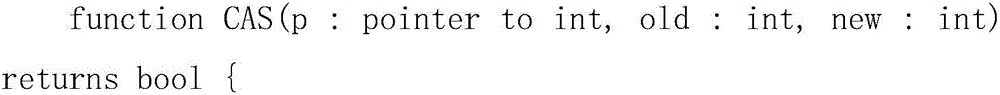Patents
Literature
108 results about "Shared variables" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
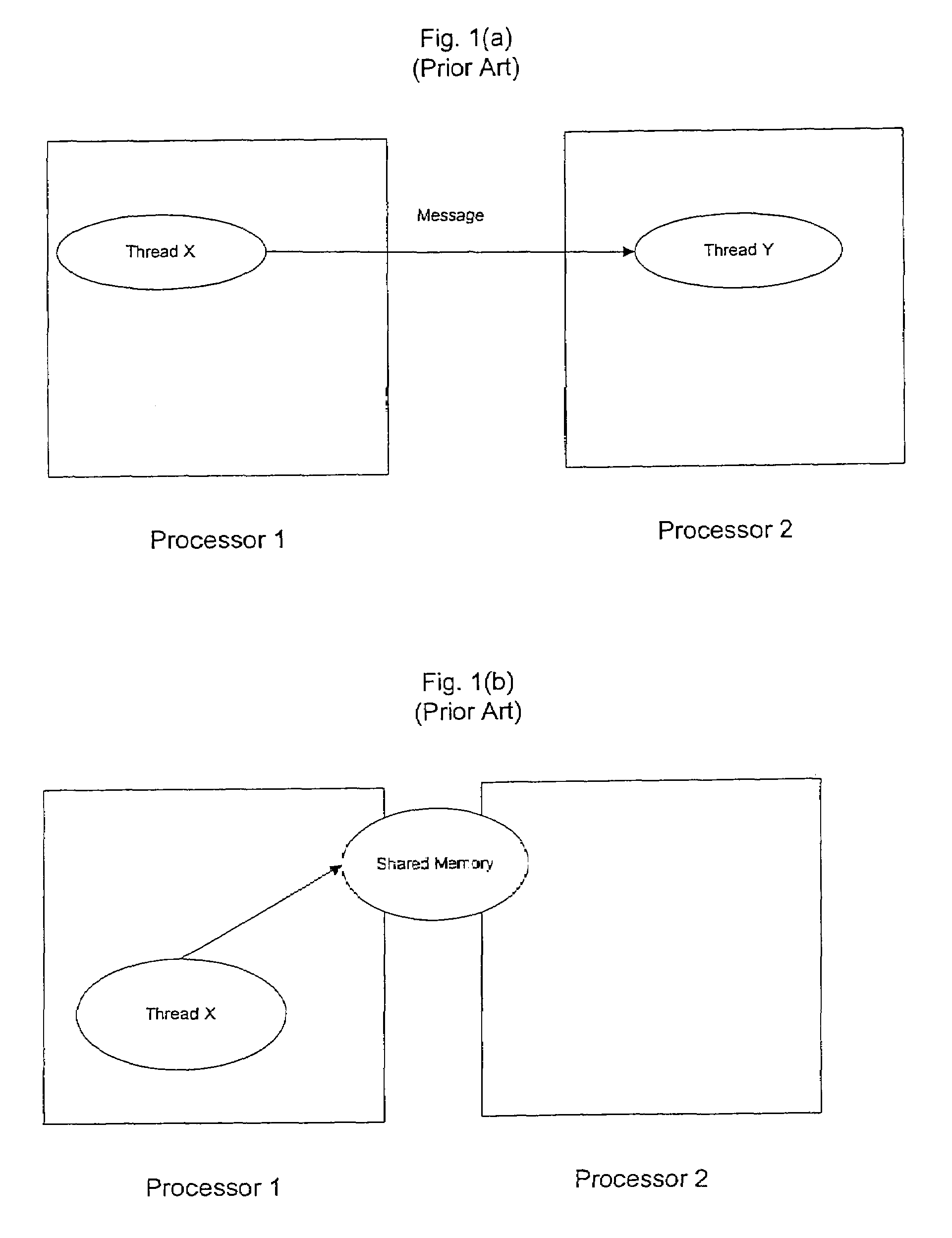
Shared Variables. Shared Variables are a feature of the programming language APL which allows APL programs running on one processor to share information with another processor. Although originally developed for mainframe computers, Shared Variables were also used in personal computer implementations of APL.
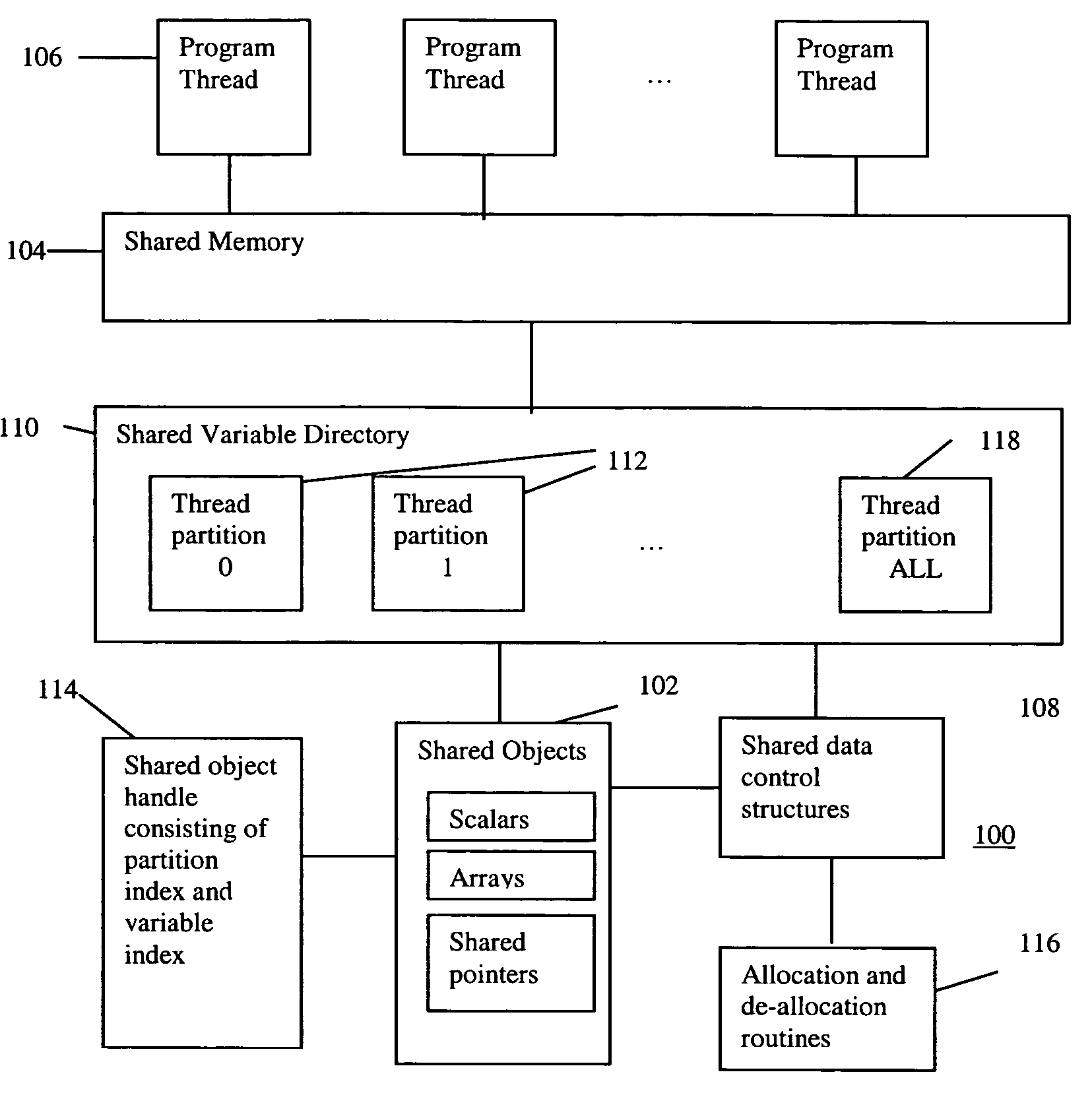
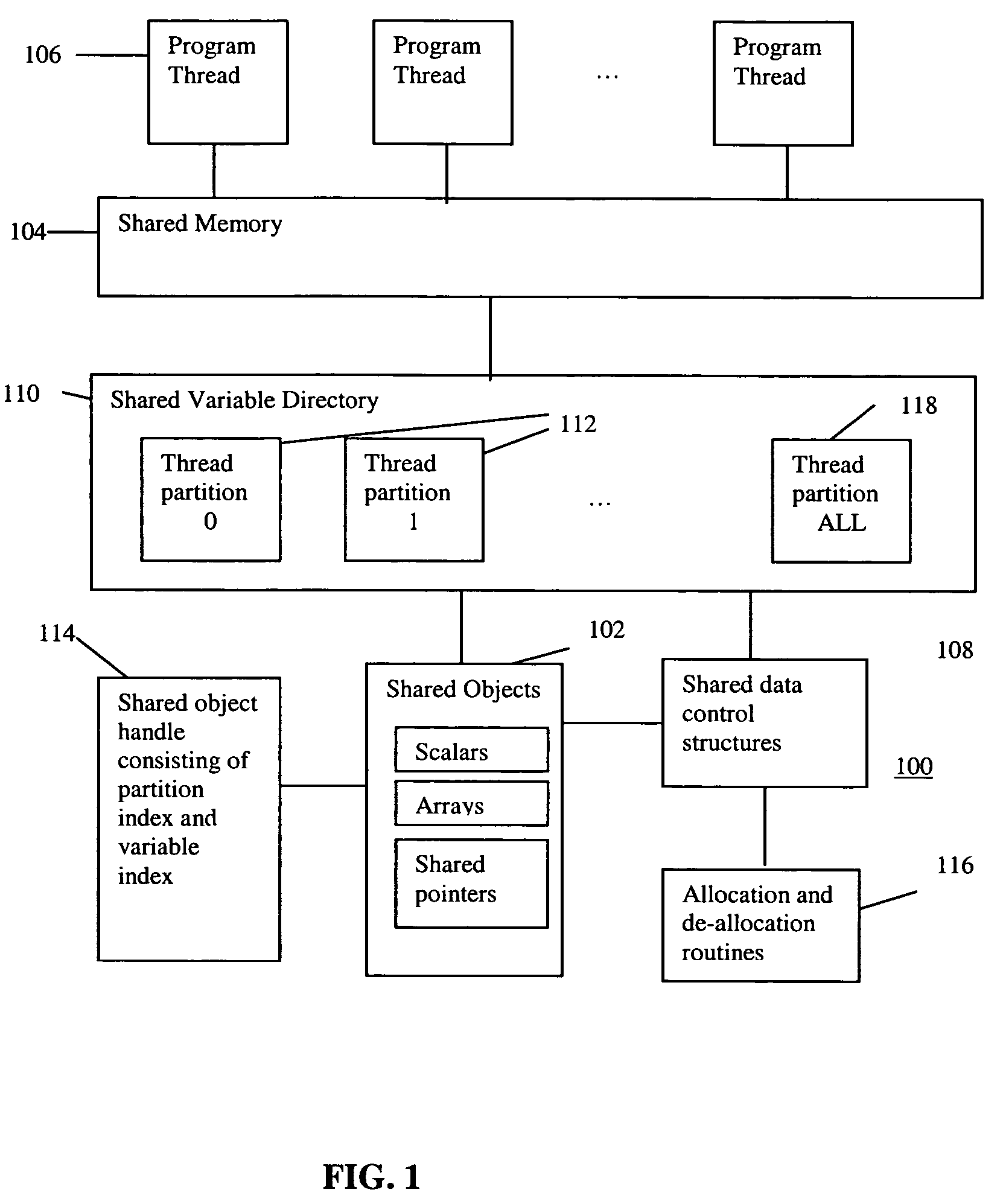
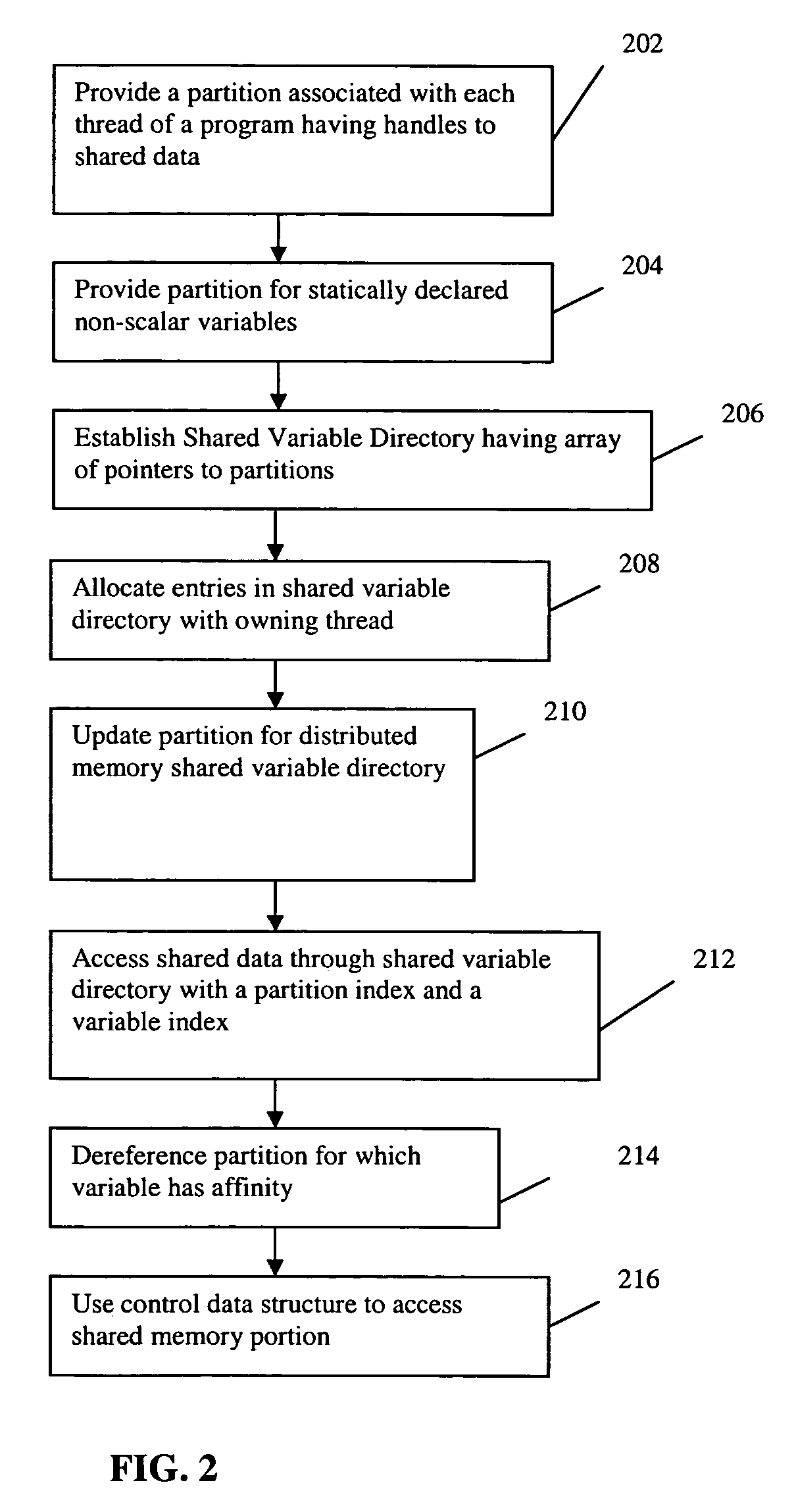
Scalable runtime system for global address space languages on shared and distributed memory machines
ActiveUS20050149903A1Improve scalabilityResource allocationSpecific program execution arrangementsExtensibilityGlobal address space
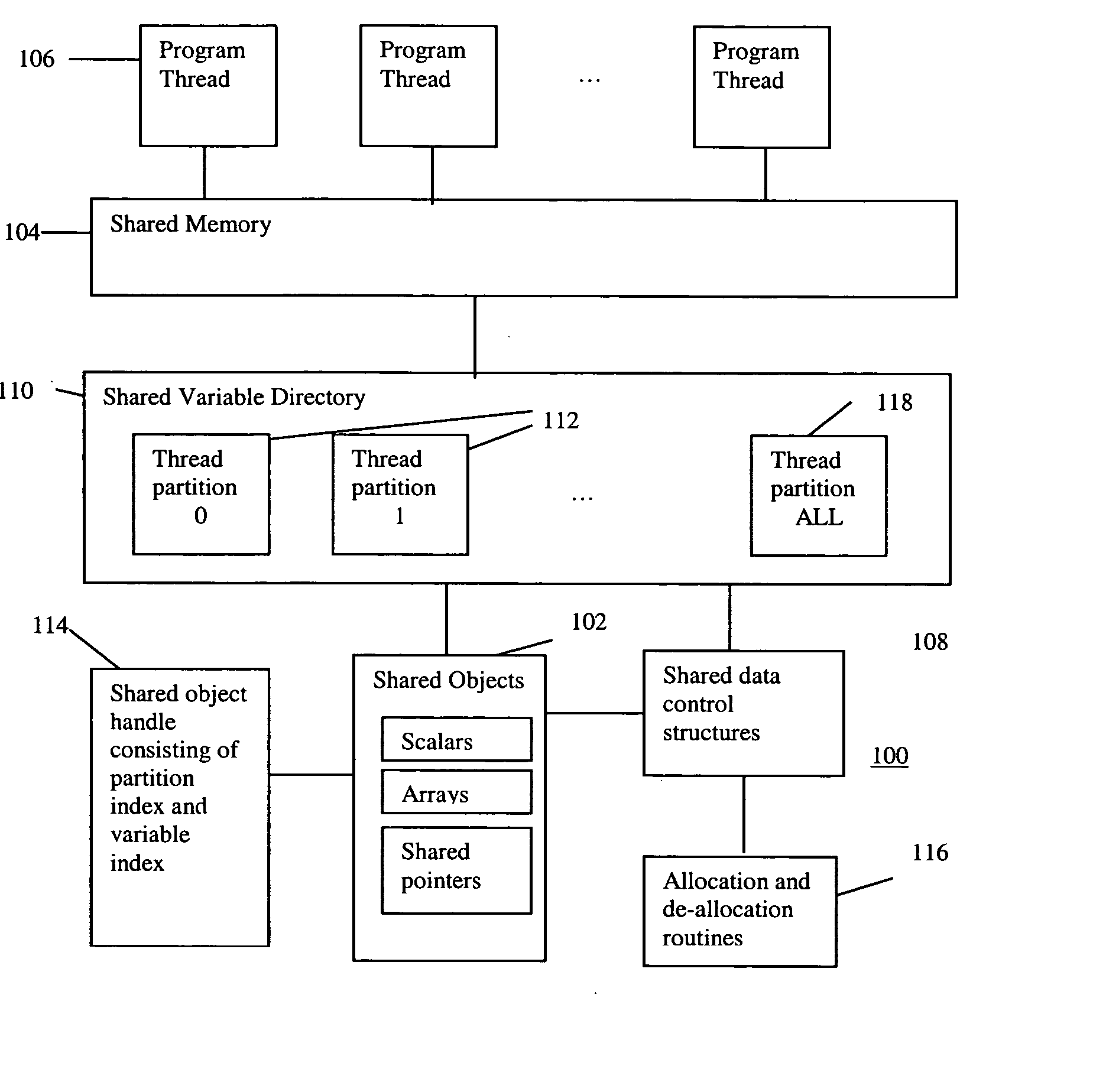
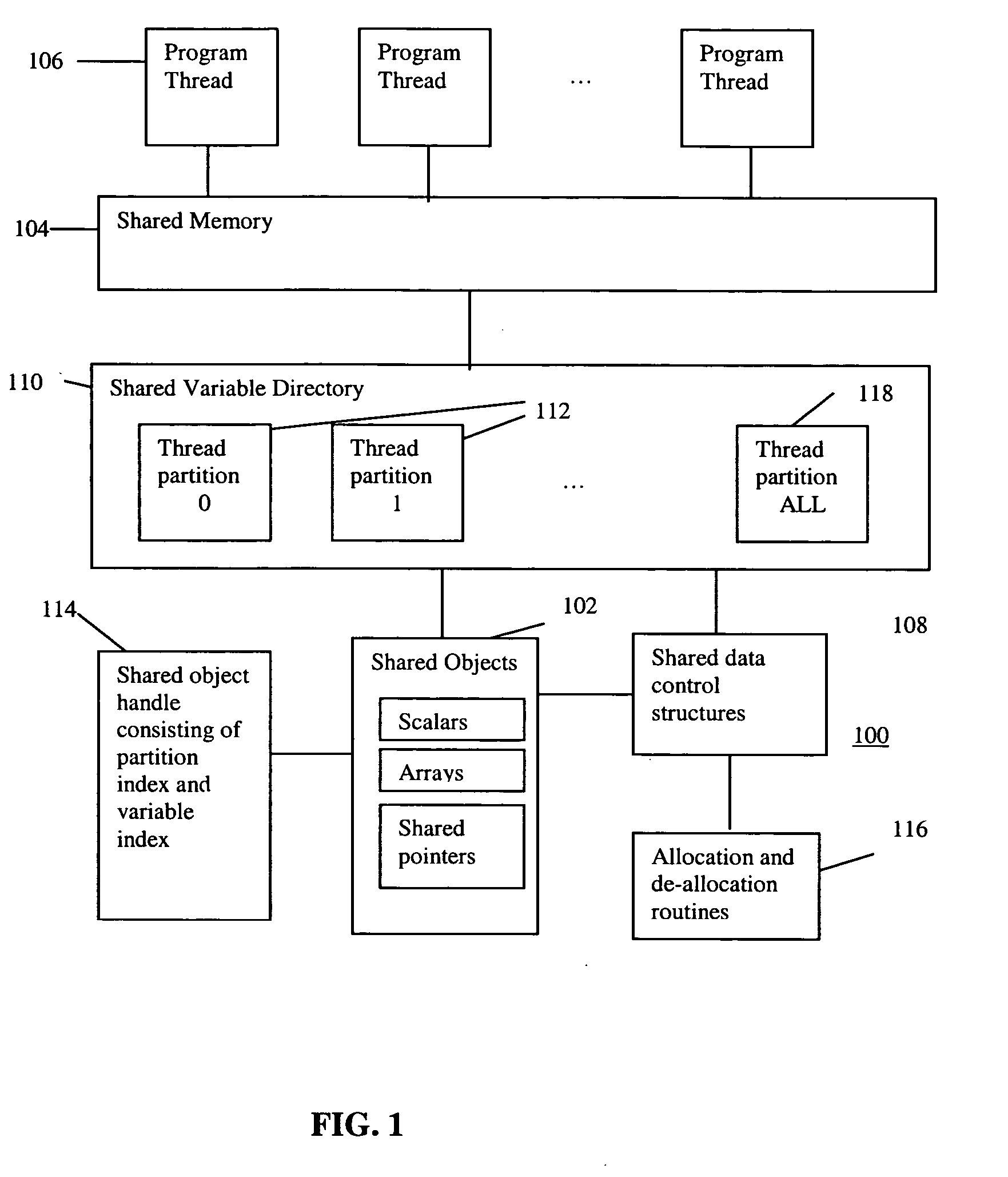
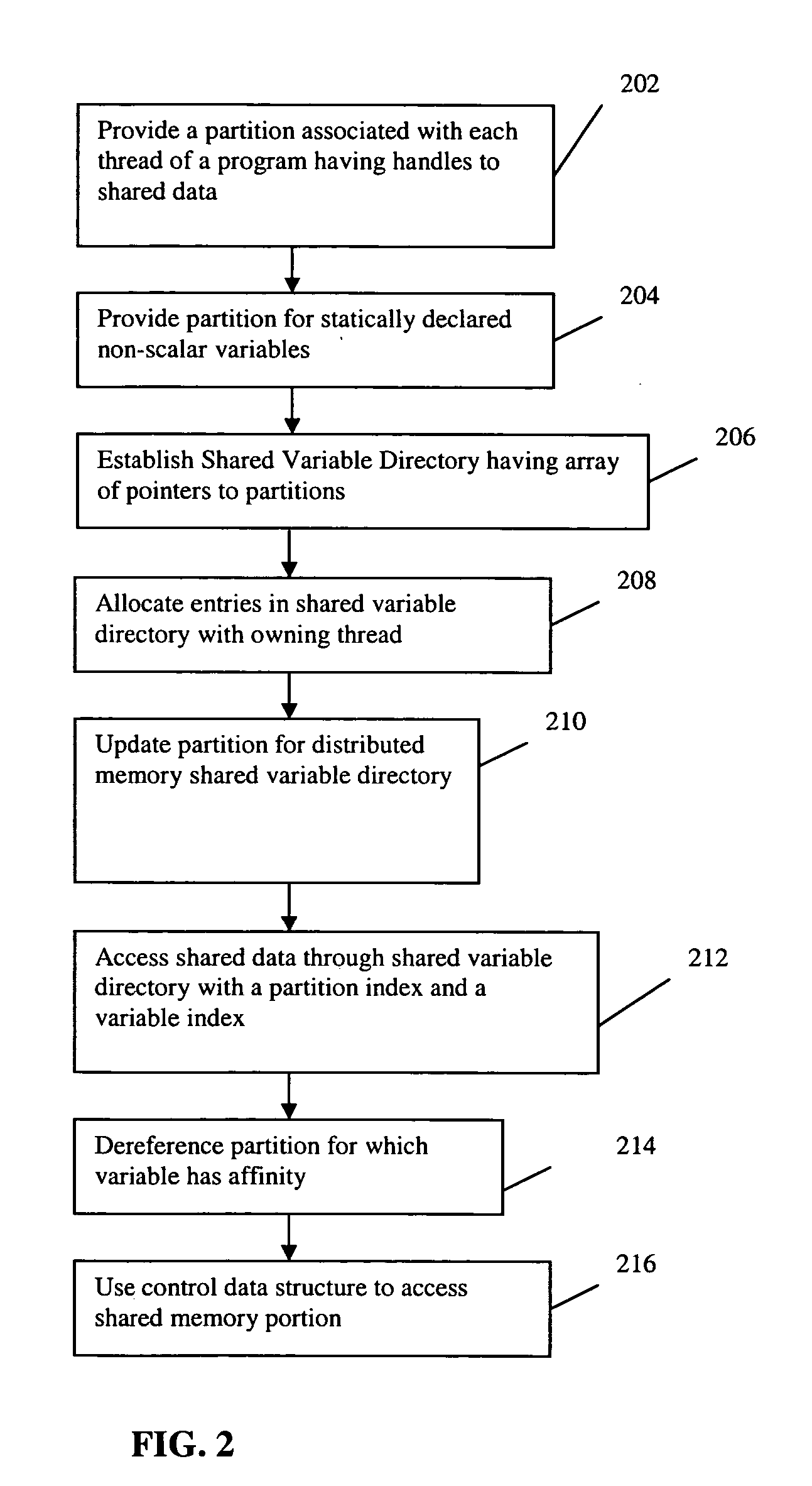
An improved scalability runtime system for a global address space language running on a distributed or shared memory machine uses a directory of shared variables having a data structure for tracking shared variable information that is shared by a plurality of program threads. Allocation and de-allocation routines are used to allocate and de-allocate shared variable entries in the directory of shared variables. Different routines can be used to access different types of shared data. A control structure is used to control access to the shared data such that all threads can access the data at any time. Since all threads see the same objects, synchronization issues are eliminated. In addition, the improved efficiency of the data sharing allows the number of program threads to be vastly increased.
