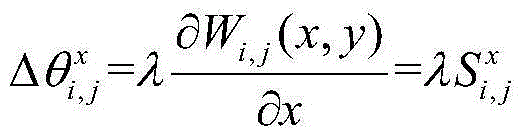Patents
Literature
69 results about "Photon density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In principle, the number density of photons include all photons, both of cosmic origin (e.g. the cosmic microwave background; CMB) and of astrophysical origin (starlight, gamma rays from gamma-ray bursts, radio waves from quasars, etc.). However, CMB photons outnumber all other types of photons by more than 200:1.
Reactor and method of processing a semiconductor substrate
InactiveUSRE37546E1Accurately determineEliminate needThermometer detailsRadiation pyrometryGas syringeEngineering
Owner:KOKUSAI SEMICON EQUIP CORP
Intra-serum and intra-gel for modeling human skin tissue
InactiveUS6475800B1Diagnostics using spectroscopyScattering properties measurementsConfocalCrosslinking reagent
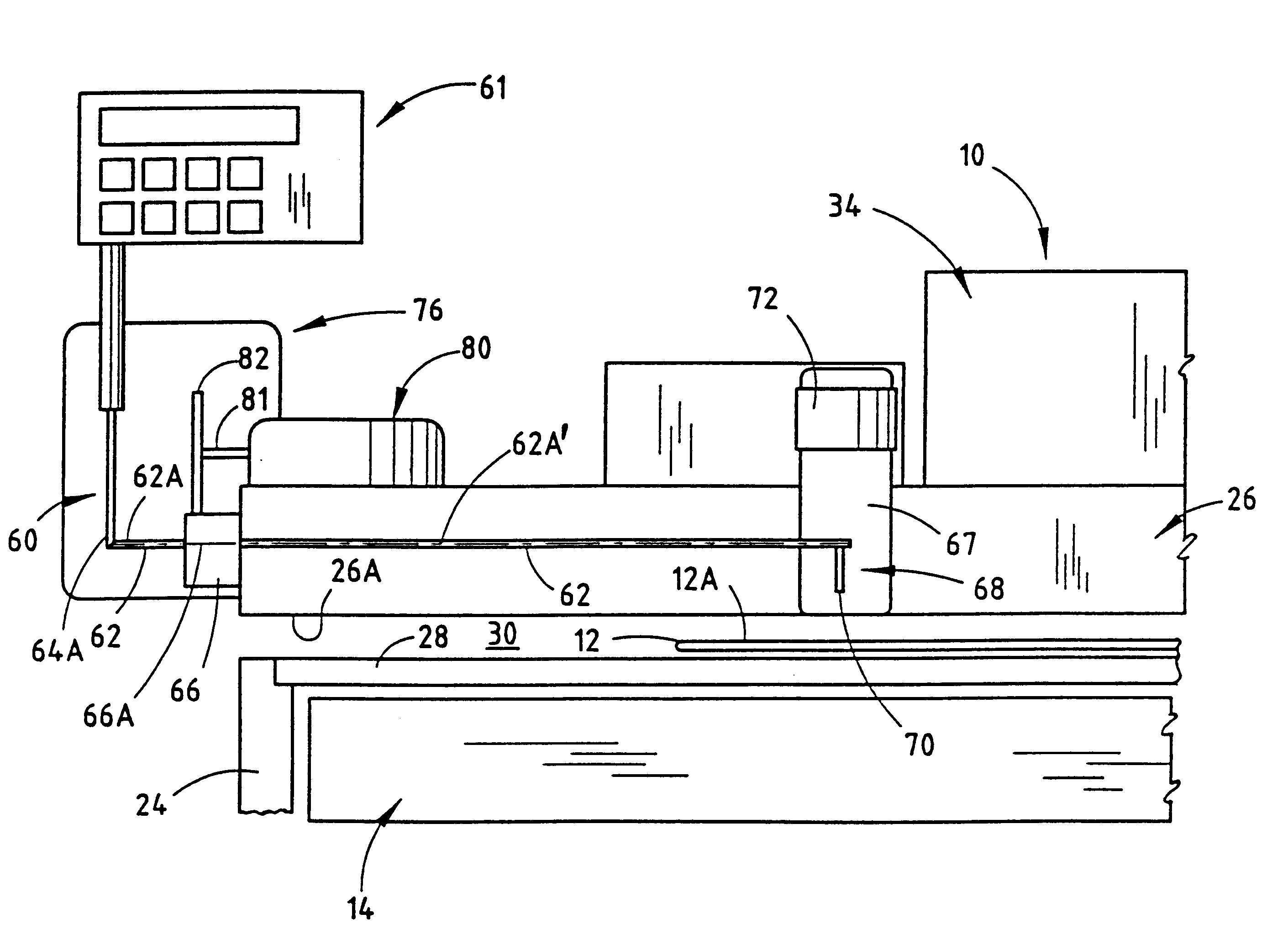
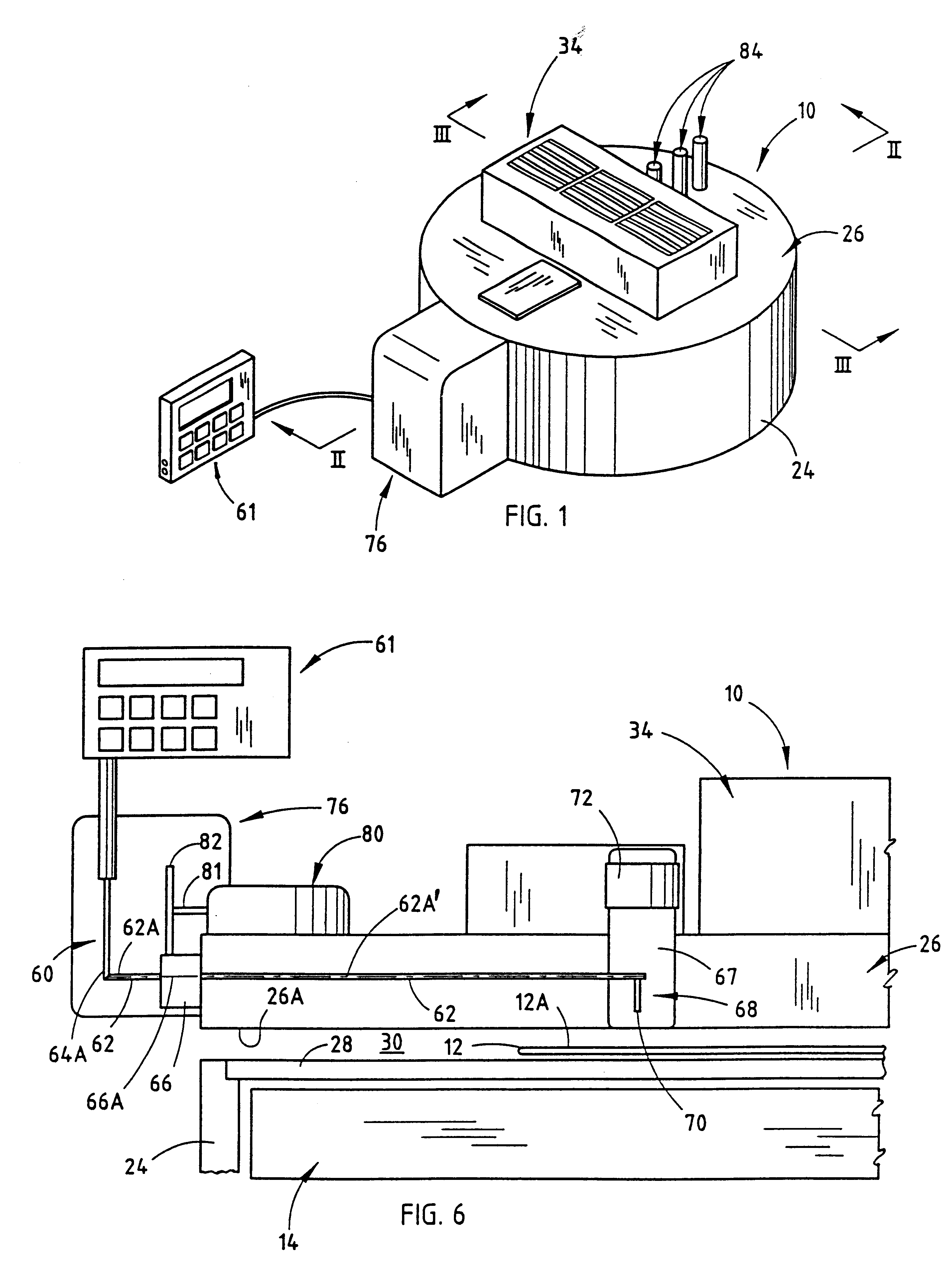
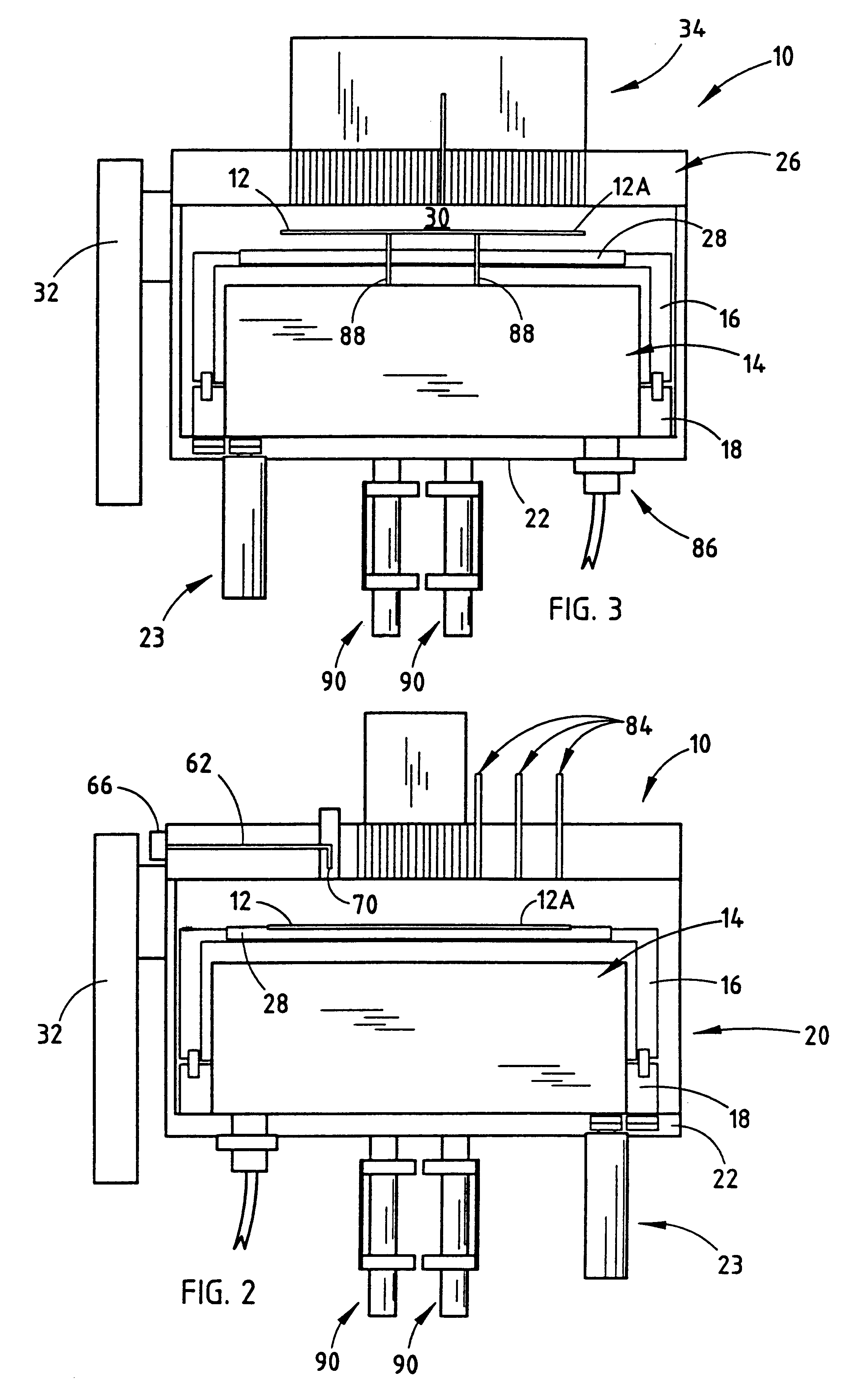
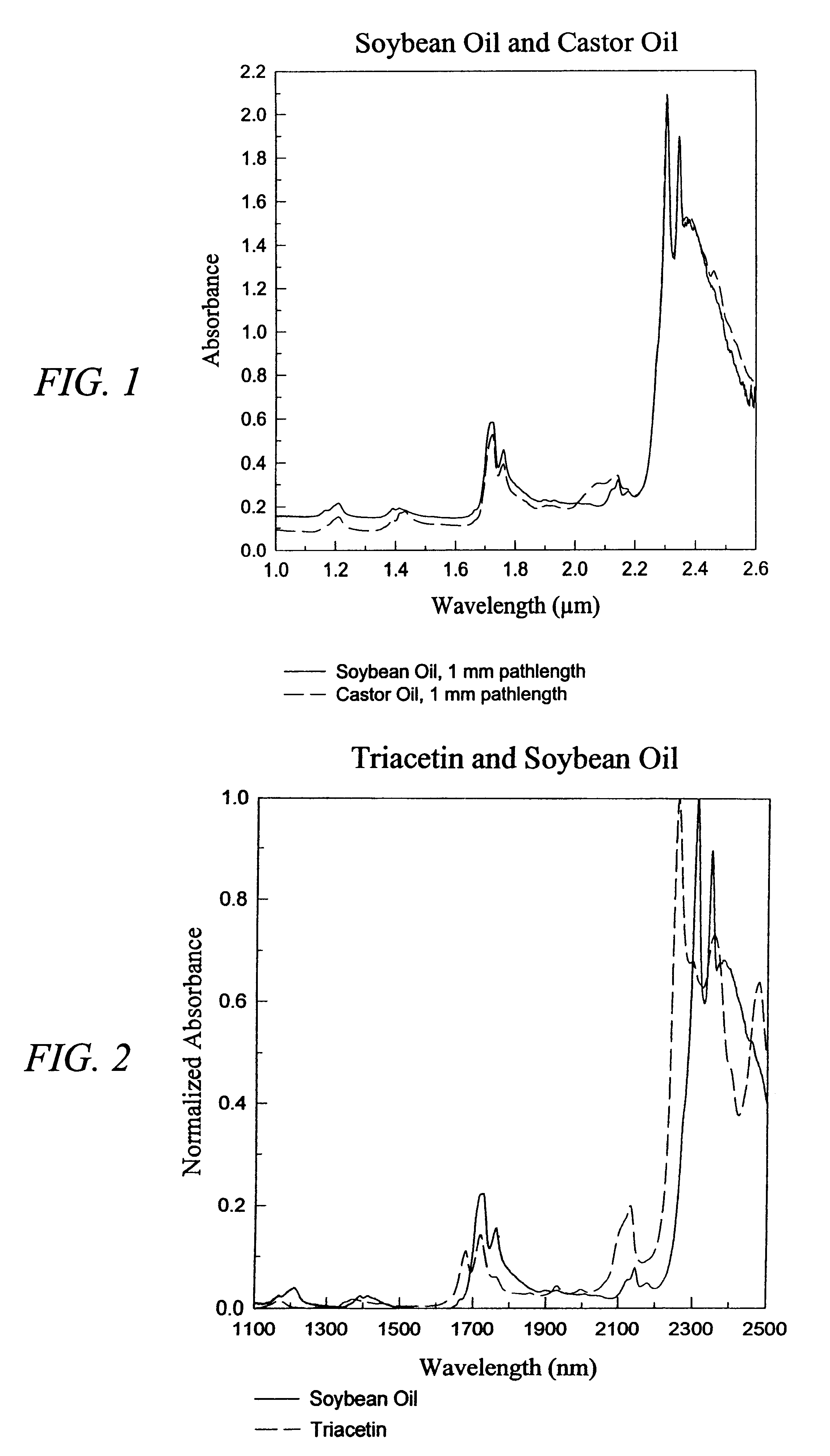
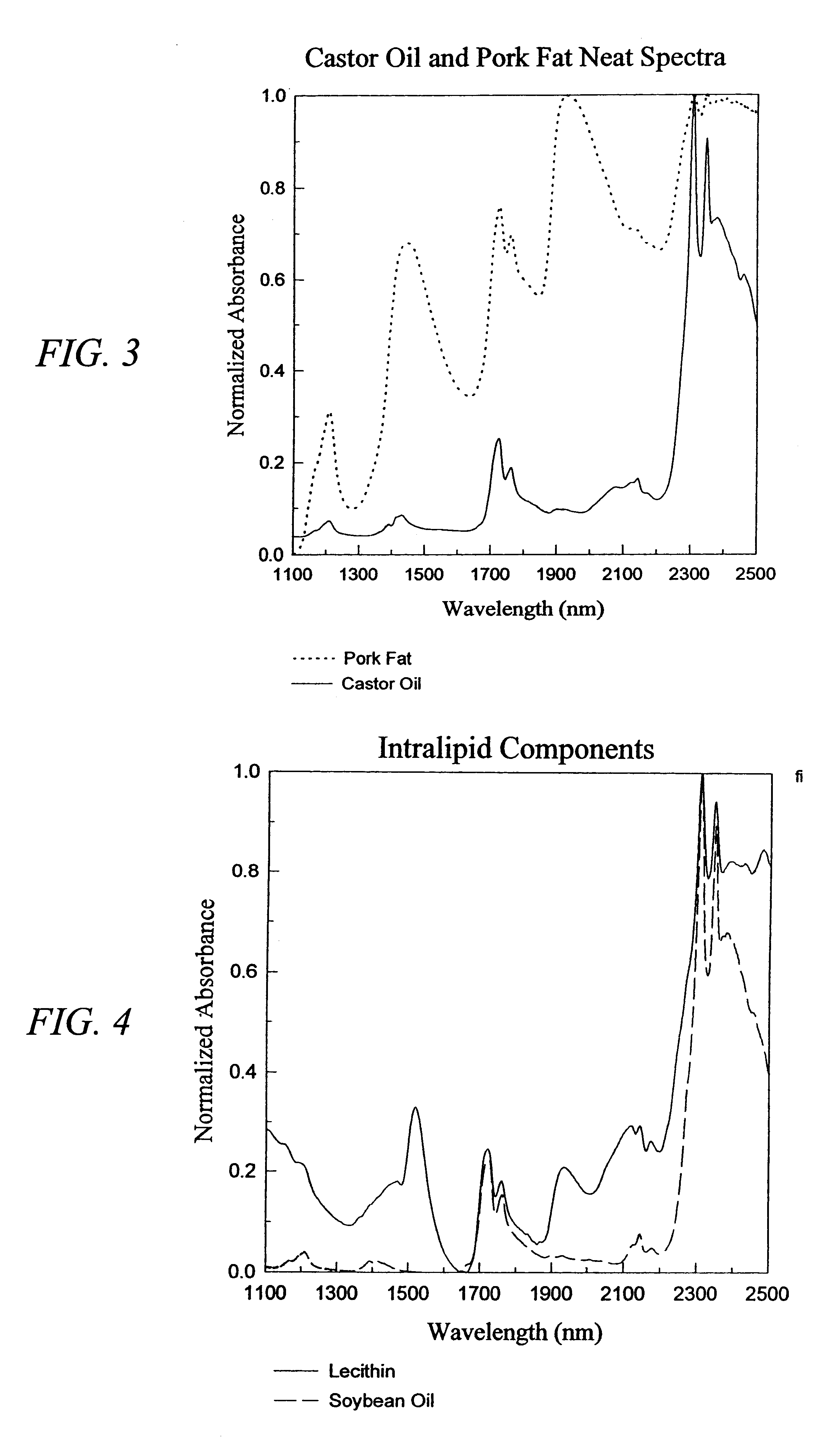
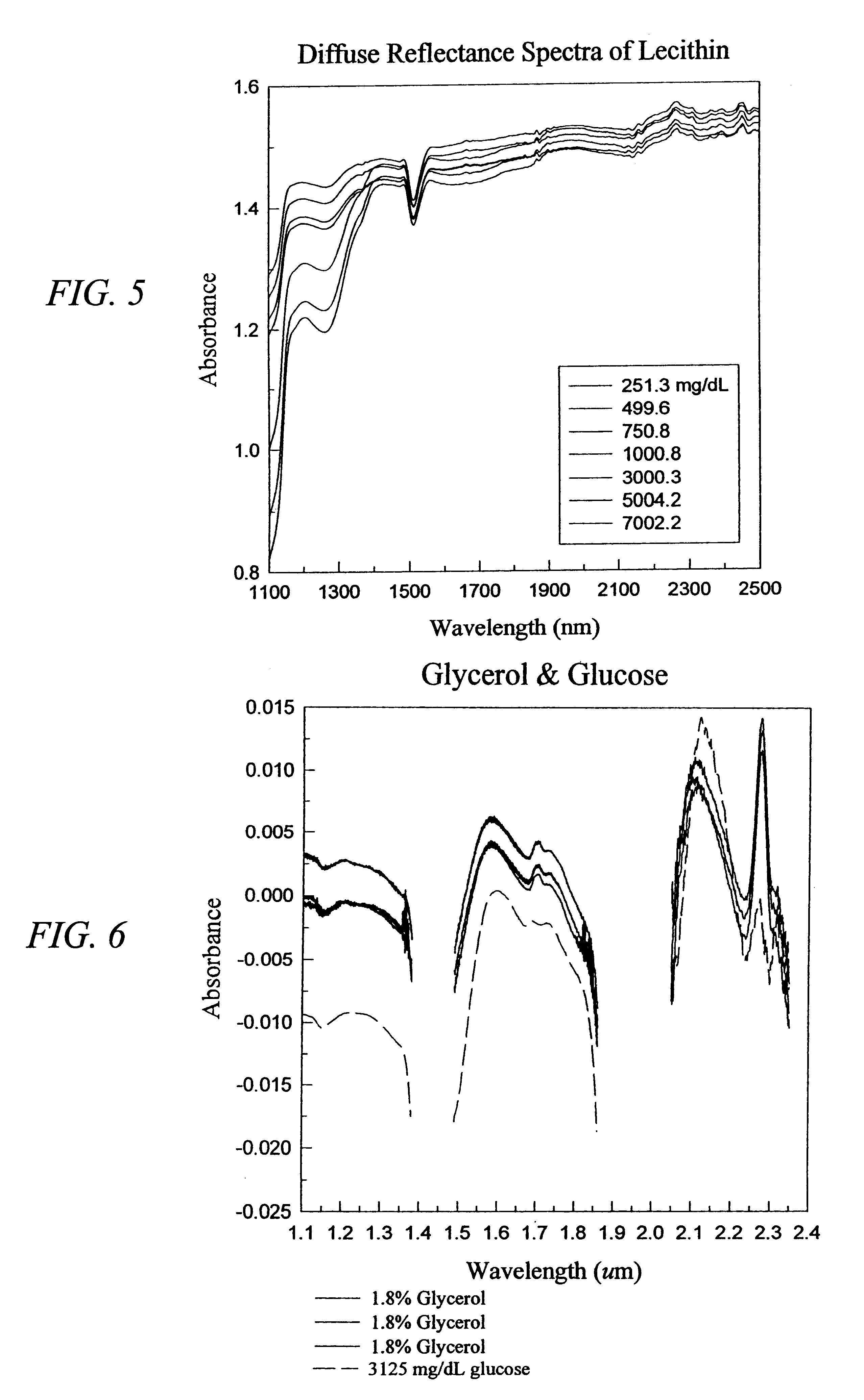
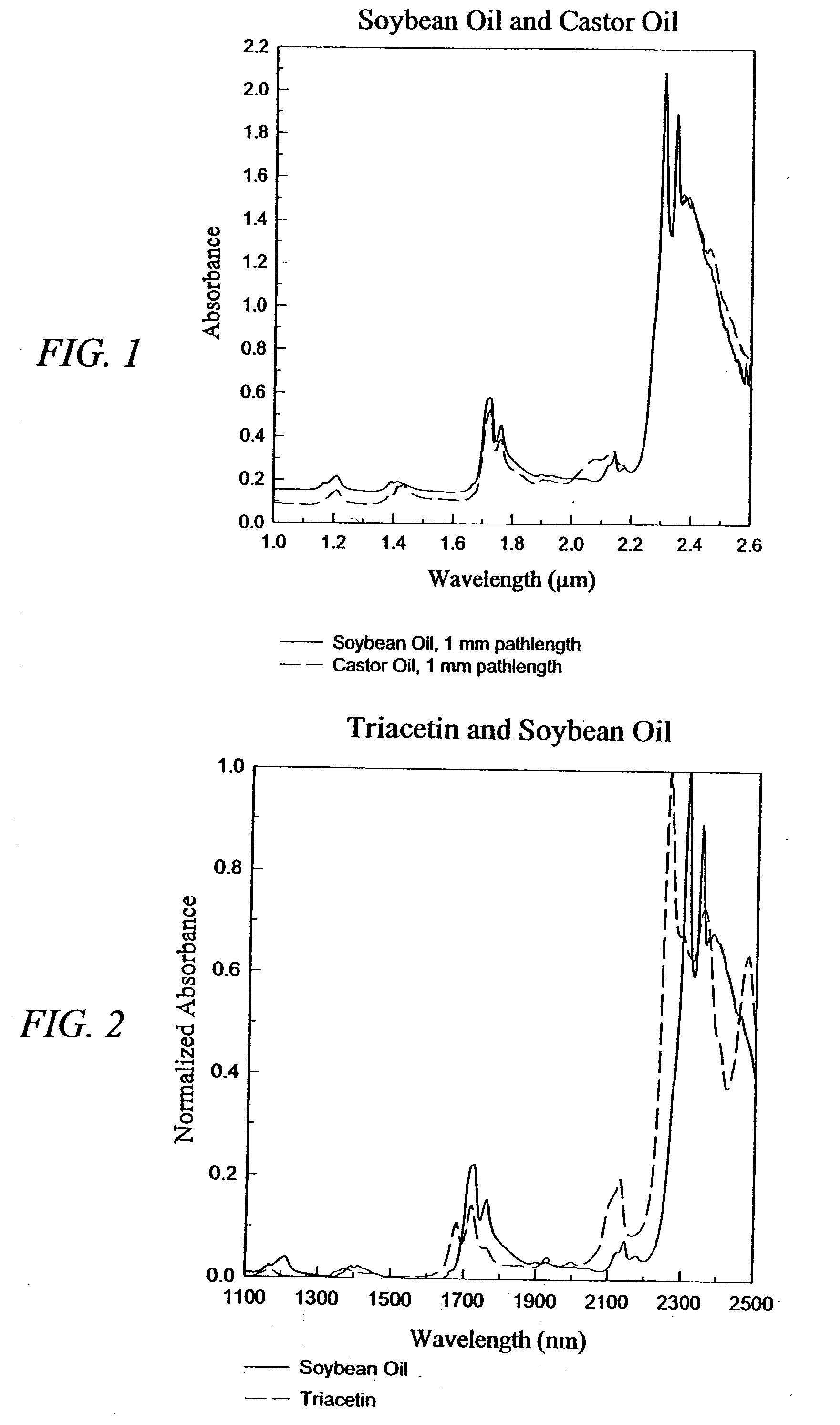
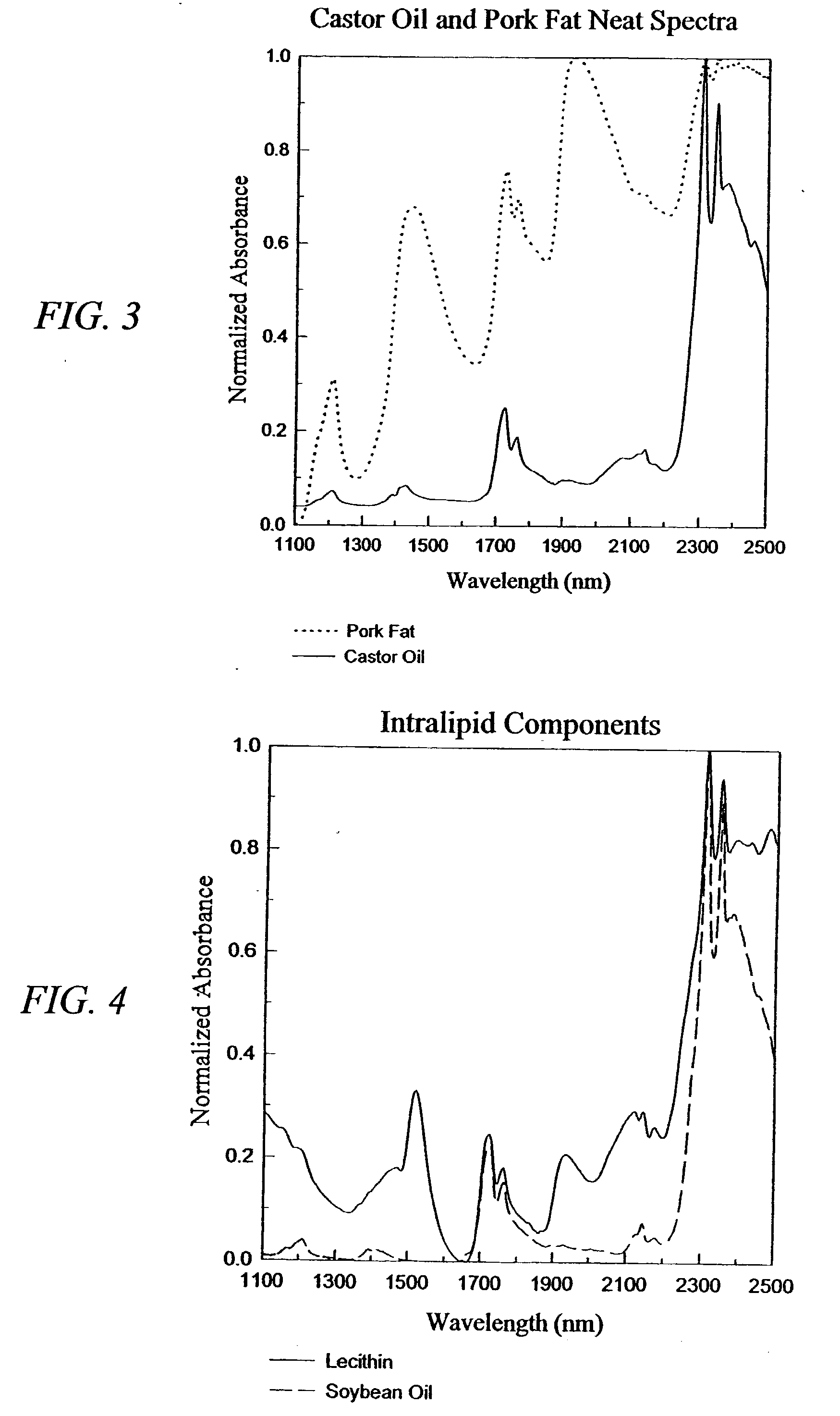
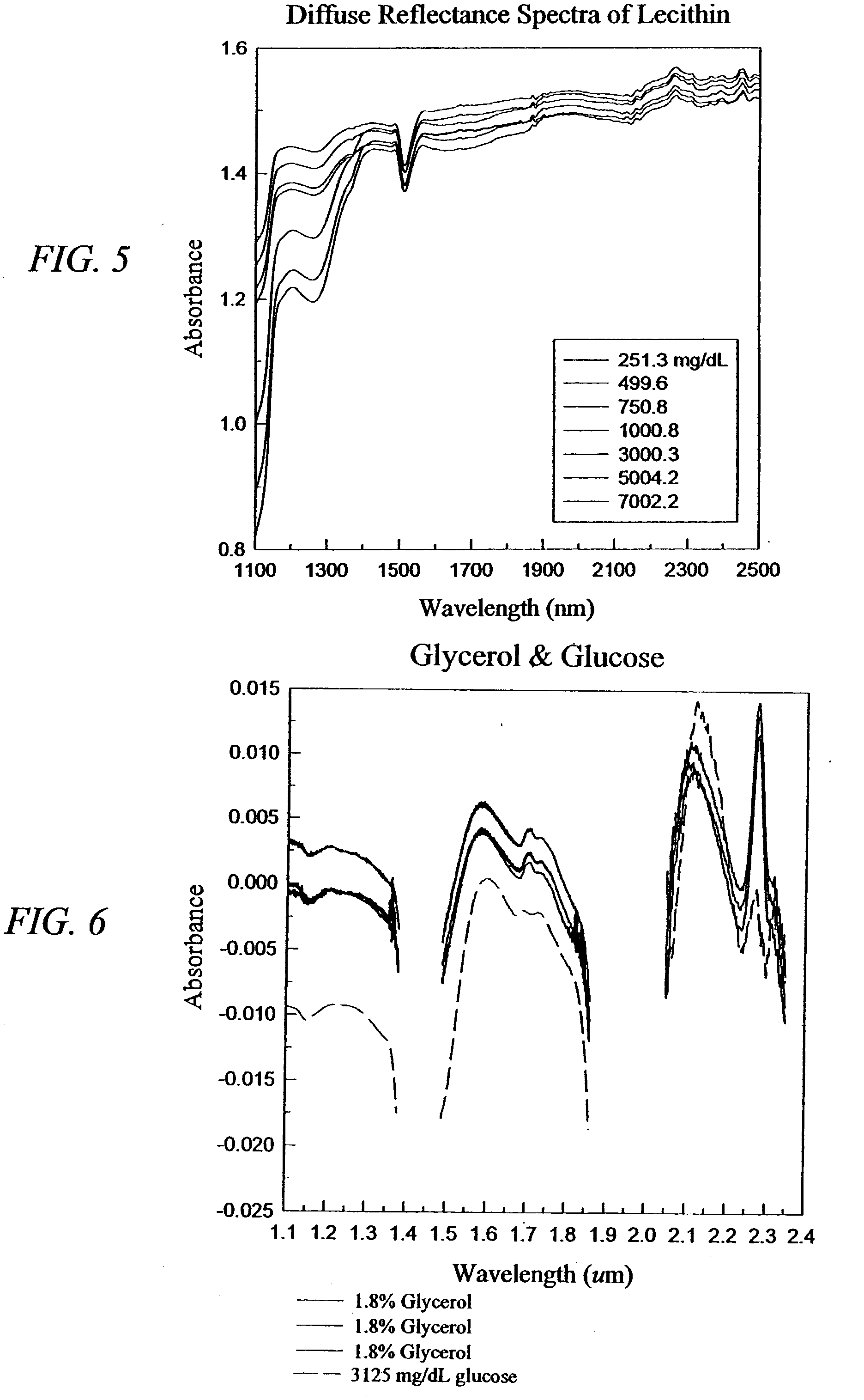
The invention provides a class of samples that model the human body. This family of samples is based upon emulsions of oil in water with lecithin acting as the emulsifier. These solutions that have varying particle sizes may be spiked with basis set components (albumin, urea and glucose) to simulate skin tissues further. The family of samples is such that other organic compounds such as collagen, elastin, globulin and bilirubin may be added, as can salts such as Na+, K+ and Cl-. Layers of varying thickness with known index of refraction and particle size distributions may be generated using simple crosslinking reagents, such as collagen (gelatin). The resulting samples are flexible in each analyte's concentration and match the skin layers of the body in terms of the samples reduced scattering and absorption coefficients, mums and muma. This family of samples is provided for use in the medical field where lasers and spectroscopy based analyzers are used in treatment of the body. In particular, knowledge may be gained on net analyte signal, photon depth of penetration, photon radial diffusion, photon interaction between tissue layers, photon density (all as a function of frequency) and on instrument parameter specifications such as resolution and required dynamic range (A / D bits required). In particular, applications to delineate such parameters have been developed for the application of noninvasive glucose determination in the near-IR region from 700 to 2500 nm with an emphasis on the region 1000 to 2500 nm (10,000 to 4,000 cm-1).
