Recombinant yarrowia lipolytica strain for producing protopanoxadiol by utilizing xylose and construction method and application of recombinant yarrowia lipolytica strain
A technology of protopanaxadiol and lipolytic Yarrowia, which is applied in the field of recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica strain and construction, can solve the problems of high cost of separation and purification, long growth cycle of ginseng, complex components of ginseng extract, etc., and achieve effective Applied effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
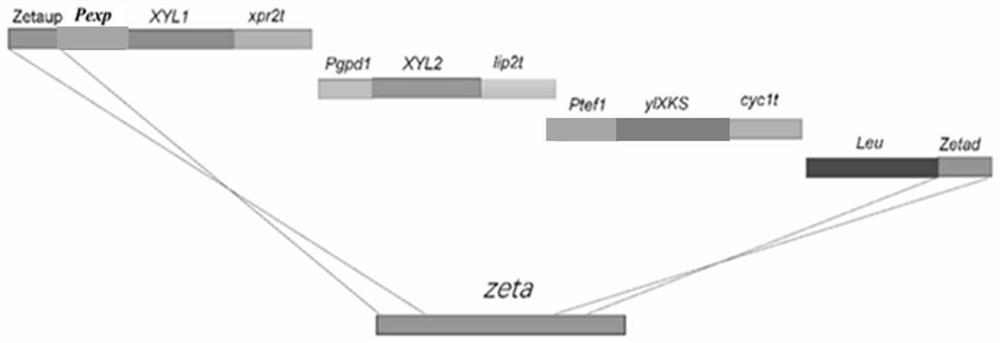
[0030] Embodiment 1, construction of Yarrowia lipolytica recombinant strain 1
[0031] Introduce the optimized xylose reductase gene XYL1 expression cassette and xylitol dehydrogenase gene XYL2 expression cassette into Yarrowia lipolytica, as well as the endogenous xylulokinase gene XKS expression cassette to obtain recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica Bacteria 1, the nucleotide sequence of the optimized xylose reductase gene XYL1 is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; the nucleotide sequence of the optimized xylitol dehydrogenase gene XYL2 is shown in SEQ ID NO.2 shown; the nucleotide sequence of the xylulokinase gene XKS is shown in SEQ ID NO.3;
[0032] 1. Module construction
[0033] Both xylose reductase gene (XYL1) and xylitol dehydrogenase (xylitoldehydrogenase) gene (XYL2) are derived from Pichia stipitis; Synthesized by chemical synthesis, optimized codons for Yarrowia lipolytica, and mutated XYL1 (K270R / N272D), to obtain optimized xylose reductase gene XYL1 (SEQ ID NO.1) and xylose ...
Embodiment 2
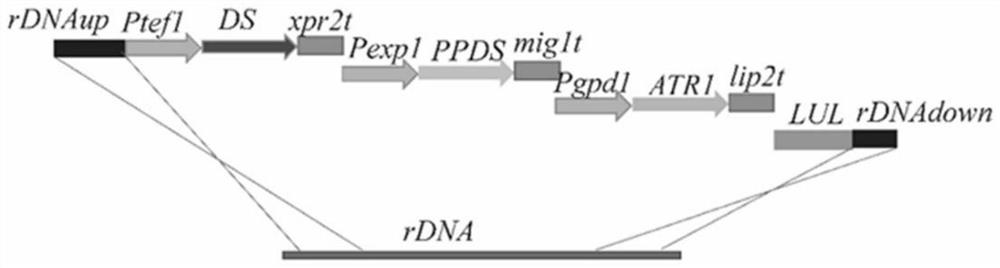
[0044] Embodiment 2, construction of recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica strain 2
[0045] Into the recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica yeast 2, the optimized dammarenediol synthase encoding gene DS expression cassette, the optimized protopanaxadiol synthase encoding gene PPDS expression cassette and the optimized cytochrome-NADPH- The expression cassette of the gene encoding reductase 1 was used to obtain the recombinant Y. lipolytica 2 that utilizes xylose to produce protopanaxadiol.
[0046] The dammarenediol synthase coding gene (DS) is derived from the plant ginseng (Panax ginseng), and the gene is synthesized by chemical synthesis by Wuhan Jinkairui Bioengineering Co., Ltd., and the codons are modified for Yarrowia lipolytica Optimized to obtain the optimized dammarenediol synthase coding gene DS (SEQ ID NO.4);
[0047] The protopanaxadiol synthase coding gene PPDS is derived from the plant ginseng (Panax ginseng), and the gene was synthesized by chemical synthesis by Wuhan Jin...
Embodiment 3
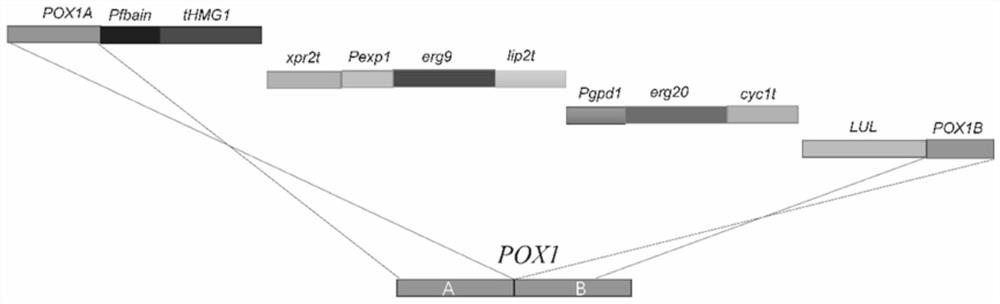
[0059] Embodiment 3, the construction of recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica 3
[0060] Into the recombinant strain 2 that uses xylose to produce protopanaxadiol, introduce the tHMG1 expression cassette of the gene encoding 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase that is truncated by 1500 nucleotides at the 5' end, The farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase gene ERG20 expression cassette, the squalene synthase coding gene ERG9 expression cassette, obtained the recombinant Y. lipolytica 3 that utilizes xylose to produce protopanaxadiol;
[0061] The nucleotide sequence of the gene tHMG1 encoding 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase is shown in SEQ ID NO.7, and the nucleotide sequence of the farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase gene ERG20 It is shown in SEQ ID NO.8; the nucleotide sequence of the squalene synthase gene ERG9 is shown in SEQ ID NO.9.
[0062] 1. Module construction
[0063] Gene POX1A (SEQ ID NO.72), Pfbain (SEQ ID NO.73), xpr2t (SEQ ID NO.12), Pexp1 (SEQ ID NO.11), lip2t ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com