Patents
Literature
57 results about "Proteome profiling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
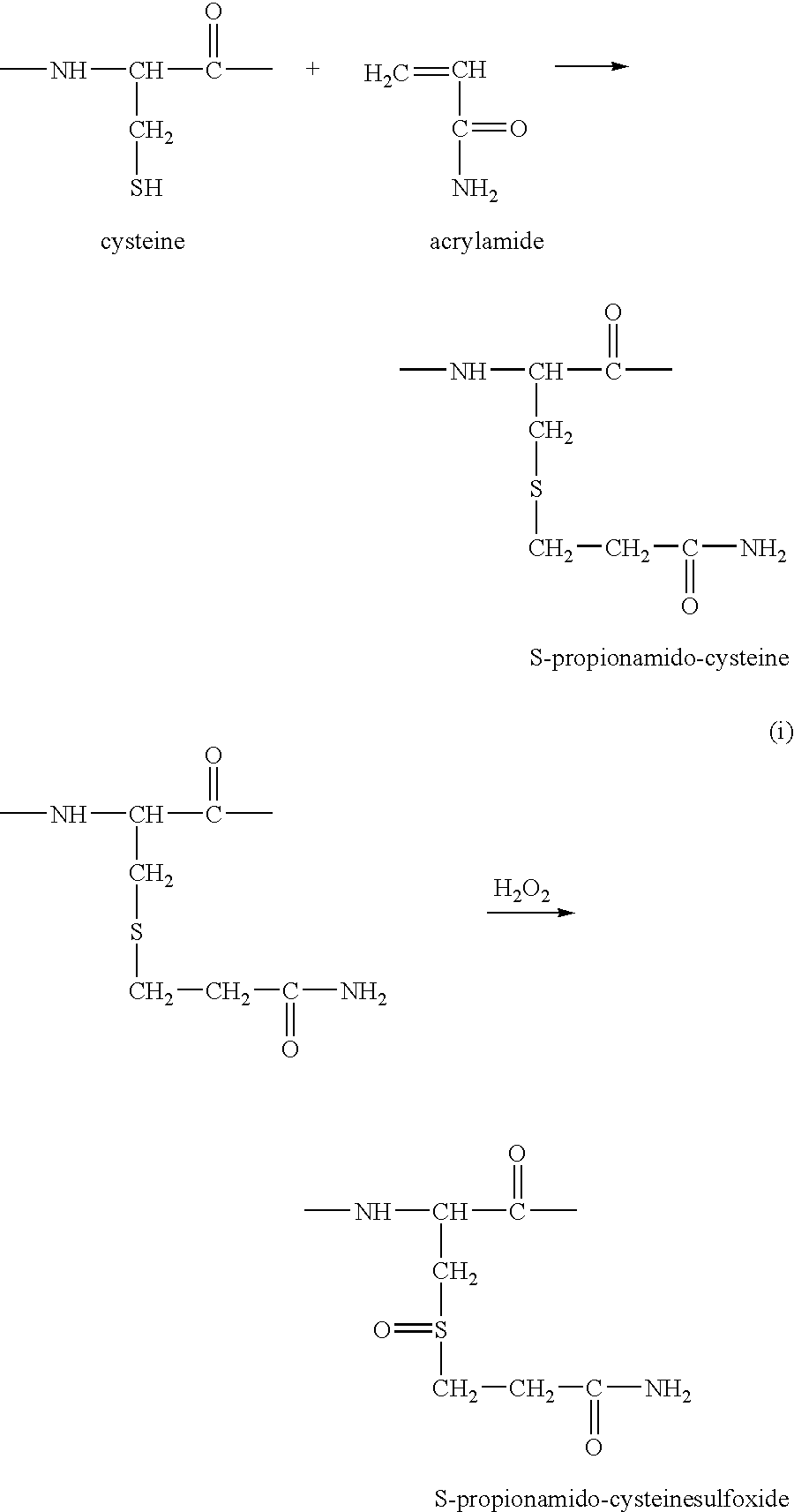
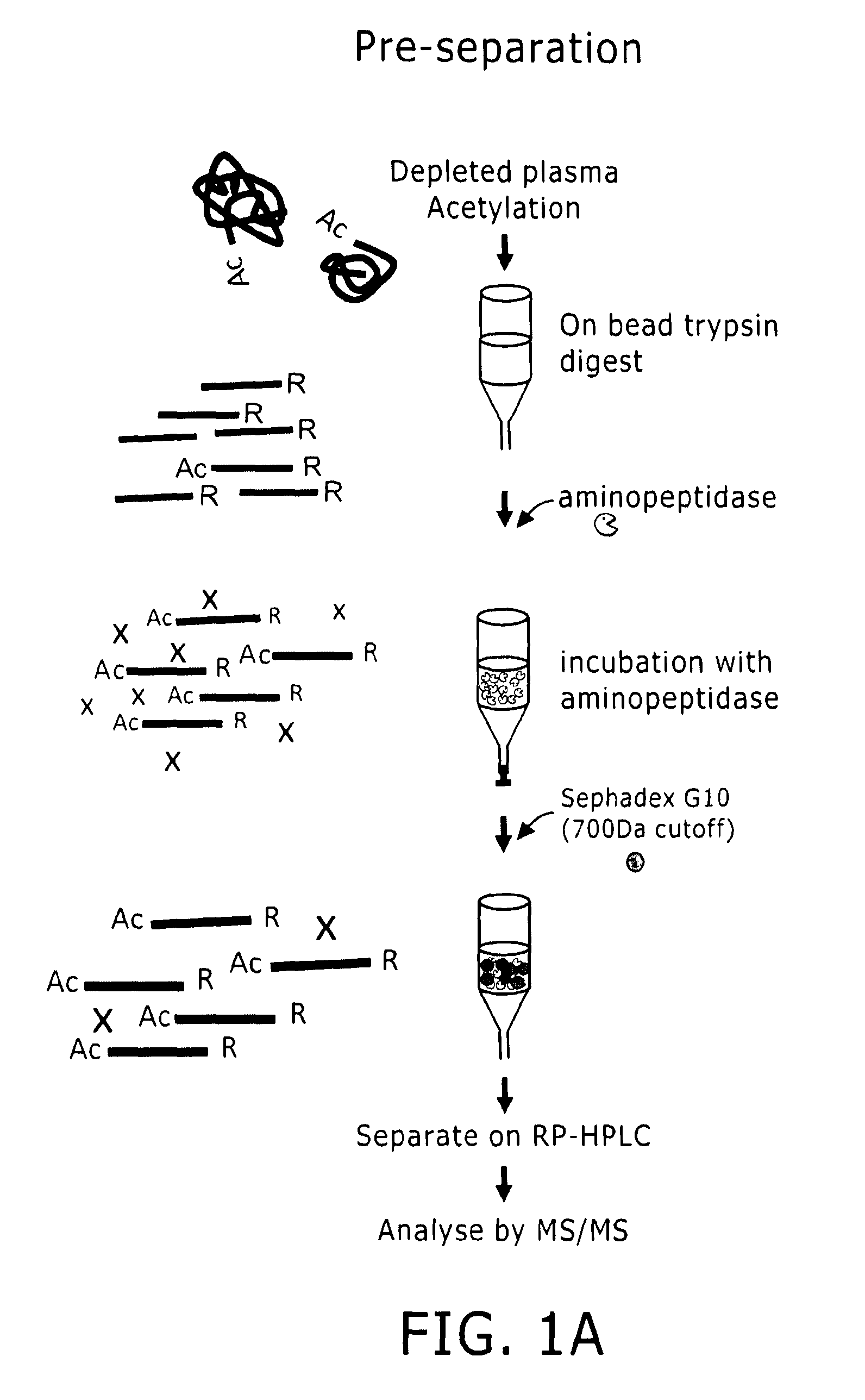
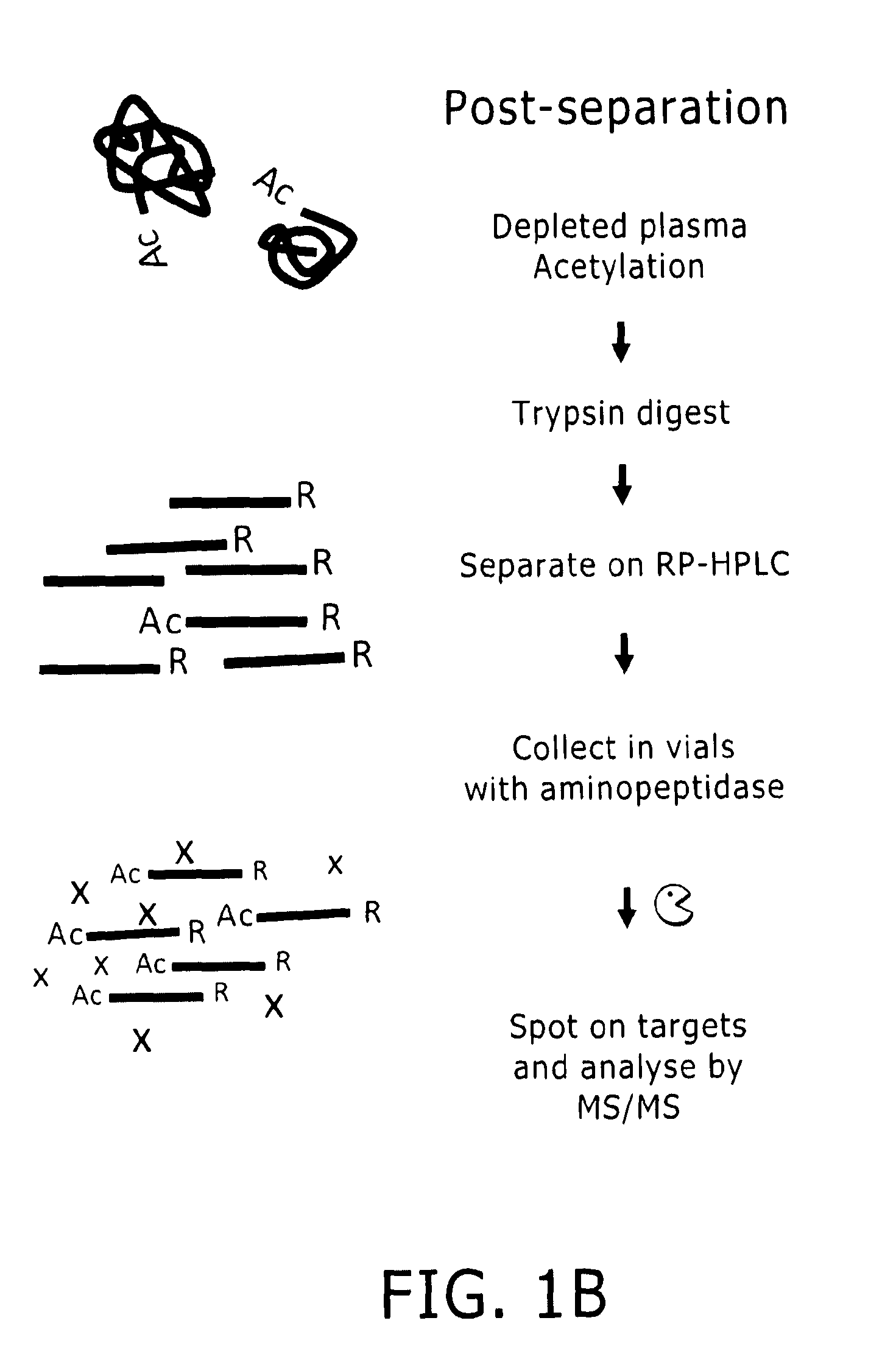
Proteome Profiling. Characterization of proteins from organisms, their body fluids or extracts is the main aim of Proteome profiling. Thus profiling of a proteome serves as a foundation for the study of quantitative changes and modification of the targeted proteins.
Full-length plant cDNA and uses thereof
Owner:NAT INST OF AGROBIOLOGICAL SCI +1
Proteomic analysis of biological fluids
ActiveUS20070161125A1Eliminate needMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesDiseaseGynecology
The invention concerns the identification of proteomes of biological fluids and their use in determining the state of maternal / fetal conditions, including maternal conditions of fetal origin, chromosomal aneuploidies, and fetal diseases associated with fetal growth and maturation. In particular, the invention concerns a comprehensive proteomic analysis of human amniotic fluid (AF) and cervical vaginal fluid (CVF), and the correlation of characteristic changes in the normal proteome with various pathologic maternal / fetal conditions, such as intra-amniotic infection, pre-term labor, and / or chromosomal defects. The invention further concerns the identification of biomarkers and groups of biomarkers that can be used for non-invasive diagnosis of various pregnancy-related disorders, and diagnostic assays using such biomarkers.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
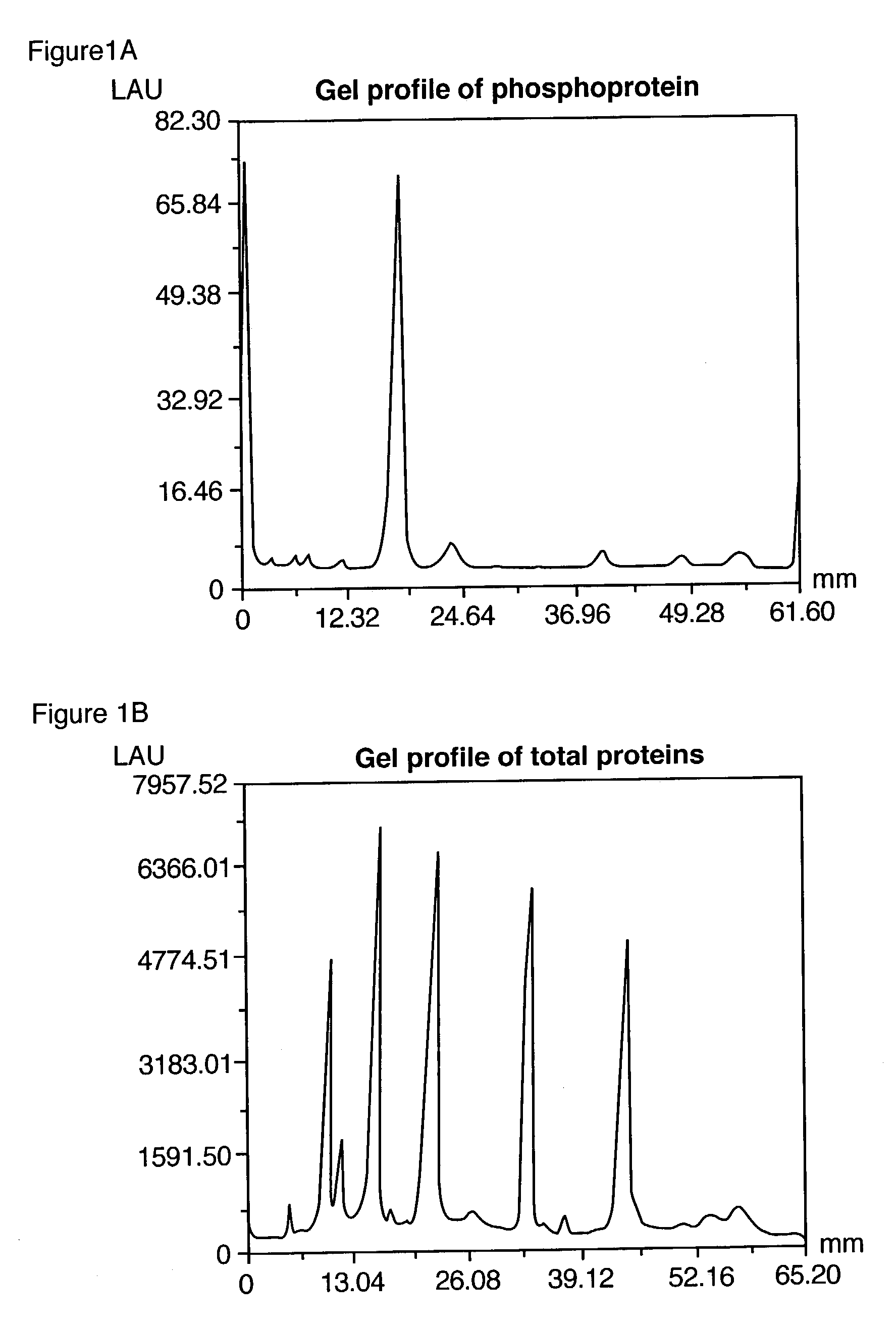
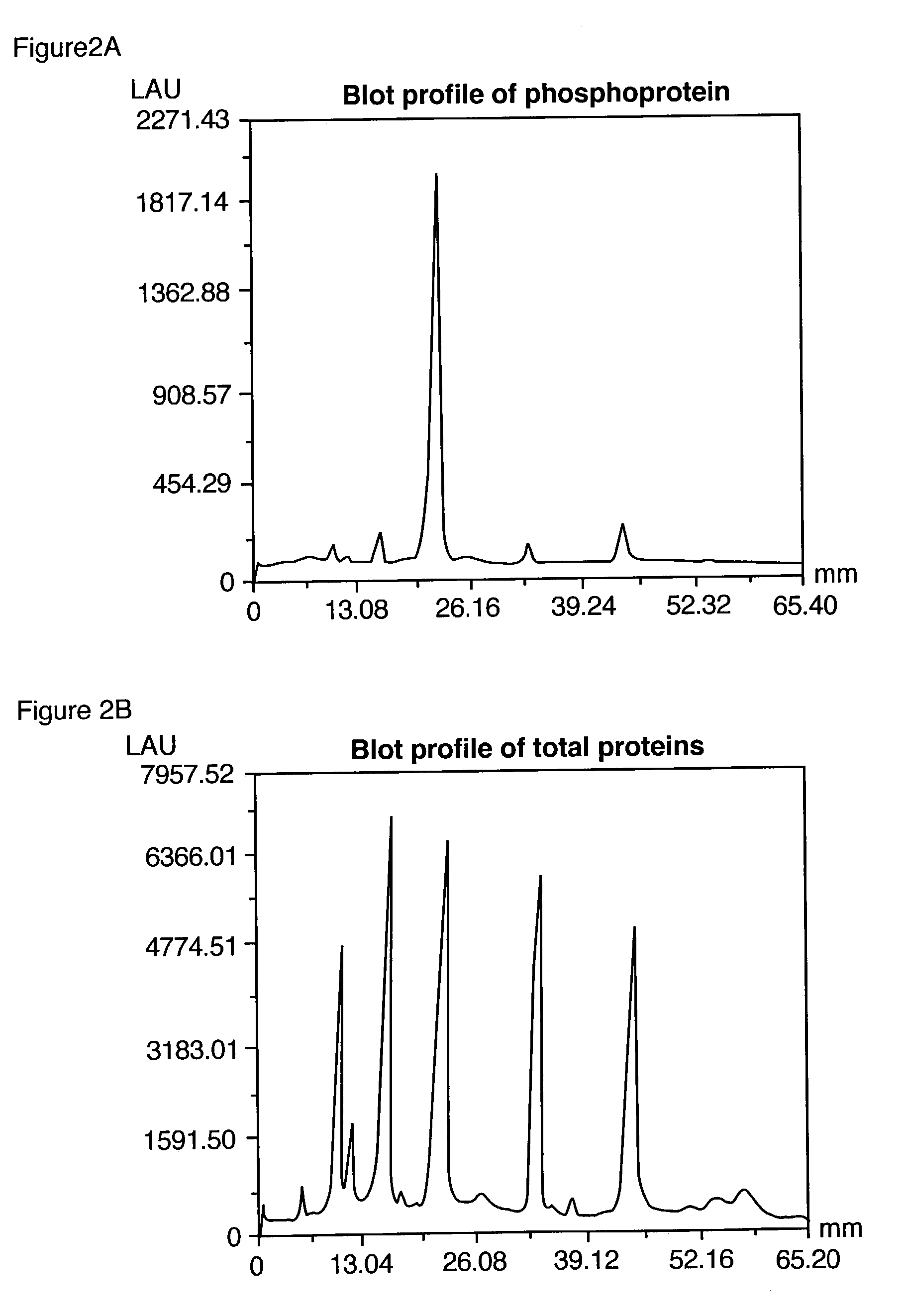
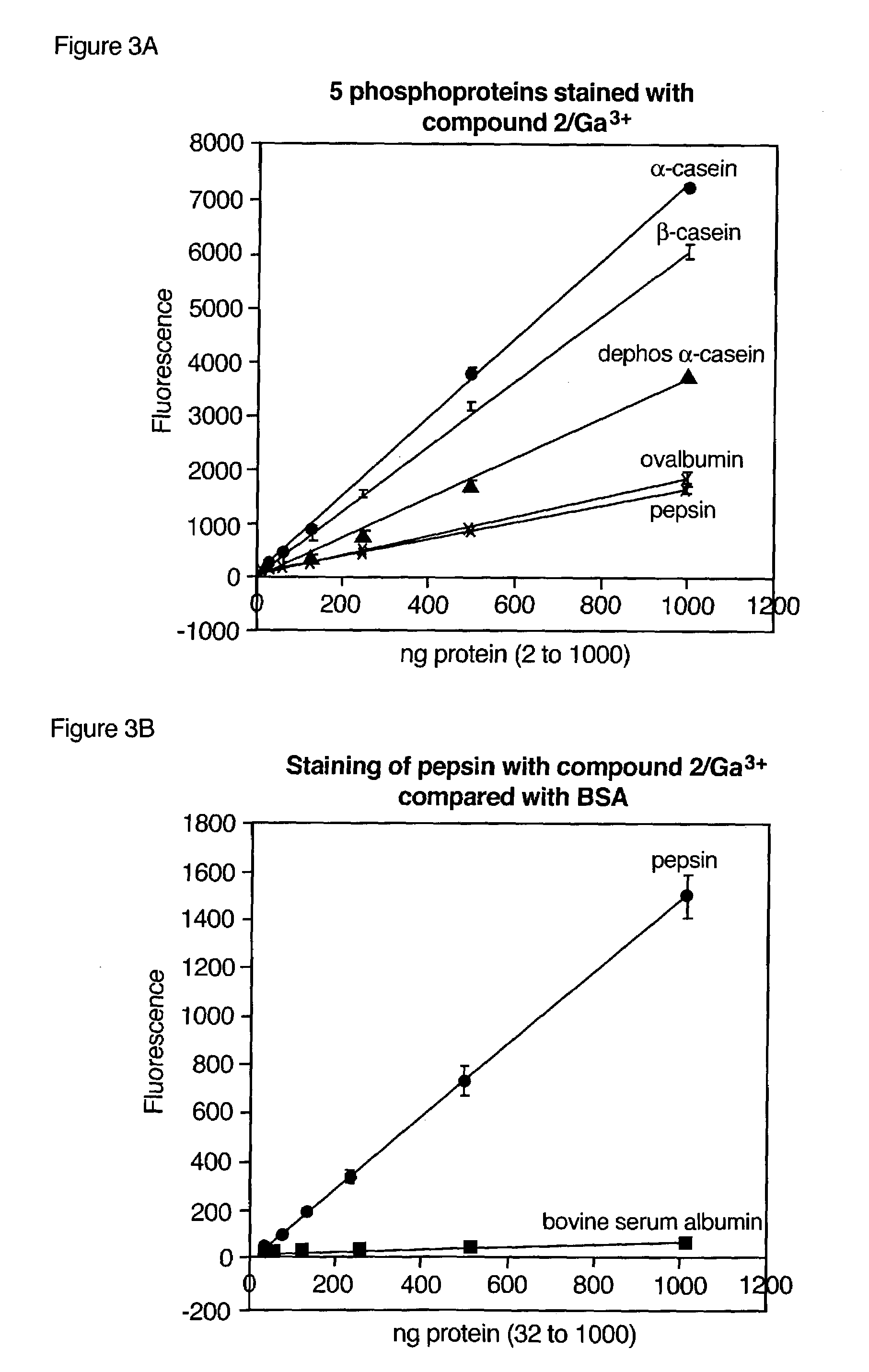
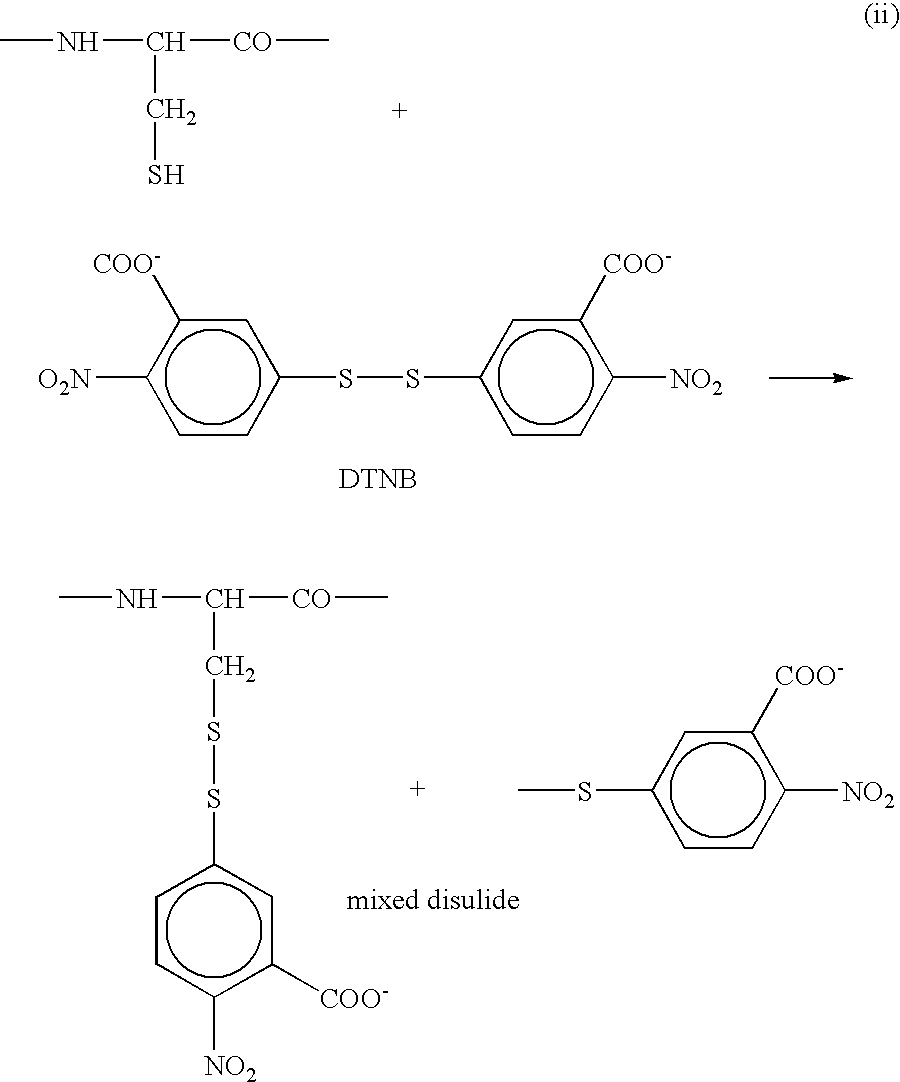
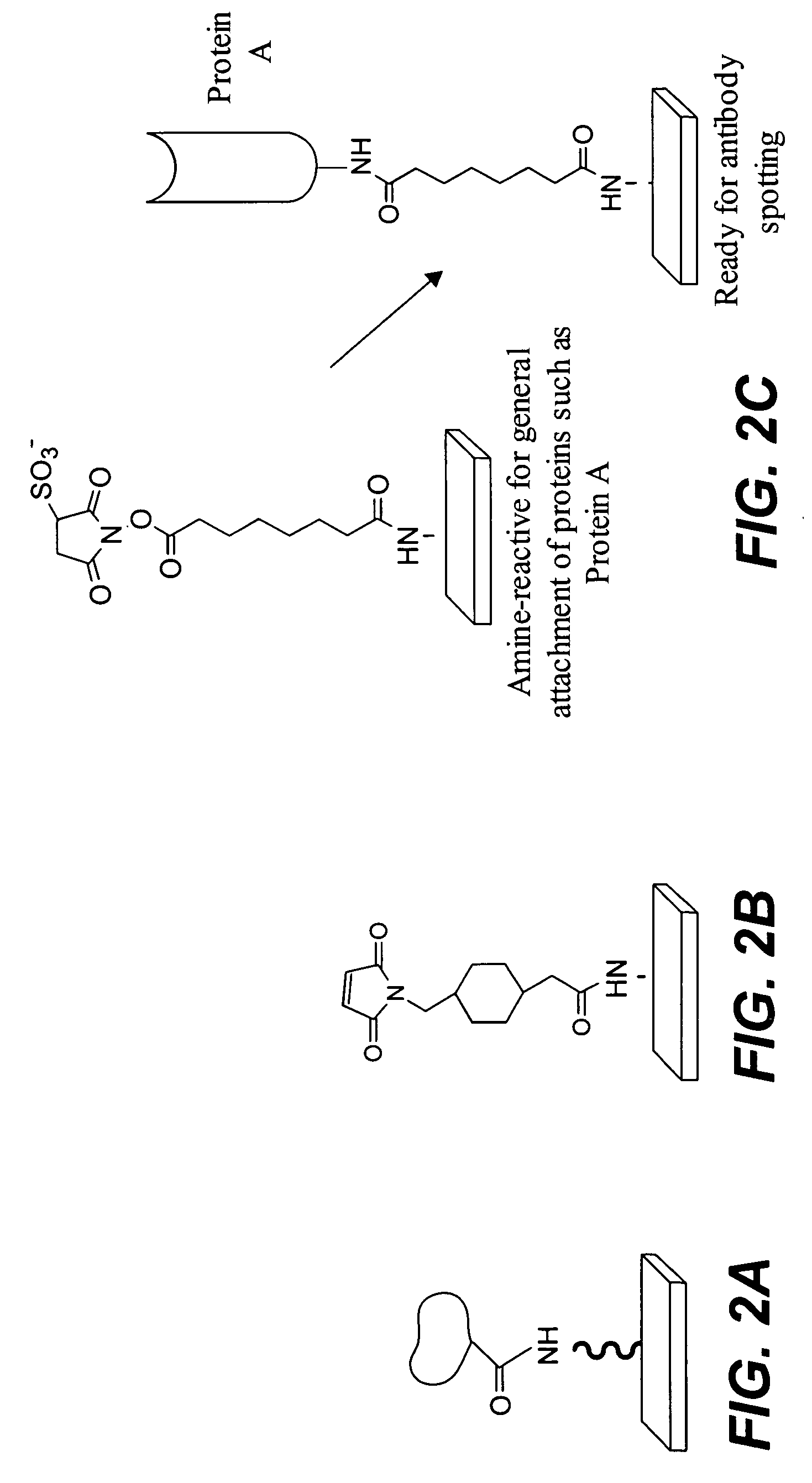
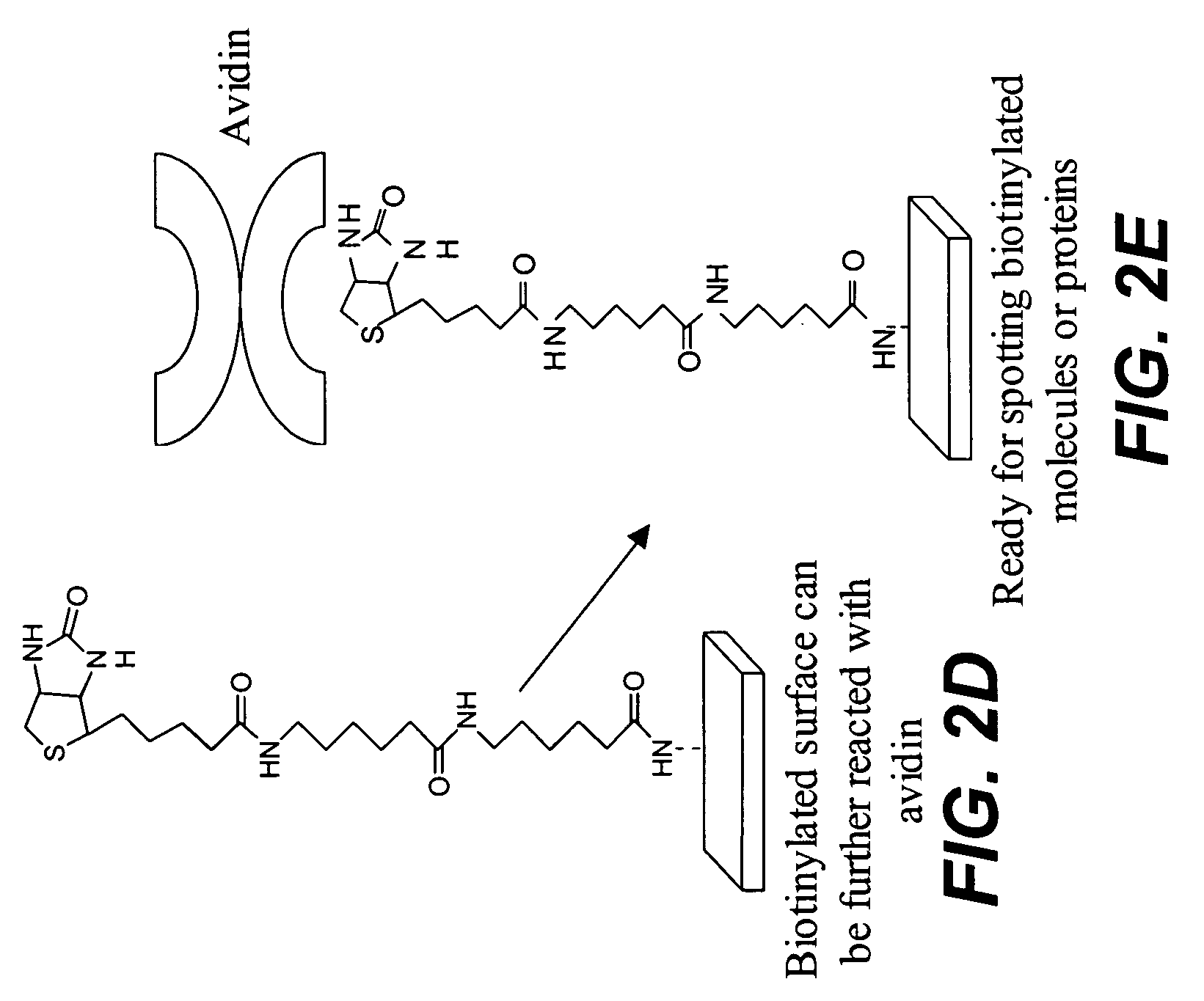
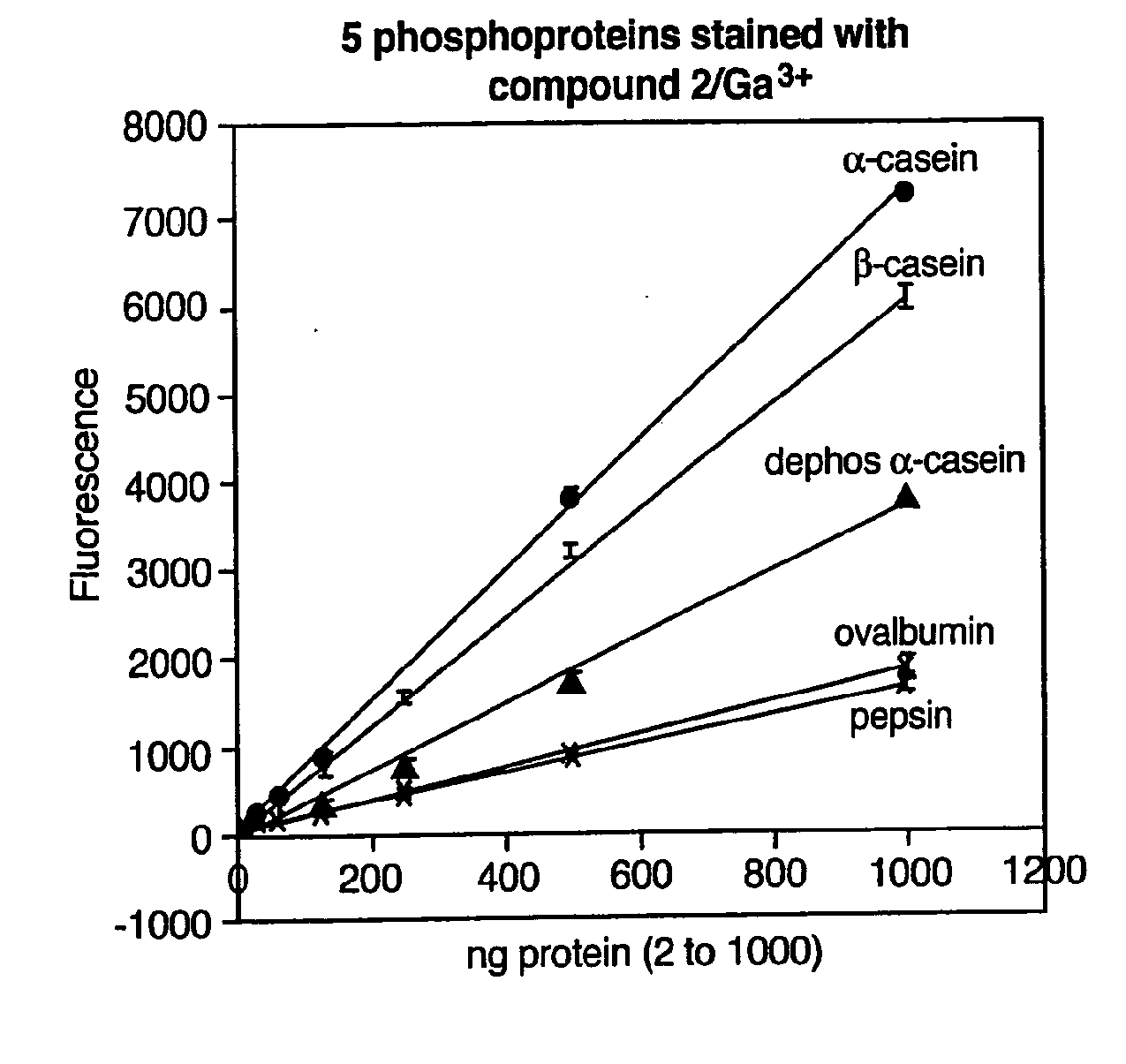
Compositions and methods for detection and isolation of phosphorylated molecules
ActiveUS7102005B2Simplifies subsequent analysisSilicon organic compoundsOther chemical processesTernary complexPhosphorylation
Owner:MOLECULAR PROBES
Assay for simultaneous genomic and proteomic analysis
InactiveUS20180208975A1High throughput screeningEfficient captureMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsAssay
The present invention is directed to a biochemical assay for simultaneous genomic and proteomic analysis.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
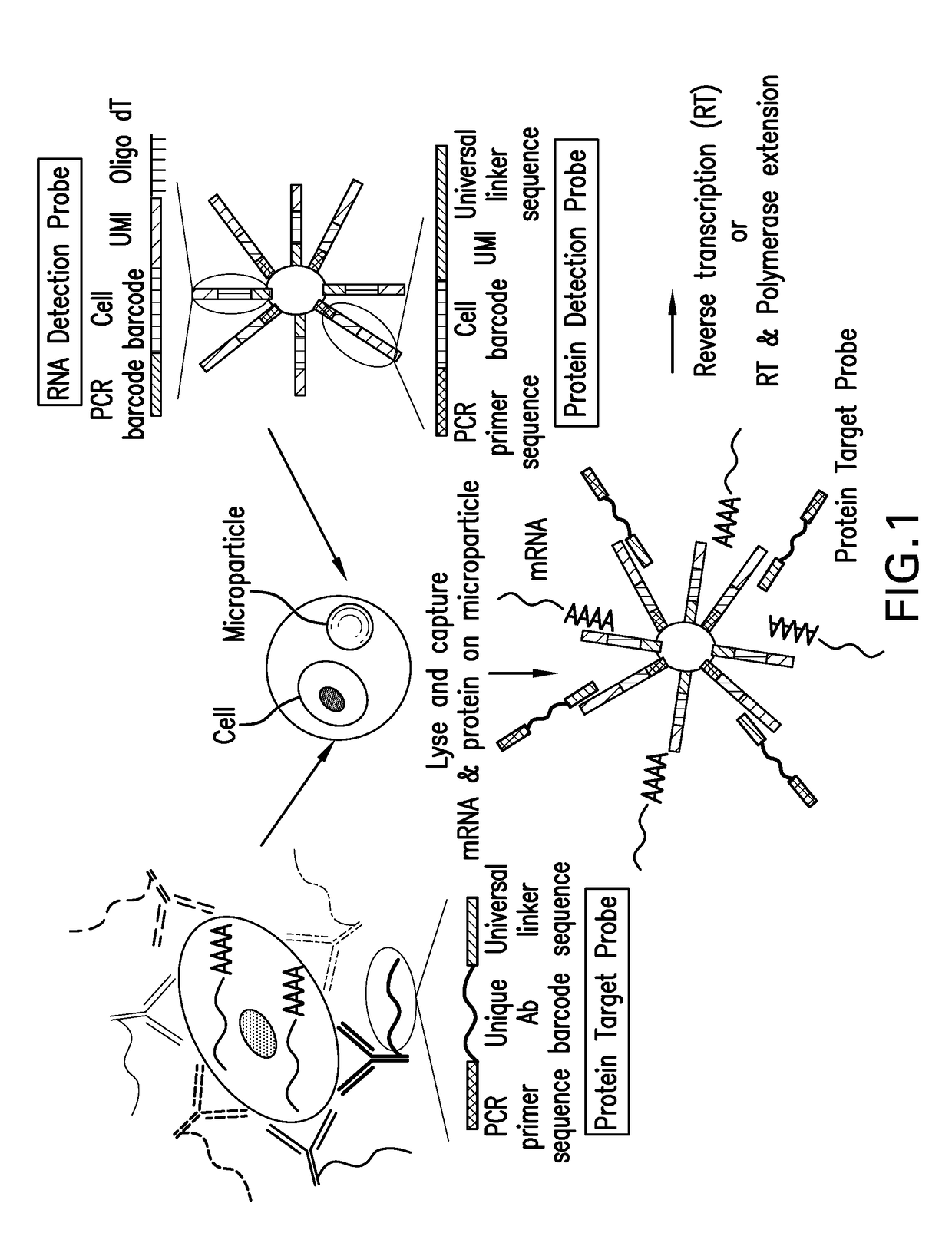
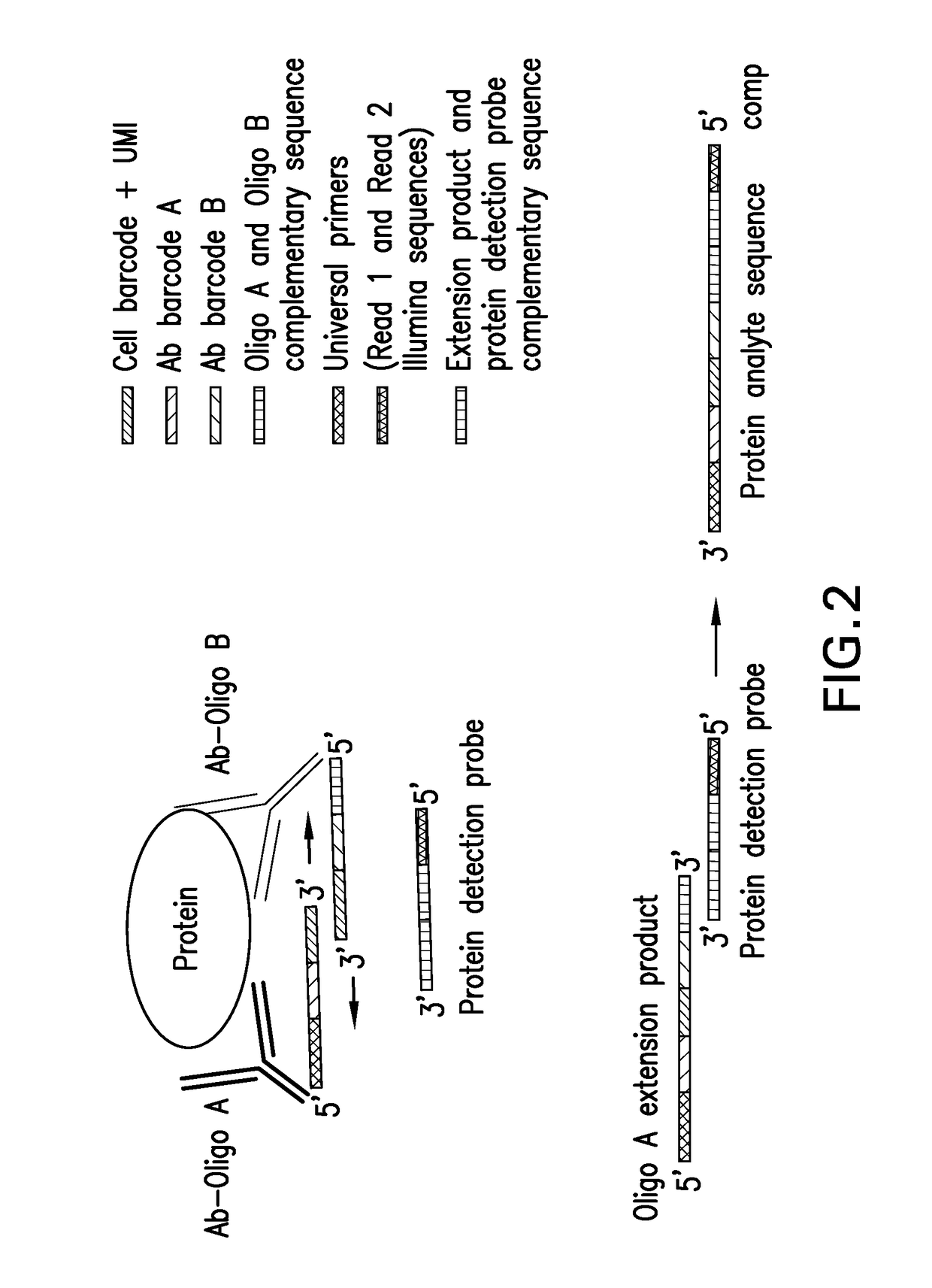
Digital protein quantification
PendingUS20170192013A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsLibrary tagsQuantification methodsQuantitative proteomics
