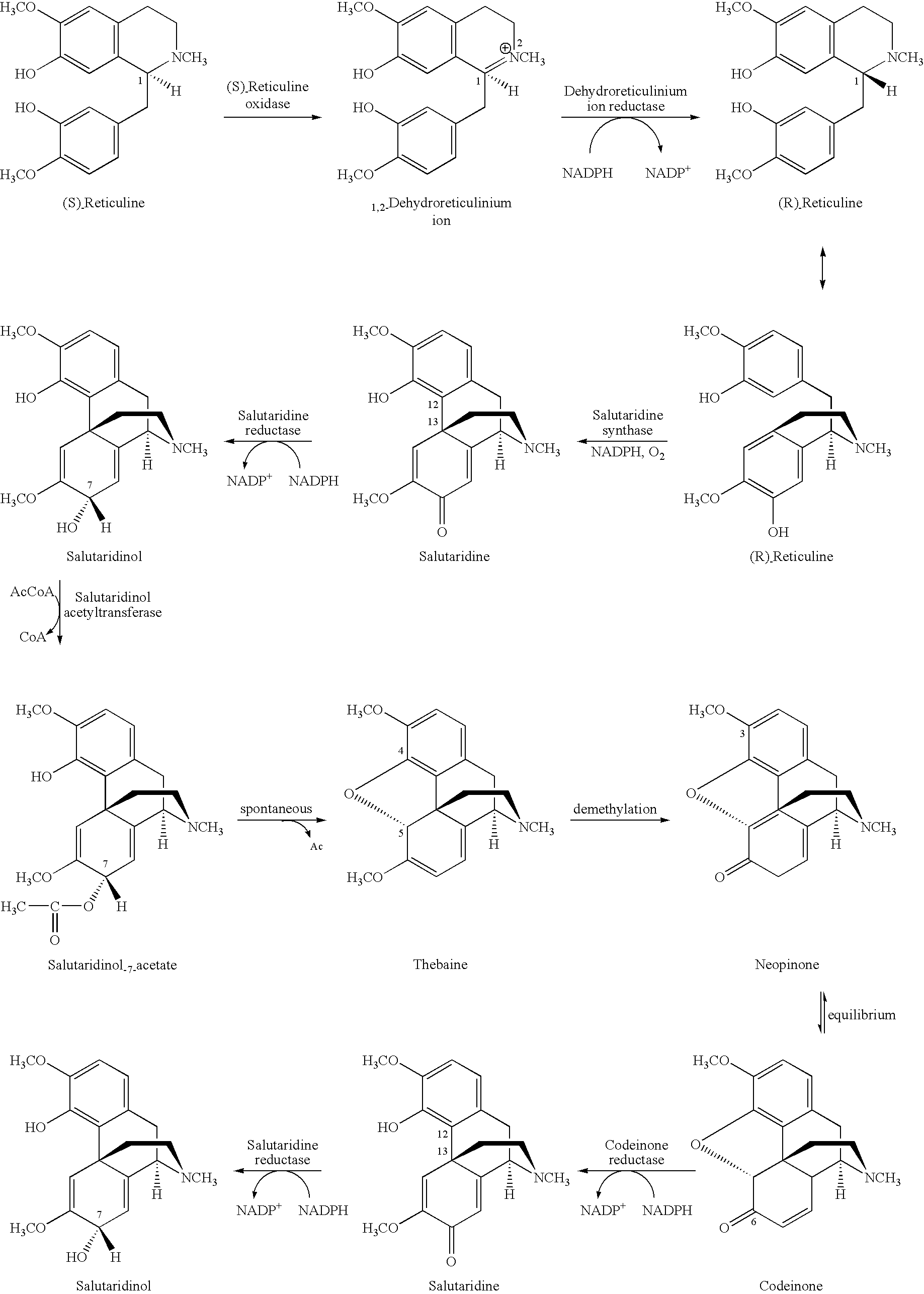
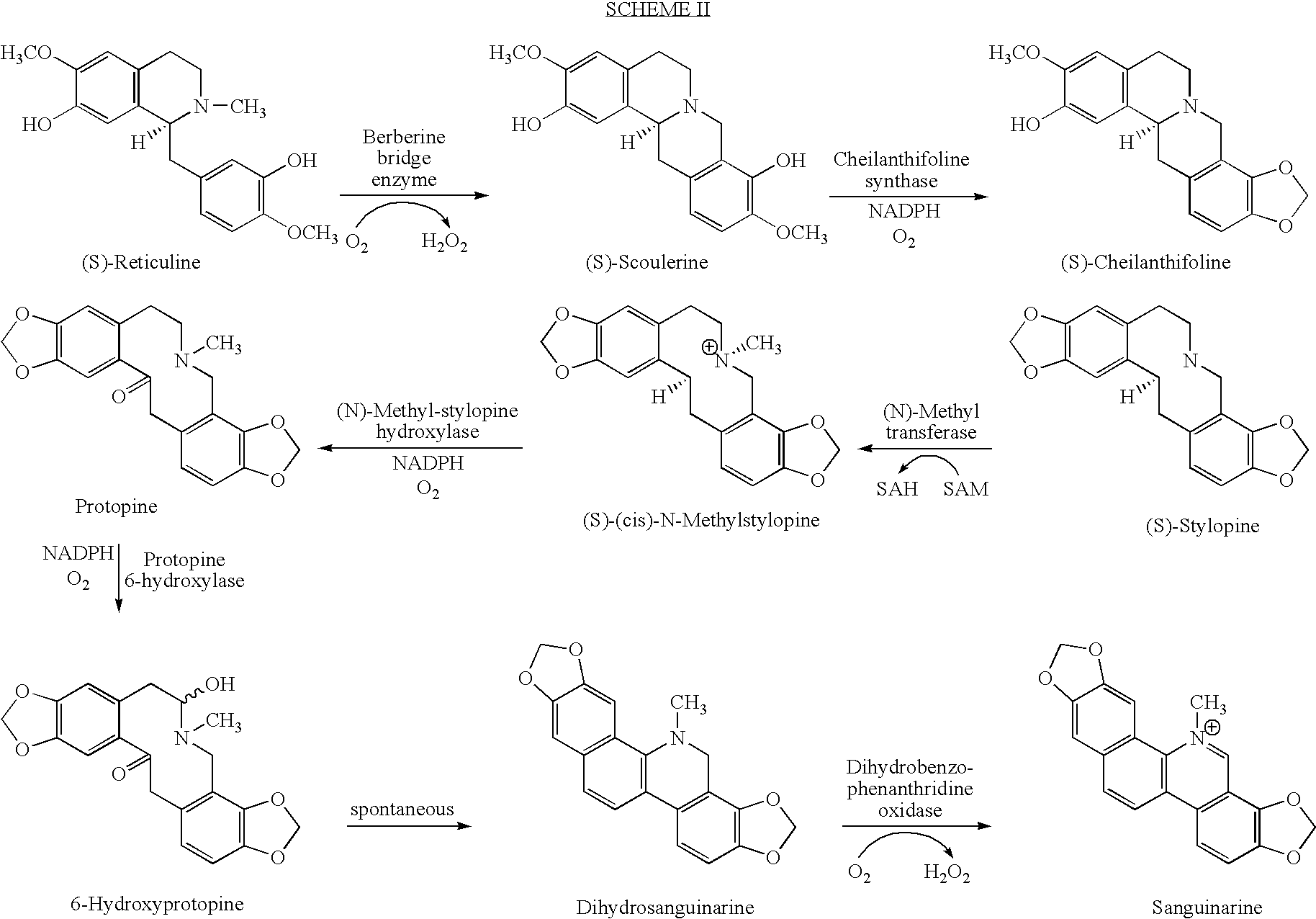
Cytochrome P450 reductases from poppy plants
a technology of cytochrome p450 and reductases, which is applied in the field of poppy alkaloids production, can solve the problems of limiting the activity rate of cytochrome p450, poor transferability of reductases from diverged species, and not being able to establish the exact nature of “bottlenecks”
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Enzyme Purification and Amino Acid Sequencing
[0085] Plant cell cultures. Cell suspension cultures of P. somniferum and E. californica were routinely grown in 1-litre conical flasks containing 400 mL of Linsmaier-Skoog medium (17) over 7 days at 23° C. on a gyratory shaker (100rpm) in diffuse light (750 lux). Elicitation of E. californica cell suspension cultures was achieved by the aseptic addition of methyl jasmonate to a final concentration of 100 μM to the medium (18).
