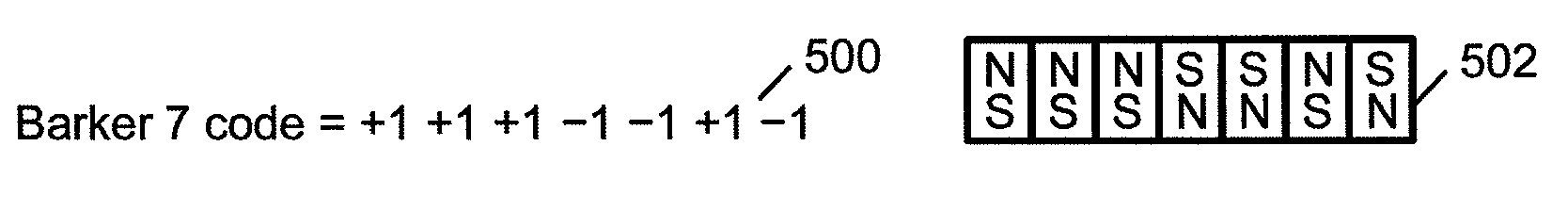Patents
Literature
229 results about "Force function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
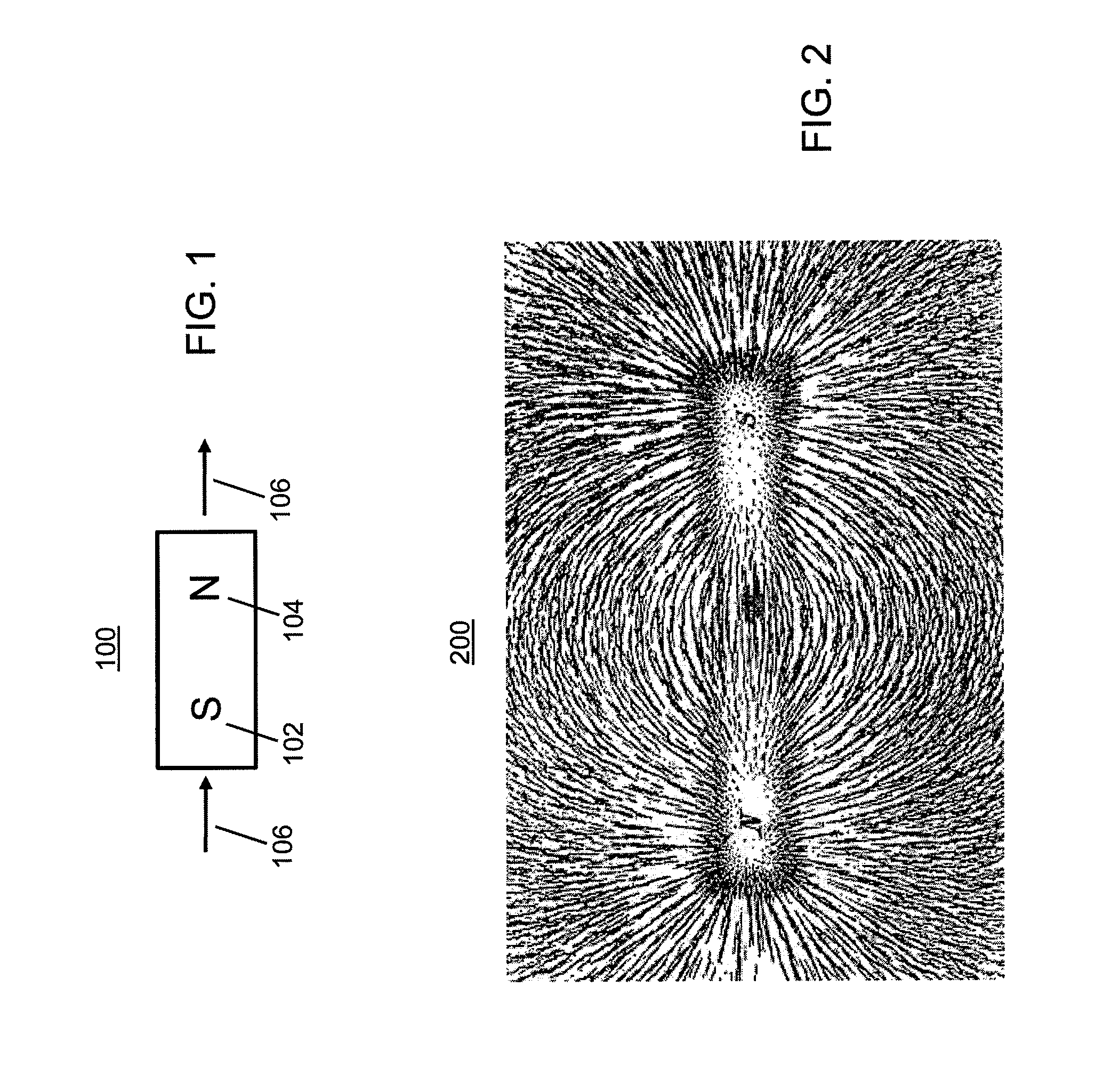
Forcing function. Forcing function can mean: In interaction design, a behavior-shaping constraint, a means of preventing undesirable user input usually made by mistake. A forcing function is any task, activity or event that forces you to take action and produce a result.
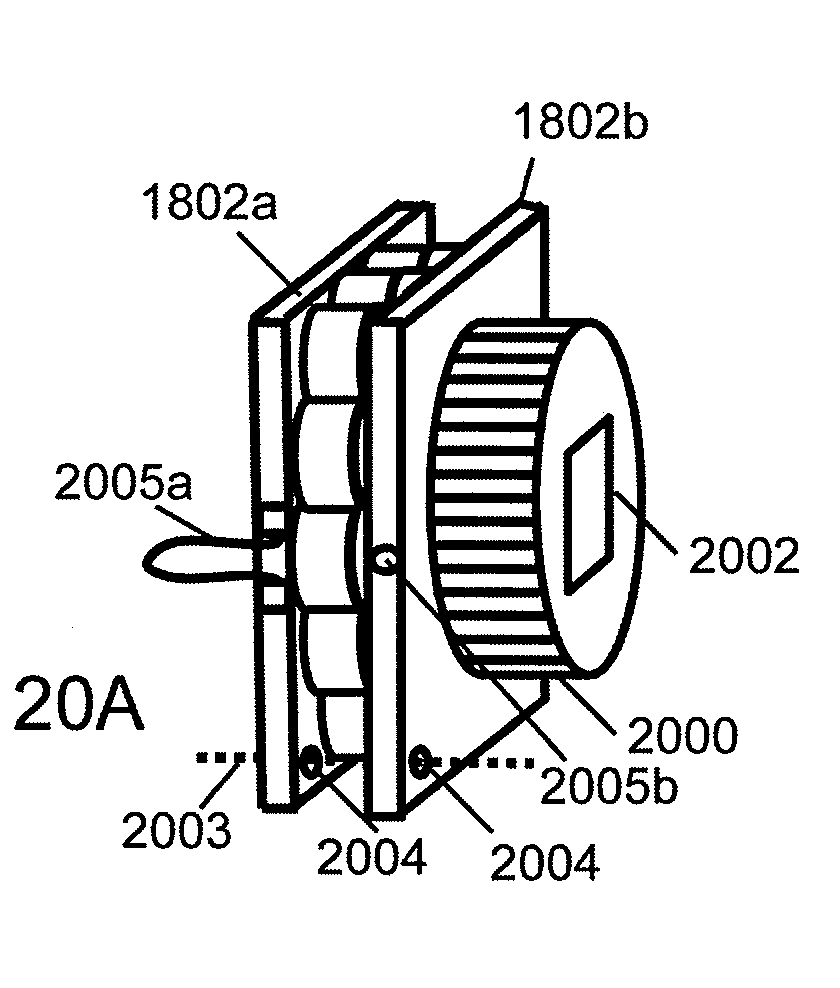
Field emission system and method
InactiveUS20090278642A1Electromagnets without armaturesPermanent magnetsElectric fieldAtomic physics
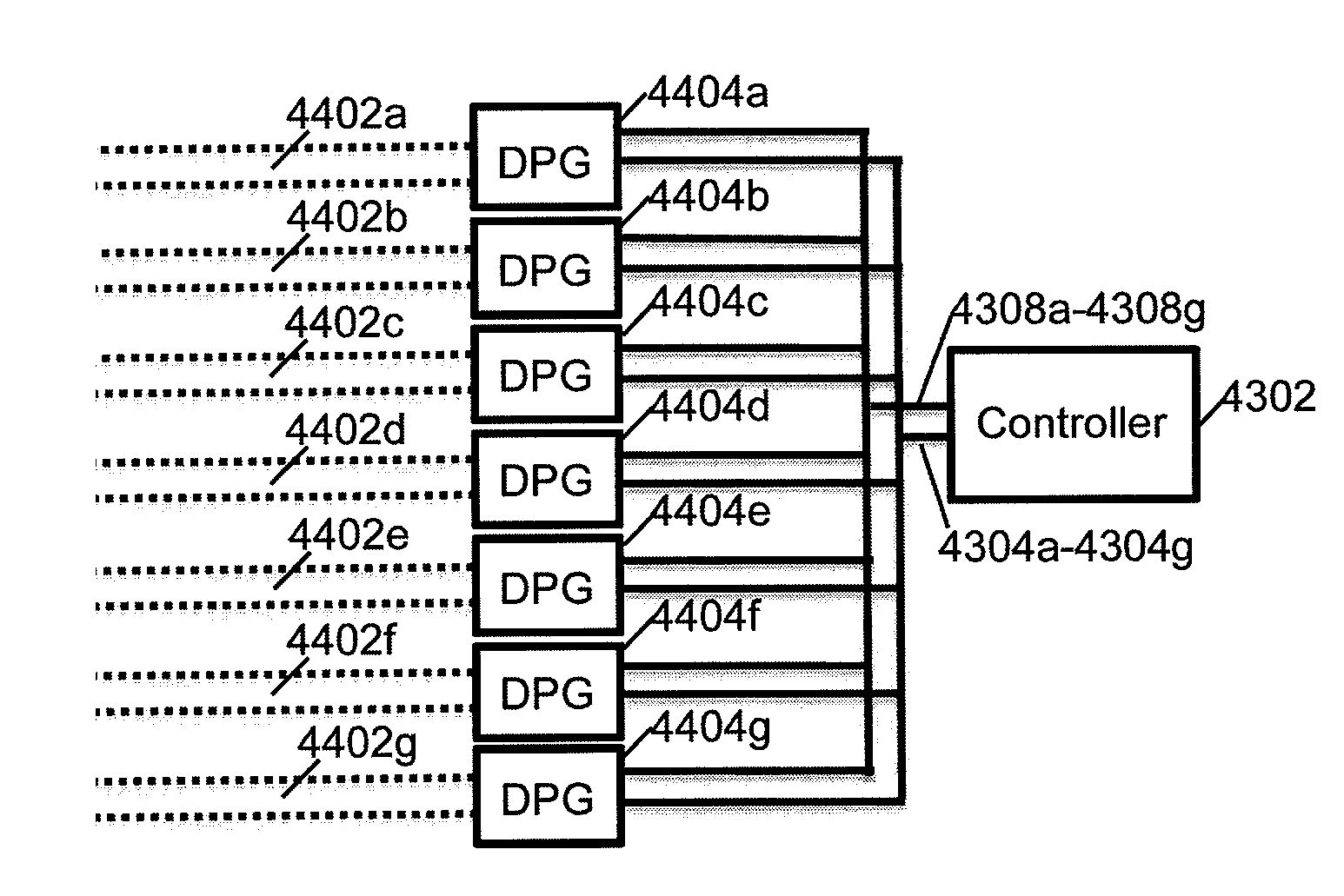
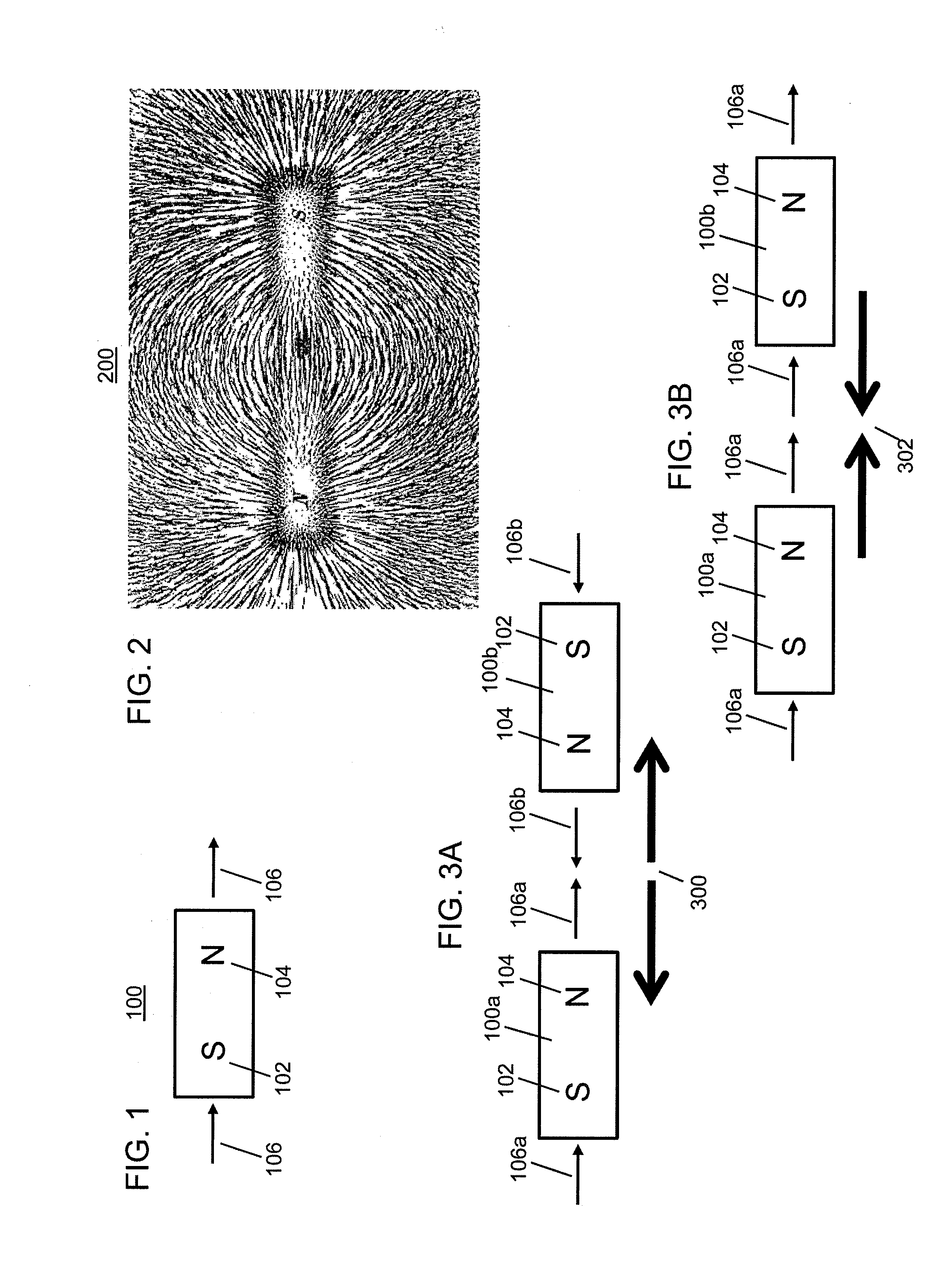
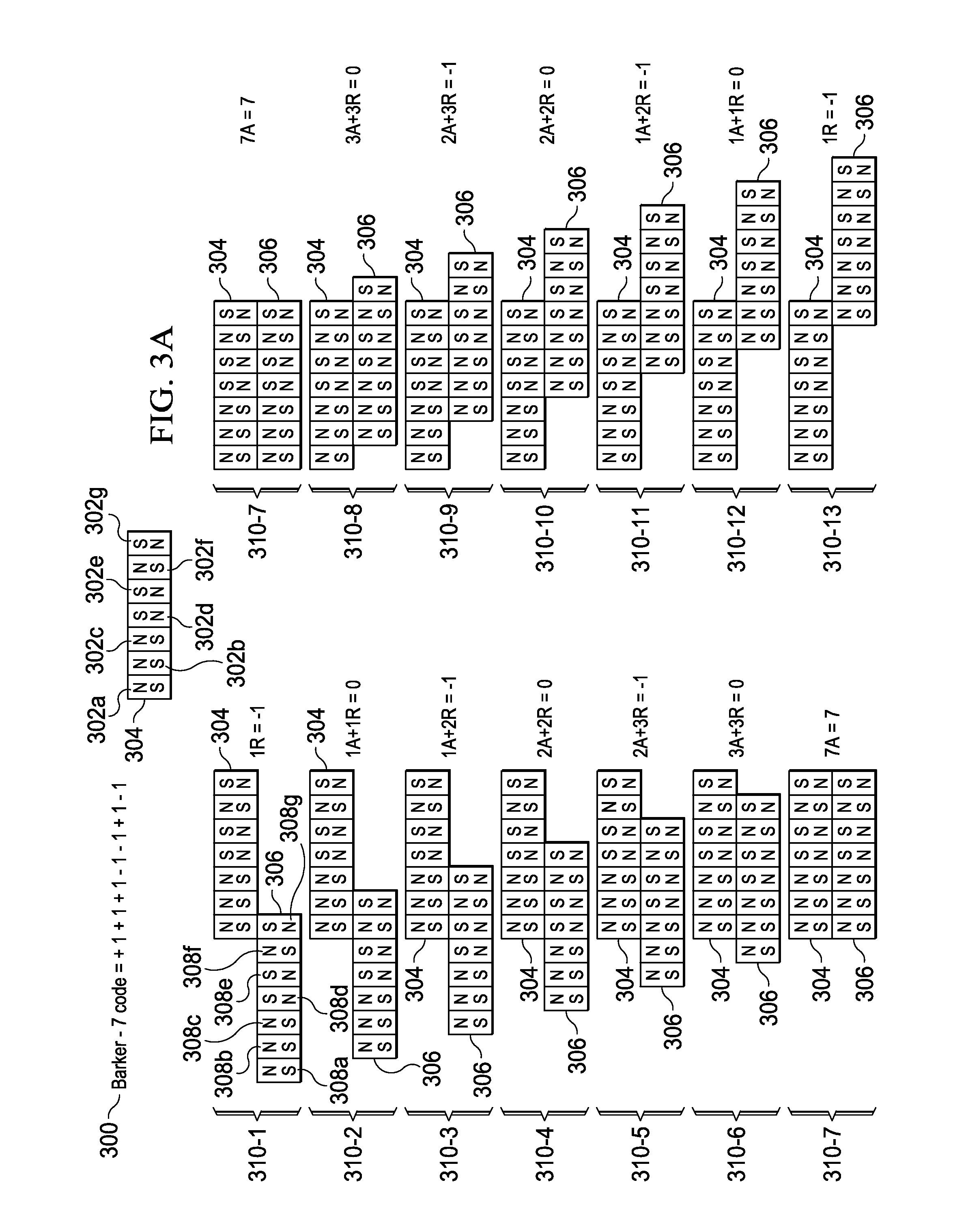
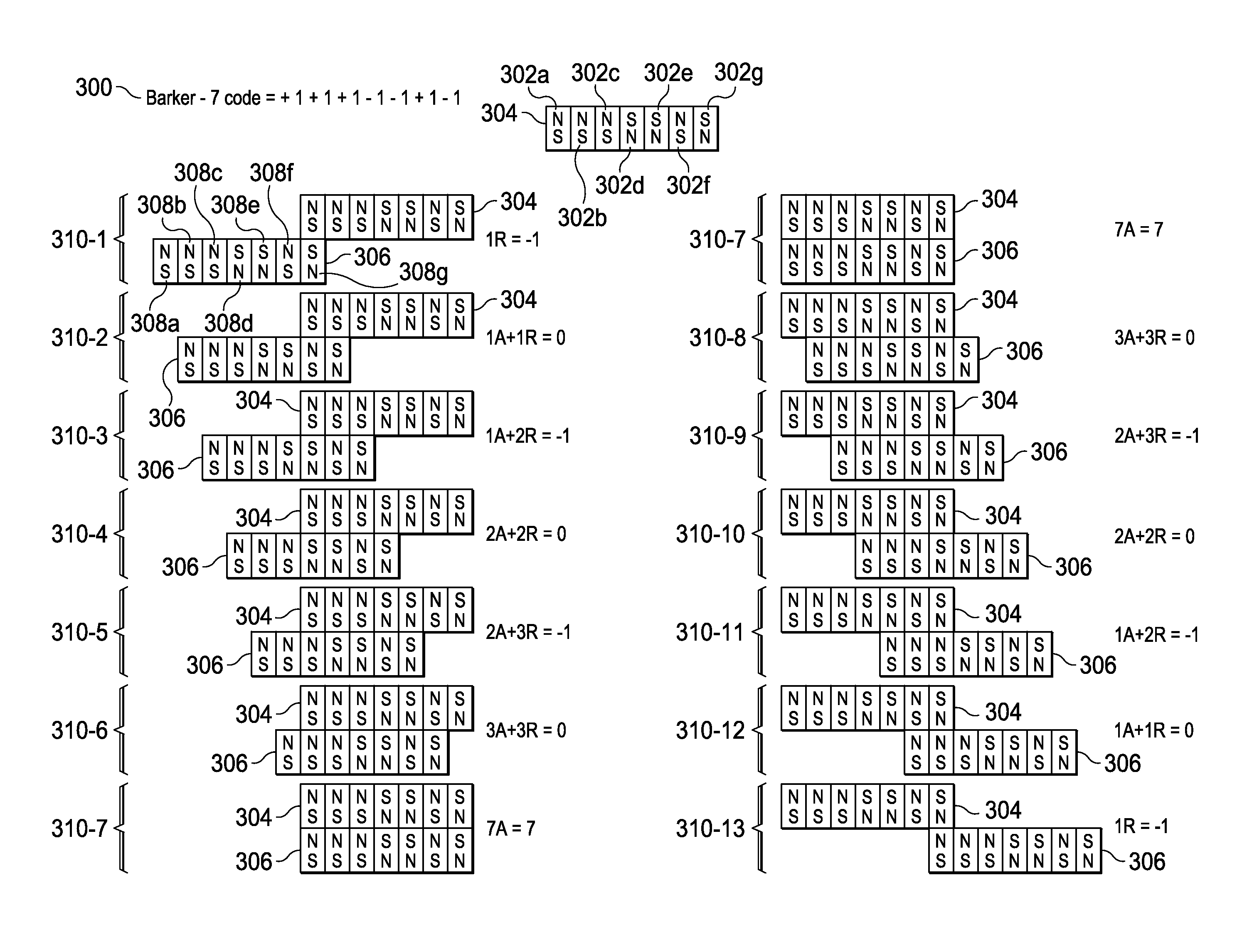
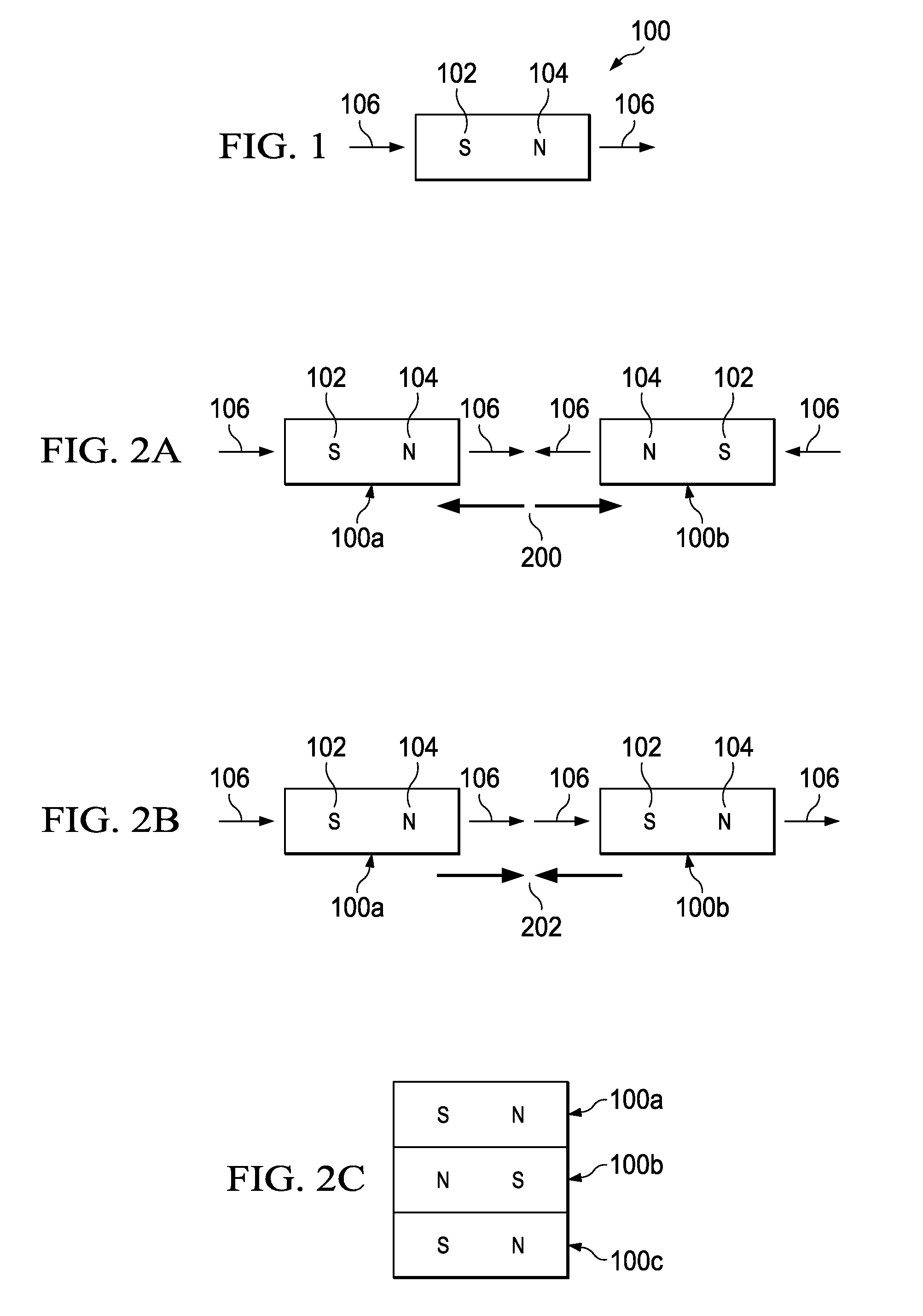
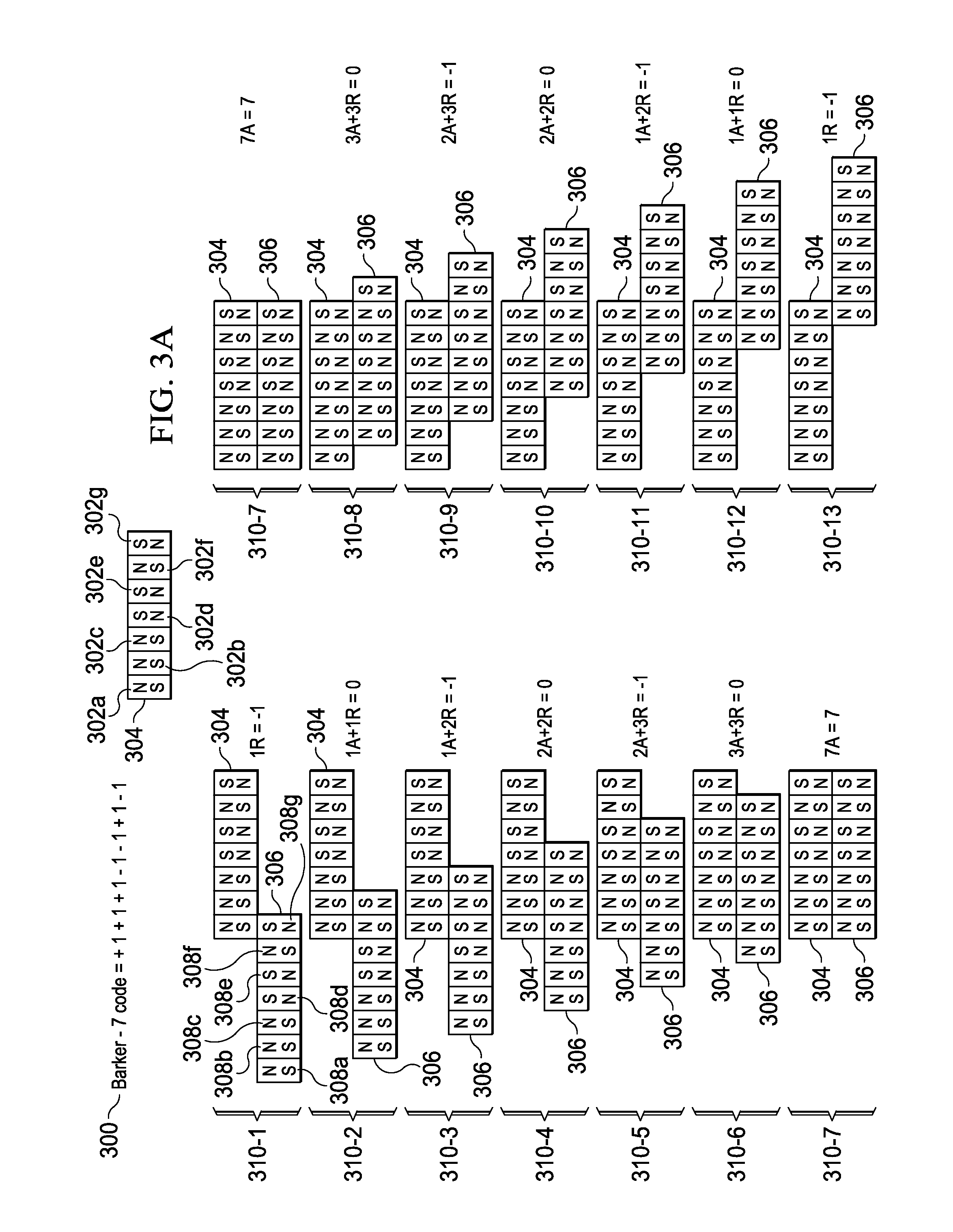
