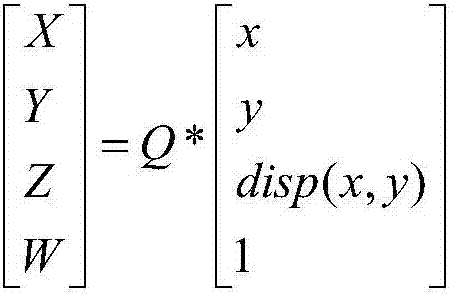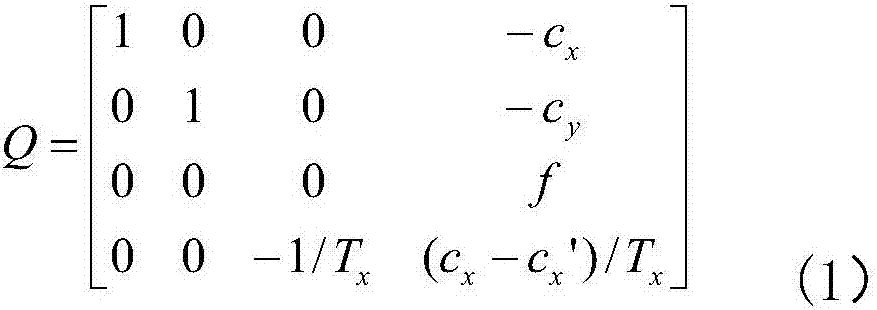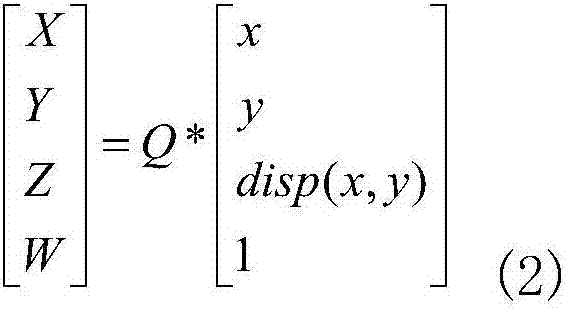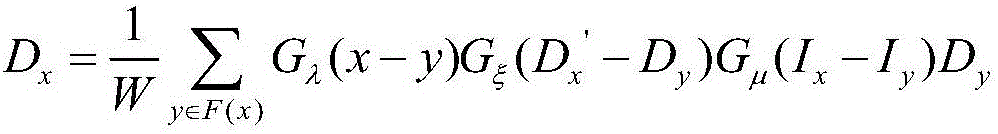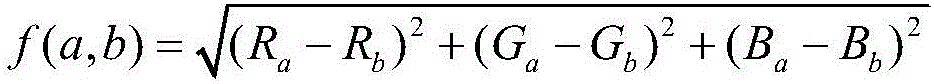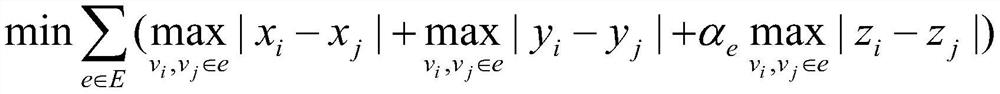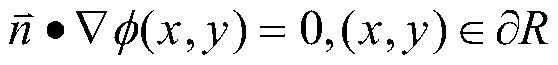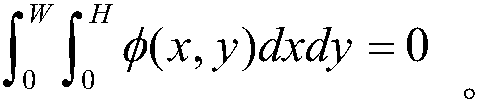Patents
Literature
91 results about "Poisson's equation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, Poisson's equation is a partial differential equation of elliptic type with broad utility in mechanical engineering and theoretical physics. It arises, for instance, to describe the potential field caused by a given charge or mass density distribution; with the potential field known, one can then calculate gravitational or electrostatic field. It is a generalization of Laplace's equation, which is also frequently seen in physics. The equation is named after the French mathematician, geometer, and physicist Siméon Denis Poisson.
Real-time image and video matting
InactiveUS20110038536A1Reduce errorsImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionColor vector
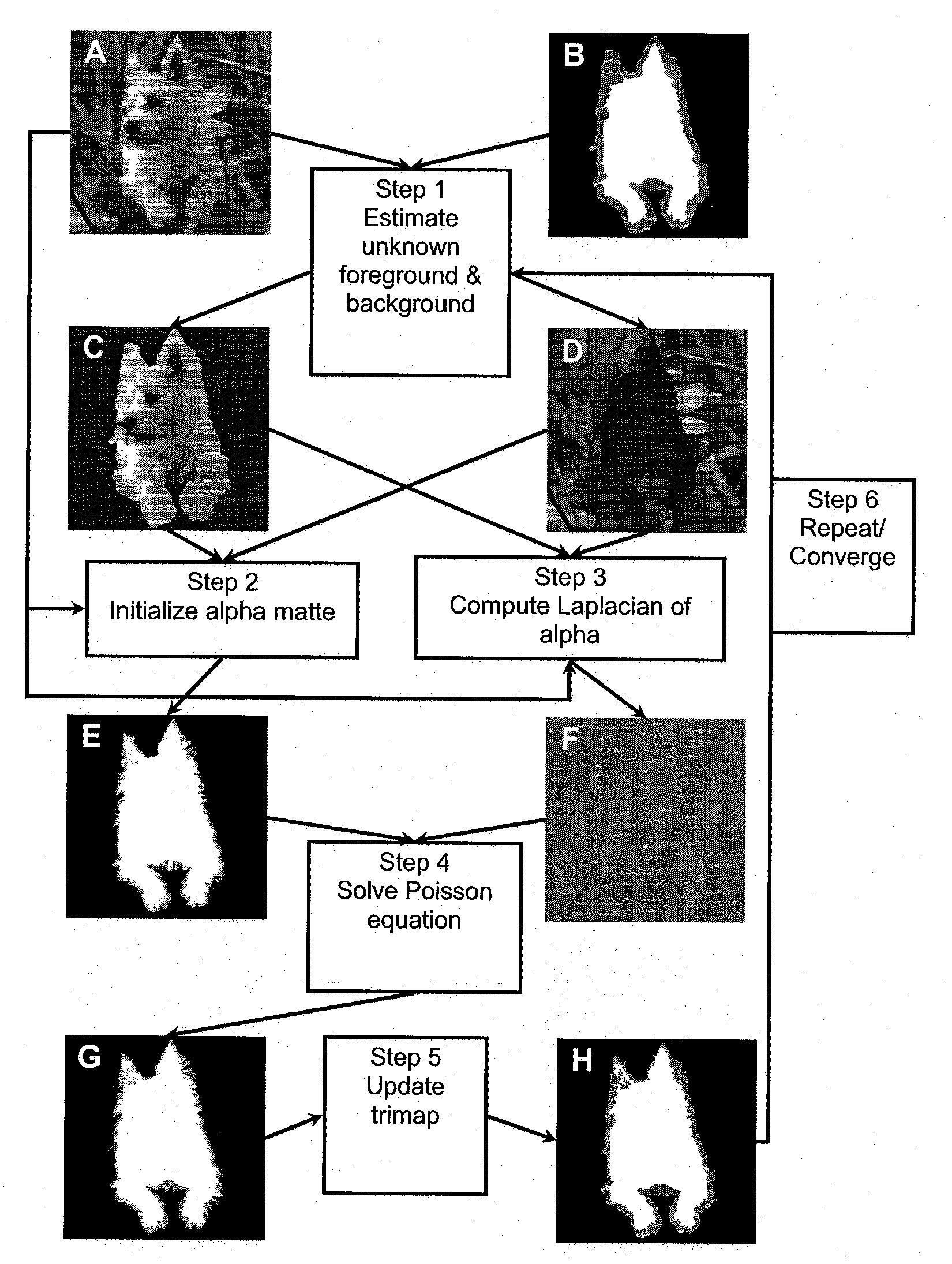
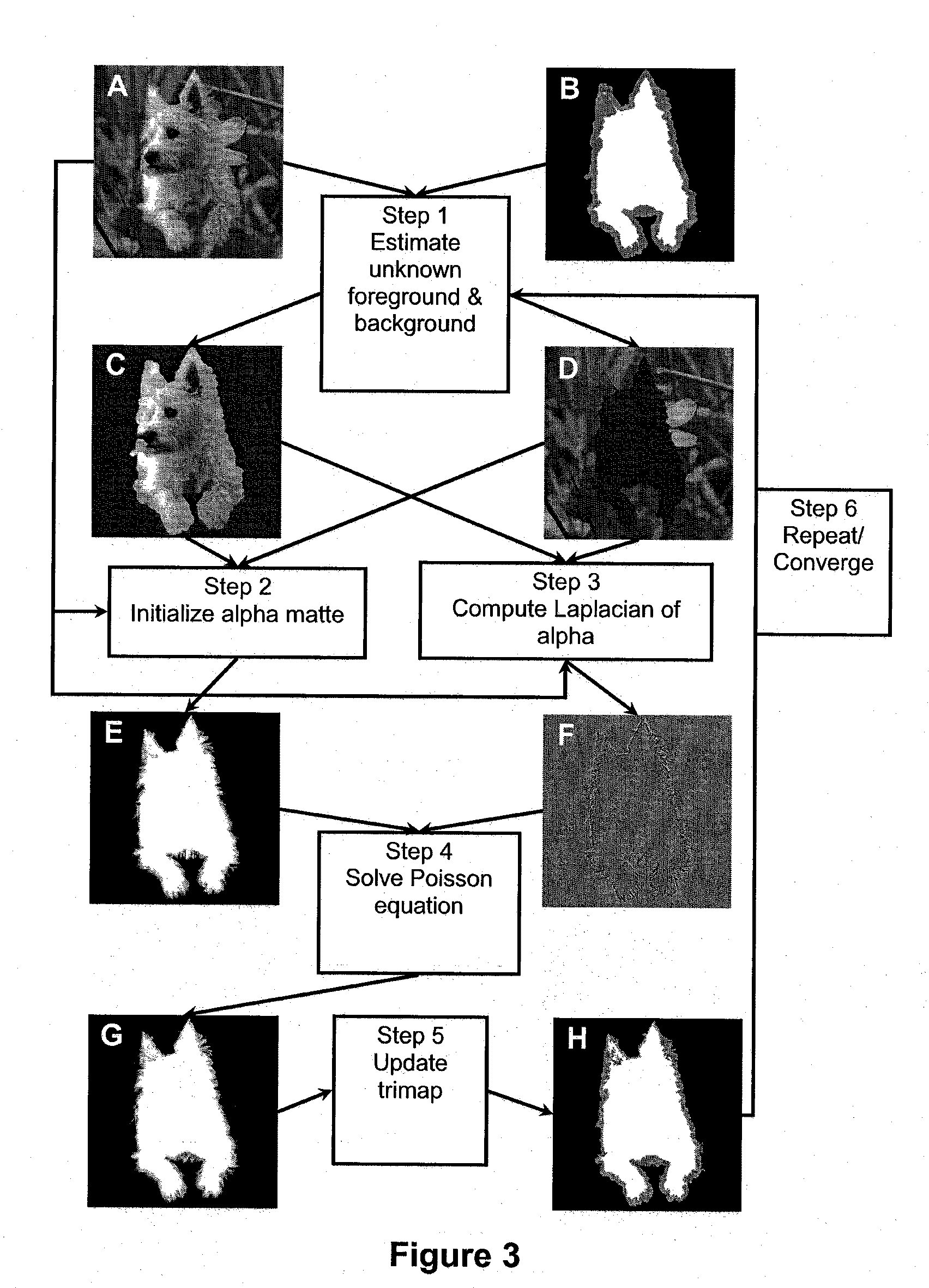
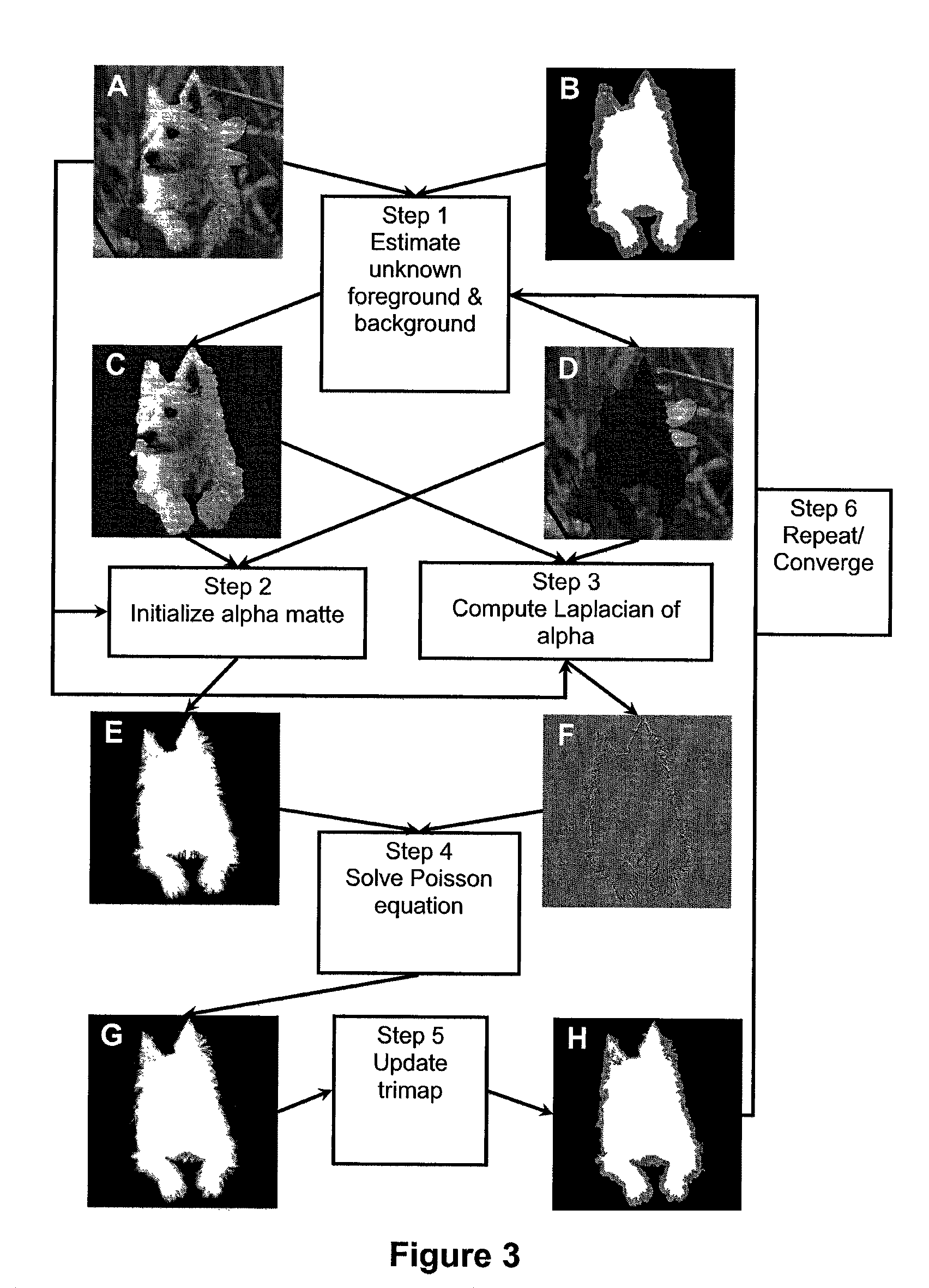
A system and method implemented as a software tool for generating alpha matte sequences in real-time for the purposes of background or foreground substitution in digital images and video. The system and method is based on a set of modified Poisson equations that are derived for handling multichannel color vectors. Greater robustness is achieved by computing an initial alpha matte in color space. Real-time processing speed is achieved through optimizing the algorithm for parallel processing on the GPUs. For online video matting, a modified background cut algorithm is implemented to separate foreground and background, which guides the automatic trimap generation. Quantitative evaluation on still images shows that the alpha mattes extracted using the present invention has improved accuracy over existing state-of-the-art offline image matting techniques.
Owner:GENESIS GROUP
Method and apparatus for simulating manufacturing, electrical and physical characteristics of a semiconductor device
InactiveUS6826517B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsDetecting faulty computer hardwareElement modelMaterial Design
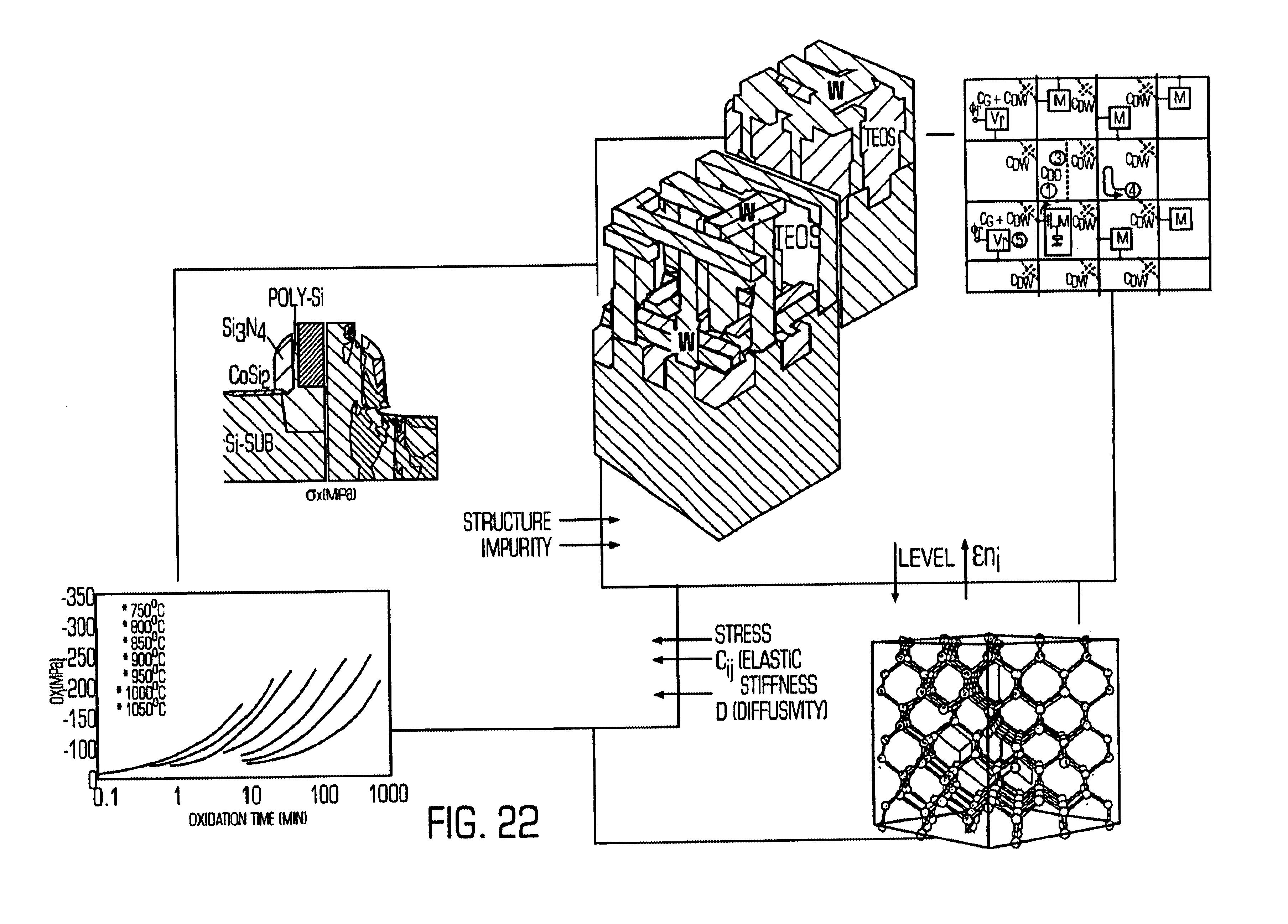
An electronic device simulator includes a three-dimensional lumped device model, a three-dimensional visco-elastic process simulation model and a material design model that are interlinked with each other. The three-dimensional lumped device element model comprises a Poisson's equation model, an electron continuity equation model, a hole continuity equation model, a Maxwell's equations model, an eddy current equation model, and an Ohm's law equation model. The simulator accounts for the three dimensional characteristics of the circuit to determine circuit performance.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Real-time image and video matting
InactiveUS8320666B2Reduce processingImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionColor vector
A system and method implemented as a software tool for generating alpha matte sequences in real-time for the purposes of background or foreground substitution in digital images and video. The system and method is based on a set of modified Poisson equations that are derived for handling multichannel color vectors. Greater robustness is achieved by computing an initial alpha matte in color space. Real-time processing speed is achieved through optimizing the algorithm for parallel processing on the GPUs. For online video matting, a modified background cut algorithm is implemented to separate foreground and background, which guides the automatic trimap generation. Quantitative evaluation on still images shows that the alpha mattes extracted using the present invention has improved accuracy over existing state-of-the-art offline image matting techniques.
