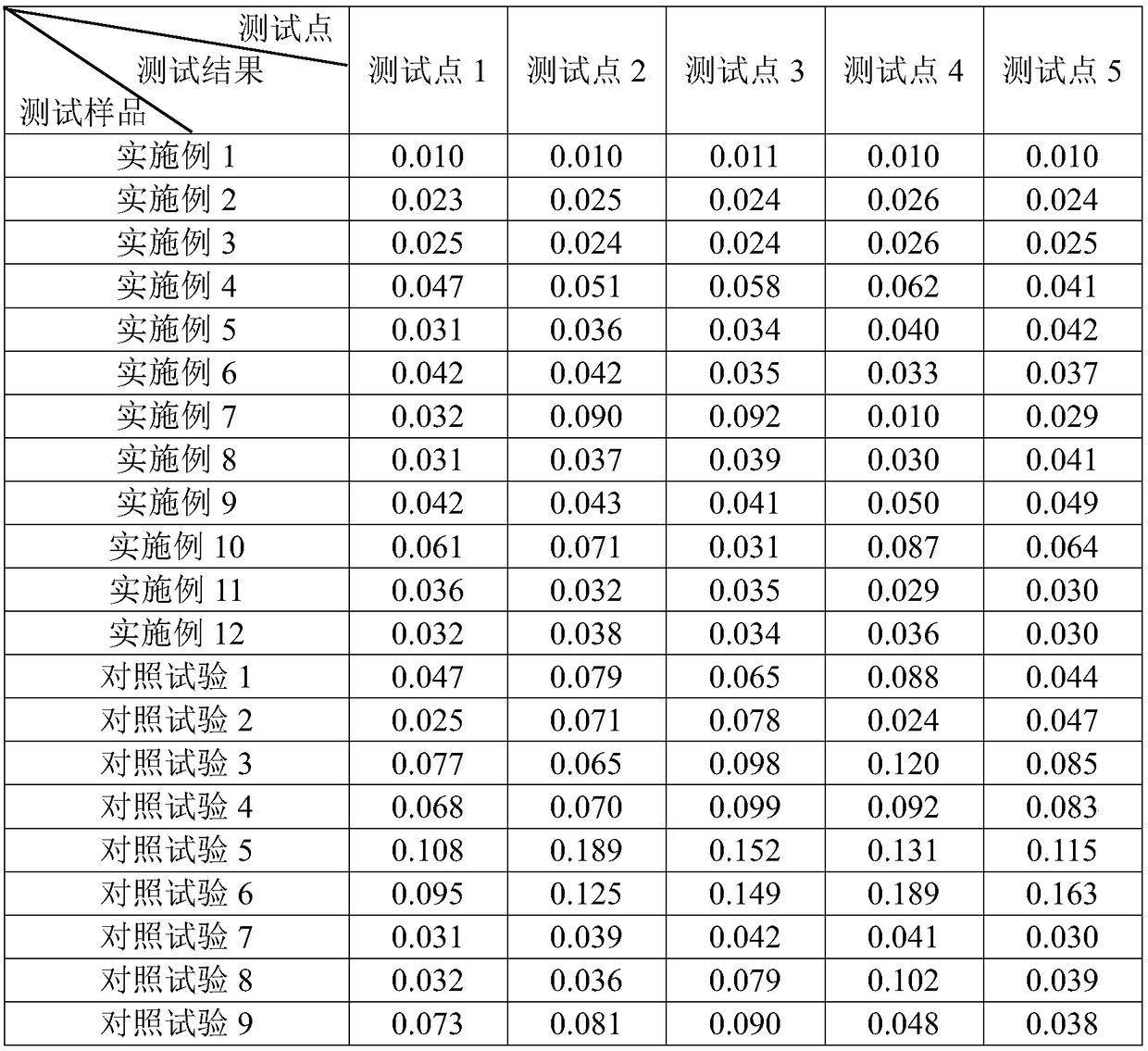
Patents
Literature
33results about How to "Smooth surface roughness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
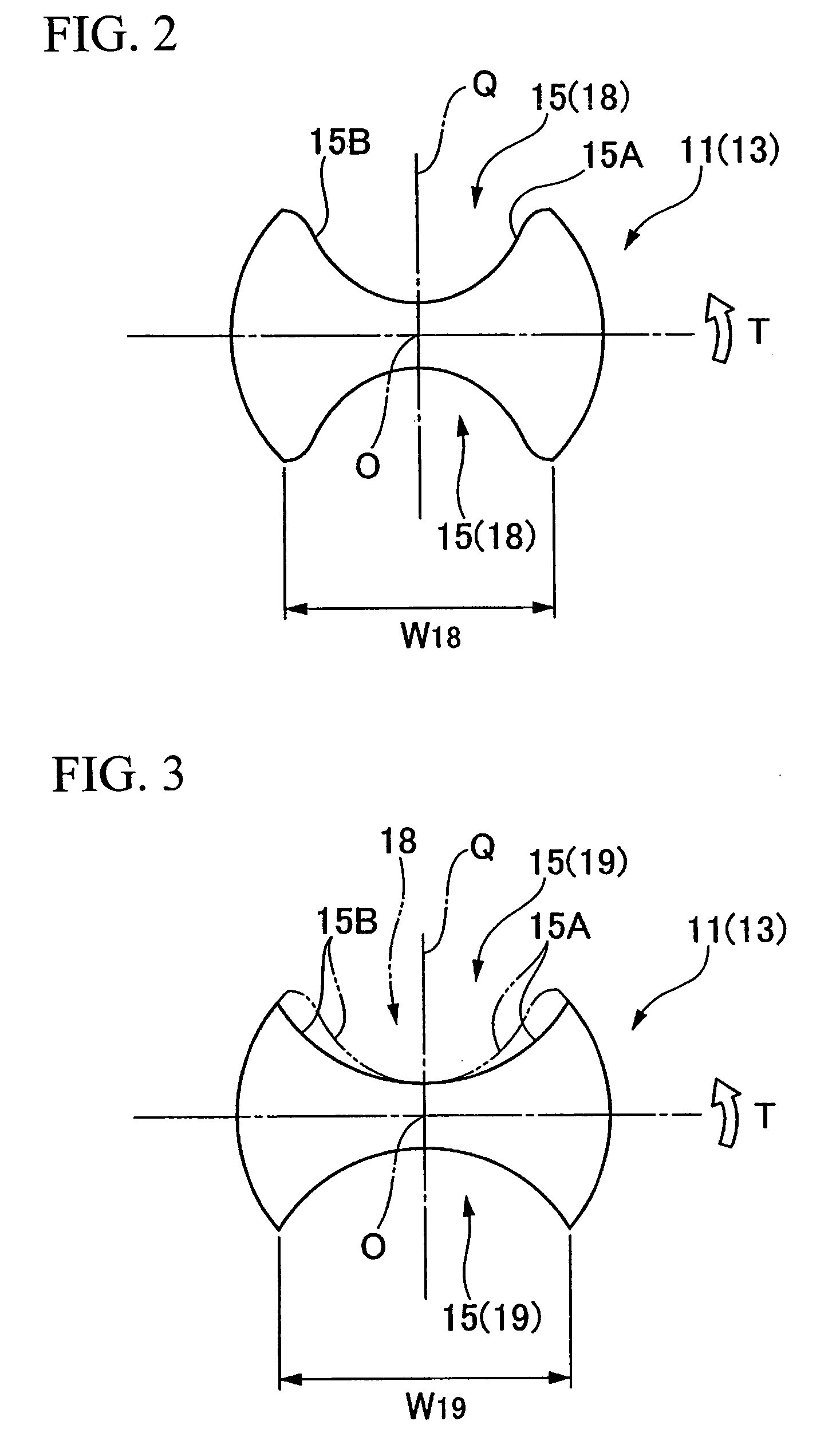
Gate oxides
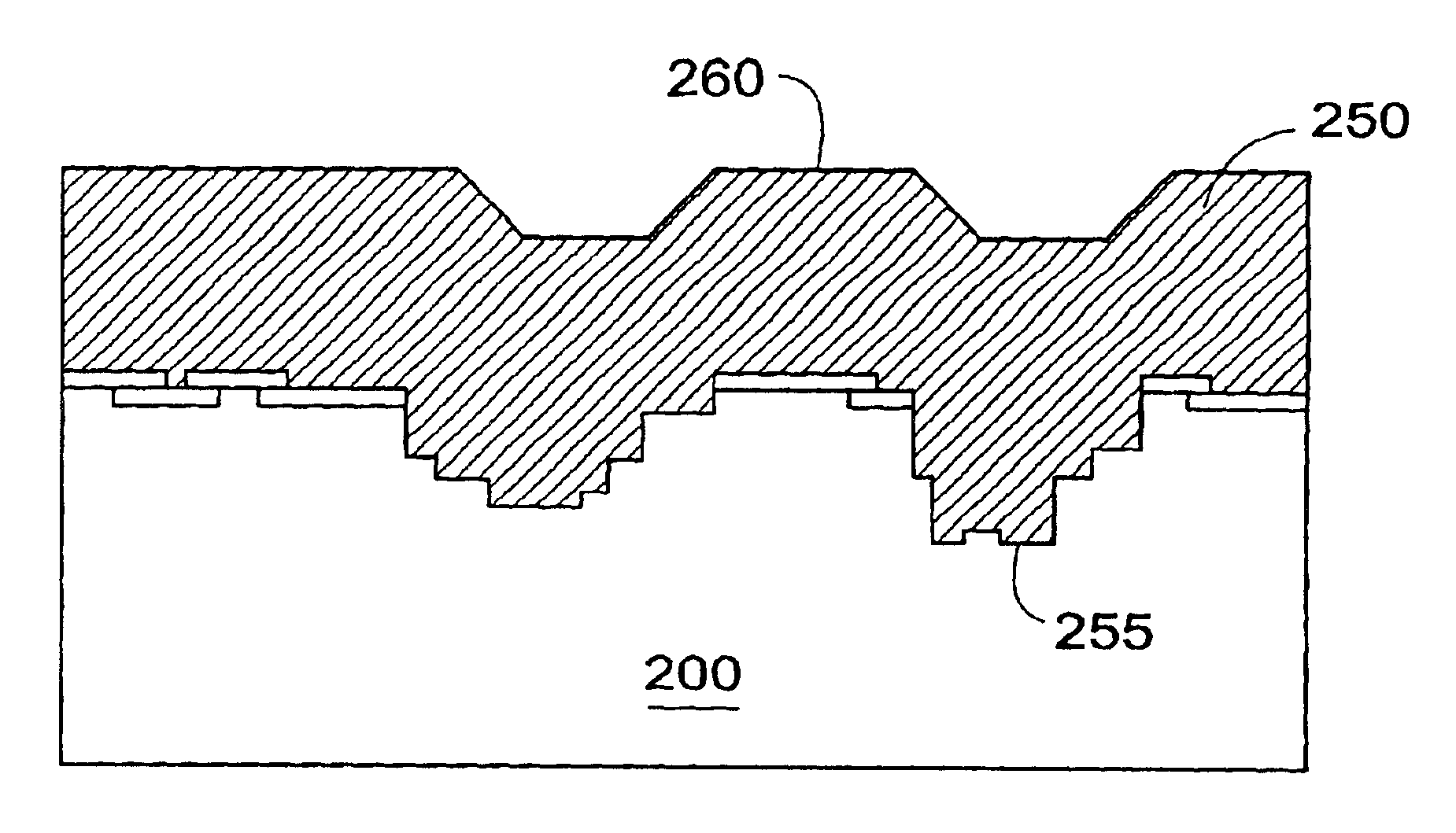
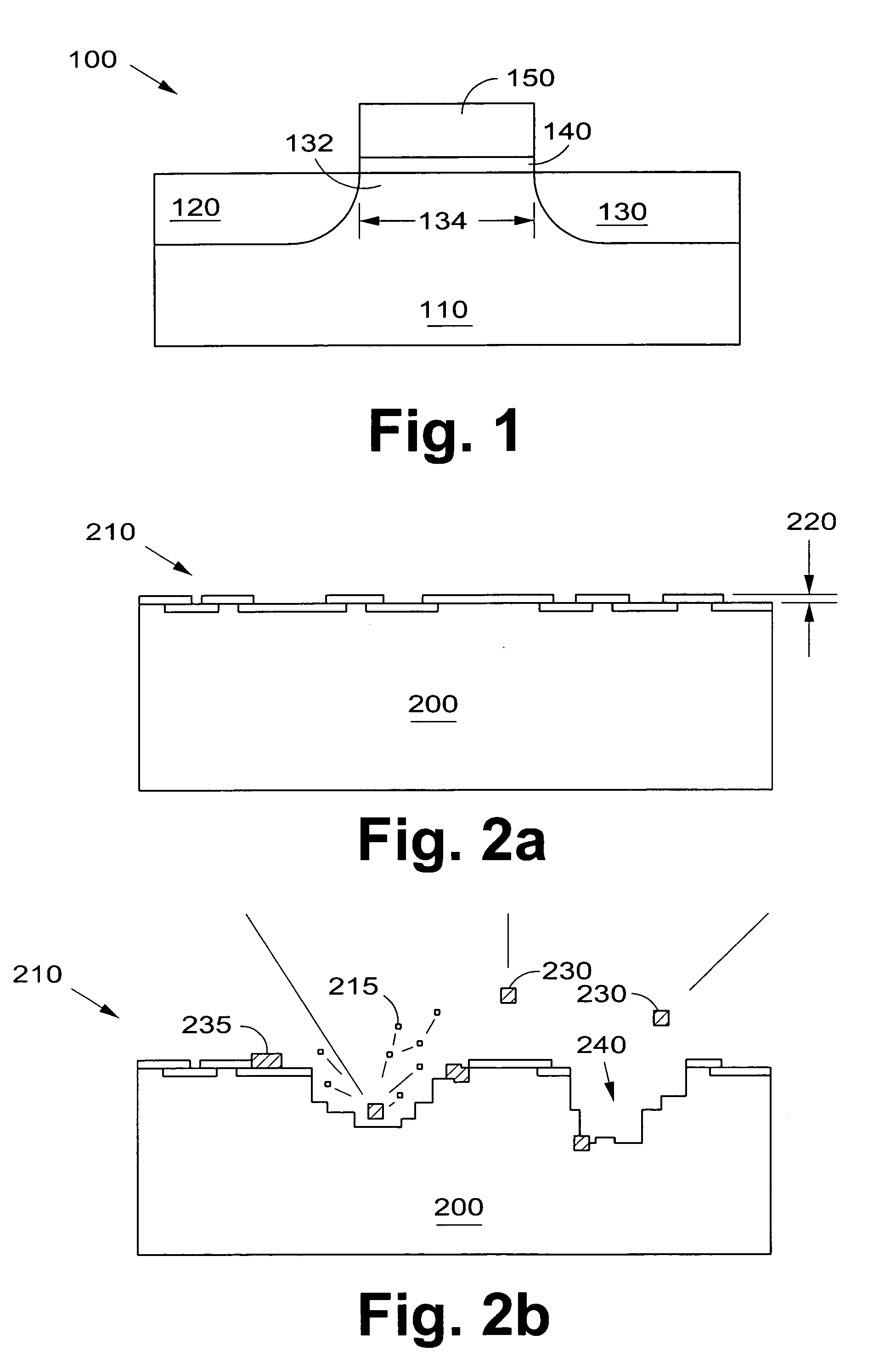
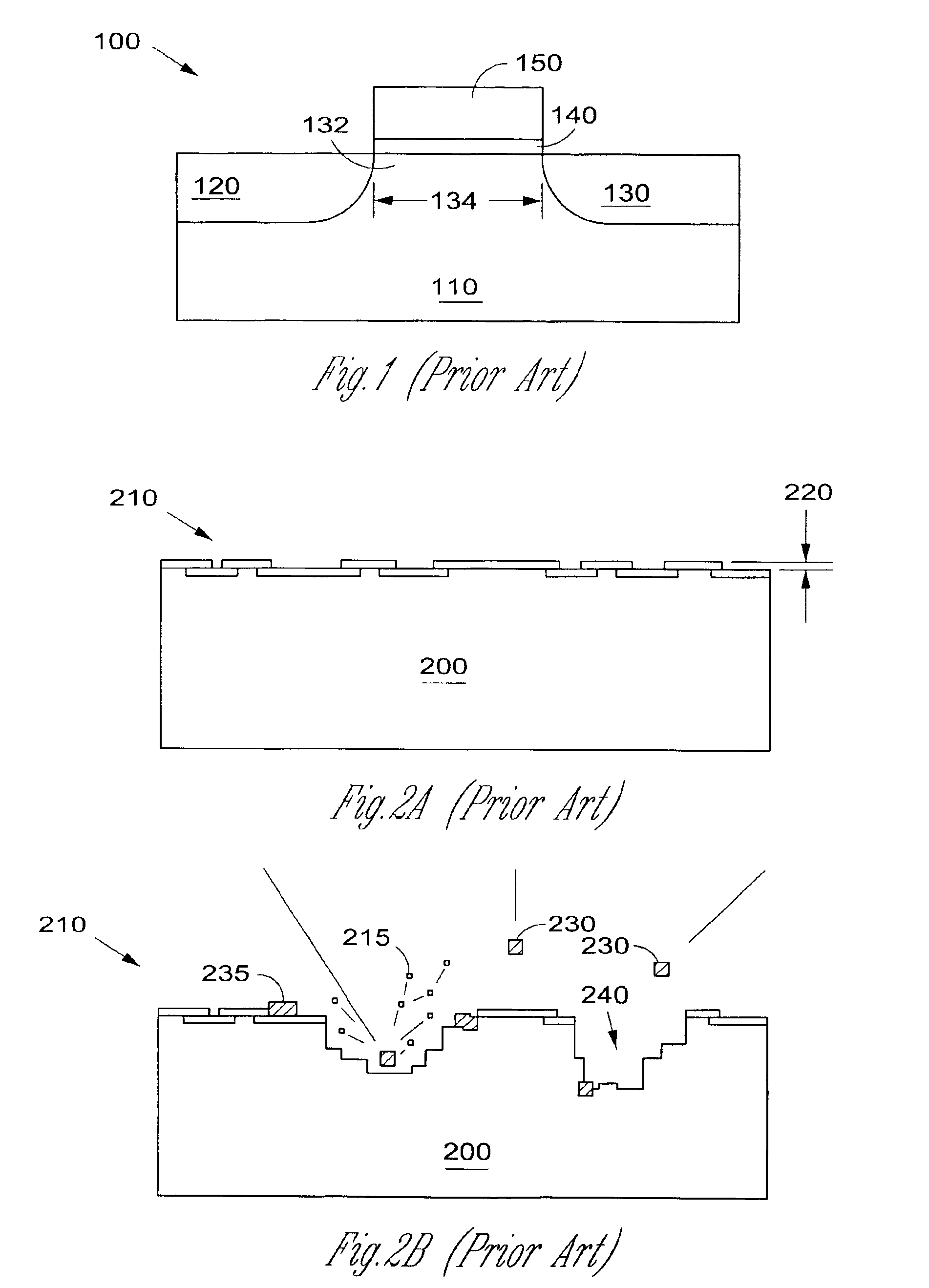
InactiveUS6844203B2Improve surface roughnessSmooth surface roughnessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEquivalent oxide thicknessGadolinium
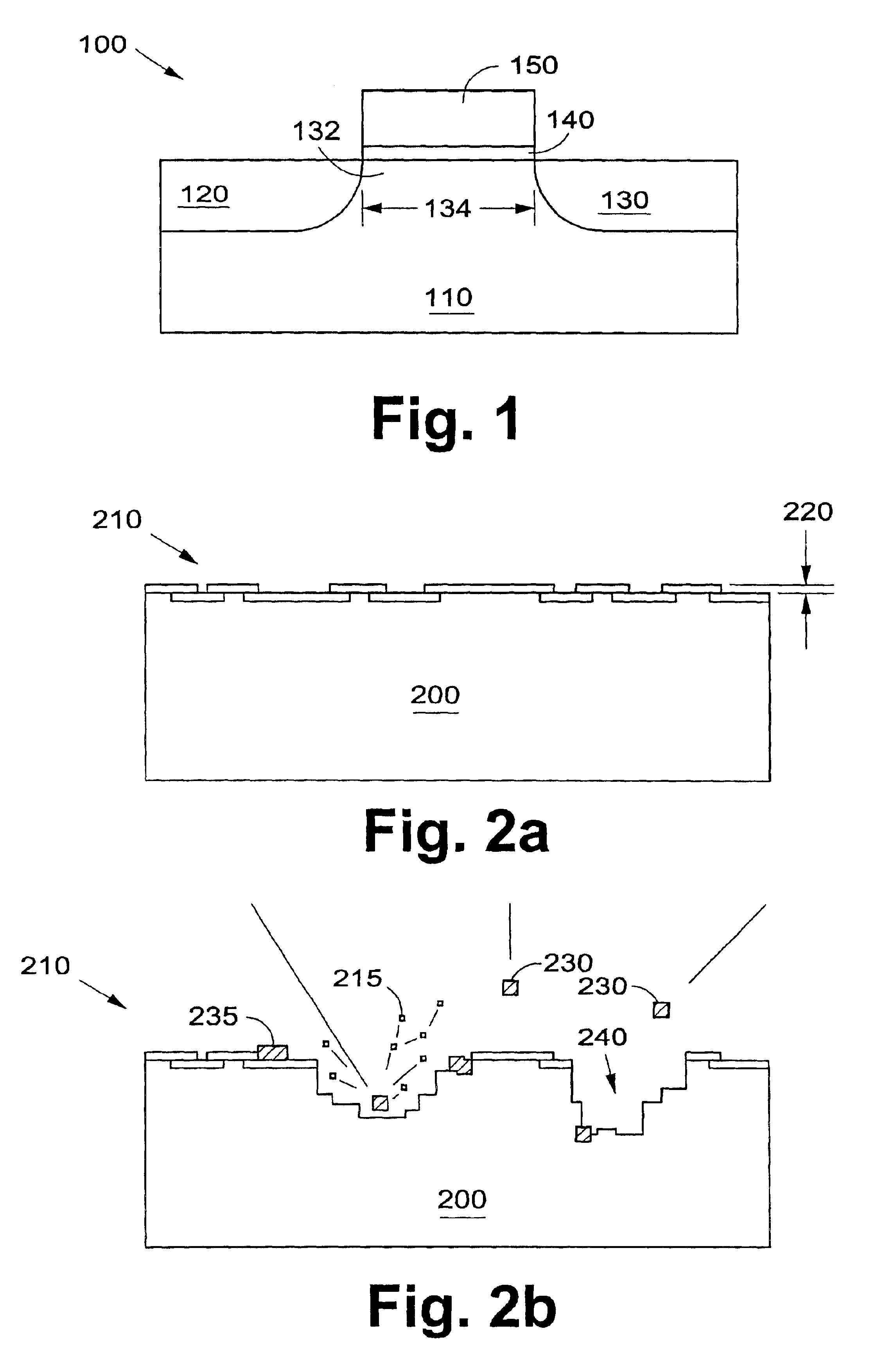
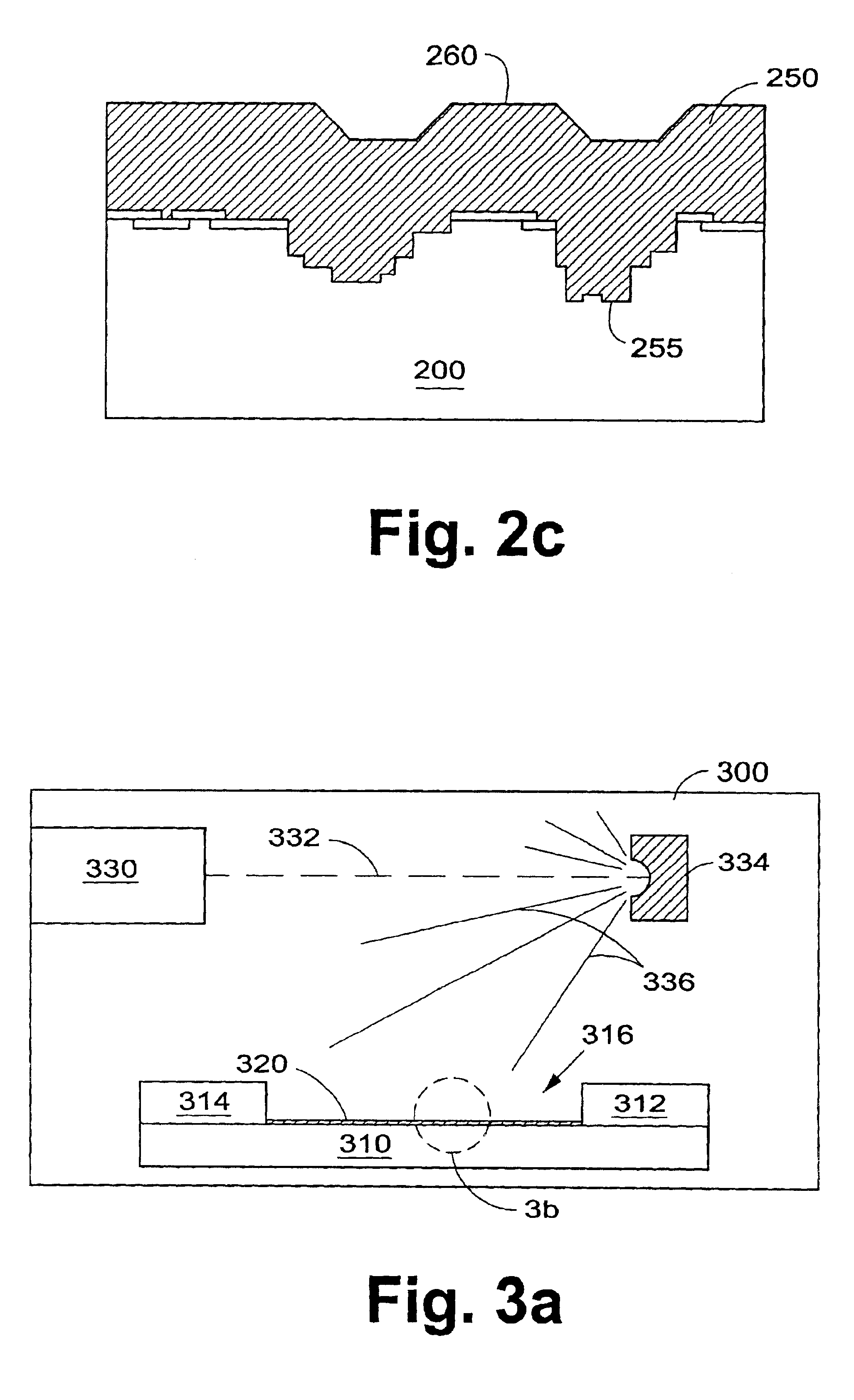
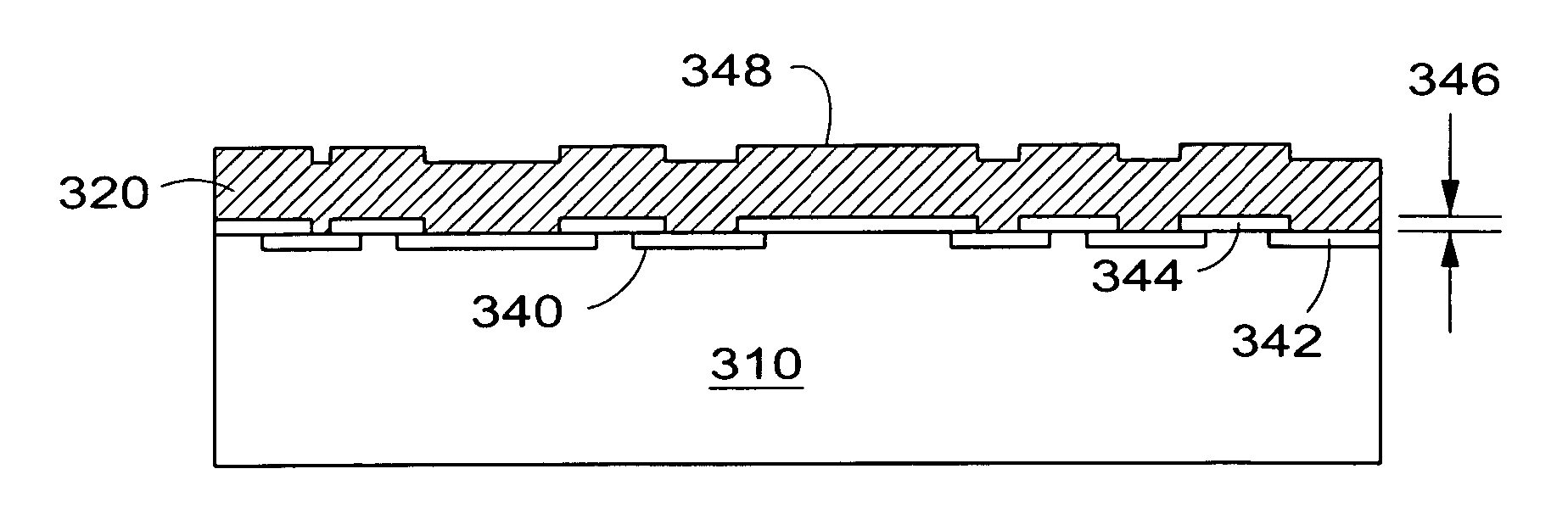
A gate oxide and method of fabricating a gate oxide that produces a more reliable and thinner equivalent oxide thickness than conventional SiO2 gate oxides are provided. Also shown is a gate oxide with a conduction band offset of 2 eV or greater. Gate oxides formed from elements such as yttrium and gadolinium are thermodynamically stable such that the gate oxides formed will have minimal reactions with a silicon substrate or other structures during any later high temperature processing stages. The process shown is performed at lower temperatures than the prior art, which further inhibits reactions with the silicon substrate or other structures. Using a thermal evaporation technique to deposit the layer to be oxidized, the underlying substrate surface smoothness is preserved, thus providing improved and more consistent electrical properties in the resulting gate oxide.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD CO +1
Highly reliable amorphous high-k gate oxide ZrO2
InactiveUS20050029605A1Improve surface roughnessSmooth surface roughnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysicsConduction band
A gate oxide and method of fabricating a gate oxide that produces a more reliable and thinner equivalent oxide thickness than conventional SiO2 gate oxides are provided. Also shown is a gate oxide with a conduction band offset in a range of approximately 5.16 eV to 7.8 eV. Gate oxides formed from elements such as zirconium are thermodynamically stable such that the gate oxides formed will have minimal reactions with a silicon substrate or other structures during any later high temperature processing stages. The process shown is performed at lower temperatures than the prior art, which further inhibits reactions with the silicon substrate or other structures. Using a thermal evaporation technique to deposit the layer to be oxidized, the underlying substrate surface smoothness is preserved, thus providing improved and more consistent electrical properties in the resulting gate oxide.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Evaporation of Y-Si-O films for medium-K dielectrics
InactiveUS6930346B2Improve surface roughnessSmooth surface roughnessTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectricEquivalent oxide thickness
A gate oxide and method of fabricating a gate oxide that produces a more reliable and thinner equivalent oxide thickness than conventional SiO2 gate oxides are provided. Gate oxides formed from yttrium, silicon, and oxygen are thermodynamically stable such that the gate oxides formed will have minimal reactions with a silicon substrate or other structures during any later high temperature processing stages. The process shown is performed at lower temperatures than the prior art, which inhibits unwanted species migration and unwanted reactions with the silicon substrate or other structures. Using a thermal evaporation technique to deposit the layer to be oxidized, the underlying substrate surface smoothness is preserved, thus providing improved and more consistent electrical properties in the resulting gate oxide.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
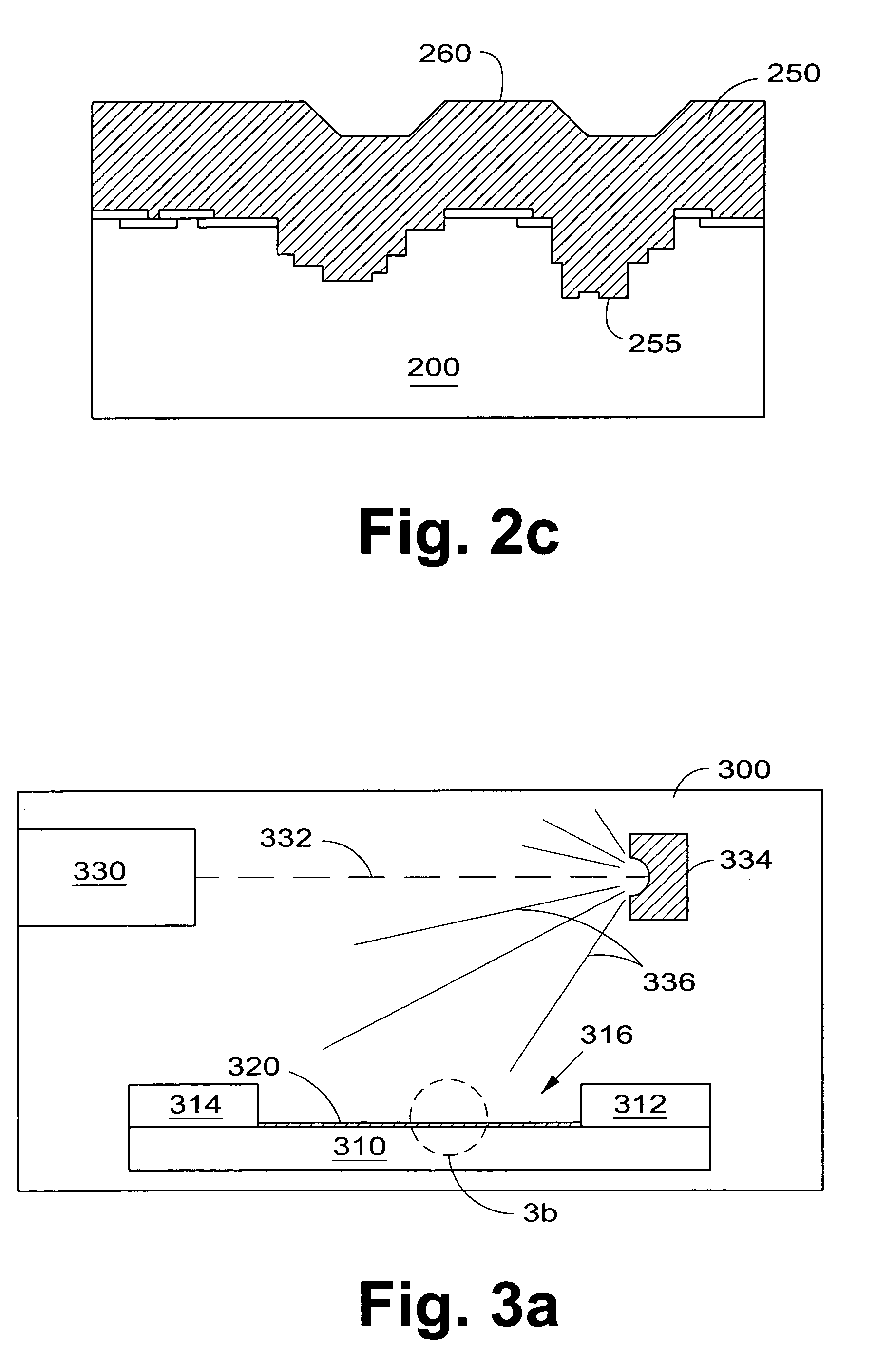
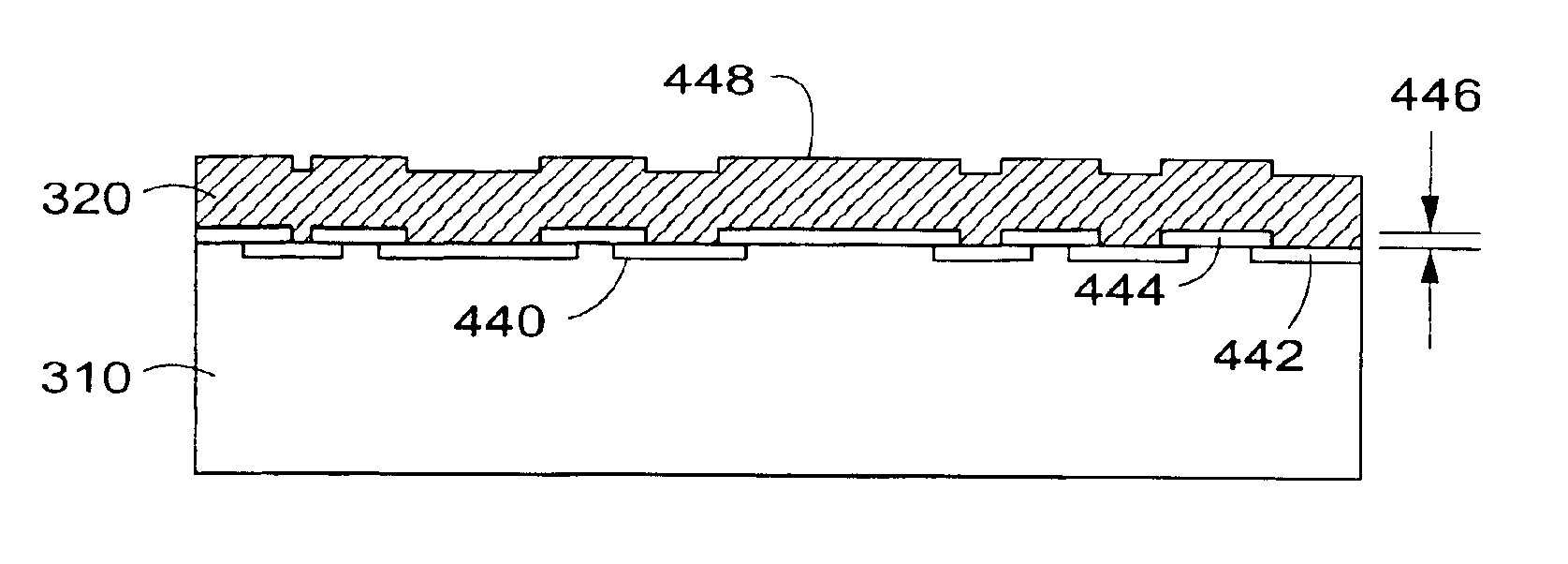
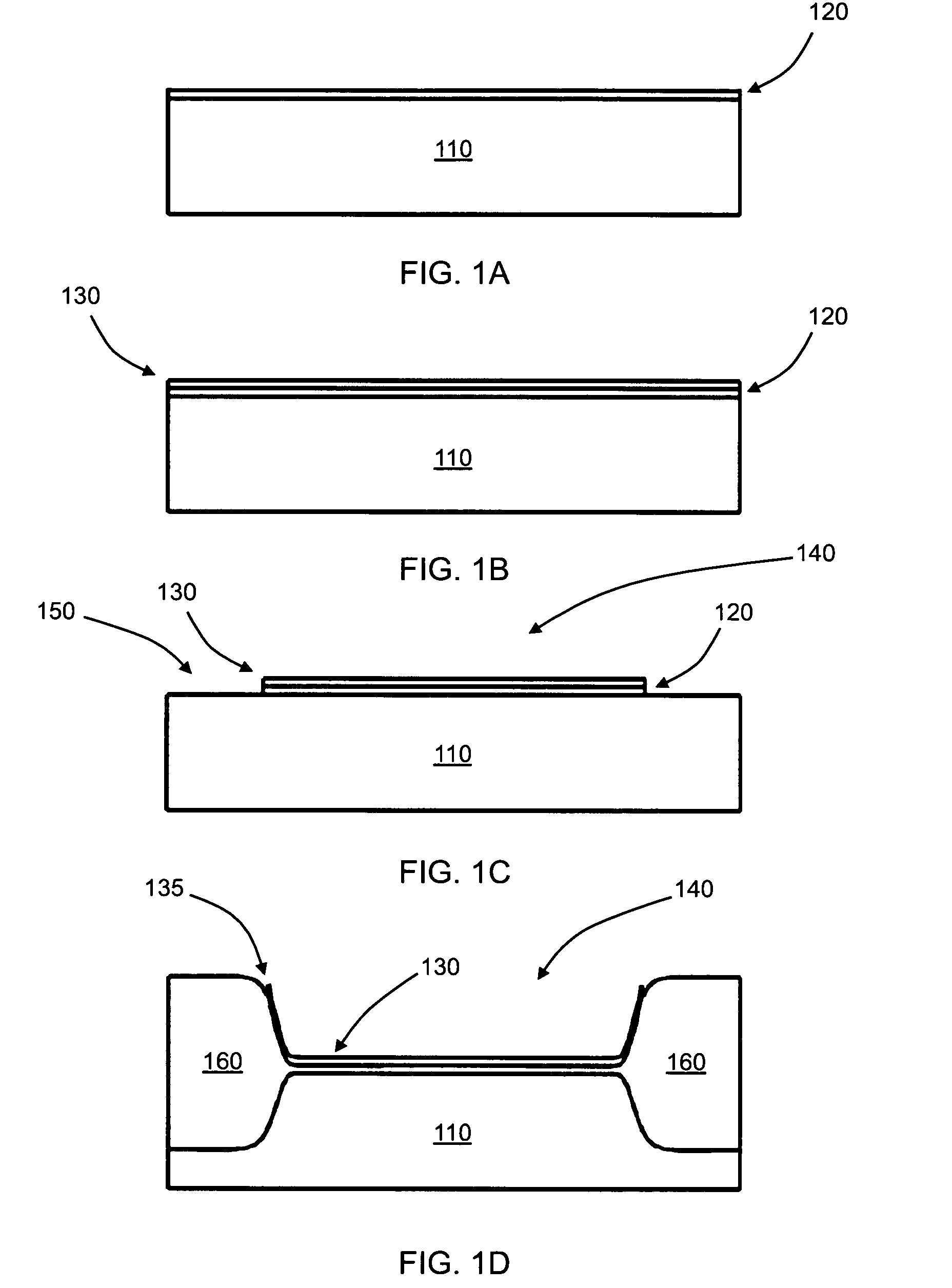
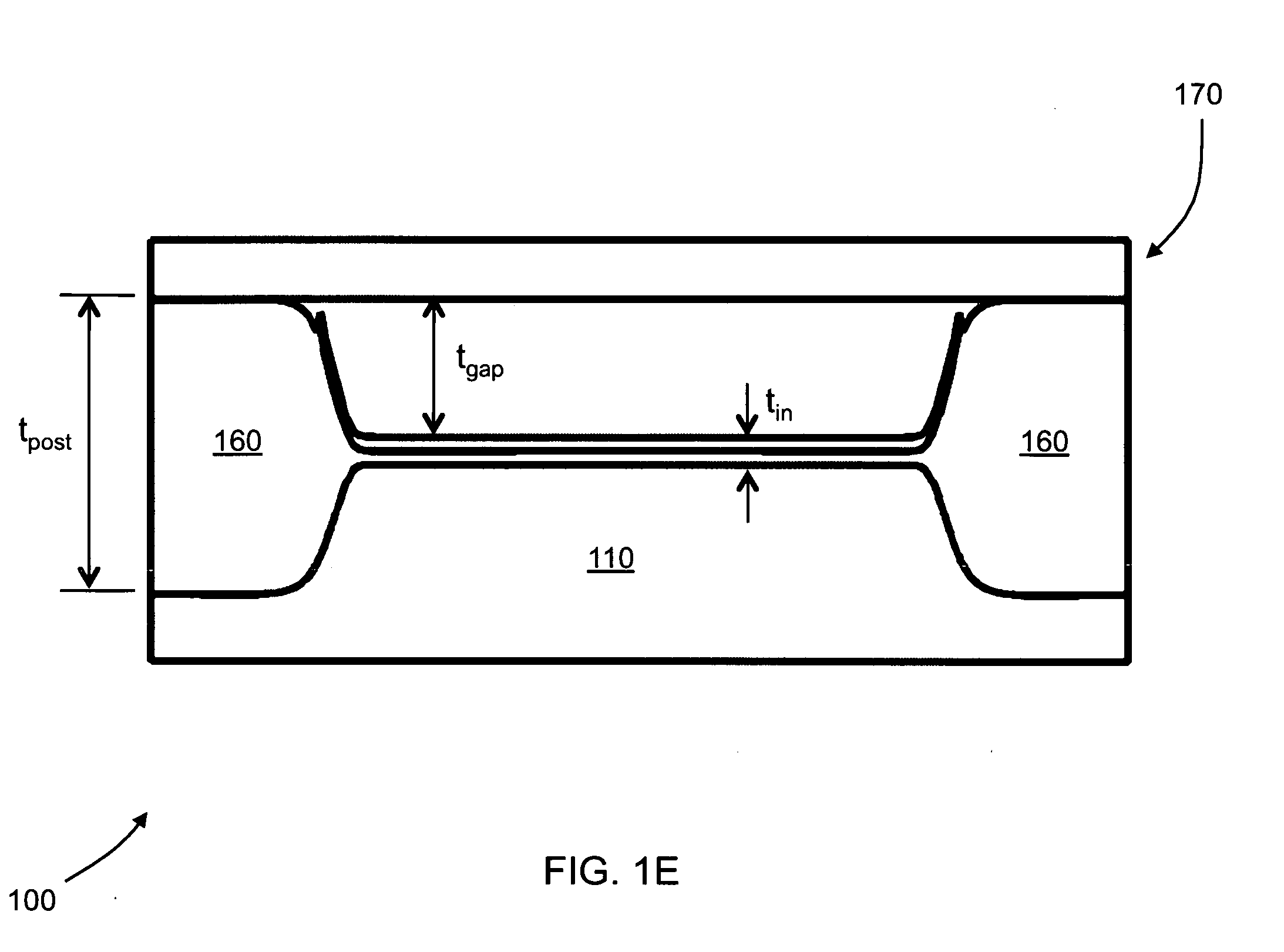
Fabrication of capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers by local oxidation
ActiveUS7745248B2Reduce parasitic capacitanceImprove breakdown voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMechanical vibrations separationCapacitanceCapacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers