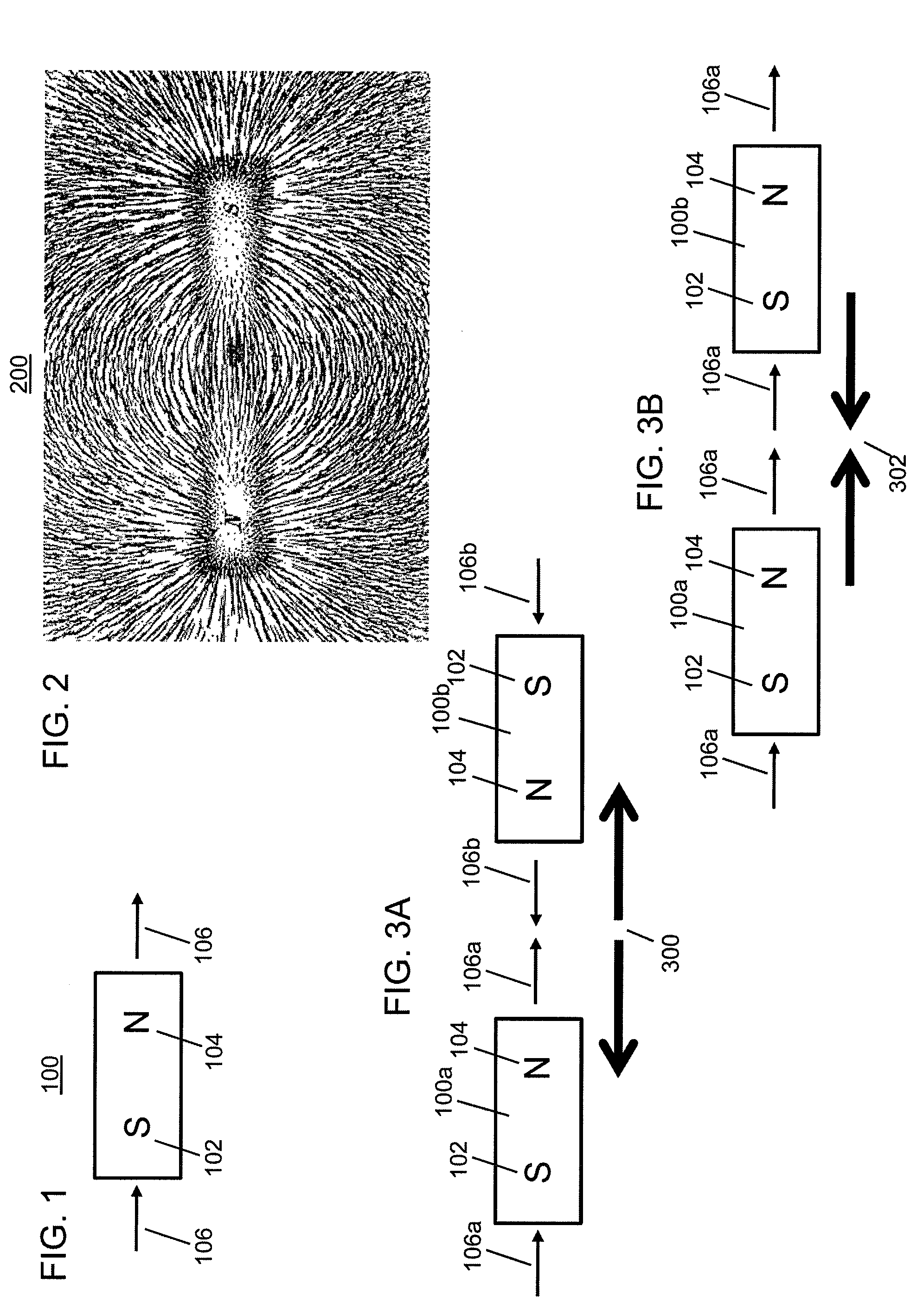
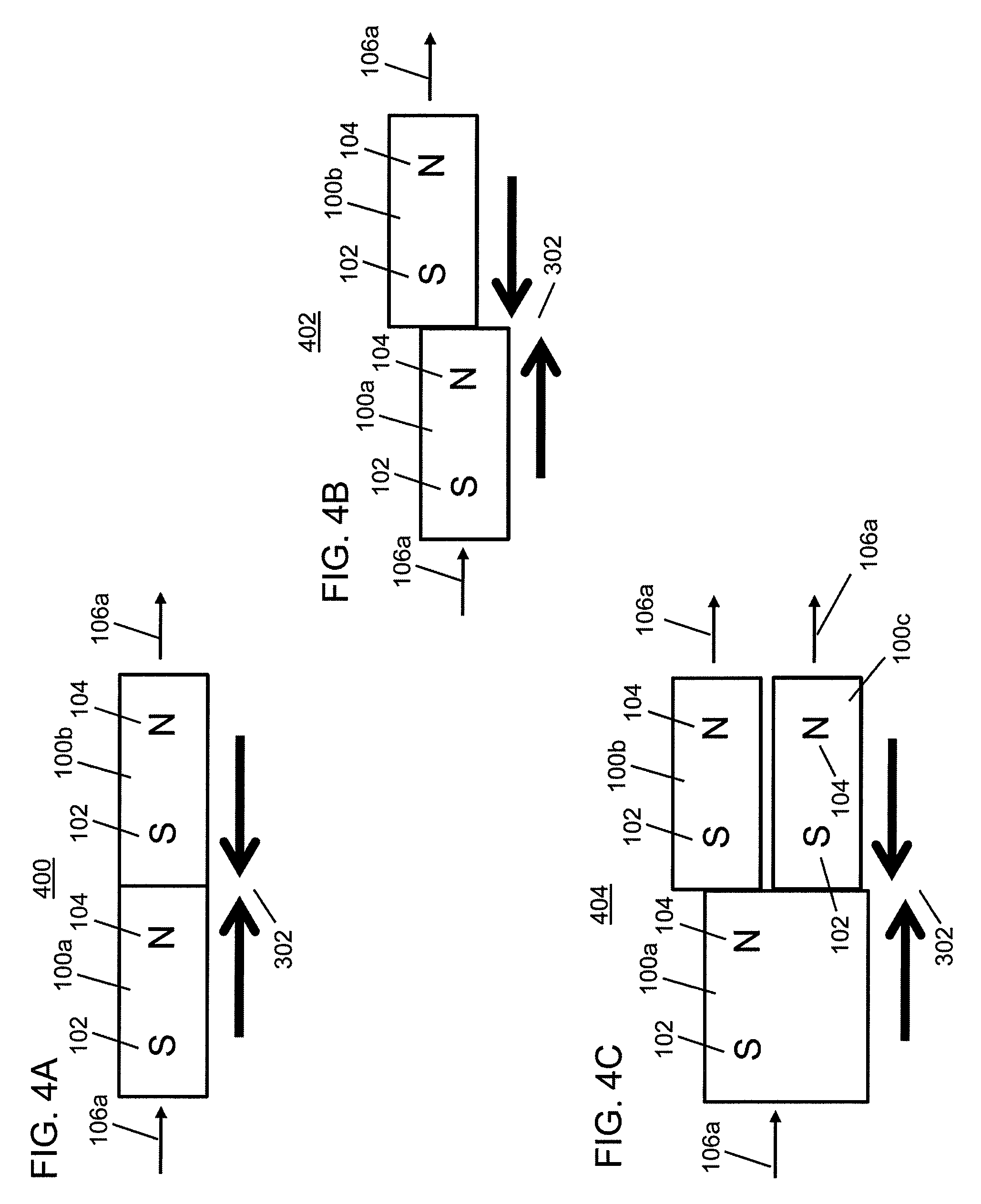
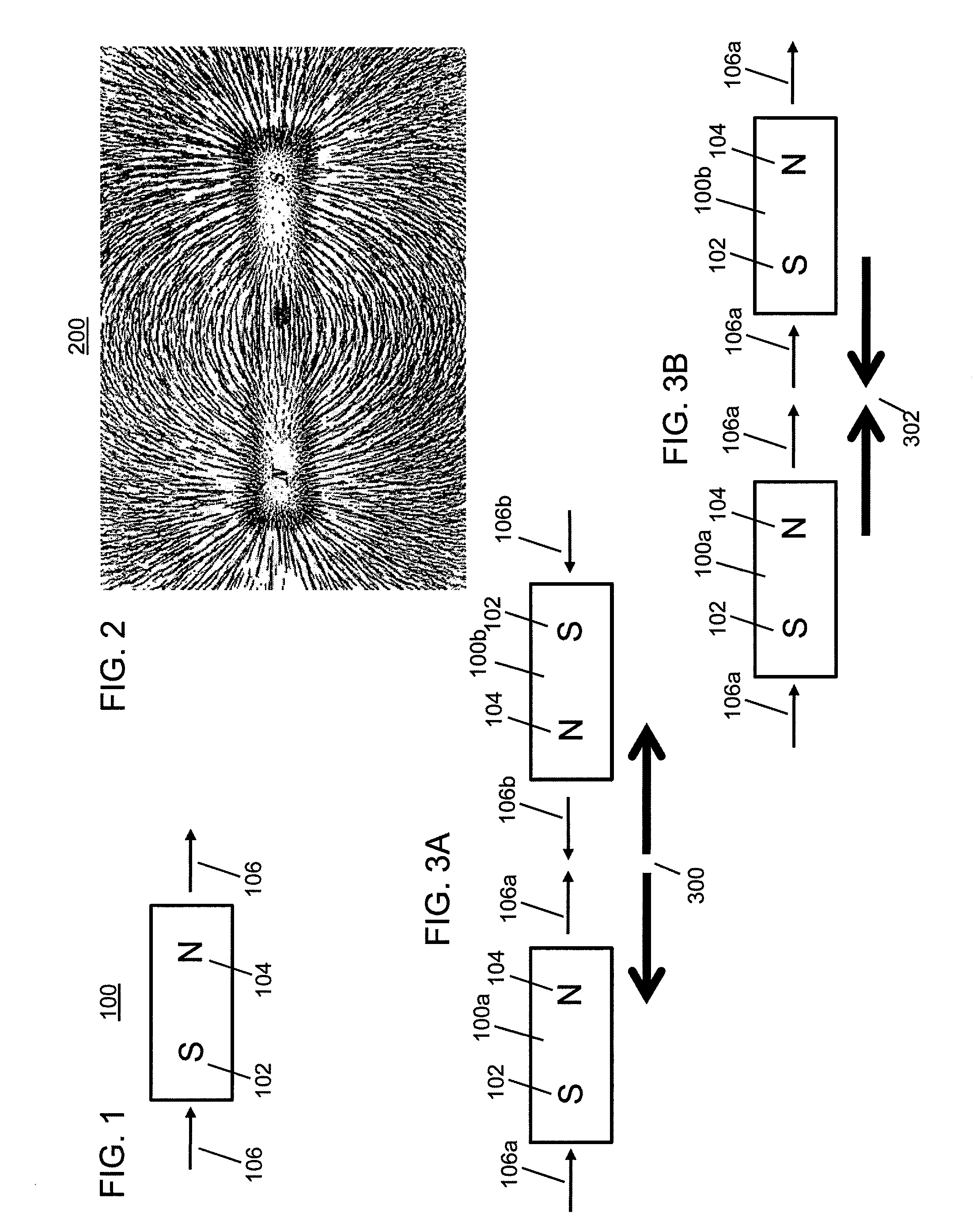
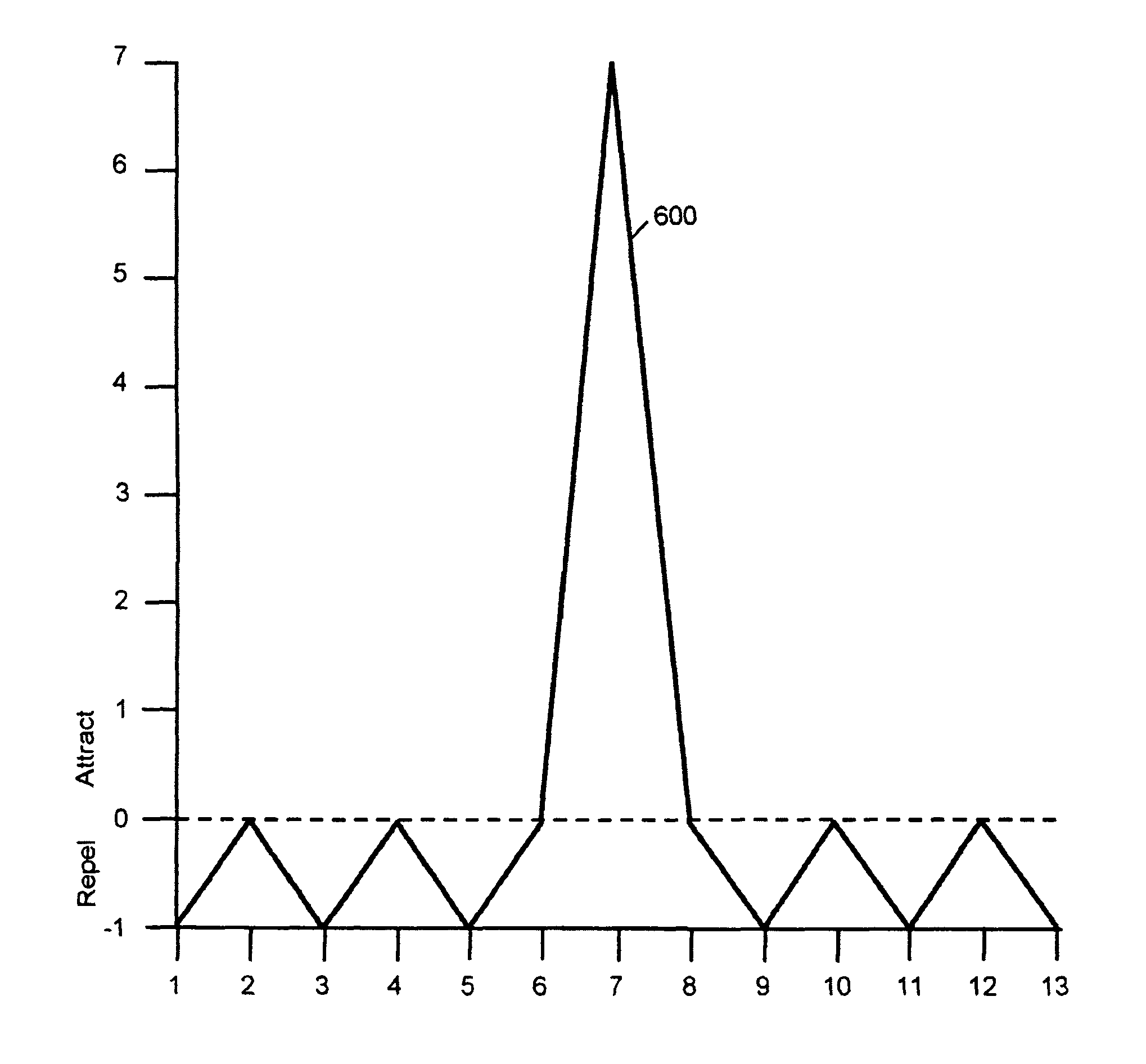
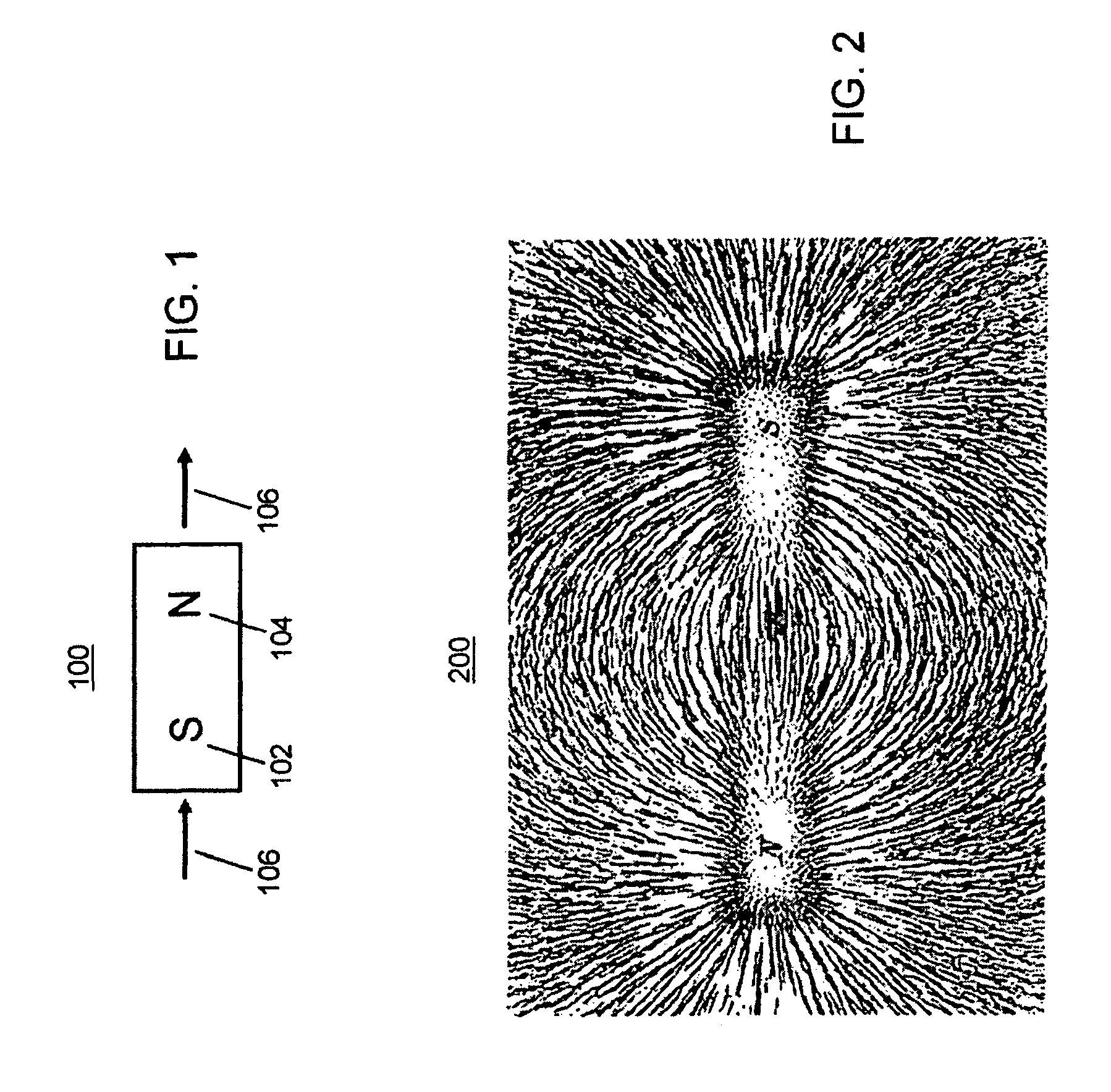
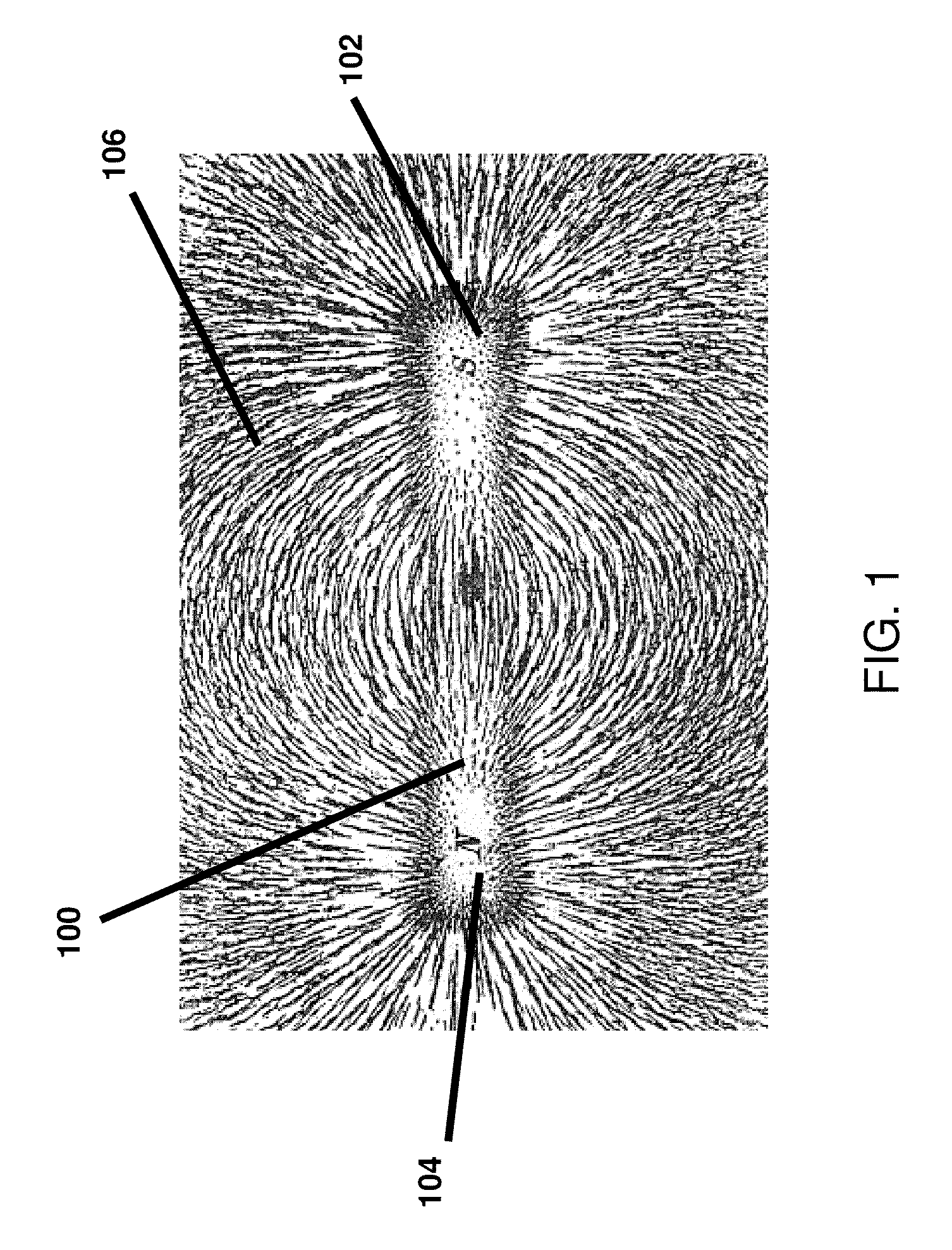
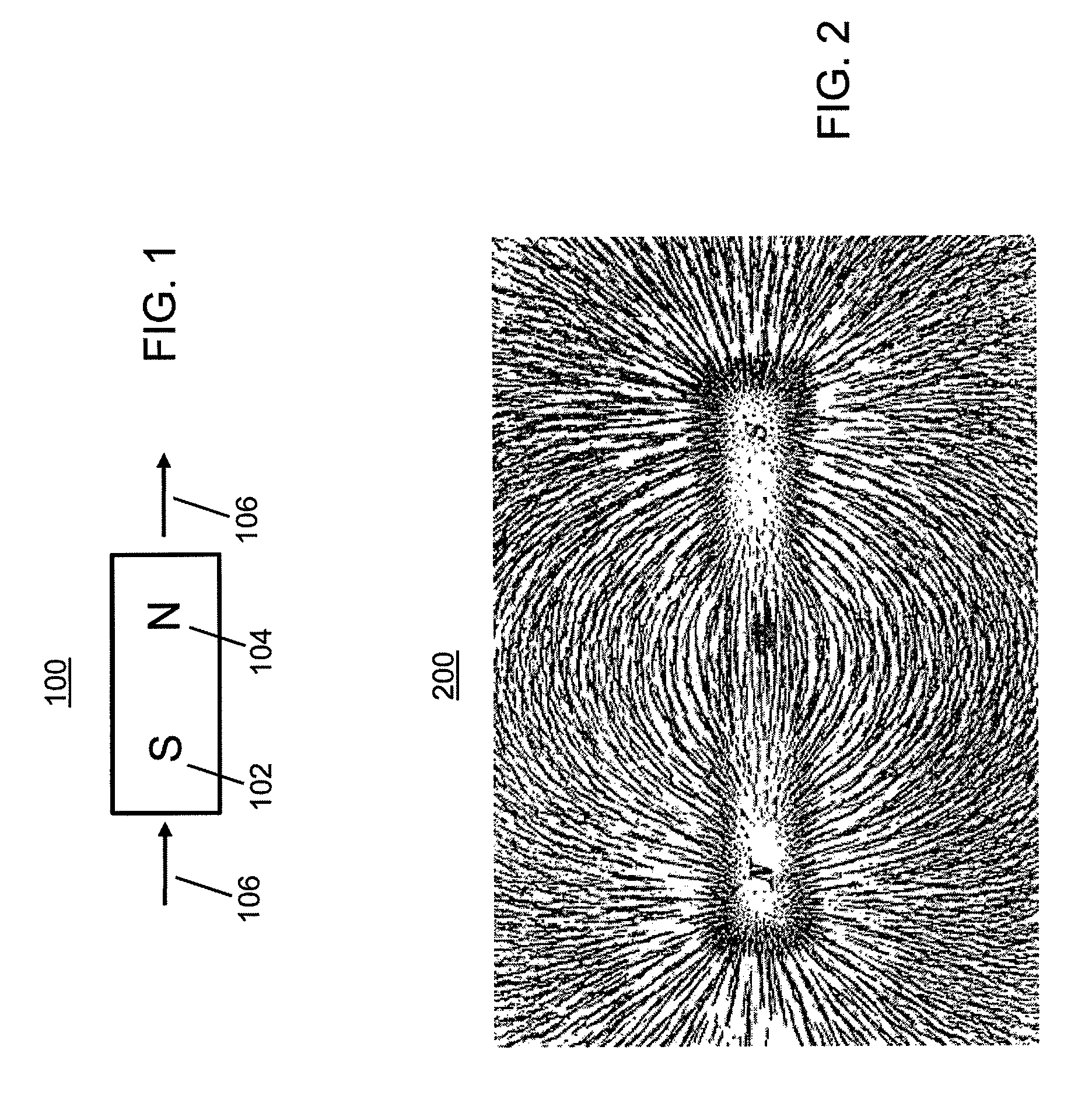
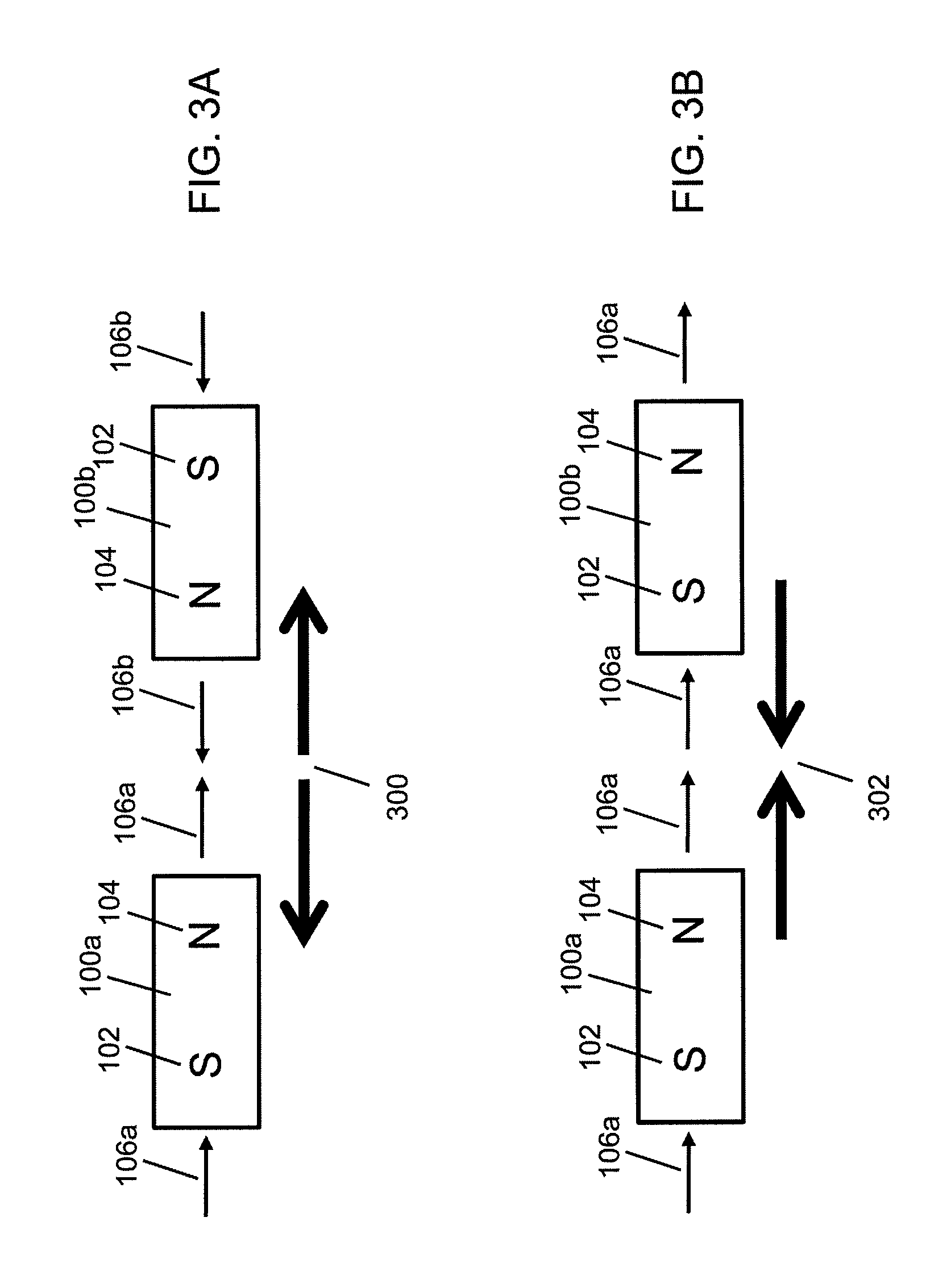
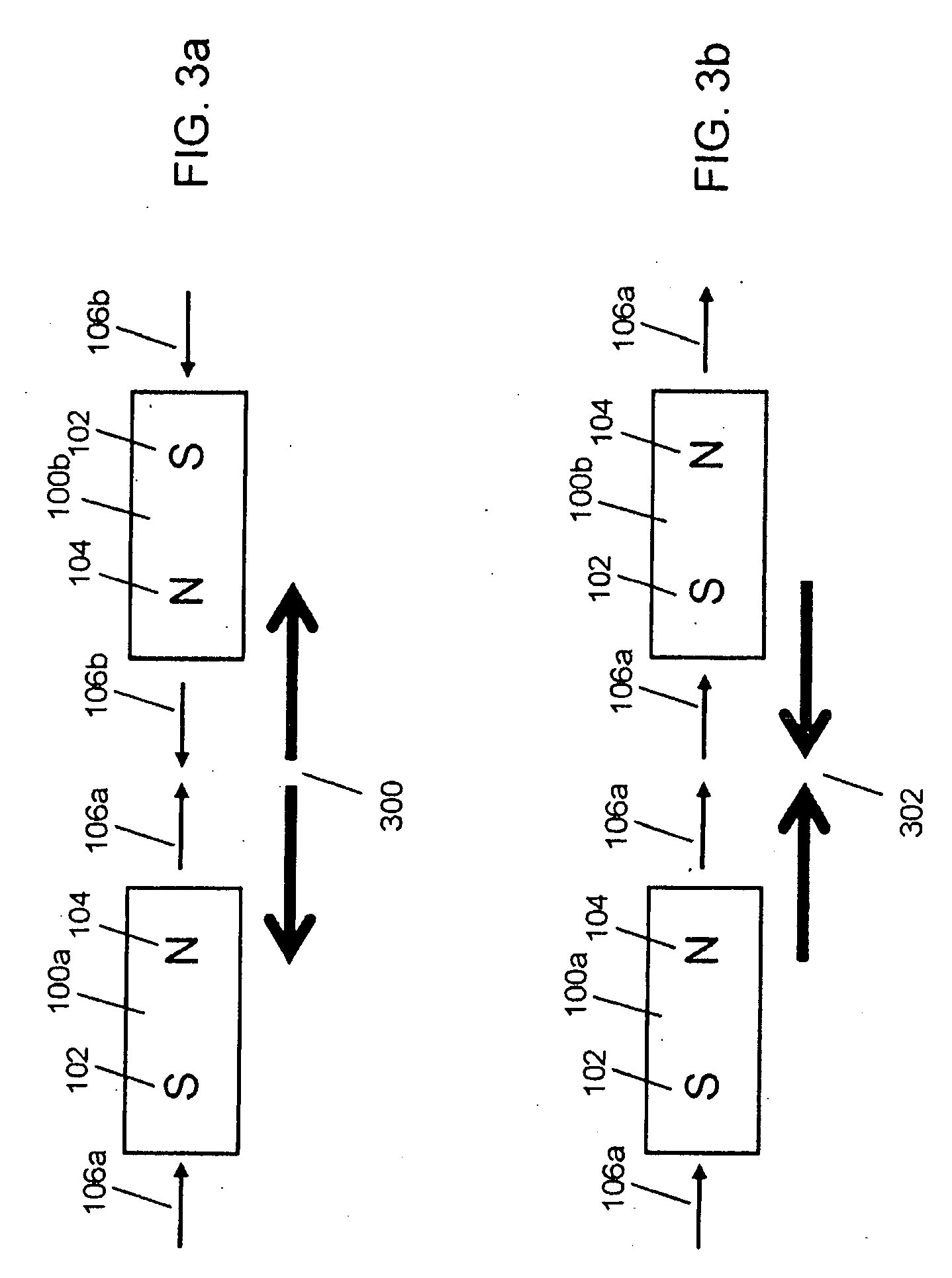
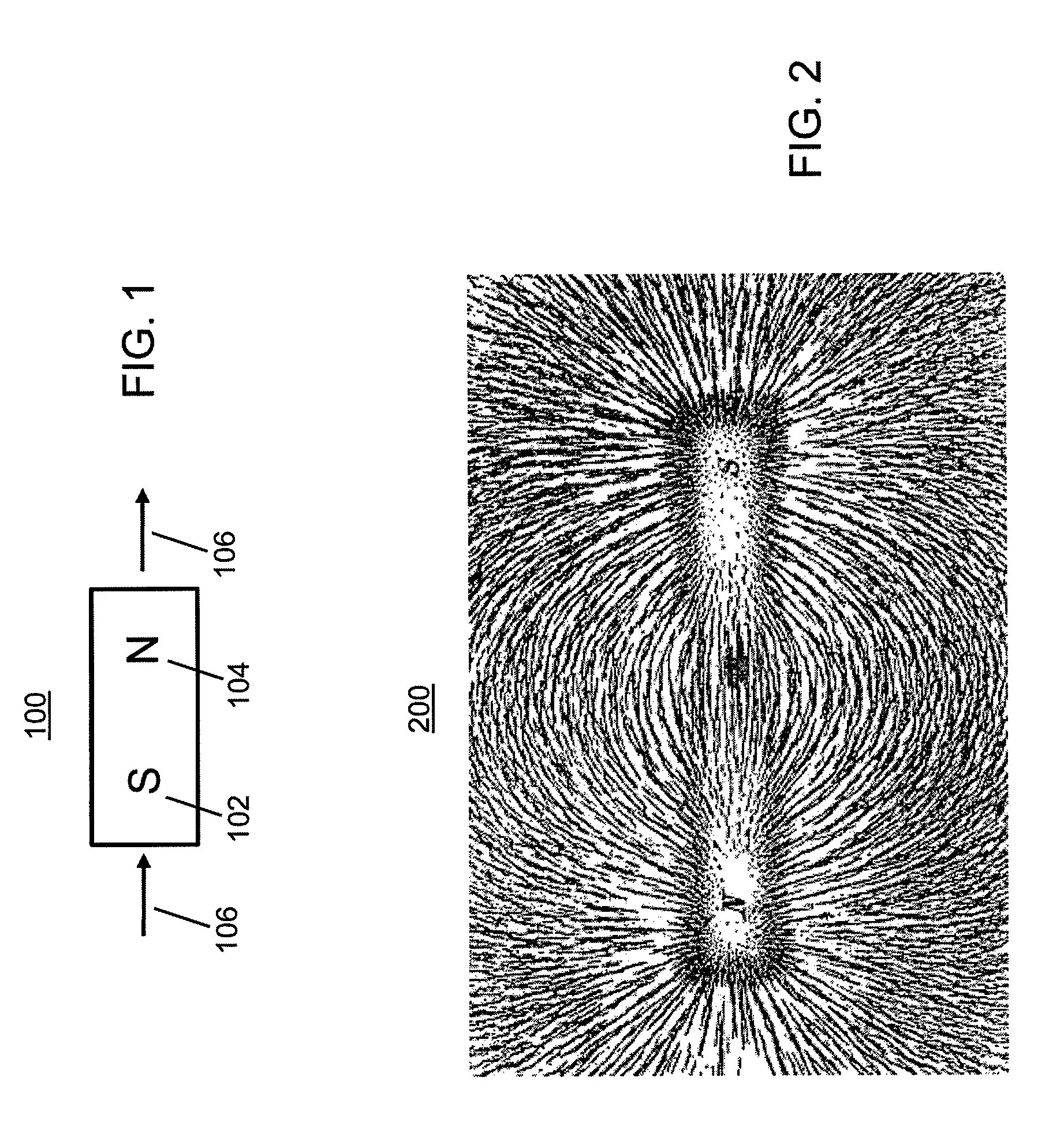
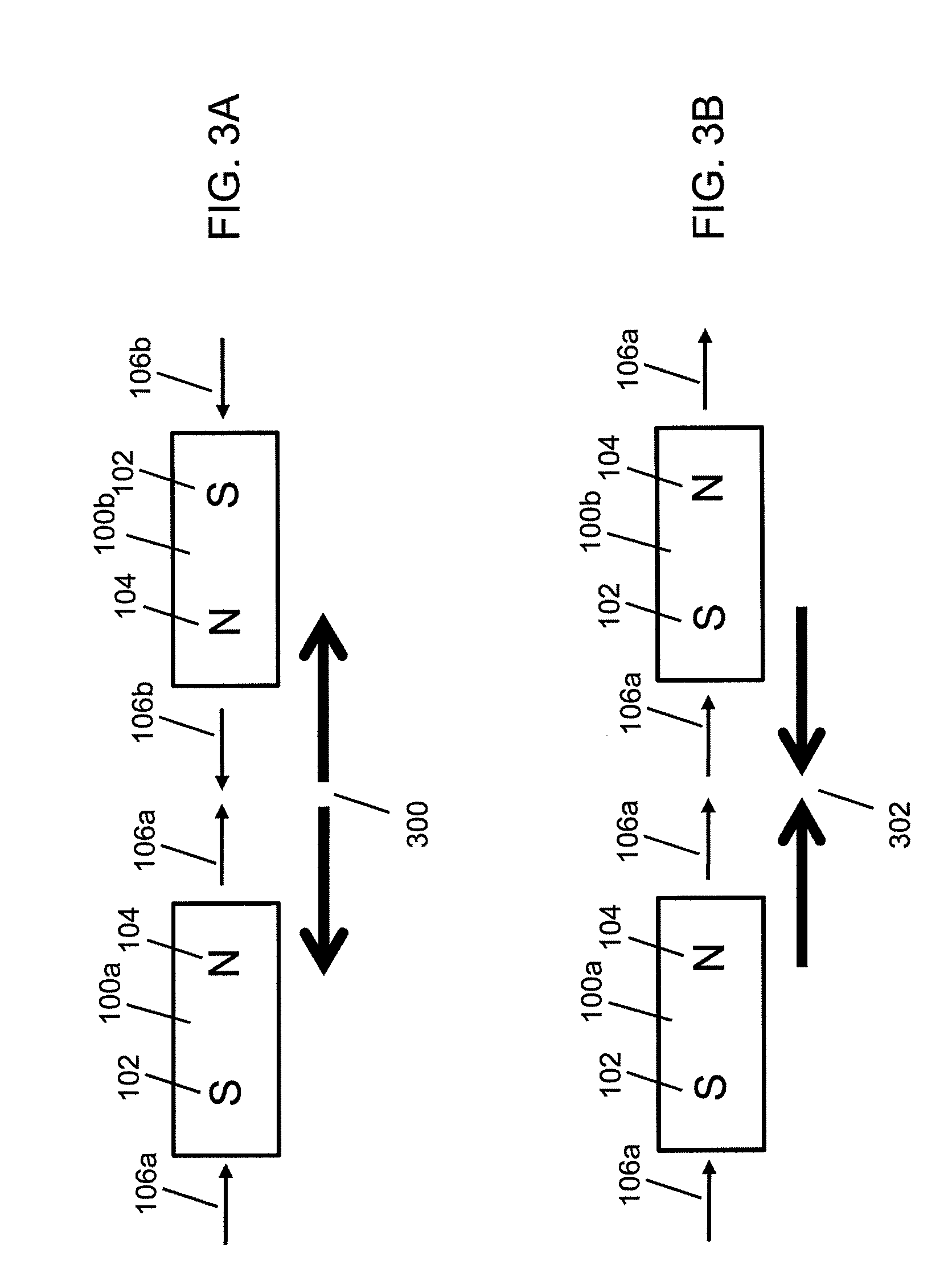
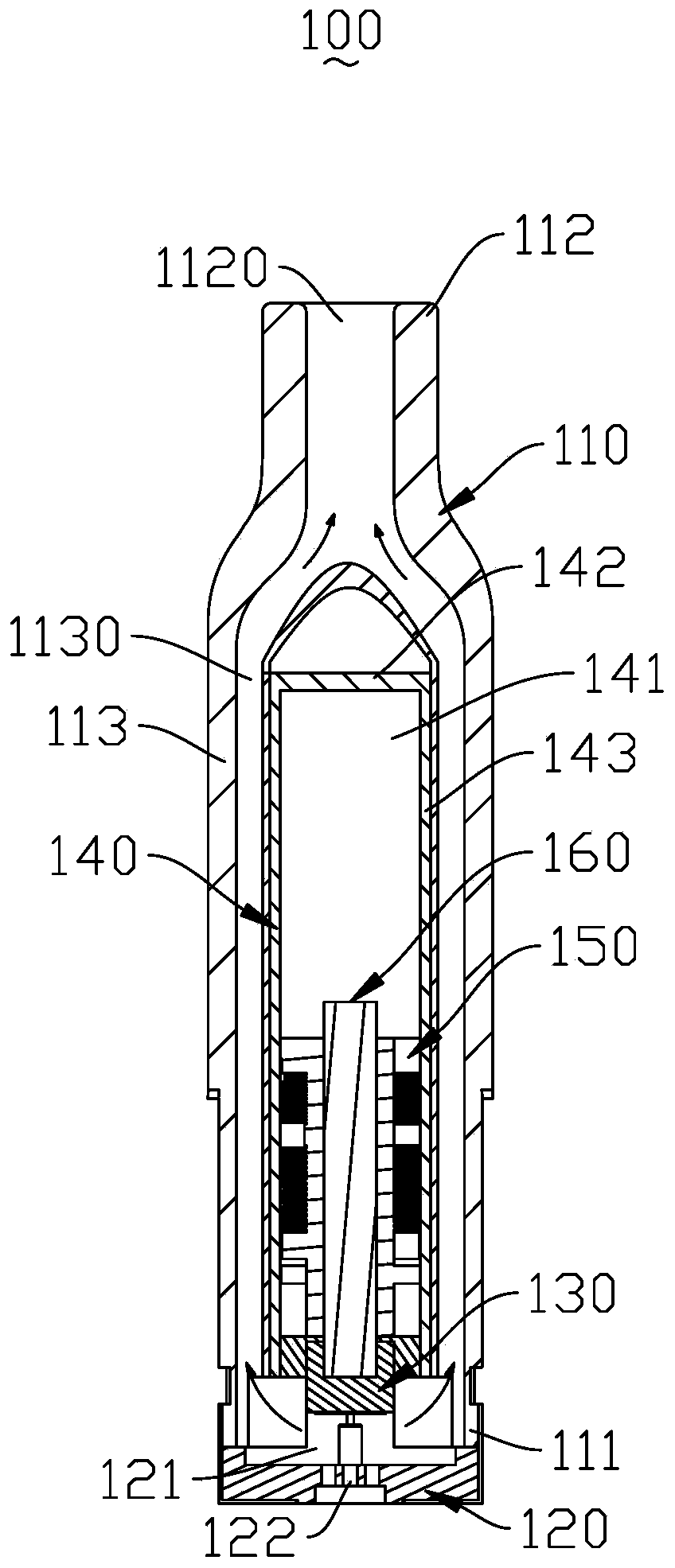
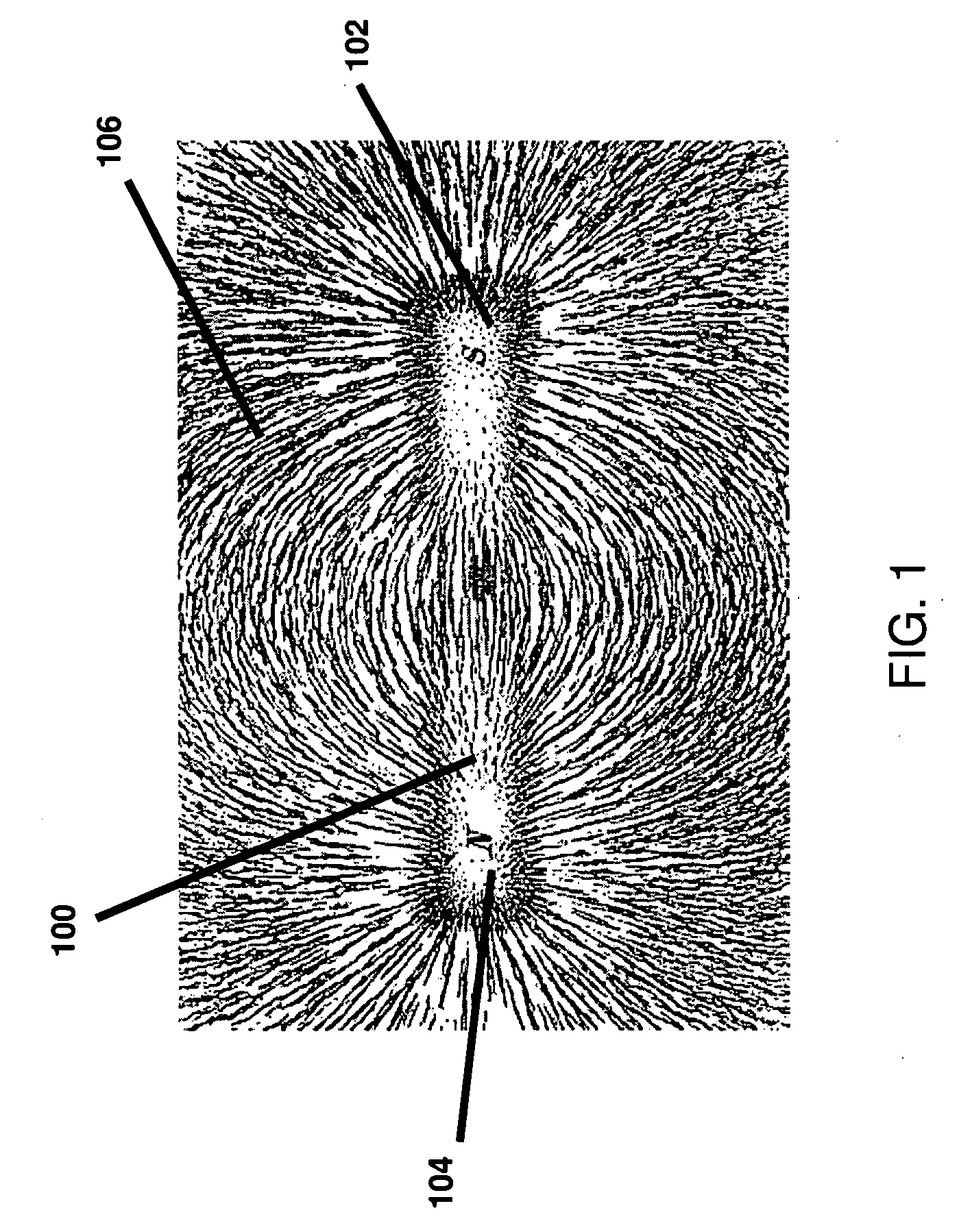
An improved field emission system and method is provided that involves field emission structures having electric or magnetic field sources. The magnitudes, polarities, and positions of the magnetic or electric field sources are configured to have desirable correlation properties, which may be in accordance with a code. The correlation