Methods and compositions are described for single cell resolution, quantitative proteomic analysis using high throughput sequencing.
Owner:BIO RAD INNOVATIONS SAS +1
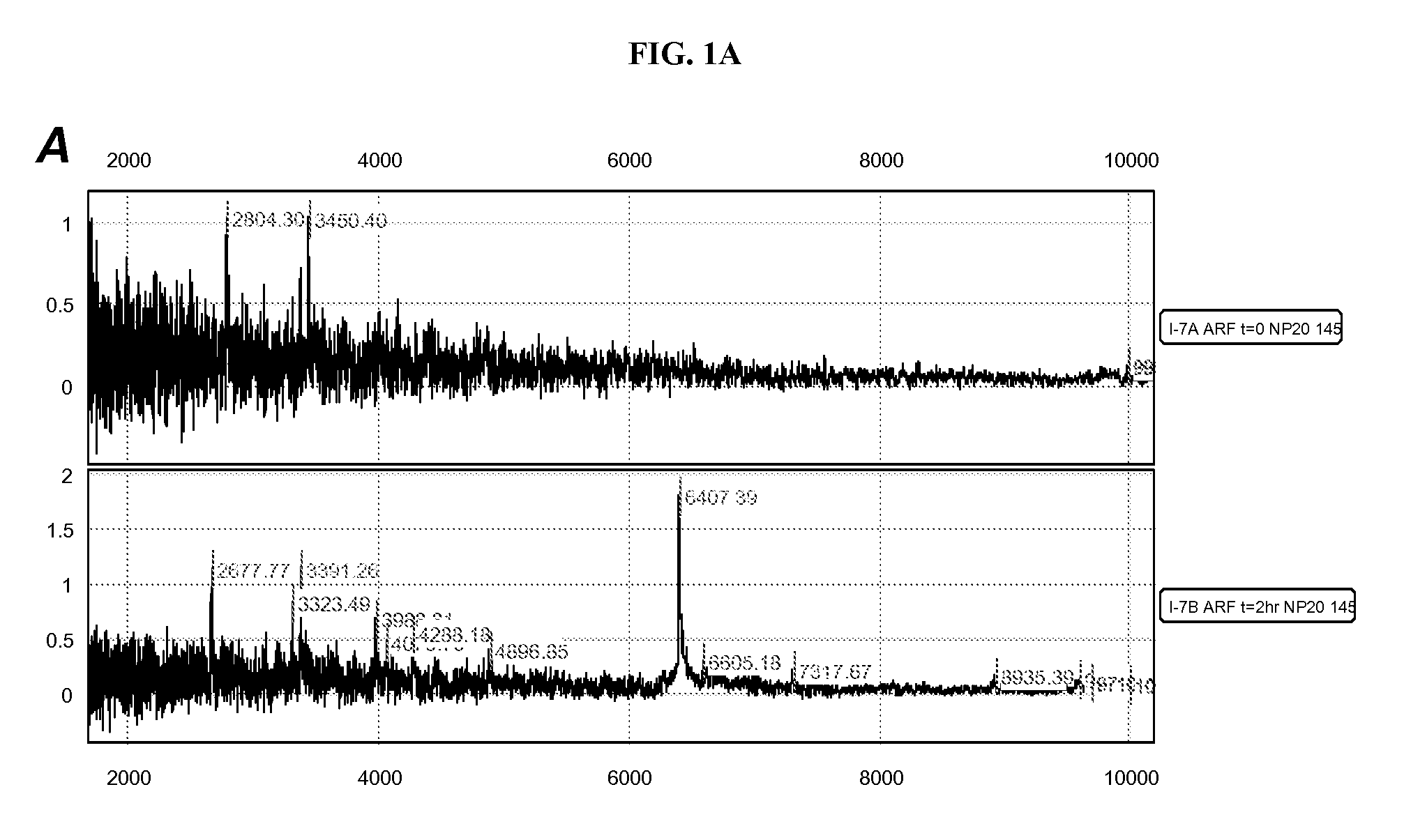
Method for the Early Detection of Renal Disease Using Proteomics
A method for the detection of an early biomarker for assessing a change in renal status in a mammalian subject following a renal event. The method typically includes the steps of (a) providing a body fluid sample obtained from a mammalian subject; (b) analyzing the molecular weight of the proteins in the sample using proteome analysis; and (c) identifying the presence of a protein in the sample selected from the group consisting of a 6.4 kDa protein, a 28.5 kDa protein, a 33 kDa protein, a 44 kDa protein, a 67 kDa protein, and combinations thereof. The presence of one of these proteins can serve as an early biomarker for assessing a change in renal status. The levels of these proteins can be compared to predetermined levels, and thus provide a determination of the subject's renal status. The invention also includes a method of assessing the administration of aprotinin during cardio-pulmonary bypass surgery and provides for methods where the level of the 6.4 kDa biomarker in the subject's urine directs a caregiver's therapeutic decision regarding the intra-operative administration of aprotinin.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Compositions and methods for detection and isolation of phosphorylated molecules
ActiveUS20050014197A1Simplifies subsequent analysisSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsTernary complexPhosphorylation
The present invention relates to phosphate-binding compounds that find use in binding, detecting and isolating phosphorylated target molecules including the subsequent identification of target molecules that interact with phosphorylated target molecules or molecules capable of being phosphorylated. A binding solution is provide that comprises a phosphate-binding compound, an acid and a metal ion wherein the metal ion simultaneously interacts with an exposed phosphate group on a target molecule and the metal chelating moiety of the phosphate-binding compound forming a bridge between the phosphate-binding compound and a phosphorylated target molecule resulting in a ternary complex. The binding solution of the present invention finds use in binding and detecting immobilized and solubilized phosphorylated target molecules, isolation of phosphorylated target molecules from a complex mixture and aiding in proteomic analysis wherein kinase and phosphatase substrates and enzymes can be identified.