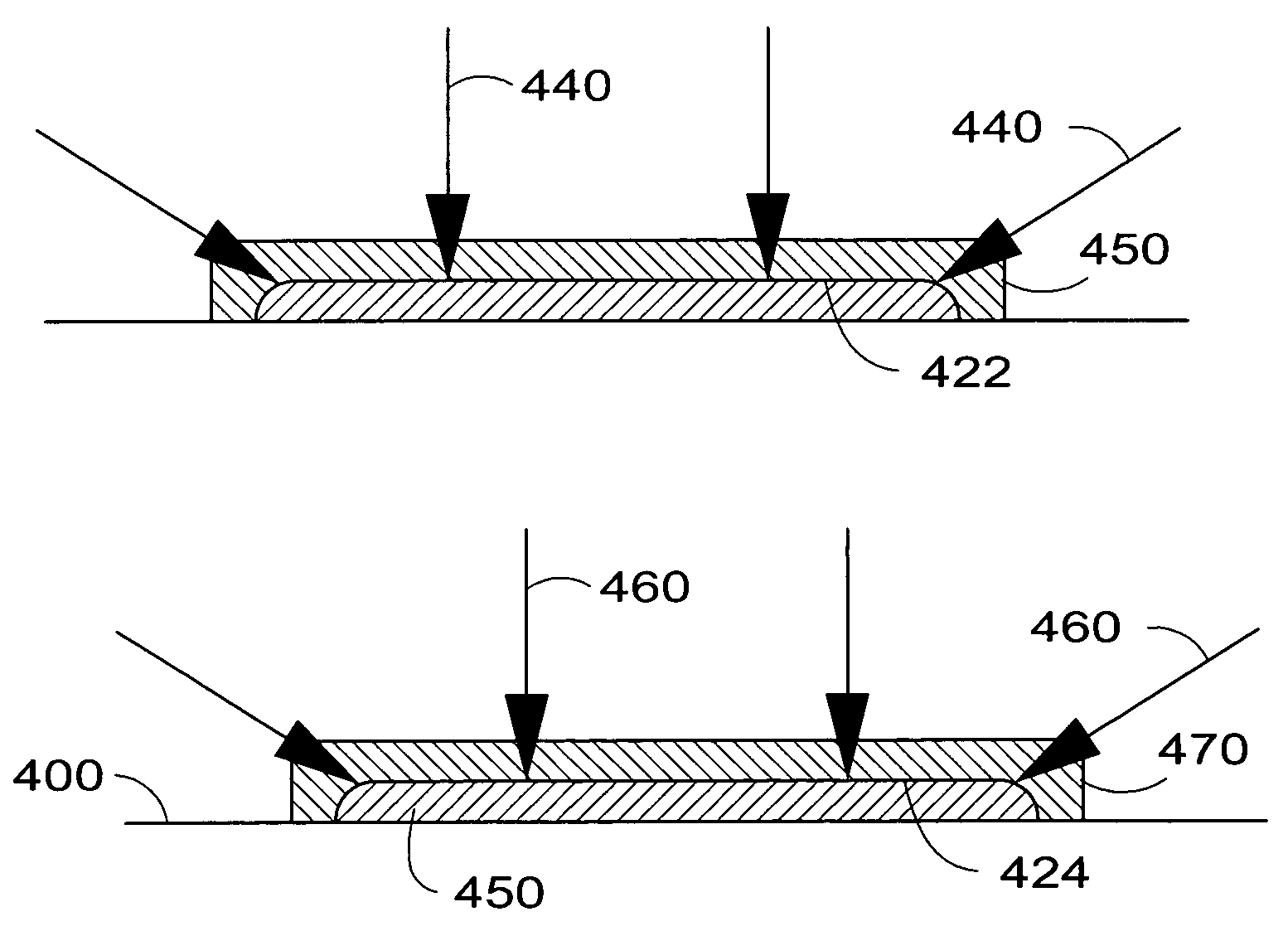
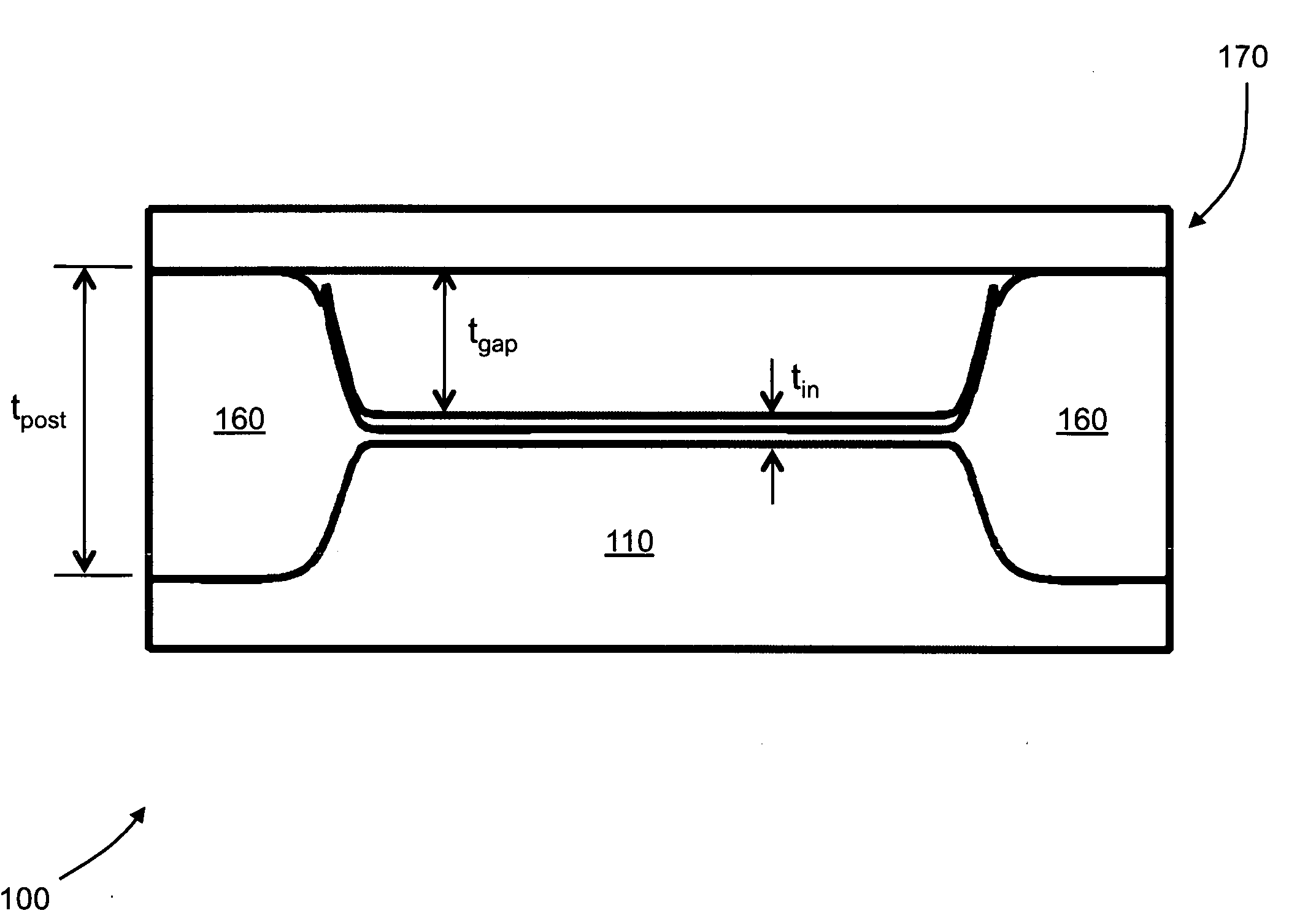
The current invention provides methods of fabricating a capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducer (CMUT) that includes oxidizing a substrate to form an oxide layer on a surface of the substrate having an oxidation-enabling material, depositing and patterning an oxidation-blocking layer to form a post region and a cavity region on the substrate surface and remove the oxidation-blocking layer and oxide layer at the post region. The invention further includes thermally oxidizing the substrate to grow one or more oxide posts from the post region, where the post defines the vertical critical dimension of the device, and bonding a membrane layer onto the post to form a membrane of the device. A maximum allowed second oxidation thickness t2 can be determined, that is partially based on a desired step height and a device size, and a first oxidation thickness t1 can be determined that is partially based on the determined thickness t2.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Highly reliable amorphous high-k gate dielectric ZrOxNy
InactiveUS7205620B2Improve surface roughnessSmooth surface roughnessVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEquivalent oxide thicknessGate dielectric
A gate dielectric and method of fabricating a gate dielectric that produces a more reliable and thinner equivalent oxide thickness than conventional SiO2 gate oxides are provided. Gate dielectrics formed from metals such as zirconium are thermodynamically stable such that the gate dielectrics formed will have minimal reactions with a silicon substrate or other structures during any later high temperature processing stages. The addition of nitrogen to the microstructure of the gate dielectric promotes an amorphous phase that further improves the electrical properties of the gate dielectric. The process shown is performed at lower temperatures than the prior art, which inhibits unwanted species migration and unwanted reactions with the silicon substrate or other structures. By using a thermal evaporation technique to first deposit a metal layer, the underlying substrate surface smoothness is preserved, thus providing improved and more consistent electrical properties in the resulting gate dielectric.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Fabrication of capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers by local oxidation
ActiveUS20090142872A1Improve breakdown voltageReduce parasitic capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMechanical vibrations separationParasitic capacitorCapacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers
Fabrication methods for capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers (CMUTS) with independent and precise gap and post thickness control are provided. The fabrication methods are based on local oxidation or local oxidation of silicon (LOCOS) to grow oxide posts. The process steps enable low surface roughness to be maintained to allow for direct wafer bonding of the membrane. In addition, methods for fabricating a step in a substrate are provided with reduced or minimal over-etch time by utilizing the nonlinearity of oxide growth. The fabrication methods of the present invention produce CMUTs with unmatched uniformity, low parasitic capacitance, and high breakdown voltage.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
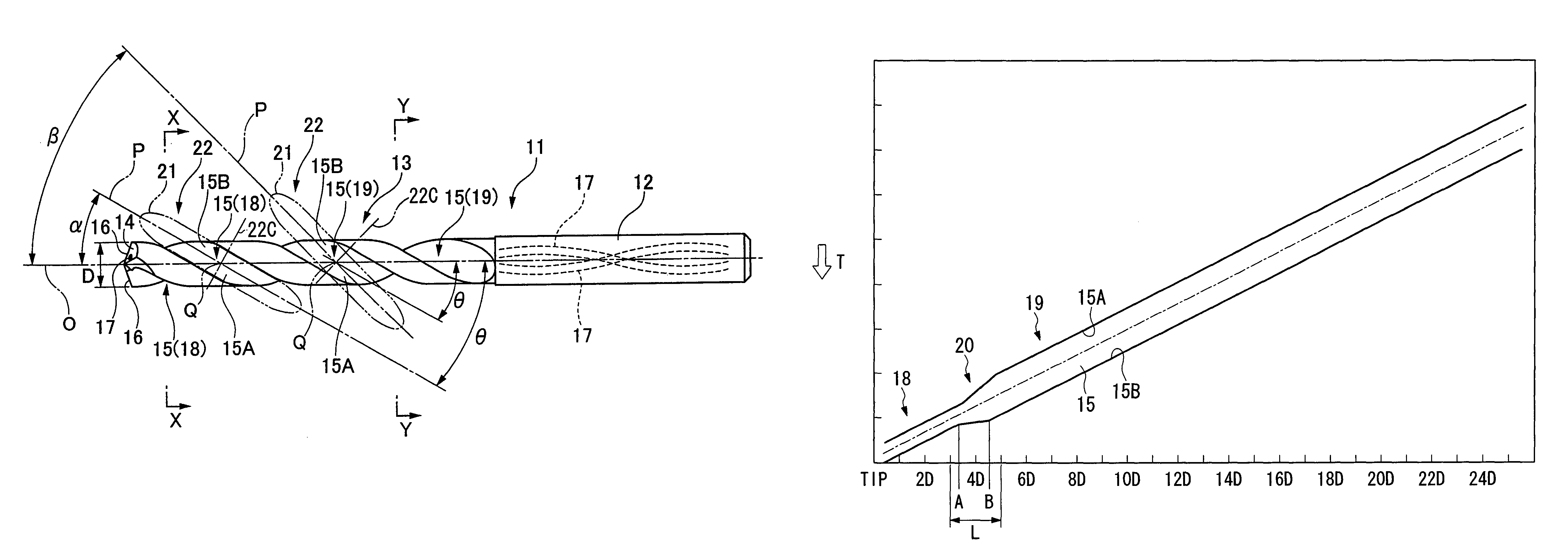
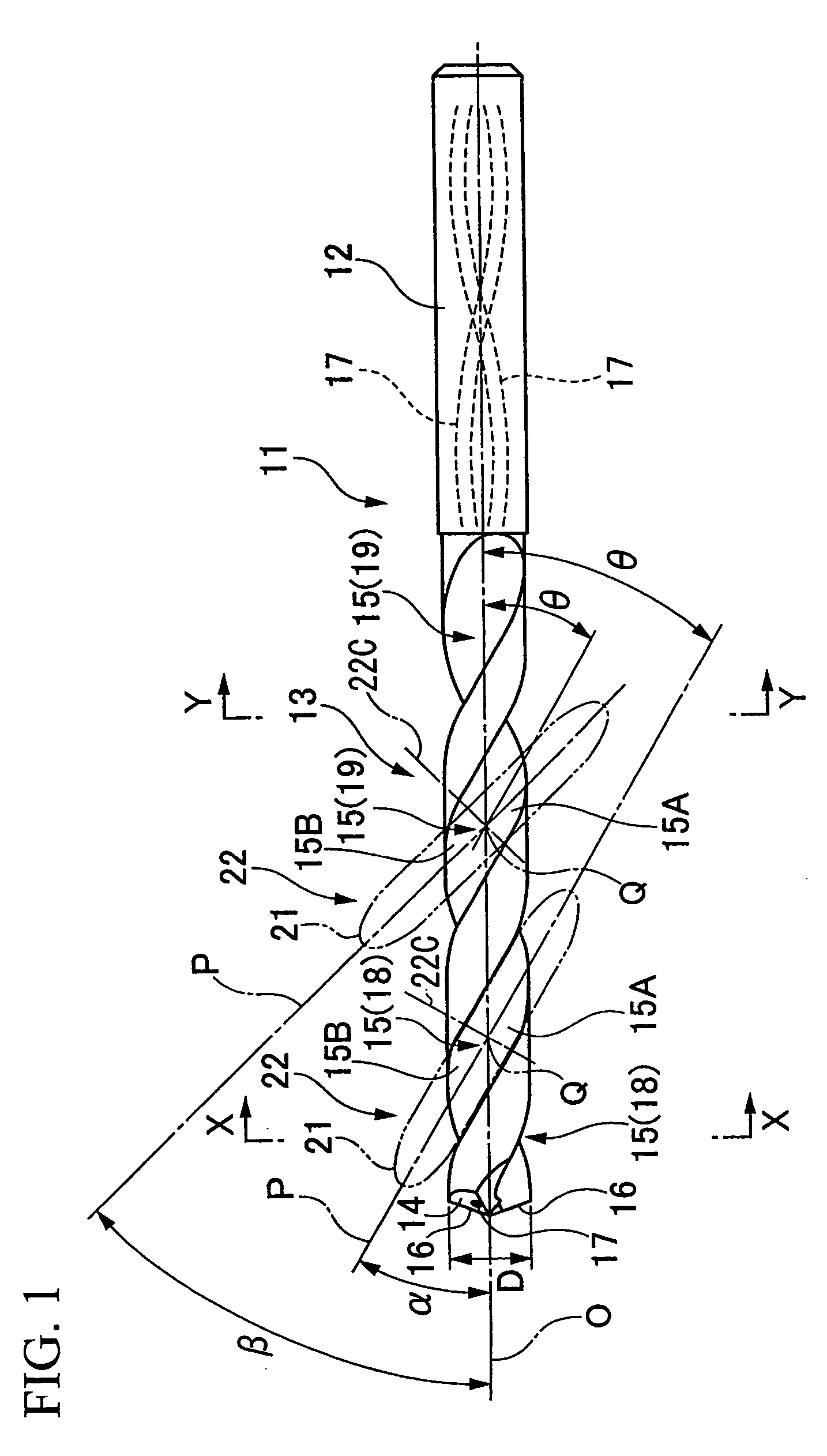
Drill with groove width variation along the drill and double margin with a thinning section at the tip
InactiveUS7306411B2Reliable dischargeImprove surface roughnessWood turning toolsTransportation and packagingGroove widthEngineering
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Highly crystalline silver powder and process for production of the same
InactiveCN101218051AExcellent heat shrinkage resistanceSmooth surface roughnessTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusFiltrationMicroparticle
