A method, system and device for optimizing high-speed downlink packet access to multiple streams
An optimization method and high-speed technology, applied in the direction of network traffic/resource management, wireless communication, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem that RNC cannot know the maximum capacity of tributaries, and cannot realize the effective application of HSDPA multi-stream technology.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0117] Embodiment 1: NodeB1 meets the preset air interface rate threshold, and NodeB2 does not meet the preset air interface rate threshold.
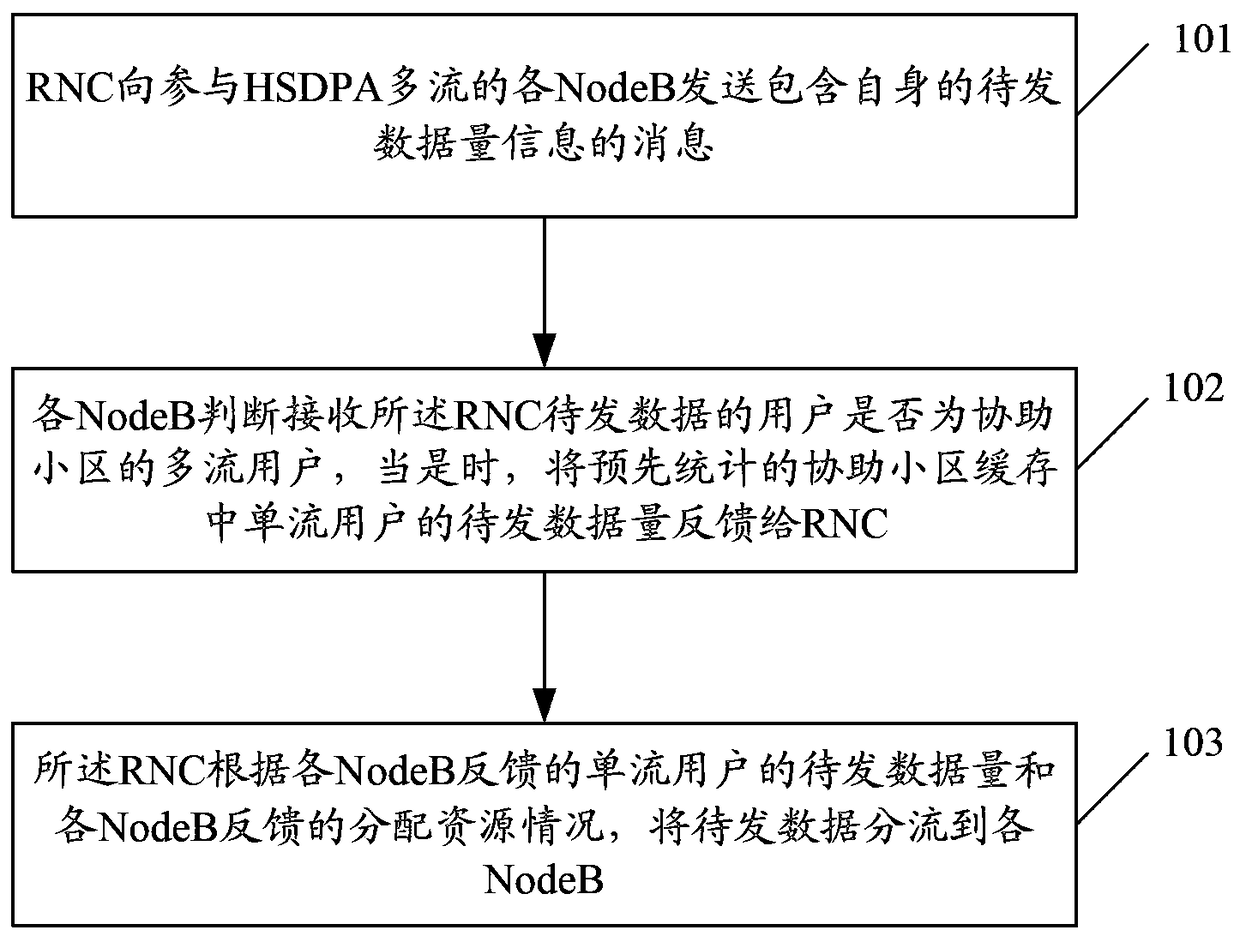
[0118]Step 1, the RNC receives the user data of the UE from the CN and puts it into the buffer, and the total amount of user data is Y1 bytes;
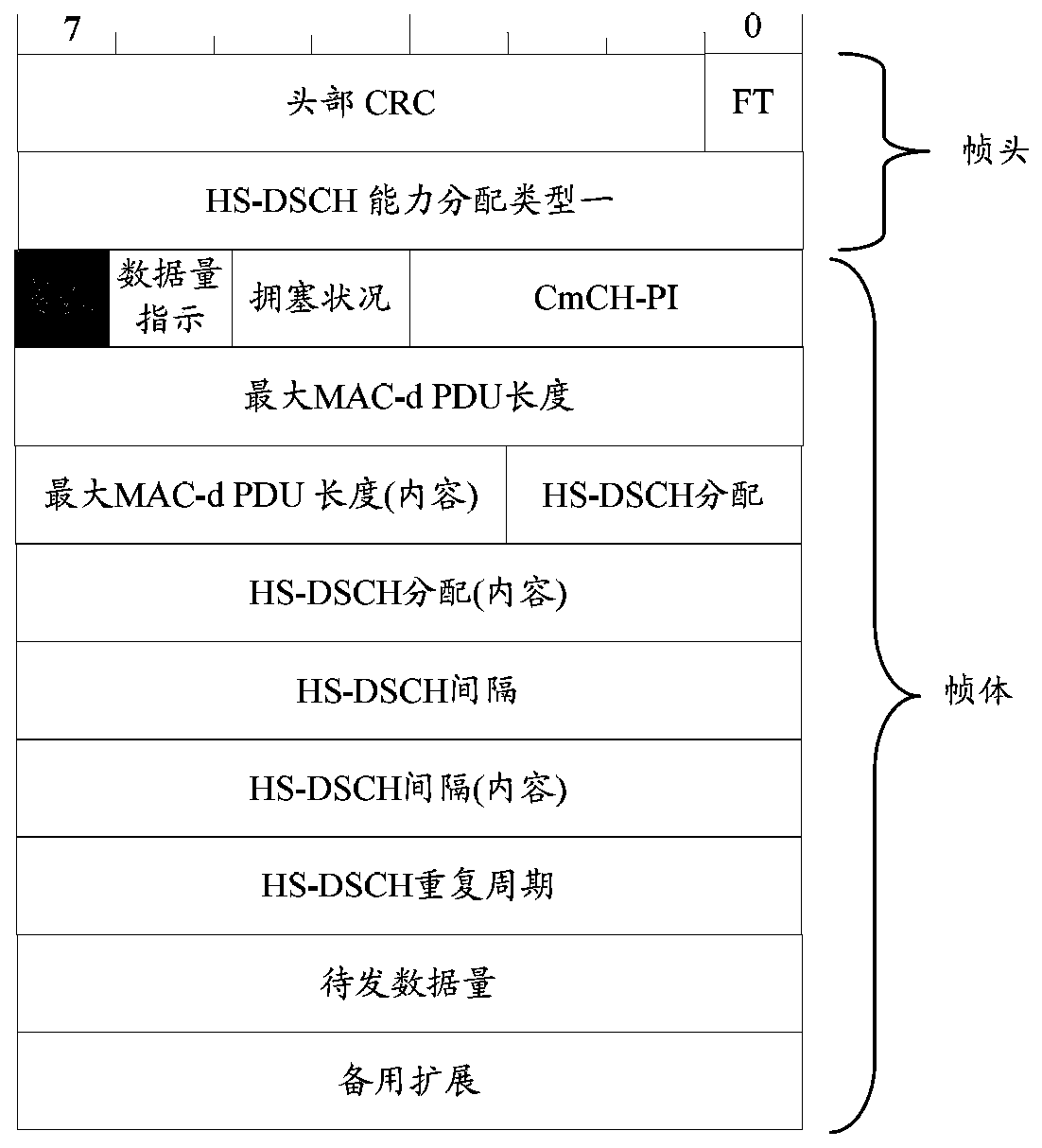
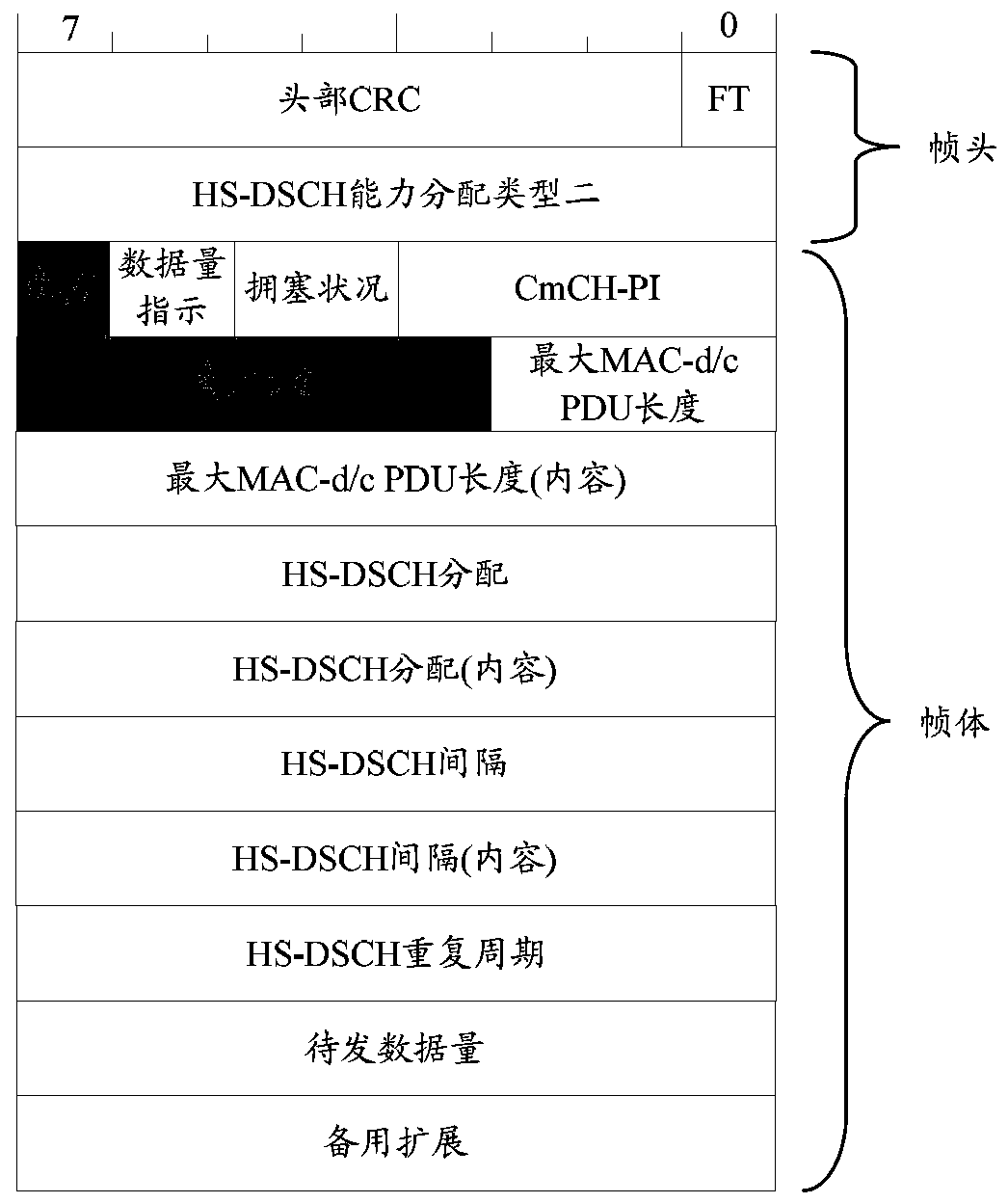
[0119] Step 2, RNC sends HS-DSCH capability request frames to NodeB1 and NodeB2 respectively, where User BufferSize fills in Y1bytes;
[0120] Step 3: NodeB1 allocates an air interface rate of 36M for the corresponding priority queue according to the size of the data to be sent, buffer size, and air interface capacity, and feeds back to RNC1 through the HS-DSCH capacity allocation frame;