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
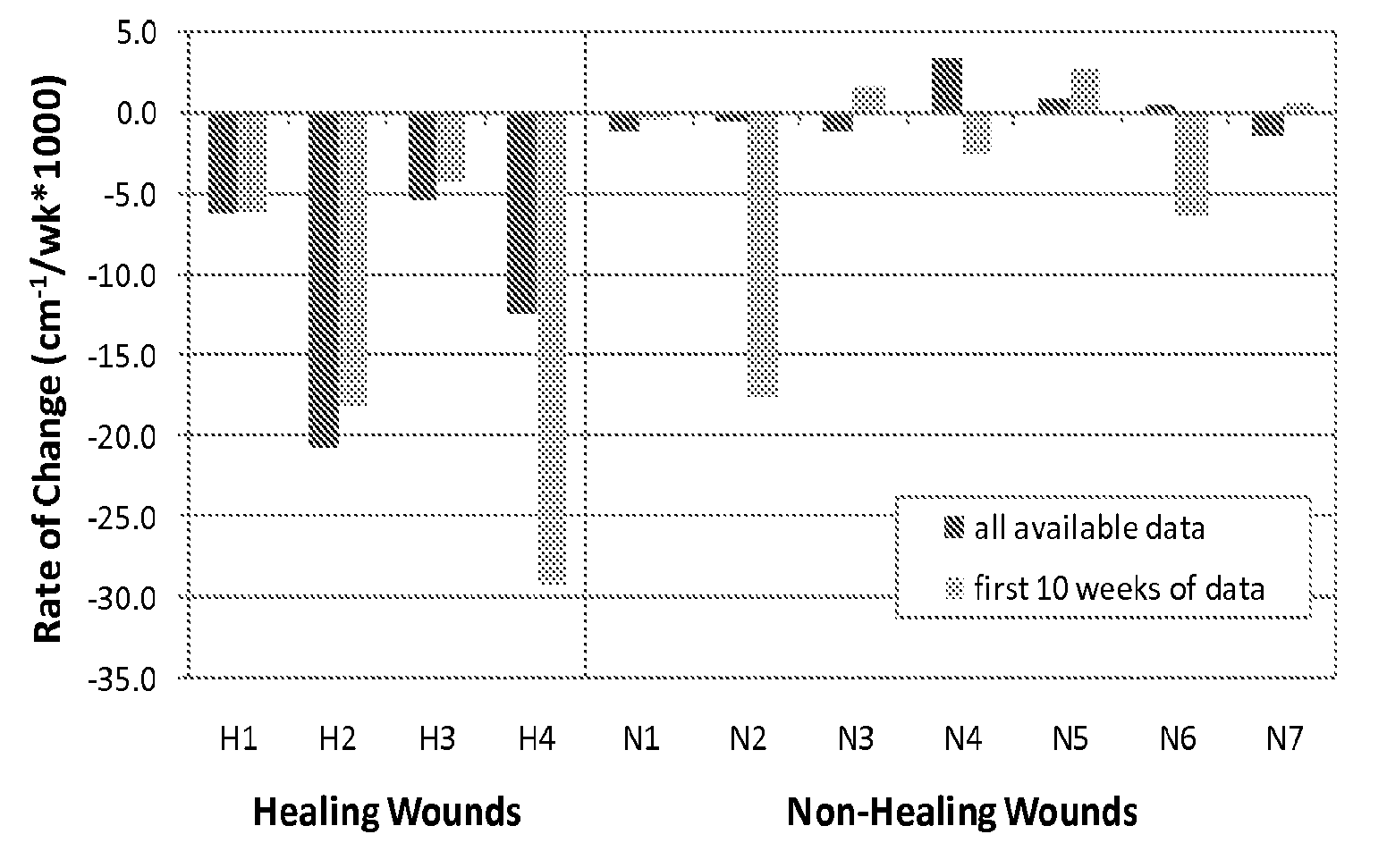
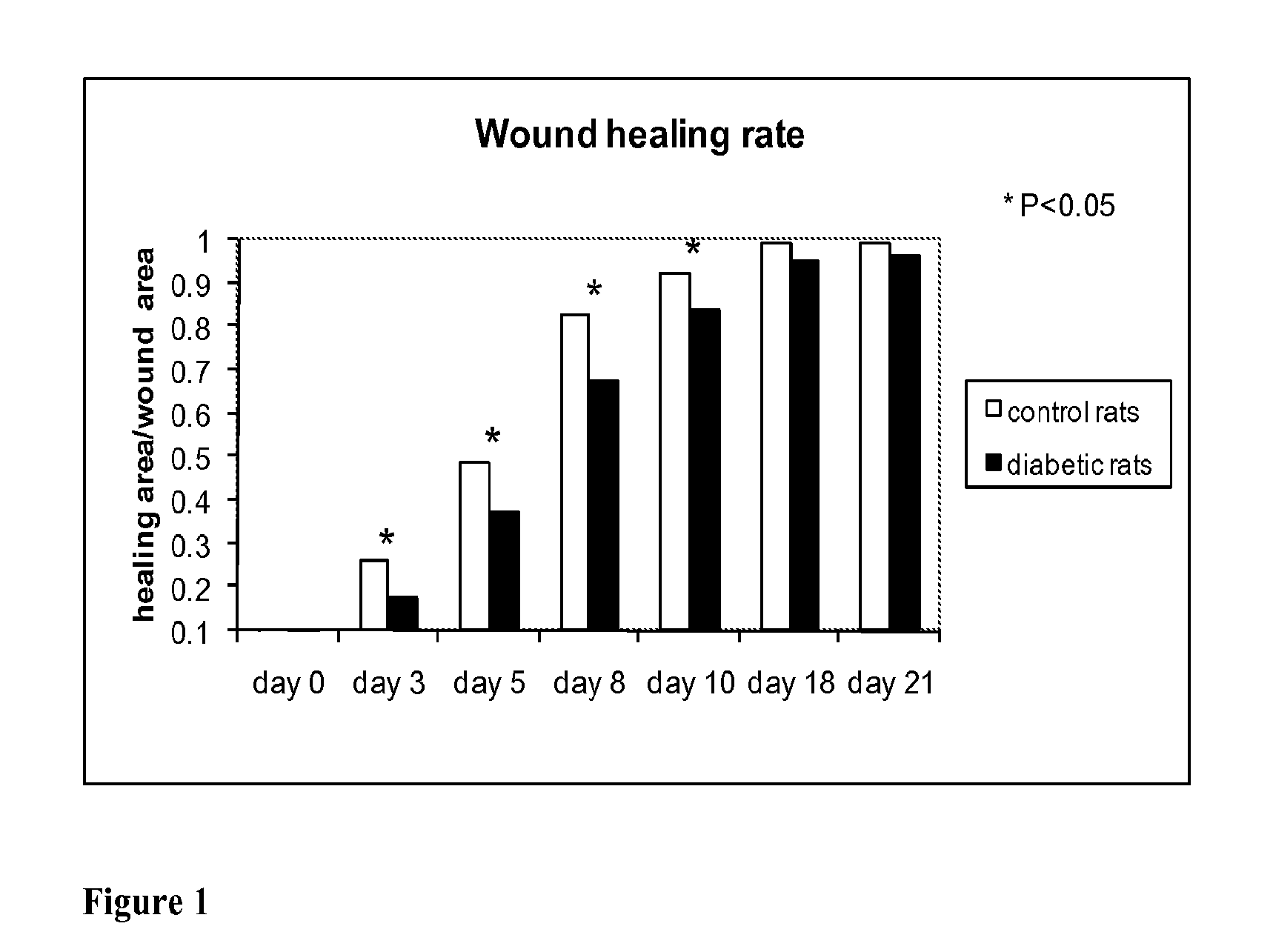
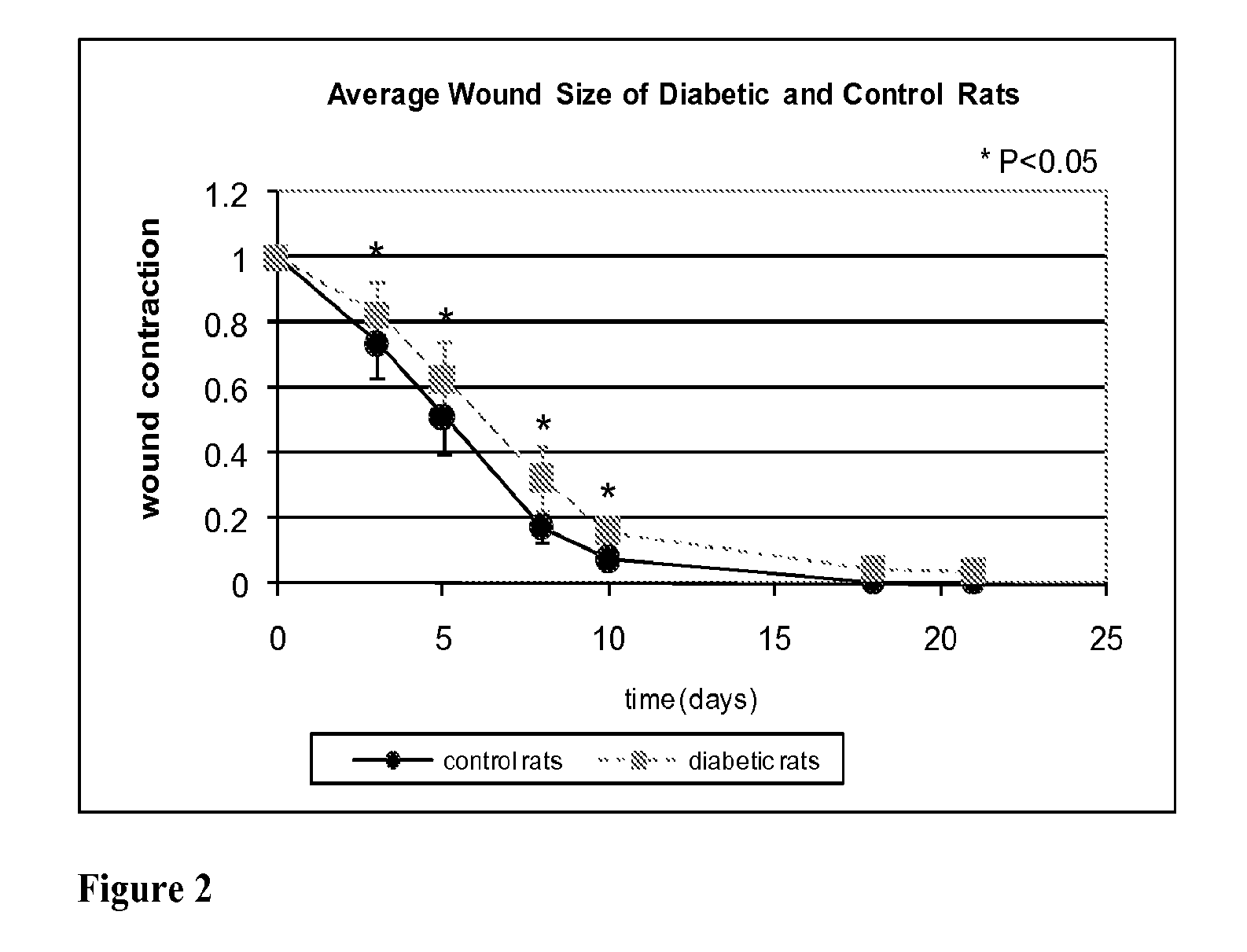
Methods for Measuring Changes in Optical Properties of Wound Tissue and Correlating Near Infrared Absorption (FNIR) and Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy Scattering (DRS) With Tissue Neovascularization and Collagen Concentration to Determine Whether Wound is Healing
ActiveUS20110124987A1Reduction factorDiagnostics using lightDiagnostics using spectroscopyReflectance spectroscopyDiffusion equation
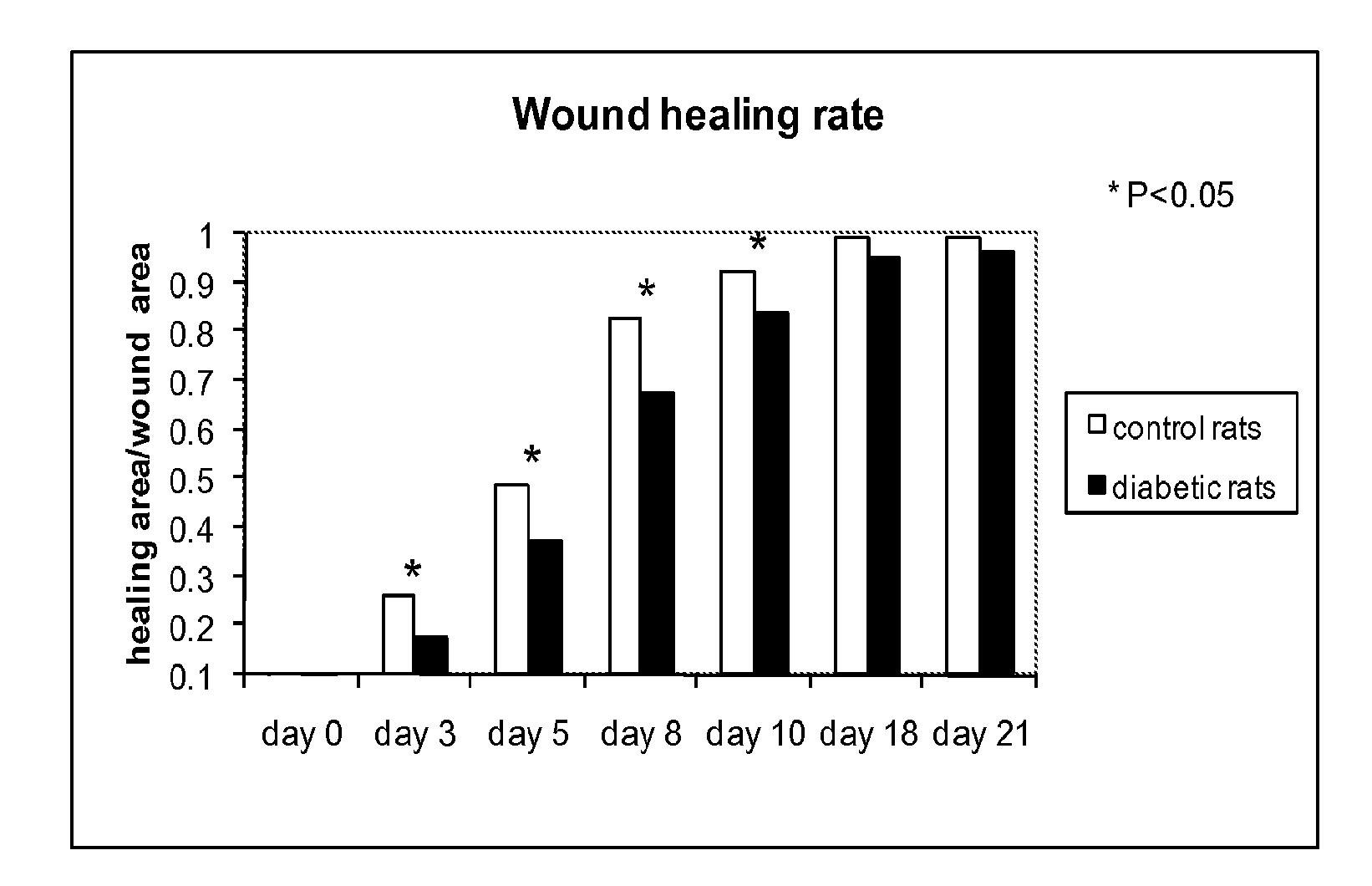
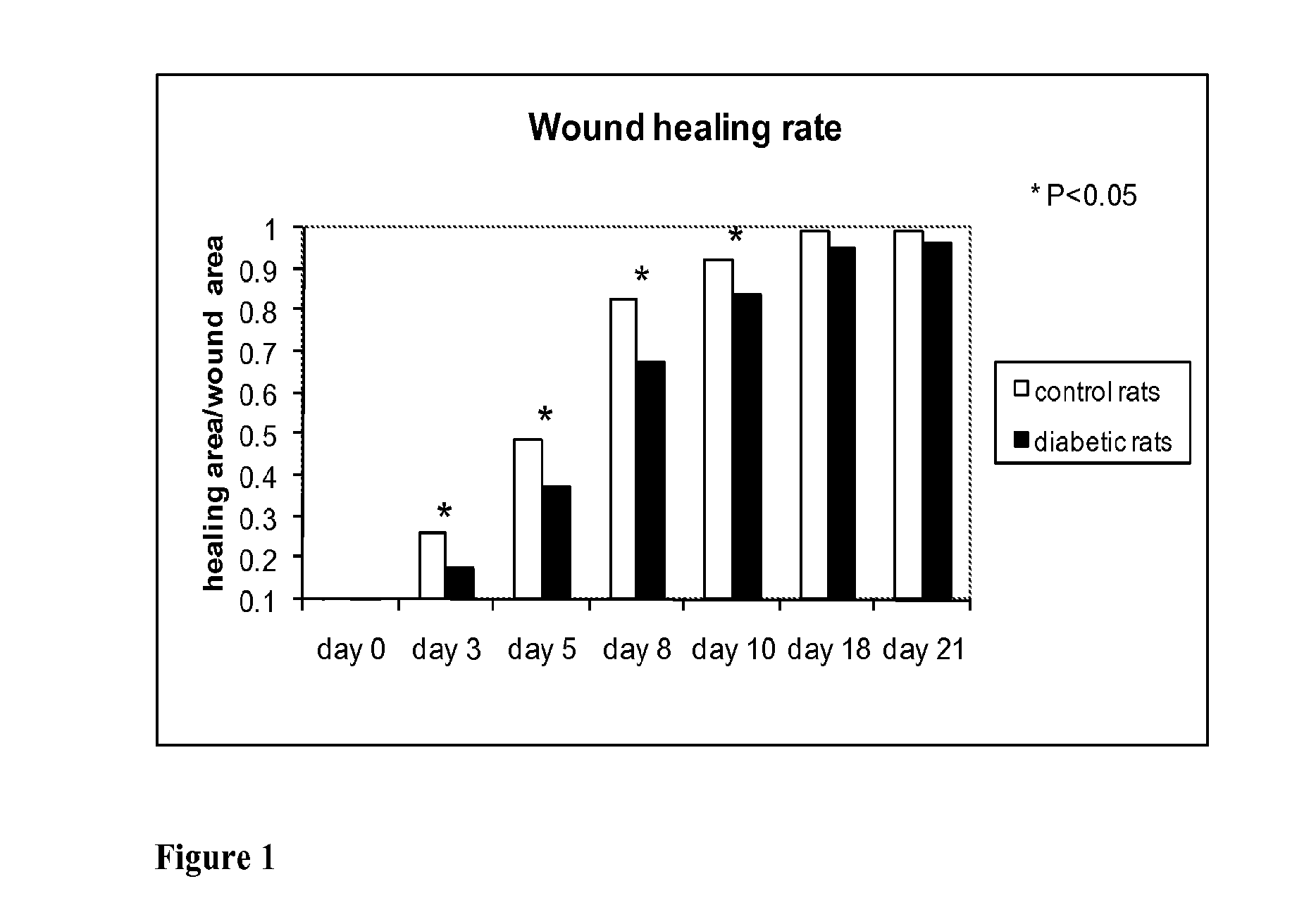
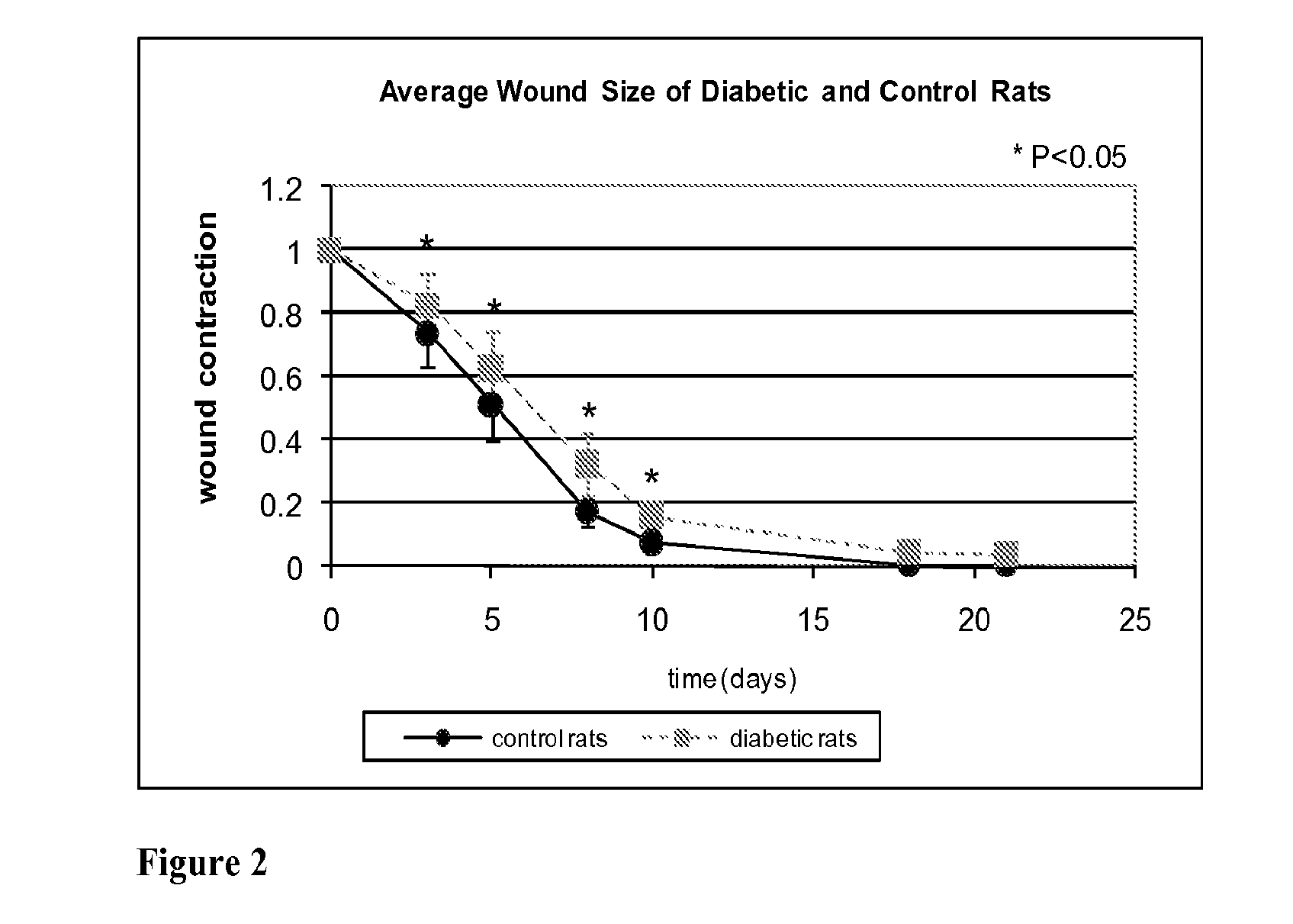
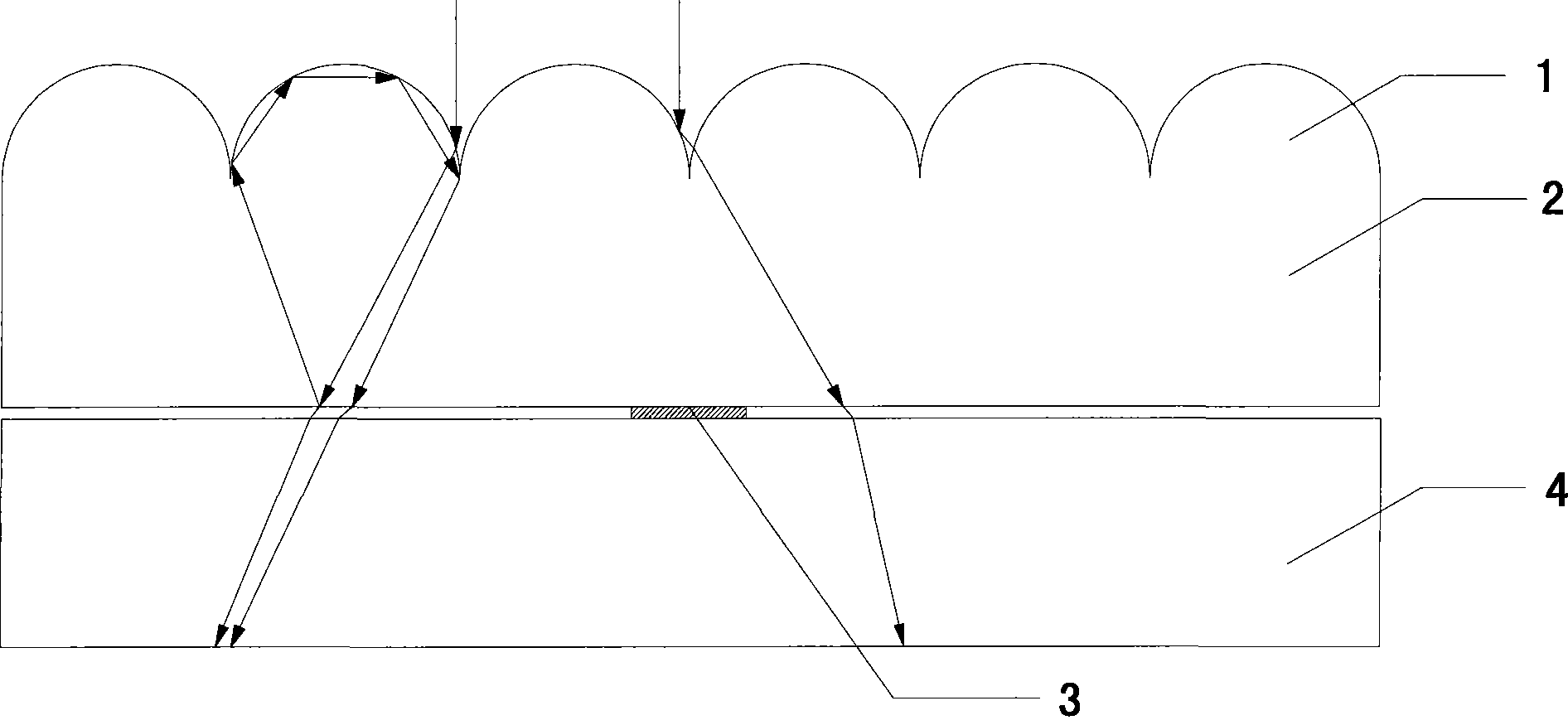
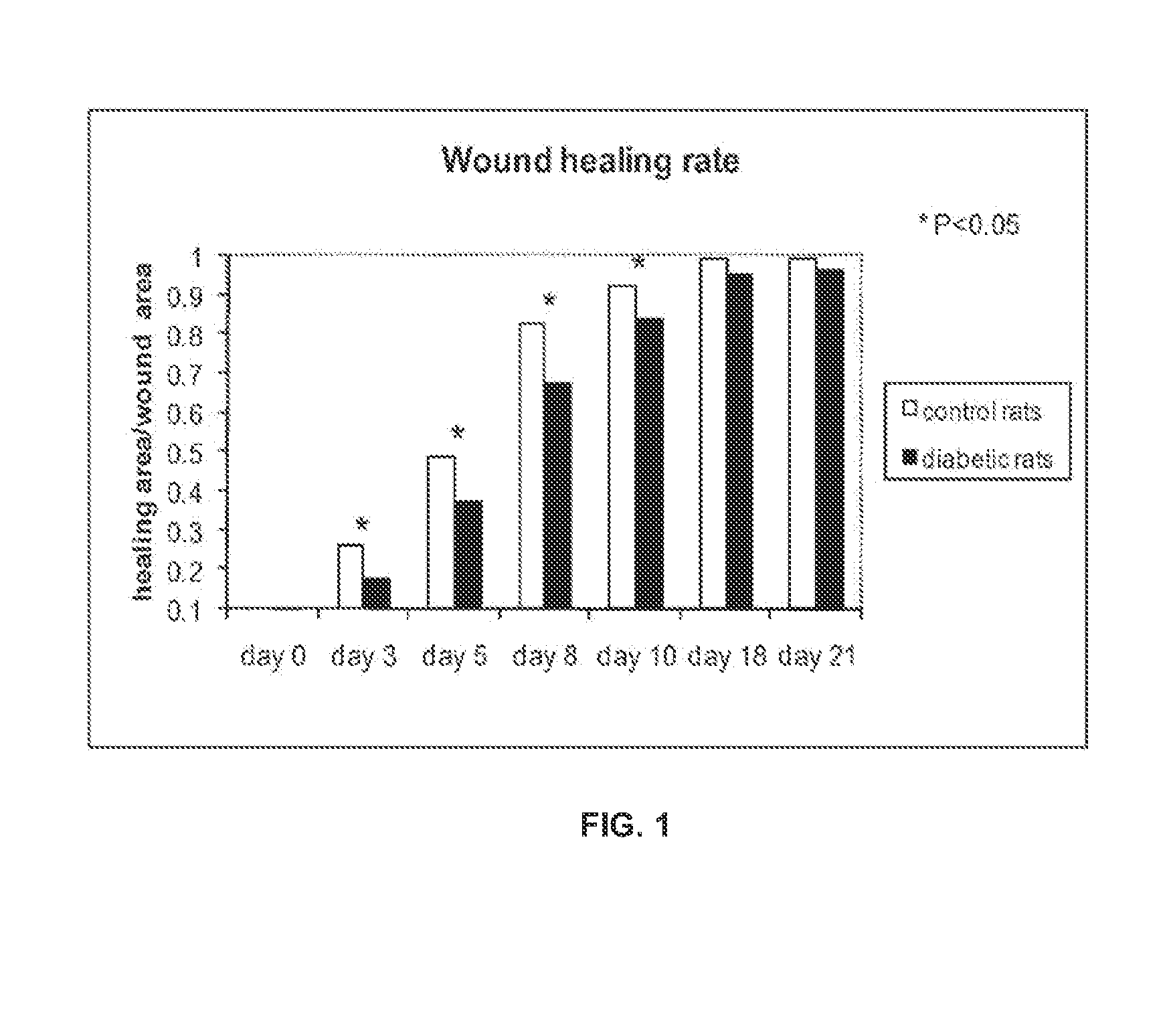
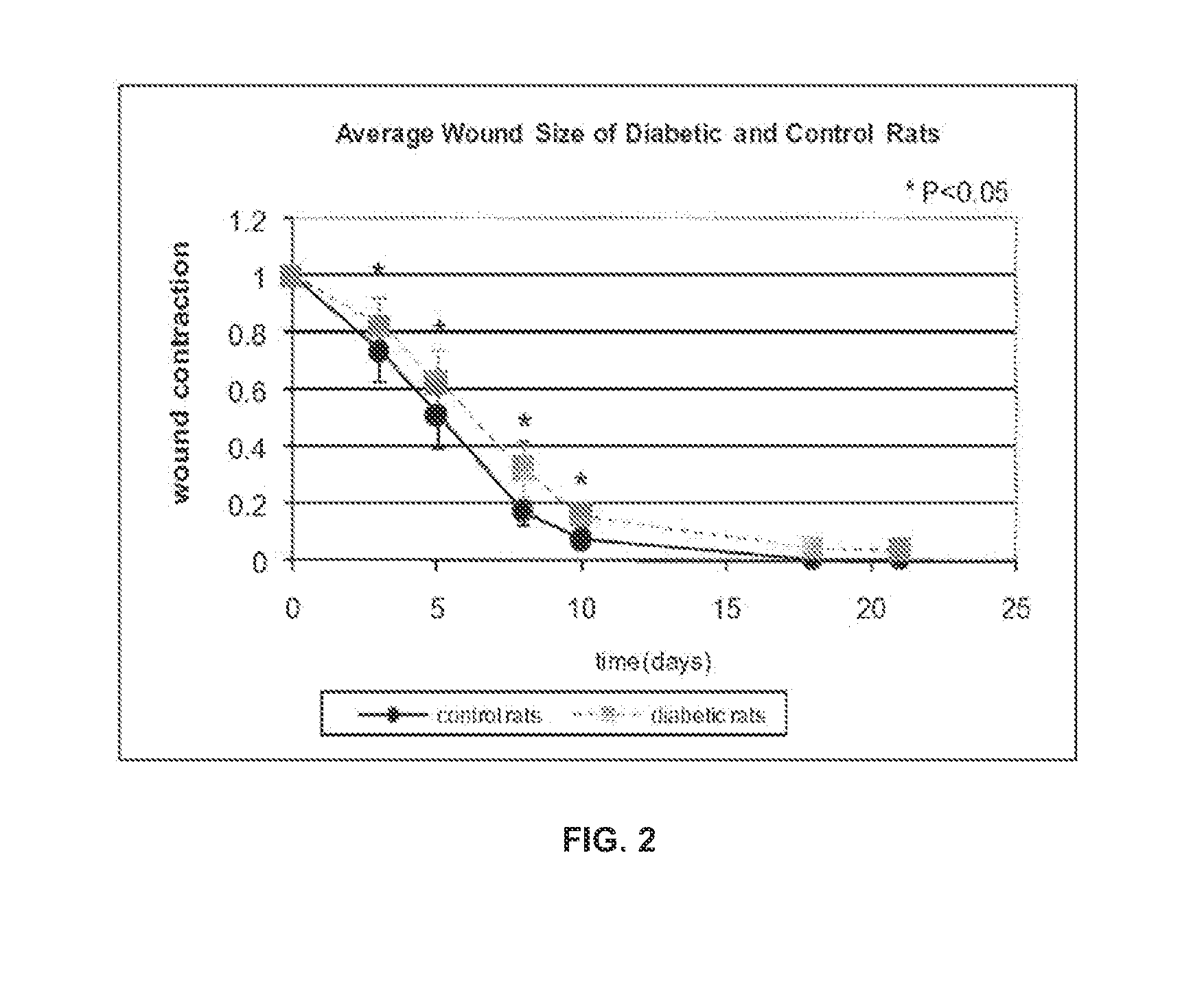
Optical changes of tissue during wound healing measured by Near Infrared and Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy are shown to correlate with histologic changes. Near Infrared absorption coefficient correlated with blood vessel in-growth over time, while Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy (DRS) data correlated with collagen concentration. Changes of optical properties of wound tissue at greater depths are also quantified by Diffuse Photon Density Wave (DPDW) methodology at near infrared wavelengths. The diffusion equation for semi-infinite media is used to calculate the absorption and scattering coefficients based on measurements of phase and amplitude with a frequency domain or time domain device. An increase in the absorption and scattering coefficients and a decrease in blood saturation of the wounds compared to the non wounded sites was observed. The changes correlated with the healing stage of the wound. The methodologies used to collect information regarding the healing state of a wound may be used to clinically assess the efficacy of wound healing agents in a patient (e.g., a diabetic) and as a non-invasive method
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
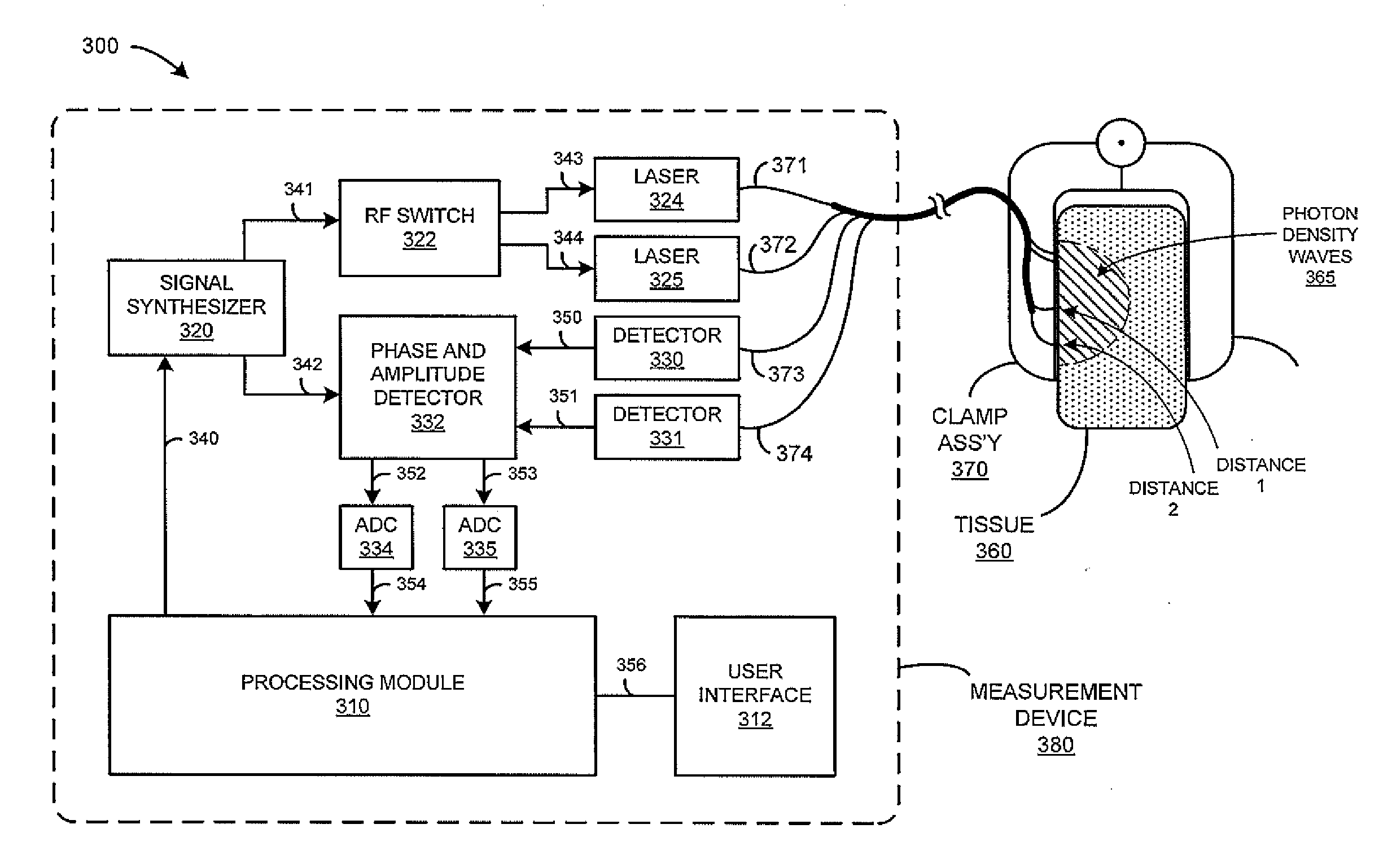
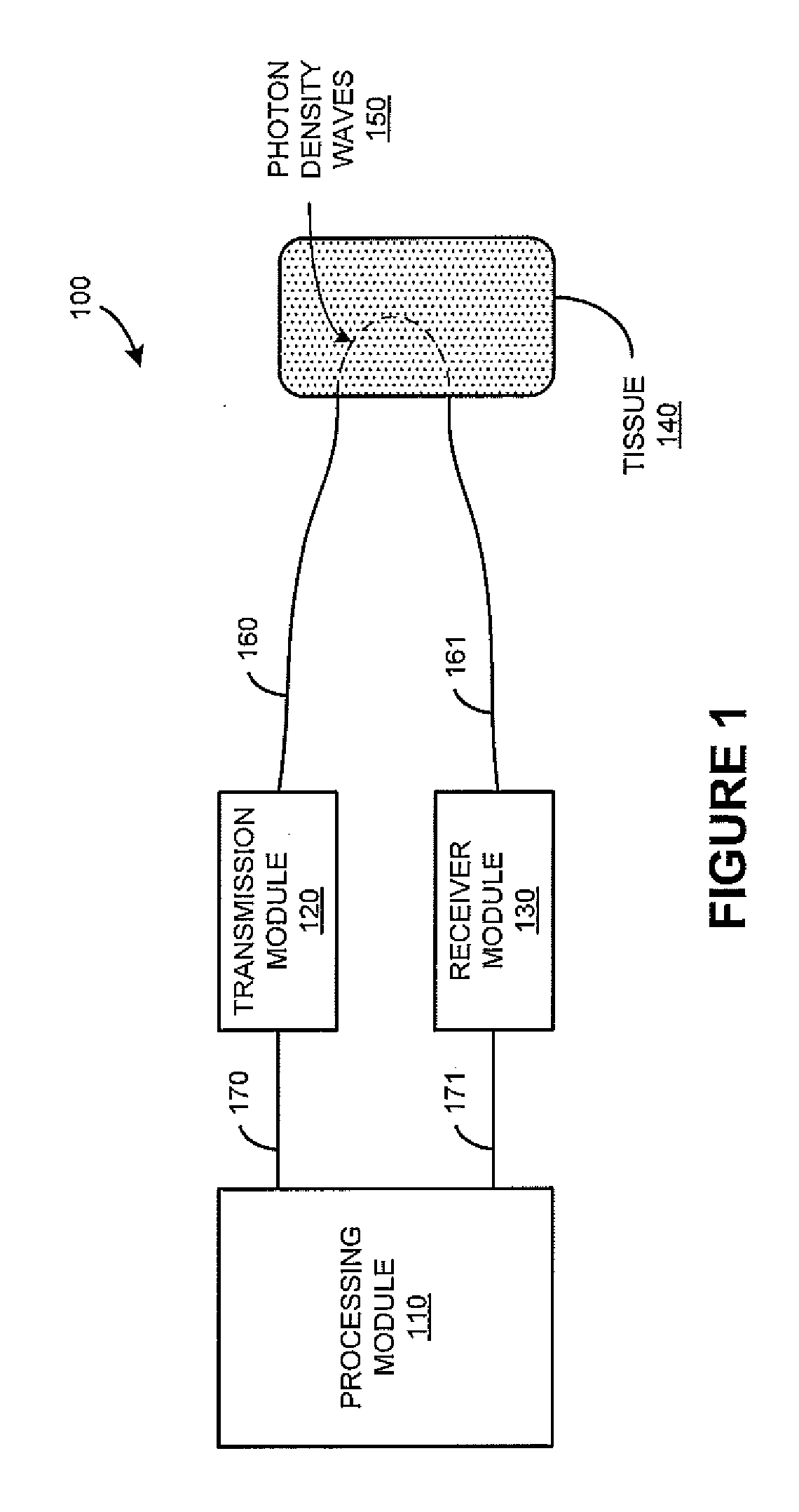
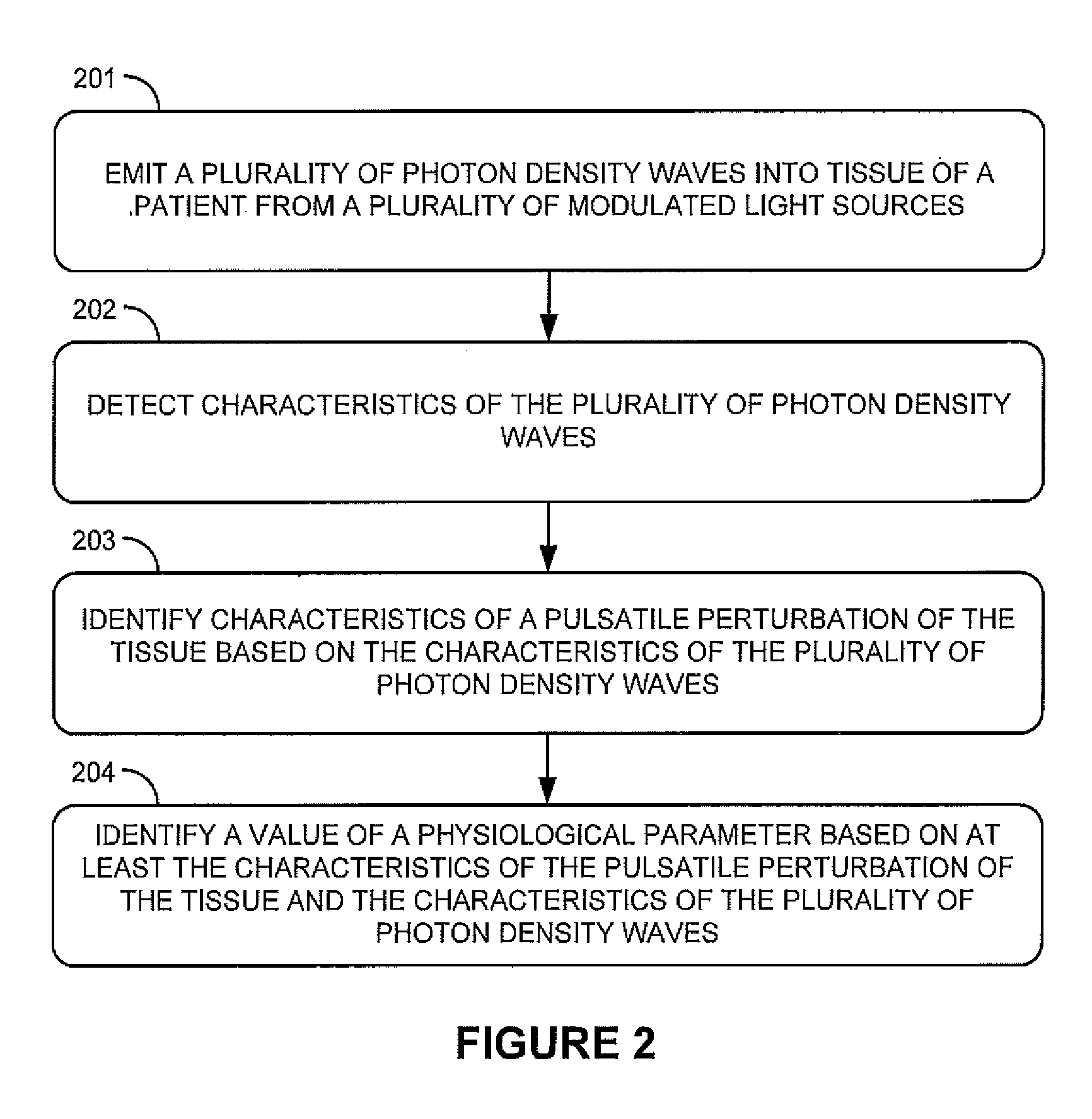
Photon density wave based determination of physiological blood parameters
A method for measuring a physiological parameter of blood in a patient is presented. The method includes emitting light from a modulated light source into tissue of the patient to generate a photon density wave in the tissue, detecting the photon density wave during pulsatile perturbation of the tissue, and processing an amplitude and phase of the photon density wave over the pulsatile perturbation to determine a value of the physiological parameter.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Auto-fluorescence molecule image system
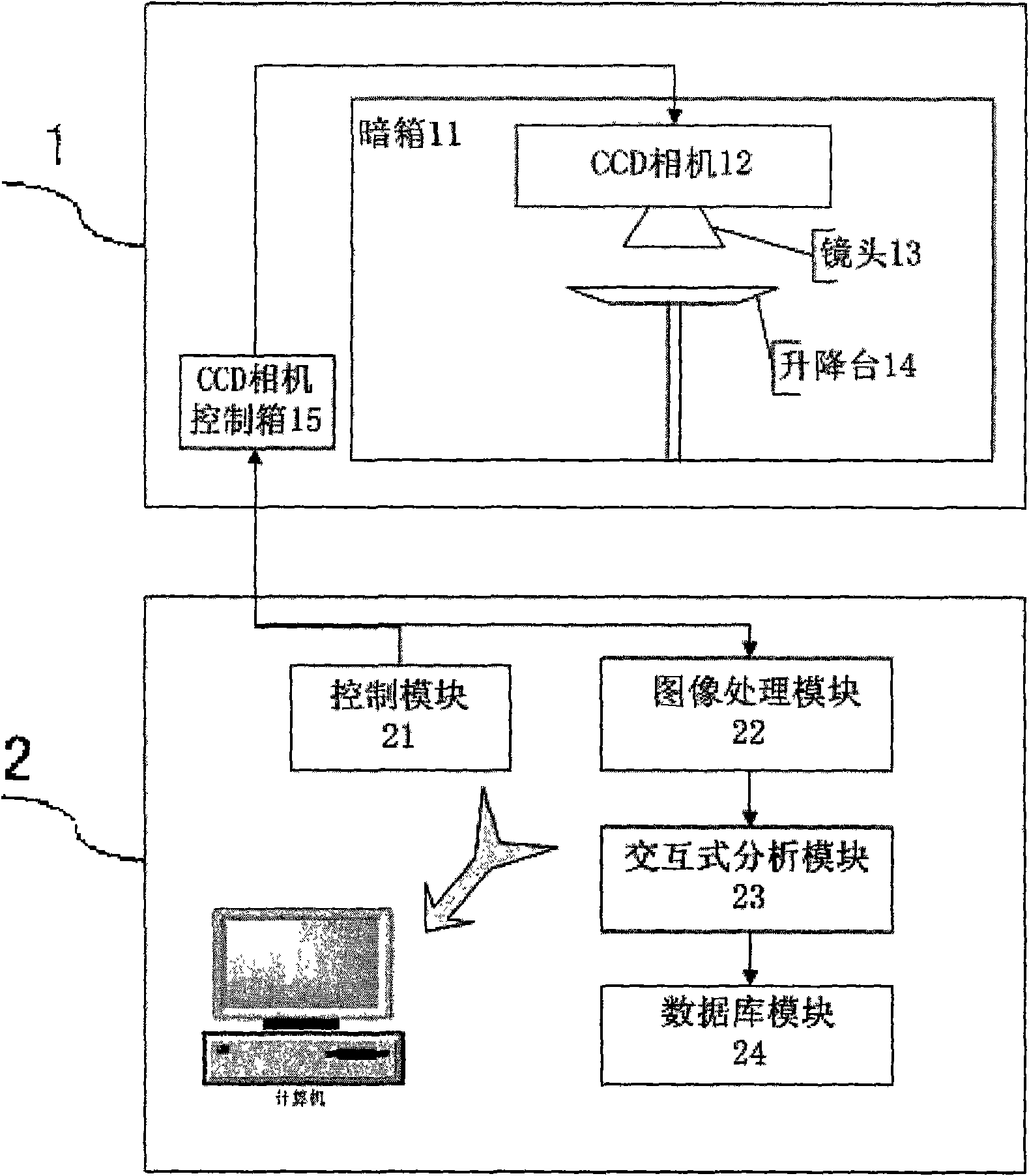
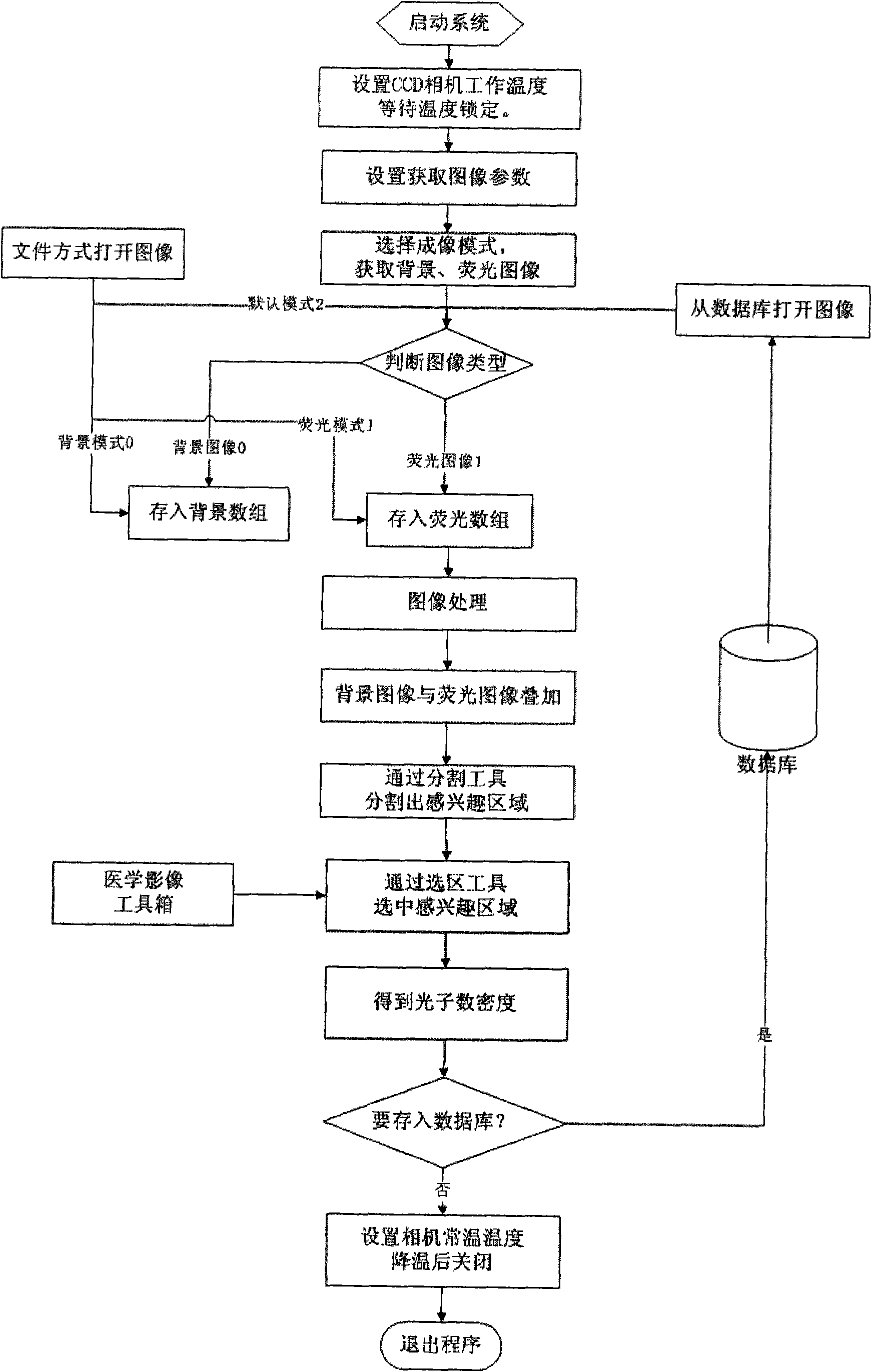
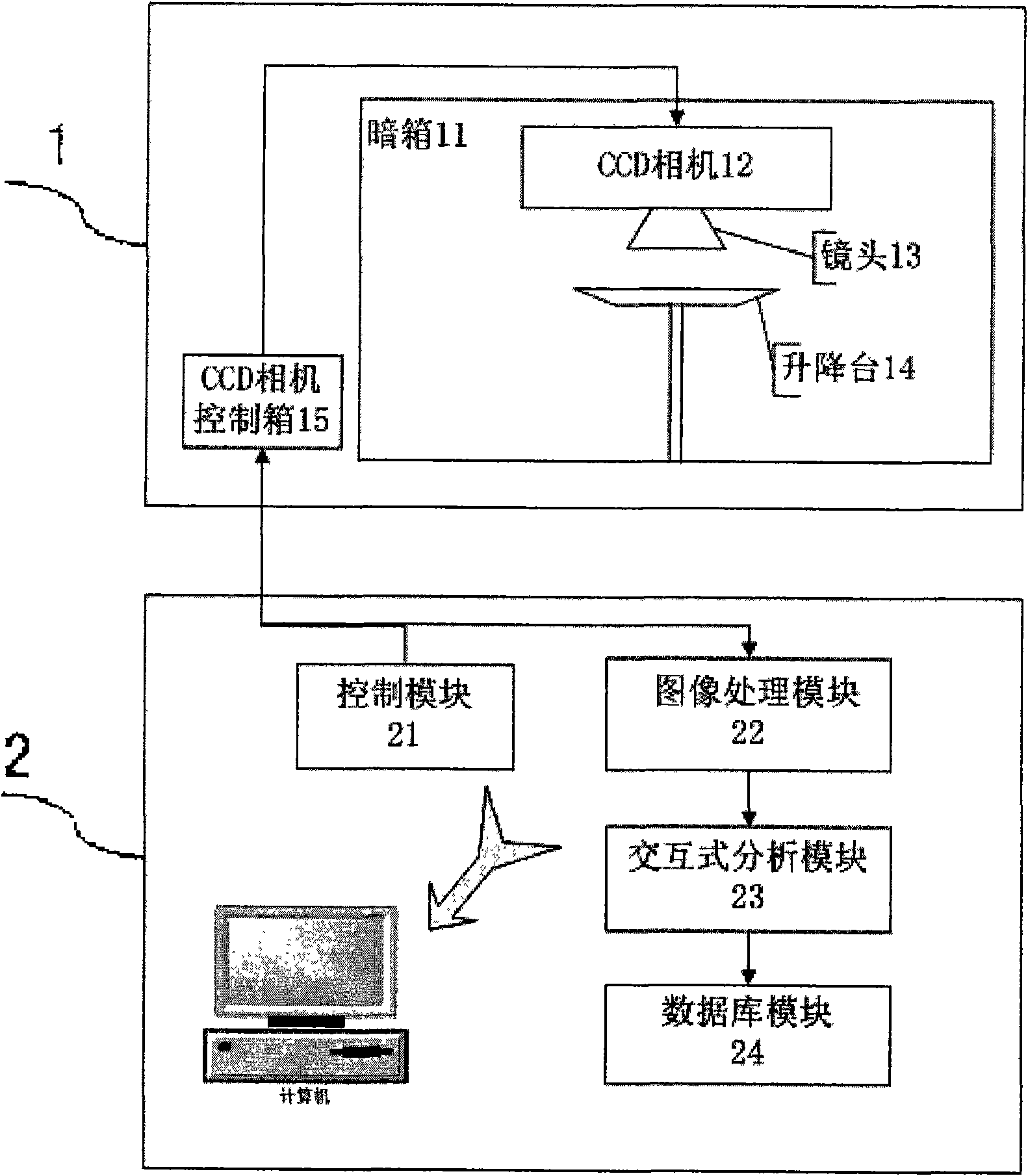
ActiveCN101766476AAccurate analysisPrecise positioningImage analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringKnowledge FieldCcd camera