The invention aims at providing a process for the production of highly crystalline silver powder which comprises silver particles falling within the fine particle region and has an excellent particle size distribution and highly crystalline silver powder obtained by the process. The aim is attained by a process for the production of highly crystalline silver powder which is characterized by preparing the first aqueous solution containing gelatin, silver nitrate and nitric acid and having a temperature of 45 to 55 C and the second aqueous solution containing erythorbic acid and / or ascorbic acid and a water-soluble organic acid, adding the second aqueous solution mildly to the first aqueous solution, stirring the mixed solution after the completion of the addition to form silver particles through particle growth, allowing the resulting system to stand to settle the silver particles, removing the supernatant, and then subjecting the remainder to filtration and washing to recover the silver particles.
Owner:MITSUI MINING & SMELTING CO LTD
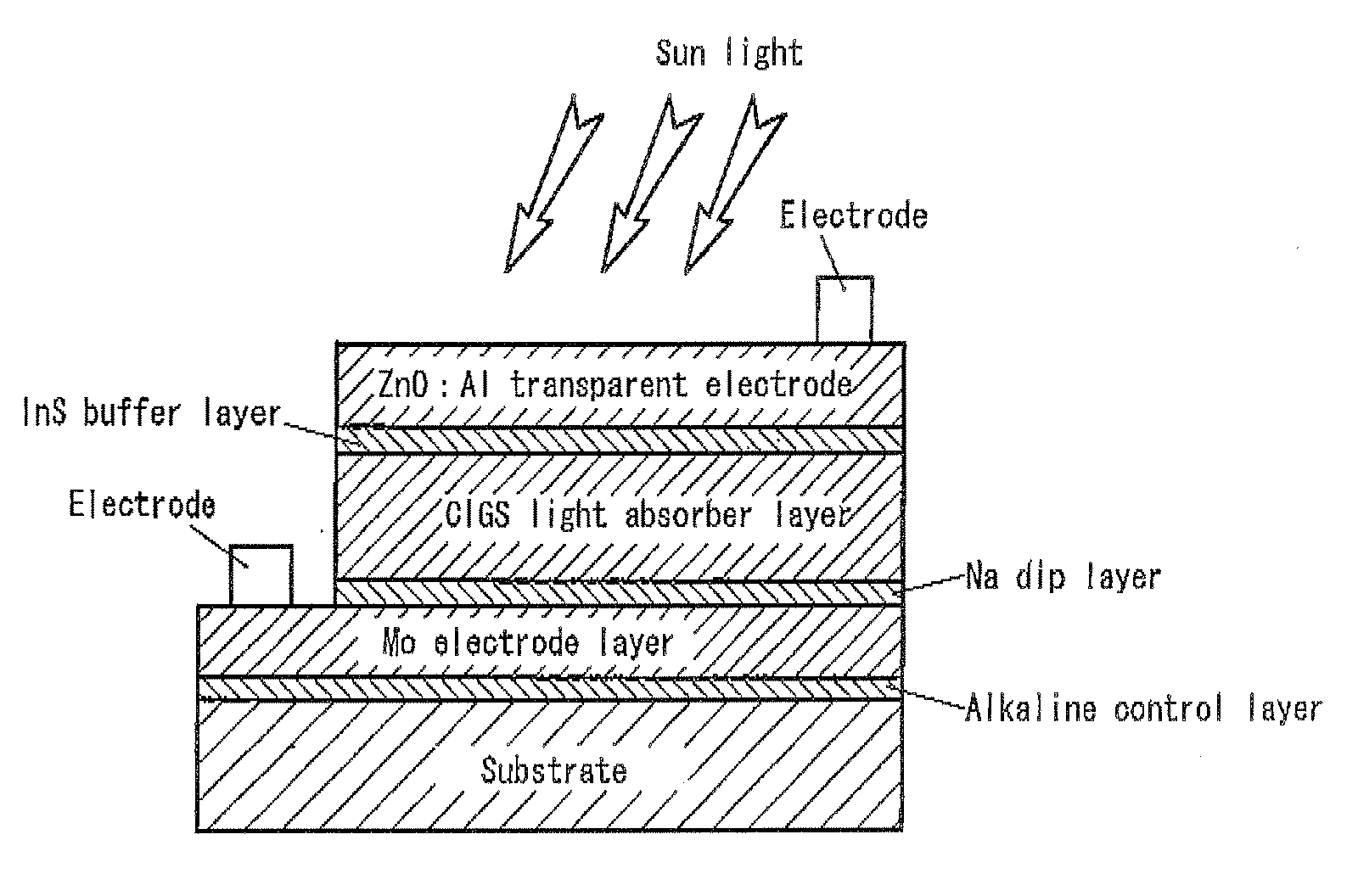
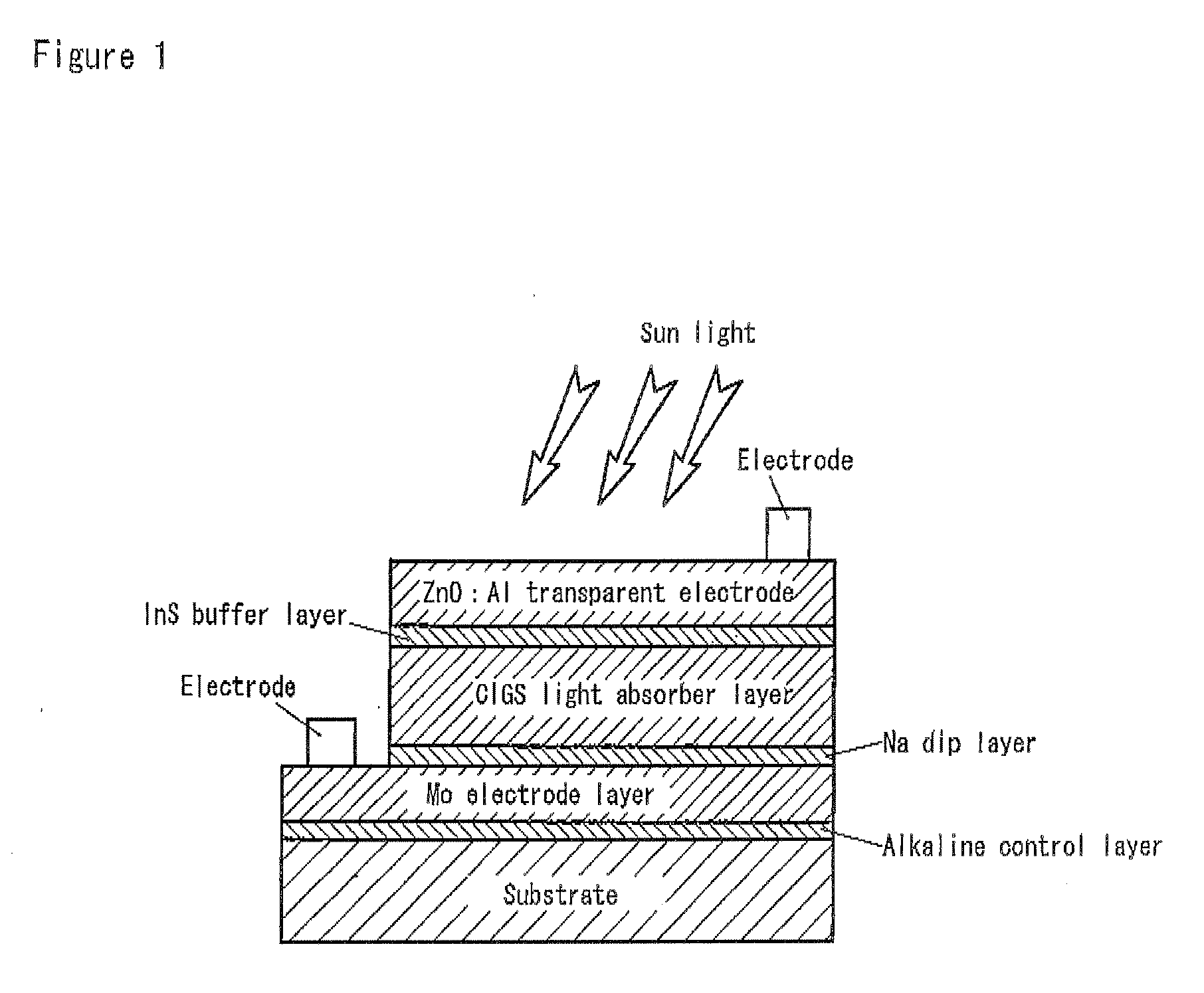
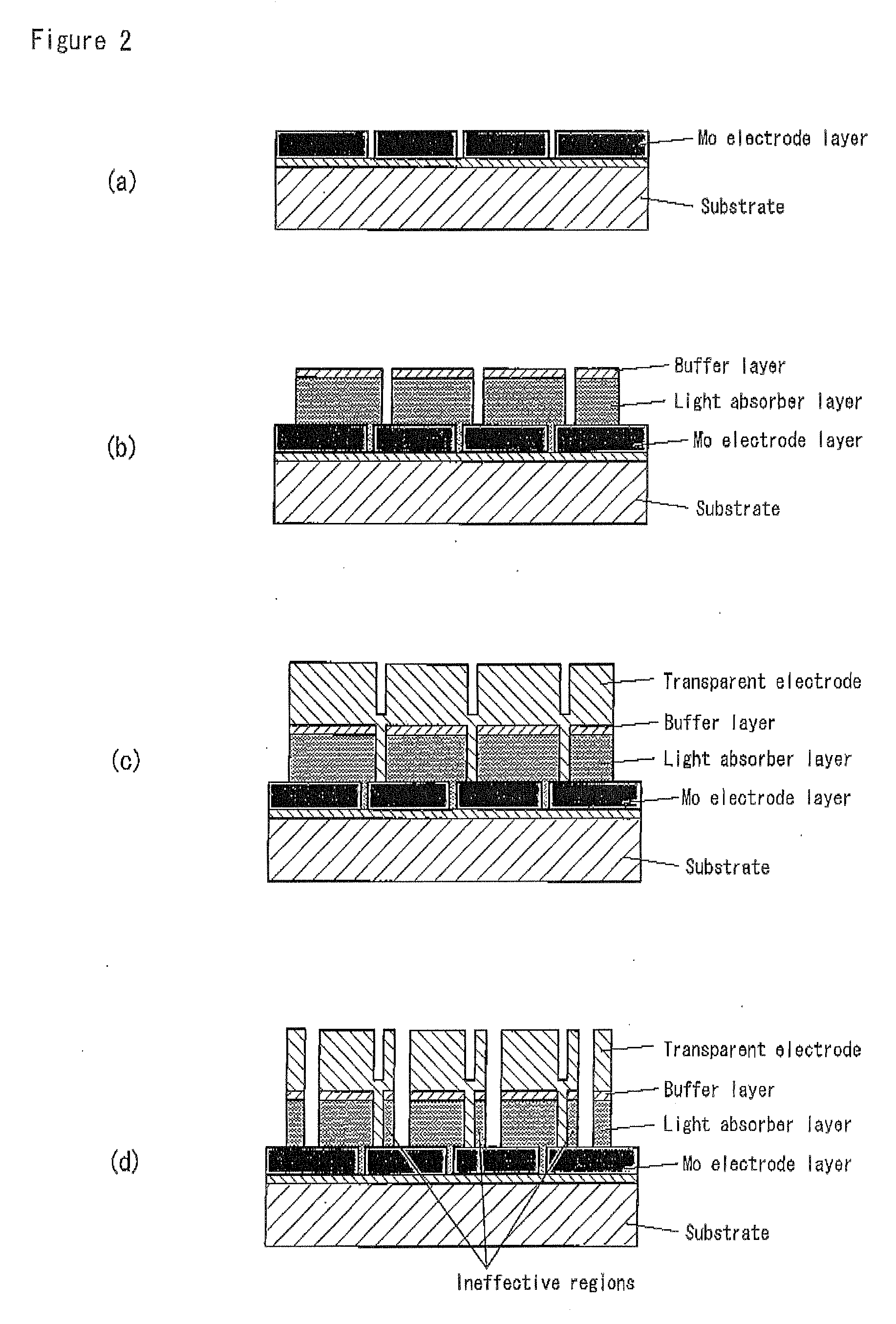
Solar Cell
InactiveUS20090242022A1Improve reliabilityBreakage of substrate can be preventedFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorCopper indium gallium selenide
A flexible solar cell is achieved which has a high photoelectric conversion efficiency and no aged deterioration. A cell 10 (unit cell) is formed as a unit, comprising: a lower electrode layer 2 (Mo electrode layer) formed on a flexible mica sheet substrate 1 (substrate); a light absorber layer 3 (CIGS light absorber layer) which contains copper indium gallium selenide; a highly resistant buffer layer thin film 4 formed of InS, ZnS, CdS, or the like on the light absorber layer 3; and an upper electrode layer 5 (TCO) formed of ZuOAl or the like, and furthermore, a contact electrode section 6 for connecting between the upper electrode layer 5 and the lower electrode layer 2 is formed in order to connect a plurality of unit cells 10 in series. The contact electrode section 6 has a Cu / In ratio higher than that of the light absorber layer 3, and in other words, has less In contained therein to have a property of p+ (plus) type or a conductor relative to the light absorber layer 3 which is a p-type semiconductor.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Preparation process for plate roller for printing
ActiveCN107020793AReduce surface roughnessSmooth surface roughnessPhotomechanical apparatusPlate printingCopper platingLaser engraving
The invention discloses a preparation process for a plate roller for printing. The process comprises the following steps that (1) manufacturing of a plate roller base body: the plate roller base body is manufactured from a specific formula of seamless steel tube; (2) copper plating treatment of the plate roller base body: the plate roller base body is subjected to copper plating in a plating tank containing a specific copper plating solution, and the thickness of a copper layer is 12-15 microns; (3) surface treatment of the plate roller base body: the copper surface is subjected to grinding treatment; (4) gumming of the plate roller: the plate roller subjected to copper plating and surface treatment is coated with a layer of glue solution with the thickness being 0.08-0.12mm and then is aired; (5) manufacturing of a laser image, laser engraving of the plate roller and developing of the plate roller; (6) corrosion to the plate roller: the plate roller is subjected to spray-type corrosion treatment with specific corrosive liquid; (7) cleaning of the plate roller: the plate roller is subjected to spray-type cleaning with specific cleaning fluid; and (8) chromium plating of the plate roller: the plate roller is subjected to chromium plating treatment in a plating tank containing a specific chromium plating solution, the thickness of a chromium layer is 5-8 microns. The preparation process has the advantage that the difference of the surface flatness of different positions of the same plate roller is reduced.