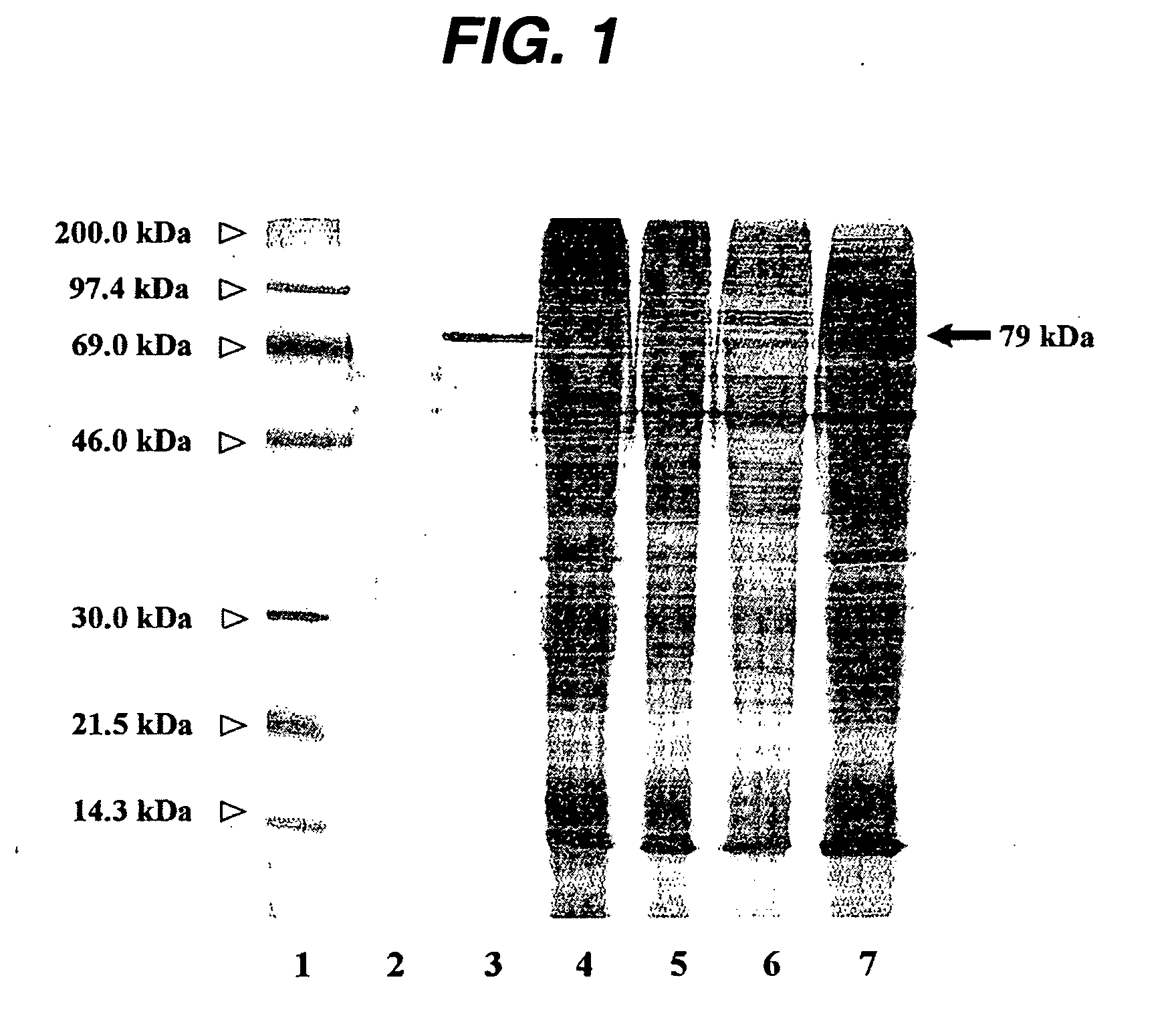
[0086] Purification and sequence analysis. Cells were harvested from seven-day-old suspension cultures of P. somniferum by vacuum filtration, immediately shock frozen and stored at −20° C. All of the following operations were carried out at 4° C. 500 g frozen tissue were then homogenised with a mortar and pestle in 1 litre 0.1 M tricine / NaOH, pH 7.5 containing 15 mM thioglycolic acid. Cell debris was removed by centrifugation at 10,000×g, 30 min. The supernatant was filtered through four layers of cheesecloth and ...
example 2
Generation of Partial cDNAs From P. somniferum and E. californica
[0091] Optimised PCR primers were then designed based on highly homologous sites on both the amino acid and nucleotide levels in the plant cytochrome P-450 reductase sequence comparison (FIG. 3). The precise sequence of the primers used for the first round of PCR was:
5′-CA ITI CII CCT CCT TTC CC-3′ and T3′-ACC TAC TTC TTA CGI CAA GG-5′. C TGC
[0092] Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) generated partial cDNAs encoding cytochrome P-450 reductases from P. somniferum and E. californica were produced by PCR using cDNA produced by reverse transcription of total RNA isolated from 3 to 5-day-old suspension cultured cells. DNA amplification was performed under the following conditions: 5 cycles of 94° C., 30 sec; 45° C., 1 min; 72° C., 1 min; 25 cycles of 94° C., 30 sec; 55° C., 30 sec, 72° C., 1 min. At the end of 30 cycles, the reaction mixtures were incubated for an additional 5 min at 72° C. prior to c...
example 3
cDNA Isolation and Heterologous Expression of Cytochrome P-450 Reductase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
[0099] cDNA clones encoding the Papaver and Eschscholzia cytochrome P-450 reductases were isolated by screening of cDNA libraries prepared in either 1-ZAP II or Uni-ZAP XR (Stratagene) using the partial clones generated by PCR as hybridization probe. The clones that yielded positive results through a third screening were converted to pBluescript KS (+) by excision. After determination of the nucleotide sequence on both strands, the full length reading frame, free of the 5′- and 3′-flanking sequences, was generated by PCR using either Taq DNA polymerase (Perkin Elmer) and was subcloned into pGEM-T (Promega) or Pfu DNA polymerase and was subcloned into pCR-Script SK (+) (Stratagene).
[0100] The P. somniferum cytochrome P-450 reductase cDNA in pGEM-T, designated pGEM-T / PsoCPR, was digested with the restriction endonucleases Not I and Hin dIII and the 2096 bp fragment was ligated into No...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com