Owner:MOLECULAR PROBES
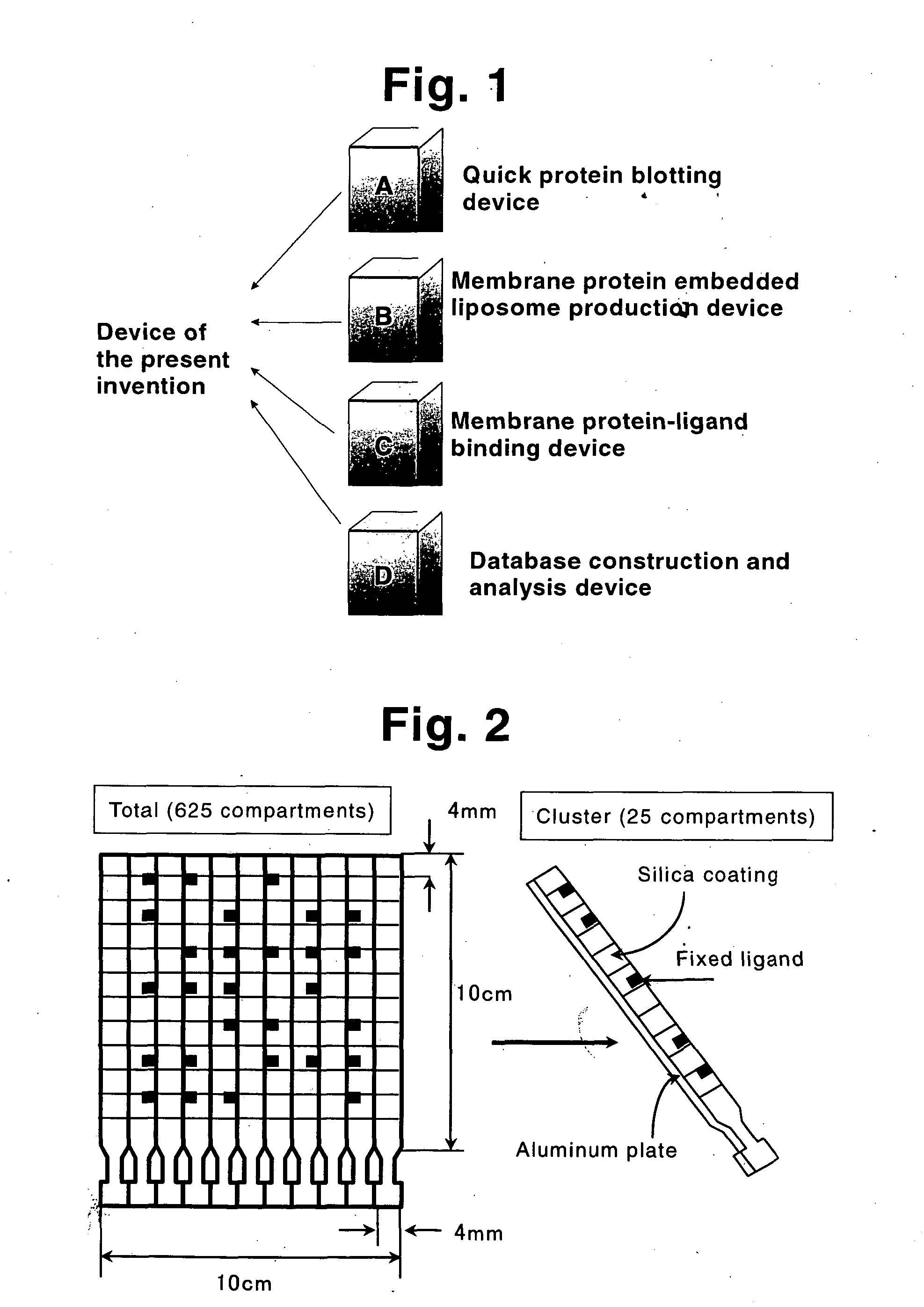
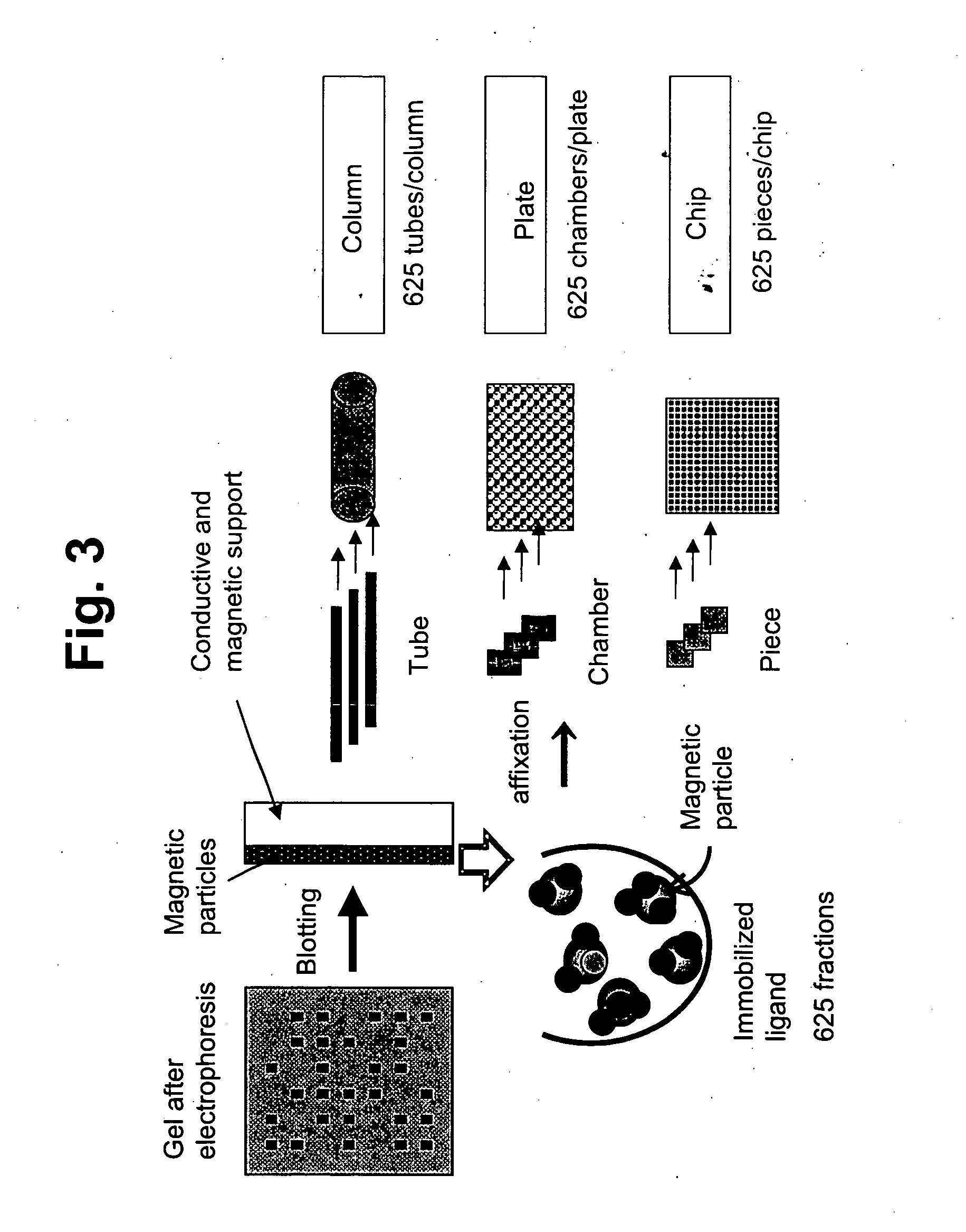
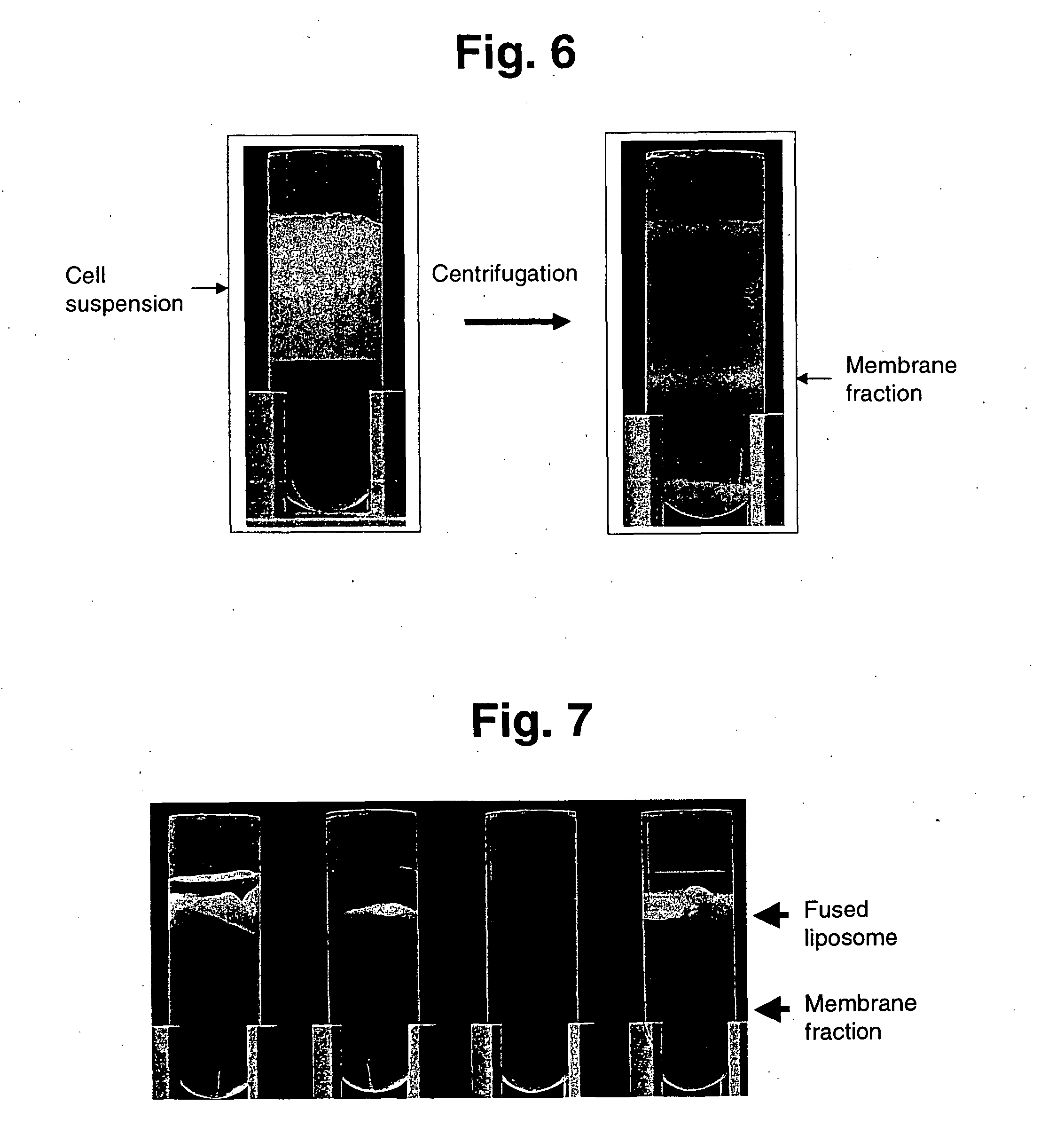
Membrane protein library for proteome analysis and method for preparing same
InactiveUS20050032113A1Useful for developmentPeptide librariesMicroencapsulation basedCell Membrane ProteinsLiposome
The present invention provides a library of membrane protein-embedded liposomes suitable for proteome analysis, a method for preparing same and a proteome analysis method using same.
Owner:PROTOSERA
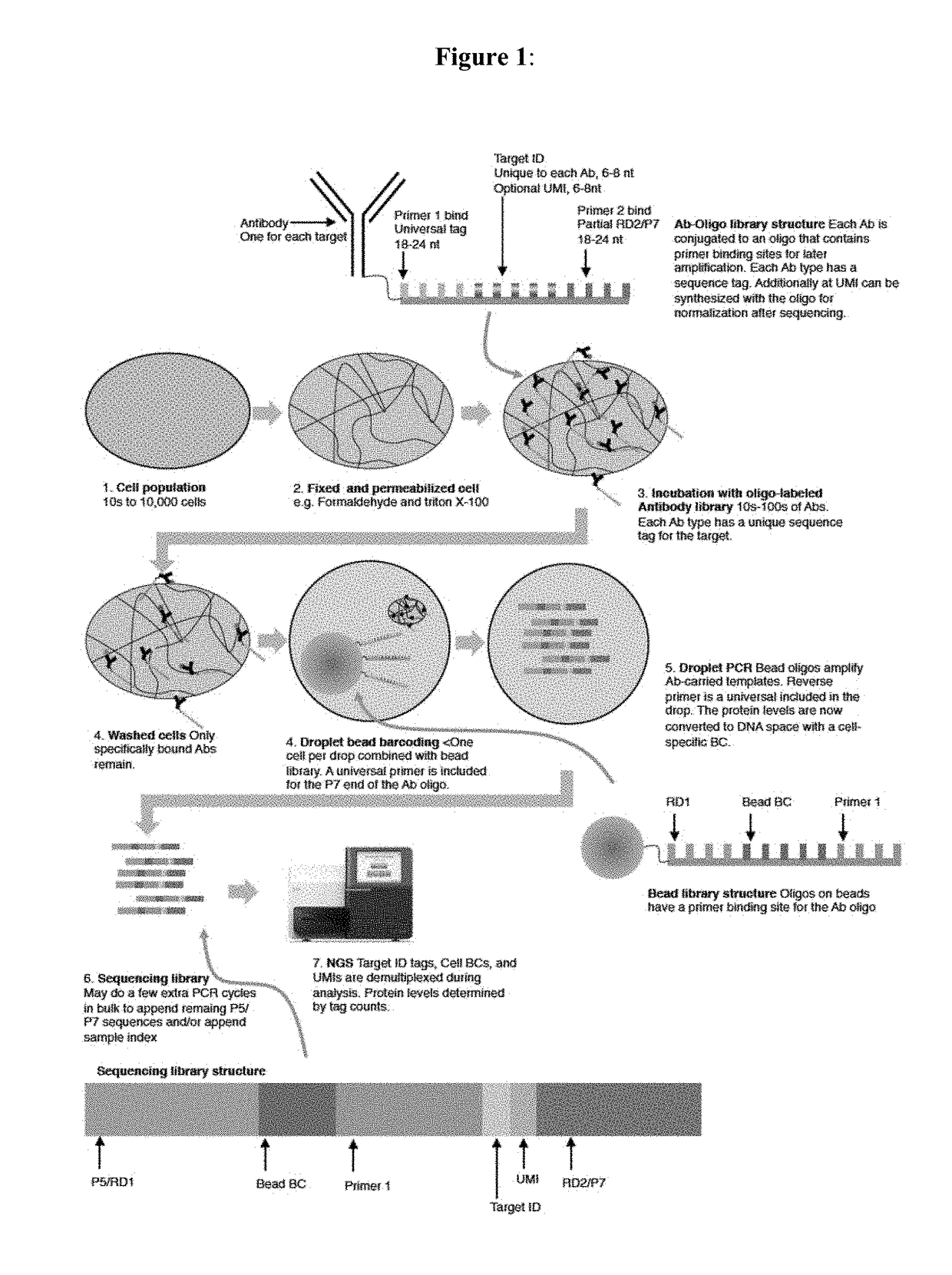
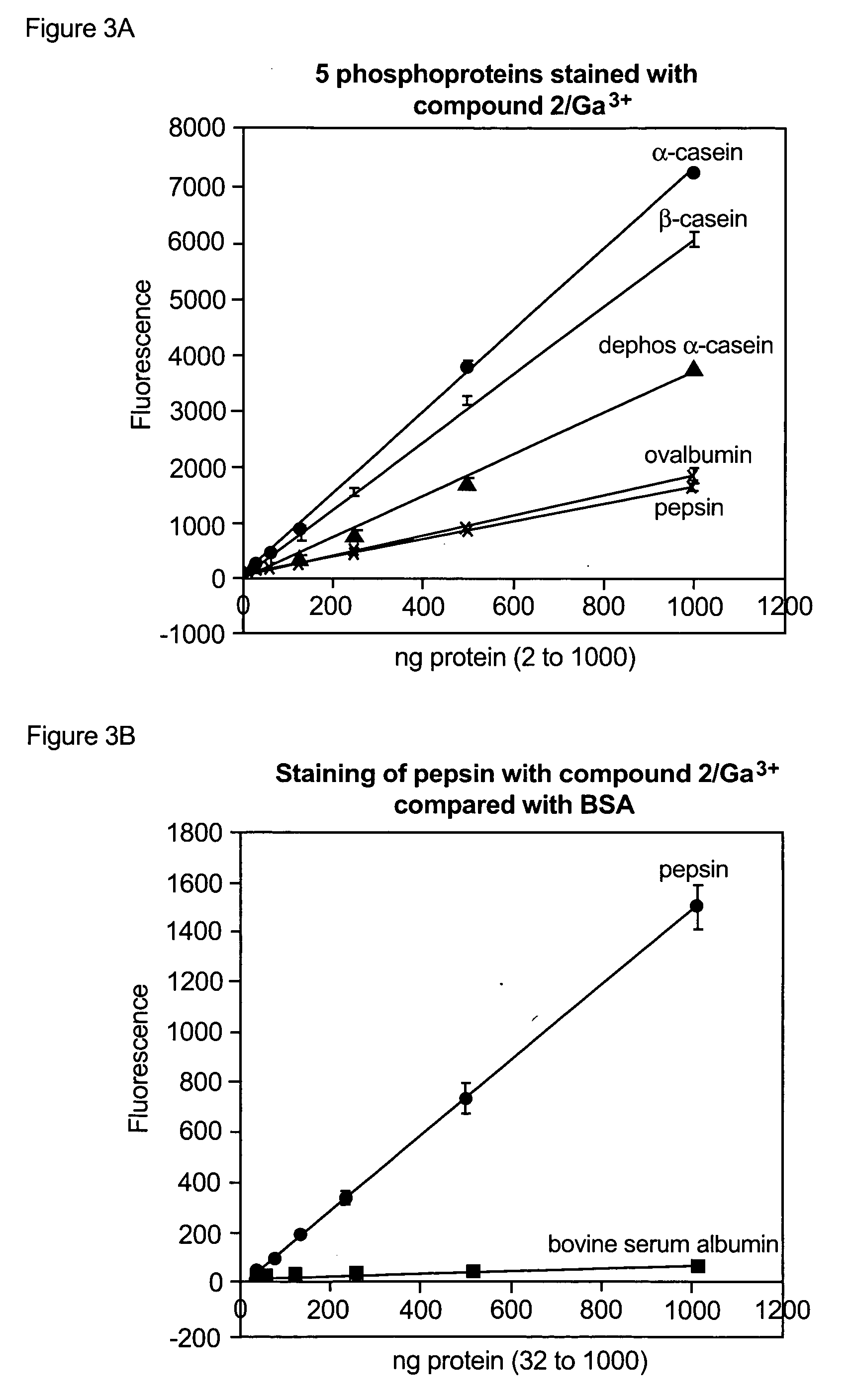
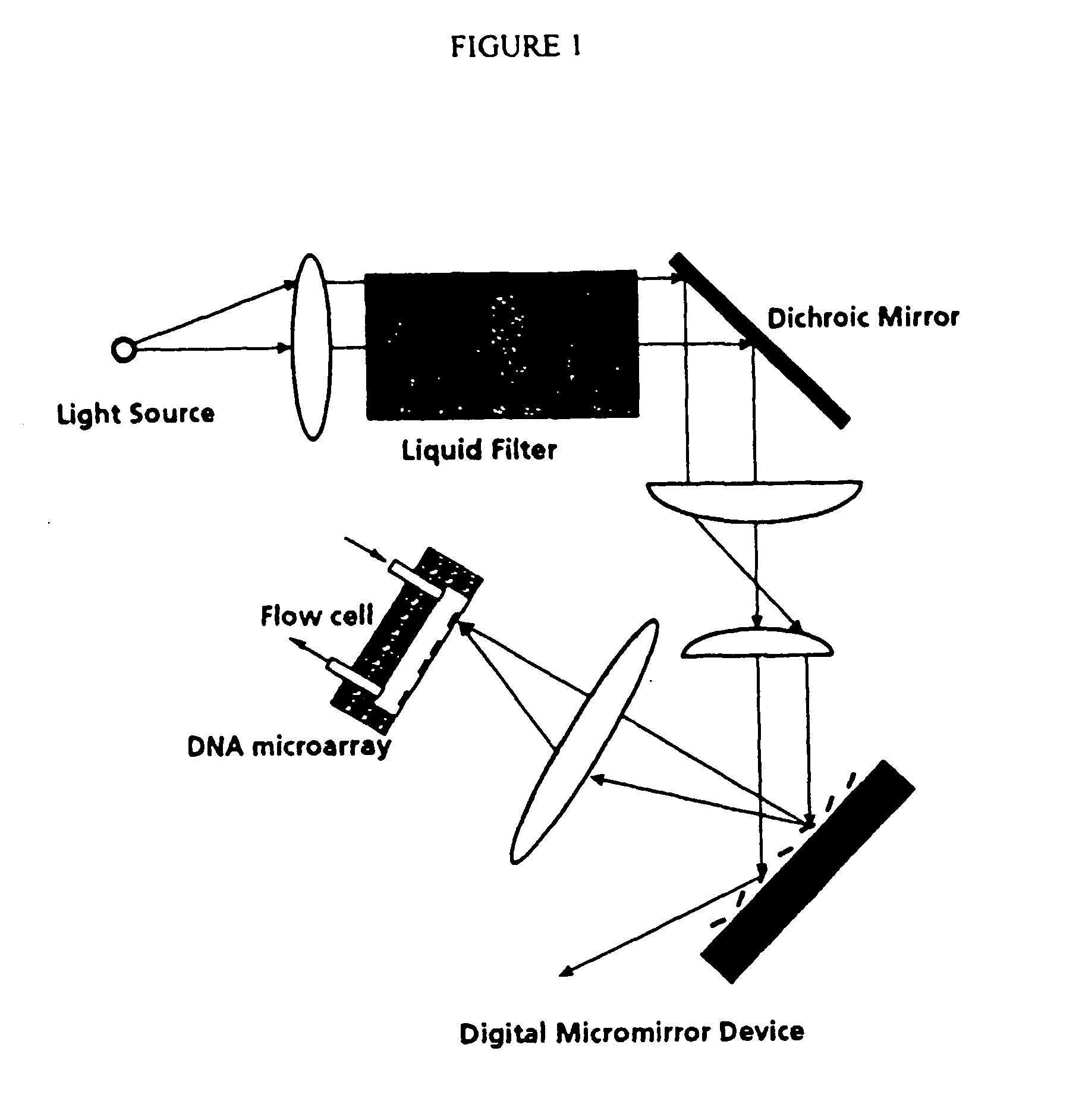
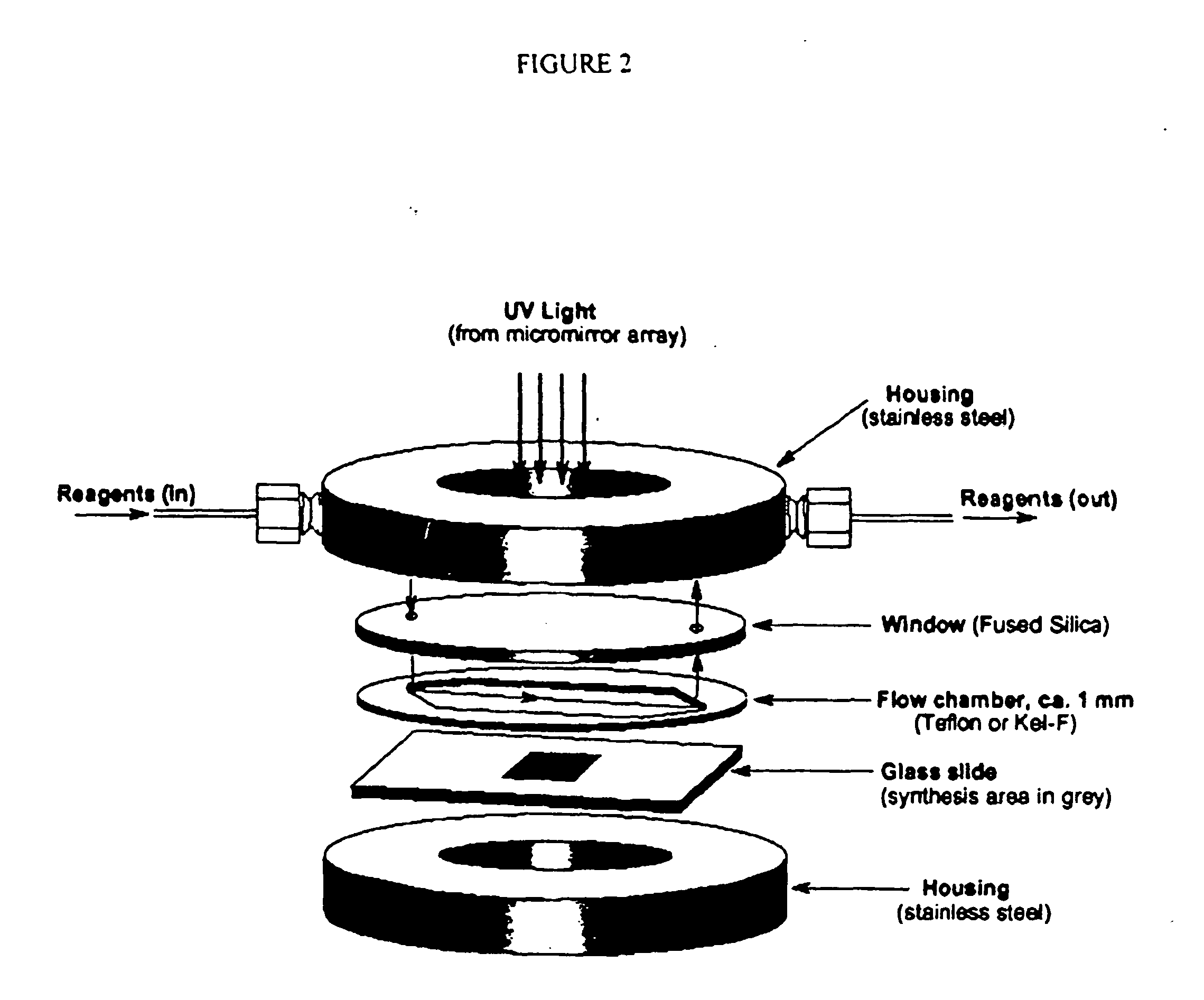
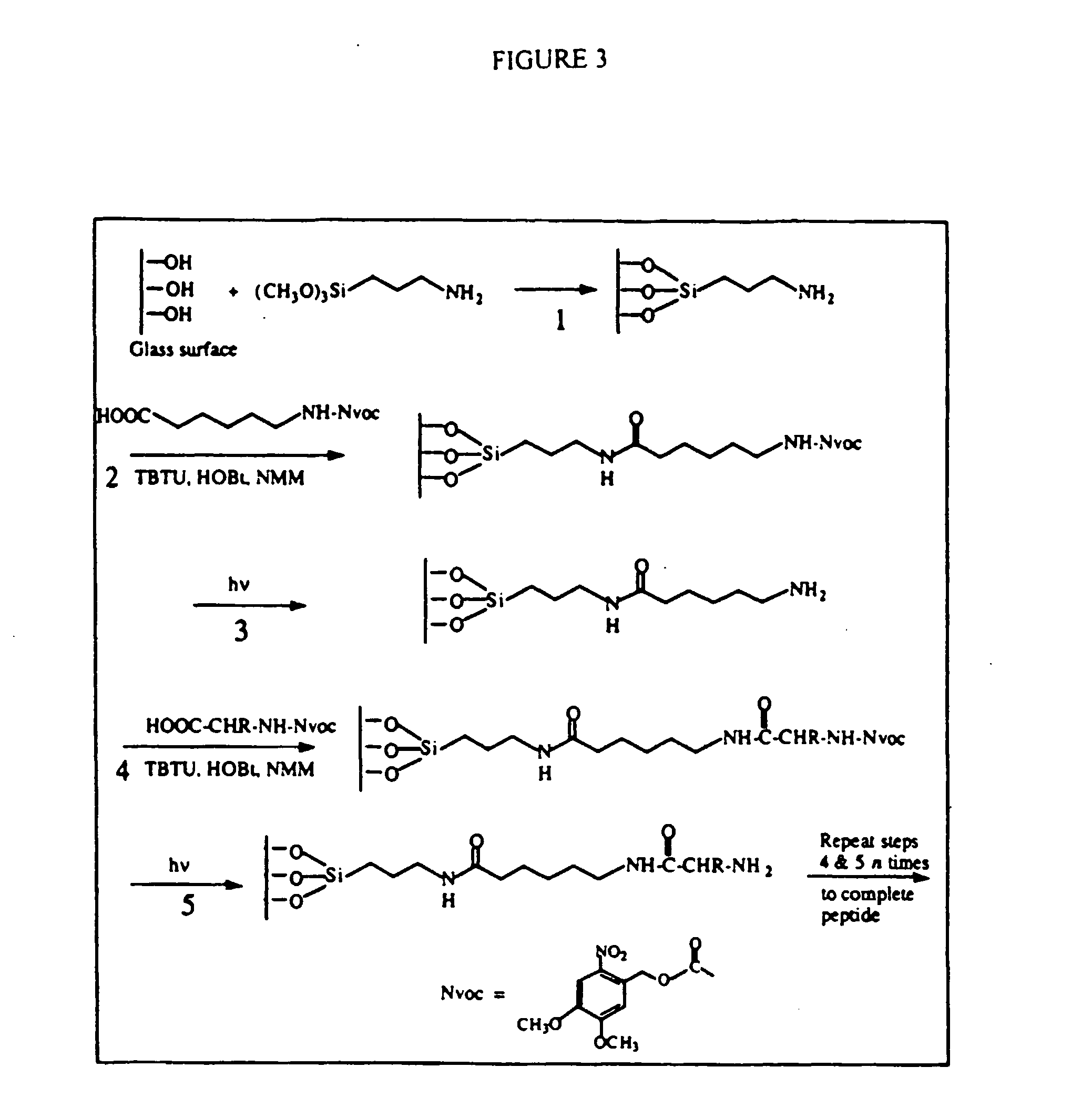
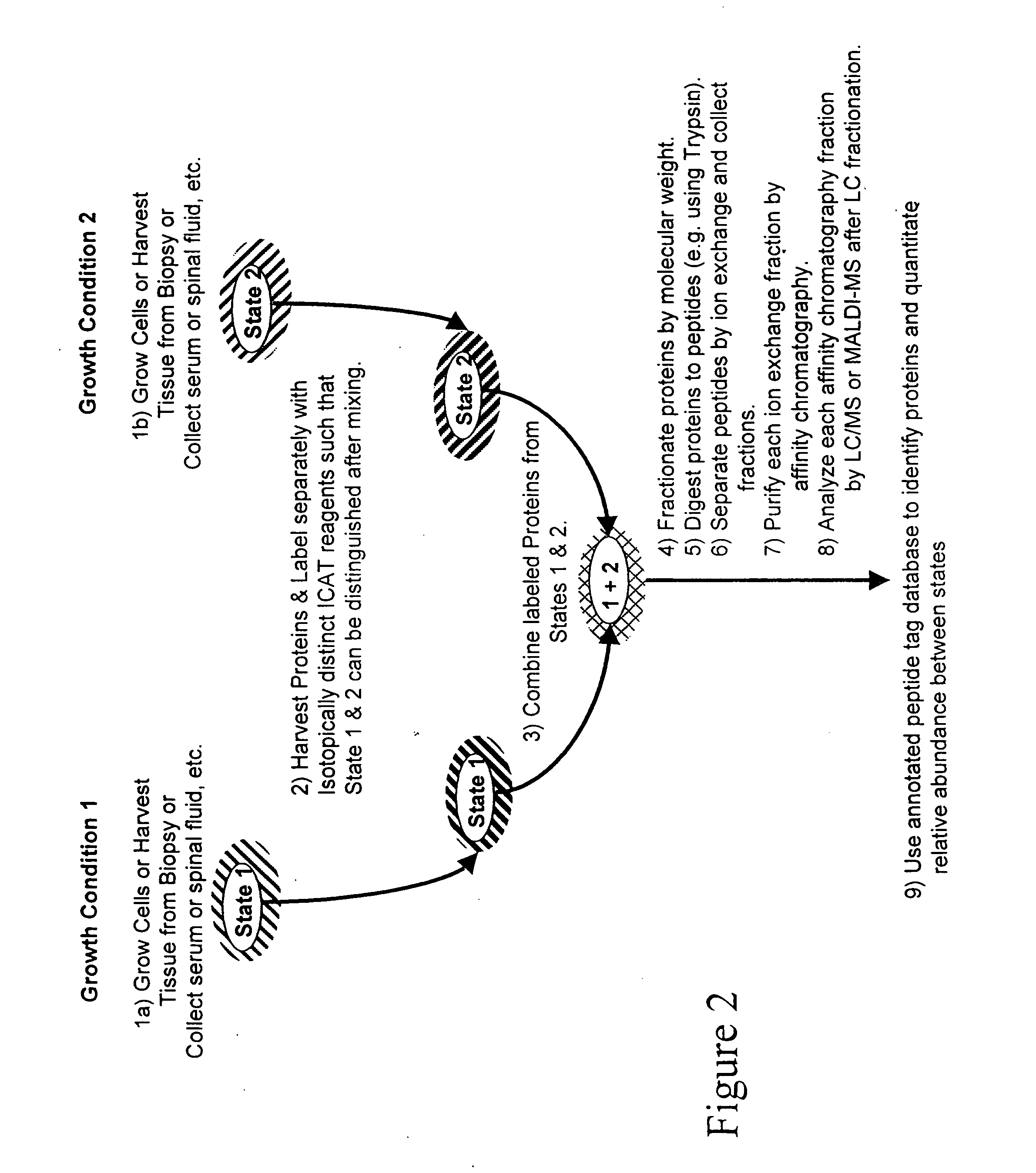
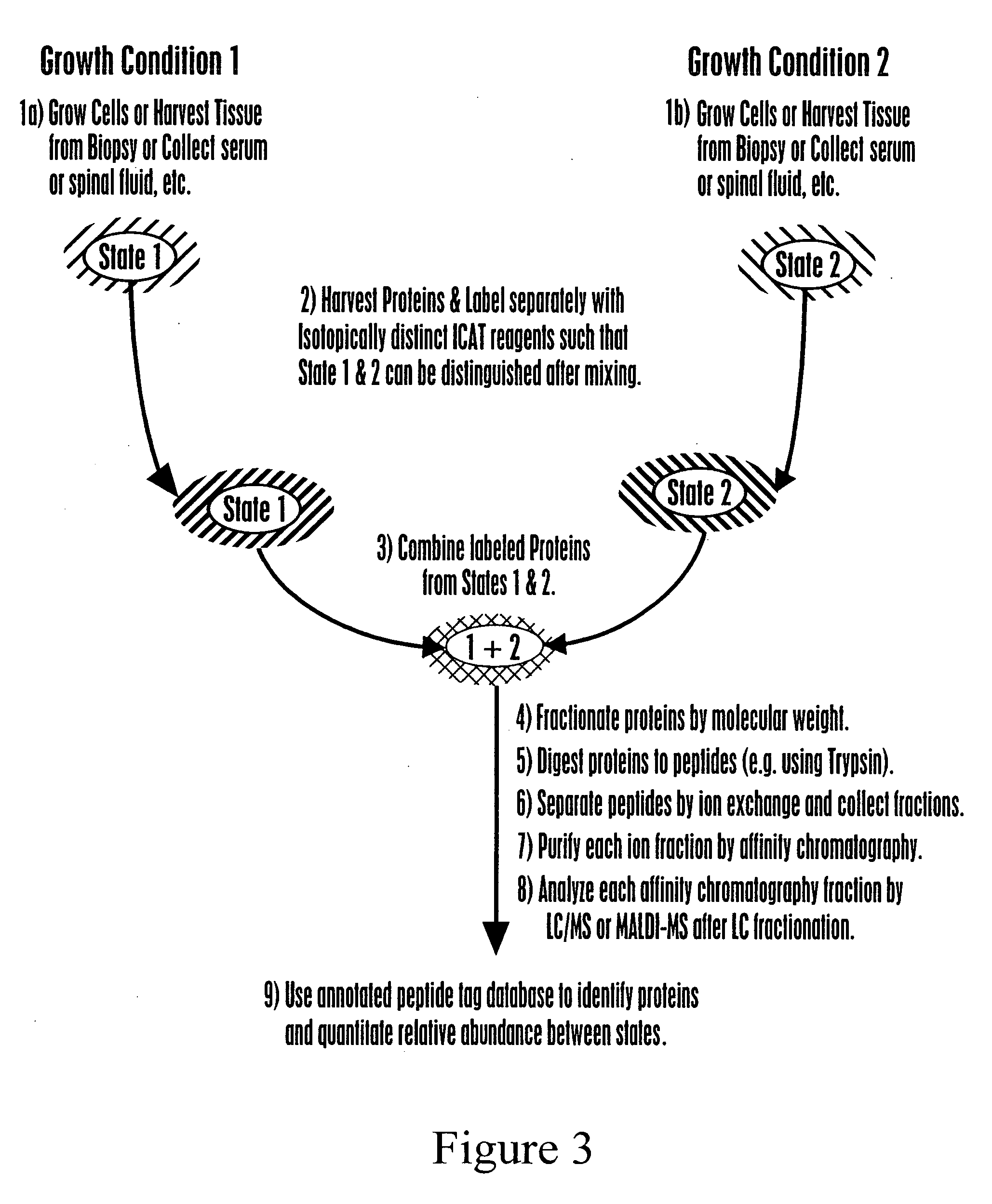
Apparatus, composition and method for proteome profiling
InactiveUS20050048566A1Sure easyPeptide librariesLibrary screeningProtein expression profileProtein abundance
The present invention is directed to a high throughput method for producing a large number of different antibodies, more specifically organized antibody microarrays. These antibodies and antibody microarrays can be used to rapidly assay protein abundance and identify types of proteins that are expressed in cells and tissues under a variety of conditions, or to compare protein expression profiles of different cells.
Owner:DELISI CHARLES +5
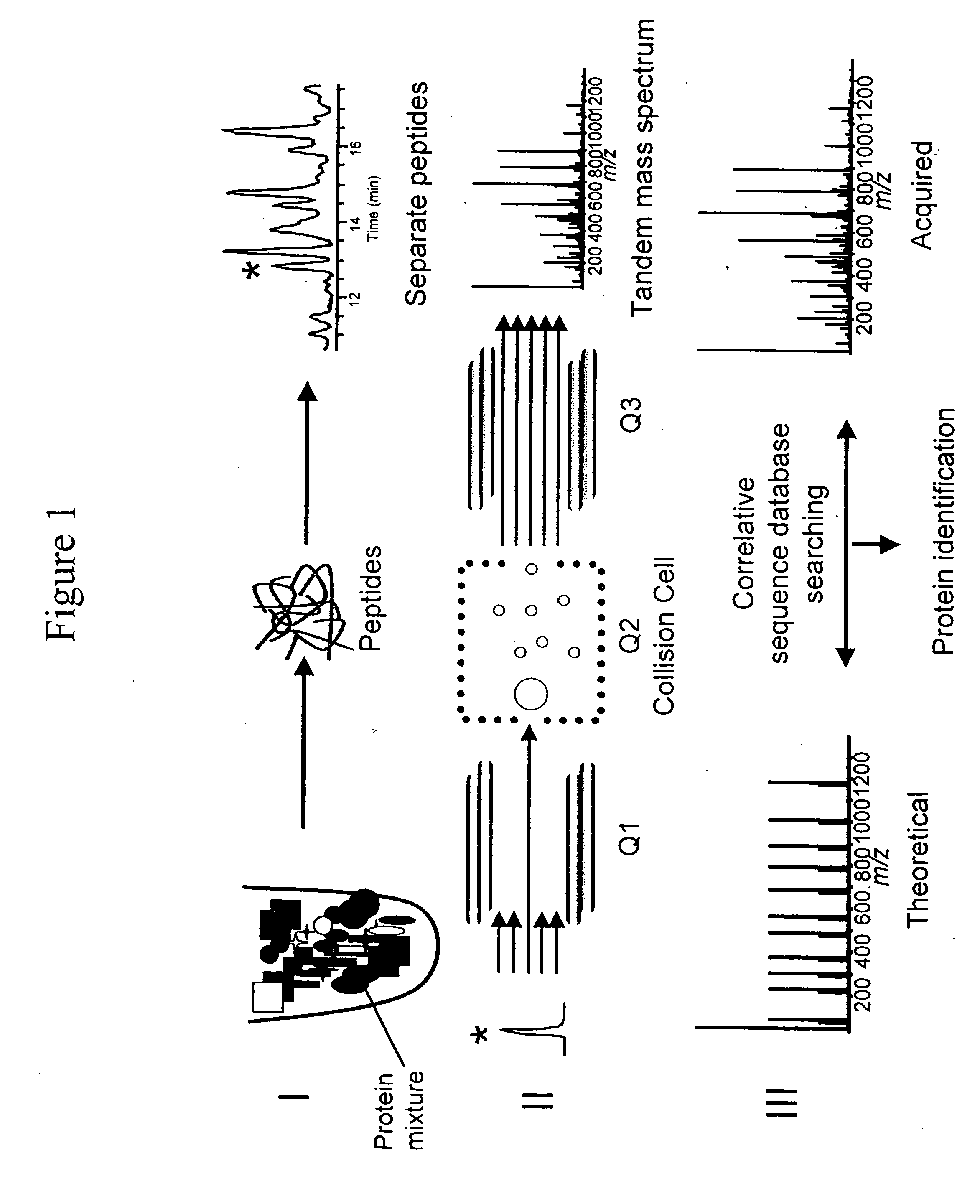
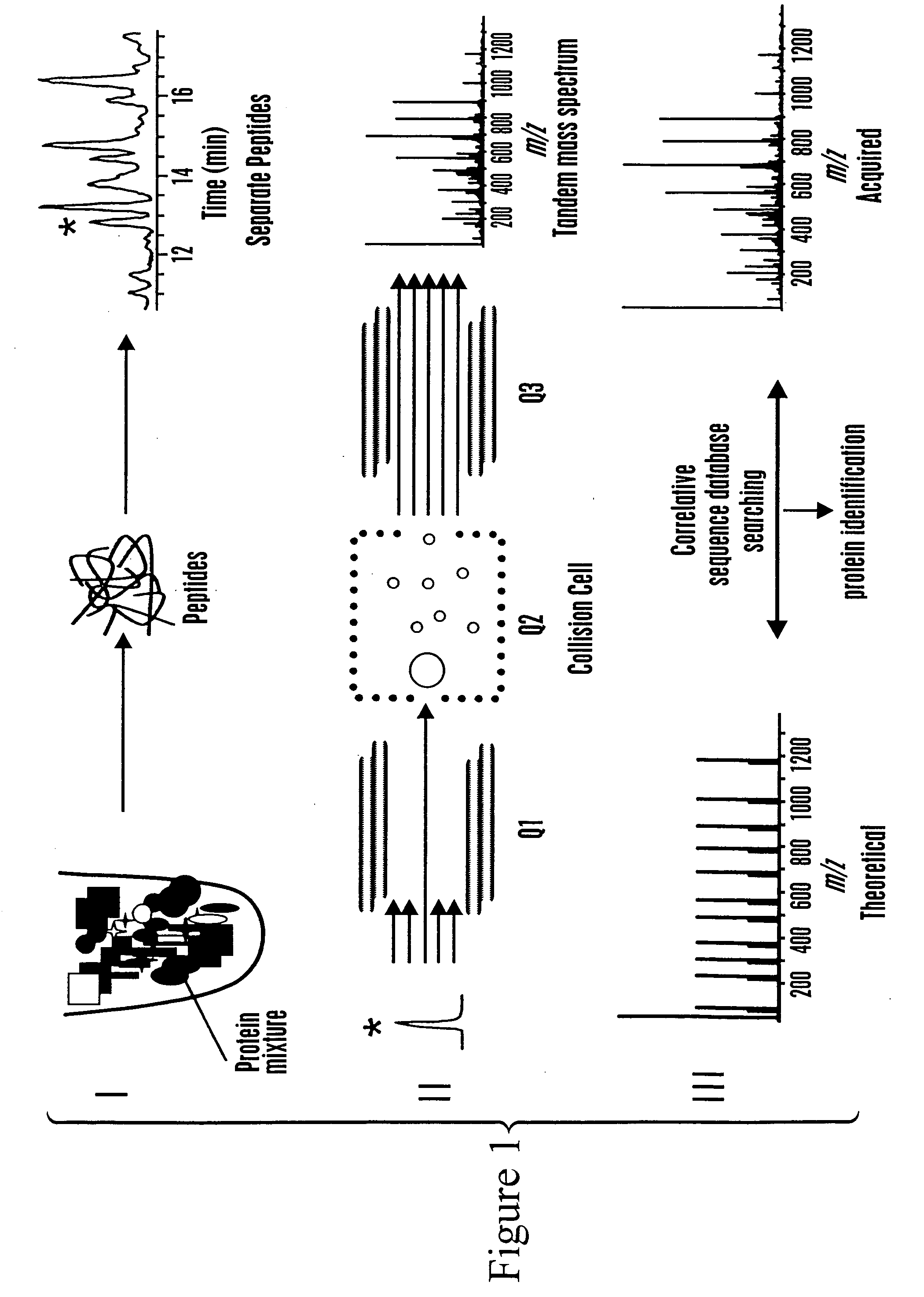
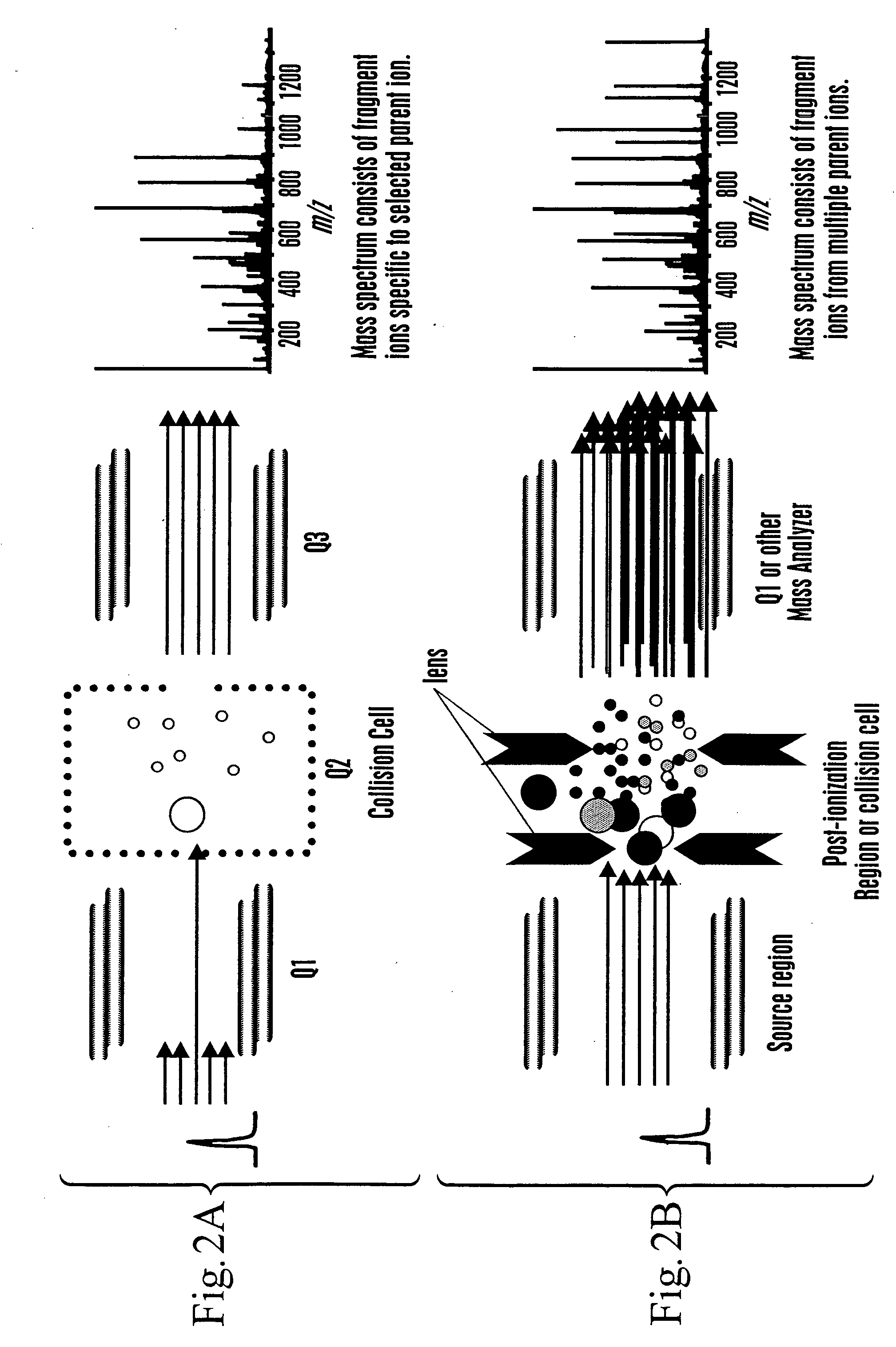
Methods for rapid and quantitative proteome analysis
The invention provides methods for identifying a polypeptide. The method can include determining two or more characteristics associated with the polypeptide, or a fragment thereof, one of the characteristics being mass of a fragment of the polypeptide, the fragment mass being determined by mass spectrometry; comparing the characteristics associated with the polypeptide to an annotated polypeptide index; and identifying one or more polypeptides in the annotated polypeptide index having the characteristics. The method can further include the steps of determining one or more additional characteristics associated with the polypeptide; comparing the determined characteristics to the annotated polypeptide index; optionally repeating the steps one or more times, wherein a set of characteristics is determined that identifies a single polypeptide in the annotated polypeptide index, and optionally quantitating the amount of identified polypeptide in a sample containing the polypeptide. The invention also provides methods for generating a polypeptide identification index.