Owner:ZIBO YUNCHENG PLATE MAKING
Short range cutting method of wire quick-moving type electrospark wire-electrode cutting machine tool and device
The invention discloses a short-range cutting method and device of rapid yarn electric spark wire cutting machine, which is characterized by the following: when the device adapts rapid yarn electric spark wire cutting machine to cut the element through electrode yarn, it makes the yarn cylinder motor of rapid yarn electric spark wire cutting machine rotate positively for t1 time to manufacture the element positively for t1 time; then the yarn cylinder motor is off for t2 time, which rotates yarn cylinder inversely for t3 time to cut element along inversed direction for t3 time; then the yarn cylinder motor is off for t2 time, which rotates yarn cylinder positively for t1 time to cut element for t1 time; the circulation continues with t1 different from t3.
Owner:贵州科邦科技实业有限责任公司
Radius end mill
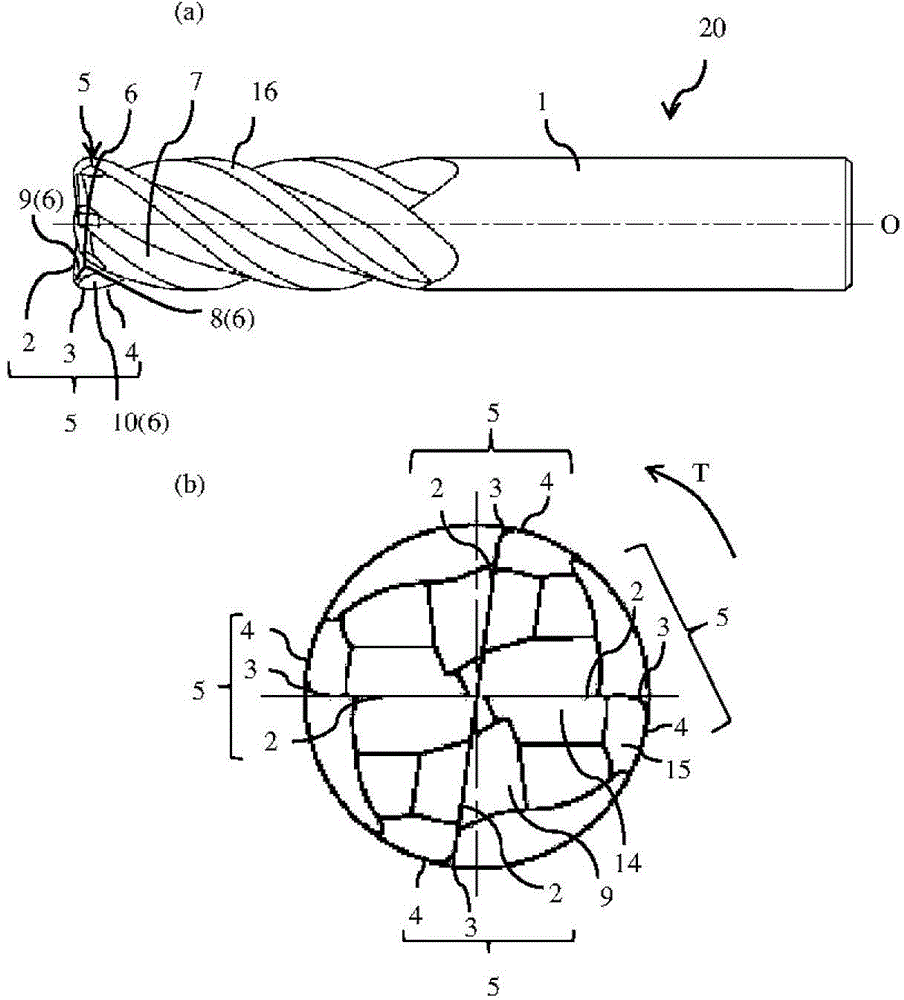
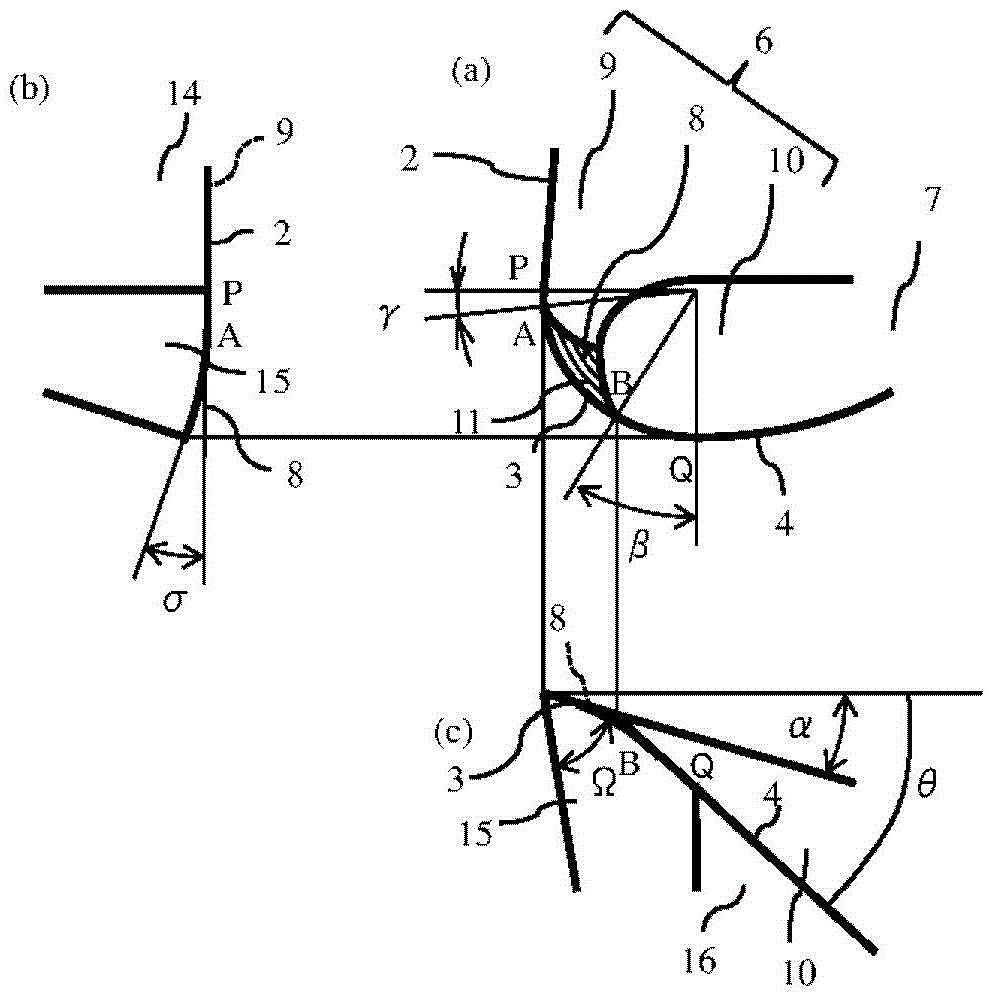
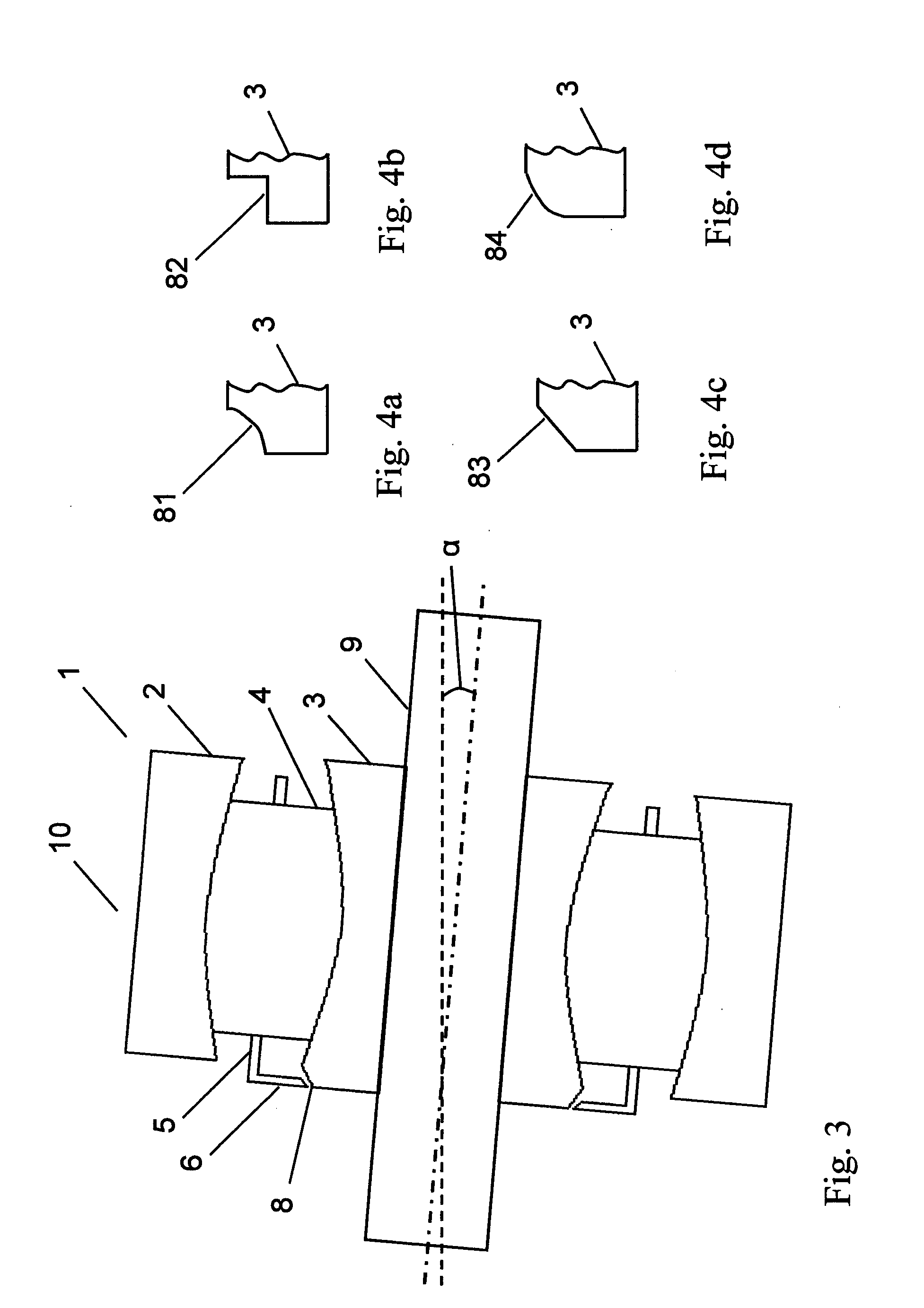
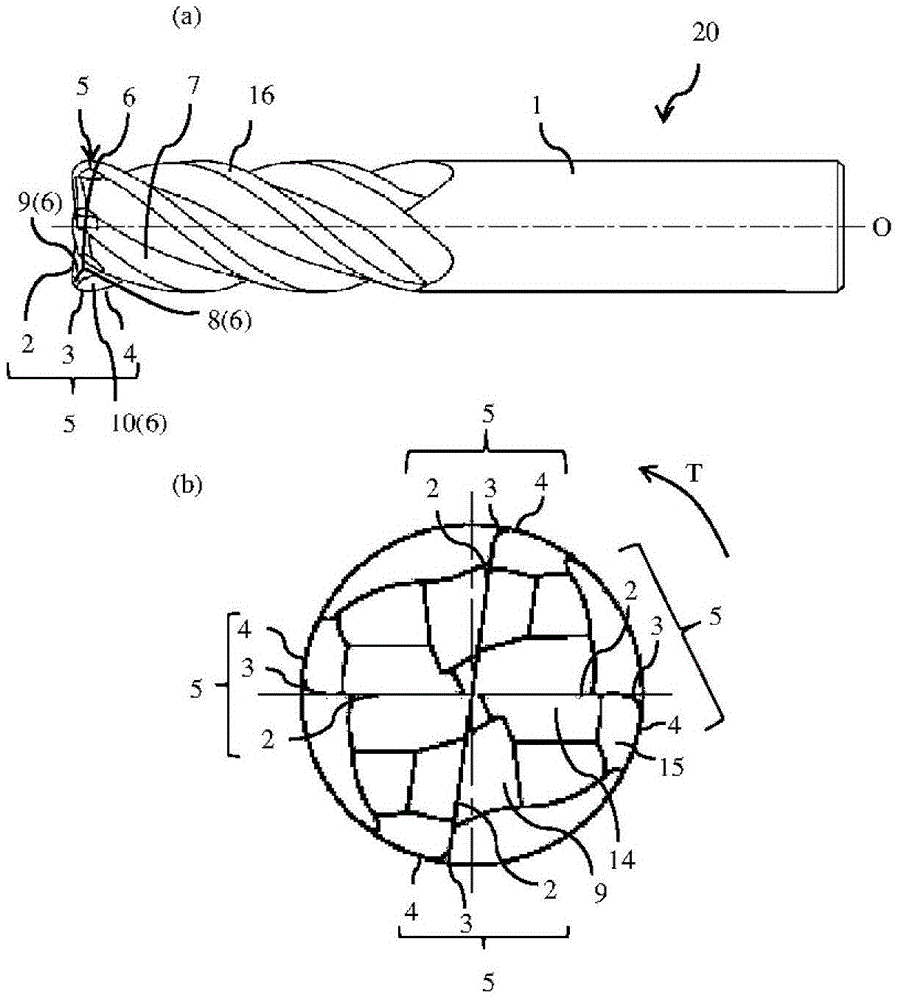
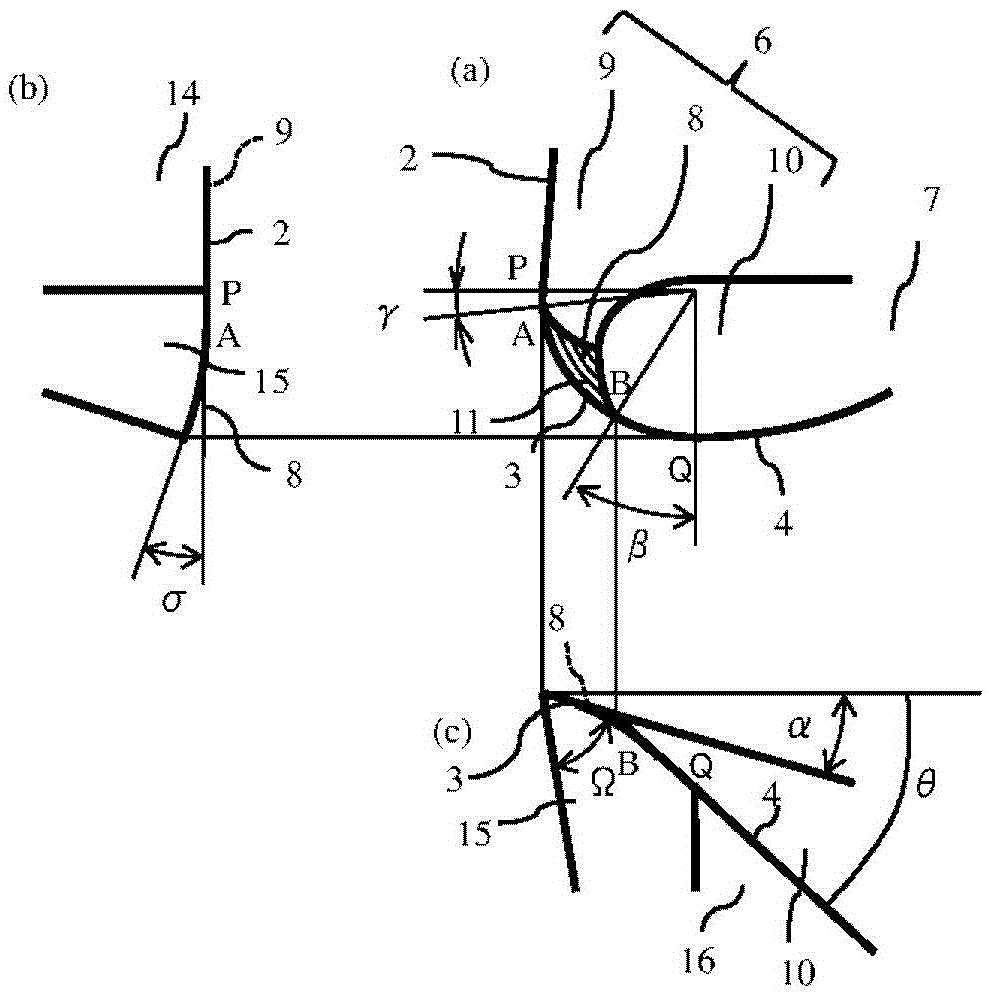
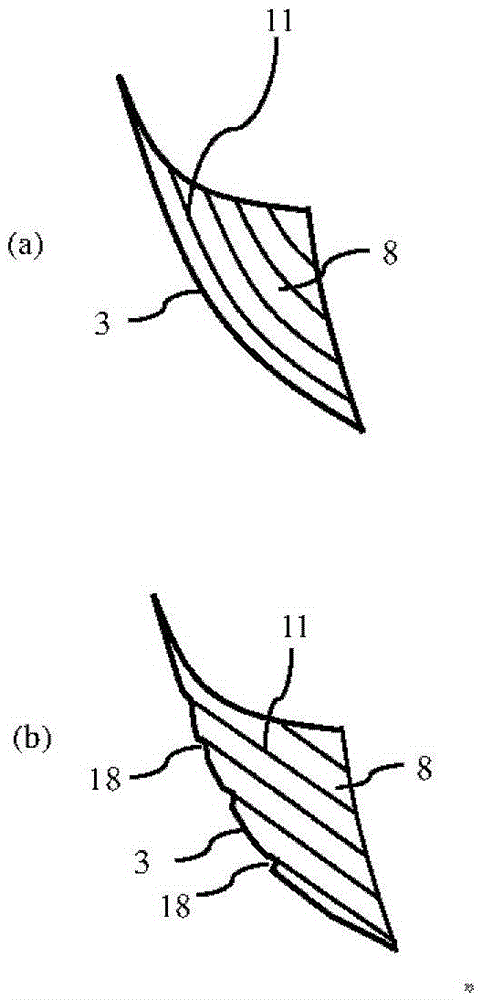
ActiveCN104023884ASuppression of chippingAvoid cloggingMilling cuttersShaping cuttersMachined surfaceEngineering
[Problem] To provide a radius end mill minimizing the appearance of steps and angles on the connecting points between a corner (R) cutting edge and an outer circumferential cutting edge, with good sharpening performance and little machined surface roughness. [Solution] A radius end mill (20) provided with: a tool main body (1) for rotating around a central axis (O); a bottom cutting edge (2) located on the distal end portion of the tool main body (1); an outer circumferential cutting edge (4) located on the outer circumference of the tool main body (1); a corner (R) cutting edge (3) connecting the space between the bottom cutting edge (2) and the outer circumferential cutting edge (4); a plurality of cutting edges (5) comprising a series; a rake surface (6) of the bottom cutting edge (2), the corner (R) cutting edge (3), and the outer circumferential cutting edge (4); a chip discharge groove (7) extending to the rear of the rake surface (6); and a corner gash (8) adjacent to the corner (R) cutting edge (3) of the rake surface (6). The planar corner gash (8) is provided so that part of the edge is the central portion of the corner (R) cutting edge (3), and the axial rake (alpha) on the end portion of the bottom cutting edge (2) touching the corner gash (8) of the corner (R) cutting edge (3) is between 5-20 DEG .