The invention belongs to an auto-fluorescence molecule image system which comprises a camera bellows, a CCD camera lens control module, an image processing module, an interactive analysis module and a database module. A system factor corrected by an integrating sphere can be converted into a photon density in an interesting area by the system through a pixel value. The system can work after a temperature value of the CCD camera is set and locked. Firstly, the light source in the camera bellows is opened to shoot an outline of a target object, then the light source is closed to capture a fluorescence signal which projects the outline of the detected object, and the signal is superposed with the outline image. User can choose the interesting area by using a selecting tool so as to acquire a photon density value for performing scientific research. The system of the invention can provide a database function for the user to conveniently manage the data and preview the images. The system of the invention has the advantages of reasonable structure, obvious function, convenient operation, low cost, wide application in the field of researching the small animals in non-invasive biologic experiment.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Laser fabrication of continuous nanofibers
This invention provides a continuous process of making continuous nanofibers of all kinds, such as SiC, BN, AlN, and C. Laser heating a vapor of feed-material made of all atomic elements needed to grow chosen nanofibers results in growth of nanofibers onto seed-nanostructures attached to a filament, which is then pulled up continuously at a rate controlled by a rate of growth of the nanofibers. More feed-material is supplied at a rate sufficient to enable the nanofibers to grow longer continuously without limit. Laser light focused into a doughnut shape provides a photon density gradient, which constrains the nanofibers to grow parallel to each other and in the form of cylinders, so that industrially useful structures like cables and cylinders can be made in one low cost operation and in large quantities.
Owner:SHIMOJI YUTAKA +1
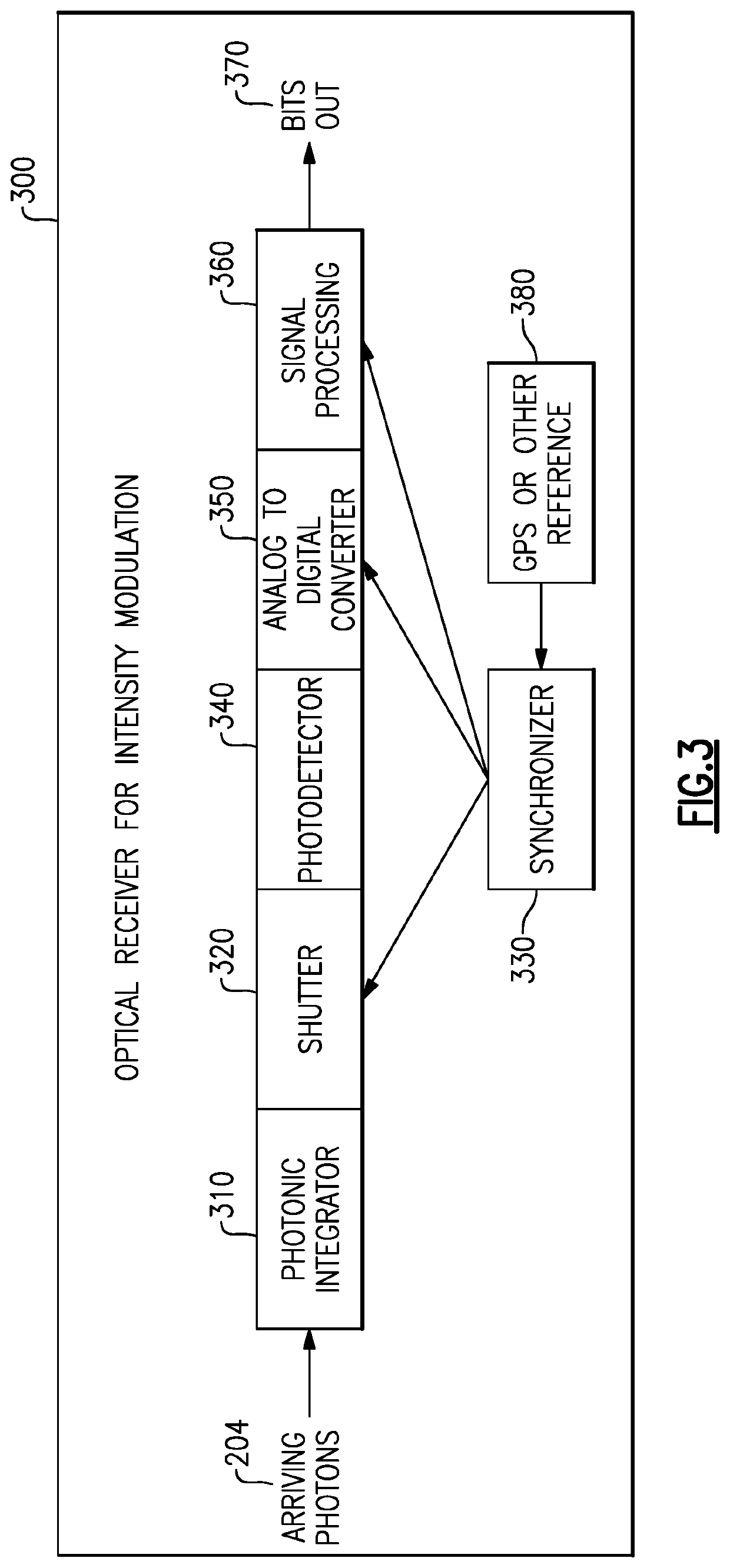
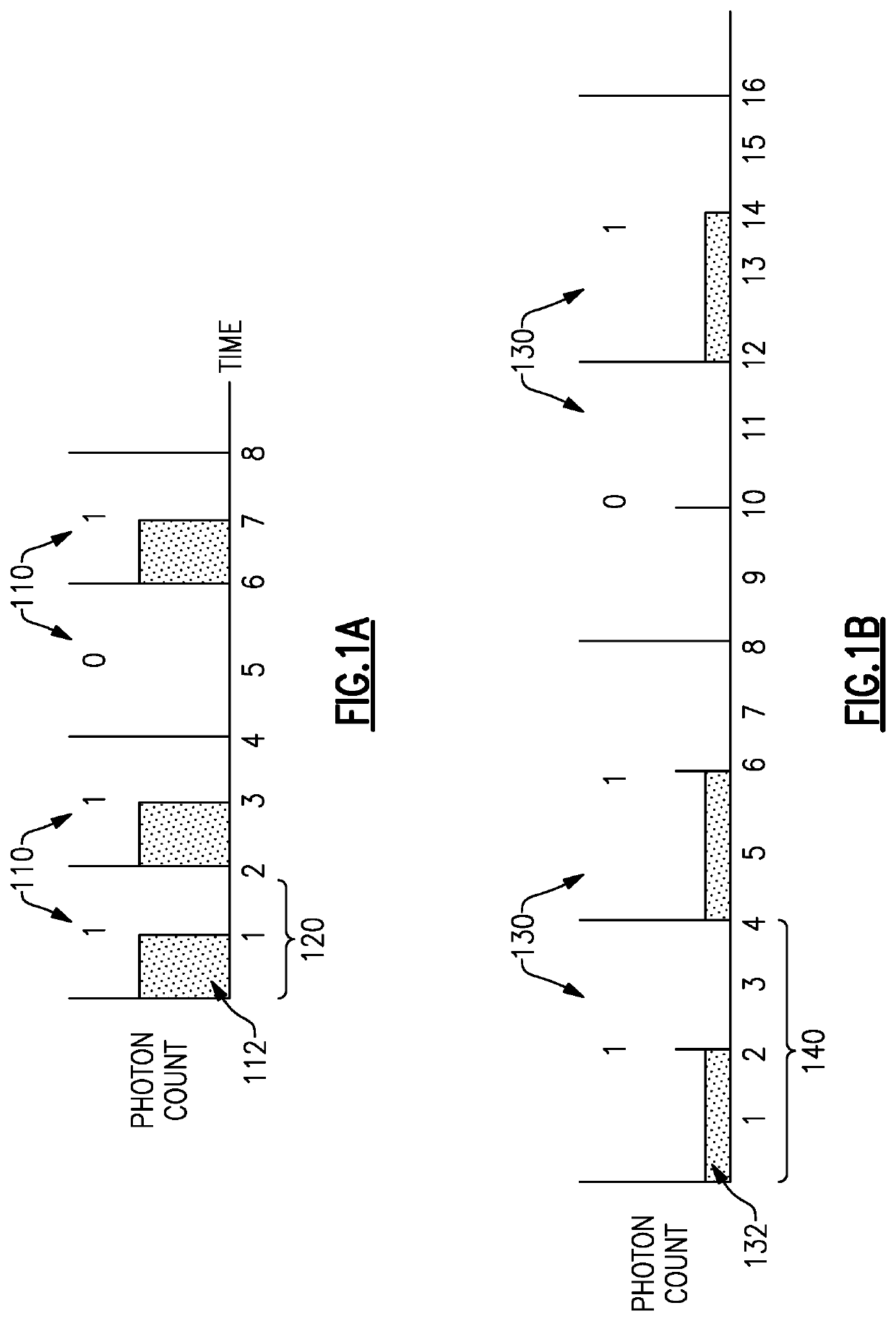
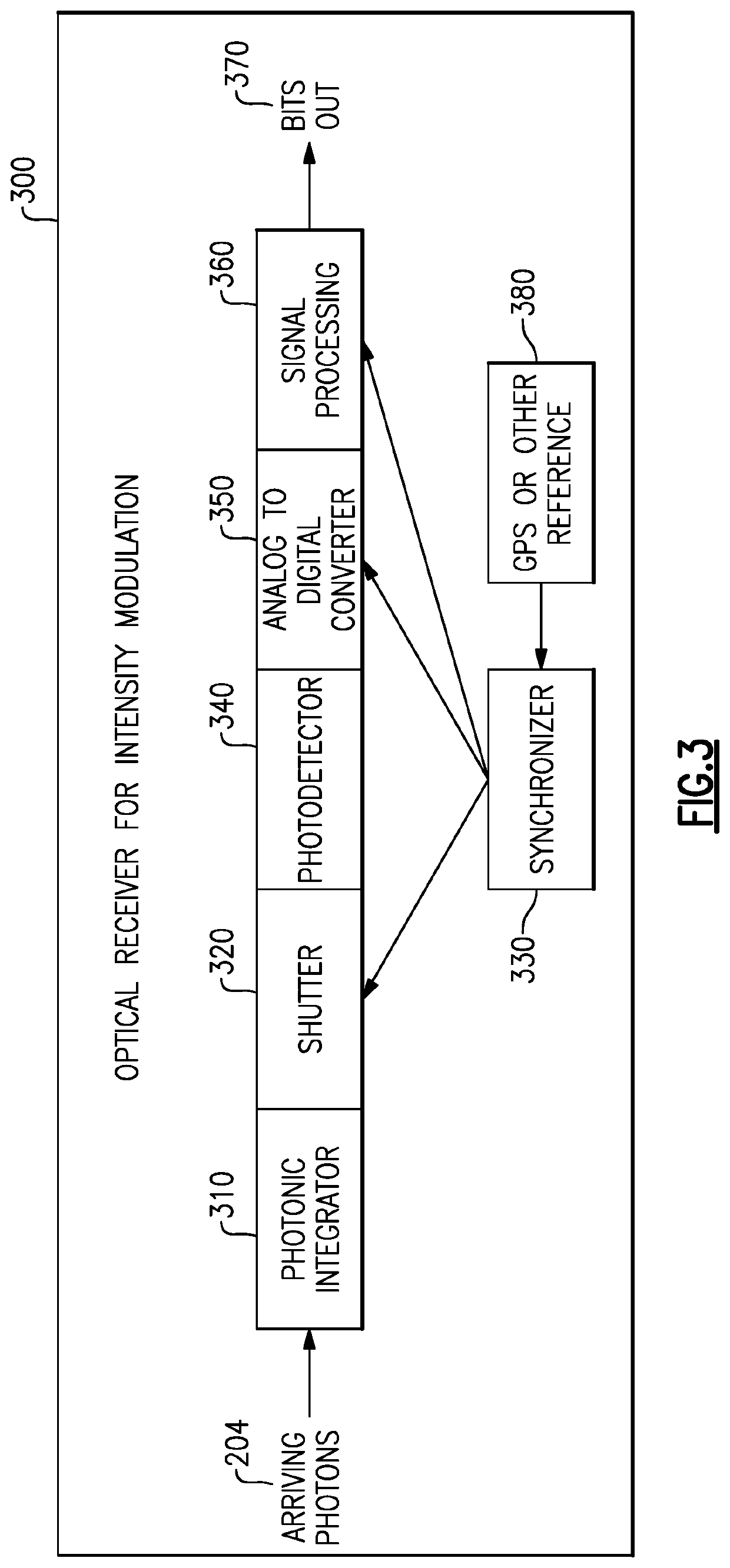
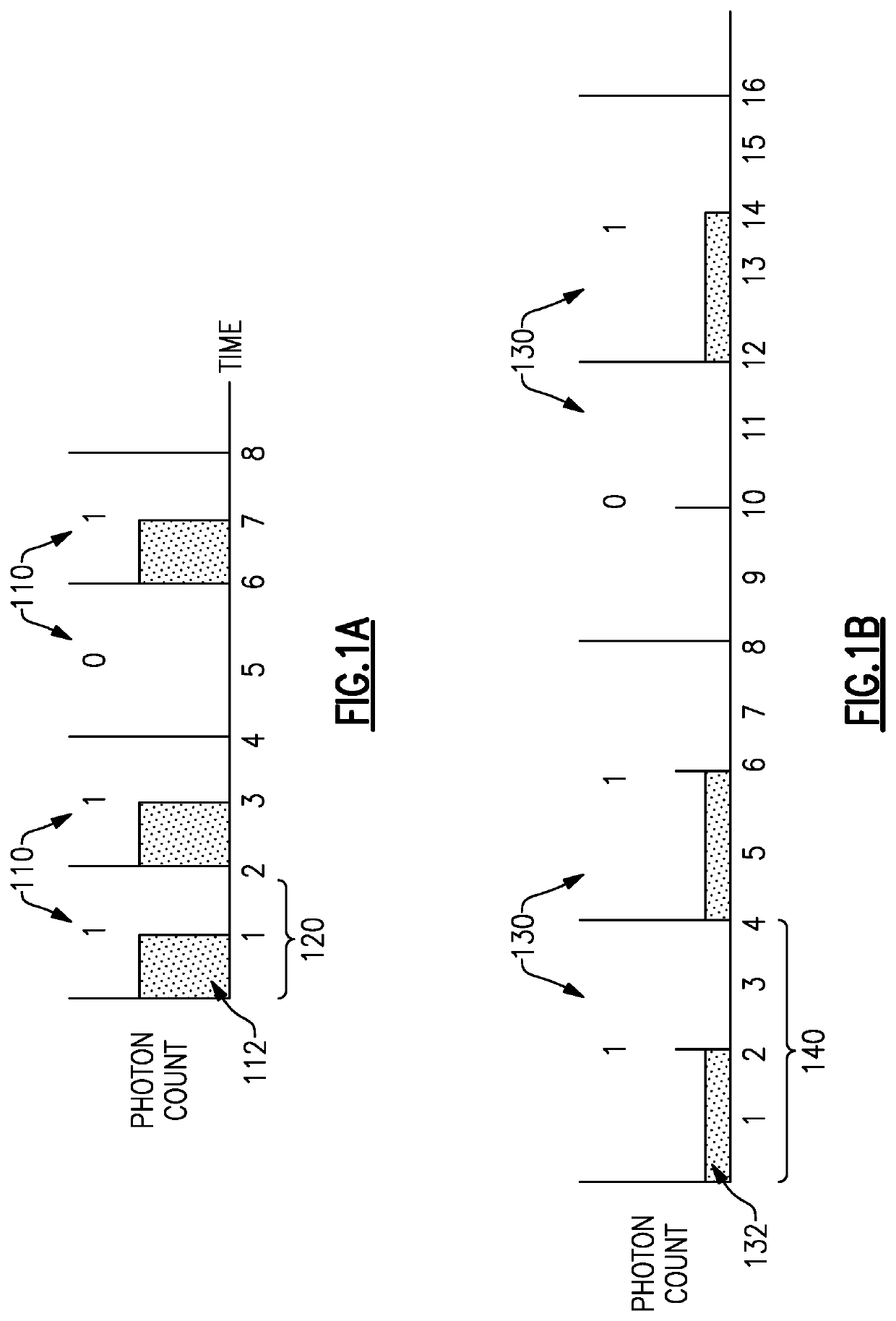
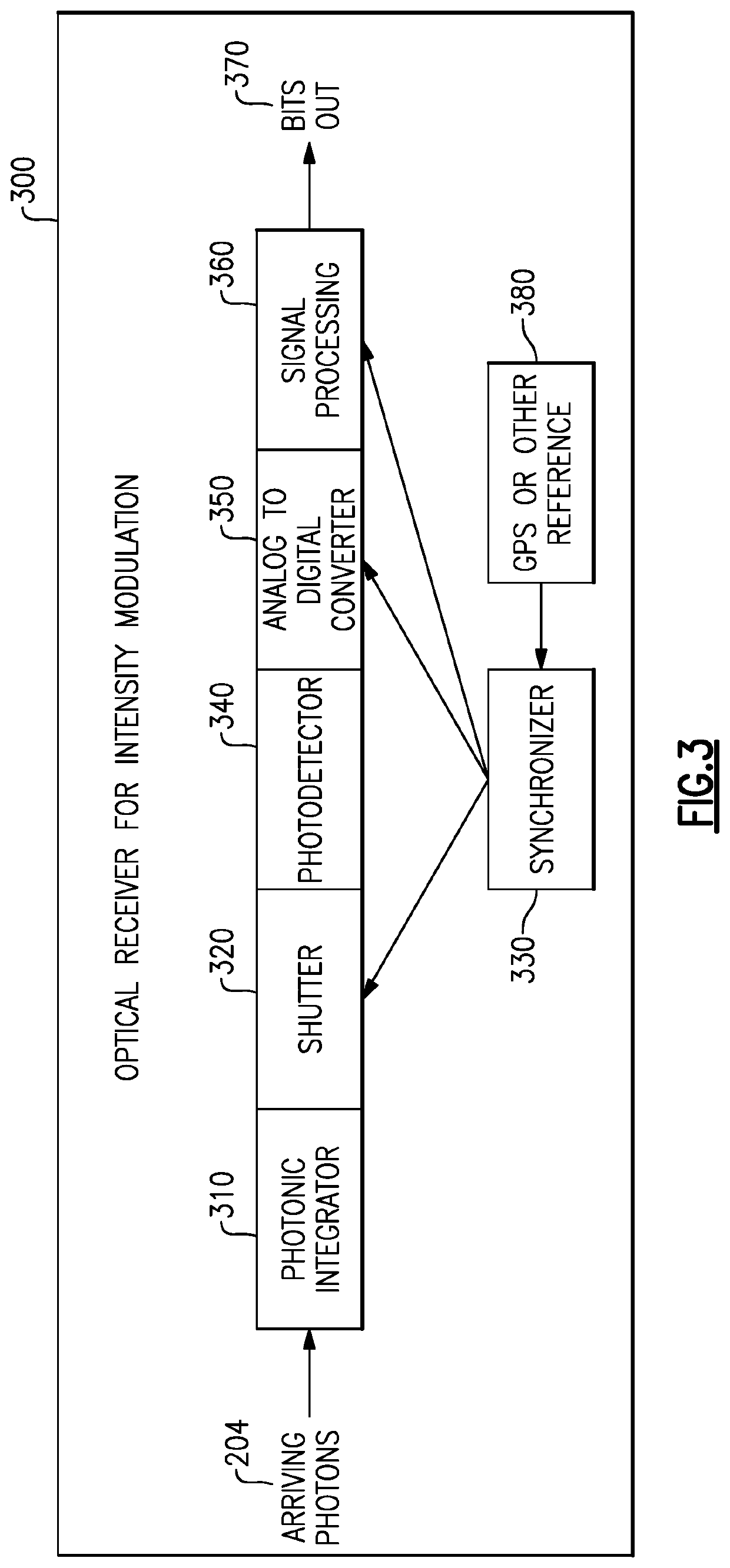
Methods and apparatus for reception of low photon density optical signals
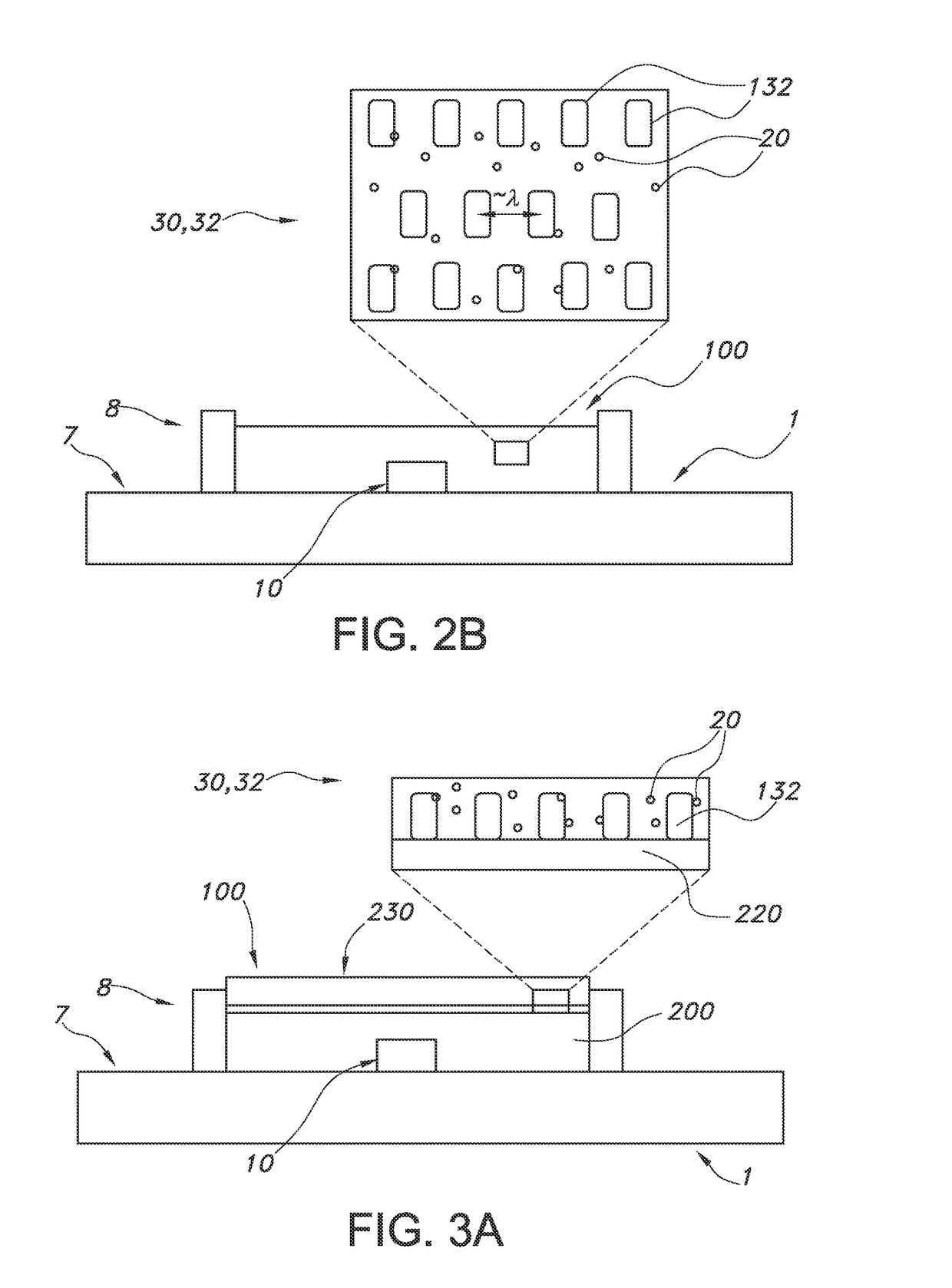
ActiveUS20210099234A1Improved optical sensitivityIncrease rangeLine-of-sight transmissionPhotonic quantum communicationPhotodetectorShutter
An optical receiver includes a photonic integrator configured to accumulate optical signal energy corresponding to the input optical signal during an integration period, and to produce an output optical signal at an end of the integration period, the output optical signal having a higher intensity than the input optical signal, a shutter operable between a closed position and an open position, the shutter configured to prevent the output optical signal from exiting the photonic integrator when in the closed position and to allow the output optical signal to exit the photonic integrator when in the open position, a synchronizer coupled to the shutter and configured to control the shutter between the open position and the closed position; and a photodetector configured to receive the output optical signal when the shutter is in the open position and to produce an electrical signal corresponding to the output optical signal.