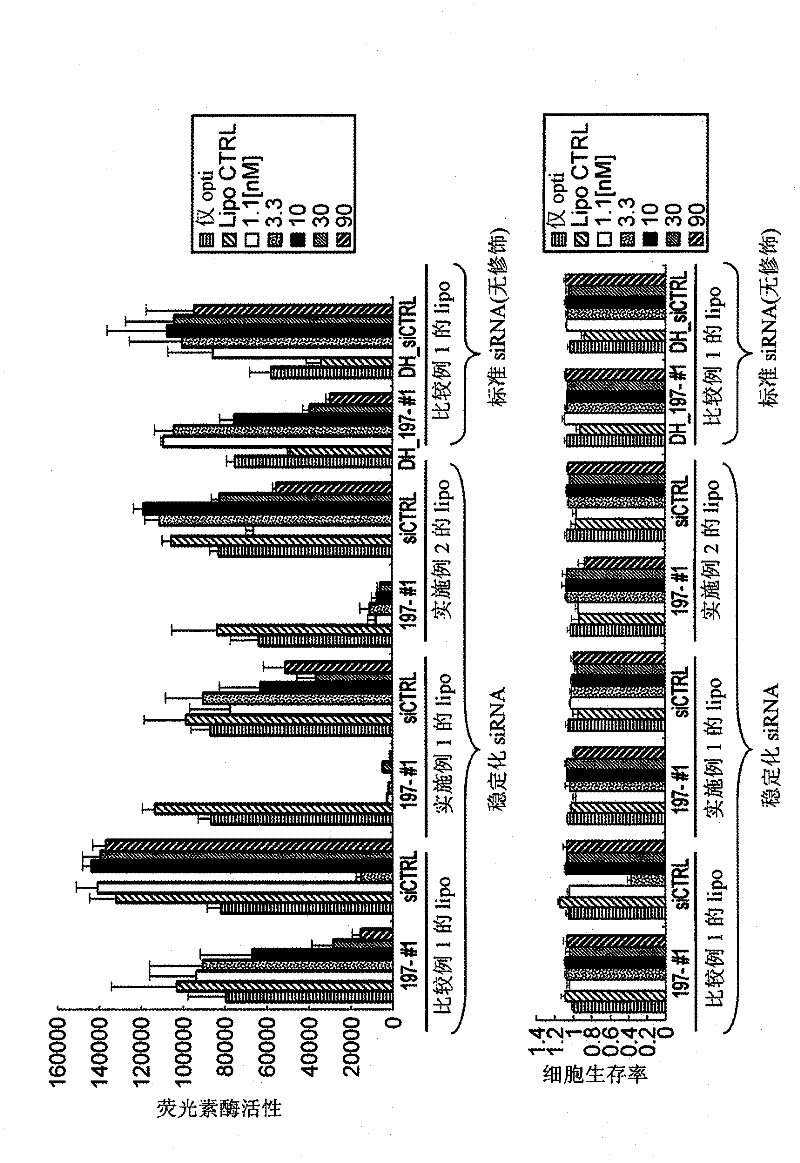
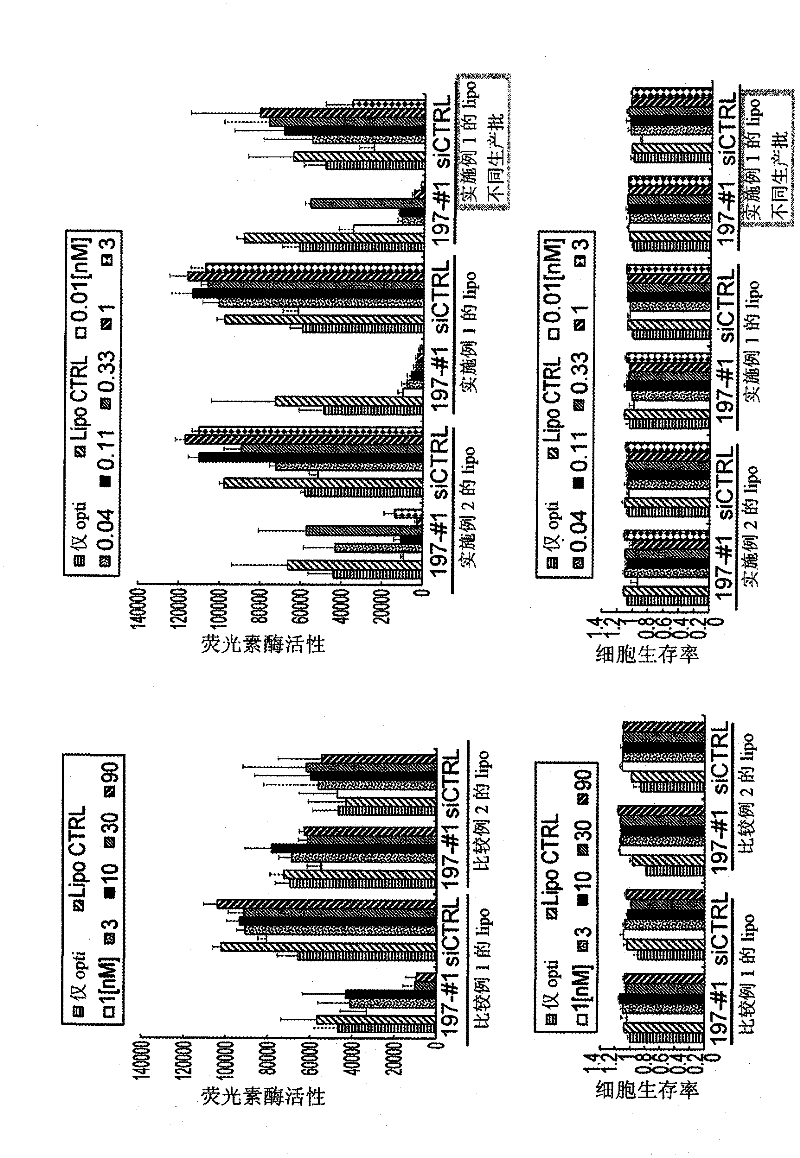
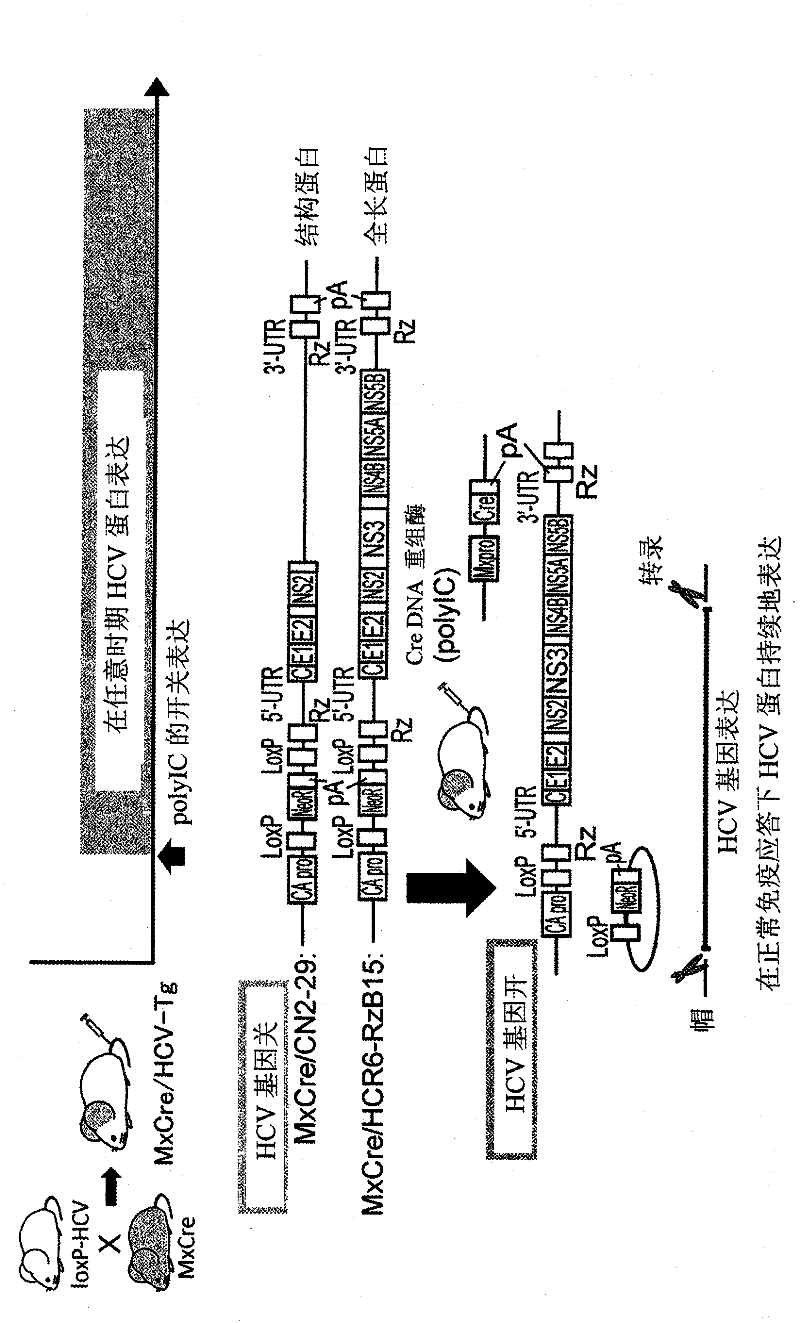
Vesicle preparation
A technology of vesicles and substances, which is applied in the directions of antiviral agents, medical preparations with non-active ingredients, and medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of undeveloped hepatic parenchymal cell delivery particles, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0146] N-(α-trimethylammonium acetyl)-dioleyl-D-glutamic acid chloride (Mutual Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Japan; trade name: DC-3-18:1), dioleoylphosphatidyl Ethanolamine (NOF Corporation, Japan) and cholesterol (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., Japan) were dissolved in an appropriate amount of chloroform at a mixing ratio of 40:30:30 (molar ratio), and the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure. Dried to make a lipid mixture.