properties correspond to a desired spatial force function where spatial forces between field emission structures correspond to relative alignment, separation distance, and the spatial force function.
Owner:CORRELATED MAGNETICS RES LLC
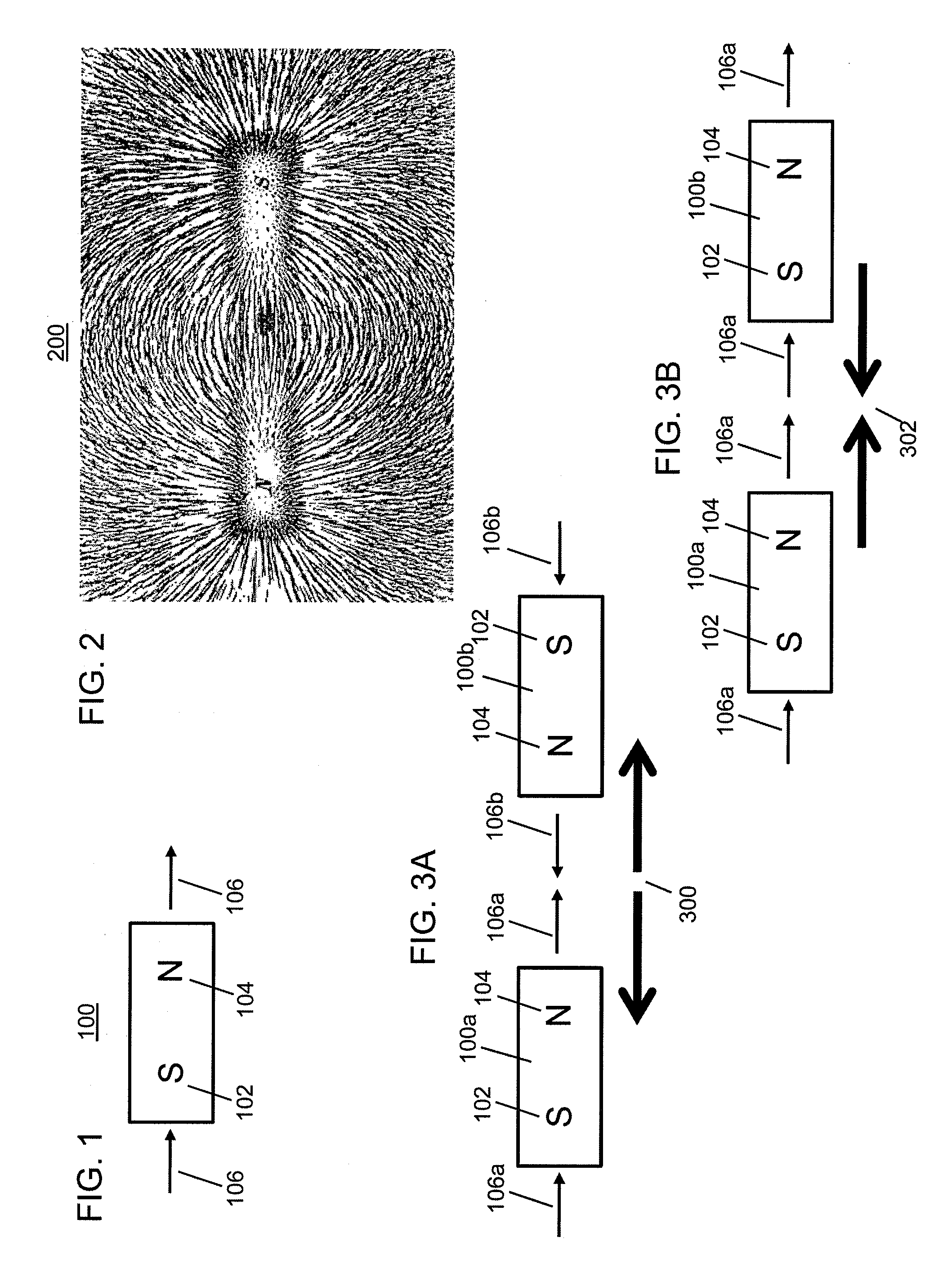
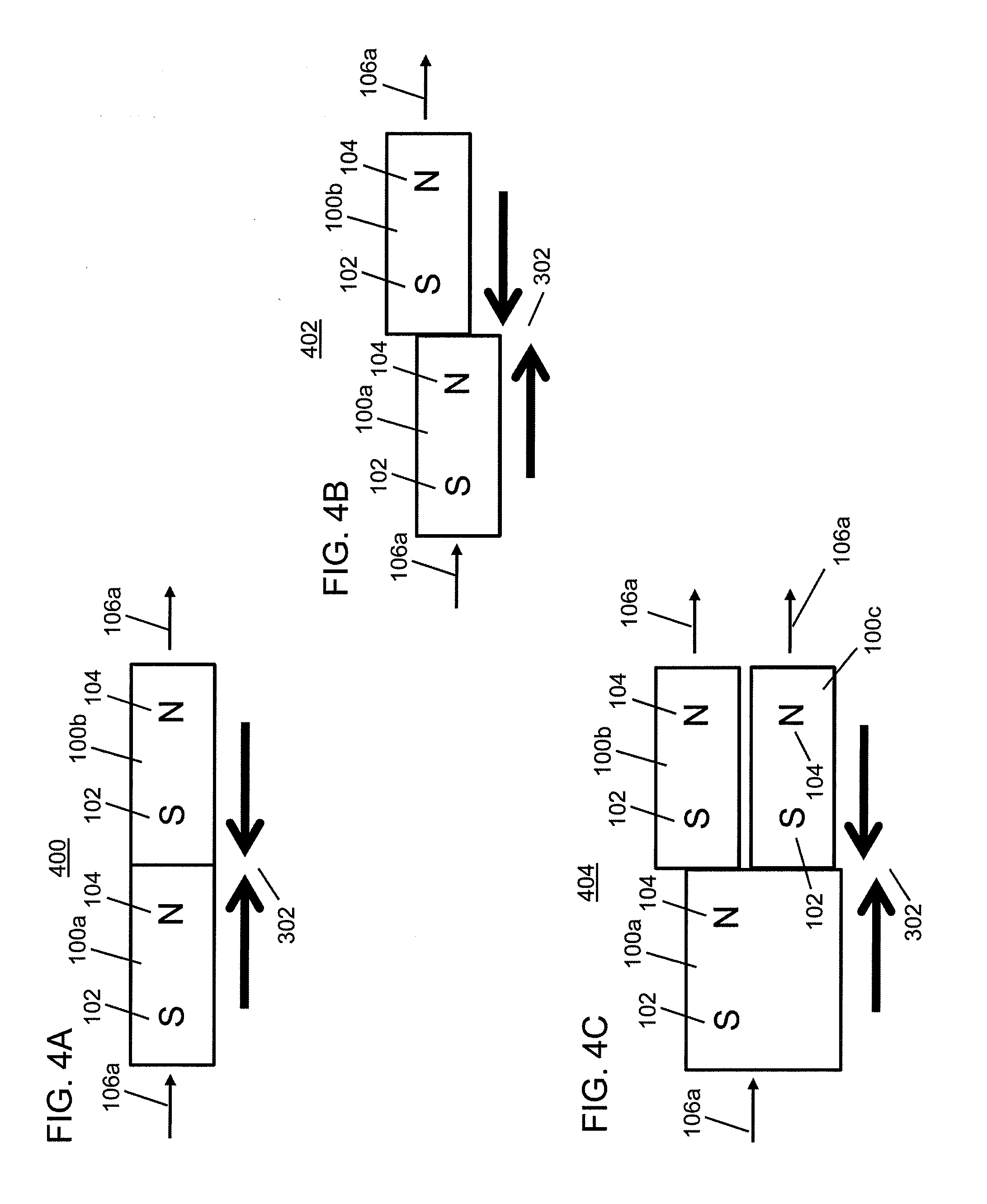
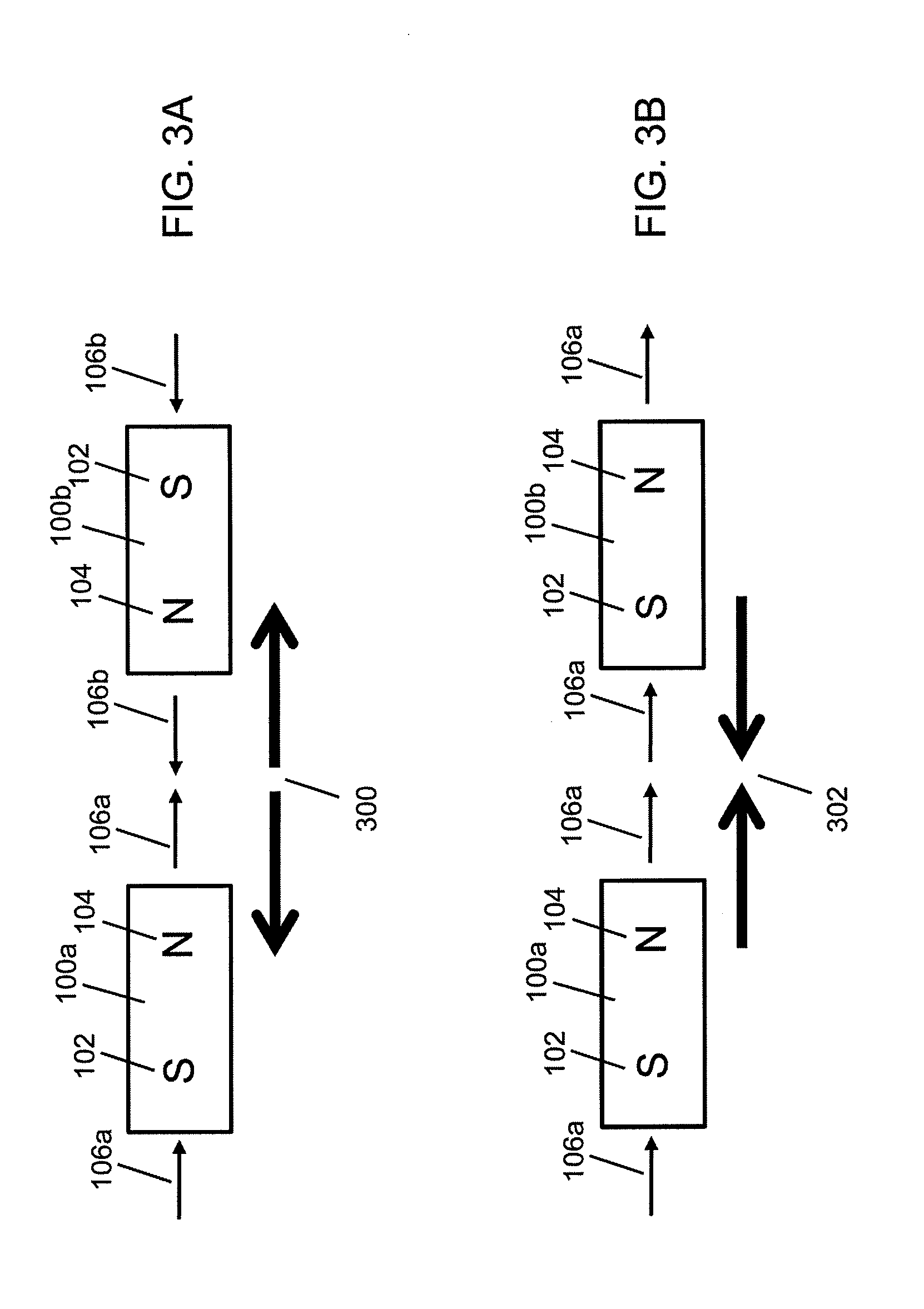
Coded Linear Magnet Arrays in Two Dimensions
InactiveUS20090251256A1Improve and extend operationElectromagnets without armaturesPermanent magnetsClassical mechanicsPeak value
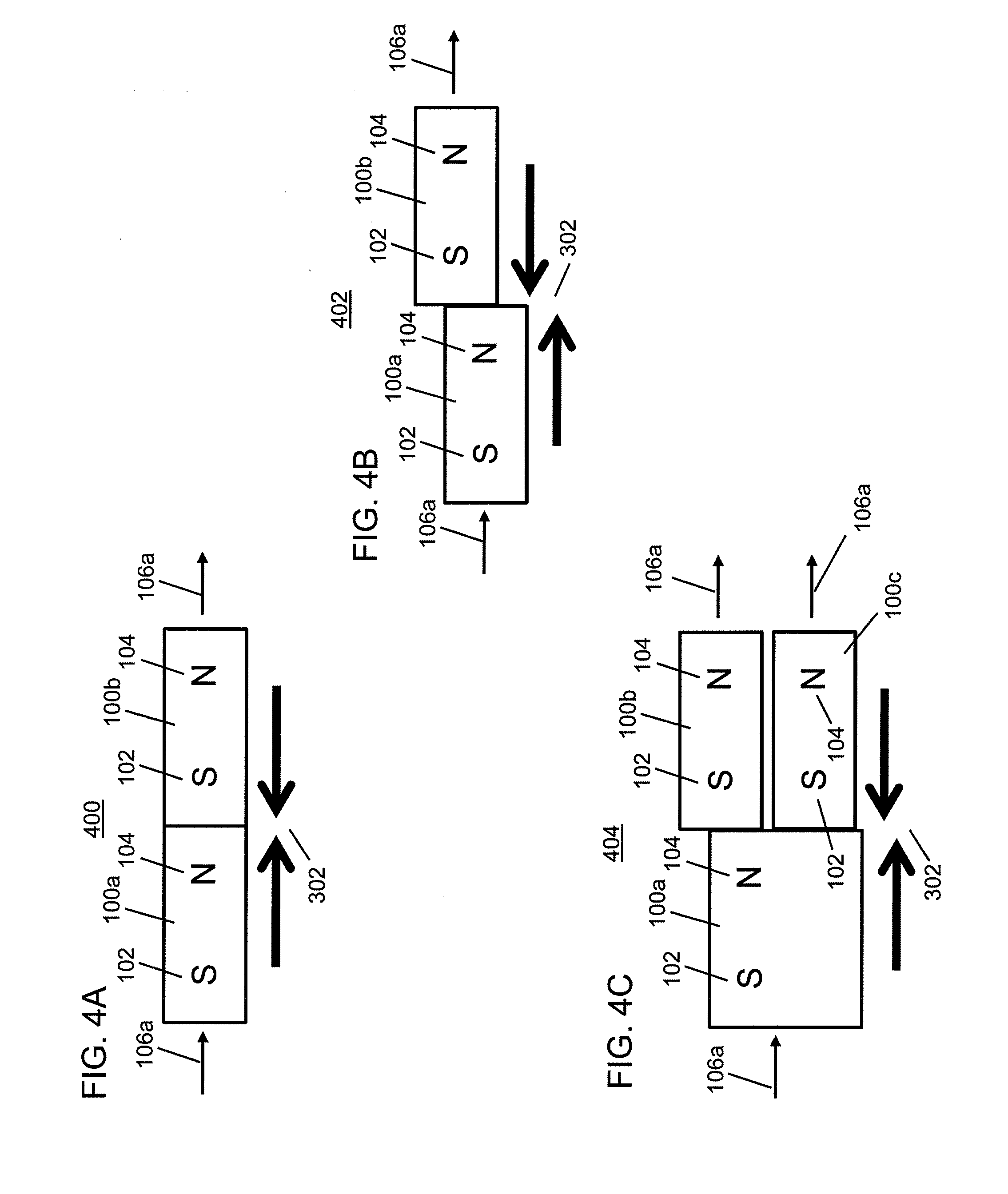
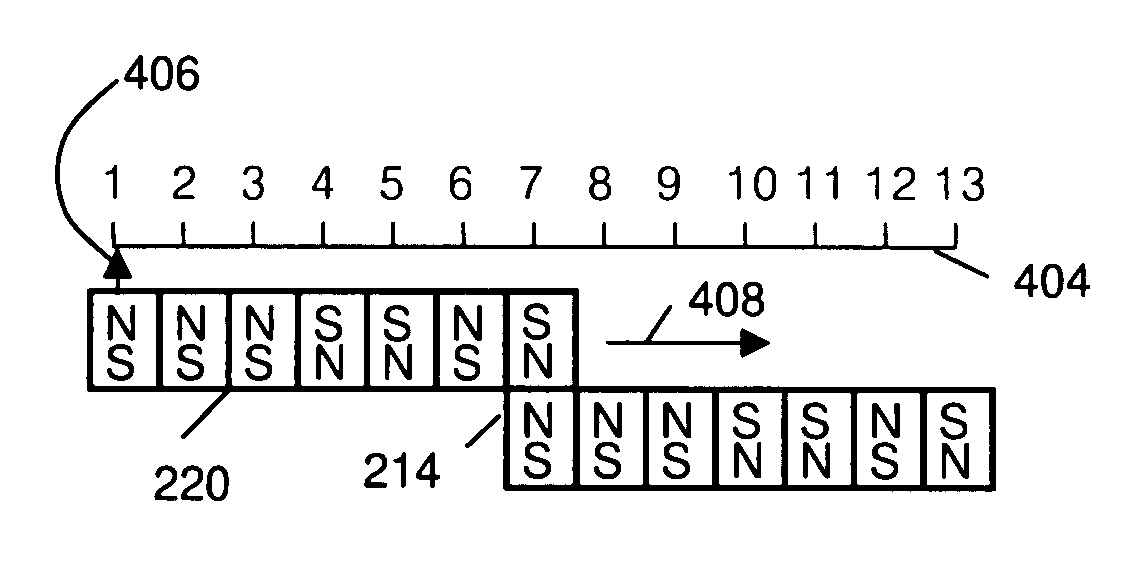
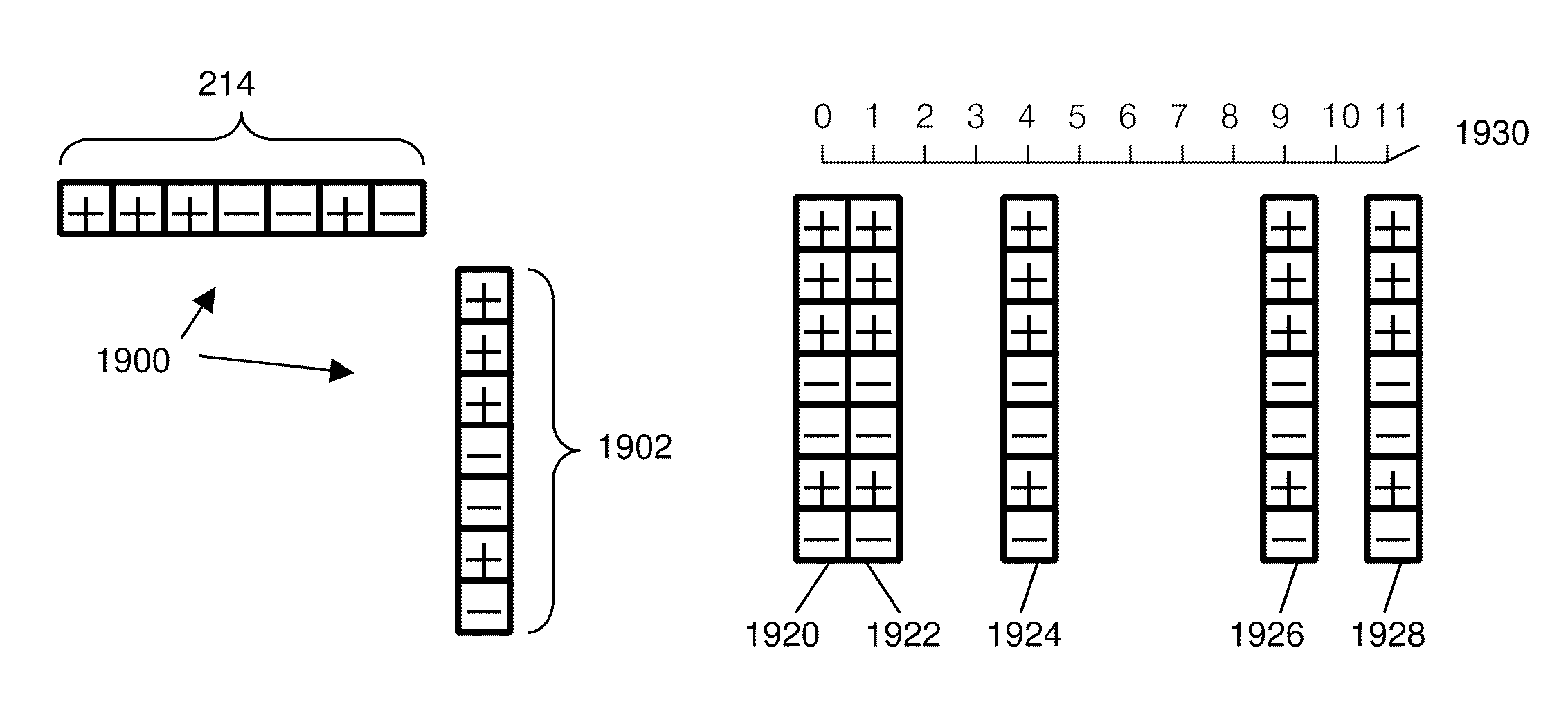
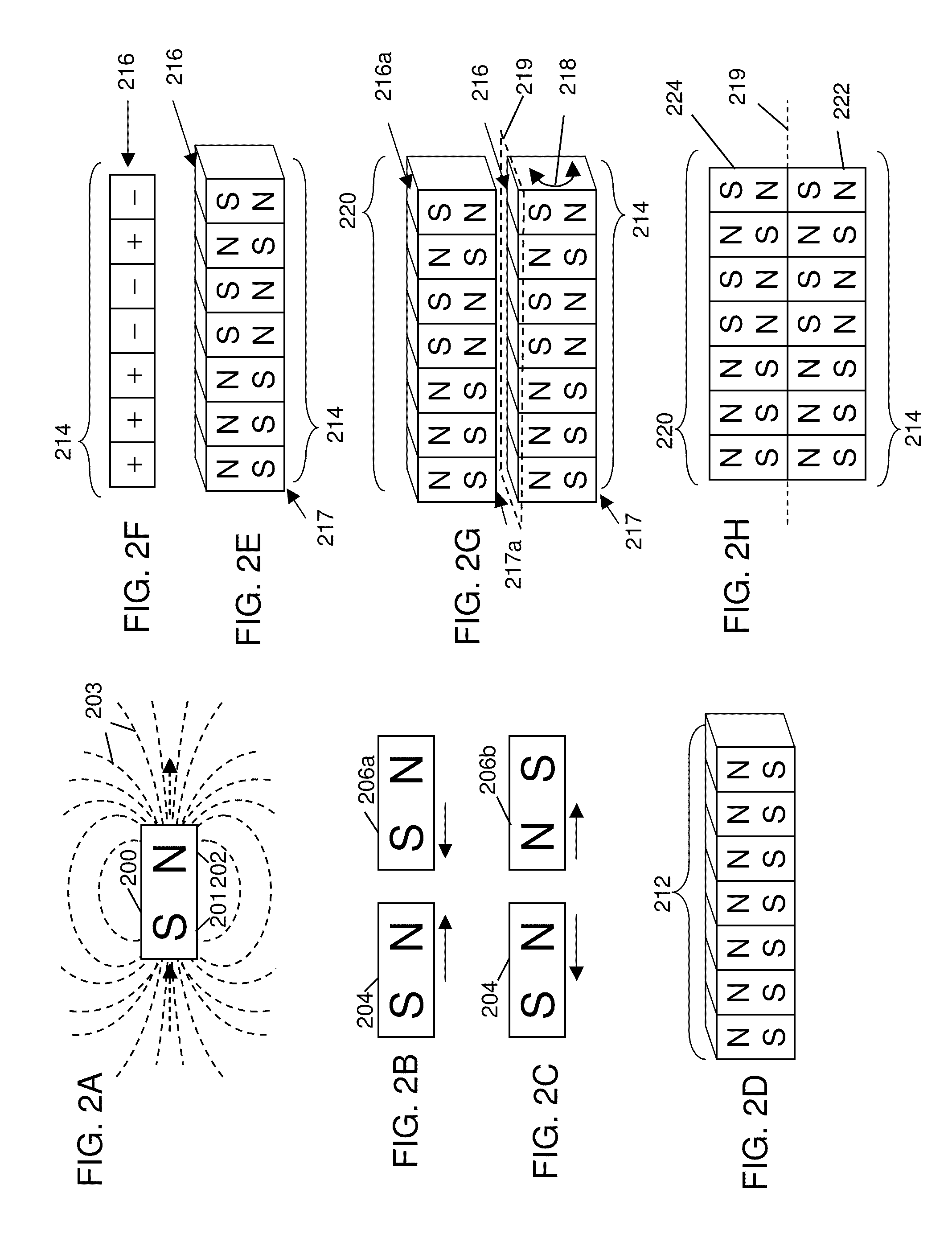
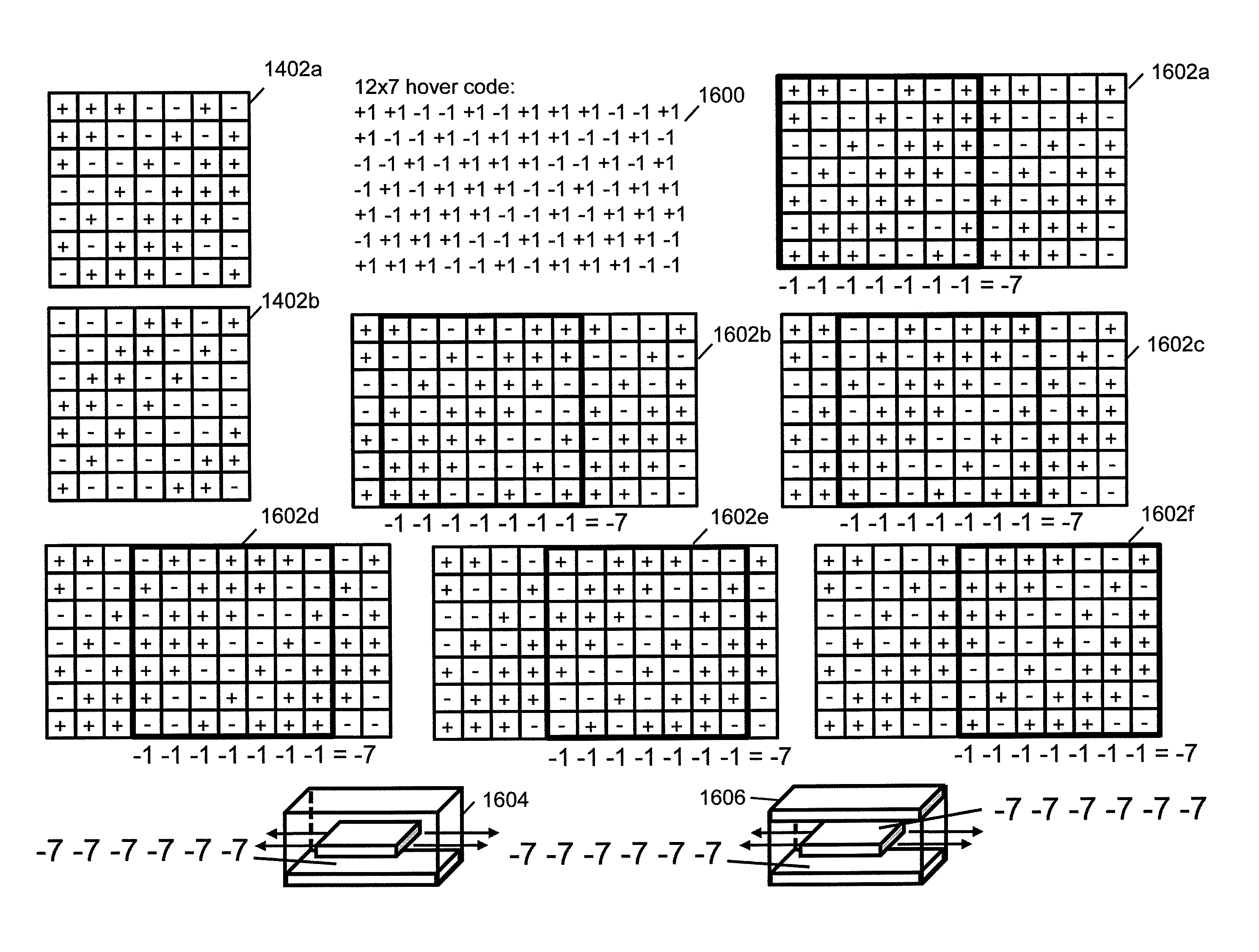
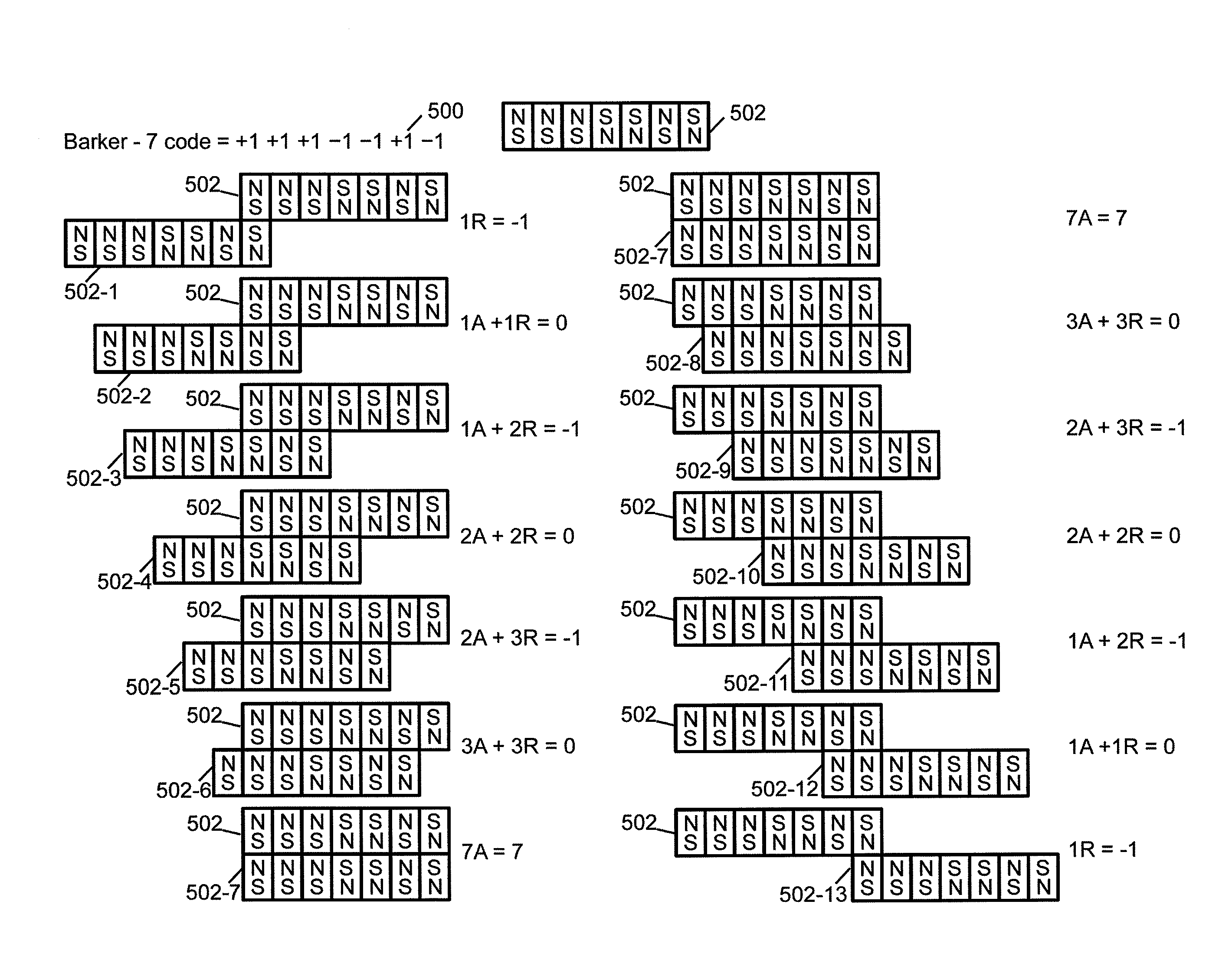
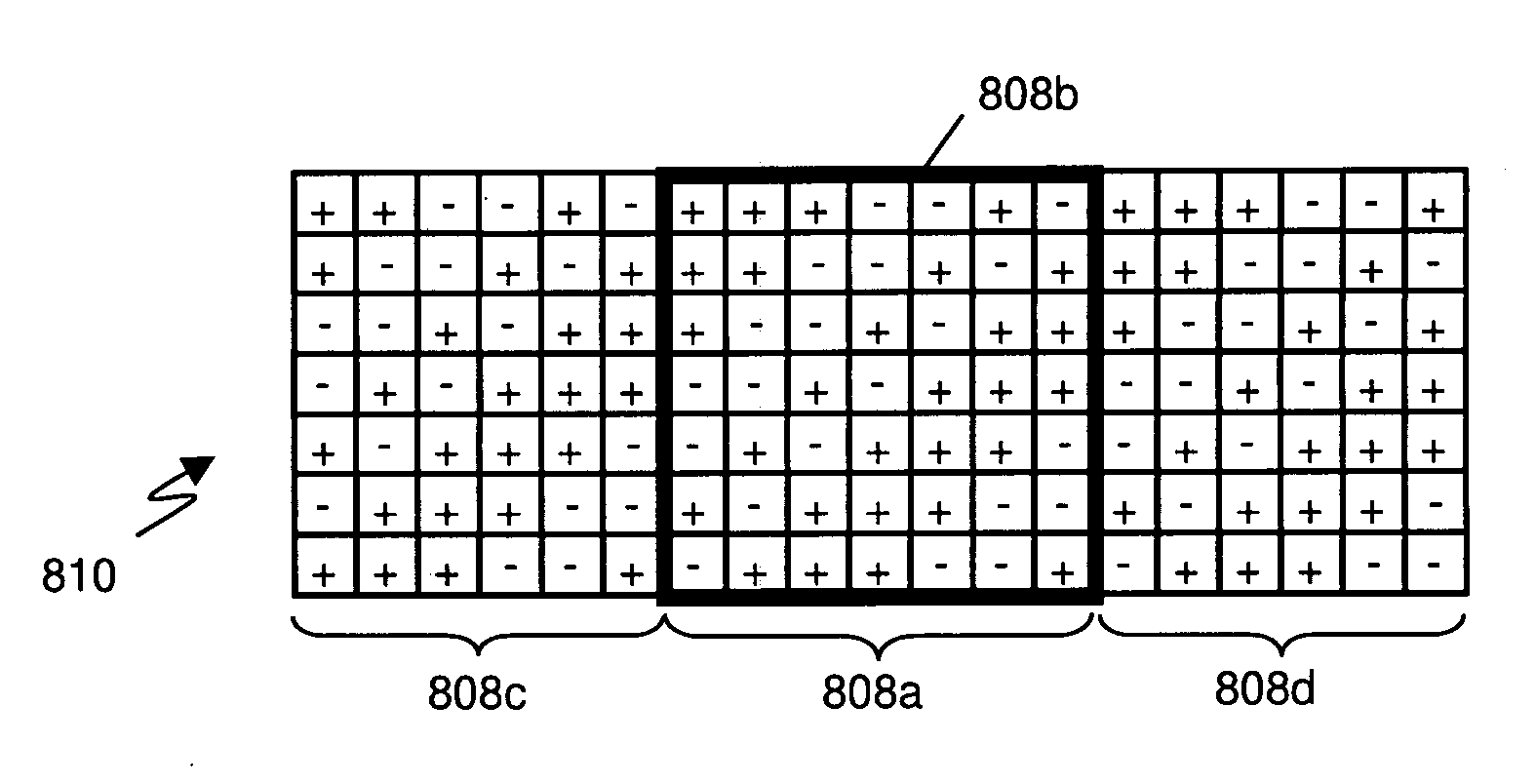
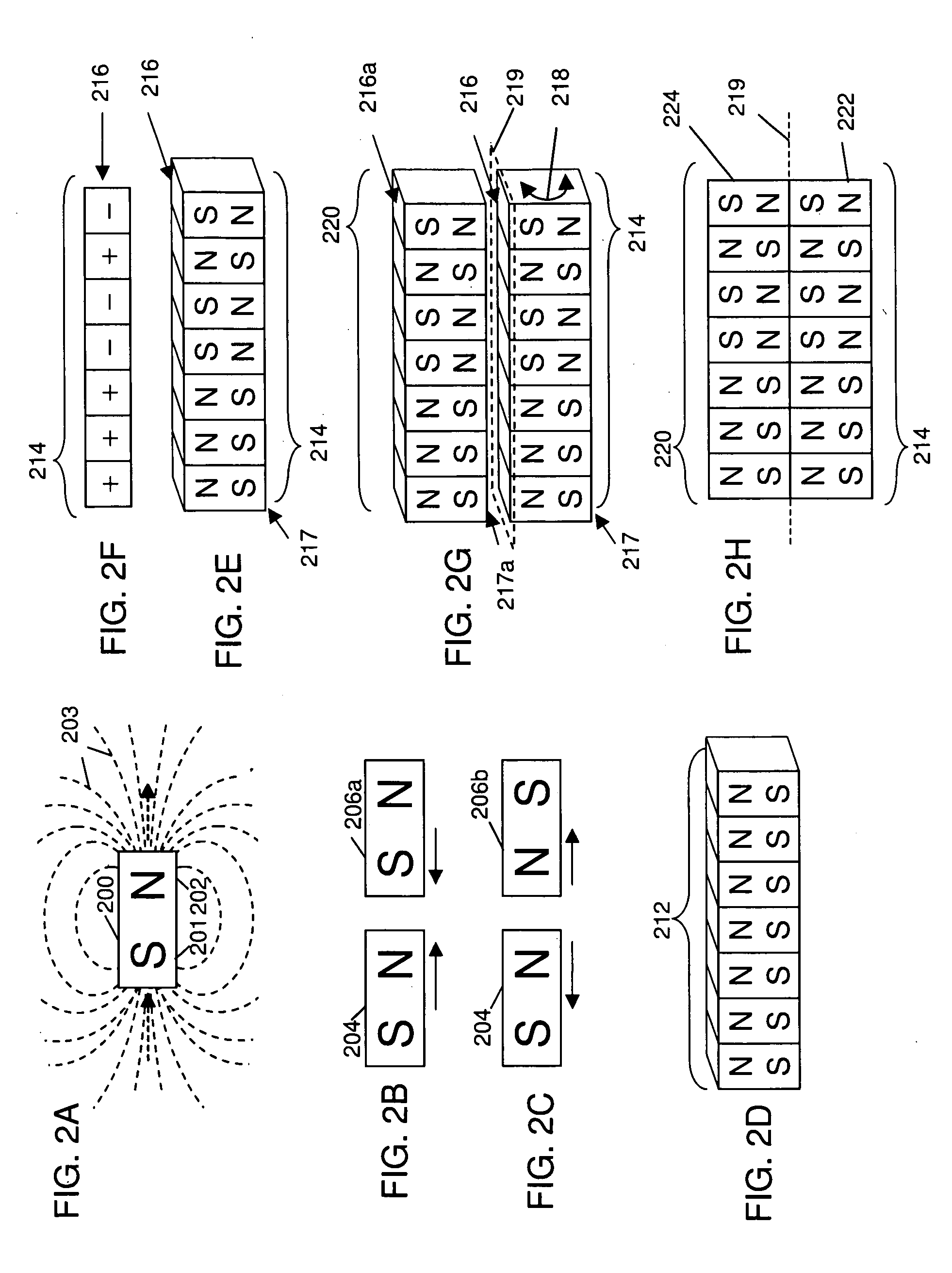
Field emission structures comprising electric or magnetic field sources having magnitudes, polarities, and positions corresponding to a desired spatial force function where a spatial force is created based upon the relative alignment of the field emission structures The magnetic field sources may be arranged according to a code having a desired autocorrelation function. In particular, a high peak to sidelobe autocorrelation performance may be found desirable. Specific exemplary embodiments are described having non-parallel linear substructures. The non-parallel linear substructures may use the same or different codes and may have none, one, or more magnets in common. Other embodiments include substructures spaced according to a spacing code. Exemplary spacing codes include, but are not limited to Golomb ruler or Costas array. A polarity code may be applied across the substructures.
