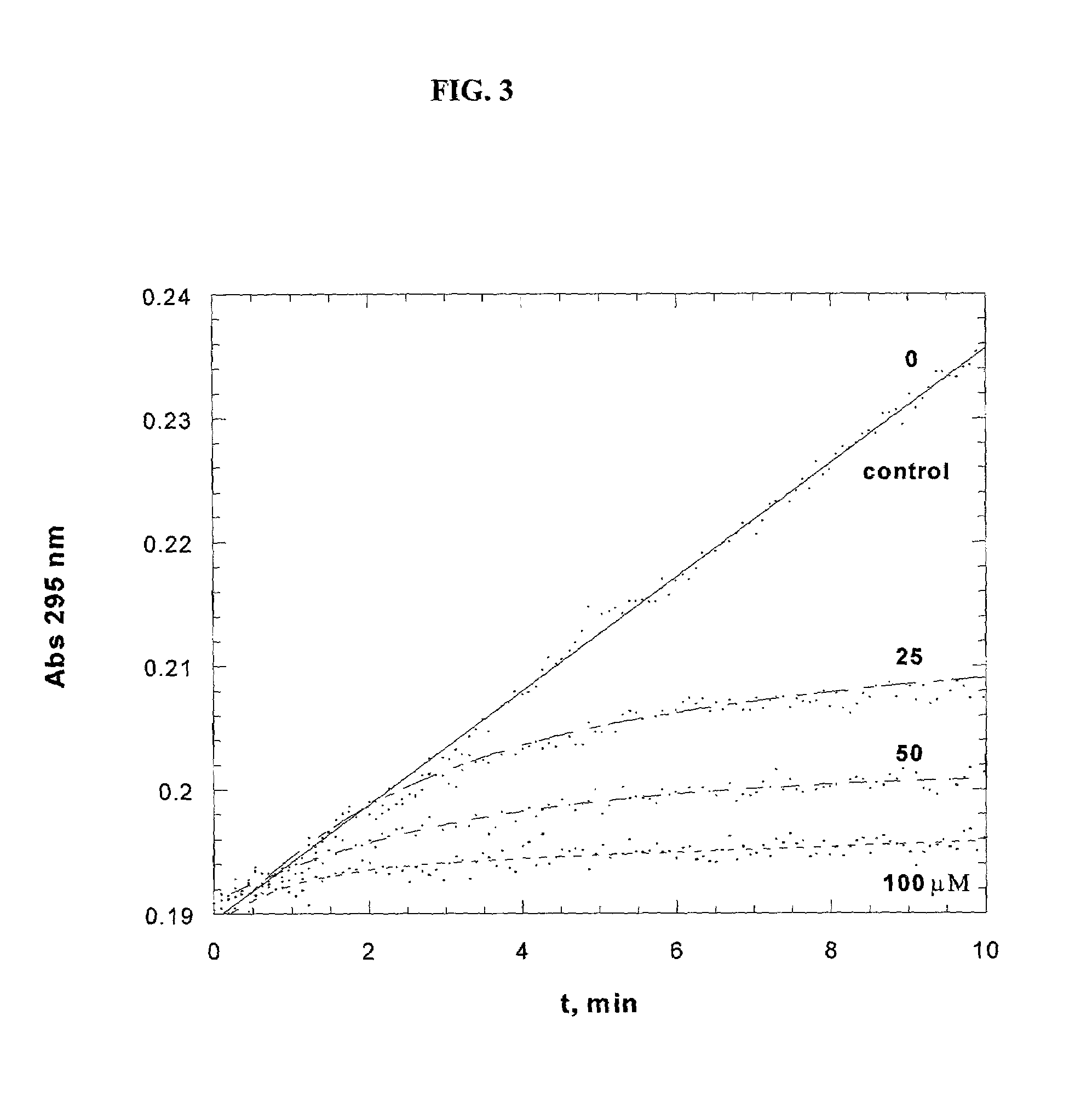
The present invention provides a method for testing quickly and easily the manner in which an antithrombotic agent inhibits the acceleration of blood coagulation when a platelet agonist causes acceleration of blood coagulation. The invention is a test method wherein a system in which an anticoagulant is added to a portion of blood sampled from a patient being administered an antithrombotic agent (X system blood), and a system in which an anticoagulant and adenosine diphosphate or collagen are added to a portion of the abovementioned blood (Y system blood) are simultaneously measured by thromboelastograph; and the efficacy of the antithrombotic agent is assessed by comparing the R values of the X system blood and the Y system blood. If the R value of the Y system blood is not found to differ significantly from the R value of the X system blood, the drug is judged to be working. Adenosine diphosphate and collagen can be used as the anticoagulant. The present invention provides a heretofore unknown method for easily assessing the efficacy of an antithrombotic agent.
Owner:KAWASAKI CORP KK +1
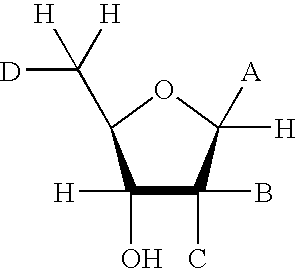
Inhibitors of ADP-ribosyl transferases, cyclases, and hydrolases
The present invention provides compounds having the formula: wherein A is a nitrogen-, oxygen-, or sulfur-linked aryl, alkyl, cyclic, or heterocyclic group, the group being further substituted with an electron contributing moiety; B is hydrogen, or a halogen, amino, or thiol group; C is hydrogen, or a halogen, amino, or thiol group; and D is a primary alcohol, a hydrogen, or an oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, or sulfur linked to phosphate, a phosphoryl group, a pyrophosphoryl group, or adenosine monophosphate through a phosphodiester or carbon-, nitrogen-, or sulfur-substituted phosphodiester bridge, or to adenosine diphosphate through a phosphodiester or carbon-, nitrogen-, or sulfur-substituted pyrophosphodiester bridge. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions containing the above compounds, methods of using the above compounds as pharmaceuticals, and processes for preparing the above compounds. Also provided are methods for inhibiting an ADP-ribosyl transferase, ADP-ribosyl cyclase, ADP-ribosyl hydrolase, or NAD-dependent deacetylase enzyme, and methods for treating a disease or condition associated with an ADP-ribosyl transferase, ADP-ribosyl cyclase, ADP-ribosyl hydrolase, or NAD-dependent deacetylase enzyme in a subject in need of treatment thereof.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
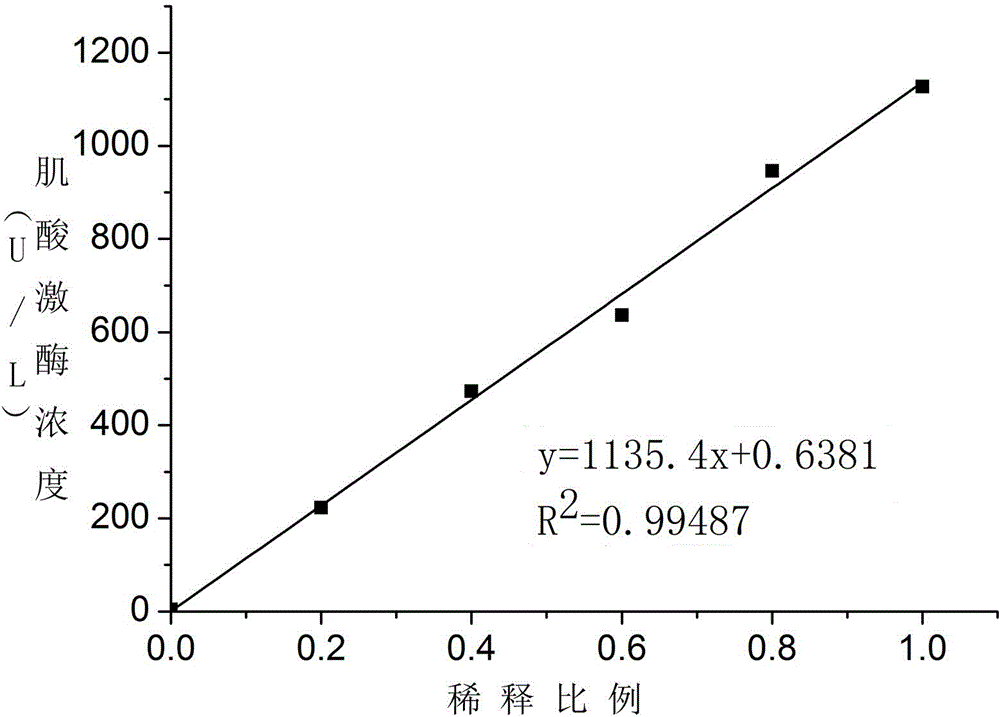
Creatine jubase MB isozyme activity detection reagent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102154443AHigh precisionImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementAntiendomysial antibodiesCreatine kinase
The invention discloses a creatine jubase MB isozyme activity detection reagent which comprises sulfide-oxidizing coenzyme, 6-phosphaogluconate dehydrogenase, sulfhydryl reagent, magnesium salt, glucokinase or hexoxinase, anti-CK-M antibody, phosphocreatine, adenosine diphosphate, glucose and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. The preparation method of the reagent is as follows: dissolving all components in a buffer solution with pH of 5.0 to 9.5. The creatine jubase MB isozyme activity detection reagent can enlarge detection sensitivity several times; and the determination result has high precision and degree of accuracy.