[0147] Dry with a desiccator until the solvent can be reliably removed, then add 9% sucrose solution to the lipid mixture, and indirectly irradiate with ultrasonic waves using an ultrasonic generator under heating at 65°C, thereby obtaining a total lipid concentration of 2.5mM liposome coarse dispersion. Next, in order to make the liposome particle size uniform, two filters with a pore size of 0.2 μm were stacked and loaded into an extruder, and extruded under heat and pressure at about 65° C. (extrusion filtration). Furthermore, the same ...
Embodiment 2
[0151] DL-α-tocopherol was dissolved in a ratio of 2.5 μmol to DL-α-tocopherol (Tokyo Chemical Co., Ltd., Japan) and 400 μL of ethanol, and a filtrate (tocopherol liquid) filtered through a 0.2 μm filter was prepared.
[0152] In a 50 mL vial, 10 mL of the liposome dispersion prepared in [Example 1] was added, and 400 μL of tocopherol solution (10.0% relative to the total number of lipid moles) was added, followed by vortex mixing for 20 seconds. Further, incubation was carried out at room temperature for 1 hour to obtain a liposome dispersion in which vitamin E was adsorbed. The average particle diameter is 136.7 nm.
Embodiment 3
[0154] DL-α-tocopherol was dissolved in a ratio of 3.75 μmol to DL-α-tocopherol (Tokyo Chemical Co., Ltd., Japan) and 400 μL of ethanol, and a filtrate (tocopherol liquid) filtered through a 0.2 μm filter was prepared.
[0155] Into a 50 mL vial, 10 mL of the liposome dispersion prepared in [Example 1] was added, and 400 μL of the tocopherol solution (15.0% relative to the total number of lipid moles) was added, followed by vortex mixing for 20 seconds. Further, incubation was carried out for 1 hour at room temperature to obtain a liposome dispersion in which vitamin E was adsorbed. The average particle diameter is 133.5 nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com