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR SYSTEMS BIOLOGY +1
Rapid and quantitative proteome analysis and related methods
The invention provides methods for identifying polypeptides. The method can include the steps of simultaneously determining the mass of a subset of parent polypeptides from a population of polypeptides and the mass of fragments of the subset of parent polypeptides; comparing the determined masses to an annotated polypeptide index; and identifying one or more polypeptides of the annotated polypeptide index having the determined masses. The method can further include the steps of determining one or more additional characteristics associated with one or more of the parent polypeptides; comparing the determined characteristics to the annotated polypeptide index; and optionally repeating the steps one or more times, wherein a set of characteristics is determined that identifies a parent polypeptide as a single polypeptide in the annotated polypeptide index. The method can additionally include the step of quantitating the amount of the identified polypeptide in a sample containing the polypeptide.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR SYSTEMS BIOLOGY
Methods and apparatus for gel-free qualitative and quantitative proteome analysis, and uses therefore
InactiveUS20050196823A1Component separationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiophysical chemistryCompound (substance)
Methods and apparatus for qualitative and quantitative proteome analysis are provided. The methods and apparatus allow for the isolation of a subset of peptides out of complex mixtures of peptides. The isolation is based on a specific chemical and / or enzymatic alteration of one or more types of peptides. This alteration modifies the biophysical, chemical or any other biochemical property of the affected types of peptides (e.g., net electrical charge and / or hydrophobicity) in such way that the altered peptides can be separated from the unaltered peptides.