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Apparatus and method for processing piston
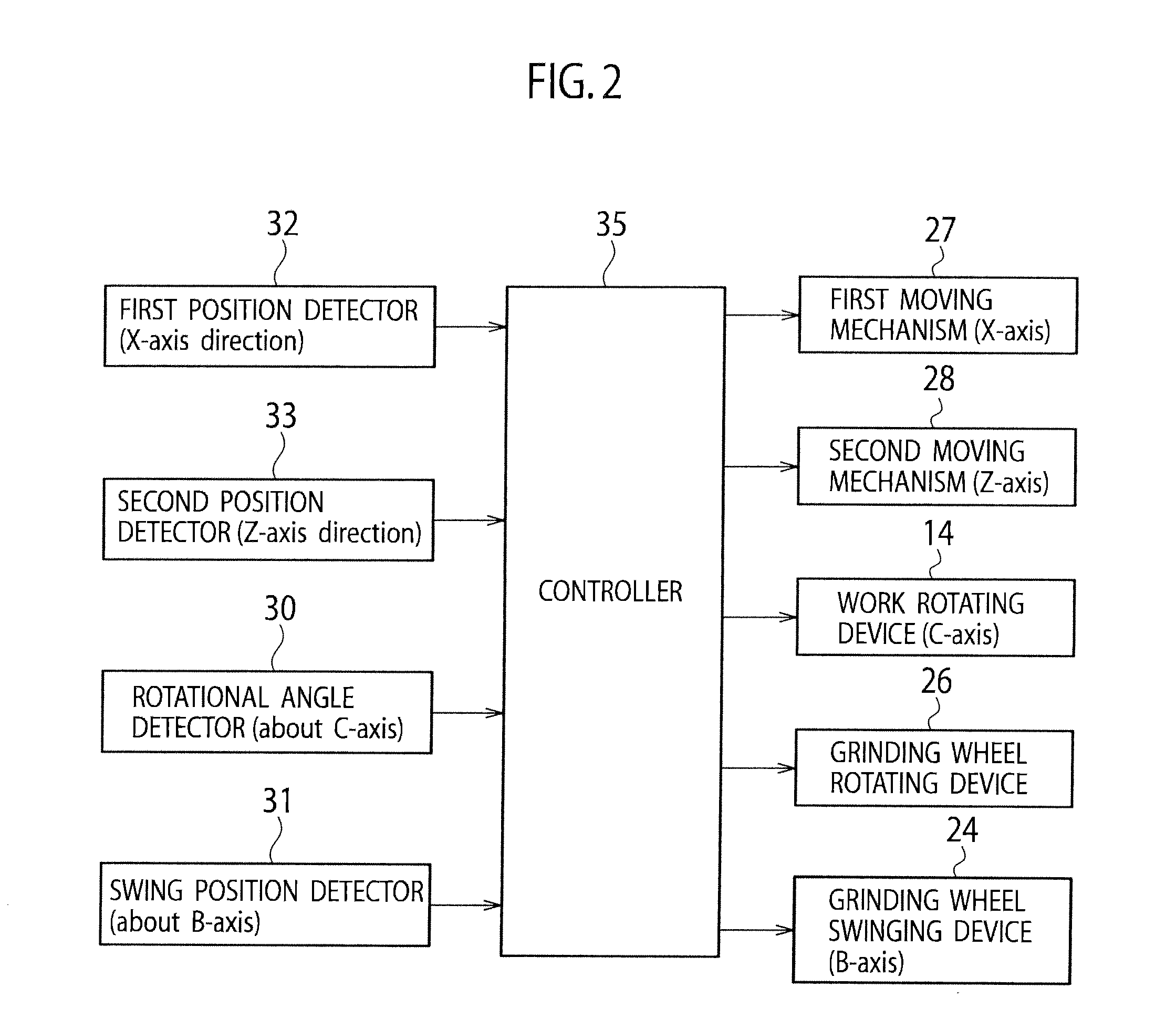
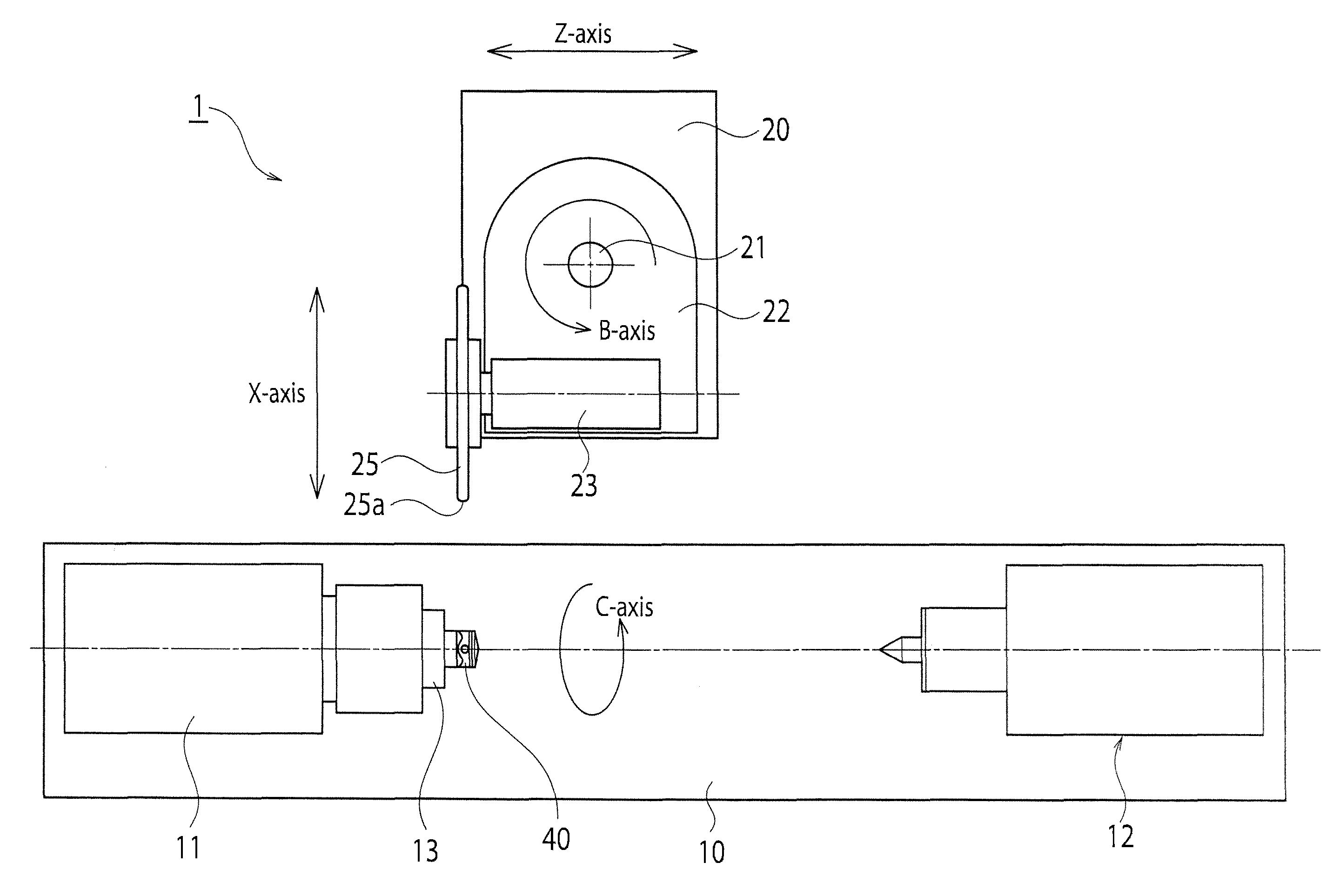
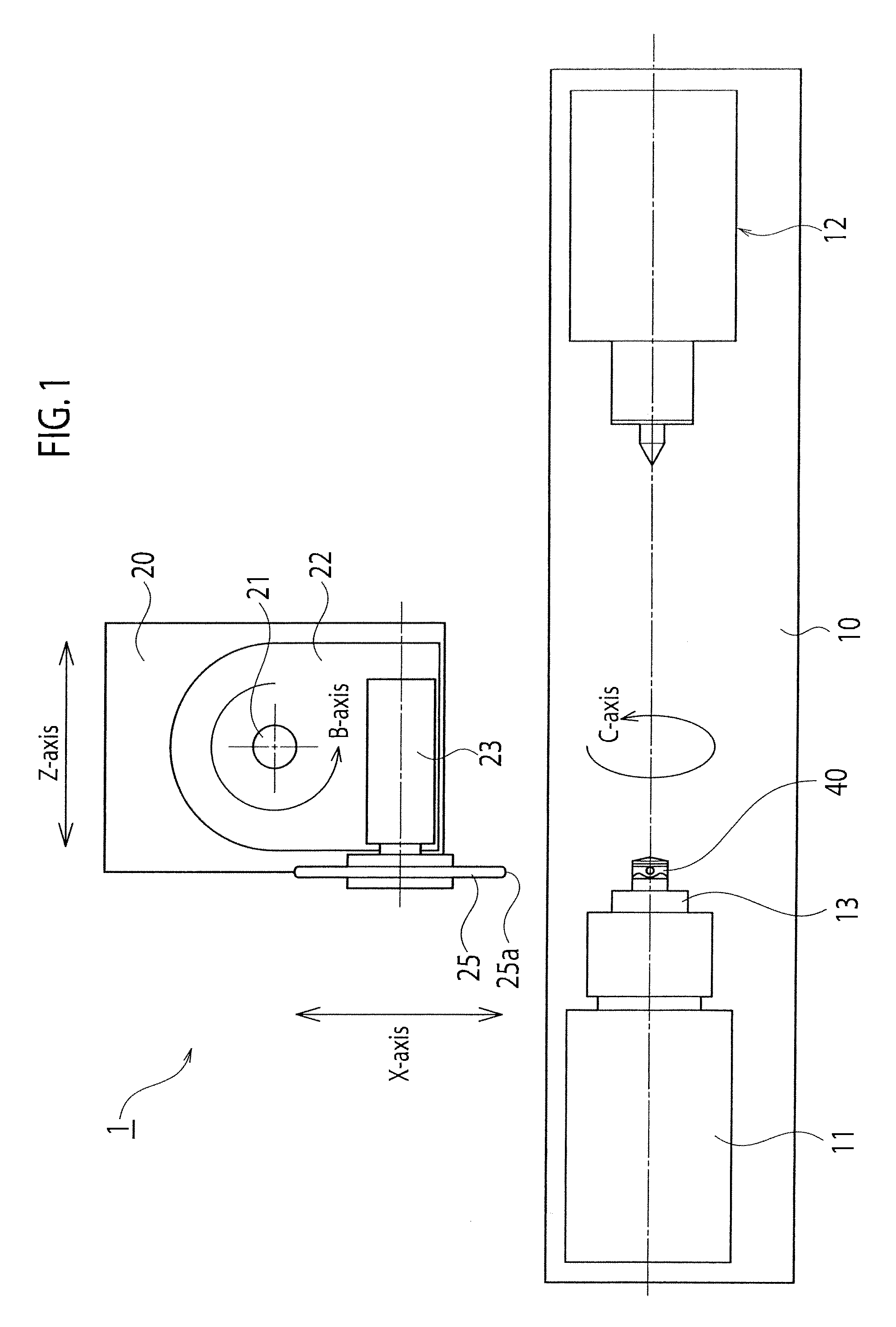
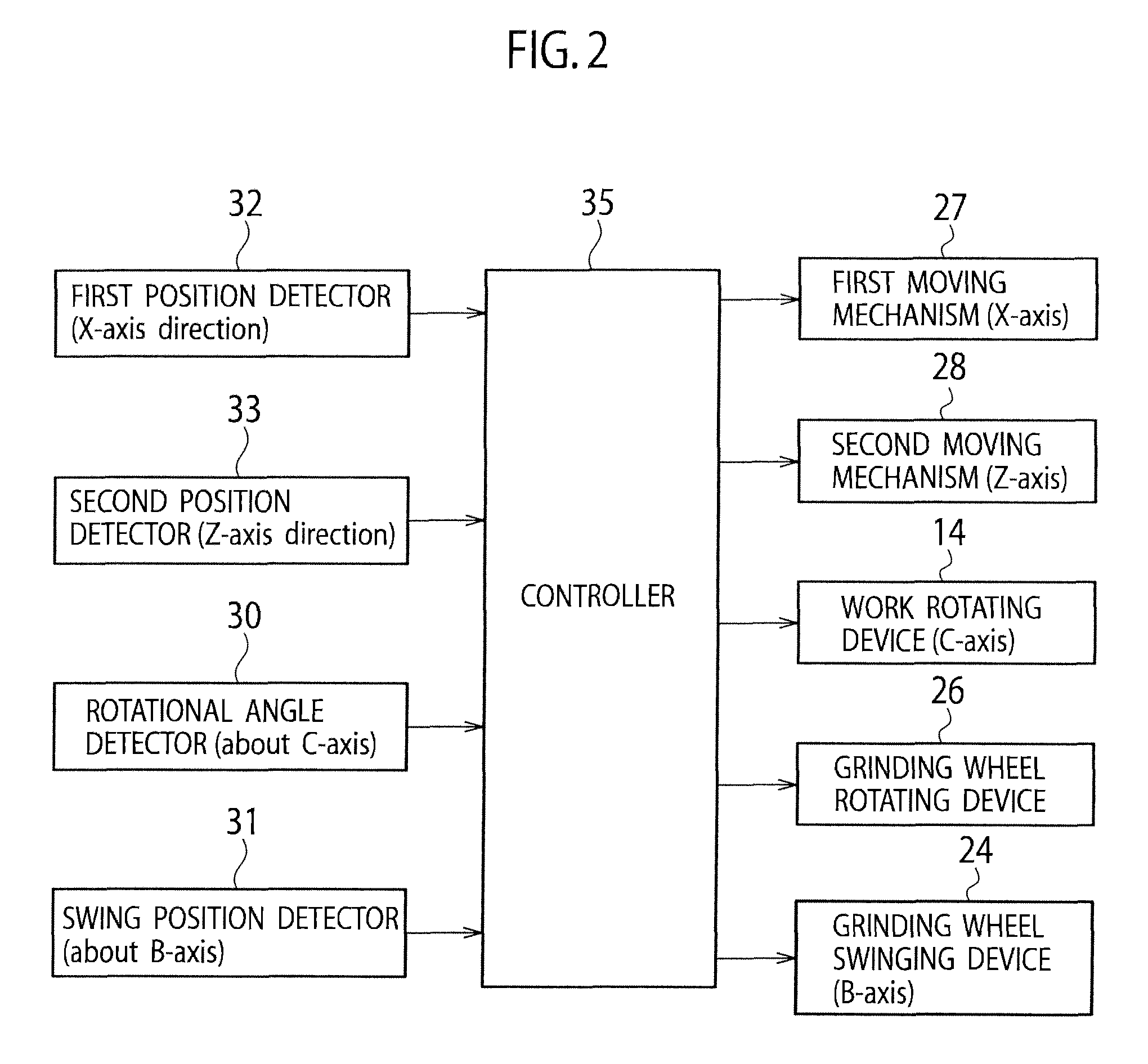
InactiveUS20120149282A1Smooth surface roughnessImprove fuel efficiencyGrinding drivesGrinding feed controlPistonThree dimensional shape
A piston processing apparatus includes a work attaching head capable of fixing a piston material, a work rotating device, a grinding wheel, a grinding wheel rotating device, first and second moving mechanisms for moving the grinding wheel, a rotational angle detector for detecting a rotational angle of the work attaching head, a first and second position detectors for detecting a position of a grinding surface of the grinding wheel, a controller controls the first and second moving mechanisms to grind the outer circumferential surface by the grinding wheel based on target-position information of the grinding surface corresponding to a position on the outer circumferential surface of the piston material. According to the piston processing apparatus, the outer circumferential surface of the piston material can be processed into a three-dimensional shape with high-accuracy, and a piston that can improve fuel efficiency.
Owner:KOGANEI SEIKI
Apparatus and method for processing piston
InactiveUS8500514B2Improve fuel efficiencySmooth surface roughnessEdge grinding machinesGrinding drivesFuel efficiencyThree dimensional shape
A piston processing apparatus includes a work attaching head capable of fixing a piston material, a work rotating device, a grinding wheel, a grinding wheel rotating device, first and second moving mechanisms for moving the grinding wheel, a rotational angle detector for detecting a rotational angle of the work attaching head, a first and second position detectors for detecting a position of a grinding surface of the grinding wheel, a controller controls the first and second moving mechanisms to grind the outer circumferential surface by the grinding wheel based on target-position information of the grinding surface corresponding to a position on the outer circumferential surface of the piston material. According to the piston processing apparatus, the outer circumferential surface of the piston material can be processed into a three-dimensional shape with high-accuracy, and a piston that can improve fuel efficiency.
Owner:KOGANEI SEIKI
Die head coating, coating device, and method of manufacturing die head for coating
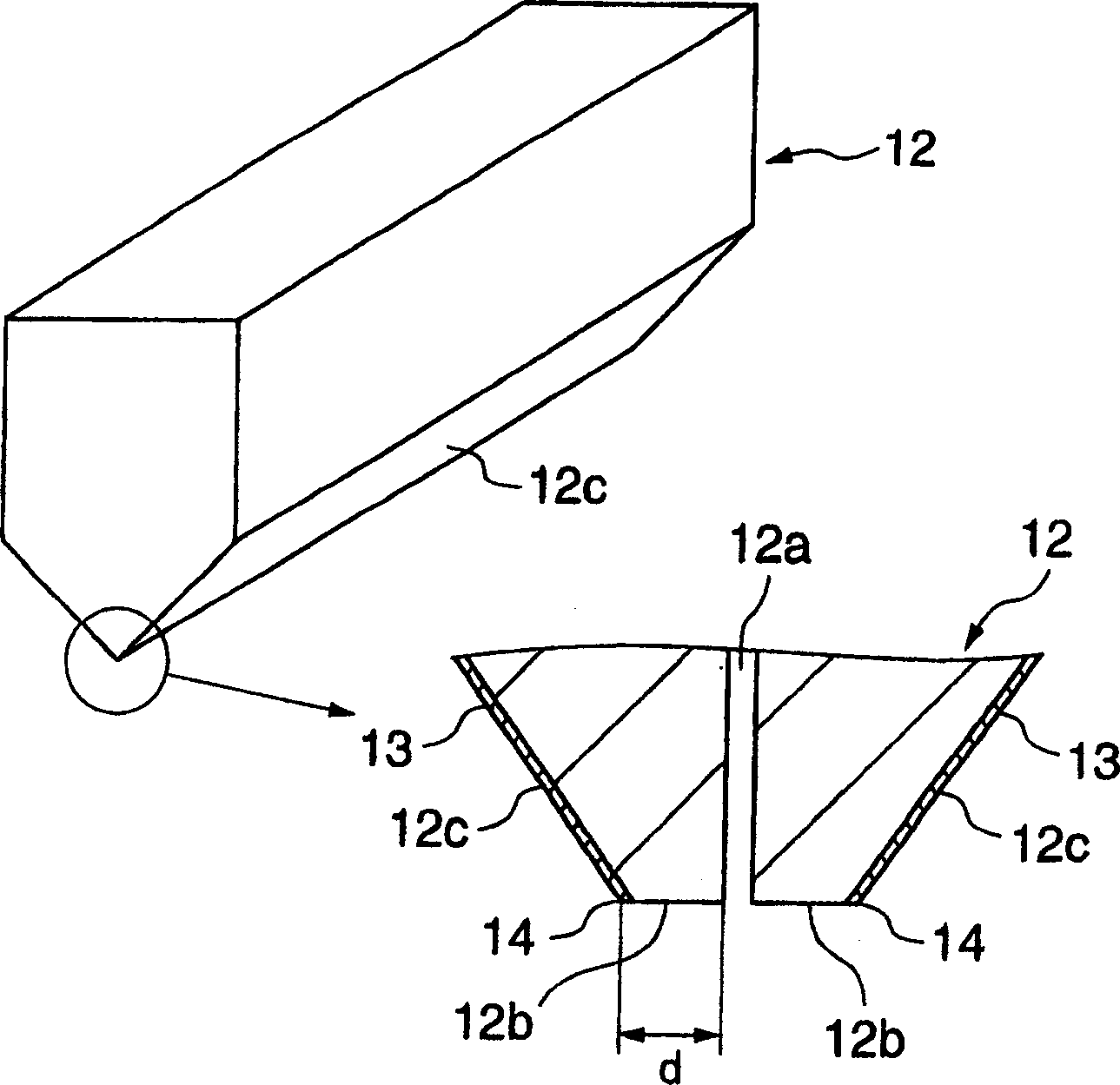
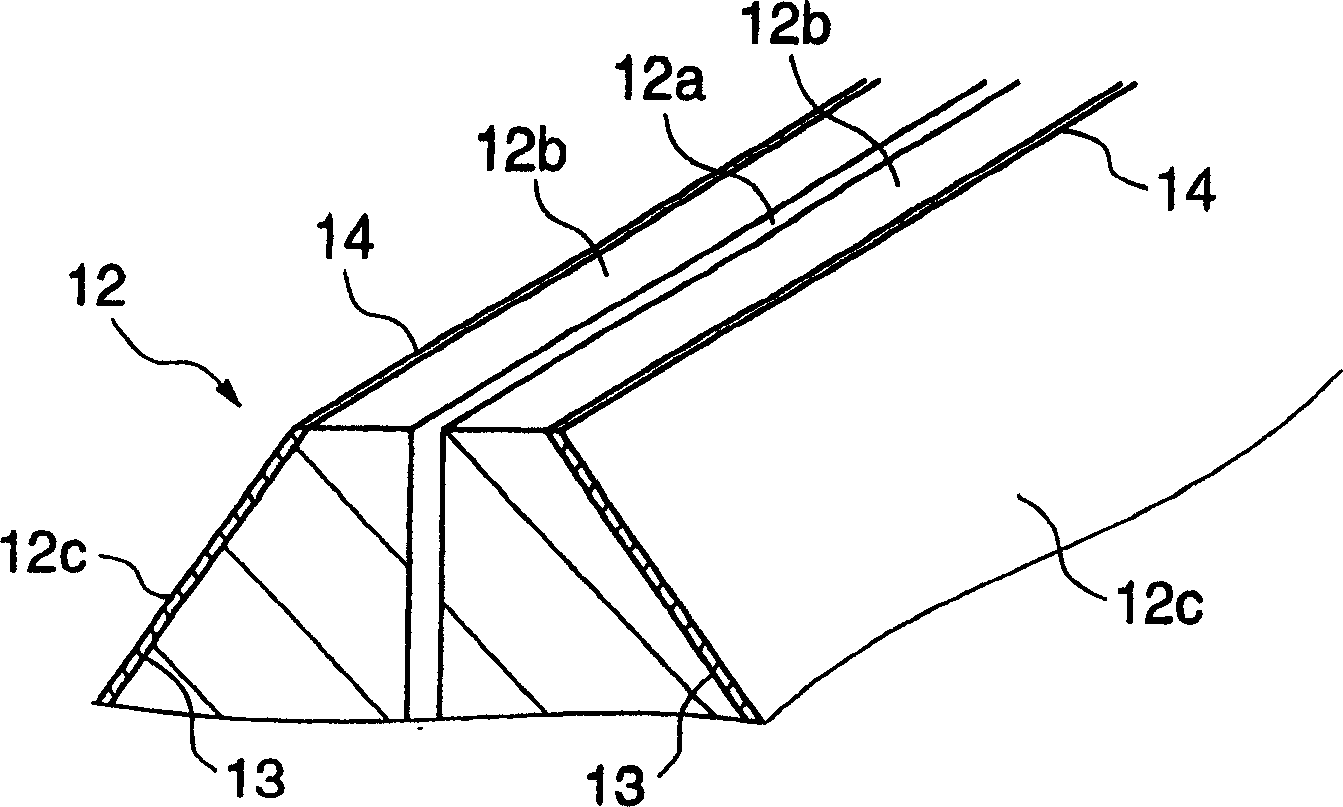
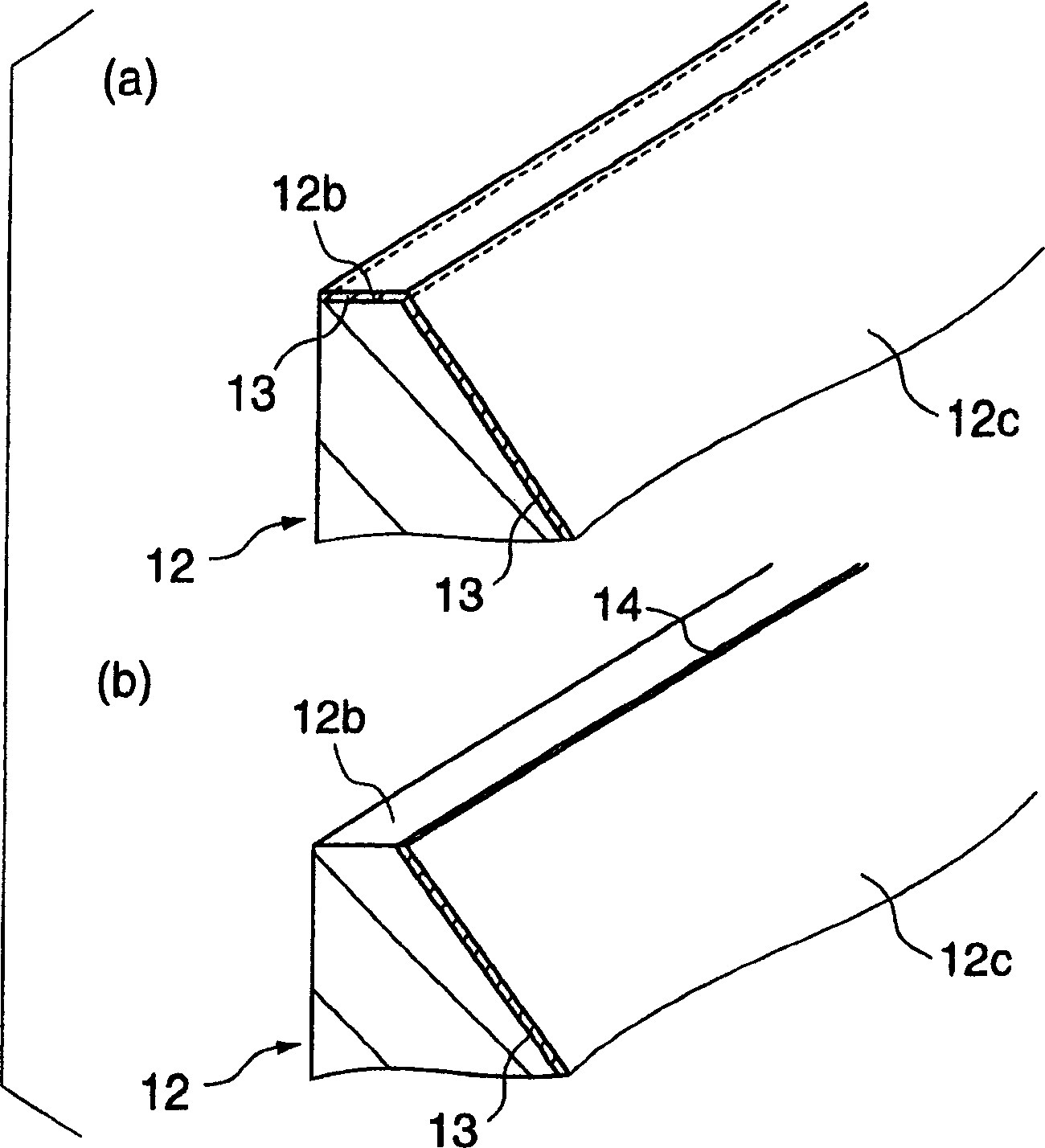
InactiveCN1668389ALow costSufficiently smooth surface roughnessLiquid surface applicatorsCoatingsLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
During displacement relative to a substrate 1, a coating die head emits coating liquid out of a slot 12a to a surface of the substrate. The coating die head includes a lip 12b having a lip surface 12b and a side having a side surface 12c. A contact angle of the surface 12c with respect to the coating liquid is greater than a contact angle of the surface 12b with respect to the coating liquid. This configuration enhances stabilization of bead of the coating liquid during application process of the coating liquid, preventing stripes and steps from appearing in the coating layer. This coating die head makes it possible to carry out high precision coating required for fabrication of color filters for liquid crystal displays.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Mould for optic lens
InactiveCN102935694ASpeed up the flowImprove the problem of poor demouldingOptical articlesOptic lensLens plate
The invention provides a mould for an optic lens. The mould comprises an upper mould and a lower mould, wherein the end face of the lower mould forms a top surface, the outer edge around the top surface serves as an edge portion, and an inwards-recessed cavity is arranged at the center of the top surface. A runner and a sprue are sequentially arranged on the edge of the cavity towards the edge portion, an edge cutting area is defined by the intersecting edge of the cavity and the runner and the lateral wall of the cavity close to two sides of the runner, and the runner is communicated with the sprue through a communication channel. A step is formed at the intersecting position of the bottom surface of the edge cutting area and the bottom surface of the cavity, and the horizontal height of the bottom surface of the cavity is lower than that of the bottom surface of the edge cutting area at the position of the step. The edge of the original cavity close to the runner is inclined, so that when ejected, one side of the mould is free of extrusion of the lateral wall, labor is saved, and the product is not damaged. The step is arranged at the bottom of the cavity, and the deckle edge and the assembly face of the manufactured lens are not on the same plane, so that uneven stacking is avoided.
Owner:YINGTAN YONGWEI PHOTOELECTRIC INSTR
Method of fabricating SOI wafer by ion implantation
ActiveUS9735045B2Low densitySmooth surface roughnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenOptoelectronics
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Toroidal roller bearing
ActiveUS20150098671A1Reduce coefficient of frictionSmooth surface roughnessRoller bearingsShaftsAxial displacementRoller bearing
A toroidal roller bearing, which comprises an outer ring, an inner ring and a plurality of roller elements interposed between the outer and inner rings, wherein the toroidal roller bearing allows for angular and axial displacement between the outer ring and the inner ring. The bearing includes a cage for holding the roller elements, wherein the cage provides an axial guiding feature for axially guiding the roller elements against at least one of the outer ring, inner ring and a separate element located outside the toroidal roller bearing.