Owner:浙江东瓯诊断产品有限公司
Pyrimidoimidazole compound and pharmaceutical composition and preparation method and use thereof
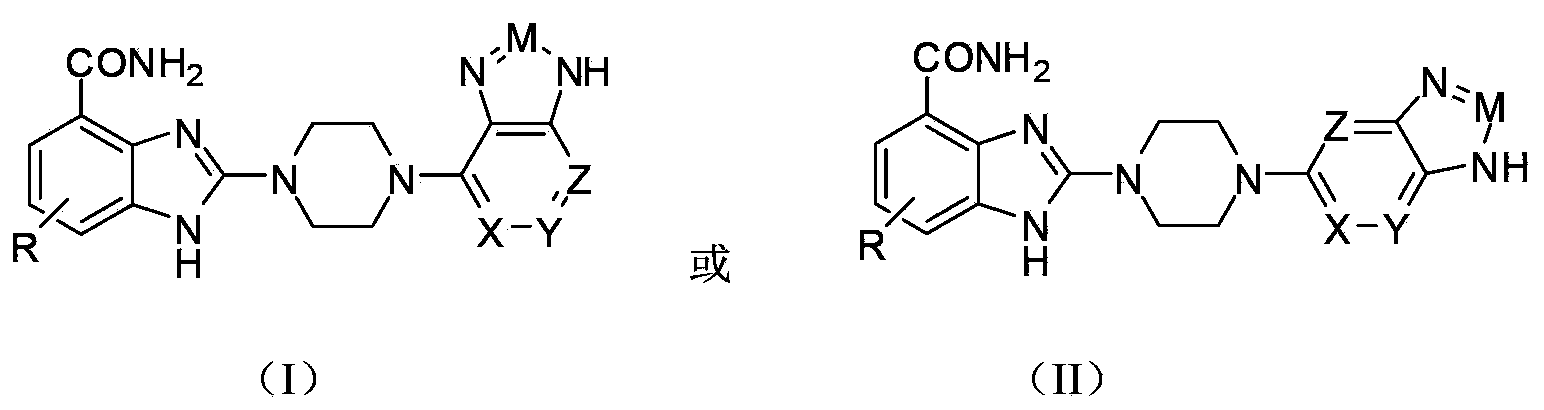
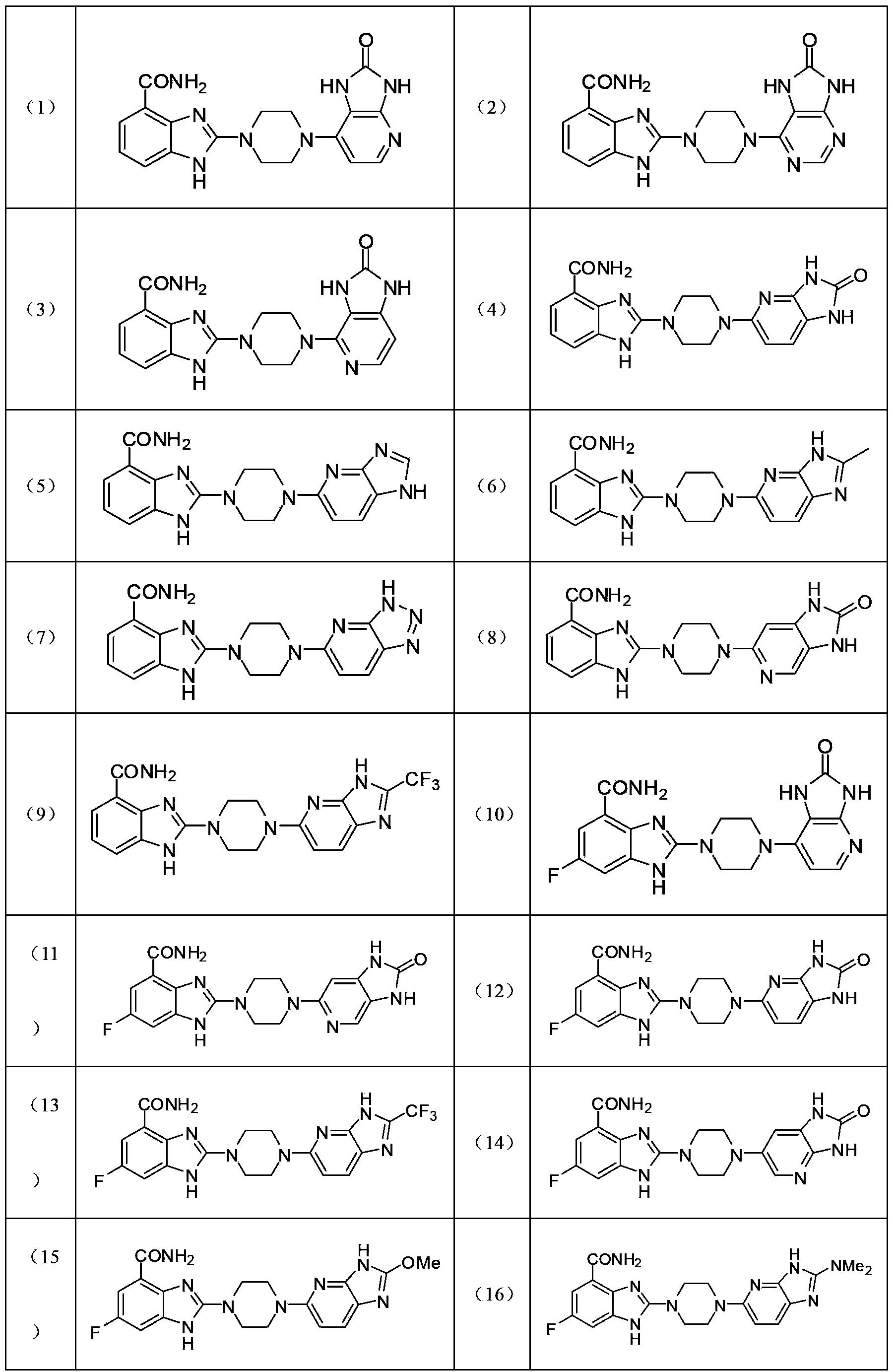
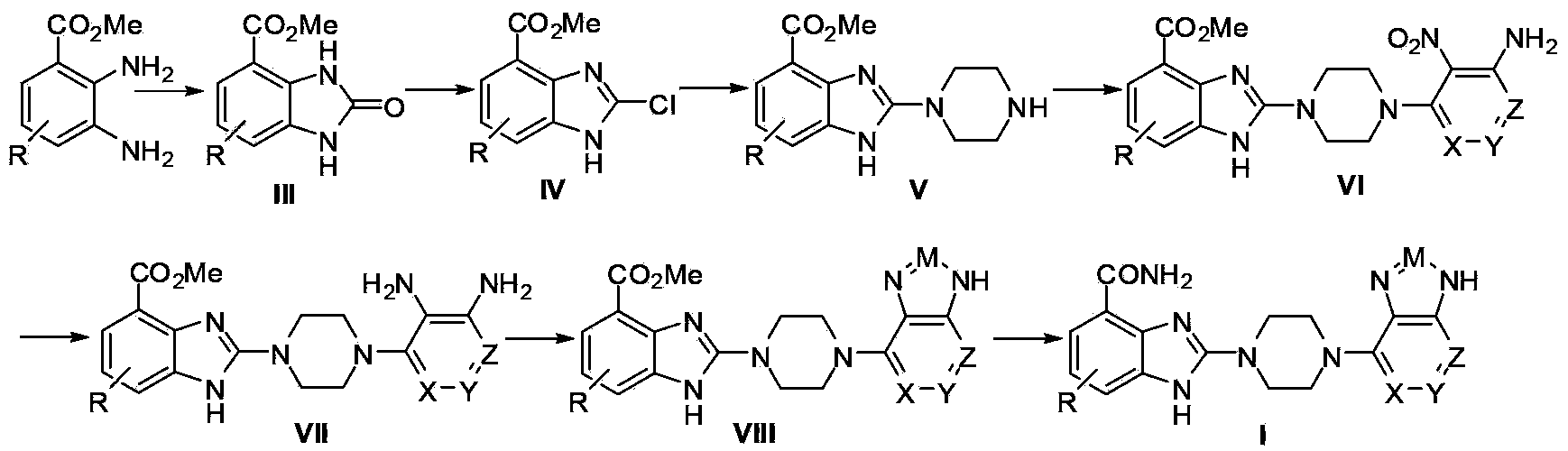
The invention relates to a pyrimidoimidazole derivative, a preparation method and medical use thereof, and particularly relates to a new pyrimidoimidazole derivative as shown in a general formula (I) or formula (II), a preparation method thereof, a pharmaceutical composition containing the new pyrimidoimidazole derivative, and use thereof as a therapeutic agent in particular as a poly (ADP(adenosine diphosphate)-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor.
Owner:上海壹典医药科技开发有限公司
Method for synthesis of glutathione in vitro
ActiveCN102220400ALow costChemically stableFermentationGamma-Glutamylcysteine synthetaseAdenosine diphosphate
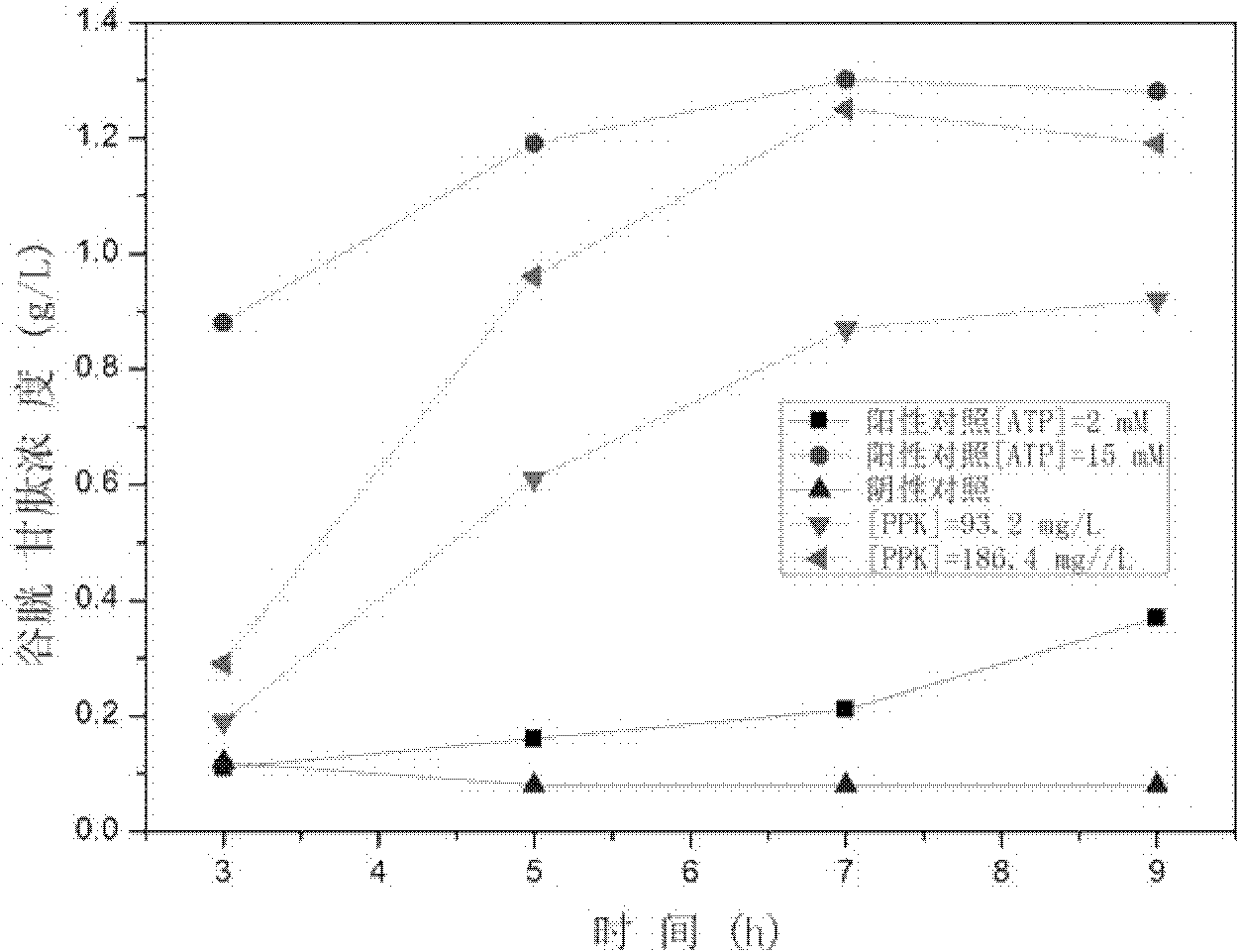
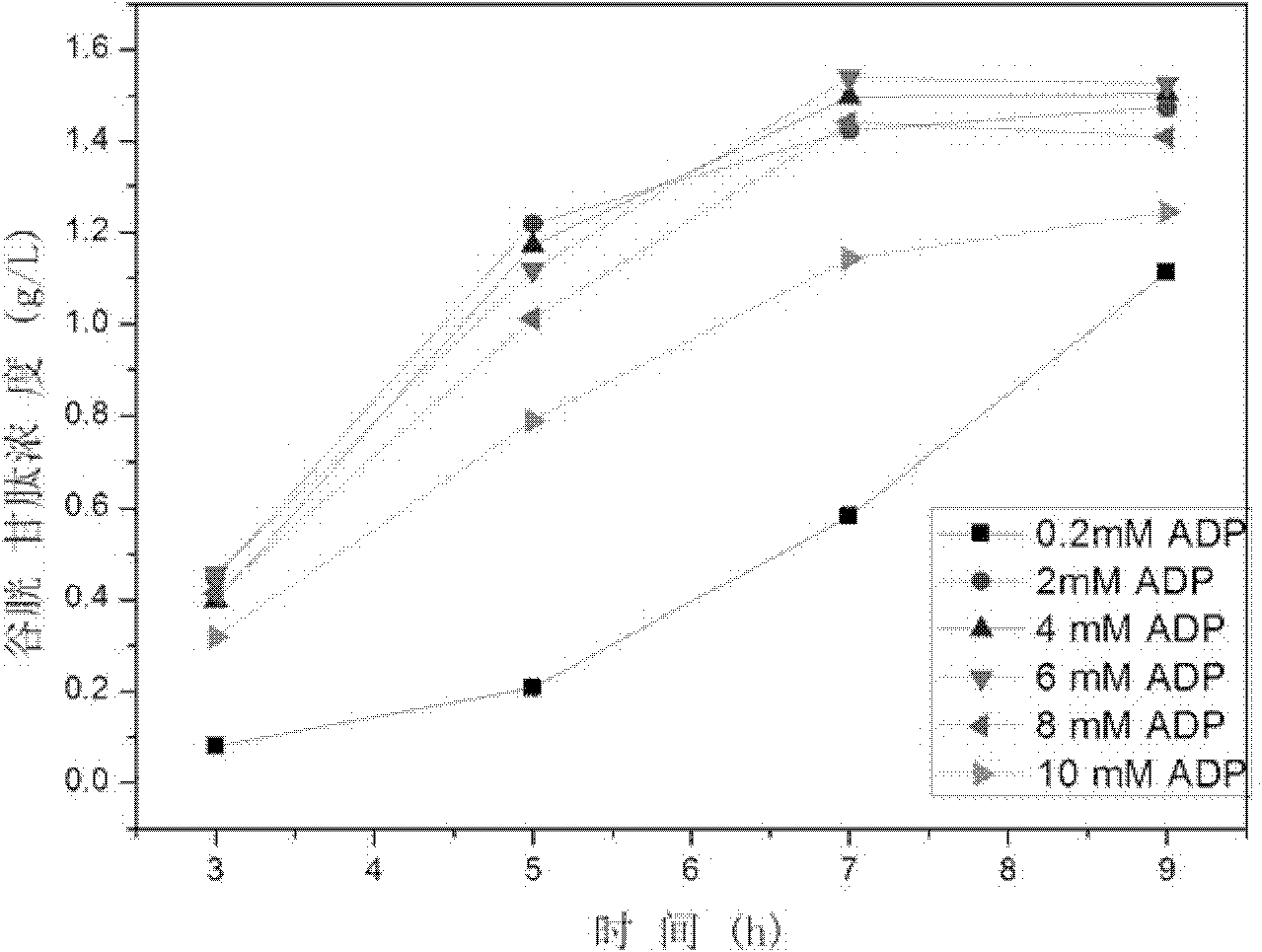
The invention relates to a method for synthesis of glutathione in vitro, comprising the step of: generating ATP (adenosine triphosphate) from ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and polyphosphoric acid compound under the catalysis of polyphosphate kinase; under the catalysis of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase and glutathione synthetase, synthesizing glutathione in vitro by glutamic acid, cysteine and glycine with the energy provided by the ATP. Compared with the prior art, the method of the invention can bring enzymes into complete contact with a substrate so as to improve the mass transfer efficiency and the utilization rate of enzymes. And the reaction system of the method is simple and strong in controllability. In addition, the method can solve the problem of great investment of ATP during production and reduce the production cost.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
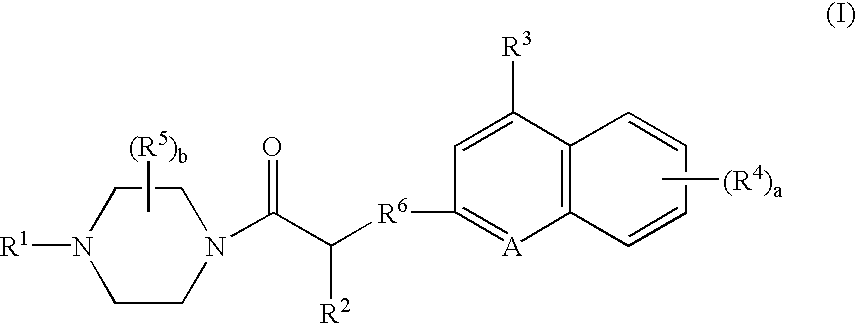
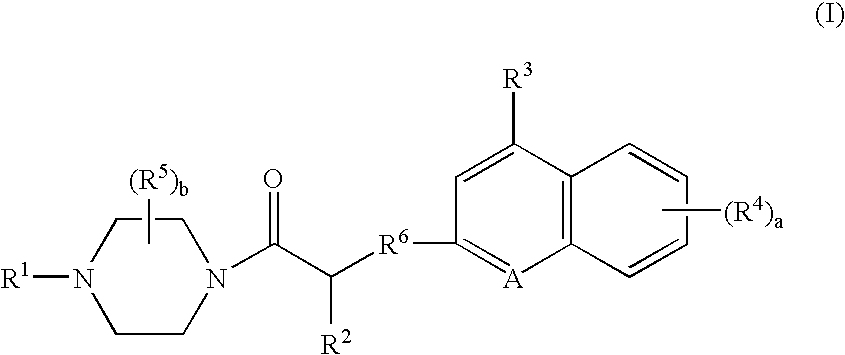
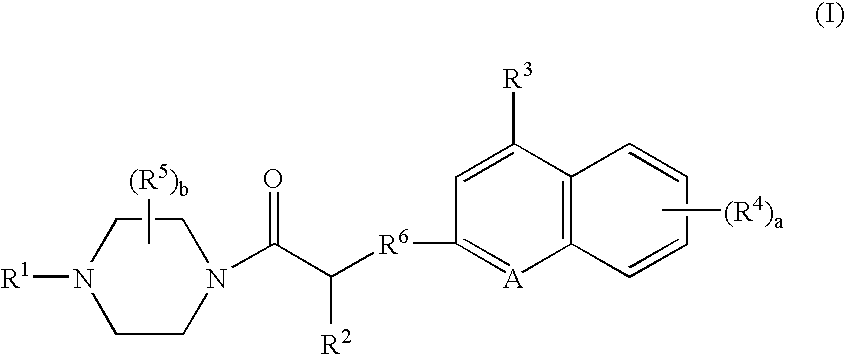
Platelet adenosine diphosphate receptor antagonists
InactiveUS6861424B2Organic chemistryBlood disorderAdenosine Diphosphate Receptor AntagonistsAntithrombotic Agent
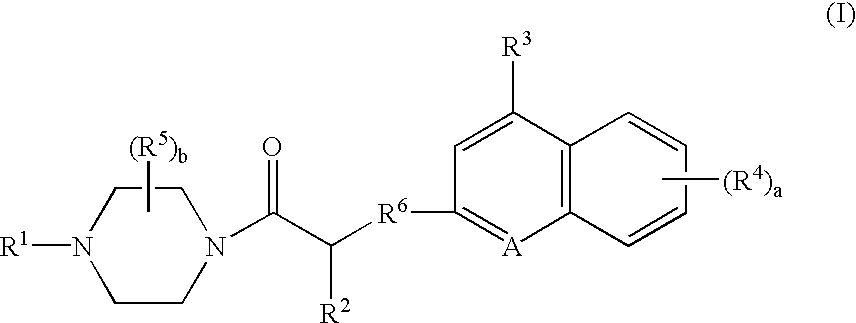
Compounds of the following formula (I): where a, b, R1, R2, R3, R4 and R6 are described herein, are useful as inhibitors of platelet adenosine diphosphate. Pharmaceutical compositions containing these compounds, methods of using these compounds as antithrombotic agents and processes for synthesizing these compounds are also described herein.
Owner:SCHERING AG
Platelet adenosine diphosphate receptor antagonists
InactiveUS20050038037A1Organic chemistryBlood disorderAdenosine Diphosphate Receptor AntagonistsAntithrombotic Agent
Compounds of the following formula (I): where a, b, R1, R2, R3, R4 and R6 are described herein, are useful as inhibitors of platelet adenosine diphosphate. Pharmaceutical compositions containing these compounds, methods of using these compounds as antithrombotic agents and processes for synthesizing these compounds are also described herein.
Owner:SCHERING AG
Medical prosthetic devices and implants having improved biocompatibility