[0121] Step 4: NodeB2 allocates an air interface rate of 16M for the corresponding priority queue according to the amount of data to be sent, buffer size, and air interface capability, and feeds back to RNC1; at the same time, feeds back to RNC1 the current single-stream users of CELL2 and the multi-stream of...
Embodiment 2
[0123] Embodiment 2: NodeB1 does not meet the preset air interface rate threshold, and NodeB2 meets the preset air interface rate threshold.
[0124] Step 1, RNC1 receives UE1's user data from CN1 and puts it into the buffer, the total amount of user data is Y1bytes;
[0125] Step 2, RNC1 sends HS-DSCH capability request frames to NodeB1 and NodeB2 respectively, where User BufferSize fills in Y1bytes;
[0126] Step 3: NodeB1 assigns an air interface rate of 12M to the corresponding priority queue according to the size of the data to be sent, buffer size, and air interface capability, and feeds back to RNC1 through the HS-DSCH capability allocation frame;
[0127] Step 4: NodeB2 assigns an air interface rate of 36M to the corresponding priority queue according to the size of the data to be sent, the buffer size, and the air interface capacity, and feeds back to RNC1; at the same time, feeds back to RNC1 the current single-stream users of CELL2 and the multi-stream of the servin...
Embodiment 3
[0133] Embodiment 3: Neither NodeB1 nor NodeB2 meets the preset air interface rate threshold.
[0134] Step 1, RNC1 receives UE1's user data from CN1 and puts it into the buffer, the total amount of user data is Y1bytes;
[0135] Step 2, RNC1 sends HS-DSCH capability request frames to NodeB1 and NodeB2 respectively, where User BufferSize fills in Y1bytes;
[0136] Step 3: NodeB1 assigns an air interface rate of 12M to the corresponding priority queue according to the size of the data to be sent, buffer size, and air interface capability, and feeds back to RNC1 through the HS-DSCH capability allocation frame;
[0137] Step 4, NodeB2 allocates an air interface rate of 20M for the corresponding priority queue according to the size of the data to be sent, the buffer size, and the air interface capability, and feeds back to RNC1;
[0138] Step 5, RNC1 judges that the air interface rate of NodeB1 does not meet the preset air interface rate threshold, that is, 12M<40M*0.8, and the a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com