Owner:AB SKF
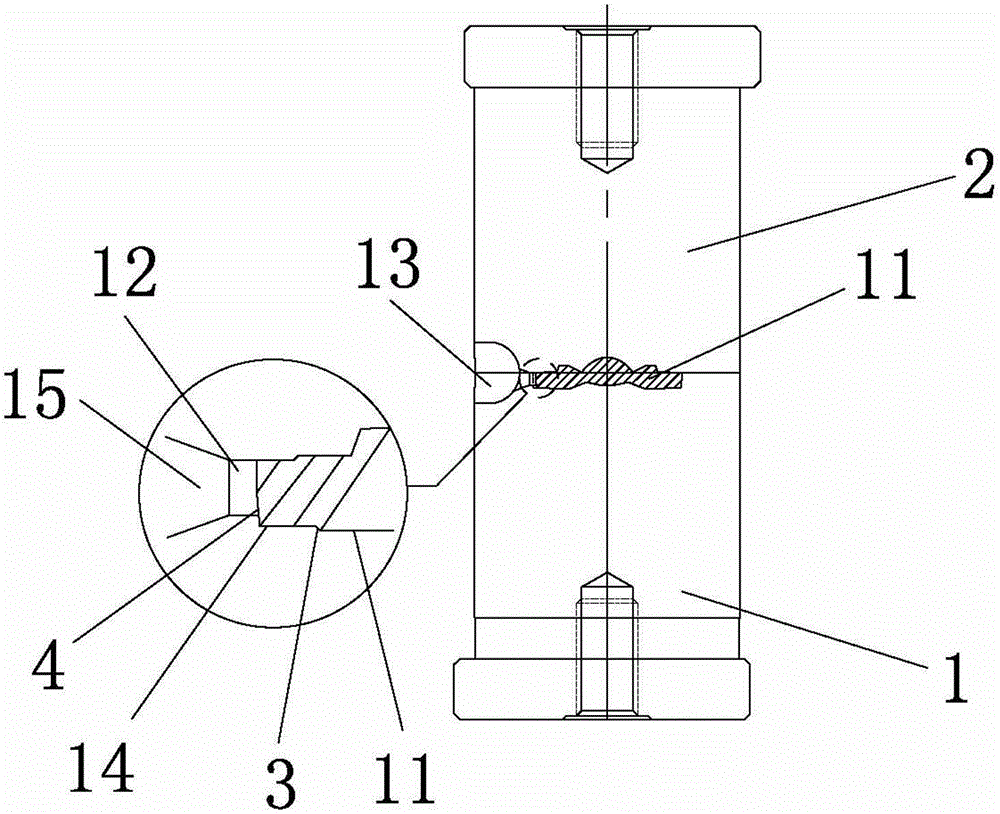
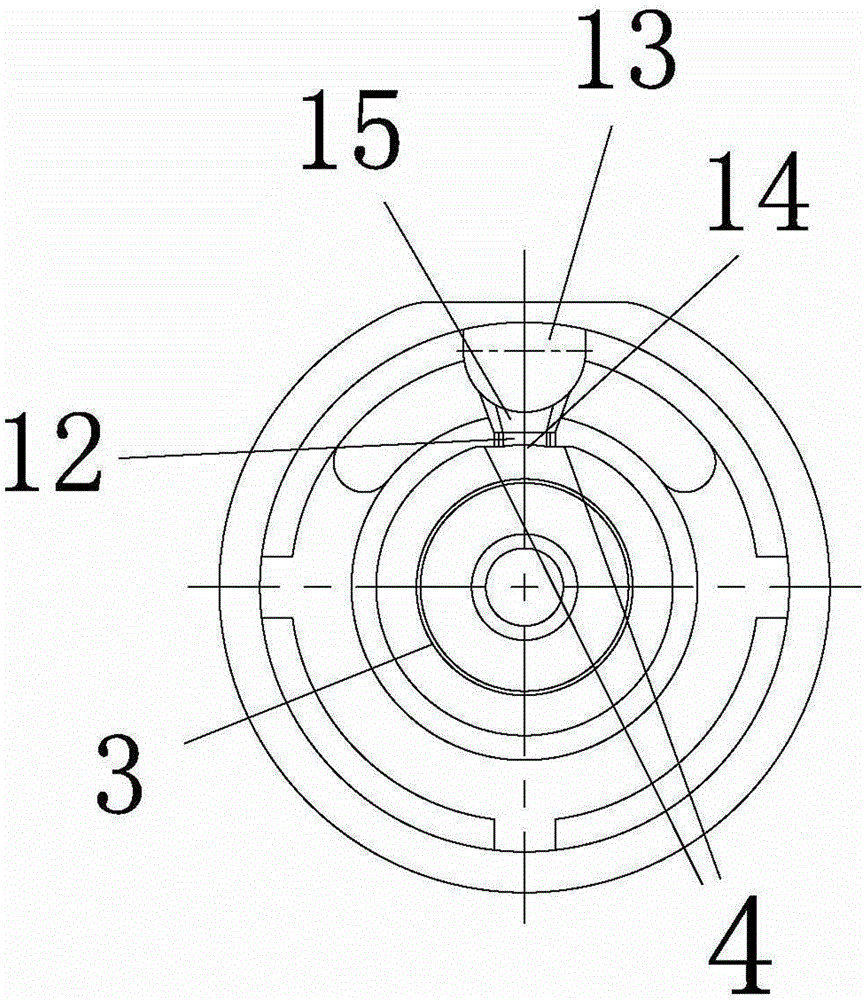
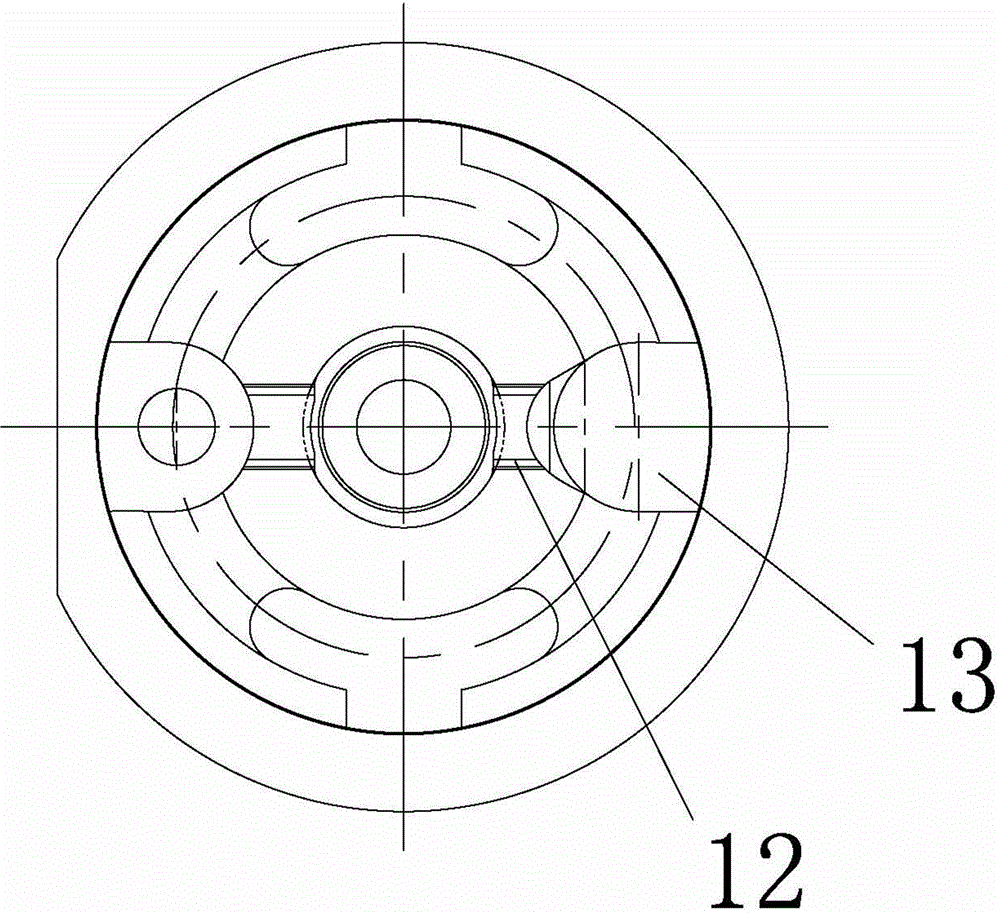
Boring device for tuyere large sleeve of blast furnace
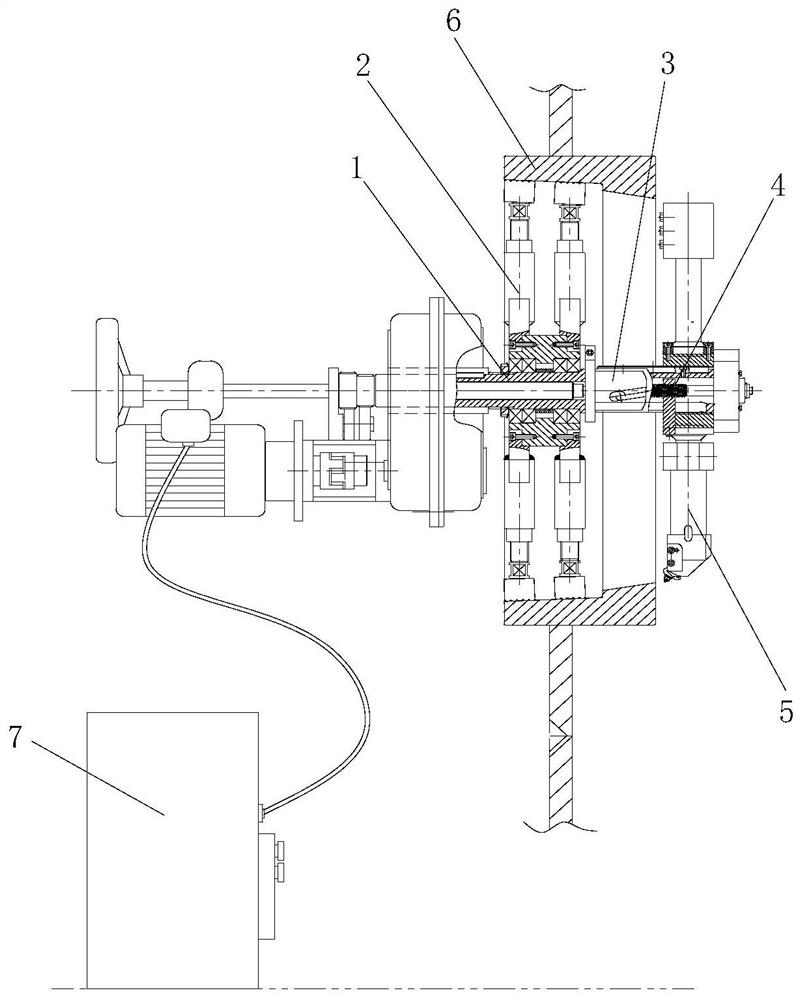
PendingCN113510264AImprove sealingExtended service lifeAutomatic control devicesMeasurement/indication equipmentsScrew threadIndustrial engineering
The embodiment of the invention provides a boring device for a tuyere large sleeve of a blast furnace. The boring device comprises a power system, a main shaft assembly, a positioning support, a feeding frame, a broach mechanism and a tool rest assembly, wherein the main shaft assembly comprises a hollow main shaft, and the main shaft is in transmission connection with the power system; the positioning support is connected with the main shaft assembly, and the positioning support is used for positioning the main shaft relative to the tuyere large sleeve; the feeding frame is fixedly connected with the main shaft, a strip-shaped groove is formed in the feeding frame, and the included angle between the strip-shaped groove and the axis of the main shaft is equal to the machining inclination of the tuyere large sleeve; the broach mechanism comprises a feeding lead screw, the feeding lead screw is arranged in the main shaft in a penetrating mode, and the feeding lead screw is in transmission connection with the main shaft; the tool rest assembly is in threaded connection with the feeding lead screw, and the feeding lead screw drives the tool rest assembly to conduct axial feeding; and the tool rest assembly is in sliding fit with the strip-shaped groove of the feeding frame, and when the tool rest assembly conducts axial feeding, the feeding frame drives the tool rest assembly to conduct radial feeding. The boring device has the characteristics of uniform cutting and convenience in operation.
Owner:QINHUANGDAO QINYE HEAVY IND
Using plated surface for recording media without polishing
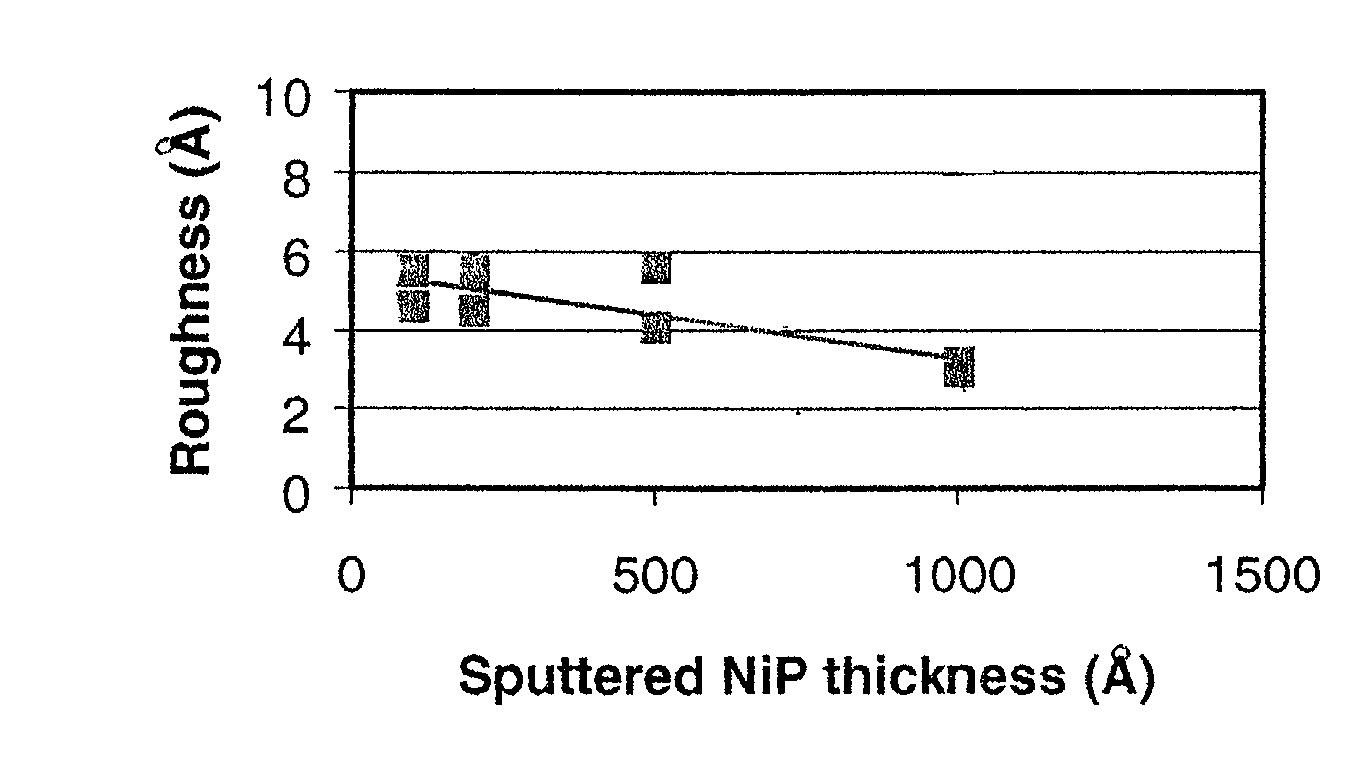
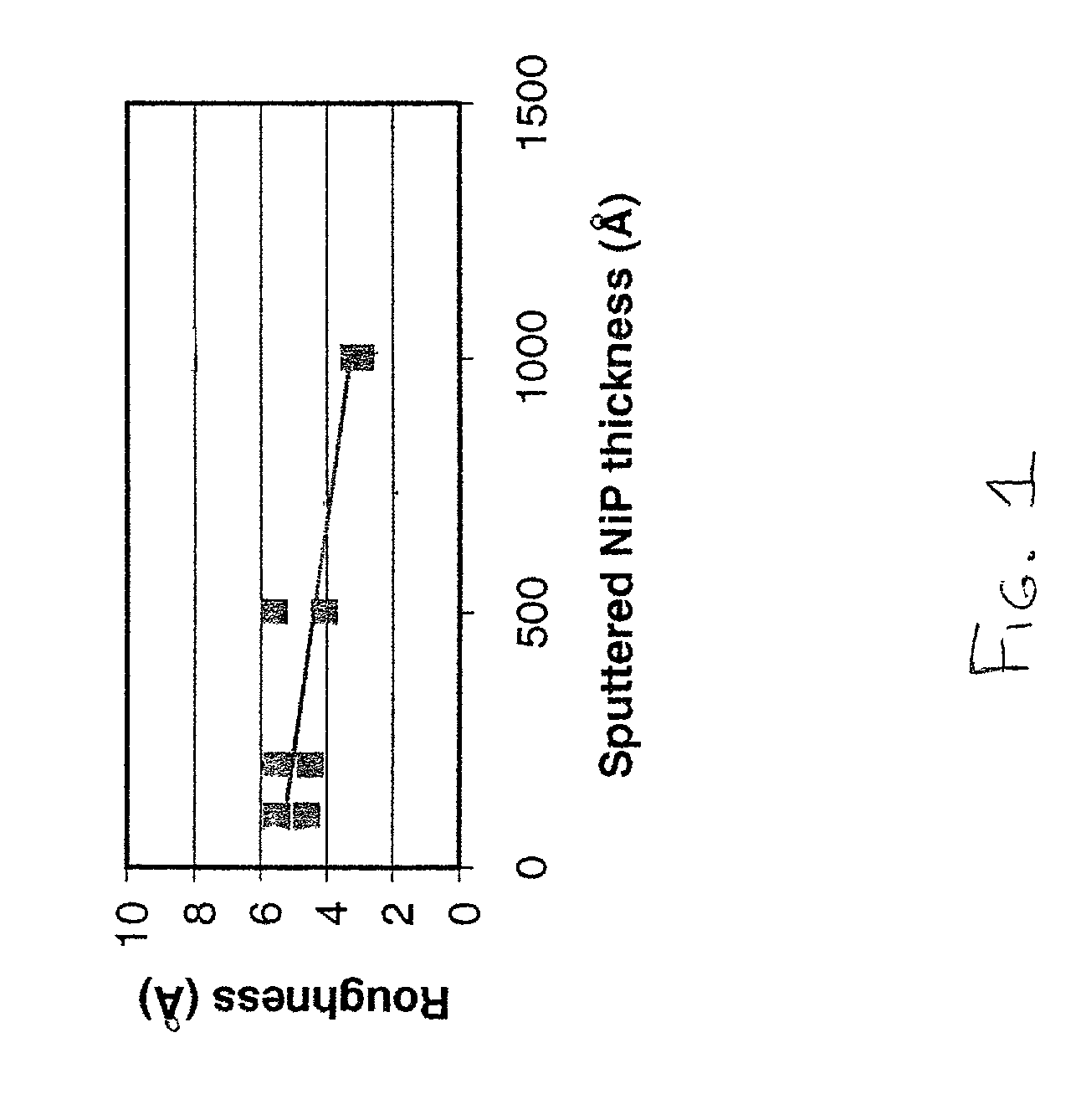
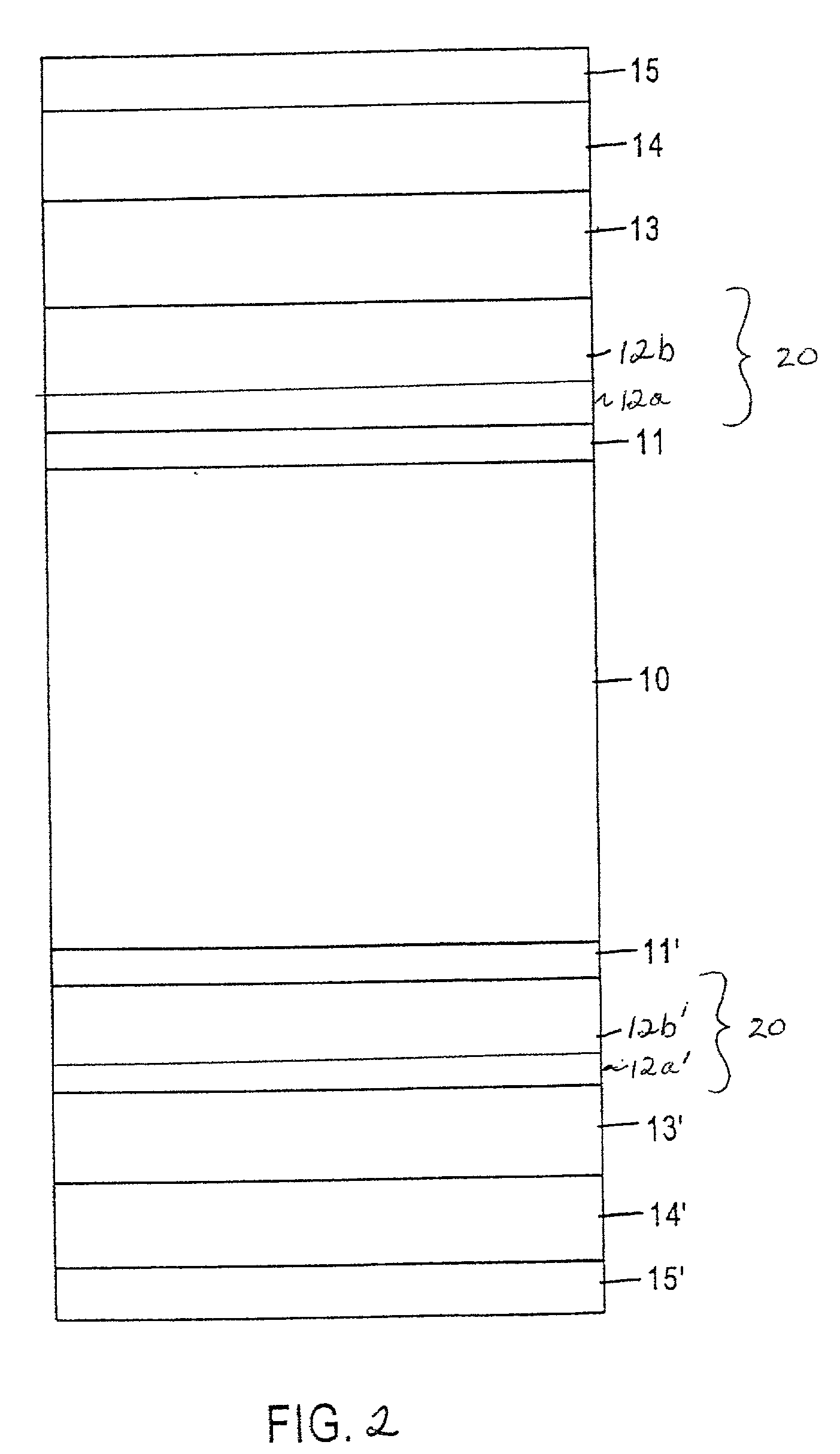
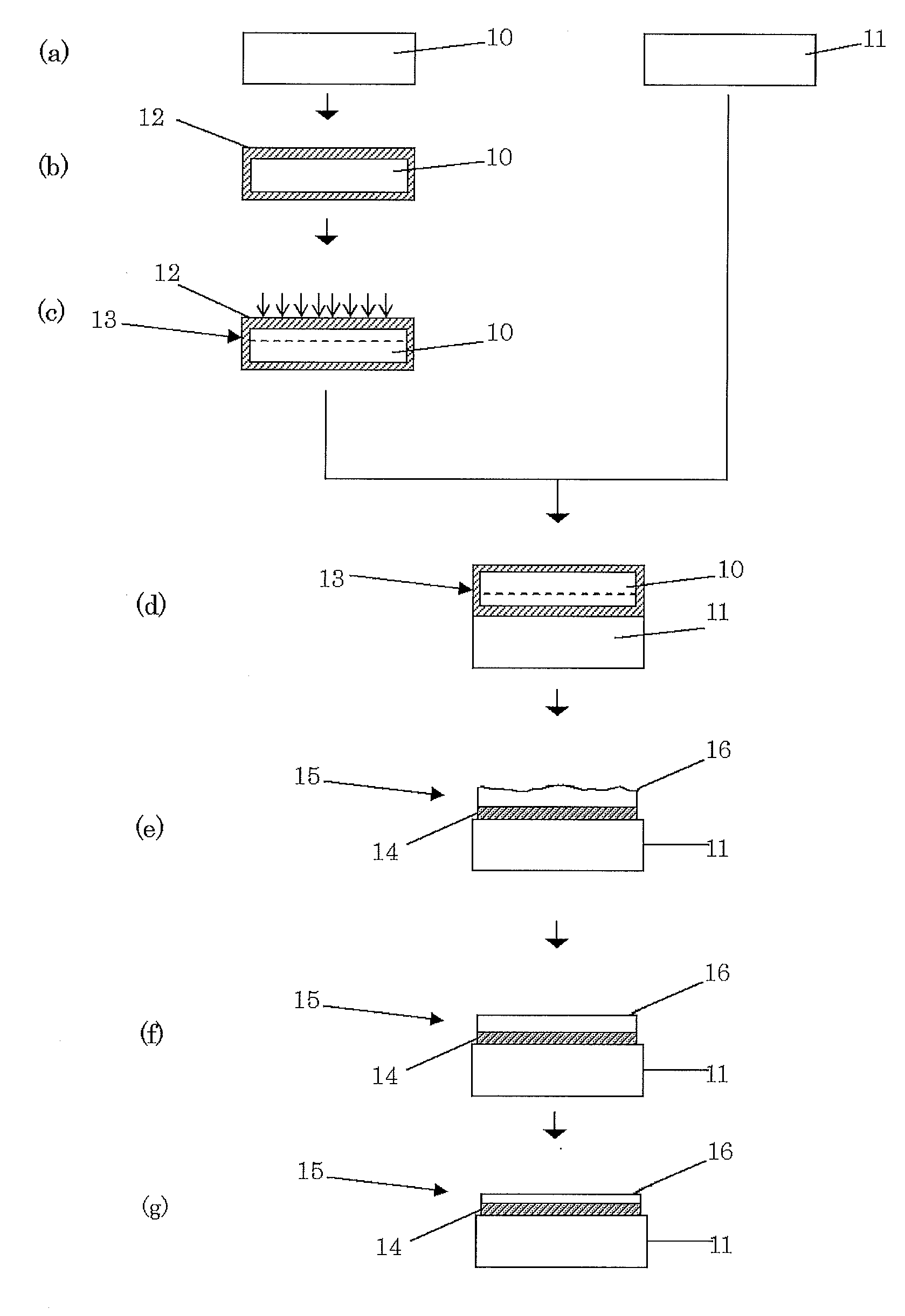
InactiveUS20020071968A1Improve processing throughputHigh degreeBase layers for recording layersVacuum evaporation coatingSurface roughnessSputter deposition
Ultra smooth as-deposited composite nickel coatings for use in an information storage system are provided. The composite nickel coatings include an electrolessly deposited nickel layer formed on a sputter deposited nickel layer. The composite nickel coatings have an as-deposited surface roughness of less than about 10 Å. Embodiments include formation of the composite nickel coating on a disk, followed by deposition of an underlayer and magnetic layer thereon to form a magnetic recording medium.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Method of manufacturing bonded wafer
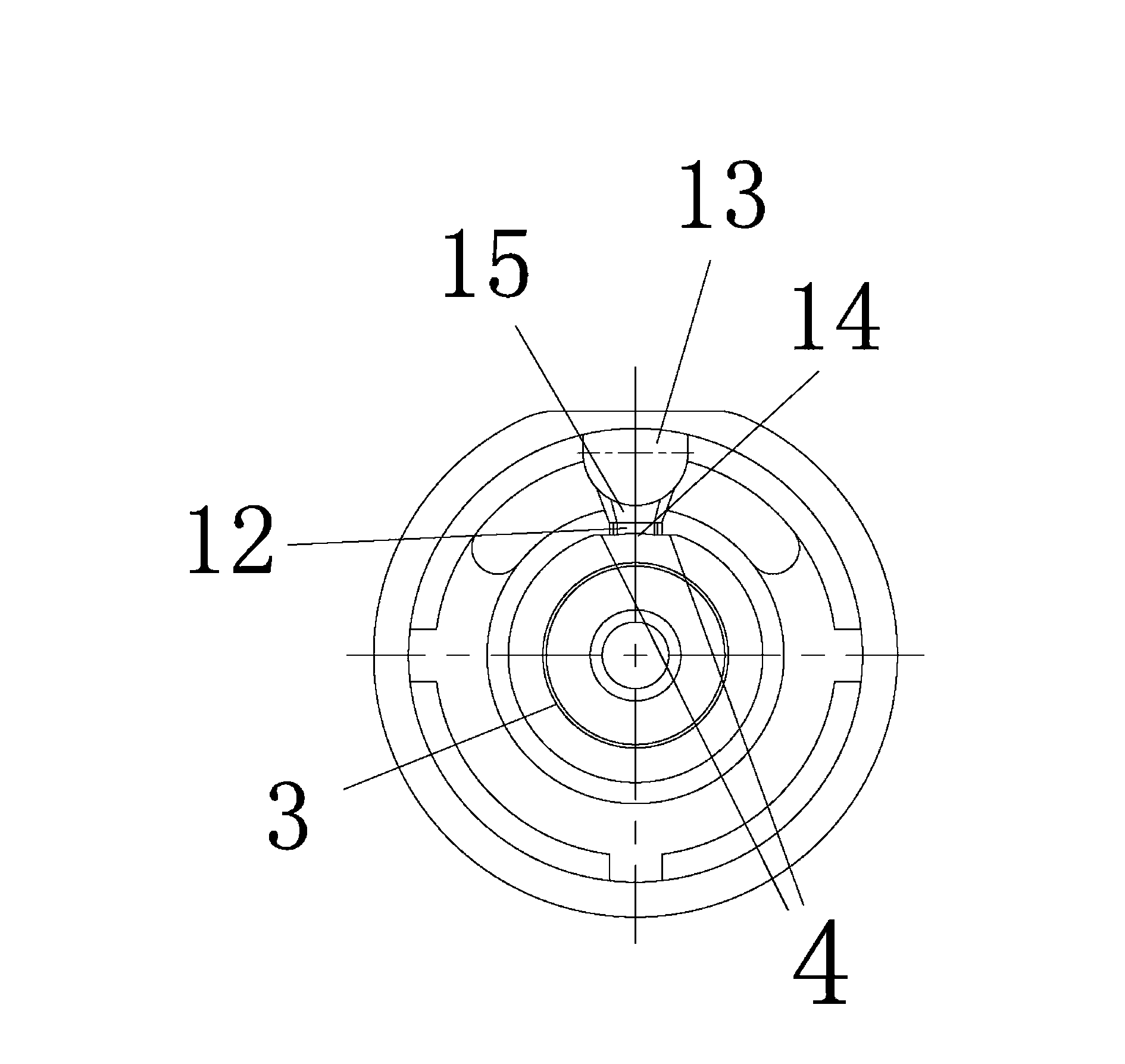
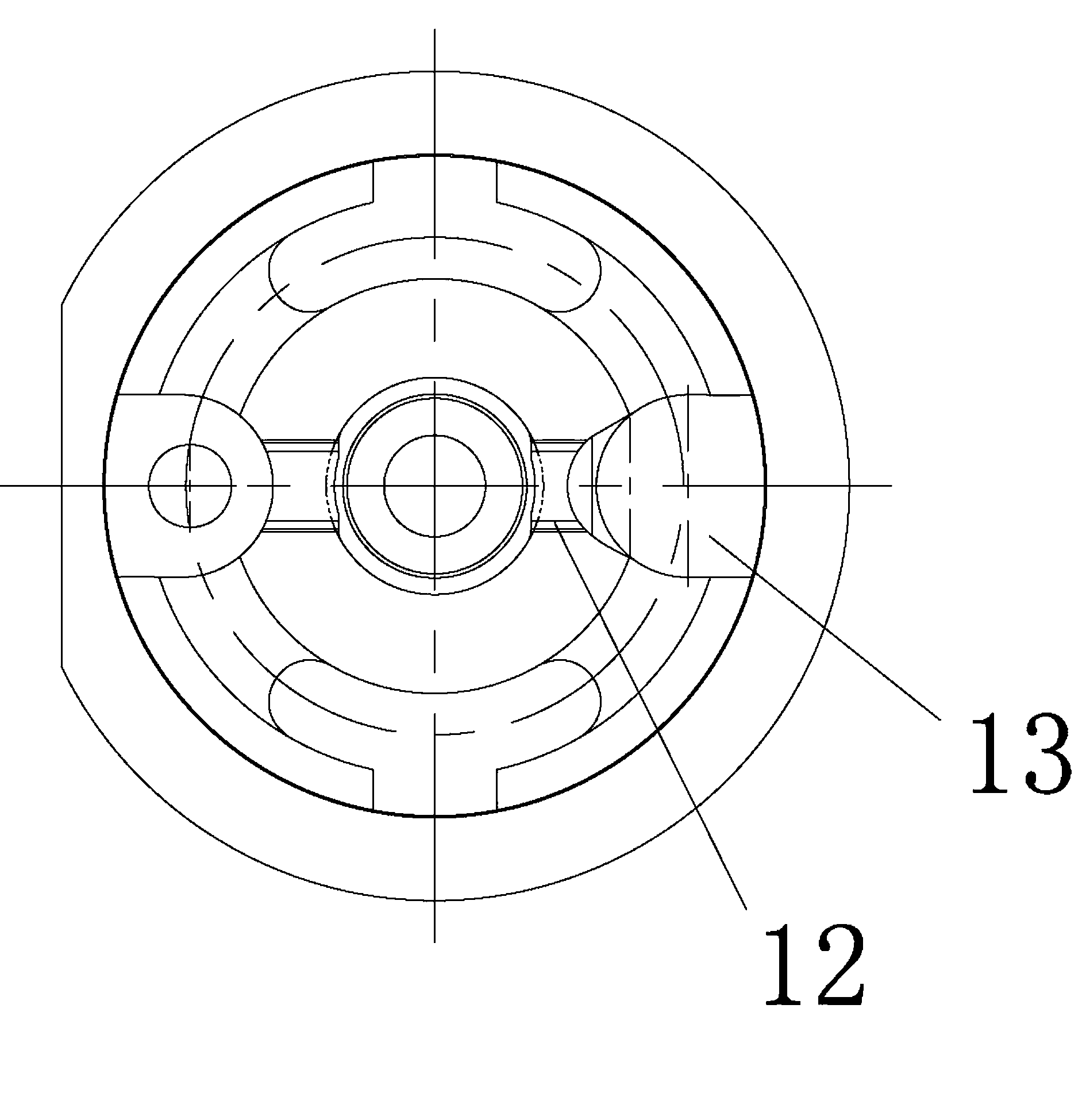
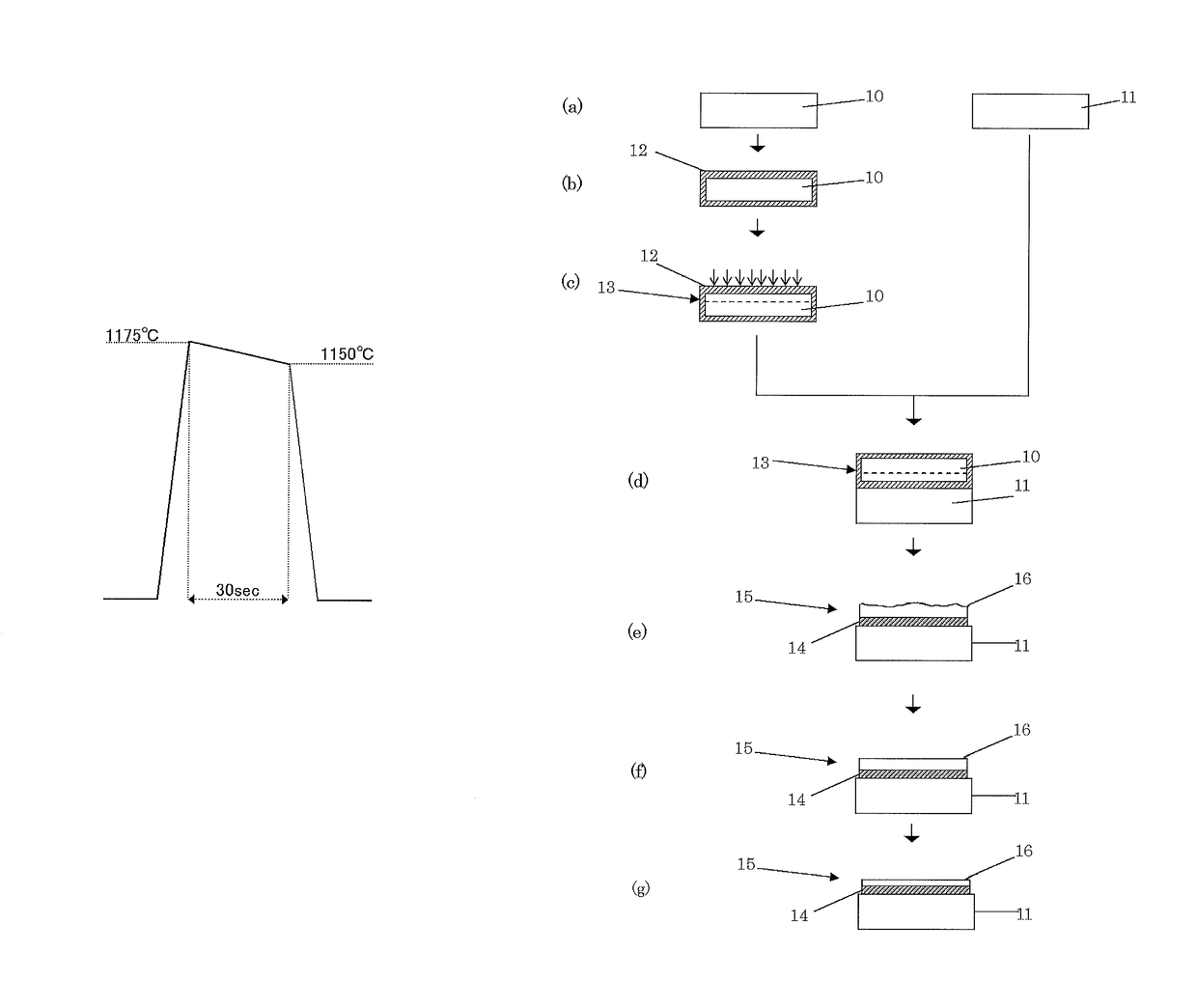
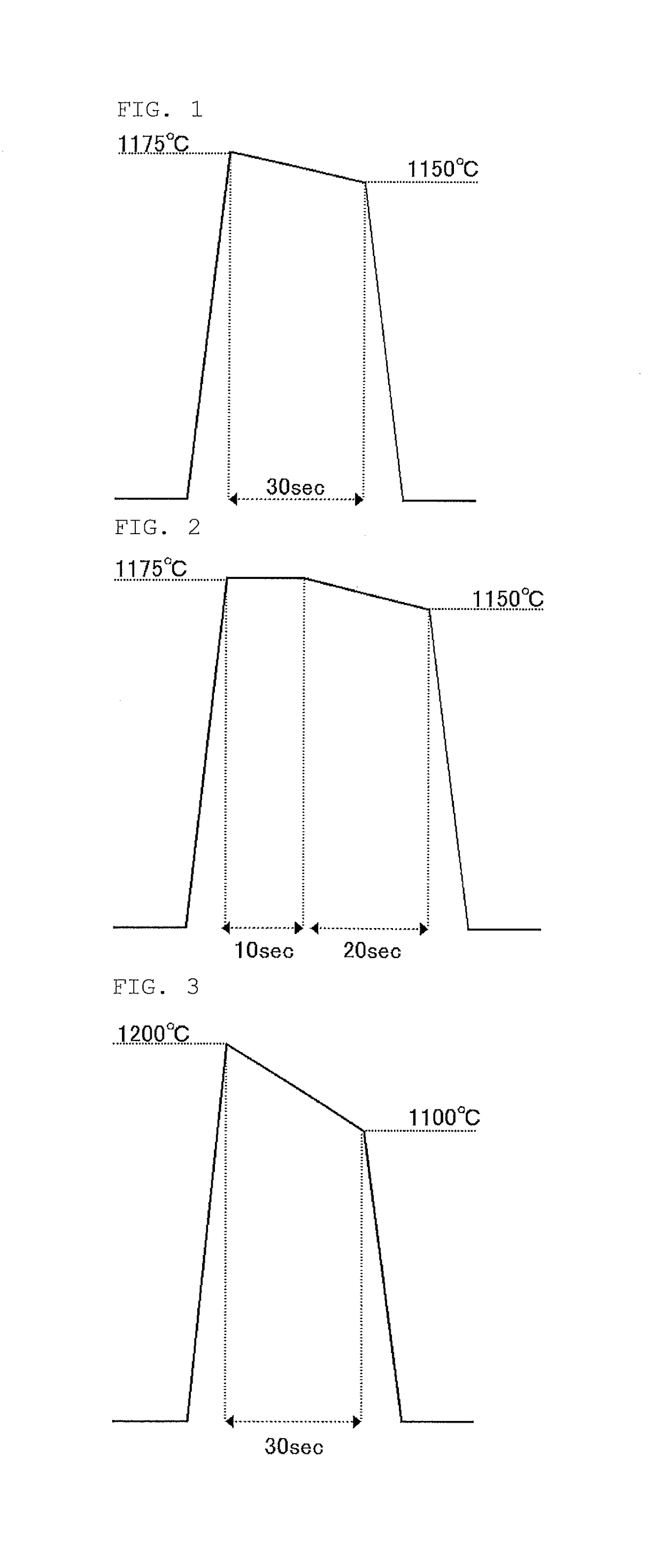
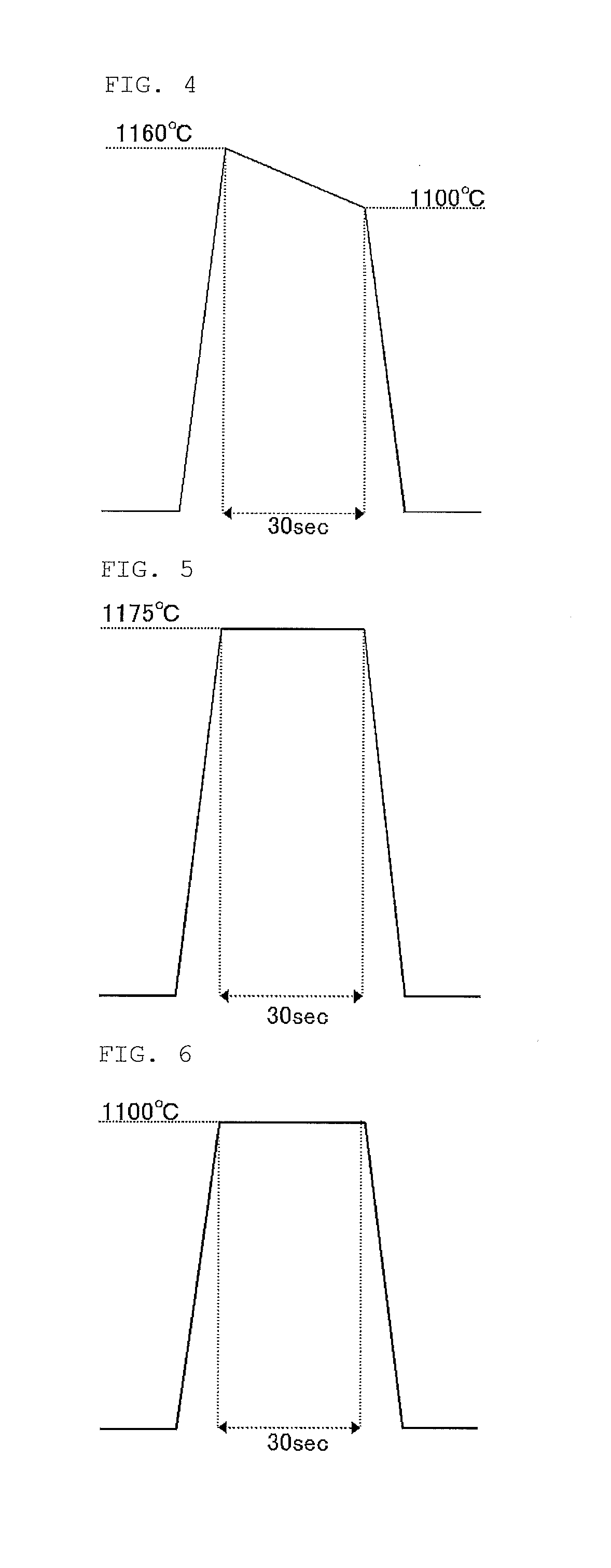
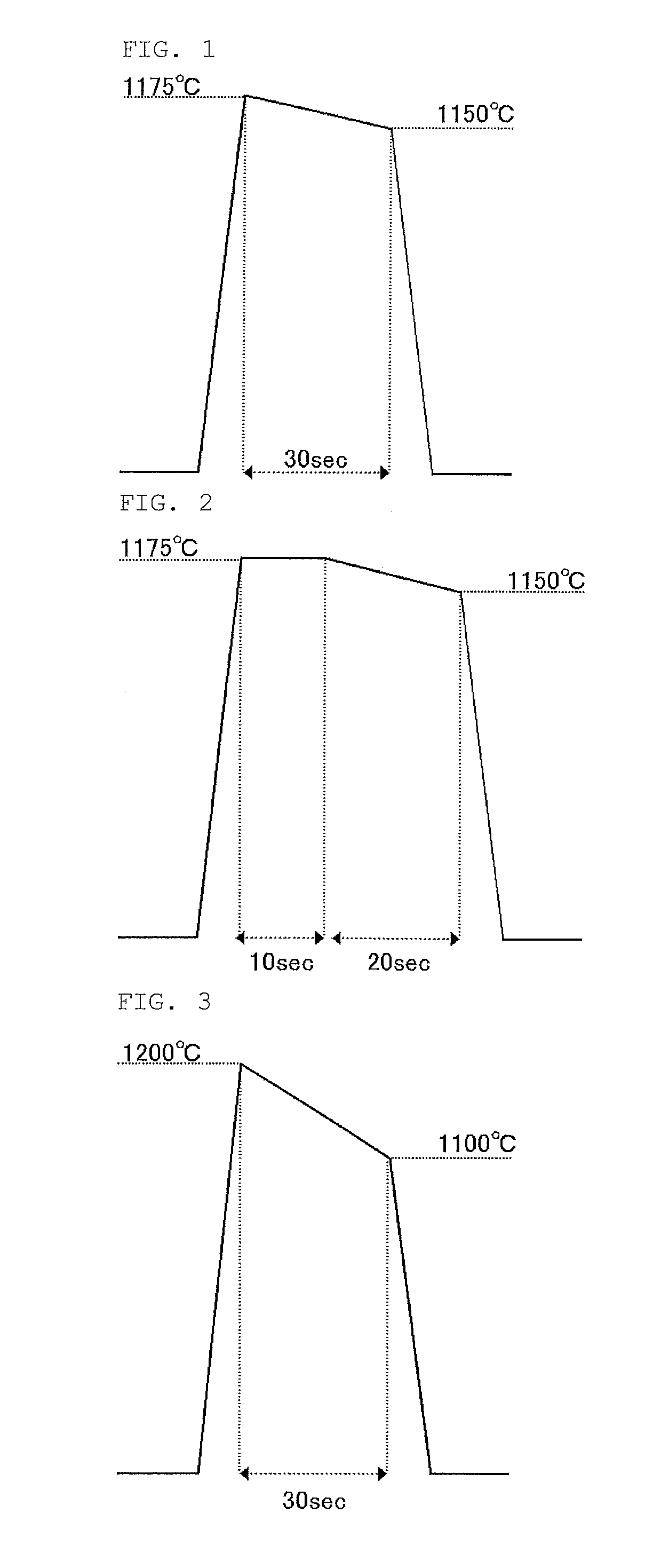
