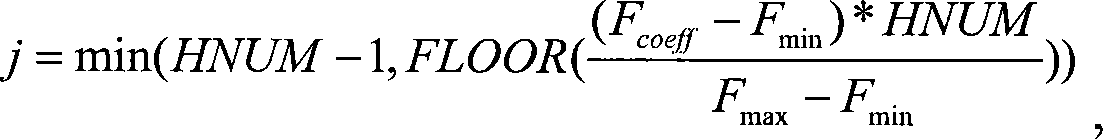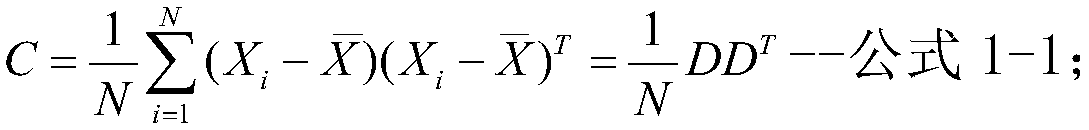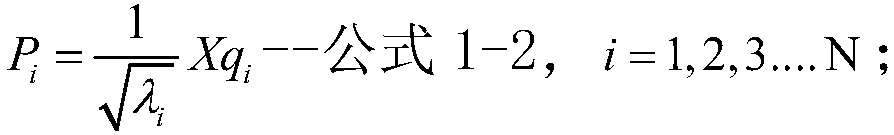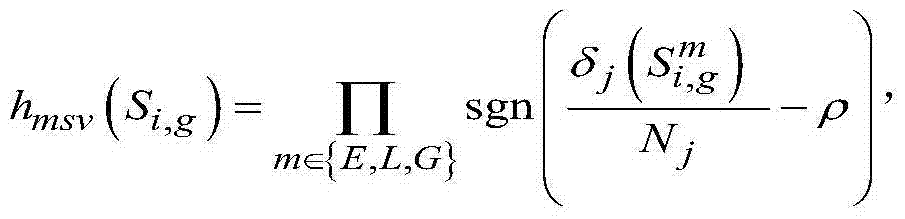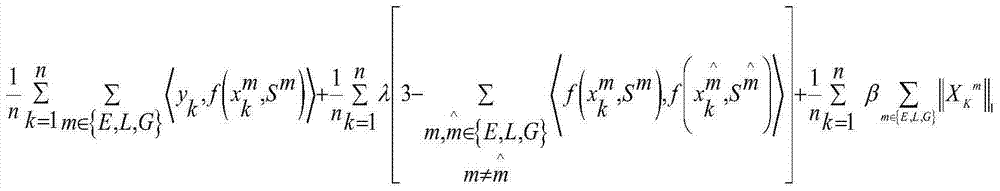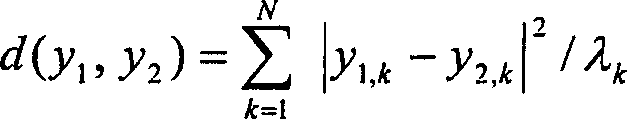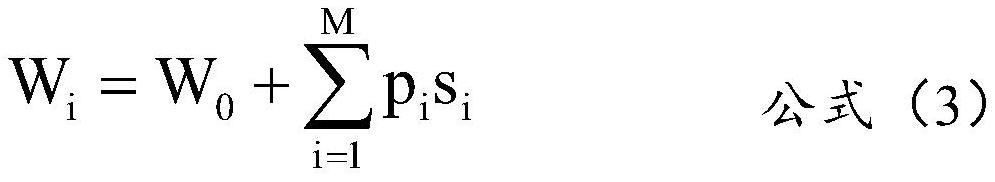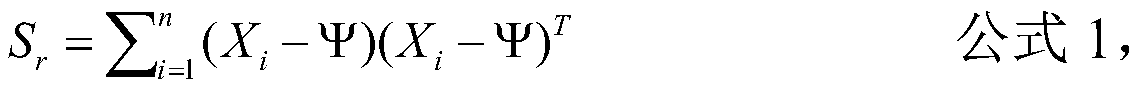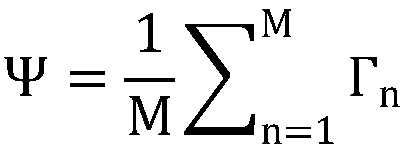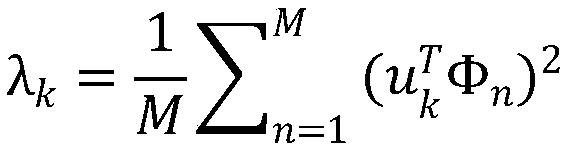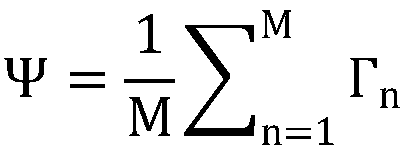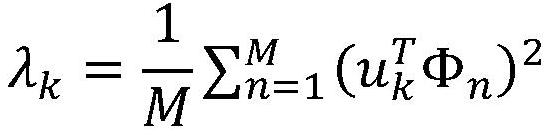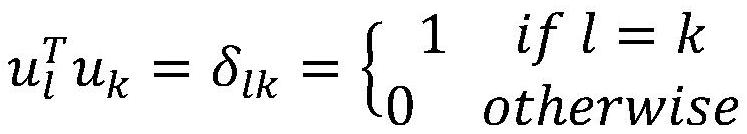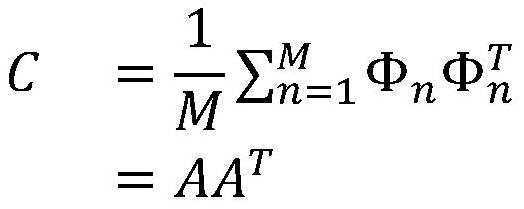Patents
Literature
45 results about "Eigenface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
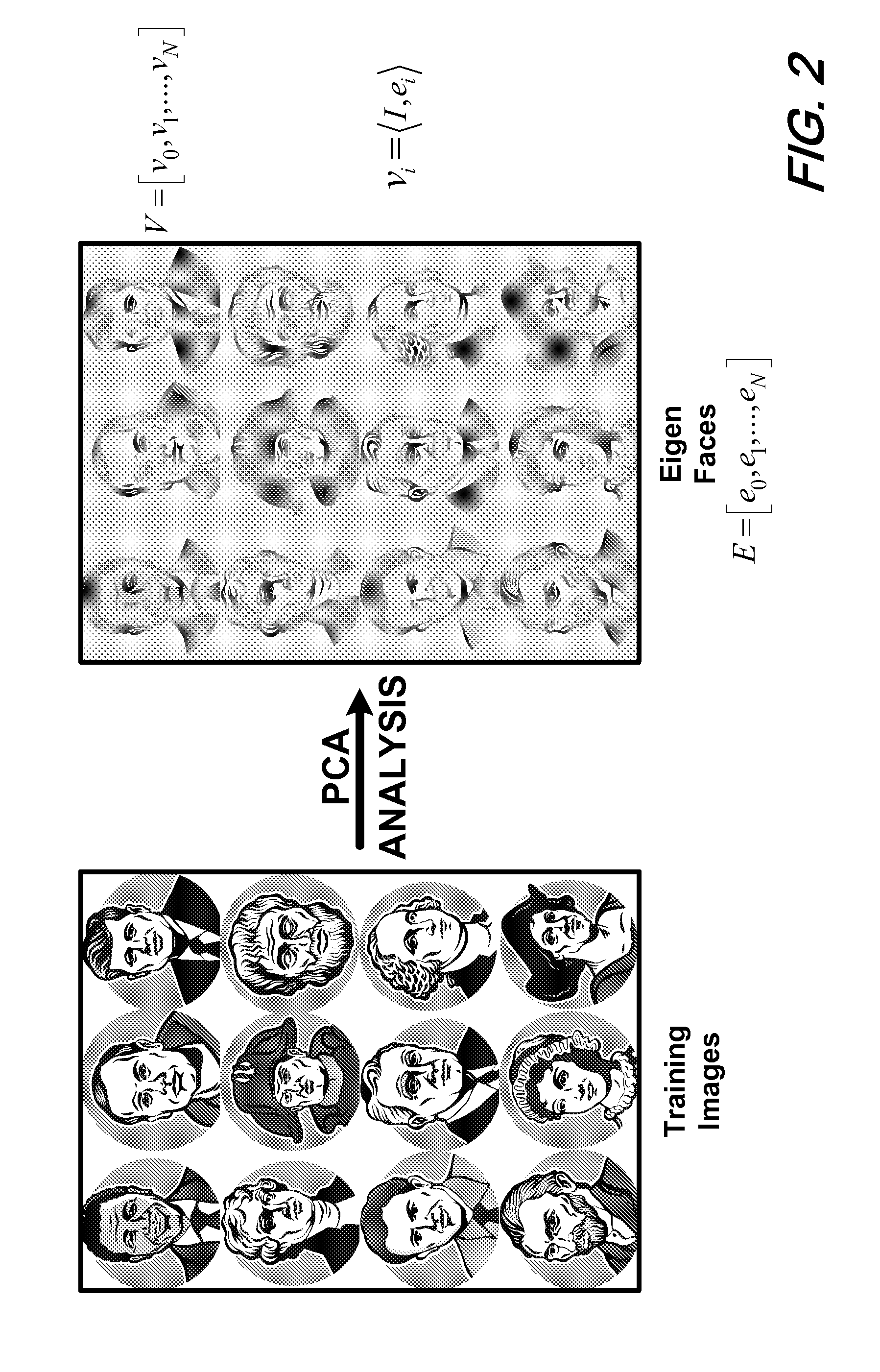
Eigenfaces is the name given to a set of eigenvectors when they are used in the computer vision problem of human face recognition. The approach of using eigenfaces for recognition was developed by Sirovich and Kirby (1987) and used by Matthew Turk and Alex Pentland in face classification. The eigenvectors are derived from the covariance matrix of the probability distribution over the high-dimensional vector space of face images. The eigenfaces themselves form a basis set of all images used to construct the covariance matrix. This produces dimension reduction by allowing the smaller set of basis images to represent the original training images. Classification can be achieved by comparing how faces are represented by the basis set.
Pose-invariant face recognition system and process
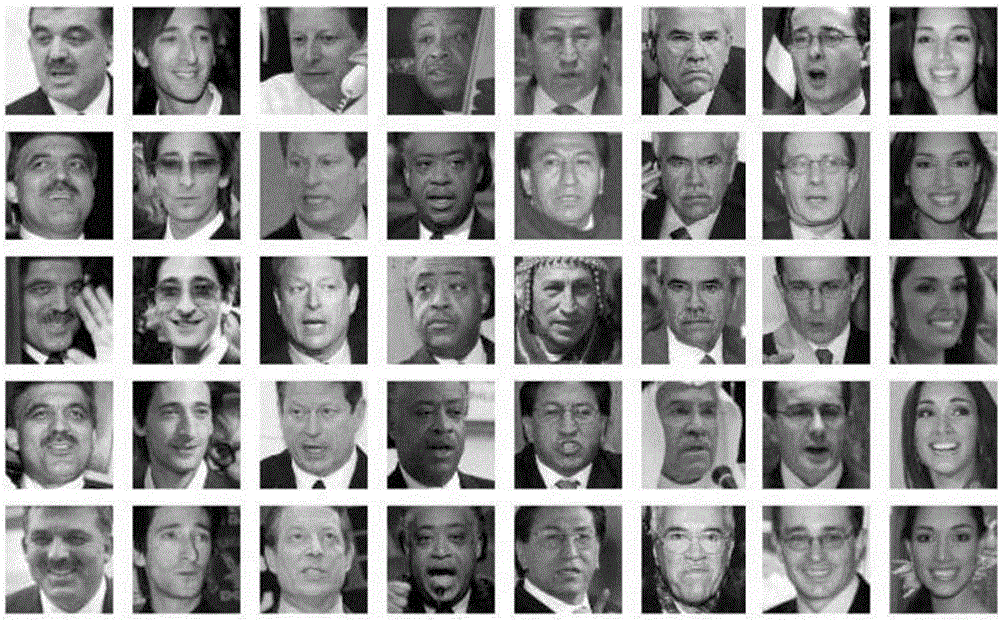
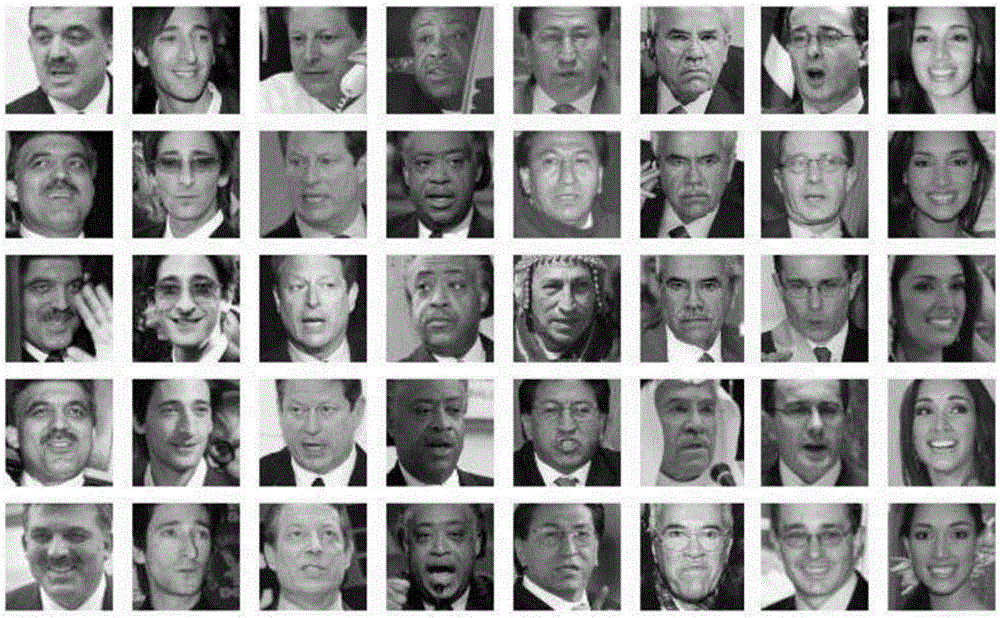
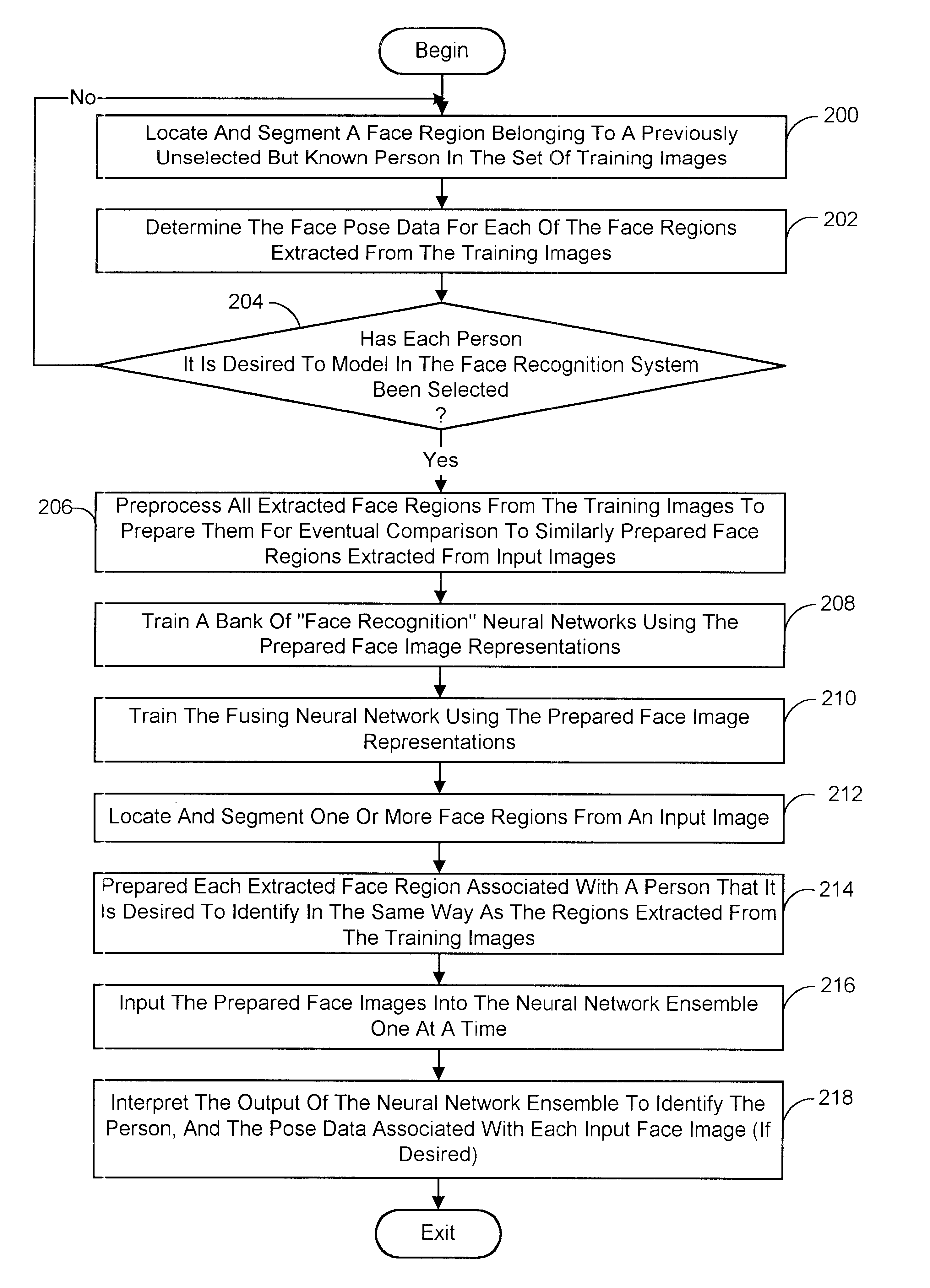
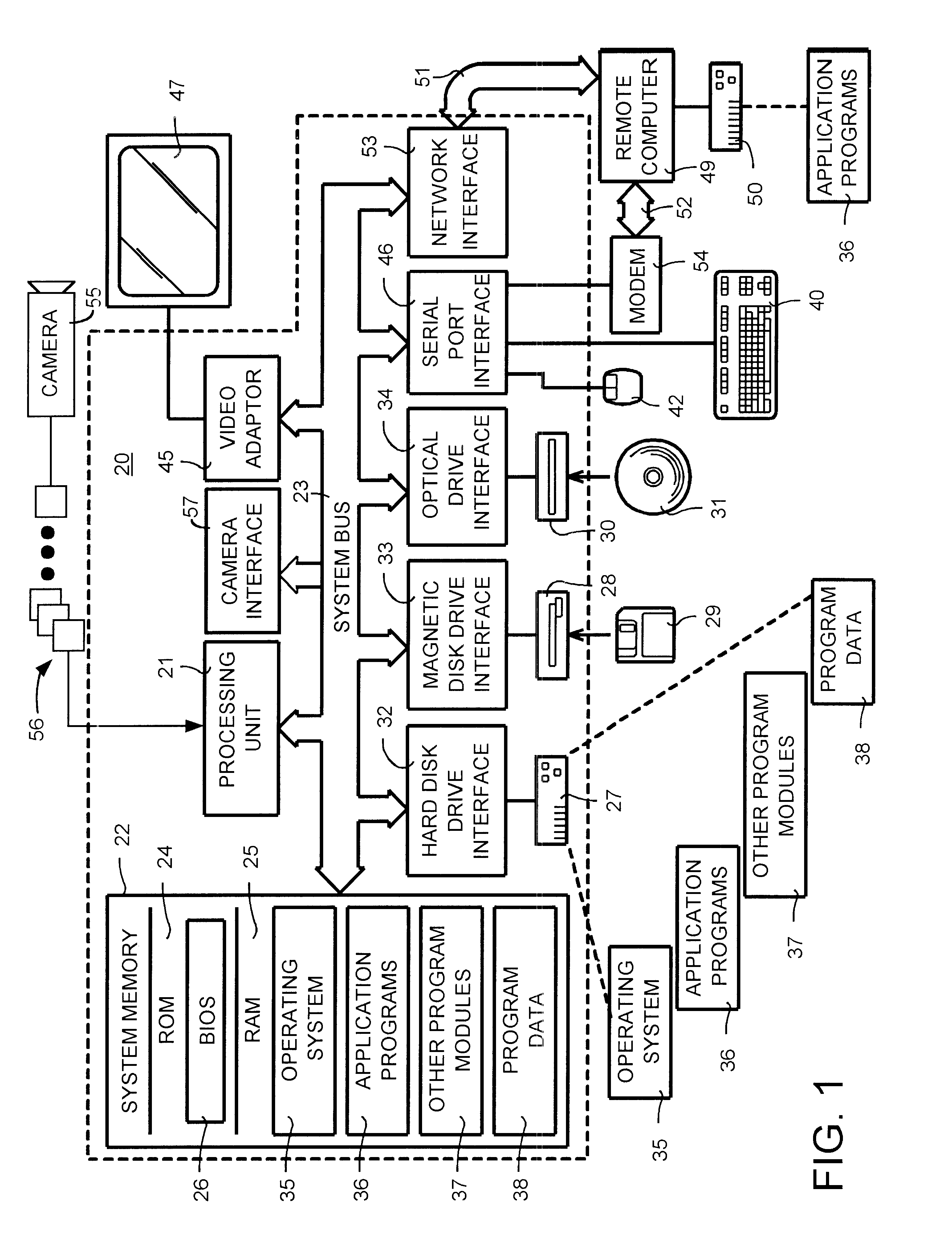
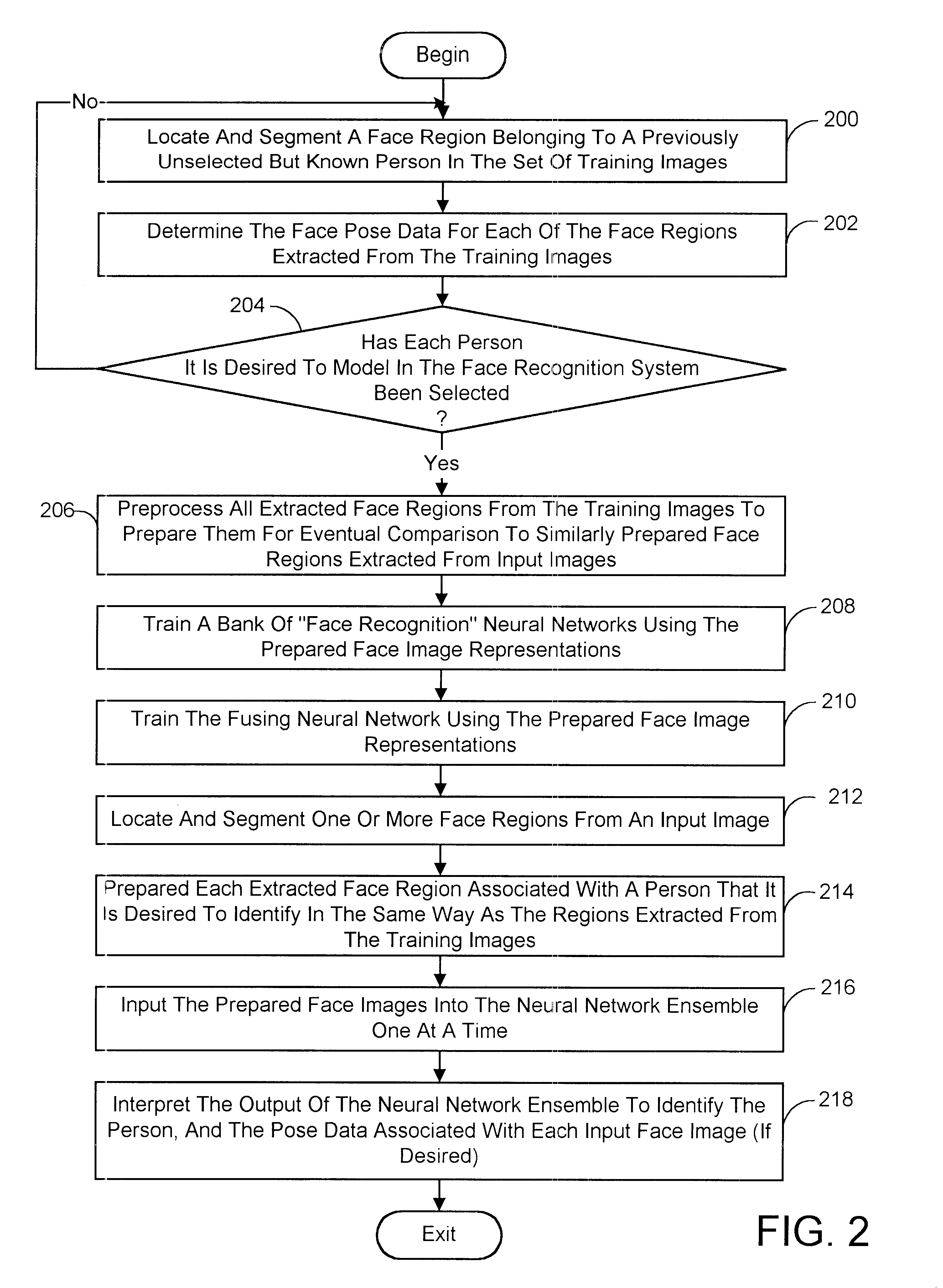
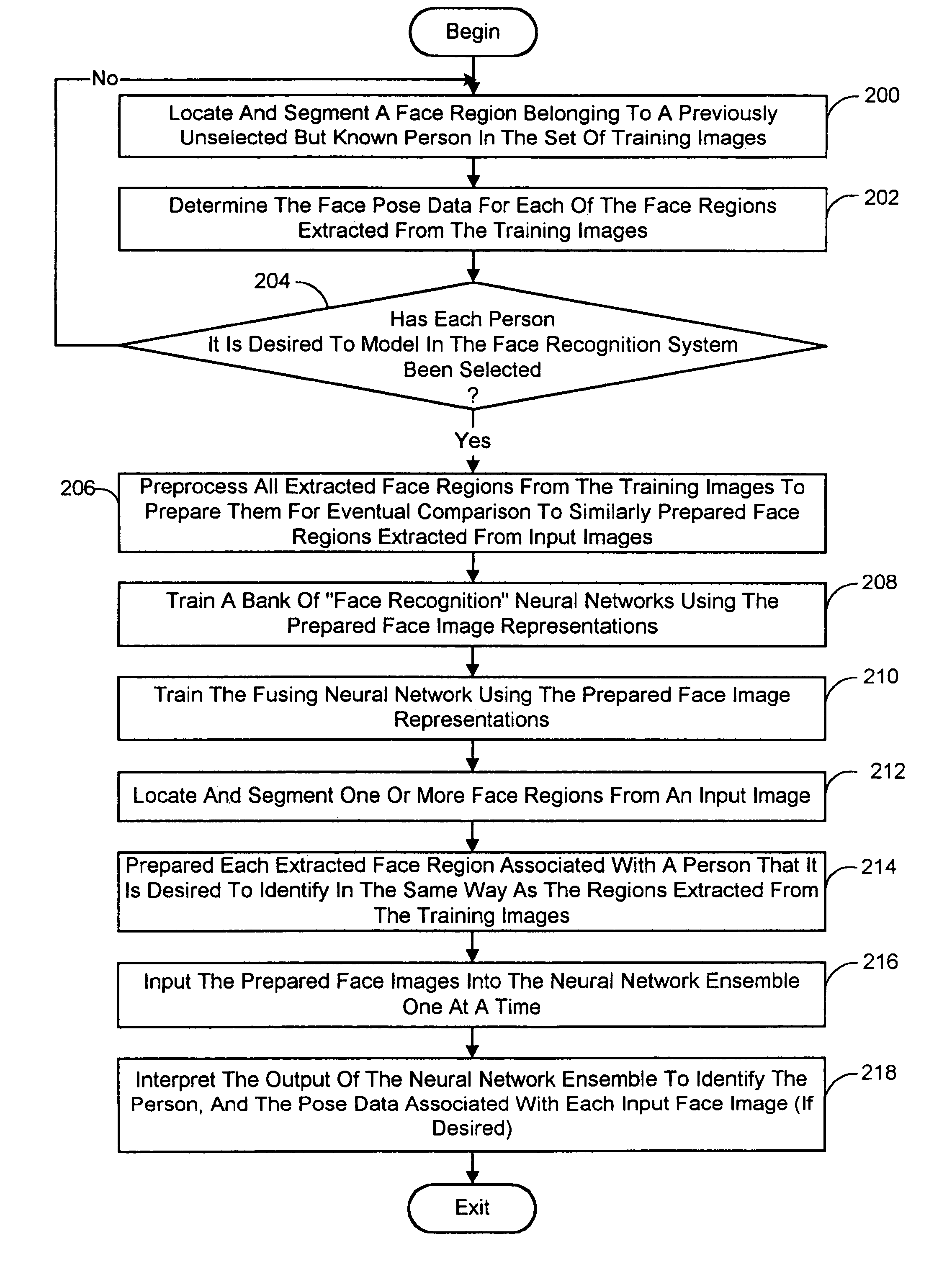
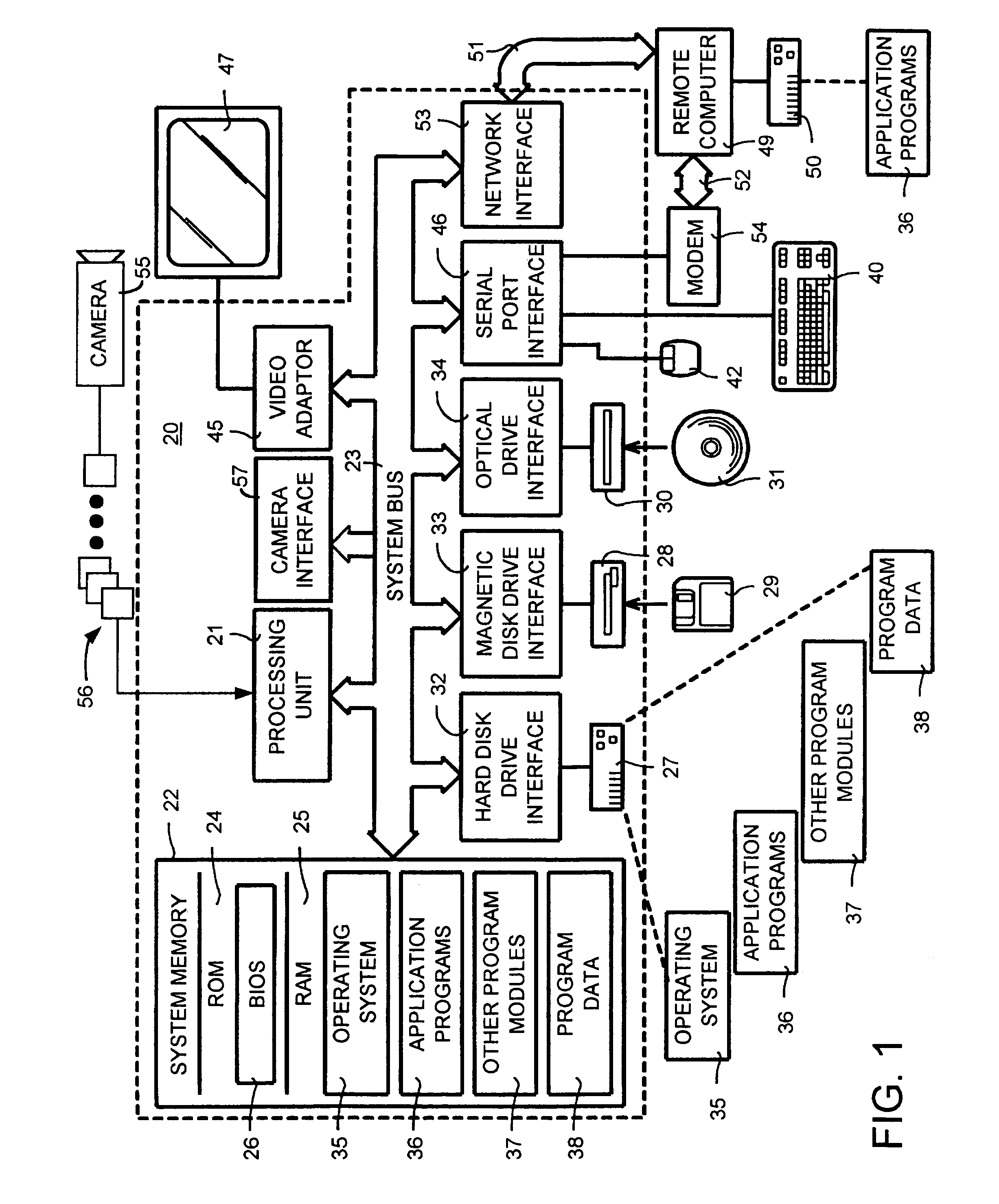
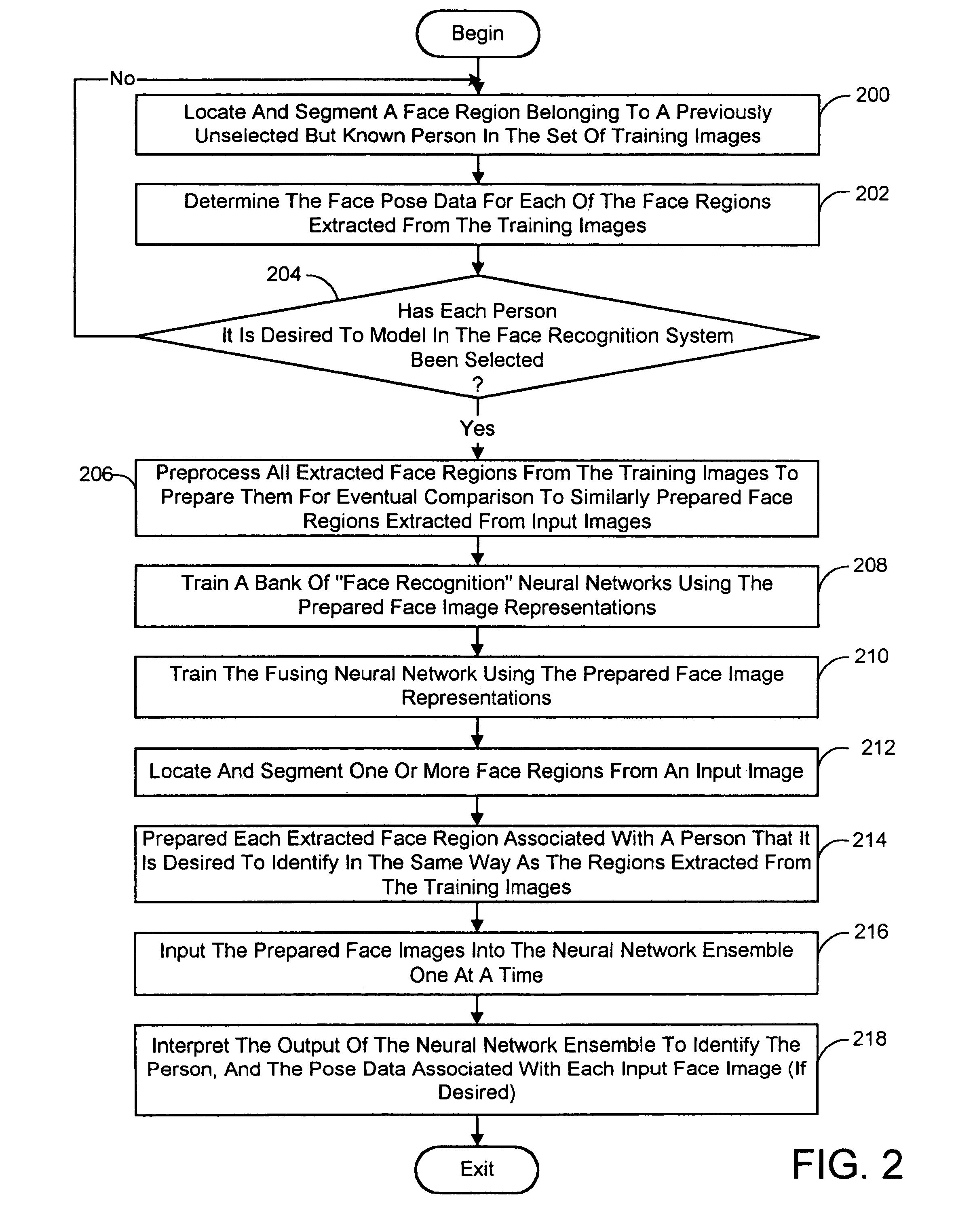
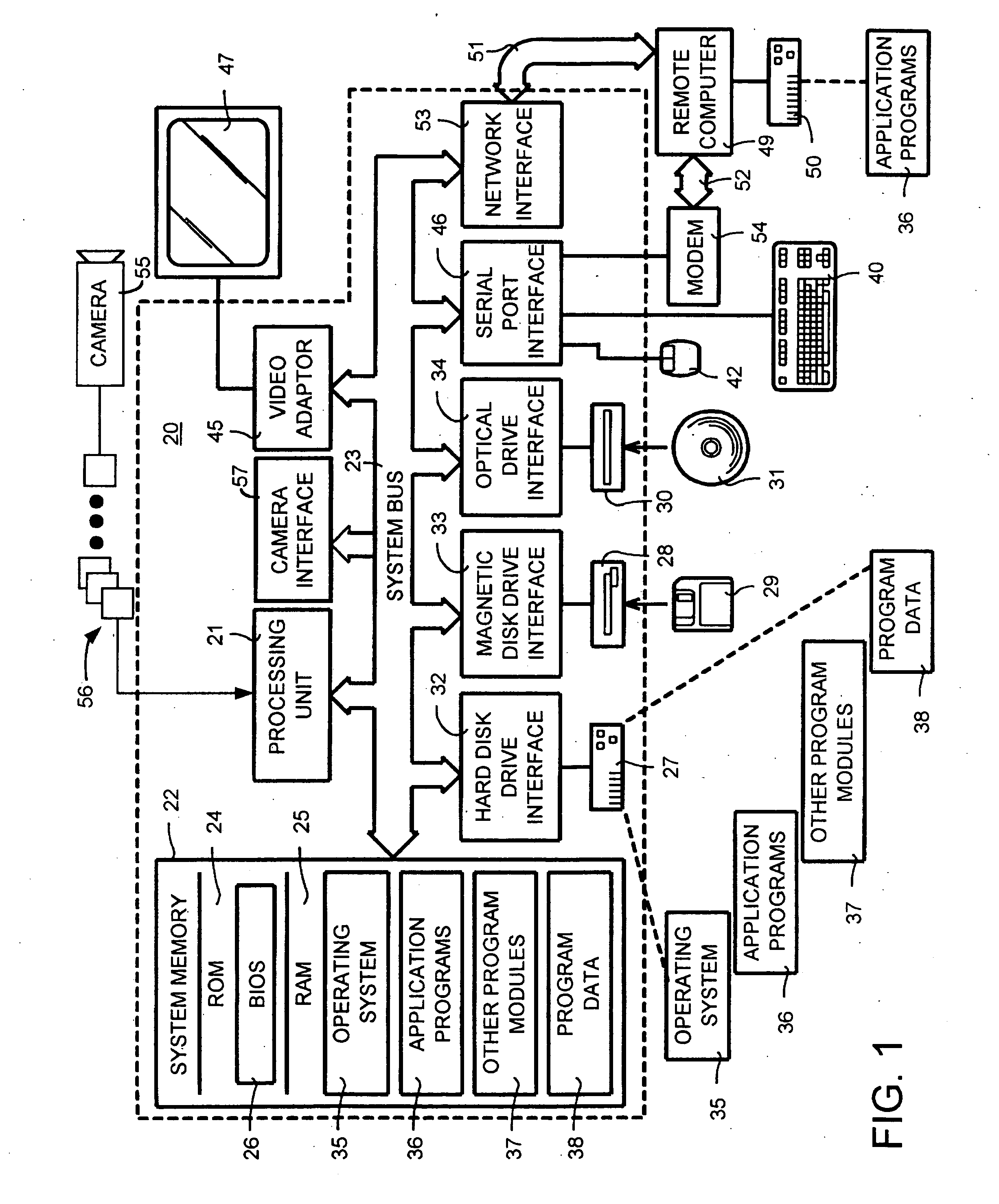
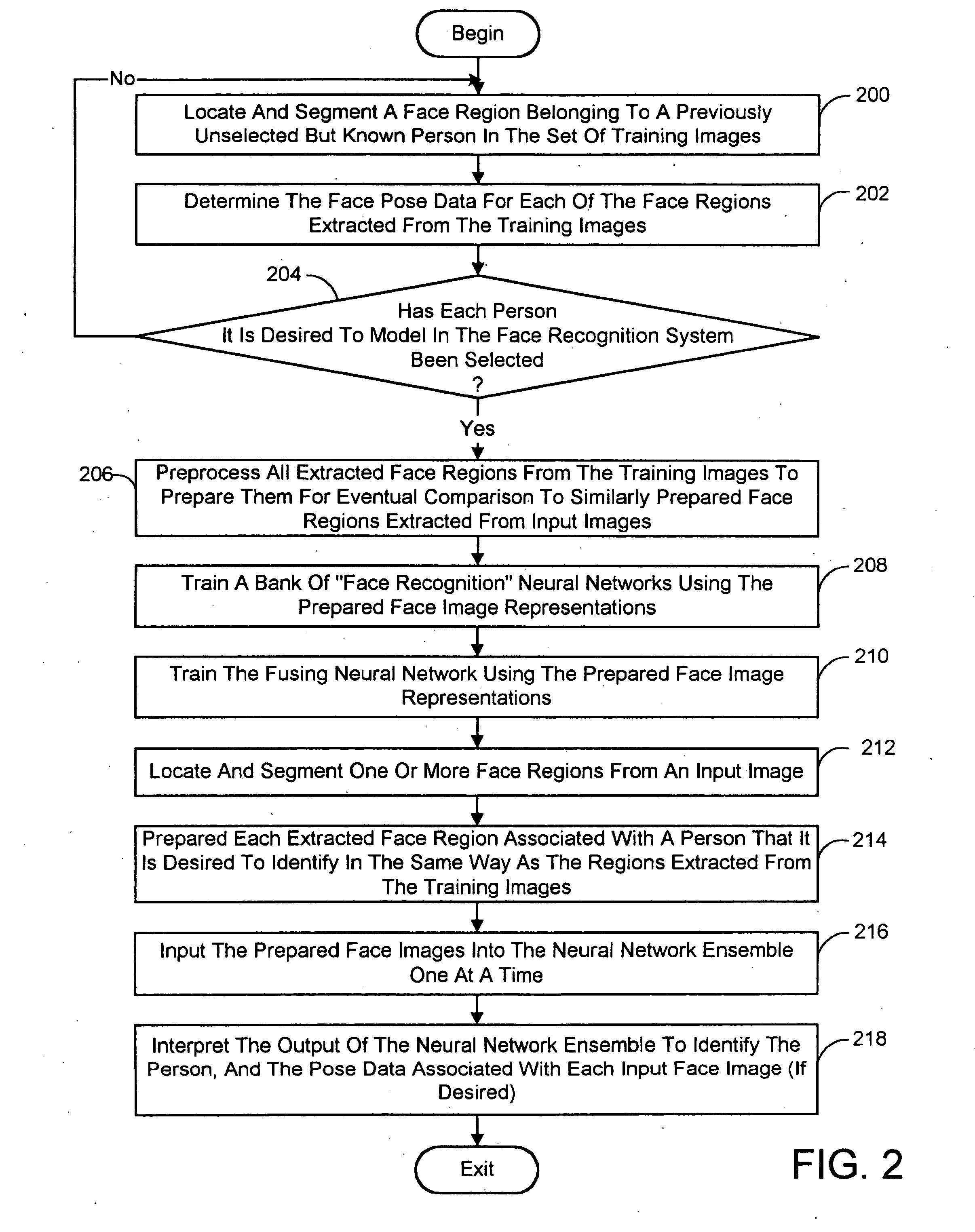
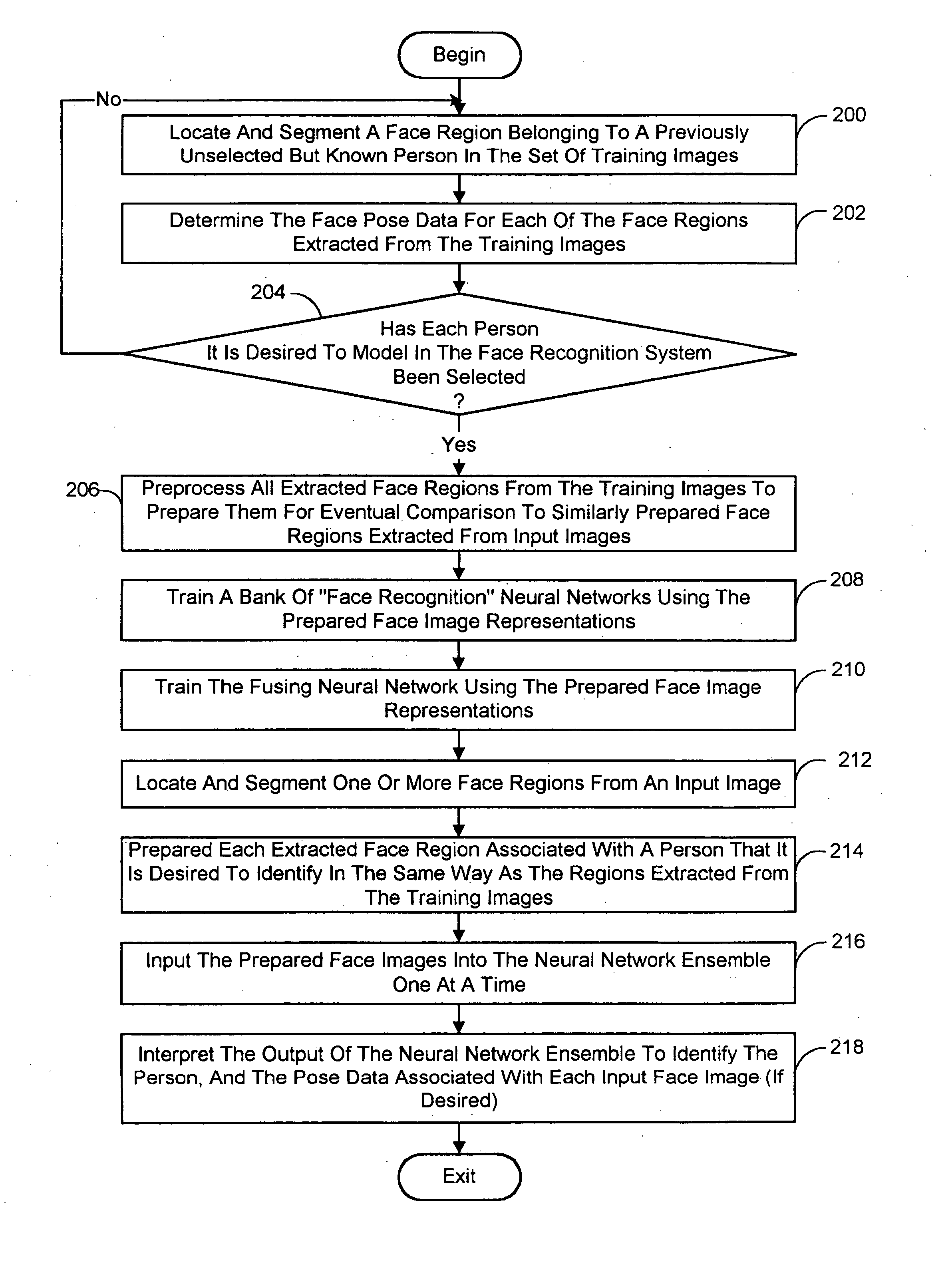
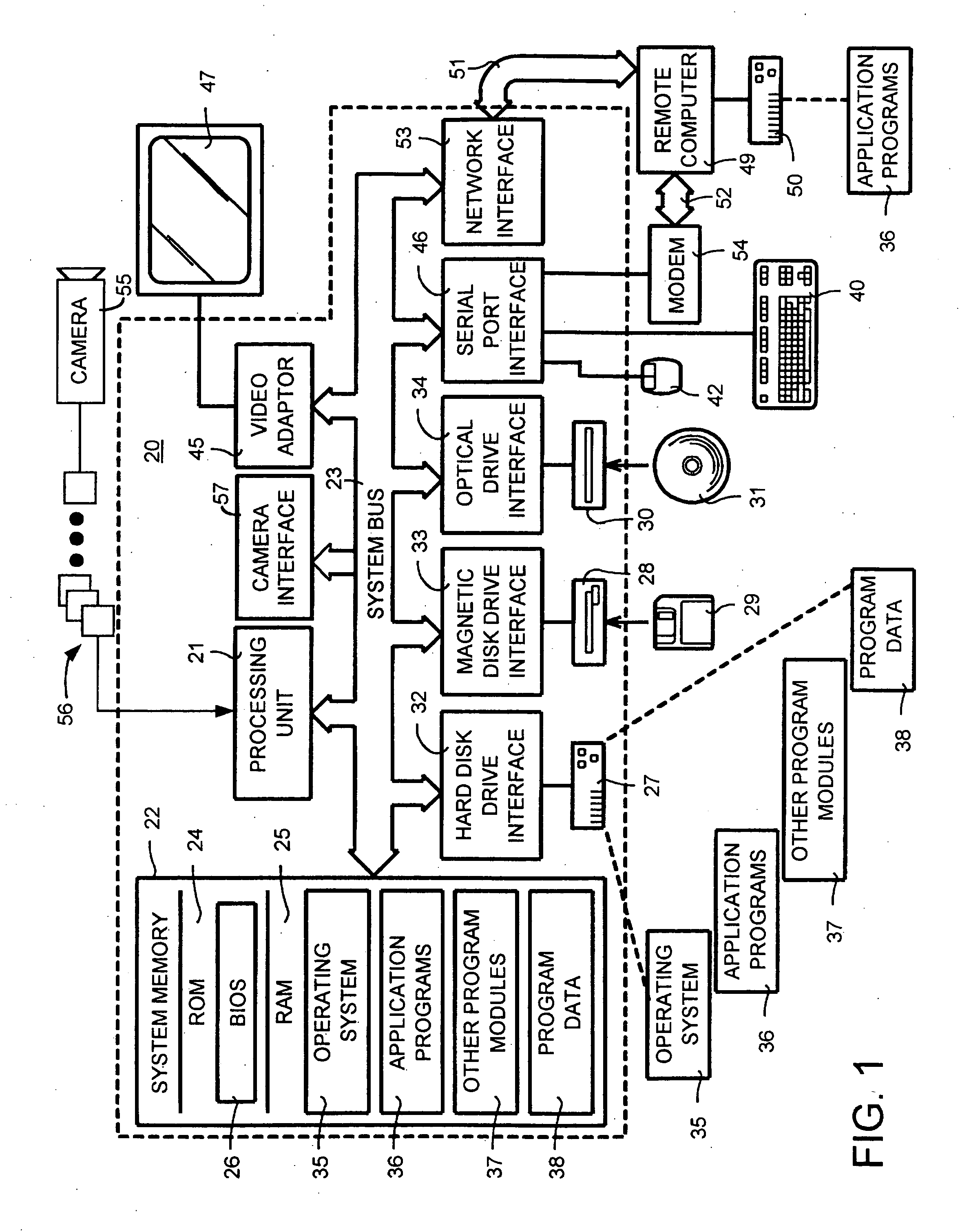
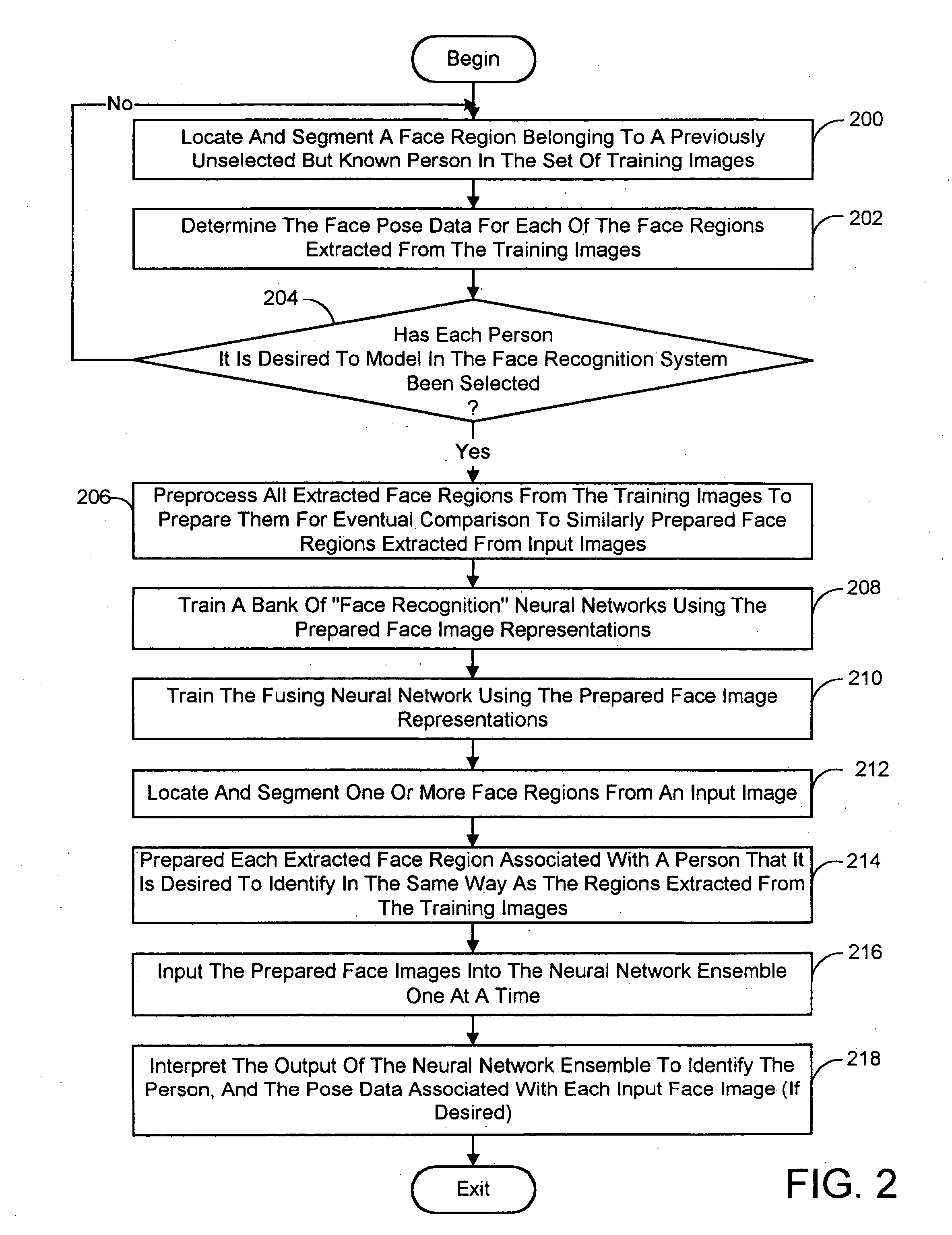
A face recognition system and process for identifying a person depicted in an input image and their face pose. This system and process entails locating and extracting face regions belonging to known people from a set of model images, and determining the face pose for each of the face regions extracted. All the extracted face regions are preprocessed by normalizing, cropping, categorizing and finally abstracting them. More specifically, the images are normalized and cropped to show only a person's face, categorized according to the face pose of the depicted person's face by assigning them to one of a series of face pose ranges, and abstracted preferably via an eigenface approach. The preprocessed face images are preferably used to train a neural network ensemble having a first stage made up of a bank of face recognition neural networks each of which is dedicated to a particular pose range, and a second stage constituting a single fusing neural network that is used to combine the outputs from each of the first stage neural networks. Once trained, the input of a face region which has been extracted from an input image and preprocessed (i.e., normalized, cropped and abstracted) will cause just one of the output units of the fusing portion of the neural network ensemble to become active. The active output unit indicates either the identify of the person whose face was extracted from the input image and the associated face pose, or that the identity of the person is unknown to the system.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
Pose-invariant face recognition system and process
InactiveUS7127087B2Sure easyElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisEigenfaceRecognition system