Owner:CORRELATED MAGNETICS RES LLC
Apparatuses and methods relating to precision attachments between first and second components
InactiveUS7817006B2Electromagnets without armaturesPermanent magnetsPrecision attachmentAtomic physics
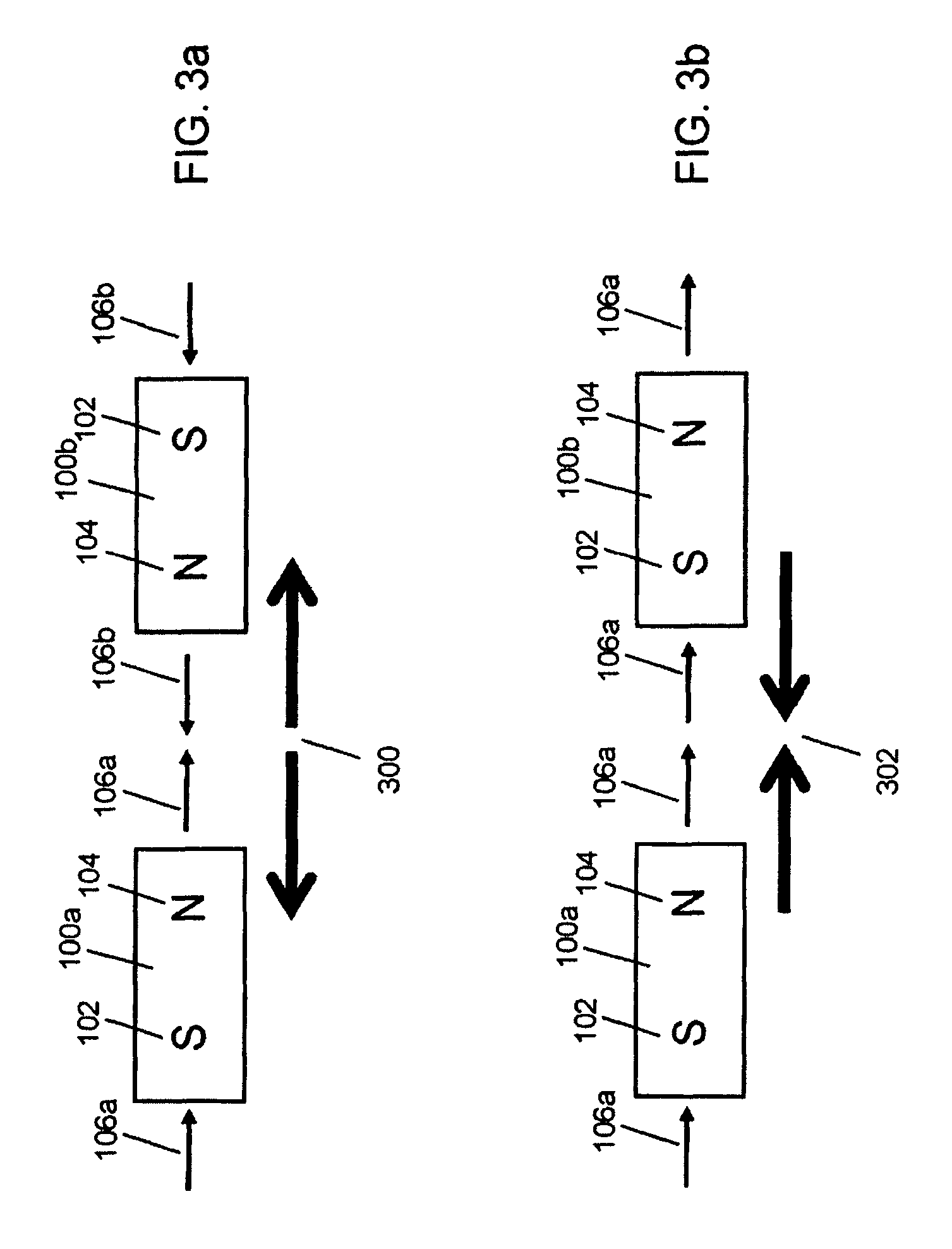
First and second components may be precisely attached to form an apparatus. In an example embodiment, a first component includes a first field emission structure, and a second component includes a second field emission structure. The first and second components are adapted to be attached to each other with the first field emission structure in proximity to the second field emission structure such that the first and second field emission structures have a predetermined alignment with respect to each other. Each of the first and second field emission structures include multiple field emission sources having positions and polarities relating to a predefined spatial force function that corresponds to the predetermined alignment of the first and second field emission structures within a field domain. The first and second field emission structures are configured responsive to at least one precision criterion to enable a precision attachment.
Owner:CORRELATED MAGNETICS RES LLC
Apparatuses and Methods Relating to Precision Attachments Between First and Second Components
InactiveUS20090289749A1Accurate attachmentElectromagnets without armaturesPermanent magnetsPrecision attachmentAtomic physics
Owner:CORRELATED MAGNETICS RES LLC
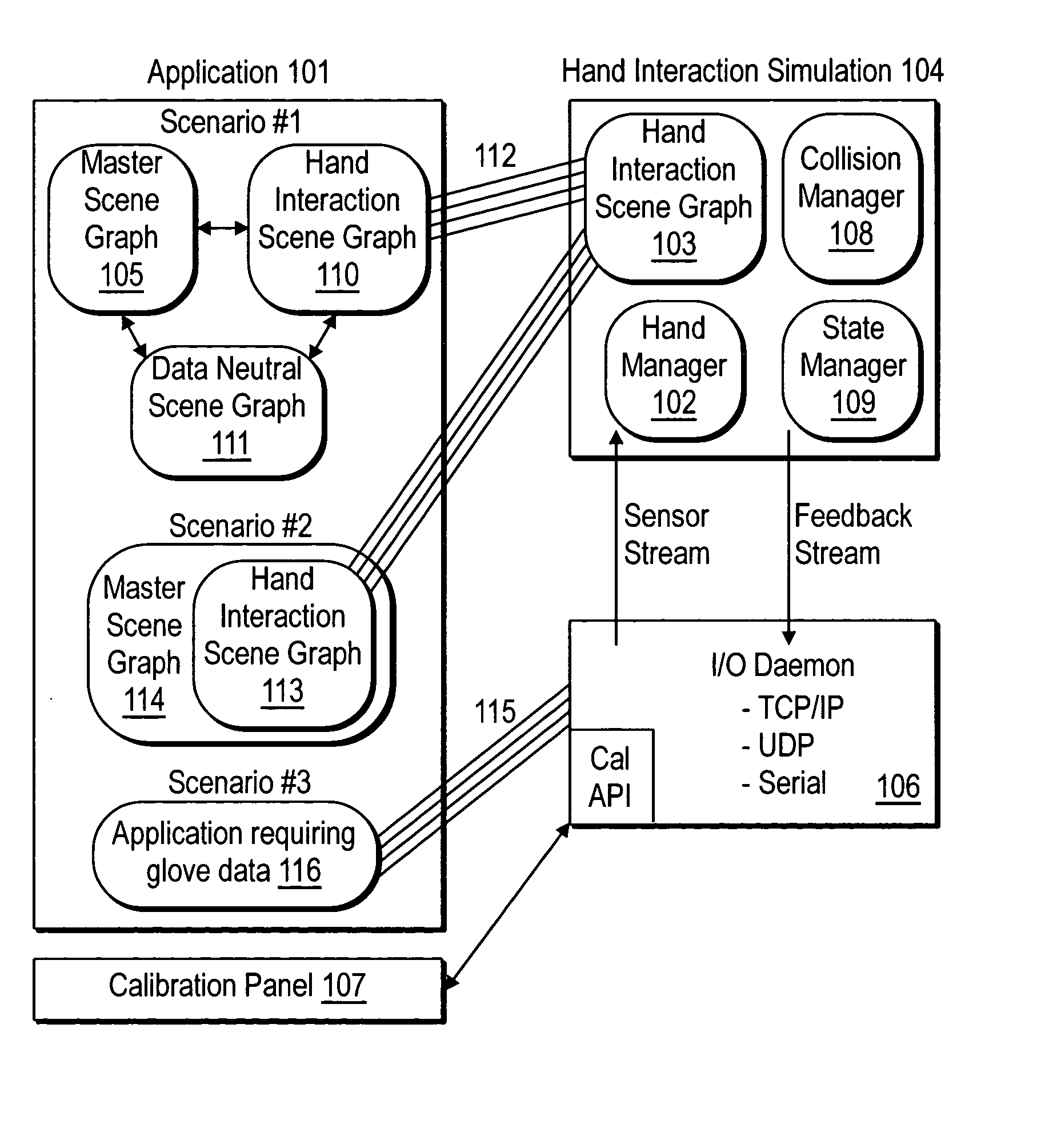
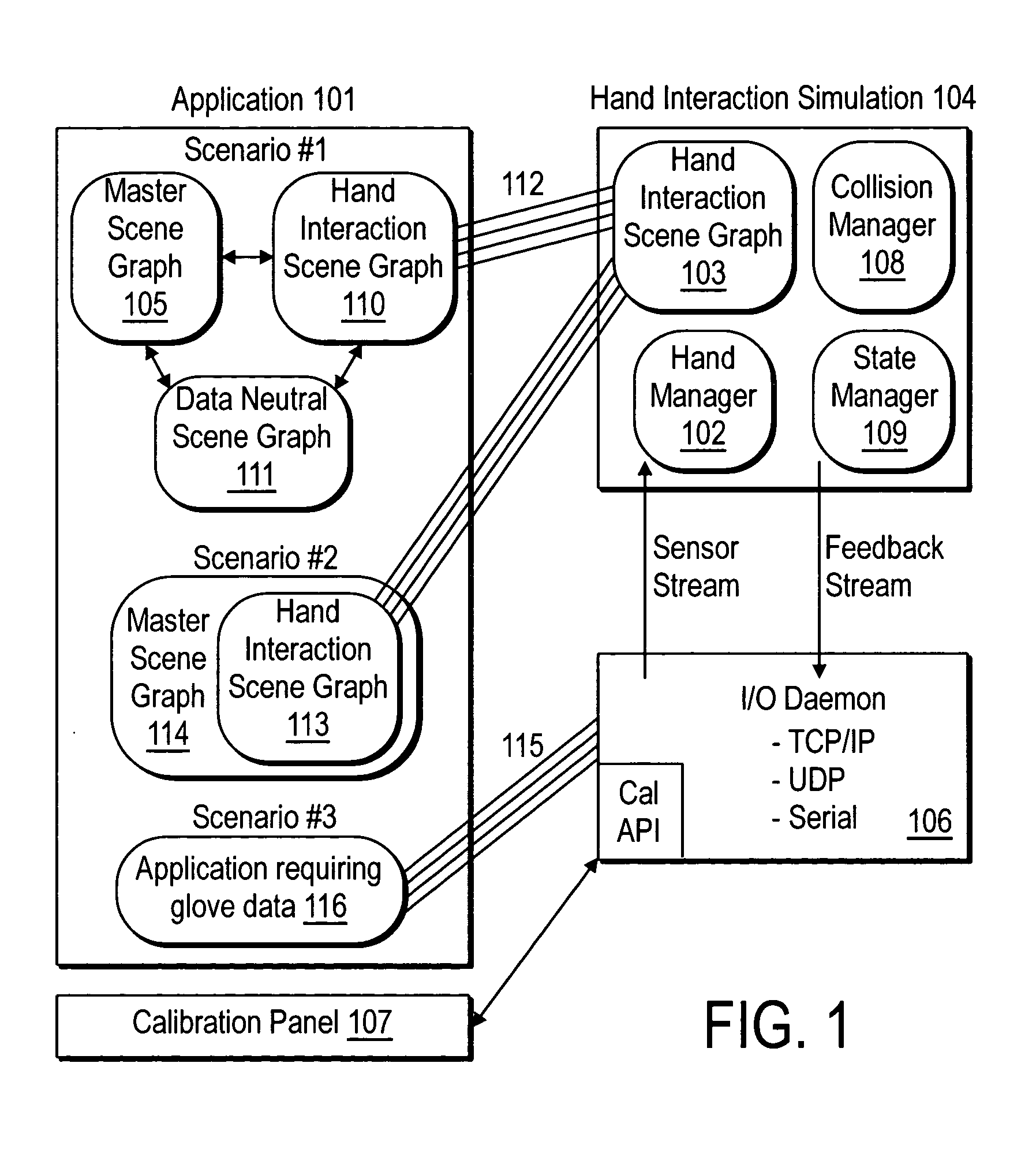
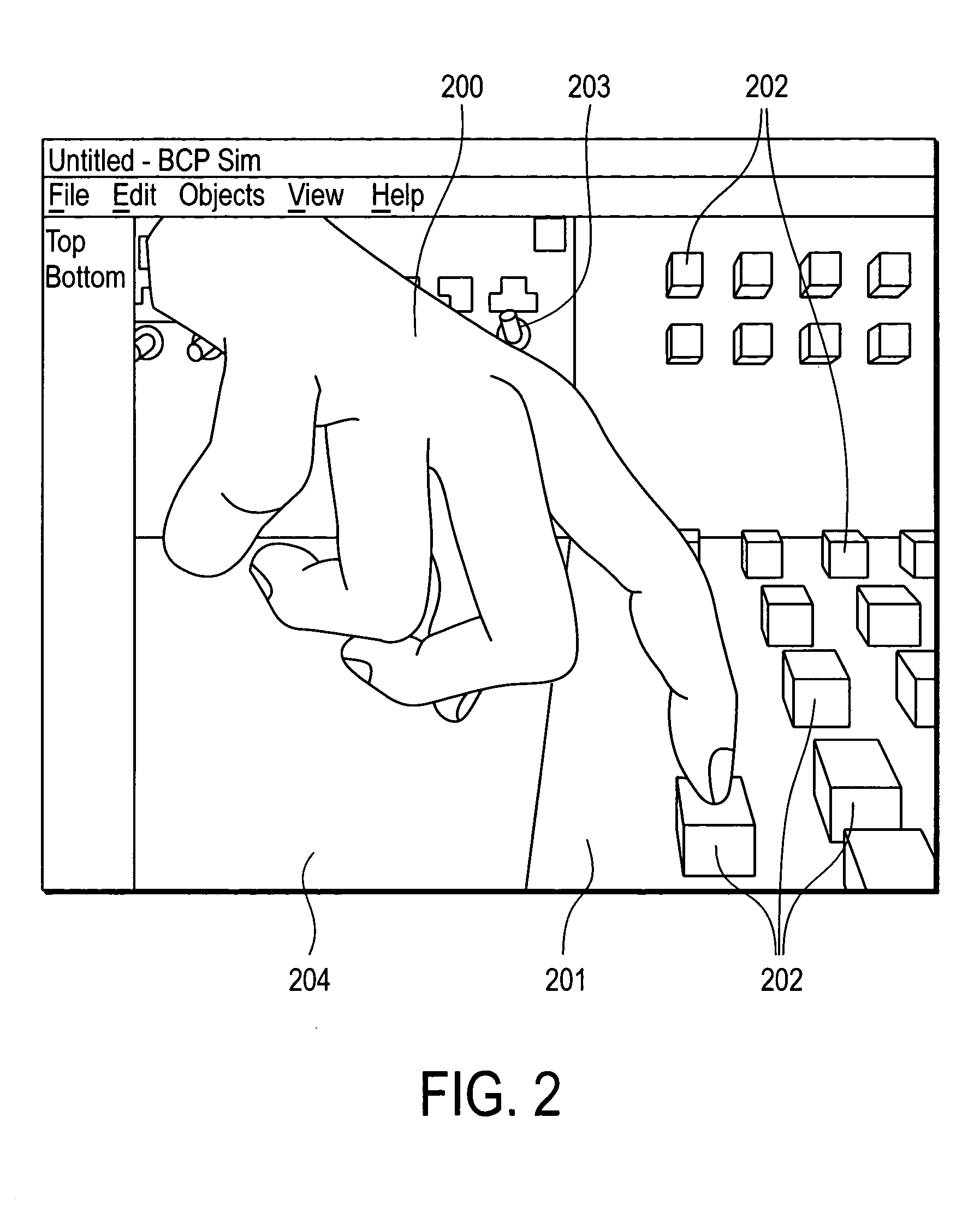
System and method for constraining a graphical hand from penetrating simulated graphical objects
An apparatus, system, method, and computer program and computer program product are provided for constraining the movement of a graphical hand when the physical hand controlling the graphical hand does not have a similar physical constraint. The constraining technique may comprise use and analysis of a revolute-joint-link-spring model. In such a model, an uncompressed / unextended spring position represents the corresponding measured joint angle or link position. In addition to linear springs which follow Hook's Law, i.e., F=k*x, non-linear springs or other non-linear force functions may be employed to obtain the desired result of allowing a graphical joint or link to deviate from what the corresponding measured joint or link provides. In particular, if a graphical hand configuration corresponding to measured joint and link positions causes a portion of the hand to penetrate a simulated graphical solid object, a mathematical determination is used to compute modified joint and link positions such that the graphical hand part will no longer penetrate the graphical solid object. Such a constraint technique may include solving a spring model such that the various joint and link springs compress or extend to produce modified joint and link positions. Such a constraint technique may also be applied to constrain other graphical body parts and graphical inanimate objects, where corresponding physical controlling, i.e., measured, body parts and inanimate objects do not possess a similar constraint or impediment.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
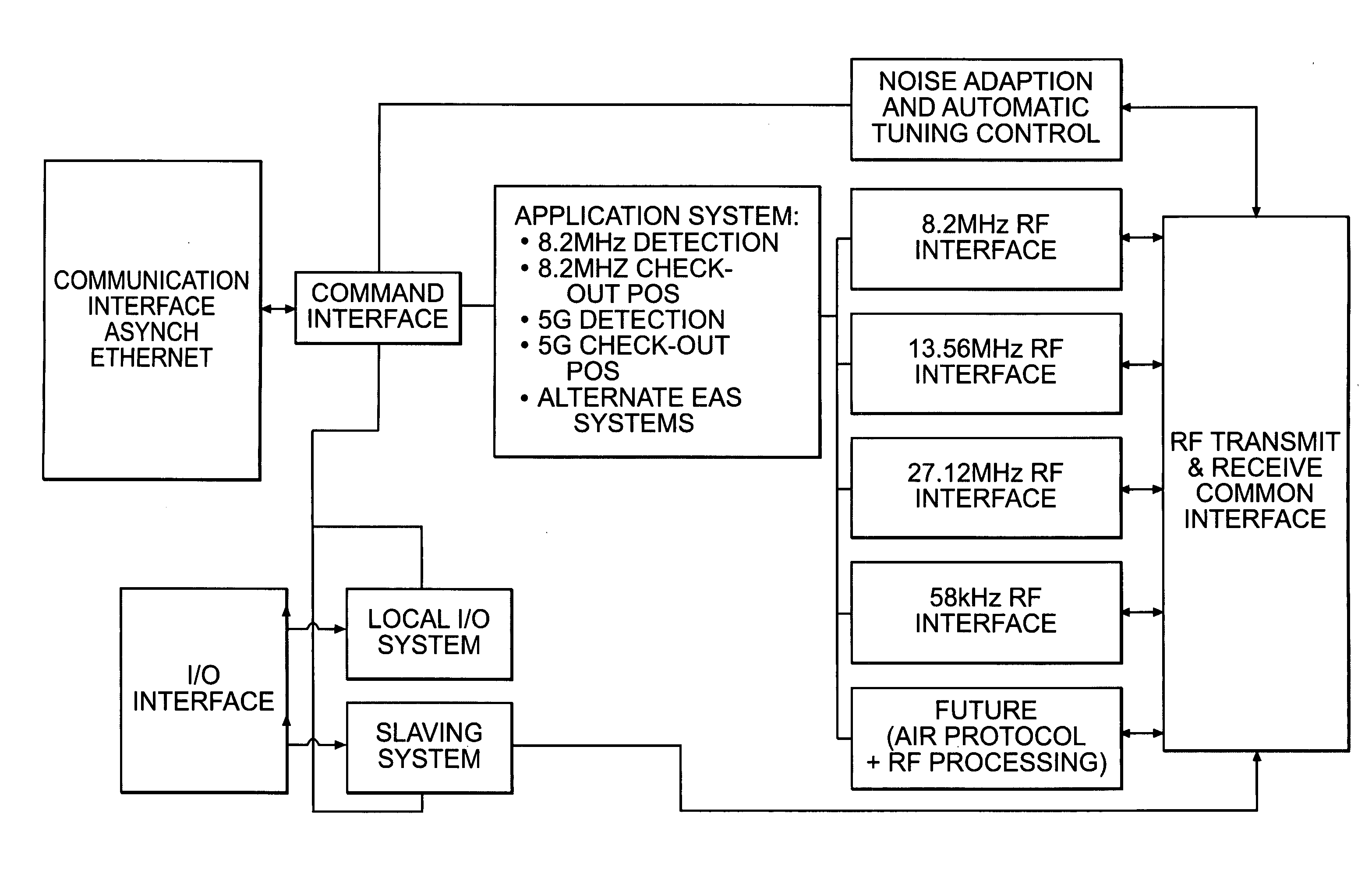
Multiple frequency detection system
InactiveUS20060158316A1Easy to packSubscribers indirect connectionBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalMultiple frequencyEmbedded system
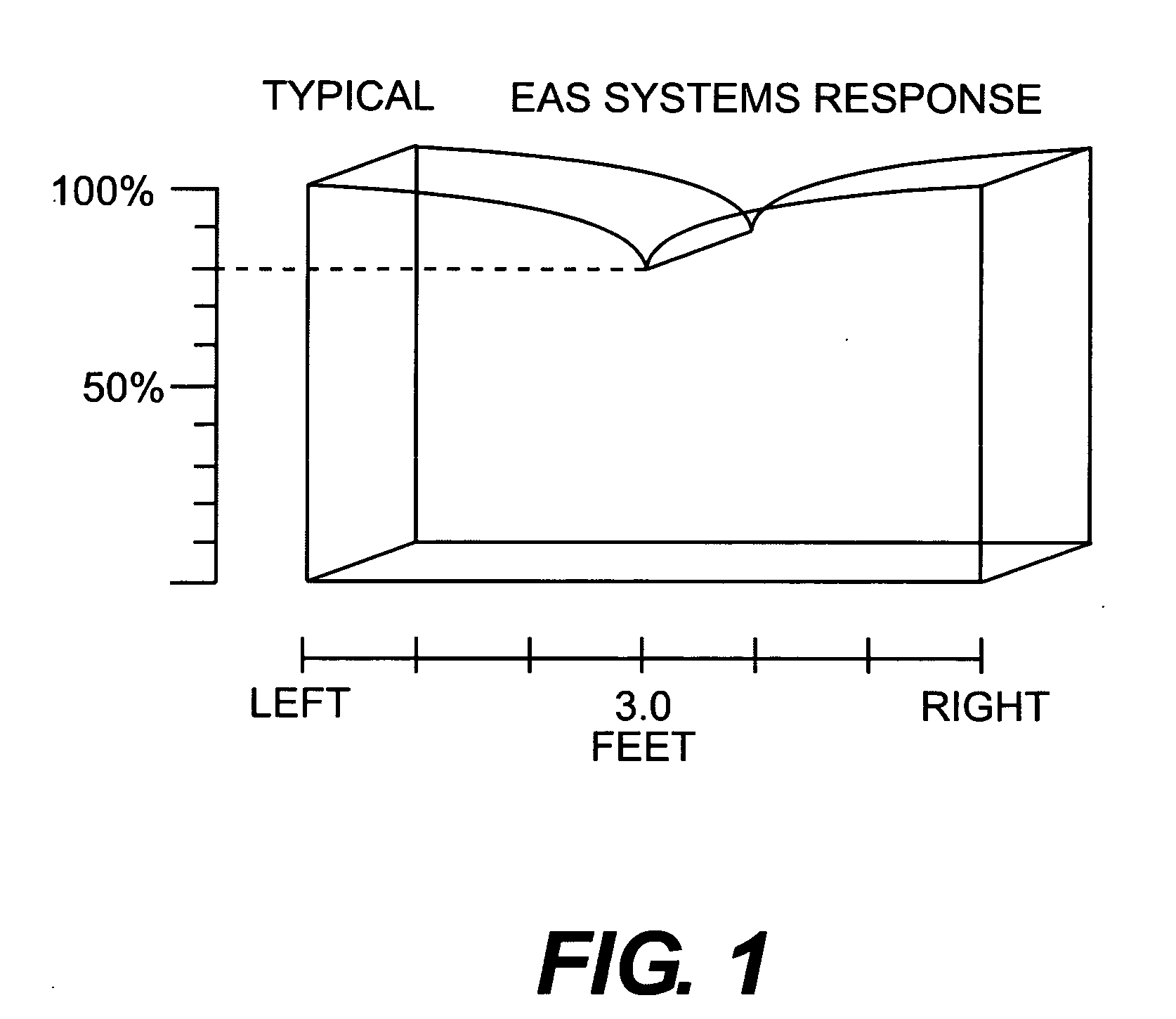
A multiple frequency detection system allows the seamless integration of an almost ideal EAS function with an RFID function. While not being limited to a particular theory, the preferred embodiments integrate EAS technology at, for example, 8.2 MHz or 14 MHz, and RFID technology at, for example, 13.56 MHz in a common antenna package. The use of standard RFID frequencies as forcing functions will allow for the easy packaging of EAS with RFID and have a true roadmap of a scalable technology.
Owner:CHECKPOINT SYST INC
Apparatus and method for measuring weight of an occupying item of a seat
InactiveUS6958451B2Improve performanceReduce crew damageVehicle seatsBelt retractorsAccelerometerRoad surface roughness
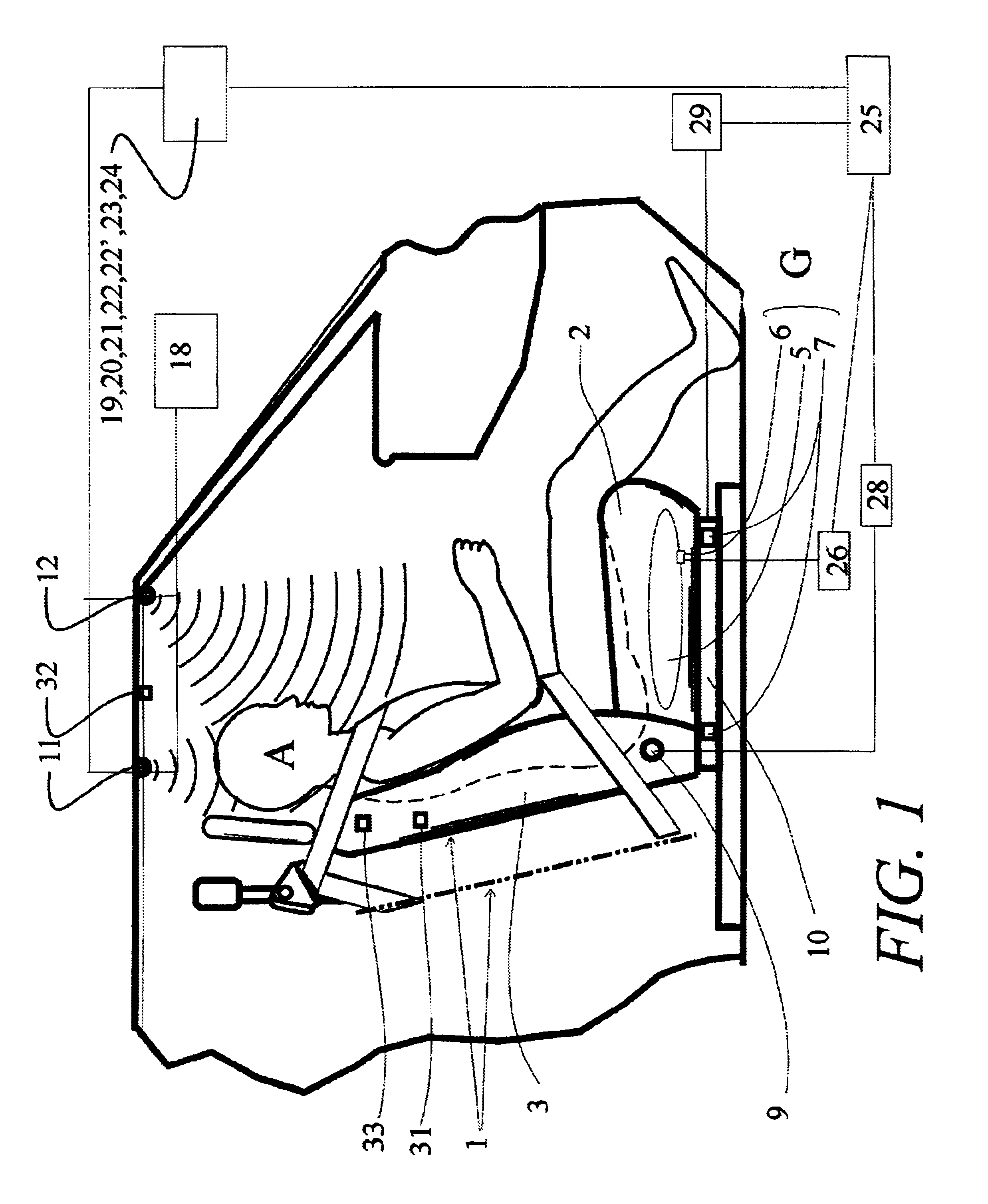
Arrangement and method for determining weight of an occupying item in a seat including one or more weight sensors arranged to obtain a measurement of the force applied to the seat, a forcing function determination arrangement for measuring a forcing function of the seat and a processor coupled to the weight sensor(s) and forcing function determination arrangement for receiving the measurement of the force applied to the weight sensor(s) and the measurement of the forcing function from the forcing function measurement system and determining the weight of the occupying item based thereon. The forcing function determination arrangement may include an accelerometer and measures effects on the seat caused by load of a seatbelt associated with the seat and / or effects on the seat of road roughness, steering maneuvers, and a vehicle suspension system.
Owner:AUTOMOTIVE TECH INT
Ring magnet structure having a coded magnet pattern
InactiveUS7755462B2Electromagnets without armaturesPermanent magnetsMagnetic polarityCondensed matter physics
Field emission structures comprising a plurality of electric or magnetic field sources having magnitudes, polarities, and positions corresponding to a desired spatial force function where a spatial force is created based upon the relative alignment of a field emission structure and a complementary field emission structure. The magnetic field sources may be arranged according to a code having a desired autocorrelation function. Specific exemplary embodiments are described with magnetic field sources arranged in a ring structure. The ring structure may include one or more concentric rings of component magnets. Additional magnets may be included. Magnet polarities and / or spacings may be defined by the code Mechanical constraints may be employed to limit lateral motion. Exemplary codes are described and applied to magnetic field source arrangements. Specific codes found by the inventors are described.
