Compositions and methods for detection and isolation of phosphorylated molecules
a technology of phosphorylation status and composition, which is applied in the field of metal chelating composition and methods for the detection and isolation of phosphorylated target molecules, can solve the problems of insufficient research capacity to simply identify, inability to perform systematic parallel analysis of the phosphorylation status of large sets of proteins involved in the regulatory circuitry of cells and tissues, and inability to achieve simple identification. , to achieve the effect of simplifying the subsequent analysis of the sampl
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Determination of BAPTA Selectivity for Gallium and Gallium Ions for Phosphorylated Target Molecules and a Screening Method for Phosphate-Binding Compounds
[0306](A) BAPTA with Trivalent Gallium Ions Selectively Detects Phosphoproteins.
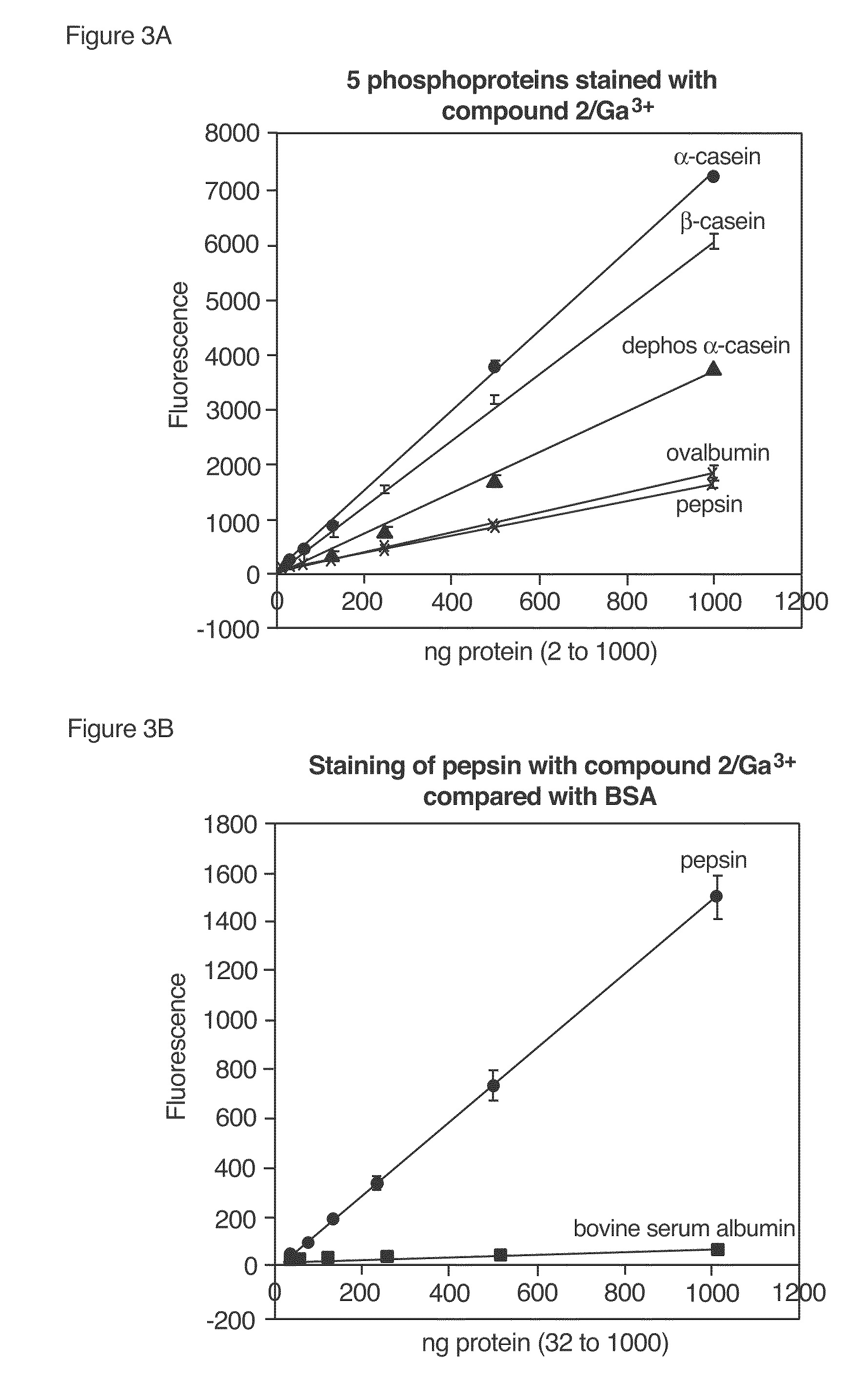
[0307]A comprehensive search of metal-chelating compounds was performed to identify fluorescent reagents that when combined with a gallium salt (gallium chloride) would selectively detect phosphorylated target molecules (particularly phosphopeptides and phosphoproteins) in a mixture of phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated target molecules. The compounds were tested in a fluorescence spectrophotometer for their ability to bind gallium (III) ion and selectively detect the phosphoprotein ovalbumin. Binding to gallium (III) ion was determined by a fluorescence increase of the same compound in the presence of up to 5 μM gallium chloride in 75 mM NaOAc (pH 4.0) and 140 mM NaCl. Ovalbumin detection was also judged by a fluorescence increase; however, the compo...