A face recognition system and process for identifying a person depicted in an input image and their face pose. This system and process entails locating and extracting face regions belonging to known people from a set of model images, and determining the face pose for each of the face regions extracted. All the extracted face regions are preprocessed by normalizing, cropping, categorizing and finally abstracting them. More specifically, the images are normalized and cropped to show only a persons face, categorized according to the face pose of the depicted person's face by assigning them to one of a series of face pose ranges, and abstracted preferably via an eigenface approach. The preprocessed face images are preferably used to train a neural network ensemble having a first stage made up of a bank of face recognition neural networks each of which is dedicated to a particular pose range, and a second stage constituting a single fusing neural network that is used to combine the outputs from each of the first stage neural networks. Once trained, the input of a face region which has been extracted from an input image and preprocessed (i.e., normalized, cropped and abstracted) will cause just one of the output units of the fusing portion of the neural network ensemble to become active. The active output unit indicates either the identify of the person whose face was extracted from the input image and the associated face pose, or that the identity of the person is unknown to the system.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
Video flow based three-dimensional dynamic human face expression model construction method
InactiveCN1920886AImprove efficiencyRich expressivenessAnimation3D-image renderingDecompositionPersonalization
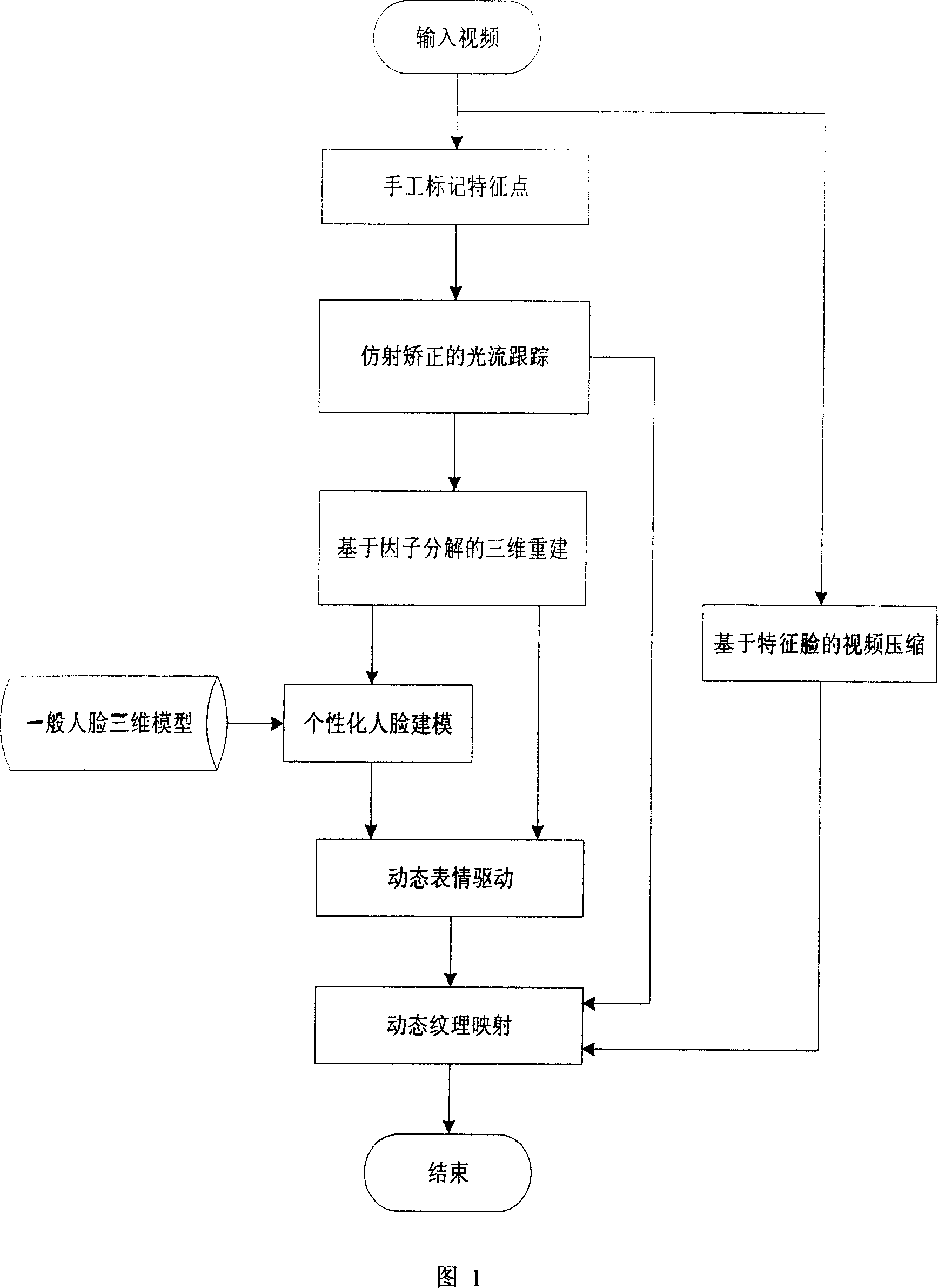
The invention relates to a three-dimension dynamic face pathetic model construction method based on video flow, which can return the three-dimension face pathetic based on input video flow, wherein the algorism comprises: (1) marking face character point at the first frame of input video; (2) using light stream method of affine correction to track the character point; (3) rebuilding the two-dimension track data based on factor decomposition into three-dimension data; (4 using rebuilt three-dimension date to match general face model, to generate personal face and dynamic pathetic motion; (5) using character face technique to compress the original video; (6) using character face to rebuild input video and projecting dynamic pattern, to compose true virtual appearance. The invention has high time / spatial efficiency and high value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Pose-invariant face recognition system and process
InactiveUS20050147292A1Sure easyElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisEigenfaceRecognition system
A face recognition system and process for identifying a person depicted in an input image and their face pose. This system and process entails locating and extracting face regions belonging to known people from a set of model images, and determining the face pose for each of the face regions extracted. All the extracted face regions are preprocessed by normalizing, cropping, categorizing and finally abstracting them. More specifically, the images are normalized and cropped to show only a persons face, categorized according to the face pose of the depicted person's face by assigning them to one of a series of face pose ranges, and abstracted preferably via an eigenface approach. The preprocessed face images are preferably used to train a neural network ensemble having a first stage made up of a bank of face recognition neural networks each of which is dedicated to a particular pose range, and a second stage constituting a single fusing neural network that is used to combine the outputs from each of the first stage neural networks. Once trained, the input of a face region which has been extracted from an input image and preprocessed (i.e., normalized, cropped and abstracted) will cause just one of the output units of the fusing portion of the neural network ensemble to become active. The active output unit indicates either the identify of the person whose face was extracted from the input image and the associated face pose, or that the identity of the person is unknown to the system.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
Pose-invariant face recognition system and process
