Method for constructing hepatitis B virus (HBV) infected mouse model
A hepatitis B virus, mouse model technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of complex process, toxicity of adenovirus, limited application, etc., and achieve the effects of simple construction process, easy technical means and low construction cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
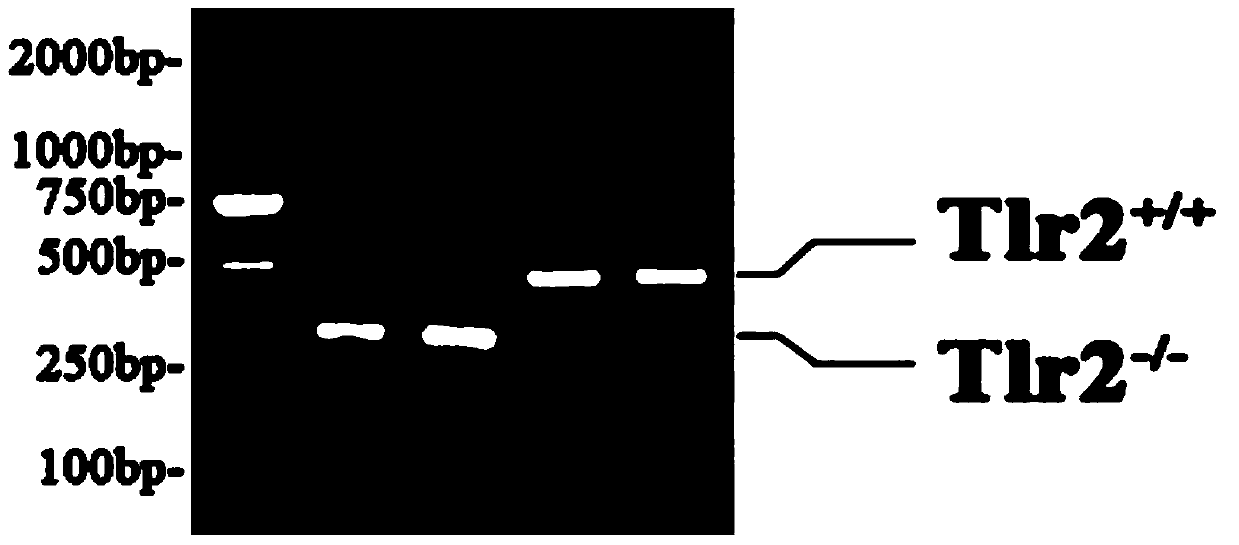
[0048] Identification of Mouse Tlr2 Genotypes:
[0049] (1) Extract the genomic DNA of the experimental mouse: cut the tail of the mouse about 0.8 cm, lyse it with 50 μl proteinase K solution (10 mg / mL), put it in a water bath at 56 °C overnight, and centrifuge the next day (12000 rpm, room temperature for 10 Minutes), add 0.5ml of 70% ethanol, inhale several times until a flocculent precipitate appears, centrifuge at 13200 rpm for 3 minutes at room temperature, discard the supernatant and dry it, add 200μl ddH 2 Mouse genomic DNA was obtained by dissolving in O and stored at 4°C.
[0050] (2) Identification of mouse genotype by PCR and gel electrophoresis experiments:
[0051] PCR system preparation (50μl):
[0052]
[0053] Table 1
[0054]
[0055] The PCR amplification program is shown in Table 2:
[0056] Table 2
[0057]
[0058]
[0059] The products obtained by PCR were subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis: the Tlr2 genotype of the mouse was identi...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Sampling for detection of virological indicators:
[0062] Tail vein high pressure injection: within 5 to 10 seconds, inject 2 ml of Ringer solution in which the corresponding plasmid was dissolved through the tail vein of the mouse within 5 to 10 seconds, and each mouse was injected once in total. The experimental mice in the R subgroup of each group were only injected with 2ml of Ringer solution without any plasmid, each mouse in the K subgroup was injected with 20 μg of empty vector plasmid, and each mouse in the W subgroup was injected with 20 μg of Wild-type HBV plasmid, M subgroup was injected with 20 μg of mutant HBV plasmid per mouse.
[0063] Peripheral blood collection and processing: Peripheral blood was collected through the infraorbital venous plexus of mice, and about 200 μl of whole blood was collected each time. The blood collection time points were blood collection before tail vein hyperbaric injection (day0), and 3 days after tail vein hyperbaric injec...
Embodiment 3
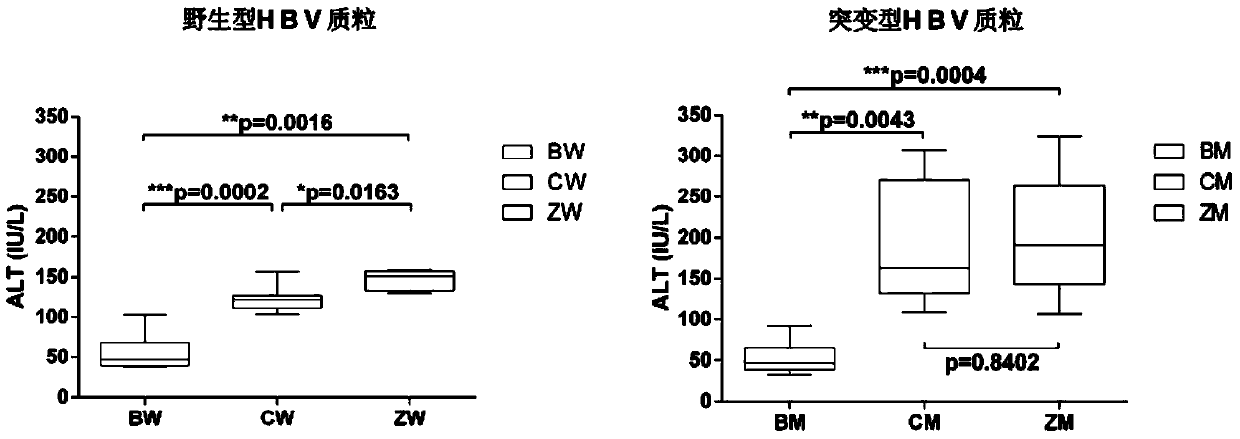
[0065] Serum ALT detection: Take 50 μl of mouse serum at each time point of day0, day3, day7, day10, day14, day17, day21 and day28 of each group, add 0.9% normal saline (NS) at a ratio of 1:1, and mix well Afterwards, the ALT level was detected with a Beckman Coulter automatic biochemical analyzer, and the unit of the measured value was IU / L. The changes of serum ALT levels in experimental mice were as follows: Figure 4 Shown, prove that the acute HBV infection mouse model (comprising homozygous and heterozygous Tlr2 gene deficient mouse) that the present invention builds by experiment than the HBV infection model that existing C57BL / 6 (B6) mouse builds, has more A high ALT level can better simulate the biochemical manifestations of hepatitis caused by HBV infection. Additionally, if figure 1 As shown, compared with the data after three weeks of injecting the plasmid, the mouse model of the present invention (CW, ZW, CM, ZM group mice) has significantly increased serum ALT ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com