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Methods of optically monitoring wound healing
ActiveUS8812083B2Diagnostics using lightDiagnostics using spectroscopyReflectance spectroscopyDiffusion equation
Optical changes of tissue during wound healing measured by Near Infrared and Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy are shown to correlate with histologic changes. Near Infrared absorption coefficient correlated with blood vessel in-growth over time, while Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy (DRS) data correlated with collagen concentration. Changes of optical properties of wound tissue at greater depths are also quantified by Diffuse Photon Density Wave (DPDW) methodology at near infrared wavelengths. The diffusion equation for semi-infinite media is used to calculate the absorption and scattering coefficients based on measurements of phase and amplitude with a frequency domain or time domain device. An increase in the absorption and scattering coefficients and a decrease in blood saturation of the wounds compared to the non wounded sites was observed. The changes correlated with the healing stage of the wound. The methodologies used to collect information regarding the healing state of a wound may be used to clinically assess the efficacy of wound healing agents in a patient (e.g., a diabetic) and as a non-invasive method to detect the progress of wound healing, particularly chronic wounds due to diabetes. The methodology applies to ischemic environments, impaired healing states, and emerging subsurface tissue deterioration, such as in pressure ulcers, venous ulcers, and ubiquitous ulcers.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Adaptive optical correcting device and method based on sodium layer structured beacon
ActiveCN105223691ANo focus anisotropic effectReduce image qualityOptical elementsSodium layerTechnology research
The invention discloses an adaptive optical correcting device and method based on a sodium layer structured beacon, belonging to the adaptive optical technology research field, and is used for detecting and correcting wavefront distortion caused by atmospheric turbulence. The adaptive optical correcting device comprises a structured sodium laser beam array generating device, a ground telescope system, a wavefront distortion extraction device, and a wavefront distortion correcting device. The correcting device and method do not exist focusing anisoplanatism effects, do not require a separate aperture mode with a hartmann sensor as a representative to detect a wavefront, receive backward diffusion photons in a full aperture mode, thereby have low requirements for backward diffusion photon density, and are especially suitable for a large field of view. The invention provides a brand new wavefront distortion extraction method for the large aperture foundation telescope adaptive optical technology.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
