Nucleic acid aptamer and screening method thereof, and application of nucleic acid aptamer in prostate cancer cell strain detection
A nucleic acid aptamer and screening method technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, measuring devices, individual particle analysis and other directions, can solve the problems that restrict the development of targeted diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer, and it is difficult to determine the site and location of tumor recurrence, It is difficult for clinicians to choose a treatment plan to achieve the effect of short cycle, small molecular weight and strong binding ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0080] Example 1: Screening of prostate cancer cell-specific nucleic acid aptamers
[0081] 1. Design and synthesis of random nucleic acid library
[0082] Design and synthesize a nucleic acid sequence library containing 20 nucleotides (primers) at both ends and a random sequence of 45 nucleotides in the middle as follows:
[0083] 5'-ACGCTCGGATGCCACTACAG-(45N)-CTCATGGACGTGCTGGTGAC-3'.
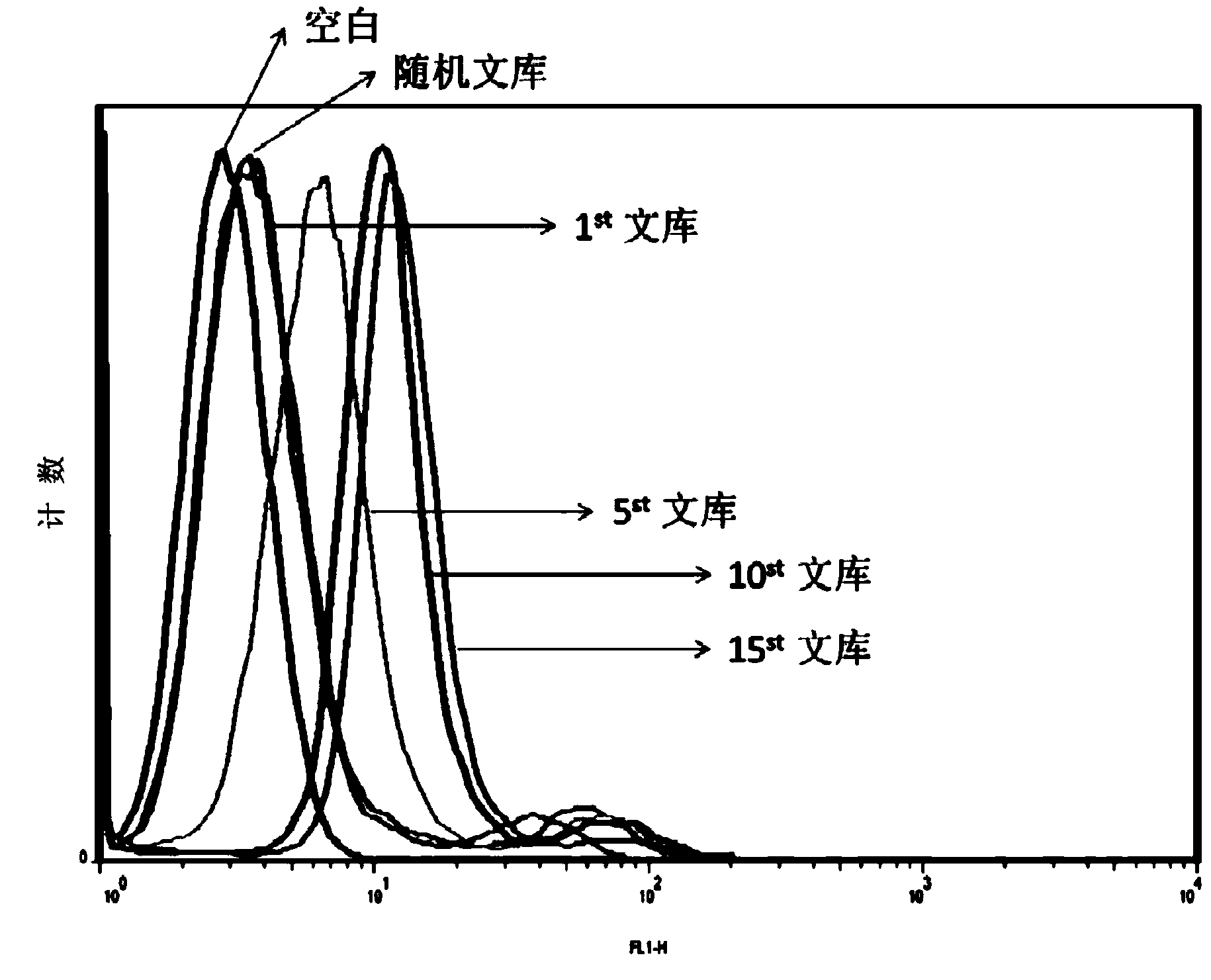
[0084] 2. Cell-SELEX screening to obtain nucleic acid aptamers
[0085] 2.1 Incubation: use binding buffer solution (PBS, containing 0.45% glucose, 5mM MgCl 2 , 0.1mg / mL herring sperm DNA) to dissolve the above random nucleic acid library, shake at 95°C for 5 minutes, and quickly put it on ice; then incubate with the cultured and pretreated prostate cancer cell line PC-3 on ice for 1 hour .