Owner:DAEDALUS BLUE LLC
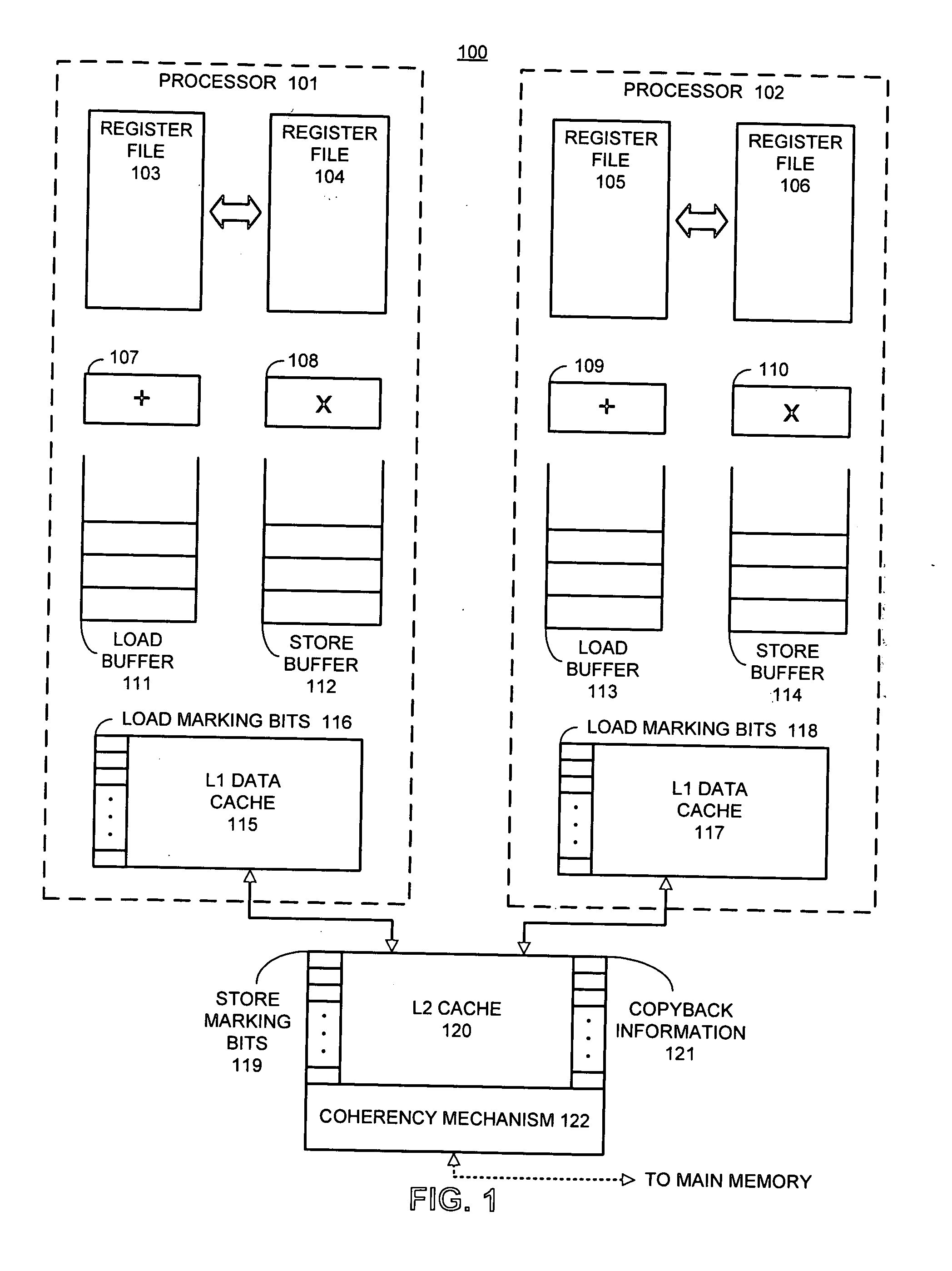
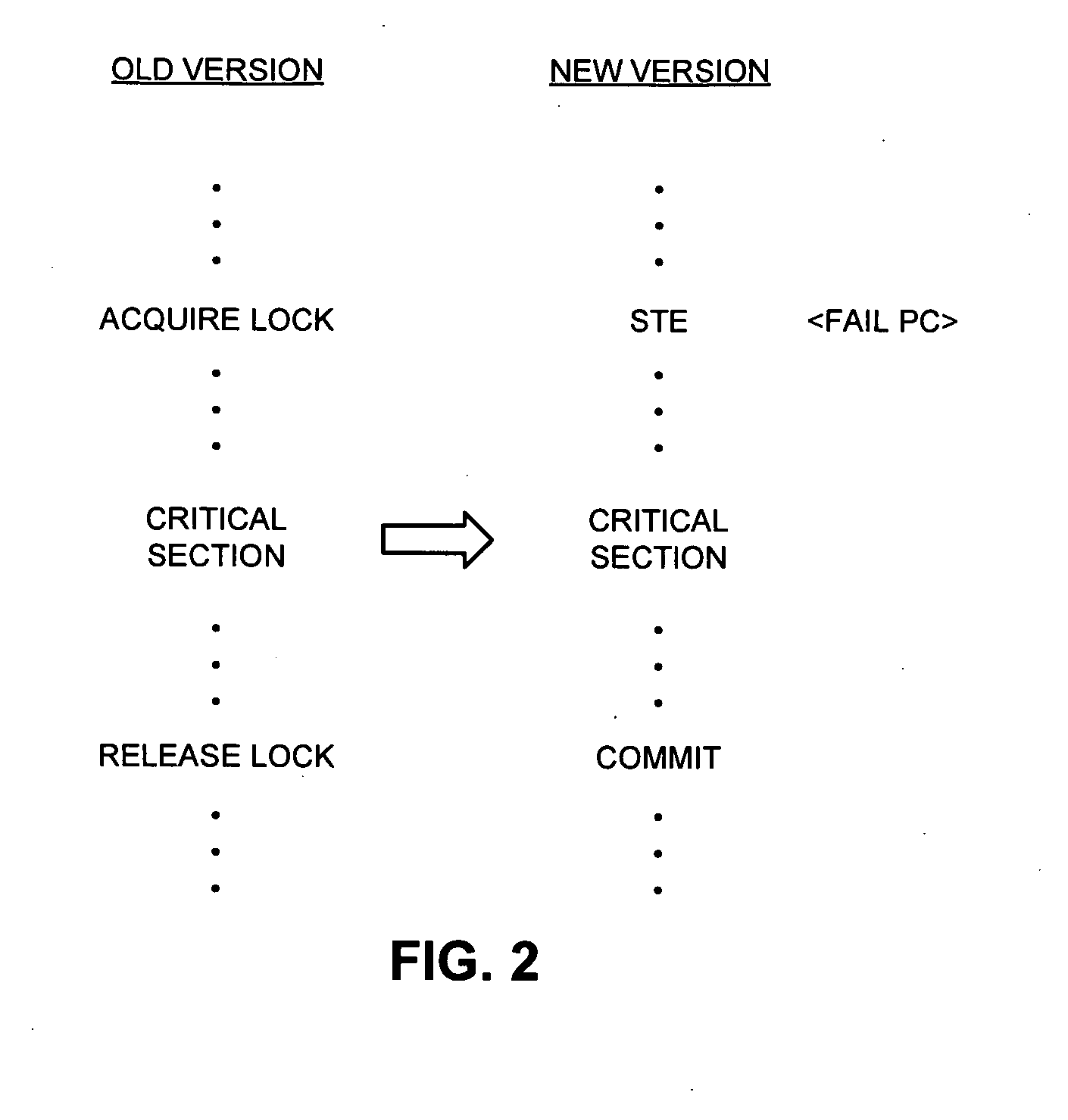
Method and apparatus for synchronizing threads on a processor that supports transactional memory
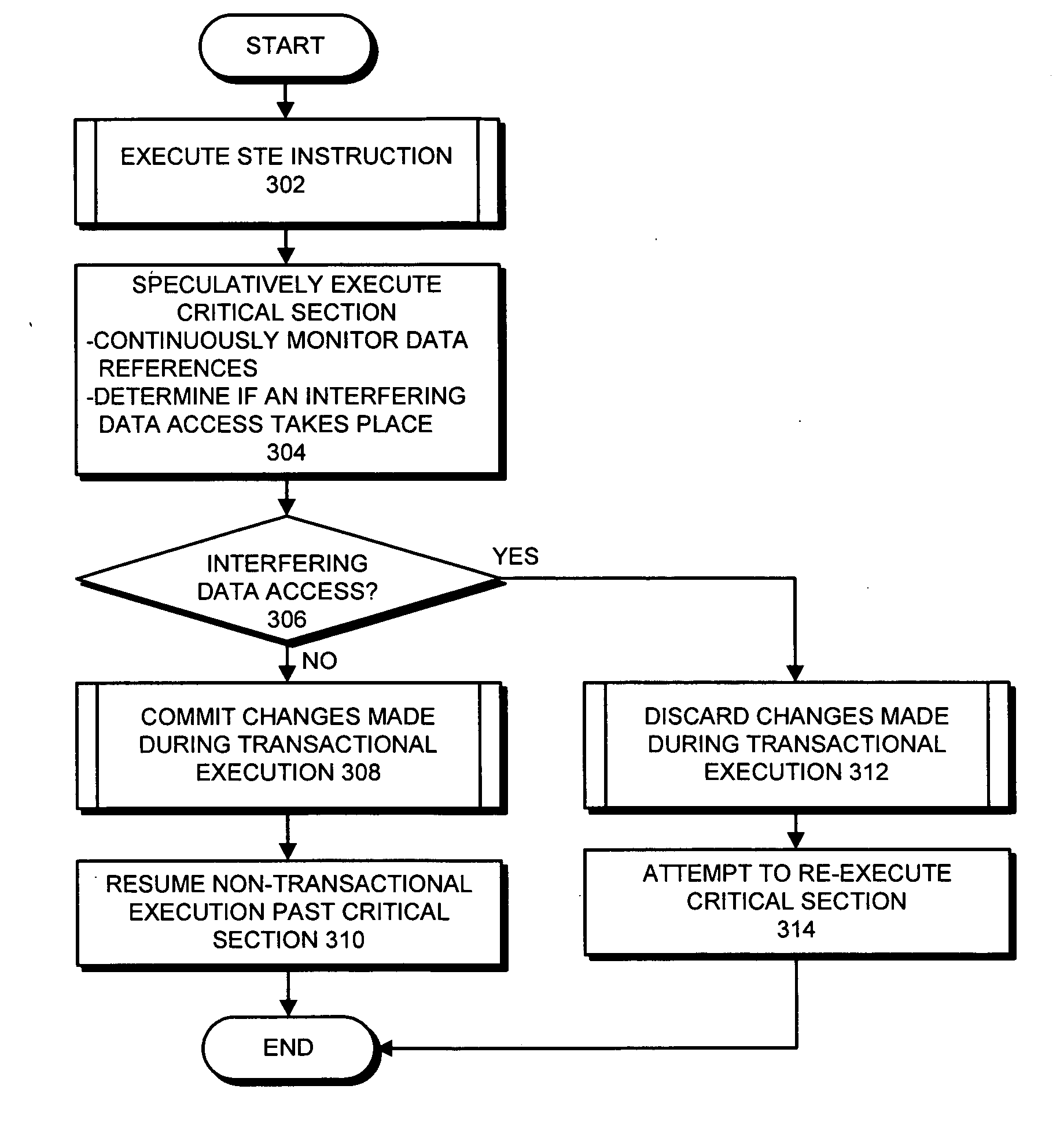
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that synchronizes threads on a multi-threaded processor. The system starts by executing instructions from a multi-threaded program using a first thread and a second thread. When the first thread reaches a predetermined location in the multi-threaded program, the first thread executes a Start-Transactional-Execution (STE) instruction to commence transactional execution, wherein the STE instruction specifies a location to branch to if transactional execution fails. During the subsequent transactional execution, the first thread accesses a mailbox location in memory (which is also accessible by the second thread) and then executes instructions that cause the first thread to wait. When the second thread reaches a second predetermined location in the multi-threaded program, the second thread signals the first thread by accessing the mailbox location, which causes the transactional execution of the first thread to fail, thereby causing the first thread to resume non-transactional execution from the location specified in the STE instruction. In this way, the second thread can signal to the first thread without the first thread having to poll a shared variable.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
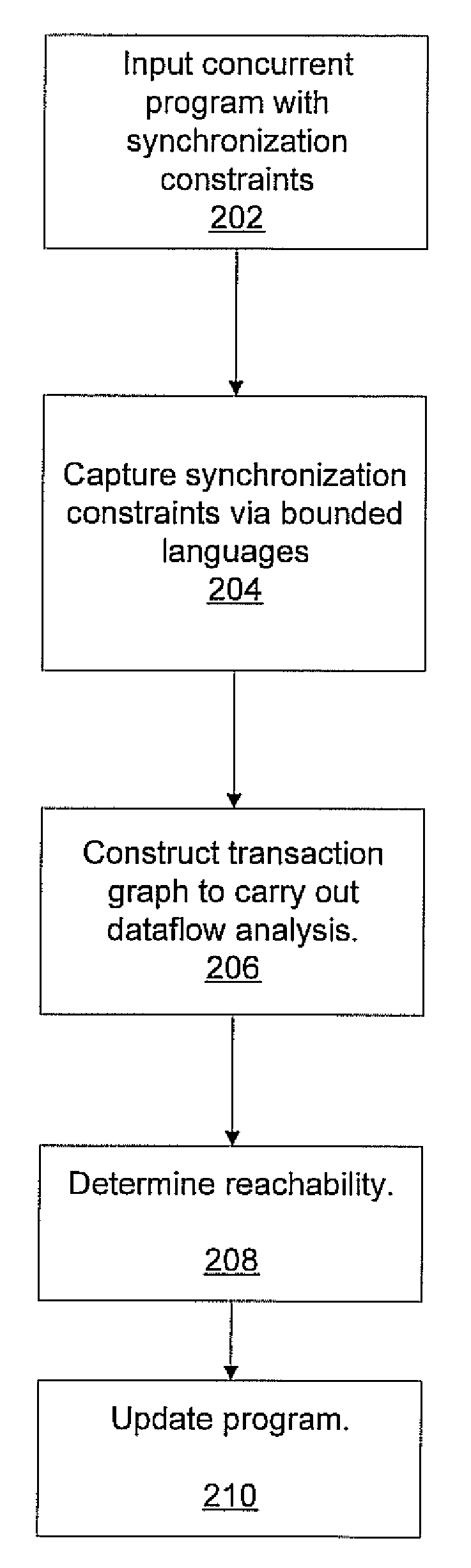
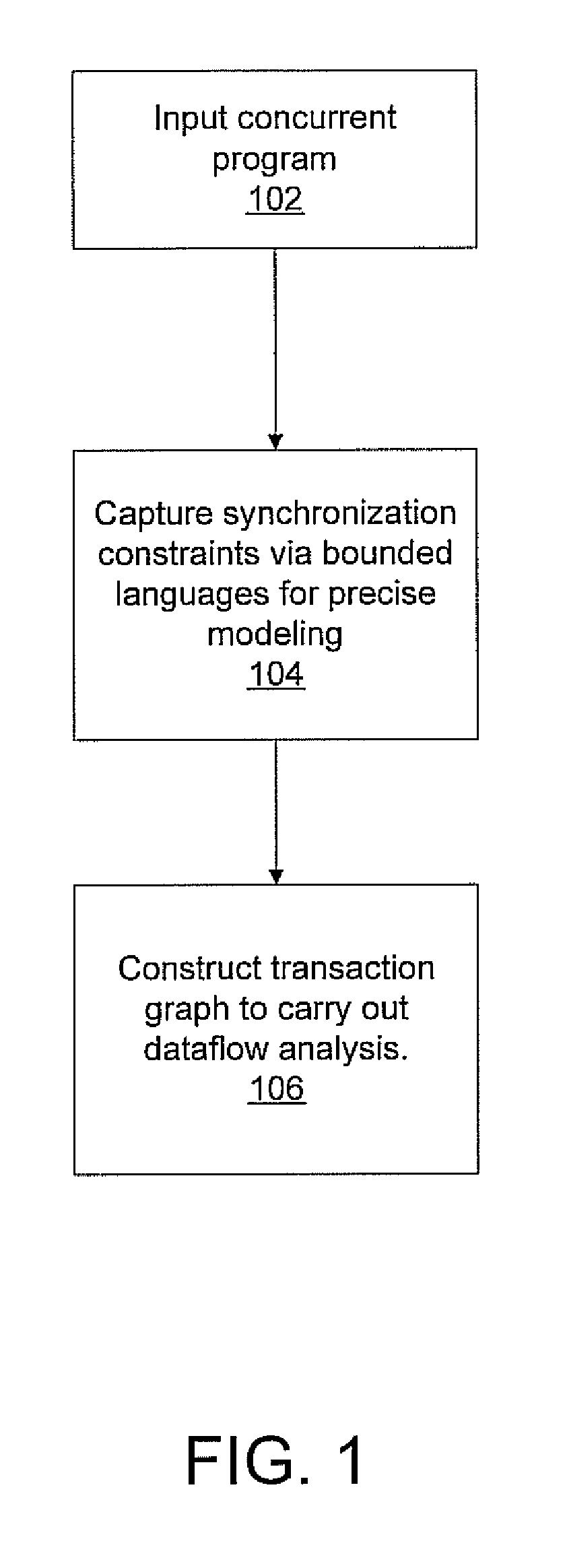
Tractable dataflow analysis for concurrent programs via bounded languages
InactiveUS20090193417A1Enhanced couplingError detection/correctionMultiprogramming arrangementsHuman languageDataflow
A system and method for dataflow analysis includes inputting a concurrent program comprised of threads communicating via synchronization primitives and shared variables. Synchronization constraints imposed by the primitives are captured as an intersection problem for bounded languages. A transaction graph is constructed to perform dataflow analysis. The concurrent program is updated in accordance with the dataflow analysis.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA
System and method for performing distributed policing
InactiveUS20060221819A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDistributed algorithmShared variables
Various systems and methods that synchronize local copies of a variable used in a distributed algorithm, such as that used in distributed policing, are disclosed. For example, one system includes several distributed algorithm participants that are coupled to communicate with each other. Each of the each of the distributed algorithm participants maintains a shared variable in order to implement the distributed algorithm. One of the distributed algorithm participants is a synchronizer. The synchronizer is configured to calculate a new value of the shared variable and to communicate the new value to each of the other distributed algorithm participants. The distributed algorithm can be a distributed policing algorithm, and the shared variable can be a global bucket.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
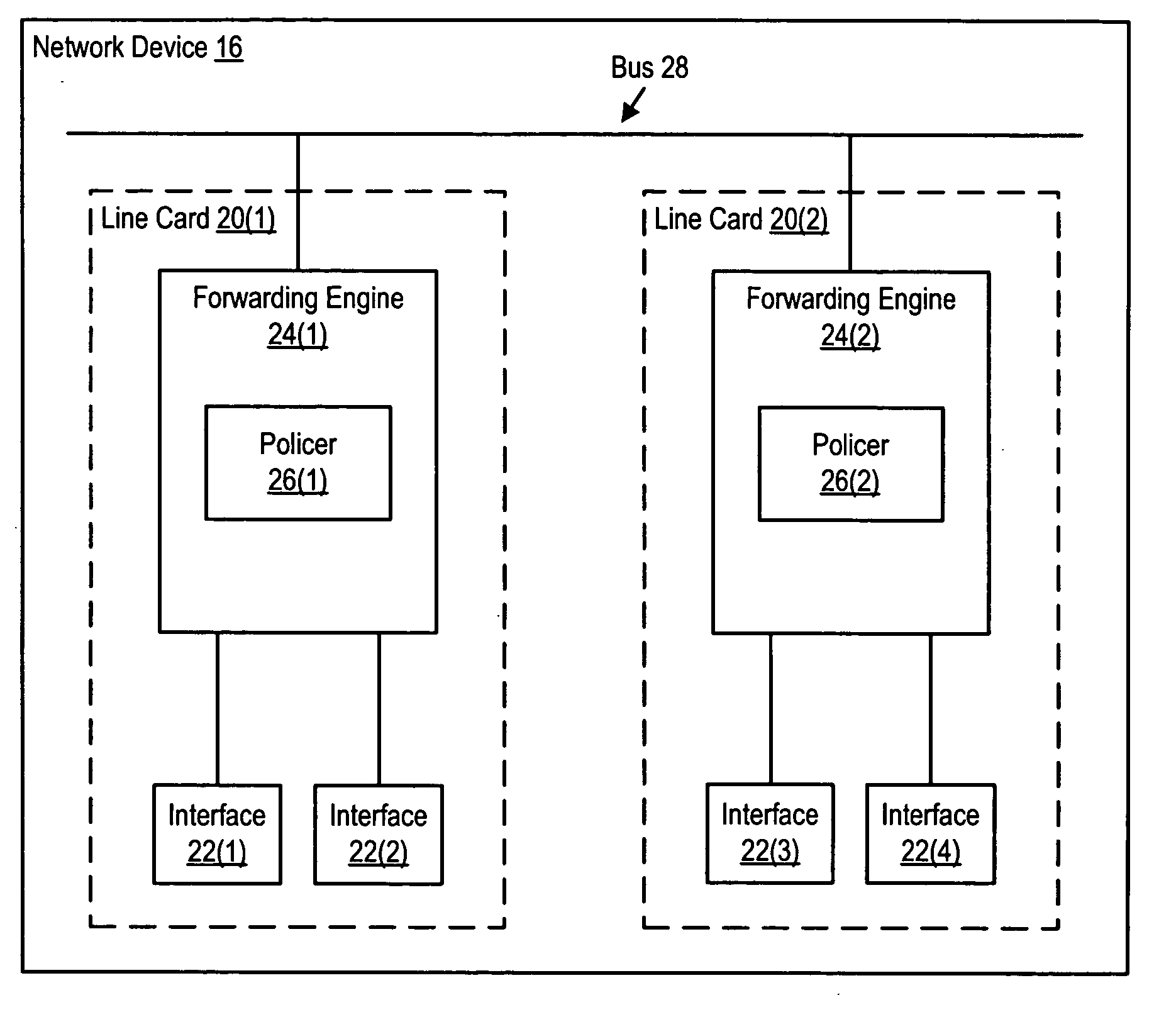
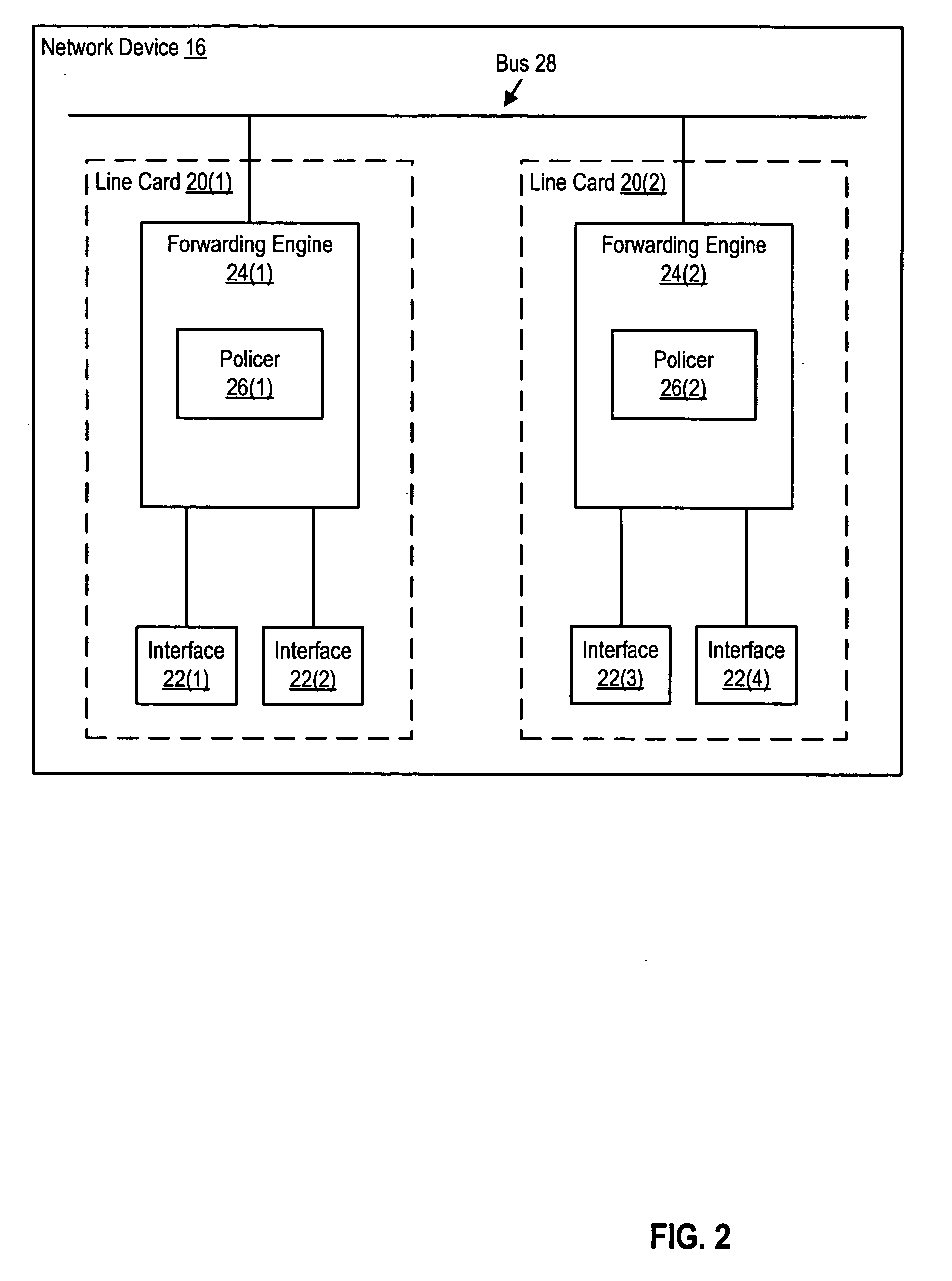
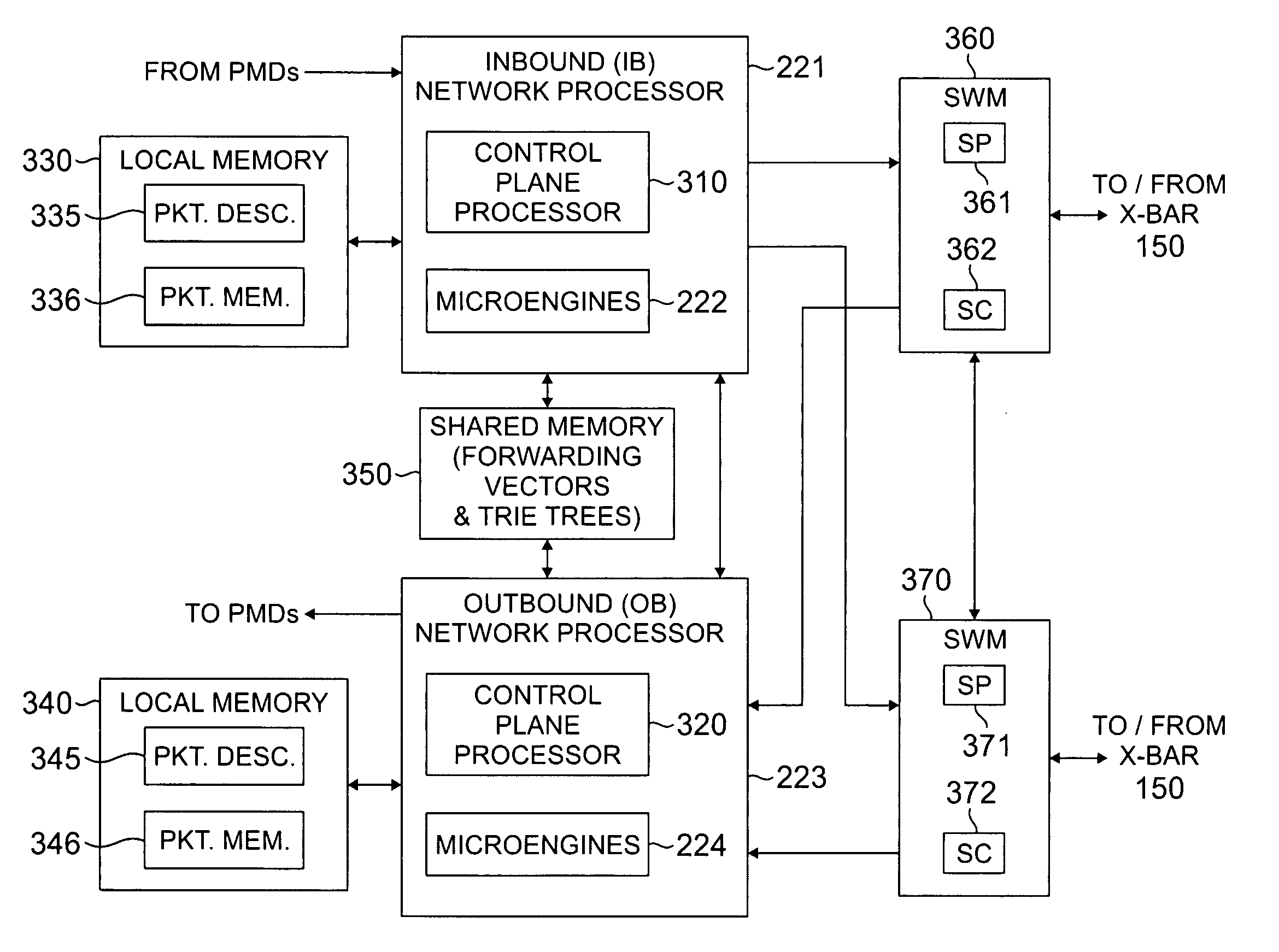
Apparatus and method for sharing variables and resources in a multiprocessor routing node
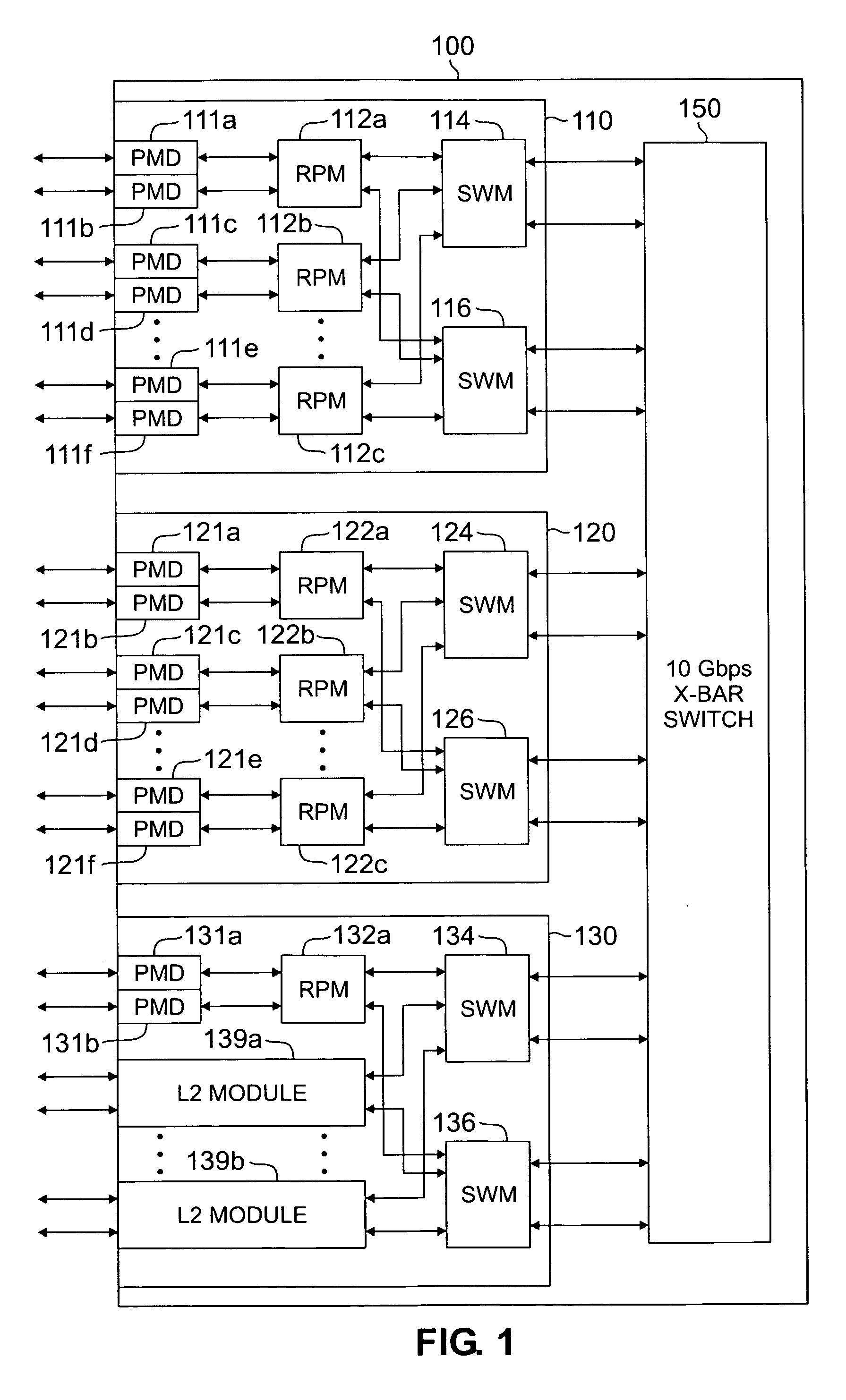
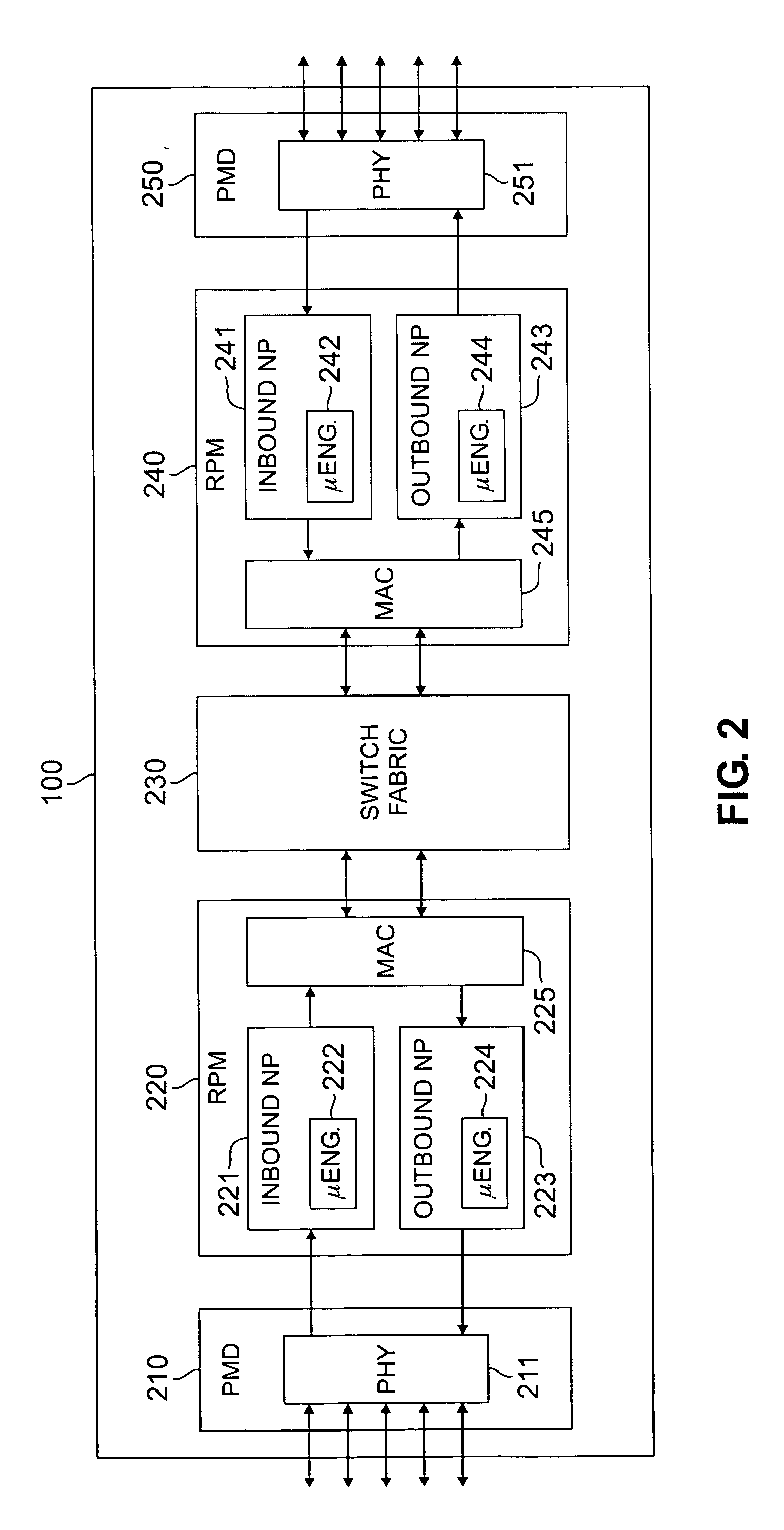
InactiveUS20060133389A1Improve throughputFast and efficientData switching by path configurationMulti processorNetwork processor
A router for transferring data packets between external devices. The router comprises: 1) a switch fabric; and 2) R routing nodes coupled to the switch fabric. Each routing node exchanges data packets with the external devices and with other routing nodes via the switch fabric. A first routing node comprises: i) an inbound network processor comprising a first plurality of microengines capable of forwarding incoming data packets from external ports to the switch fabric; ii) an outbound network processor comprising a second plurality of microengines capable of forwarding outgoing data packets from the switch fabric to the external ports; and iii) an asynchronous variables circuit for controlling access of the inbound and outbound network processors to at least one of i) a shared resource and ii) a shared variable in the router.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
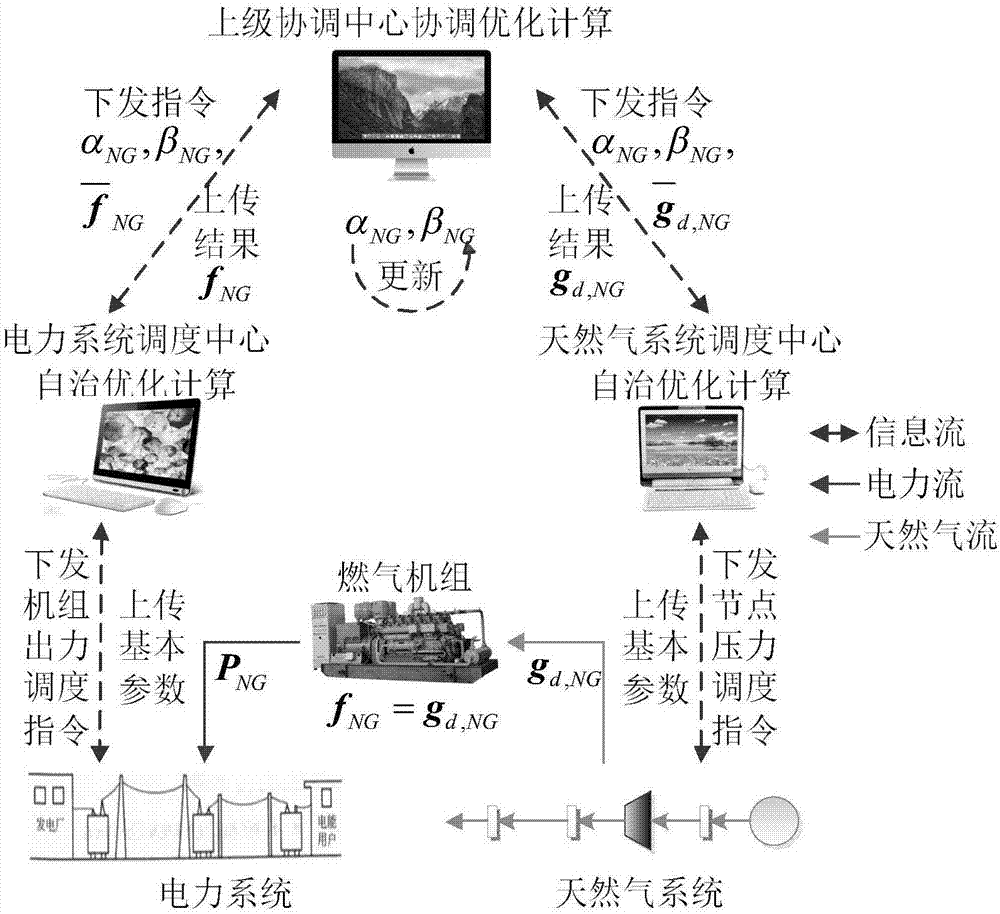
Power-gas energy flow distributed cooperative optimization calculation method based on alternating direction multiplier method
InactiveCN107292456AAchieving OptimizabilityOvercome deficienciesForecastingShared variablesResearch Object
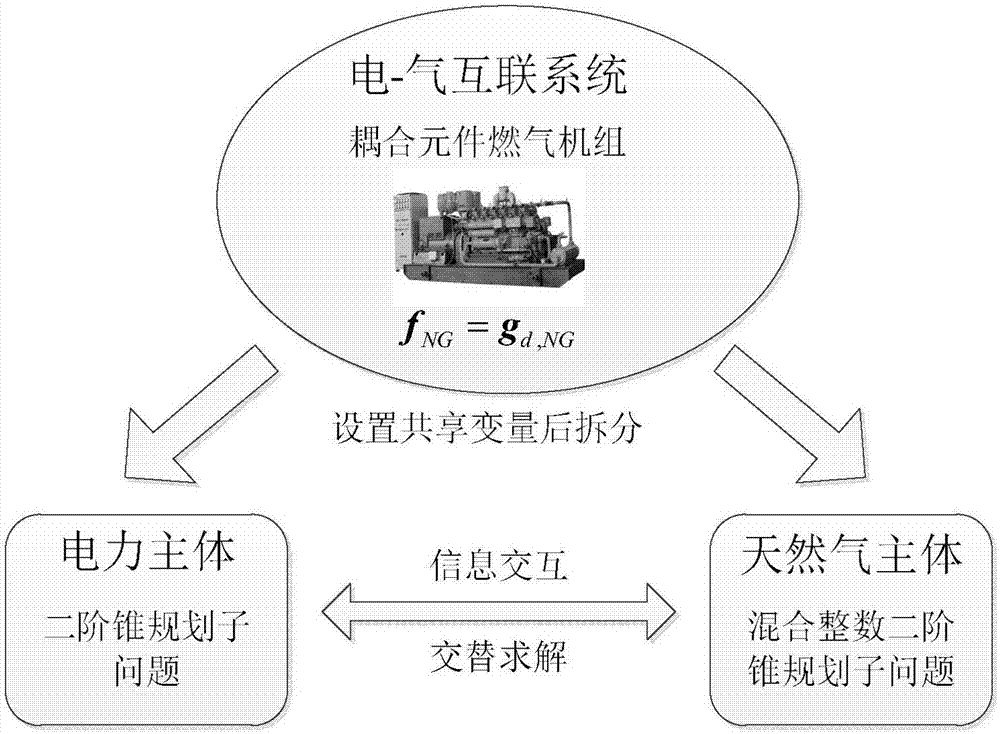
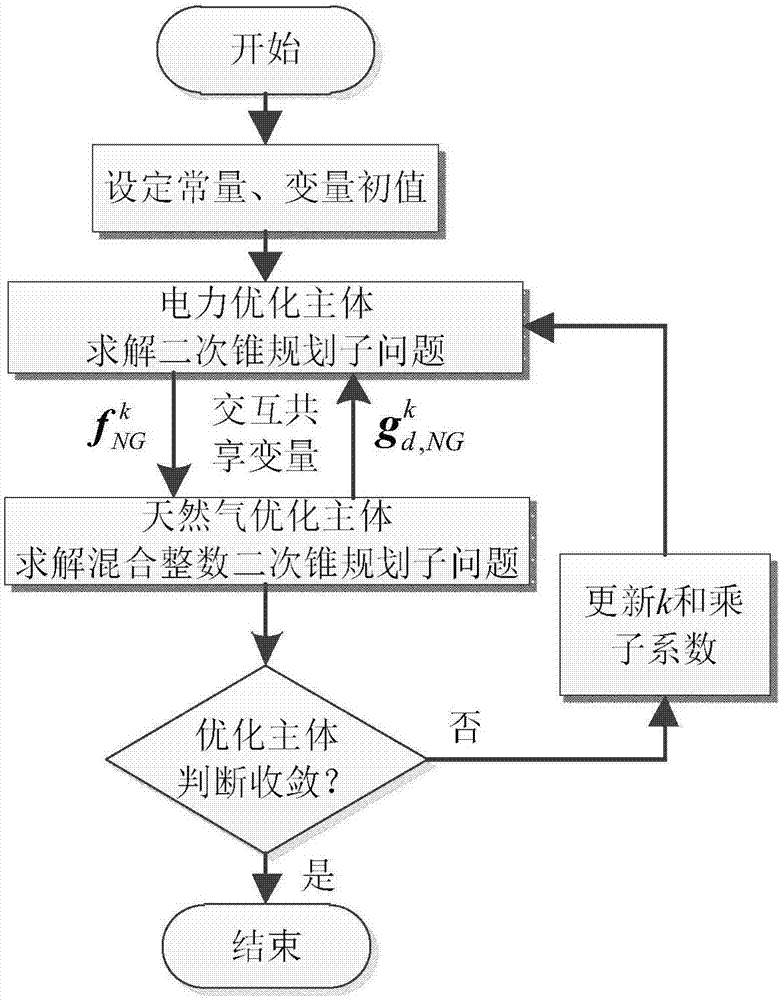
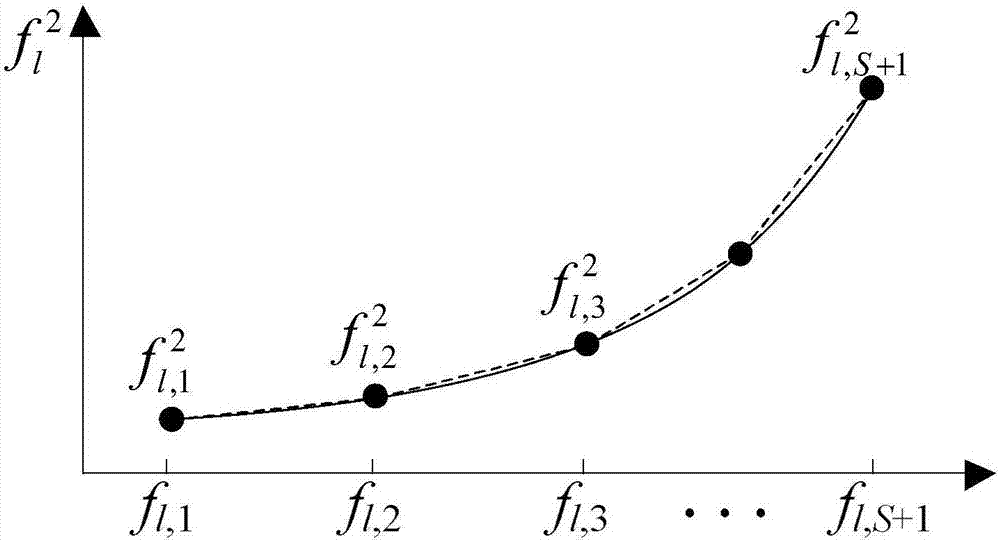
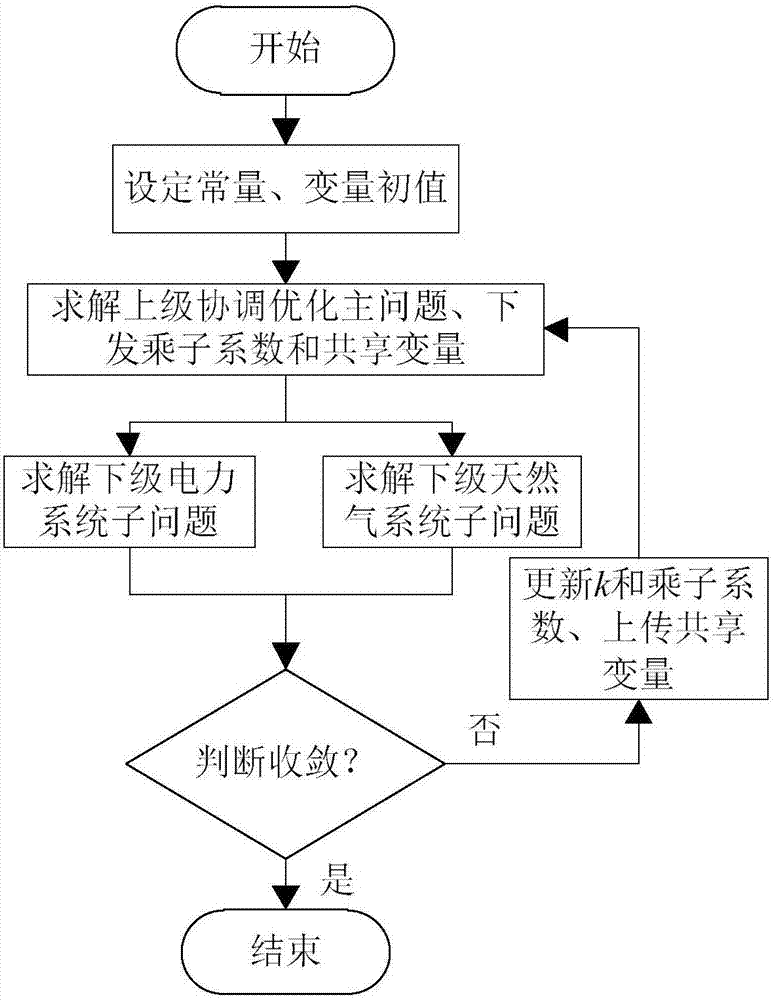