InactiveUS20060155384A1Electrolytic inorganic material coatingBone implantZirconium hydrideEnzyme Inhibitor Drugs
A medical prosthetic device or medical implant containing a metal material (A) selected from the group consisting of titanium or an alloy thereof, zirconium or an alloy thereof, tantalum or an alloy thereof, hafnium or an alloy thereof, niobium or an alloy thereof and a chromium-vanadium alloy, wherein surface parts of the metal material (A) are coated with a layer of a corresponding hydride material (B) selected from titanium hydride, zirconium hydride, tantalum hydride, hafnium hydride, niobium hydride and chromium and / or vanadium hydride, respectively, said device or implant being characterised in that the layer of hydride material (B) comprises one or more biomolecule substances (C) associated therewith. The device or implant exhibits improved biocompatibility. The metal material (A) is preferably titanium. The biomolecule substance (C) may be selected from the following types of substances: Natural or recombinant bio-adhesives; natural or recombinant cell attachment factors; natural, recombinant or synthetic biopolymers; natural or recombinant blood proteins; natural or recombinant enzymes; natural or recombinant extracellular matrix proteins; natural or synthetic extracellular matrix biomolecules; natural or recombinant growth factors and hormones; natural, recombinant or synthetic peptide hormones; natural, recombinant or synthetic deoxyribonucleic acids; natural, recombinant or synthetic ribonucleic acids; natural or recombinant receptors; enzyme inhibitors; drugs; biologically active anions and cations; vitamins; adenosine monophosphate (AMP), adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or adenosine triphosphate (A TP); marker biomolecules; amino acids; fatty acids; nucleotides (RNA and DNA bases); and sugars.
Owner:NUMERICAL TECH INC
Method for measuring royal jelly
InactiveCN101320030AFreshness JudgmentHigh sensitivityComponent separationMaterial analysis by optical meansInosinic acidPhosphoric acid
The invention relates to a freshness detecting method used for royal jelly. In the specific detecting method, the contents of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), adenosine diphosphate (ADP), single phosphoric acid adenosine (AMP), inosinic acid (IMP), hypoxanthine riboside (HxR), hypoxanthine (Hx), adenine and adenosine of the royal jelly are quantitatively determined through methods of liquid chromatography or ultraviolet spectrometry, and the like; the ratio (F value) between the accumulation amount of adenine, adenosine, HxR and Hx and the sum of the qualities of the eight substances (degradation products of ATP and nucleic acid)is calculated; the F value of the royal jelly is used for detecting the freshness of the royal jelly and judging the quality of the royal jelly. Compared with a present royal jelly quality detecting method, the freshness detecting method can judge the quality and the freshness of the royal jelly more accurately and sensitively, can improve the quality standard of the present royal jelly and effectively monitor the quality of the royal jelly.