Owner:CORRELATED MAGNETICS RES LLC
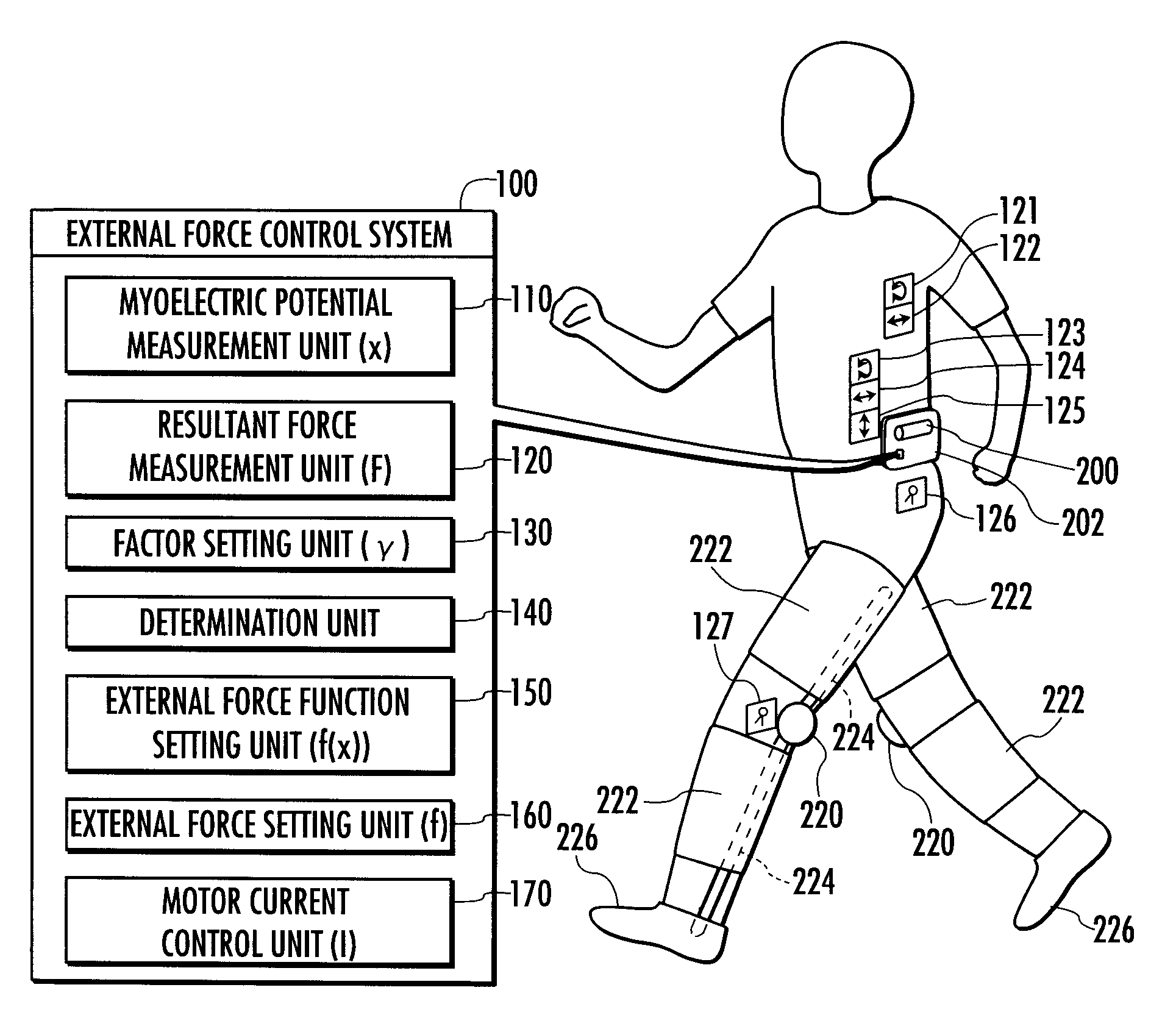
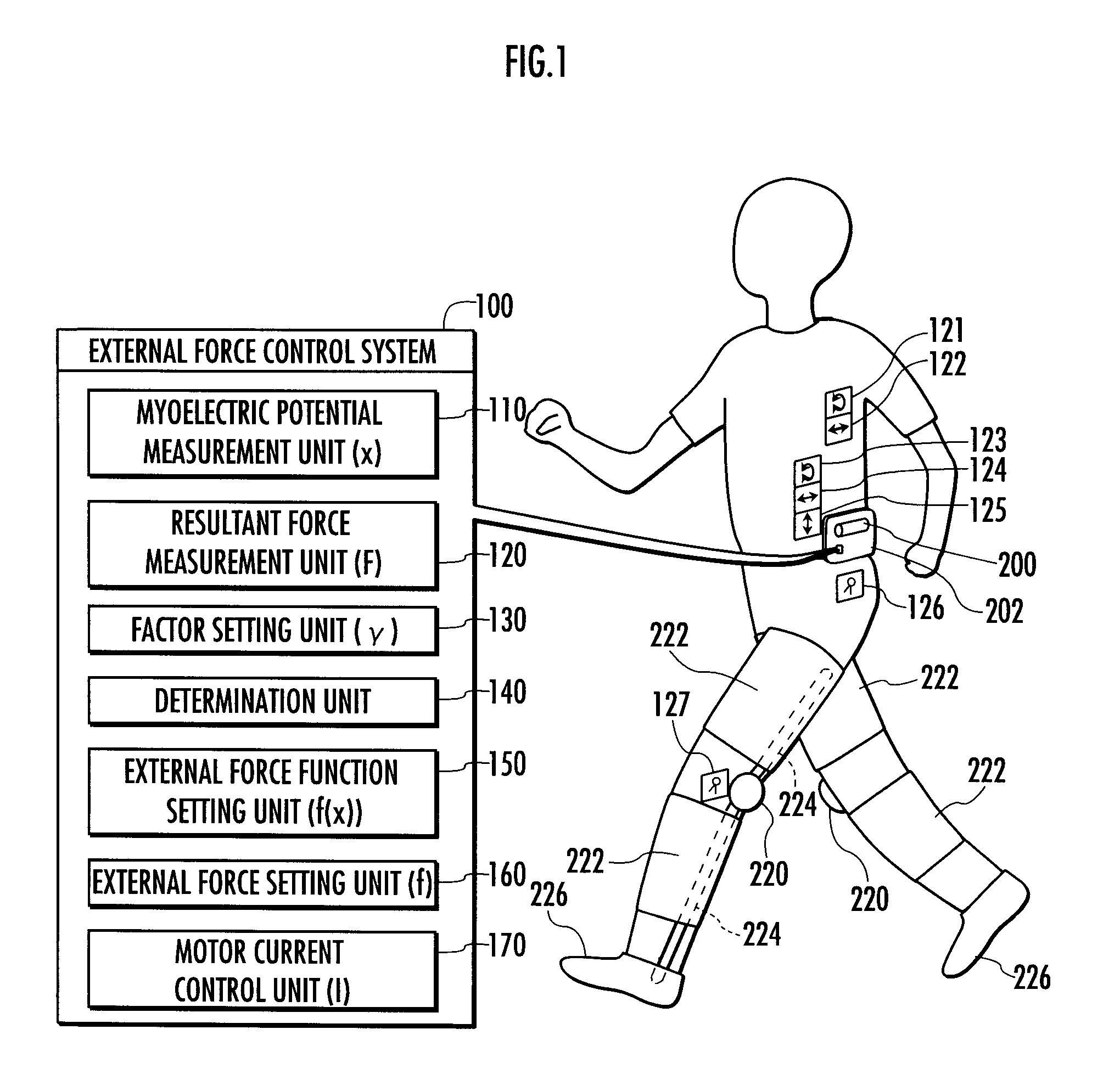
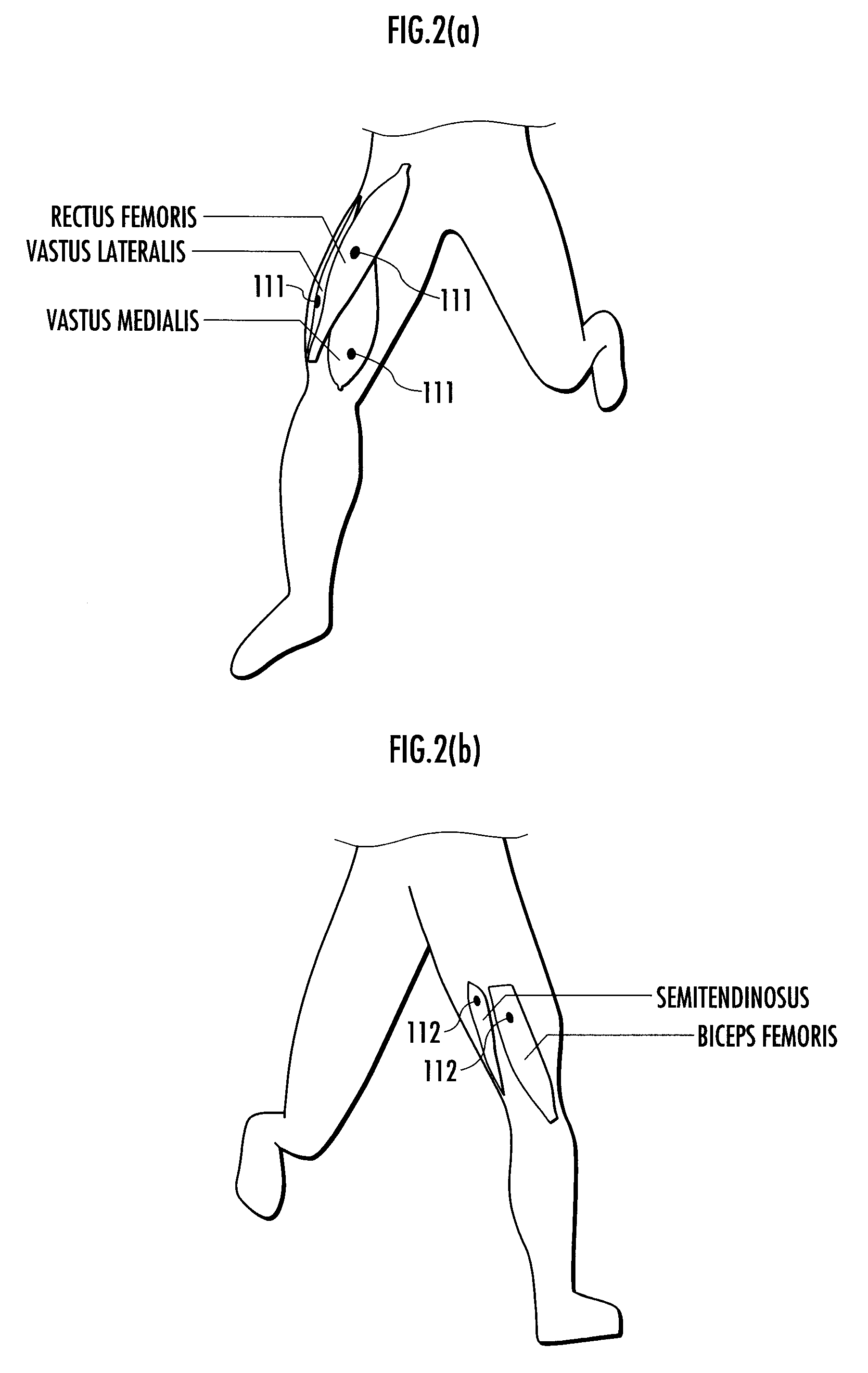
External Force Control Method, External Force Control System and External Force Control Program
A method of controlling an external force applied to an animal to achieve as a target relation the relation between the external force and a motion variable varying with the motion of the animal.A value of an external force f applied to a human leg according to an external force function f(x) on the basis of a measured value of a myoelectric potential x that occurs in the human leg, current I of a motor 220 is controlled according to the set value, and the external force f is applied to the leg through an orthosis 222. A resultant force (the sum of an internal torque and an external torque around a knee joint) F is measured as “a motion variable.” Moreover, a value of a factor γ is set according to a factor function γ(f, F) on the basis of the set value of the external force f and the measured value of the resultant force F. If a deviation δ between the set value of the factor γ and target value γt thereof is equal to or greater than a reference value ε, a new external force function f(x) is set in such a way that the set value of the factor γ approaches the target value γt.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Field emission system and method
Owner:CORRELATED MAGNETICS RES LLC
Field emission system and method
InactiveUS20090273422A1Electromagnets without armaturesPermanent magnetsElectrical polarityElectric field
An improved field emission system and method is provided that involves field emission structures having electric or magnetic field sources. The magnitudes, polarities, and positions of the magnetic or electric field sources are configured to have desirable correlation properties, which may be in accordance with a code. The correlation properties correspond to a desired spatial force function where spatial forces between field emission structures correspond to relative alignment, separation distance, and the spatial force function.
Owner:CORRELATED MAGNETICS RES LLC
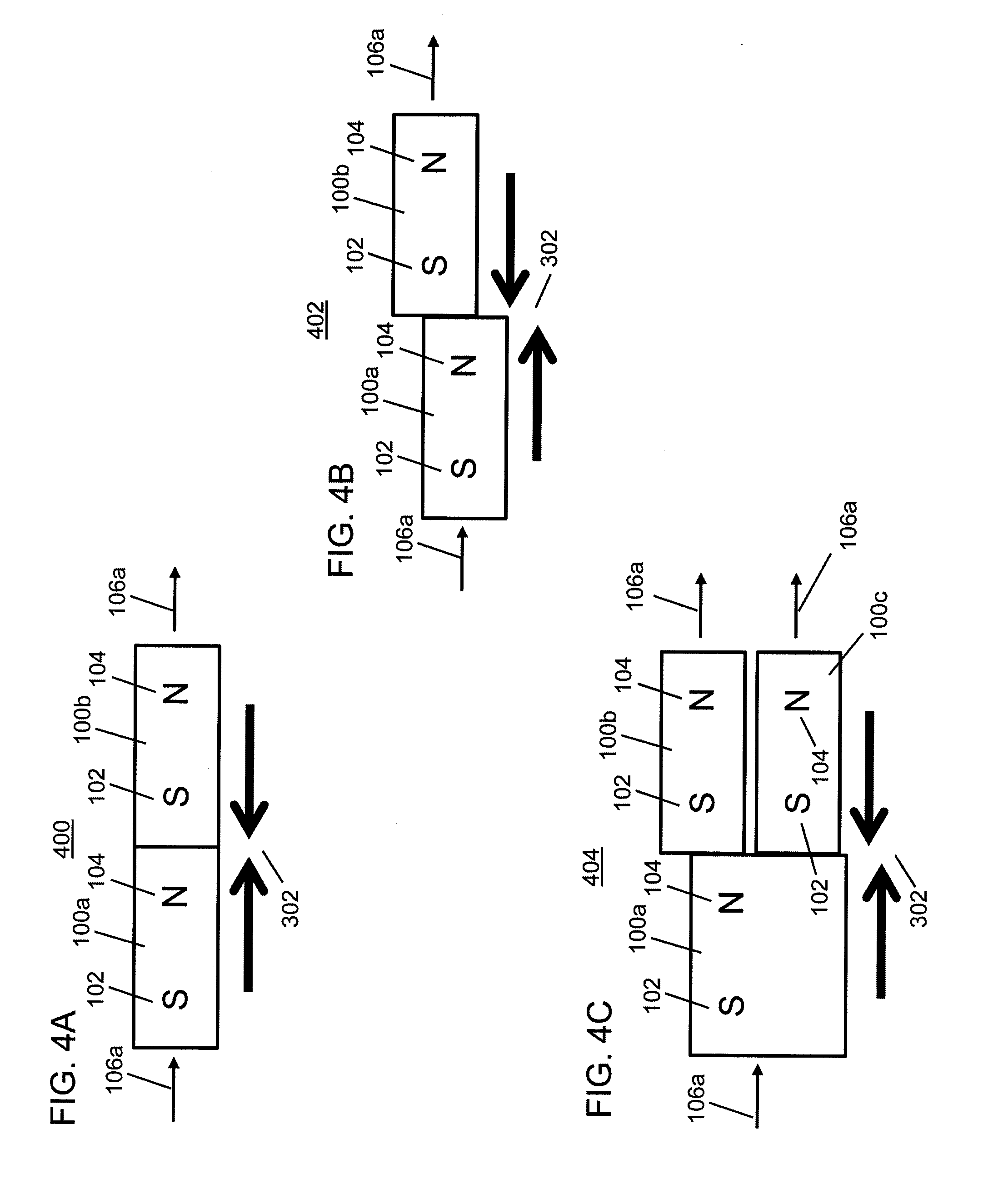
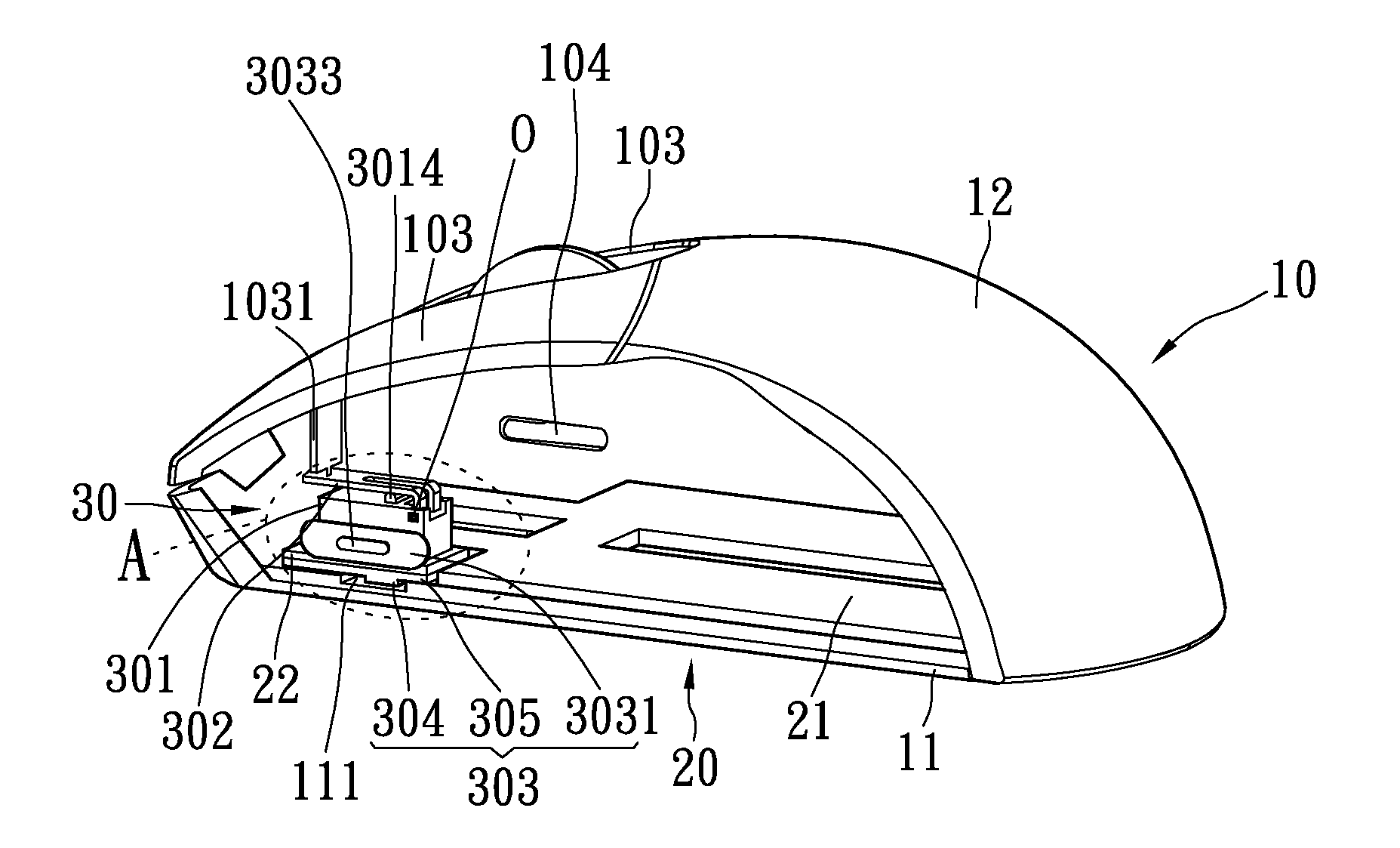
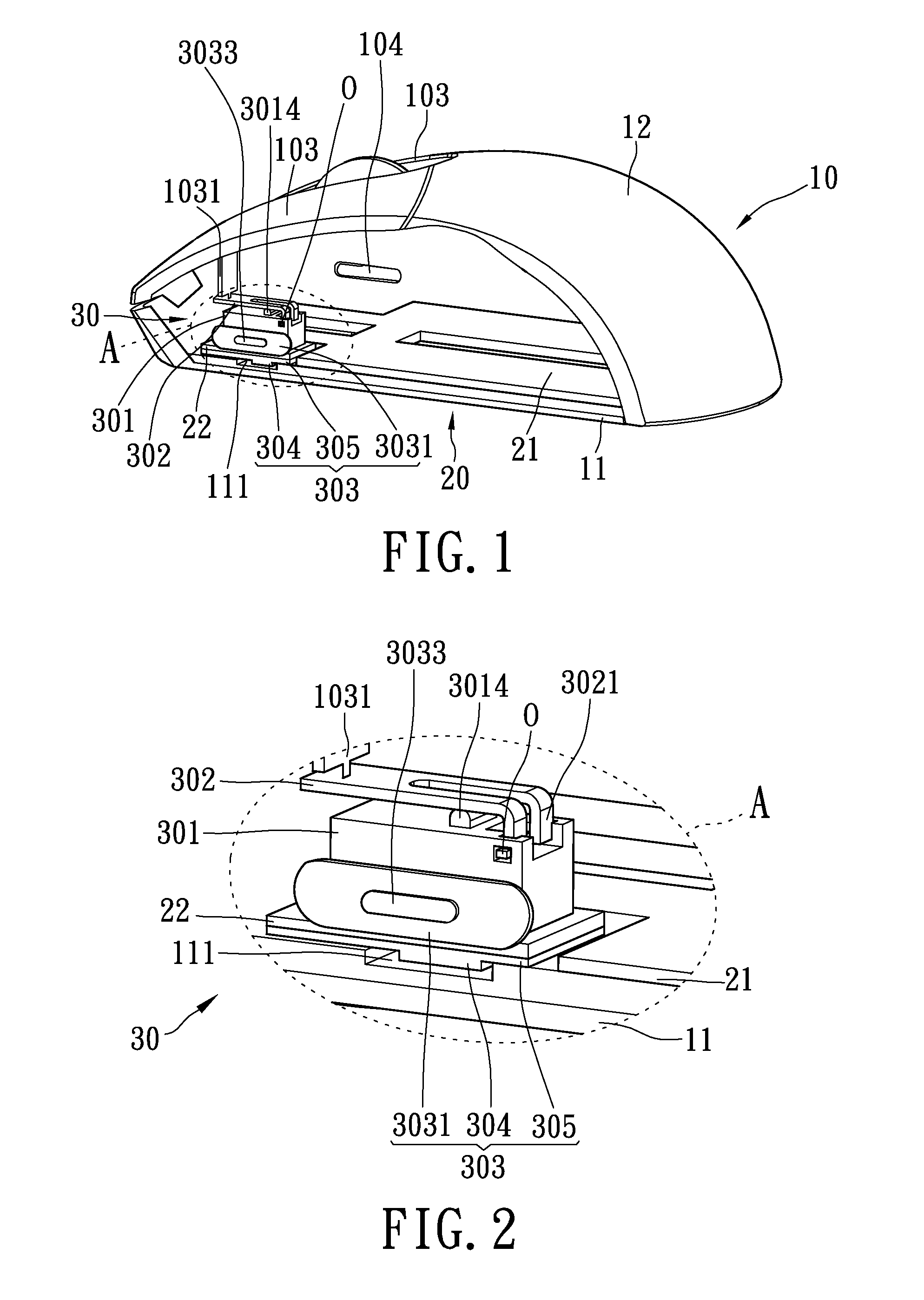
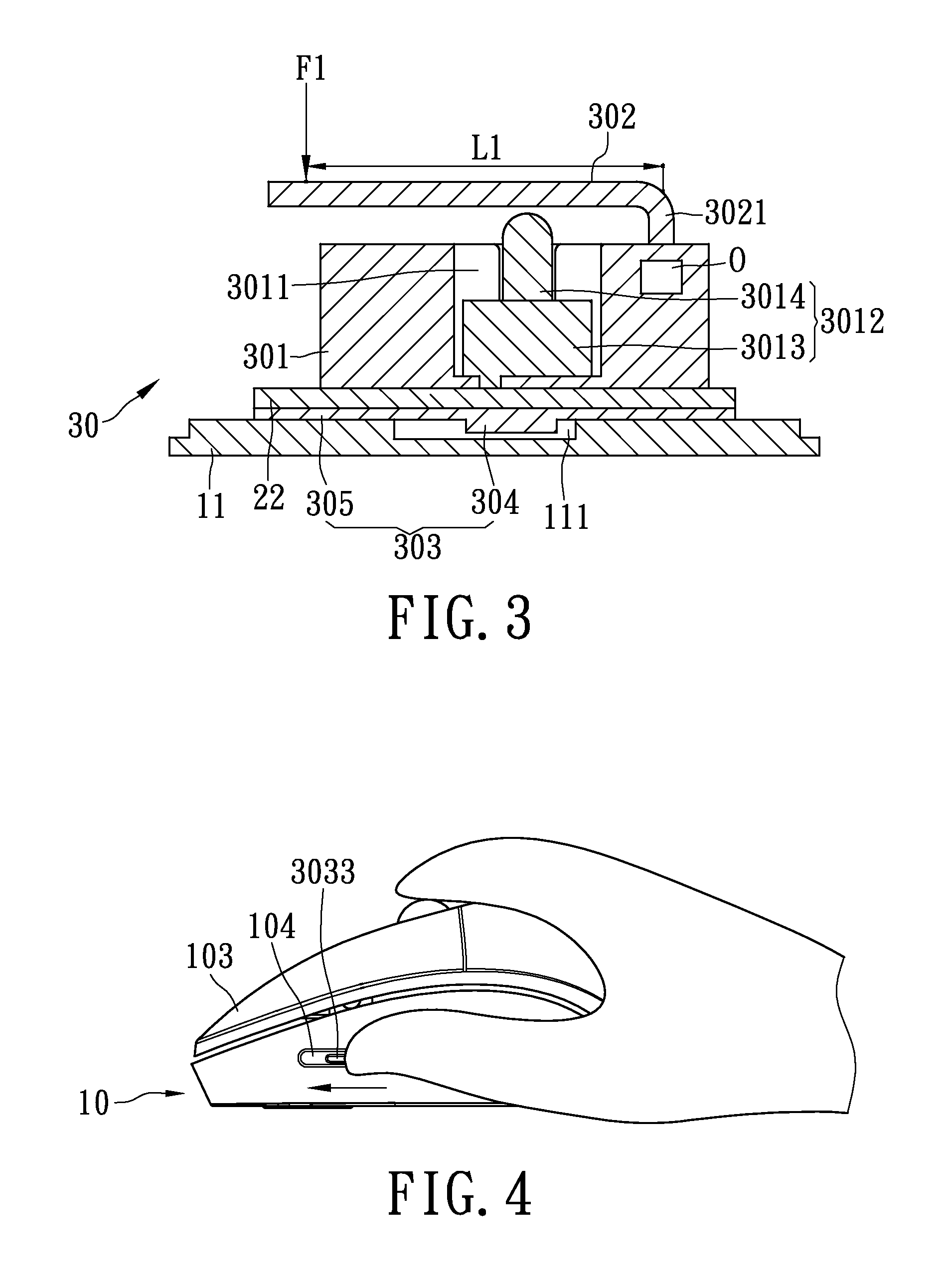
Mouse structure with adjustable clicking force function
InactiveUS20110069008A1Easy to operateEasy to moveCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectric switchesEngineeringForce function
Owner:LITE ON ELECTRONICS (GUANGZHOU) LTD +1
System and method for controlling movement of an object
An improved field emission system and method is provided that involves field emission structures having electric or magnetic field sources. The magnitudes, polarities, and positions of the magnetic or electric field sources are configured to have desirable correlation properties, which may be in accordance with a code. The correlation properties correspond to a desired spatial force function where spatial forces between field emission structures correspond to relative alignment, separation distance, and the spatial force function.
Owner:CORRELATED MAGNETICS RES LLC
Coded linear magnet arrays in two dimensions
Field emission structures comprising electric or magnetic field sources having magnitudes, polarities, and positions corresponding to a desired spatial force function where a spatial force is created based upon the relative alignment of the field emission structures The magnetic field sources may be arranged according to a code having a desired autocorrelation function. In particular, a high peak to sidelobe autocorrelation performance may be found desirable. Specific exemplary embodiments are described having non-parallel linear substructures. The non-parallel linear substructures may use the same or different codes and may have none, one, or more magnets in common. Other embodiments include substructures spaced according to a spacing code. Exemplary spacing codes include, but are not limited to Golomb ruler or Costas array. A polarity code may be applied across the substructures.
Owner:CORRELATED MAGNETICS RES LLC
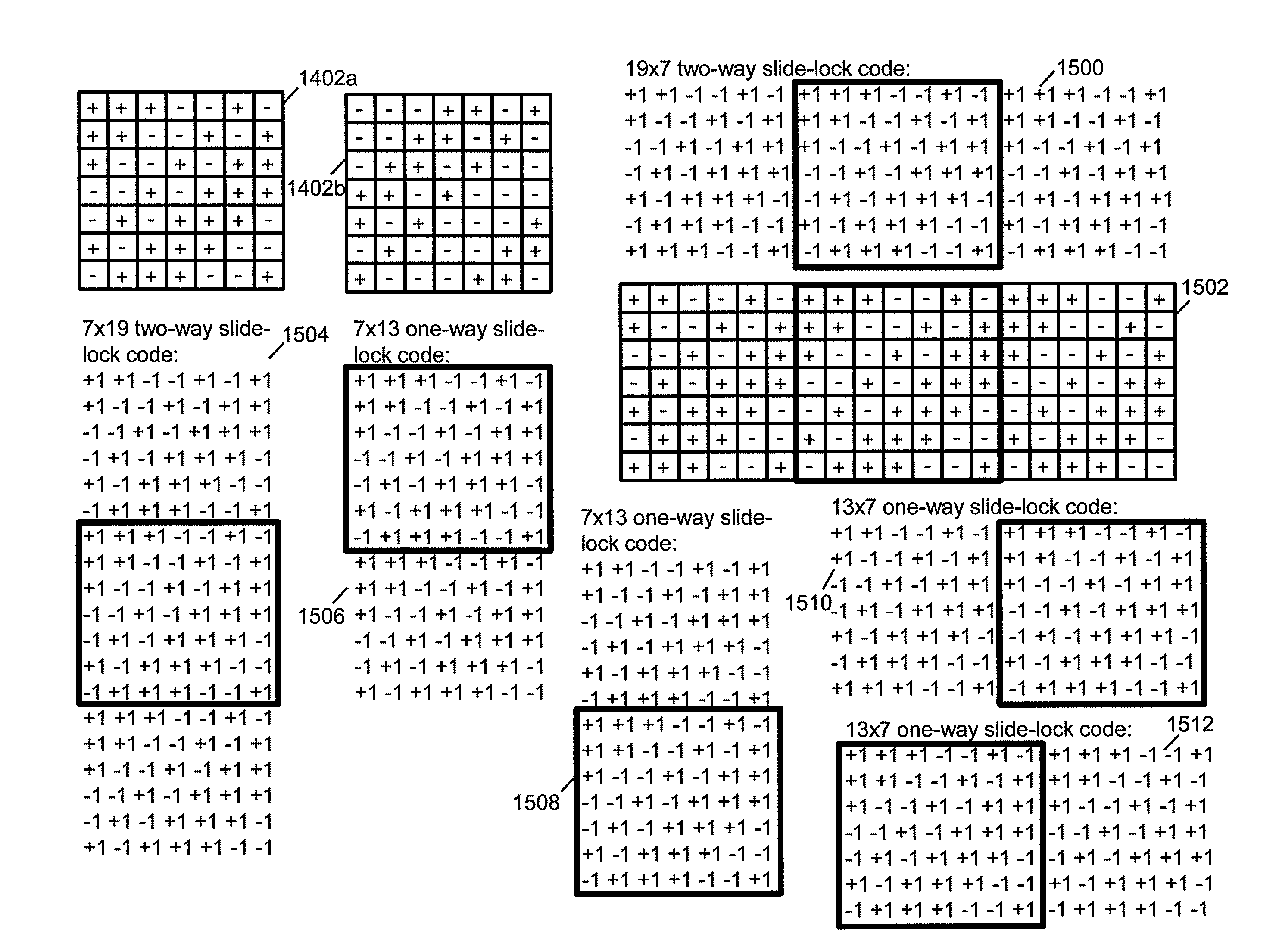
System and method for producing a slide lock mechanism
An improved field emission system and method is provided that involves field emission structures having electric or magnetic field sources. The magnitudes, polarities, and positions of the magnetic or electric field sources are configured to have desirable correlation properties, which may be in accordance with a code. The correlation properties correspond to a desired spatial force function where spatial forces between field emission structures correspond to relative alignment, separation distance, and the spatial force function.