Owner:GENESIS GROUP
Modeling gravity and tensor gravity data using poisson's equation for airborne, surface and borehole applications
InactiveUS6993433B2Seismic signal processingAnalogue computers for heat flowPotential fieldPoisson's equation
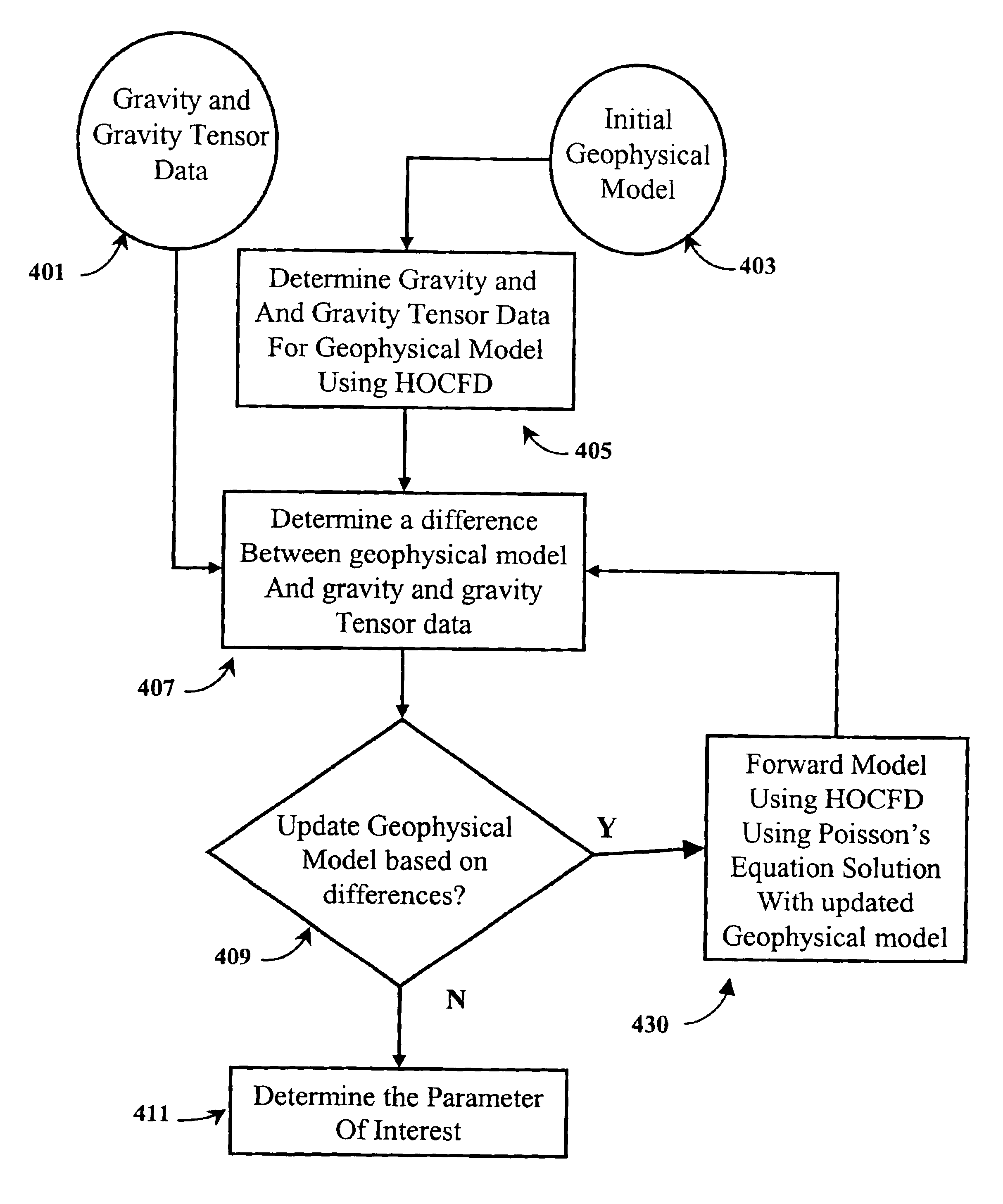
The present invention is a method for determining a parameter of interest of a region of interest of the earth. At least one component of potential fields data is measured at a plurality of locations over a region of interest including a subterranean formation of interest. The potential fields data are selected from magnetic data and gravity data. An initial geophysical model is determined for the region including the subterranean formation of interest. For the model, geophysical tensor data is updated using a forward model at a plurality of locations using a High Order Compact Finite Difference method. A difference between the estimated model value and the measured value of the potential field measurements are determined, and the geophysical model is updated. The model is iteratively updated and compared to the measured data until the differences reach an acceptable level and the parameter of interest has been determined.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Method and apparatus for simulating manufacturing, electrical and physical characteristics of a semiconductor device
InactiveUS20020123872A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElement modelMaterial Design
An electronic device simulator includes a three-dimensional lumped device model, a three-dimensional visco-elastic process simulation model and a material design model that are interlinked with each other. The three-dimensional lumped device element model comprises a Poisson's equation model, an electron continuity equation model, a hole continuity equation model, a Maxwell's equations model, an eddy current equation model, and an Ohm's law equation model. The simulator accounts for the three dimensional characteristics of the circuit to determine circuit performance.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
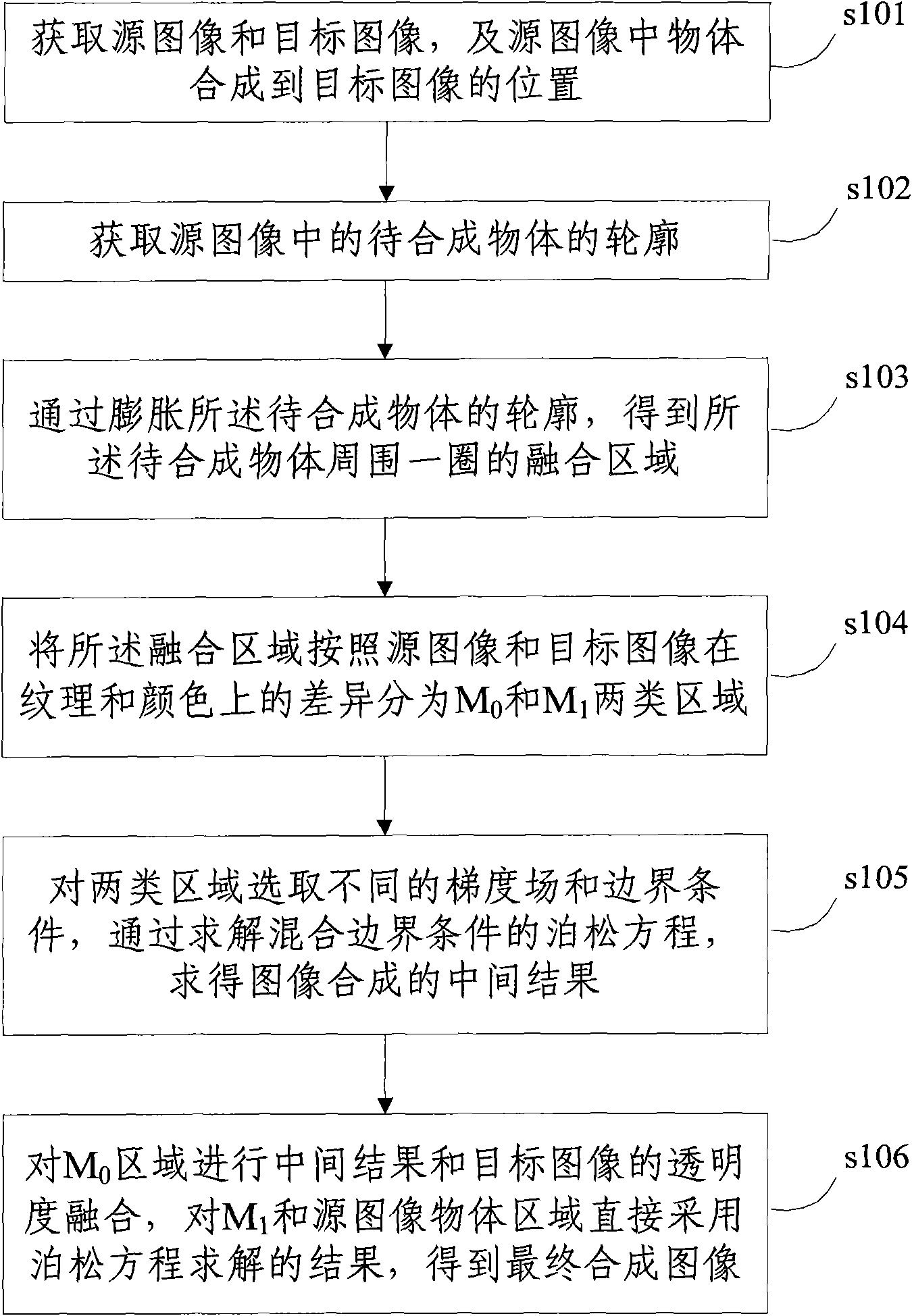
Image synthesis method and apparatus based on mixed gradient field and mixed boundary condition
ActiveCN101551904ARealisticReduce synthesis errorsImage enhancementMixed boundary conditionPoisson's equation
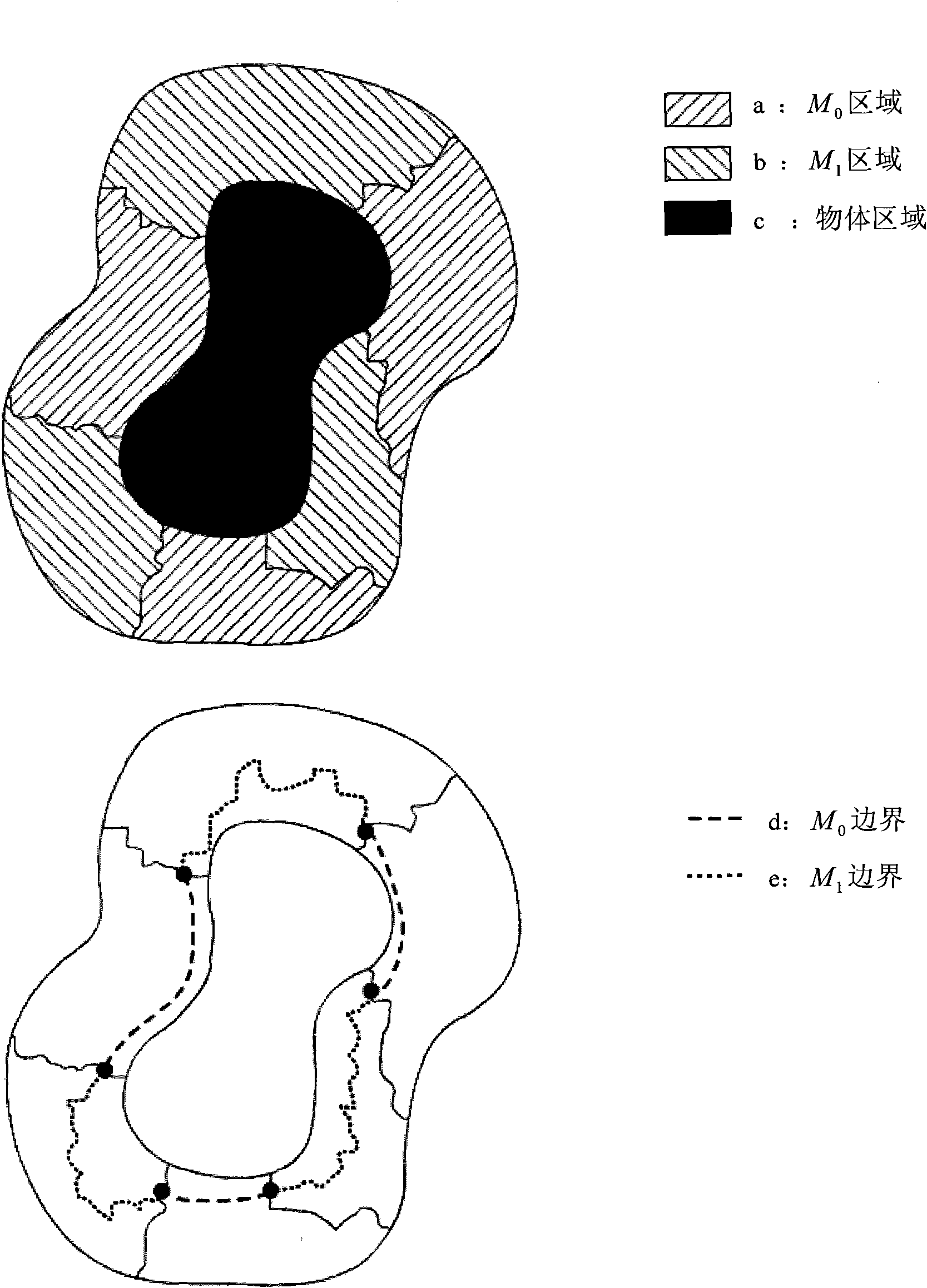
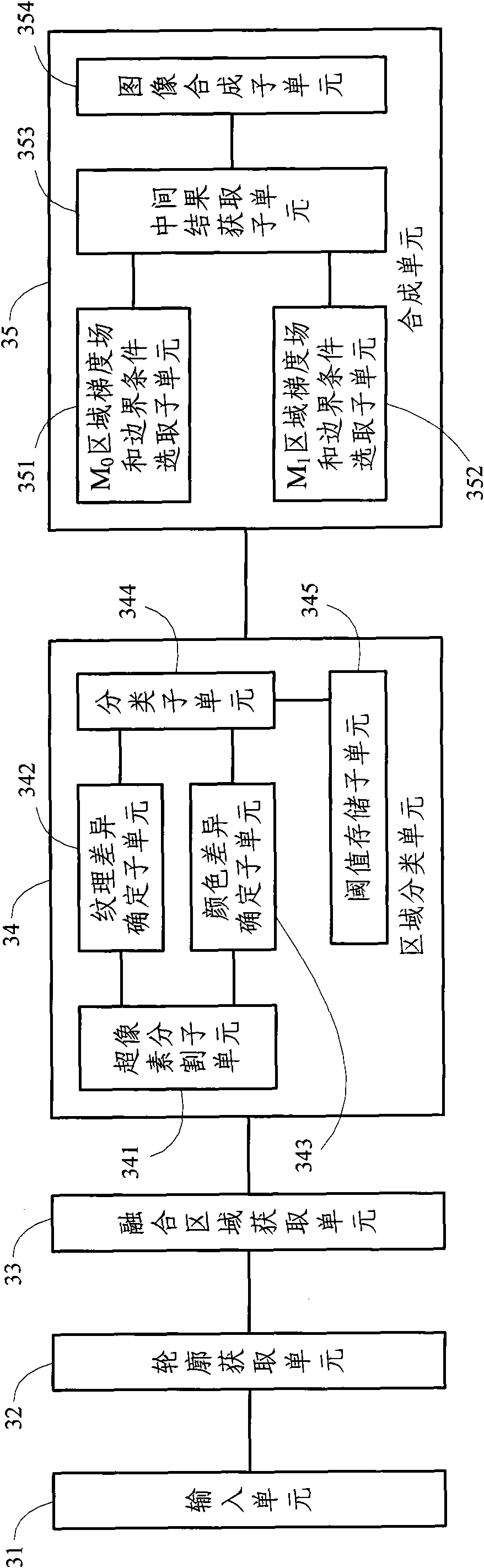