Owner:BEE RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Inhibitors of ADP-ribosyl transferases, cyclases, and hydrolases
The present invention provides compounds having the formula: wherein A is a nitrogen-, oxygen-, or sulfur-linked aryl, alkyl, cyclic, or heterocyclic group, the group being further substituted with an electron contributing moiety; B is hydrogen, or a halogen, amino, or thiol group; C is hydrogen, or a halogen, amino, or thiol group; and D is a primary alcohol, a hydrogen, or an oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, or sulfur linked to phosphate, a phosphoryl group, a pyrophosphoryl group, or adenosine monophosphate through a phosphodiester or carbon-, nitrogen-, or sulfur-substituted phosphodiester bridge, or to adenosine diphosphate through a phosphodiester or carbon-, nitrogen-, or sulfur-substituted pyrophosphodiester bridge.The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions containing the above compounds, methods of using the above compounds as pharmaceuticals, and processes for preparing the above compounds.Also provided are methods for inhibiting an ADP-ribosyl transferase, ADP-ribosyl cyclase, ADP-ribosyl hydrolase, or NAD-dependent deacetylase enzyme, and methods for treating a disease or condition associated with an ADP-ribosyl transferase, ADP-ribosyl cyclase, ADP-ribosyl hydrolase, or NAD-dependent deacetylase enzyme in a subject in need of treatment thereof.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
Serum creatine kinase detection reagent
ActiveCN104374905AHigh activityEfficient removalMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAcyl CoA dehydrogenaseSODIUM DODECYL BENZENE SULFONATE
The invention discloses a creatine jubase detection reagent. The reagent disclosed by the invention consists of a reagent R1 and a reagent R2 according to a volume ratio being 4 to 1, wherein the reagent R1 consists of an imidazole buffer solution, glucose, nano particles, N-acetylcysteine, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt, adenosine diphosphate, coenzyme I, adenine ribonucleotide, pyruvate decarboxylase, 6-phosphogluconic dehydrogenase, hexokinase and sodium dodecyl benzene sulphonate; and the reagent R2 consists of an imidazole buffer solution, phosphocreatine, a preservative and sodium dodecyl benzene sulphonate. Pyruvate decarboxylase and gamma-Fe2O3 nano particles are added into the creatine jubase detection reagent disclosed by the invention, so that interfering substances in a serum sample can be effectively eliminated, metal ions in the serum sample are chelated by matching sodium dodecyl benzene sulphonate and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt, the influence on reaction enzymes is alleviated, and the reagent is a stable, accurate and sensitive detection reagent with high interference resistance.
Owner:BIOBASE BIODUSTRY (SHANDONG) CO LTD
Energy-protective composition comprising adenosine phosphates
Compositions comprising the nucleotides adenosine diphosphate and adenosine monophosphate, and their use for neutralizing effects of excess incident energy on the human body, particularly effects of ionizing radiation from nuclear or radiological energy sources, are disclosed and claimed.
Owner:N R YOUSSEF
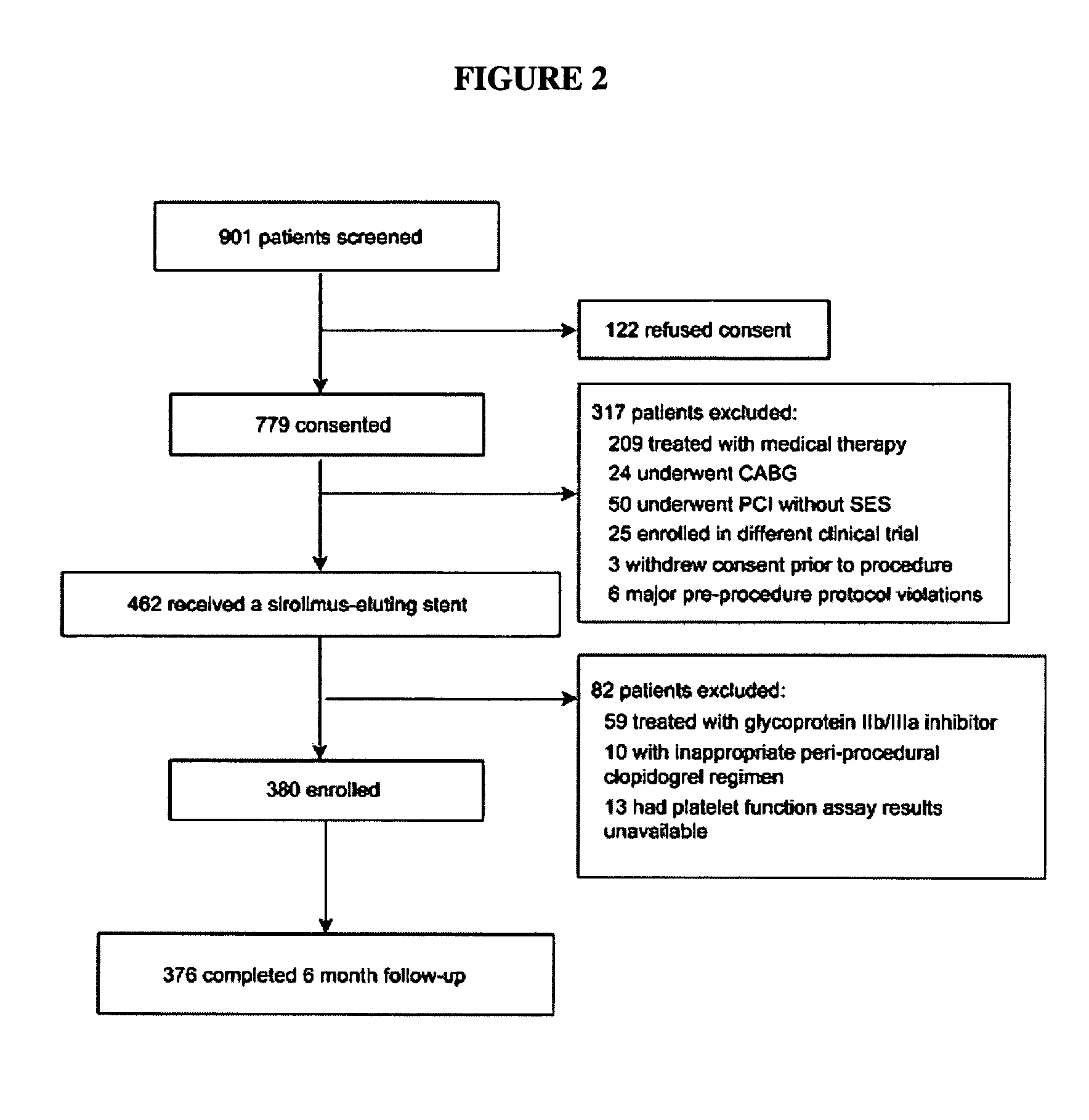
Methods for measuring platelet reactivity of individuals treated with drug eluting stents
ActiveUS9506938B2Elcosanoid active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAdenosineAdenosine diphosphate
A method is provided for measuring inhibition of platelet reactivity in an individual treated with a drug-eluting stent (DES). First, a blood sample is obtained from an individual treated with a DES and a P2Y12 antagonist. The blood sample is then mixed with particles comprising an attached GPIIb / IIIa receptor ligand, adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and prostaglandin E1 (PGE1). The mixture is incubated under conditions suitable for agglutinating particles, and platelet-mediated agglutination is assessed in the mixture. The absence or reduction of agglutination indicates that the individual treated with a DES has reduced platelet reactivity. Also provided is a kit for measuring inhibition of platelet aggregation by a P2Y12 receptor antagonist that includes a GPIIb / IIIa receptor ligand immobilized on a particle, adenosine diphosphate (ADP), prostaglandin E1 (PGE1), an anticoagulant, and a buffer to maintain the anticoagulated blood in a condition suitable for platelet aggregation.
Owner:INSTR LAB
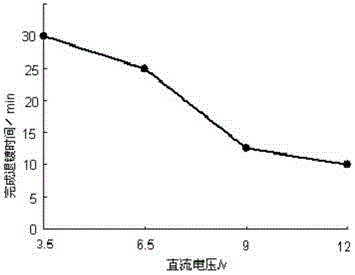
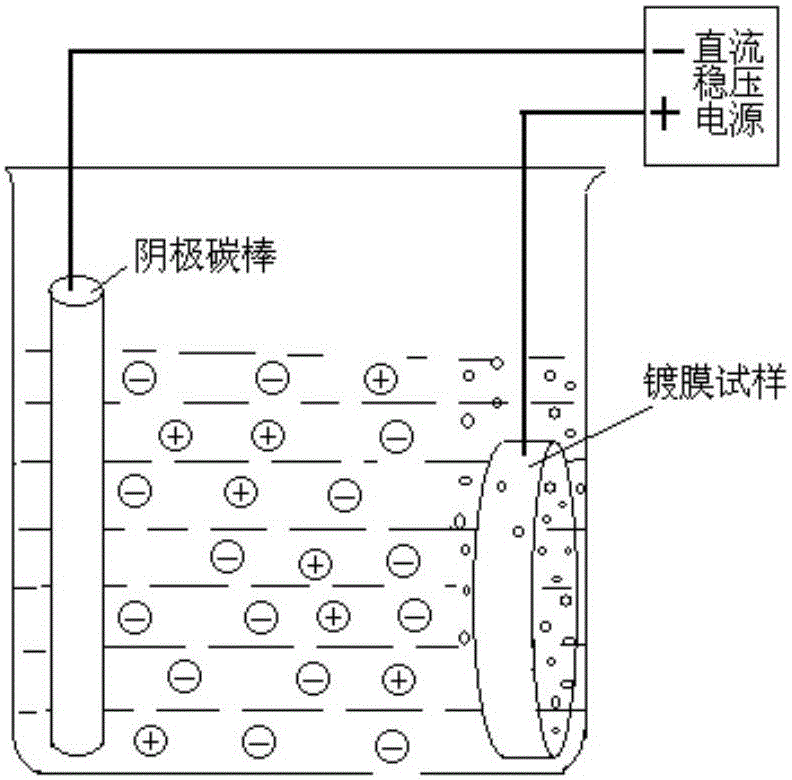
Deplating method for magnetic control sputtering graphite carbon film
ActiveCN105088325AImprove stabilityGood stability, can efficiently remove high-efficiencyCarbon filmElectrolysis
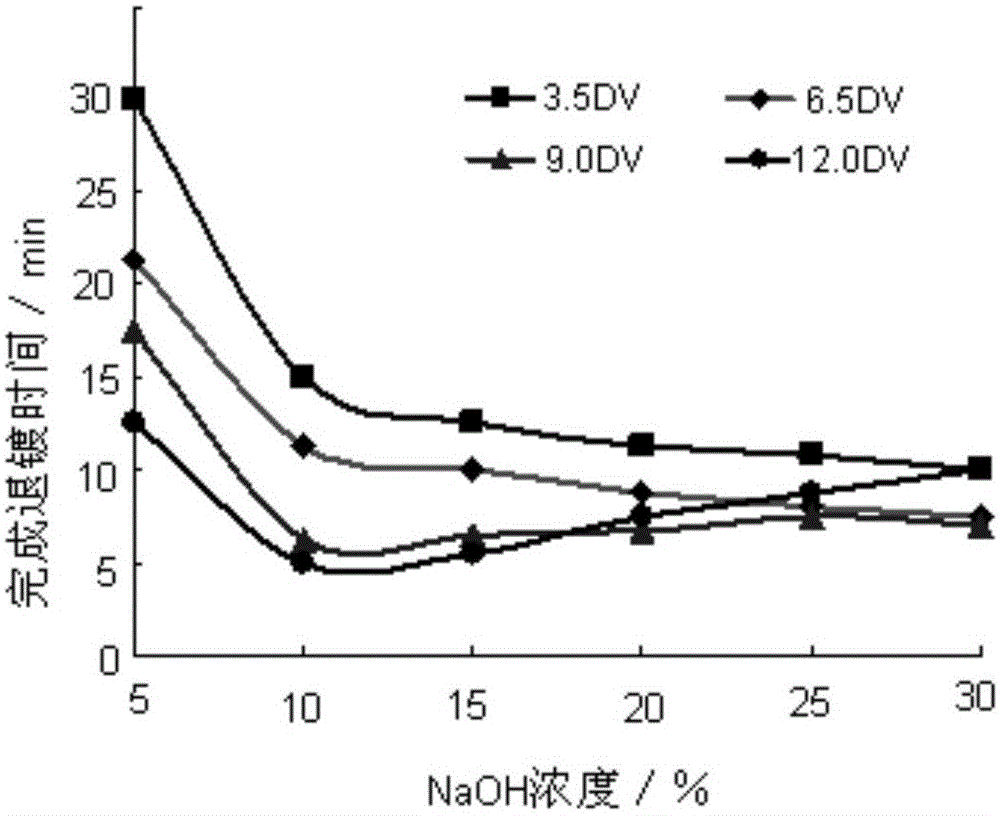
The invention provides a deplating method for a magnetic control sputtering graphite carbon film. According to the deplating method, 1 L of distilled water is taken, 10-200 g of sodium hydroxide and 5-50 g of sodium carbonate are added to be stirred evenly, 5-20 g of surfactant dodecyl alcohol amine is added to the obtained solution to be evenly stirred, and 3-15 g of antiseptic complexing agent trimerization ammonium phosphate and 1-4 g of corrosion inhibitor adenosine diphosphate are added into the mixture; a formed substrate of the magnetic control sputtering graphite carbon film is soaked in deplating liquid at the temperature of 50 DEG C to 90 DEG C, the deplating liquid serves as electrolyte, electrolysis is conducted at the direct-current voltage of 3.5 V to 12 V, the electrolysis time ranges from 5 minutes to 30 minutes, the magnetron sputtering graphite carbon film is removed, the deplated substrate is washed and dried, and the deplating process is completed. The method is efficient and good in stability and has higher practical value.