example 2
Detection of Phosphoproteins in SDS-Polyacrylamide Gels
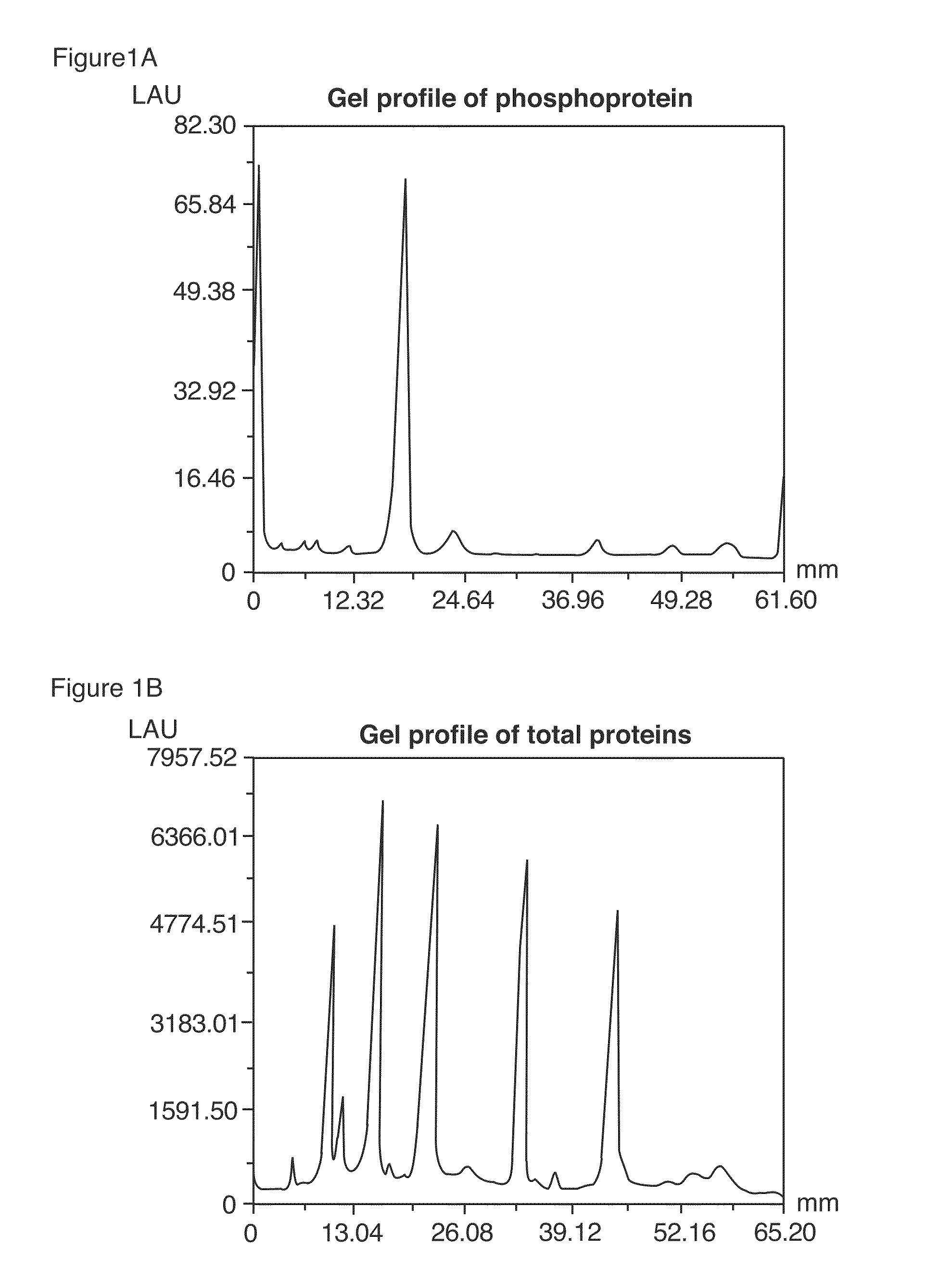
[0312]Phosphoproteins were separated by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis utilizing a 4% T, 2.6% C stacking gel, pH 6.8 and 13% T, 2.6% C separating gel, and pH 8.8, according to standard procedures. % T is the total monomer concentration (acrylamide+crosslinker) expressed in grams per 100 mL and % C is the percentage crosslinker (e.g., N,N′-methylene-bis-acrylamide, N,N′-diacryloylpiperazine or other suitable agent). The separating gels were 8 cm wide by 5 cm high and 0.75 cm in thickness. After electrophoresis, the gels were fixed by immersing them in 100 mL 45% methanol and 5% acetic acid for 90 minutes. The gels were washed twice in water for a total of 30 minutes. The gels were then added to a binding solution of the invention (Example 1E) and incubated for 120 minutes at room temperature with gentle orbital shaking, typically 50 rpm. The binding buffer contained 50 mM NaOAc (pH 4.0), 250 mM sodium chloride, 20% v / v 1,...