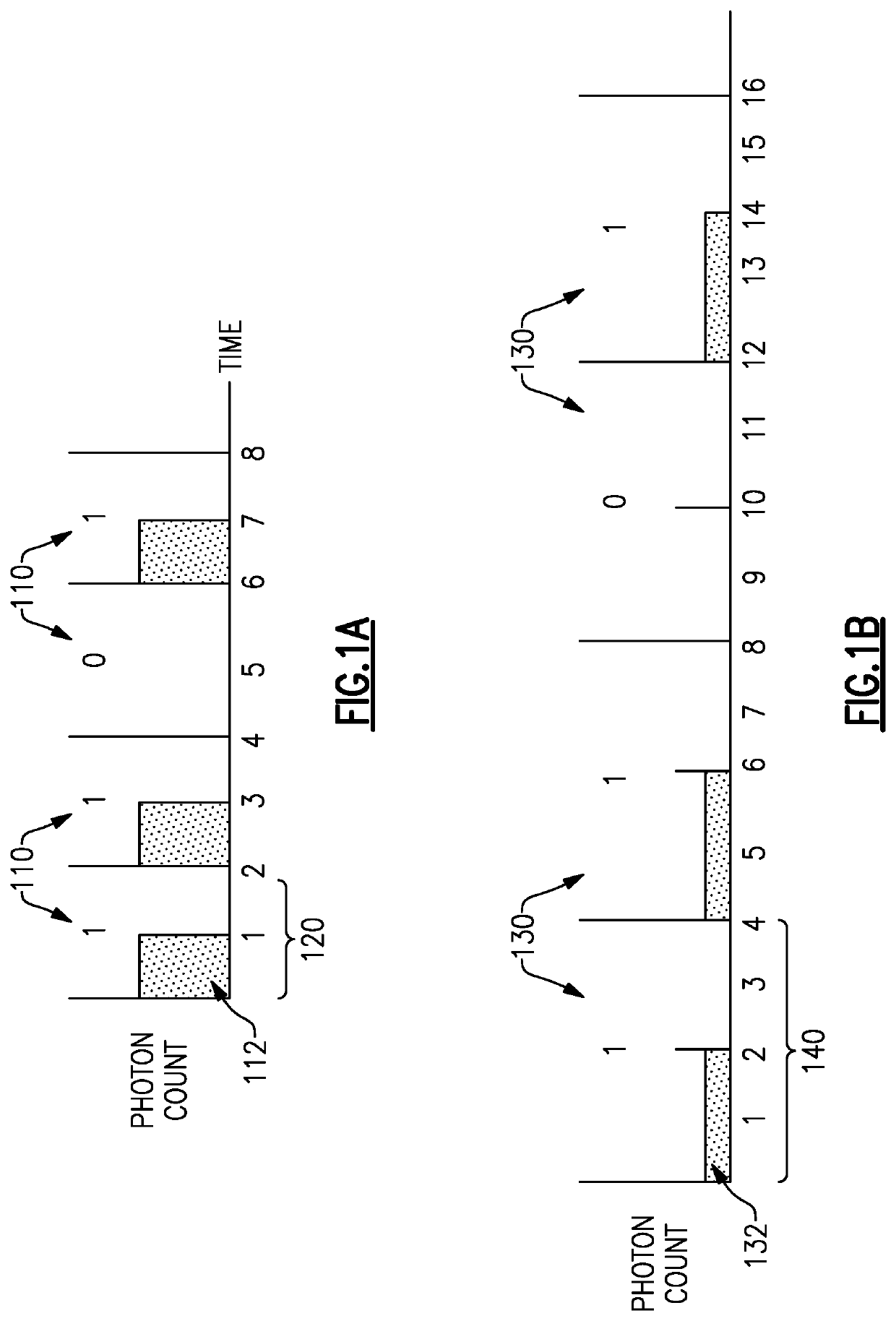
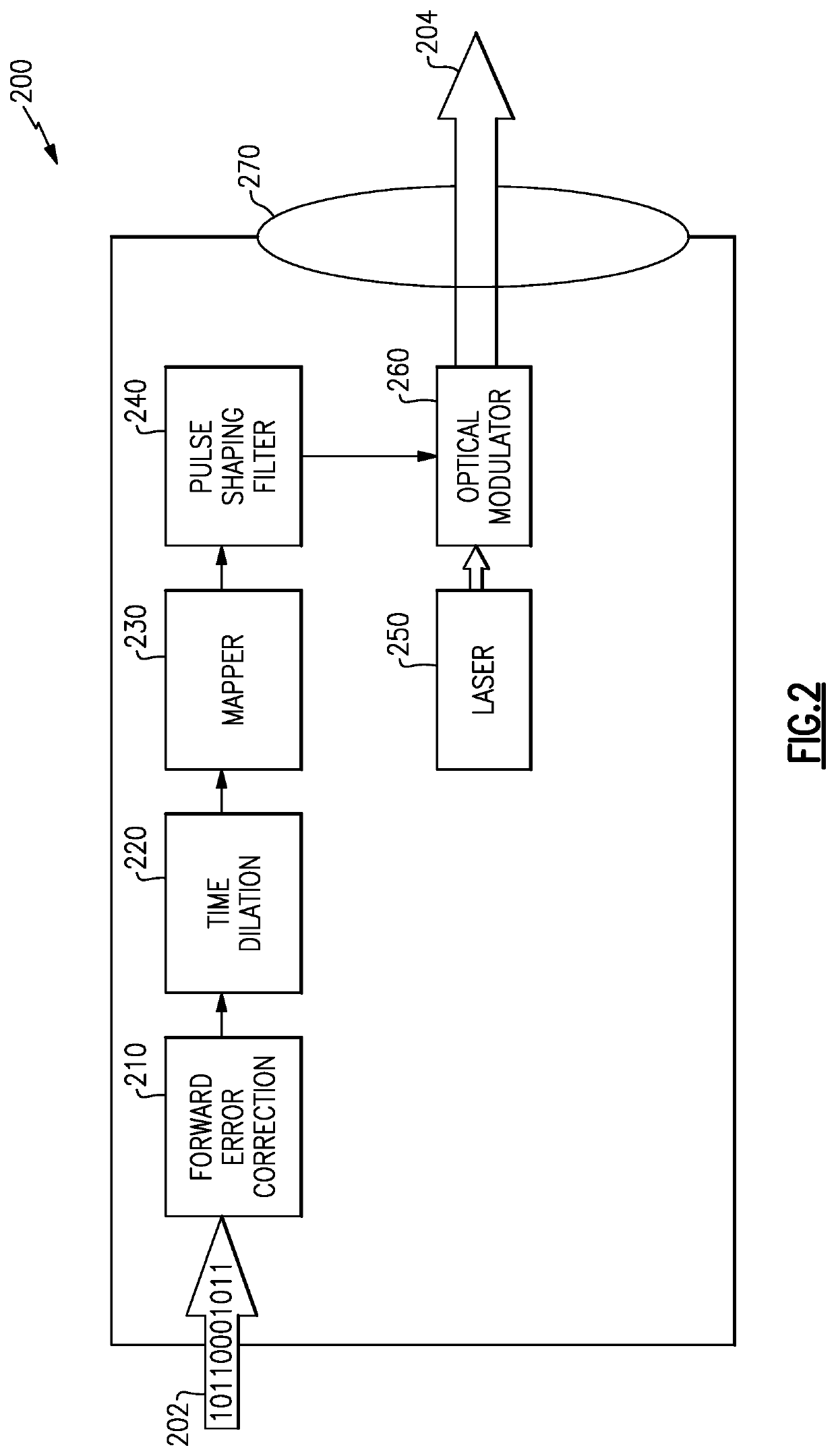
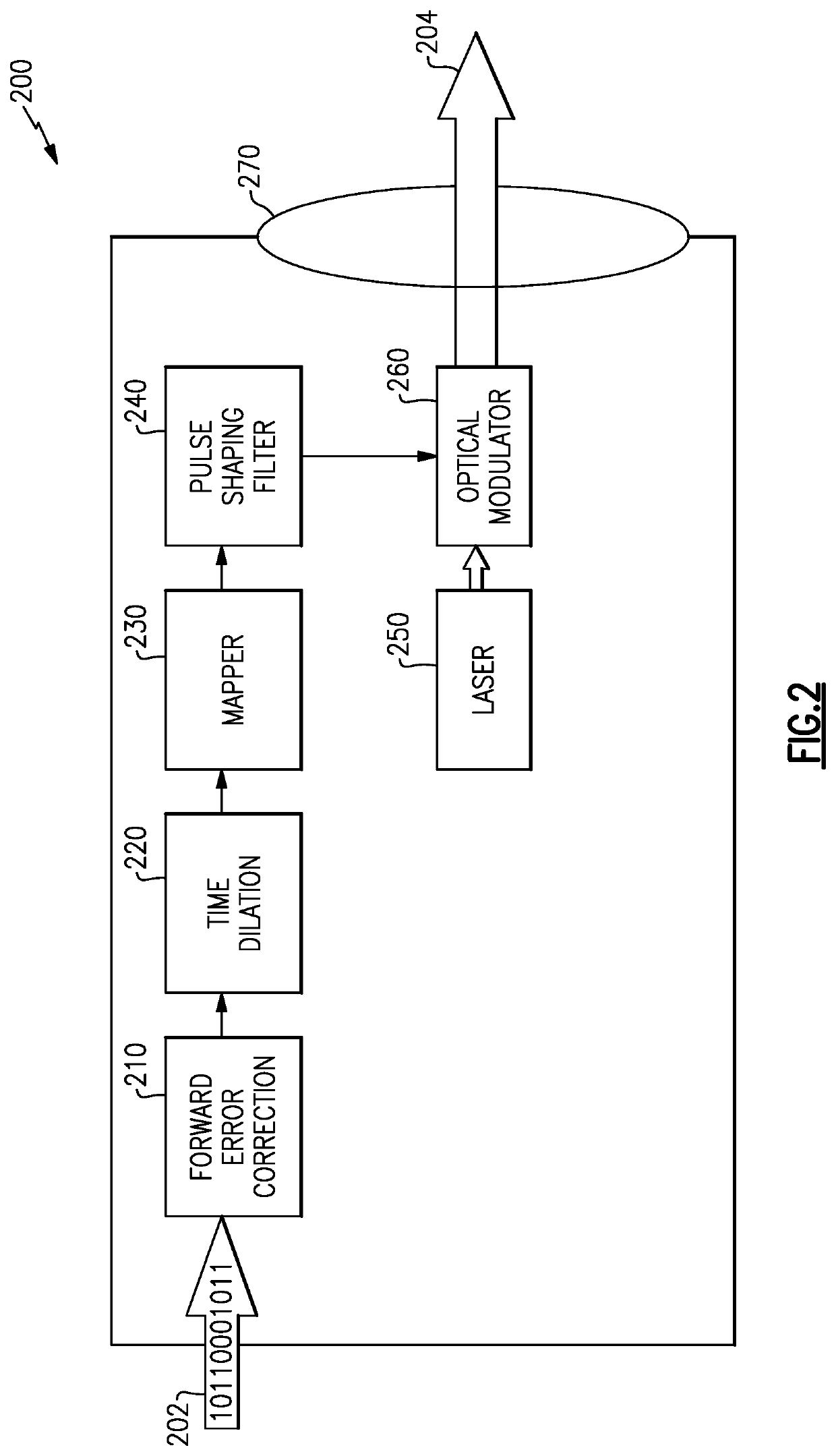
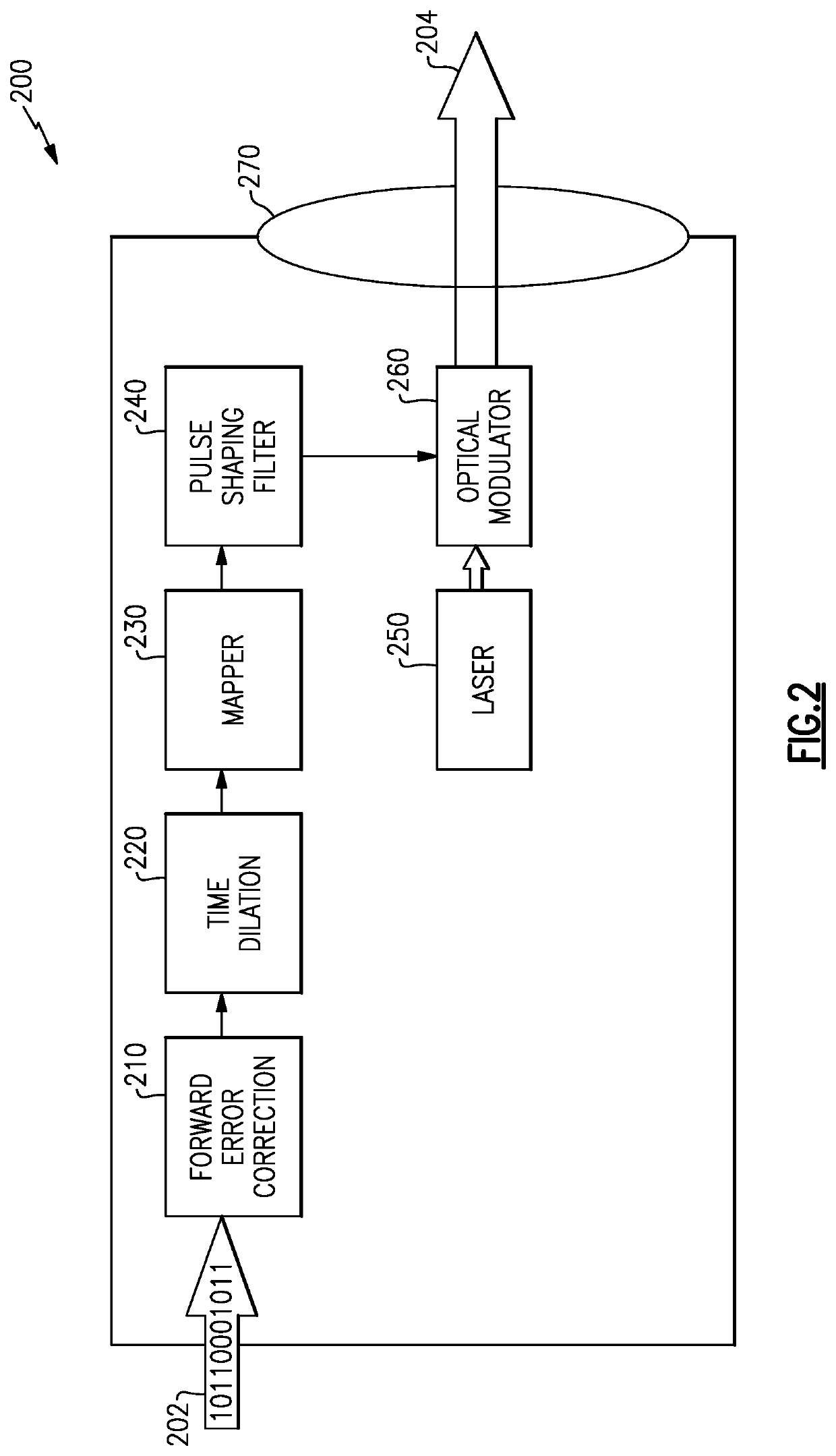
Methods and apparatus for transmission of low photon density optical signals
ActiveUS20210099232A1Diminishing detectabilityHigh sensitivityLine-of-sight transmissionPhotonic quantum communicationContinuous lightComputational physics
An optical transmitter and a method of producing a low-photon-density modulated optical signal are disclosed. The optical transmitter and method include an optical source configured to emit a continuous optical carrier waveform, a dilation module configured to apply a spreading code to a data payload to spread each of the plurality of symbols in time to expand the symbol duration by a dilation factor and produce a corresponding plurality of time-dilated symbols, the plurality of time-dilated symbols having a lower photon density than the plurality of symbols; a mapping module configured to map the plurality of time-dilated symbols to a modulation scheme; and a modulator configured to modulate the optical carrier waveform with the plurality of time-dilated symbols according to the modulation scheme to produce the low-photon-density modulated optical signal encoded with the plurality of time-dilated symbols corresponding to the data payload.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Measuring arrangement for an optical spectrometer
ActiveUS20100284004A1Improved light coupling-inImproved coupling-out propertyRadiation pyrometryDiagnostics using lightCouplingLight guide
The invention relates to a measuring arrangement for an optical spectrometer, in particular a photon density wave spectrometer, having a measuring chamber, which can be loaded with a sample to be measured, and a coupling-in / coupling-out device which is configured to receive excitation light from a light source and couple it into the sample to be measured in the measuring chamber and to receive measuring light formed in the sample to be measured on account of the excitation light which has been coupled in and to emit said measuring light to a detection device, wherein the coupling-in / coupling-out device has an optical switching device and a plurality of light guide elements which couple to the latter, have a respective optical waveguide and can be connected according to at least one selectable measuring configuration using the optical switching device in order to couple in the excitation light and receive the measuring light according to the at least one selectable measuring configuration, and wherein outputs of the plurality of light guide elements are positioned according to a spiral arrangement in the viewing direction of the outputs.