Owner:CSIC NO 12 RES INST
Creatine kinase isoenzyme detection reagent
ActiveCN104374925AHigh activityEfficient removalBiological testingSodium acetateAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention discloses a creatine kinase isoenzyme detection reagent. The reagent consists of a reagent R1 and a reagent R2 according to the volume ratio of 4 to 1, wherein the reagent R1 consists of an imidazole buffer liquid, glucose, nano particles, N-acetylcysteine, sodium ethylene diamine tetracetate, adenosine diphosphate, cozymase I, ribonucleotide, pyruvate decarboxylase, glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase, hexokinase, a goat anti-human CK-M polyclonal antibody and trehalose; the reagent R2 consists of an imidazole buffer liquid, phosphocreatine, sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate and a preservative. The reagent disclosed by the invention is a creatine kinase isoenzyme detection reagent which is stable, accurate, and high in anti-interference, and has very high clinical application value.
Owner:BIOBASE BIODUSTRY (SHANDONG) CO LTD
Creamy o/w emulsion composition and production process thereof
ActiveUS20110112045A1Improve emulsion stabilityEffective displayBiocideCosmetic preparationsEmulsionAlcohol
A major object of the present invention is to provide a creamy O / W emulsion composition containing an adenosine phosphate ester, more specifically, to provide a creamy O / W emulsion composition containing an adenosine phosphate ester, which ensures emulsification stability and a superior feel during use. Specifically, the present invention provides a creamy O / W emulsion composition containing the following Components (A) to (F) at the following proportions based on its total amount:(A) not less than 0.1 wt. % of adenosine phosphate ester selected from at least one member selected from the group consisting of cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate, adenosine monophosphate, adenosine diphosphate, adenosine triphosphate, and salts thereof;(B) 0.5 to 6 wt. % of polyglycerin fatty acid ester;(C) 0.05 to 0.7 wt. % of acrylic acid-alkyl methacrylate copolymer;(D) 0.5 to 10 wt. % of amphiphilic lipid;(E) 0.5 to 20 wt. % of polyhydric alcohol; and(F) 0.3 to 5 wt. % of self-emulsifiable glycerin fatty acid ester.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
Polypeptide used for prevention and treatment of acute coronary syndrome and anticoagulation antithrombotic therapy and application thereof
ActiveCN102241735ATetrapeptide ingredientsTripeptide ingredientsHuman plateletFemoral artery thrombosis
Owner:SHAANXI MICOT TECH LTD
Fluorescent probe for selectively identifying ATP based on aggregation-induced fluorescence enhancement characteristic, synthetic method and application thereof
ActiveCN106814057AOvercoming easy bleachingOvercoming detectionFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh concentrationATP Hydrolase
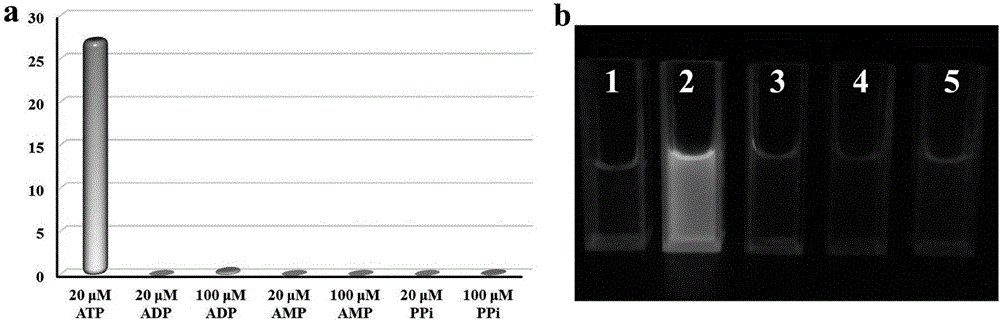
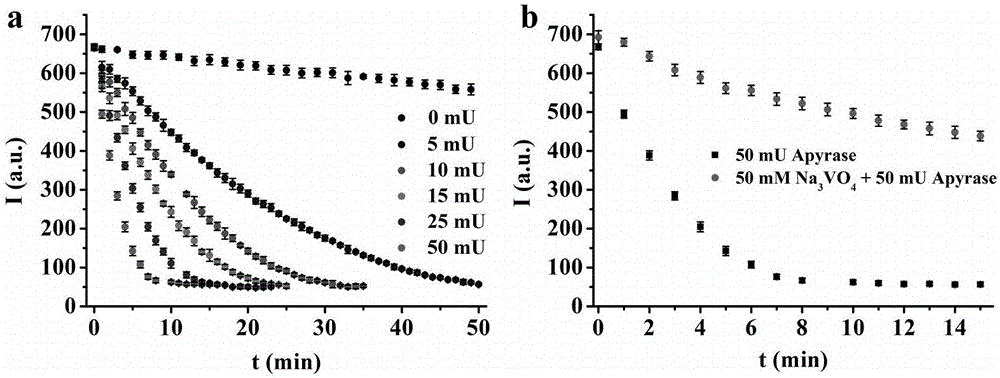
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe for selectively identifying ATP (adenosine triphosphate) based on an aggregation-induced fluorescence enhancement characteristic, a synthetic method and an application thereof. The fluorescent probe 1 is synthesized by taking a benzophenone derivative as a starting material. The invention carries out a detection research on ATP, ADP (adenosine diphosphate), AMP (adenosine monophosphate) and pyrophosphoric acid (PPi) with the fluorescent probe 1, and discoveries that the fluorescent probe has very good sensitivity and selectivity to ATP; compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages that the synthetic raw material is easy to obtain, the fluorescent probe has high fluorescence quantum yield and strong photobleaching resistance, and the like, and avoids the defect that a conventional fluorescent dye is not suitable for detection under a high concentration; in addition, the fluorescent probe 1 is successfully used for monitoring a reaction process of ATP hydrolase Apyrase in a solution, and is also used for imaging research of ATP in cells. Therefore, the fluorescent probe 1 has a great application prospect in the aspect of detecting the content of in vivo ATP.
Owner:GANNAN NORMAL UNIV
Stable compound coenzyme preparation as well as preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104623626AGood repeatabilityReduce lossOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryFlavin adenine dinucleotideDisease
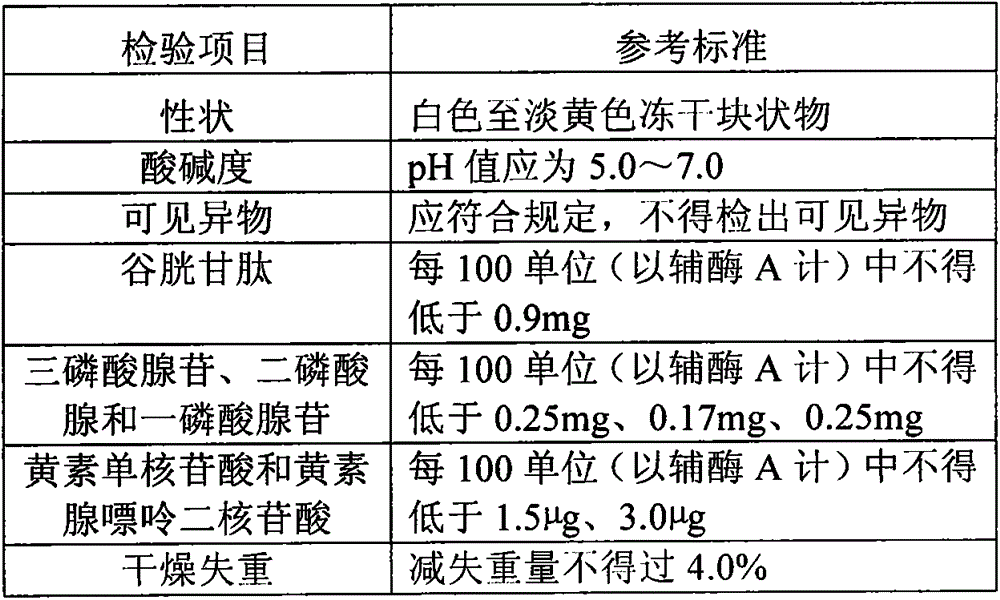
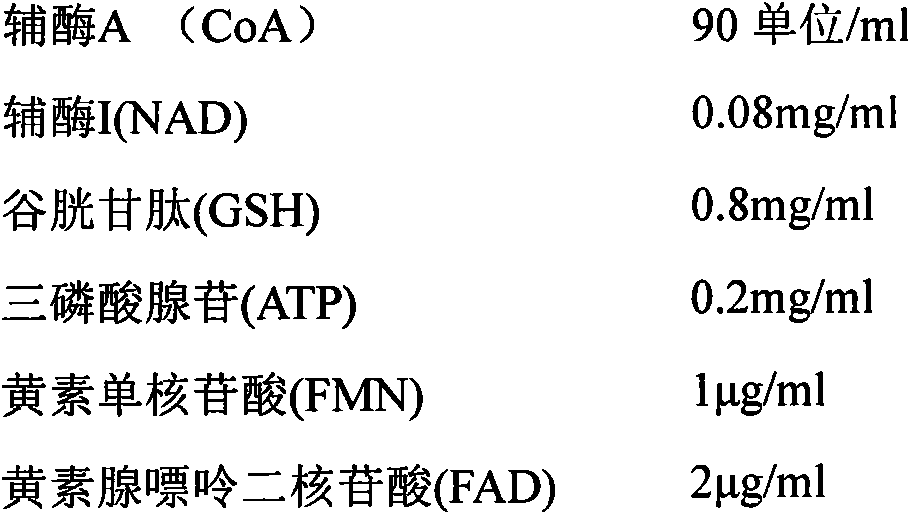
The invention provides a stable compound coenzyme preparation and a preparation method thereof. The main compositions and proportions of the stable compound coenzyme preparation are as follows: 90-120 U of coenzyme A (CoA), 0.1-0.3 mg / ml coenzyme I (NAD), 1-5 mg / ml glutathione (GSH), 1-2.5 mg / ml adenosine triphosphate (ATP), 1.8-12 mu g / ml flavin mononucleotide (FMN), 3-13 mu g / ml flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), 0.1-0.4 mg / ml adenosine diphosphate (ADP), 0.2-0.4 mg / ml adenosine monophosphate (AMP), 1.2-15 mu g / ml of adenosine methionine (SAM), 1-5 mg / ml calcium gluconate, 0.5-1.5 mg / ml cysteine hydrochloride, and 0.6-5 mg / ml mannitol. The preparation method overcomes the defects that high-speed centrifugalization is adopted, freeze-drying conditions are not clear and the product stability is poor in the existing method, and the stable compound coenzyme preparation is widely applied to the practices of preparing drugs for treating cardia-cerebrovascular diseases and digestive system diseases.