The invention provides a power-gas energy flow distributed cooperative optimization calculation method based on an alternating direction multiplier method. Firstly distributed independent optimization bodies-a power optimization body and a natural gas optimization body are determined according to the research object power-gas interconnection system, and both of the bodies are in the same position; the connection features of the power-gas interconnection system are analyzed, a coupling element model is researched and abstracted as the corresponding coupling constraint, and power flow and natural gas flow shared variables are determined; second-order cone programming sub-problems corresponding to the bodies are constructed accordingly for aiming at the problem of natural gas system pipeline gas flow direction optimization by adopting the McCormick equation and the relaxation technology; and mutual interaction and alternating solution of all the optimization sub-problems can be performed according to the alternating direction multiplier method solving mode, and the convergence can be judged according to the convergence criterion so that distributed cooperative optimization calculation of the power flow and the natural gas flow can be realized.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Scalable runtime system for global address space languages on shared and distributed memory machines
ActiveUS7380086B2Improve scalabilityResource allocationSpecific program execution arrangementsGlobal address spaceDistributed memory
An improved scalability runtime system for a global address space language running on a distributed or shared memory machine uses a directory of shared variables having a data structure for tracking shared variable information that is shared by a plurality of program threads. Allocation and de-allocation routines are used to allocate and de-allocate shared variable entries in the directory of shared variables. Different routines can be used to access different types of shared data. A control structure is used to control access to the shared data such that all threads can access the data at any time. Since all threads see the same objects, synchronization issues are eliminated. In addition, the improved efficiency of the data sharing allows the number of program threads to be vastly increased.
Owner:DAEDALUS BLUE LLC
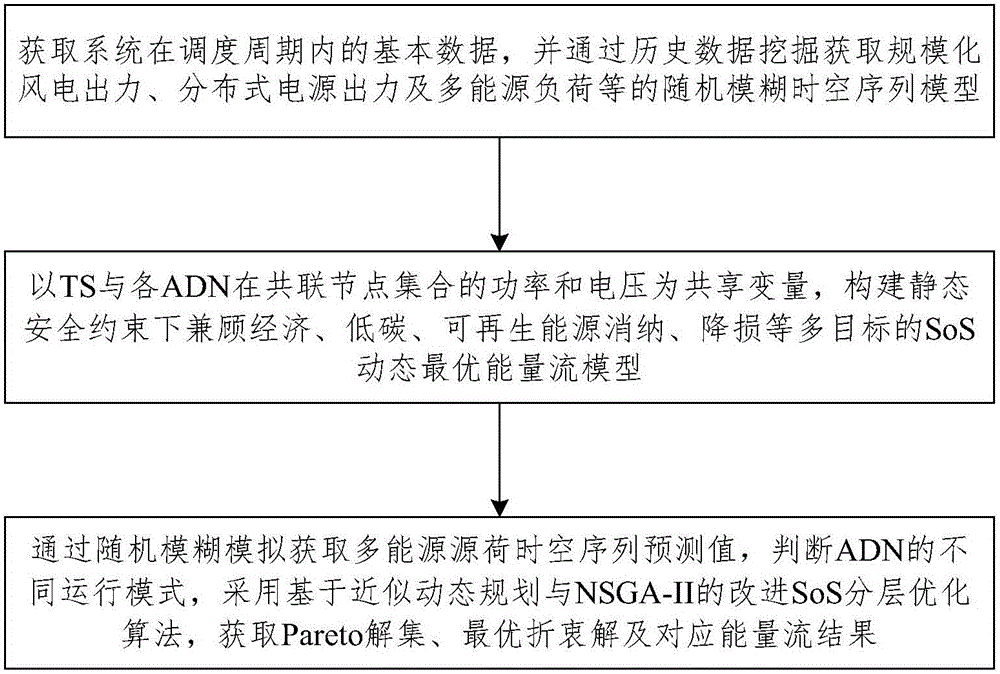
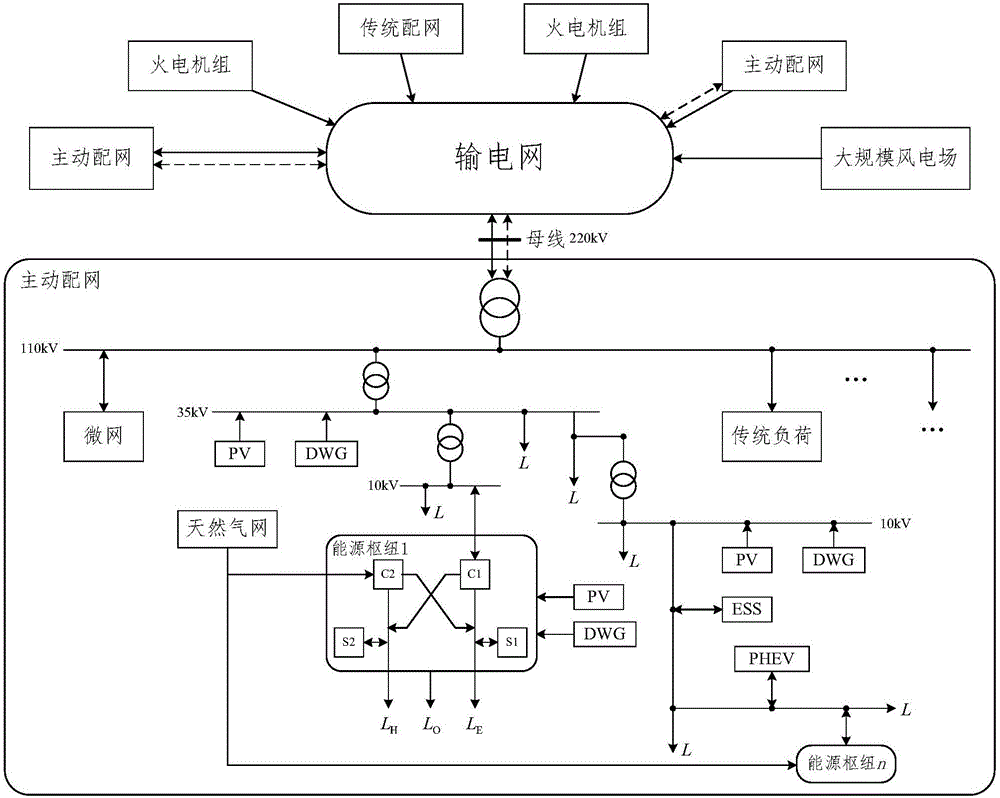
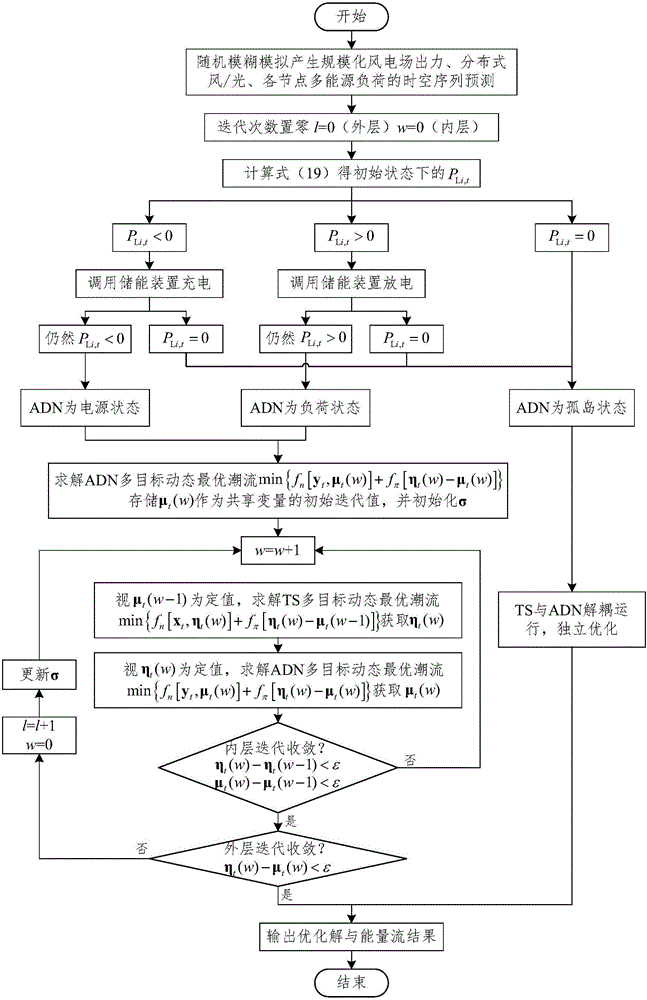
Multi-target random fuzzy dynamic optimal energy flow modeling and solving method for multi-energy coupling transmission and distribution network
ActiveCN105703369ARealize comprehensive coordination and optimization of schedulingAc networks with different sources same frequencyElectric power systemEnergy coupling
Owner:马瑞
Distributed collaborative optimization calculation method of electricity-gas energy flow based on target cascade analysis
The invention discloses a distributed collaborative optimization calculation method of an electricity-gas energy flow based on target cascade analysis. Firstly, a coupling element model is analyzed according to the connection characteristics of an electricity-gas interconnection system, and the coupling element model is abstracted into a corresponding coupling constraint to determine shared variables of an electricity flow and a natural gas flow; on the basis of this, an electricity-gas flow decomposition collaborative mechanism based on the target cascade analysis is constructed; and further an electricity-gas flow collaborative optimization problem is split into a higher-level coordination primal problem and lower-level optimization sub-problems (including: an electricity optimization sub-problems and a natural gas optimization sub-problem), and the upper-level and lower-level problems are alternatively solved in sequence to convergence to achieve the distributed collaborative optimization of the electricity flow and the natural gas flow.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
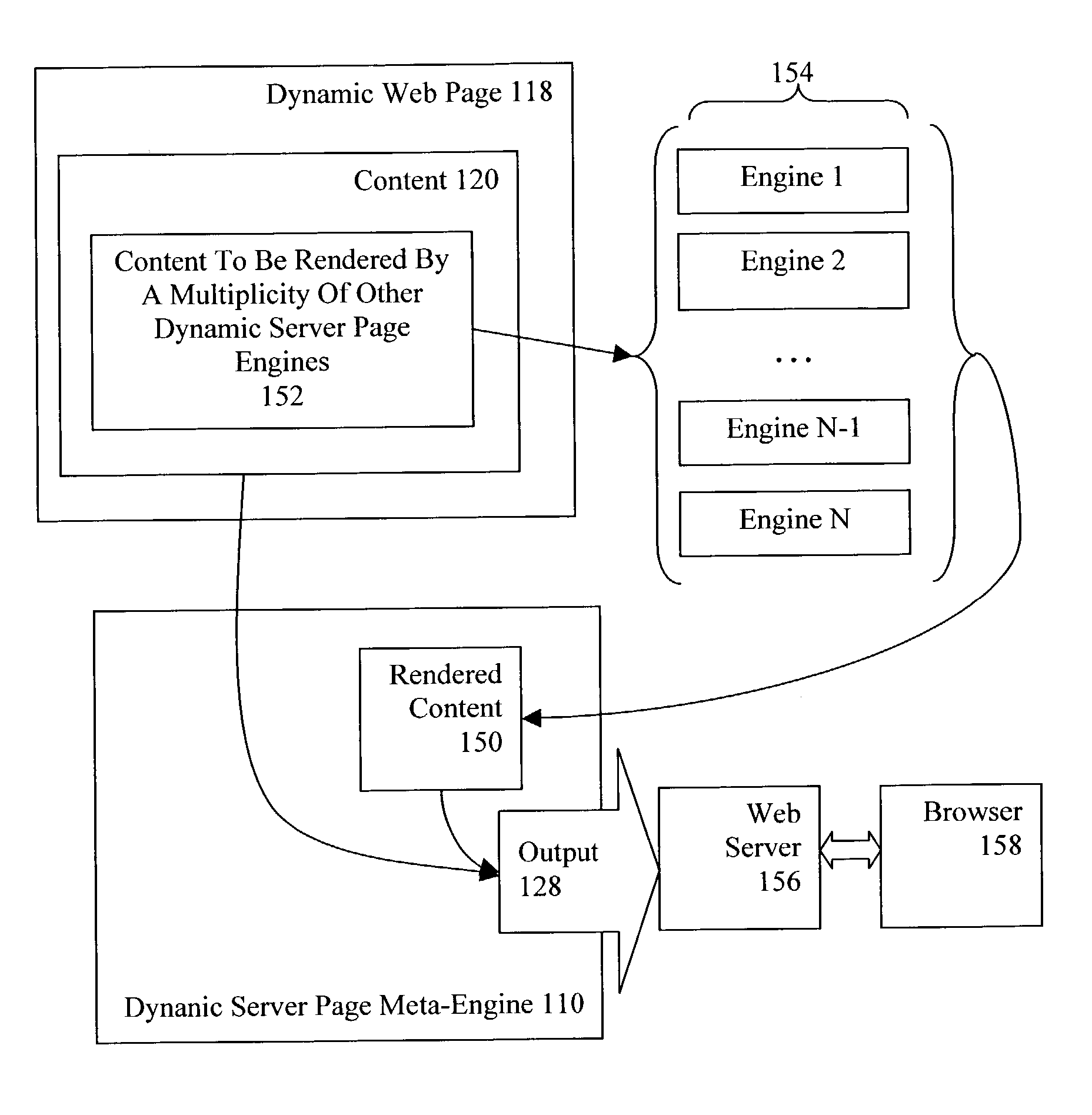
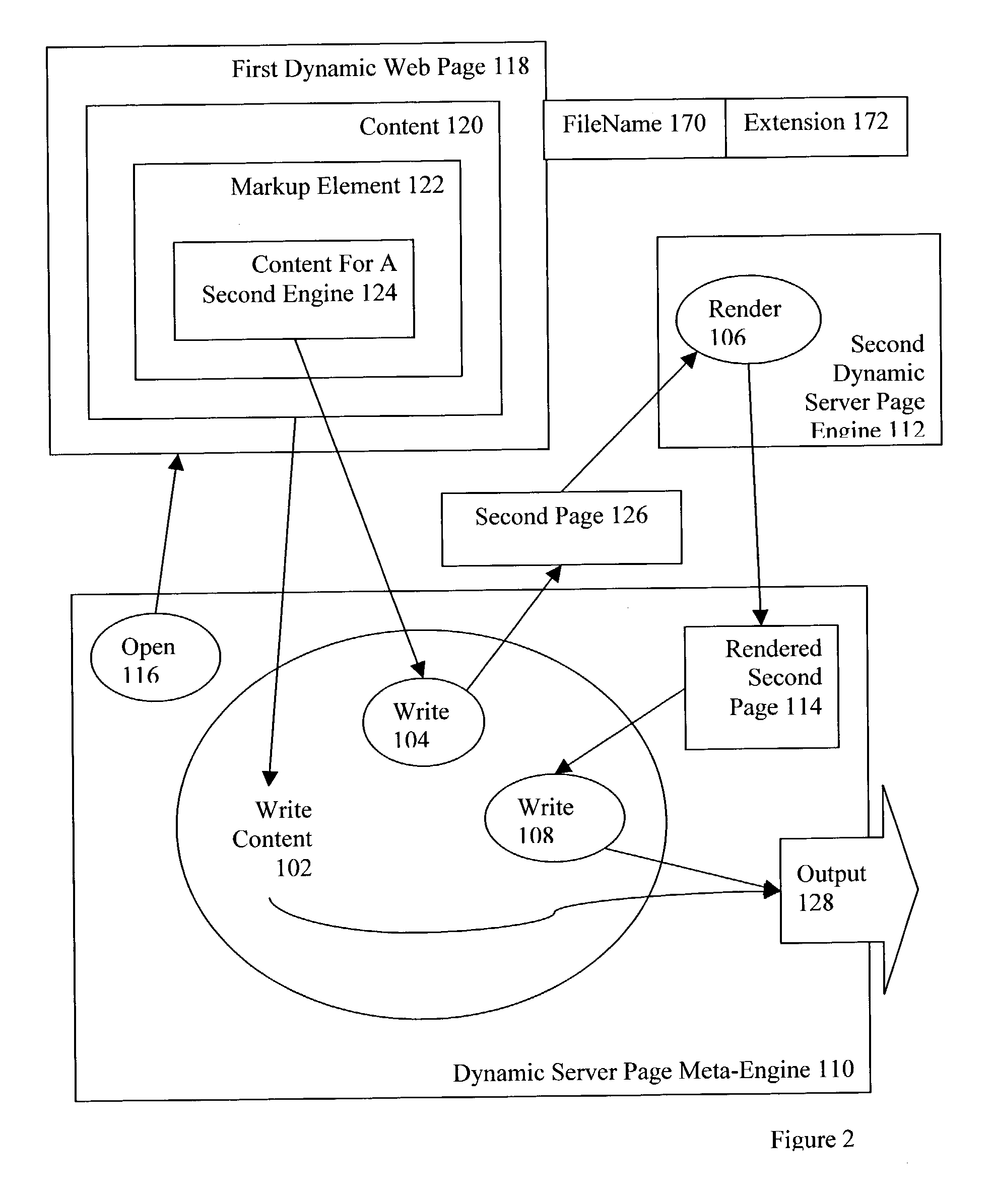
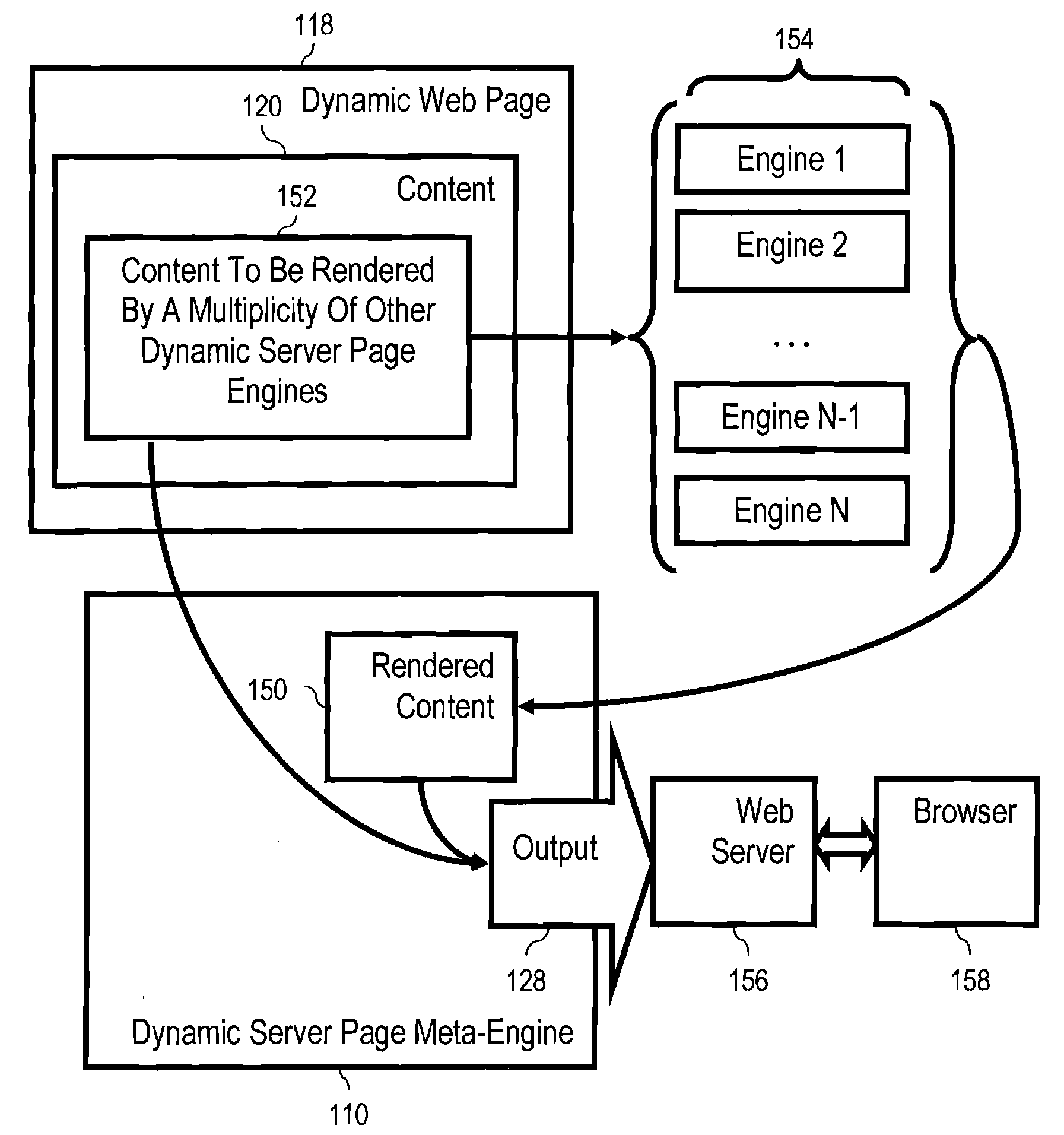
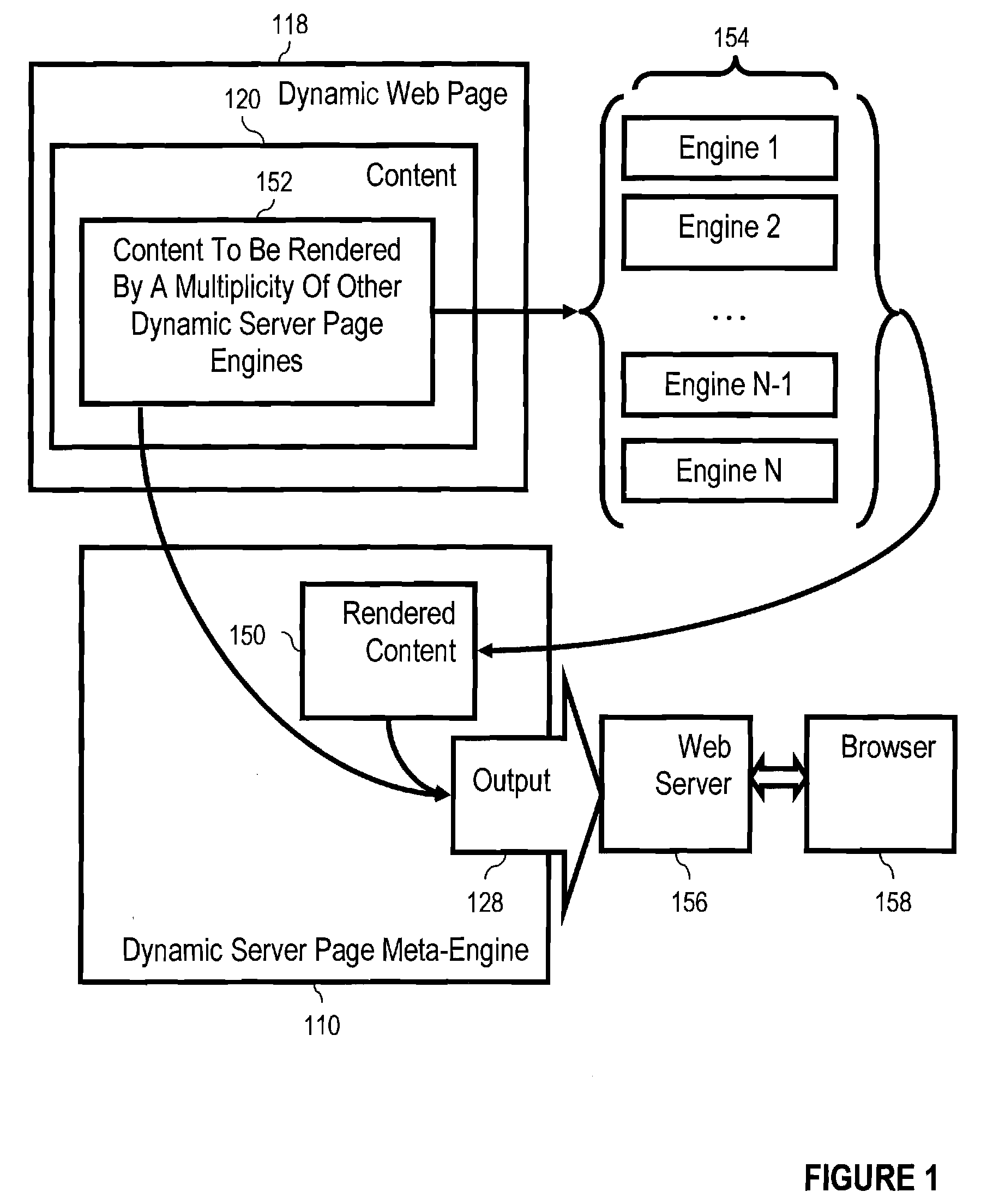
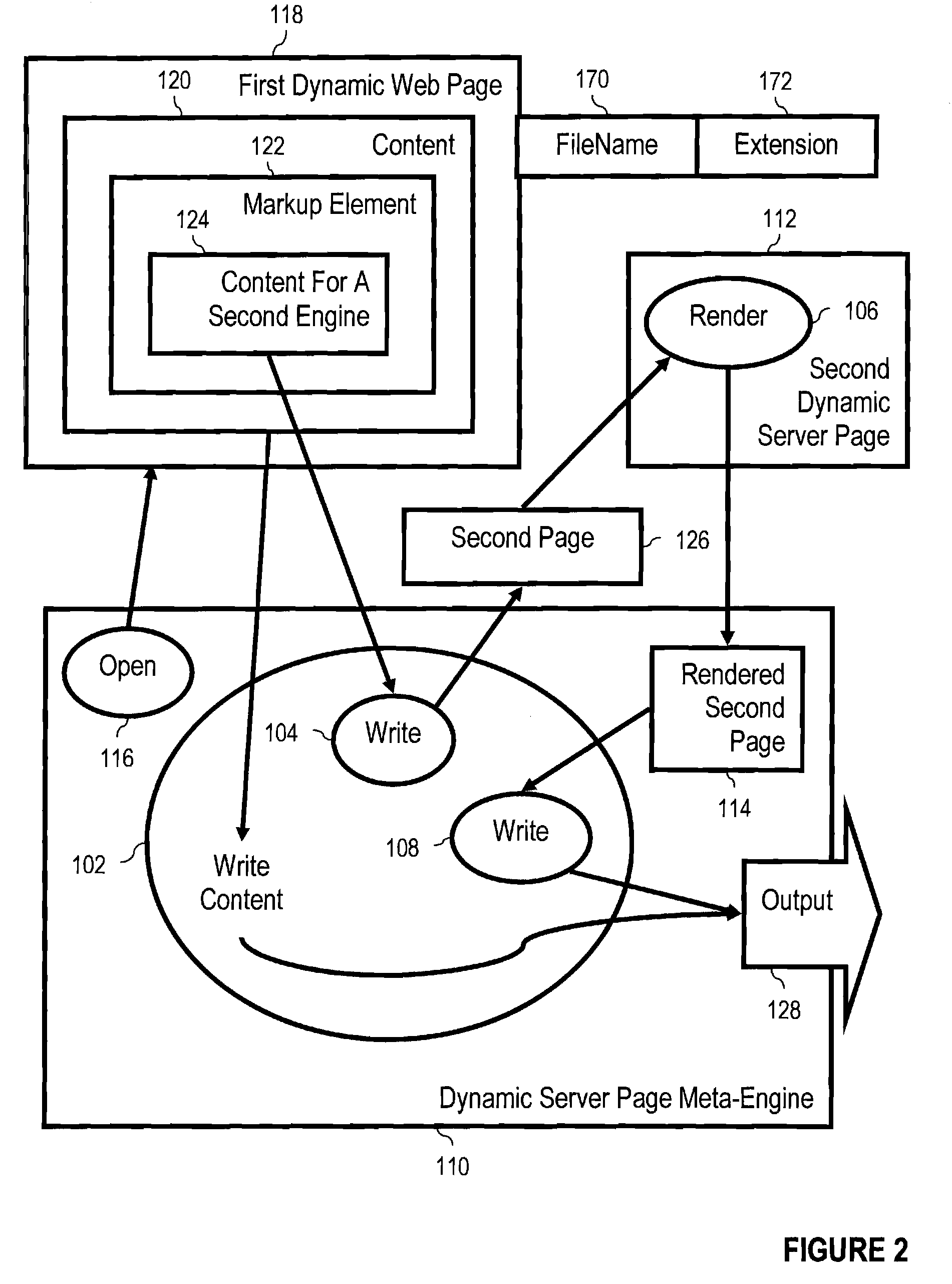
Dynamic server page meta-engines with data sharing for dynamic content and non-JSP segments rendered through other engines
InactiveUS20040187136A1Multiple digital computer combinationsWebsite content managementData sharingWorld Wide Web
Rendering a meta-page through a meta-engine, the meta-engine including a tag handler, the meta-page including static content, JSP dynamic content and one or more types of non-JSP dynamic content, and identifications of shared variables. Embodiments include writing to output the static content of the meta-page, rendering the JSP dynamic content to the output of the meta-engine, and inserting into the non-JSP dynamic content additional non-JSP dynamic content identifying current values of shared variables. Embodiments include rendering the non-JSP dynamic content through dynamic server page engines, including passing current values of shared variables to the dynamic server page engines, reading from the non-JSP additional dynamic content as rendered the current values of shared variables, deleting from the non-JSP dynamic content as rendered the additional non-JSP dynamic content as rendered, and writing the non-JSP dynamic content as rendered, at its location among the static content, to the output of the meta-engine.