The present invention discloses an image synthesis method and apparatus based on mixed gradient field and mixed boundary condition, the method includes: acquiring a source image and a target image and a position of target image synthesized by object in the source image; acquiring outline of the object to be synthesized in the source image; getting a fusion area by expanding the outline; dividing the fusion area into two kinds according to differences of the source image and the target image in texture and color; choosing different gradient field and different boundary condition for the two kinds of areas, and obtaining a intermediate result by solving the poisson equation of the mixed boundary condition; proceeding transparency fusion to the intermediate result and the target image of one kind area, the other areas using the results solved by the poisson equation to synthetize final image. The invention can use accurate boundary of the synthesized object to reduce synthesis error, and can use gradient field transmission and solving of the poisson equation to keep consistency of the synthesized image in illumination and color, using simple interaction of users to generate synthesized image with third dimension.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
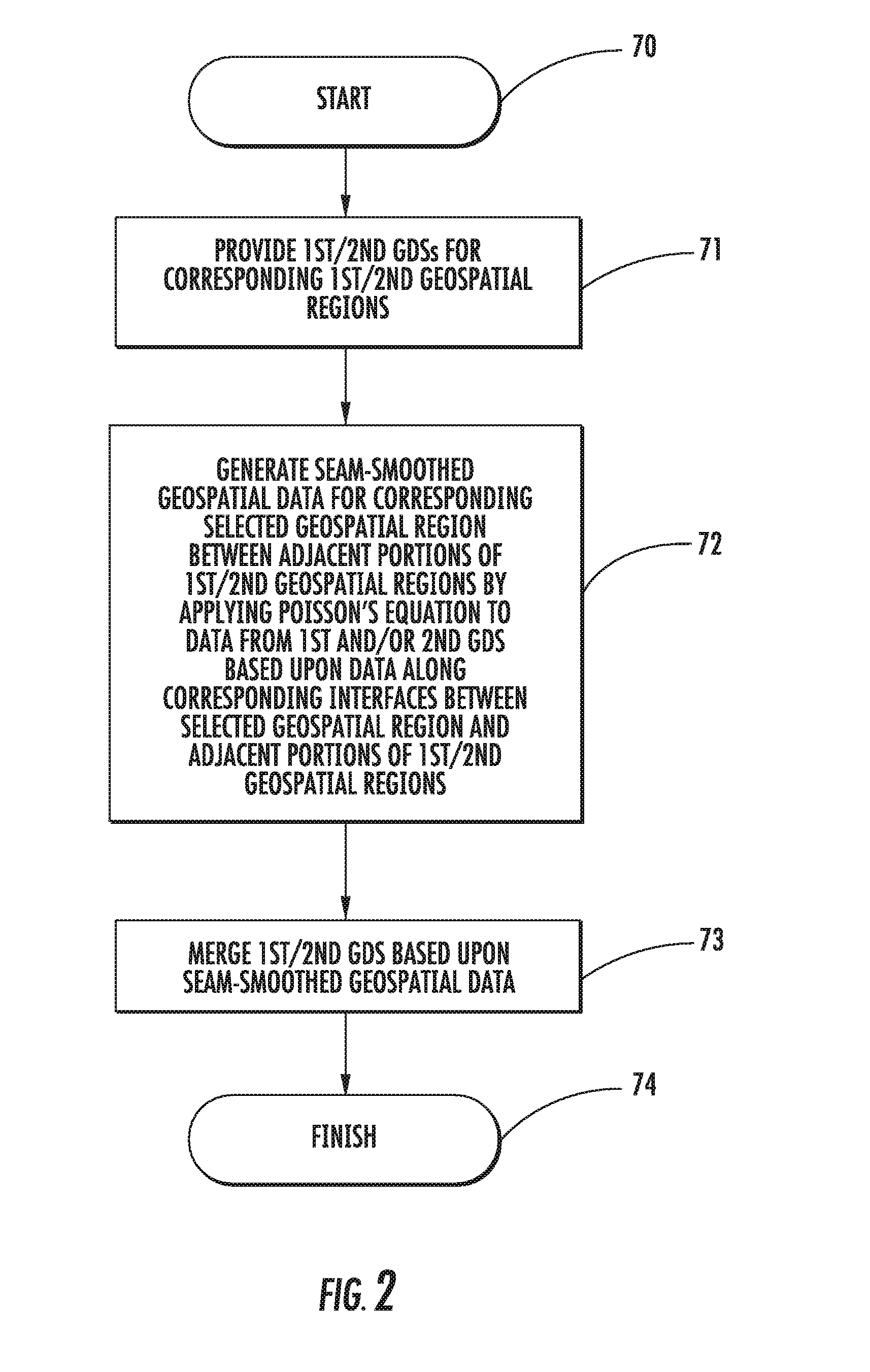
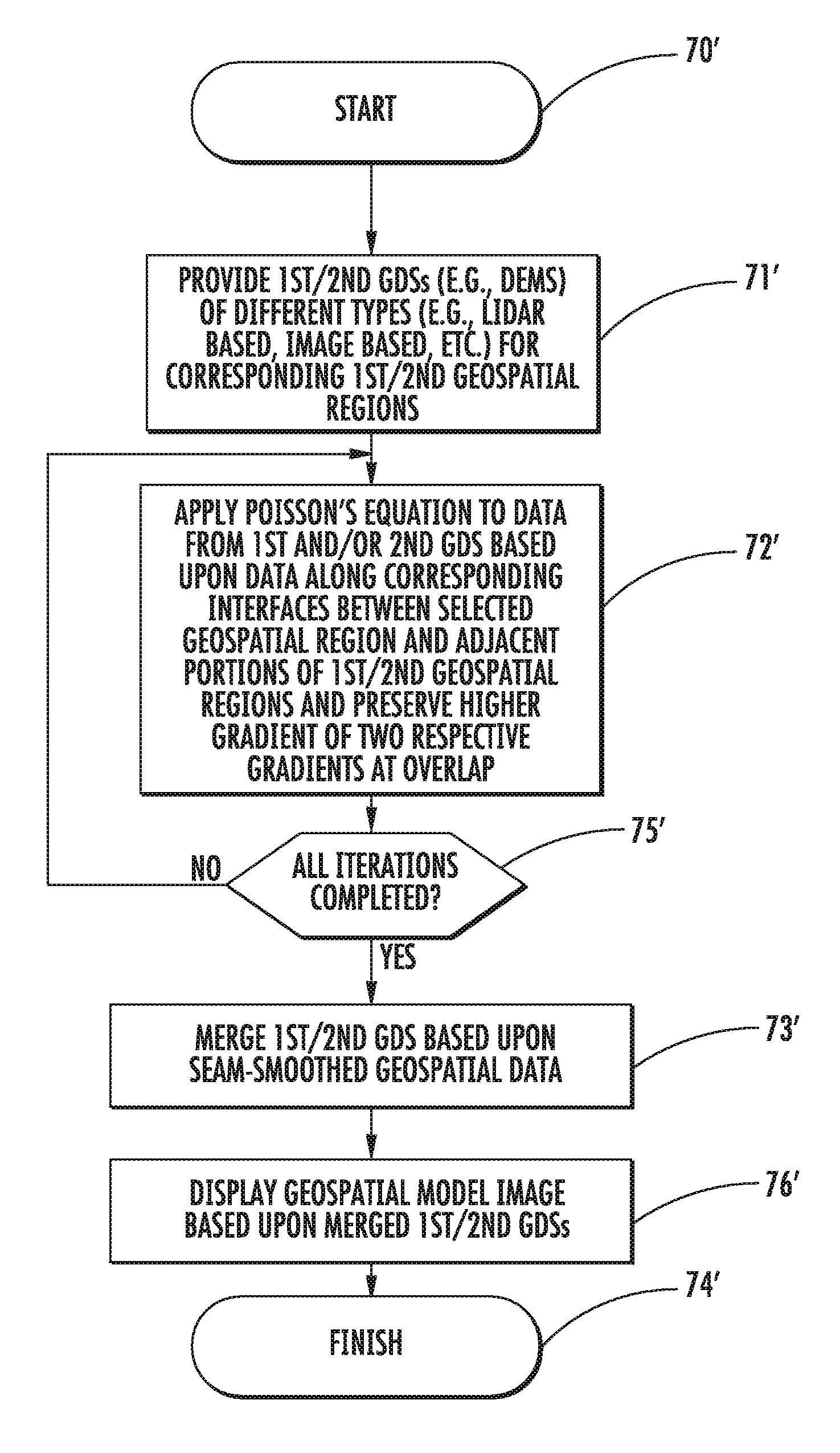
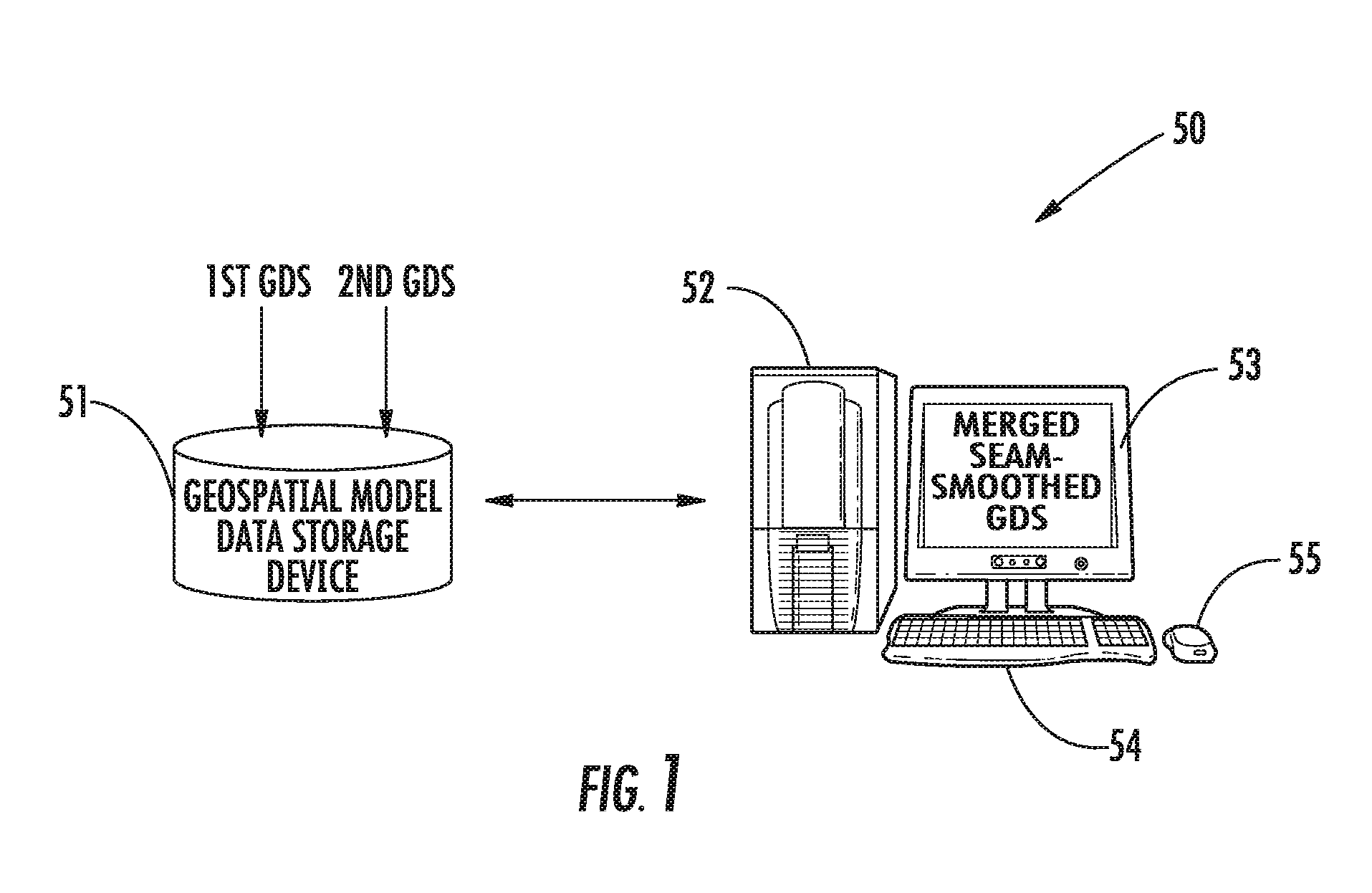
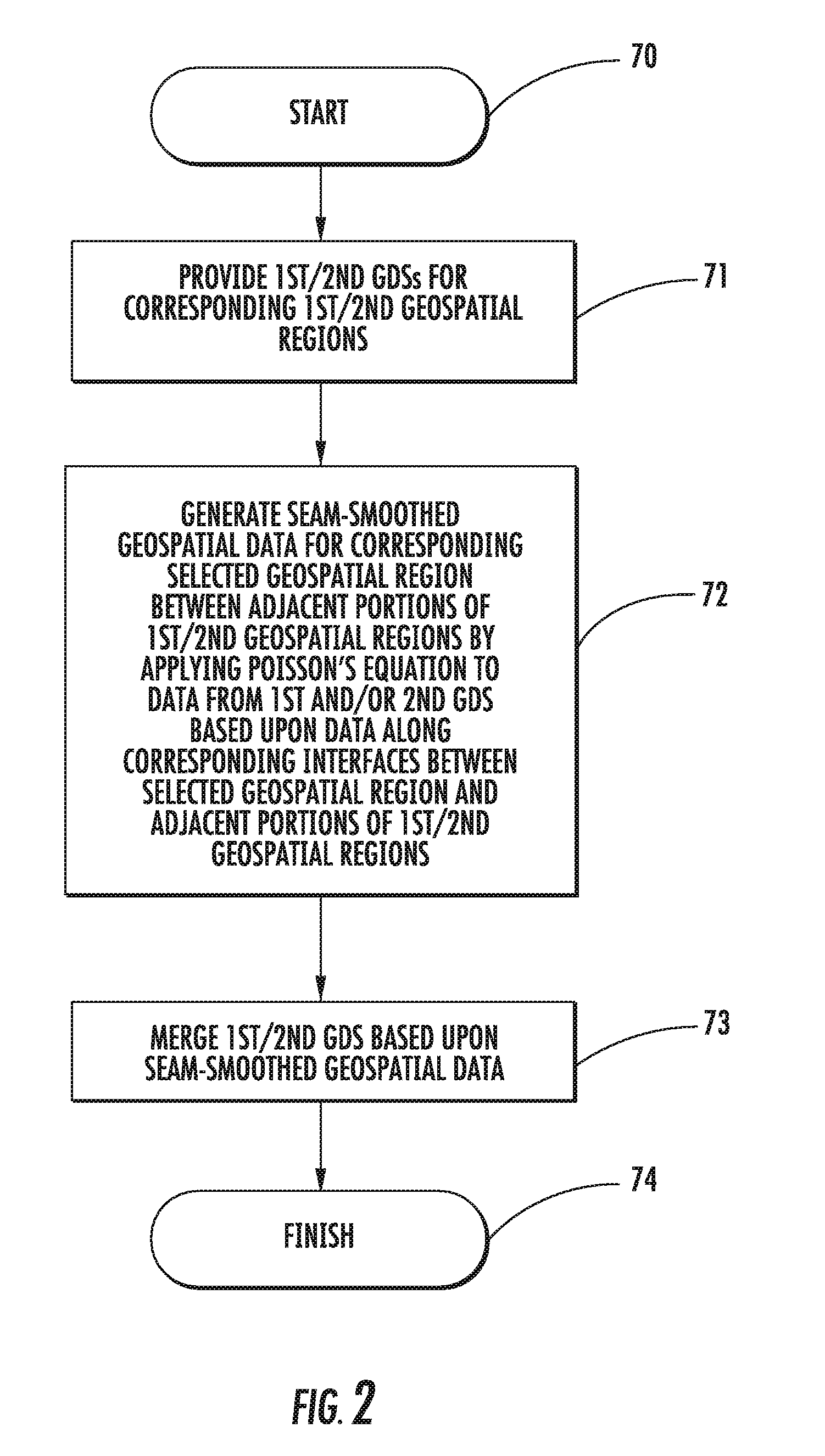
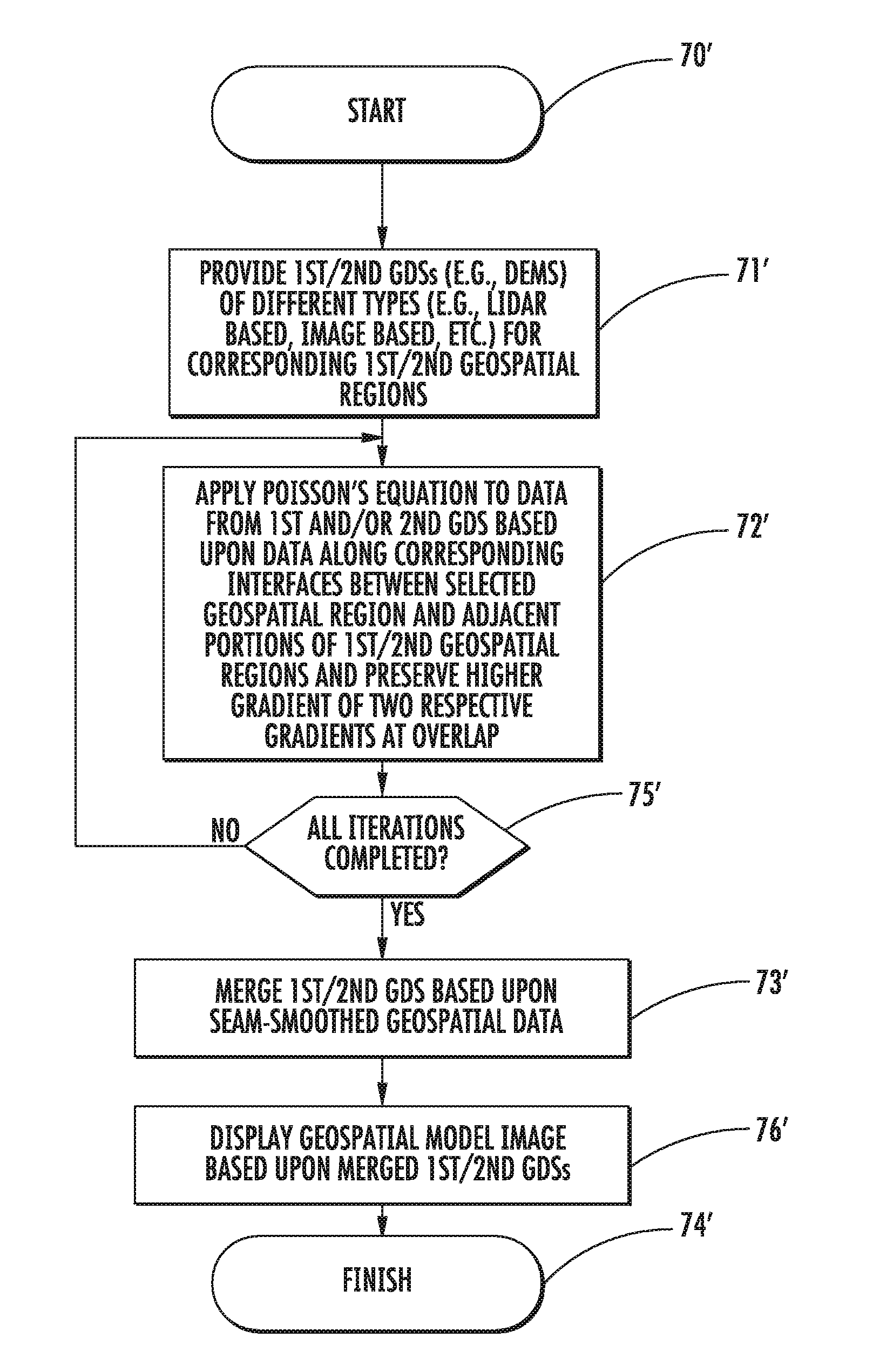
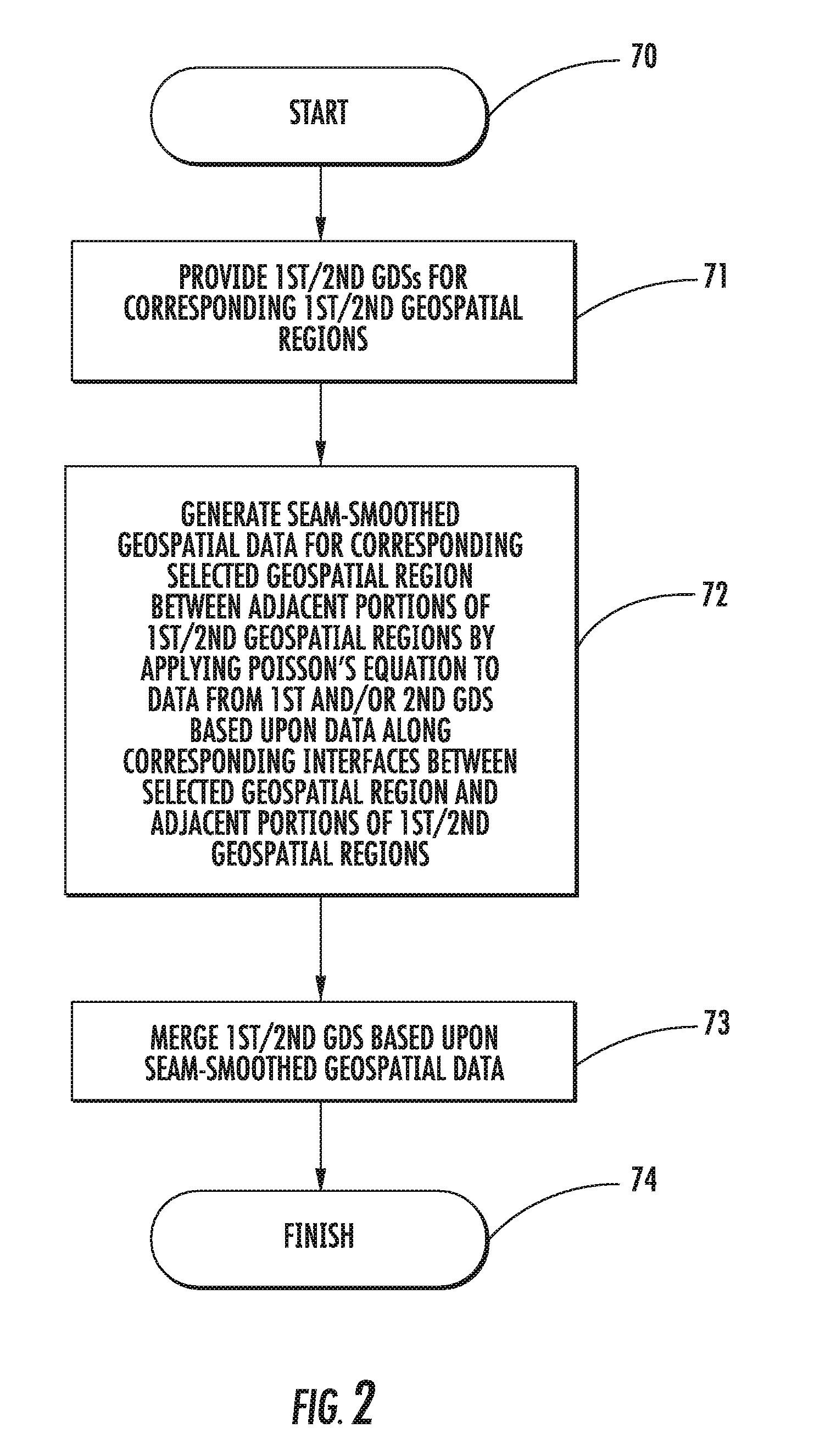
Geospatial modeling system providing poisson-based void inpainting and related methods
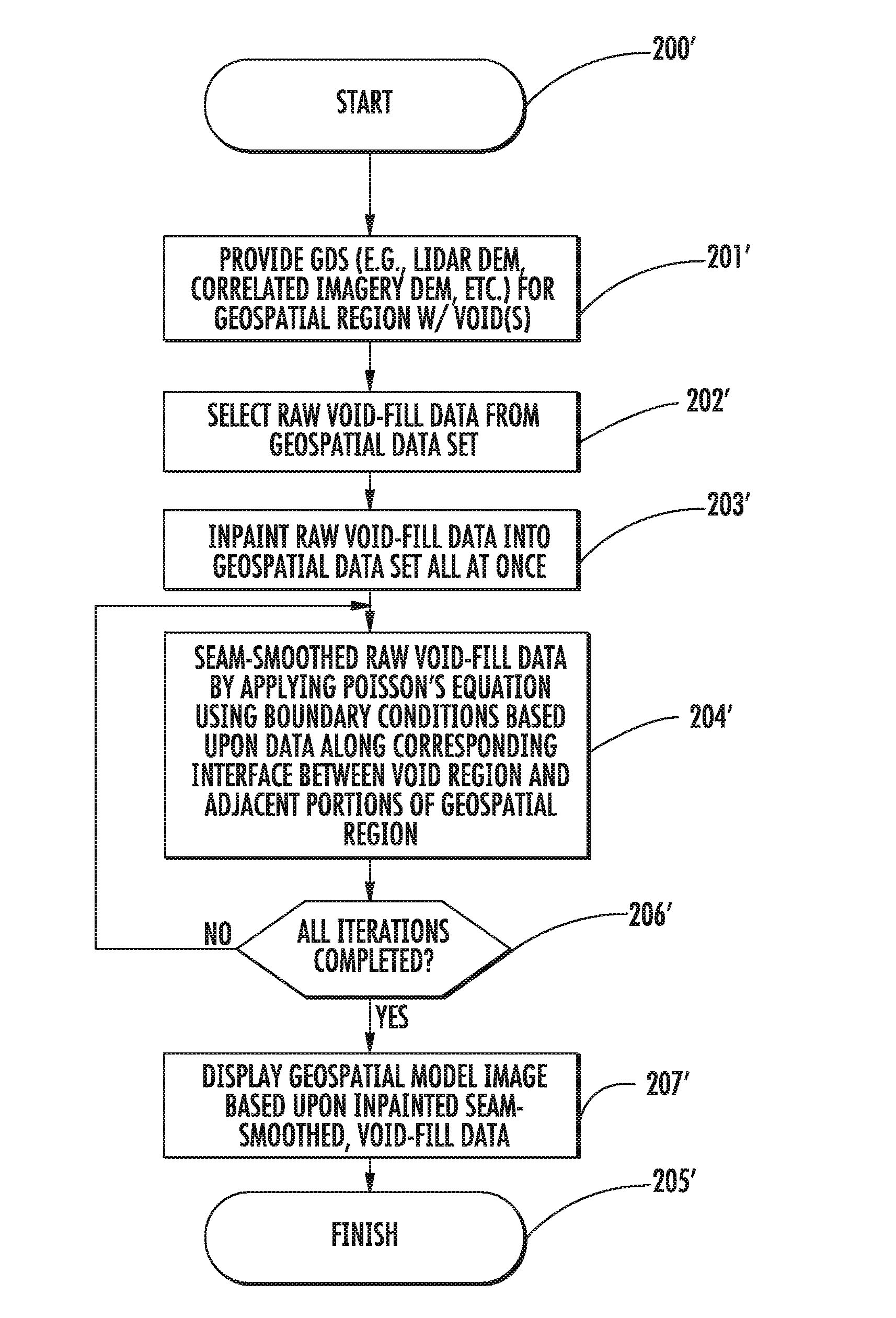
A geospatial modeling system may include a geospatial model data storage device and a processor cooperating with the geospatial model data storage device for inpainting seam-smoothed, void-fill data into a void in a geospatial data set for a geospatial region. The processor may select raw void-fill data from the geospatial data set, and generate the seam-smoothed, void-fill data by applying Poisson's equation to the raw void-fill data using boundary conditions based upon data along a corresponding interface between the void region and adjacent portions of the geospatial region.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
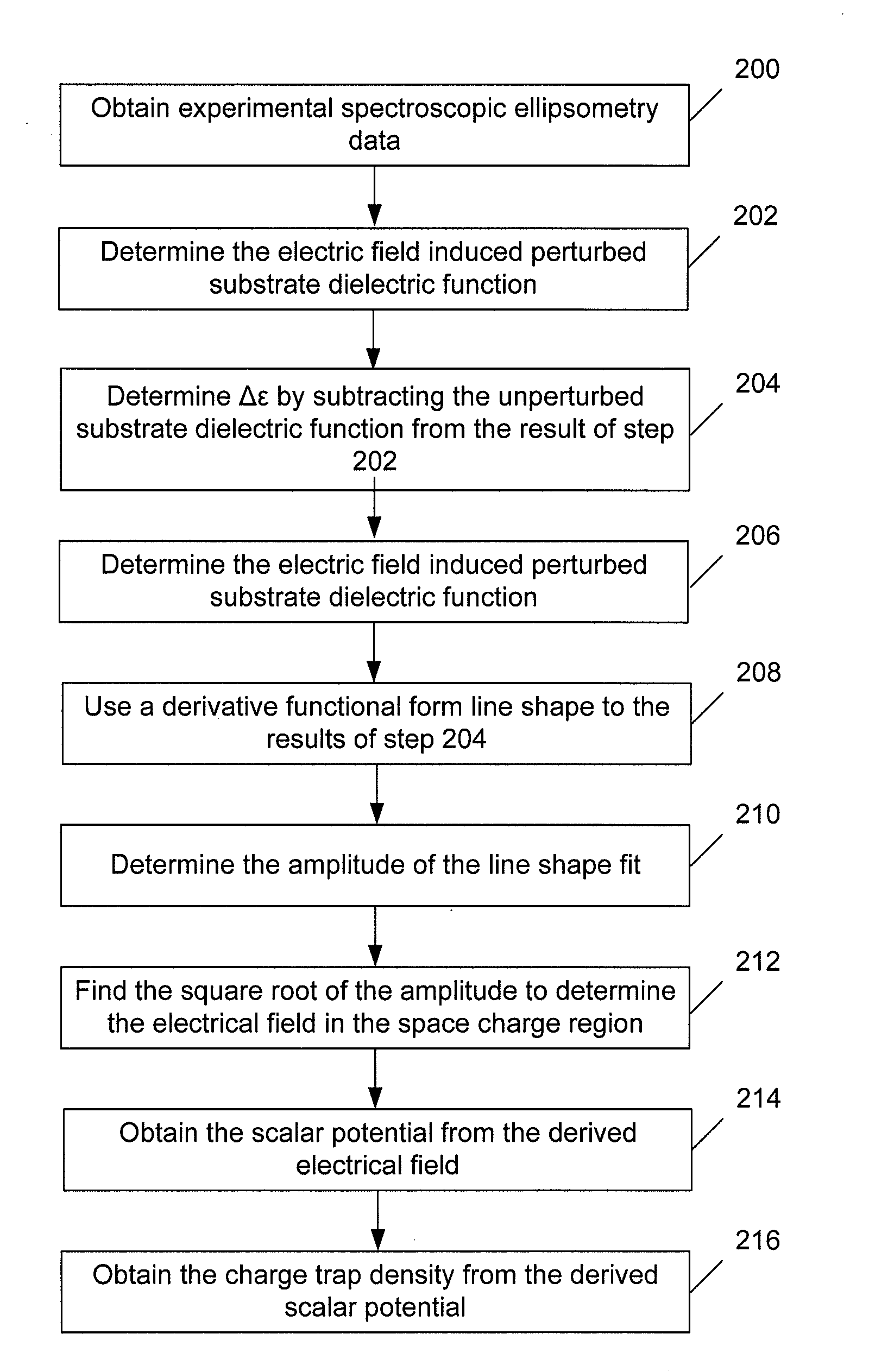
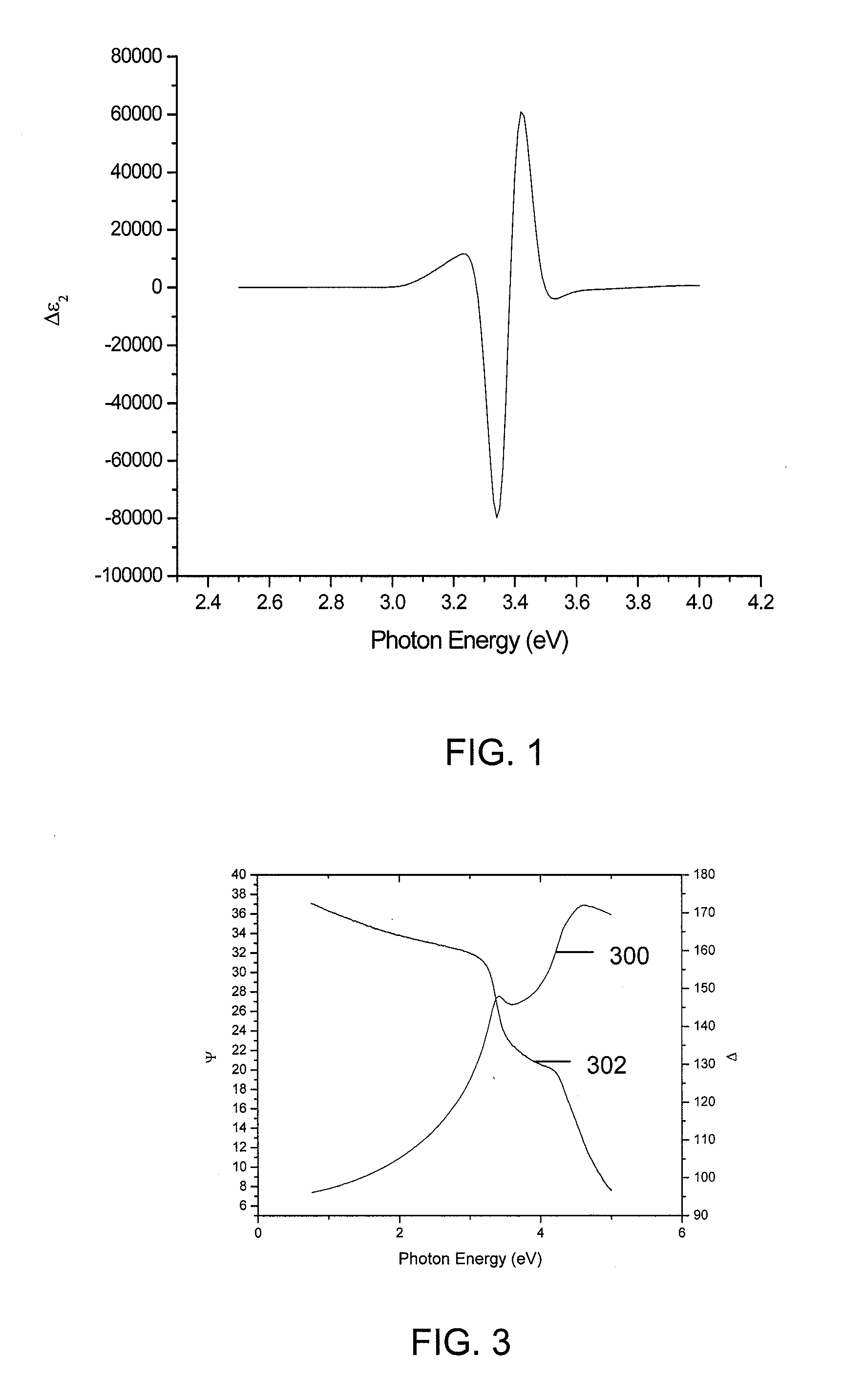
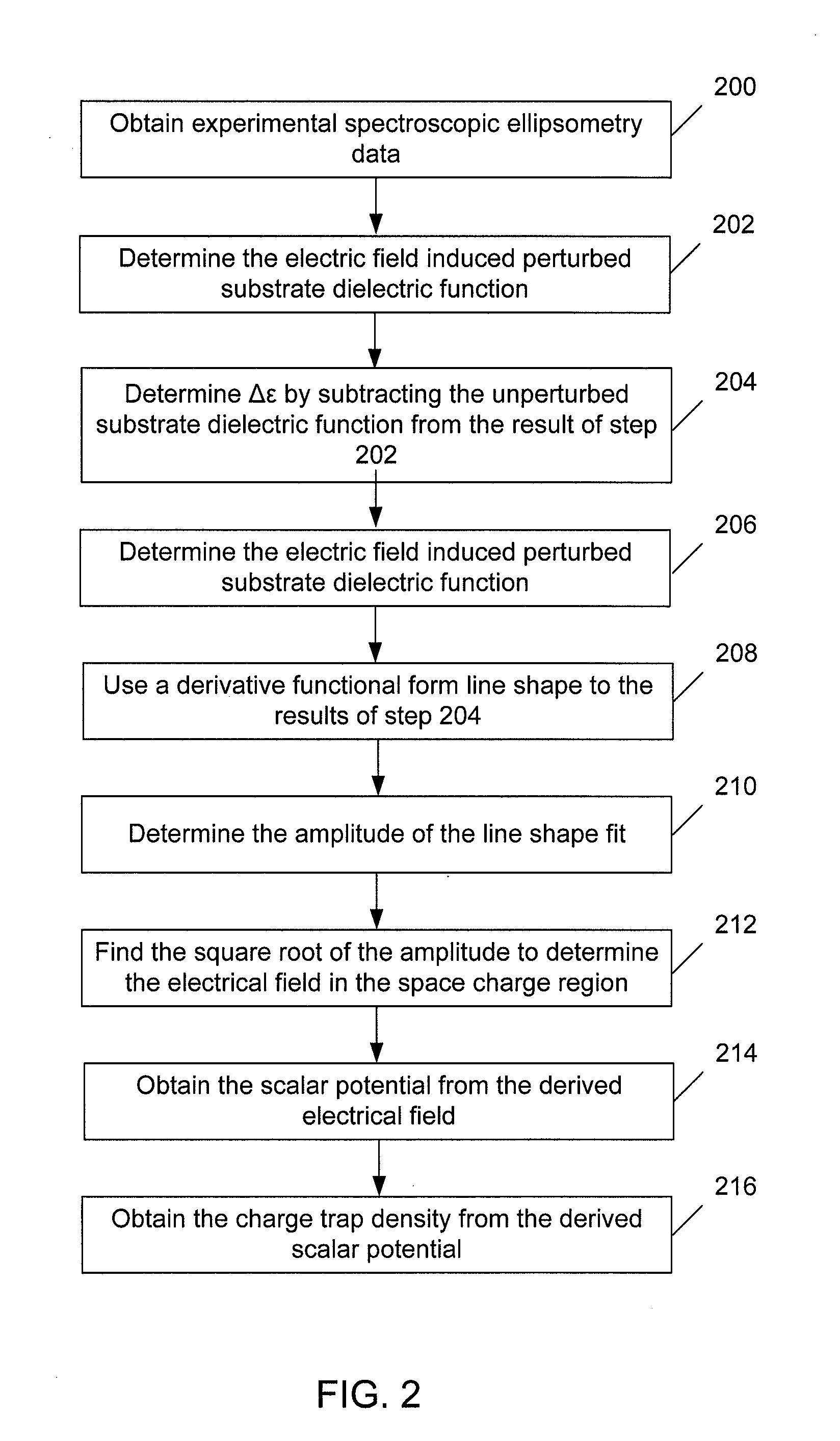
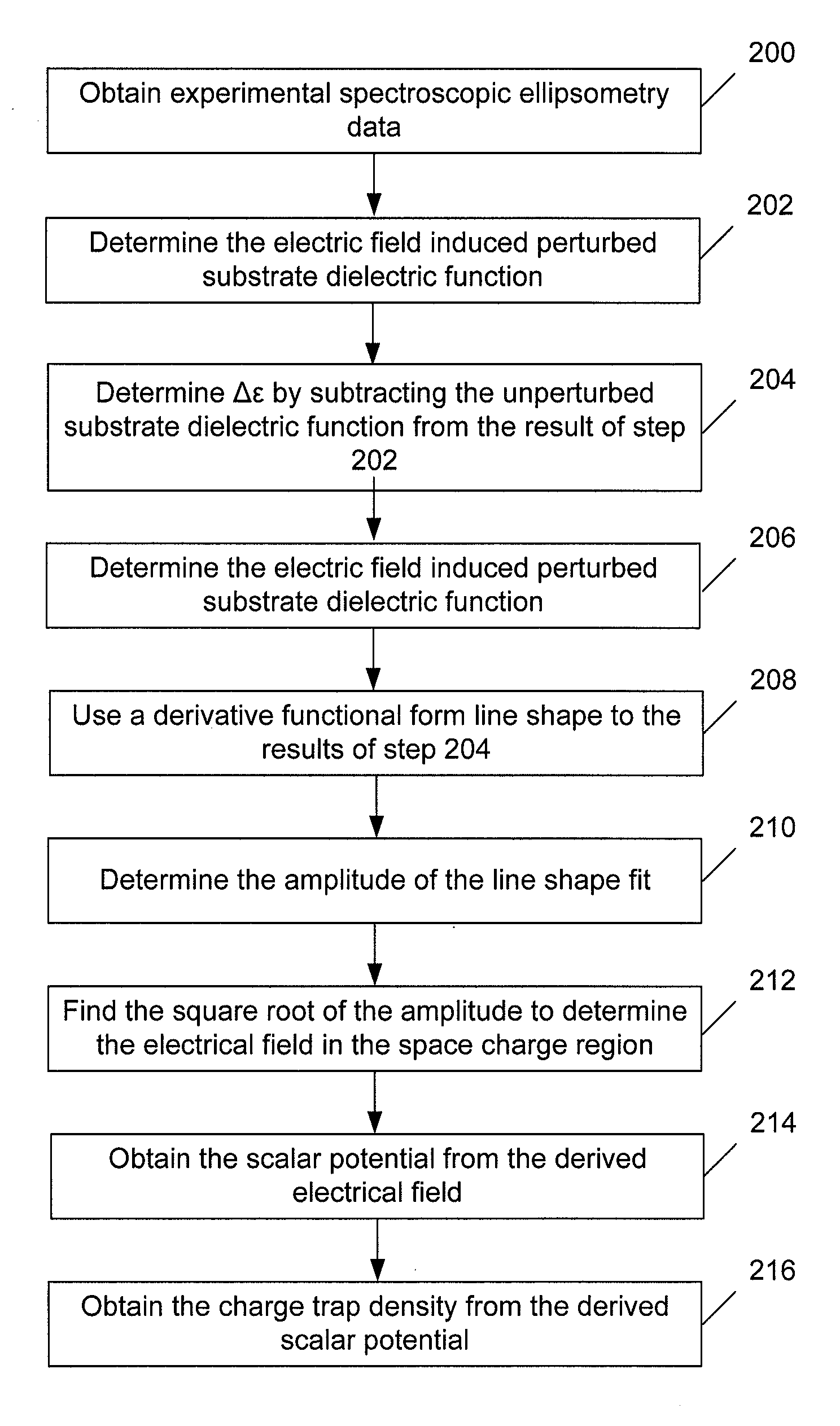
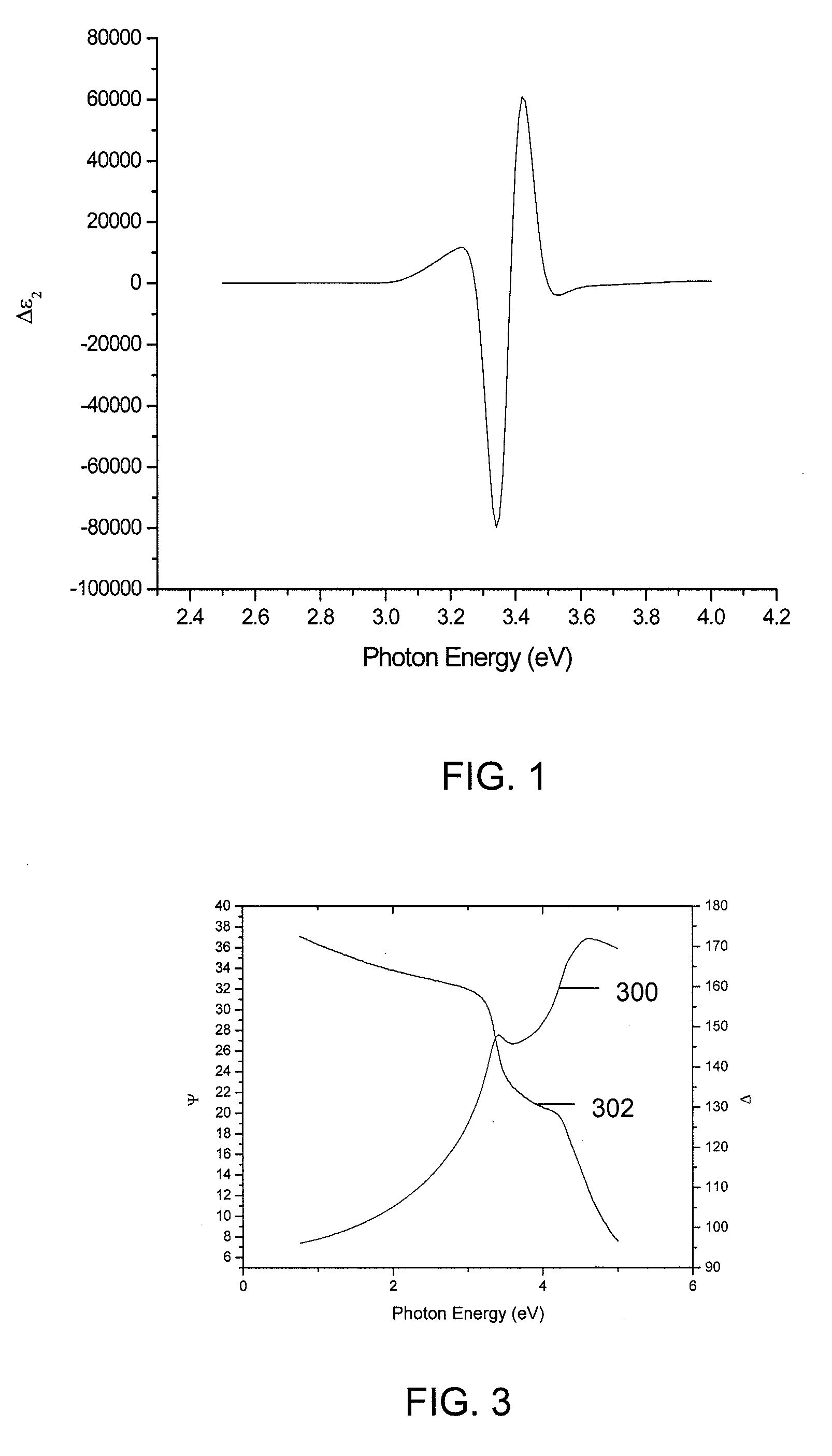
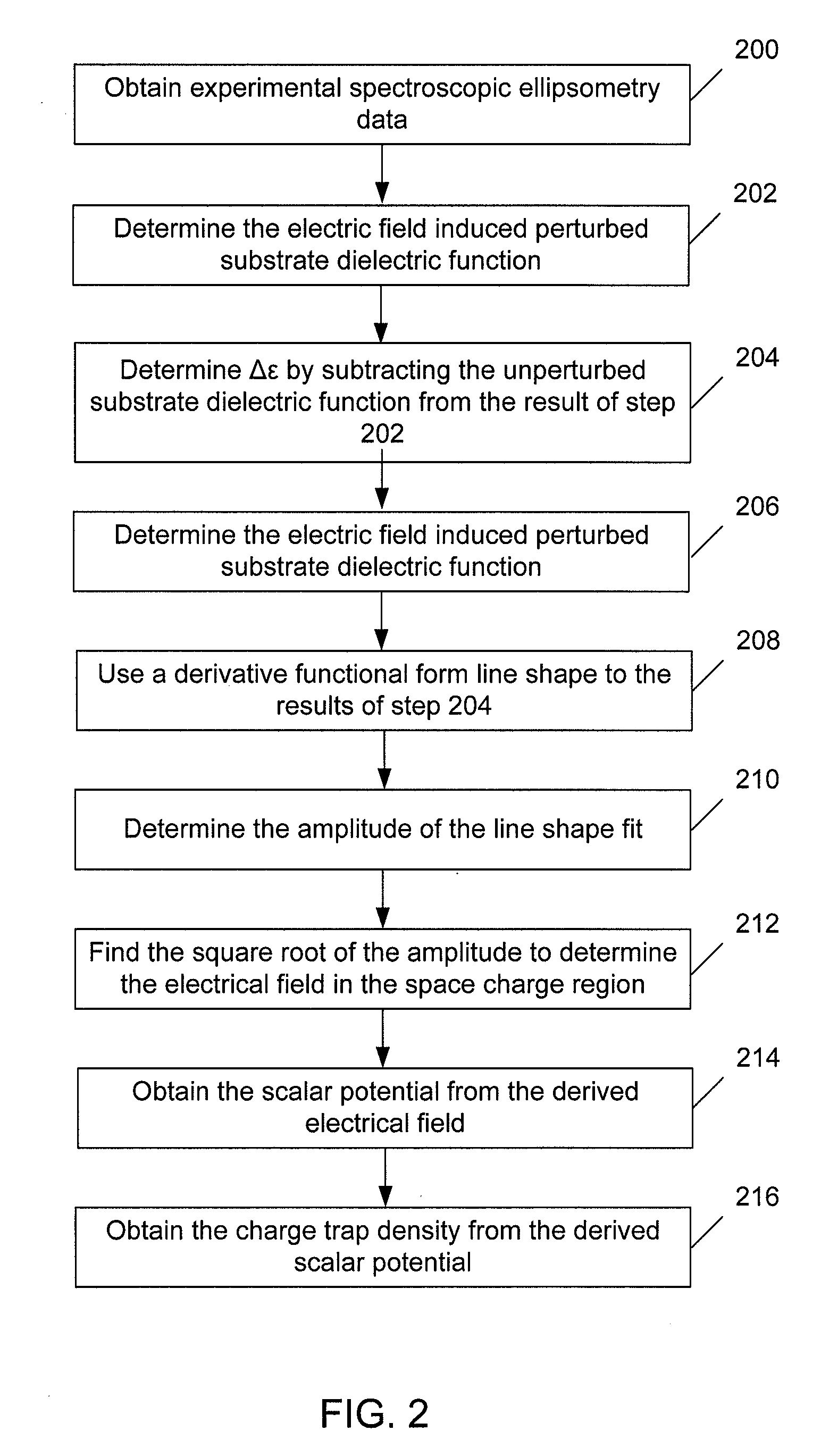
Methods and Systems for Determining Trapped Charge Density in Films
InactiveUS20070213954A1Improve accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesScalar potentialSemiconductor materials