Owner:PRONOTA NV
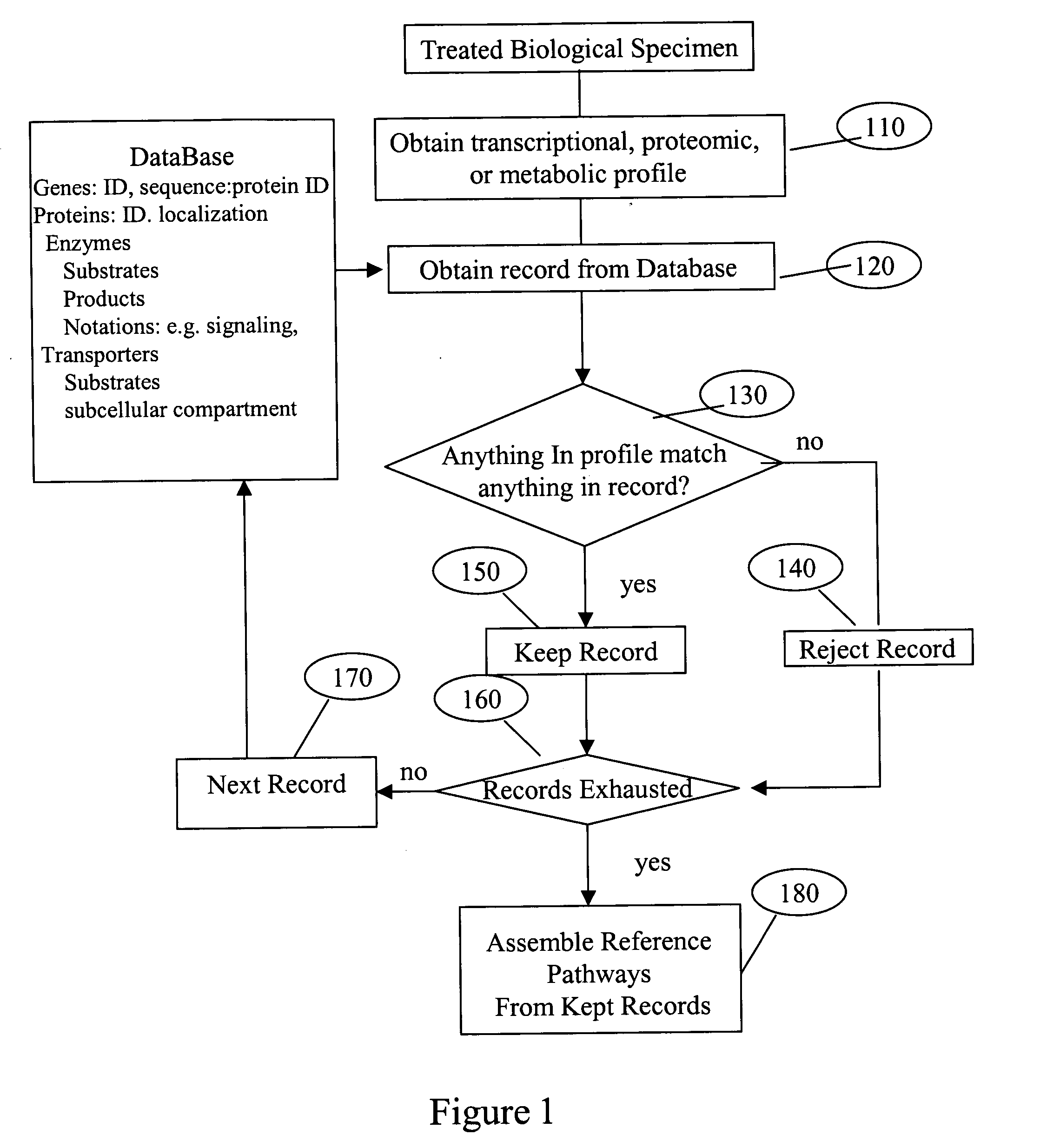
System and process of determining a biological pathway based on a treatment of a biological specimen
InactiveUS20050260615A1Rapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMetabolomeOrganism
Provided herein is a system and method for analyzing microarray data (transcriptome profiles), metabolite data (metabolome profiles), protein level data (proteome profiles), or any combination thereof to determine the biochemical pathways affected by a treatment. The system and method can be used to generate biochemical pathway information for any organism for which metabolic profile data can be obtained. The system and method may allow users to query the pathways generated and to filter the results of queries based on the -omic profile data, pathways involving molecules of interest, notions of biochemical importance, milestone molecules, and other factors. The system and method may also be suitable for discovery of regulatory sequences in genes. In an exemplary use, the system and method can be utilized to identify three genes involved in “de novo” ammonia “biosynthesis” that are induced by light, and was able to identify a putative cis-element, GWTTGTGG, that is likely involved in the regulation of those genes.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
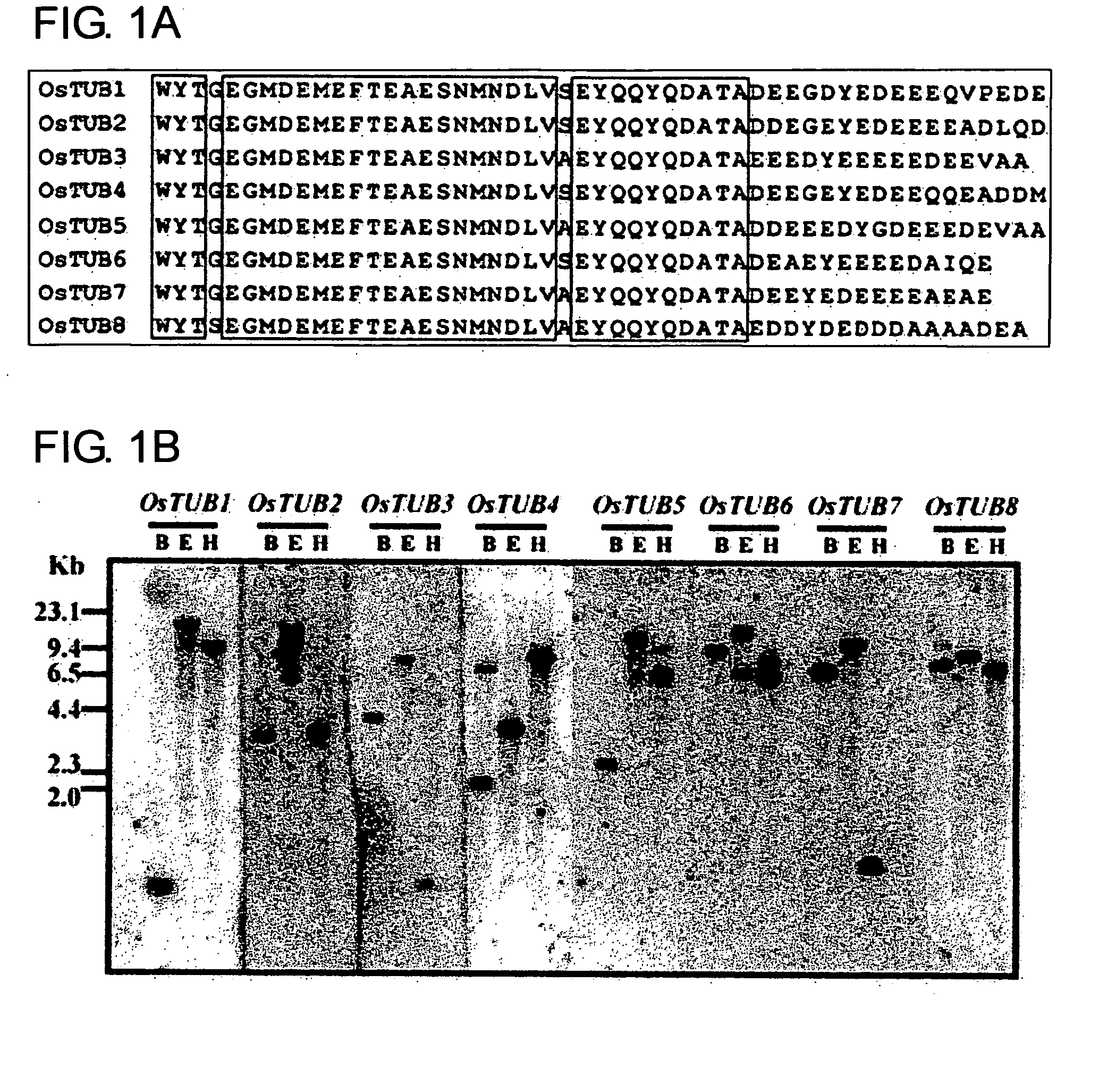
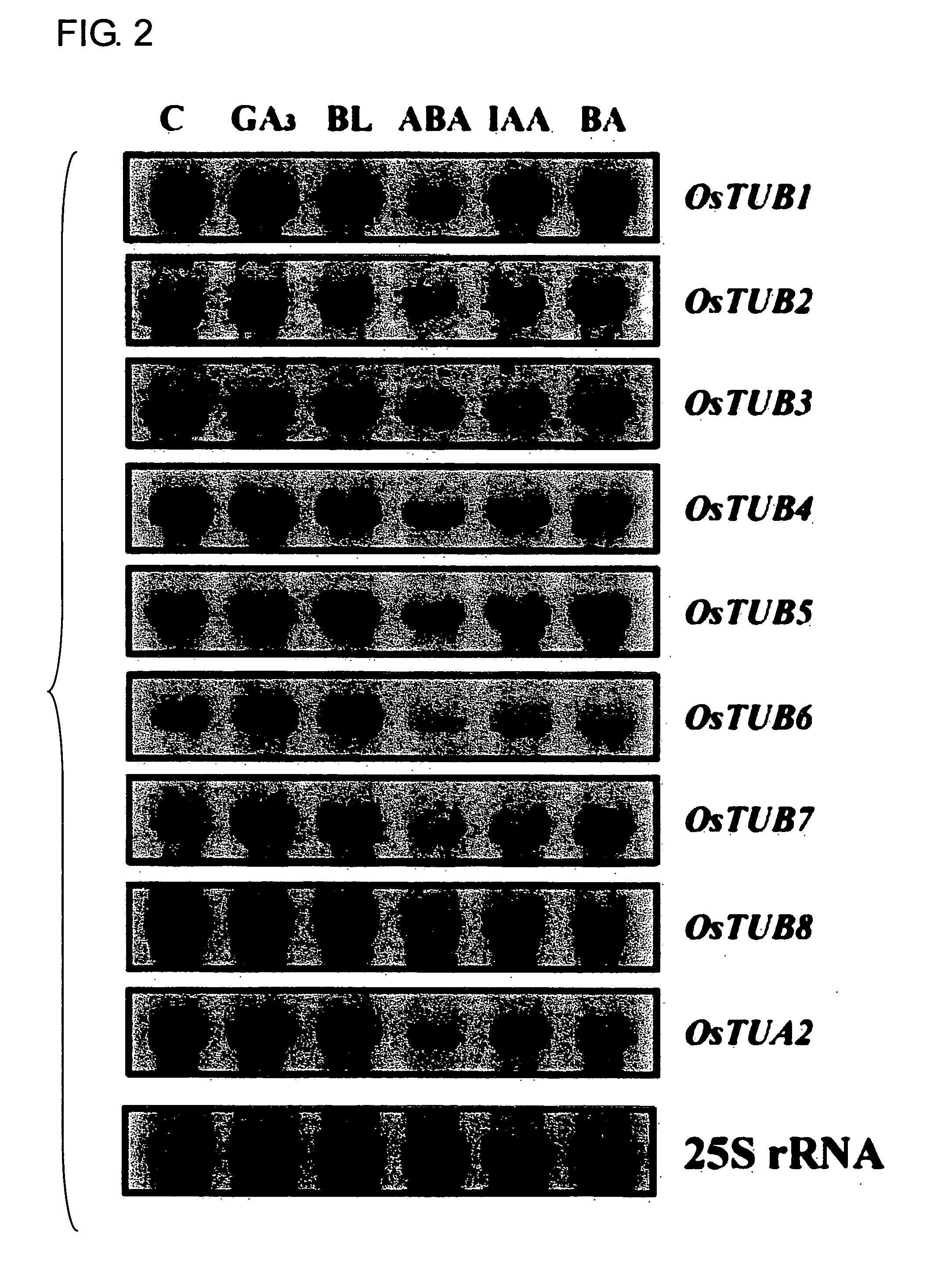
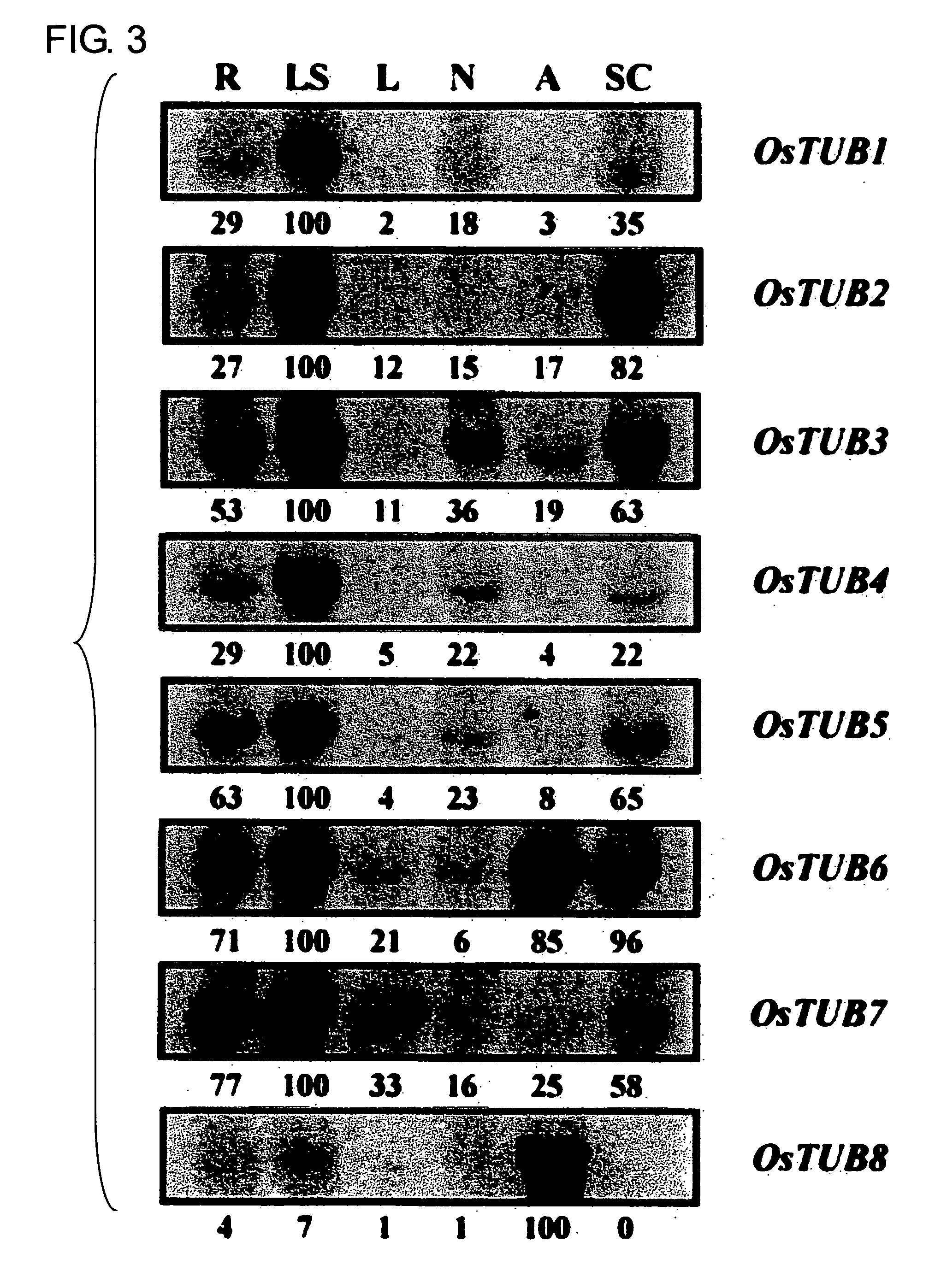
Anther-specific genes, their promoters, and uses of the same
The present invention provides novel anther-specific genes, their promoters, and uses of the same. Rice seedlings were treated with gibberellin, and then genes and proteins with up-regulated expression were screened using DNA microarray analysis and proteome analysis. As a result, eight types of β-tubulins were identified. Among them, OsTUB8 was expressed specifically in the anther. Thus OsTUB8 was suggested to be involved in male sterility in rice, and it was thought that regulating OsTUB8 expression in plants could alter plant fertility. In addition, OsTUB8 promoters were thought to comprise anther-specific activity. Thus, the present invention can be said to be highly valuable when used as a tool for anther-specific gene expression.
Owner:NAT INST OF AGROBIOLOGICAL SCI
Compositions and methods for detection and isolation of phosphorylated molecules
InactiveUS20100009381A1Simplifies subsequent analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingTernary complexPhosphorylation
The present invention relates to phosphate-binding compounds that find use in binding, detecting and isolating phosphorylated target molecules including the subsequent identification of target molecules that interact with phosphorylated target molecules or molecules capable of being phosphorylated. A binding solution is provide that comprises a phosphate-binding compound, an acid and a metal ion wherein the metal ion simultaneously interacts with an exposed phosphate group on a target molecule and the metal chelating moiety of the phosphate-binding compound forming a bridge between the phosphate-binding compound and a phosphorylated target molecule resulting in a ternary complex. The binding solution of the present invention finds use in binding and detecting immobilized and solubilized phosphorylated target molecules, isolation of phosphorylated target molecules from a complex mixture and aiding in proteomic analysis wherein kinase and phosphatase substrates and enzymes can be identified.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Treatment solution, method for pretreatment, method for acquiring information and method for detection
InactiveUS20080268497A1High sensitivityHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationProtein targetPretreatment method
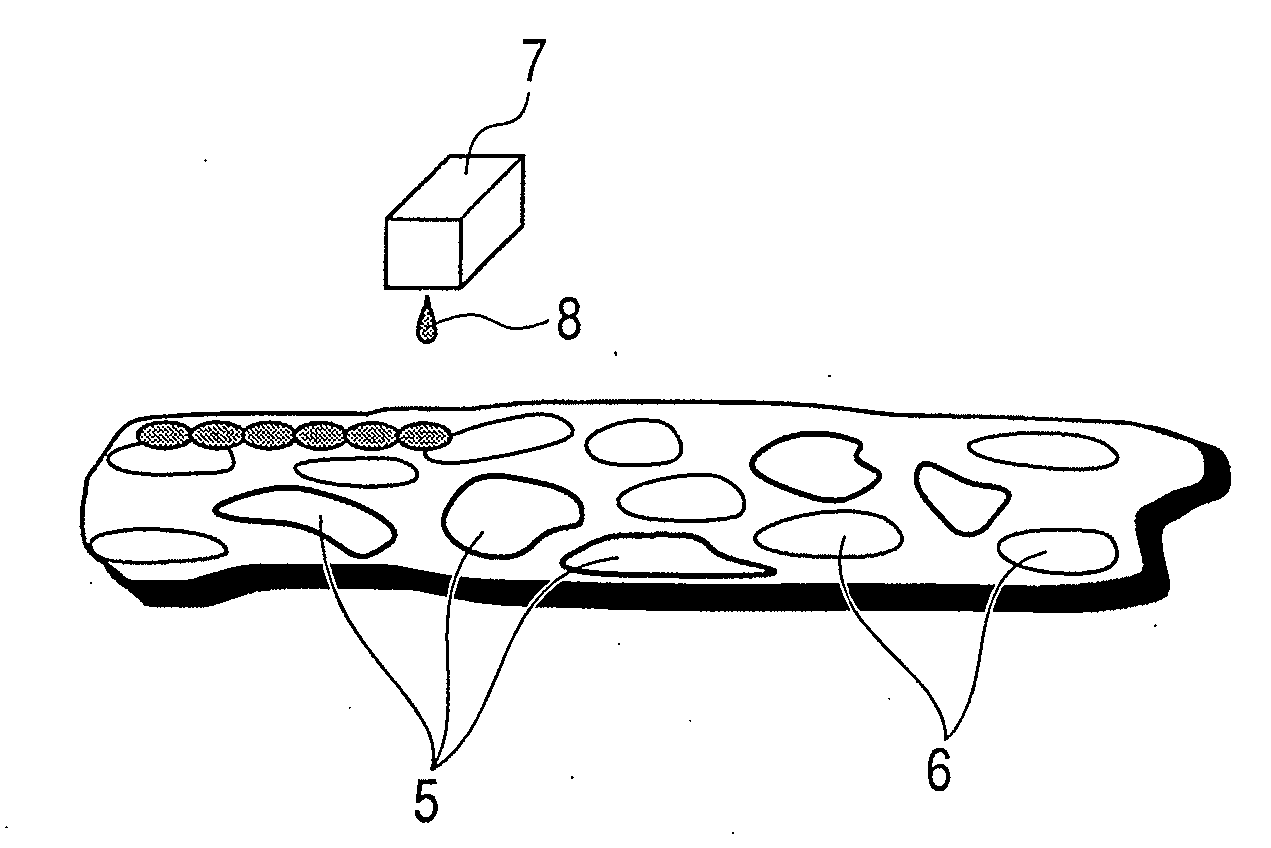
The present invention intends to provide a high sensitivity method for identifying the type of a protein contained in each cell with a diameter of ten to several tens μm and a sample treatment solution required for it. The above is achieved by three steps of (1) treating a slice of a diseased tissue with an aqueous solution containing gold particles and a digestive enzyme, and digesting restrictively a protein of interest, (2) measuring a 2-dimensional distribution of fragmented peptides by TOF-SIMS, and (3) visualizing a 2-dimensional distribution of the target protein in the slice of the diseased tissue using the results of the proteome analysis and by means of a numerical analysis.