Owner:CORRELATED MAGNETICS RES LLC
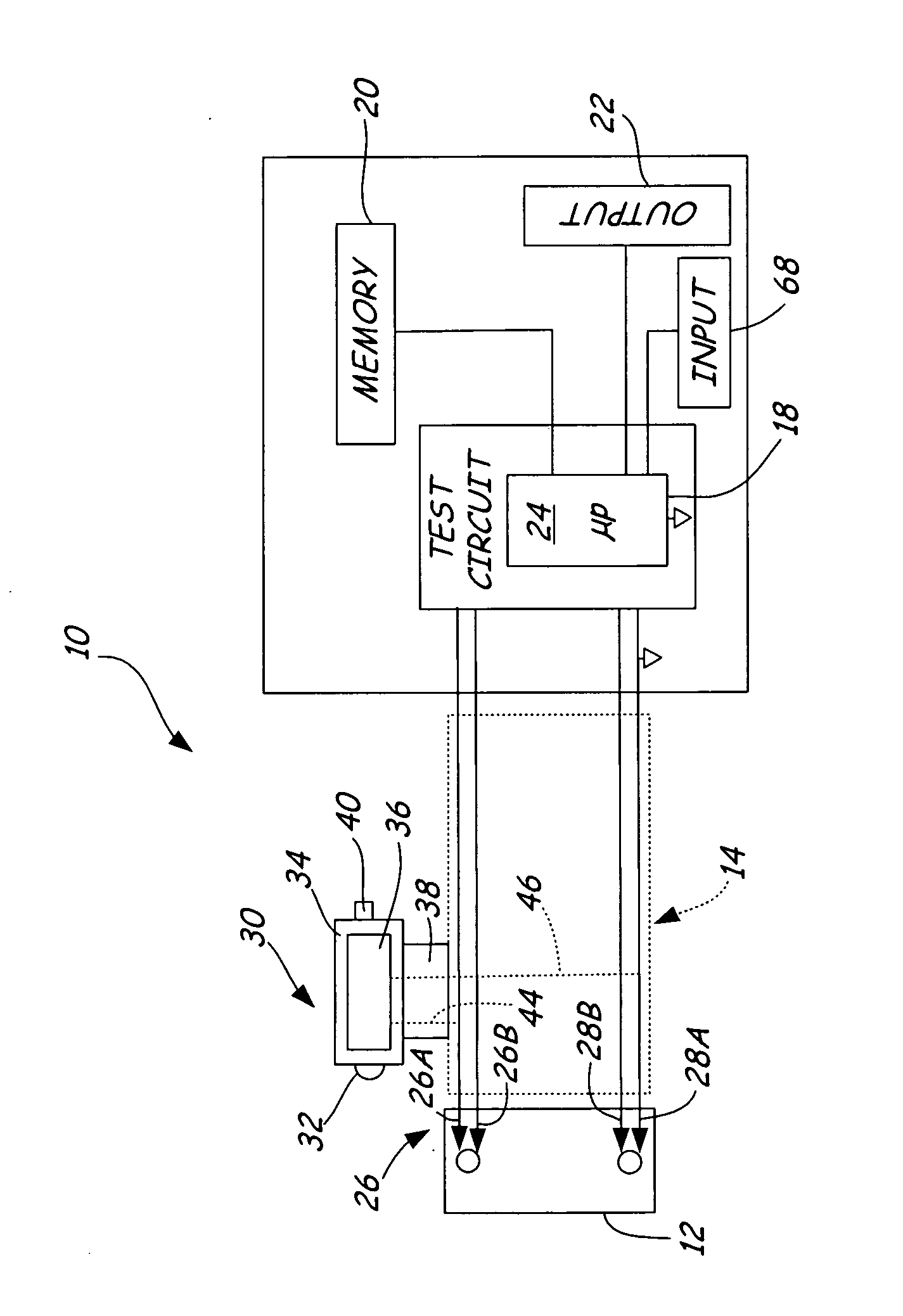
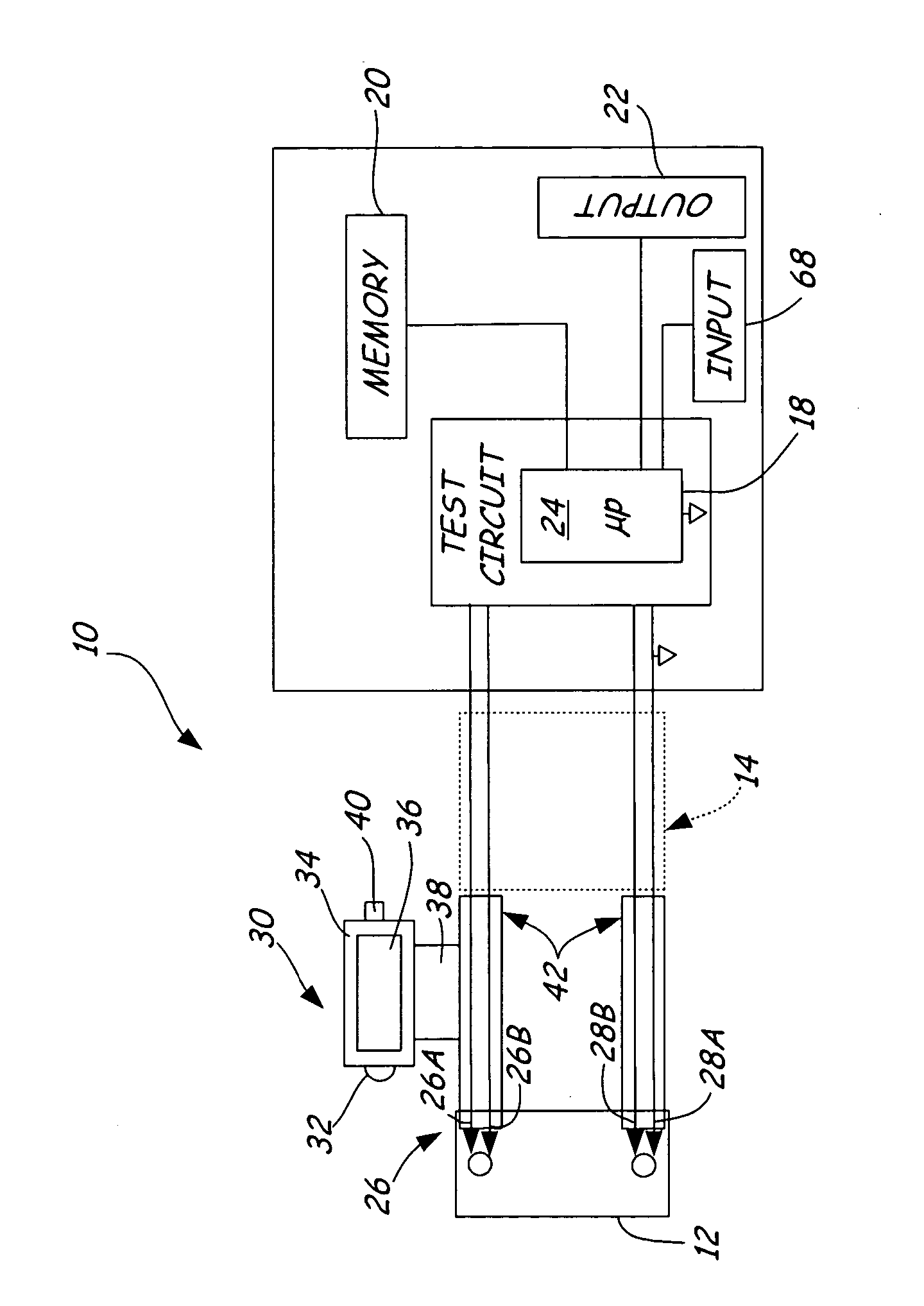
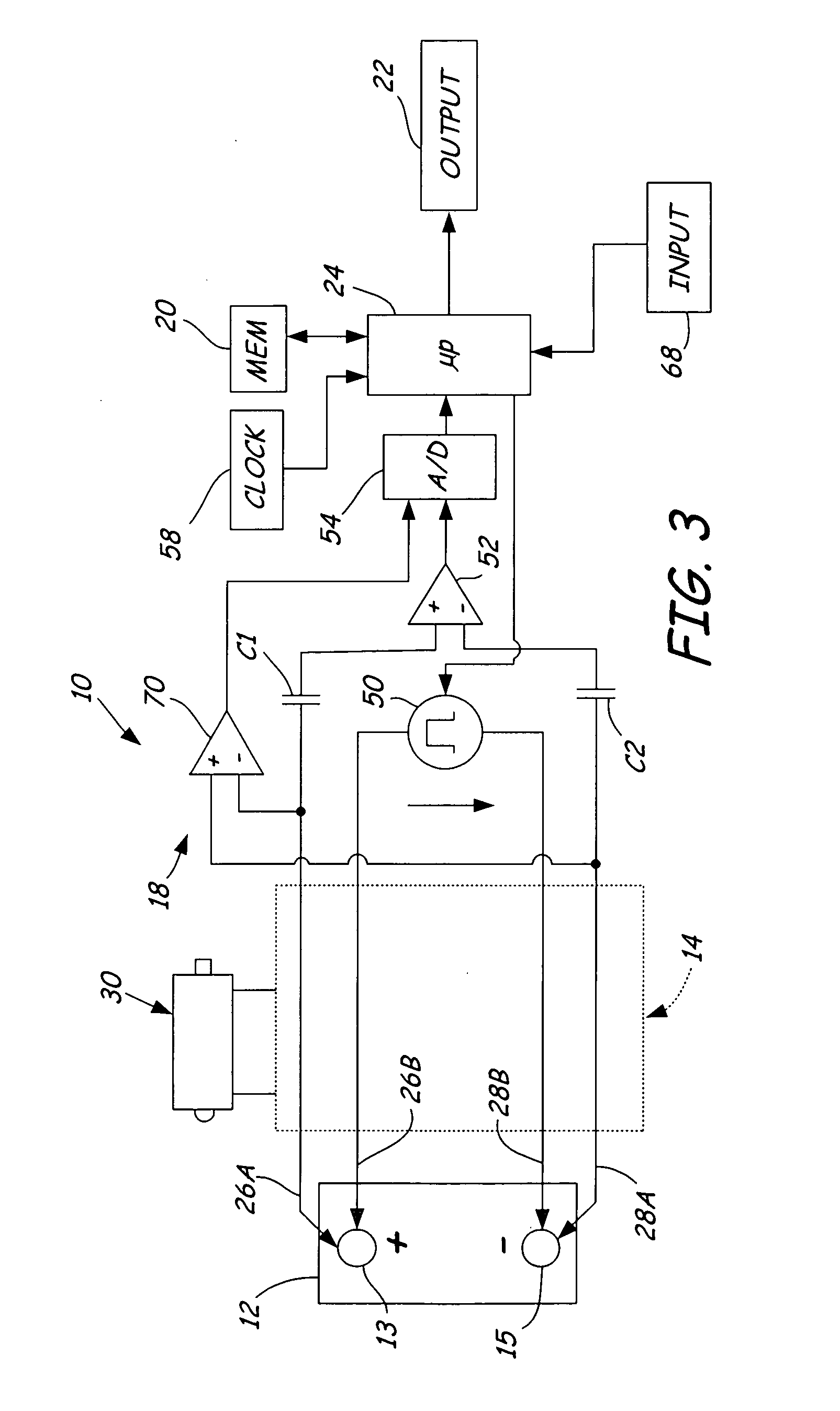
Electronic battery tester with probe light
InactiveUS20050077904A1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical testingTester deviceElectron
An electronic battery tester for testing a storage battery includes first and second Kelvin connections configured to couple to the battery. A forcing function applies a time varying signal to the battery through the first and second Kelvin connections. Further, a probe light is configured to couple to at least one of the first and second Kelvin connections. A microprocessor tests the storage battery as a function of a dynamic parameter measured through the first and second Kelvin connections in response to the applied time varying signal.
Owner:MIDTRONICS
Magnetic attachment system
An improved magnetic attachment system is provided that involves field emission structures having electric or magnetic field sources. The magnitudes, polarities, and positions of the magnetic or electric field sources are configured to have desirable correlation properties, which may be in accordance with a code. The correlation properties correspond to a desired spatial force function where spatial forces between field emission structures correspond to relative alignment, separation distance, and the spatial force function.
Owner:CORRELATED MAGNETICS RES LLC
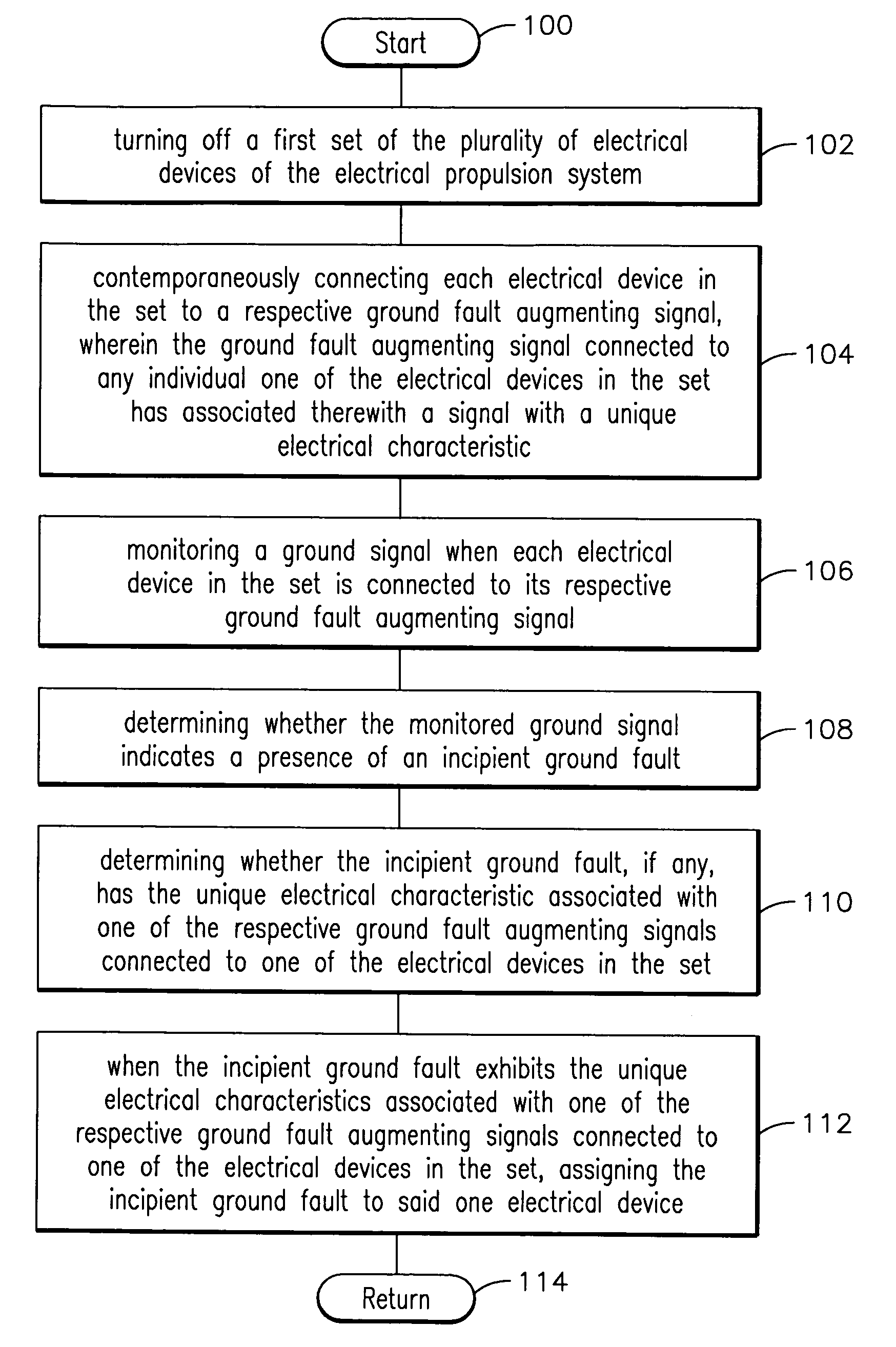
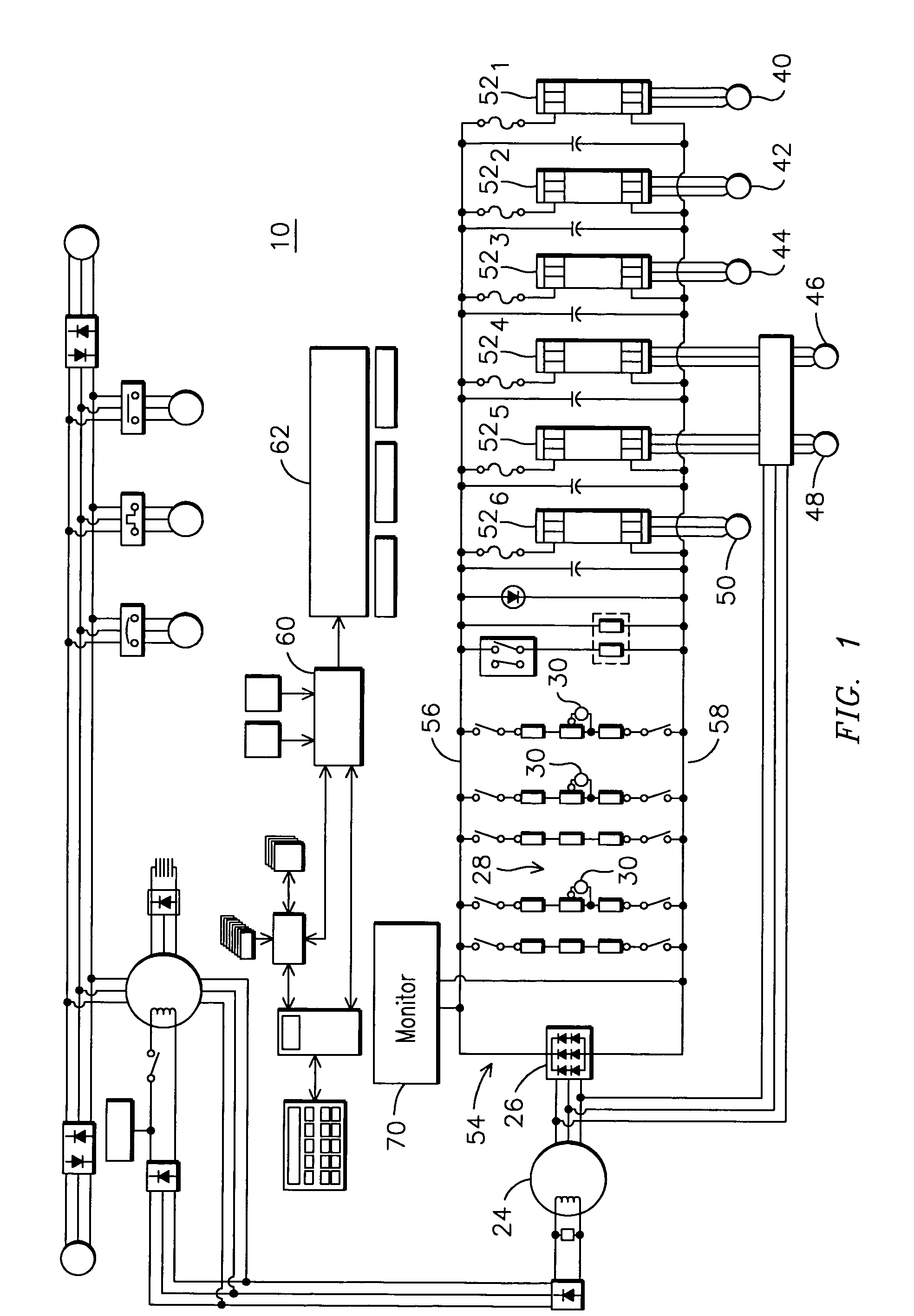
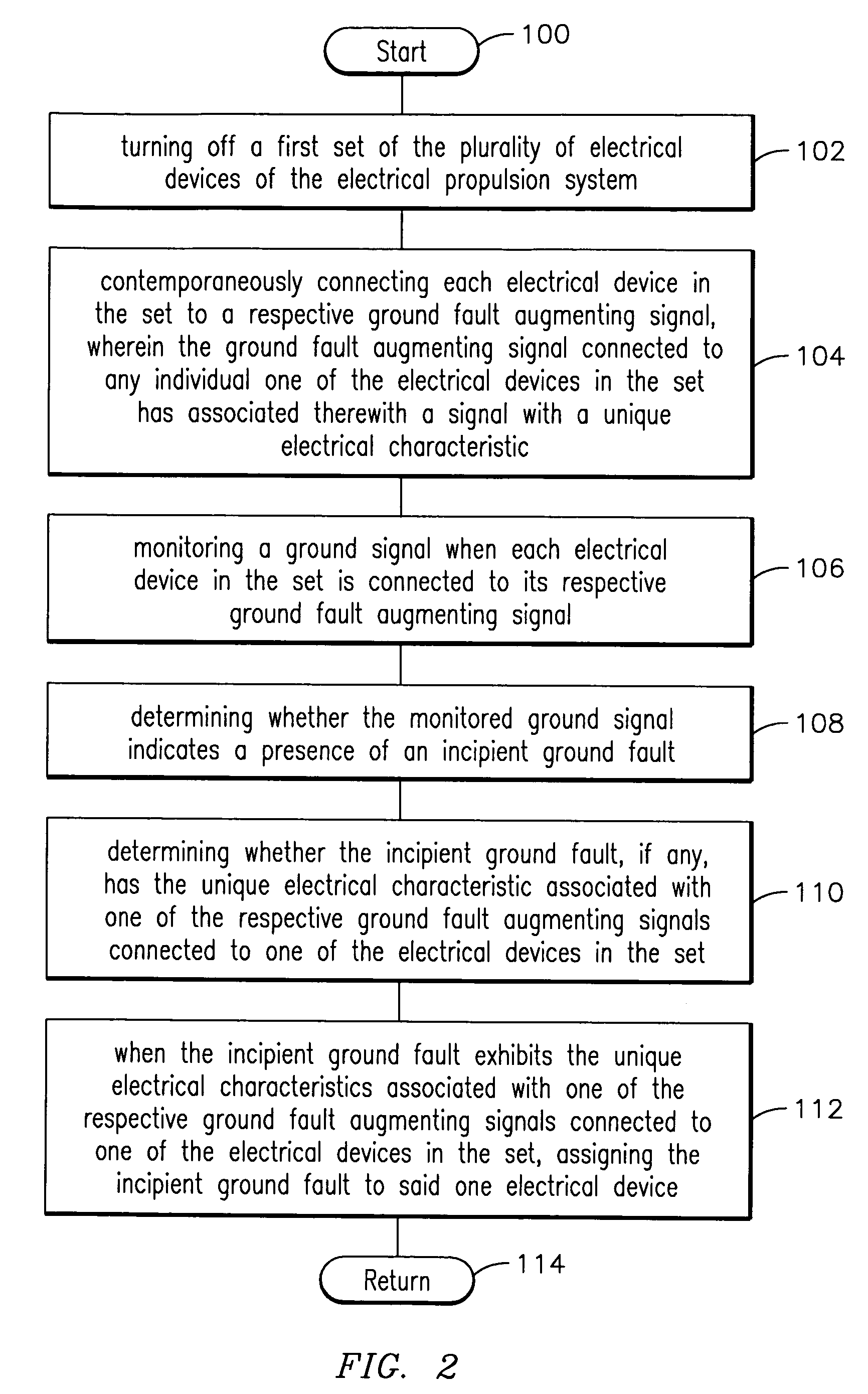
Method, apparatus and computer-readable code for magnifying an incipient ground fault and enable quick detection of such fault
Method, apparatus and computer-readable code are provided for detecting a location of an incipient ground fault in an electrical propulsion system of a relatively large land-based vehicle, such as a locomotive. A method embodying aspects of the present invention allows to simultaneously apply a forcing function to one or more electrical devices connected to a direct current (dc) bus. The forcing function is configured to magnify (without voltage stress to such devices) an incipient ground fault that may be directly associated with a given electrical device. This enables to quickly identify the incipient ground fault and to uniquely identify the electrical device likely to be experiencing the incipient ground fault.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE AIR BRAKE TECH CORP
System and method for affecting field emission properties of a field emission structure
An improved field emission system and method is provided that involves field emission structures having electric or magnetic field sources. The magnitudes, polarities, and positions of the magnetic or electric field sources are configured to have desirable correlation properties, which may be in accordance with a code. The correlation properties correspond to a desired spatial force function where spatial forces between field emission structures correspond to relative alignment, separation distance, and the spatial force function.
Owner:CORRELATED MAGNETICS RES LLC
System and method for producing a hover surface
An improved field emission system and method is provided that involves field emission structures having electric or magnetic field sources. The magnitudes, polarities, and positions of the magnetic or electric field sources are configured to have desirable correlation properties, which may be in accordance with a code. The correlation properties correspond to a desired spatial force function where spatial forces between field emission structures correspond to relative alignment, separation distance, and the spatial force function.
Owner:CORRELATED MAGNETICS RES LLC
Electronic atomizing device and atomizer thereof
ActiveCN110250576AEasy dischargePrevent dry burningTobacco devicesMedical atomisersEngineeringAtmospheric pressure
The invention discloses an electronic atomizing device and an atomizer thereof. The atomizer includes an atomizing assembly, a liquid storage cavity connected with the atomizing assembly in a liquid-leading mode and a mist channel which communicates with the atomizing assembly in an air-leading mode; the atomizer further includes an air-liquid balancing component and an air inlet opening which communicates with the air-liquid balancing component; the air-liquid balancing component includes a liquid storage groove with a capillary force function and an air-returning groove, one end of the air-returning groove communicates with the liquid storage groove, and the other end of the air-returning groove communicates with the air inlet opening; and the air-returning groove communicates with the liquid storage groove, and the liquid storage groove communicates with the liquid storage cavity. According to the atomizer, the air-liquid balancing component is arranged, air pressure in the liquid storage cavity can be balanced, liquid discharging is convenient, the phenomenon of burning to be dried is prevented, and at the same time, the problem that liquid leakage caused by unbalance of the air pressure is prevented.
Owner:SHENZHEN SMOORE TECH LTD
System and method for producing a spatial force
An improved field emission system and method is provided that involves field emission structures having electric or magnetic field sources. The magnitudes, polarities, and positions of the magnetic or electric field sources are configured to have desirable correlation properties, which may be in accordance with a code. The correlation properties correspond to a desired spatial force function where spatial forces between field emission structures correspond to relative alignment, separation distance, and the spatial force function.