Methods and systems for determining a charge trap density between a semiconductor material and a dielectric material are disclosed. In one respect, spectroscopic data of the semiconductor material may be determined and used to determine a change in dielectric function. A line shape fit of the change in the dielectric function may be applied using derivative function form. The amplitude of the line shape fit may be determined and used to determine an electric field of a space charge region of the semiconductor material. By applying Poisson's equations, the scalar potential due to the electric field in the space charge region may be determined. Subsequently, using the scalar potential the charge trap density may be determined.
Owner:SEMATECH
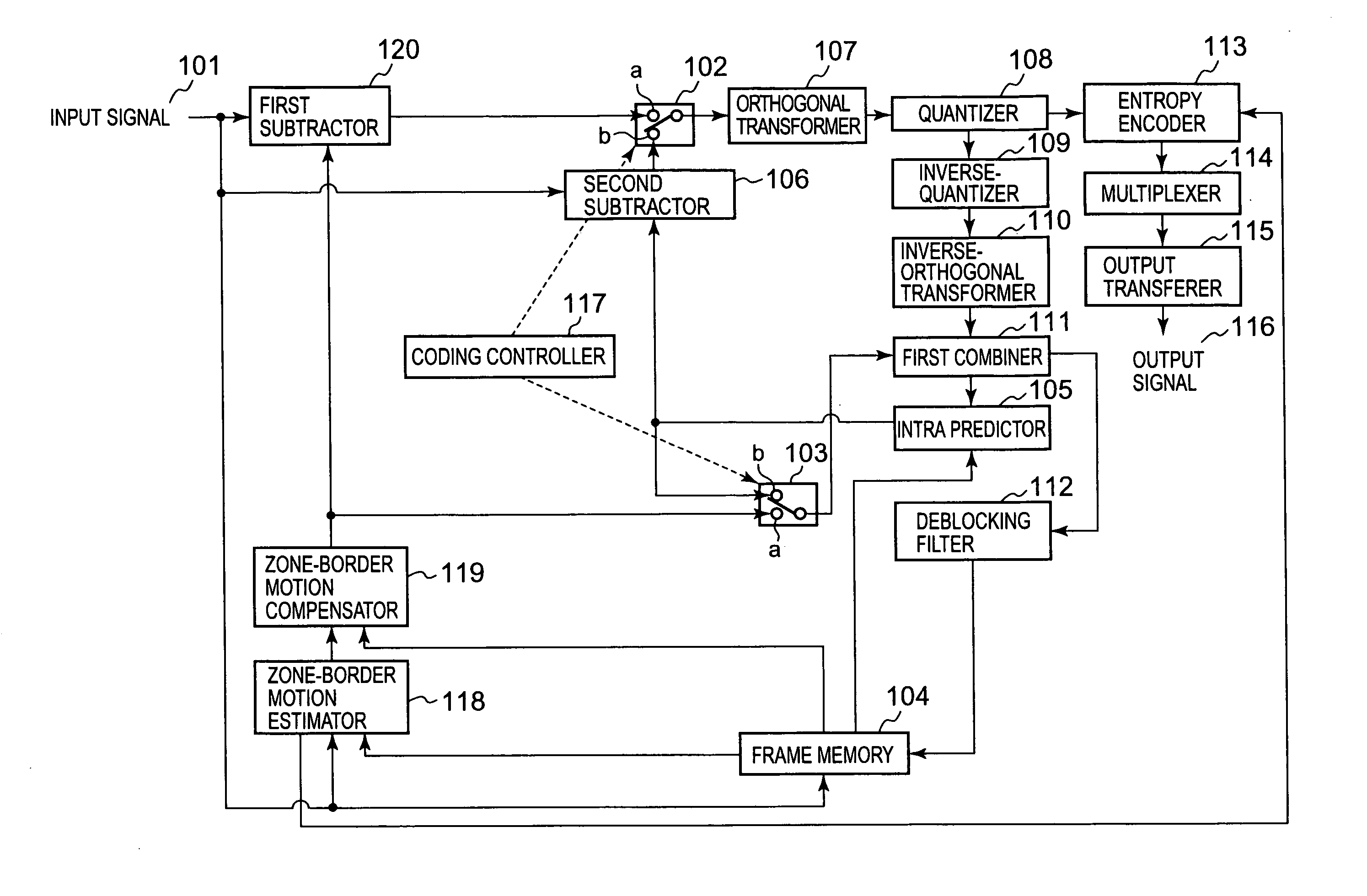
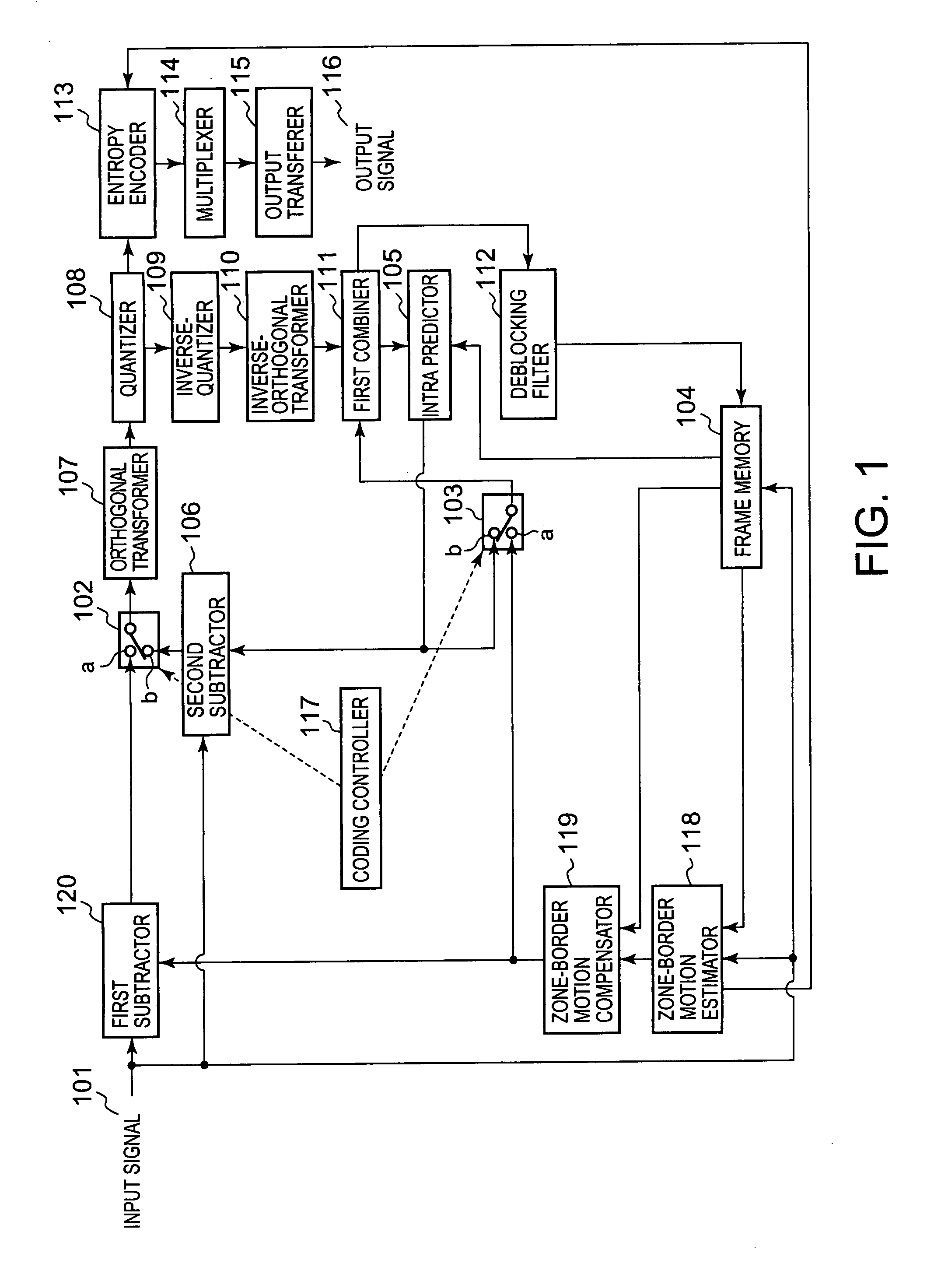
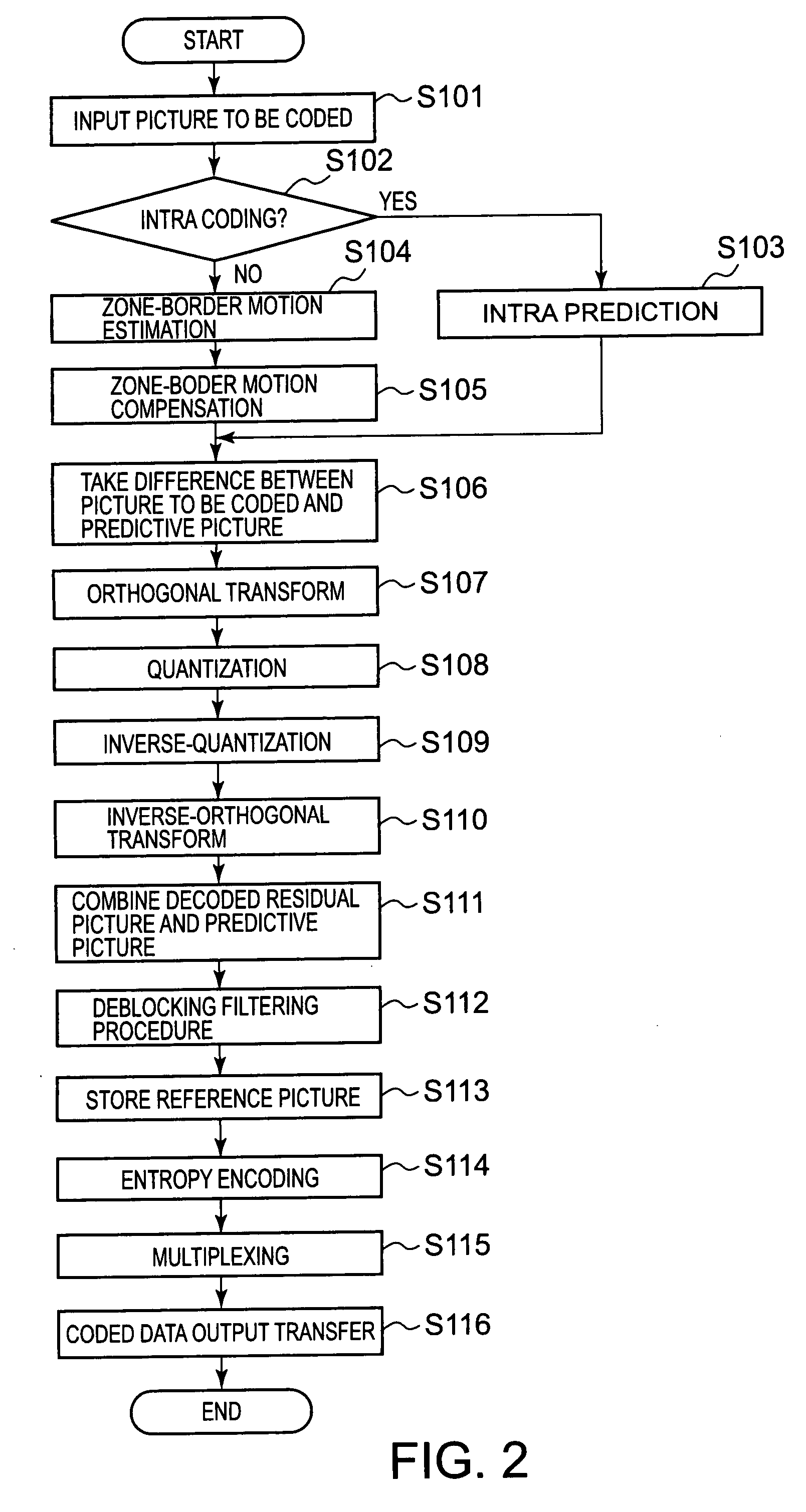
Moving-picture coding apparatus, method and program, and moving-picture decoding apparatus, method and program
ActiveUS8090025B2Maintain continuityEfficient transferColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorComputer graphics (images)
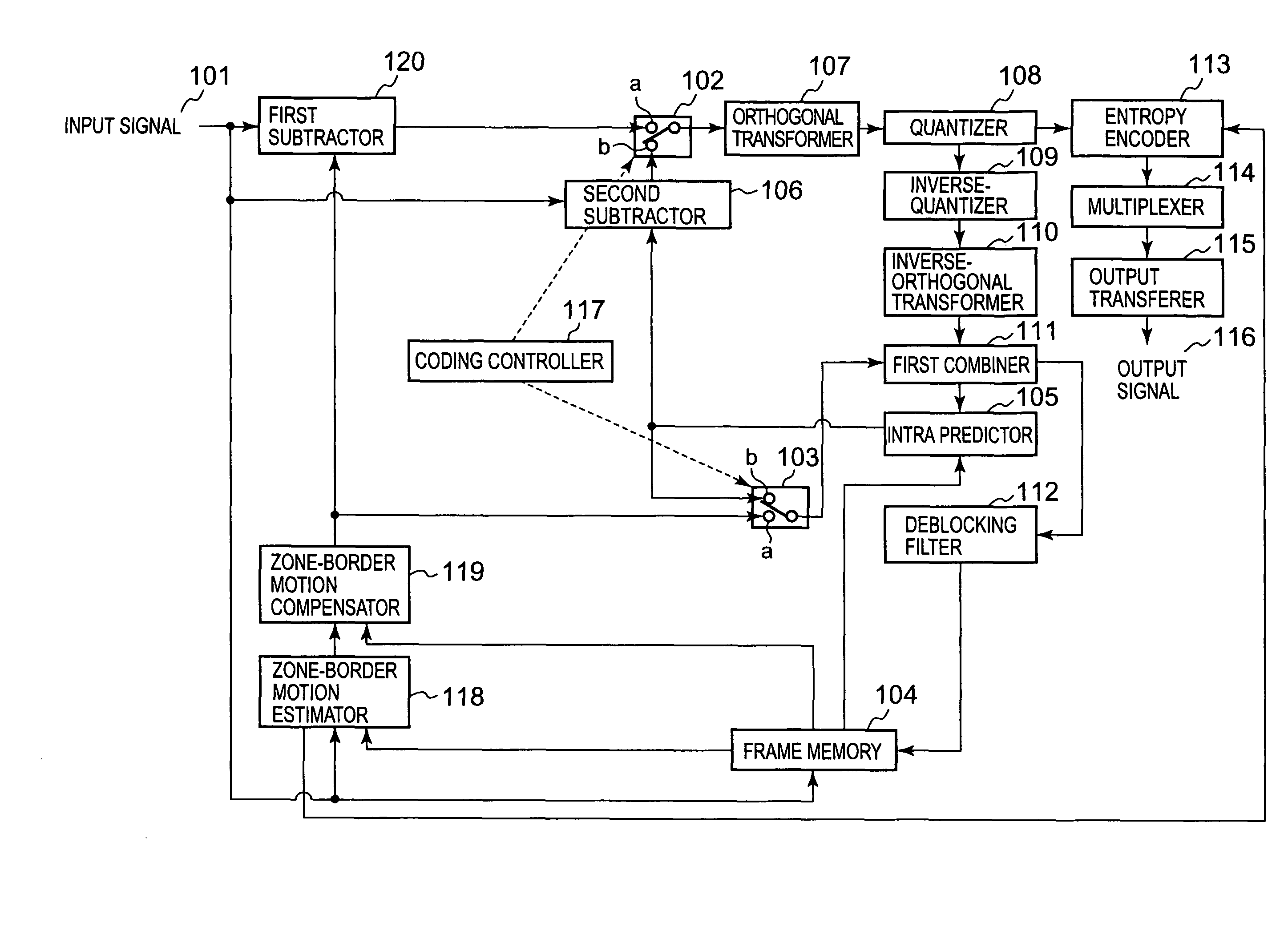
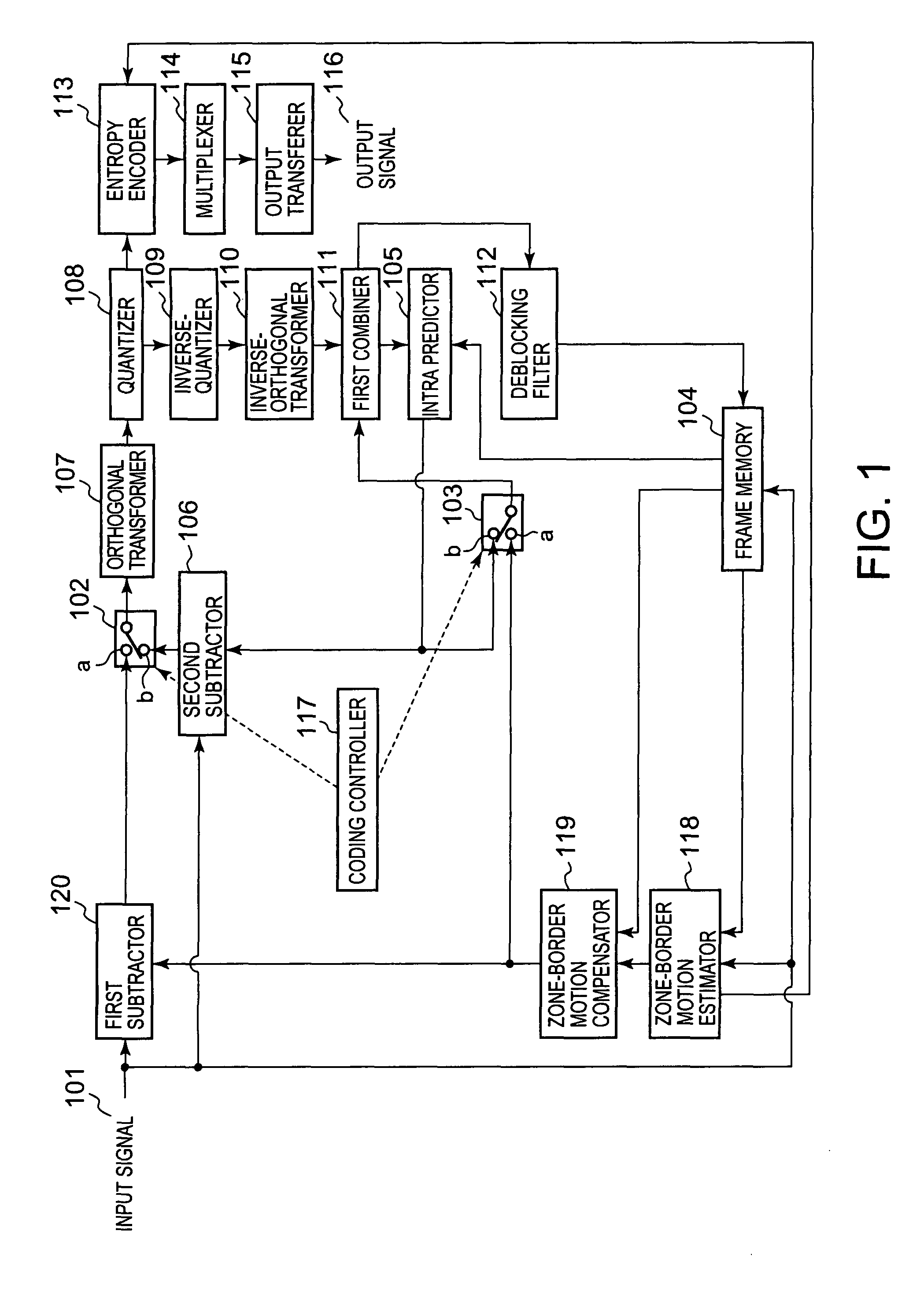
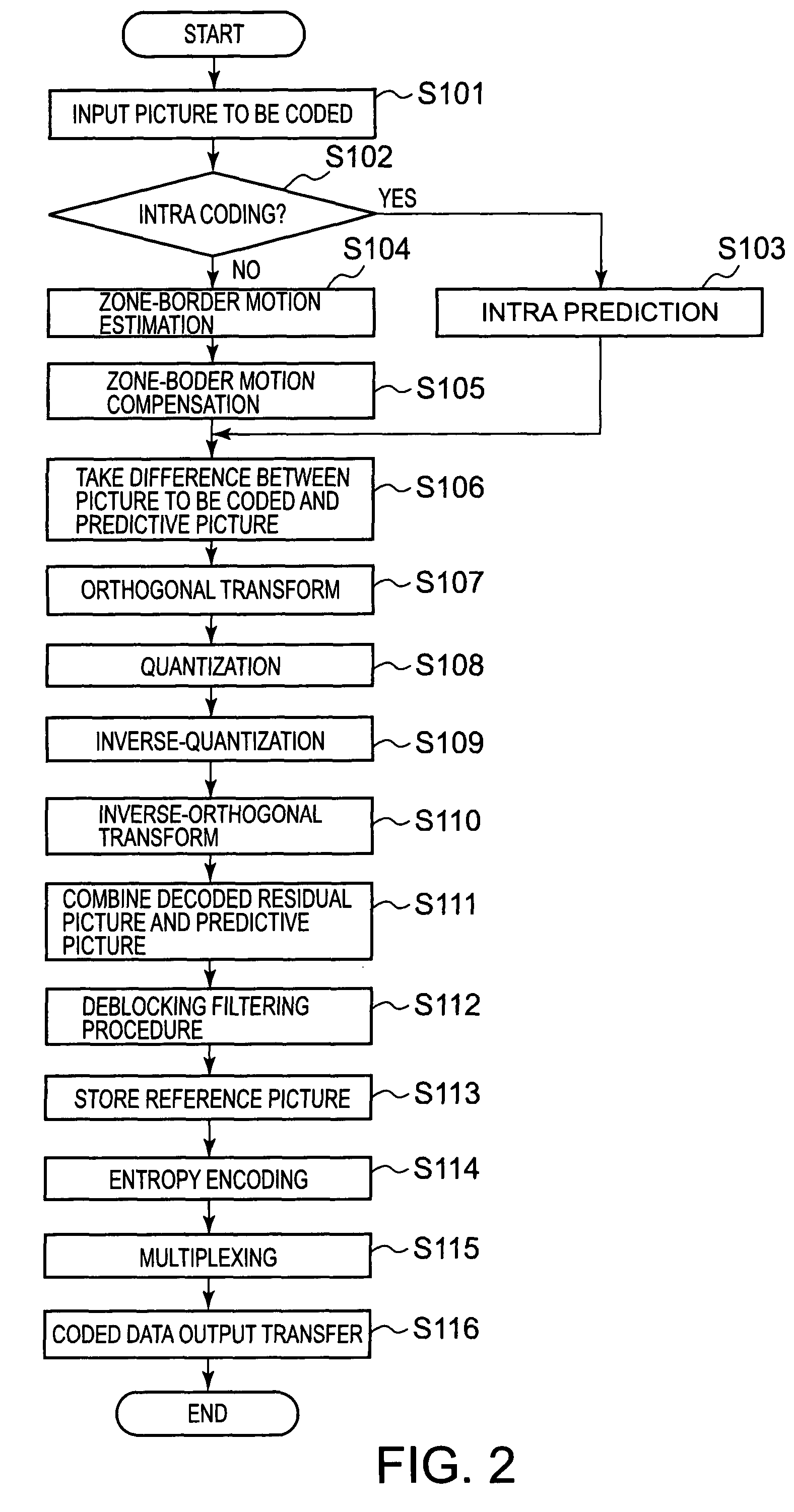
A residual picture is produced and encoded that is a residual picture that is a residual signal between a picture to be coded that is an input moving-picture video signal to be subjected to coding and a predictive picture produced from a reference picture that is a local decoded video signal for each of a plurality of rectangular zones, each composed of a specific number of pixels, into which a video area of the moving-picture video signal is divided. A boundary condition of each of a plurality of borders is obtained between the rectangular zones and another plurality of rectangular zones adjacent to the rectangular zones, and a border, of the reference picture, having a boundary condition that matches the boundary condition, is found by motion-vector search in the reference picture, and border motion-vector data is generated that is data on a motion vector from a border of the rectangular zone in the picture to be coded to the border of the reference picture thus found. A boundary condition of a border that corresponds to the border motion vector data is defined from the reference picture based on the border motion-vector data, and an estimated video signal is generated in each rectangular zone in the picture to be coded, that satisfies Poisson's Equation, thus producing a first predictive picture. The residual picture is then produced with the first predictive picture as the predictive picture and encodes the residual picture.