Owner:UNIV POSTDAM
Method and device for transplantation of femtosecond laser nucleus
InactiveCN101177664AIncrease success rateShort pulse widthStress based microorganism growth stimulationMicro nanoSomatic cell
The invention relates to a method and equipment for femtosecond laser somatic cell nuclear transplantation, in particular to a micro-nano control method which adopts a light knife effect induced by femtosecond laser two-photon and optical tweezers gradient force induced by high photon density. A pump laser is started-up; the laser produced by the pump laser is introduced into a resonator of a femtosecond laser; when the oscillation is done, the energy of the ultrashort femtosecond laser pulse is amplified through a regenerative amplifier, and the pulse number and the repeated frequency of laser output are chosen. The emitted femtosecond laser is divided into two beams of light, one of which used for realizing the femtosecond optical tweezers, and the other of which is used for realizing the function of the femtosecond optical tweezers through a half-permeable and semi-reflecting mirror, and then the two beams of light are coupled with an optical path through another half-permeable andsemi-reflecting mirror to realize the amplification of a spot light area; then the light beams is focused on a target cell, and the harmless transplantation operation of the somatic cell nuclear is done. A switch for controlling a light valve is arranged in a software control system, which can not only realize the operation of the laser spot on the target cell, but also adjust the scanning speed and change the exposure time to meet different requirements and enhance the success rate of the somatic cell nuclear transplantation.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method and device for nervus damnification and regeneration renovation by using femtosecond laser
InactiveCN101220332AAvoid damageShort pulse widthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicro nanoNerve cells
The invention adopts the femtosecond laser two-photon induced photo knife effect and the high photon density induced optical tweezers gradient force function for carrying out a micro-nano manipulation, which is applicable to the study of the injury, regeneration and repair of various biological cells. The invention consists of a laser generation system, an external optical path system, a high precision imaging system and a software control system. The laser generation system includes two parallel branches, one branch consists of a lock mould knob and a femtosecond laser sequentially, and the other branch consists of a digital delay / pulse signal generator and a regeneration amplifier sequentially. The external optical path system consists of a dual-branch optical path, a semi-transparent semi-reflection mirror, an optical gate and a beam expander sequentially. The dual-branch optical path includes two parts: one part consists of a movable convex lens, a fixed convex lens, a rotatable total reflection mirror and an attenuation mirror sequentially, and the other part is an attenuation mirror. The device can realize the whole process of nano-injury and regeneration study of the nerve cells and can adopt the femtosecond optical tweezers to realize the choice of the super-sophisticated target position during an axon regeneration process.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
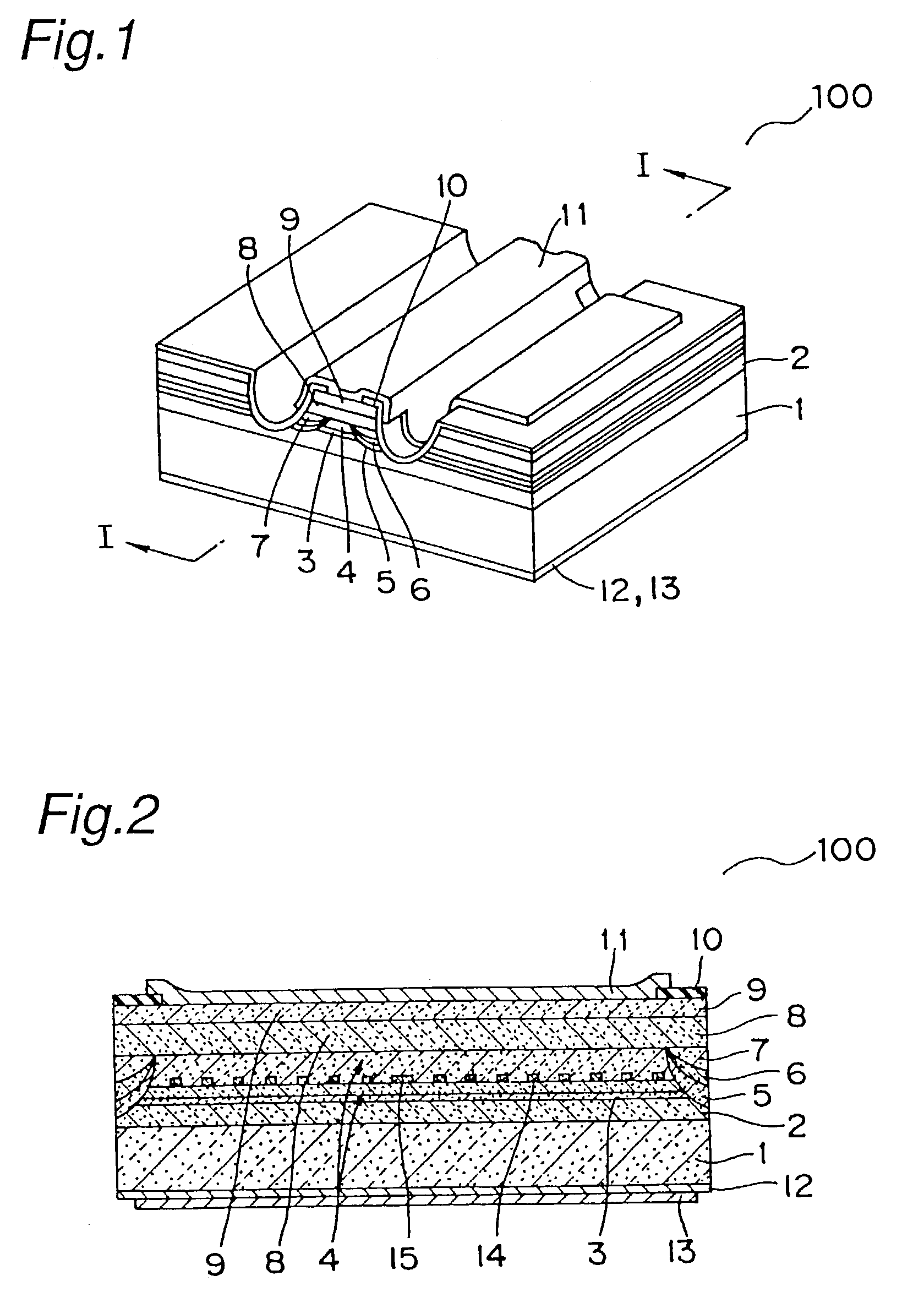
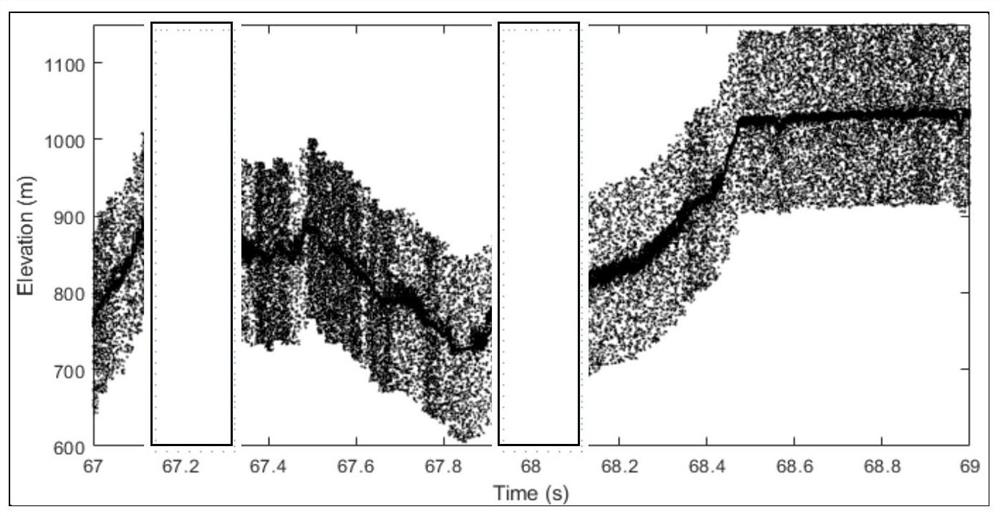
Semiconductor optical device
InactiveUS6999485B2Reduce variationLow refractive indexLaser optical resonator constructionLaser active region structureRefractive indexLight beam
A kink-free semiconductor optical device stabilizing laser oscillation and producing a high optical performance. The semiconductor optical device includes a beam waveguide extending in a longitudinal direction between a pair of end surfaces. The beam waveguide includes an active layer having a quantum well structure with at least one well layer and two barrier layers, and a pair of cladding layers sandwiching the active layer. The active layer has first and second regions in the longitudinal direction, the photon density in the first region being larger than in the second region. The first region has a differential gain greater than the second region so that variation of refractive index across the beam waveguide is reduced.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
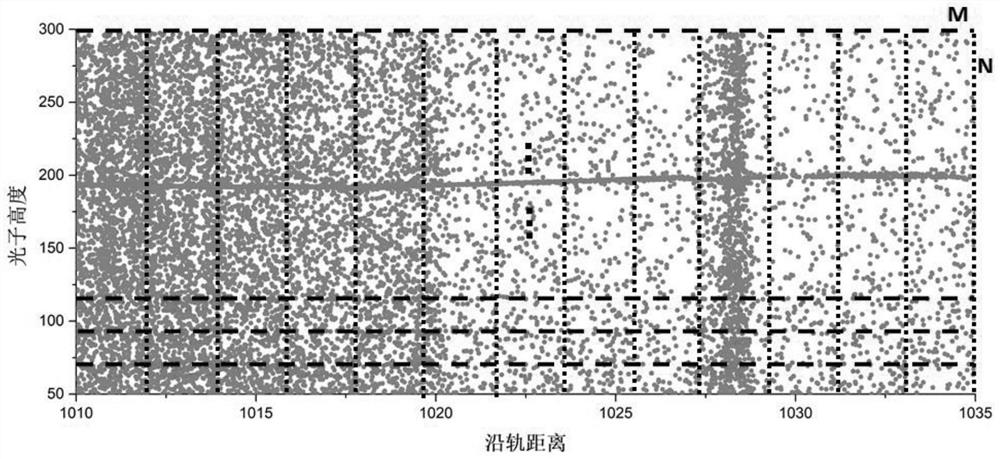
Single-photon laser height measurement data denoising method and device based on density statistics
ActiveCN111665517AImprove denoising effectImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionElectromagnetic wave reradiationComputational physicsLaser altimetry
The invention relates to a single-photon laser height measurement data denoising method and device based on density statistics. The method comprises the following steps: 1) obtaining single-photon laser altimetry data; 2) performing data preprocessing; 3) carrying out photon density calculation by using an ellipse search area whose direction and size change adaptively with the gradient; and 4) adaptively calculating segmented threshold separation signal photons and noise photons by adopting an OTSU method, and removing discrete noise points by adopting a K nearest neighbor distance. Compared with the prior art, the method is not influenced by non-uniform background noise photons, and is high in adaptability, the direction of the search ellipse can be changed adaptively along with the slope, the size can be changed, signal photons and noise photons of each segment are separated by using the segmentation threshold, and a small number of discrete noise points left after rough denoising are further removed; and the method is complete in signal extraction, high in denoising precision and high in efficiency.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
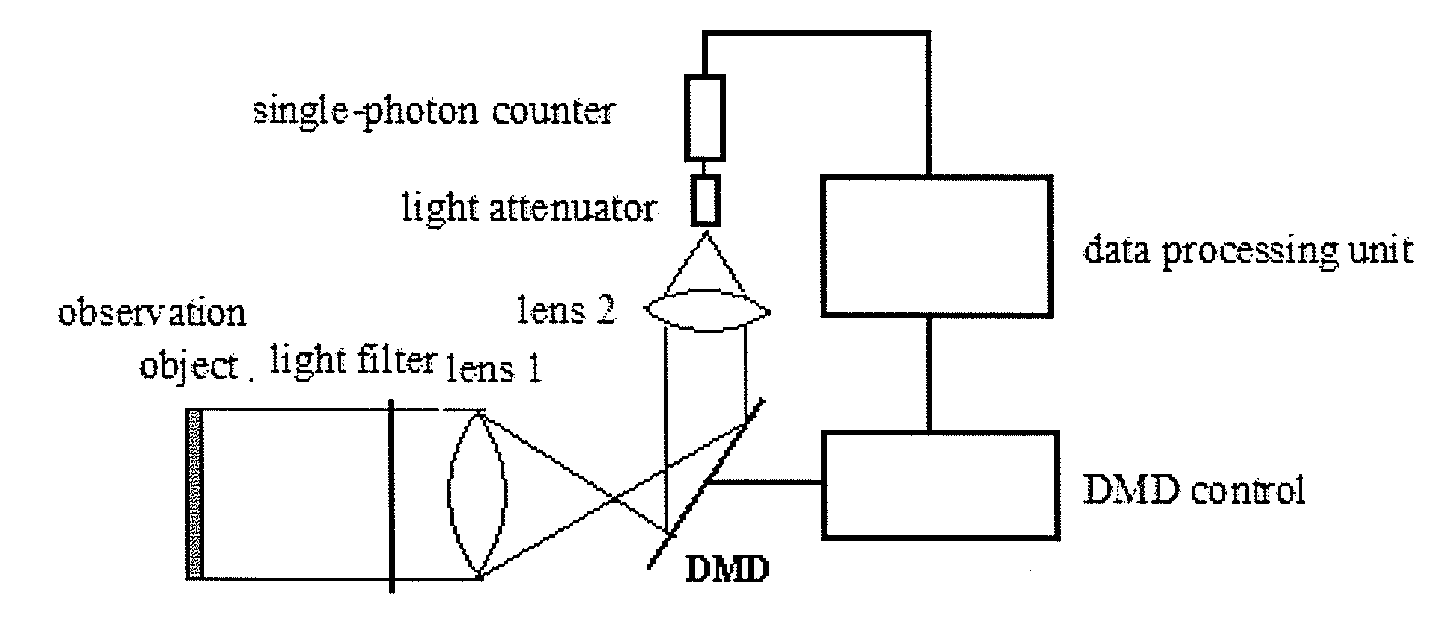
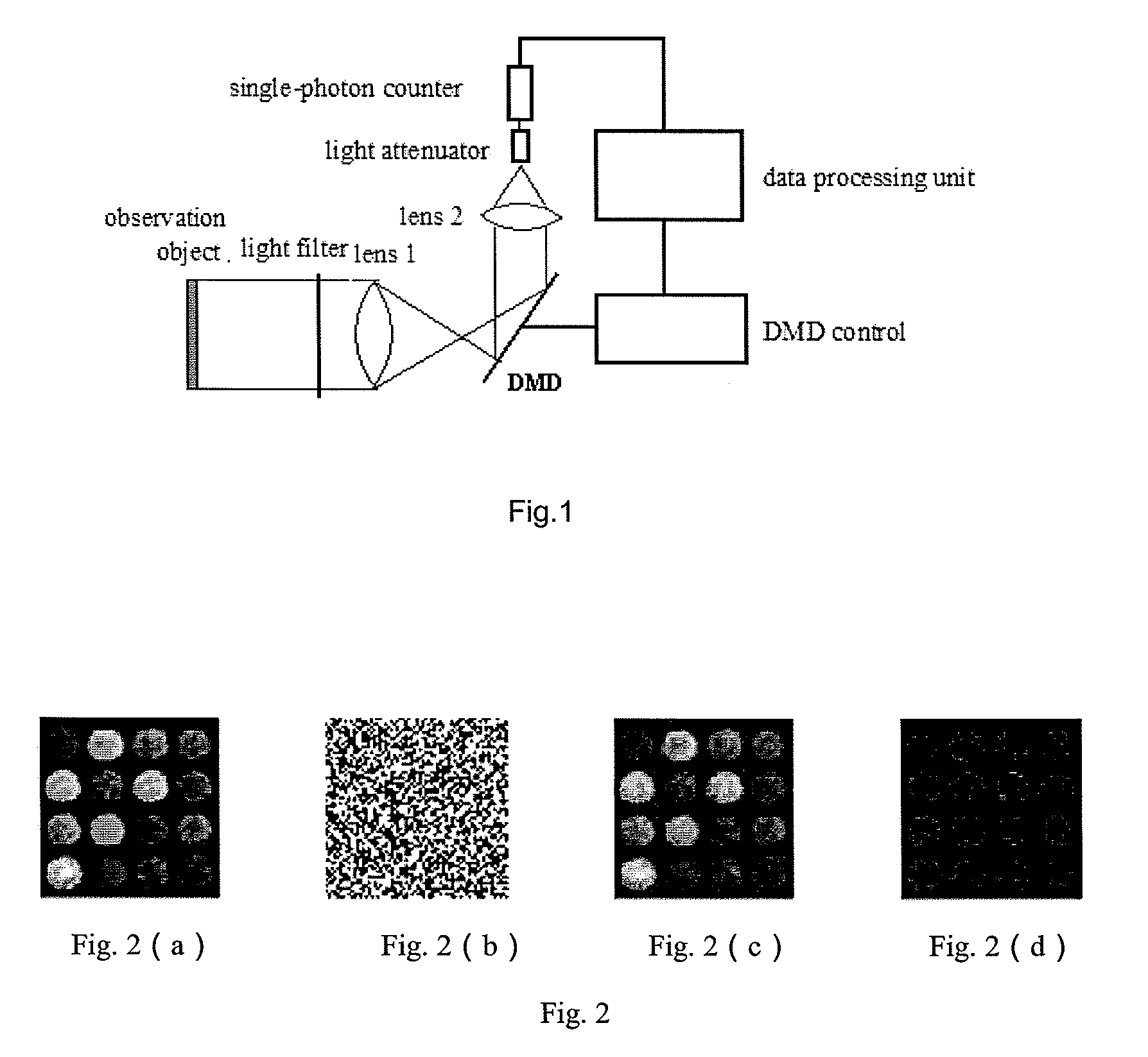
Single Photon-Counting Imaging System and Method Thereof
InactiveUS20130341487A1High detection sensitivityHigh resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesDigital micro mirror deviceControl system
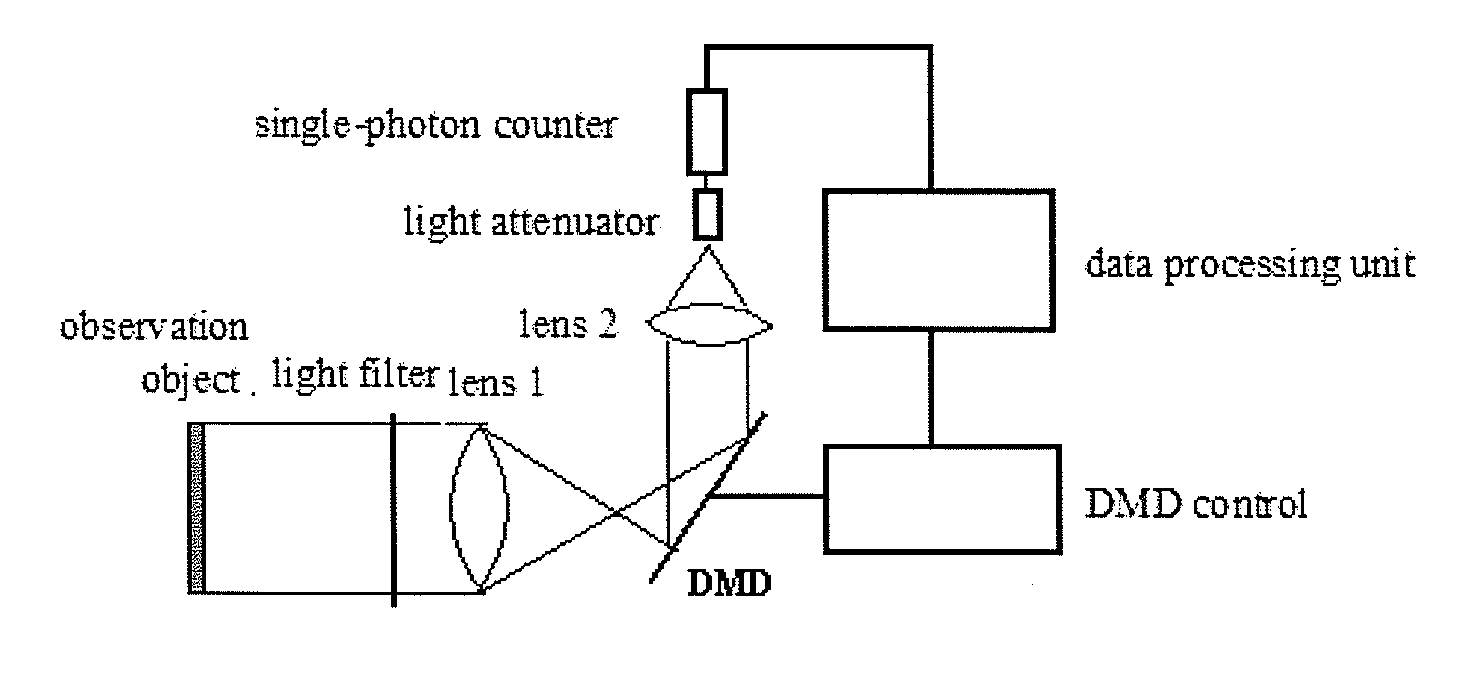
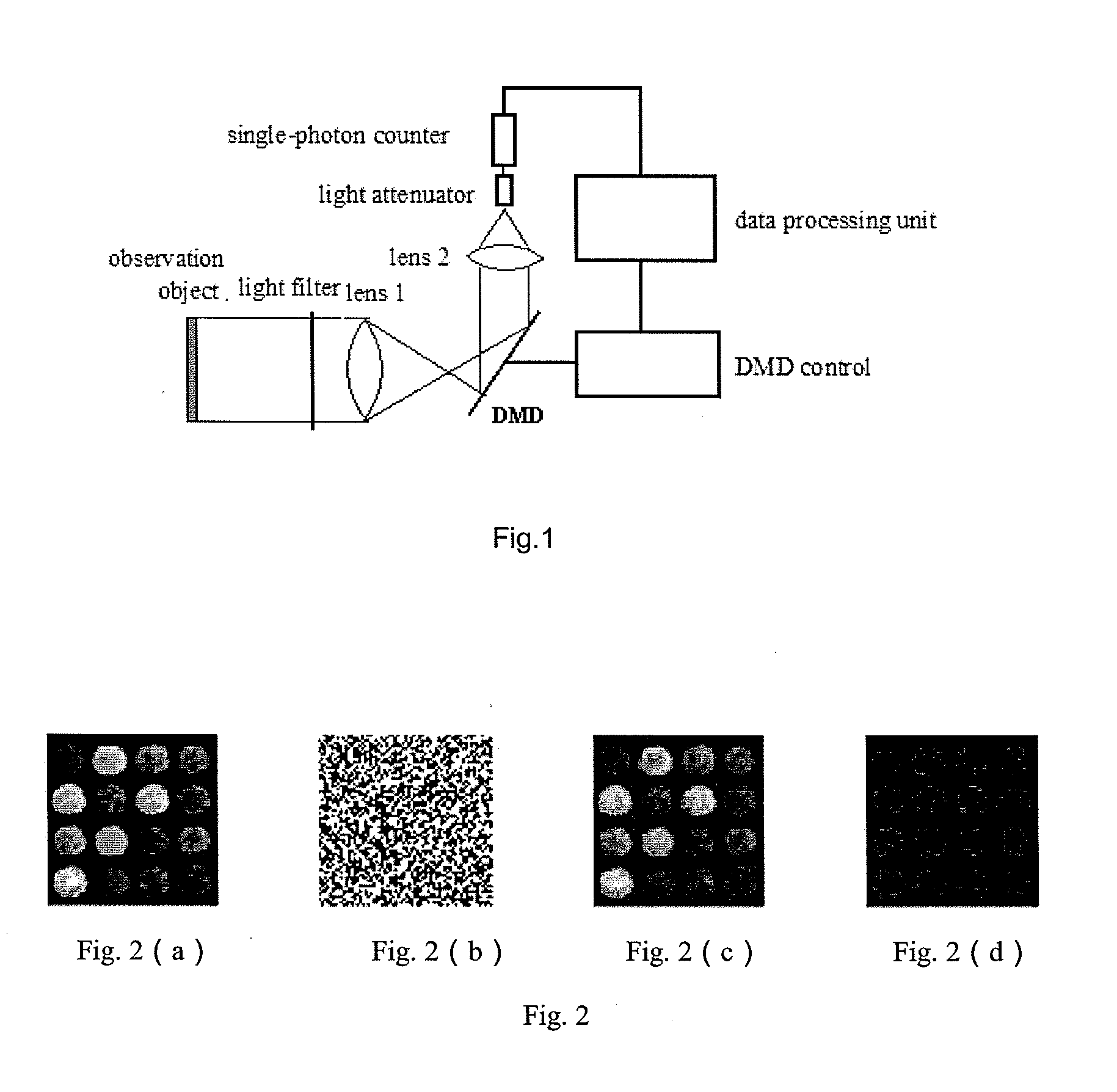
The invention relates to a single-photon counting imaging system and a single-photon counting imaging method. The system comprises a optical filter, a first lens, a digital micro-mirror device (DMD) control system, a second lens, a single-photon counter and a data processing unit, where the DMD together with the first lens and the second lens are used for converting two-dimensional image data into a one-dimensional sequence to complete sampling of measured signals; the ultra-weak light is filtered by the optical filter, after which the ultra-weak light image onto the DMD through the first lens, and the DMD control system controls the probability of the photons reflected to the second lens and the second lens controls the focusing of the photons; and the data processing unit together with the single-photon counter to complete sparse reconstruction, and the data processing unit converts the number of photons counted by the single-photon counter within a certain period of time into the probability of detected photon counts, as the measured value, and a photon density image is reconstructed by adopting an optimization algorithm based on the measurement matrix on the DMD and the measured value, thereby solving out the two-dimensional image.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Solar cell synergistic film
InactiveCN101510565AImprove current efficiencyImprove conversion efficiencyPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesFill factorEngineering
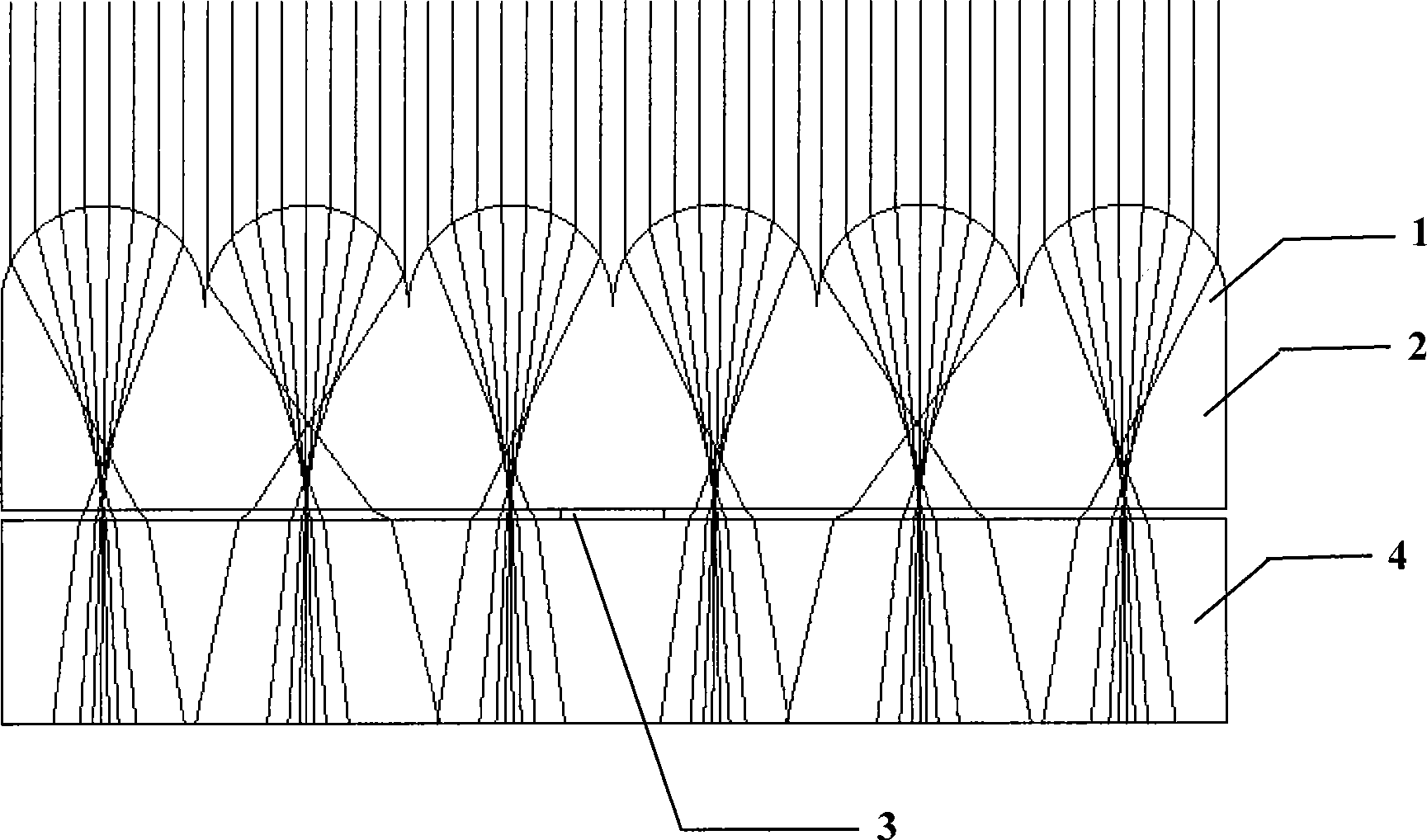
The invention discloses a solar battery synergy membrane which is characterized by consisting of a transparent membrane structure, on the surface of which focus lenticule structures are distributed; the parallel sunlight can be focused on the photosensitive area of the surface of the solar battery by the array of lenticules, therefore, the photon density on the surface of the photosensitive area is increased, which is equivalent to the reduction of the area of the photosensitive area to the same output power, thus effectively improving conversion efficiency and reducing production costs; and with the flexion reflection and refraction of the array of lenticules, the light reflected by the surface of the solar battery can be reflected to the photosensitive area, thus improving the utilization rate of the light. No obvious temperature change takes place on the solar battery, and therefore the fill factors and service life of the solar battery are not reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV +1
Methods for measuring changes in optical properties of wound tissue and correlating near infrared absorption(fNIR) and diffuse refelectance spectroscopy scattering (DRS) with tissue neovascularization and collagen concetration to determine whether wound is healing