Owner:CANON KK
Biomarker for diagnosis of liver disease
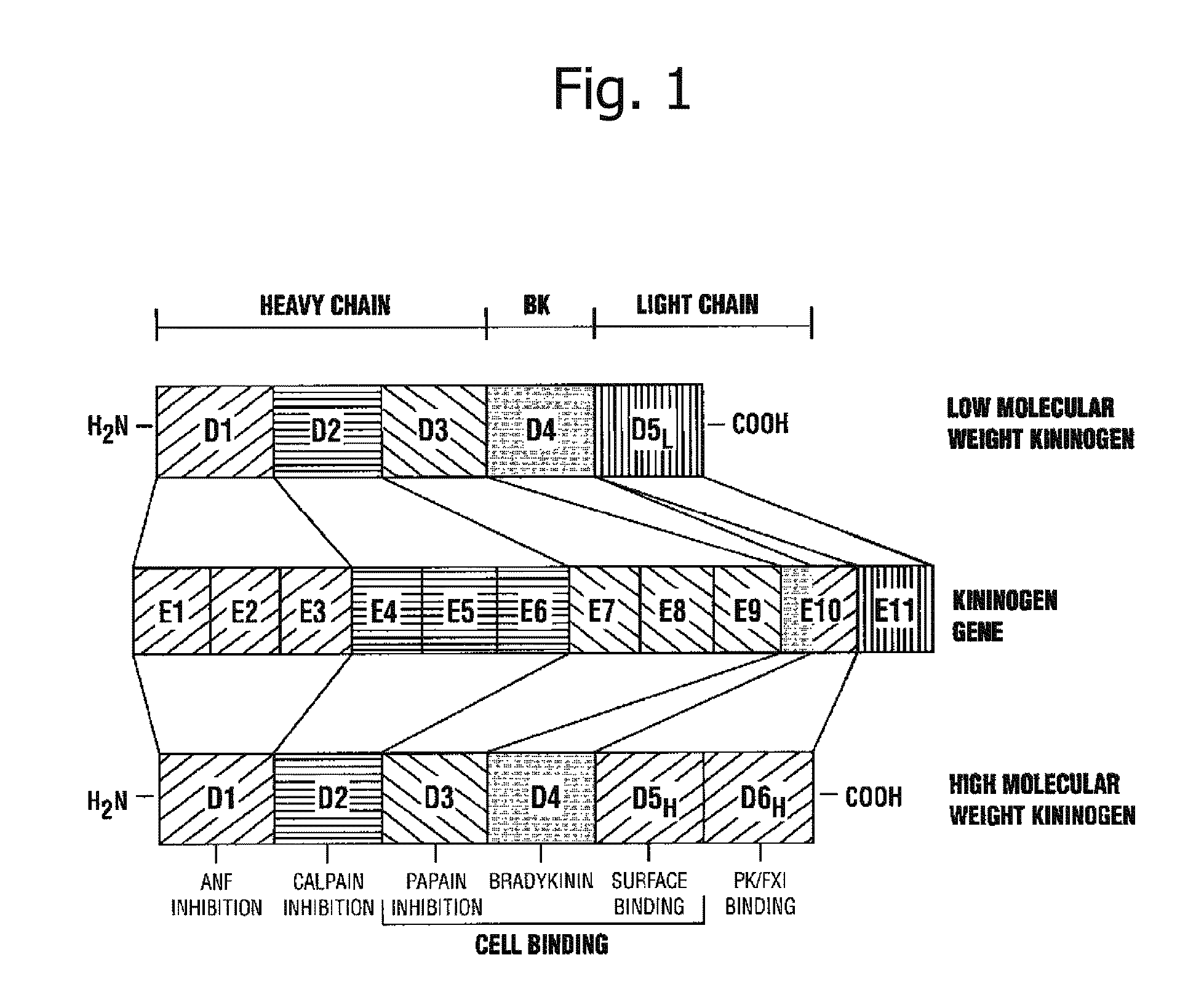
InactiveUS20110129859A1Conveniently and correctly diagnosedHeavy burdenPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansKininChronic hepatitis
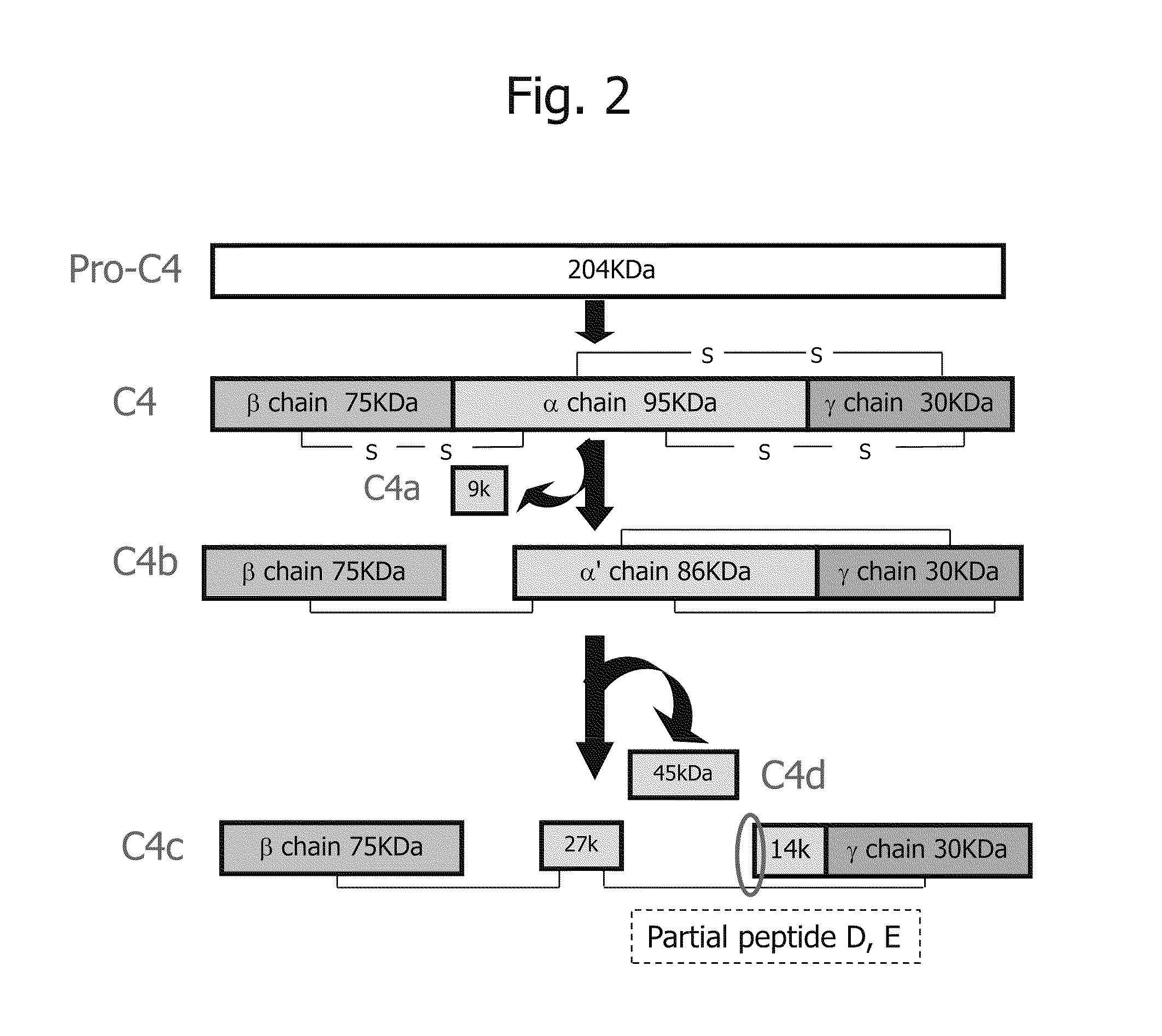
Disclosed are: a marker for the diagnosis of a liver disease, which can determine the disease in a simple manner; an antibody directed against the marker; a diagnostic agent; a diagnosis method; and a method for marker detection in blood or serum. Proteome analysis revealed that quantities of the full-length kininogen and three partial peptides thereof (sequence A: position-440 to position-456, sequence B: position-439 to position-456, and sequence C: position-438 to position-456) in sera of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease are significantly different from those in sera of healthy individuals; and a diagnostic agent and a detecting method for the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease that can be conveniently used for medical examination are established. The use of a combination of a kininogen-based marker and a C4-based marker (the full length sequence or partial peptides thereof) enables identification of chronic hepatitis and an asymptomatic virus carrier, as well as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Owner:KAGOSHIMA UNIV
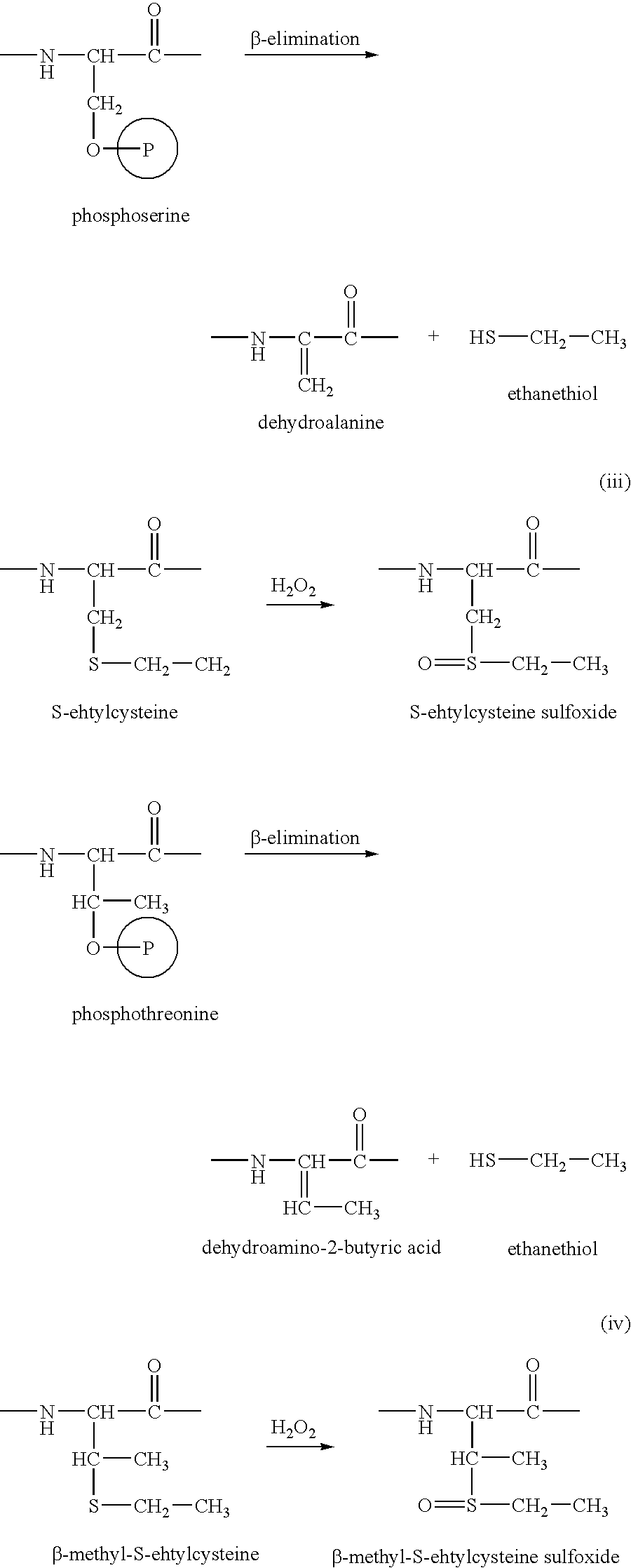
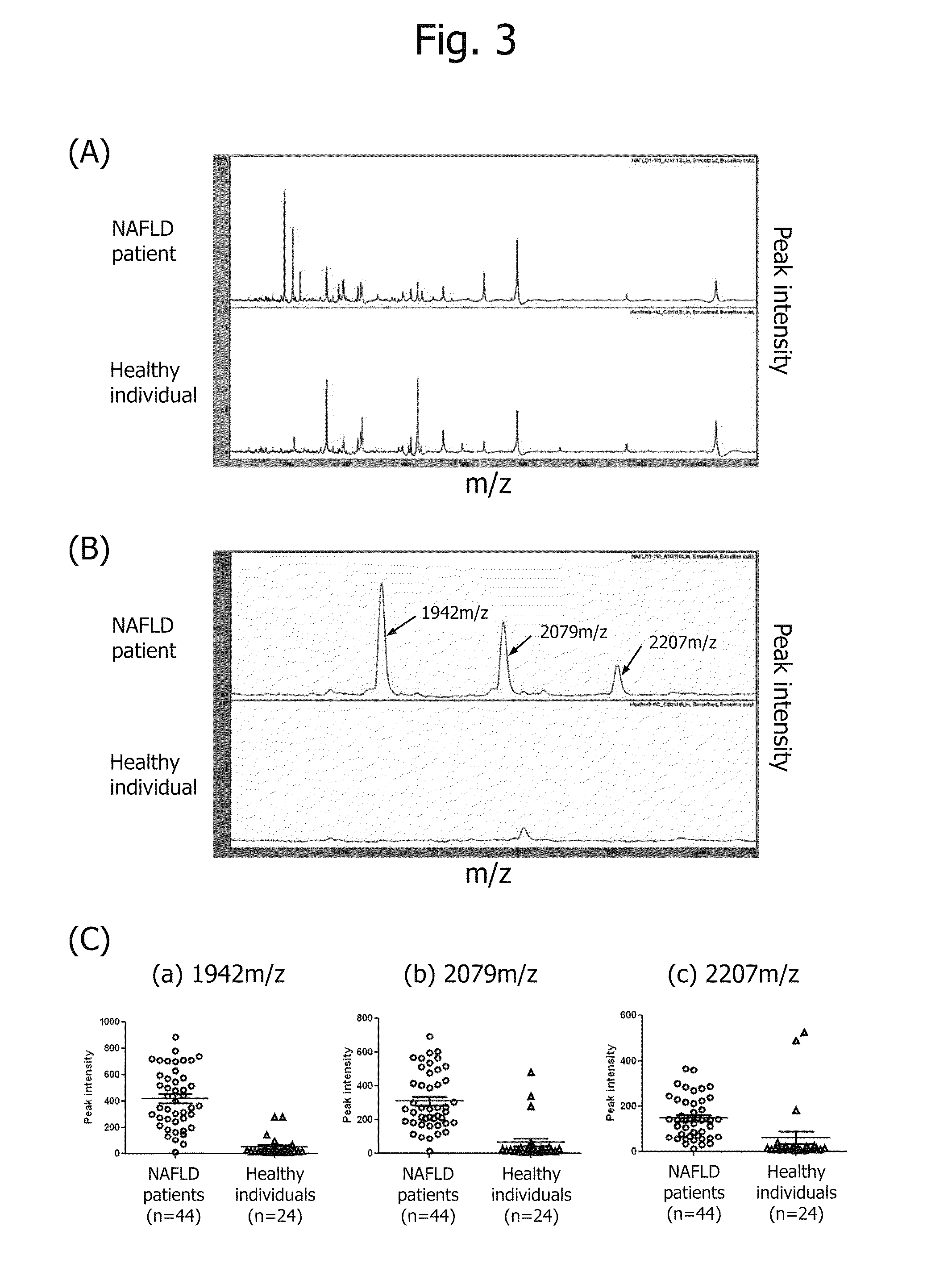
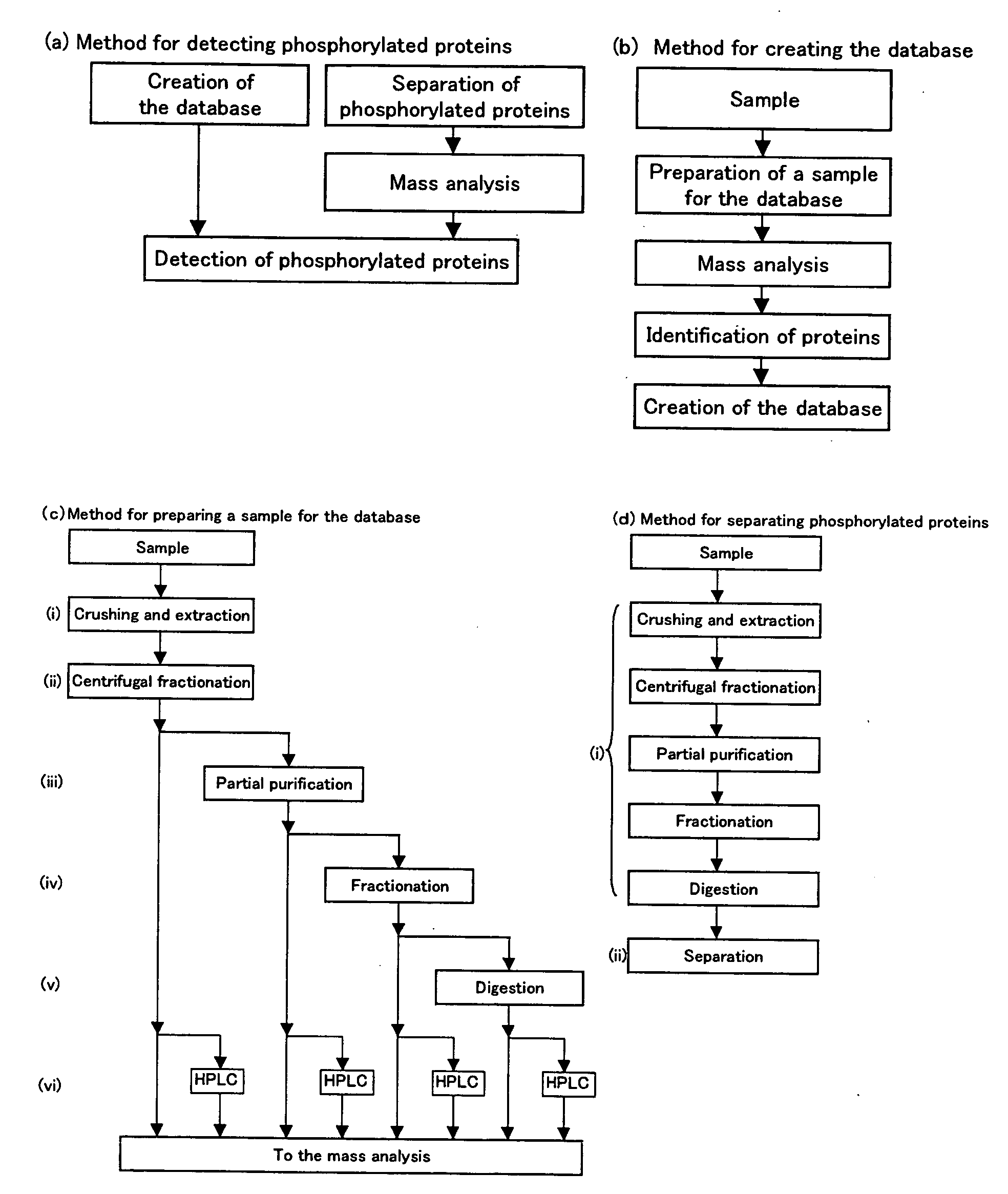
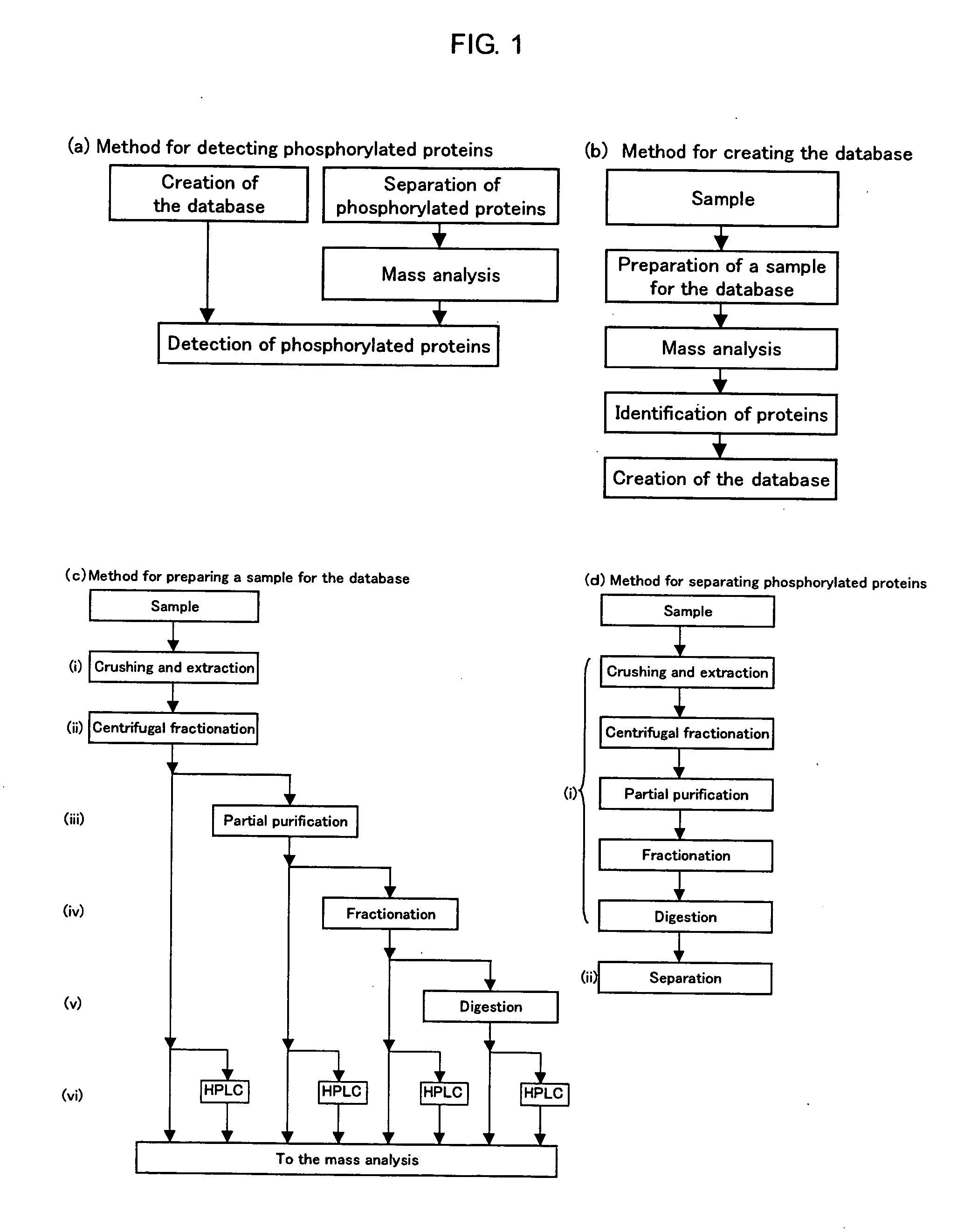
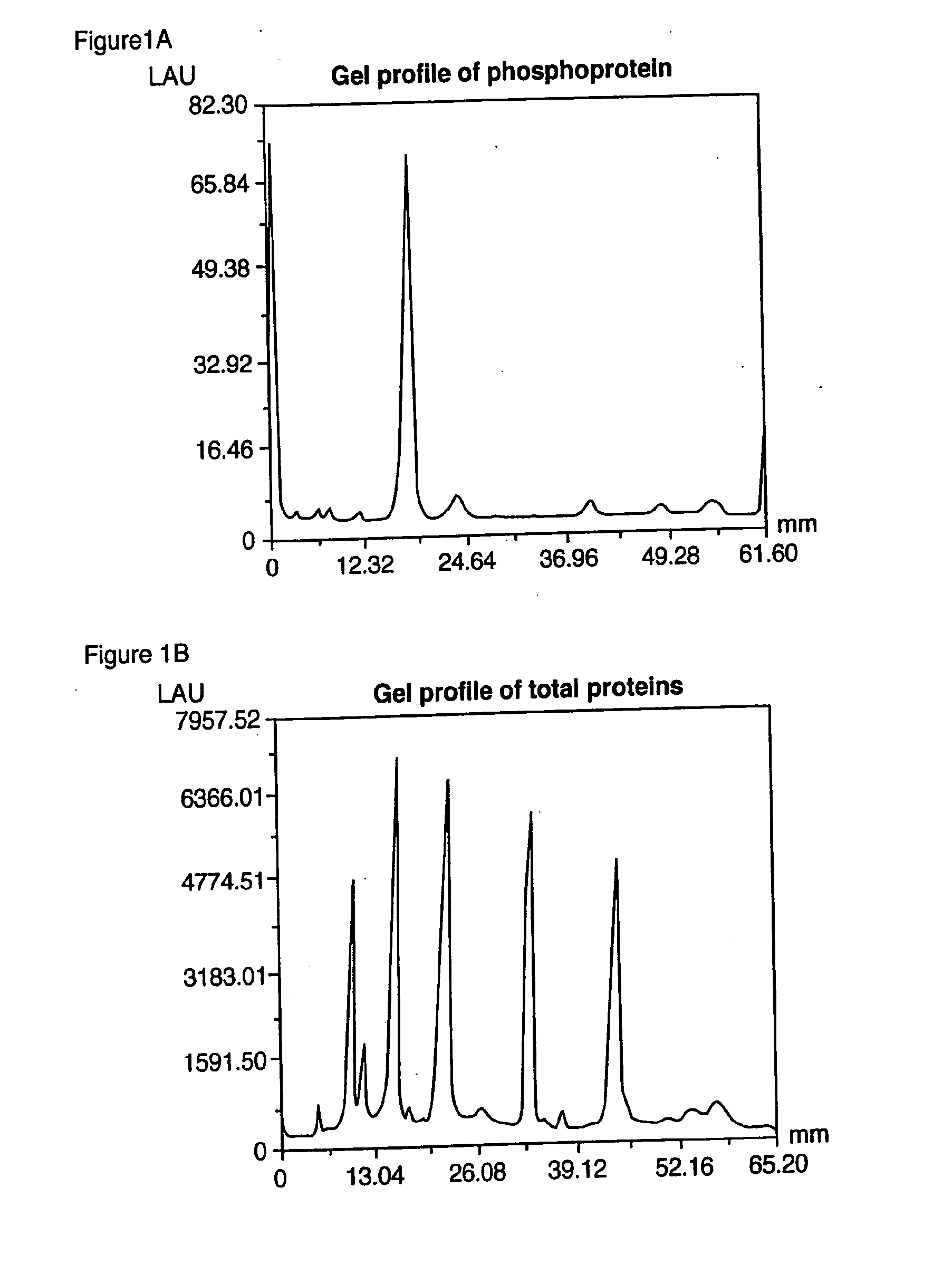
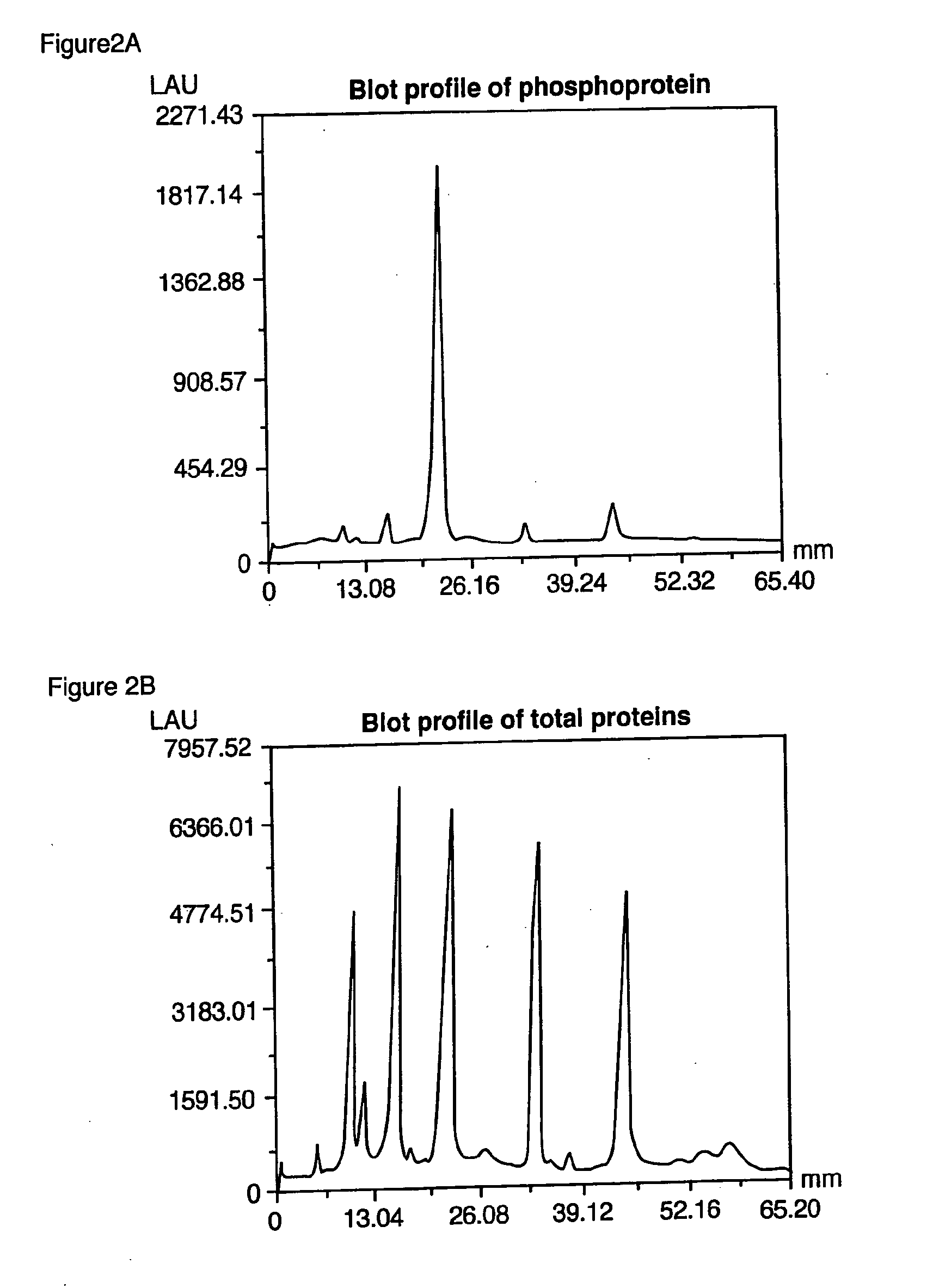
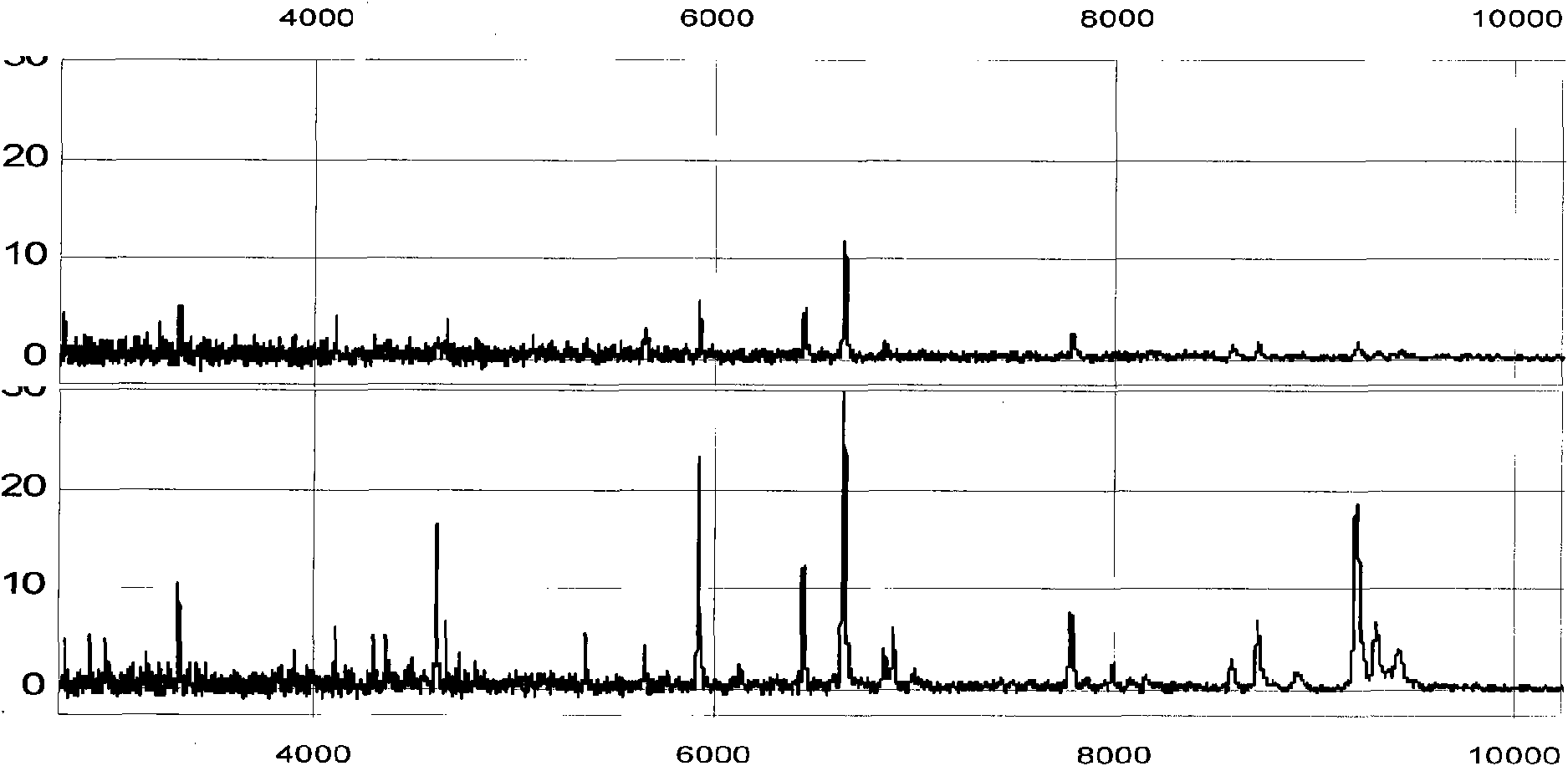
Method of Proteome Analysis for Phosphorylated Protein
InactiveUS20080221802A1Improve accuracyShort timeParticle separator tubesComponent separationAcetonitrileProteome
A method for detecting plural types of phosphorylated proteins in a sample, wherein a database consisting of data regarding plural types of proteins in the sample is used; and a method for purifying phosphorylated proteins using an immobilized metal carrier or a titania carrier, wherein a solution containing acetonitrile in a range of 40% (v / v) or greater but 60% (v / v) or less is used.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Protein microarrays on mirrored surfaces for performing proteomic analyses
InactiveUS20070042442A1Enhanced signalImprove understandingMaterial nanotechnologyCompound screeningAntigenStructure analysis
Provided are protein microarrays, their manufacture, use, and application. Protein microarrays in accordance with the present invention are useful in a variety preoteomic analyses. Various protein arrays in accordance with the present invention may immobilize large arrays of proteins that may be useful for studying protein-protein interactions to improve understanding of disease processes, facilitating drug discovery, or for identifying potential antigens for vaccine development. The protein array elements of the invention are native or modified proteins (e.g., antibodies or fusion proteins). The protein array elements may be attached directly to a organic functionalized mirrored substrate by a binding reaction between functional groups on the substrate (e.g., amine) and protein (e.g., activated carboxylic acid). Techniques for chemical blocking of the arrays are also provided. The invention contemplates spotting of array elements onto solid planar substrates, labeling of complex protein mixtures, and the analysis of protein binding to the array. The invention also enables the enrichment or purification, and subsequent sequencing or structural analysis of proteins that are identified as differential by the array screen. Kits including protein-binding microarrays for proteomic analysis in accordance with the present invention are also provided.
