Method for preparing blood vessel cells through transdifferentiation of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells, and blood vessel cells and application thereof
A technology of mesenchymal stem cells and vascular cells, applied in the field of transdifferentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells to prepare vascular cells, can solve the problems of low efficiency of iPS cells, restriction of iPS cell differentiation, cumbersome operation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0080] Construction of Adenovirus Recombinant Plasmid
[0081] Use Stbl3 competent cells to amplify pShuttle-CMV-ETV2 plasmids and pAdEasy-2 plasmids (addgene, Plasmid#16401), and extract pShuttle-CMV-ETV2 plasmids, pAdEasy-2 plasmids, and For the pAdEasy-2 plasmid, the pShuttle-CMV-ETV2 plasmid was digested with PacI from NEB Company, identified by electrophoresis, and the linear pShuttle-CMV-ETV2 plasmid was recovered. Wherein, the pShuttle-CMV-ETV2 plasmid is obtained by inserting the ETV2 transcription factor into the plasmid pShuttle-CMV (addgene, Plasmid #16403).
[0082] The linear pShuttle-CMV-ETV2 plasmid and the pAdEasy-2 plasmid were mixed at a molar ratio of 2:1, and transferred into BJ5183E.coli competent cells for intracellular recombination to obtain a bacterial solution containing the adenovirus recombinant plasmid. Spread the bacterial solution on a kanamycin-resistant LB culture dish and culture it upside down at 37°C for 12 hours, pick white, small-diameter...
Embodiment 2
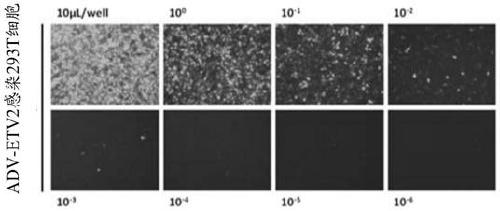
[0084] Preparation of adenovirus carrying ETV2 transcription factor (ie ADV-ETV2)
[0085] 1) Digest the adenovirus recombinant plasmid with Pac I from NEB Company, then extract the digested adenovirus recombinant plasmid through phenol-chloroform extraction, desalting, and ethanol precipitation to recover the linearized adenovirus recombinant plasmid, and wash it with sterile water Dissolve to obtain a linearized adenovirus recombinant plasmid solution with a concentration not lower than 500ng / uL.
[0086] 2) Inoculate 293A cells into a 35mm culture dish at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultured in an incubator to a confluence of 60%. Based on the amount of 5ug linearized adenovirus recombinant plasmid added to each 35mm culture dish, and according to the amount of 3uL transfection agent added per 1ug linearized adenovirus recombinant plasmid, the linearized adenovirus recombinant plasmid and transfection Reagent (FuGene 6 (Promega)) was mixed and acted for 15 minutes to form a transfectio...
Embodiment 3
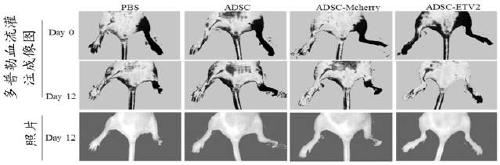
[0115] Transdifferentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells to prepare vascular cells (i.e. endothelial cells)
[0116] 1. Cell inoculation
[0117] Day-1: Inoculate mesenchymal stem cells (ASC cells) into 12 wells of a 12-well plate, 3.5×10 4 cells / well, placed at 37°C, 5.0% CO 2 cultured in an incubator.
[0118] The experiment was divided into two groups, and each group had two parallel controls. The settings of each group are shown in Table 1 below.
[0119] Table 1: Grouping situation
[0120]
[0121]
[0122] Wherein, "negative control" means no virus infection, and "ADV-ETV2" means adenovirus carrying ETV2 transcription factor.
[0123] 2. Virus infection
[0124] 1) Day0: digest the ASC cells in the 12-well plate, and count the number of cells. Put the ASC cell complete medium into a 37°C water bath to heat, add ADV-HR (Shandong Weizhen Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) to obtain ADV-HR complete medium containing 10 μg / mL, add 10 μg / mL The adenovirus car...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com