Owner:ADVANCED CODING TECH LLC
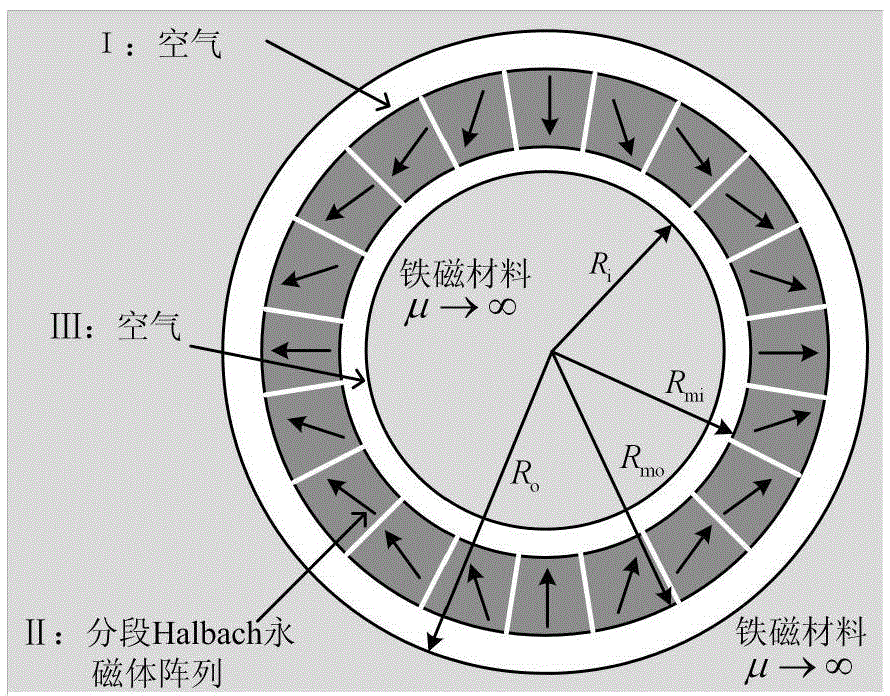
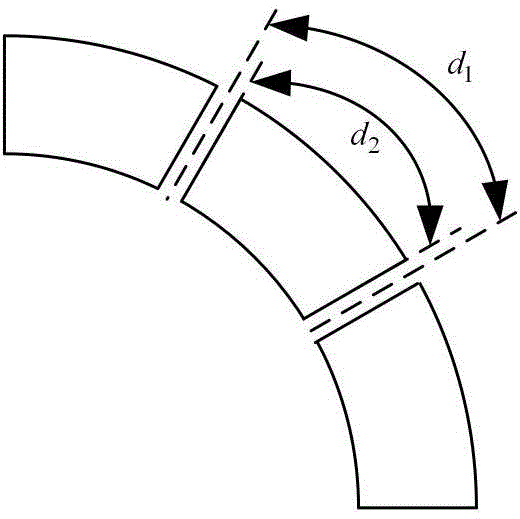
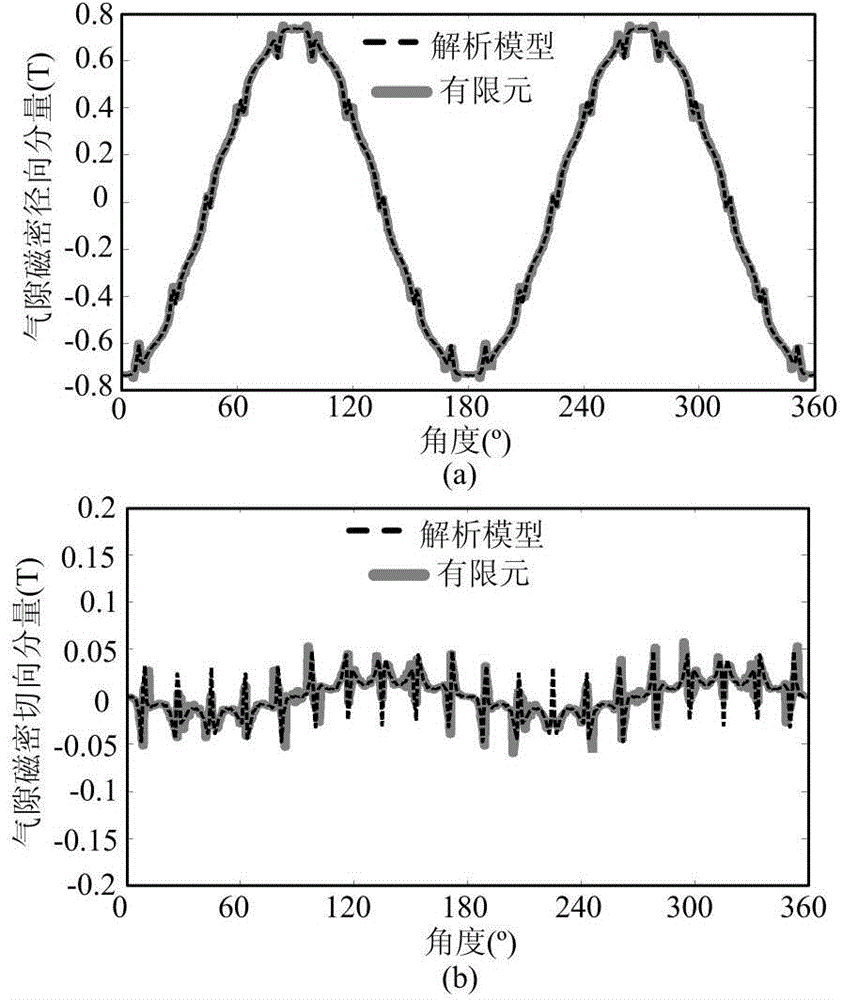
Sectional type Halbach array permanent magnet motor magnetic field calculation method
ActiveCN104091060AAccurate distributionSpecial data processing applicationsHarmonicPermanent magnet motor
The invention relates to a sectional type Halbach array permanent magnet motor magnetic field calculation method. The sectional type Halbach array permanent magnet motor magnetic field calculation method comprises the steps of determining solution areas, respectively building Laplace's equations or Poisson's equations for the different solution areas, calculating the interval between magnetic blocks of a sectional type Halbach array, solving the radial and tangential component amplitudes under each order of harmonic waves of residual magnetization intensity of a permanent magnet, solving the built Laplace's equations or Poisson's equations, obtaining an expression of a scalar magnetic potential in the solution areas, and further obtaining radial and tangential components of flux densities of the areas. The sectional type Halbach array permanent magnet motor magnetic field calculation method can accurately solve the magnetic field of an inner and outer rotor sectional type Halbach array permanent magnet motor with any magnetic block number of each pole and any number of pole pairs.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
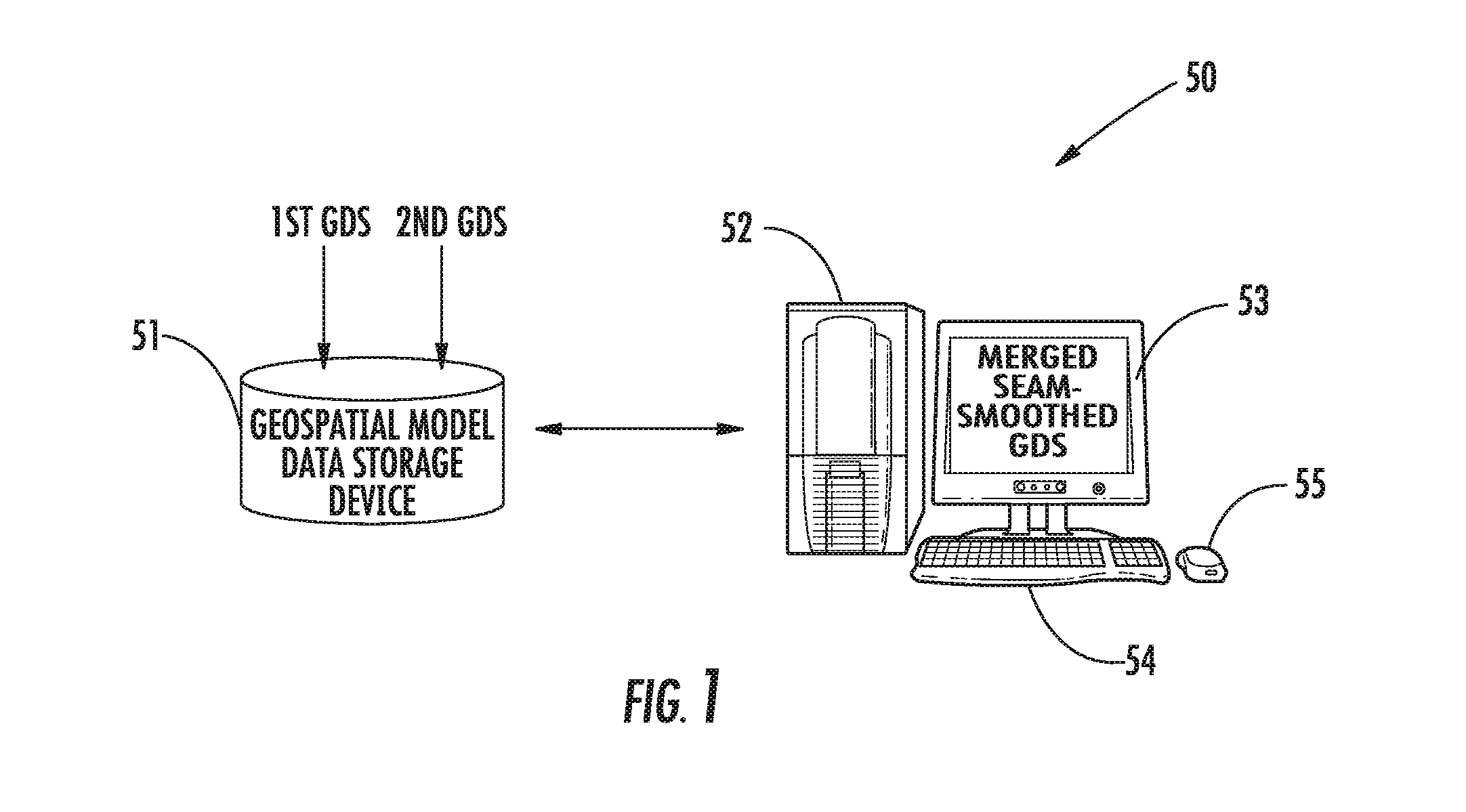
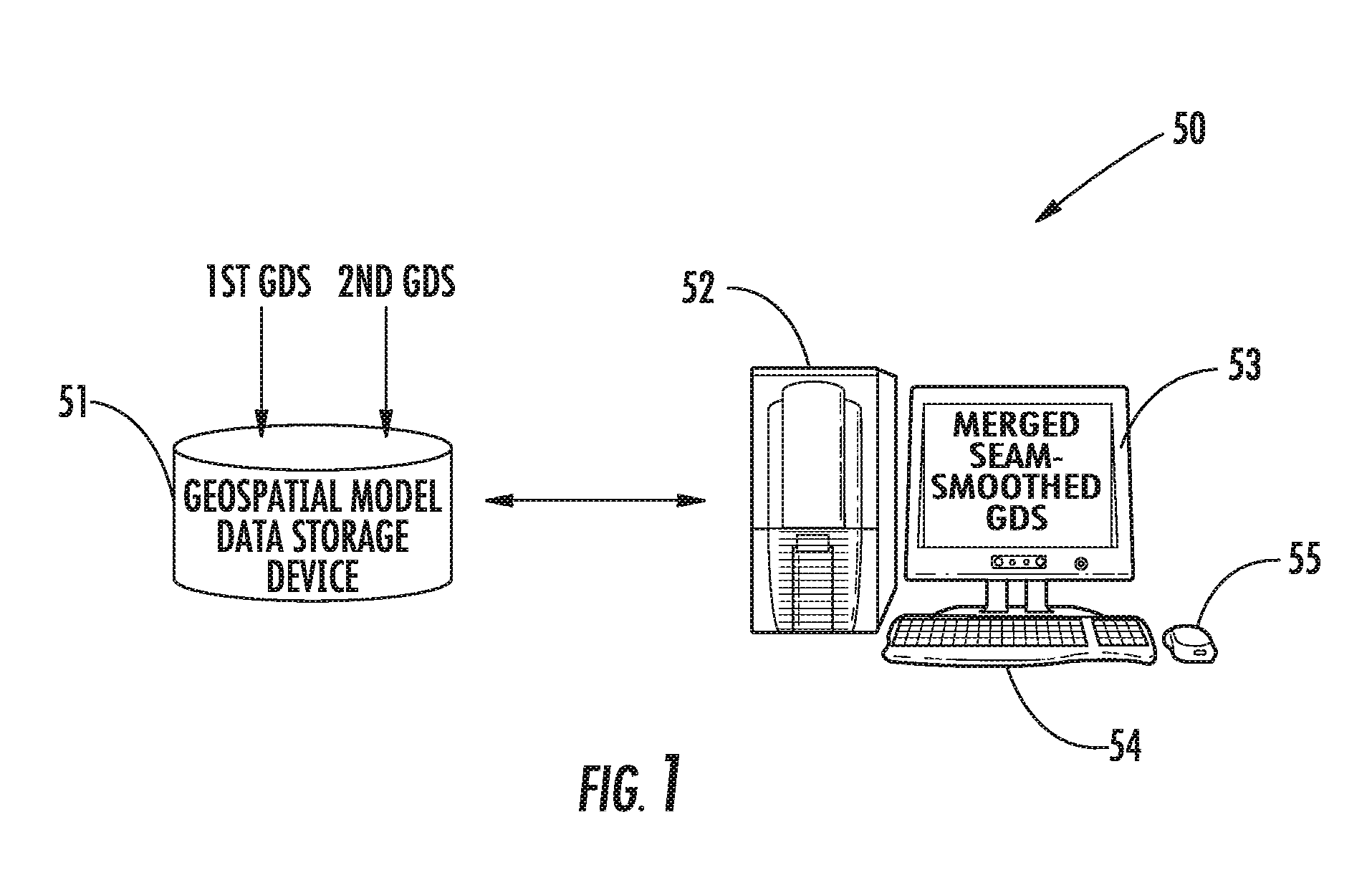
Geospatial modeling system providing poisson-based geospatial data set merging and related methods
InactiveUS8239175B2Character and pattern recognitionComputation using non-denominational number representationData setPoisson's equation
A geospatial modeling system may include a geospatial model data storage device, and a processor cooperating with the geospatial model data storage device for merging first and second geospatial data sets for corresponding first and second geospatial regions. The processor may be for generating seam-smoothed geospatial data for a corresponding selected geospatial region between adjacent portions of the first and second geospatial regions by applying Poisson's equation to data from at least one of the first and second geospatial data sets for the selected geospatial region using boundary conditions based upon data along corresponding interfaces between the selected geospatial region and adjacent portions of the first and second geospatial regions.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Moving-picture coding apparatus, method and program, and moving-picture decoding apparatus, method and program
ActiveUS20070268968A1Maintain continuityEfficient transferColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer graphics (images)Motion vector
A residual picture is produced and encoded that is a residual picture that is a residual signal between a picture to be coded that is an input moving-picture video signal to be subjected to coding and a predictive picture produced from a reference picture that is a local decoded video signal for each of a plurality of rectangular zones, each composed of a specific number of pixels, into which a video area of the moving-picture video signal is divided. A boundary condition of each of a plurality of borders is obtained between the rectangular zones and another plurality of rectangular zones adjacent to the rectangular zones, and a border, of the reference picture, having a boundary condition that matches the boundary condition, is found by motion-vector search in the reference picture, and border motion-vector data is generated that is data on a motion vector from a border of the rectangular zone in the picture to be coded to the border of the reference picture thus found. A boundary condition of a border that corresponds to the border motion vector data is defined from the reference picture based on the border motion-vector data, and an estimated video signal is generated in each rectangular zone in the picture to be coded, that satisfies Poisson's Equation, thus producing a first predictive picture. The residual picture is then produced with the first predictive picture as the predictive picture and encodes the residual picture.
Owner:ADVANCED CODING TECH LLC
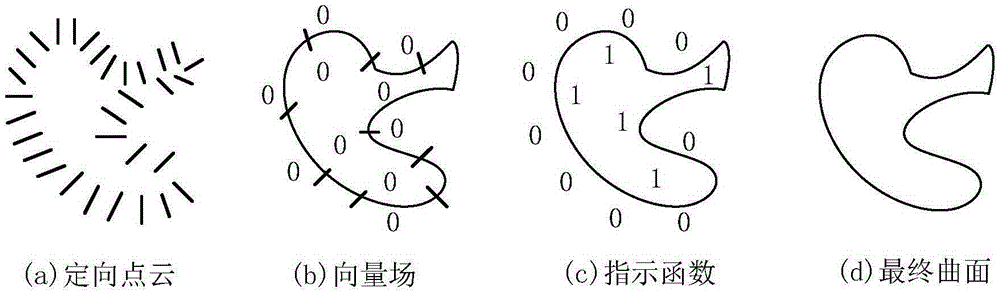
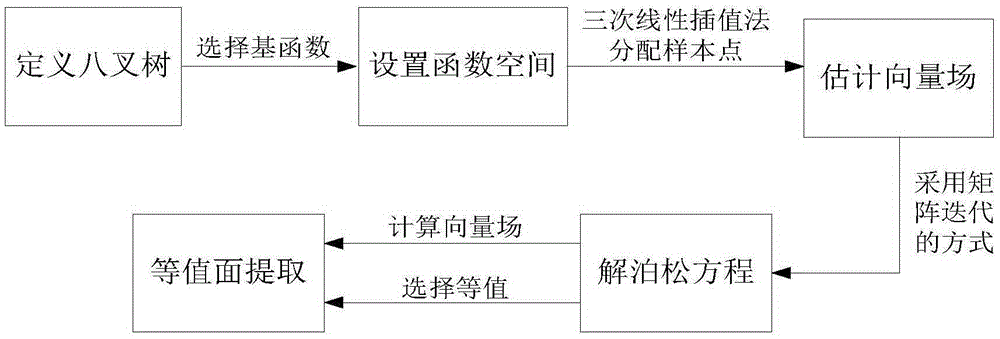
Complex structure point cloud processing algorithm bases on Poisson reconstruction
The invention discloses a complex structure point cloud processing algorithm bases on Poisson reconstruction. Curved surface reconstruction carried out through a point cloud processing technical method based on Poisson reconstruction adopts an indicator function to describe a curved surface; a vector field based on normal vector is constructed through Gaussian filtering; and a Poisson equation is solved through a multi-grid method to obtain a transition portion of the indicator function of directional point cloud to finish the curved surface reconstruction. The curved surface reconstruction technology based on Poisson is mainly formed by five parts: defining an octree, setting function space, estimating the vector field, solving the Poisson equation and extracting contour surface. With the fast development of a 3D laser scanning device, the point cloud obtaining technology also has considerable progress. The point cloud processing algorithm can be widely applied to the fields of reverse engineering, hybrid modeling, visual inspection, medical images and archaeological and cultural relic modeling and the like.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Methods and systems for determining trapped charge density in films
InactiveUS7595204B2Improve accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesScalar potentialSemiconductor materials
Methods and systems for determining a charge trap density between a semiconductor material and a dielectric material are disclosed. In one respect, spectroscopic data of the semiconductor material may be determined and used to determine a change in dielectric function. A line shape fit of the change in the dielectric function may be applied using derivative function form. The amplitude of the line shape fit may be determined and used to determine an electric field of a space charge region of the semiconductor material. By applying Poisson's equations, the scalar potential due to the electric field in the space charge region may be determined. Subsequently, using the scalar potential the charge trap density may be determined.