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Compositions and methods for detection and isolation of phosphorylated molecules
InactiveUS20080044804A1Simplifies subsequent analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementTesting metalsTernary complexPhosphorylation
The present invention relates to phosphate-binding compounds that find use in binding, detecting and isolating phosphorylated target molecules including the subsequent identification of target molecules that interact with phosphorylated target molecules or molecules capable of being phosphorylated. A binding solution is provide that comprises a phosphate-binding compound, an acid and a metal ion wherein the metal ion simultaneously interacts with an exposed phosphate group on a target molecule and the metal chelating moiety of the phosphate-binding compound forming a bridge between the phosphate-binding compound and a phosphorylated target molecule resulting in a ternary complex. The binding solution of the present invention finds use in binding and detecting immobilized and solubilized phosphorylated target molecules, isolation of phosphorylated target molecules from a complex mixture and aiding in proteomic analysis wherein kinase and phosphatase substrates and enzymes can be identified.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
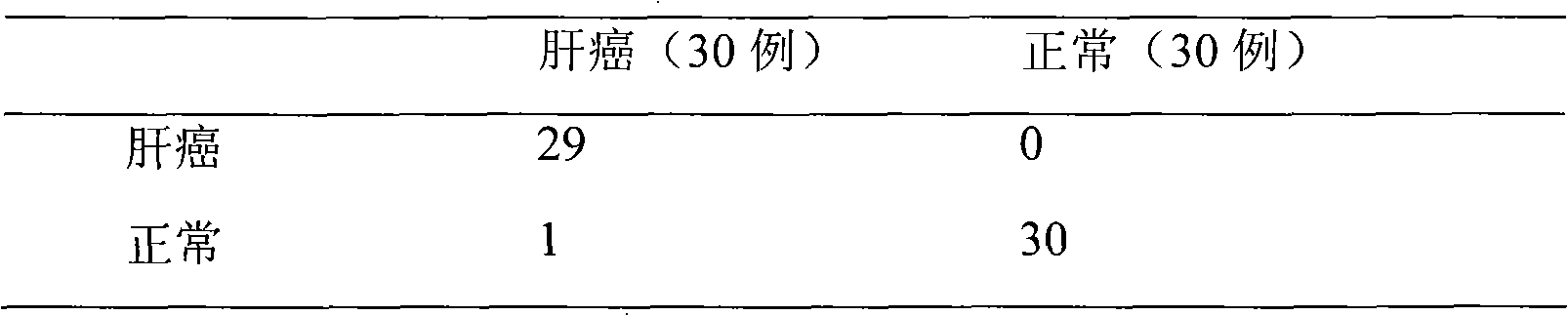
Method for analyzing proteome in biological sample
ActiveCN101685080AEarly diagnosisSensitive diagnosisPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCancer cellCancer Early Diagnosis
The invention aims to provide a method for analyzing proteome in a biological sample. The method can detect unique proteome generated by cancer cells through blood or body fluid in an early stage of tumors; and the method can diagnose cancers more sensitively and more early so as to make early diagnosis and treatment of the cancers possible.
Owner:苏州云泰生物医药科技有限公司 +1
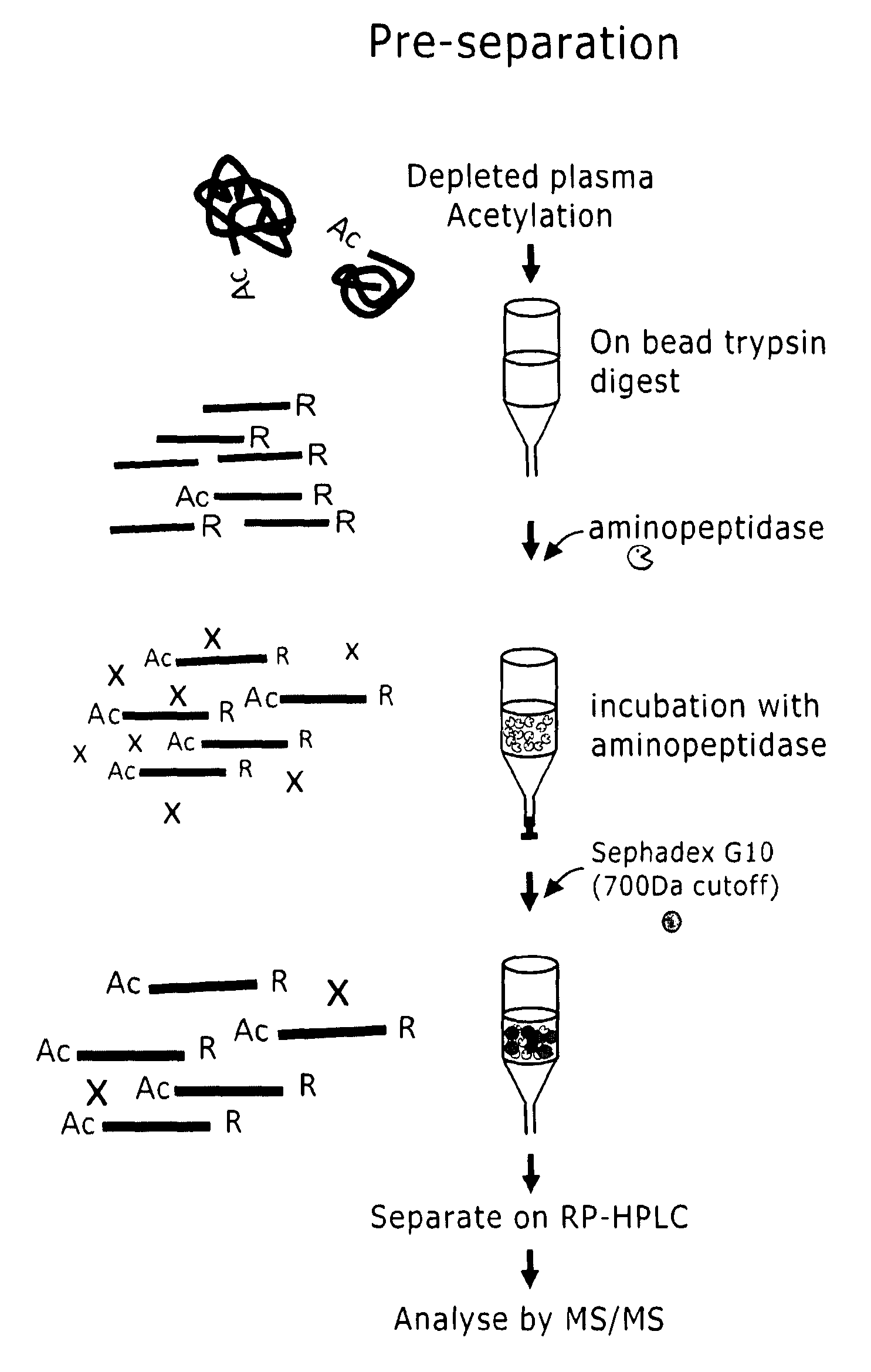
Preparation of samples for proteome analysis
InactiveUS20100311114A1Improve sensitivity and specificityImprove representationHydrolasesPeptide preparation methodsProtein formationProteome
The invention mainly concerns methods and systems for the preparation of biological samples for proteome analysis, N-terminal or C-terminal peptides of proteins are enriched using exopeptidase.
Owner:PRONOTA NV
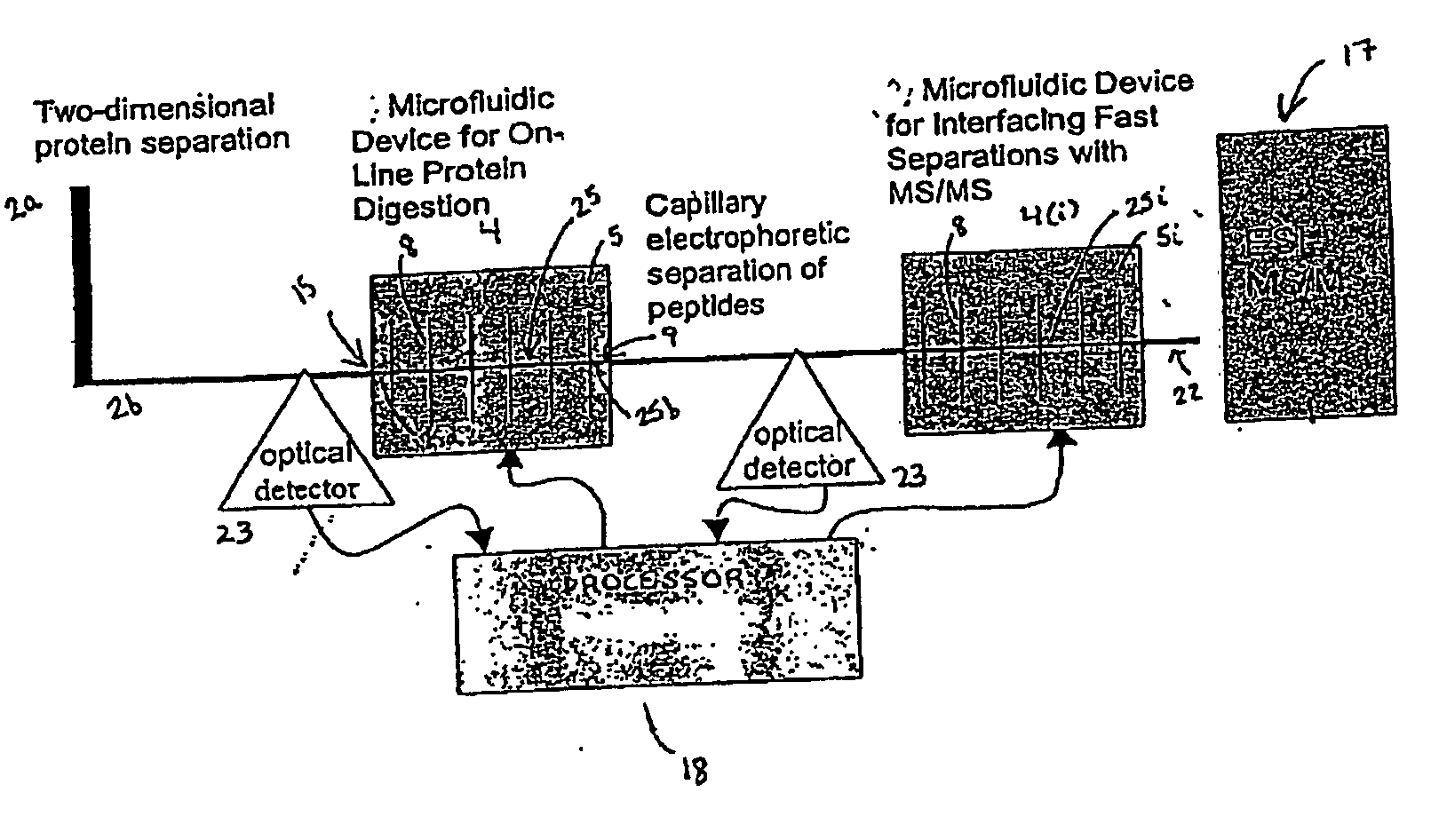
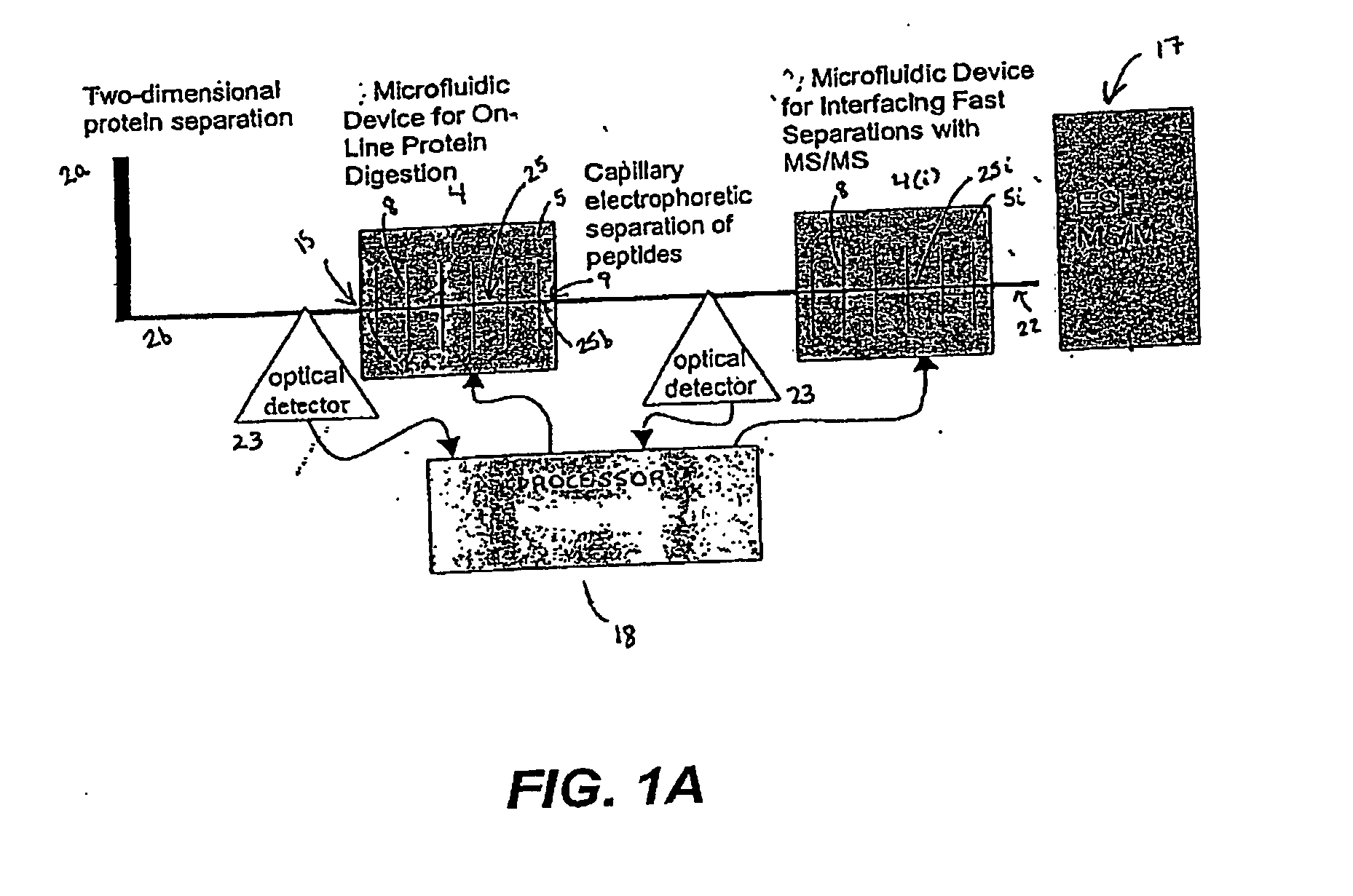
Microfluidic system for proteome analysis
InactiveUS20080076143A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioApparatus sterilizationMicrobiological testing/measurementCell signaling pathwaysMulti dimensional
The invention provides a microfluidic system and method to rapidly analyze large numbers of compounds or complex mixtures of compounds, particularly, low abundance cellular proteins involved in cell signaling pathways. In one aspect, an integrated microfluidic system comprises an upstream separation module (preferably, a multi-dimensional separation device), a microfluidic device for on-device protein digestion of substantially separated proteins received from the upstream separation module, a downstream separation module for separating digestion products of said proteins, a peptide analysis module and a processor for determining the amino acid sequence of said proteins. Preferably, the system comprises an interfacing microfluidic device between the downstream separation module and the peptide analysis module.