Owner:BEIJING SL PHARMA +2
Cracking aptamer sensor for ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) detection and application thereof
ActiveCN109406467ASignificant signal amplificationGood choiceFluorescence/phosphorescenceAptamerSerum samples
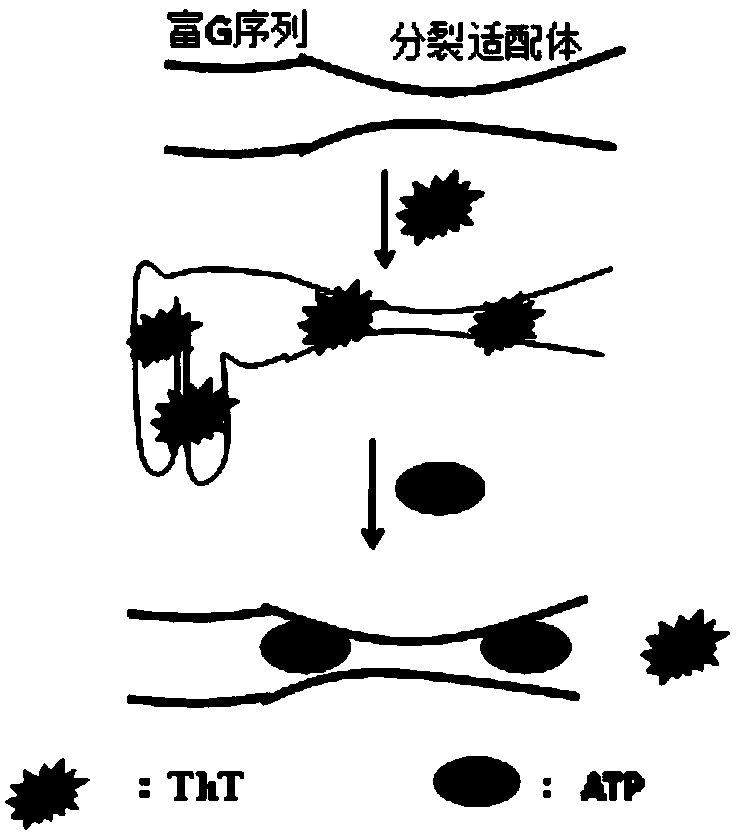
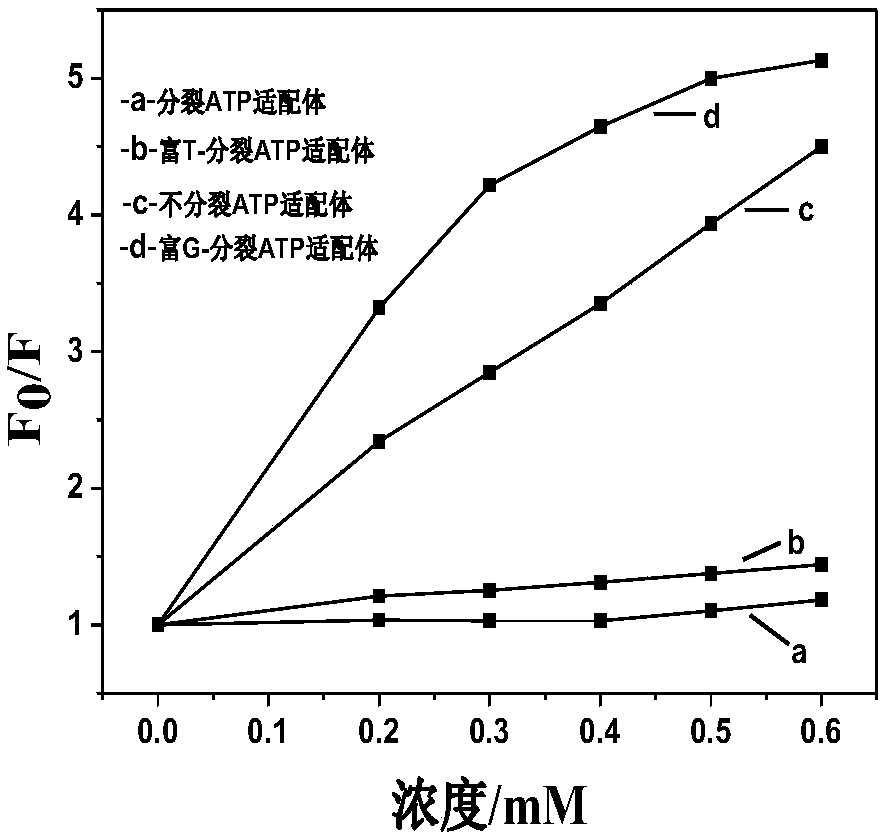
The invention discloses a cracking aptamer sensor for ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) detection and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of biochemistry. According to the cracking aptamer sensor, G-enriched sequences are modified to tail ends of two cracked ATP aptamer segments. ThT and two G-enriched ATP cracking aptamers have a mutual effect to form a fluorescence compound which is better than a complete aptamer / ThT compound. The G-enriched sequences can be used for improving a fluorescence signal, so that the sensitivity of a novel method is improved. With the help of the G-enriched sequences, the detection limit of the ATP aptamer sensor is 5 nM. The method has a good linear relation on ATP from 100 nM to 120 muM. Compared with a ThT substitution based complete aptamer for the ATP detection, which is reported before, the aptamer sensor provided by the invention is more sensitive and has a wider dynamic linear range; the selectivity to ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate), AMP(Adenosine Monophosphate) and the like is obviously improved. The aptamer sensor can be used for detecting the ATP in a complicated biological serum sample.
Owner:SHANGQIU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
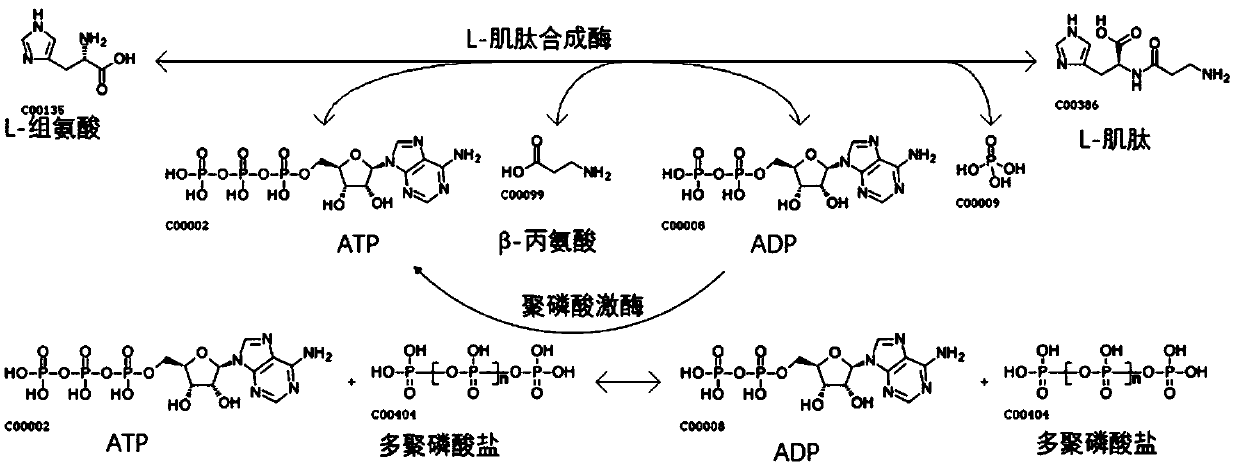
Method of synthesizing L-carnosine using L-amino acid ligase by one-step method
ActiveCN109593805AAchieve recyclingWide variety of sourcesTransferasesNucleic acid vectorPhosphorylationL-Carnosine
The invention discloses a method of synthesizing L-carnosine using L-amino acid ligase by a one-step method. The method comprises the steps of taking beta-alanine, L-histidine, ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and polyphosphate as raw materials, and MgCl2 as an activator, adding L-amino acid ligase and polyphosphate kinase, and synthesizing L-carnosine through an enzymatic reaction and coupled coupleunder conditions of a pH of 6.5-8.5 and a temperature of 30-45 DEG C. According to the method, a sequence optimized L-amino acid ligase gene is successfully expressed in escherichia coli, and beta alanine and L-histidine can be catalyzed to synthesize L-carnosine at one step. A substrate is not required to be methylated or subjected to group protection; ATP required by a catalytic reaction is continuously regenerated by allowing polyphosphate kinase to catalyze phosphorylation of ADP (adenosine diphosphate); cyclic regeneration of ATP can be achieved only by consuming a small amount of ADP; and a renewable raw material, sodium hexametaphosphate, is wide in source, low in cost, simple to operate and easy in large-scale production.