ActiveUS20160079114A1Smooth surface roughnessLow BMD densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetallurgyAtmosphere
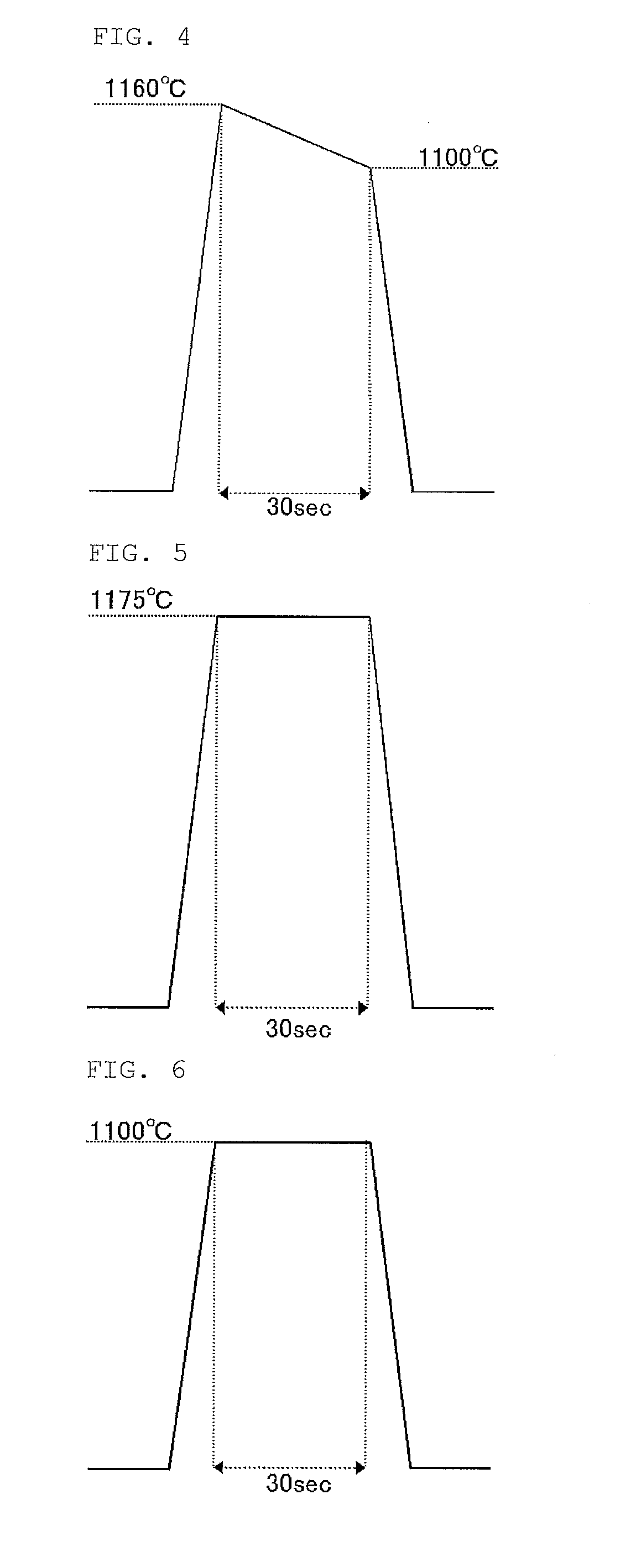
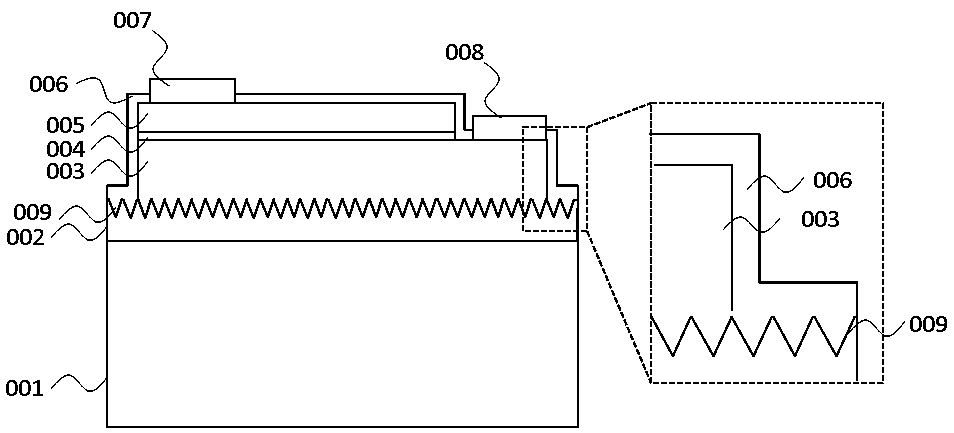
The present invention provides a method of manufacturing a bonded wafer, including performing RTA under an atmosphere containing hydrogen on a bonded wafer after separating the bond wafer constituting the bonded wafer, and subsequently performing a sacrificial oxidation process to reduce the thickness of the thin film, wherein the RTA is performed under conditions of a retention start temperature of more than 1150° C. and a retention end temperature of 1150° C. or less. The invention can inhibit the BMD density from increasing and sufficiently flatten the surface of a thin film when the thin film of the bonded wafer is flattened and thinned by the combination of the RTA and sacrificial oxidation processes.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Inverted light-emitting element
ActiveCN110571318AImprove reliabilityInterface void reductionSemiconductor devicesQuantum wellEngineering
The invention discloses an inverted light-emitting element. The inverted light-emitting element structurally comprises a transparent substrate, a transparent bonding layer, an epitaxial layer, an insulating protection layer, a first welding electrode and a second welding electrode which are distributed from bottom to top; the epitaxial layer comprises a p-type conductive layer, a quantum well andan n-type conductive layer; the p-type conductive layer is connected with the transparent bonding layer, and the contact surface of the p-type conductive layer and the transparent bonding layer is a roughened surface; the edge of the epitaxial layer is etched until the transparent bonding layer is also etched and thinned to form a step; the surface of the thinned transparent bonding layer is at least lower than the lowest point of the roughened surface; partial regions of the n-type conductive layer and the quantum well are etched until the p-type conductive layer is exposed; the insulating protection layer covers the above structure; and the first welding electrode and the second welding electrode contact with the p-type conductive layer and the n-type conductive layer through the throughholes of the insulating protection layer. The reliability of the inverted light-emitting element is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN SANAN OPTOELECTRONICS
Toroidal roller bearing
ActiveUS9243664B2Reduce coefficient of frictionSmooth surface roughnessRoller bearingsShaftsAxial displacementRoller bearing
A toroidal roller bearing, which comprises an outer ring, an inner ring and a plurality of roller elements interposed between the outer and inner rings, wherein the toroidal roller bearing allows for angular and axial displacement between the outer ring and the inner ring. The bearing includes a cage for holding the roller elements, wherein the cage provides an axial guiding feature for axially guiding the roller elements against at least one of the outer ring, inner ring and a separate element located outside the toroidal roller bearing.