Owner:IBM CORP
Dynamic Server Page Meta-Engines with Data Sharing for Dynamic Content and Non-JSP Segments Rendered Through Other Engines
InactiveUS20060282501A1Multiple digital computer combinationsWebsite content managementData sharingWorld Wide Web
Owner:IBM CORP
Dynamic data race detection method based on static shared variable recognition
ActiveCN102760095ASolve the bloat problemReduce overheadSoftware testing/debuggingControl flowDynamic data
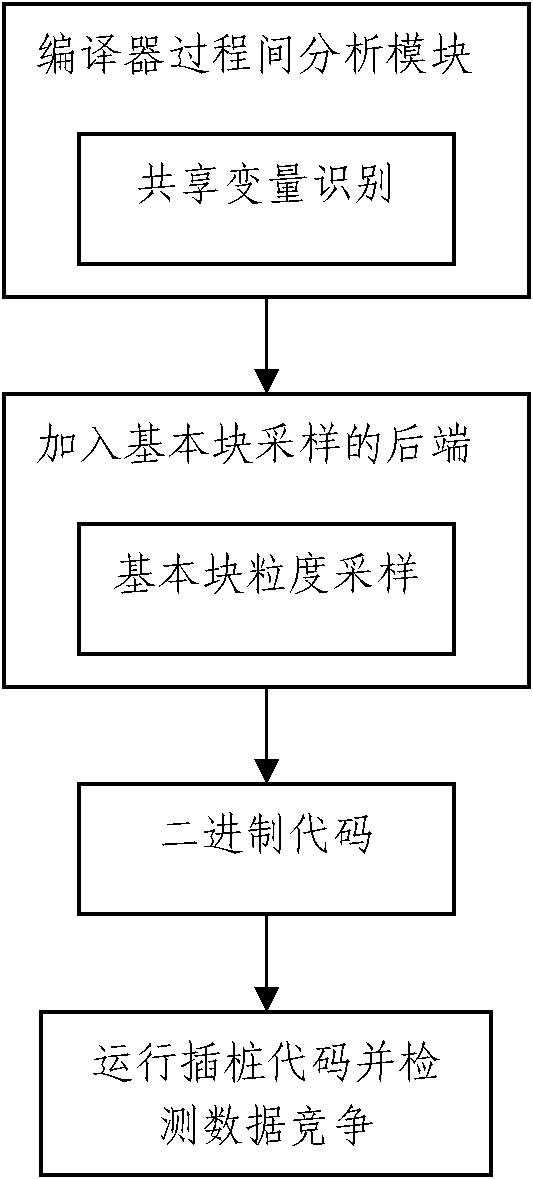
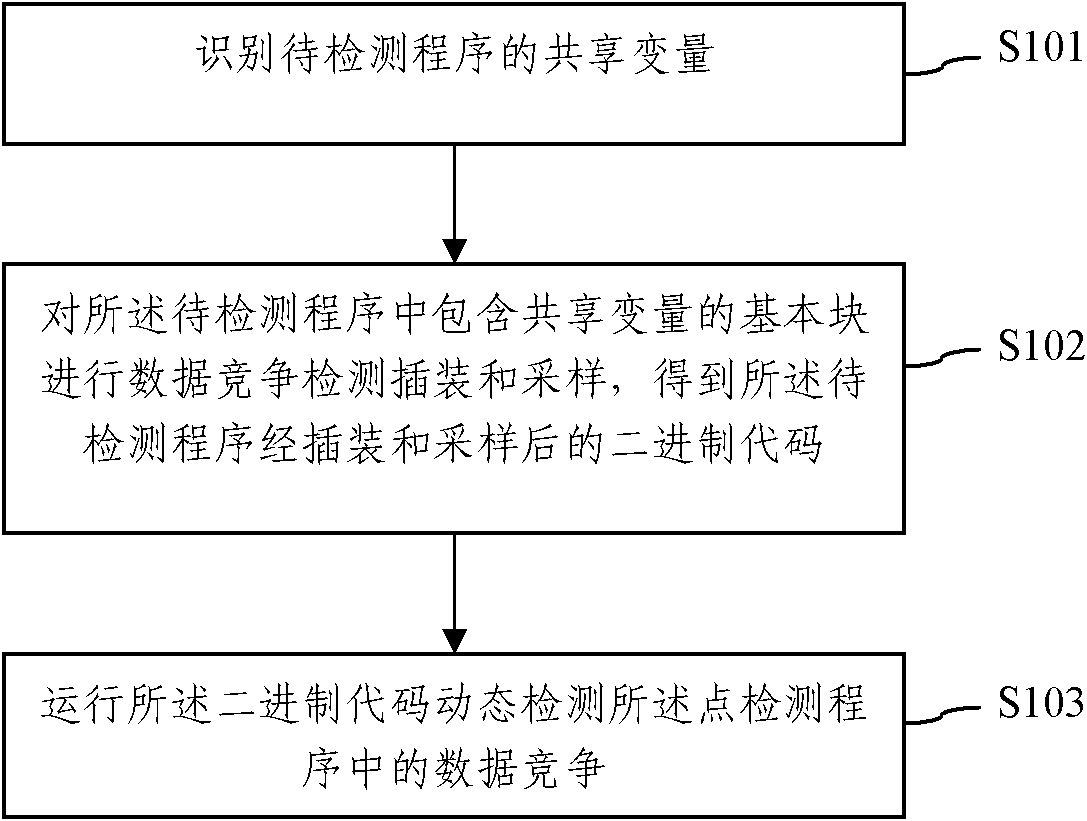
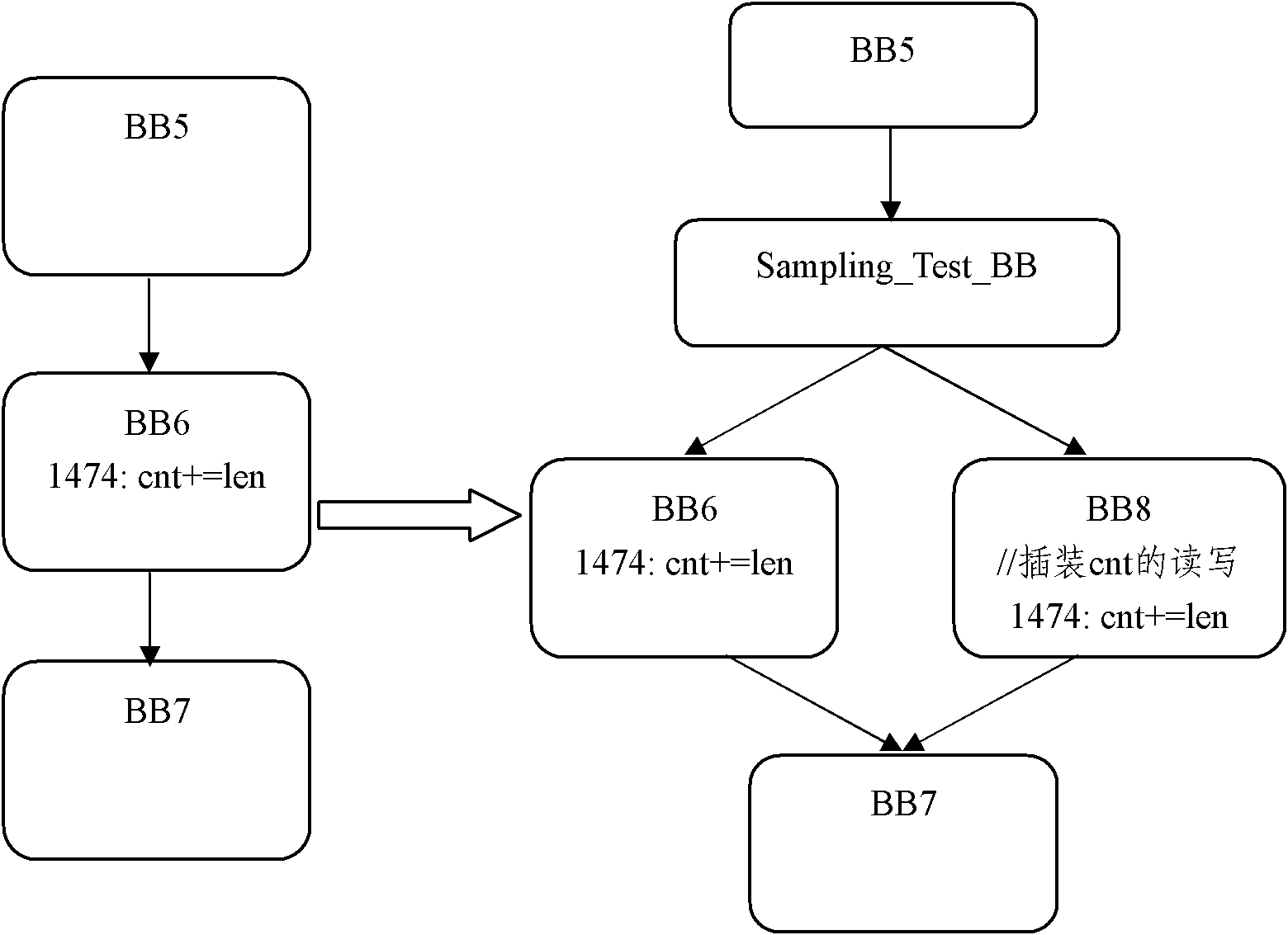
The invention discloses a dynamic data race detection method based on static shared variable recognition. The method comprises the steps: S1, recognizing a shared variable of a program to be detected; S2, performing data race detection instrumenting and sampling on a basic block of the shared variable contained in the program to be detected, to obtain instrumented and sampled binary code of the program to be detected, wherein the basic block references to a continuous program statement sequence, a control flow starts entering from the continuous program sentence sequence and leaves from the end without interruption or branch; and S3, running the binary code to dynamically detect data race in spot detection. The method can be used for instrumenting and sampling the basic block containing the shared variable, thus avoiding the problem of code bloat, and greatly reducing the system overhead.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Systems and methods for parallel distributed programming
ActiveUS7712080B2Software engineeringGeneral purpose stored program computerParallel computingComputer programming
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
System and method for test generation with dynamic constraints using static analysis and multidomain constraint reduction
ActiveUS7870523B1Quantity minimizationError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsStatic timing analysisA domain
The present invention provides a system and method for resolving a test generation problem involving constraint resolution problems where a verification environment includes constraints that are suitable for resolution using one type of solver for a first domain and other constraints that are suitable for resolution using a different solver in a second domain. The invention further comprises variables and, in instances where at least one variable is in each of the first and second domains, using these solvers to restrict the set of permissible values of