Owner:苏州百因诺生物科技有限公司
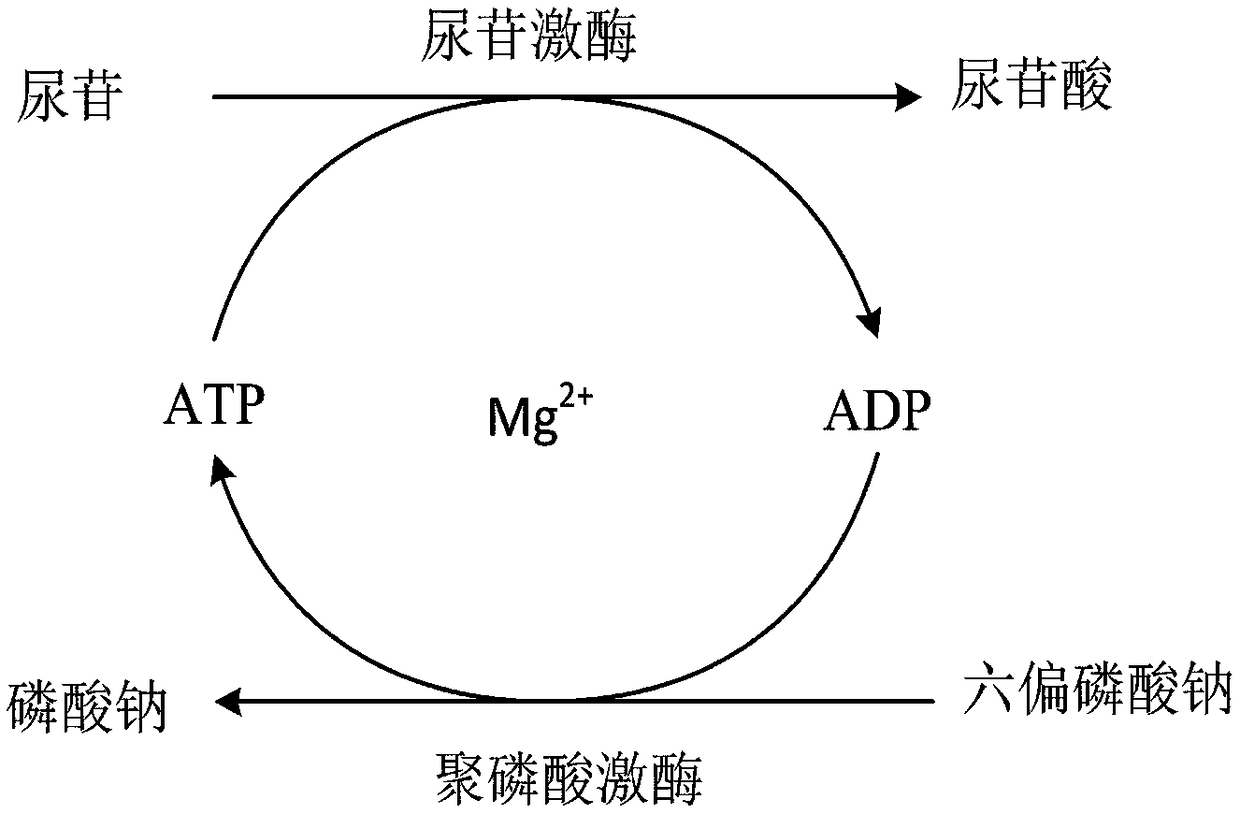
Enzyme preparation for preparing uridylic acid and method for preparing uridylic acid through enzyme catalysis
ActiveCN109161536AWide variety of sourcesPromote regenerationBacteriaTransferasesPhosphorylationEnzyme catalysis
The invention relates to an enzyme preparation for preparing uridylic acid and a method for preparing the uridylic acid through enzyme catalysis. The method comprises the following steps: taking a material liquid containing uridine as a substrate, adding an escherichia coli cell crushing liquid with activity of uridine kinase and poly-phosphokinase, sodium hexametaphosphate, magnesium sulfate anda small amount of ATP (Adenosintriphosphat), and carrying out an enzymatic reaction under conditions that the pH value is 8.0 and the temperature is 30 DEG C to synthesize the uridylic acid. In a coupling catalysis reaction system, the uridine and the ATP are catalyzed by the uridine kinase to generate the uridylic acid, and ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate) is formed along with the dephosphorylation ofthe ATP. Poly-phosphokinase is in charge of catalyzing the sodium hexametaphosphate and the ADP to generate the ATP, so that the regeneration of the ATP is achieved in reactions. The uridylic acid production method provided by the invention has the advantages of being low in raw material price, short in period, simple and convenient to operate, green and environmentally-friendly and high in yield, and has good industrial application value.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
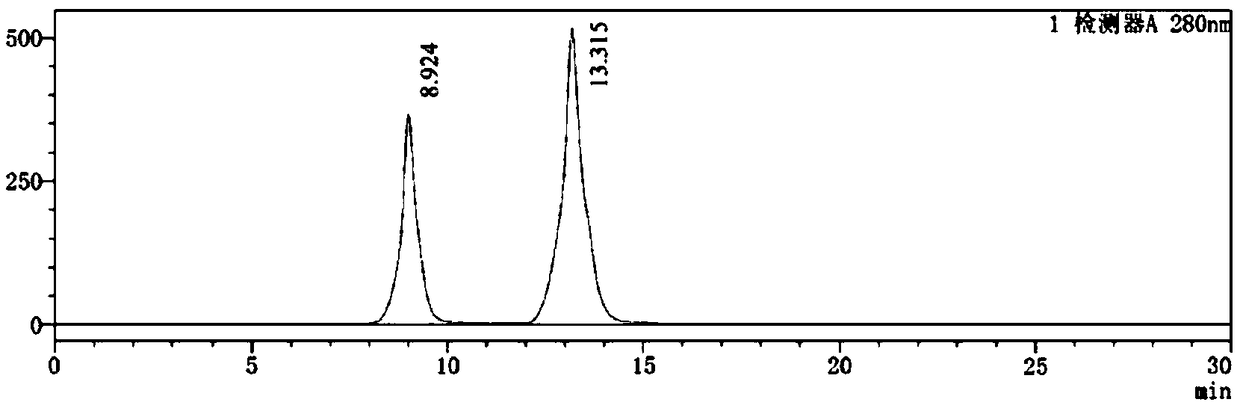
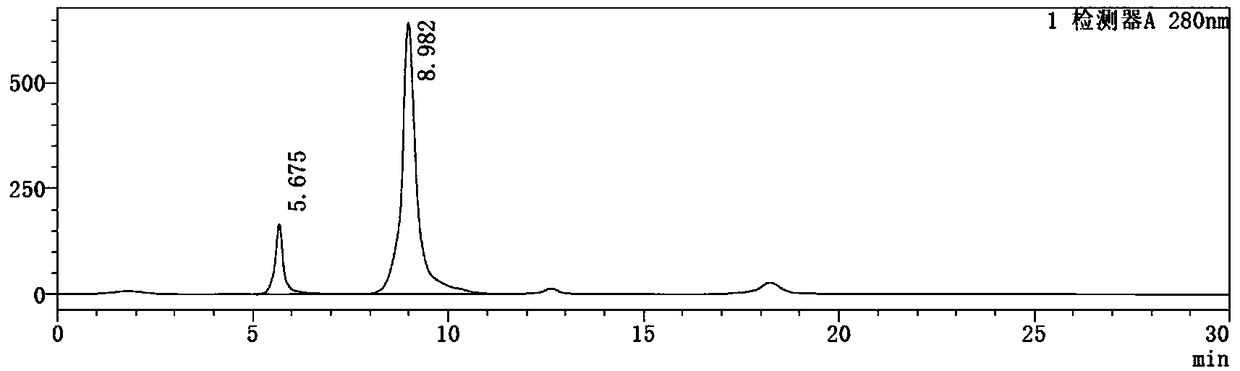
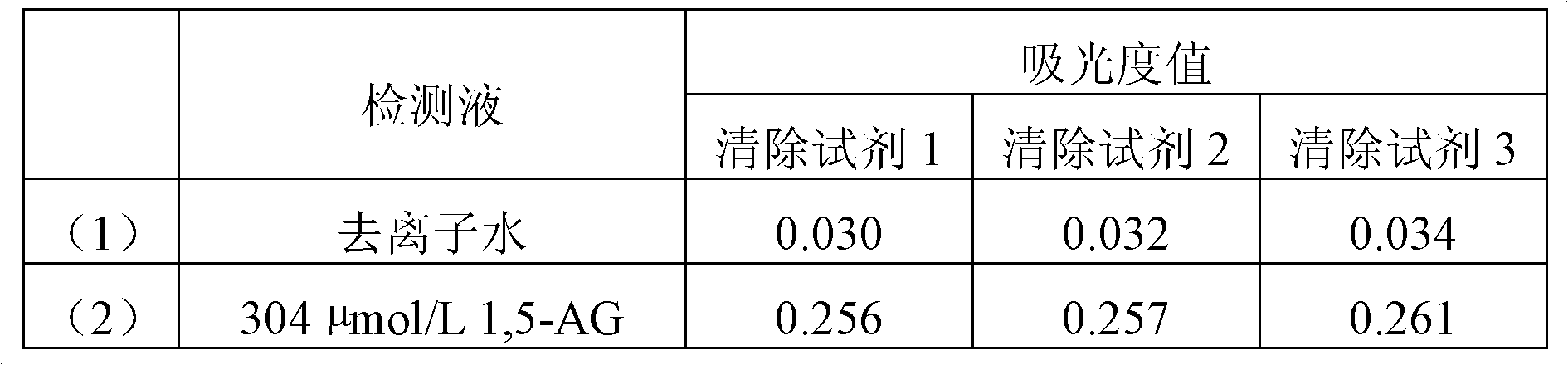
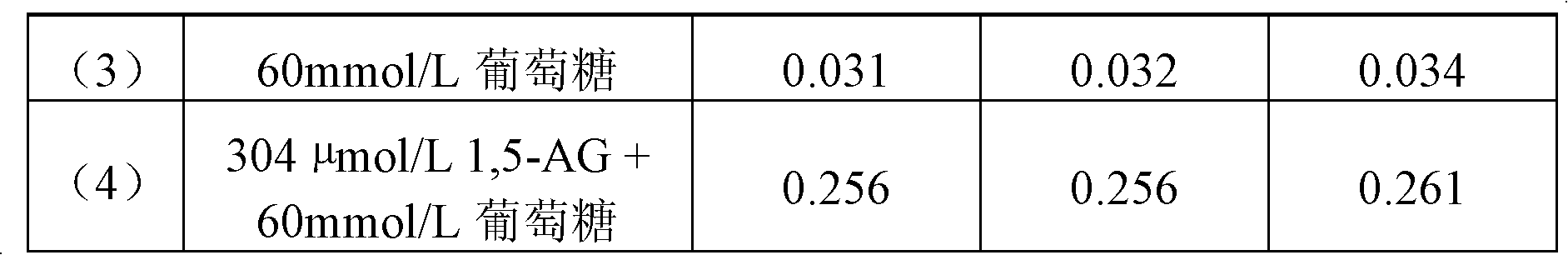
High-concentration glucose removal method and kit for determining serum 1,5 anhydro-D-glucitol based on pyranose oxidase method
The invention discloses a high-concentration glucose removal method for determining serum 1,5 anhydro-D-glucitol based on a pyranose oxidase method, which comprises the following steps: preparing a 2-morpholinoethanesulfonic acid (MES) buffer solution having a pH value of 6.0-9.0, wherein the MES buffer solution contains a certain amount of glucokinase (GK), glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP), pyruvate kinase (PK), phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP); and adding into a serum sample containing glucose (Glu), and reacting at 20-50 DEG C for 3-5 minutes, wherein the GK converts the Glu into glucose-6-phosphoric acid (G6P) in the presence of the ATP, and adenosine diphosphate (ADP) is generated at the same time; the G6P is further converted into glucose-6-phosphate lactone (G6PL) by the G6PD in the presence of the NADP+; and the ADP generated in the reaction is converted into ATP again under the action of thePK in the presence of the PEP. The glucose removal agent prepared by the method can be stably stored at 2-8 DEG C for 14 months, and can be used for a clinical biochemical autoanalyzer extensively used at present.
Owner:浙江夸克生物科技有限公司
Medicine for treating ischemic angiocardiopathy and cerebrovascular disease and its preparation method
InactiveCN1413655AImprove blood and oxygen supplyBlood supply and oxygen supply adjustmentUnknown materialsCardiovascular disorderDiseaseAcute myocardial ischaemia
A Chinese medicine for treating ischemic cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases is prepared from 3 Chinese-medicinal materials ginseng, red sage root and corydalis tuber through extracting, separating by adsorptive resin, eluting and concentrating. Its advantages are high curative effect and low cost.
Owner:刘建勋
Brewer's yeast recombined hepatitis B virus surface antigen stream plus addition femrentation
ActiveCN1552857AImprove toleranceIncreased weight-to-weight productivityFungiImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHepatitis B Surface AntigensAdenosine diphosphate
A hepatitis B surface antigen is produced with beer yeast engineering bacteria. The process is carried out by: 1) fermenting seeds of the beer yeast engineering bacteria, 2) fermenting by the said seeds, and 3) separating and purifying fermented mixture to obtain hepatitis B surface antigen, specially, flow adding adenine, adenosine, adenosine monophosphate, adenosine diphosphate or adenosine triphosphate at the rate of 14mg / L.h by weight into its culture medium in the said step 2. It achieves in higher expression level of recombined HBsAg.