InactiveUS20050147291A1Sure easyElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisEigenfaceRecognition system
A face recognition system and process for identifying a person depicted in an input image and their face pose. This system and process entails locating and extracting face regions belonging to known people from a set of model images, and determining the face pose for each of the face regions extracted. All the extracted face regions are preprocessed by normalizing, cropping, categorizing and finally abstracting them. More specifically, the images are normalized and cropped to show only a persons face, categorized according to the face pose of the depicted person's face by assigning them to one of a series of face pose ranges, and abstracted preferably via an eigenface approach. The preprocessed face images are preferably used to train a neural network ensemble having a first stage made up of a bank of face recognition neural networks each of which is dedicated to a particular pose range, and a second stage constituting a single fusing neural network that is used to combine the outputs from each of the first stage neural networks. Once trained, the input of a face region which has been extracted from an input image and preprocessed (i.e., normalized, cropped and abstracted) will cause just one of the output units of the fusing portion of the neural network ensemble to become active. The active output unit indicates either the identify of the person whose face was extracted from the input image and the associated face pose, or that the identity of the person is unknown to the system.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
Identification of people using video and audio eigen features
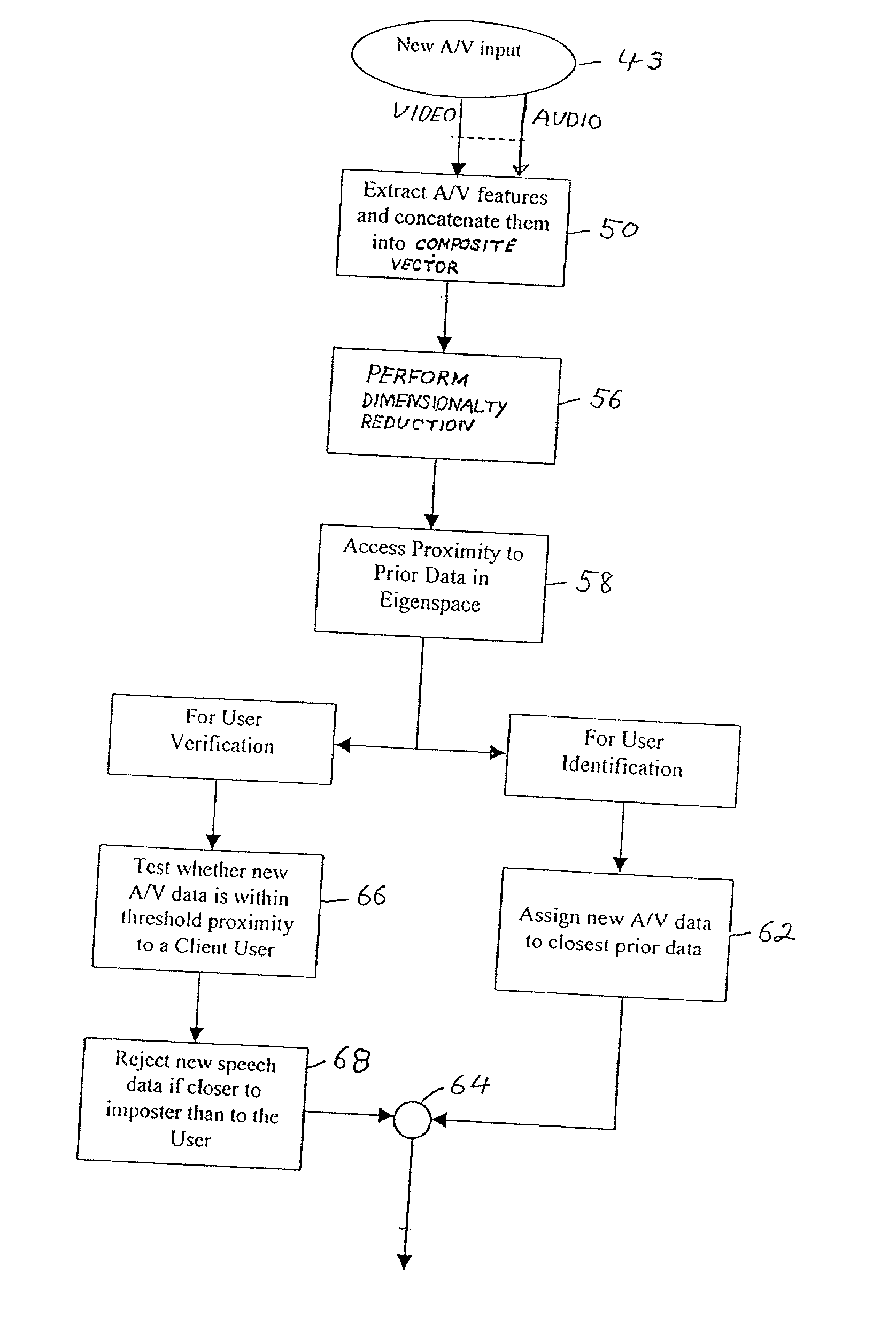
A method and system for concatenating eigenvoice vector data with eigenface vector data to obtain a new basic eigenvector to more positively and accurately identify a person. More specifically, for a specific person, the data of an eigenface vector is concatenated with the data of an eigenvoice vector to form a single vector, and this single vector is compared to reference vectors also obtained by concatenting the data of eigenface vectors and eigenvoice vectors to obtain a single vector of each persons in a defined group of people to determine if a person that is a member of a defined group of people. Using this single eiginvector gives a higher success rate for identifying a person than an eigenface vector or an eigenvoice vector used separately or together as separate vectors.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
A face authentication method and device
ActiveCN101187977AImprove recognition rateEasy to classifyCharacter and pattern recognitionLookup tableEigenface
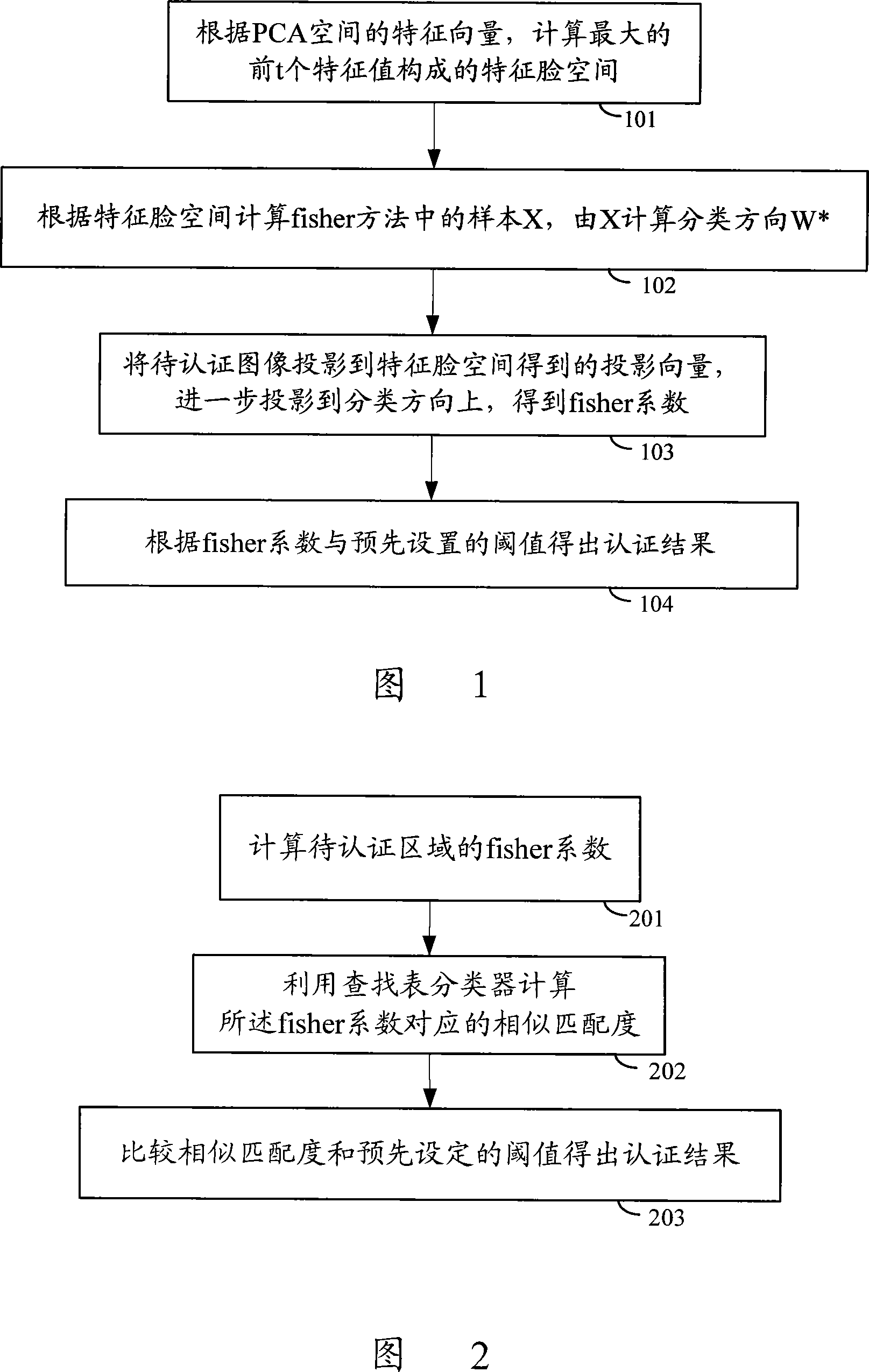
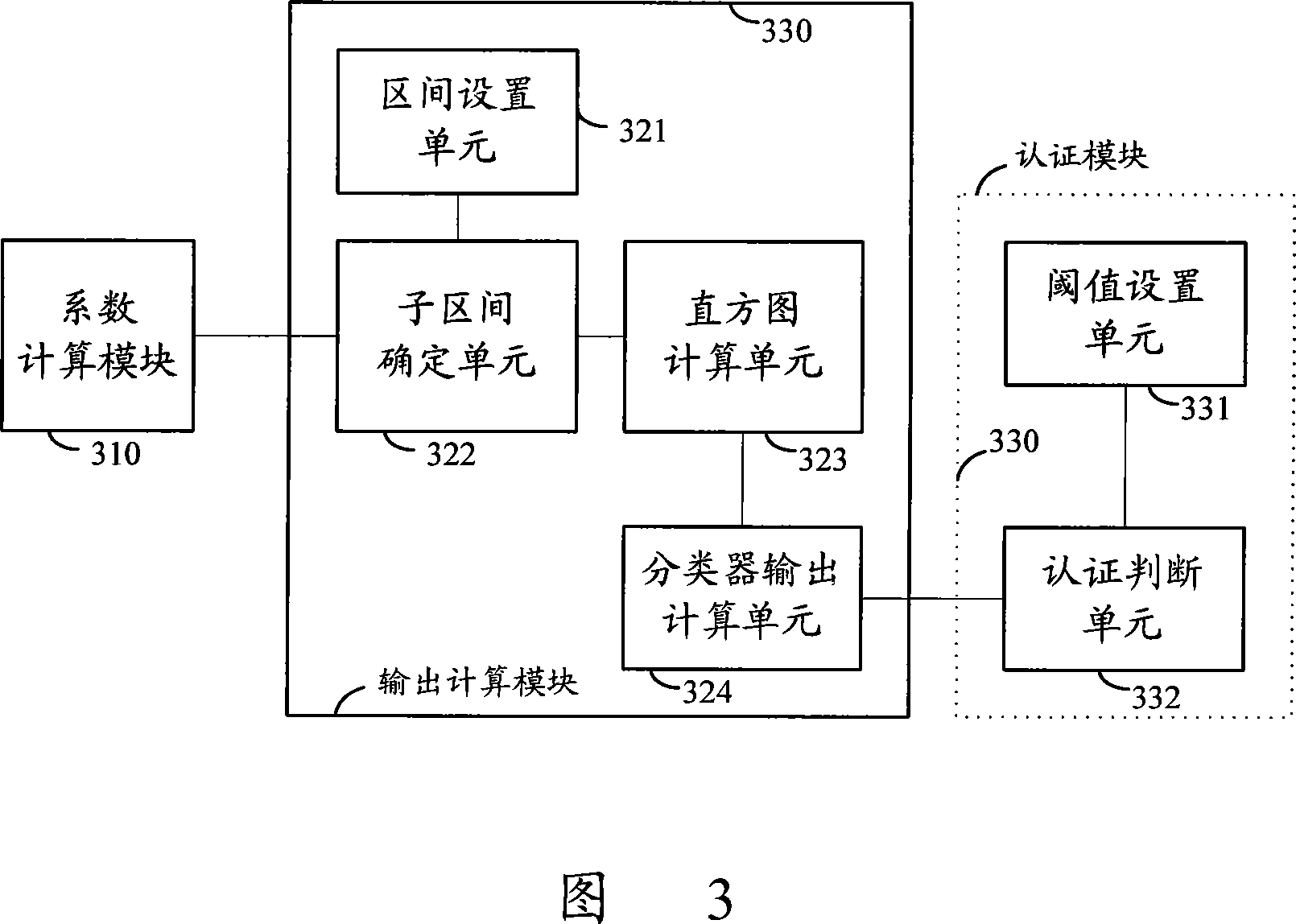
The invention discloses a method for human face authentication. The method comprises the following steps: the fisher coefficient of a target to be authenticated is calculated with the fisher eigenface method based on principal component analysis; the similarity matching degree corresponding to the fisher coefficient is calculated by utilizing a lookup table classifier; the similarity matching degree and a preset threshold are compared to get the authentication result. The invention also discloses a device for human face authentication. The device comprises a coefficient computing module, which computes the fisher coefficient of a target to be authenticated; an output computing module, which computes the similarity matching degree corresponding to the fisher coefficient with a lookup table classifier; and an authenticating module, which compares the similarity matching degree and the preset threshold to get the authentication result. The method and the device for the human face authentication of the invention, by introducing the lookup table classifier with more powerful expressing ability than a single threshold, can perform better classification on training samples, thereby improving the recognition rate of human face authentication and reducing the mis-detection possibility.