variables to be consistent in multiple domains, preferably in all relevant domains.A constraint resolution problem is divided into clusters of constraints connected within a domain, and connected clusters of clusters that are connected through shared variables that are subject to constraints in more than one cluster.A preferred solver is applied to constraints in each of various domains such that constraints in multiple clusters and domains in a connected cluster are consistent for connected constraints in a domain, and preferably all constraints in all clusters in all domains within the connected cluster are consistent.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Systems and methods for parallel distributed programming
ActiveUS20050039159A1Software engineeringGeneral purpose stored program computerParallel computingComputer programming
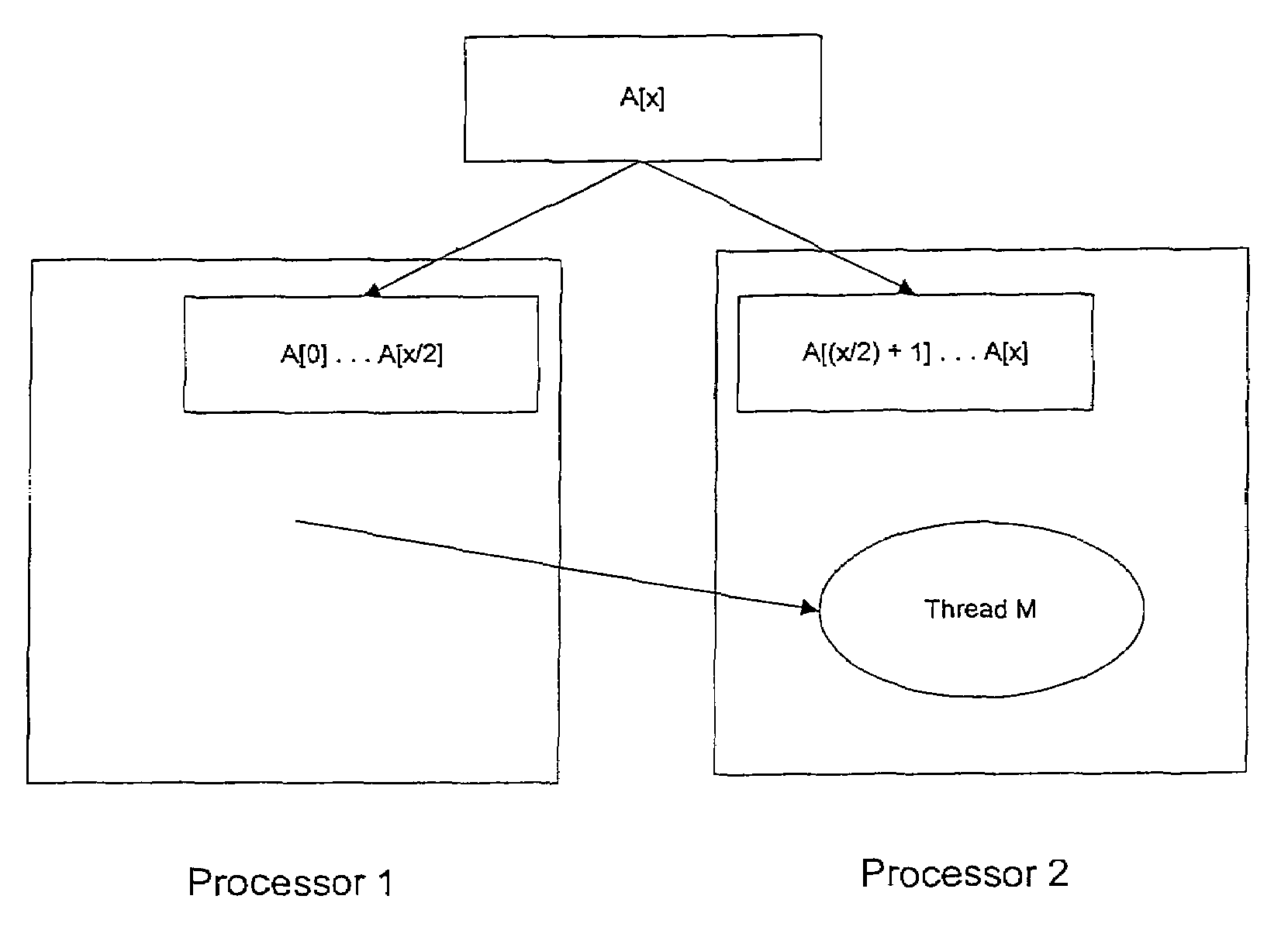
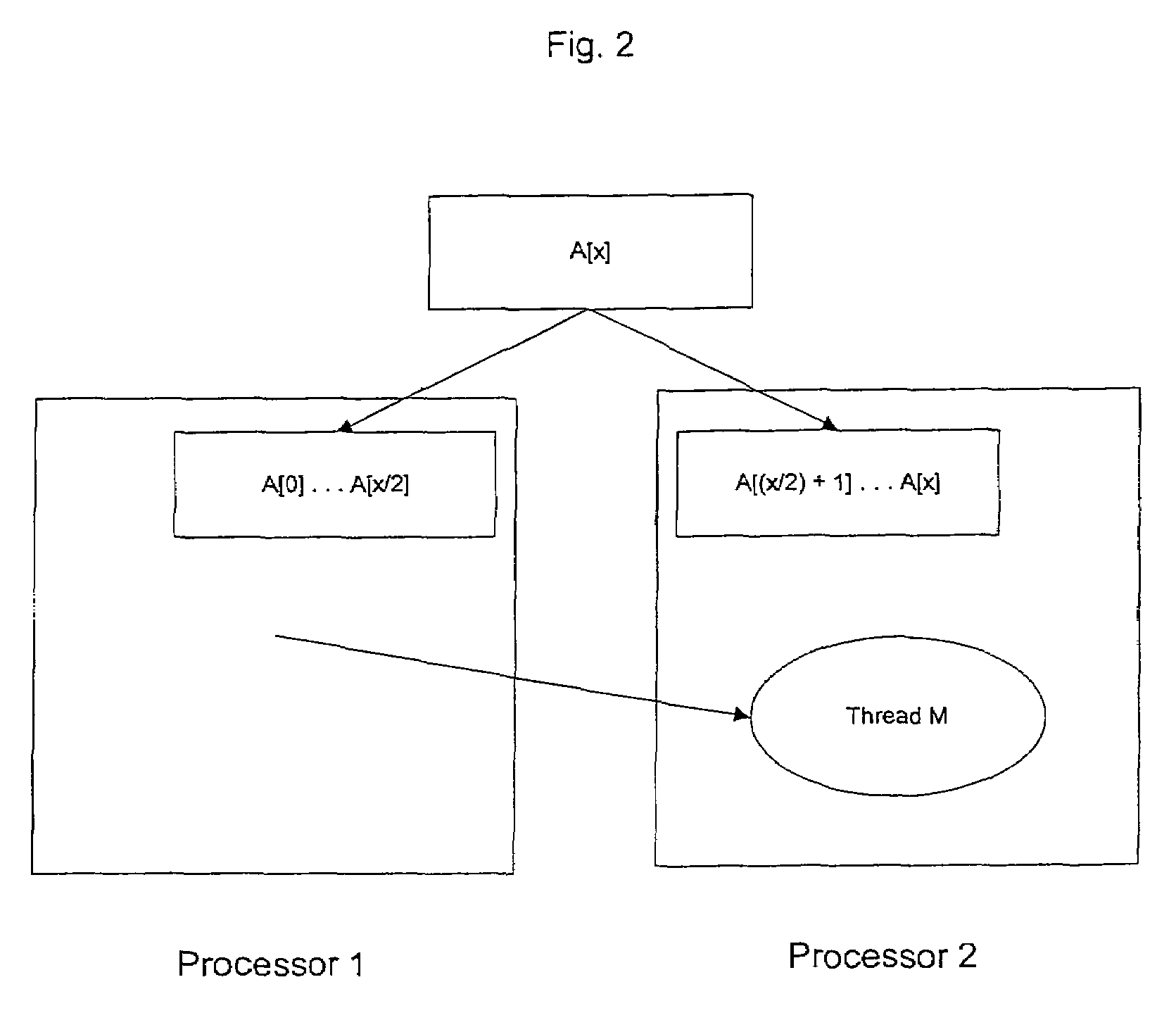
The present invention relates generally to computer programming, and more particularly to systems and methods for parallel distributed programming. Generally, a parallel distributed program is configured to operate across multiple processors and multiple memories. In one aspect of the invention, a parallel distributed program includes a distributed shared variable located across the multiple memories and distributed programs capable of operating across multiple processors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Information flow analysis method based on system source code searching concealed channel
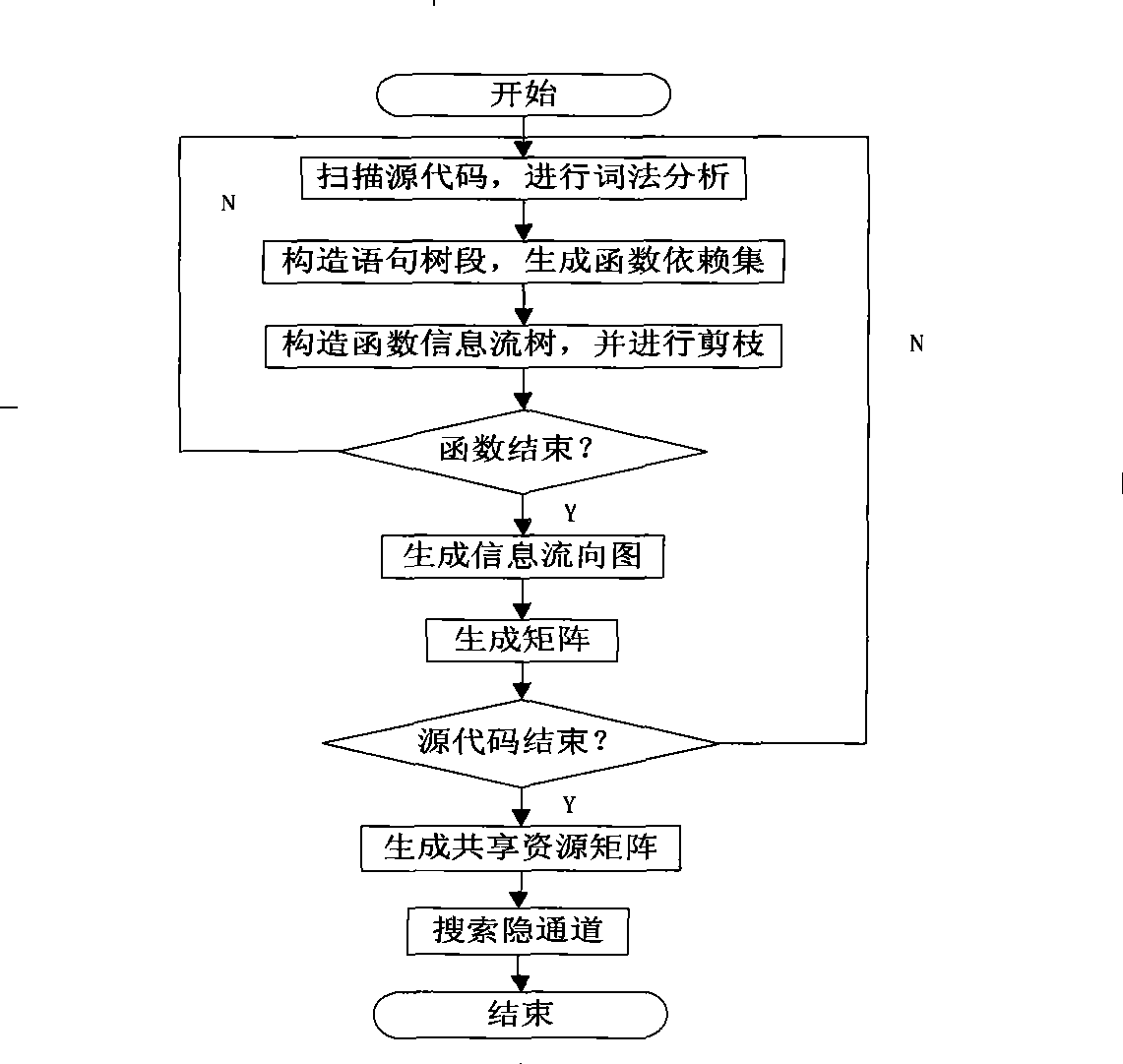
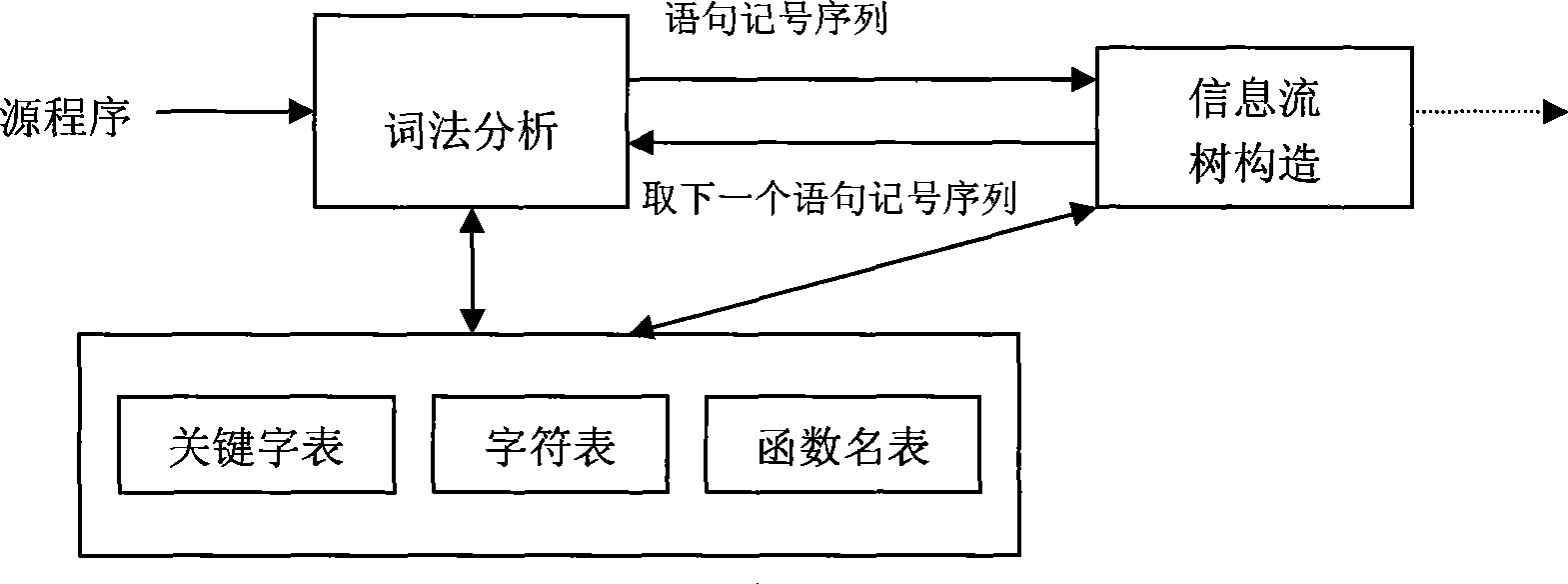
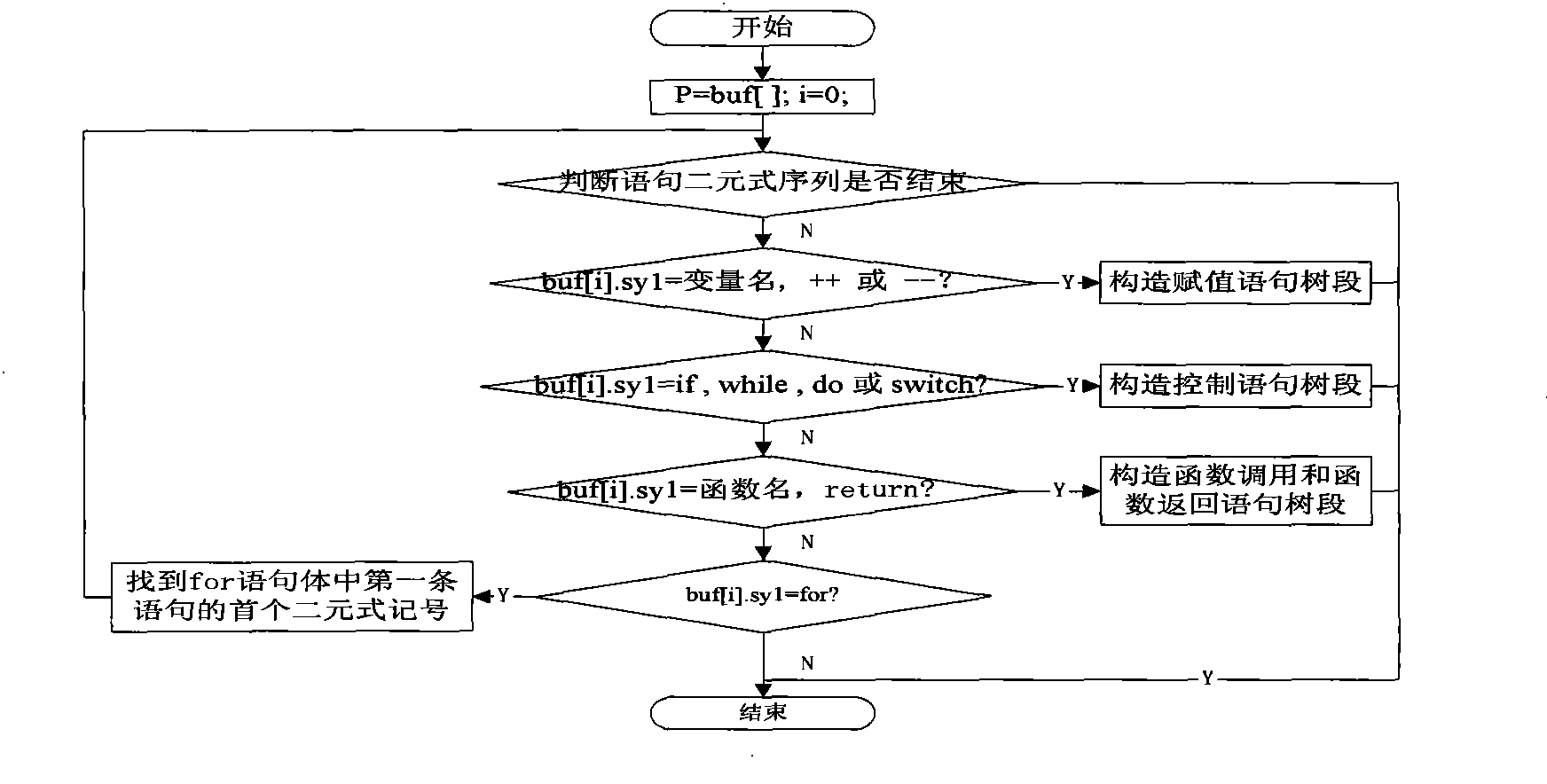
InactiveCN101377806AHigh precisionAvoid introducingPlatform integrity maintainanceTransmissionVisibilitySource code
The invention provides an information flow analytic method based on the searched convert channels of system source codes, which comprises the following steps: functions in the source codes and the statements and the variables in the functions are identified by dint of lexical analyzers and scanning system source codes; the call relations of the functions are determined, statement tree fields are constructed and functional dependence gathers of each function are given according to the functions and the function call statements identified by scanners; function information flow trees are constructed and are lopped with the statements and the variables which can generate information flow and are identified by the scanners as the input for information flow analysis; the