Owner:SEMATECH
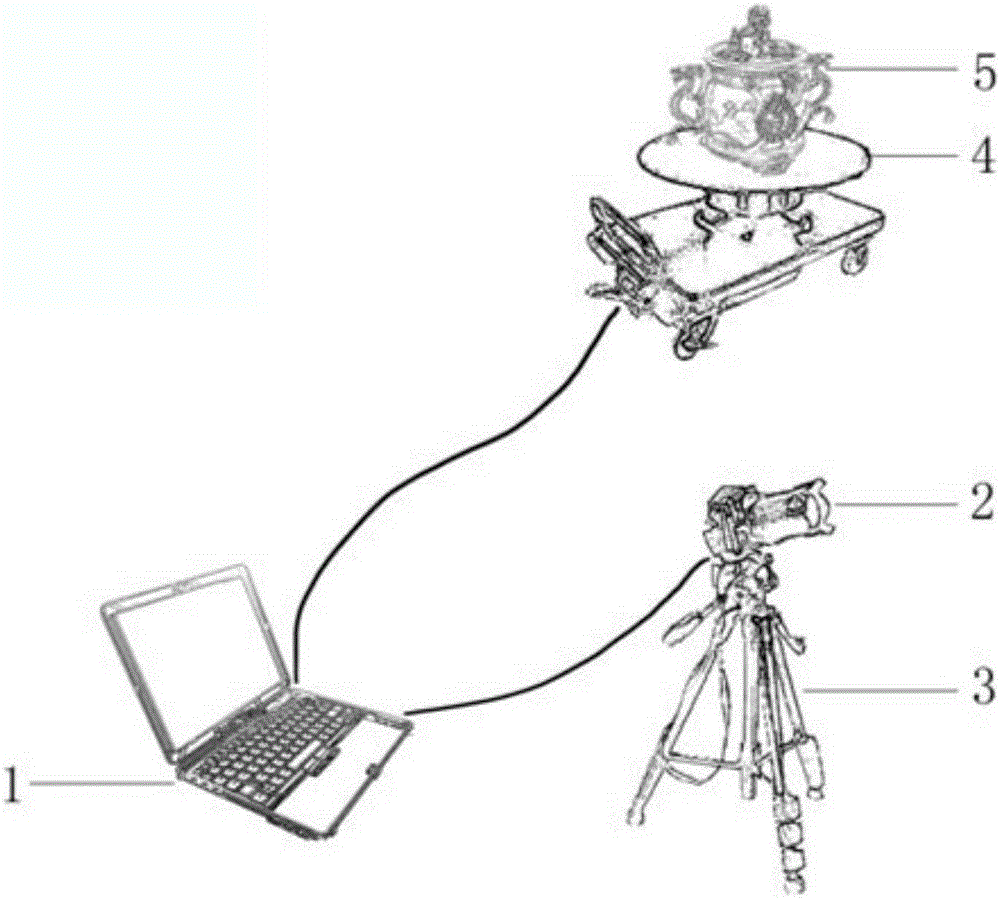
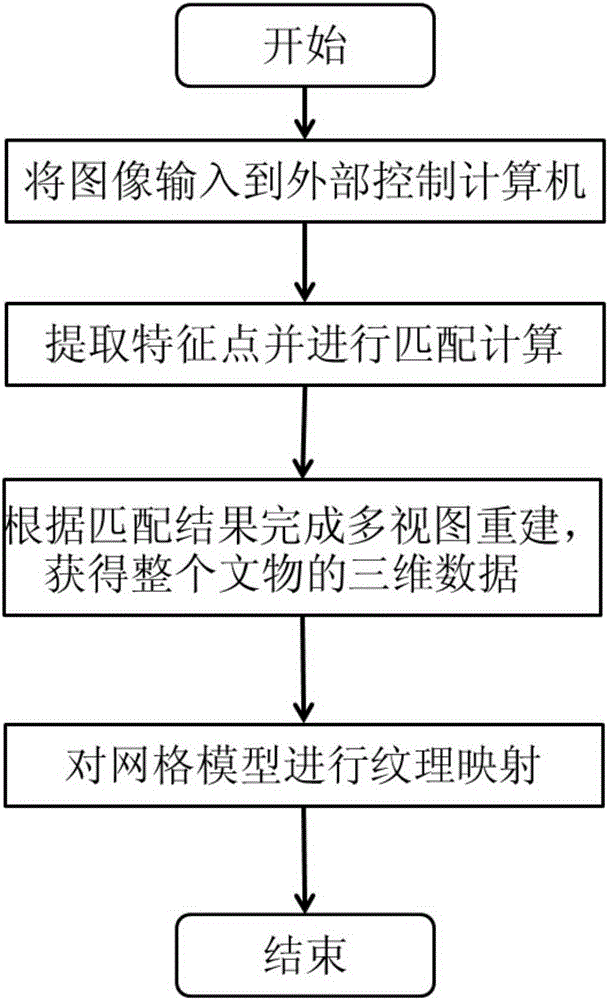
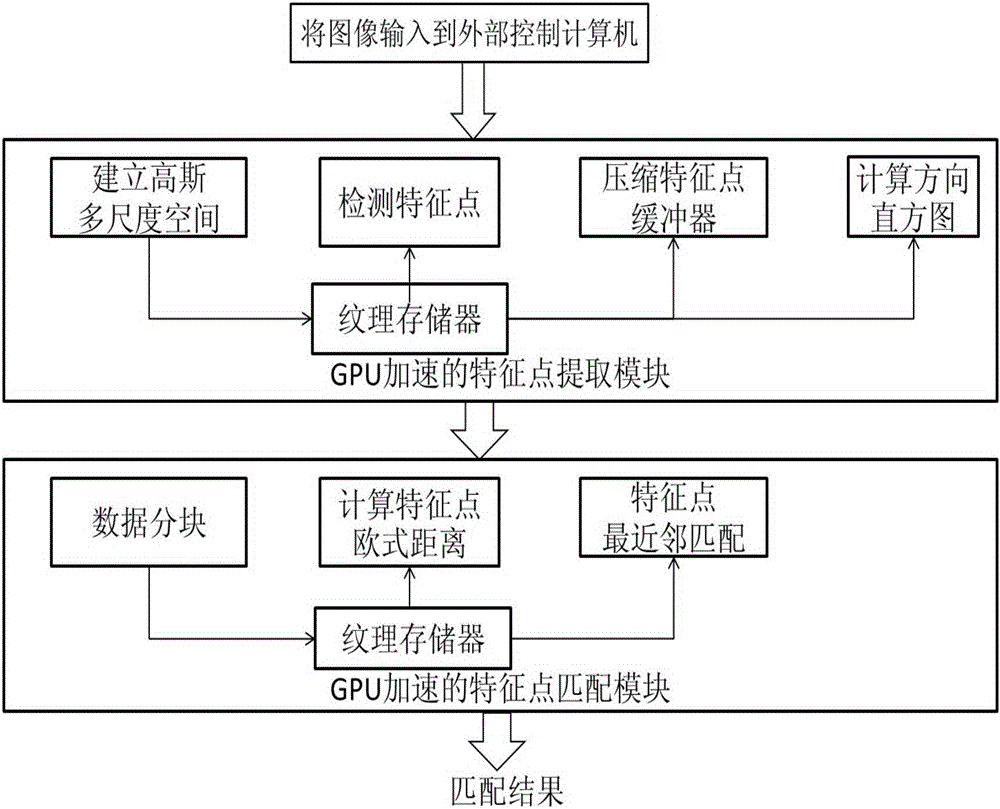
Three-dimensional cultural relic reconstruction system and three-dimensional cultural relic reconstruction method based on computer stereo vision
The invention relates to a three-dimensional cultural relic reconstruction system and a three-dimensional cultural relic reconstruction method based on computer stereo vision. The system is composed of a computer, a rotating platform, a digital camera and a camera support. The method comprises the steps of firstly inputting a cultural relic image into the computer, extracting feature points of the image, and establishing a matching relation; then carrying out multi-view reconstruction according to the feature points and the matching relation, and acquiring three-dimensional data of the cultural relic; and finally, carrying out texture mapping on the three-dimensional data of the cultural relic by adopting a Poisson equation, and outputting a textured three-dimensional cultural relic model. The beneficial effects lie in that (1) the method provided by the invention is simple and low in cost, and does not need additional control equipment; (2) the system provided by the invention is simple to use and convenient to operate, people only need to put the cultural relic on the rotating platform and presses a start button, and the system can output the texture indicating three-dimensional cultural relic data; and (3) the reconstruction efficiency is effectively improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
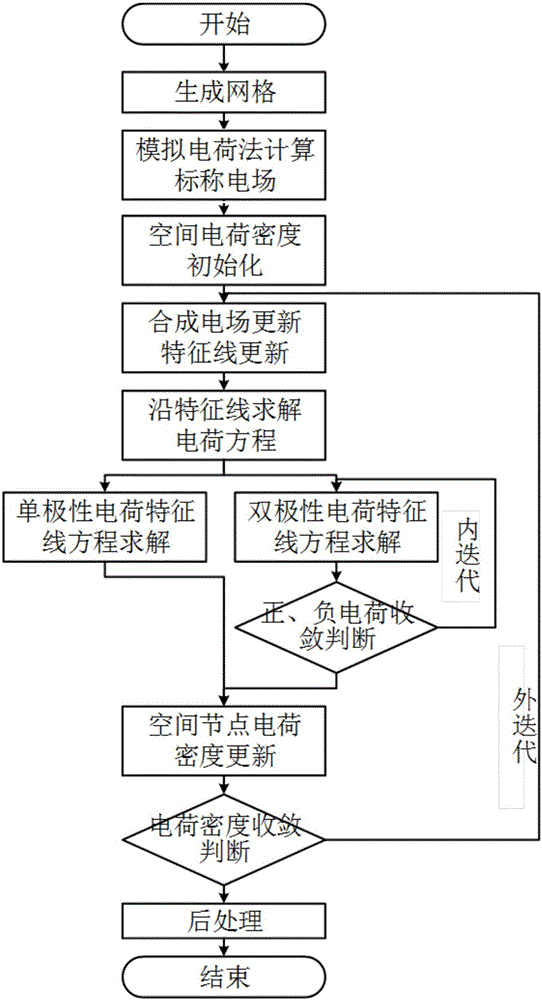
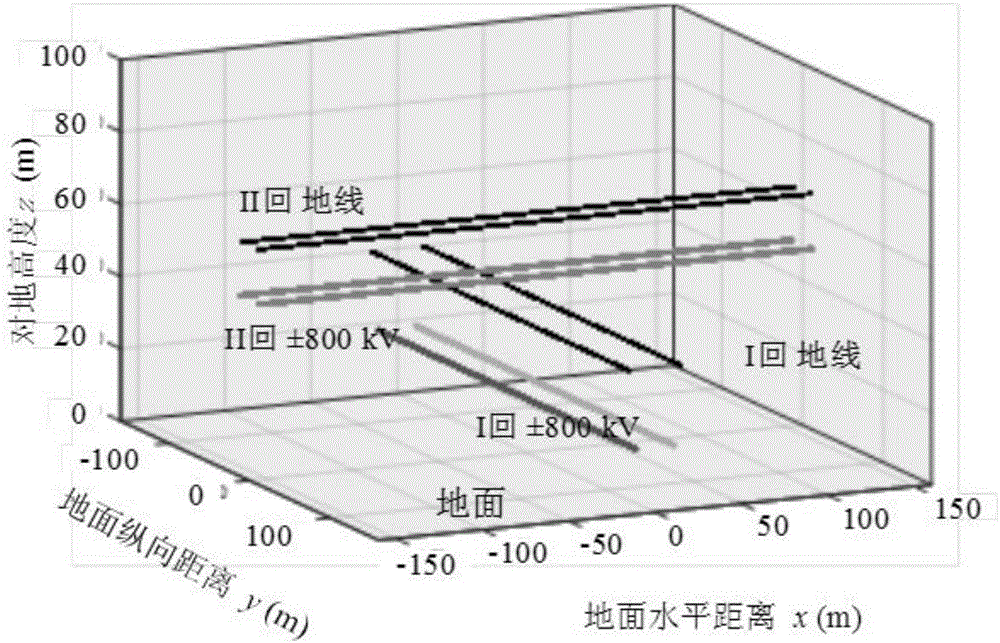
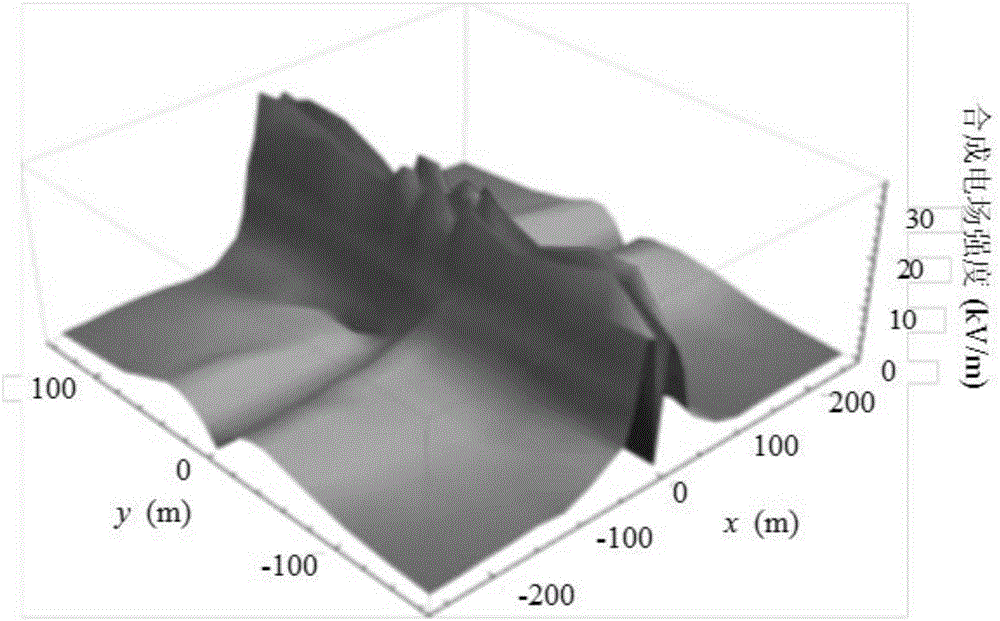
Method for calculation of characteristic lines of three-dimensional ionized field of direct current transmission line
ActiveCN106680603ACalculation speedCalculation speed is accurateElectrostatic field measurementsEngineeringElectric field
The present invention discloses a method for calculation of characteristic lines of a three-dimensional ionized field of a direct current transmission line. The method can be used for calculation of direct current three-dimensional ionized fields of line crossing and around the surface structures and insulators. The method comprises: giving an assumed distribution of a space electric field and of space charges, calculating a new space electric field distribution by employing the space charges through the Poisson equation, and painting characteristic lines; solving the charge distribution on the characteristic lines according to the new space electric field distribution through the ion current equation and the current continuity equation; and repeating the steps mentioned above until the distributions of two successive space charges is in an allowable error range, and performing calculation of combination of the electric field and the ion current density. Compared to the Deutsch hypothesis method, the method for calculation of characteristic lines of the three-dimensional ionized field of direct current transmission line considers the influence of the space charges and is more accurate in calculation result; and moreover, compared to the finite element method, the method for calculation of characteristic lines of the three-dimensional ionized field of direct current transmission line greatly increases the update efficiency of charges and is obviously better than the finite element method on the computational efficiency.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
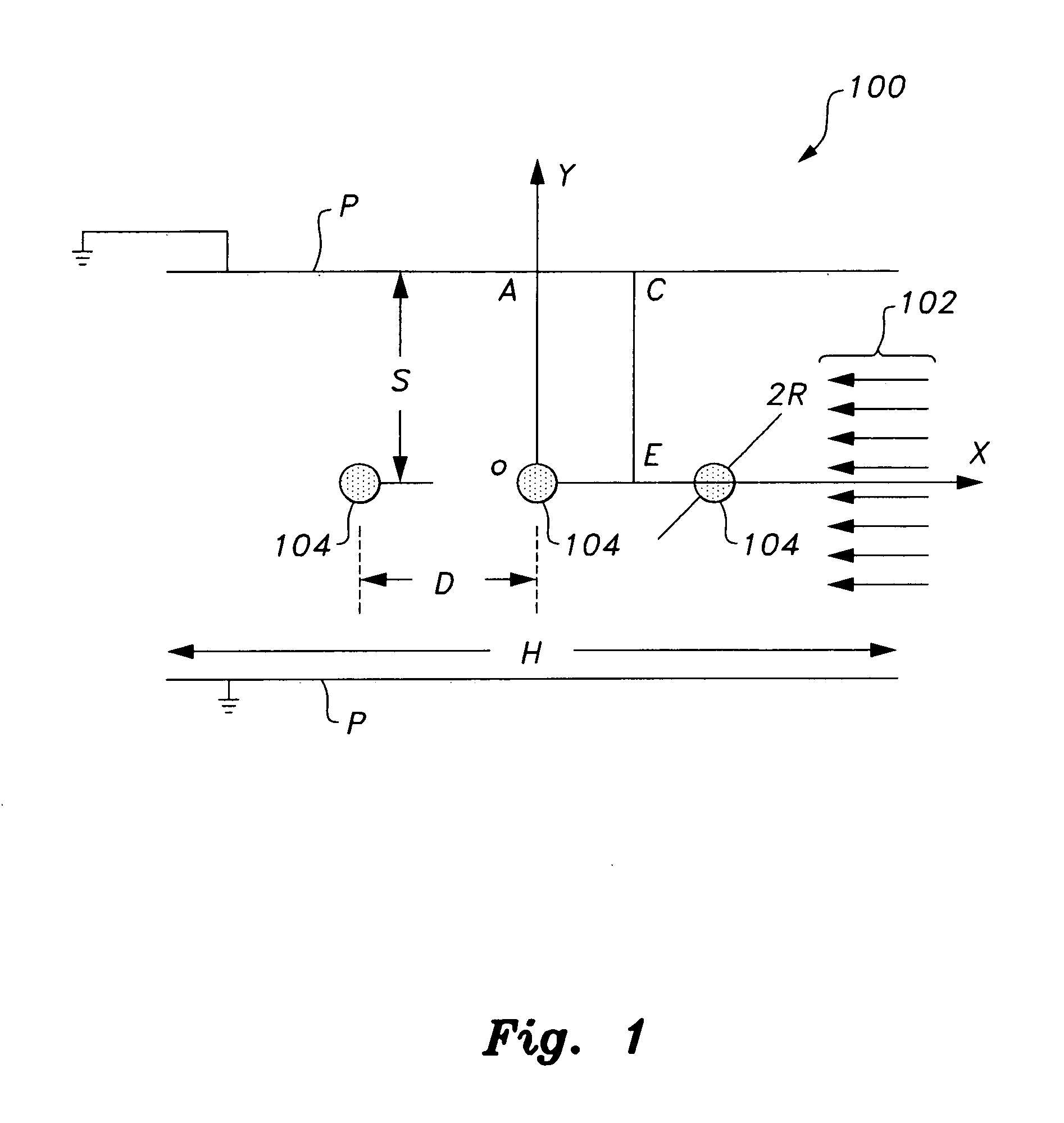
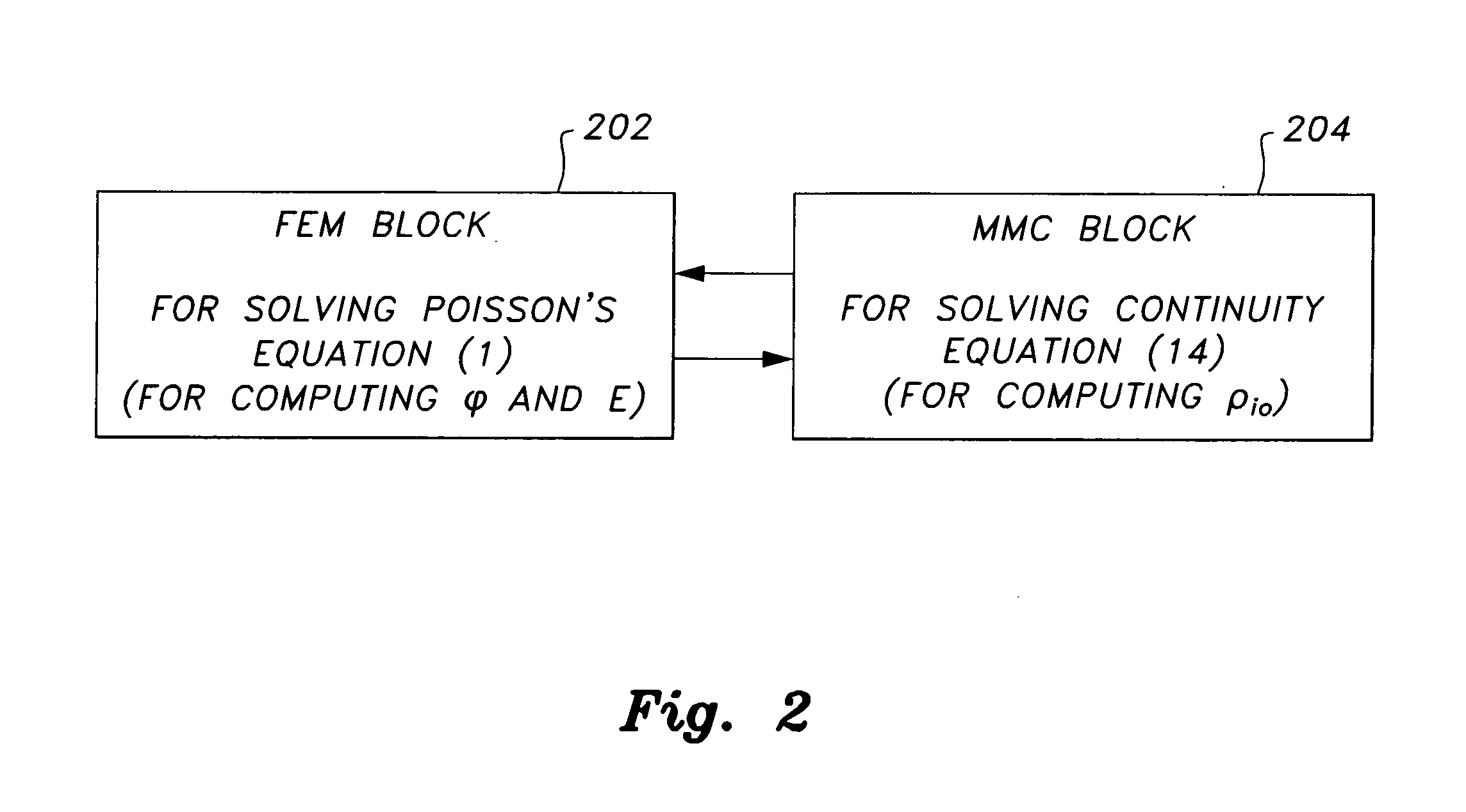
System and method for estimating corona power loss in a dust-loaded electrostatic precipitator
InactiveUS20110307198A1Readily apparentFast convergenceElectric devicesResistance/reactance/impedenceVoltage polarityEngineering
The method for estimating corona power loss in a dust-loaded electrostatic precipitator numerically solves Poisson's equation and current continuity equations in which the finite element method (FEM) and a modified method of characteristics (MMC) are used. The system is a computerized system that produces results showing how different parameters such as discharging wire radius, wire-to-wire spacing, wire-to-plate spacing, fly ash flow speed and applied voltage polarity influence corona power loss and current density profiles.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Geospatial modeling system providing poisson-based geospatial data set merging and related methods
InactiveUS20120179433A1Character and pattern recognitionComputation using non-denominational number representationData setPoisson's equation
A geospatial modeling system may include a geospatial model data storage device, and a processor cooperating with the geospatial model data storage device for merging first and second geospatial data sets for corresponding first and second geospatial regions. The processor may be for generating seam-smoothed geospatial data for a corresponding selected geospatial region between adjacent portions of the first and second geospatial regions by applying Poisson's equation to data from at least one of the first and second geospatial data sets for the selected geospatial region using boundary conditions based upon data along corresponding interfaces between the selected geospatial region and adjacent portions of the first and second geospatial regions.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
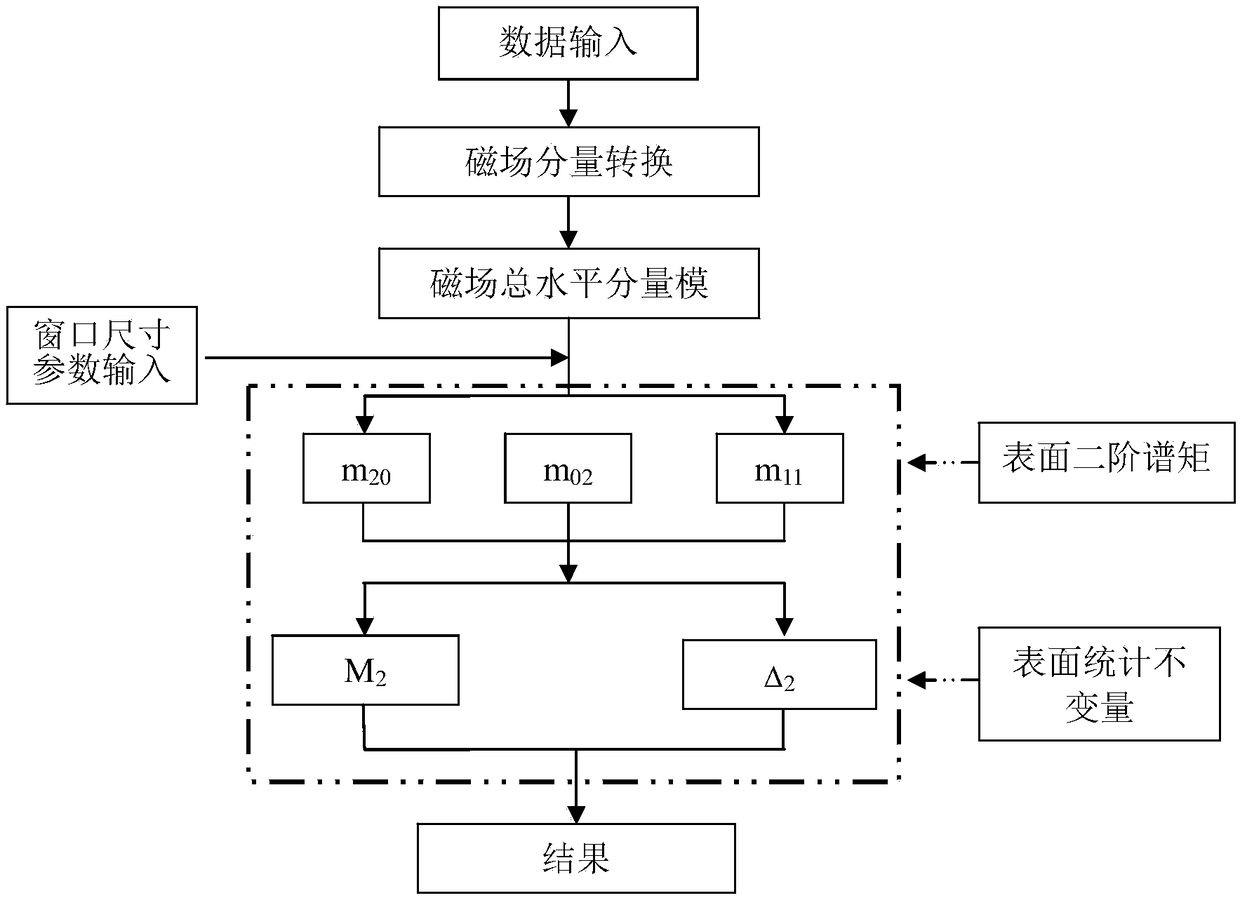
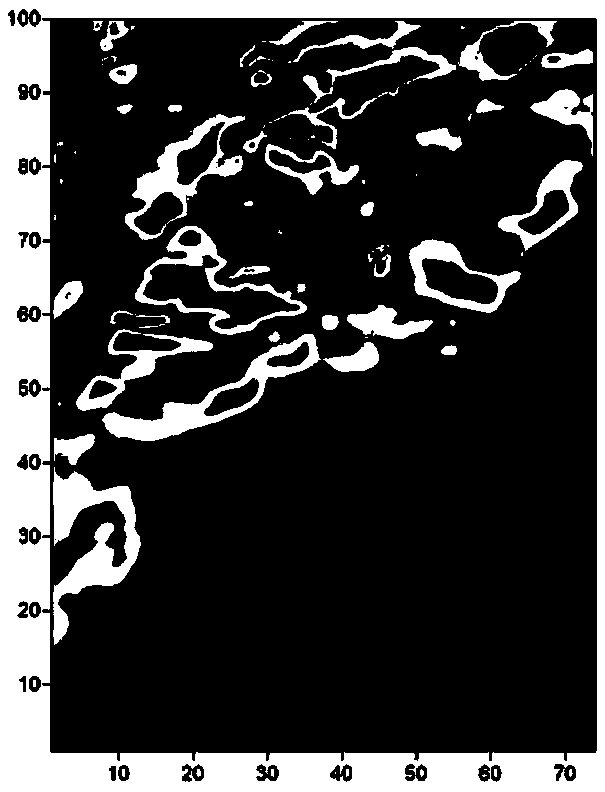
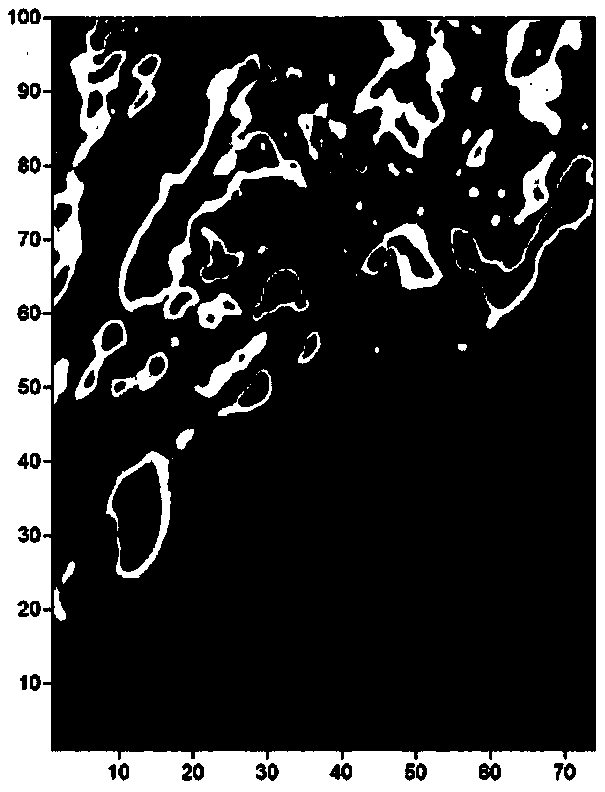
Magnetic field nicking analysis method for extraction of physical geography magnetic anomaly field boundary
ActiveCN109407161AEliminate false bordersEfficient extractionElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationTectonicsNoise suppression
The present invention discloses a magnetic field nicking analysis method for extraction of a physical geography magnetic anomaly field boundary. An analysis relation between a magnetic field and a gravitational field is employed, namely a Poisson's equation, to deduce three components of a second-order spectral moment at the surface of the magnetic field to obtain result parameters of magnetic field surface nicking analysis. The method comprises the four steps of: 1, magnetic field component conversion; 2, total magnetic field modulus anomaly [Delta]T total horizontal component module surfacelocal surface element second-order spectral moment; 3, total magnetic field modulus anomaly [Delta]T total horizontal component module surface local surface element invariant statistics; and 4, boundary coefficient extracted from the magnetic field surface. The magnetic field nicking analysis method is employed to perform boundary extraction of the magnetic field to eliminate the false boundary caused by associated anomaly while retaining the high enhancement capacity, resolving power and noise suppression capacity of the gravity nicking analysis for the weak boundary so as to provide more efficient reference information for the interpretation of the geologic structure.