Owner:AB SKF
Processing method of high-cleanness stainless steel cable
The invention discloses the structure of highly clean stainless steel cables, and a treatment method thereof, comprising the following steps: after being knitted and made into required finished products, stainless steel wires or stainless steel cables are treated with electrolytic degreasing to reach complete ungrease treatment, after water washing, the stainless steel wires or the stainless steel cables are treated with electrolytic polishing so as to carry out accurate leveling improvement to the rough surface of the surface layer of the finished product and improve the corrosion resistance of the finished product; subsequently, weak acid activation and water washing are carried out for drying the finished product so as to cause the surface of the stainless steel wires or the stainless steel cables to have better corrosion resisting performance and increase the luster of the surface of the finished product.
Owner:YUEN NENG
Mould for optic lens
InactiveCN102935694BSpeed up the flowImprove the problem of poor demouldingOptical articlesOptic lensEngineering
The invention provides a mould for an optic lens. The mould comprises an upper mould and a lower mould, wherein the end face of the lower mould forms a top surface, the outer edge around the top surface serves as an edge portion, and an inwards-recessed cavity is arranged at the center of the top surface. A runner and a sprue are sequentially arranged on the edge of the cavity towards the edge portion, an edge cutting area is defined by the intersecting edge of the cavity and the runner and the lateral wall of the cavity close to two sides of the runner, and the runner is communicated with the sprue through a communication channel. A step is formed at the intersecting position of the bottom surface of the edge cutting area and the bottom surface of the cavity, and the horizontal height of the bottom surface of the cavity is lower than that of the bottom surface of the edge cutting area at the position of the step. The edge of the original cavity close to the runner is inclined, so that when ejected, one side of the mould is free of extrusion of the lateral wall, labor is saved, and the product is not damaged. The step is arranged at the bottom of the cavity, and the deckle edge and the assembly face of the manufactured lens are not on the same plane, so that uneven stacking is avoided.
Owner:YINGTAN YONGWEI PHOTOELECTRIC INSTR
Sub-resolutional laser annealing mask
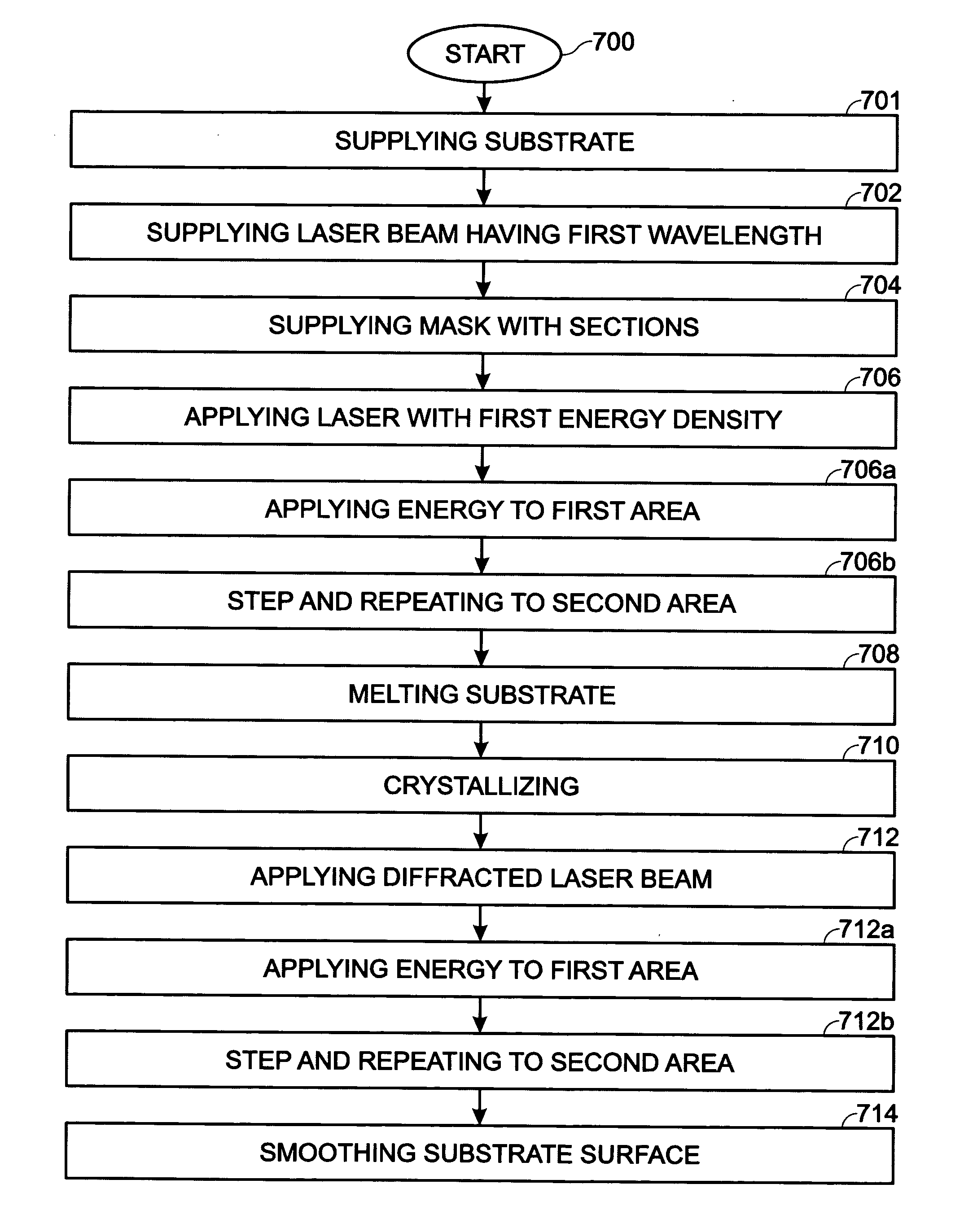
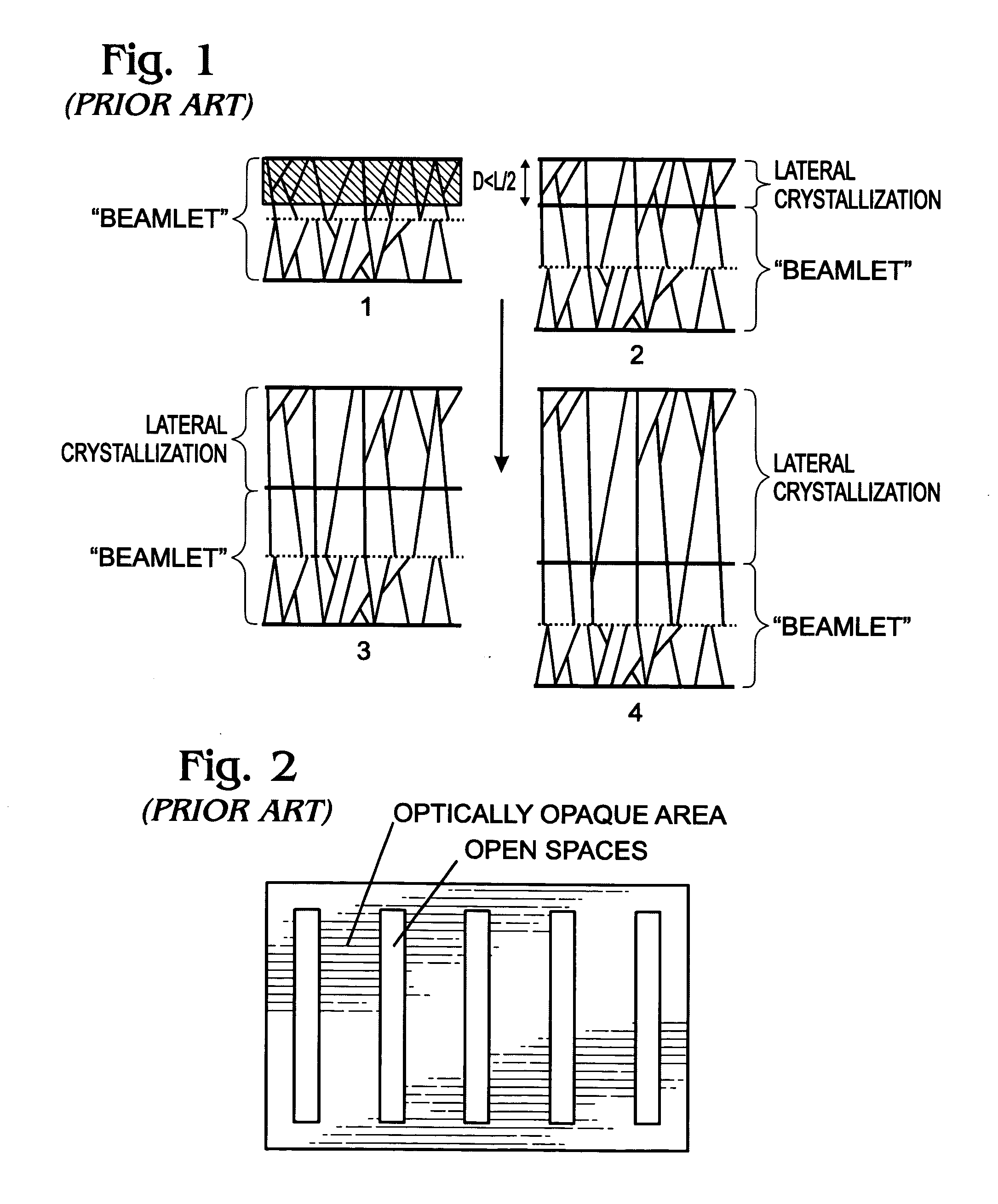
InactiveUS20070107655A1Improve performanceImprove reliabilityPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsVolumetric Mass DensityLength wave
A mask with sub-resolution aperture features and a method for smoothing an annealed surface using a sub-resolution mask pattern are provided. The method comprises: supplying a laser beam having a first wavelength; supplying a mask with a first mask section having apertures with a first dimension and a second mask section with apertures having a second dimension, less than the first dimension; applying a laser beam having a first energy density to a substrate region; melting a substrate region in response to the first energy density; crystallizing the substrate region; applying a diffracted laser beam to the substrate region; and, in response to the diffracted laser beam, smoothing the substrate region surface. In some aspects of the method, applying a diffracted laser beam to the substrate area includes applying a diffracted laser beam having a second energy density, less than the first energy density, to the substrate region. The second energy density is in the range of 40% to 70% of the first energy density, and preferably in the range of 50% to 60% of the first energy density.
Owner:SHARP KK
5G chip processing technology
InactiveCN112518552APrevent rustAvoid pollutionPolishing machinesGrinding drivesWaferingGallium nitride
The invention discloses a 5G chip processing technology. The 5G chip processing technology comprises the following steps of: 1, carrying out primary cutting, grinding and lapping treatment on a gallium nitride wafer; 2, placing the lapped gallium nitride wafer on a precision polishing instrument for fine polishing treatment; and 3, washing the surfaces of the gallium nitride wafer after fine polishing with a cleaning agent, and then drying to obtain a radio-frequency chip material, wherein the precision polishing instrument in the step 2 comprises a protection box, a polishing bin, a driving bin, a bearing plate, a polishing groove, a maintaining mechanism, an ejecting device, a polishing device, a stroke device, an upper cover plate, a supercharging device arranged on the upper cover plate and a liquid feeding device arranged on the polishing bin. The flatness of the surfaces including the front surface and the back surface of the gallium nitride wafer can be improved to a new level through the precision polishing instrument, so that a 5G chip with better quality is produced, and the requirement of 5G communication is met.
Owner:谢贝贝
A method of manufacturing a plate roll
ActiveCN106994817BReduce surface roughnessSmooth surface roughnessForme preparationCopper platingMicrometer
Owner:TIANJIN YUNCHENG PLATE MAKING
Wear-resistant pvd tool coating containing tialn nanolayer film
ActiveCN111032915BHigh coating rateSmooth surface roughnessMilling cuttersVacuum evaporation coatingPolycrystalline diamondPhysical chemistry
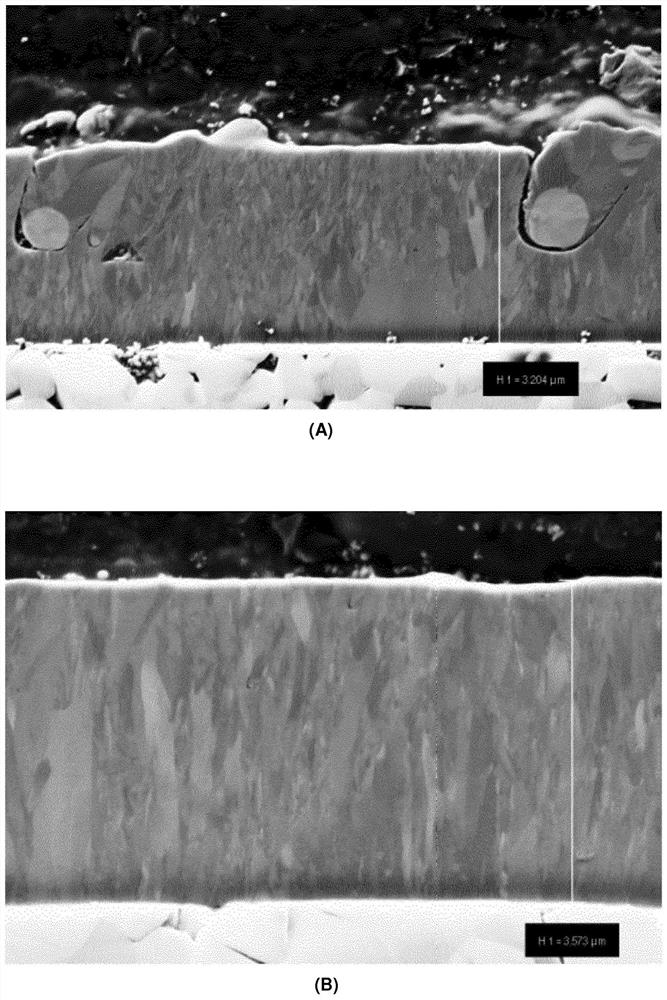
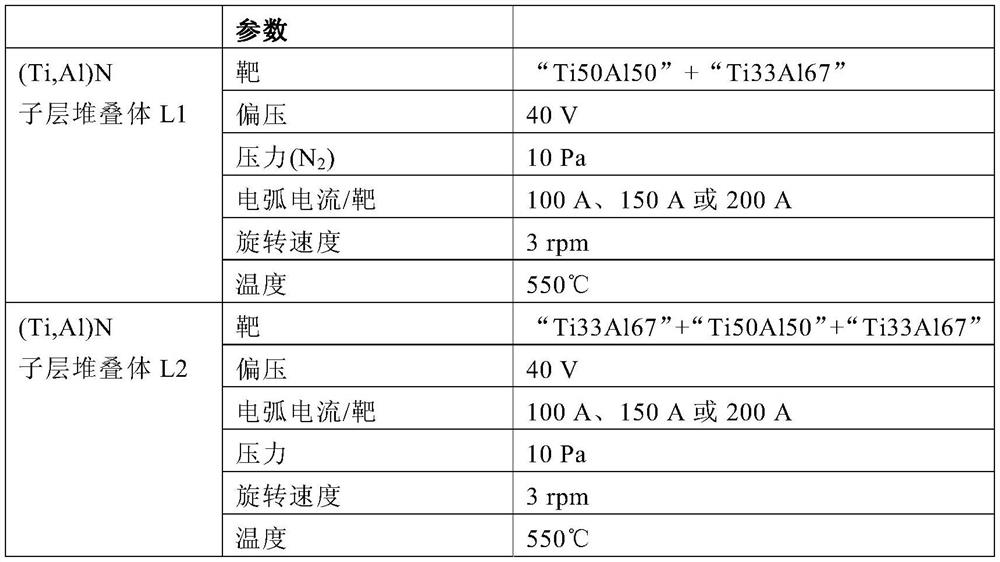
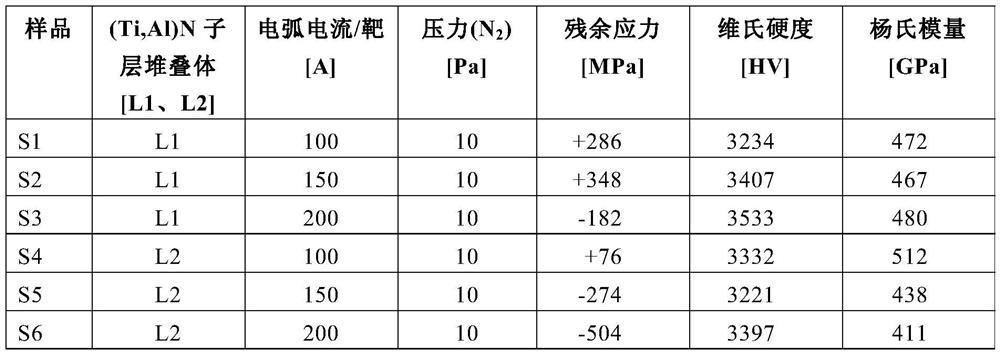
The invention relates to a coating cutting tool and a manufacturing method thereof. The coating cutting tool is composed of a base material and a hard material coating, and the base material is selected from cemented carbide, cermet, ceramic, cubic boron nitride (cBN), polycrystalline diamond (PCD) or high speed steel (HSS), wherein the hard material coating comprises a (Ti,Al)N layer stack (L) of alternately stacked (Ti,Al)N sublayers , said layer stack (L) is characterized in that: - the total atomic ratio of Ti:Al in said (Ti,Al)N layer stack (L) is in the range of 0.33:0.67 to 0.67:0.33; - The total thickness of the (Ti,Al)N layer stack (L) is in the range of 1 μm to 20 μm; - in the (Ti,Al)N layer stack of alternately stacked (Ti,Al)N sublayers Each individual (Ti,Al)N sublayer within (L) has a thickness in the range of 0.5 nm to 50 nm; Each individual (Ti,Al)N sublayer within the stack (L) differs from the immediately adjacent (Ti,Al)N sublayer in the atomic ratio Ti:Al; On the thickness of the (Ti, Al)N layer stack (L), from the interface of the (Ti, Al)N layer stack (L) aligned toward the substrate to the at the interface of the (Ti,Al)N layer stack (L) in the direction of the outer surface of the coating, the Al content increases and the Ti content decreases; - at the (Ti,Al)N layer perpendicular to the substrate surface , Al)N layer stack (L), from the interface of the (Ti,Al)N layer stack (L) aligned towards the substrate to the layer aligned towards the outside of the coating At the interface of said (Ti,Al)N layer stack (L) in the direction of the surface, the residual stress σ drops by an amount of at least 150 MPa to at most 900 MPa, whereby applying the sin based on (200) reflection 2 Ψ method to measure the residual stress σ by X-ray diffraction; Said residual stress σ in a portion of a thickness of at least 100 nm to at most 1 μm from the interface of the layer stack (L) is in the range of 0 MPa to +450 MPa.
Owner:WALTER AG
Fillet End Mills
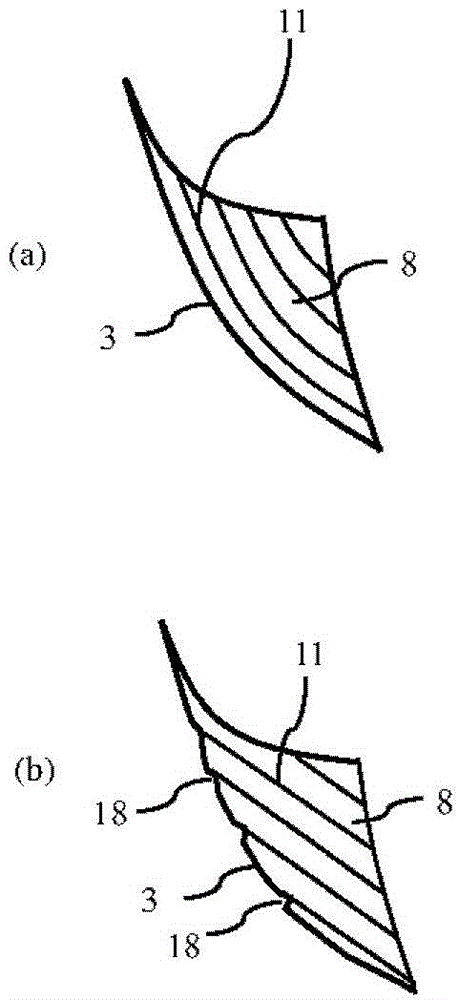
ActiveCN104023884BSuppression of chippingAvoid cloggingMilling cuttersShaping cuttersMachined surfaceEngineering
[Object] To provide a radius end mill that prevents a stepped or edged portion from being formed on the cutting edge at the connection between the corner R cutting edge and the outer peripheral cutting edge, has a good cutting sharpness, and improves a surface roughness on the machined surface. [Solution] A radius end mill 20 includes a tool body 1 that rotates around a center axis O; a series of a plurality of cutting edges 5 composed of an end cutting edge 2 disposed at a distal end of the tool body 1, an outer peripheral cutting edge 4 disposed on an outer periphery of the tool body 1, and a corner R cutting edge 3 which extends between the end cutting edge 2 and the outer peripheral cutting edge 4; a rake face 6 of the end cutting edge 2, the corner R cutting edge 3 and the outer peripheral cutting edge 4; a chip removal flute 7 which extends at the back of the rake face 6; and a corner gash 8 disposed adjacent to the corner R cutting edge 3 of the rake face 6, wherein the corner gash 8 in a planar shape has an edge, part of which is located at the center portion of the corner R cutting edge 3, and an axial rake 2 at an end portion on the side of the end cutting edge 2 which is in contact with the corner gash 8 on the corner R cutting edge 3 is in the range of 5 to 20 degrees.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com