Owner:GUANGDONG VIMICRO
A method for detecting and recognizing human face in vivo
InactiveCN109145817AJudging face spoofing behaviorAvoid defectsNeural learning methodsSpoof detectionColor imagePattern recognition
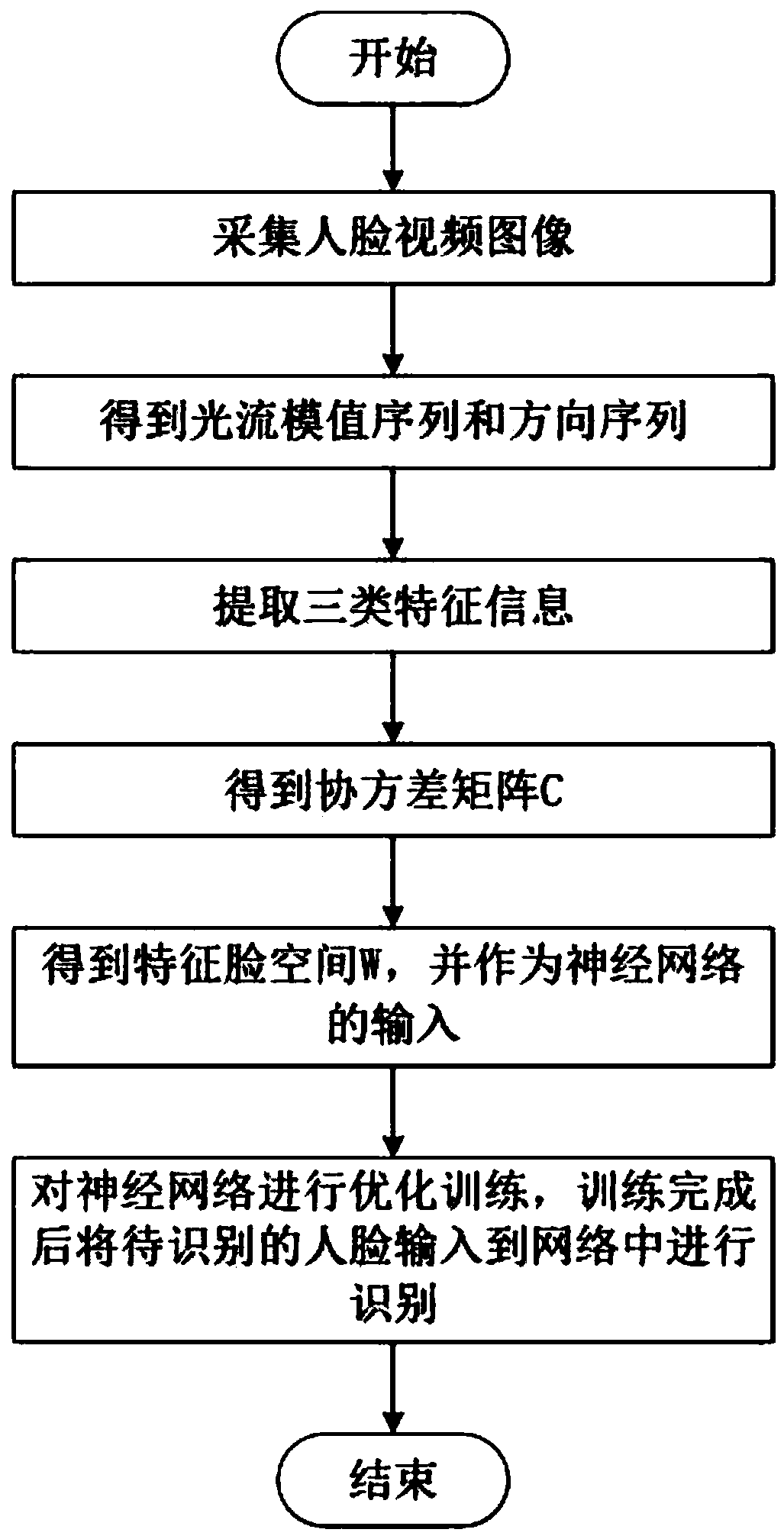
A method for detecting and recognizing human face in vivo comprises the steps of: a video human face image is acquired; the face part of the video frame image is segmented to get the optical flow modulus sequence and direction sequence; three kinds of feature information are extracted from the sequence, and the extracted feature is trained to get an SVM classifier to judge whether it is a living face or not; according to the living face image detected by infrared image, the face part in the color image is segmented, the color face image is extracted by using PCA algorithm, and the collected face image is represented by one-dimensional vector, and the covariance matrix C of the vector is obtained; the eigenface space W is obtained from the covariance matrix C, and the eigenface space W is used as the input of the neural network; the neural network is optimized and trained; after the training, the face images to be recognized are input into the network for face recognition. In order to solve the cheating behavior of photographs in face recognition method, the difference between living face and image video face can be judged effectively.
Owner:FOSHAN NANHAI GUANGDONG TECH UNIV CNC EQUIP COOP INNOVATION INST +1
Method for generating intuitive quasi-eigen paces
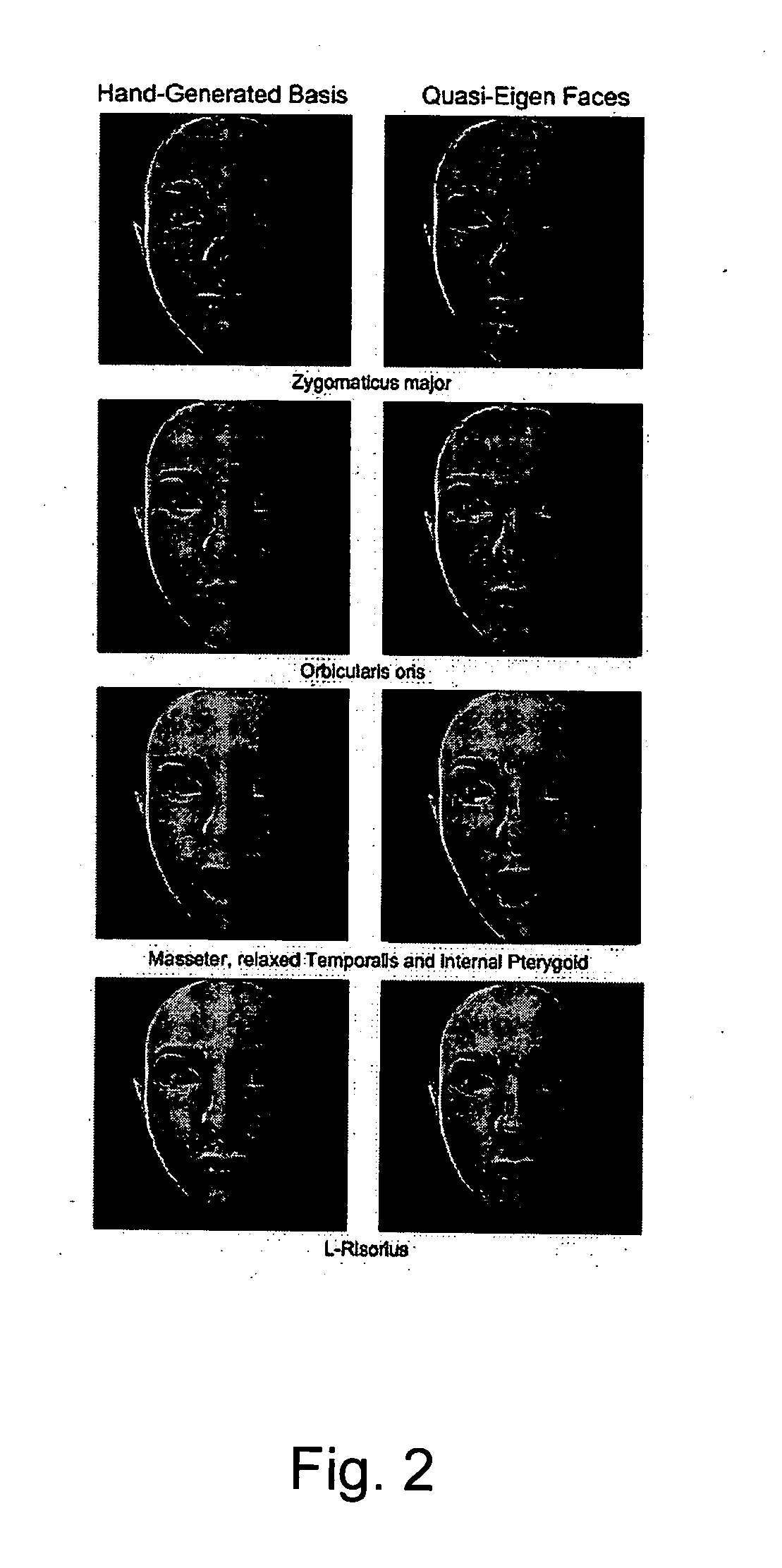
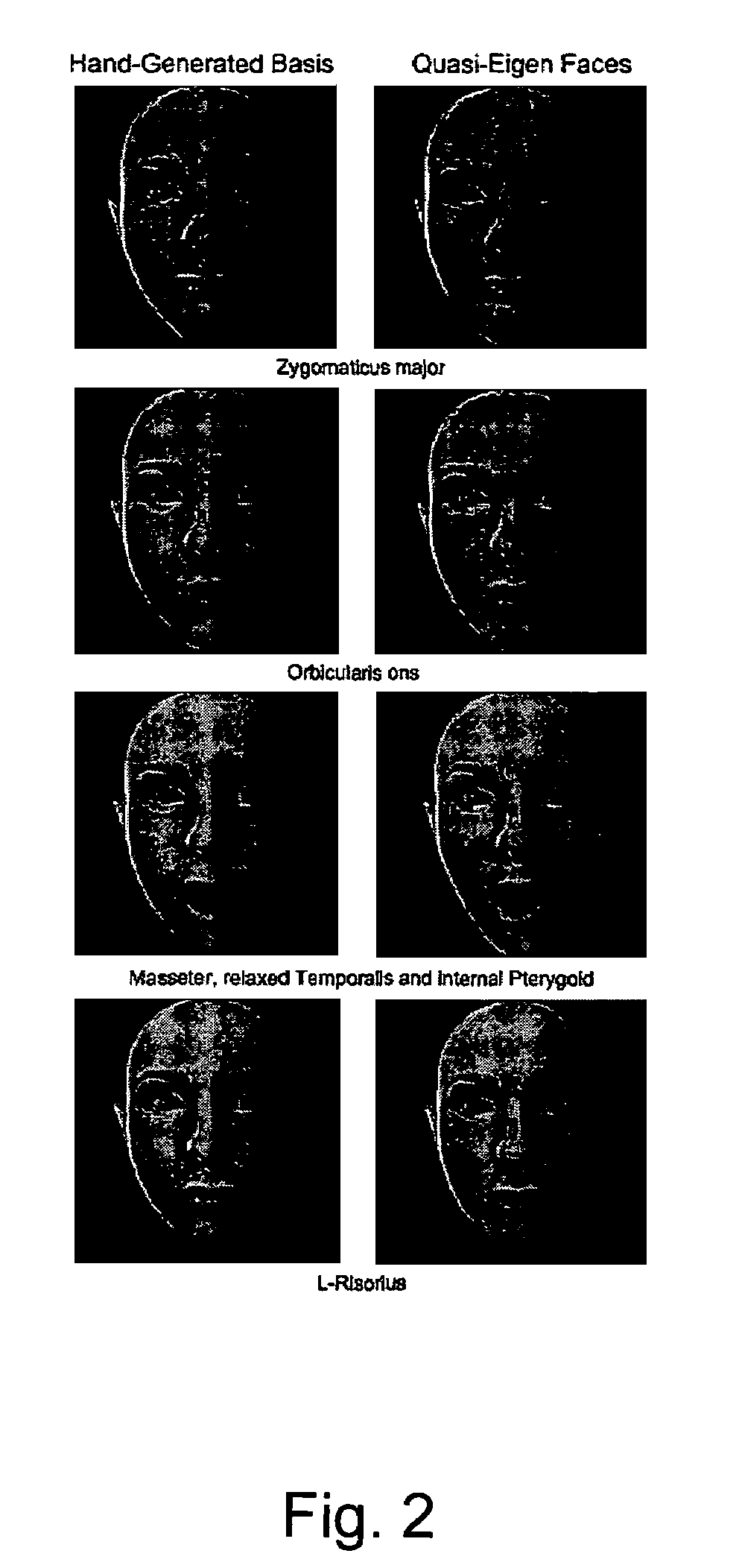
InactiveUS20070236501A1Reduce reconstruction errorReduce errorsAnimation3D-image renderingAnimationTheoretical computer science
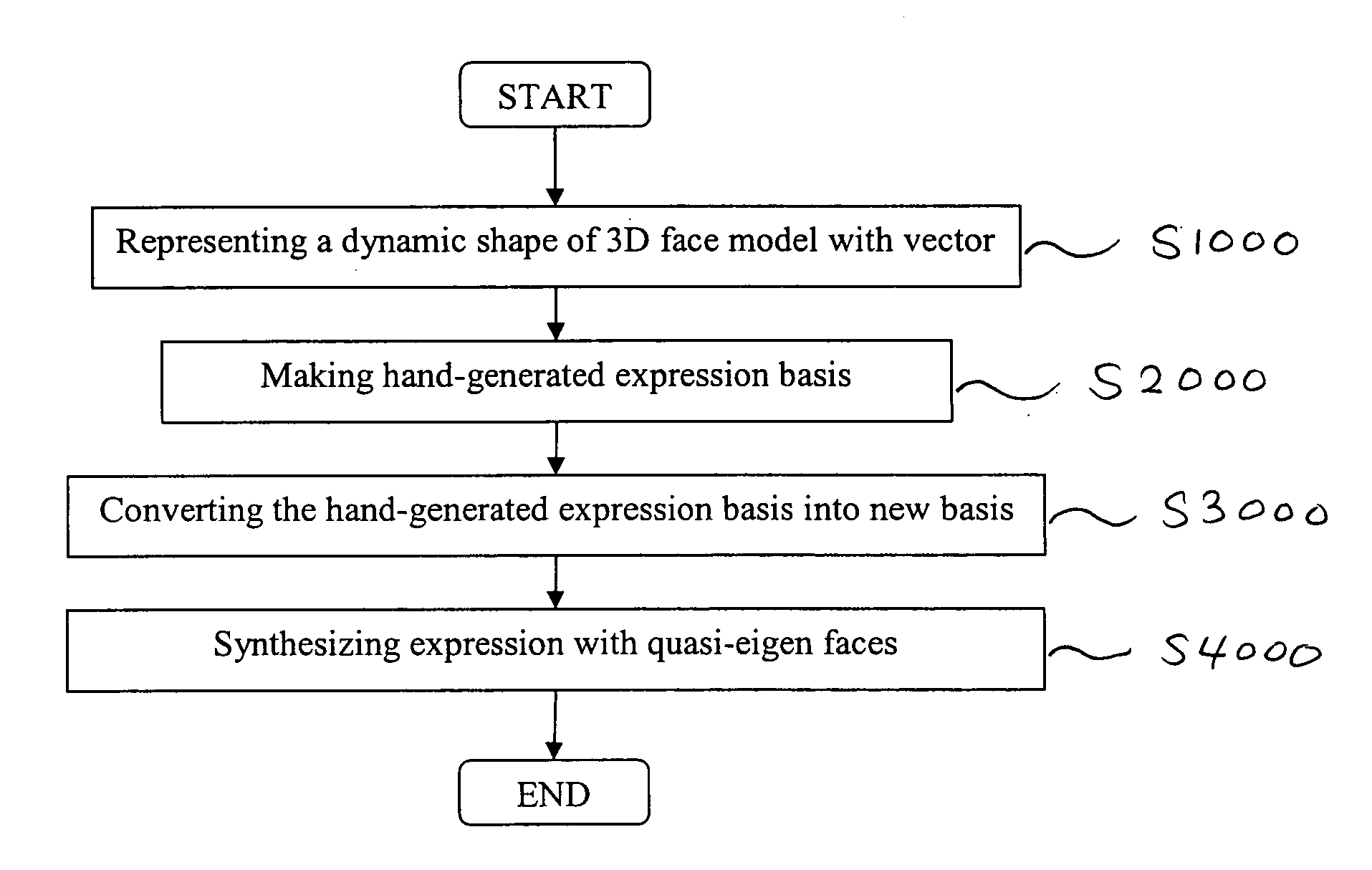
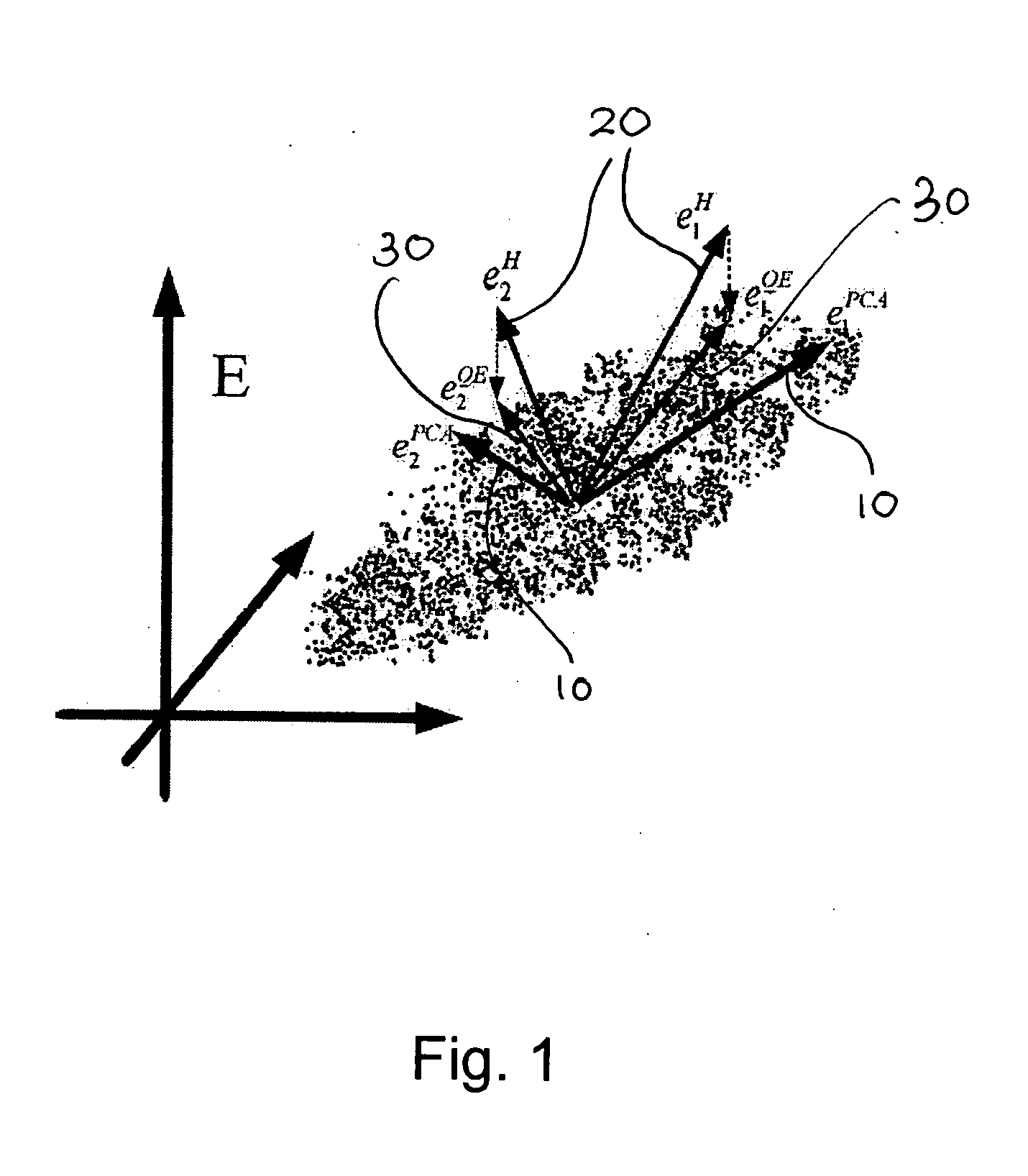
In blendshape-based facial animation, two main approaches are used to create the key expressions: manual sculpting and statistically-based techniques. Hand-generated expressions have the advantage of being intuitively recognizable, thus allowing animators to use conventional keyframe control. However, they may cover only a fraction of the expression space, resulting in large reproduction animation errors. On the other hand, statistically-based techniques produce eigenfaces that give minimal reproduction errors but are visually non-intuitive. In the invention the applicants propose a technique to convert a given set of hand-generated key expressions into another set of so-called quasi-eigen faces. The resulting expressions resemble the original hand-generated expressions, but have expression space coverages more like those of statistically generated expression bases. The effectiveness of the proposed technique is demonstrated by applying it to hand-generated expressions.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Low-rank matrix and eigenface-based human face identification method
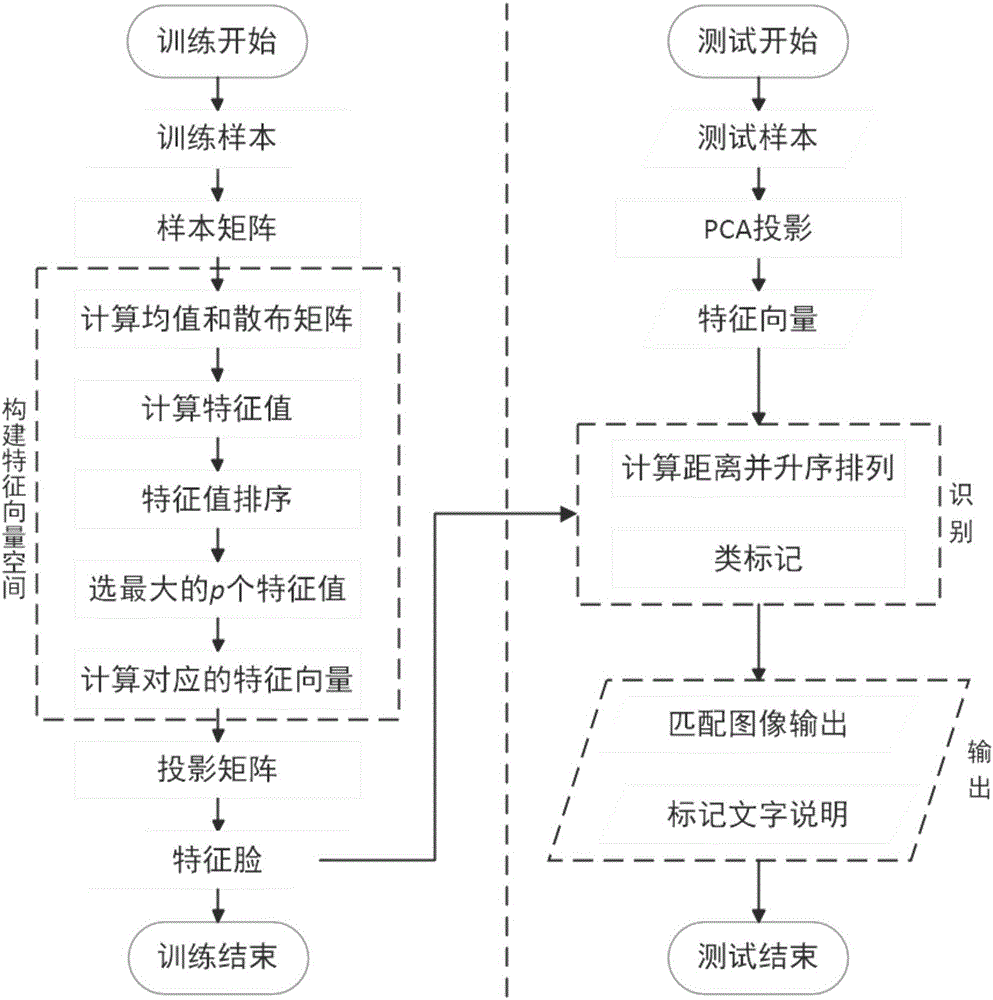
InactiveCN106096517AEnhance expressive abilityHigh expressionCharacter and pattern recognitionShortest distanceSample image
The invention discloses a low-rank matrix and eigenface-based human face identification method, which relates to the technical fields of digital image processing, mode identification, computer vision, physiology and the like, and is used for solving the problem in human face identification based on static images or video images in various scenes. A low-rank matrix is applied to preprocessing of a human face picture based on a low-rank matrix concept, and the influence of changes of illumination, expressions and the like is reduced through low-rank processing on a training picture, so that the algorithm robustness and the identification accuracy are improved. According to the key points of the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps of firstly acquiring a human face sample picture and establishing a sample library; secondly during a training stage, constructing an eigenvector space through operations of calculating a sample mean value, an eigenvalue, an eigenvector and the like, and projecting the eigenvector to obtain an eigenface; and finally during a test stage, performing PCA projection on a test sample to obtain an eigenvector, calculating a distance between the eigenvector and the eigenface, taking a shortest distance as an identification result, and outputting the identification result.