function information flow trees are traversed, and the information flow graphs of each function are output; the shared variable visibility between dependence concentration functions and the modifiability information are acquired in functional dependence gathers according to the functional dependence gathers and the information flow graphs, thus generating shared resource matrices; covert channels are searched with the shared resource matrices as the input, and the covert channel sequences in the system are output. By adopting the information flow analytic method, the search work precision of the covert channels is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
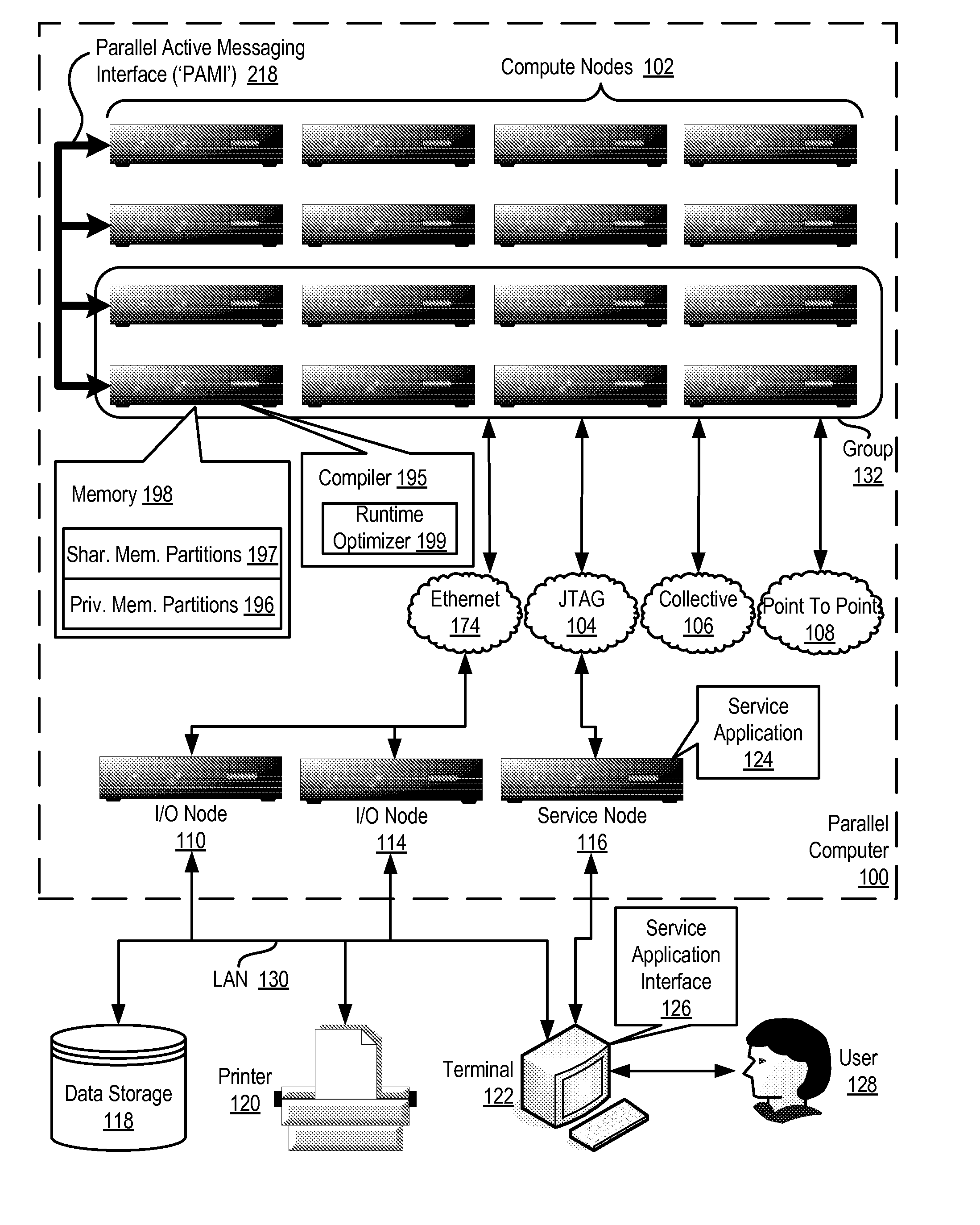
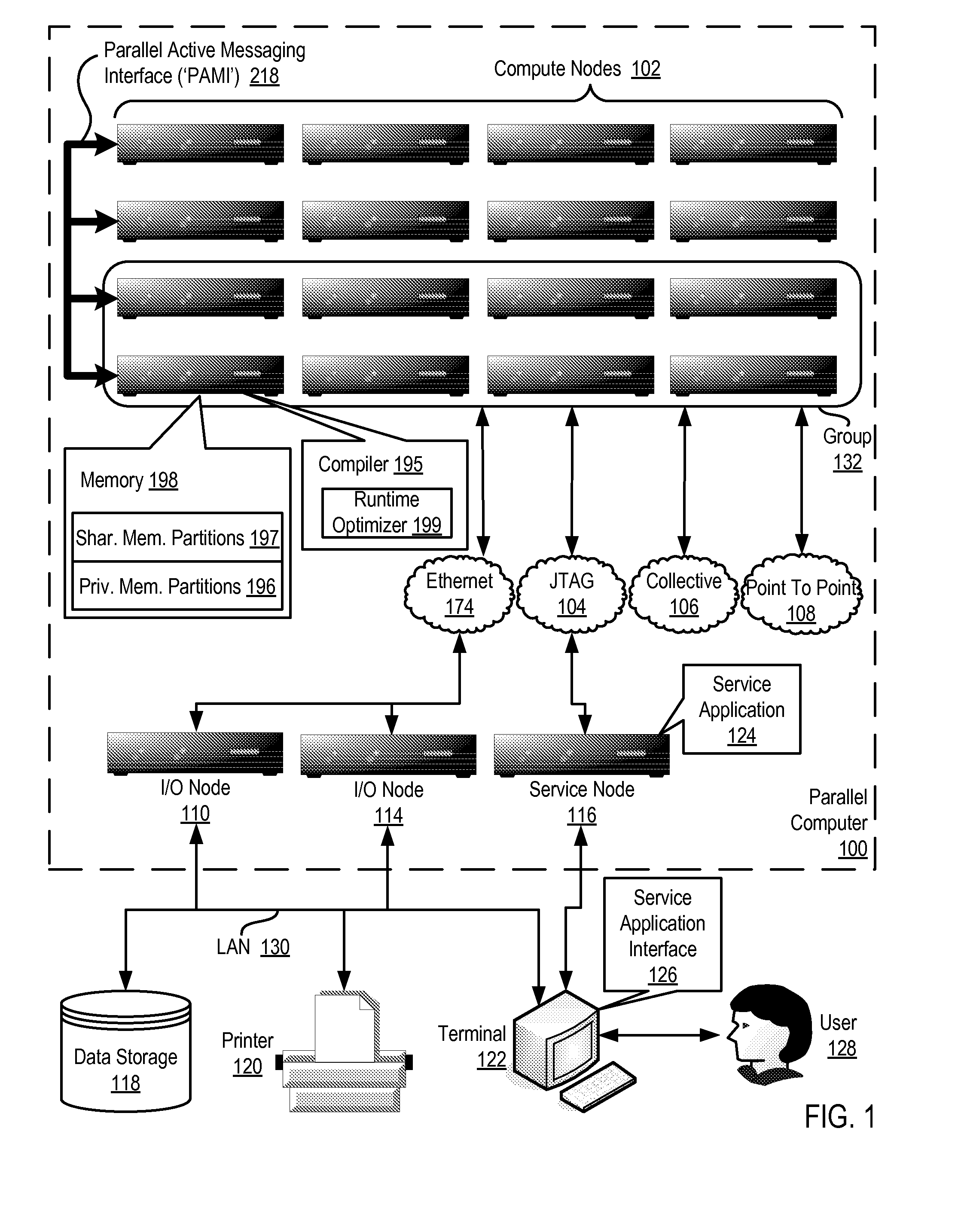
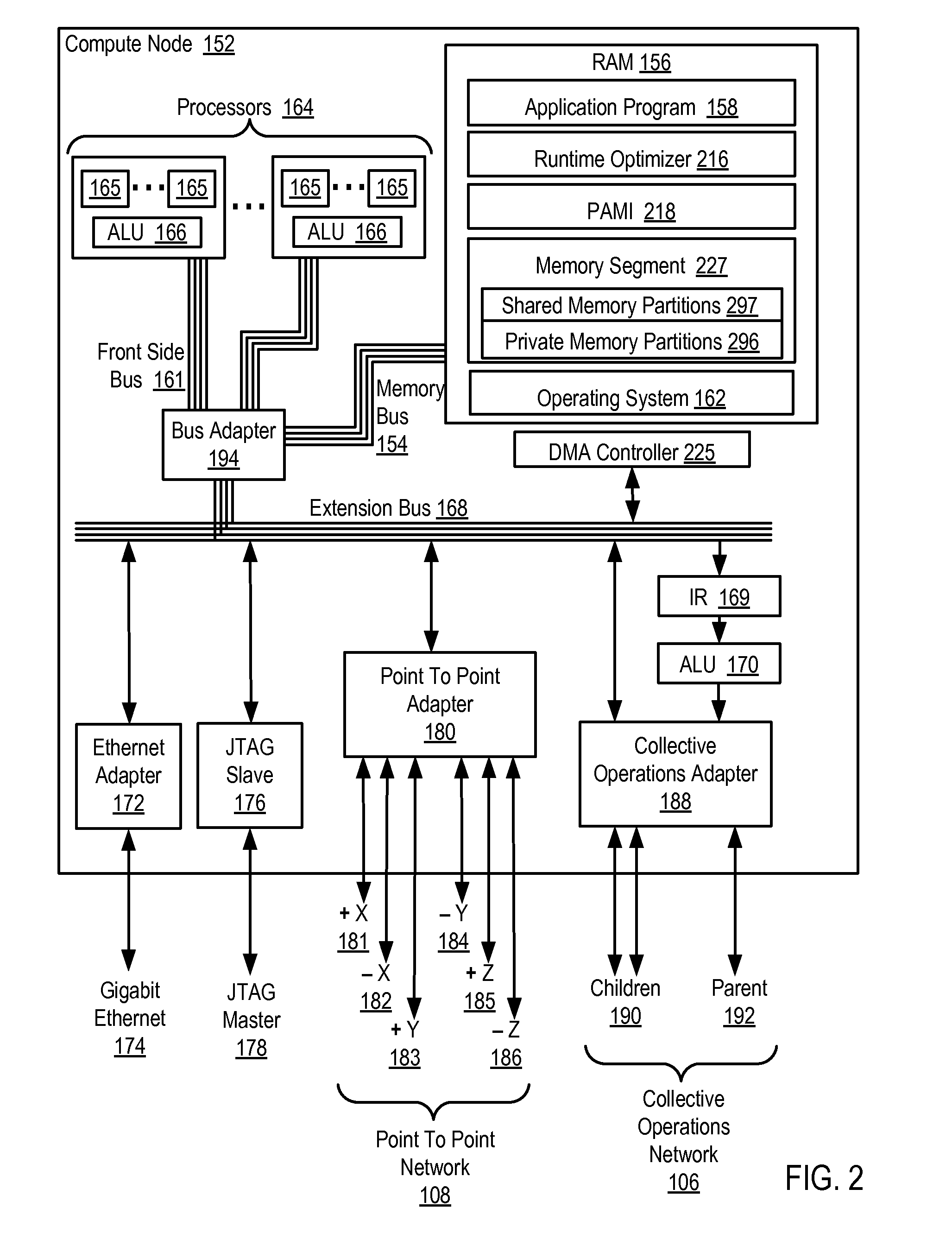
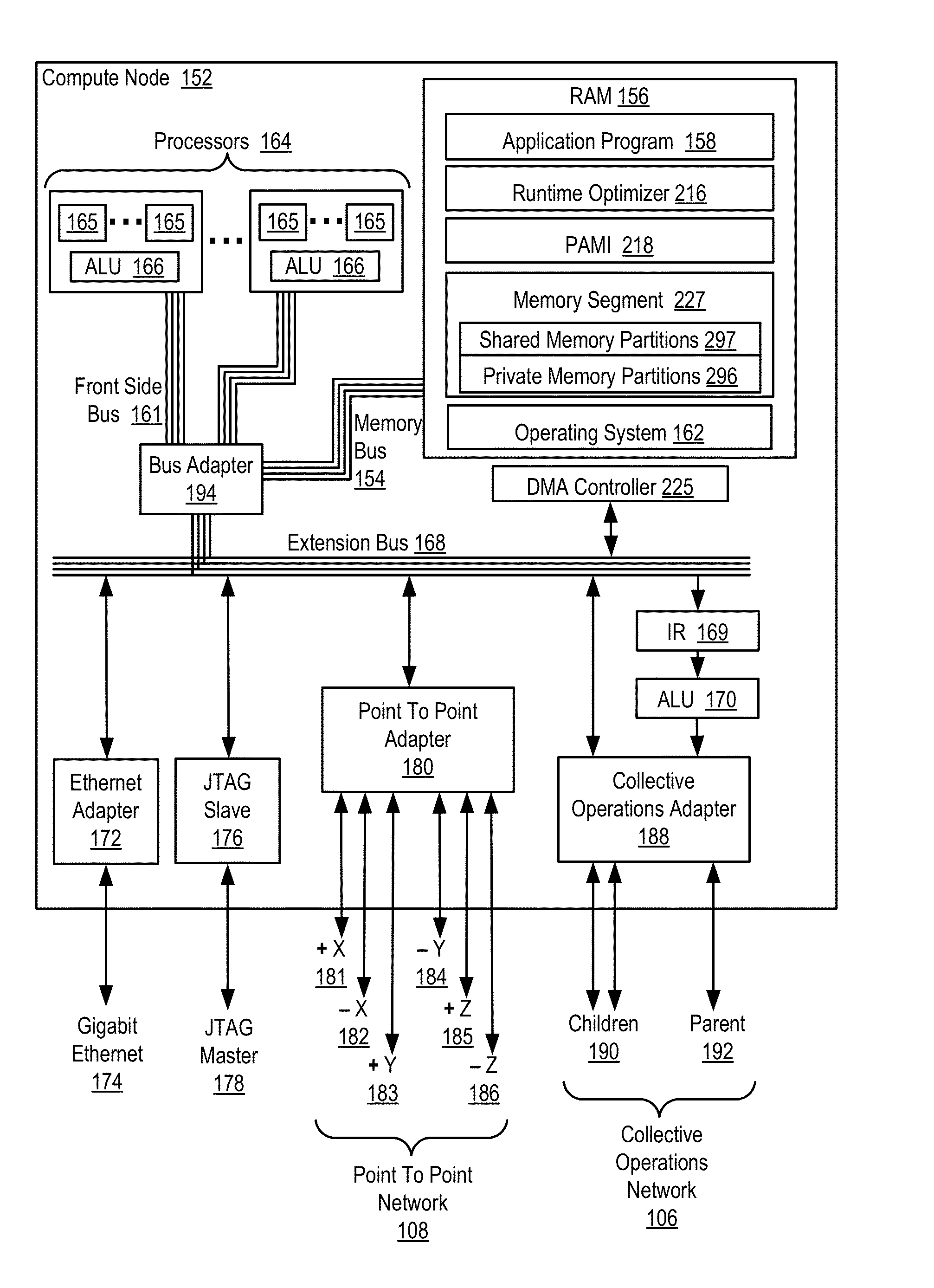
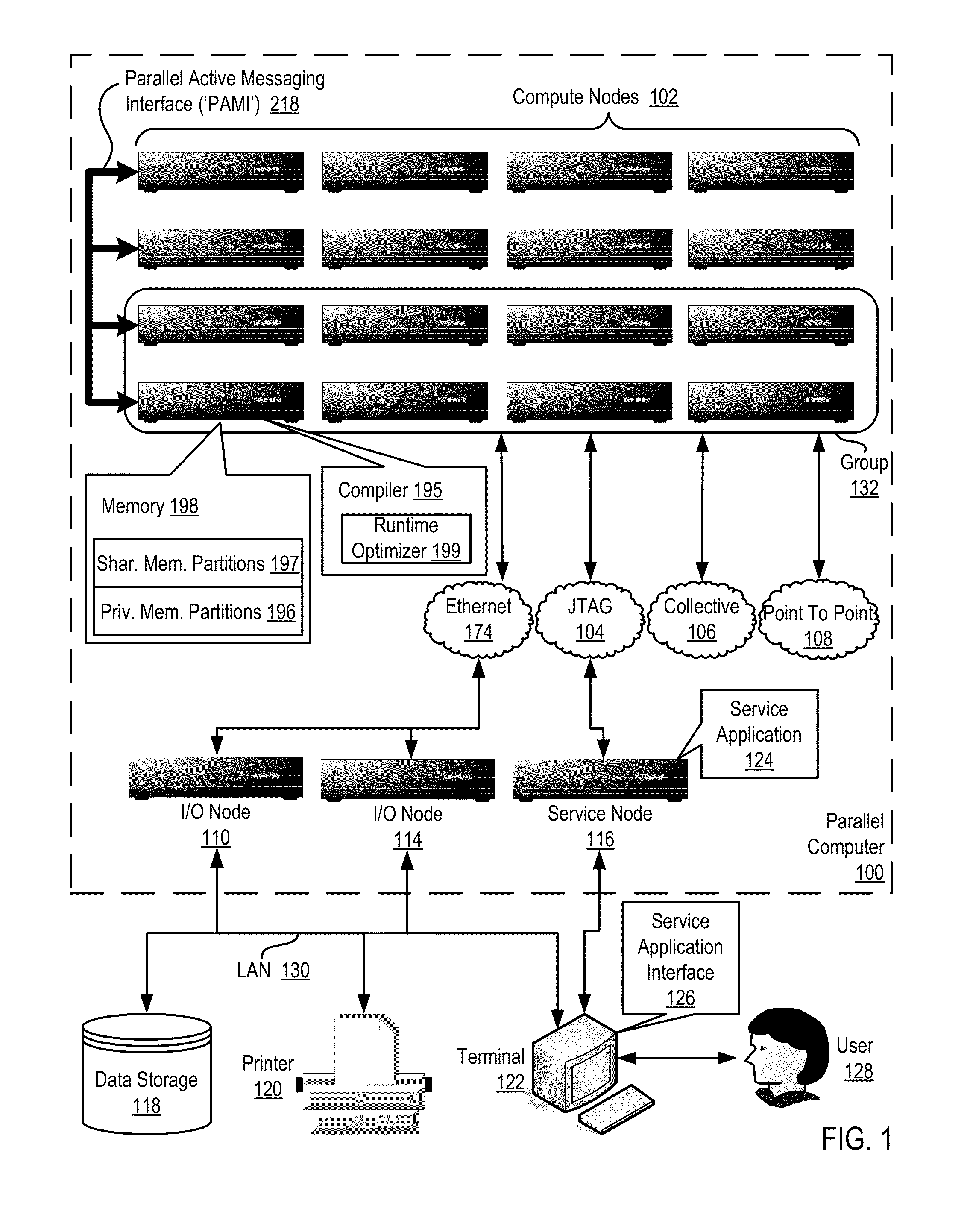
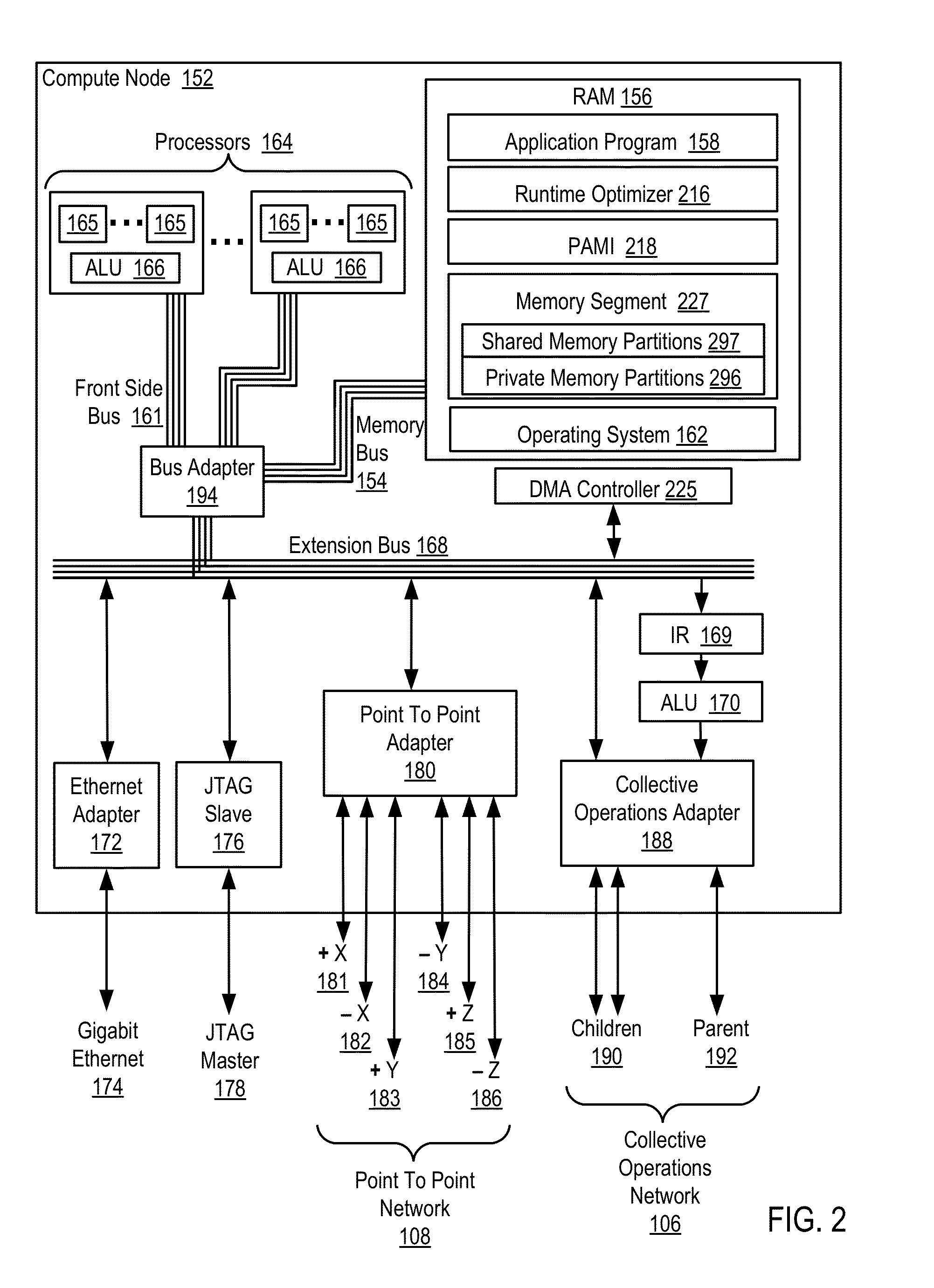
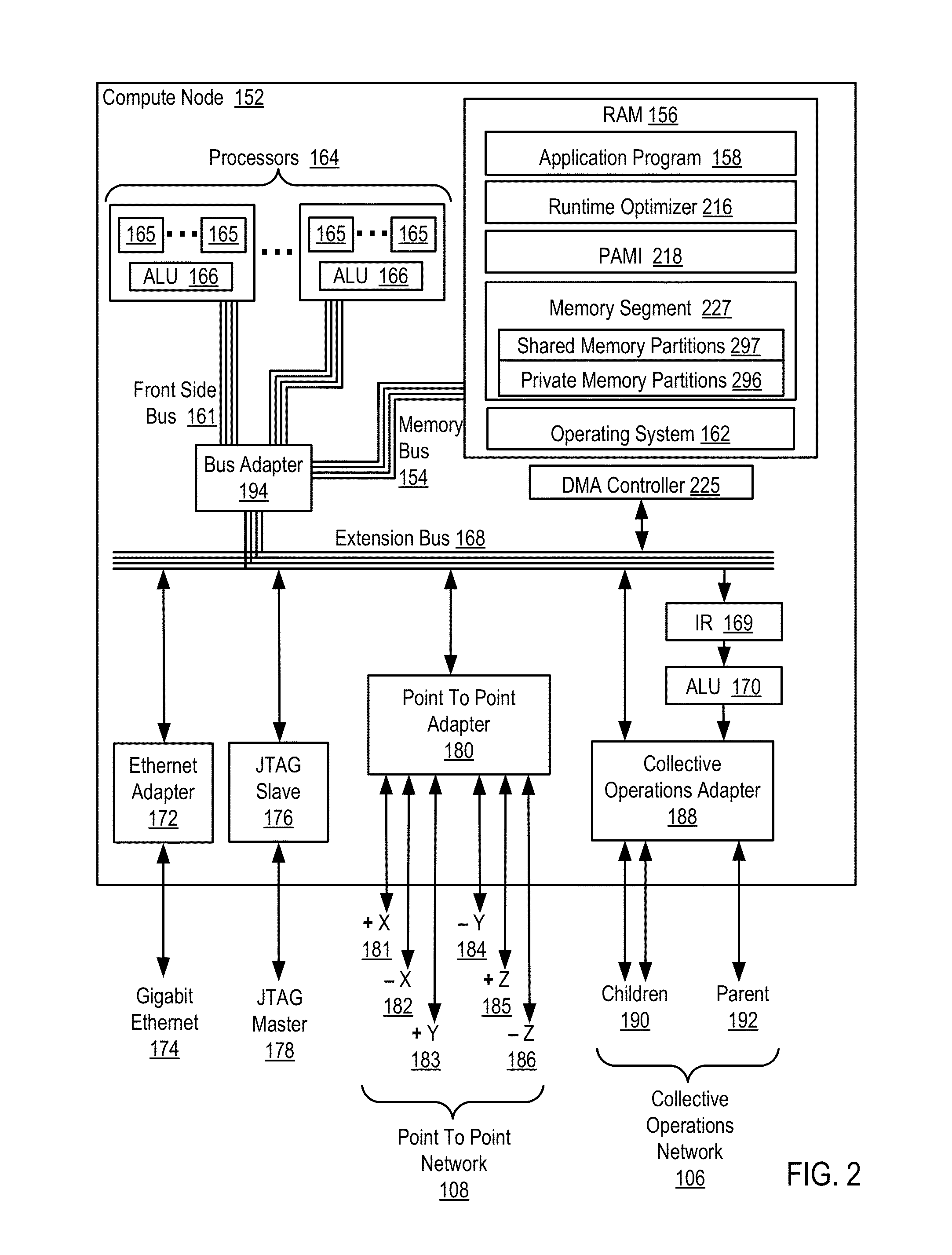
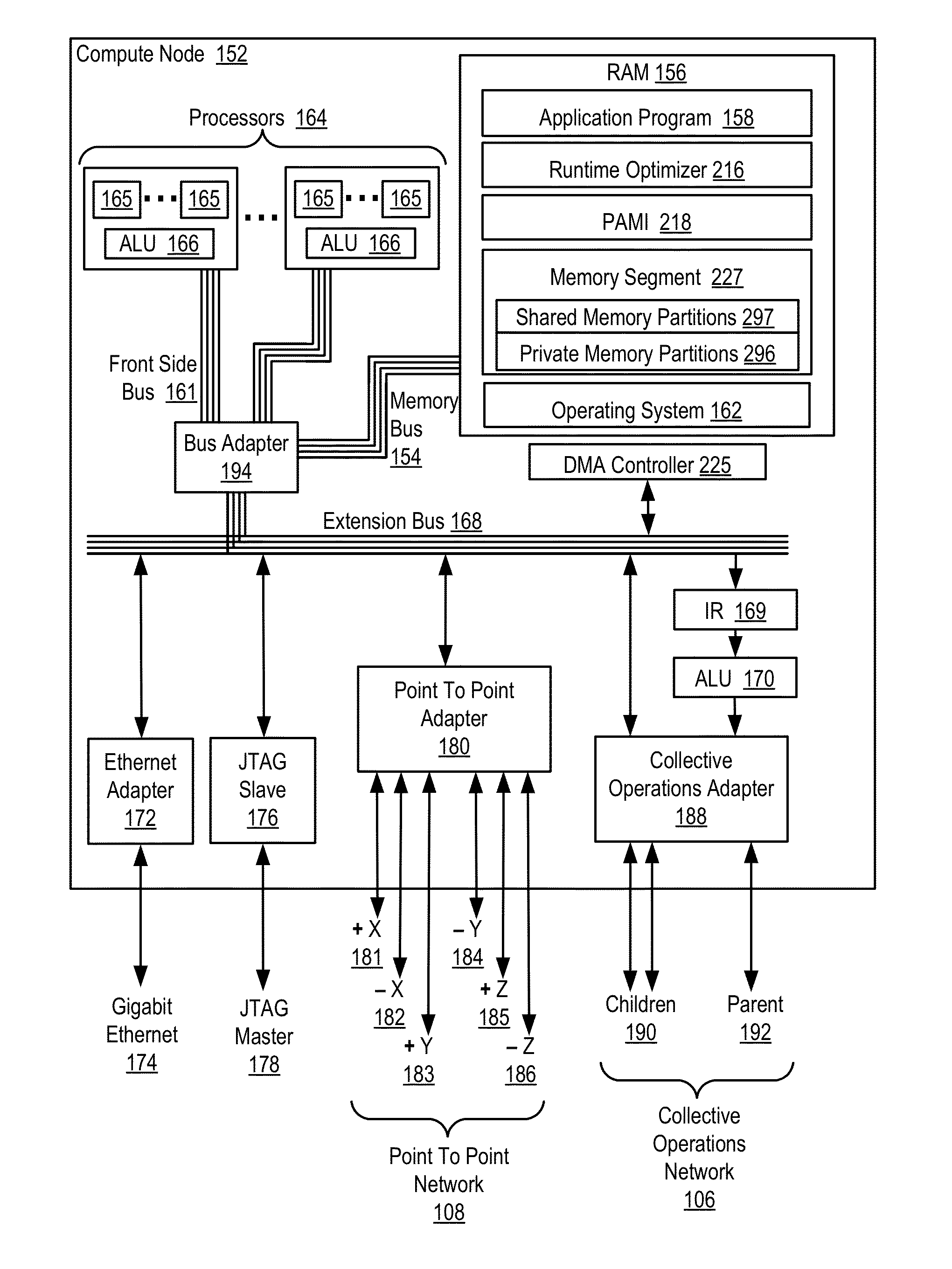
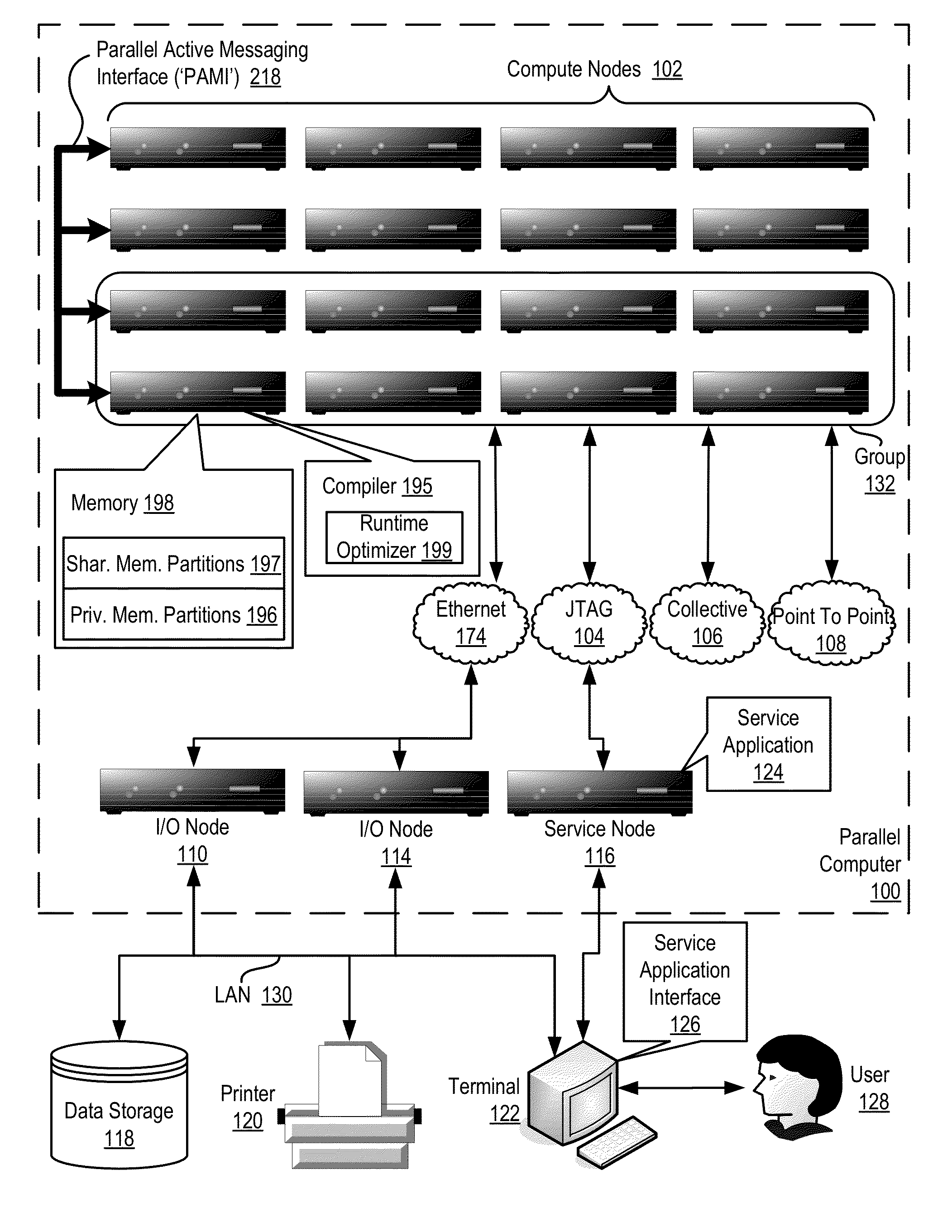
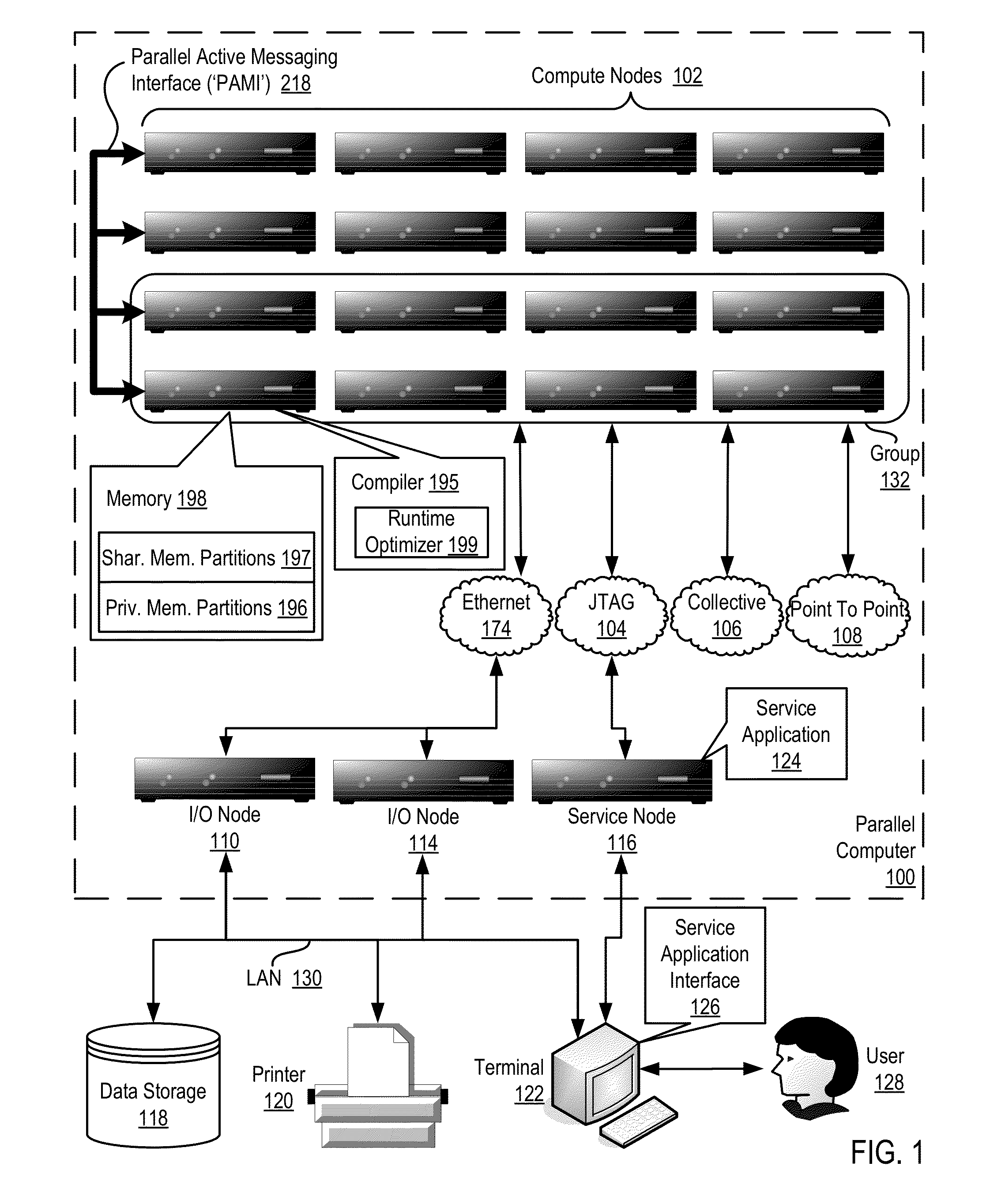
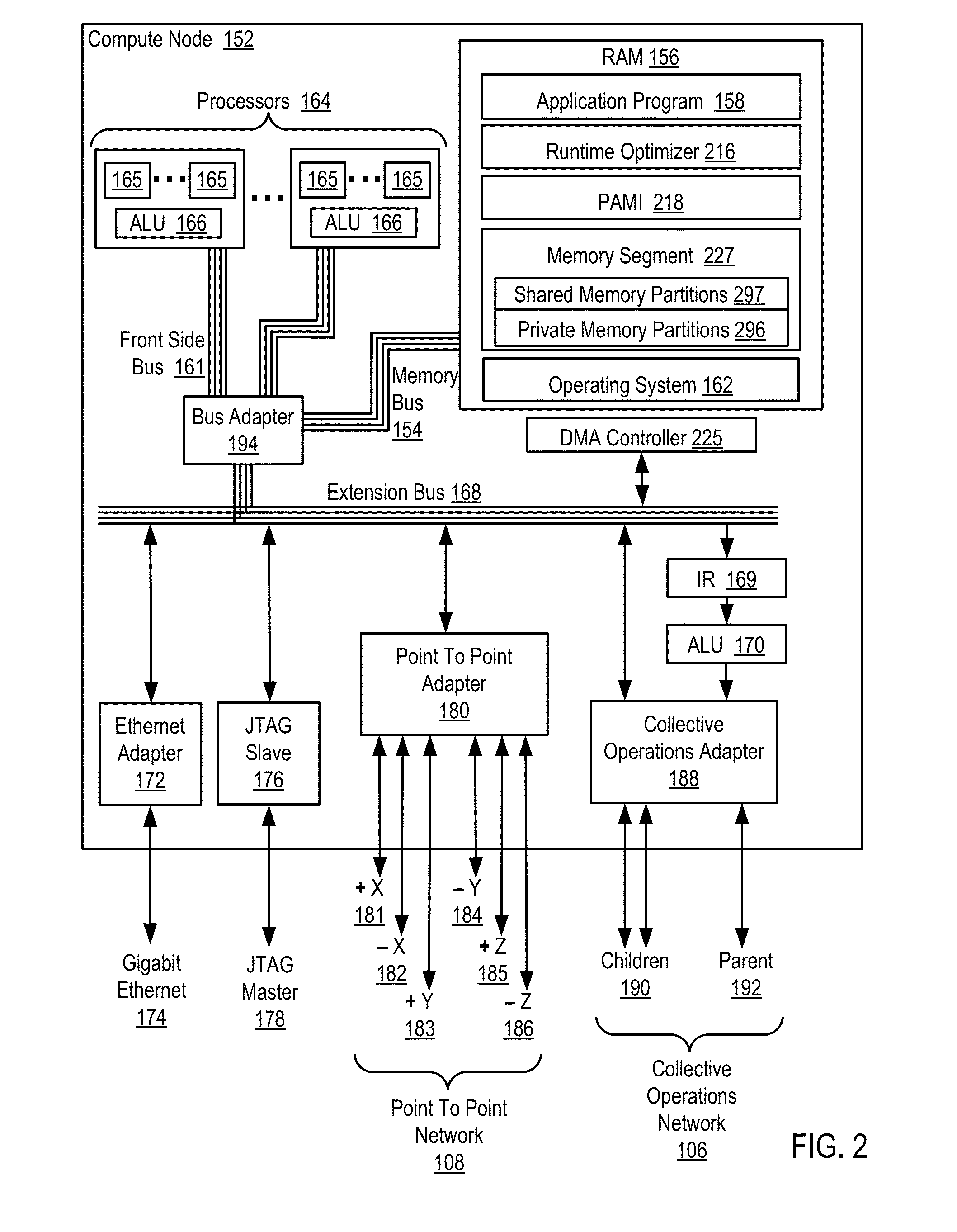
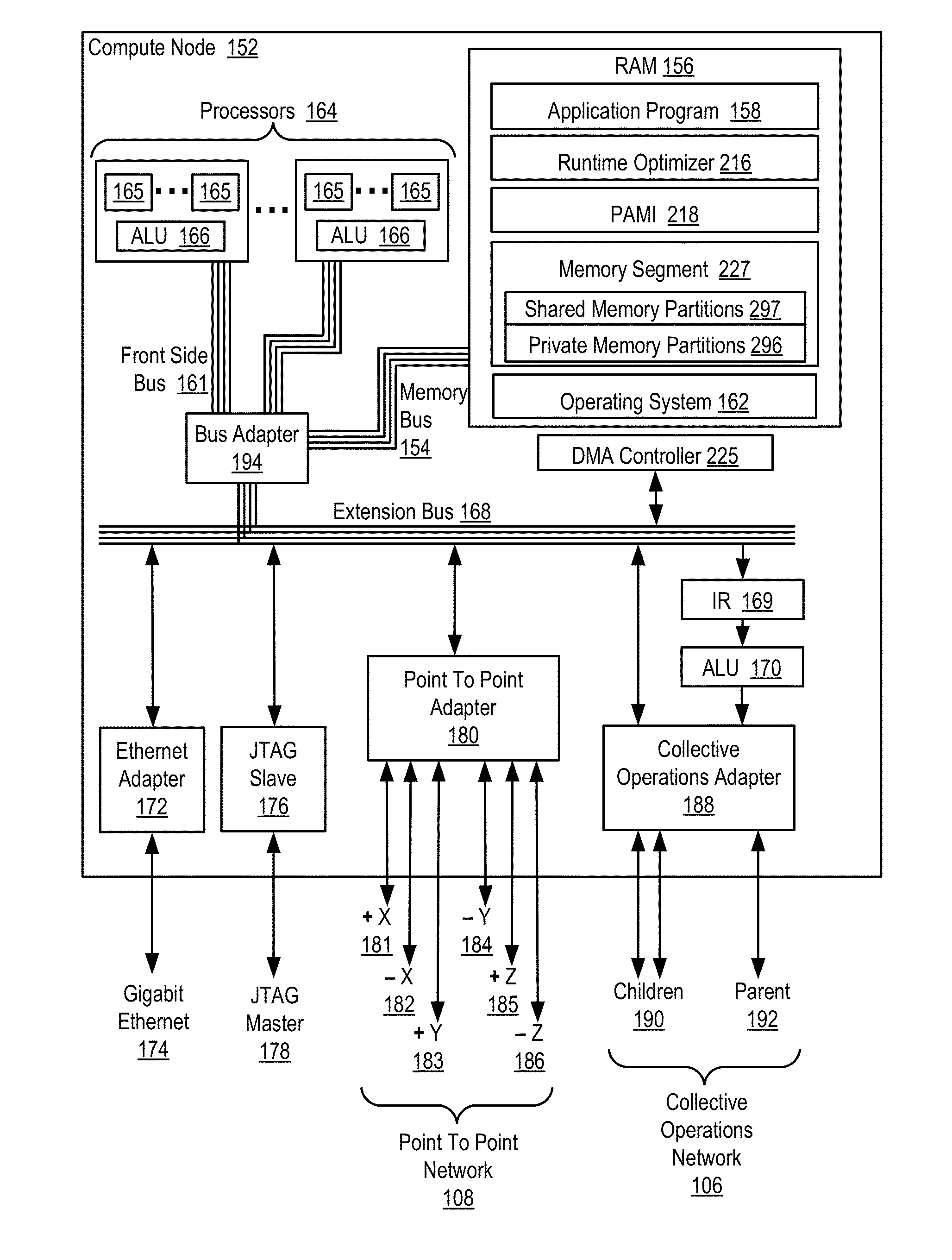
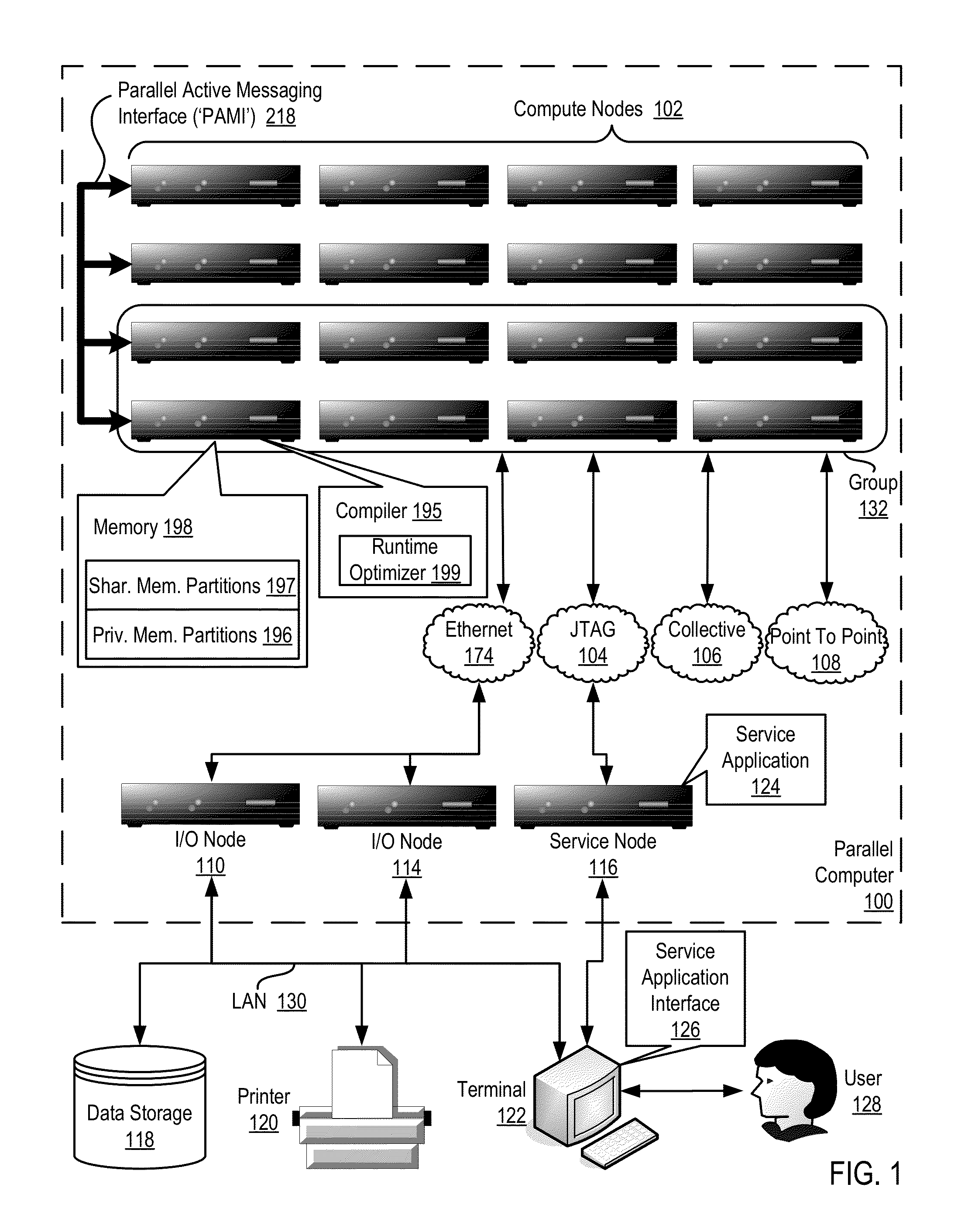
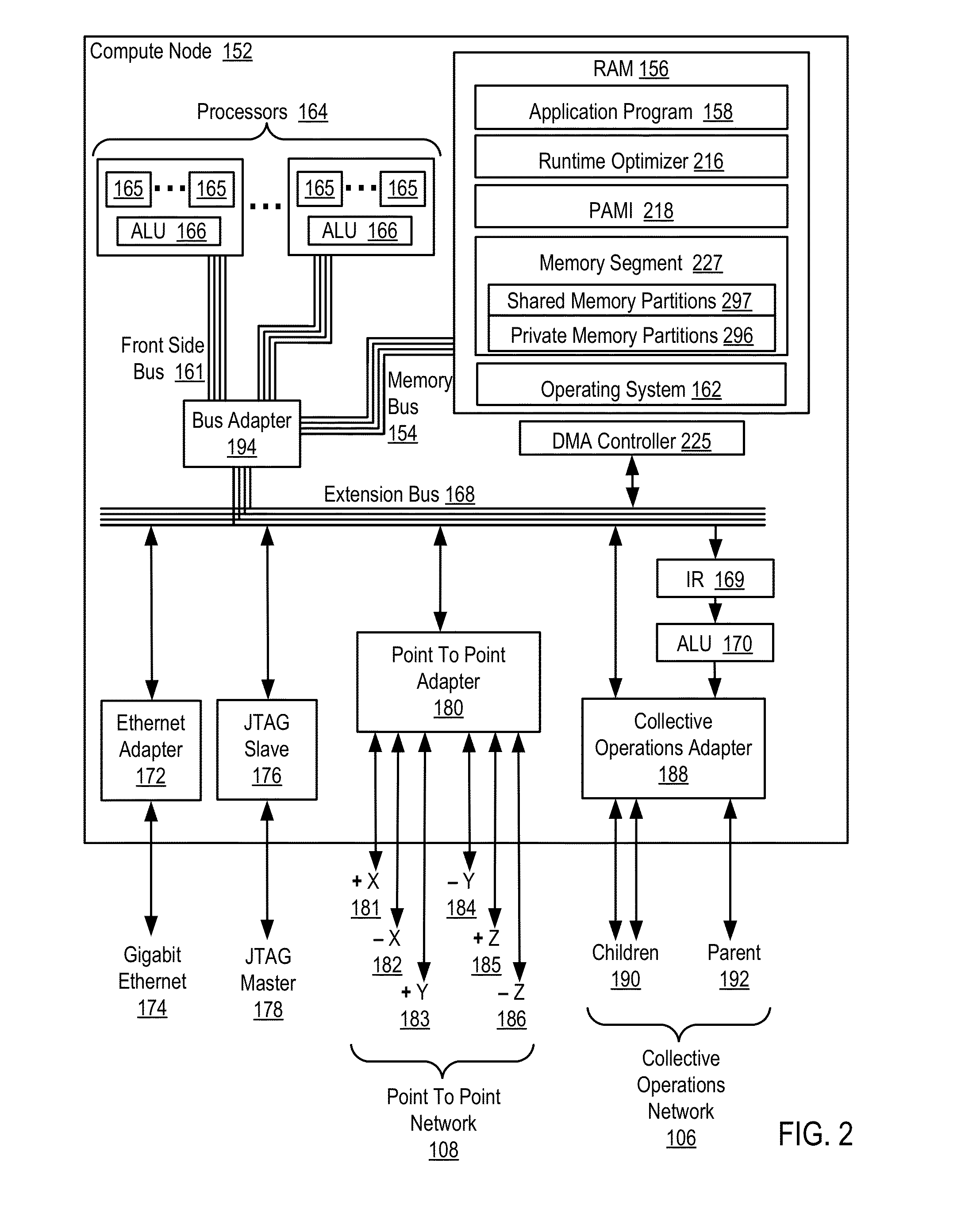
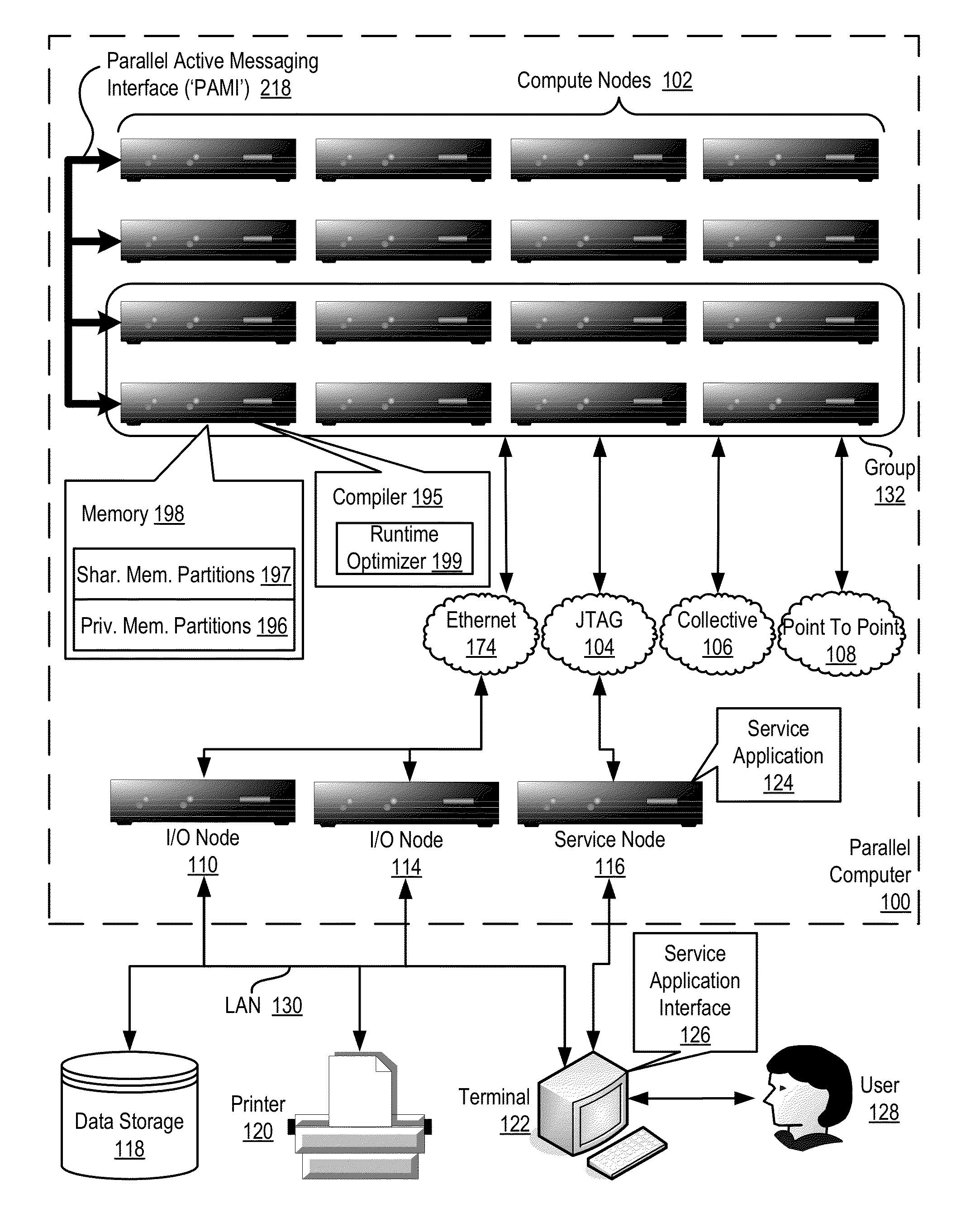
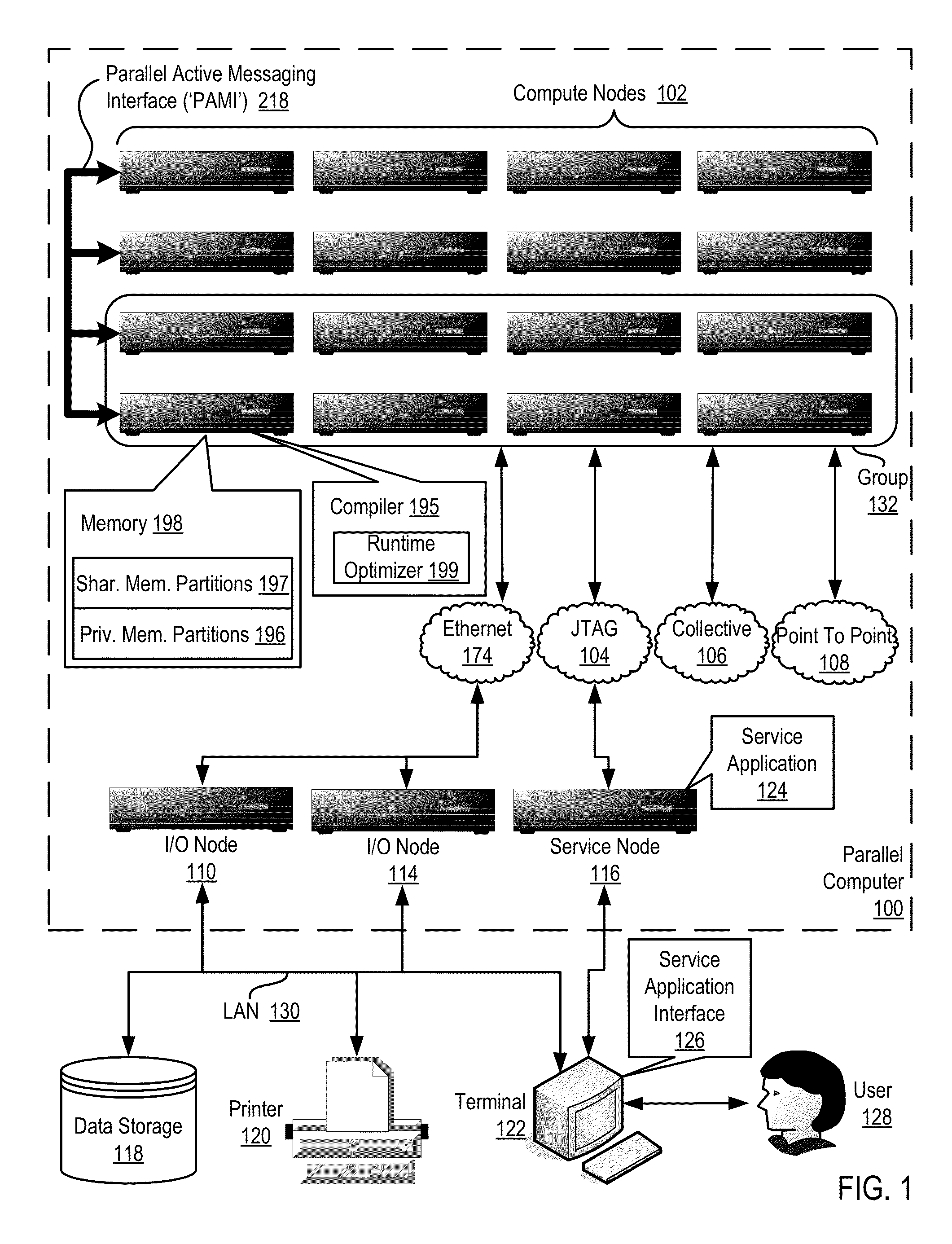
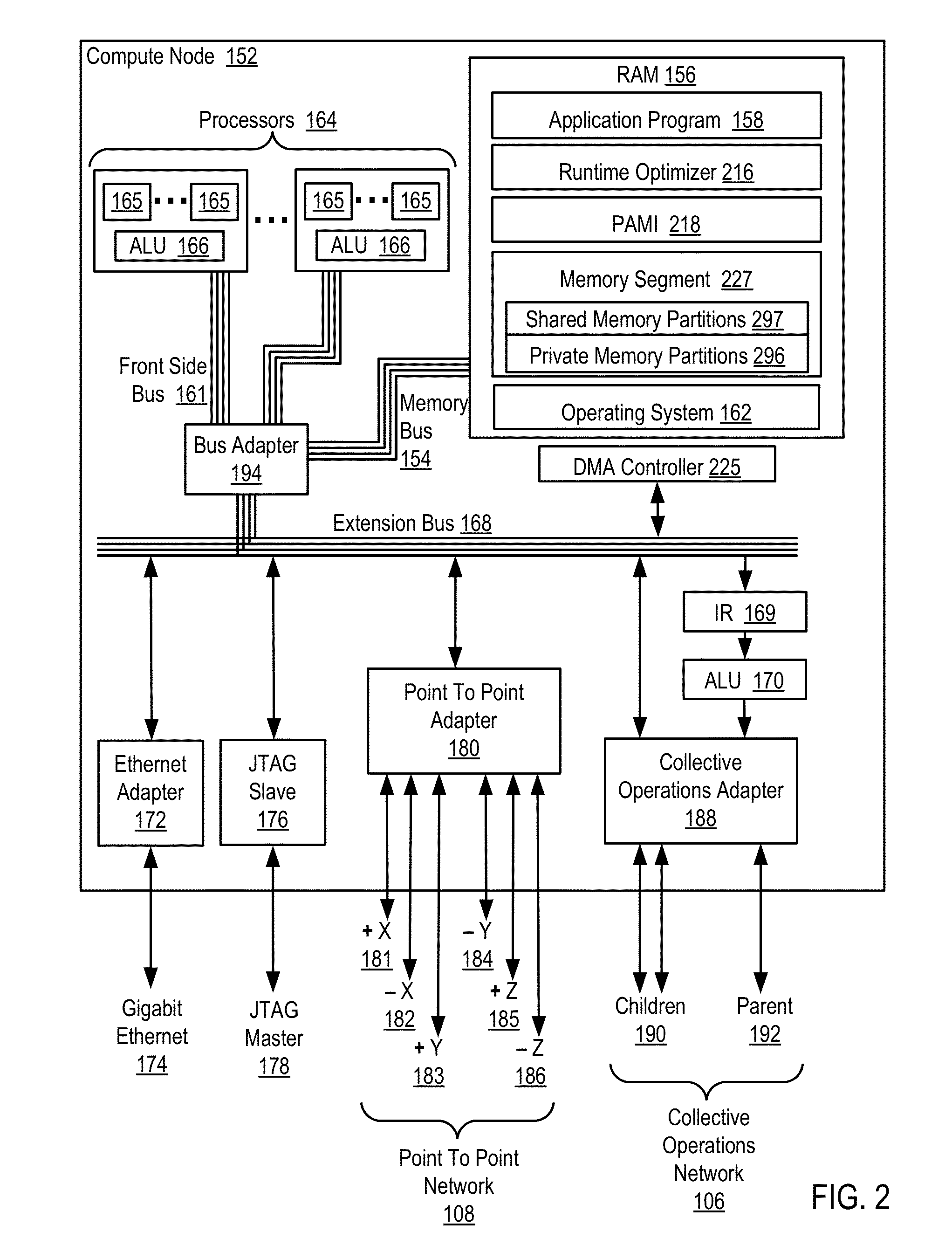
Conditionally updating shared variable directory (SVD) information in a parallel computer
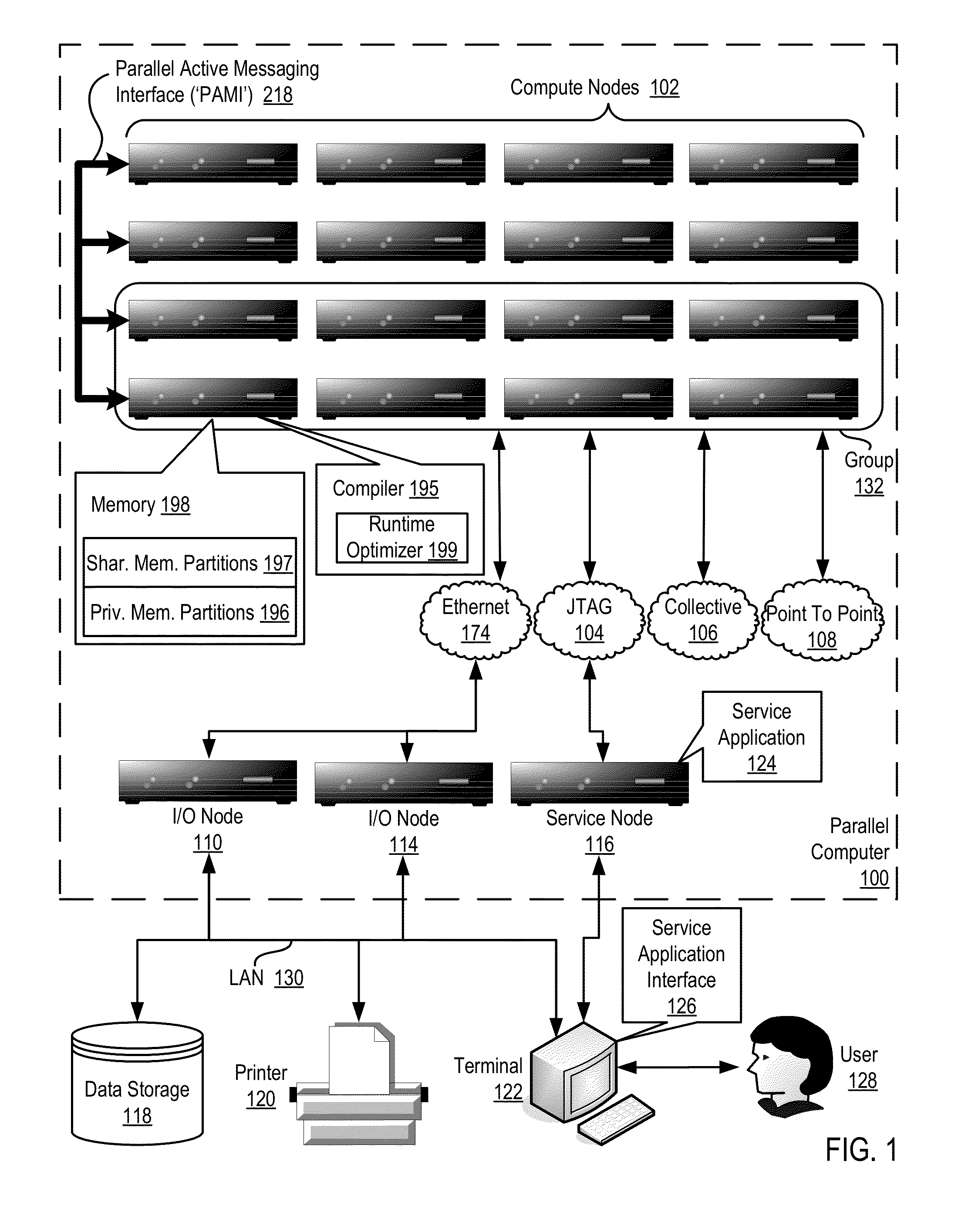
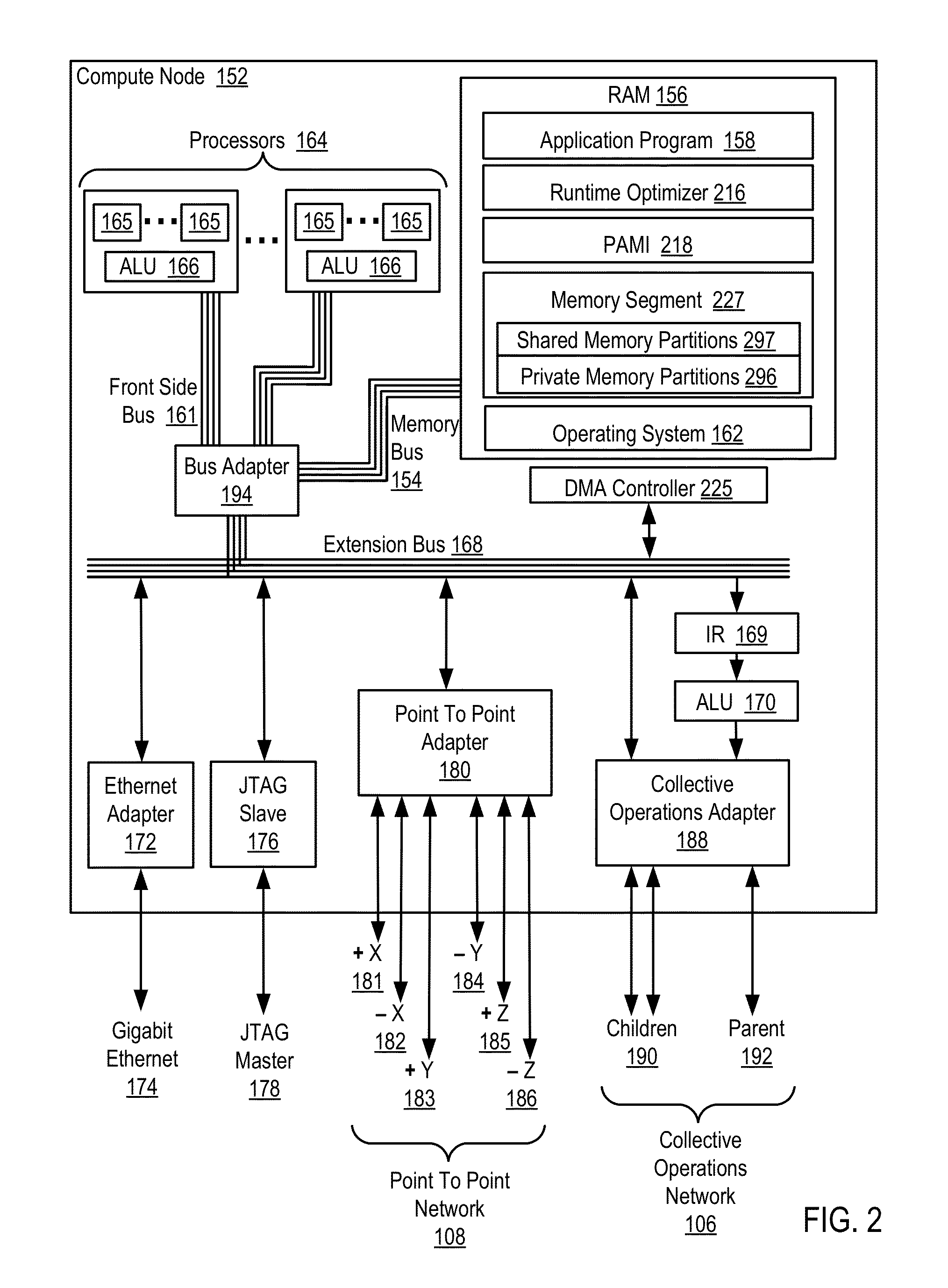
InactiveUS20140173604A1Database updatingMultiprogramming arrangementsParallel computingComputer program
Methods, parallel computers, and computer program products for conditionally updating shared variable directory (SVD) information in a parallel computer are provided. Embodiments include a runtime optimizer receiving a broadcast reduction operation header. The broadcast reduction operation header includes an SVD key and a first SVD address. The first SVD address is associated with the SVD key in a first SVD associated with a first task. Embodiments also include the runtime optimizer retrieving from a remote address cache associated with the second task, a second SVD address indicating a location within a memory partition associated with the first SVD, in response to receiving the broadcast reduction operation header. Embodiments also include the runtime optimizer determining that the first SVD address does not match the second SVD address and updating the remote address cache with the first SVD address.