InactiveUS20150025342A1Diagnostics using lightDiagnostics using spectroscopyReflectance spectroscopyEfficacy
Optical changes of tissue during wound healing measured by Near Infrared and Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy are shown to correlate with histologic changes. Near Infrared absorption coefficient correlated with blood vessel in-growth over time, while Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy (DRS) data correlated with collagen concentration. Changes of optical properties of wound tissue at greater depths are also quantified by Diffuse Photon Density Wave (DPDW) methodology at near infrared wavelengths. The diffusion equation for semi-infinite media is used to calculate the absorption and scattering coefficients based on measurements of phase and amplitude with a frequency domain or time domain device. An increase in the absorption and scattering coefficients and a decrease in blood saturation of the wounds compared to the non wounded sites was observed. The changes correlated with the healing stage of the wound. The methodologies used to collect information regarding the healing state of a wound may be used to clinically assess the efficacy of wound healing agents in a patient (e.g., a diabetic) and as a non-invasive method
Owner:PHILADELPHIA HEALTH & EDUCATION CORP +1
Semiconductor optical amplifier
ActiveCN106785915APhoton density increaseIncreased pattern volumeLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersUltravioletDivergence angle
The invention discloses a semiconductor optical amplifier, and especially relates to a GaAs-based semiconductor optical amplifier having a parabola-shaped curved-surface waveguide structure. Material of the semiconductor optical amplifier is a GaAs-based material system. An N-type AlxGa1-xAs buffer layer, an N-type AlGaAsSb lower limit layer, an N-type N-AlxGa1-xAs lower waveguide layer, an InxGa1-xAs quantum well active region, a P-type AlxGa1-xAs upper waveguide layer and a P-type AlGaAsSb upper limit layer are epitaxially prepared on an N-type GaAs substrate in sequence. The upper waveguide layer of the semiconductor optical amplifier is in the parabola-shaped curved-surface structure; such structure can enable a parabola-shaped curved-surface tip to have higher photon density, thereby improving mode volume of the semiconductor optical amplifier and enabling the semiconductor optical amplifier to have higher gain; and meanwhile, the parabola-shaped curved-surface waveguide structure facilitates compressing divergence angle of the semiconductor optical amplifier, thereby realizing high-power output and improving fiber coupling efficiency. The parabola-shaped curved-surface structure of the upper waveguide layer of the semiconductor optical amplifier is prepared through electron beam lithography or ultra-violet lithography, and then, through a dry method and wet method combined etching process.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Intra-serum and intra-gel for modeling human skin tissue
InactiveUS20030113924A1Diagnostics using spectroscopyScattering properties measurementsConfocalNon invasive
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
Charge-exchange device
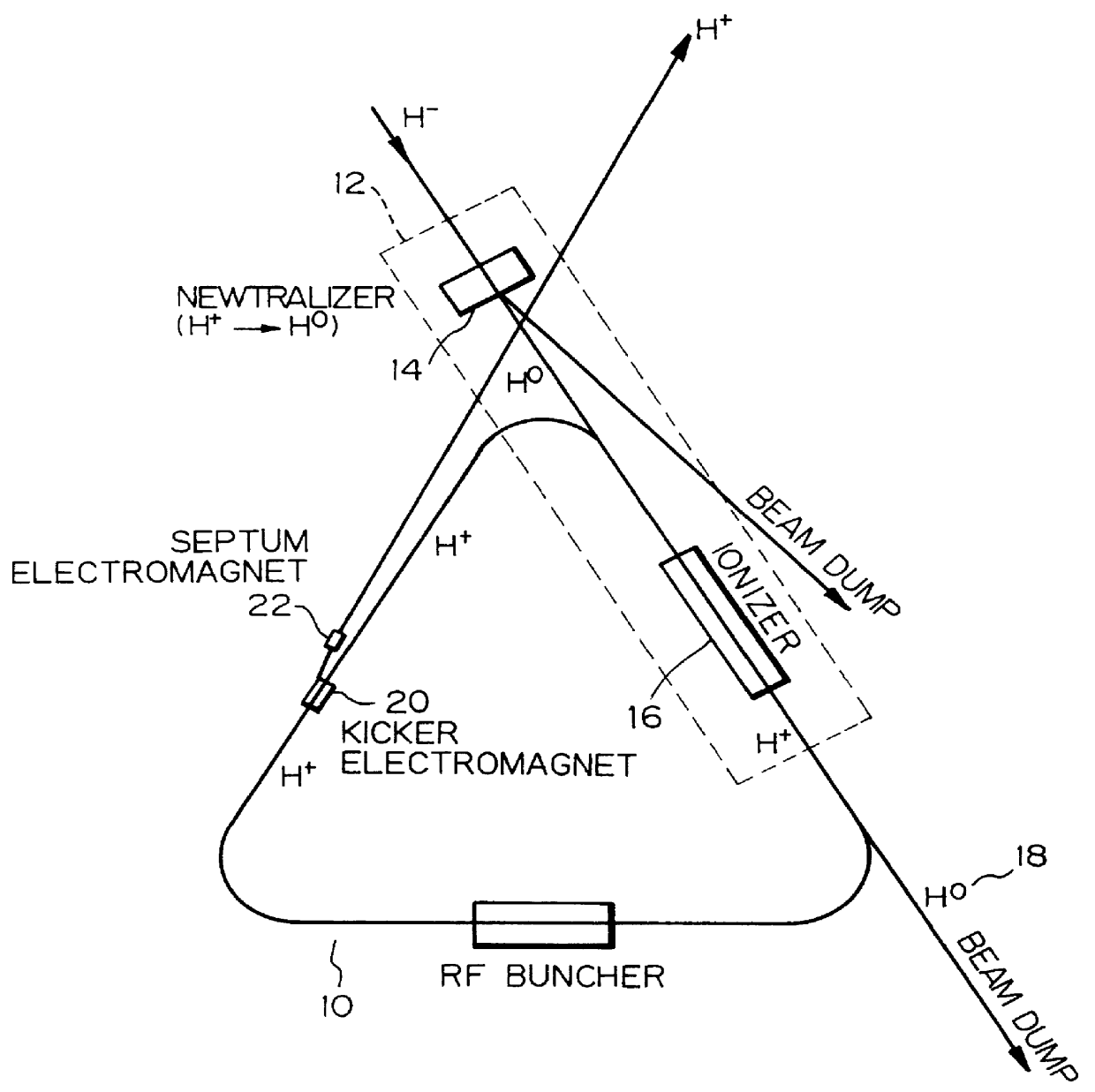
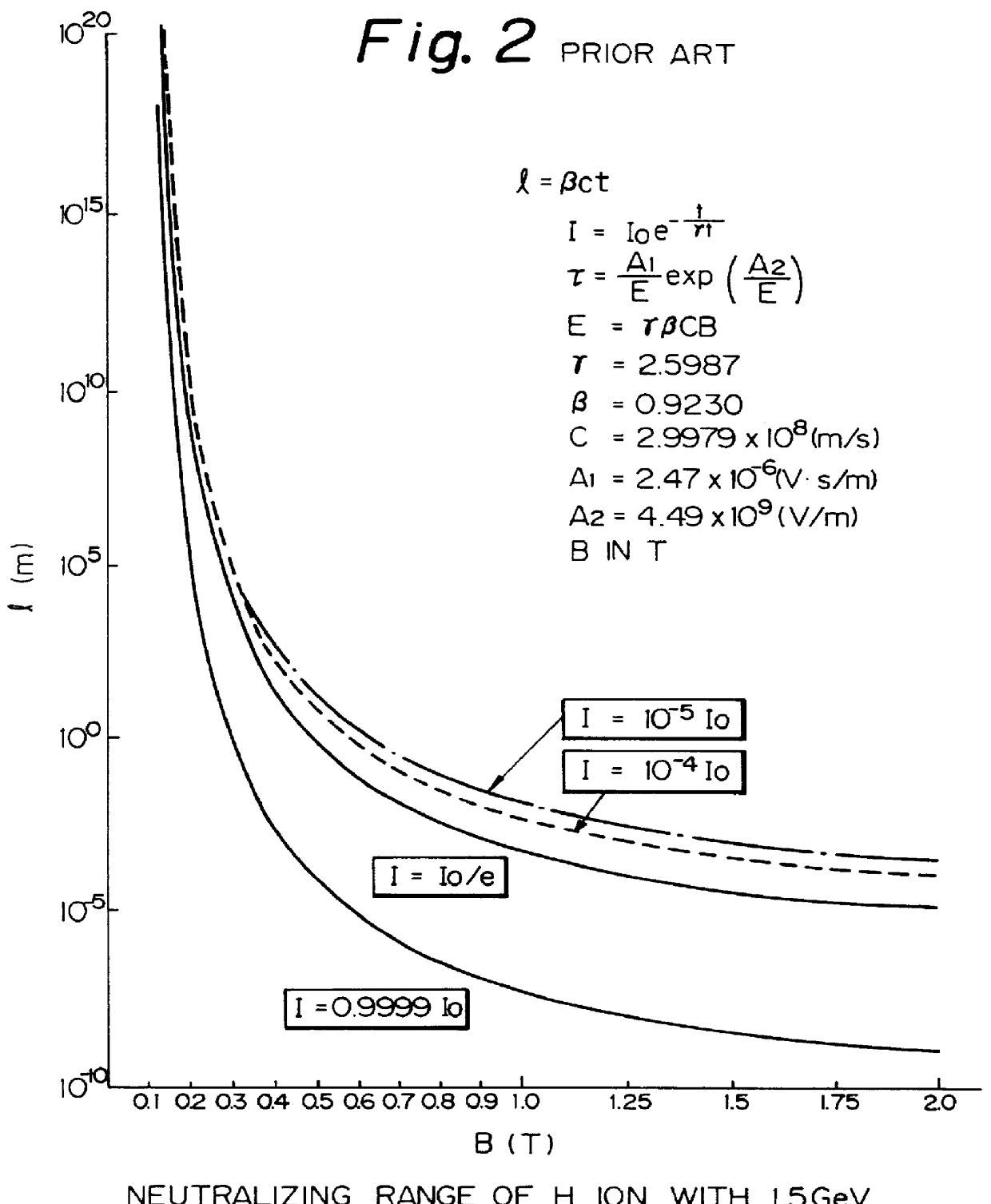
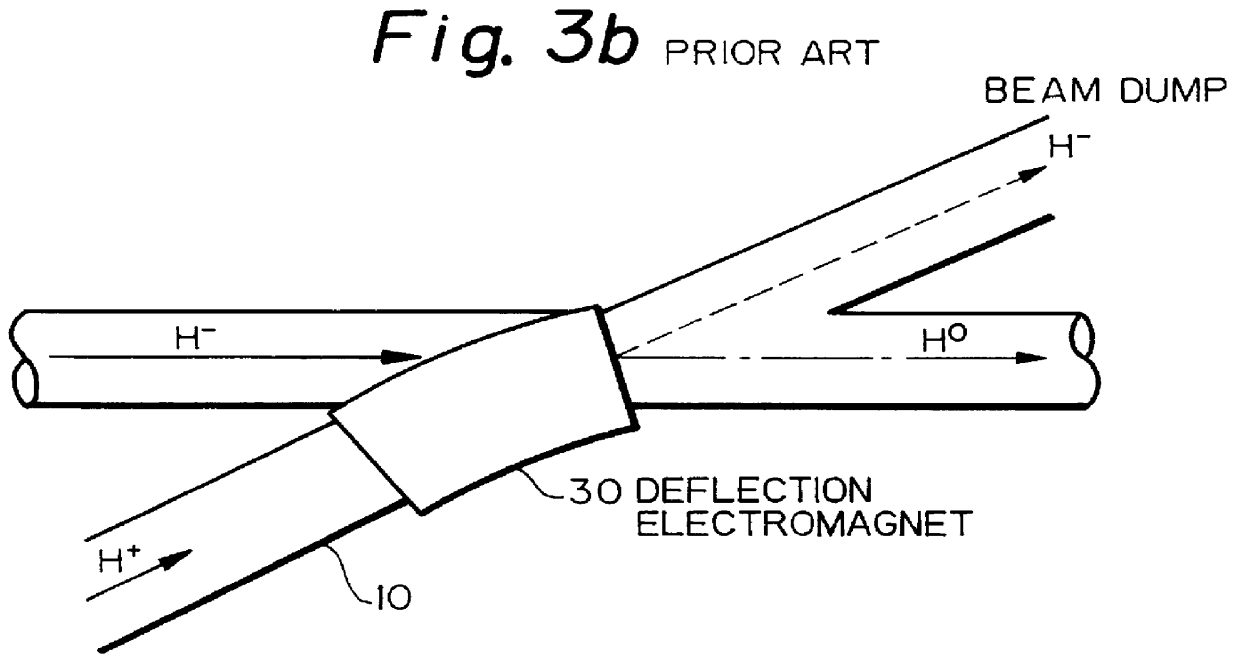
InactiveUS6137246AReduce loadReduced the adverse affectParticle separator tubesConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsRelativistic Doppler effectLaser beams
A charge-exchange device is disclosed which is able to considerably reduce, without the use of foils, radio activation caused by a beam deflection angle and, which also implements a further efficiency and reduction of a laser output. The charge-exchange device is provided with an undulator and an optical resonator. The undulator magnetic field which has been generated by the undulator generates the Lorentz electric field by interaction with the relativistic velocity of H0 neutral beam being injected. The optical resonator amplifies the photon density of the laser beam and causes it to collide against the injected H0 neutral beam, thereby resonantly exciting the H0 beam to the principal quantum number of 4. The H0 beam which has been resonantly excited or excited by the relativistic Doppler effect in the undulator magnetic field is ionized to H+ ion by the Lorentz electric field.
Owner:JAPAN ATOM ENERGY RES INST
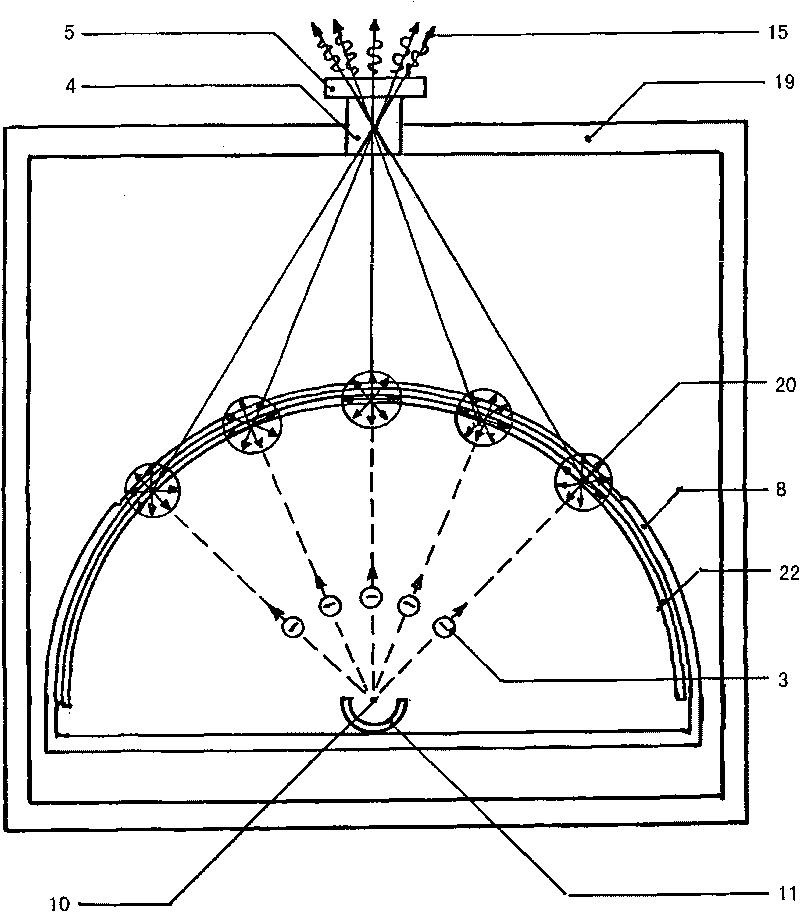
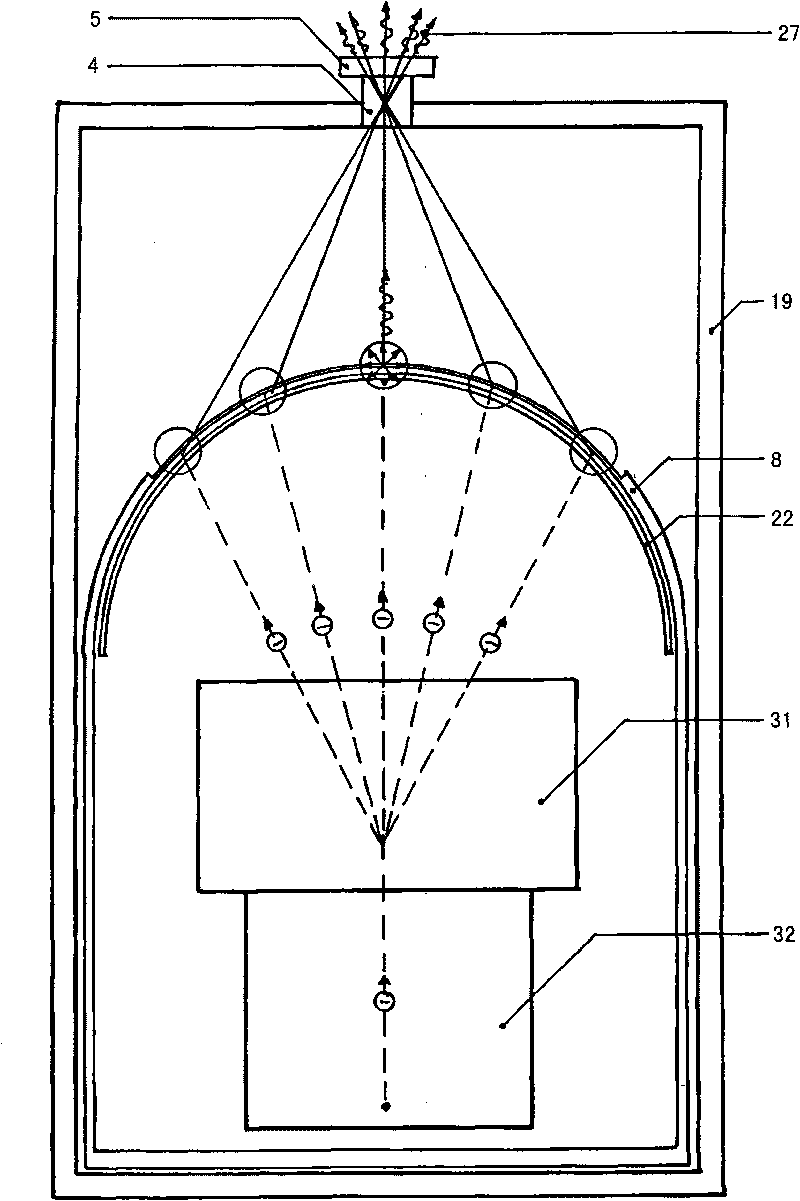
Arrangement for generation of x-ray radiation having a large real focus and a virtual focus adjusted according to requirements
An arrangement for generating X-ray radiation comprising an anode (9) formed as a part of a sphere. The arrangement further comprises at least one virtual focus element (4) which is adapted to emit generated photons to create the useful beam field. An arrangement according to the invention has a real focus which is larger than the previously known X-ray tubes and arrangements for generating X-ray with an inclined anode surface. Accordingly, an increased radiation amount per unit of time compared to previously known X-ray tubes is achieved by the arrangement according to the invention, provided that the acceleration voltage and the electron density for each anode surface unit are equal for both arrangements. The virtual focus element (4) can be adapted to a specific field of application. Time-and geometry-related imaging errors maybe avoided due to the high photon density and a focus which can be adapted to the requirements. When generating useful radiation using the arrangement according to the present invention, the photons are equally distributed in respect of mass and energy in the beam field, which makes it possible to achieve equivalent imaging conditions in the entire useful beam field.
Owner:L·蓝托
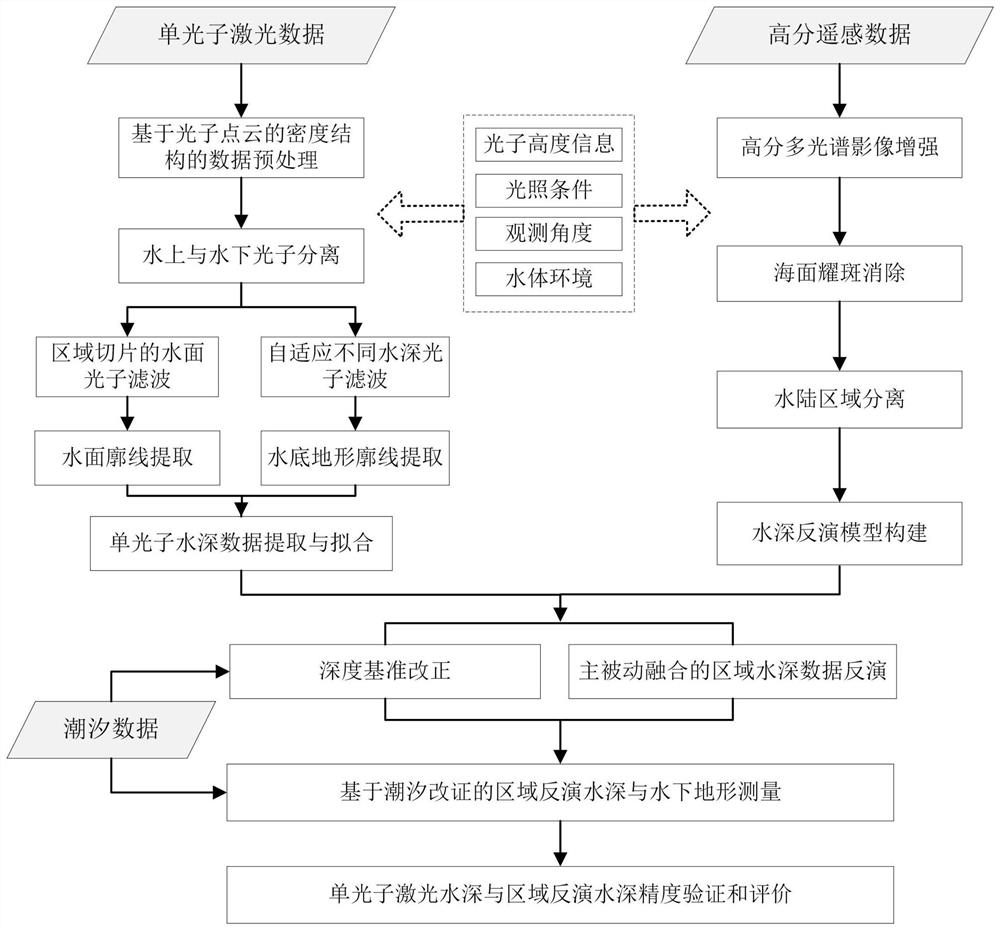
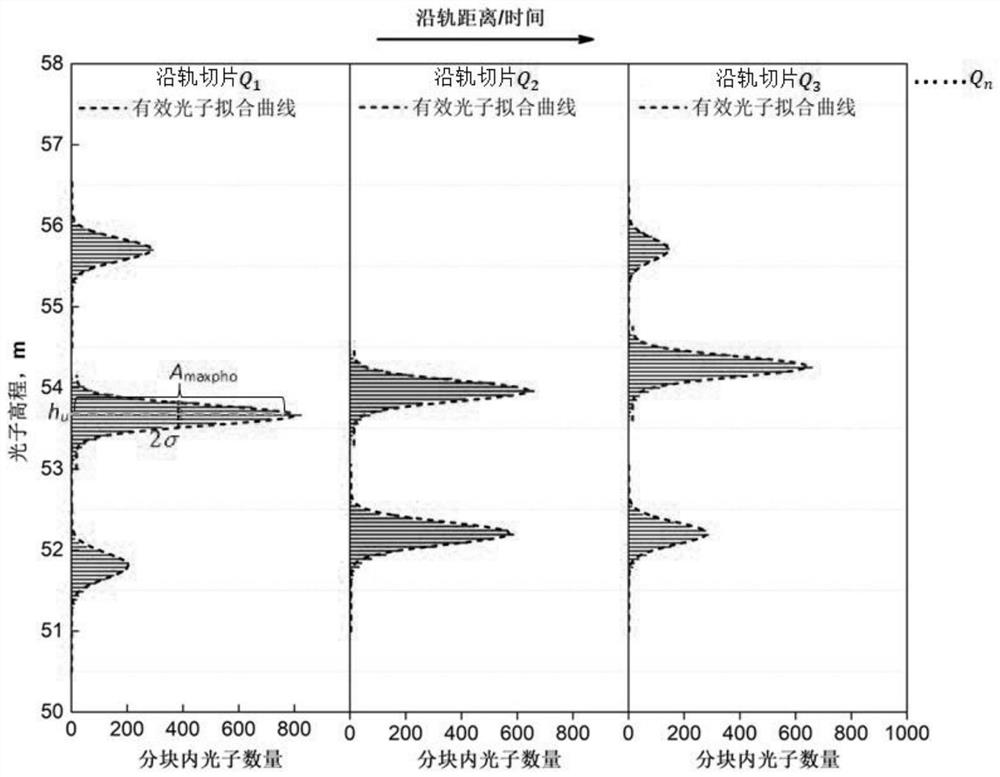
Method for measuring shallow sea water depth based on satellite-borne single-photon laser radar data
PendingCN114355367AImplement extractionAdapt to the conditionsElectromagnetic wave reradiationSensing dataSea waves
A method for measuring shallow sea water depth based on satellite-borne single-photon laser radar data comprises the following steps: firstly, analyzing photon signal and noise elevation characteristics of a satellite-borne single-photon laser radar in a shallow sea area in different environments, and constructing an initial filtering model of a photon point cloud; analyzing the spatial density distribution of the photon point clouds in different environments based on the initial filtering result, constructing a water surface and underwater photon point cloud separation model, and realizing the extraction of water surface effective photon signals and sea wave profiles; according to the spatial density distribution characteristics of underwater photon point clouds in different environments at different water depths, a self-adaptive photon density filtering model changing along with the water depth and a water depth extraction method are constructed, and the water depth measurement capability and precision of the satellite-borne single-photon laser radar are analyzed; finally, based on the relation between the water depth detection result of the satellite-borne single-photon laser radar and the remote sensing reflectivity spectrum, active-passive fusion high-precision regionalized shallow sea water depth inversion is carried out through satellite-borne multi-source remote sensing data, and domestic and overseas high-precision shallow sea water depth data extraction is achieved.
Owner:中国人民解放军61540部队
Single photon-counting imaging system and method thereof
InactiveUS8723130B2Avoid saturationKeep for a long timeSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDigital micro mirror deviceControl system
Owner:CENT FOR SPACE SCI & APPLIED RES
Apparatus and method for multiwavelength photodynamic therapy
ActiveUS20170043179A1Improve absorbed photon density gradientHigh gradientPhotodynamic therapySurgical instrument detailsPhotodynamic therapyMedicine
A method for treating a condition in a tissue, includes the steps: (1) providing a PS within the tissue; (2) irradiating the tissue containing the PS with a first light of a first wavelength; and (3) irradiating the tissue containing the PS with a second light of a second wavelength so as to treat the condition in the tissue, wherein: (a) the PS absorbs light at the first wavelength and the second wavelength; and (b) the second light is more strongly absorbed by the tissue than the first light or vice versa, so as to achieve a predetermined absorbed photon density gradient. An apparatus for conducting the method includes first and second light sources, a power supply, a focusing device, and a controller which adjusts light emission such that I(d)=I(λ1 at d=0)×exp (μeff (λ1)×d)+I(λ2 at d=0)×exp (μeff(λ2)χd).
