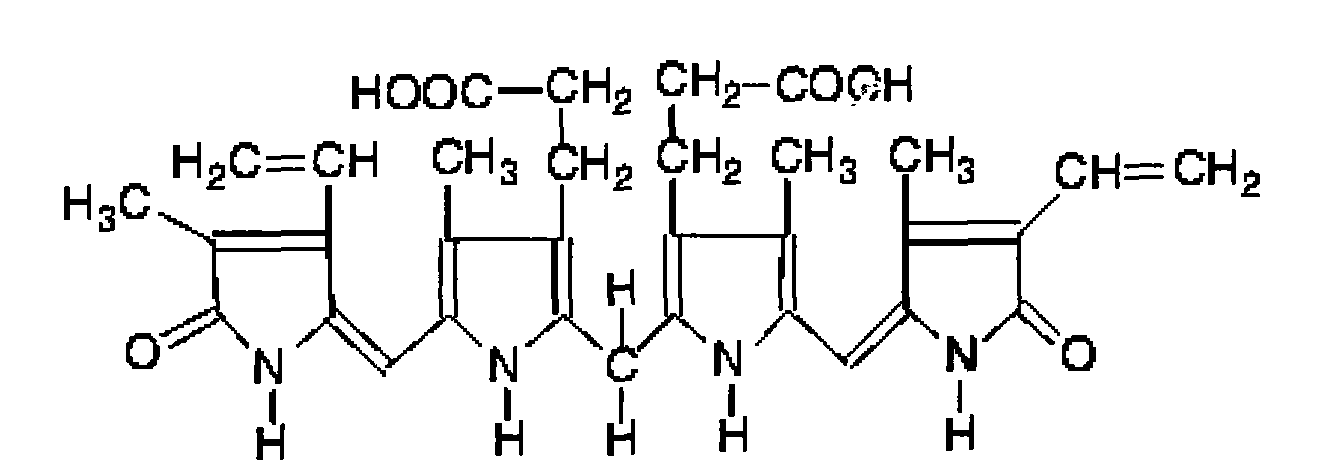
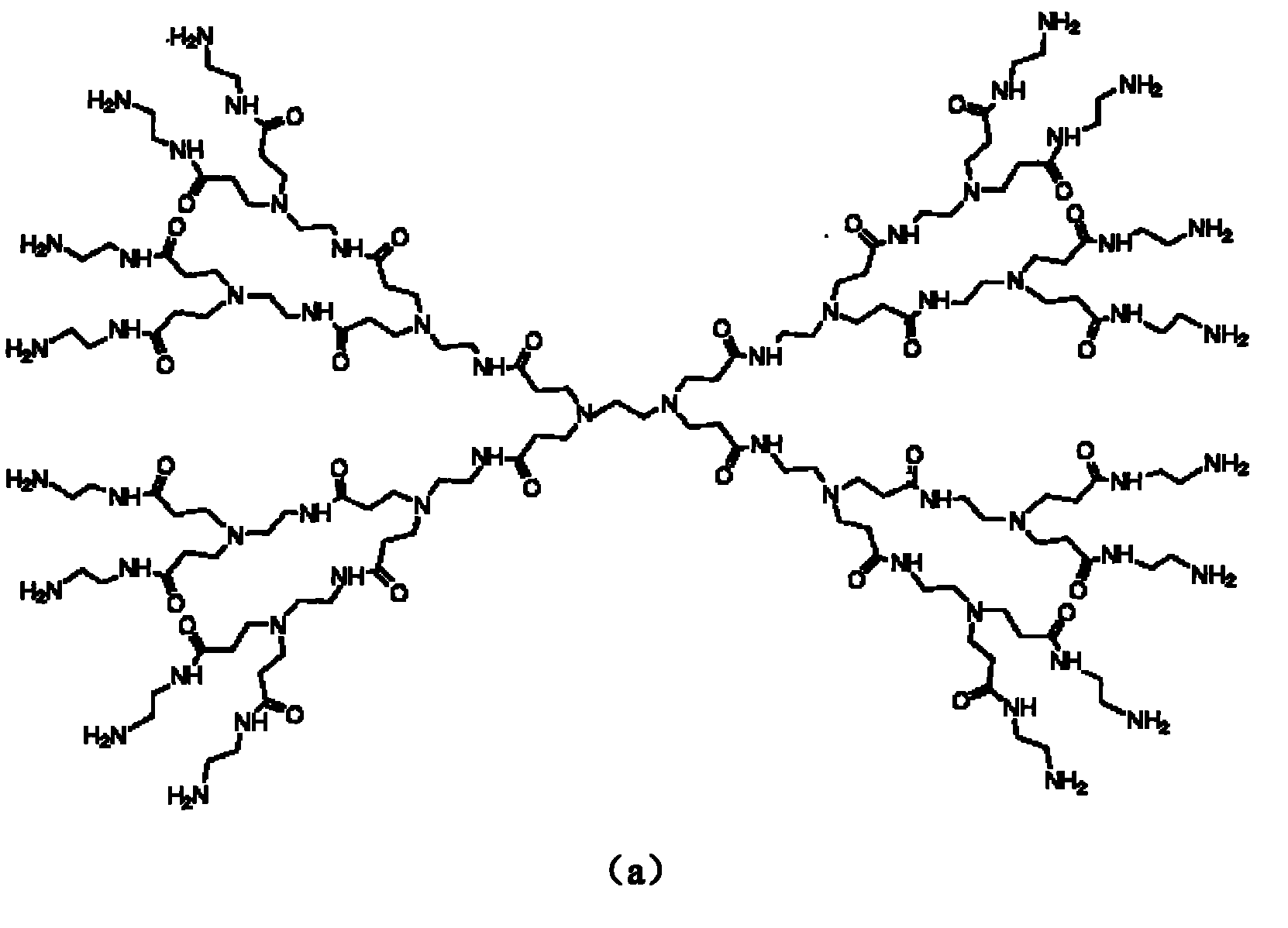
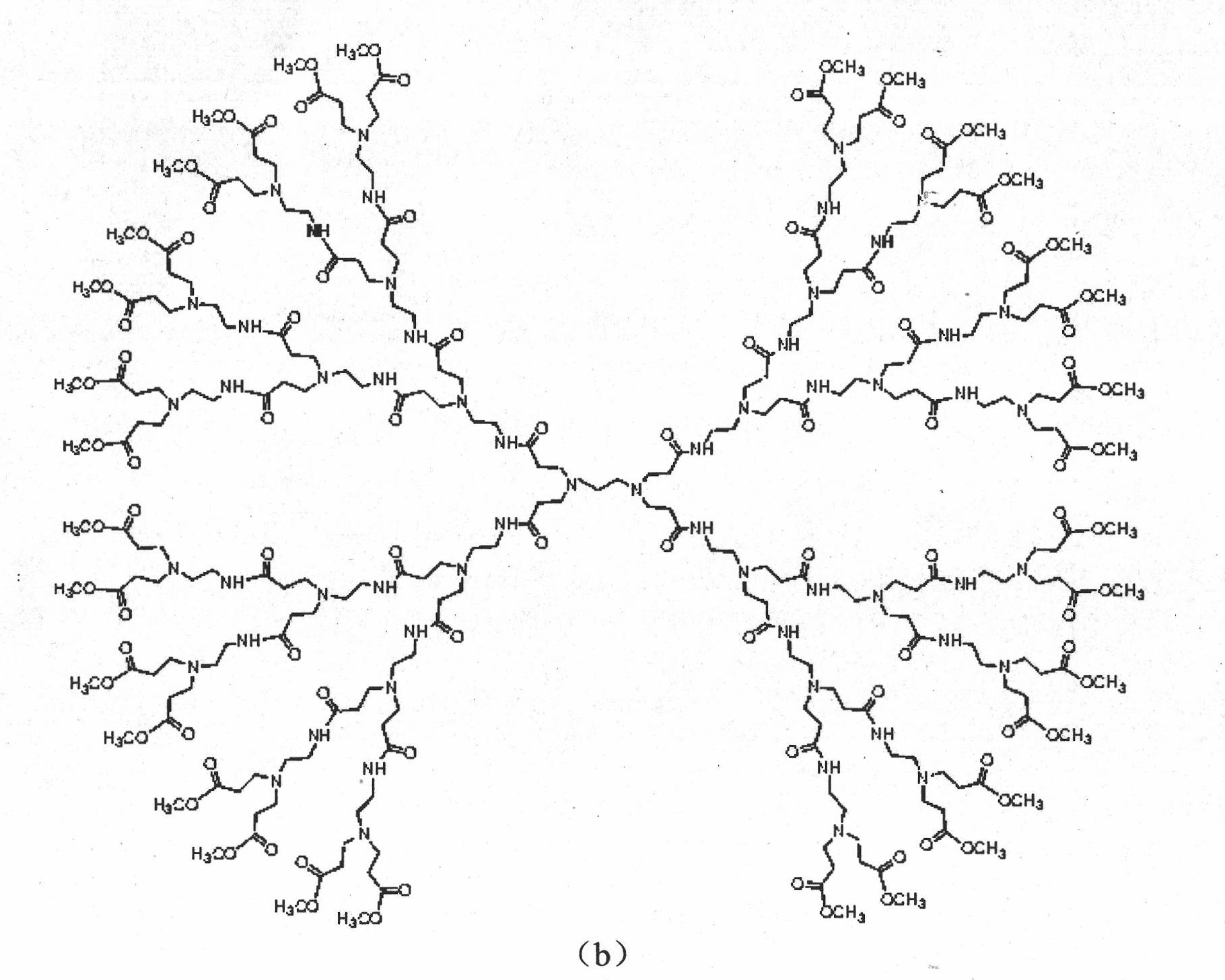
Polyamido-amine dendrimers -modified macroporous crosslinked chitosan microsphere and preparation method thereof
A technology for cross-linking chitosan and chitosan microspheres is applied in the field of preparation of bilirubin adsorption materials, which can solve the problems of low adsorption capacity, poor blood compatibility, and the inability of adsorbents to obtain satisfactory clinical effects, and the like. To achieve the effect of increasing amino content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1: Preparation of CS microspheres. In the there-necked flask of 1000ml, add 200ml carbon tetrachloride, 200ml liquid paraffin and 0.9g span-80 respectively, under electric stirring, add the chitosan of 200ml 5% (the molecular weight of chitosan is 10.6× 10 4 , degree of deacetylation is 85%) acetic acid (2%) aqueous solution and 50% sucrose solution (the volume ratio of chitosan solution and sucrose solution is 3: 1), regulate stirring speed, after 40 minutes, chitosan solution is dispersed as At room temperature, add 