Owner:BEIJING UNION UNIVERSITY
Method for generating intuitive quasi-eigen faces
In blendshape-based facial animation, two main approaches are used to create the key expressions: manual sculpting and statistically-based techniques. Hand-generated expressions have the advantage of being intuitively recognizable, thus allowing animators to use conventional keyframe control. However, they may cover only a fraction of the expression space, resulting in large reproduction animation errors. On the other hand, statistically-based techniques produce eigenfaces that give minimal reproduction errors but are visually non-intuitive. In the invention the applicants propose a technique to convert a given set of hand-generated key expressions into another set of so-called quasi-eigen faces. The resulting expressions resemble the original hand-generated expressions, but have expression space coverages more like those of statistically generated expression bases. The effectiveness of the proposed technique is demonstrated by applying it to hand-generated expressions.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
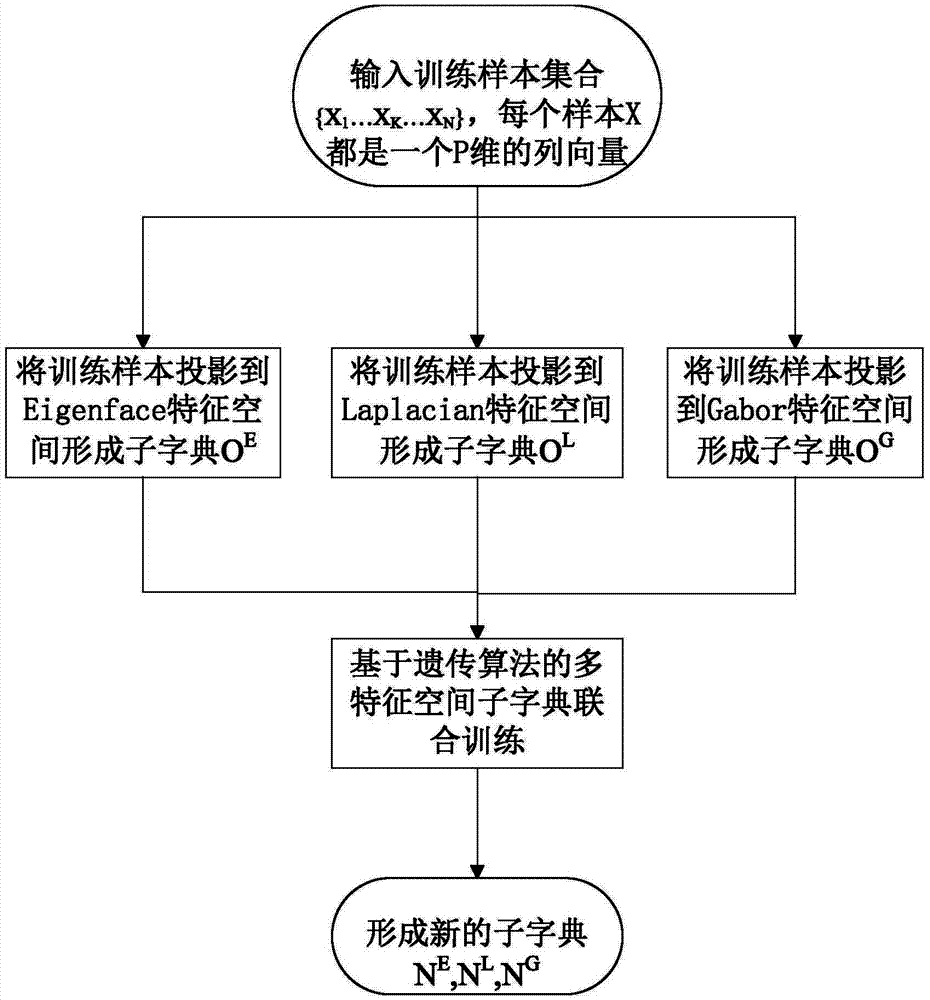
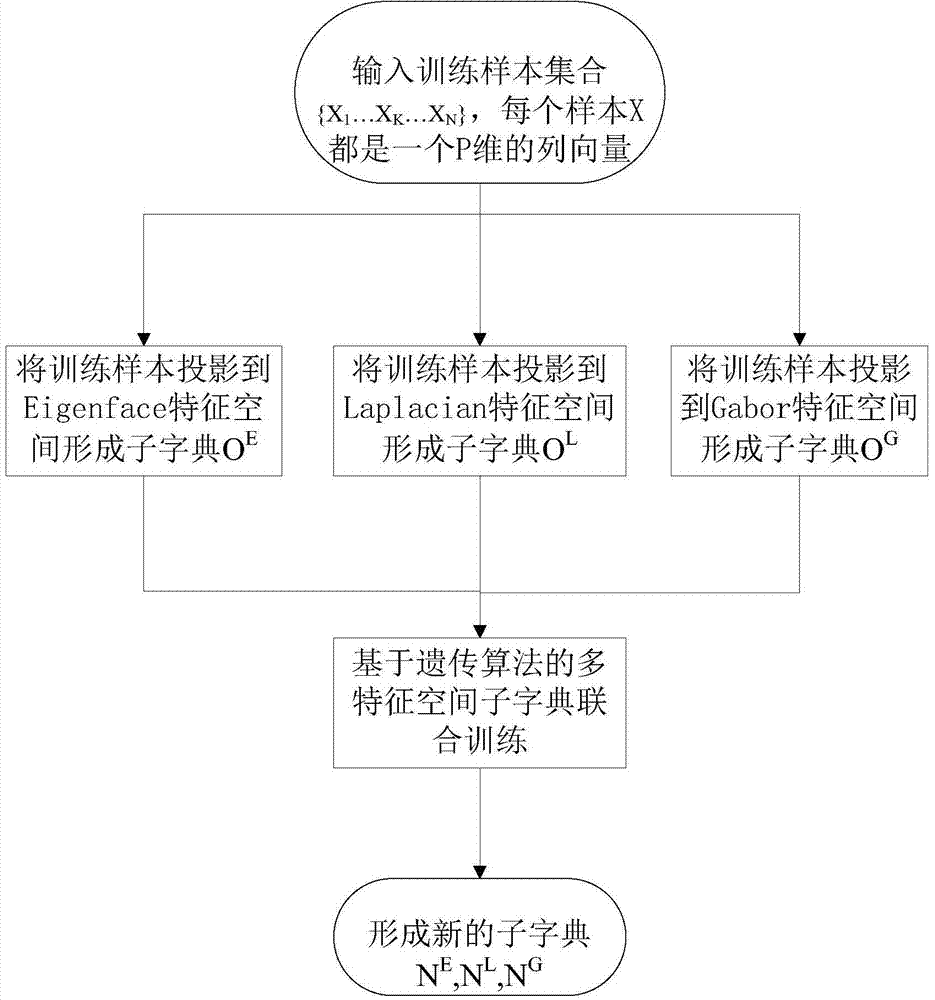
Human face recognition method based on multiple-feature space sparse classifiers
InactiveCN103793694AGood effectAccurate classificationCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionGenetic algorithm
The invention provides a human face recognition method based on multiple-feature space sparse classifiers. The human face recognition method includes the following steps that original training samples, namely X1....XN, are projected onto an Eigenface feature space, a Laplacianface feature space and a Gabor feature space respectively to form a sub-dictionary OE, a sub-dictionary OL and a sub-dictionary OG; the genetic algorithm is used for carrying out joint optimization and training on the three sub-dictionaries to obtain a sub-dictionary NE, a sub-dictionary NL and a sub-dictionary NG; the sub-dictionary NE, the sub-dictionary NL and the sub-dictionary NG are used for training the sparse classifier SRCs. Each sparse classifier carries out sparse representation on a sample to be tested and obtains residual errors corresponding to the ith training sample, wherein the residual errors are RiE, RiL and RiG respectively and then, the mean value of the residual errors corresponding to the ith training sample are calculated. A category corresponding to the minimum value of the residual error mean value E[Ri] is the category which the human face sample to be tested belongs to. According to the human face recognition method based on the multiple-feature space sparse classifiers, the adopted dictionary training method can select a sample with the best separating capacity from each sub-dictionary, so that the human face recognition accuracy based on the sparse classifiers with the dictionaries is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
System And Method For Identifying Patterns
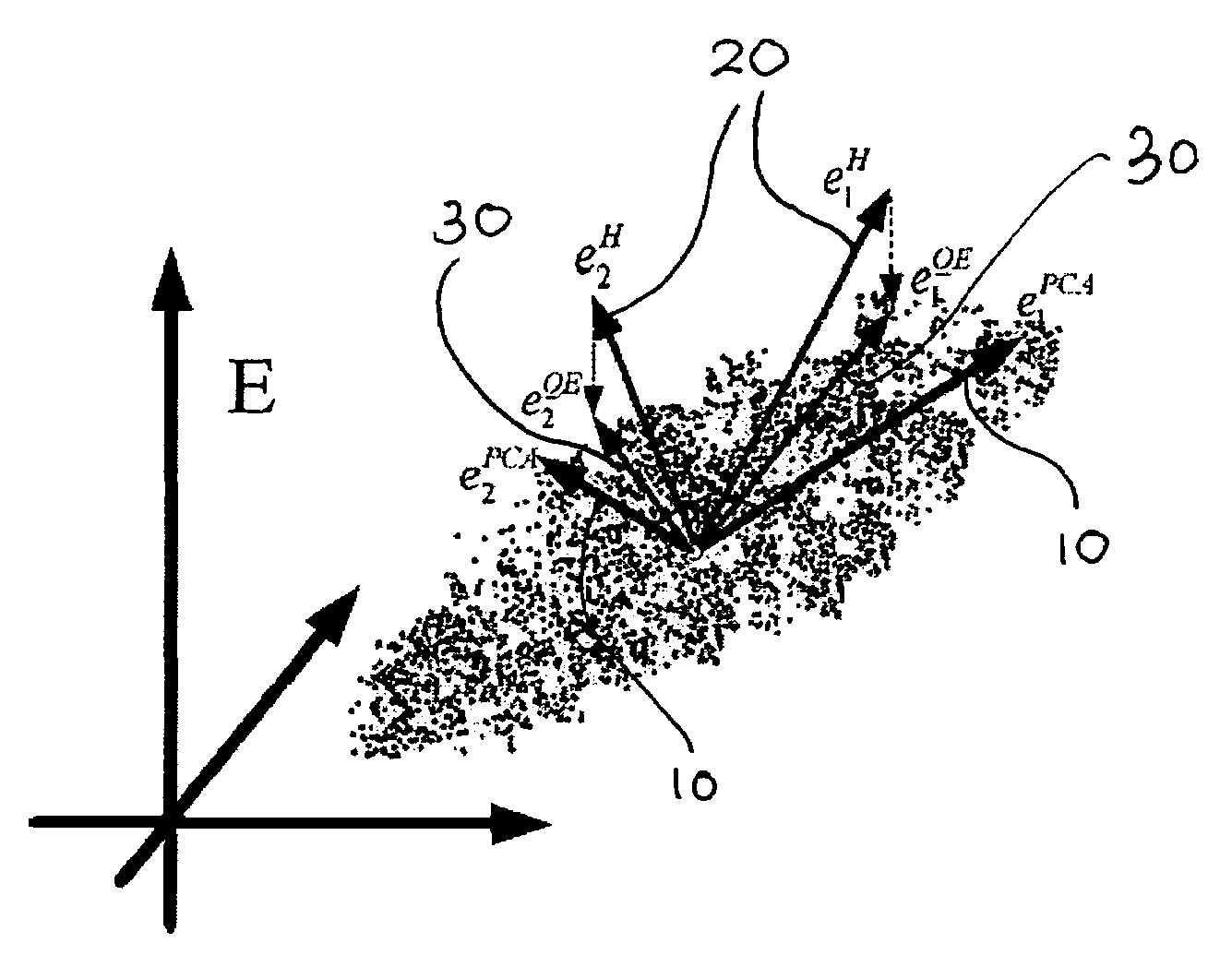
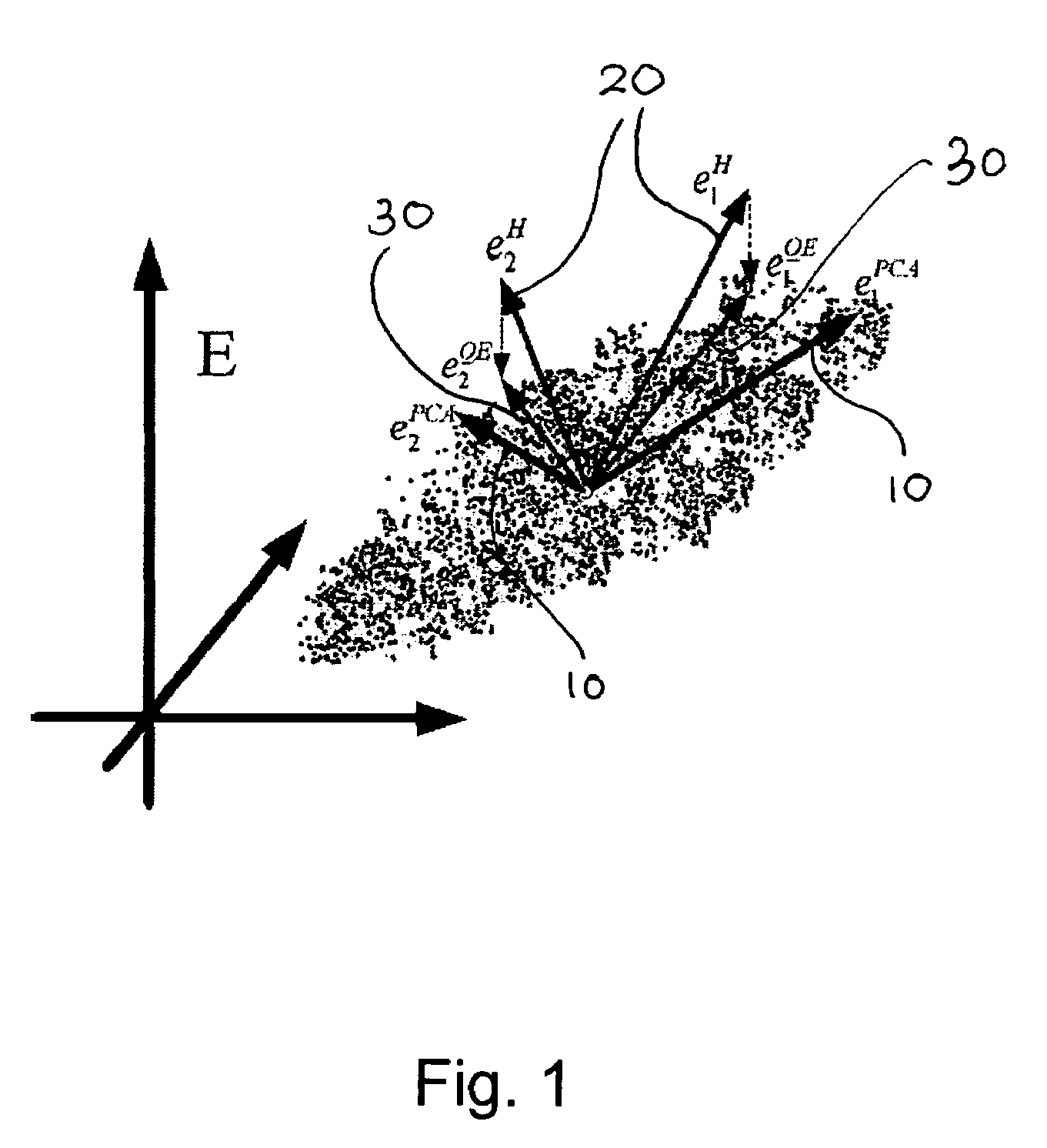
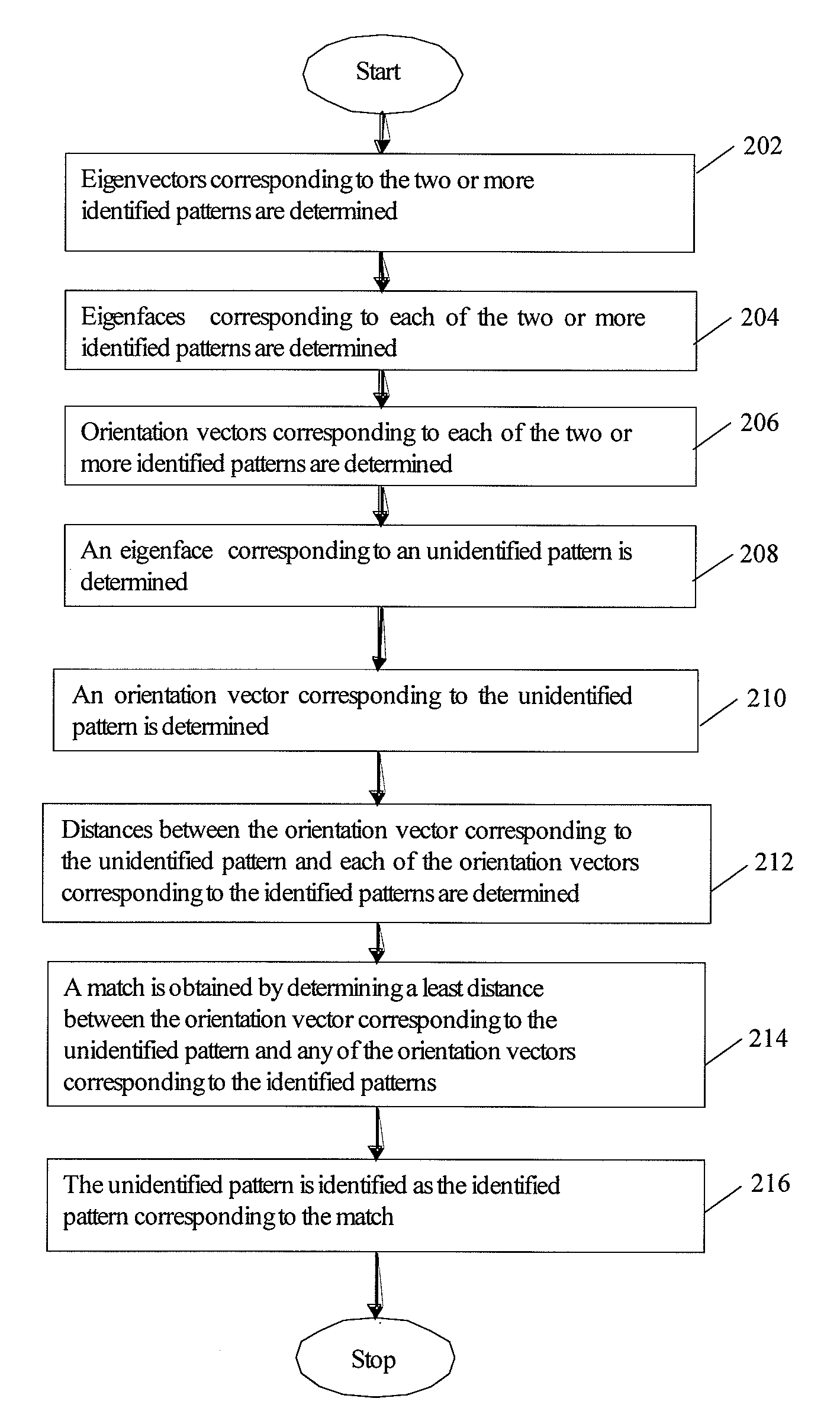
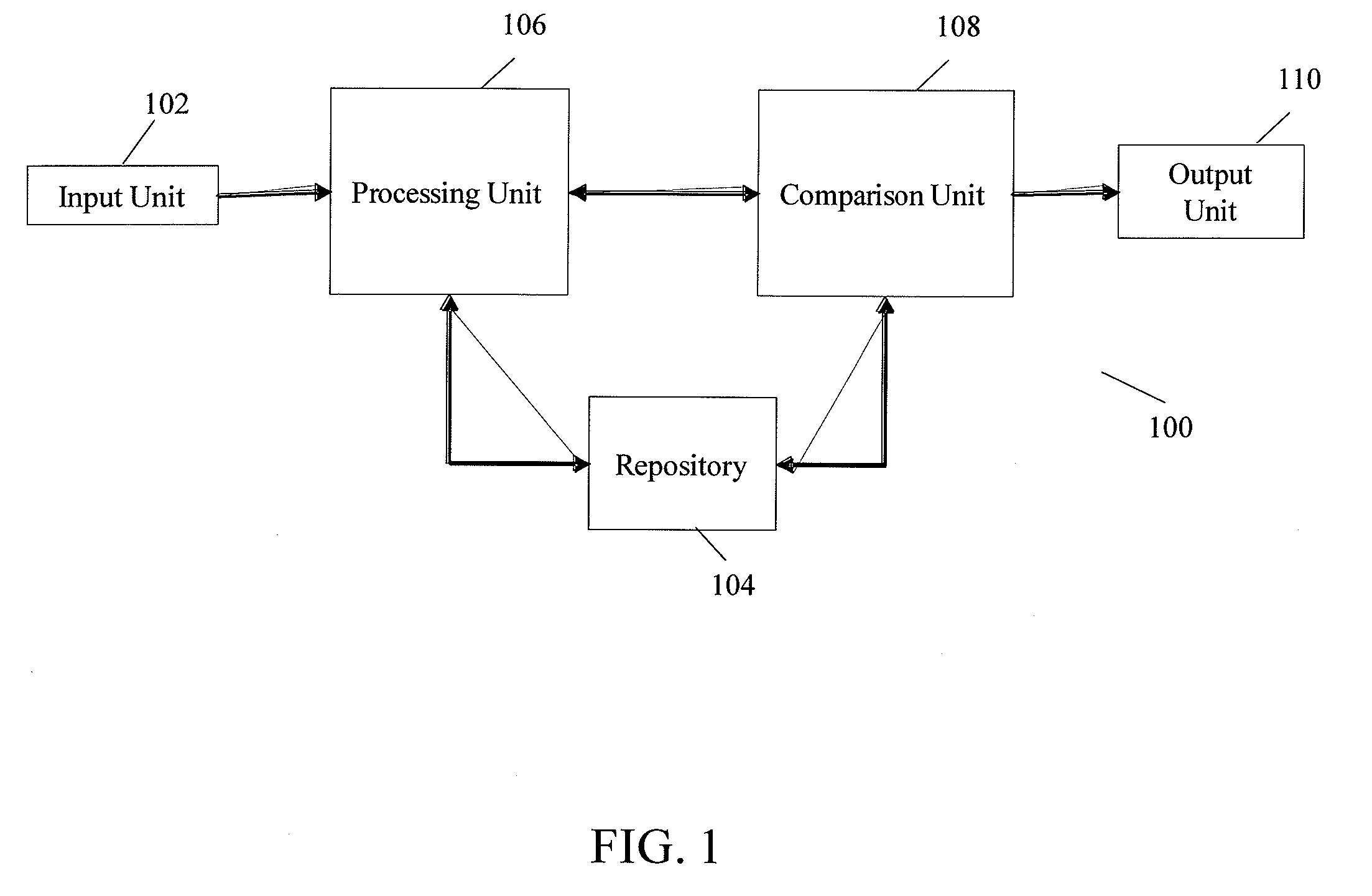
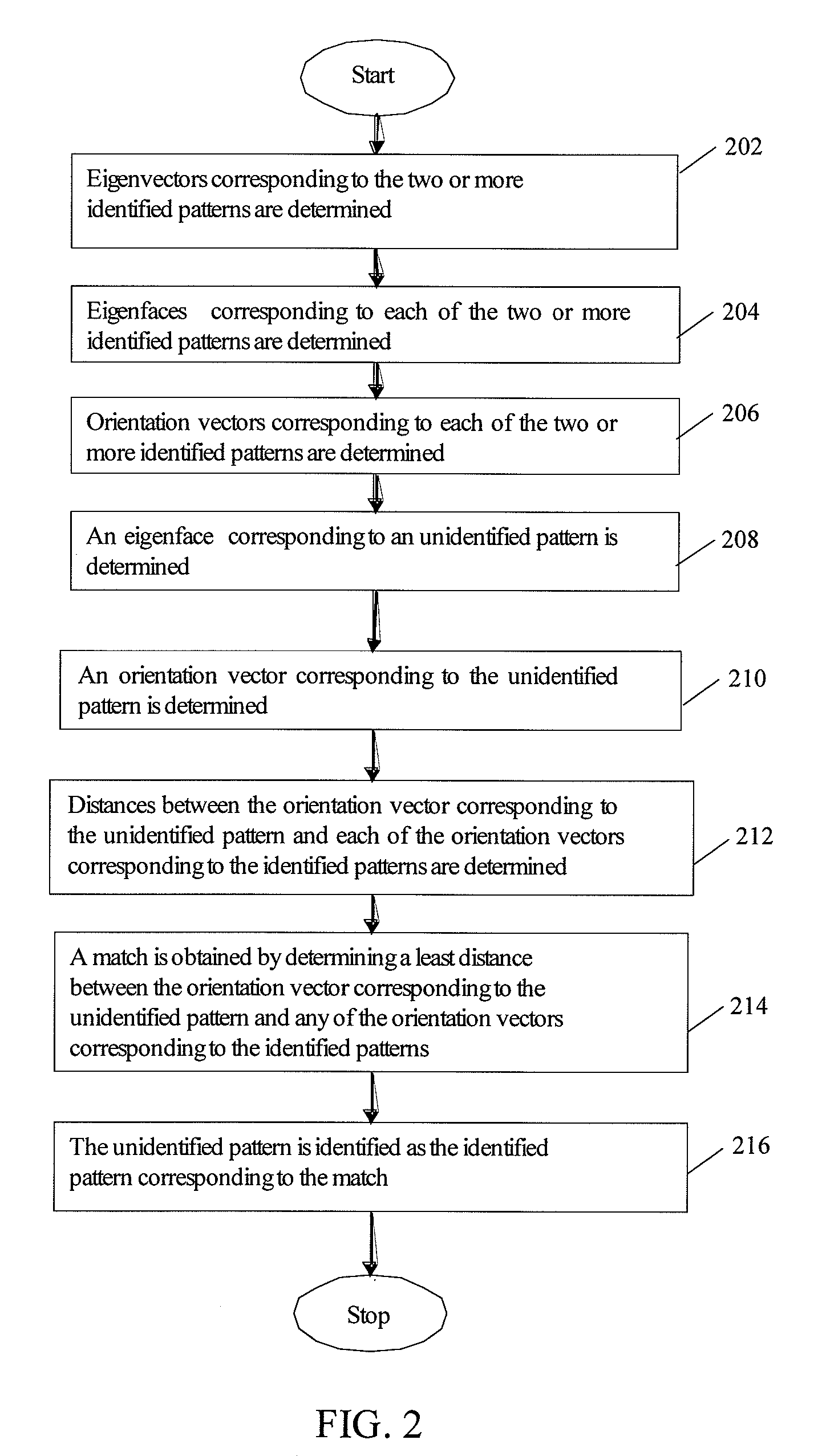
The present invention relates to a system and method for identifying of a pattern by comparing the pattern with two or more identified patterns. The system comprises an input unit for capturing a pattern for identification, a processing unit for determining eigenfaces corresponding to the captured pattern and the two or more identified patterns, and determining orientation vectors corresponding to each determined eigenface, and a comparison unit for comparing the determined orientation vector corresponding to the captured pattern with each of the determined orientation vectors corresponding to the identified patterns. The method comprises determining eigenvectors corresponding to each of the identified patterns, determining eigenfaces corresponding to each of the identified patterns and the pattern being identified, determining orientation vectors corresponding to each of the identified patterns and the pattern being identified, comparing an orientation vector corresponding to the pattern being identified with each of the orientation vectors corresponding to the identified patterns, and identifying the pattern. The present invention further provides a method of clustering a plurality of patterns into a predetermined number of clusters by using orientation vectors.