[0086] 2.2 Dissociation: After the incubation, pour out the liquid in the incubation flask, wash with washing buffer (PBS, containing 0.45% glucose, 5mM MgCl 2 ) to wash the cells in the incubation f...
Embodiment 2
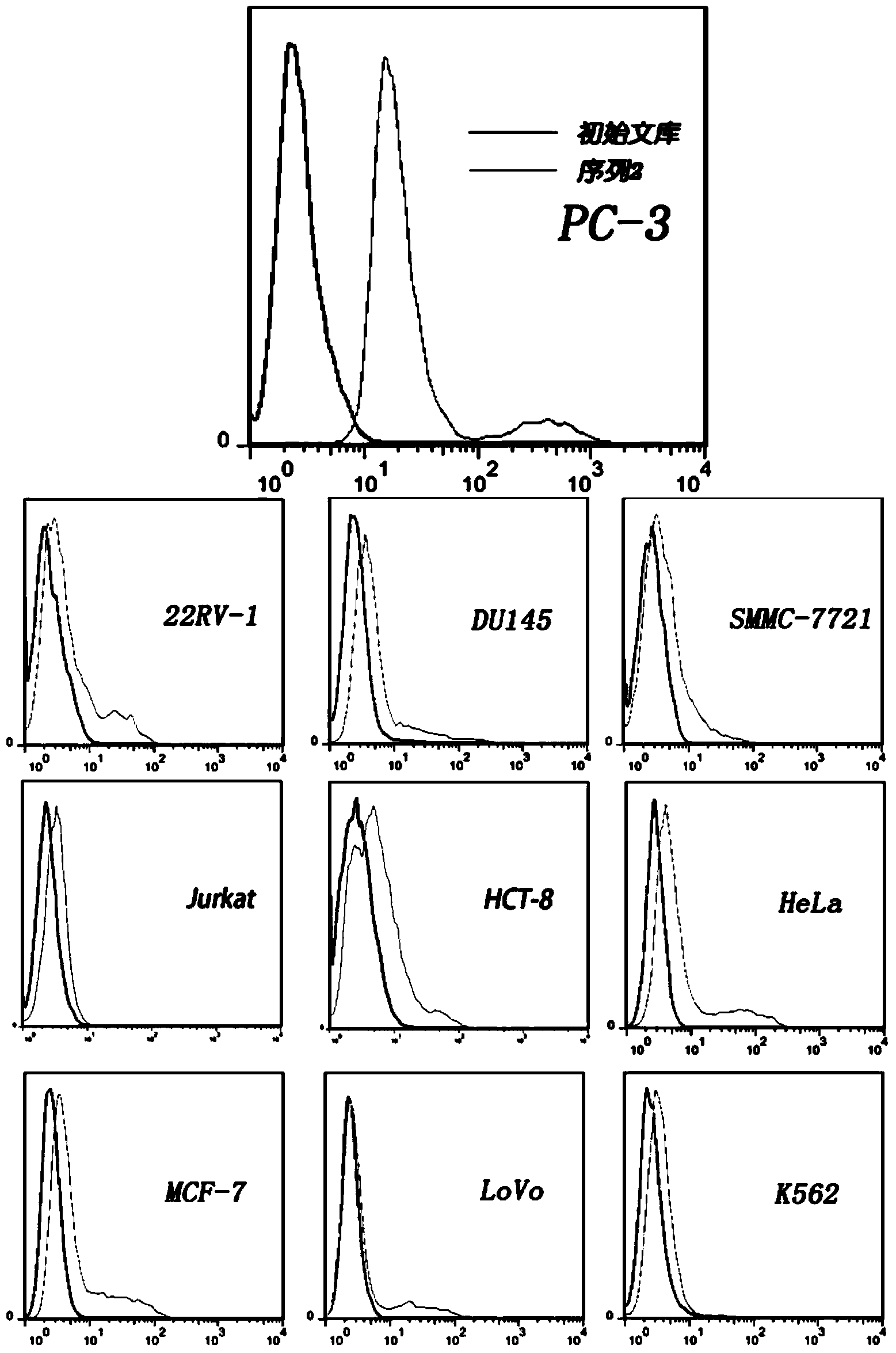
[0107] Example 2: Detection of cell specificity
[0108] A total of 12 cell lines were selected for specificity analysis: three prostate cancer cell sublines were PC-3, LNCap, DU-145, and 22RV-1; immortalized normal prostate epithelial cells RWPE-1; liver cancer cells SMMC -7721; cervical cancer cells HeLa, lung cancer cells A549, MCF-7; colon cancer sub-cell line LoVo; leukemia cells Jurkat, K562.
[0109] Each cell line was subjected to the following steps (1) and (2), repeated three times.
[0110] 1. By cell counting, take 5×10 5 The cells were dispersed in the binding buffer, and then the labeled nucleic acid aptamer was added with a final concentration of 0.25 μM.