Owner:中国自然资源航空物探遥感中心
3D tooth imaging modeling method
InactiveCN106875472AEasy accessImprove the treatment experienceImage enhancementImage analysisHat matrixTreatment experience
The invention provides a 3D tooth imaging modeling method. The method comprises the steps: obtaining a tooth image of an oral cavity through a binocular camera; carrying out the denoising filtering of the tooth image; calibrating the binocular camera, and obtaining a reprojection matrix; calculating three-dimensional coordinates of the tooth image through the reprojection matrix and the tooth image after noise reduction, and obtaining the point cloud data; and carrying out the curved surface reconstruction of the point cloud data through a space Poisson equation. Compared with a conventional method, the method can quickly obtain a tooth model, is low in cost, does not need to employ a conventional die obtaining material, reduces the waste, and can improve the treatment experience of a patient.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
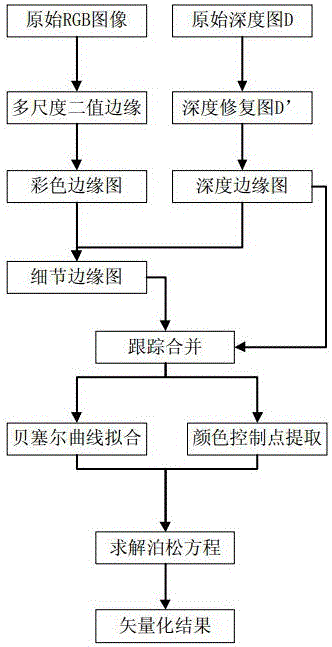
Diffusion curve-based RGBD image vectorization method
ActiveCN106504294APromote reductionGood real outlineImage analysisImage codingRgb imageEdge extraction
The invention discloses a diffusion curve-based RGBD image vectorization method. The method includes the following nine steps: inputting an original RGB color image and a depth image D which are to be processed, performing multi-scale Canny edge extraction on the RGB image, coloring the acquired multi-scale binary edge image to generate a color edge image, restoring the depth image, performing depth edge extraction on the restored depth image D' to generate a depth edge image, performing subtraction on the two edge images to obtain a detail edge image, performing tracking merging on the detail edge image and the depth edge image to generate a group of broken line sections, performing color sampling and Bezier curve fitting on the broken line sections to obtain a group of diffusion curves, using colors on the curve as constraints to solve a Poisson's equation to obtain a vectorization result. The diffusion curve-based RGBD image vectorization method provided by the invention adopts RGBD images to obtain an object outline, well restores the real outline of an object, and solves the situation of multi-scale Canny invalidation in some color environments. The method has a clear algorithm and a robust result, and is suitable for vectorization of the RGBD images.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
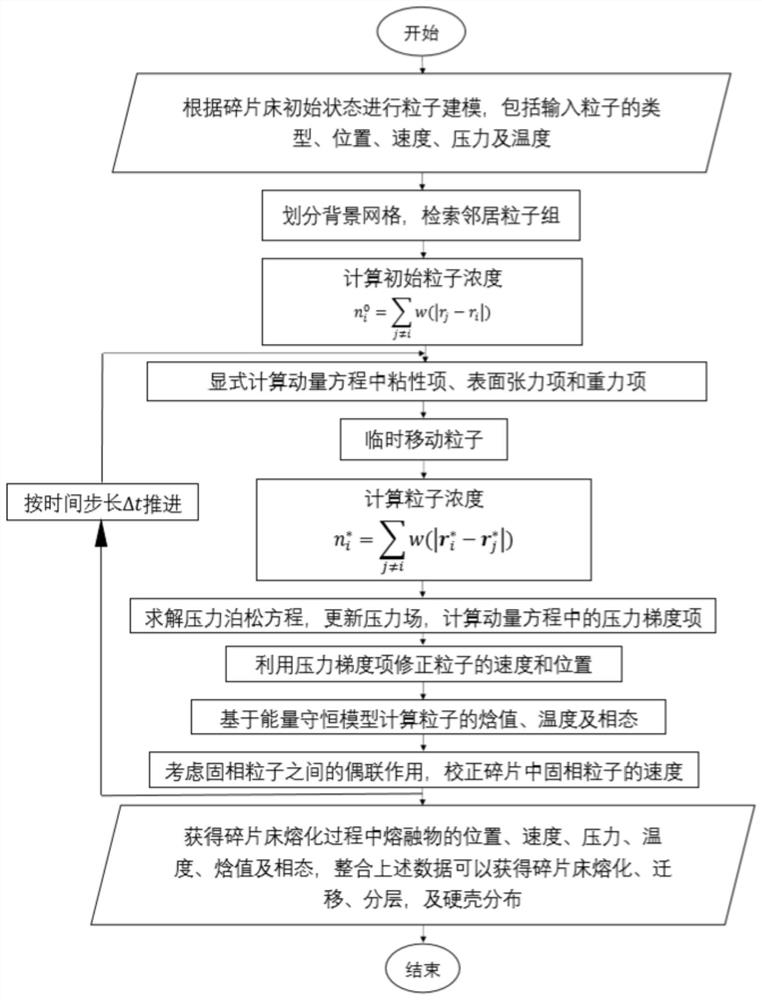
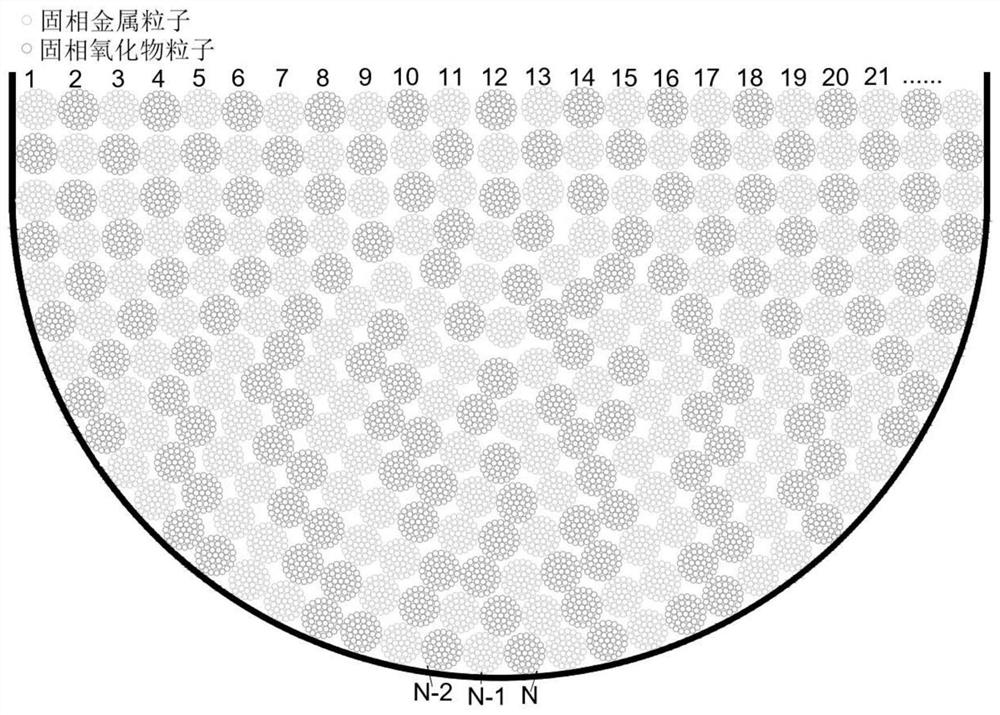
Nuclear reactor serious accident fragment bed melting process simulation method based on particle method
ActiveCN111832214AMaintain complete configurationSolving recognition problemsNuclear energy generationDesign optimisation/simulationNuclear reactorParticle method
A nuclear reactor serious accident fragment bed melting process simulation method based on a particle method comprises the following steps of 1, conducting particle modeling, setting particle initialarrangement and parameters, using particle clusters for representing solid fragments, and numbering the particles and the fragments respectively; 2, dividing background grids, and retrieving neighborparticle groups; 3, explicitly calculating a viscosity item, a surface tension item and a gravity item in the momentum equation, and estimating particle speed and displacement; 4, calculating particlepressure by adopting a Poisson equation, and correcting particle speed and displacement according to a pressure gradient model; 5, calculating a particle enthalpy value, a temperature and a phase state; 6, calculating the translation speed and the rotation speed of the fragments, and correcting the speed and the displacement of the solid-phase particles in the fragments; 7, outputting a calculation result. According to the method, small-scale particles are used for representing large-size solid fragments and numbering the large-size solid fragments, so that the identification problem of the fragments to which the particles belong is solved. In addition, a radiation heat exchange model between the solid fragments is established according to a mode of judging whether two particles are shielded by other particles or not.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
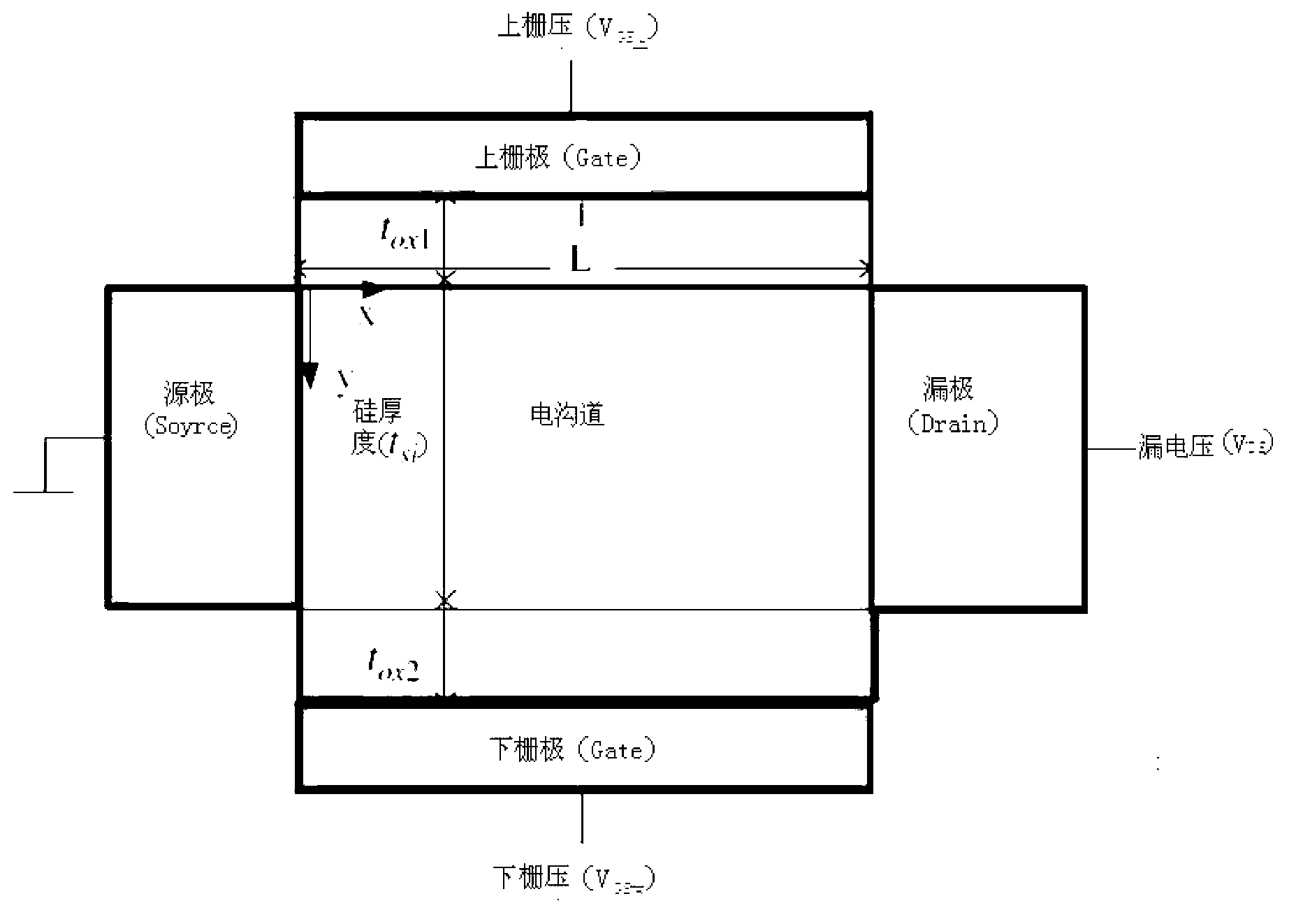
Independent double-grid FinFET channel potential distribution analysis model
InactiveCN103186691ALarge gate areaSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringPoisson's equation
The invention provides an independent double-grid FinFET (Fin Field-Effect Transistor) channel potential distribution analysis model which comprises a source electrode, wherein the source electrode is arranged on one side of a powered channel; the side of the powered channel, which is deviated from the powered channel, is provided with a drain electrode; the top surface of the powered channel is provided with an upper grid electrode; and the bottom surface of the powered channel is provided with a lower grid electrode. The independent double-grid FinFET channel potential distribution analysis model is characterized in that the device structure adopts the following potential distribution model analysis formula. The independent double-grid FinFET channel potential distribution analysis model disclosed by the invention does not use more approximate conditions and solves a two-dimensional poisson equation by using a progression method so as to establish a channel potential analysis model; the analysis model adopts more reasonable boundary condition; complex geometrical structure parameters and experimental parameters are not introduced into the analysis model; and the analysis model is suitable for different conditions such as substrate reversed bias voltages, drain voltages and the like, well accords with a numerical simulation result and has the advantages of simple form, high computing accuracy and high computing speed.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Magnetic thermoacoustic imaging conductivity reconstruction method based on linear Poisson's equation
The invention discloses a magnetic thermoacoustic imaging conductivity reconstruction method based on a linear Poisson's equation. An exciting coil generates an electromagnetic thermoacoustic signal on a conductive object; an ultrasonic transducer receives the electromagnetic thermoacoustic signal; an ultrasonic signal processing and acquiring subsystem acquires and processes the signal; and a control circuit controls the synchronization of a current excitation source, the ultrasonic transducer and the ultrasonic signal processing and acquiring subsystem. The method comprises the following steps: performing circular fault scanning on the electromagnetic thermoacoustic signal by virtue of the ultrasonic transducer, acquiring an electromagnetic ultrasonic signal on the circumference of each fault, and finally combining an image reconstruction algorithm to realize the conductivity image reconstruction. The conductivity image reconstruction method comprises the following steps: firstly defining an objective function meeting a thermoacoustic source, the conductivity, a primary magnetic dislocation spatial component and an electric scalar potential spatial component, giving the initial value of the conductivity, solving the electric scalar potential spatial component according to a current continuity theorem under the condition that the thermoacoustic source distribution is known, substituting the electric scalar potential spatial component and magnetic dislocation spatial component into the objective function, and reconstructing the conductivity distribution.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Data-driven model gradual deformation method
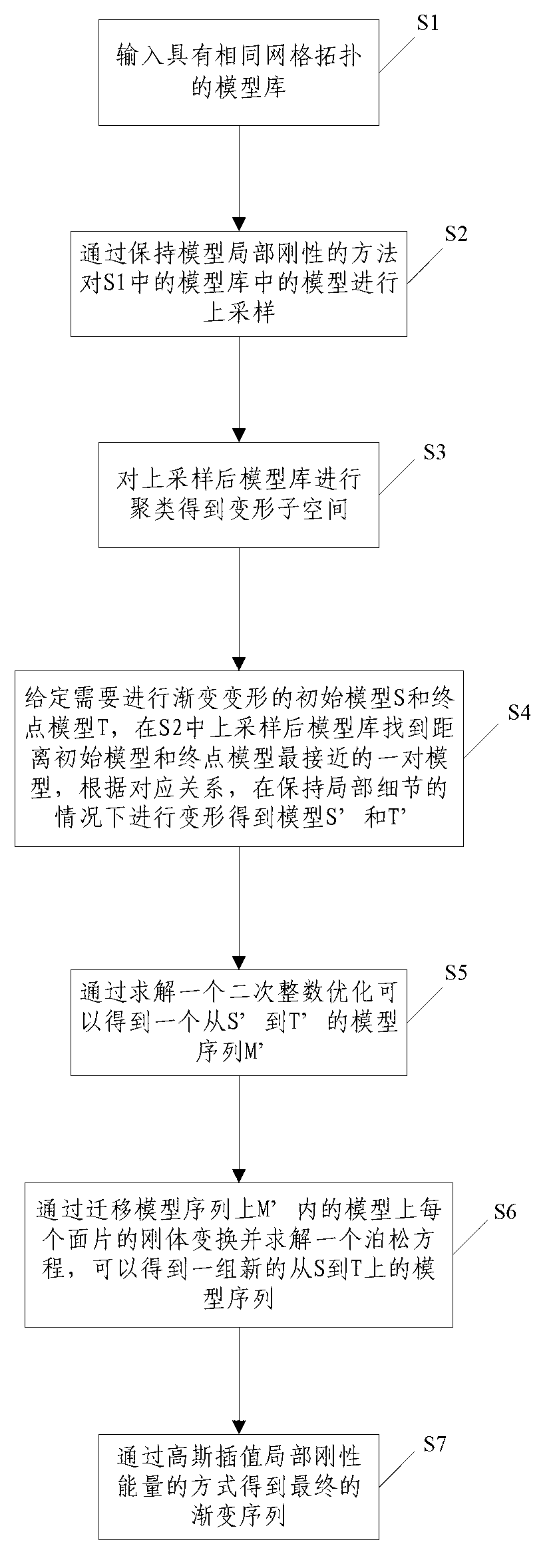
The invention discloses a data-driven model gradual deformation method, comprising the following steps of: S1, inputting model library with same mesh topologies; S2, performing up-sampling on models in the model library in the S1 through using a method of keeping the local rigidity of the model; S3, clustering the model library which is subjected to the up-sampling to get a deformation subspace; S4, providing an initial model S and a terminal point model T which need to be treated by gradual deformation, and according to the corresponding relation, performing the deformation under the condition of keeping local details to obtain models S' and T'; S5, solving a quadratic integer optimization to obtain a model sequence M' from S' to T'; S6, by rigid body transformation of each surface patch on the model in the M' on a migration model sequence and solving one poisson equation, obtaining a group of new model sequence from S to T; and S7, obtaining a final gradual deformation sequence by means of Gauss interpolation of the local rigid energy. By using the method disclosed by the invention, a relatively true and nature model gradual deformation sequence can be generated.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