Owner:BEIJING BIOLOGICAL PROD INST CO LTD +1
Detection method of poly(adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase
InactiveCN105606671AEnable label-free detectionSimple methodMaterial electrochemical variablesSignalling moleculesPolyadenosine diphosphate ribose polymerase
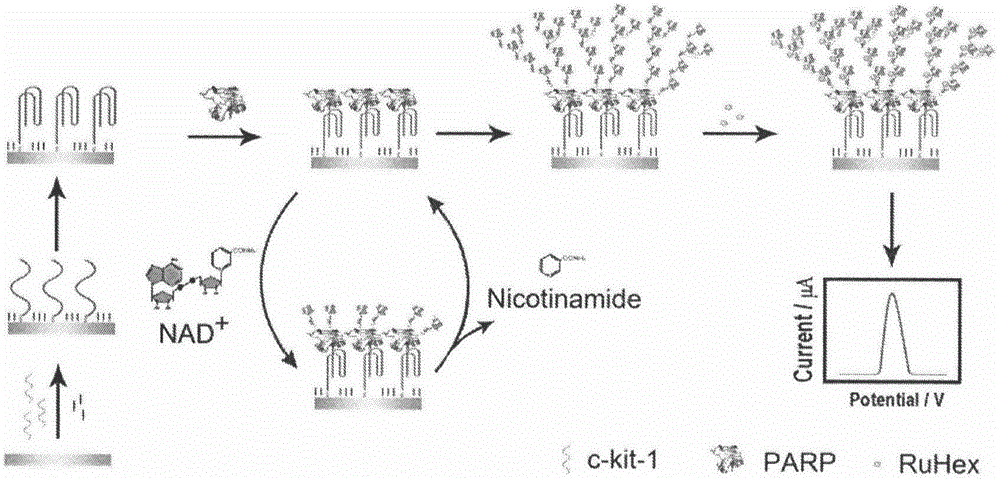
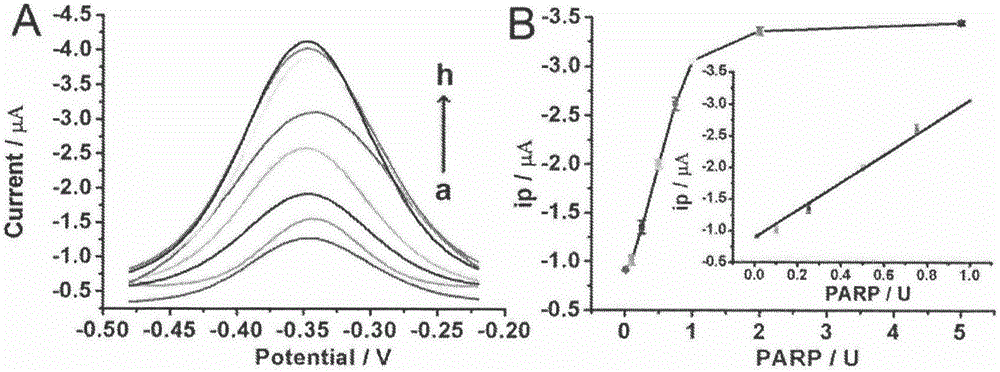
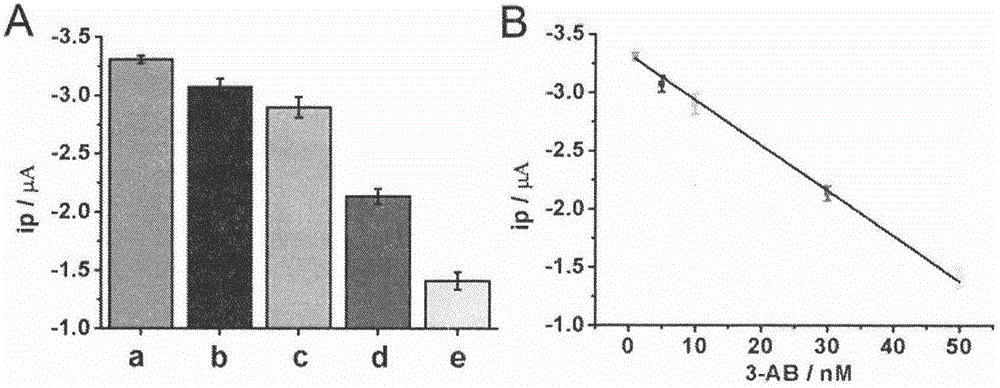
The invention belongs to the technical field of analytical chemistry and relates to a detection method and application of PARP [poly(adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase]. The detection method mainly includes: modifying a single-stranded DNA (c-kit-1) capable of specifically binding with the PARP on the surface of a gold electrode in a classical mercapto self-assembly mode and enabling c-kit-1 to form a tetramer configuration through treatment; after the tetramer configuration is incubated with the PARP, adding a specific catalytic substrate, namely NAD (nicotinamide ademinedinucleotide) of the PARP, to enable the PARP to self-catalyze to produce PAR with high negative charges; using the negative charges of the PAR for adsorbing electrical signal molecules RuHex with positive charges, quantifying the RuHex adsorbed on the surface of the electrode through an electroanalysis method, and drawing a standard curve according to a relation between electrochemical signals and PARP concentration so as to achieve sensitive PARP detection by measuring the electrochemical signals of to-be-detected samples and calculating. The detection method is high in repeatability and sensitivity and can be applied to detection of the PARP and an inhibitor 3-AB (3-aminobenzamide) thereof.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Process for determining content of potassium ion by enzyme method and kit for diagnosing potassium ion thereof
InactiveCN1786692AStrong specificityThe test result is accurateAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionColor/spectral properties measurementsLactate dehydrogenasePhosphoric acid
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
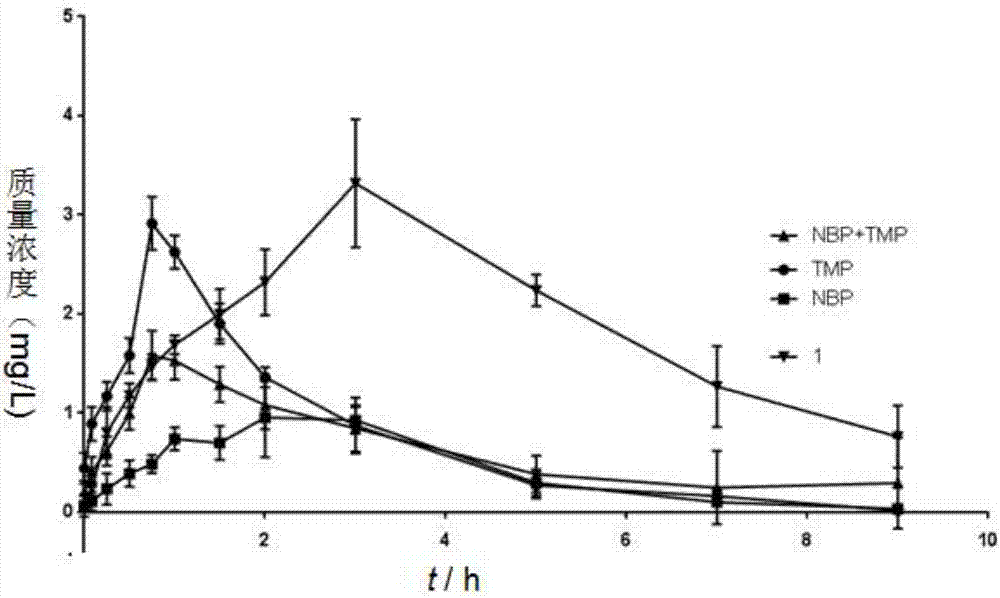
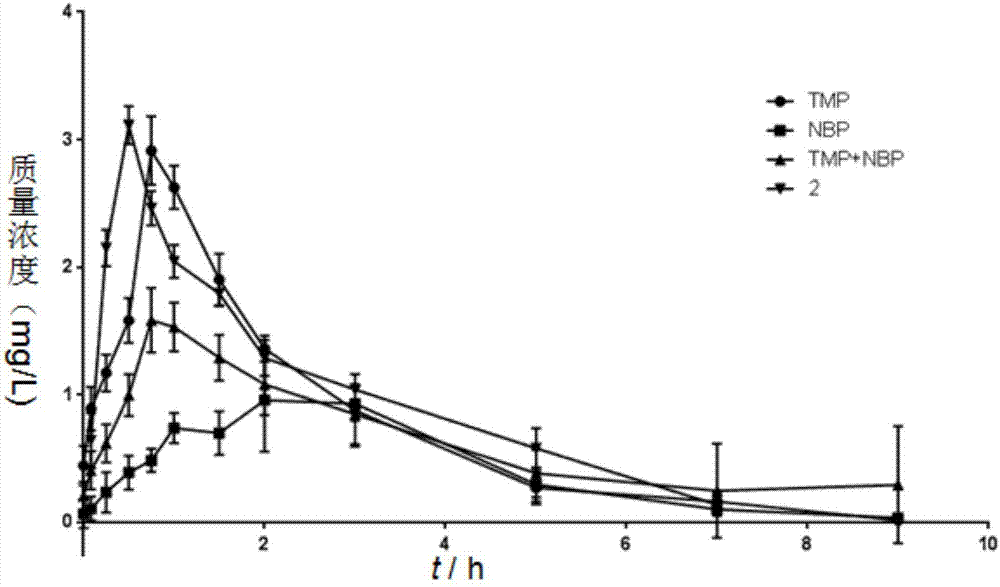
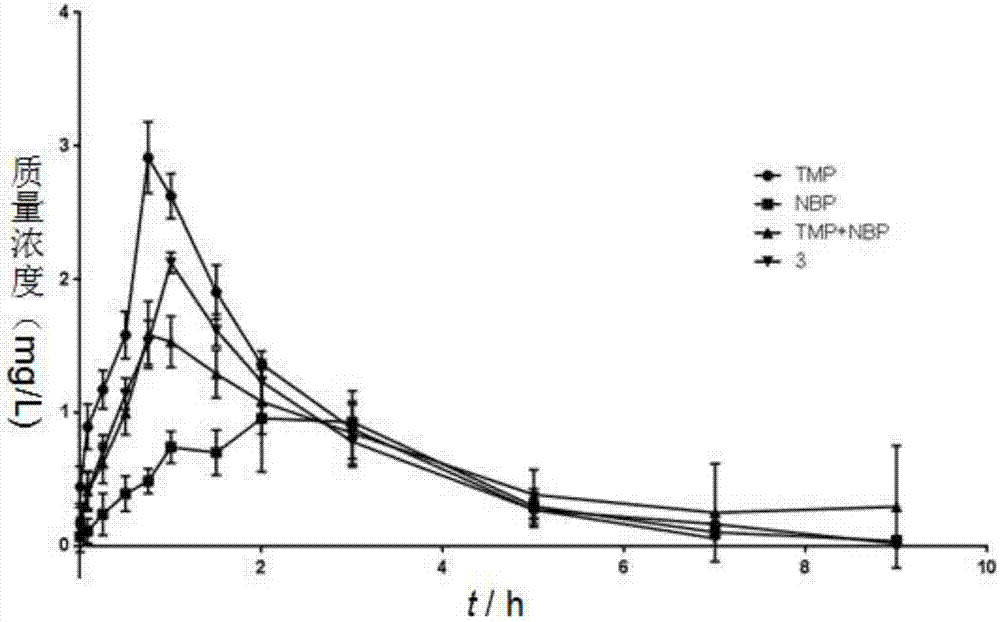
Ligustrazine-butyphthalide combination compound, preparation method of ligustrazine-butyphthalide combination compound, and application of ligustrazine-butyphthalide combination compound to pharmaceuticals
ActiveCN106928155AExtended half-lifeImprove bioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAdjuvantInduced platelet aggregation
The invention discloses a ligustrazine-butyphthalide combination compound, a preparation method of the ligustrazine-butyphthalide combination compound and an application of the ligustrazine-butyphthalide combination compound to pharmaceuticals. The ligustrazine-butyphthalide combination compound has the following structural formula I as in the description. The phthalic anhydride and the ligustrazine are taken as starting materials, bromization, nucleophilic addition, catalytic dehydration, ester hydrolysis, reduction and esterification reactions are conduced to prepare the ligustrazine-butyphthalide combination compound; a pharmaceutical composition takes the ligustrazine-butyphthalide combination compound as an active pharmaceutical ingredient and is a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, excipient, diluent, adjuvant, intermedium or a composition. The prepared ligustrazine-butyphthalide combination compound has an excellent effect of inhibiting in-vitro platelet aggregation (ADP) induced platelet aggregation, has a better in-vivo pharmacokinetics properties, and can be used for preventing and treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, vascular senile dementia and the complications.
Owner:GUIZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com