Owner:CORRELATED MAGNETICS RES LLC
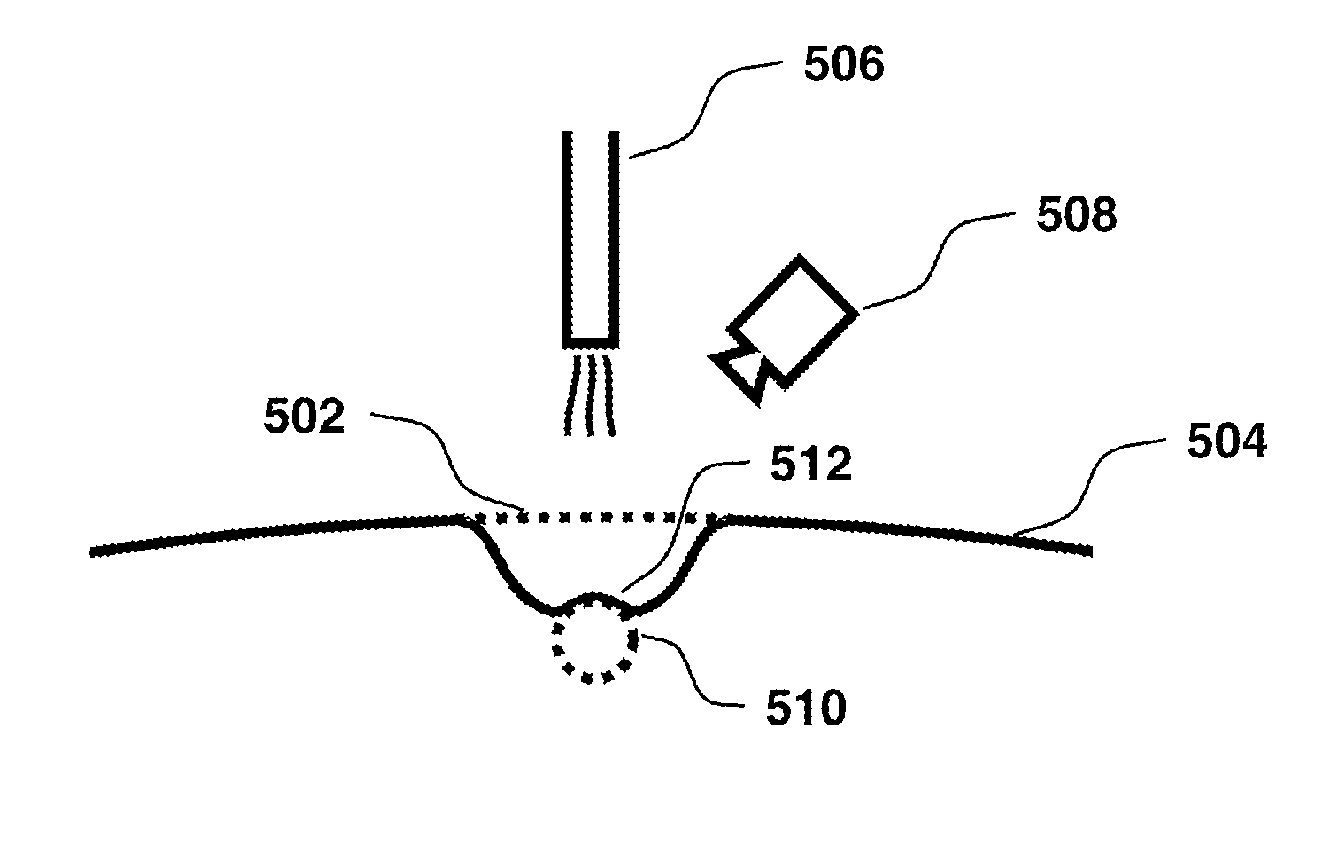
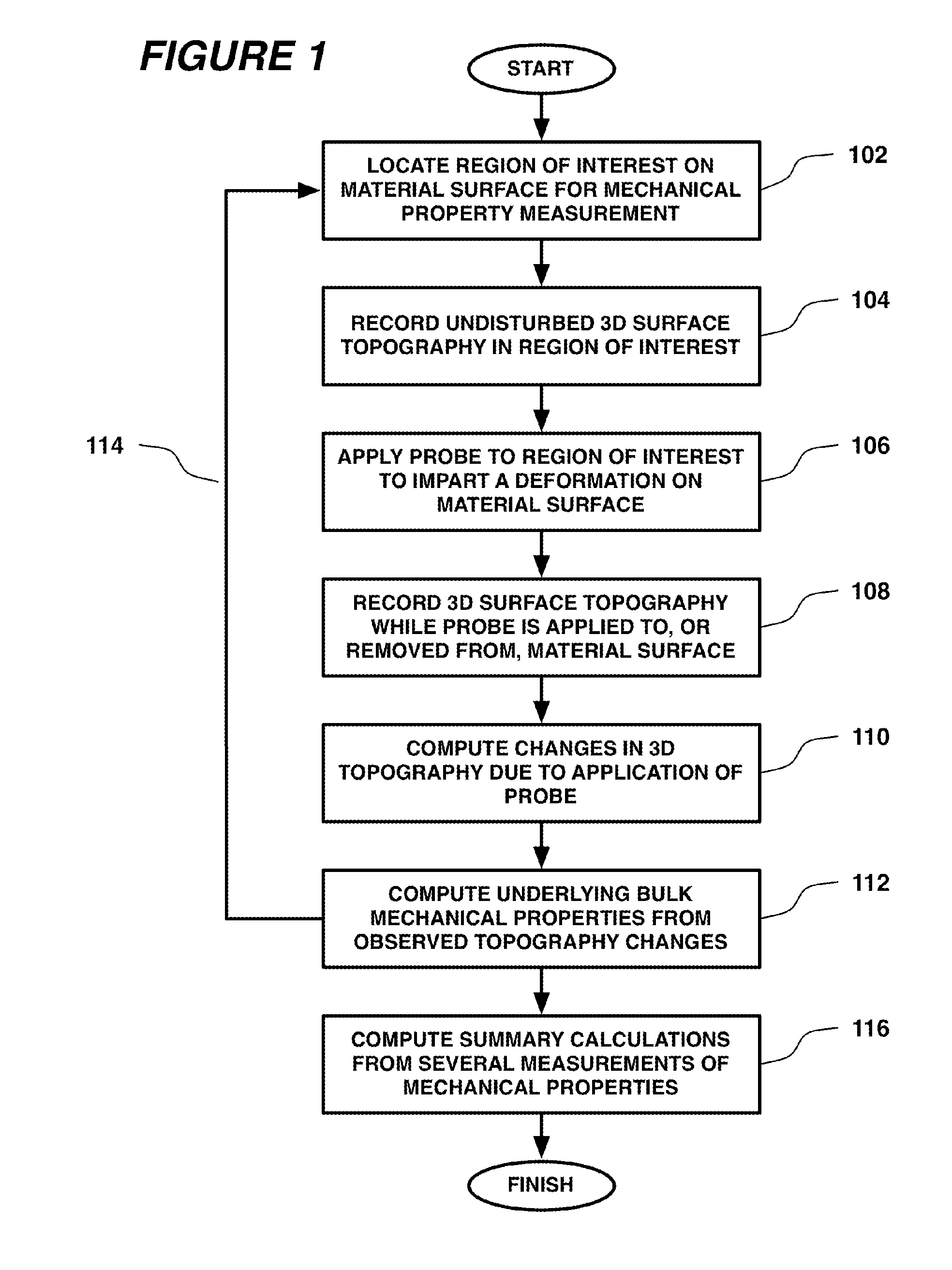
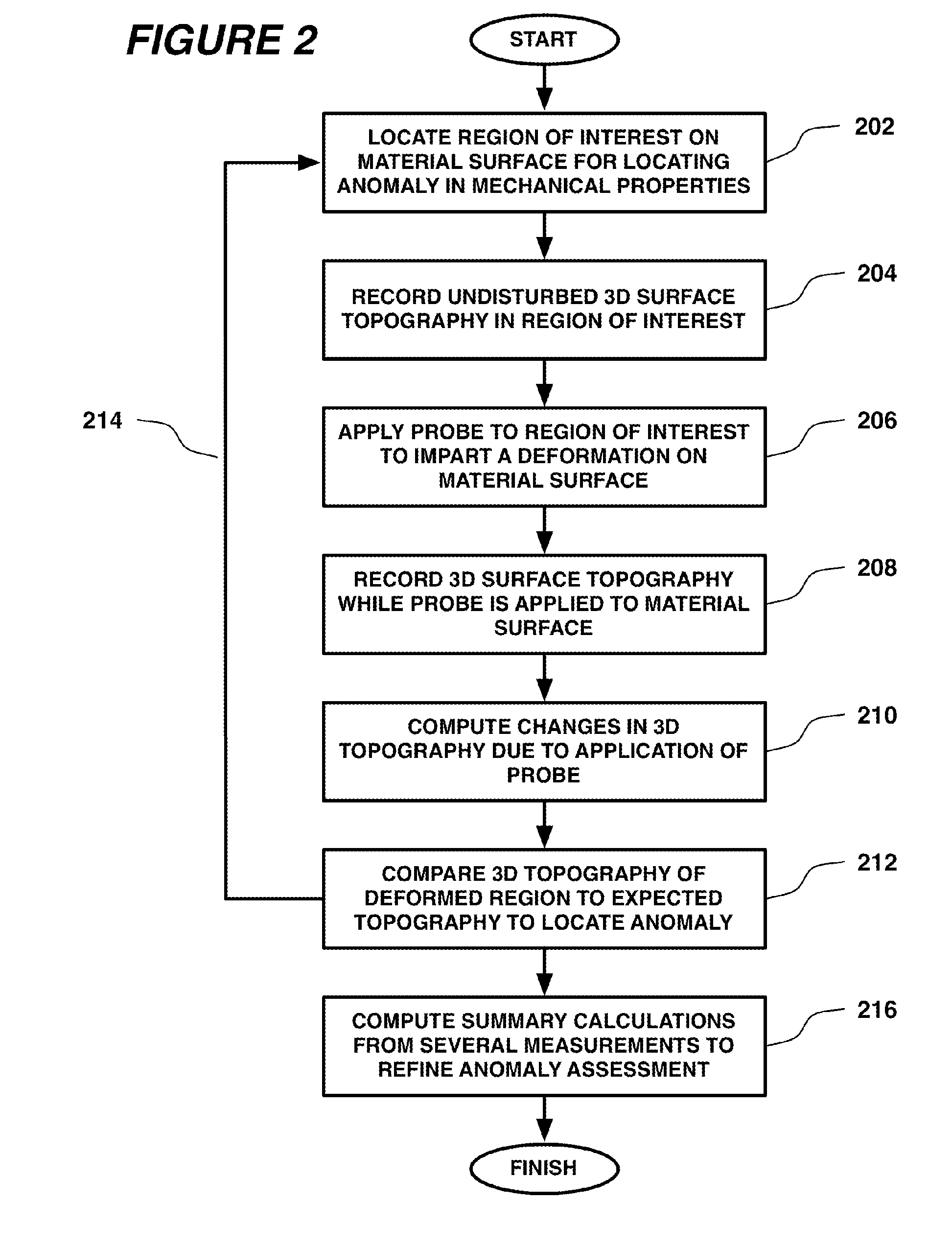
Systems and Methods for Measuring Mechanical Properties of Deformable Materials
ActiveUS20110319791A1Minimum of operator manipulationAddressing slow performanceDiagnostics using pressurePerson identificationLiquid jetEngineering
Systems and methods deform the surface of the material with a probe, such as a mechanical device or a gas / liquid jet, while optically recording in detail the three-dimensional (3D) topography of the resulting surface deformation. The probe effectively applies a forcing function to the material, the attributes of which are known by performing calibrations prior to use or by direct measurement while it is applied. The topography is effectively the system output that is measured as indicative of the underlying mechanical properties of the material. In one application, systems and methods that apply a pressure in-vivo to human tissue and analyze a three-dimensional topography of the resulting surface deformation to identify localized inhomogeneities and anomalies in the human tissue.
Owner:PHOTON +1
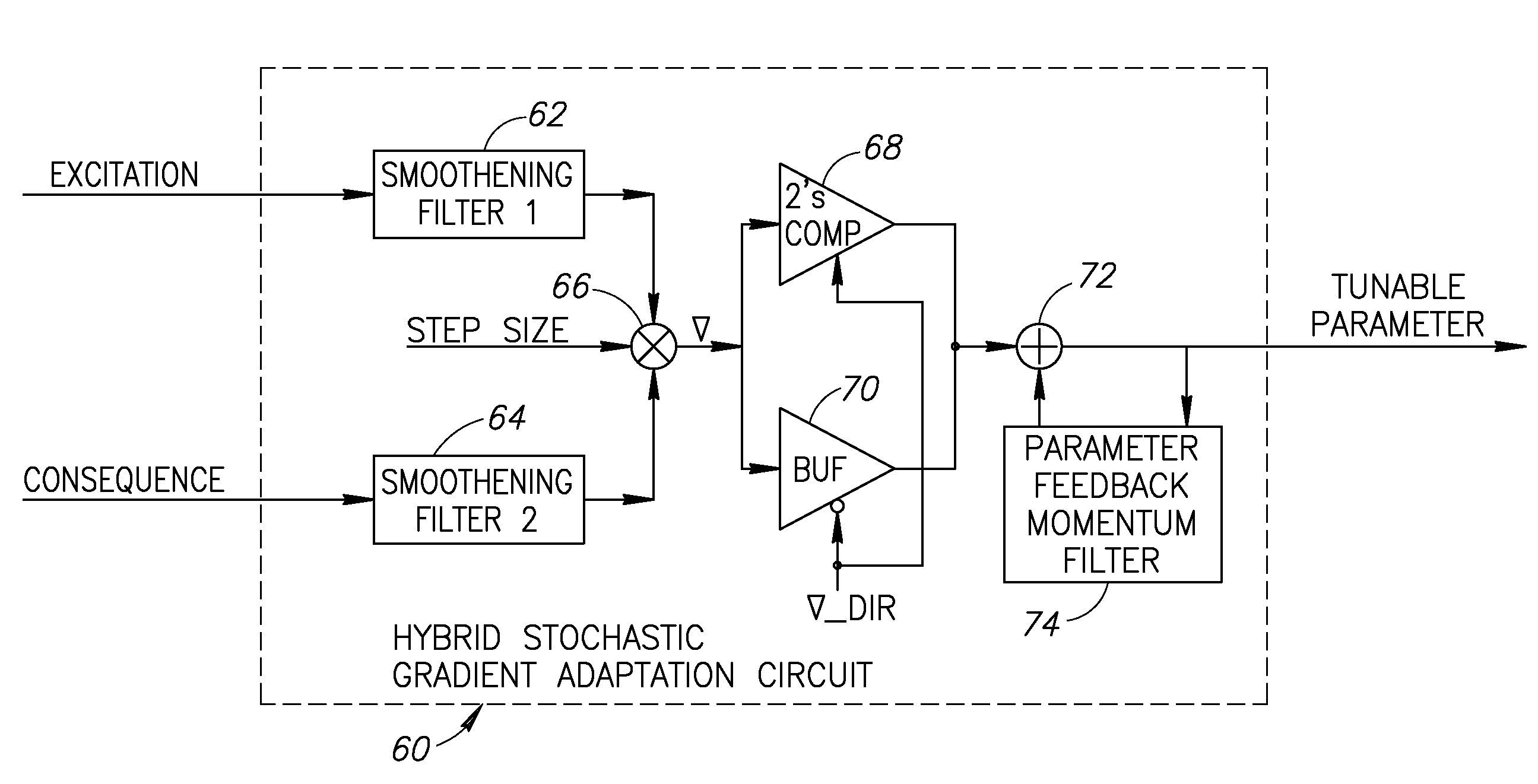
Hybrid stochastic gradient based digitally controlled oscillator gain KDCO estimation
ActiveUS7365609B2Tighter convergenceGood estimatePulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsMomentumDigital controlled oscillator
A novel hybrid stochastic gradient adaptation apparatus and method for calibrating the gain of an RF or non-RF digitally controlled oscillator (DCO). The adaptation algorithm determines a true stochastic gradient between a forcing function and its corresponding system measure to estimate the system parameters being adapted. A momentum term is generated and injected into the adaptation algorithm in order to stabilize the algorithm by adding inertia against any large transient variations in the input data. In the case of adaptation of DCO gain KDCO, the algorithm determines the stochastic gradient between time varying calibration or actual modulation data and the raw phase error accumulated in an all digital phase locked loop (ADPLL). Two filters preprocess the observable data to limit the bandwidth of the computed stochastic gradient providing a trade-off between sensitivity and settling time.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Disposable diaper
A diaper is provided in a transverse middle of a crotch region with a pad seat formed from top- and backsheets. The pad seat has a pair of extensions bifurcated from a rear end of the pad seat toward respective tape fasteners. In the course of wearing the diaper as well as during use of the diaper, a tensile force functioning to pull side flaps outward as viewed in a transverse direction of the article is transmitted to the respective extensions and pulls the pad seat so that the pad seat may be tightened so as to press a pad laid in the pad seat against the wearer's skin.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
Ring Magnet Structure Having A Coded Magnet Pattern
InactiveUS20090295521A1Electromagnets without armaturesPermanent magnetsMagnetic polarityCondensed matter physics
Field emission structures comprising a plurality of electric or magnetic field sources having magnitudes, polarities, and positions corresponding to a desired spatial force function where a spatial force is created based upon the relative alignment of a field emission structure and a complementary field emission structure. The magnetic field sources may be arranged according to a code having a desired autocorrelation function. Specific exemplary embodiments are described with magnetic field sources arranged in a ring structure. The ring structure may include one or more concentric rings of component magnets. Additional magnets may be included. Magnet polarities and / or spacings may be defined by the code Mechanical constraints may be employed to limit lateral motion. Exemplary codes are described and applied to magnetic field source arrangements. Specific codes found by the inventors are described.
Owner:CORRELATED MAGNETICS RES LLC
Gyromagnet treatment system based on magnetic nanoparticles
InactiveCN102814004AIncrease the magnetic field strengthHigh strengthMagnetotherapy using variable magnetic fieldsPatient needMagnetite Nanoparticles
The invention discloses a gyromagnet treatment system based on magnetic nanoparticles. The gyromagnet treatment system comprises the magnetic nanoparticles, n groups of magnetic field loading systems, a treatment table and a frame, wherein the treatment table is horizontally placed, the magnetic nanoparticles are injected in a body to be treated on the treatment table, the n groups of magnetic field loading systems are arranged on the frame in a mode of being opposite to or surrounding the treatment table, and the n is a natural number. The magnetic nanoparticles serve as a treating target to be directly injected in the body to be treated of an animal or a patient needing treating, the magnetic nanoparticles can form aggregation at a focus in the body through modification of surface specificity, and cancer cells are killed through hyperpyrexia under an alternating magnetic field and force functions on cells and tissues to achieve therapeutic effects. The gyromagnet treatment system is explicit in magnetic field function target, explicit in therapeutic mechanism, and capable of conducting quantitative analysis on the therapeutic effects.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
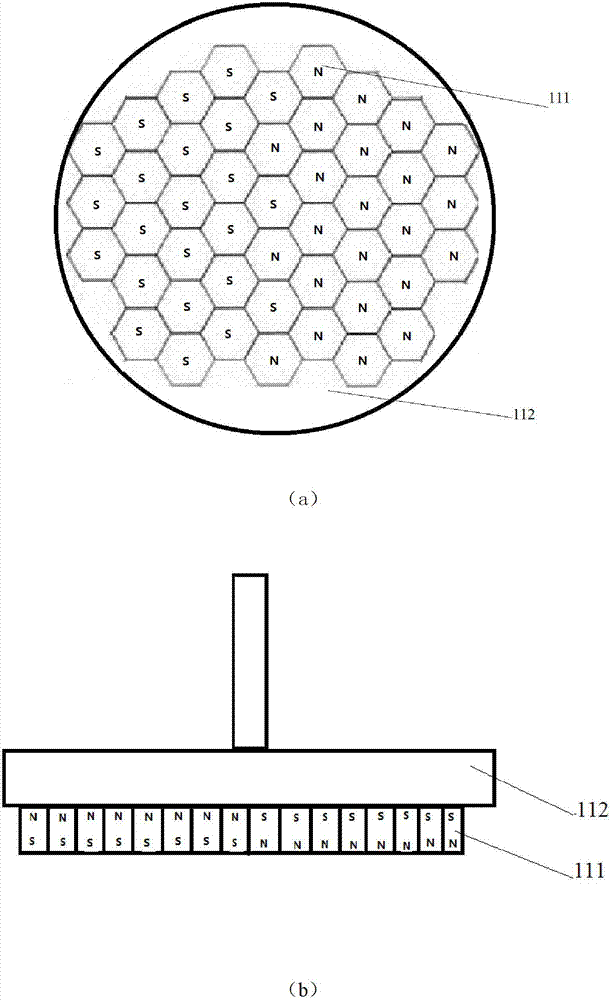
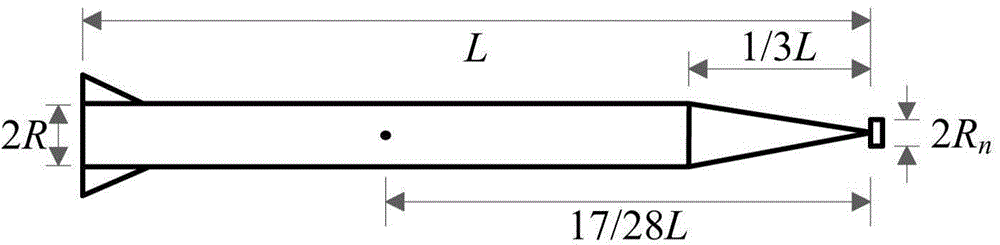
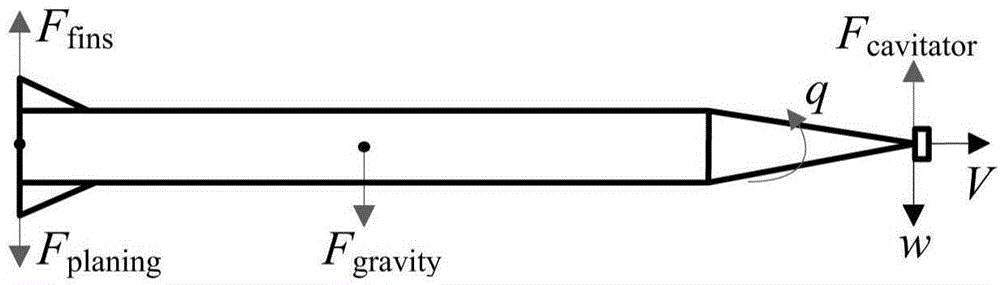
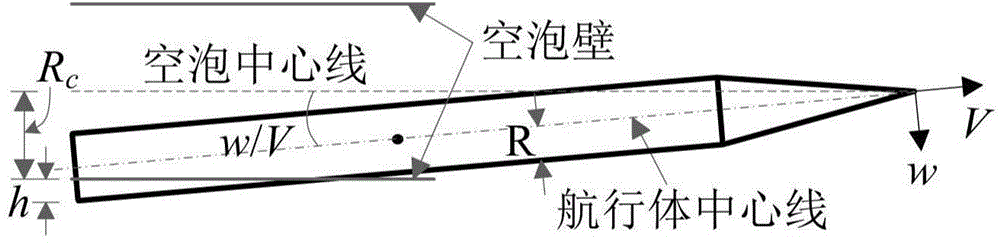
Piecewise linear method for analyzing supercavitation navigation body kinetic characteristics
InactiveCN103558009AConcise parsing expressionEasy to parseHydrodynamic testingLinearizationLinear fitting
A piecewise linear method for analyzing supercavitation navigation body kinetic characteristics includes the steps that step1, a supercavitation navigation body kinetic model is built; step2, piecewise linear fitting is performed on a non-linear sliding force function in the supercavitation navigation body kinetic model to obtain a linear sliding force function; step3, parameters of the supercavitation kinetic model are set; step4, the supercavitation kinetic model with the piecewise linear sliding force Fp function is adopted for obtaining a sole balance point of a supercavitation navigation body, linearization is performed on a system at the balance point to obtain a jacobian matrix of the system and a characteristic equation at the balance point, characteristic values of the system are obtained, and the balance point of the system is judged to be an unstable saddle focus. By the adoption of the piecewise linearization of the sliding force function, the supercavitation navigation body kinetic model is simplified, so that the balance point position and stability conditions of the model have concise analytical expressions, and the supercavitation navigation body kinetic characteristics are analyzed more conveniently.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Nanometer oxide ceramic purification and adsorption material with decomposition and bactericidal performance
InactiveCN103537255AImprove protectionKeep healthyBiocideOther chemical processesOxide ceramicHigh concentration
Owner:王泽辉
Electronic device having force touch function
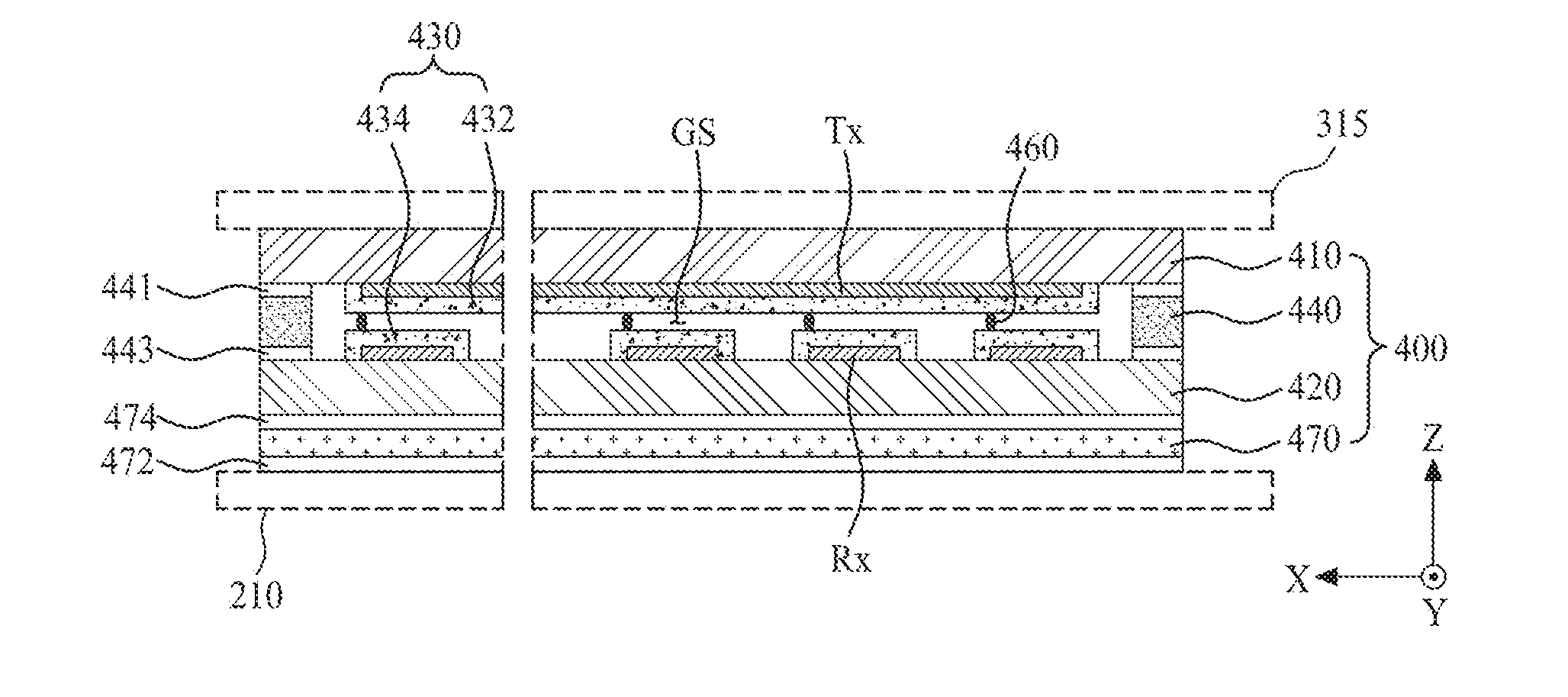
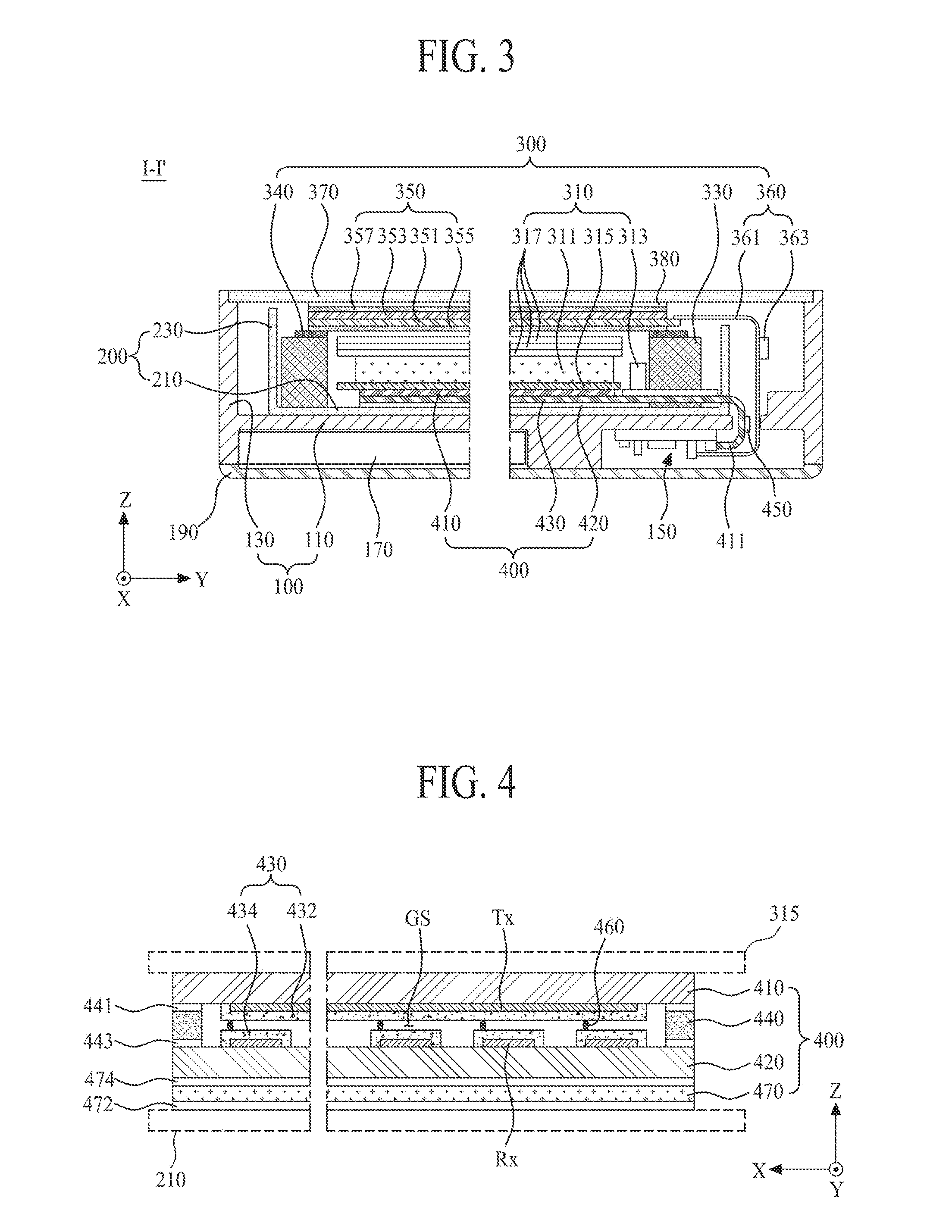
ActiveUS20170003782A1Improve heat radiation efficiencyQuality improvementMechanical apparatusLight guides for lighting systemsComputer moduleEngineering
An electronic device has a force touch function which is capable of minimizing a degradation of picture quality, wherein the electronic device may include a housing having a receiving space, an image display module disposed in the receiving space, and a force sensing panel disposed between a bottom surface of the housing and the image display module, which enables a user's force touch to be sensed through the force sensing panel, and to minimize a degradation of picture quality caused by heat.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com