Owner:ESWARAN KUMAR
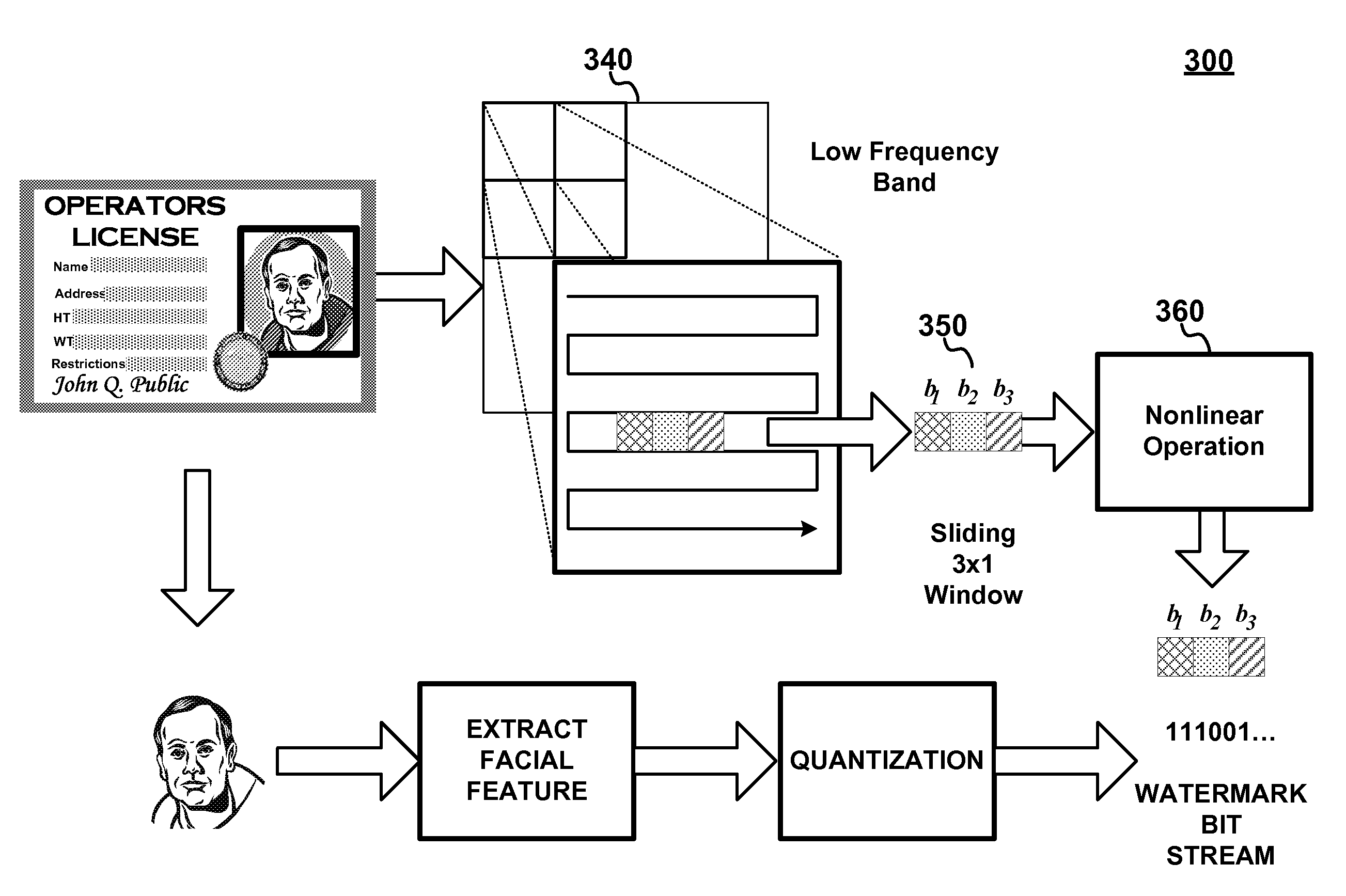
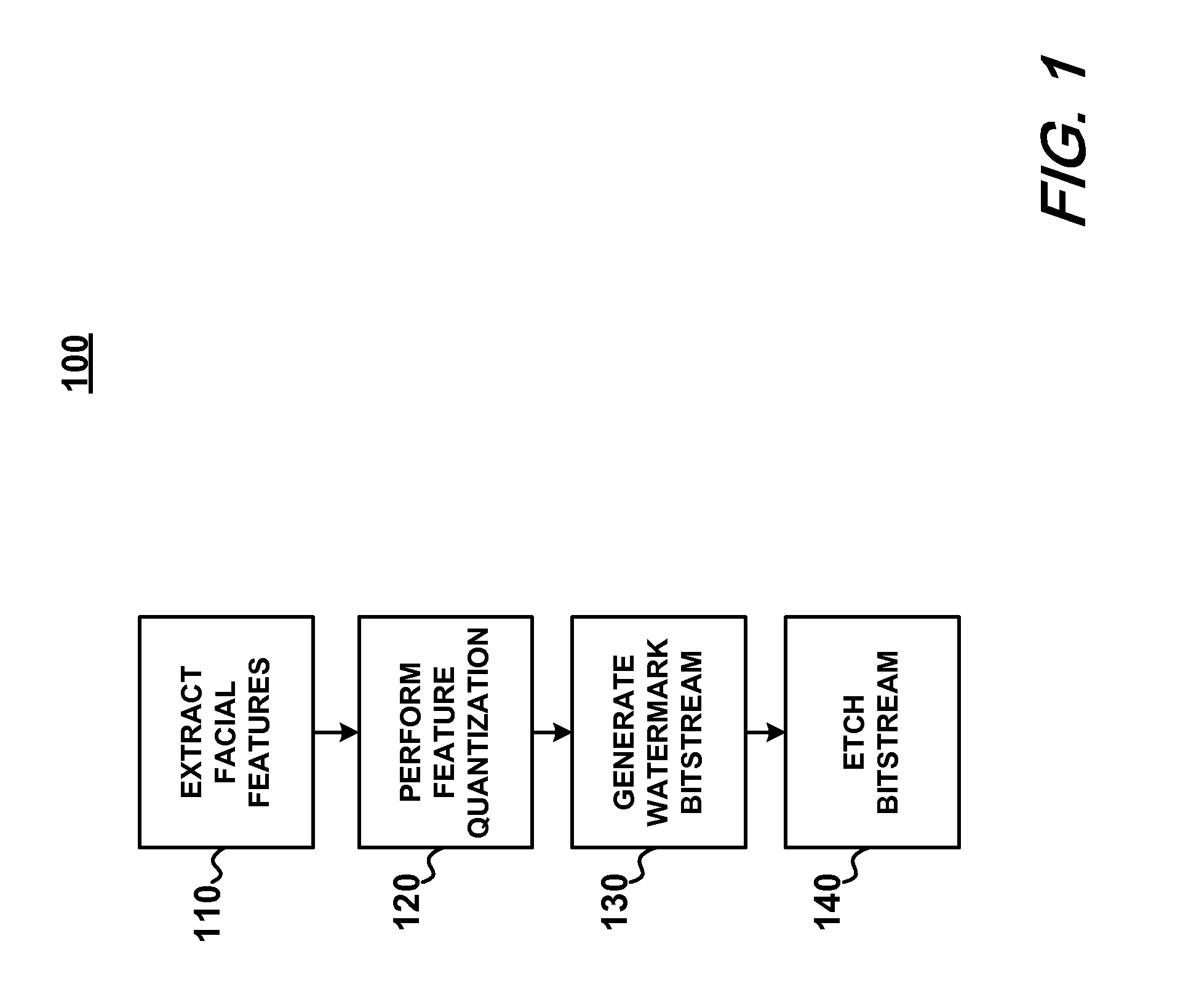
Digital watermarking of picture identity documents using Eigenface vectors of Eigenface facial features of the document facial image as the watermark key
InactiveUS7668347B2Simple methodImprove securityPaper-money testing devicesCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionDriver's license
An improved method of watermarking picture identification documents (IDs) such as passports, driver's licenses, identification cards and the like which combines biometric information with digital watermarking to provide an improved secure picture ID document and authentication of same. A facial image—that is part of the identification document—is processed such that particular facial features are extracted from the overall facial image. The extracted features are used to generate a watermark key that is subsequently used to embed a unique watermark into the facial image or other location on the identification document.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
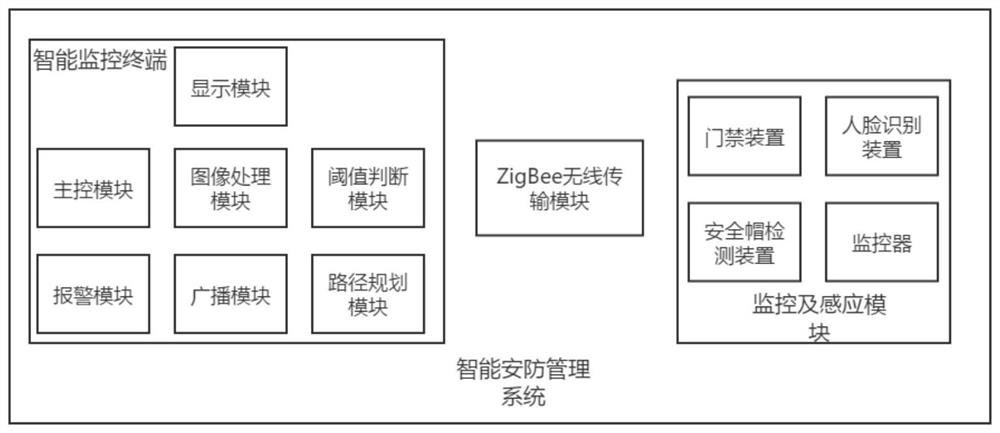
Face recognition method and device and intelligent security and protection management system
PendingCN112183394AEfficient identificationRelease work pressureCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringComputer vision
The invention discloses a face recognition method and device and an intelligent security and protection management system, and the method comprises the steps: calculating the feature face weight of ato-be-recognized face image, and then calculating the Euclidean distance between the feature face weight of the to-be-recognized face image and each value in a feature face weight vector of a trainingset, and if a certain Euclidean distance is less than or equal to a preset similar face threshold, judging that the face is the same face, if all Euclidean distances are greater than or equal to a preset non-face threshold, considering that the face is a non-face, and if all Euclidean distances are between the similar face threshold and the non-face threshold, considering that the face is a new face. Non-human faces and human faces without entrance guard permission can be effectively recognized, the intelligent security and protection management system can achieve the functions of remote monitoring, automatic alarming, entrance guard management, intelligent human face recognition, intelligent safety helmet recognition, safety early warning, video capture and the like, the working pressureof people is relieved, and the working behaviors of warehouse personnel are standardized.
Owner:江苏智库智能科技有限公司
Joint training method of sub-dictionaries in multiple characteristic spaces and for face recognition
InactiveCN103793695AImprove featuresGood distinctionCharacter and pattern recognitionGenetic algorithmCharacteristic space
The invention provides a joint training method of sub-dictionaries in multiple characteristic spaces and for face recognition. The joint training method of the sub-dictionaries in the multiple characteristic spaces and for face recognition comprises the steps that original training samples{X[1] to X[N]} are projected in the Eigenface characteristic space, the Laplacianface characteristic space and the Gabor characteristic space to form the sub-dictionary OE, the sub-dictionary OL and the sub-dictionary OG respectively, and joint optimization training is carried on the three sub-dictionaries by using a genetic algorithm to obtain the sub-dictionary NE, the sub-dictionary NL and the sub-dictionary NG. According to the joint training method of the sub-dictionaries in the multiple characteristic spaces and for face recognition, a sample, with the highest distinguishing capacity, in each sub-dictionary can be selected, and thus accuracy of face recognition on the basis of a sparse classifier using the sub-dictionaries can be improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
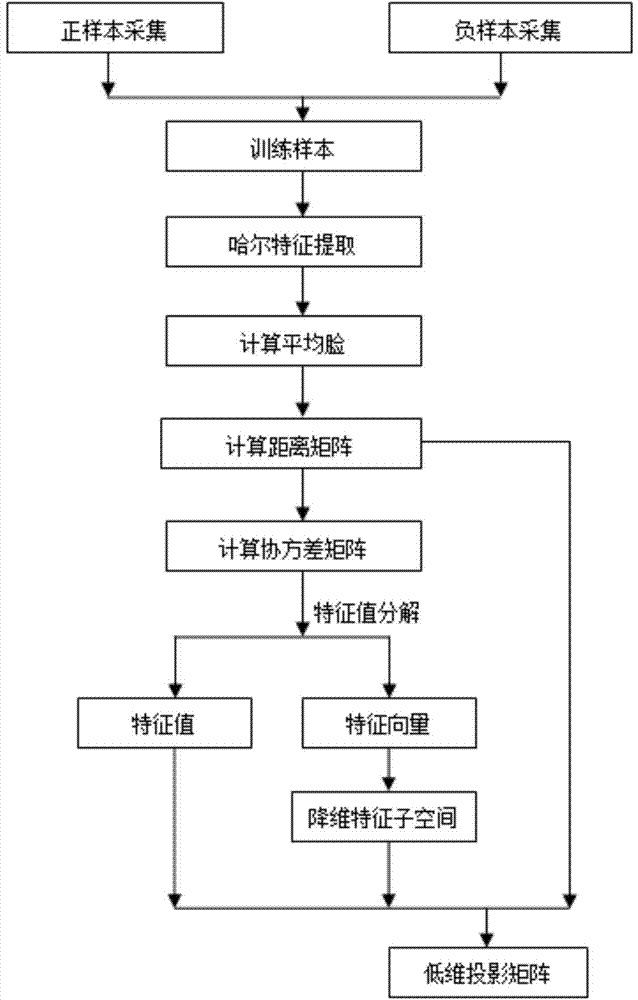
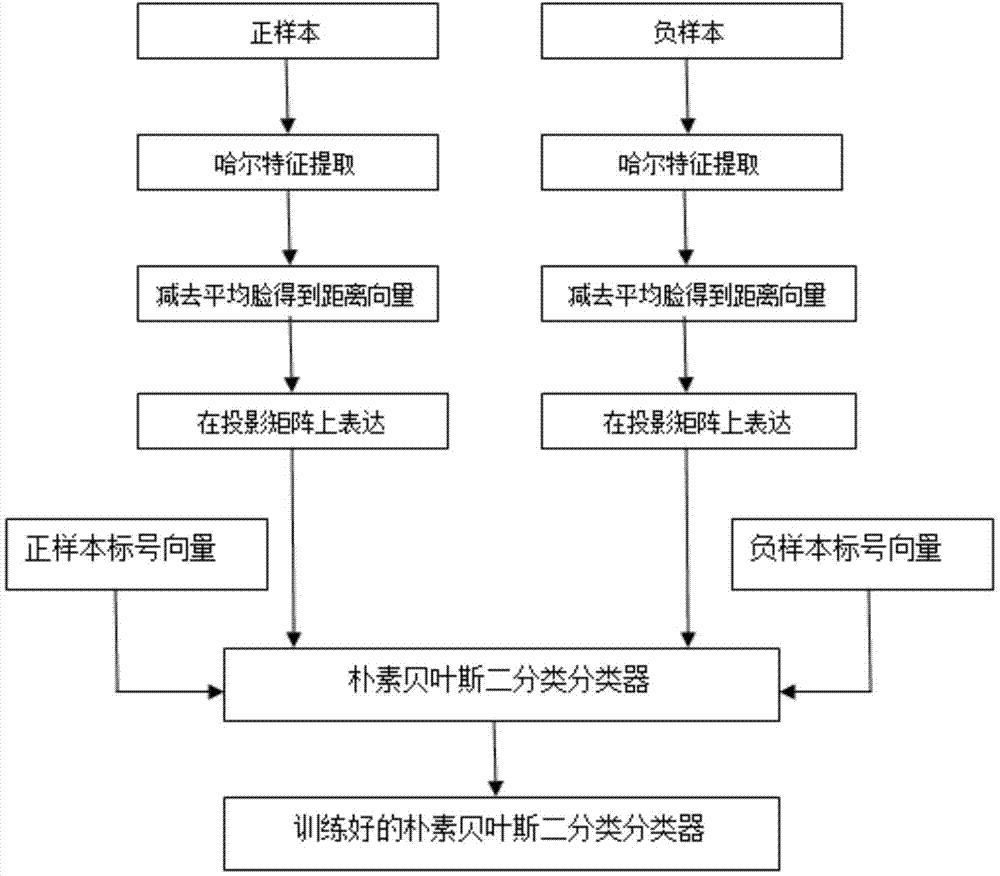
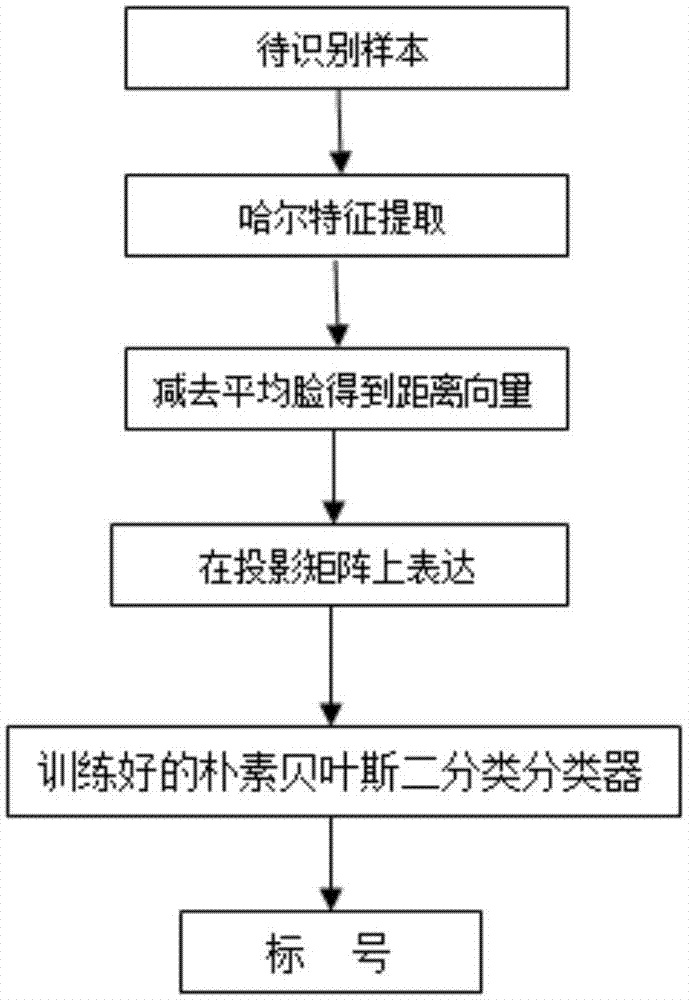
Face recognition method based on Haar-like features and eigenface recognition
InactiveCN104715263AMultiprogramming arrangementsCharacter and pattern recognitionNonlinear modelLinear model
The invention discloses a face recognition method based on Haar-like features and eigenface recognition. According to the method, on the basis that low-dimension feature space is constructed based on Haar-like features and a principal component analysis technology to perform feature extraction, a model is built by a classier technology, and a linear feature combination idea in an old method is improved; and the essence of the introduction of a classifier is to replace a traditional linear model with a nonlinear model so that the accuracy of recognition is greatly increased.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
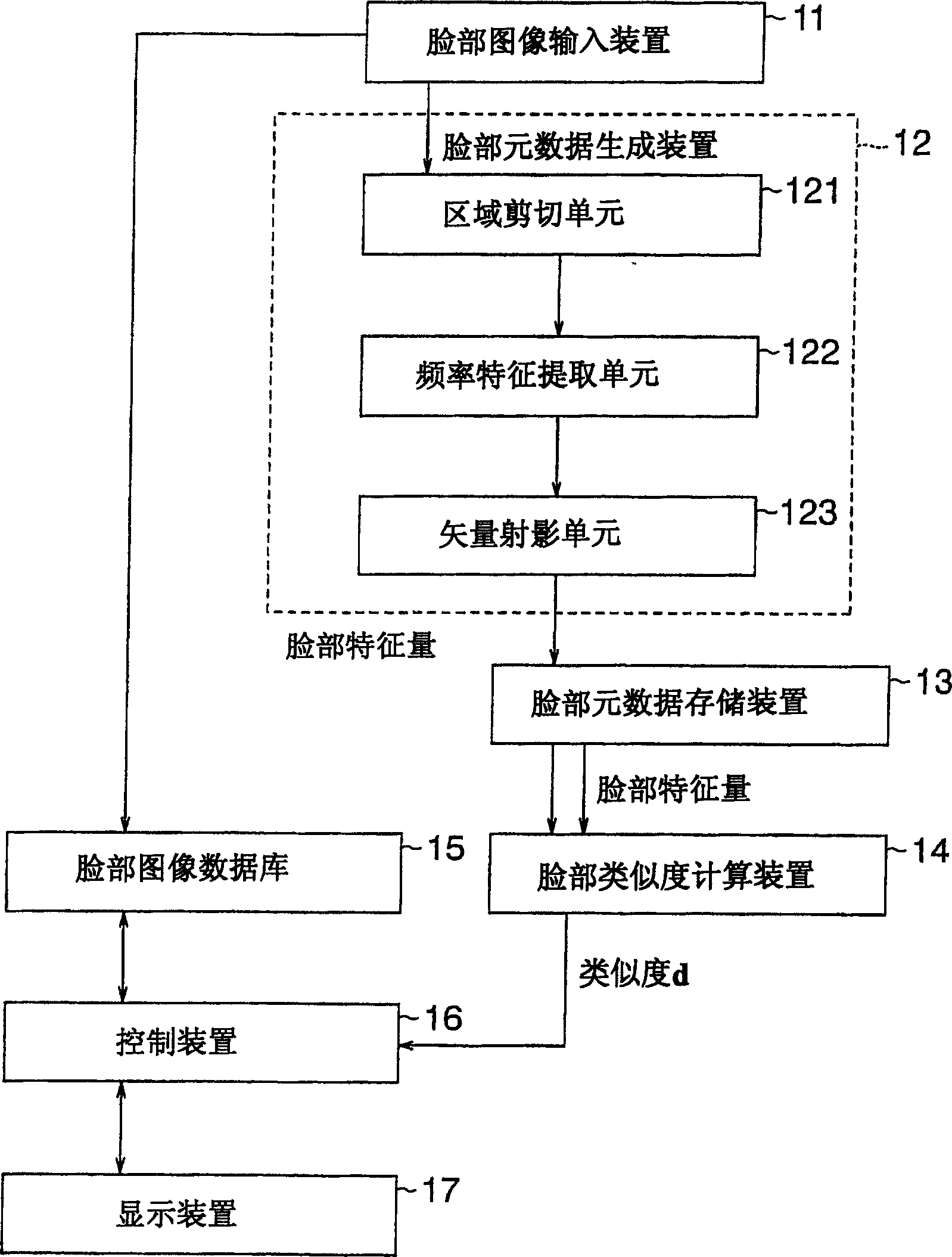
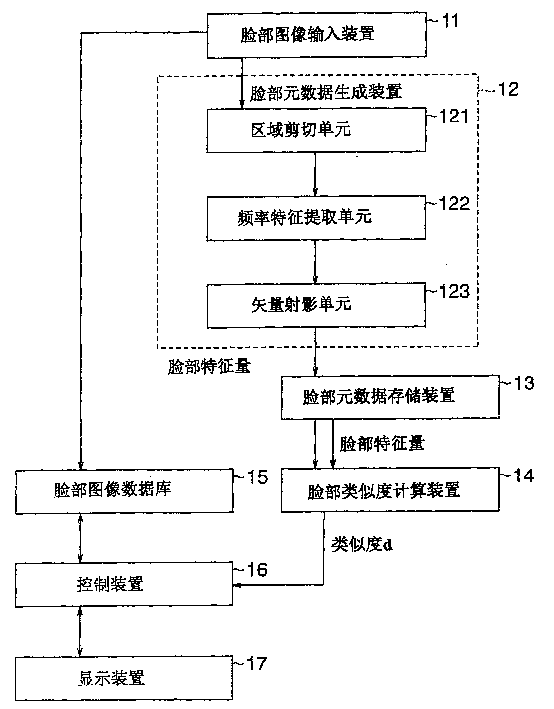
Face meta-data creation
A face meta-data creating technique in which the description length is short and which is used to extract the face feature for face recognition immune to the local error. An area cut-out section ( 121 ) cuts out a local area of a face image. Frequency feature extracting means ( 122 ) extracts the frequency spectrum of the local area. Vector projection means ( 123 ) projects the obtained frequency feature onto a partial space to extract the face feature of the local area. Aface meta-data unit ( 12 ) extracts the face features from local areas cut out in different positions, thus creating face features as face meta-data.