Owner:IBM CORP
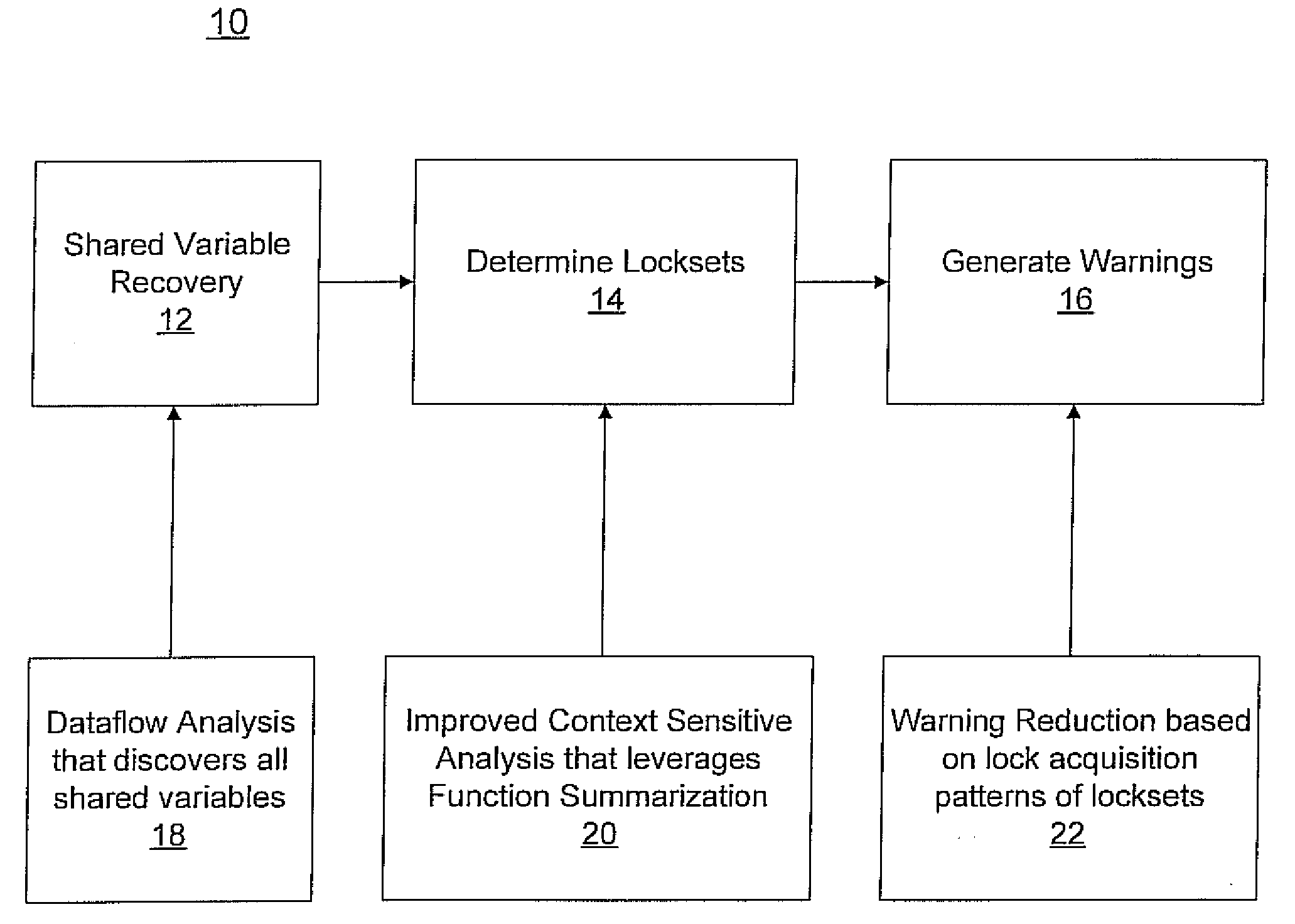
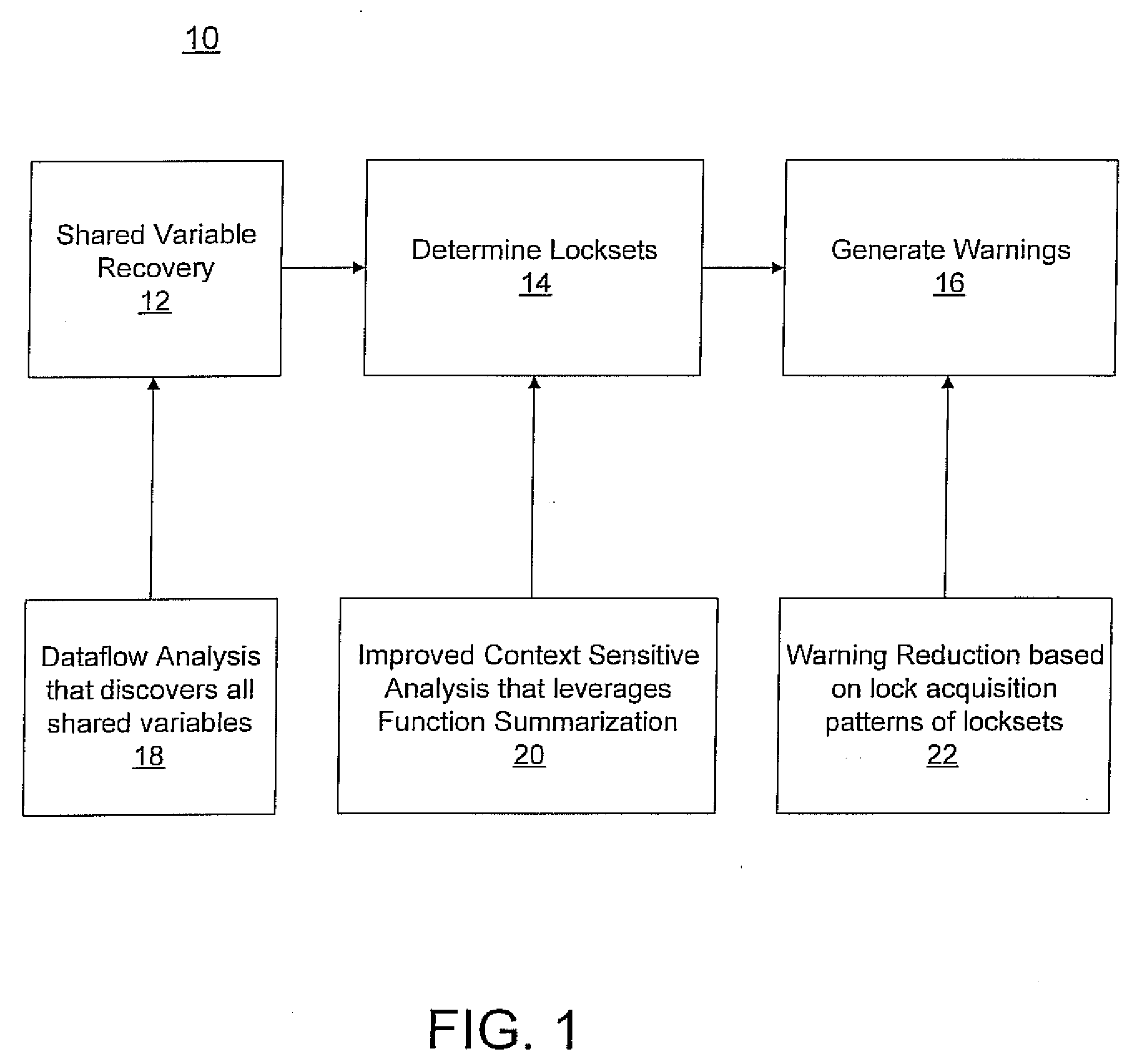
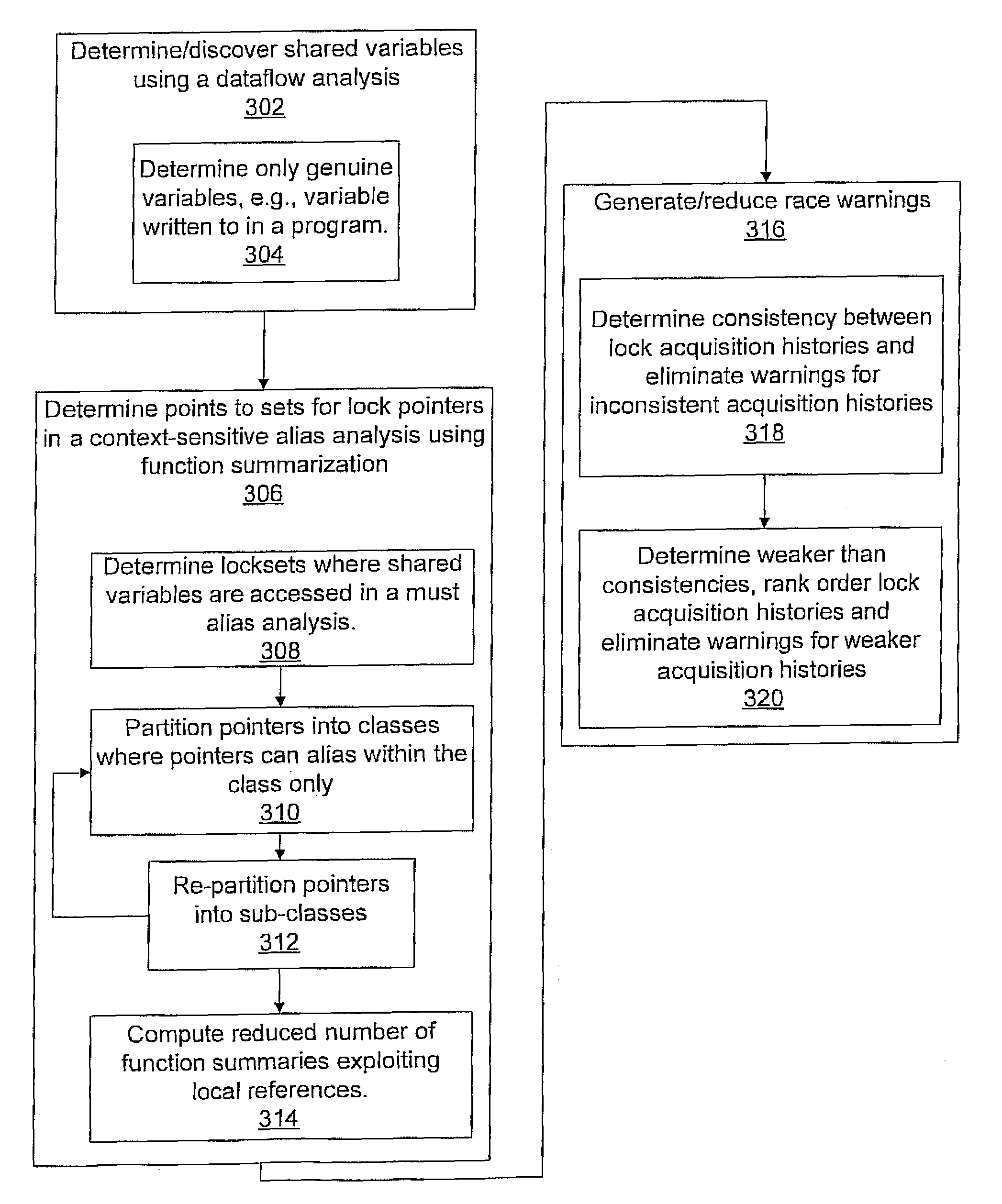
Fast and accurate static data-race detection for concurrent programs
ActiveUS20080178156A1Accurate analysisImprove scalabilityProgram synchronisationSoftware engineeringParallel computingContext sensitivity
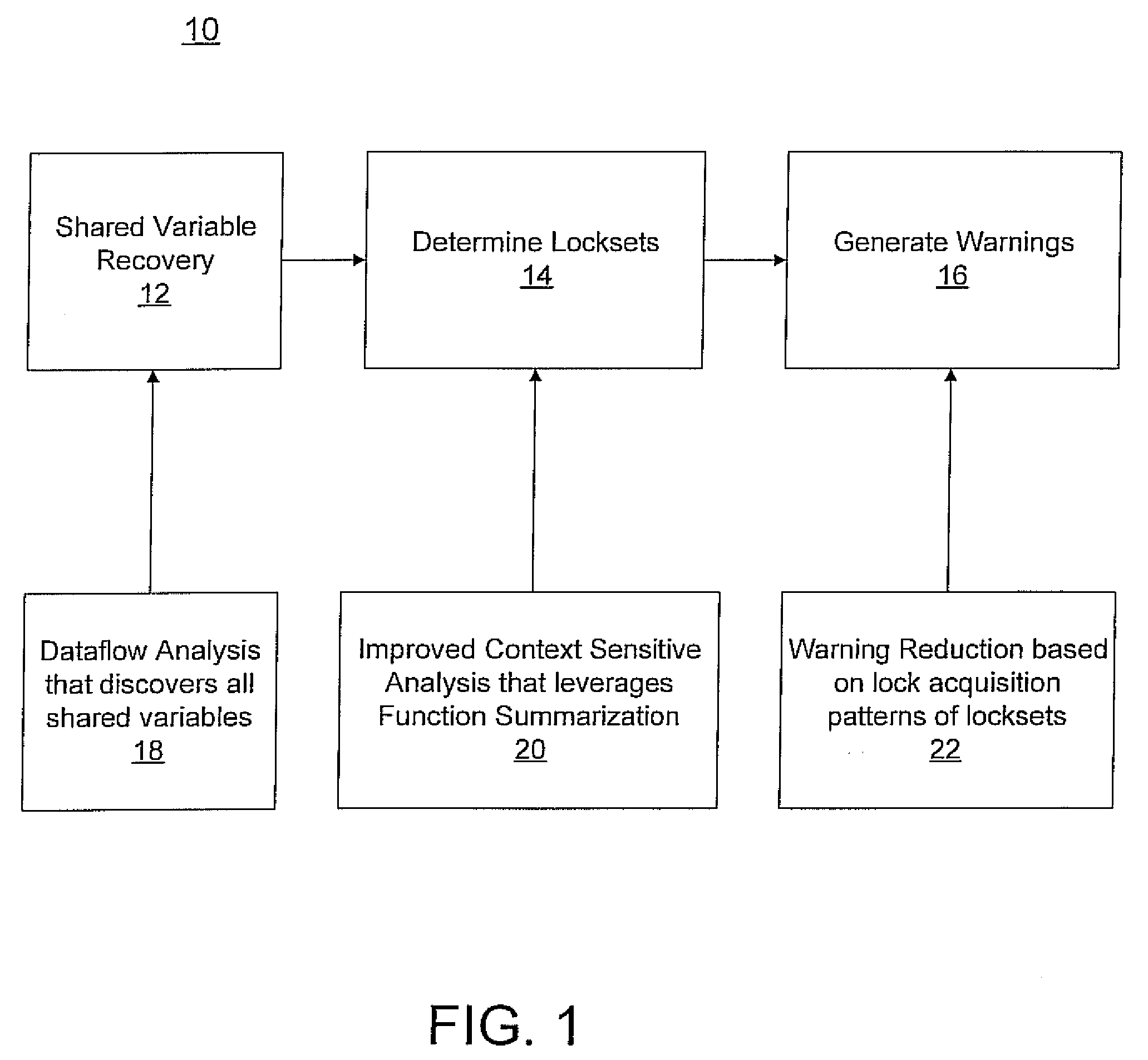
A system and method for race warning generation for computer program verification includes determining shared variables and determining context-sensitive points-to sets for lock pointers by focusing on pointers that may affect aliases of lock pointers, and by leveraging function summarization. Locksets are determined at locations where shared variables are accessed using the points-to sets for lock pointers. Warnings are based on disjointness of locksets.
Owner:NEC CORP
Program, apparatus and method for verifying program
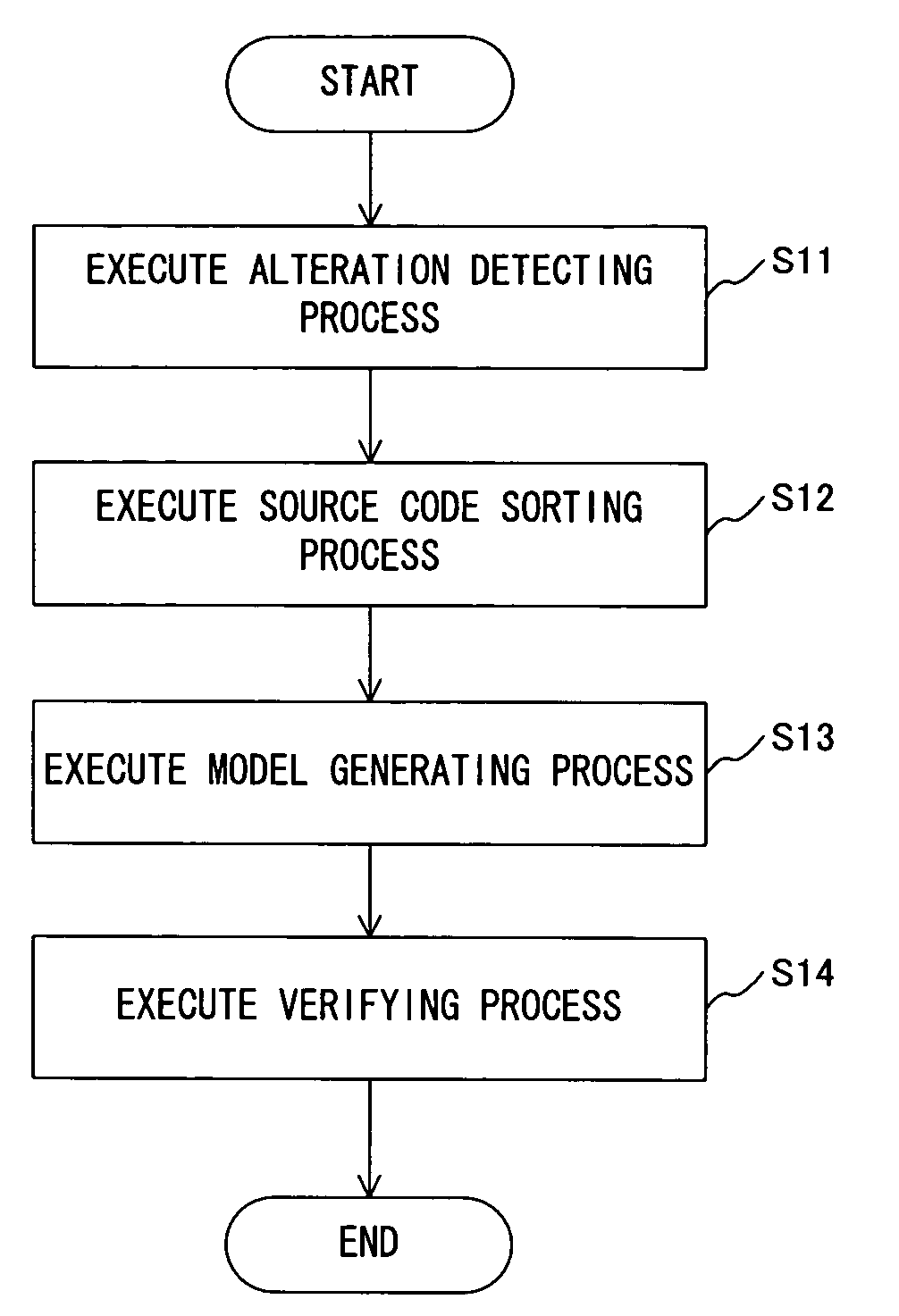
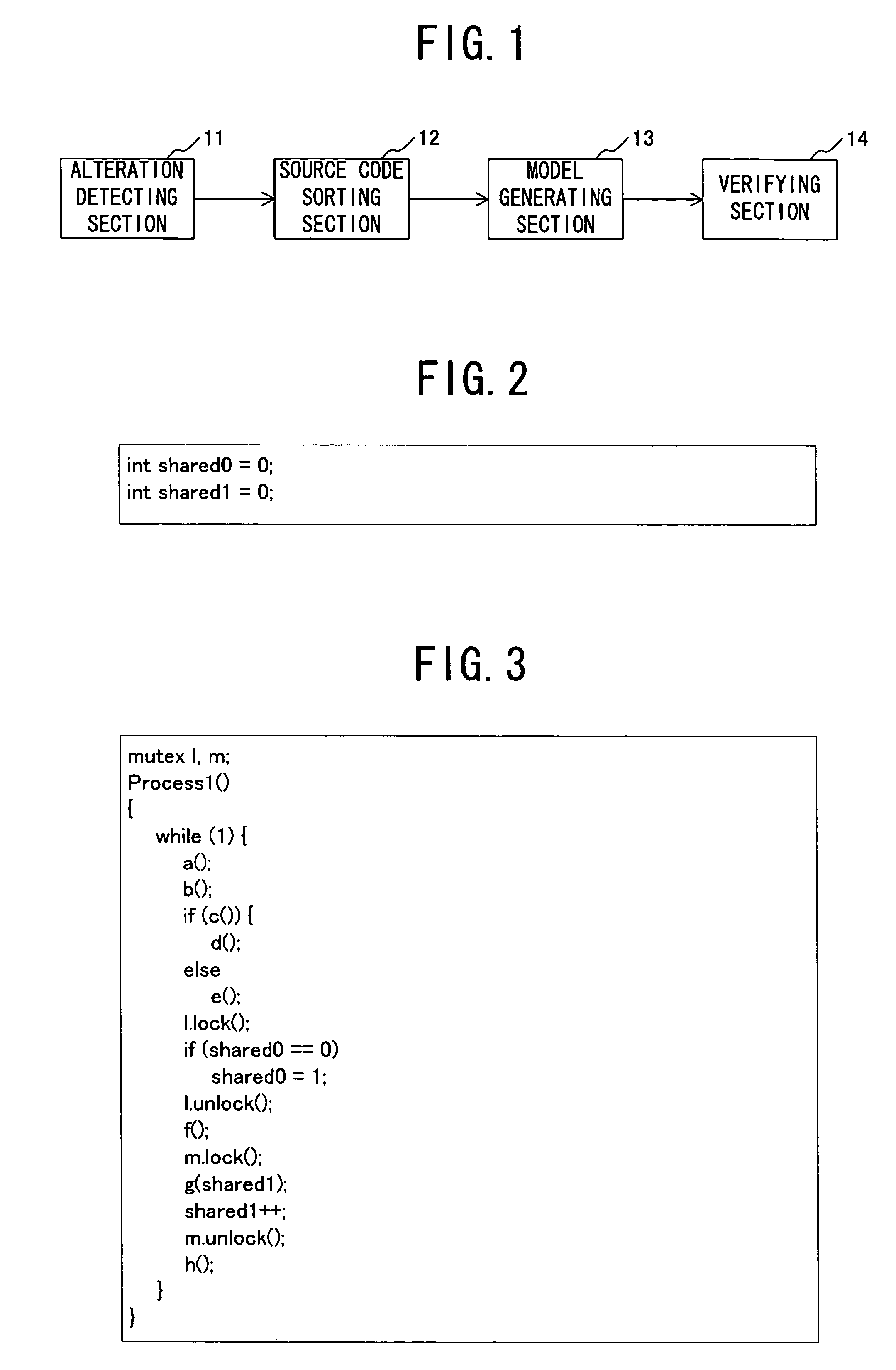
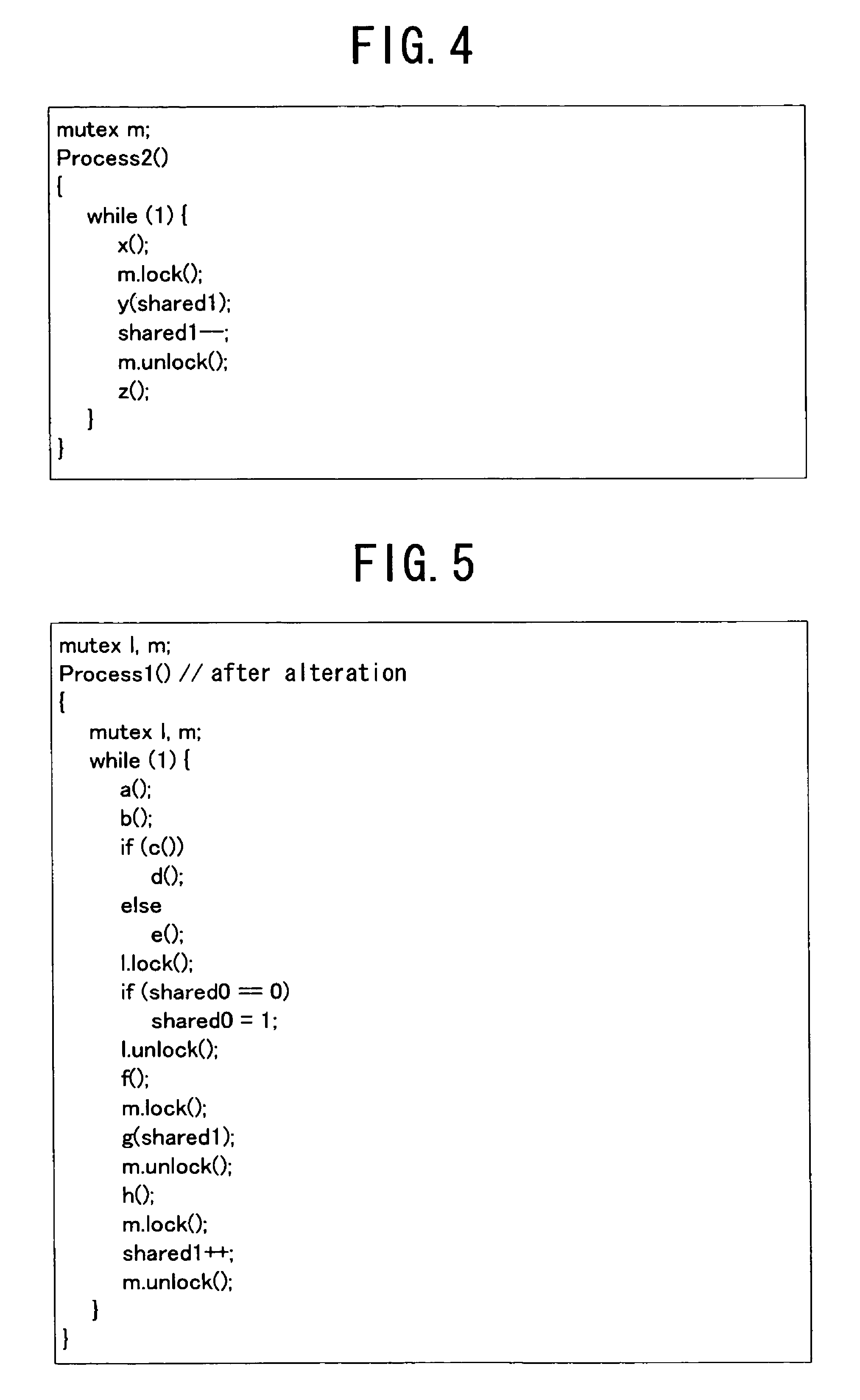
InactiveUS7844953B2Efficient verificationImprove efficiencyError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsVerified procedureGenerative model
A program, an apparatus and a method verify a program that efficiently verifies a concurrent / parallel program, allowing interactively debugging the current / parallel program. The program causes a computer to execute a detection step that detects the function that has been altered and the function that uses a shared variable influenced by the alteration out of the program to be verified before and after the alteration and also detects the part that is influenced by the alteration, the control structure part and the other parts, a model generation step that generates a model on the basis of the outcome of the detection in the detection step and a verification step that verifies the program to be verified after the alteration by comparing the model of the program to be verified before the alteration and the model of the program to be verified after the alteration.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Systems and methods for just-in-time state sharing
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Requesting shared variable directory (SVD) information from a plurality of threads in a parallel computer
InactiveUS20140173257A1Program synchronisationDigital computer detailsParallel computingComputer methods
Methods, parallel computers, and computer program products for requesting shared variable directory (SVD) information from a plurality of threads in a parallel computer are provided. Embodiments include a runtime optimizer detecting that a first thread requires a plurality of updated SVD information associated with shared resource data stored in a plurality of memory partitions. Embodiments also include a runtime optimizer broadcasting, in response to detecting that the first thread requires the updated SVD information, a gather operation message header to the plurality of threads. The gather operation message header indicates an SVD key corresponding to the required updated SVD information and a local address associated with the first thread to receive a plurality of updated SVD information associated with the SVD key. Embodiments also include the runtime optimizer receiving at the local address, the plurality of updated SVD information from the plurality of threads.