example 3
Serial Dichromatic Detection of Phosphoproteins and Total Protein in SDS Polyacrylamide Gels
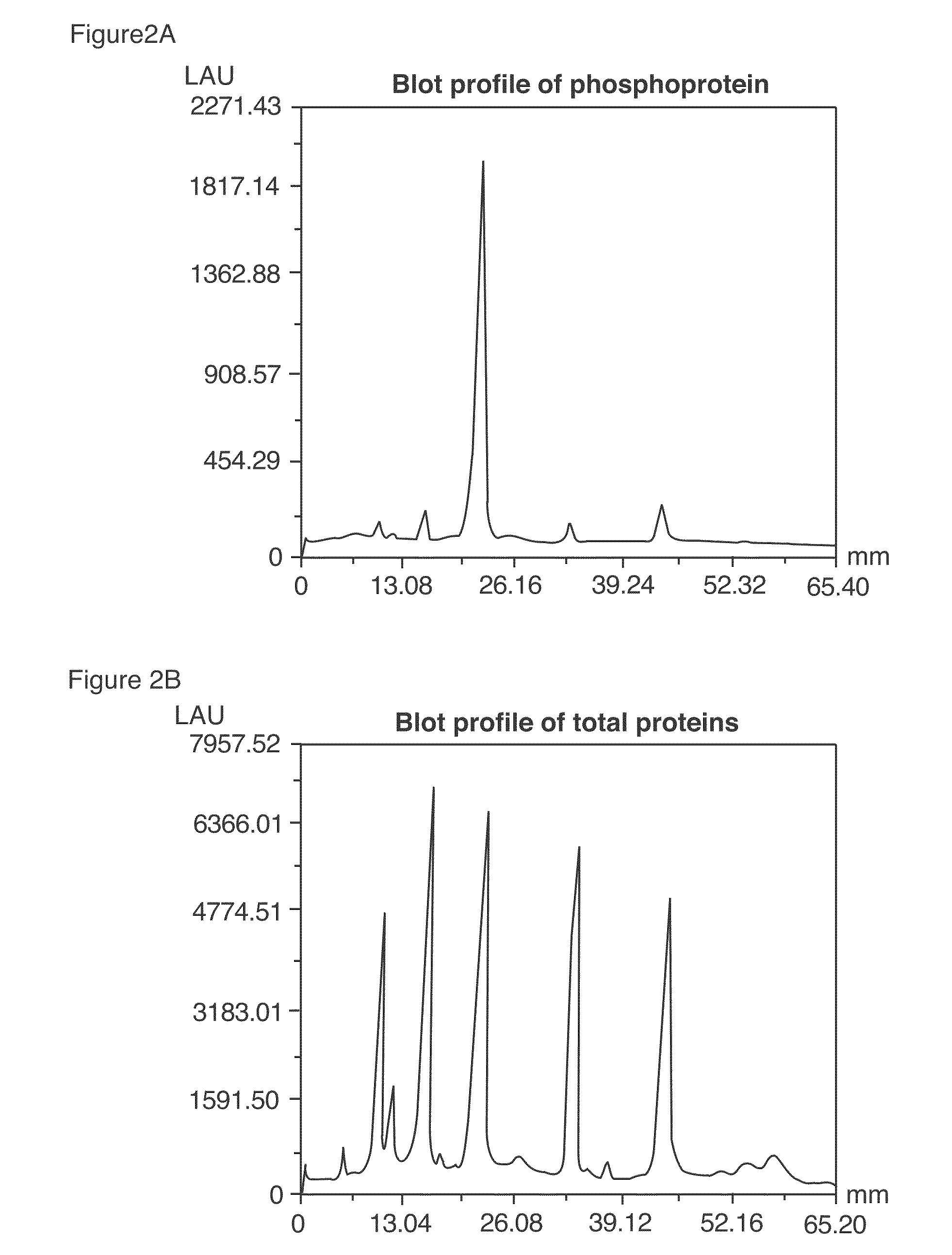
[0315]After detection of the phosphoproteins as in Example 2, the gel was incubated overnight with 60 ml SYPRO® Ruby protein gel stain (Molecular Probes, Eugene, Oreg.) with gentle orbital shaking, typically 50 rpm. The gel was then incubated in 7% acetic acid, 10% methanol for 30 minutes, also at 50 rpm. The orange signal from the phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated proteins was collected with a standard CCD camera-based imaging system with 300 nm UV light excitation and a 600 nm bandpass filter.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com