Owner:NEC CORP
Human face recognition system and method based on second-order two-dimension principal component analysis
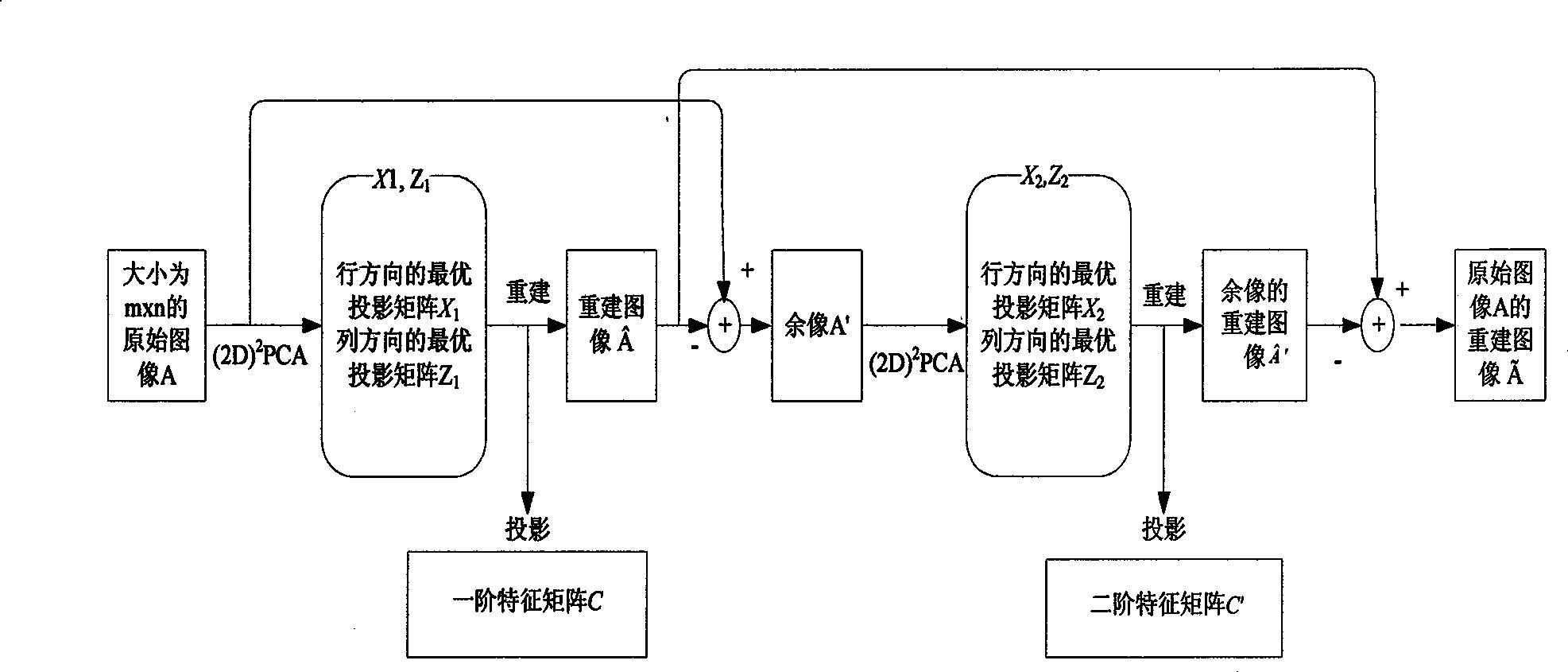
InactiveCN101482917AAvoid interferenceImprove recognition rateCharacter and pattern recognitionKernel principal component analysisComputation complexity
The invention requests to protect a face recognition system and a face recognition method which are based on the second-order two-dimensional principal component analysis, and belongs to the fields of image processing technology, computer vision technology and mode identification technology. The invention provides the face recognition method which has low computational complexity and is based on the second-order two-dimensional principal component analysis. The method researches the face recognition problem in the condition of illumination change, and provides the face recognition method of the second-order two-dimensional principal component analysis. The face recognition method comprises: respectively applying the (2D)PCA technology to an original image matrix set and a residual image matrix set to obtain a first-order feature matrix and a second-order feature matrix, thereby determining reconstructed images of sample images and reconstructed images of residual images; superimposing the two reconstructed images to obtain reconstructed images of original images. The method of the invention has higher recognition accuracy, and save more computing time than the eigenface method and the second-order eigenface method. The method of the invention can be widely used in the image recognition field.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Online passing system based on face feature recognition technology
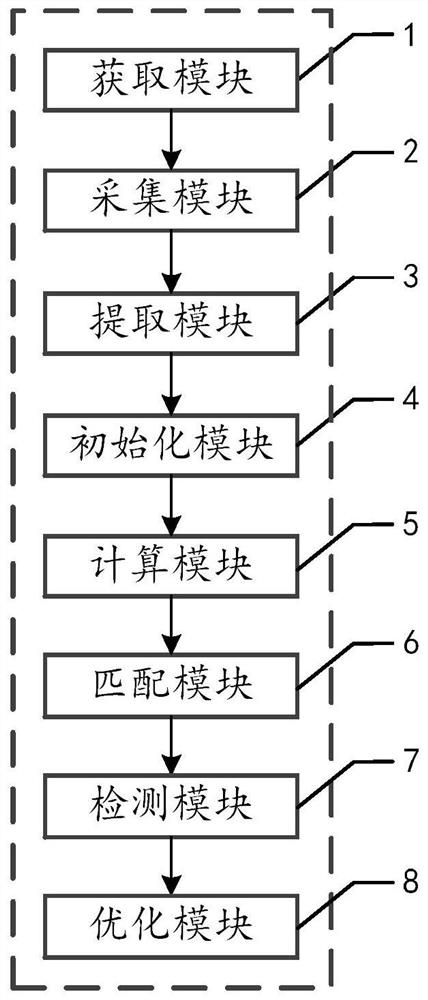
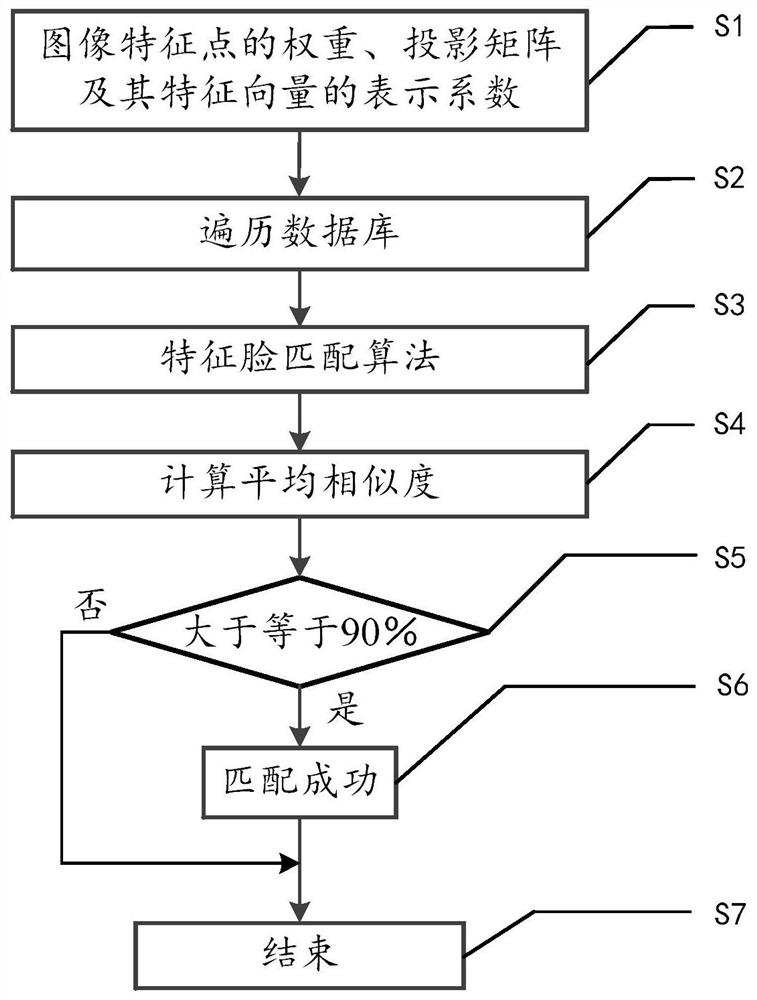
ActiveCN113505717AImprove accuracyDefend against cheatingDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmEngineering
The invention discloses an online passing system based on a face feature recognition technology. Comprising an acquisition module, an acquisition module, an extraction module, an initialization module, a calculation module, a matching module, a detection module and an optimization module. A feature face matching algorithm is adopted, so that face recognition with higher accuracy is realized; on-line / off-line living body detection service is adopted to identify whether a user is a real person or not, and cheating tools such as photos, videos and 3D molds are effectively resisted; the space and time complexity of the system is optimized by adopting a system optimization algorithm, the response time of the system is reduced, and the fluency of the system is improved. The face feature recognition system can prevent lawbreakers from cheating by using tools such as photos, videos and 3D molds of others, can effectively improve the face recognition accuracy and passing efficiency of an existing face recognition system, can be widely applied to the fields of financial industry, retail industry, security passing and the like, and the business requirements of identity verification, face attendance checking, gate passing and the like are met.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
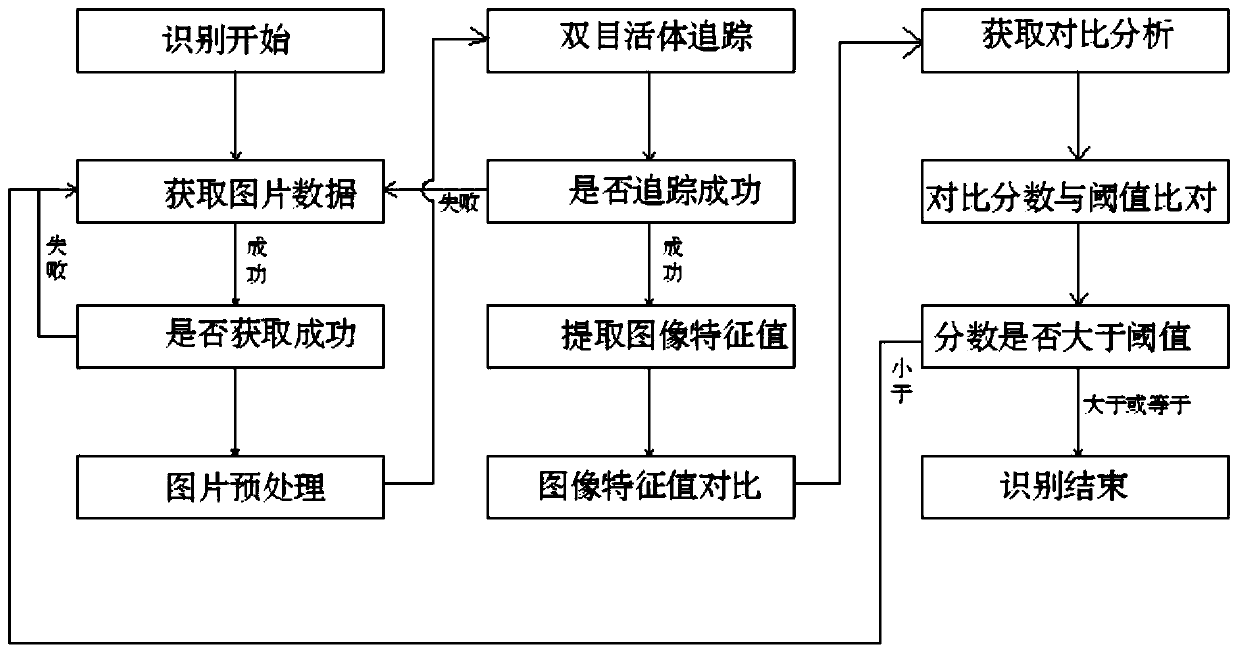
Face recognition method
The invention provides a face recognition method. The face recognition method comprises the following main steps: acquiring original image data shot by an infrared camera and an RGB camera, wherein the original image data is composed of shot image data of a face of a living body, and performing brightness adjustment on a shot image through image preprocessing; extracting a feature face of the faceby adoption of a PCA principal component analysis method so as to form a feature face matrix, carry out image data detection, carrying out synchronous processing on the image shot by the infrared camera and the RGB camera, carrying out feature contour positioning on the face by adoption of a feature point extraction algorithm, and carrying out face extraction by using a modulo mode; and calculating the Euler distance between a single-time feature face and the feature face in a face library by detecting the single-time face feature, comparing the single-time feature face with the feature facein the face library, and if the Euler distance is smaller than a threshold value, judging that face recognition succeeds. According to the invention, image preprocessing and pre-extraction are carriedout on the actual environment, so the function of increasing the recognition distance and the recognition rate is actually achieved.
Owner:成都超有范儿科技有限公司
Eye-positioning method
InactiveCN109034051APrecise positioningReduce complexityAcquiring/recognising eyesTemplate matchingCharacteristic space
An eye-positioning method is provided. At present, the disadvantage of the human eye location method is that the image of the miscellaneous background and the inclined face location are inaccurate. The template matching method has high accuracy, but it needs to calculate fractal dimension many times, so the calculation is complex. The method of the invention firstly obtains a template and a feature space when determining an eye, and determines a face used in verification; the K-L transform is used to obtain characteristic face; possible eye points are detected in a picture; all candidate eye points on the image are combined, binocular windows are selected from the original image and matched with the template of step 1, and candidate eye pairs are determined to satisfy matching conditions;the face region determined by each pair of candidate eyes is projected onto the eigenface space, and the vector coefficients are obtained. The image is reconstructed according to the vector coefficients, and the correctness of the presumed eye pairs can be verified by comparing the original image with the reconstructed image. The invention does not need to reduce the size of obtaining each objectin proportion to the input picture for many times, and greatly reduces the complexity of operation from two aspects.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Geological target recognition method based on face recognition
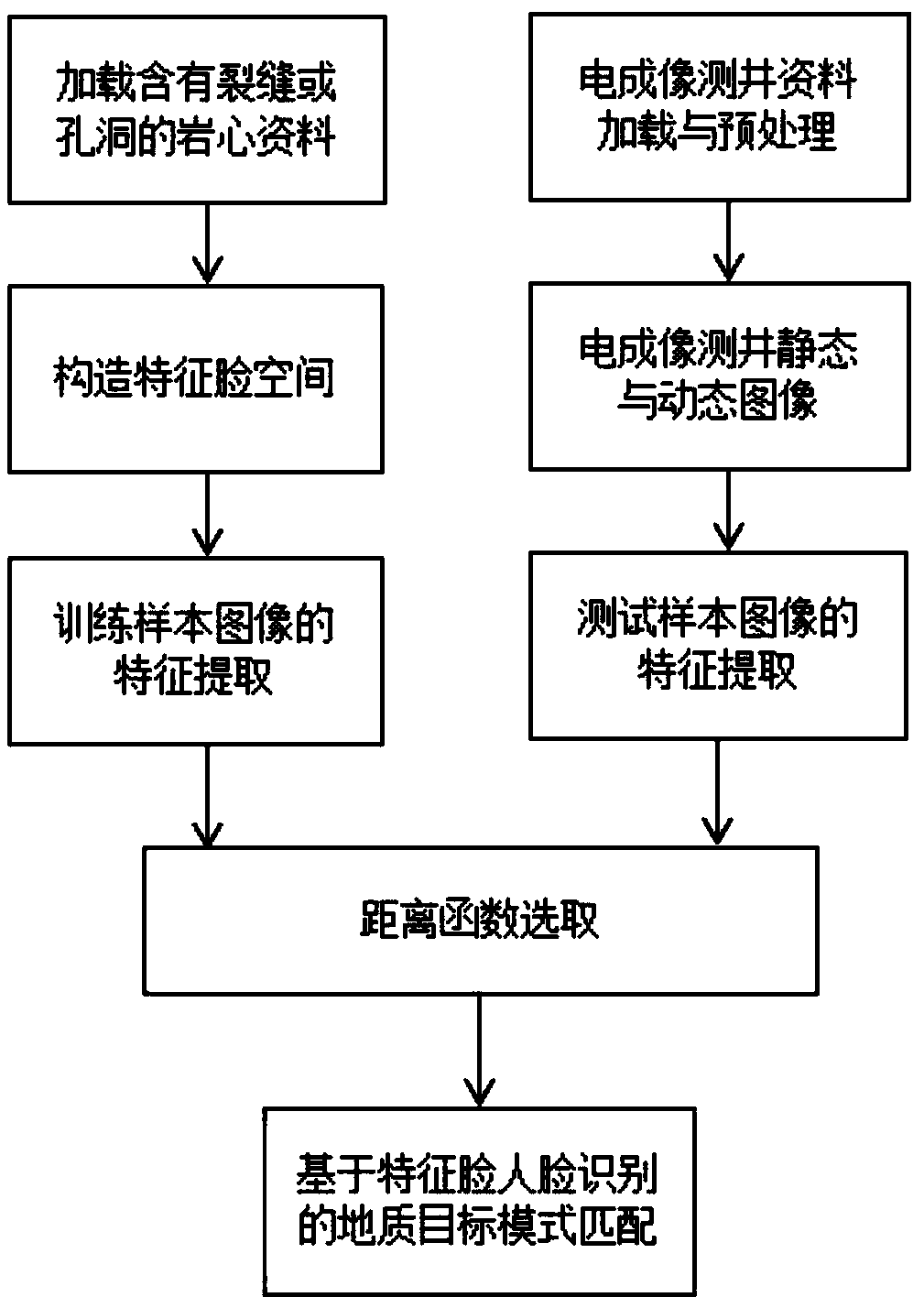
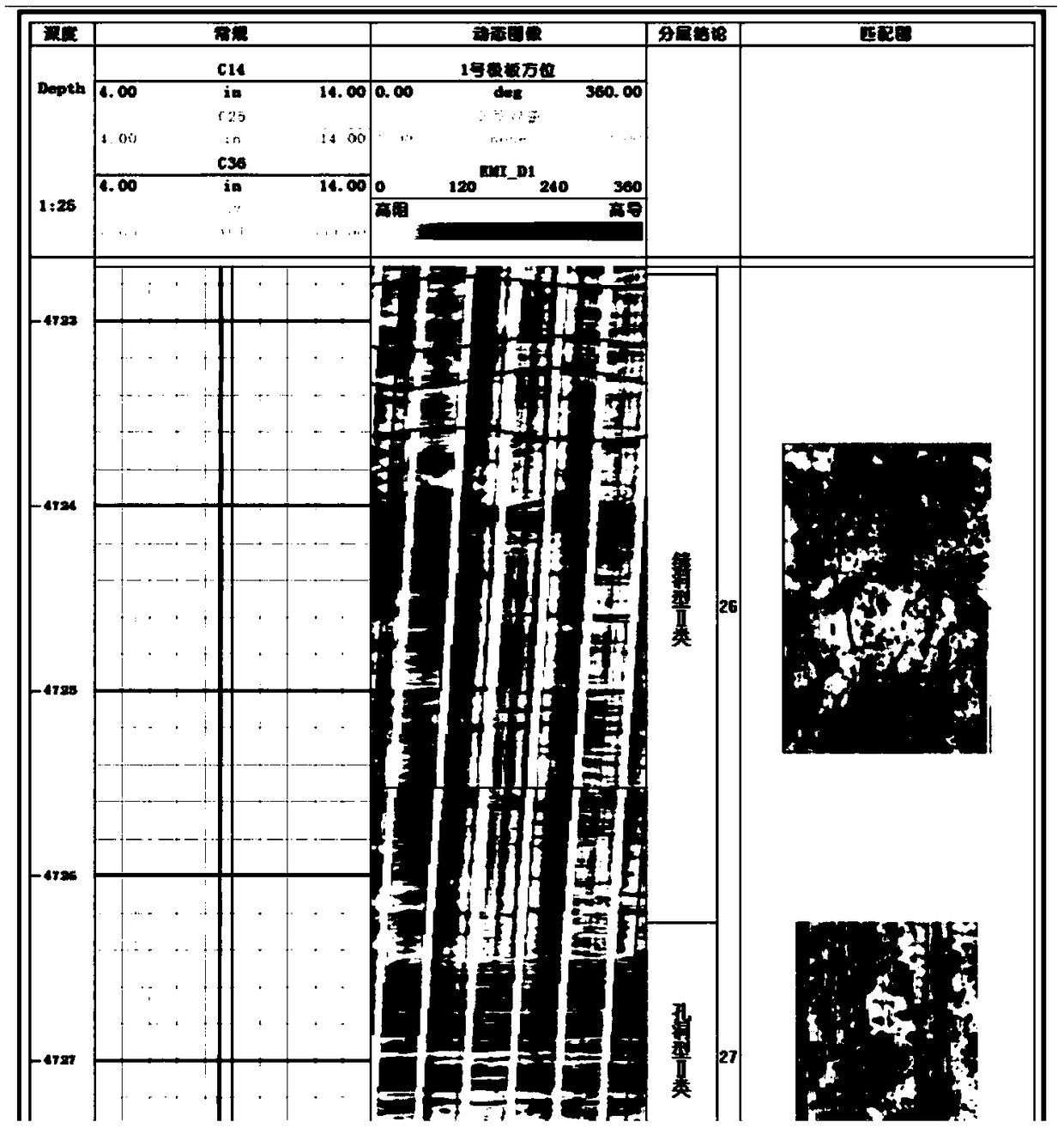
ActiveCN109344681AImprove the recognition rate of geological targetsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern matchingTest sample
The invention provides a geological target recognition method based on face recognition, which is used for recognizing geological targets such as fractures and holes of different sizes and shapes. Themethod comprises the specific steps of loading the electric imaging logging data, preprocessing and processing the electric imaging logging data, generating dynamic and static images, etc., loading core data containing fractures or cavities, structured by standard geologic target feature faces; carrying out the feature extraction of training sample image; carrying out the feature extraction of test sample image; carrying out the distance function selection; carrying out the pattern matching of geological targets based on eigenface face recognition. Because the dynamic micro-resistivity imageis formed firstly and then the face recognition technology is used to recognize the geological targets of different sizes and shapes, the method has the characteristics of high accuracy and strong reliability, and can improve the recognition rate of the geological targets.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
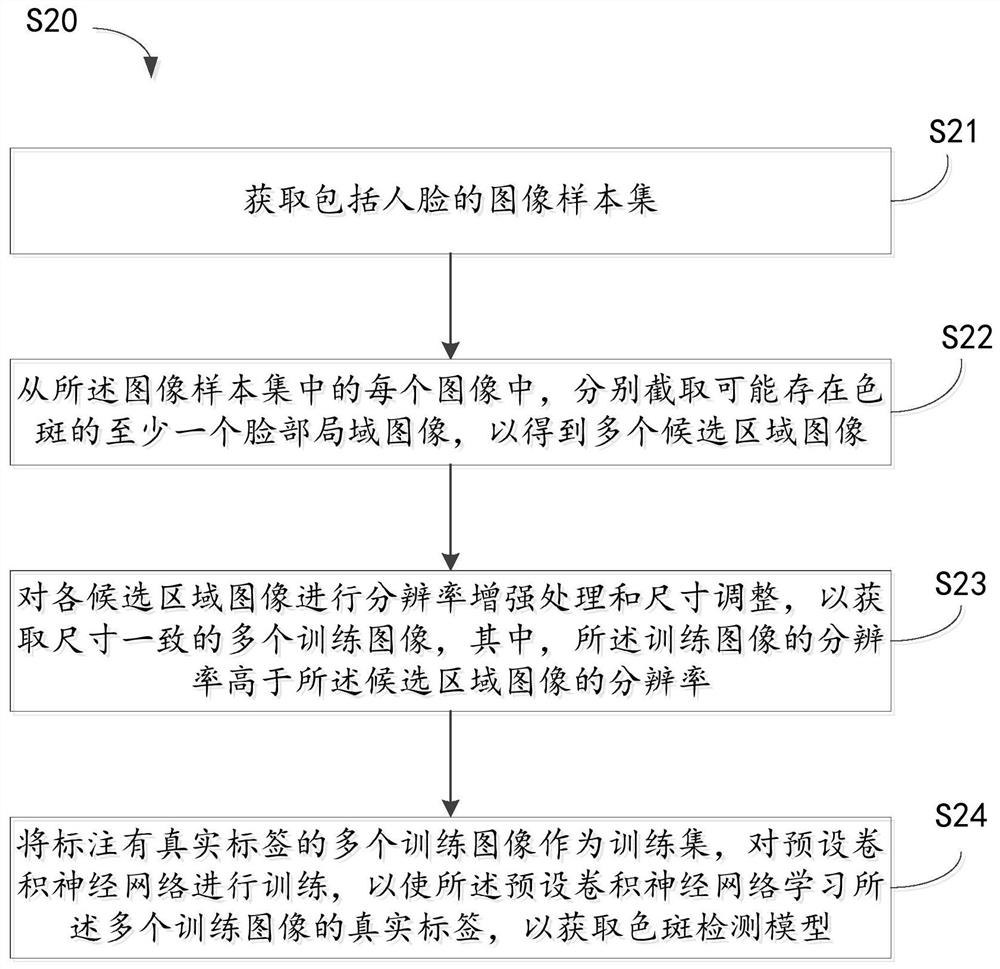
Method for training color spot detection model and related device
PendingCN112614140AHigh precisionImprove detection accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionMedicine
Owner:深圳数联天下智能科技有限公司
Face recognition method under illumination change condition
InactiveCN104573641AAchieving perspective invarianceEasy to identifyBiological neural network modelsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionSingle image
The invention discloses a face recognition method under an illumination change condition. The method comprises steps as follows: step one, acquiring a neutral network through training; step two, acquiring virtual face images of each person under target illumination conditions; step three, acquiring a simulation image of each person under each target illumination condition, and establishing N neutral networks; step four, acquiring simulation face images of each person under all target illumination conditions; step five, establishing a face training library comprising real face images and simulation face images; step six, matching to-be-tested images with images in the training library under corresponding illumination conditions. According to the face recognition method under the illumination change condition, eigenface features of all persons under rest view angle conditions are simulated through training of a radial basis function network on a single image set, recognized view angle invariance is realized to a certain extent, and the good recognition effect can be realized.