[0111] 2. Incubate the mixture of cells and nucleic acid aptamers on ice for 20 minutes, centrifuge and wash twice, and use flow cytometry to detect the combination of nucleic acid aptamers and the above-mentioned different cell lines. The cells were incubated with the FITC-labeled random library and then ...
Embodiment 3
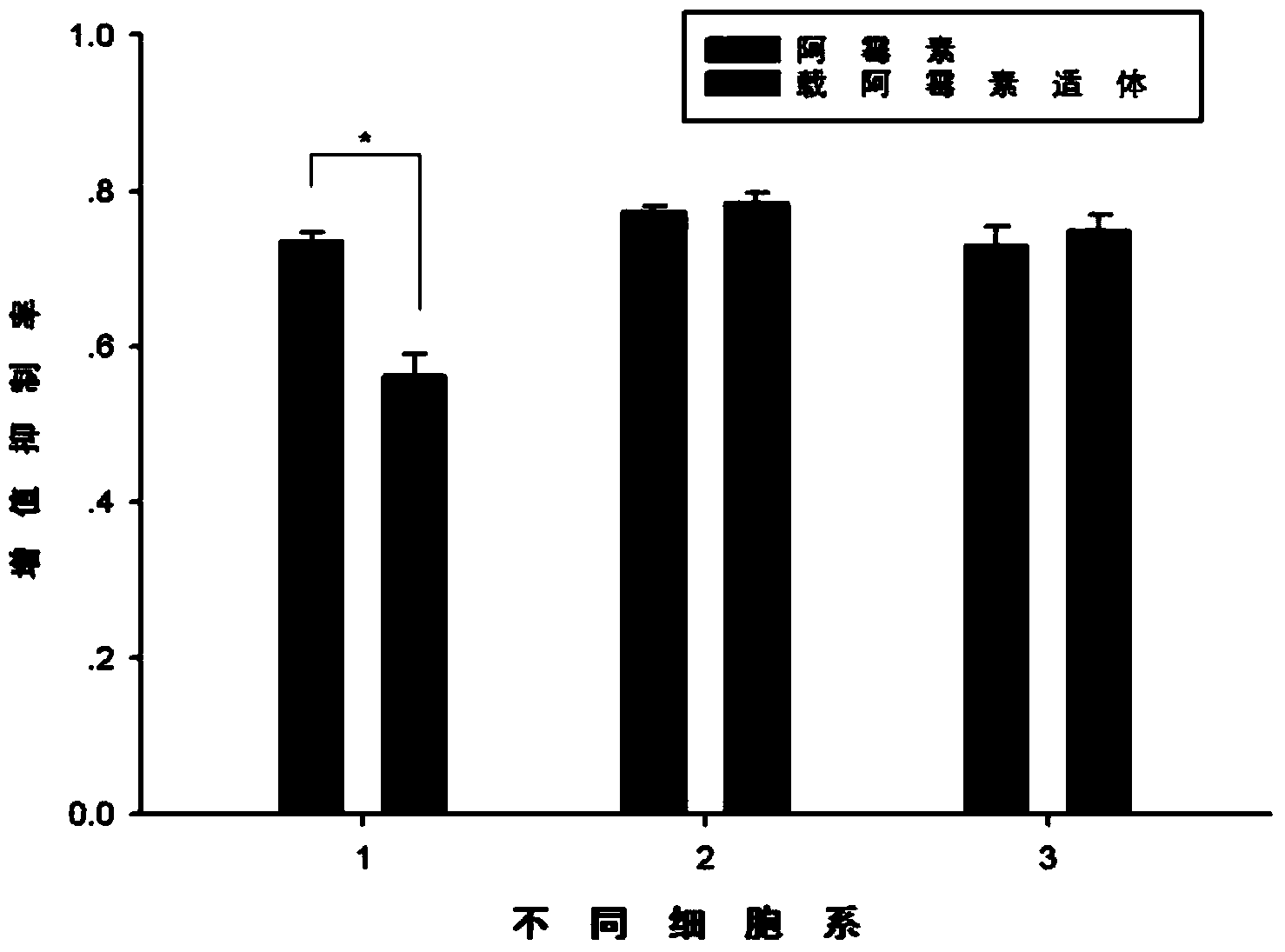
[0116] Example 3: Targeted inhibitory effect of doxorubicin-loaded aptamers on cells
[0117] Inoculate 2000 cells per well in a 96-well plate, and after culturing for 24 hours, add 2 μM doxorubicin and 0.5 μM doxorubicin-loaded aptamer every 4 hours (1 molecular sequence and 2 aptamers can carry 4 molecules of doxorubicin After incubation for 15 minutes, the drug-containing medium was withdrawn, the cells were rinsed once, and 100 μL of fresh medium was added, a total of 4 times. After continuing to cultivate for 48 hours, add 10 μL cck-8 to each well, incubate at 37°C for 40 minutes, and measure the absorbance on a microplate reader at a wavelength of 450 nm ( Figure 4 ).
[0118] Depend on Figure 4 It can be seen that the drug-loaded aptamer significantly enhanced the inhibition of the proliferation of the target cell PC-3 (1), but the inhibitory effect on HeLa (2) and SMMC-7721 (3) cells was not obvious.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com