Owner:PROTEA BIOSCI
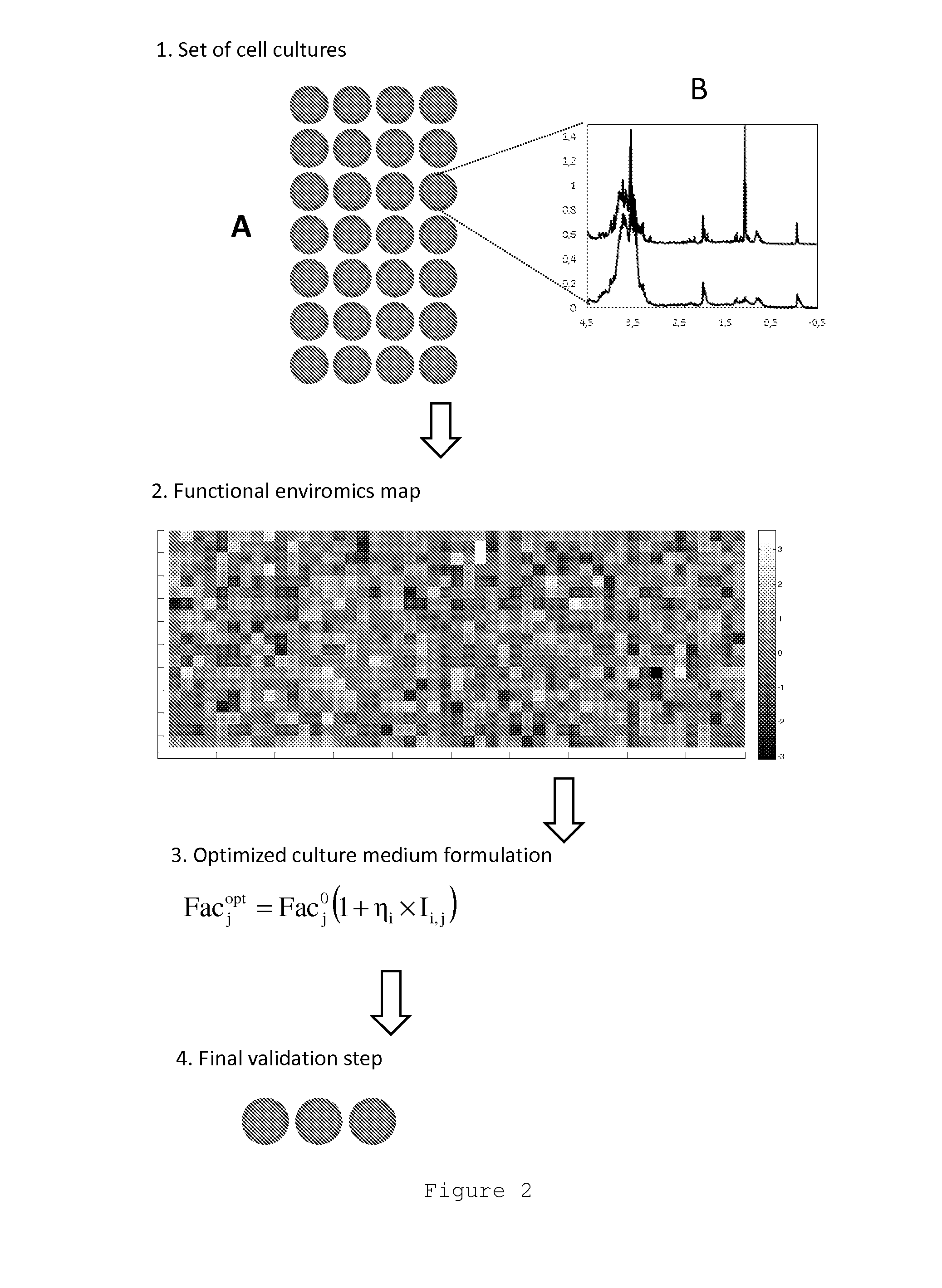
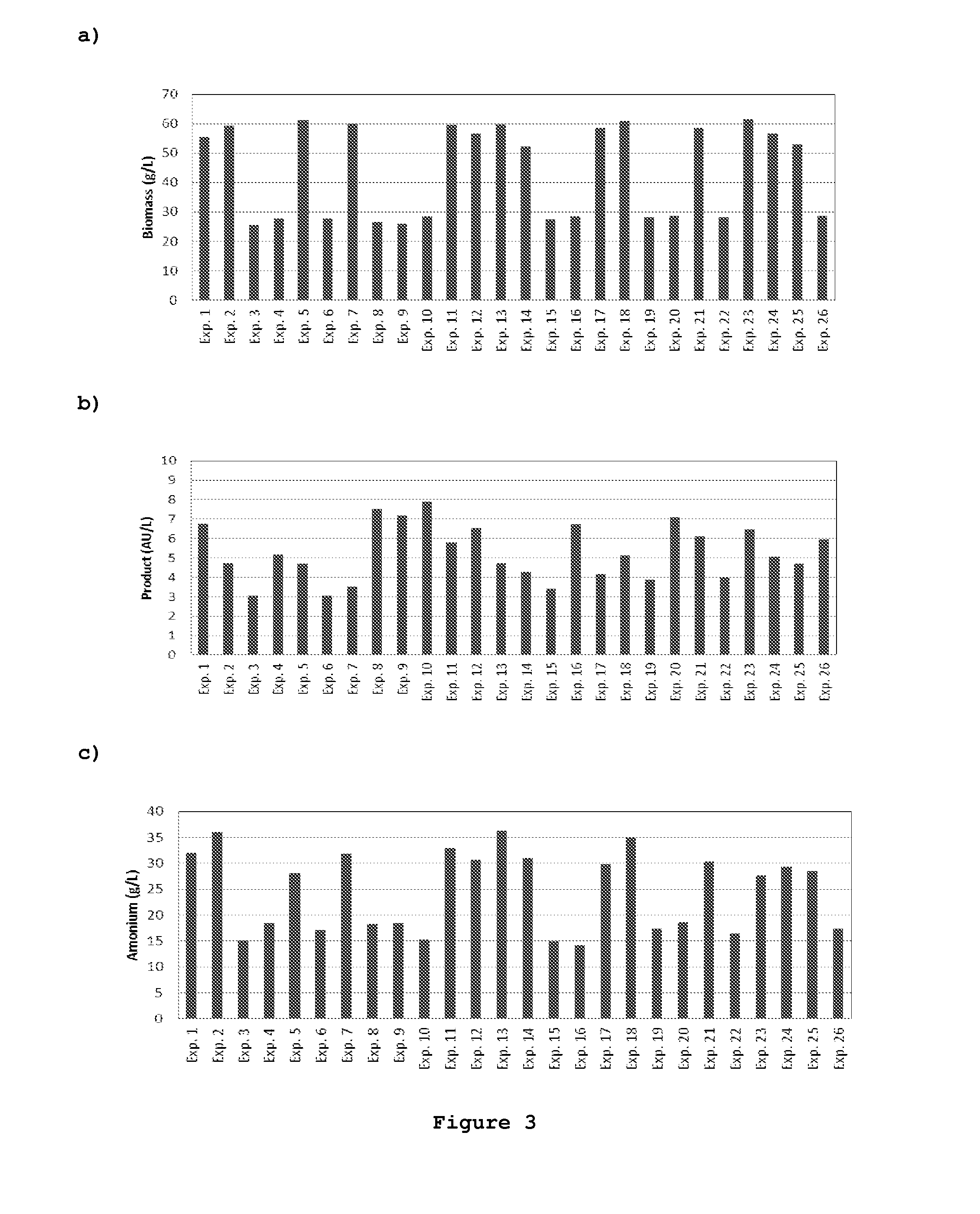
Functional enviromics method for cell culture media engineering
This invention refers to a new method for optimizing the composition of cell culture media. This new method comprises two main stages. In the first stage, a functional enviromics map is built through the joint screening of cell functions and medium factors by the execution of a specific cell culture protocol and exometabolome assays protocol. The functional enviromics map consists of a data array of intensity values of elementary cellular functions against medium factors. In the second stage, optimized cell culture medium formulations are developed that either enhance or repress target elementary cellular functions from columns of the functional enviromics map. The main advantage of this method lies in enabling metabolic engineering through the culture media composition manipulation, wherein an arbitrarily high number of cell functions are optimized through manipulation of medium factors, as opposed to previous methods, which are eminently empirical, are not cell function oriented, and require a much higher number of experiments. Furthermore, this new method is based on cost-effective exometabolome assays and does not require costly intracellular genomic or proteomic assays.
Owner:FACULDADE DE CIENCIAS E TECHA DA UNIV NOVA DE LISBOA
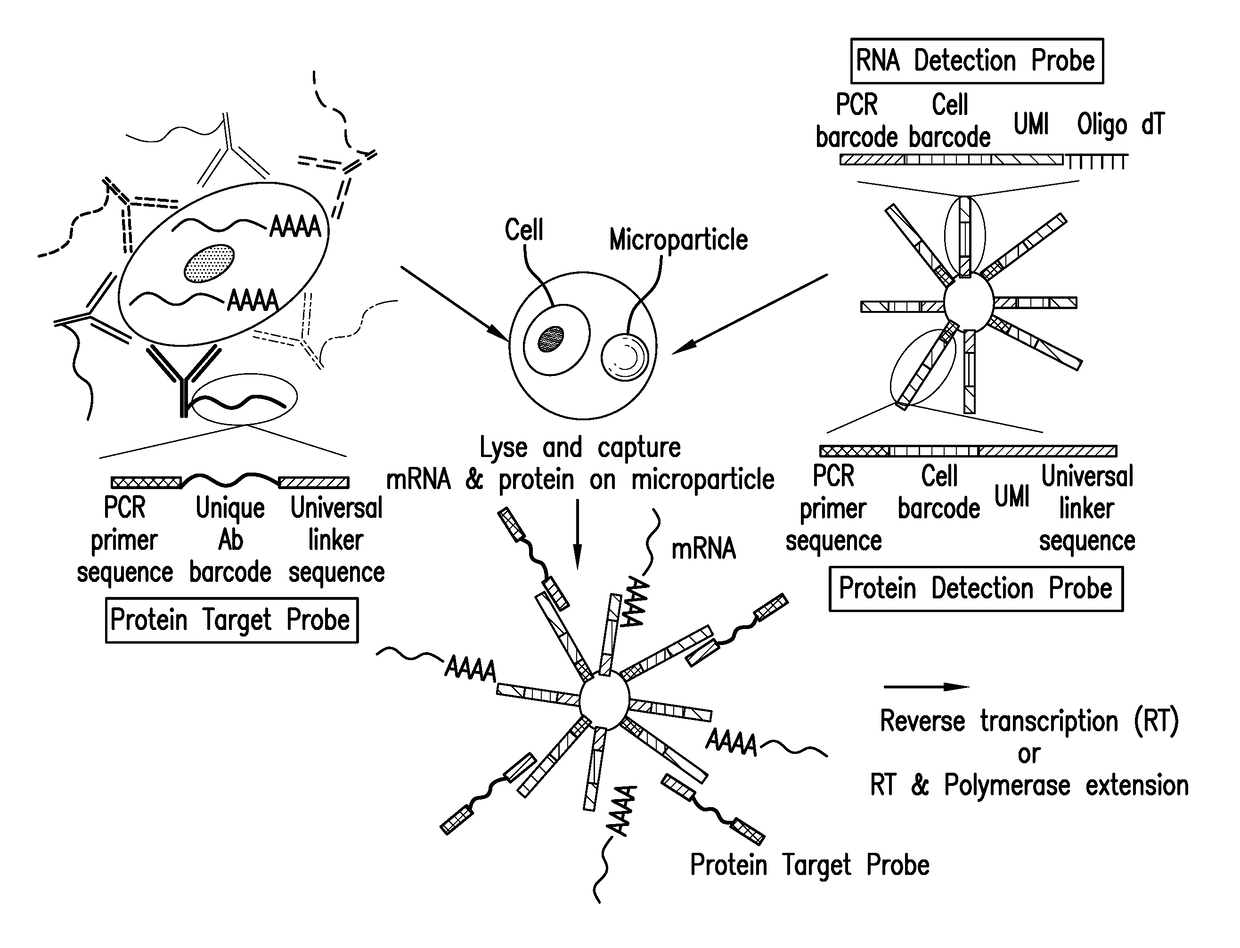
Anoliter-scale sample processing and mass spectrometry acquisition method for single cell proteomics
PendingUS20210080469A1Improve efficiencyIon-exchange process apparatusIon-exchanger regenerationMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMass analyzer
Improved methods of performing proteomic analysis are described wherein single cell samples are placed into nanowells disposed on chips that also contain a booster sample of known peptides. Once the samples are placed, these singles cells are lysed and peptides are extracted. These peptides are then labeled using TMT labels and combined with labeled boosting peptides to form a mixed sample. The mixed sample is then separated using an LC separation system and the separated sample is then passed through a mass spectrometer to acquire data of the peptide characterization data from the separated sample. Various modifications and alterations to the MS acquisition process that enhance the effectiveness of the process are also described.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Methods of detecting prostate cancer
Proteins specific for prostate epithelial cells, normal or neoplastic, are identified and used for diagnosis, development of antibodies, and for evaluating drugs that react with the neoplastic specific proteins. Affinity based probes are used that react specifically with the active site to provide a measure of the enzyme activity of the cells. Prostate epithelial neoplastic cells can be used in screening candidate drugs for their effect in changing the proteome profile as to the serine-threonine hydrolase enzymes, using the affinity based probes for determining the profile.
Owner:BURNHAM INST FOR MEDICAL RES
Methods and systems of proteome analysis and imaging
Provided herein are methods and systems for proteome analysis that are at least partially automated and / or performed robotically. In some aspects, the methods and systems described herein can rapidly and efficiently provide protein identification of each of the proteins from a proteome, or a complement of proteins, obtained from extremely small amounts of biological samples. The identified proteins can be imaged quantitatively over a spatial region. Automation and robotics facilitates the throughput of the methods and systems, which enables protein imaging and / or rapid proteome analysis.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Sample preparation method for proteomic analysis
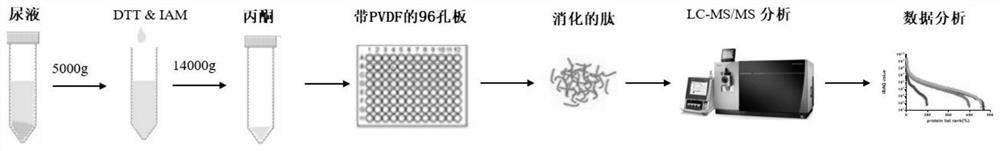
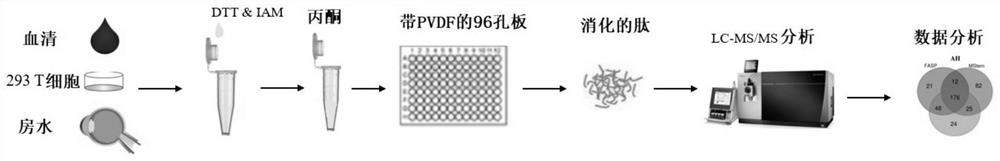
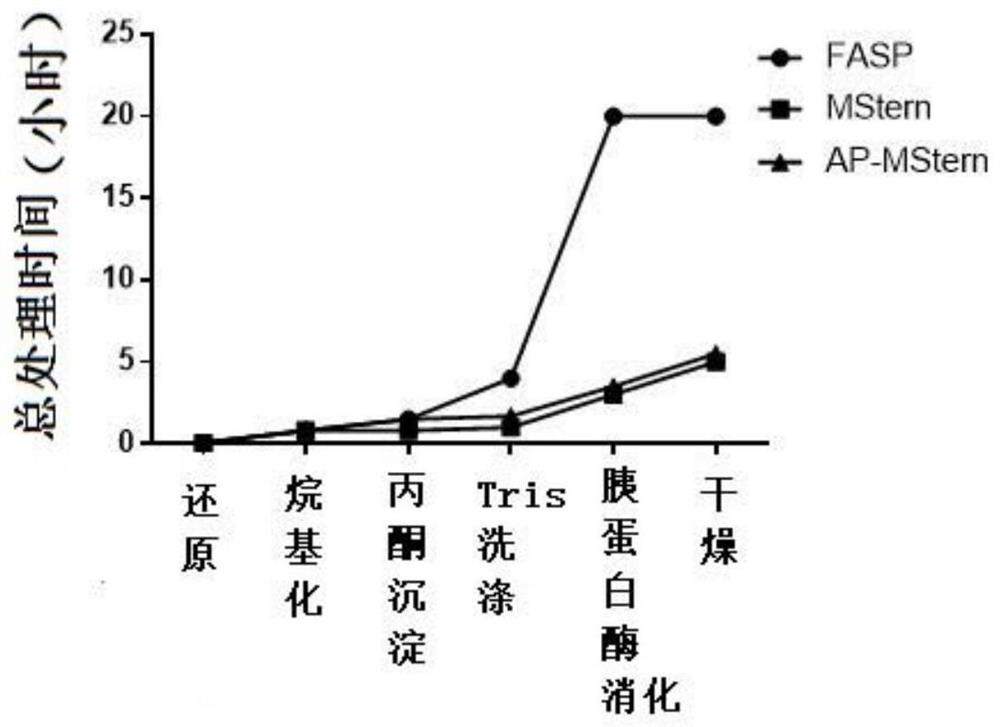
InactiveCN111635921AAdvantage protein qualitativeAdvantage detectionPeptide preparation methodsBiological testingProtein solutionProteome profiling
The invention relates to a sample preparation method for proteomic analysis. Specifically, the method comprises the following steps: reducing and alkylating proteins in a sample to be detected, addingacetone to precipitate the reduced and alkylated proteins, redissolving the proteins, adding the redissolved protein solution to a 96-well plate with a PVDF membrane, and carrying out enzymolysis onthe 96-well plate with the PVDF membrane. The sample obtained according to the method of the invention can be used for proteome analysis.
Owner:THE INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
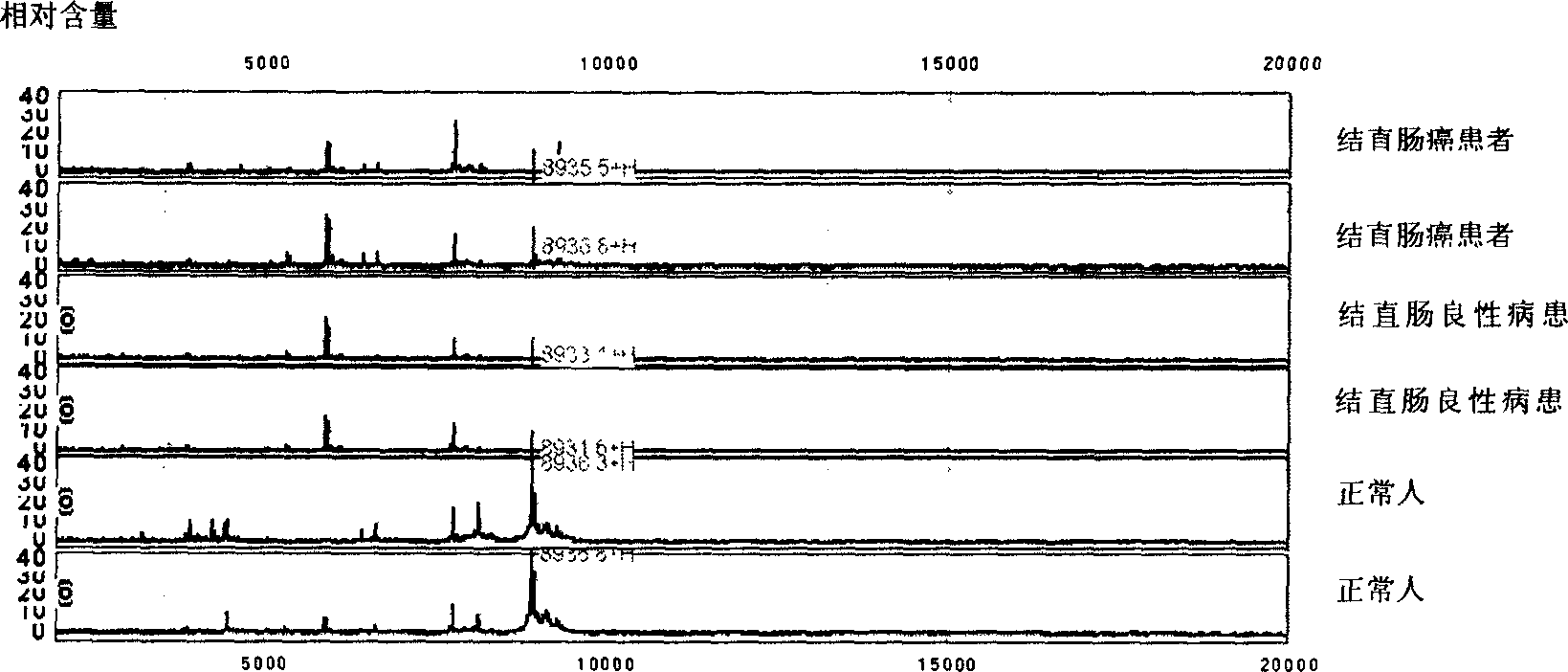
Use of protein fingerprint method in detecting protein fingerprint of colon cancer and rectum cancer in blood
InactiveCN1595138AAccurate resolutionQuick dimension descriptionComponent separationSamples introduction/extractionAdenocarcinoma polypsAnalysis data
This invention also relates to protein dactylography method for analyzing for the protein group got by retention chromatography. This method adopts mass spectroscopy to distinguish and detect protein group. The analysis data takes the form of bar code (protein dactylography) read by computer. This invention method is used to detect the protein fingerprint in the normal cell, restocarcinoma patient cell and rectal polyp patient cell.
Owner:BEIJING SELDI TECH
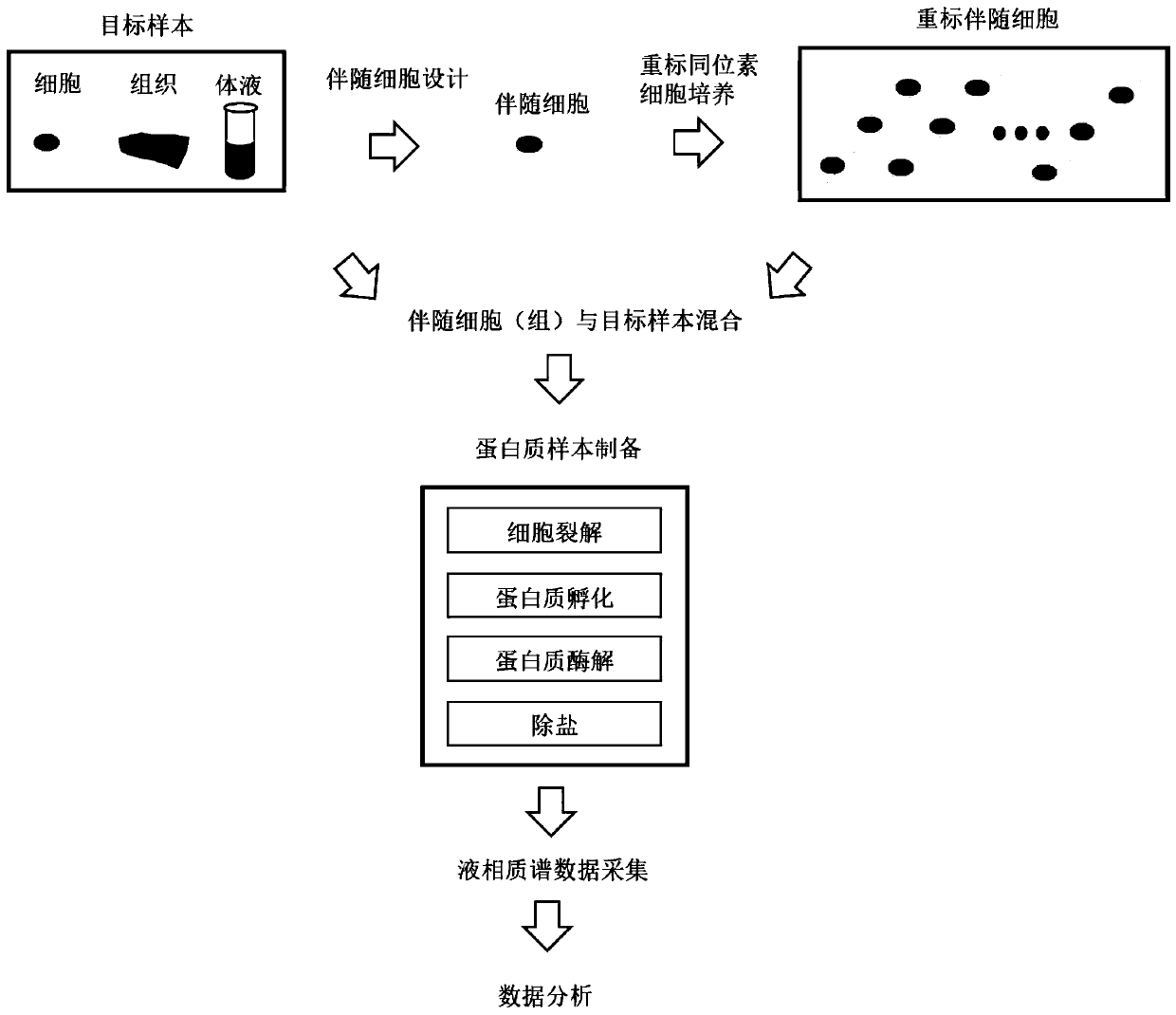
Method for quantifying trace amount of biological sample proteome by utilizing isotope labeling technology
PendingCN111239271AImprove accuracyLower technical barriersComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationProtein detectionIsotopic labeling
The invention provides a method for quantifying a trace amount of biological sample proteome by utilizing an isotope labeling technology. An accompanying sample is designed for a target sample, the accompanying sample is marked again, protein detection loss is transferred to the accompanying sample, detection of trace amount of biological sample protein is achieved, the technical obstacles existing in proteome analysis of trace amount of biological samples in the prior art are overcome, and practical information capable of being used for identification or quantification is obtained.
Owner:WESTLAKE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com