Owner:SUZHOU FUFENG TECH
Face recognition method
The invention relates to a face recognition method, which comprises the following steps of 1) elongating each human face image of a training set by one column as a vector; 2) adding up all the faces on the corresponding dimensions and then averaging them to obtain an average face; 3) subtracting that average face image from each image to obtain a data matrix of the difference image; 4) calculatingthat covariance matrix, and then decomposing the covariance matrix into eigenvalue, and obtaining a desired eigenvector (eigenface); 5) projecting that images of the train set and the test set onto these eigenvectors, and then finding the nearest neighbor of the training set for classification and recognition for each image of the test set. The method has the characteristics of accurate recognition, simple realization, safety and practicability.
Owner:江苏环宇臻视智能科技有限公司
Face recognition module and method
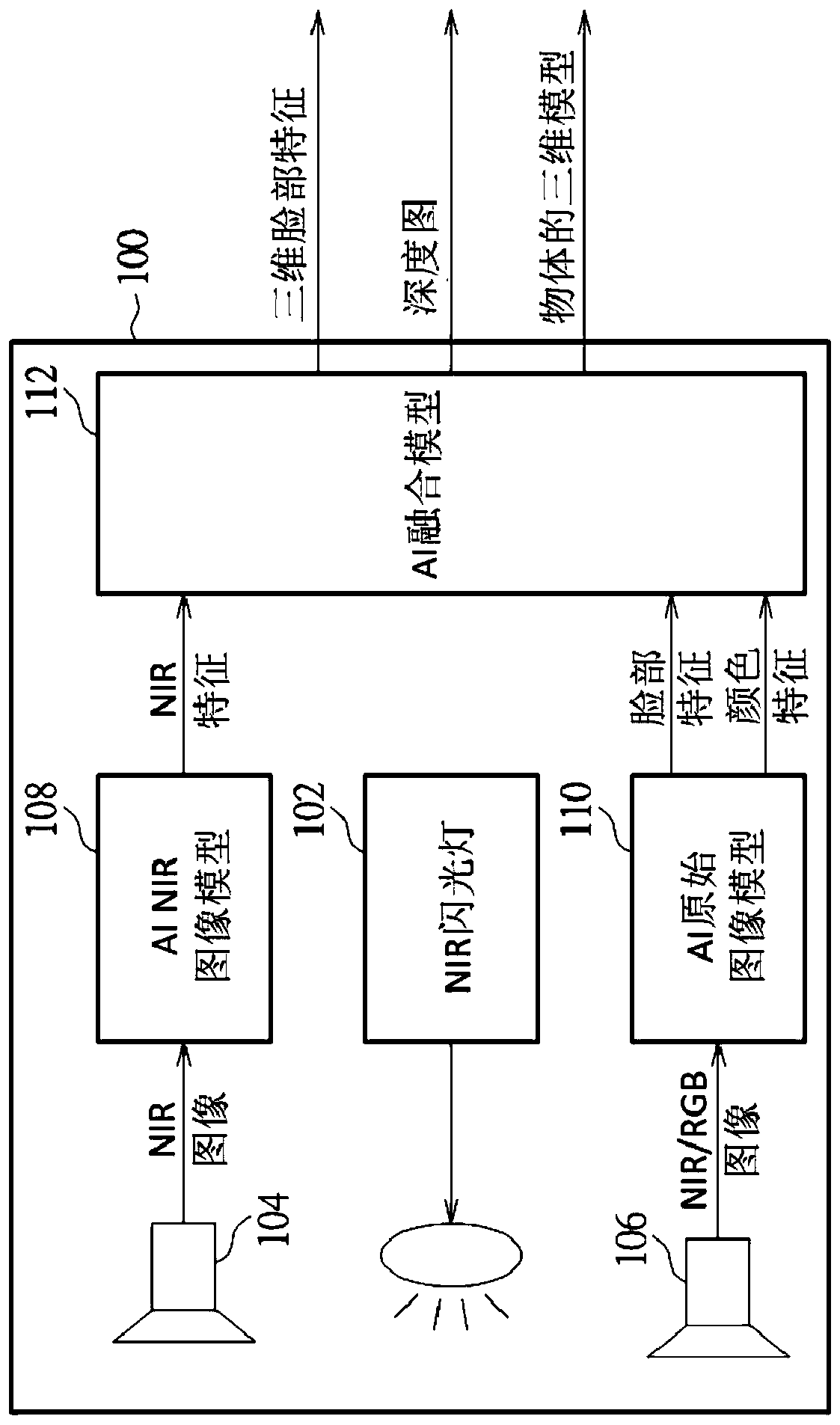
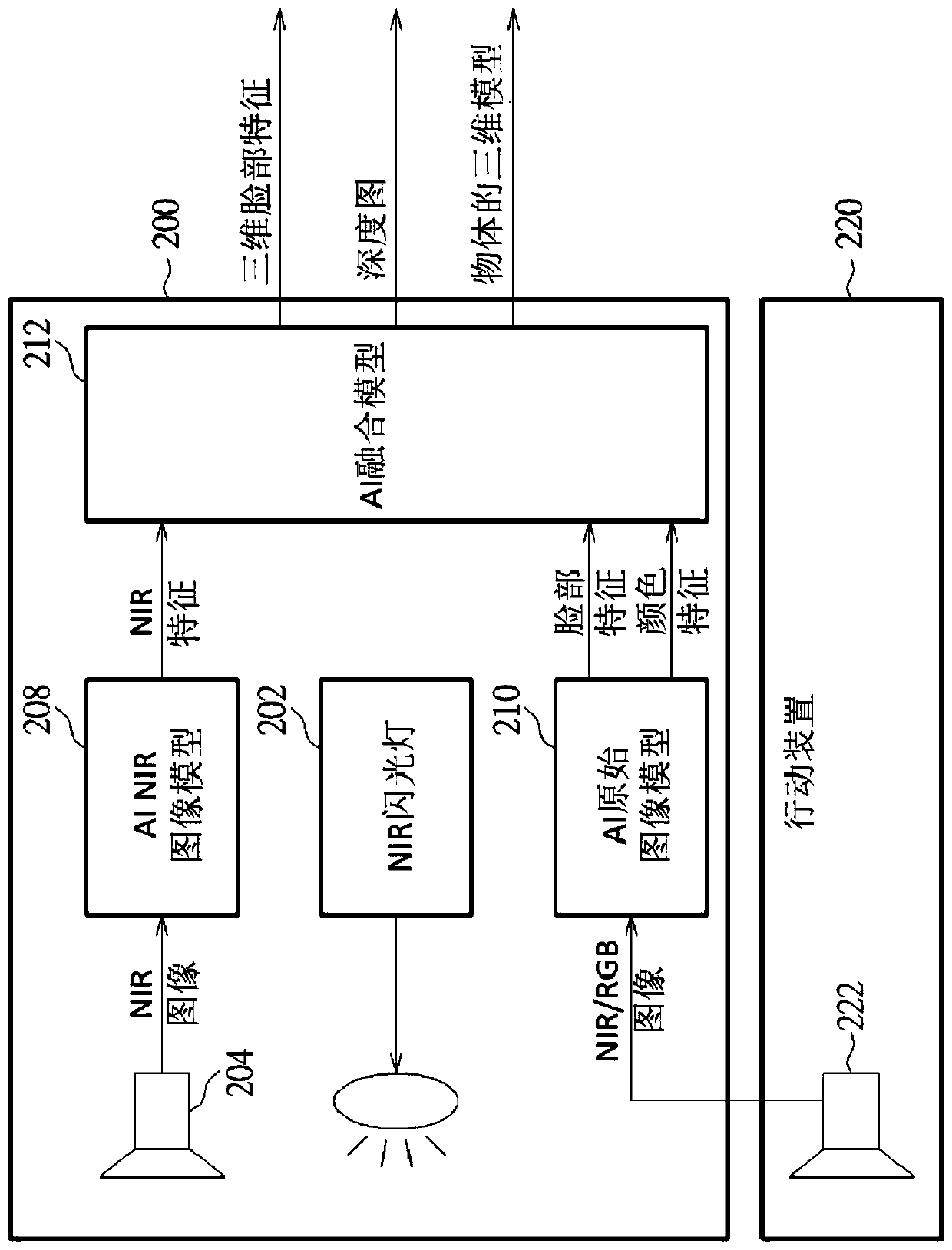
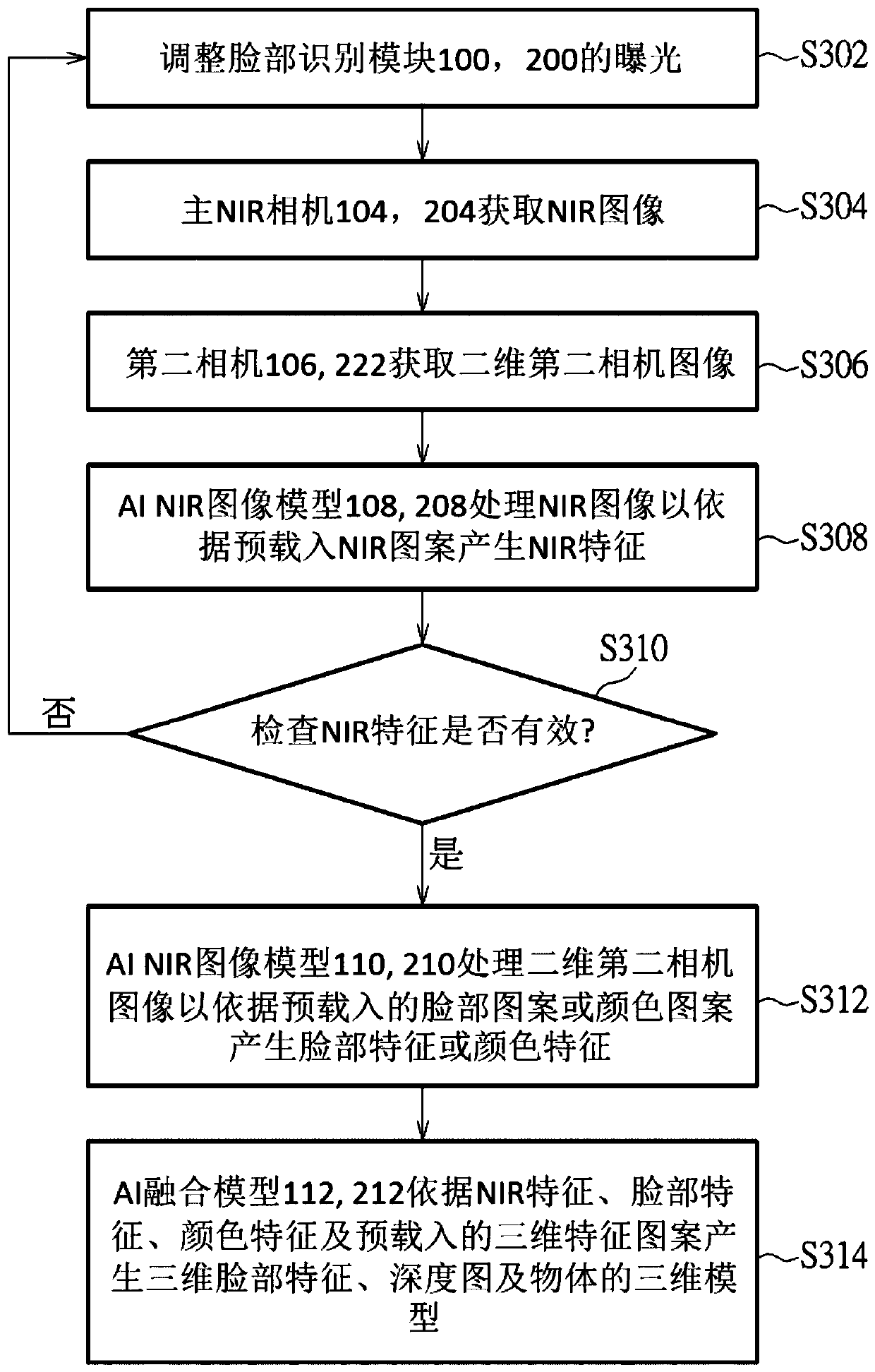
PendingCN110895678AIncrease success rateMaterial analysis by optical meansNeural learning methodsFace detectionInfrared
The invention provides face recognition module and method. The face recognition module includes a near infrared flash, a master near infrared camera, an artificial intelligence NIR image model, an artificial intelligence original image model, and an artificial intelligence fusion model. The NIR flash flashes near infrared light. The master near infrared camera captures a NIR image. The artificialintelligence NIR image model processes the NIR image to generate NIR features. The artificial intelligence original image model processes a 2 dimensional second camera image to generate face featuresor color features. The artificial intelligence fusion model generates 3 dimensional face features, a depth map and an object's 3 dimensional model according to the NIR features, the face features andthe color features. In the invention, successful rate and optimum extracted features of face recognition are improved, so that the module and method can be used for artificial intelligence face detection, artificial intelligence facial feature generation, artificial intelligence landmark generation, artificial intelligence live detection artificial intelligence depth map generation, etc.
Owner:KNERON TAIWAN CO LTD
Face recognition method and system of SVM (Support Vector Machine) based on PCA (Principal Component Analysis) and ReliefF, storage medium and equipment
InactiveCN113792678AGuaranteed classification accuracyAccelerated trainingCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorImage conversion
The invention discloses a face recognition method and system of an SVM based on PCA and ReliefF, a storage medium and equipment, applied to the field of image recognition. The method comprises the steps: converting a face image into a preset dimension vector, and storing the preset dimension vector into a face vector set; calculating a vector accumulation average value to obtain an average image; calculating a difference value between the face image and the average image, calculating a feature vector of a covariance matrix according to the difference value, and forming a feature face space; respectively calculating the feature weight of each feature face space sample according to a ReliefF algorithm, and constructing a feature weight vector; constructing and solving an optimal solution according to a preset penalty parameter and the feature weight vector, obtaining a decision function, and determining a support vector machine; and training and verifying based on a support vector machine to obtain a face recognition model, and performing face recognition by using the face recognition model. According to the technical scheme, the defect that a single ReliefF algorithm cannot remove redundant features is overcome, the data dimension is effectively reduced, and SVM training is accelerated.
Owner:华院分析技术(上海)有限公司
Human face recognition system and method based on second-order two-dimension principal component analysis
InactiveCN101482917BAvoid interferenceImprove recognition rateCharacter and pattern recognitionKernel principal component analysisComputation complexity
The invention requests to protect a face recognition system and a face recognition method which are based on the second-order two-dimensional principal component analysis, and belongs to the fields of image processing technology, computer vision technology and mode identification technology. The invention provides the face recognition method which has low computational complexity and is based on the second-order two-dimensional principal component analysis. The method researches the face recognition problem in the condition of illumination change, and provides the face recognition method of the second-order two-dimensional principal component analysis. The face recognition method comprises: respectively applying the (2D)<2>PCA technology to an original image matrix set and a residual image matrix set to obtain a first-order feature matrix and a second-order feature matrix, thereby determining reconstructed images of sample images and reconstructed images of residual images; superimposing the two reconstructed images to obtain reconstructed images of original images. The method of the invention has higher recognition accuracy, and save more computing time than the eigenface method and the second-order eigenface method. The method of the invention can be widely used in the image recognition field.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Face recognition method based on multi-dimensional Taylor network
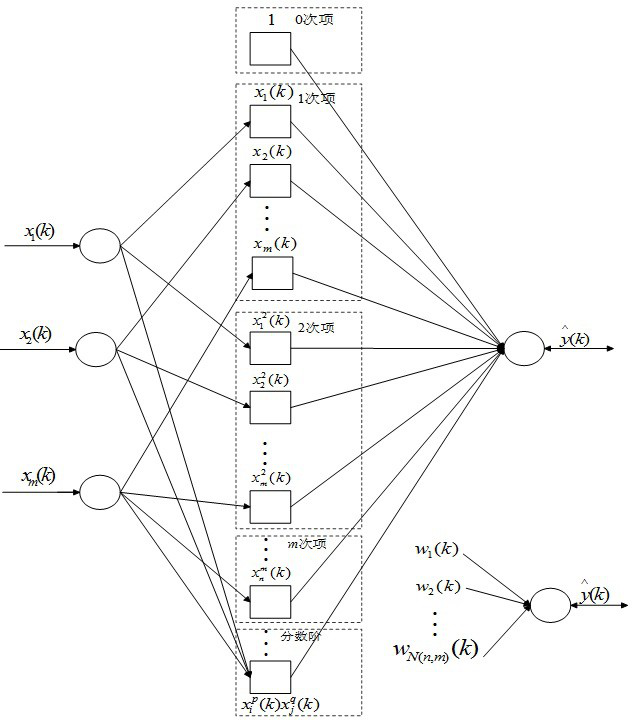
PendingCN112597890AGuaranteed structure simplificationImprove recognition accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesPattern recognitionActivation function
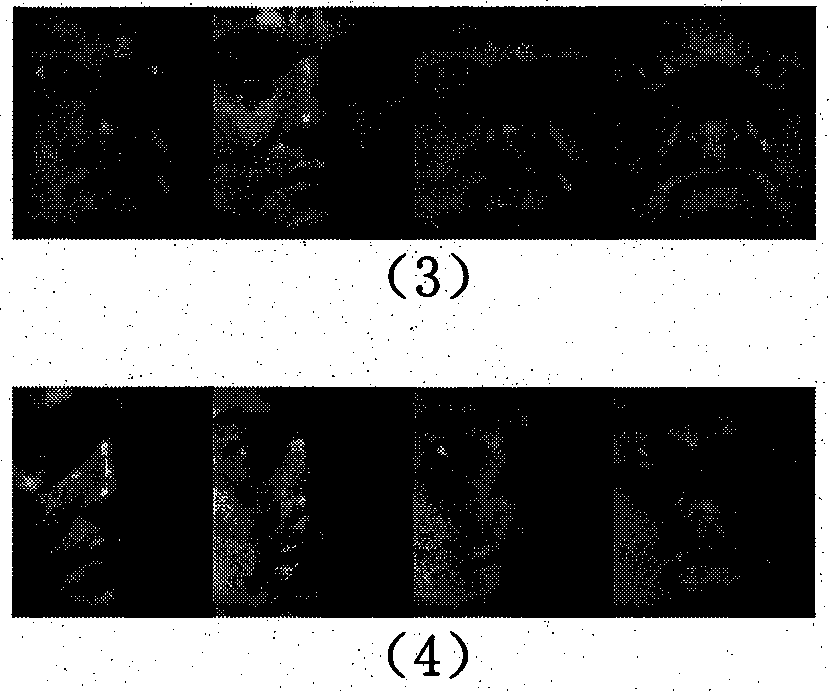
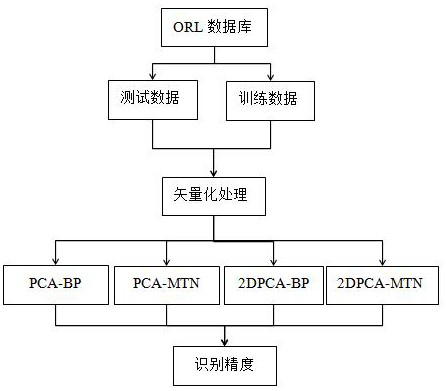
The invention discloses a face recognition method based on a multi-dimensional Taylor network. The construction process of the multi-dimensional Taylor network comprises the following steps: performing Taylor expansion on an activation function of a neural network structure, performing linear combination on the Taylor expansion of the activation function to obtain network output, and finally obtaining an optimal solution of a target function by minimizing a loss function. Through a simulation test of an ORL face data set, a feature face extracted by PCA and 2DPCA algorithms is used as networkinput, and the effectiveness of the method is verified.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com