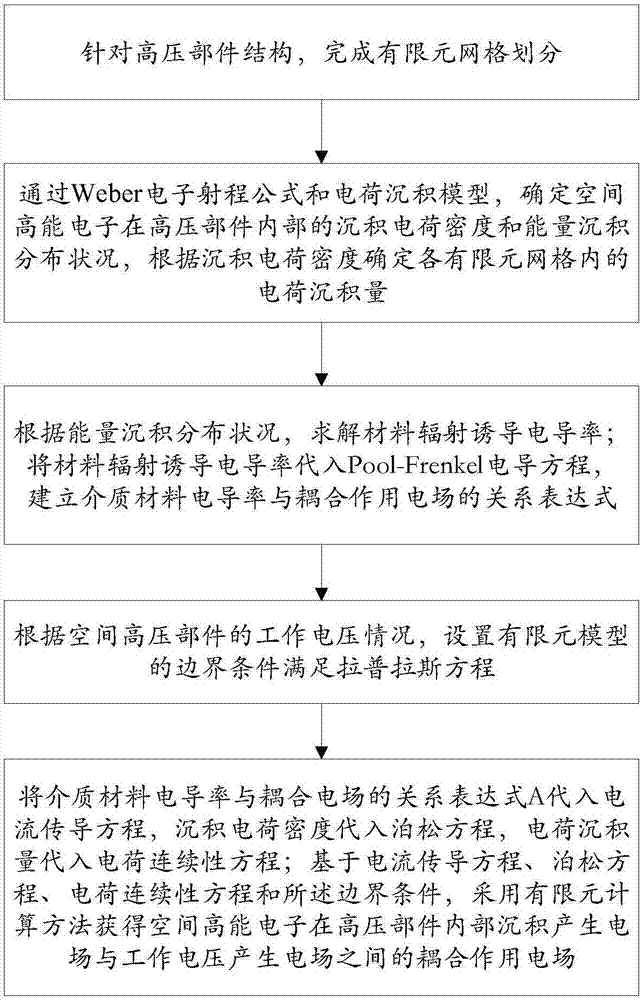
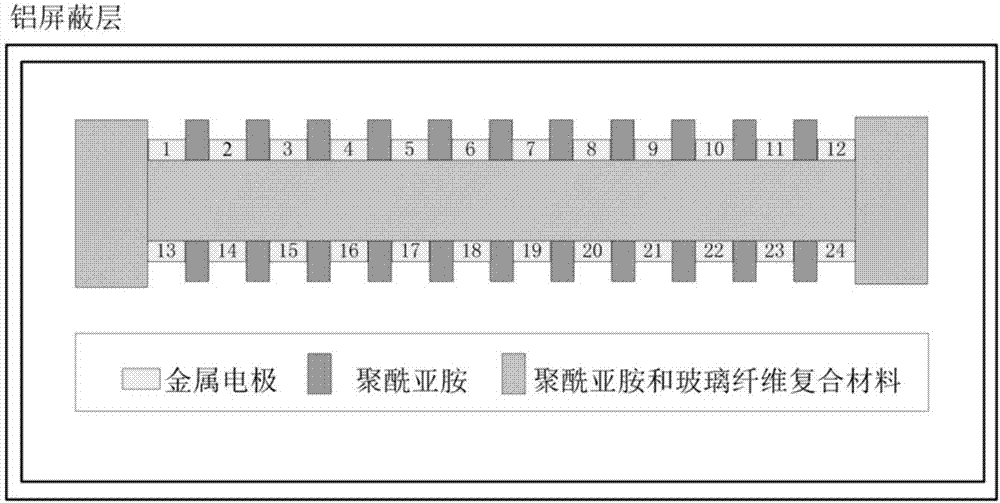
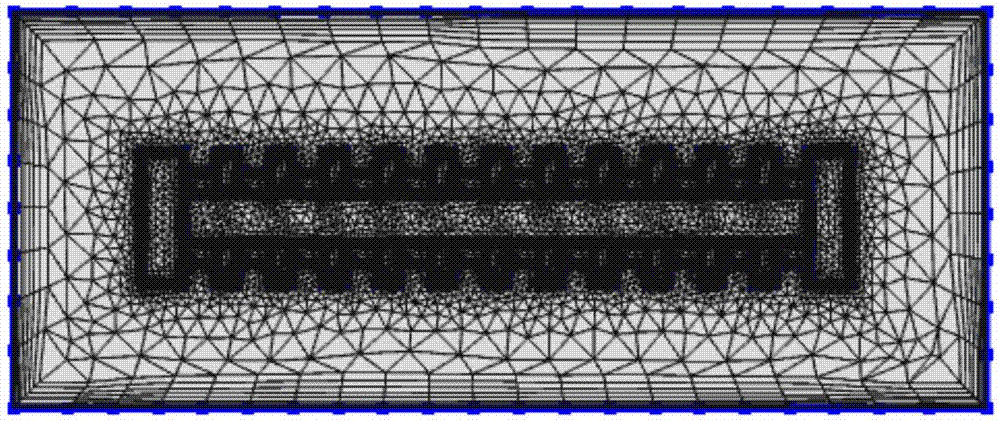
Electric field calculation method for multiple coupled electric fields in spatial high voltage part
The invention discloses an electric field calculation method for multiple coupled electric fields in a spatial high voltage part. The electric field calculation method for multiple coupled electric fields in the spatial high voltage part comprises steps of adopting a finite element difference method to determine conditions of charge deposition distribution and internal charge conduction of spatial high energy electrons in the high voltage part, setting a boundary condition according to a working voltage condition of a high voltage part, substituting a charge deposition amount and a conduction amount into a current conduction function to calculation spatial charge distribution, substituting spatial electrons into a poisson's equation, calculating to obtain a coupled electric field between an electric field produced by the spatial high energy electrons depositing in the high voltage part and an electric field produced by working voltage to obtain a distorted position of the two electric fields. The electric field calculation method for multiple coupled electric fields in the spatial high voltage part considers an affect of the working voltage on a charge-discharge effect, can improve accuracy of the electric field calculation, and provides basis to accurately evaluating the risk introduced by the charge-discharge effect of the spatial high voltage part and effectively guiding a design for protecting the high voltage part charge-discharge effect.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SPACE TECH
Global layout method for 2.5D packaged FPGA
InactiveCN113139361ASolving SLL problemsExact analytical solutionCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsLayoutEngineering
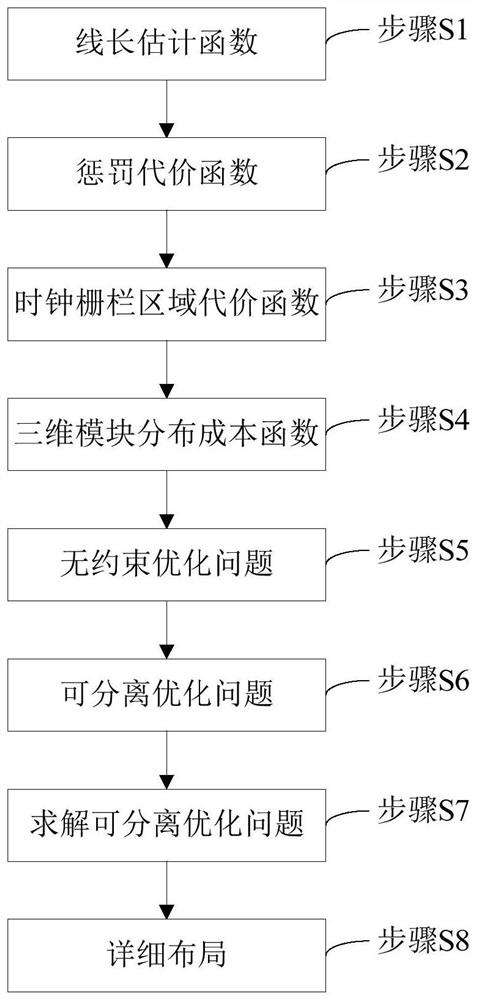
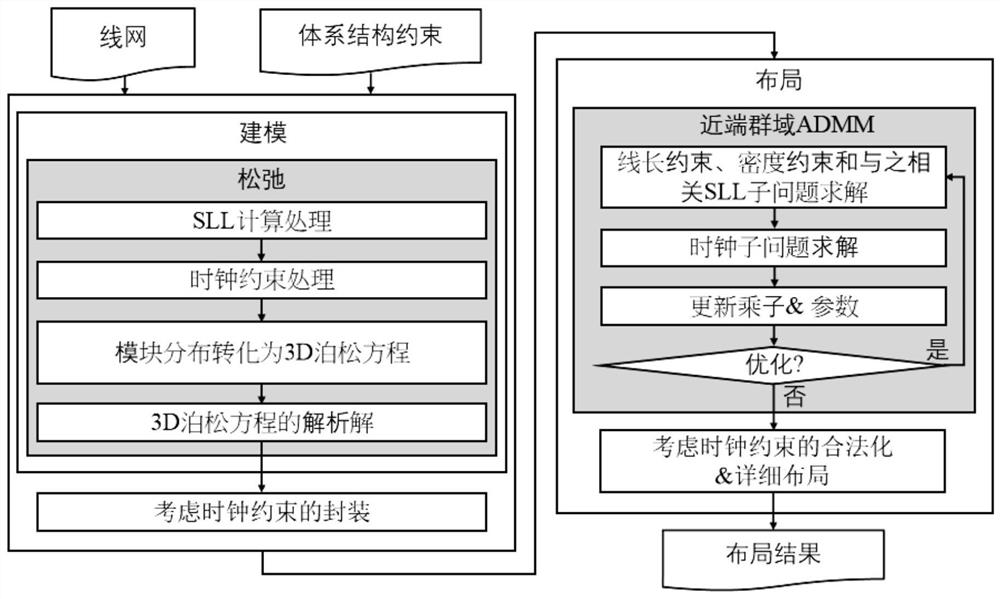
The invention relates to a global layout method for a 2.5D packaged FPGA, and the method comprises the following steps: defining a line length constraint condition through a line length estimation function, constraining a super-long line SLL through a penalty cost function, processing clock constraint through a clock fence area cost function, constraining module distribution through a three-dimensional module distribution cost function based on a 3D Poisson equation, expressing the global layout method of the 2.5D packaged FPGA as an unconstrained optimization problem including a line length estimation function, a penalty cost function, a clock fence area cost function and a three-dimensional module distribution cost function, expressing the unconstrained optimization problem as a separable optimization problem with linear constraints, and solving the separable optimization problem by adopting a near-end group domain ADMM; and carrying out detailed layout by using clock constraint legalization so as to realize layout legalization. According to the global layout method, layout calculation time is shortened, super-long lines are remarkably reduced on a base layer meeting clock constraint and line length constraint, and a more effective legalized layout result is obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI FUDAN MICROELECTRONICS GROUP
Method of analyzing numerical value of influences on performance of field effect transistor amplifier by high-power pulses
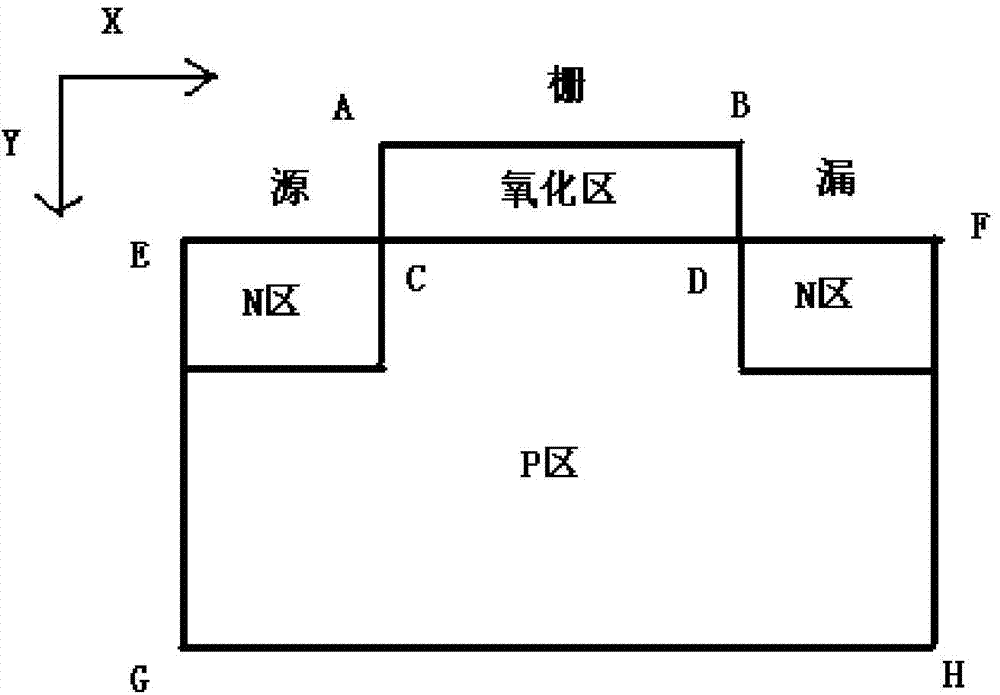
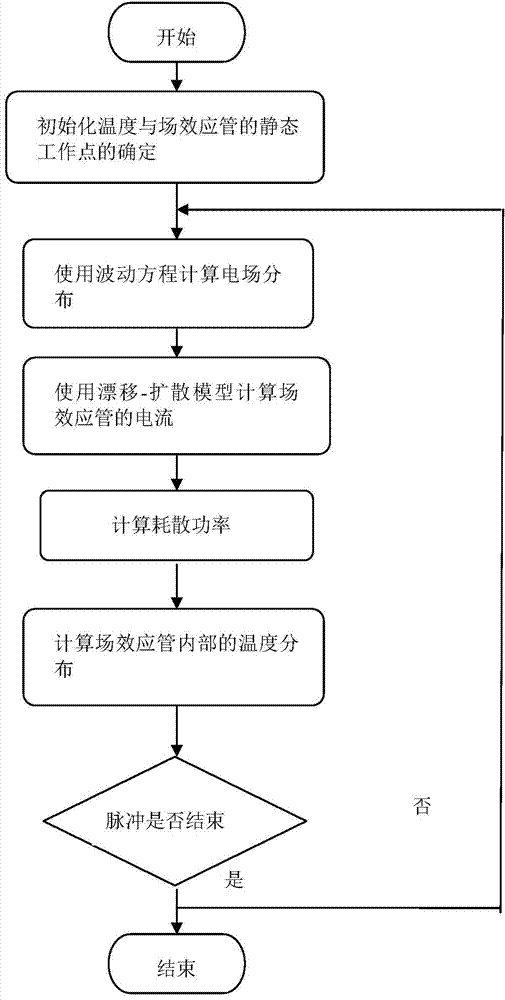
ActiveCN104752245ASemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementInformaticsFET amplifierNonlinear systems of equations
The invention discloses a method of analyzing a numerical value of influences on performance of a field effect transistor amplifier by high-power pulses. A wave equation is used for carrying out field analysis on inputted and outputted integrated circuits, the field effect transistor performs device simulation through building a three-dimensional Poisson equation and a current continuity equation, a newton iteration method is used for solving nonlinear equations formed by the Poisson equation, a potential distribution and an electron concentration distribution inside the field effect transistor are solved under effects of high-power pulses, a heat conduction equation is introduced to obtain a heat distribution inside the device, and simulation of the overall device is completed. Gains, noise factors and other performance parameters of the field effect transistor amplifier under effects of different high-power pulses can be accurately obtained, and the change process during which device performance and reliability of the field effect transistor are reduced or even quickly disabled under high-power pulses can be elaborately simulated.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
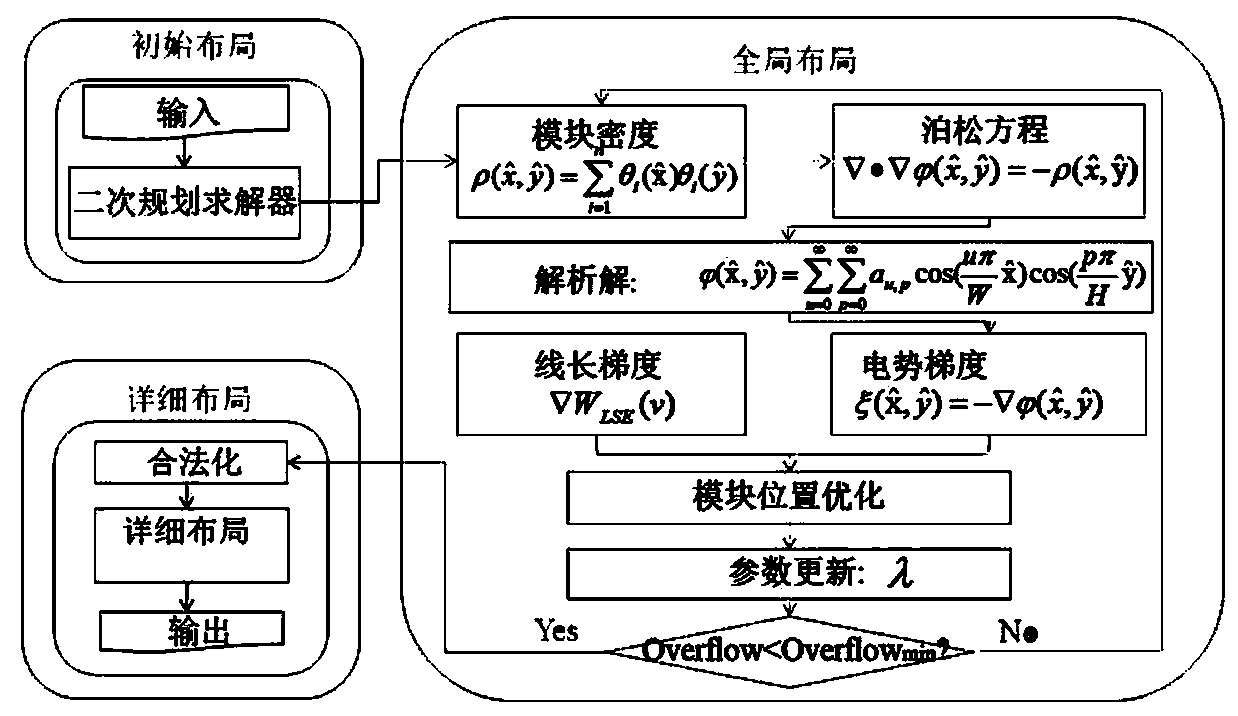
VLSI global layout model establishing method based on explicit solution of Poisson equation
ActiveCN108763777ANo numerical errorGuaranteed solution speedSpecial data processing applicationsCAD numerical modellingPoisson's equationComputer science
The invention relates to a VLSI global layout model establishing method based on an explicit solution of a Poisson equation, comprising: representing the circuit as a hypergraph model; simulating theVLSI circuit layout model as a two-dimensional electrostatic system, and converting the density constraint into the constraint of the total potential energy N(v) equal to 0 of the electrostatic system; establishing partial differential equations based on the Poisson equation, boundary conditions and compatibility conditions; establishing an analytical formula of density functions and substitutinginto the partial differential equations; determining expressions of the potential and electric field according to the density functions; determining the convergence of the expressions of the potentialand electric field; solving the expressions of the potential and electric field according to the partial sum; obtaining the potential and electric field values of each grid by the fast calculation method, obtaining the potential and electric field of the module by weighting, and establishing the VLSI circuit layout model under the action of electric field force. The invention may provide an efficient and practical global layout result, and especially for large-scale examples, may meet the requirements of the current VLSI global layout stage.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Capacitive tomographic method for sensitive field using coupled microwave imaging information
InactiveCN106153691ASensitive field is accurateCalculation speedMaterial capacitanceImaging algorithmFluidized bed
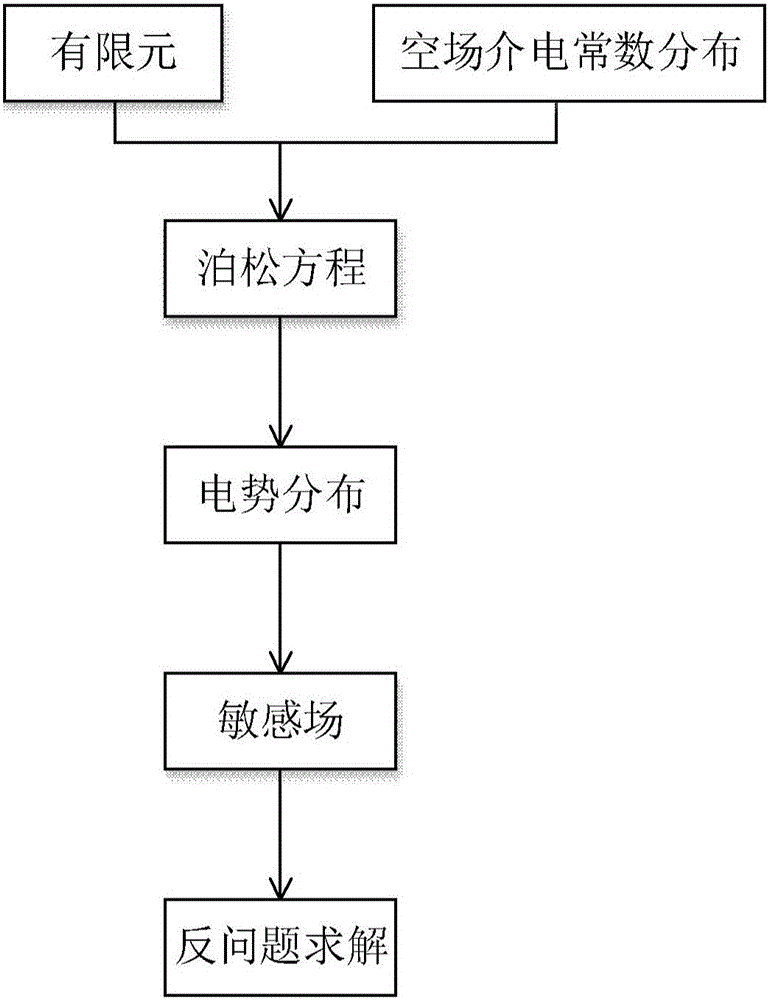
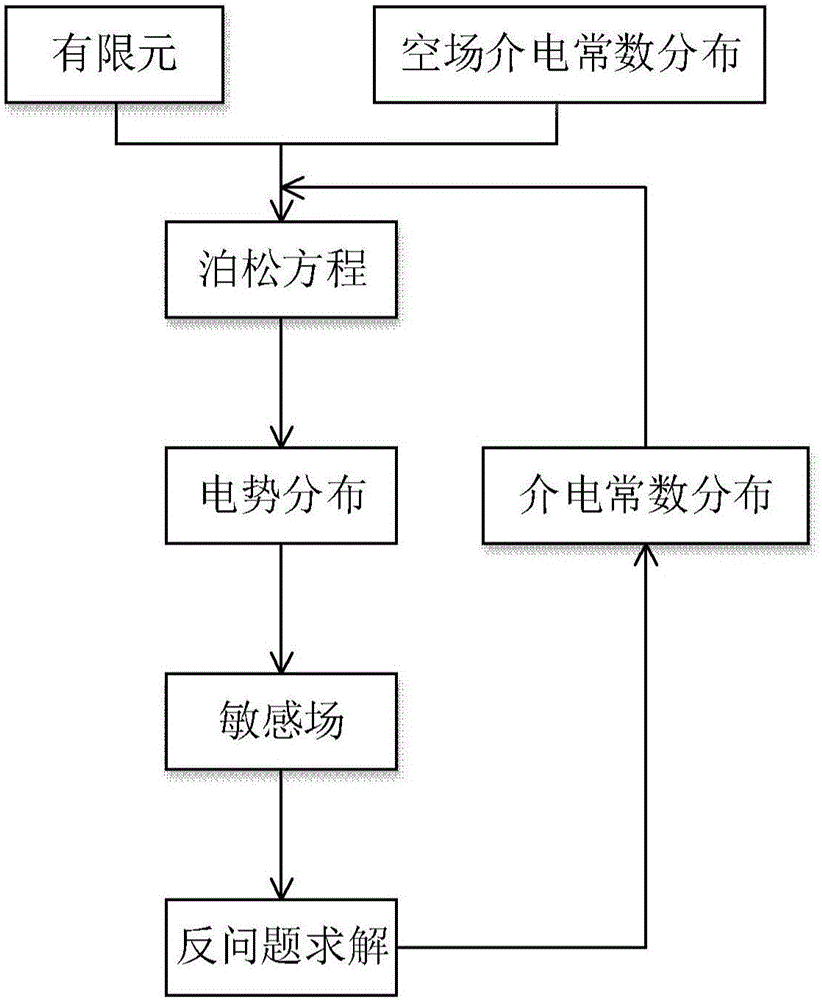
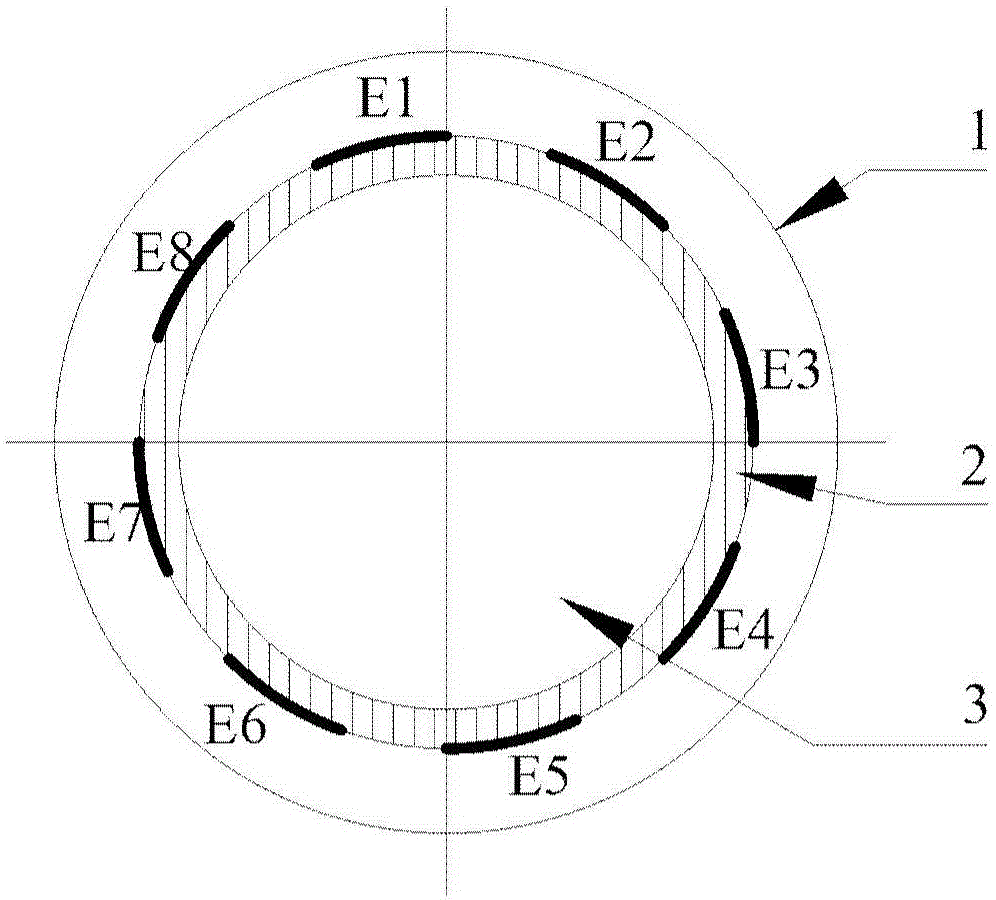
A capacitive tomographic method for a sensitive field using coupled microwave imaging information includes the steps of acquiring Poisson equation of a capacitive tomographic imaging system; acquiring distribution of dielectric constants by using microwave imaging information, and solving the Poisson equation through finite element method according to the distribution to obtain potential distribution of an area under measurement; acquiring sensitive field distribution by using the potential distribution; carrying out image reconstruction by using the sensitive field and reconstruction image algorithm. The capacitive tomographic method in fusion with microwave imaging enables reduced reconstructed image errors and increased solving speed; the imaging method can be applied to the processes such as circulating fluidized bed and coating to acquire in real time, a more precise gas-liquid concentration distribution image, and the above processes are more effectively monitored.
Owner:INST OF ENGINEERING THERMOPHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com