Owner:THERALASE TECH
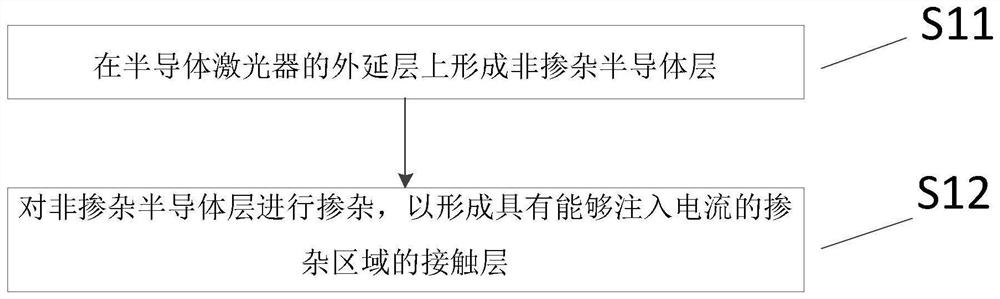
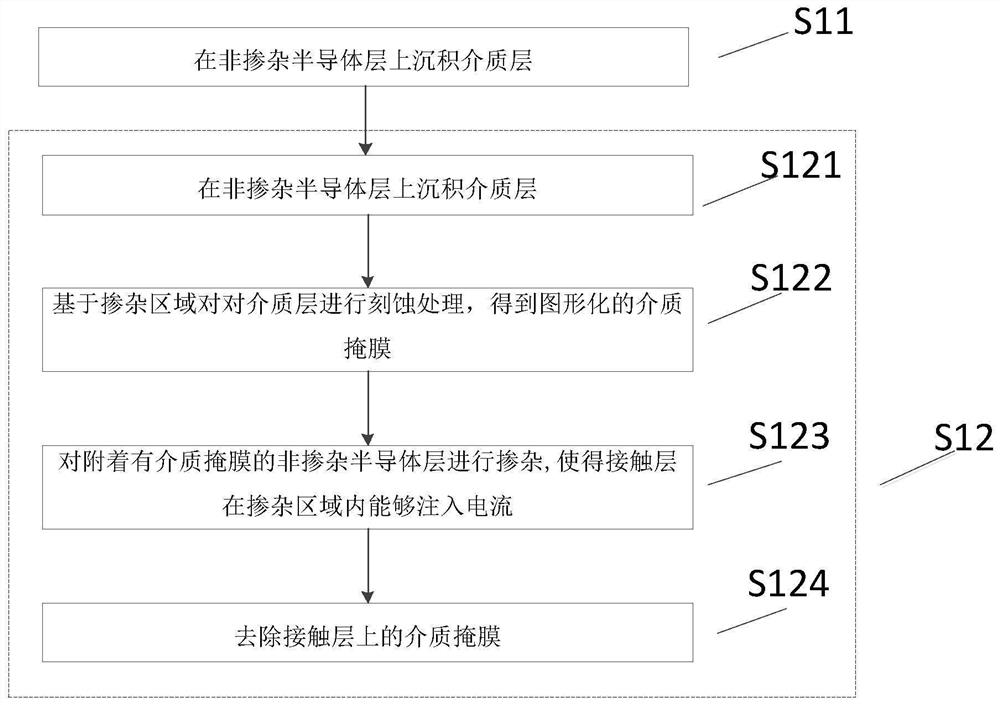
Manufacturing method of contact layer, semiconductor laser and manufacturing method of semiconductor laser
ActiveCN111682400AIncrease output powerImprove output stabilityLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersResonant cavityThin film electrode
The invention provides a manufacturing method of a contact layer, a semiconductor laser and a manufacturing method of the semiconductor laser, and the manufacturing method of the contact layer comprises the following steps: firstly, forming a non-doped semiconductor layer on an epitaxial layer of the semiconductor laser, and then doping the non-doped semiconductor layer. The contact layer manufactured by adopting the manufacturing method comprises a doped region and a non-doped region, the current cannot be injected into the non-doped region; only the doped region can be injected with current;the area of injected current in the doped region is gradually increased along the length direction of the cavity; therefore, influence of uneven distribution of carrier density and gain along the direction from a reflection enhanced film to an antireflection film due to uneven distribution of photon density in the resonant cavity is counteracted, carriers are evenly distributed in the cavity length direction, and the output power and performance stability of the semiconductor laser are improved. An electrode of the semiconductor laser is directly manufactured on the contact layer, no dielectric film is arranged between the electrode and the contact layer, and the electrode and the contact layer are firmly adhered and are not easy to fall off.
Owner:SUZHOU EVERBRIGHT PHOTONICS CO LTD +1
Quantum dots with reduced saturation quenching
ActiveUS10050184B2Convenient distanceEasy to adjustNanoopticsLight demodulationQuantum efficiencyPhotonic crystal structure
The invention provides a lighting device comprising (a) a light converter comprising a light receiving face; and (b) a solid state light source configured to generate a light source light with a photon flux of at least 10 W / cm2 at the light receiving face, wherein the light converter is configured to convert at least part of the light source light into light converter light having a first frequency, wherein the light converter comprises a semiconductor quantum dot in an optical structure selected from a photonic crystal structure and a plasmonic structure, wherein the optical structure is configured to increase the photon density of states in the light converter resonant with the first frequency for reducing saturation quenching, and wherein the quantum dot has a quantum efficiency of at least 80%.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Methods and apparatus for transmission of low photon density optical signals
ActiveUS11258516B2Diminishing detectabilityHigh sensitivityLine-of-sight transmissionPhotonic quantum communicationContinuous lightComputational physics
An optical transmitter and a method of producing a low-photon-density modulated optical signal are disclosed. The optical transmitter and method include an optical source configured to emit a continuous optical carrier waveform, a dilation module configured to apply a spreading code to a data payload to spread each of the plurality of symbols in time to expand the symbol duration by a dilation factor and produce a corresponding plurality of time-dilated symbols, the plurality of time-dilated symbols having a lower photon density than the plurality of symbols; a mapping module configured to map the plurality of time-dilated symbols to a modulation scheme; and a modulator configured to modulate the optical carrier waveform with the plurality of time-dilated symbols according to the modulation scheme to produce the low-photon-density modulated optical signal encoded with the plurality of time-dilated symbols corresponding to the data payload.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Non-invasive multi-frequency oxygenation spectroscopy device using nir diffuse photon density waves for measurement and pressure gauges for prediction of pressure ulcers
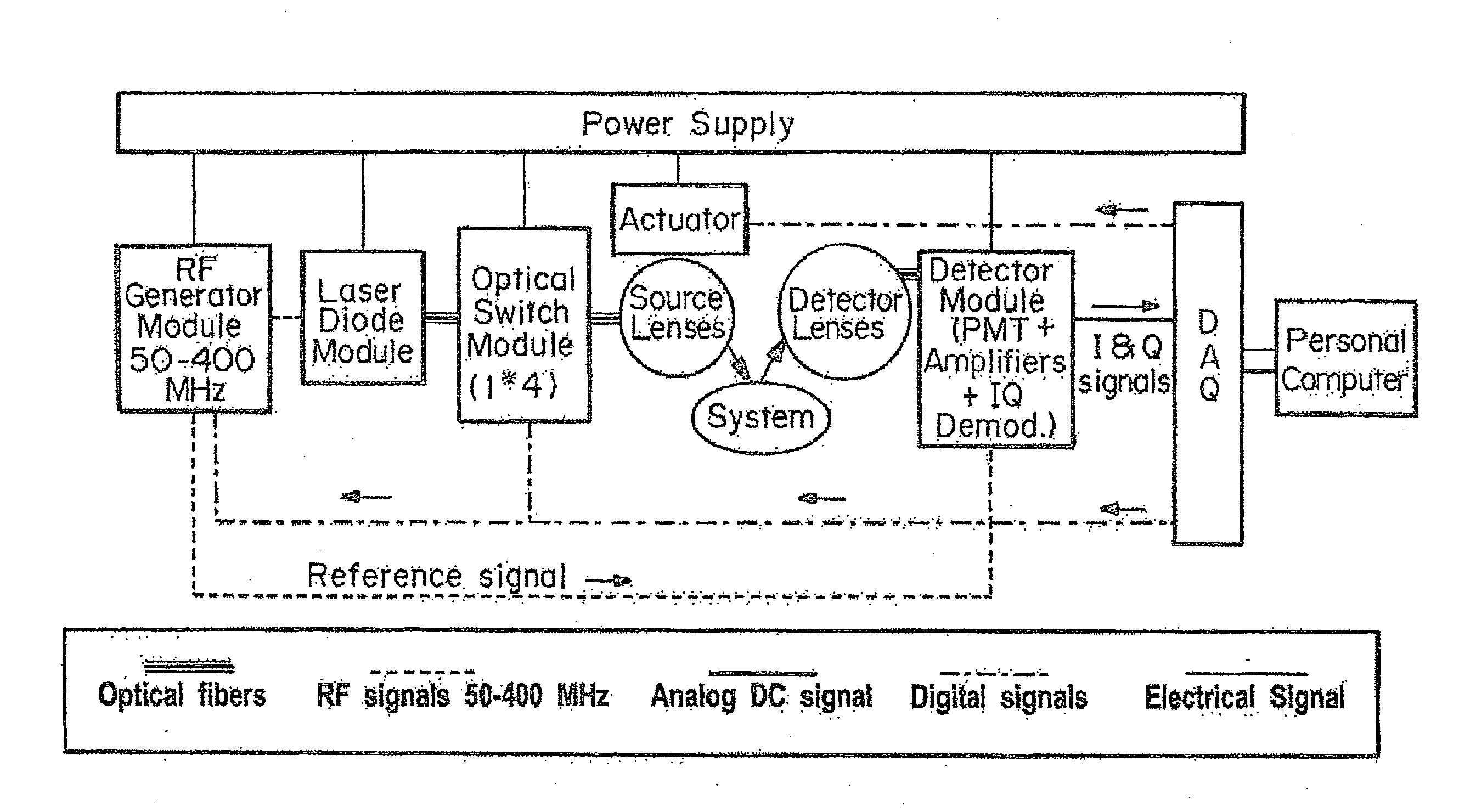
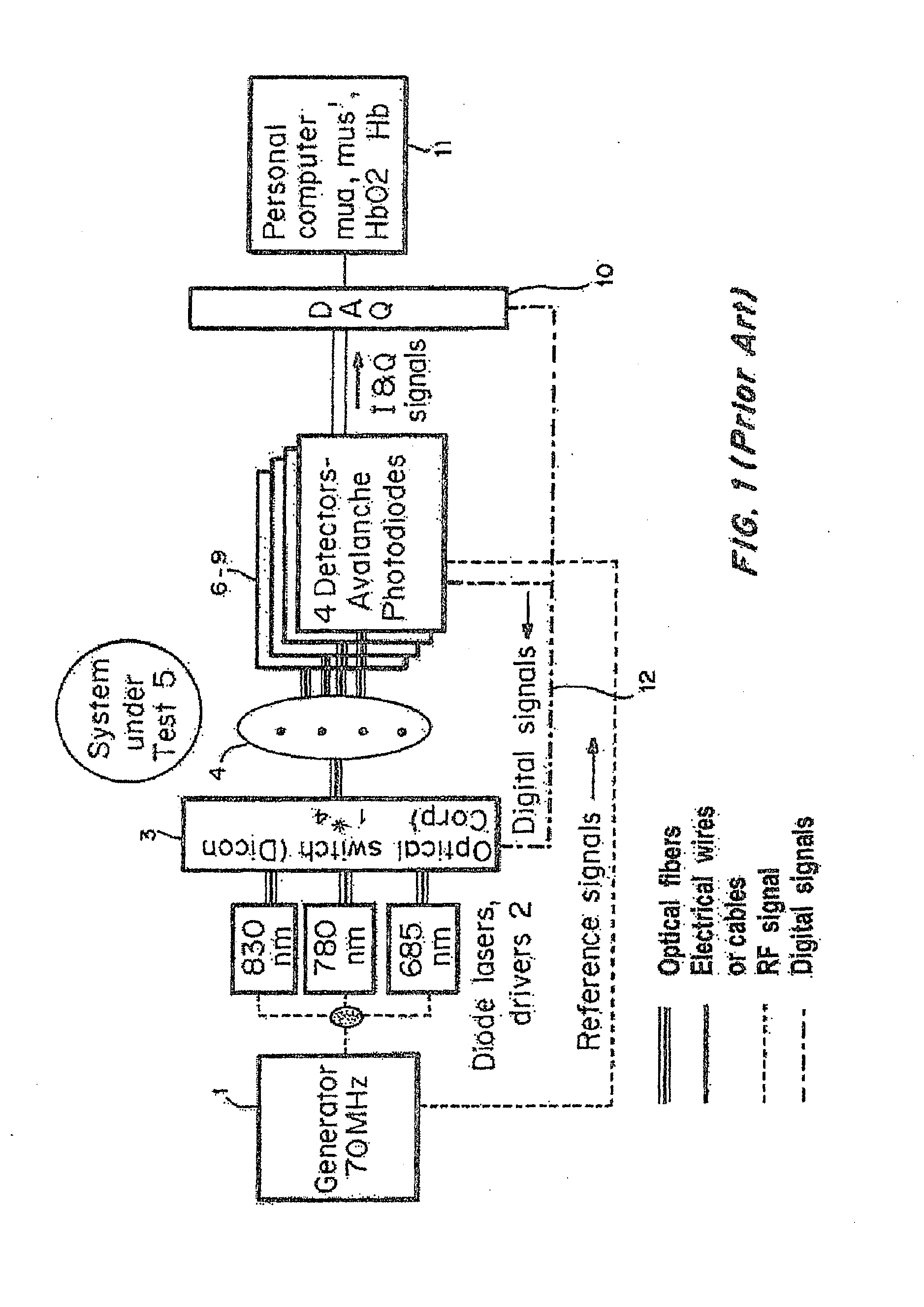
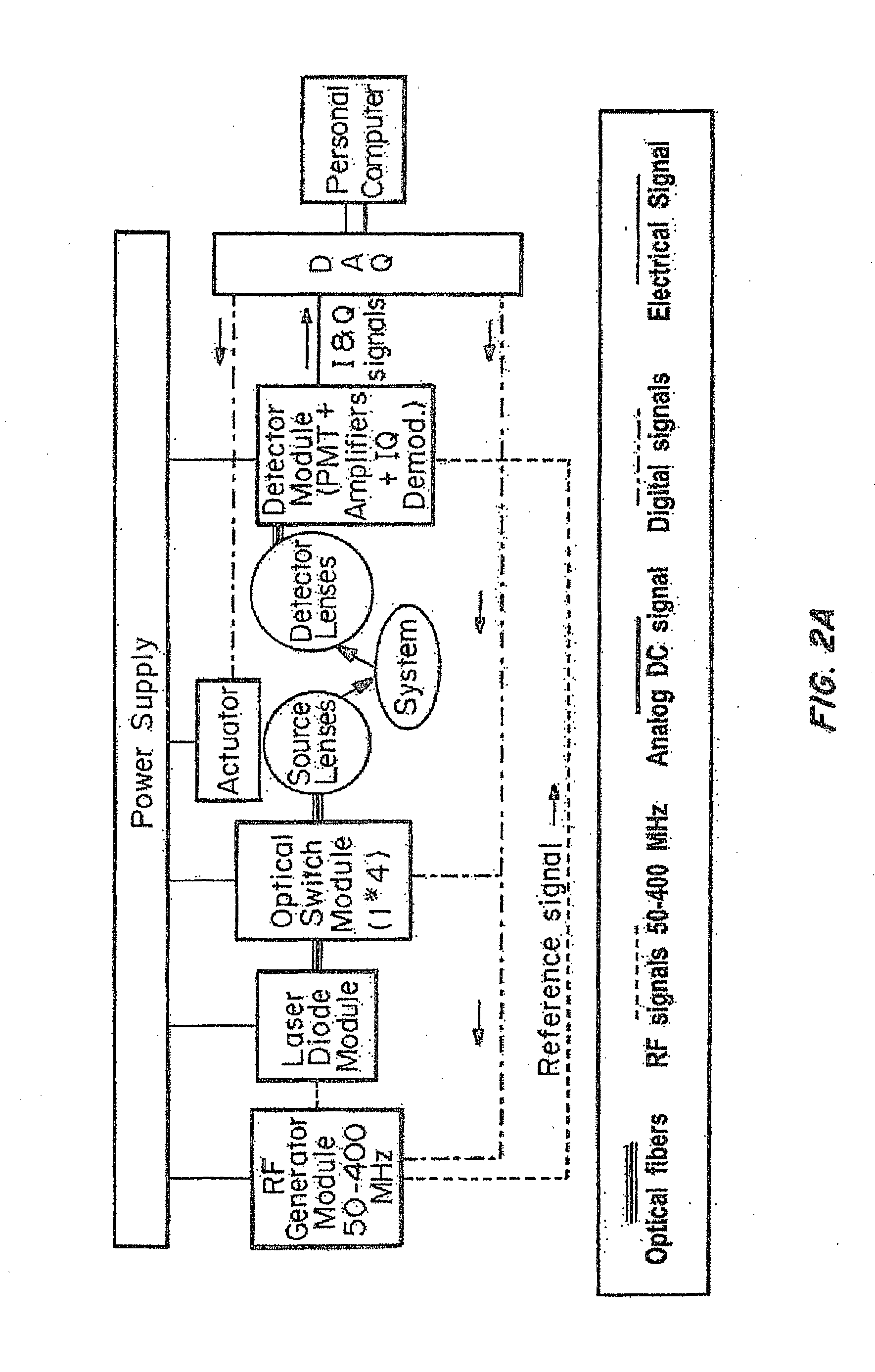
Multi-frequency Diffuse Photon Density Wave (DPDW) methodology at near infrared wavelengths is used to non-invasively measure the optical absorption and reduced scattering coefficients of tissue at depths of several millimeters to quantify the depth and degree of tissue damage. A digitally-controlled stepper motor and variable RF generator enable the user to select the distance between the light source and detector and the modulation frequency through software. This allows for the collection of virtually unlimited number of data points, enabling precise selection of the volume and depth of tissue that will be characterized.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Transistor laser electrical and optical bistable switching
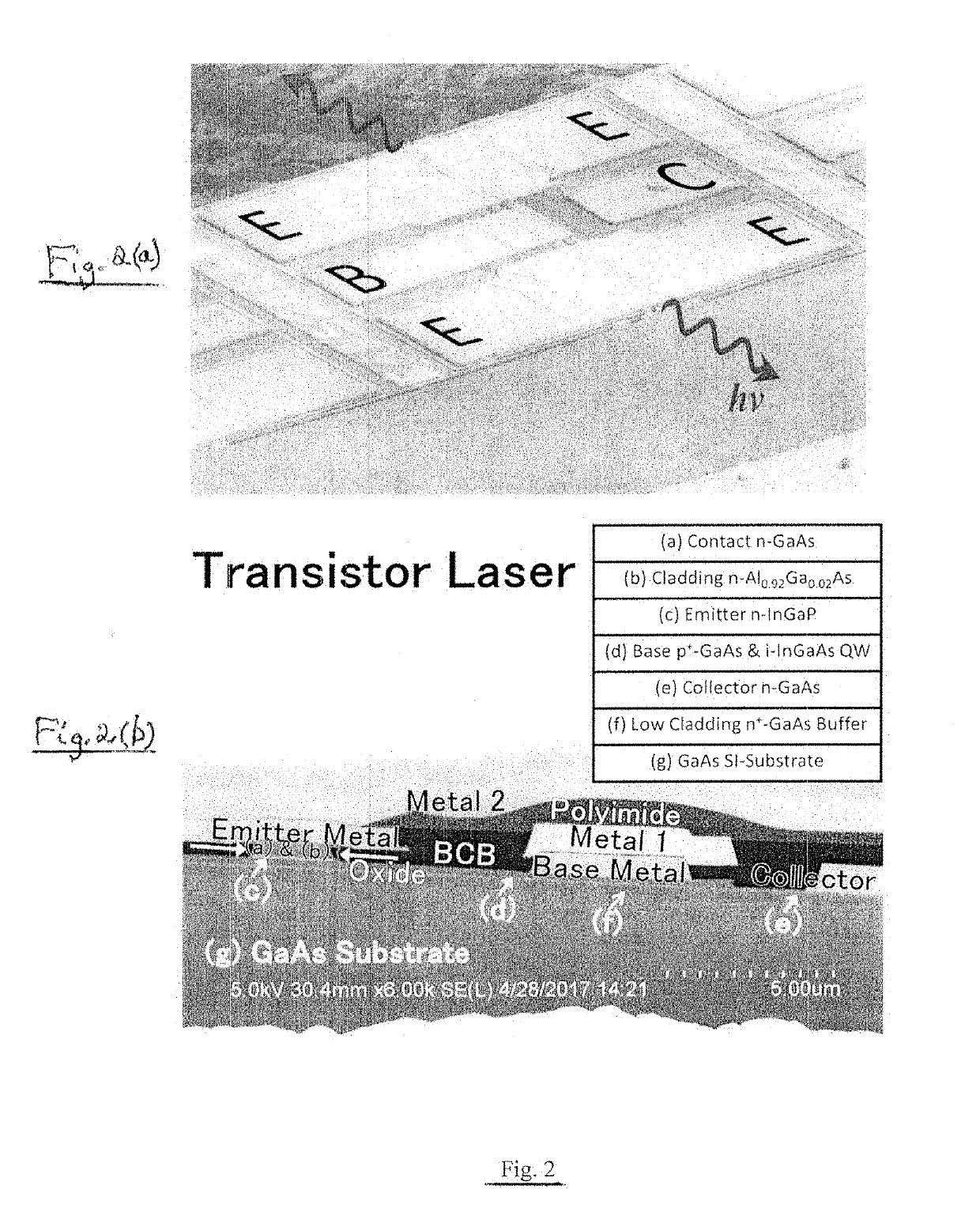
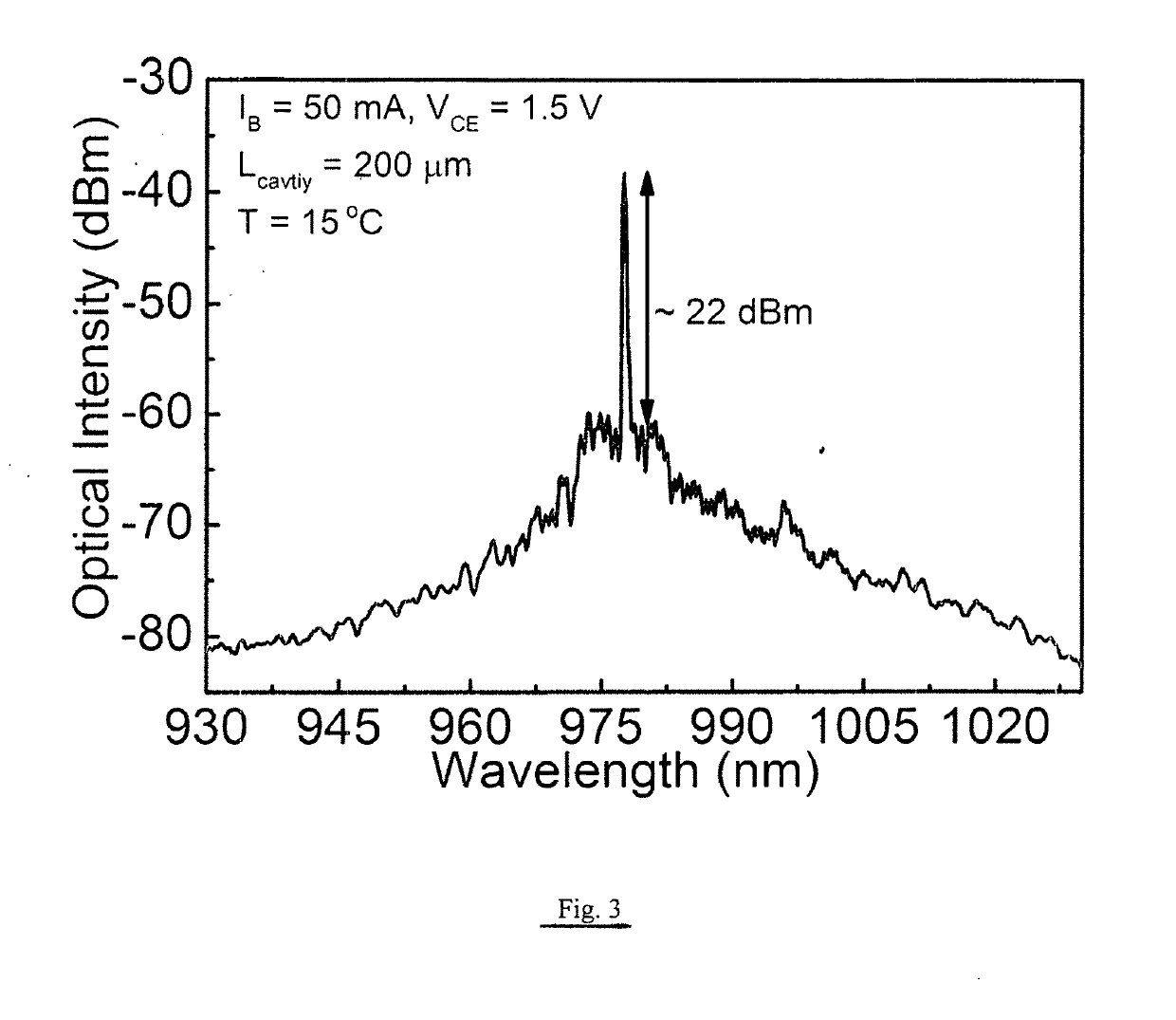
ActiveUS20190123513A1High speed computingReduce rateLaser detailsLaser active region structureElectricityResonant cavity
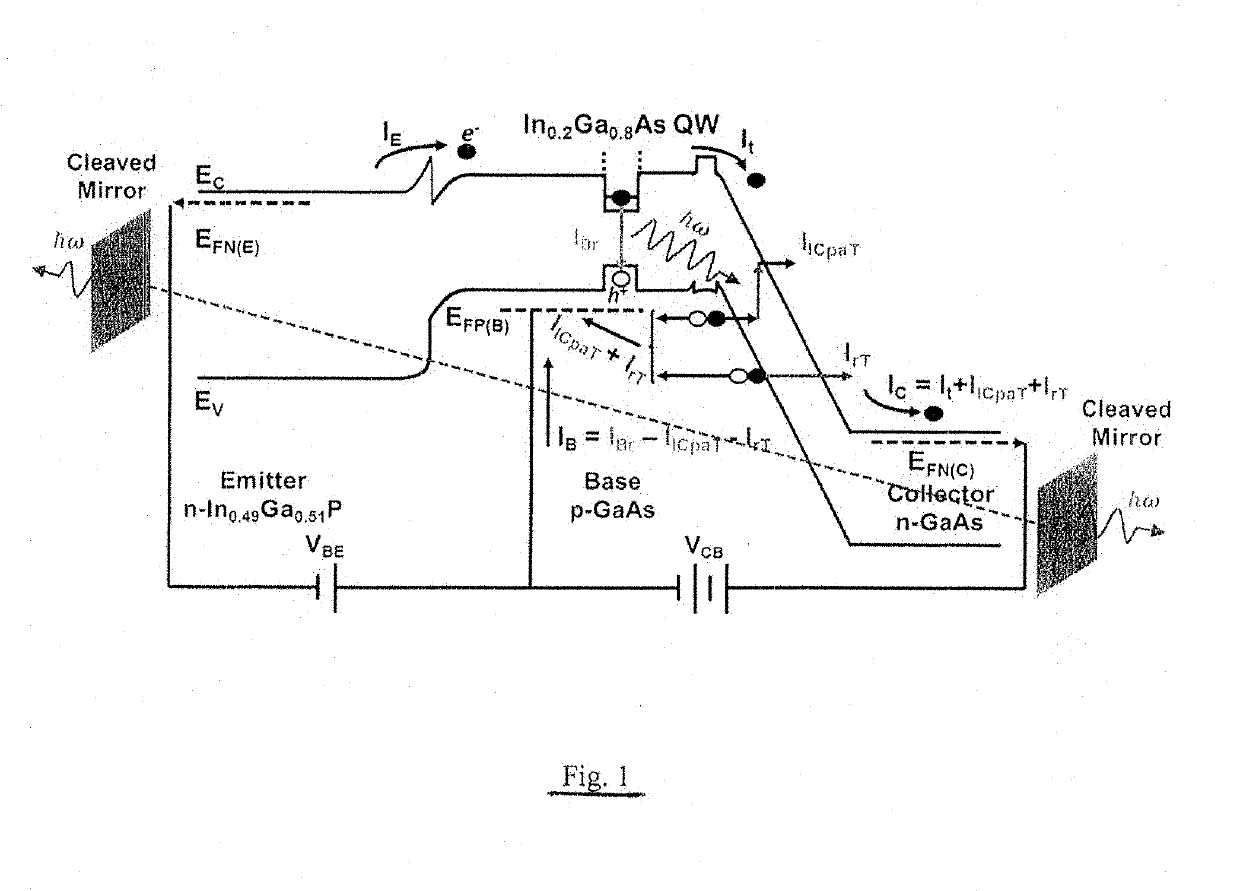
A method for electrical and optical bistable switching, including the following steps: providing a semiconductor device that includes a semiconductor base region of a first conductivity type between semiconductor collector and emitter regions of a second conductivity type, providing a quantum size region in the base region, and providing base, collector and emitter terminals respectively coupled with the base, collector, and emitter regions; providing input electrical signals with respect to the base, collector, and emitter terminals to obtain an electrical output signal and light emission from the base region; providing an optical resonant cavity that encloses at least a portion of the base region and the light emission therefrom, an optical output signal being obtained from a portion of the light in the optical resonant cavity; and modifying the input electrical signals to switch back and forth between a first state wherein the photon density in the cavity is below a predetermined threshold and the optical output is incoherent, and a second state wherein the photon density in the cavity is above the predetermined threshold and the optical output is coherent, said switching from the first to the second state being implemented by modifying the input electrical signals to reduce optical absorption by collector intra-cavity photon-assisted tunneling, and the switching from the second to the first state being implemented by modifying the input electrical signals to increase photon absorption by collector intra-cavity photon-assisted tunneling.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com