3ml of 37% formaldehyde solution dropwise to beads of appropriate size. After 1 hour, raise the temperature to 40°C and add 10ml of 50% glutaraldehyde solution dropwise. After 2 hours, the gelation was completed, the temperature was raised to 60°C, and 10% NaOH solution was added dropwise to adjust the pH value to 9-10, and reacted for 12 hours to solidify the ball, and then suction filtered. Repeatedly wash with ethanol and petroleum ether sever...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Example 2: Preparation of HPCS microspheres. Add 8g of chitosan microspheres without formaldehyde removal (particle size distribution 150-170μm, fully swell with deionized water in advance), 40ml of epichlorohydrin, electric stirring at 60°C for 0.5h, and constant pressure liquid separation into the three-necked flask Slowly add 24ml HClO dropwise through the funnel 4 , reacted for 10 hours, filtered with suction, soaked and washed the microspheres with deionized water and absolute ethanol repeatedly until neutral, dried in vacuum (0.1MPa) at 40°C for 24 hours, and obtained HPCS microspheres, whose infrared spectrum is shown in Figure 4 (b). It can be seen from the figure that the C-Cl absorption peak appears near 625cm-1, which proves that the hydroxypropyl chlorination reaction is successful.
Embodiment 3
[0028] Example 3: Preparation of CS-GO microspheres. Take 8g of HPCS microspheres (particle size distribution 150-170μm, fully swell with deionized water in advance) in a three-necked flask, add 80ml of hexamethylenediamine, 60°C, mechanically stir for 12h, filter with suction, wash the microspheres with water until neutral According to the method of Example 1, the protection of formaldehyde was removed to obtain CS-GO microspheres. Its amino content determination method is with embodiment 1, and the results are shown in Table 1. Its infrared spectrum is shown in Figure 4 (a), it can be seen from the figure that the comparison Figure 4 (b) Spectrum of HPCS microspheres at 625cm -1 The nearby C-Cl absorption peak disappeared, proving that HDA had been successfully attached to the HPCS microspheres, and the reaction was thorough; combining the amino groups of HPCS and CS-G0 microspheres in Table 1 further proved that the reaction was successful.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com