Owner:IBM CORP
Analyzing update conditions for shared variable directory information in a parallel computer
InactiveUS20140173204A1Software engineeringMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingCompare-and-swap
Methods, parallel computers, and computer program products for analyzing update conditions for shared variable directory (SVD) information in a parallel computer are provided. Embodiments include a runtime optimizer receiving a compare-and-swap operation header. The compare-and-swap operation header includes an SVD key, a first SVD address, and an updated first SVD address. The first SVD address is associated with the SVD key in a first SVD associated with a first task. Embodiments also include the runtime optimizer retrieving from a remote address cache associated with the second task, a second SVD address indicating a location within a memory partition associated with the first SVD in response to receiving the compare-and-swap operation header. Embodiments also include the runtime optimizer determining whether the second SVD address matches the first SVD address and transmitting a result indicating whether the second SVD address matches the first SVD address.
Owner:IBM CORP
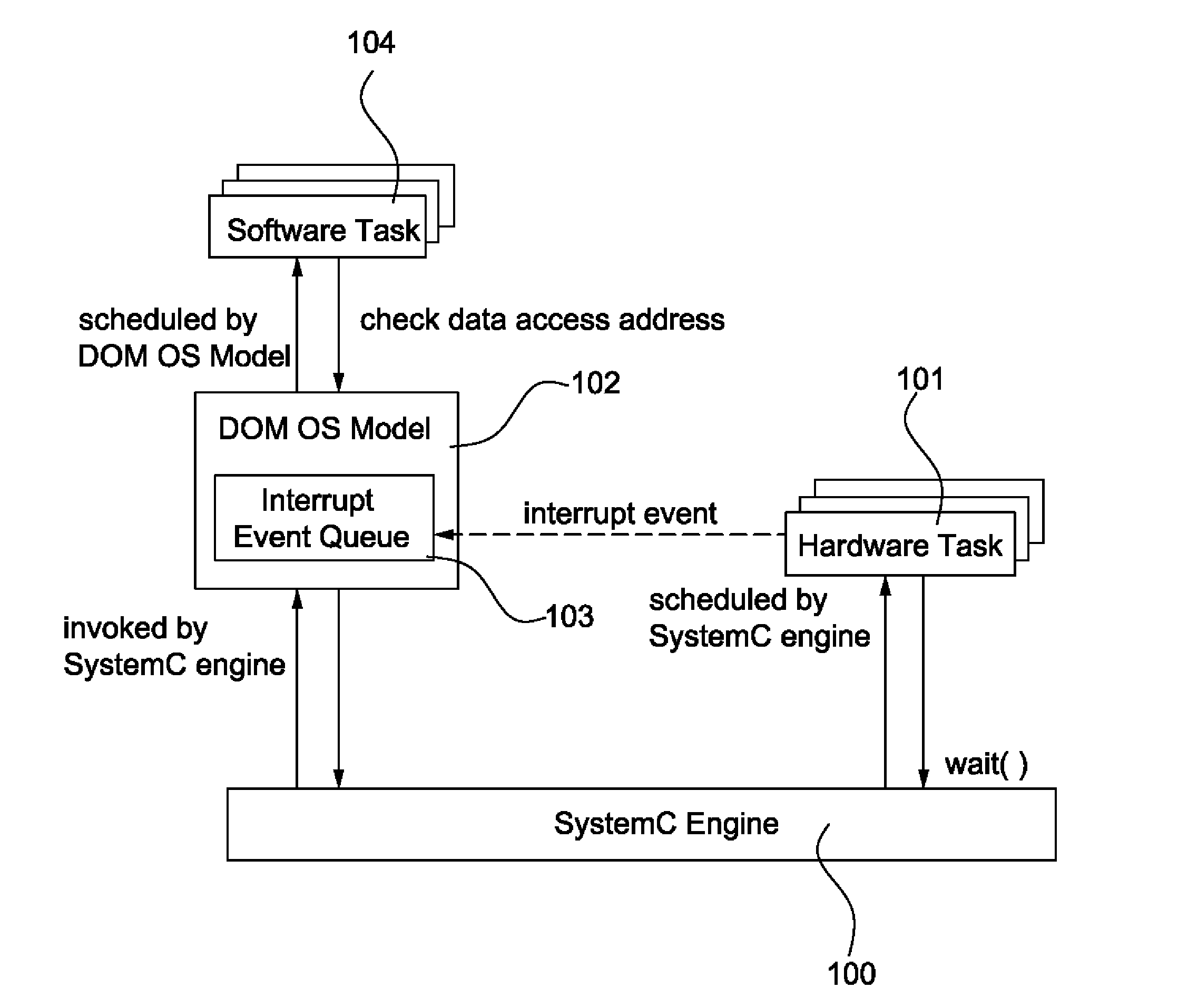
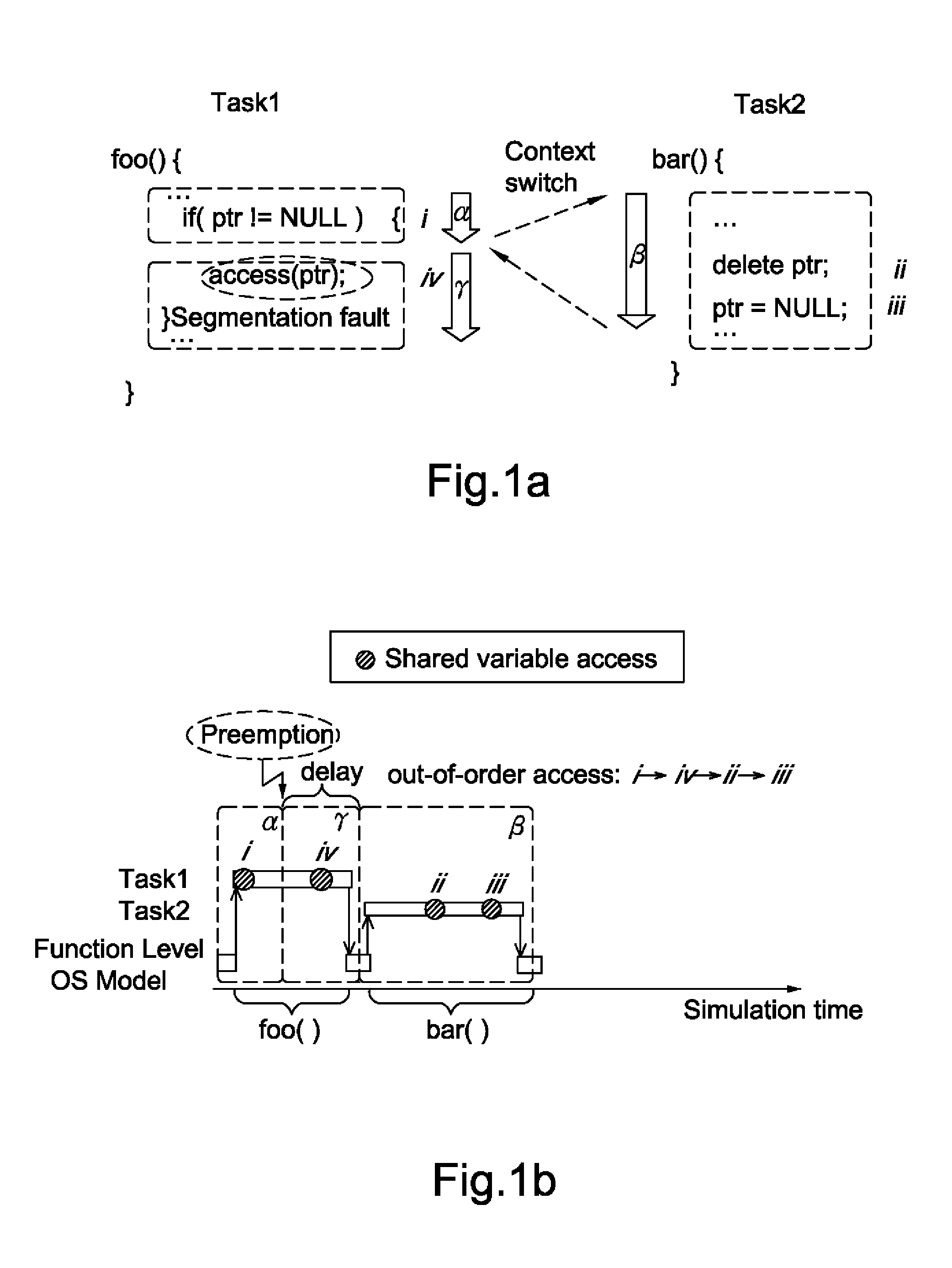
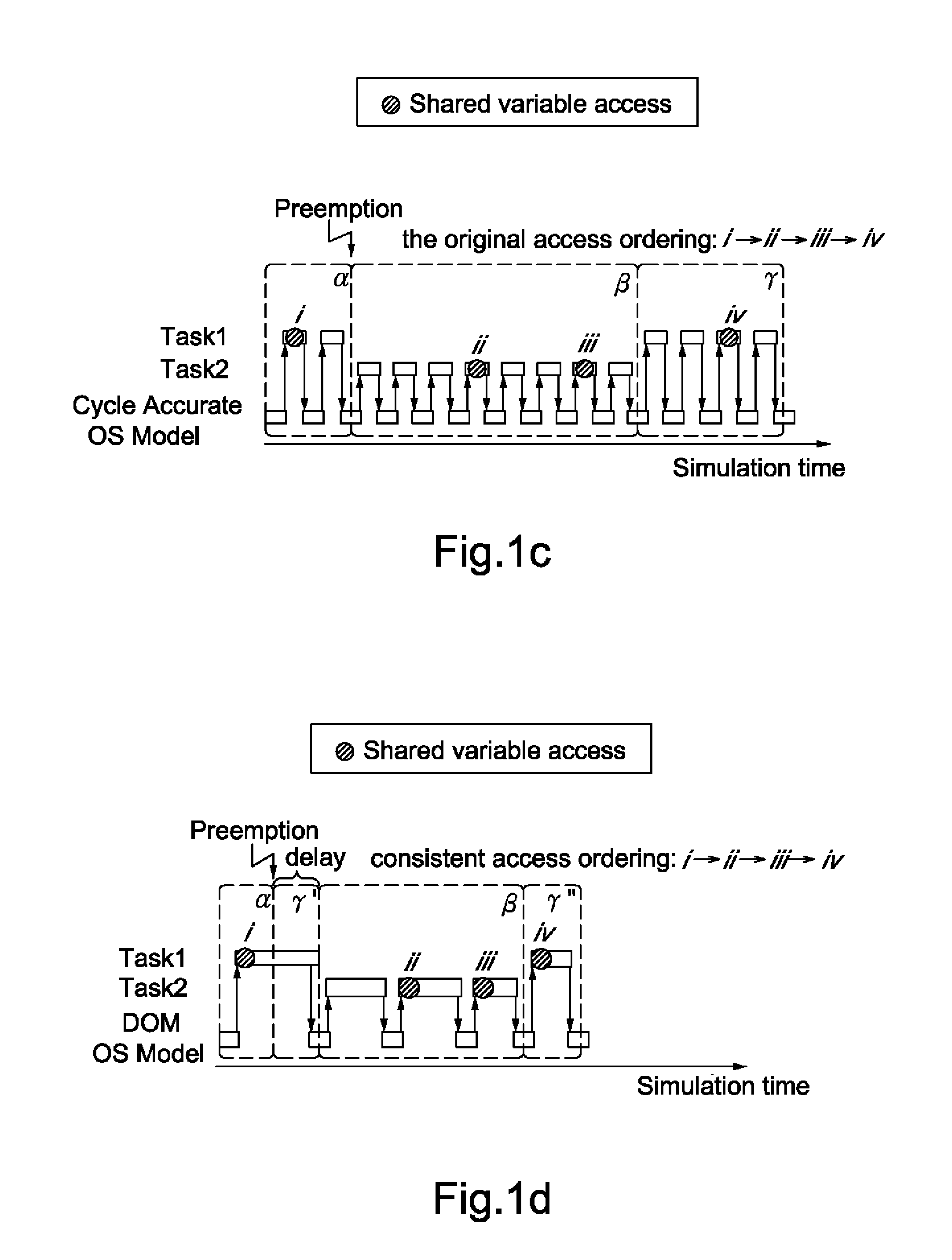
Data-dependency-Oriented Modeling Approach for Efficient Simulation of OS Preemptive Scheduling
InactiveUS20120197625A1Fast and accurate simulationReduce overheadCAD circuit designProgram controlSystemCSoftware
In the present disclosure, the DOM approach for the simulation of OS preemptive scheduling has presented and demonstrated. By maintaining the data-dependency between the software tasks, and guaranteeing the order of shared variable accesses, it can accurately simulate the preemption effect. Moreover, the proposed DOM OS model is implemented to enable preemptive scheduling in SystemC.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Requesting shared variable directory (SVD) information from a plurality of threads in a parallel computer
Methods, parallel computers, and computer program products for requesting shared variable directory (SVD) information from a plurality of threads in a parallel computer are provided. Embodiments include a runtime optimizer detecting that a first thread requires a plurality of updated SVD information associated with shared resource data stored in a plurality of memory partitions. Embodiments also include a runtime optimizer broadcasting, in response to detecting that the first thread requires the updated SVD information, a gather operation message header to the plurality of threads. The gather operation message header indicates an SVD key corresponding to the required updated SVD information and a local address associated with the first thread to receive a plurality of updated SVD information associated with the SVD key. Embodiments also include the runtime optimizer receiving at the local address, the plurality of updated SVD information from the plurality of threads.
Owner:IBM CORP
Thread lock optimization method
InactiveCN105975349AReduce conflictAvoid synchronization overheadProgram synchronisationOccupancy rateParallel computing
The present invention provides a thread lock optimization method. The method comprises the following steps: determining a key section in a memory; and using a synchronization primitive provided by the CPU, controlling a thread lock to take charge of protecting the key section, before a thread enters the key section, allowing to obtain the access right of the thread lock firstly, and ensuring that at the same time only one thread can enter the key section. The key section is a memory space stored with shared variables, and the determination of the key section is designated by a user. According to the thread lock optimization method disclosed by the present invention, the synchronization expense between the common lock threads in the original universal system is avoided, only a small number of CPU primitives is used, safety between threads is realized, the rate is increased by a hundred times, and performance of synchronous parallel access to the same locked area is improved by at least a hundred times, so that the performance is significantly enhanced, the CPU occupancy rate is significantly reduced, and the conflict between the threads is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING INTELLIGENT STEWARD CO LTD
Fast and accurate static data-race detection for concurrent programs
ActiveUS8185875B2Accurately determinedEfficiently determinedProgram synchronisationSoftware engineeringContext sensitivityComputer program
A system and method for race warning generation for computer program verification includes determining shared variables and determining context-sensitive points-to sets for lock pointers by focusing on pointers that may affect aliases of lock pointers, and by leveraging function summarization. Locksets are determined at locations where shared variables are accessed using the points-to sets for lock pointers. Warnings are based on disjointness of locksets.
Owner:NEC CORP
Acquiring remote shared variable directory information in a parallel computer
InactiveUS20140173212A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationProgram controlParallel computingData storing
Methods, parallel computers, and computer program products for acquiring remote shared variable directory (SVD) information in a parallel computer are provided. Embodiments include a runtime optimizer determining that a first thread of a first task requires shared resource data stored in a memory partition corresponding to a second thread of a second task. Embodiments also include the runtime optimizer requesting from the second thread, in response to determining that the first thread of the first task requires the shared resource data, SVD information associated with the shared resource data. Embodiments also include the runtime optimizer receiving from the second thread, the SVD information associated with the shared resource data.
Owner:IBM CORP
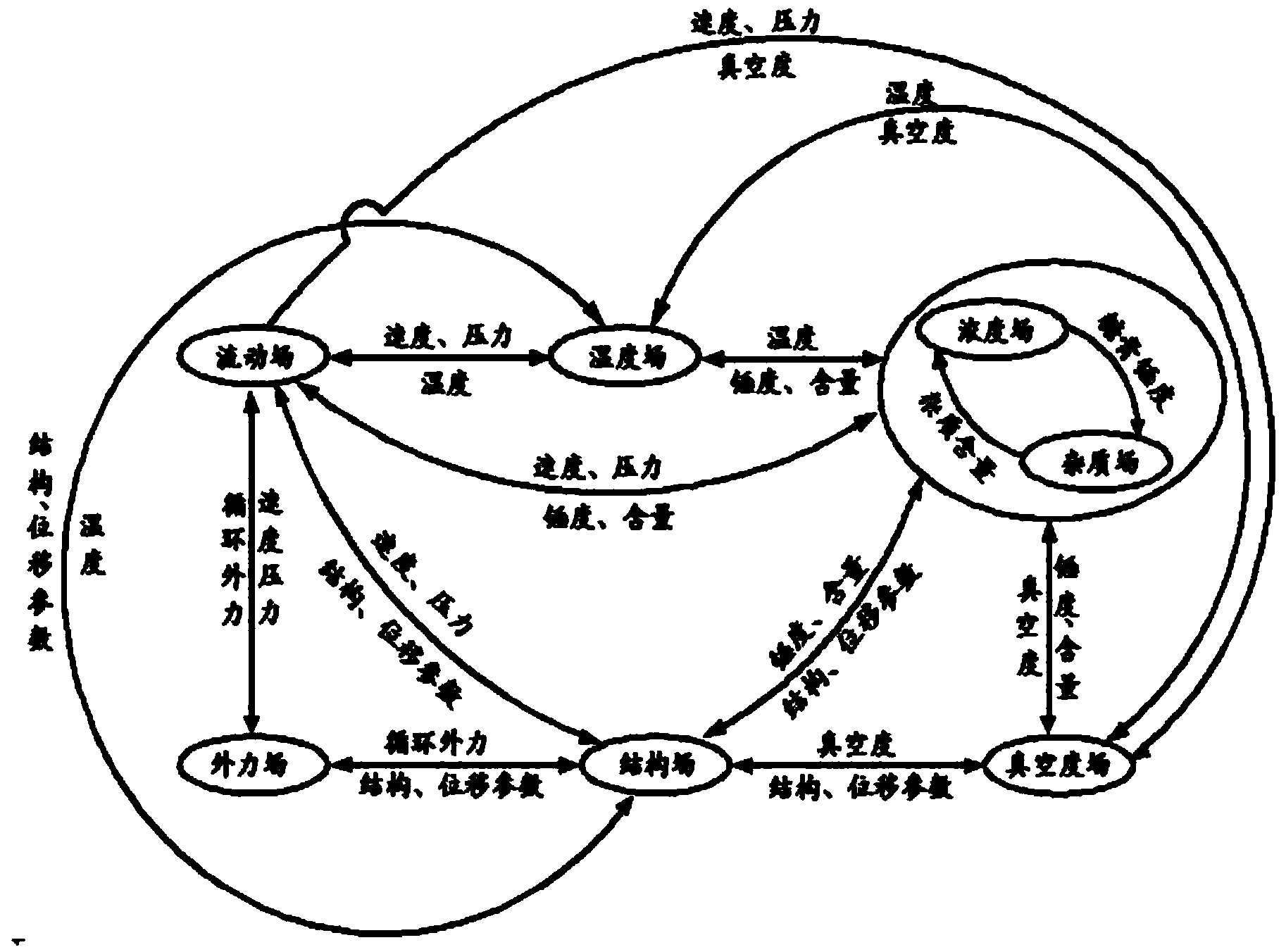
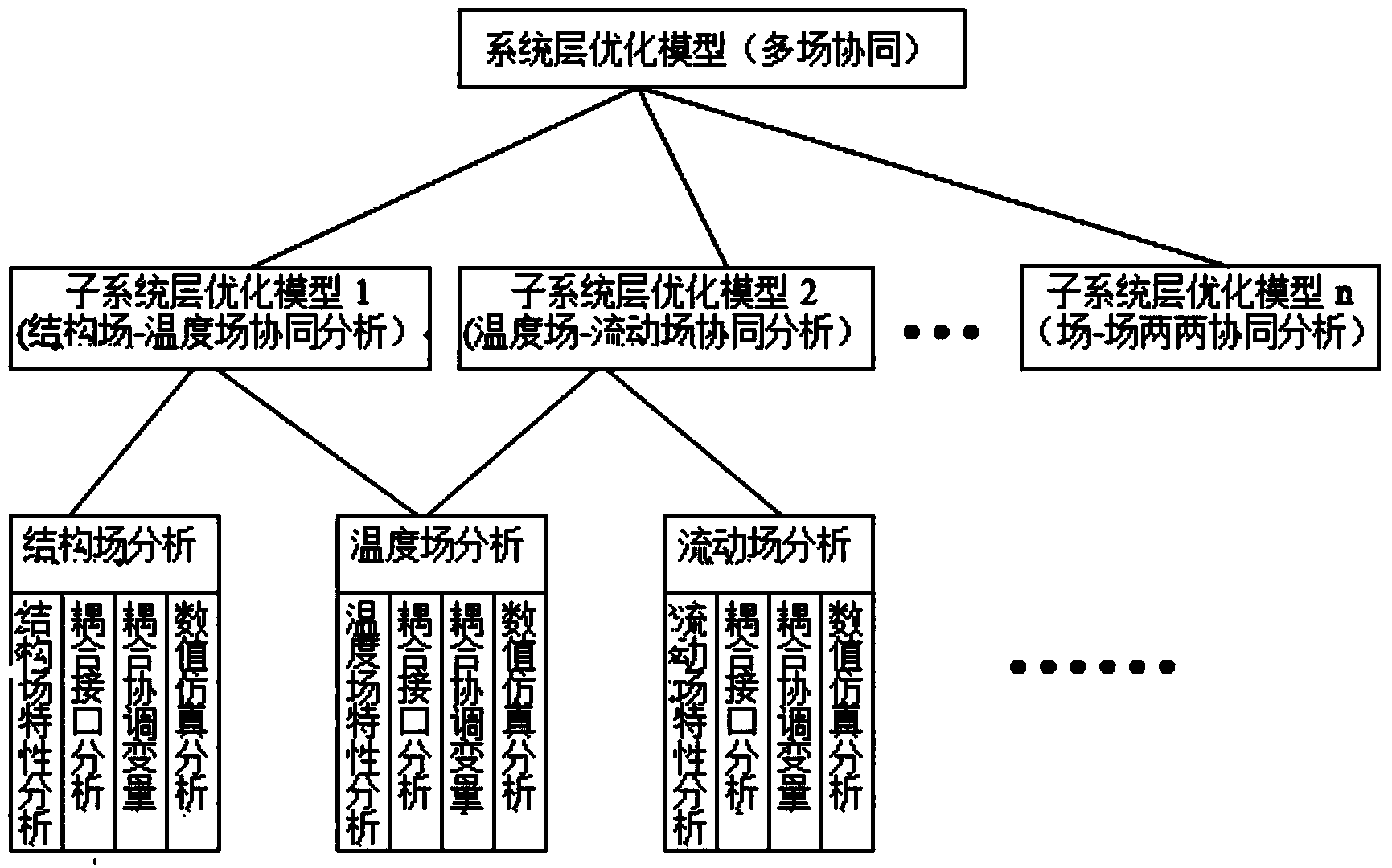
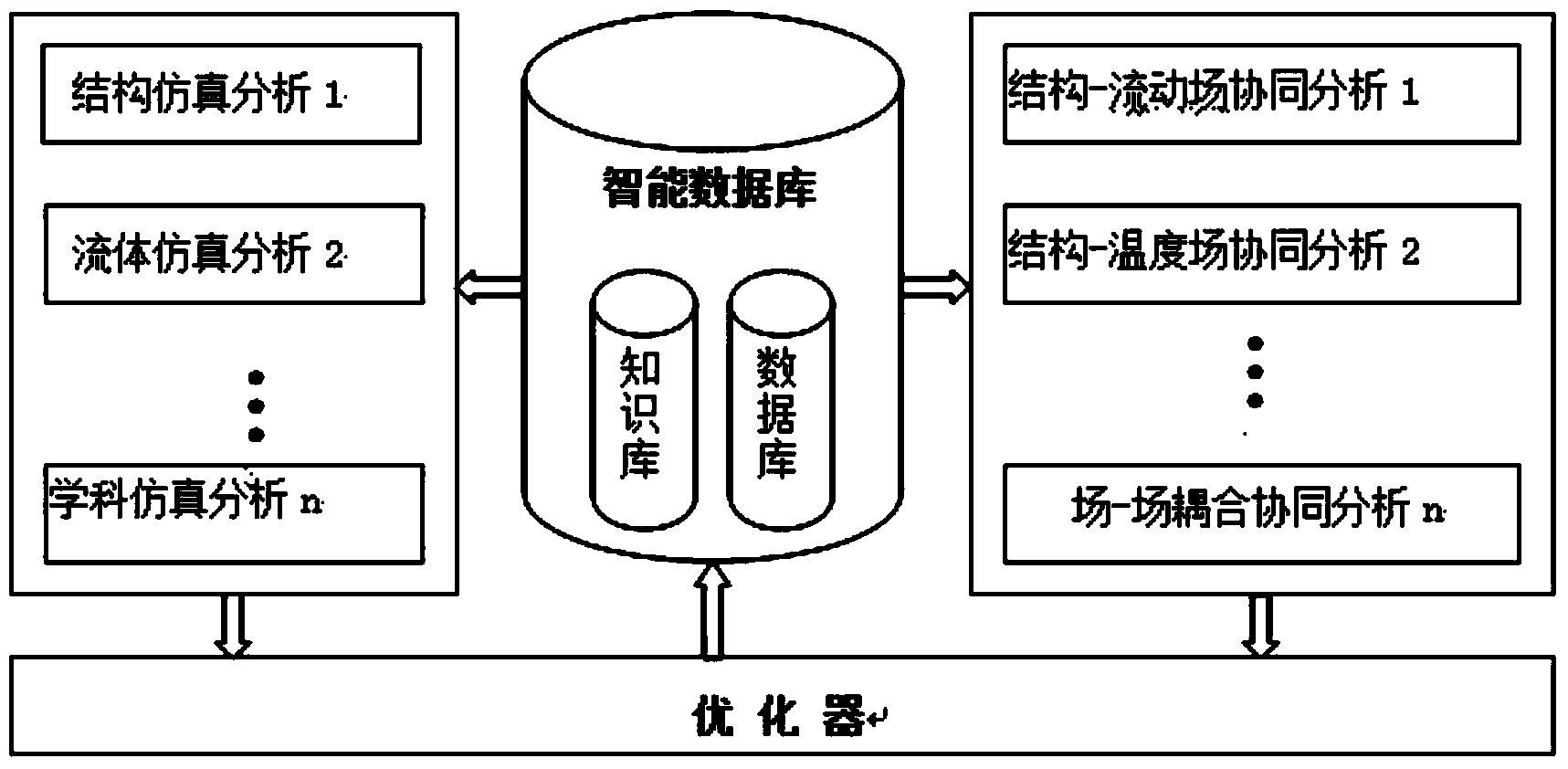
Sugarcane sugar boiling equipment optimizing design modeling and modeling method based on field synergy principle
ActiveCN103761383AIncrease productionQuality improvementSpecial data processing applicationsPhysical fieldField analysis
The invention provides a sugarcane sugar boiling equipment optimizing design modeling and modeling method based on the field synergy principle. The modeling comprises a subsystem analysis model, a subsystem optimization model and a system optimization model. The subsystem analysis model is used for analyzing a single physical field to form a module with certain functions; the module comprises field analysis, field coupling interface analysis, field coupling coordination variables and numerical simulation analysis. The subsystem optimization model is used for analyzing two different physical field coupling coordination in the subsystem analysis model; the target function is a minimized optimized function of the difference between coupling variables and shared variables, and constraint condition is the constraint of the system; the system optimization model is used for overall coordinating the system with a plurality of physical fields for boiling sugar coordinately, and constraint condition is consistent constraints of the coupling variables and shared variables of each subsystem. By the aid of the modeling method, structure, parameters and operating parameters of the batch-type sugar boiling equipment can be designed optimally, quantity of sugar is increased, quality of sugar is improved, sugar boiling time is shortened, and energy consumption is reduced.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Acquiring remote shared variable directory information in a parallel computer
InactiveUS20140173201A1Resource allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationShared variablesComputer program
Methods, parallel computers, and computer program products for acquiring remote shared variable directory (SVD) information in a parallel computer are provided. Embodiments include a runtime optimizer determining that a first thread of a first task requires shared resource data stored in a memory partition corresponding to a second thread of a second task. Embodiments also include the runtime optimizer requesting from the second thread, in response to determining that the first thread of the first task requires the shared resource data, SVD information associated with the shared resource data. Embodiments also include the runtime optimizer receiving from the second thread, the SVD information associated with the shared resource data.
Owner:IBM CORP
Broadcasting shared variable directory (SVD) information in a parallel computer
InactiveUS20140173629A1Program synchronisationInterprogram communicationComputational scienceConcurrent computation
Methods, parallel computers, and computer program products for broadcasting shared variable directory (SVD) information in a parallel computer are provided. Embodiments include a runtime optimizer detecting, by a runtime optimizer of the parallel computer, a change in SVD information within an SVD associated with a first thread. Embodiments also include a runtime optimizer identifying a plurality of threads requiring notification of the change in the SVD information. Embodiments also include the runtime optimizer in response to detecting the change in the SVD information, broadcasting to each thread of the identified plurality of threads, a broadcast message header and update data indicating the change in the SVD information.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com