Patents
Literature
127 results about "Synthetic Cells" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An artificial cell or minimal cell is an engineered particle that mimics one or many functions of a biological cell. The term does not refer to a specific physical entity, but rather to the idea that certain functions or structures of biological cells can be replaced or supplemented with a synthetic entity.
Biosensors for single cell and multi cell analysis
InactiveUS20030104512A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingElectricityBiological cell
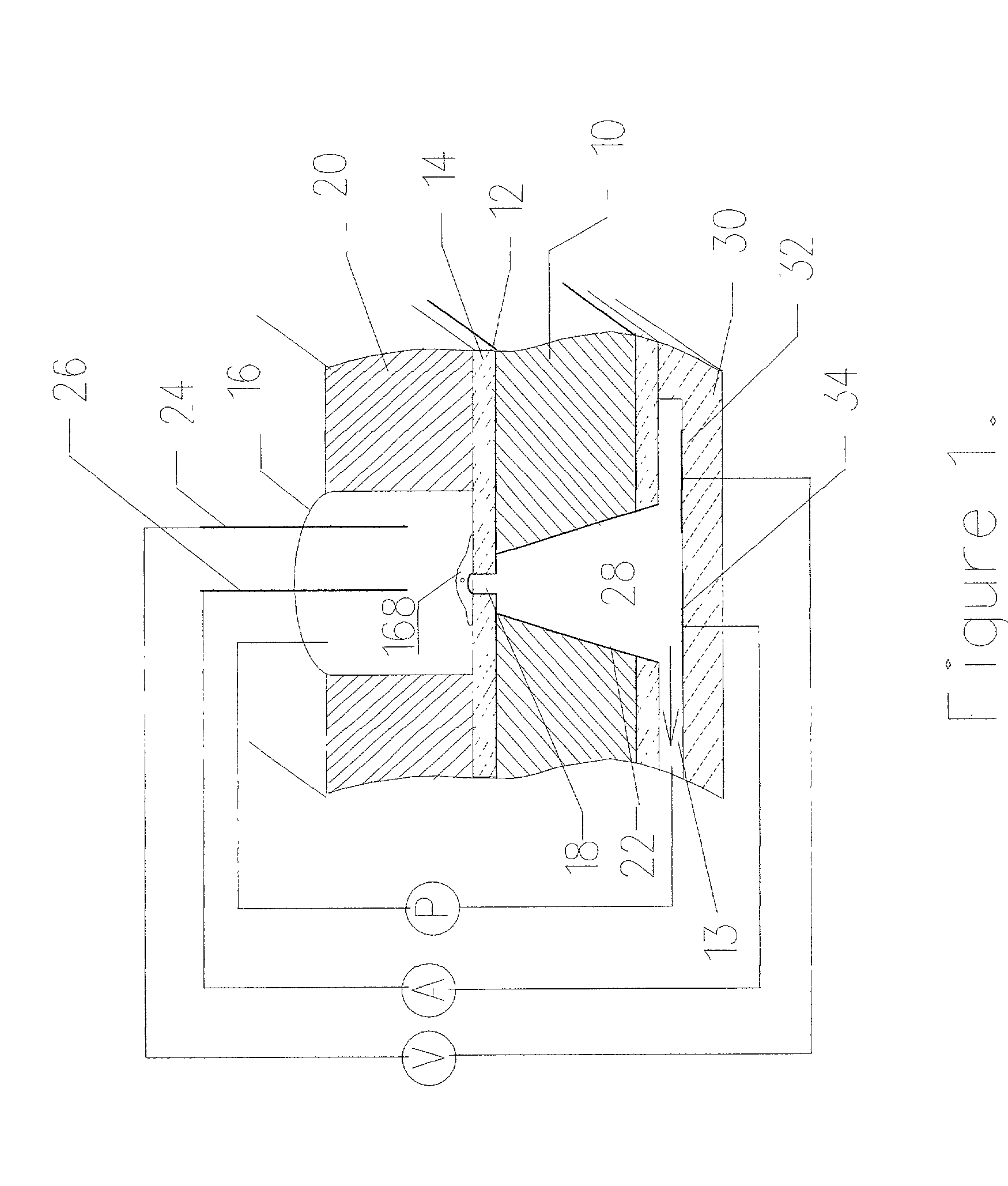
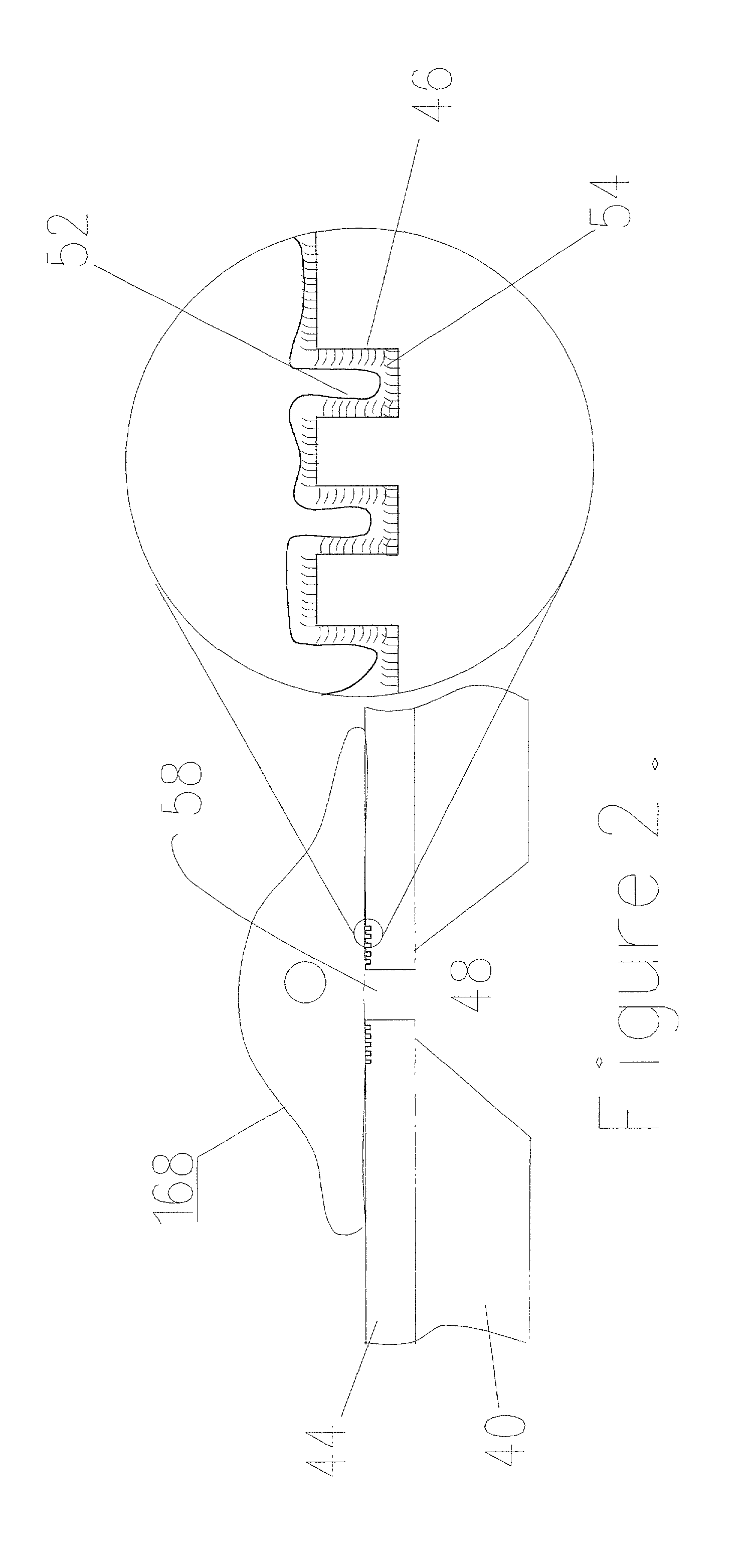
The present invention relates to a structure comprising a biological membrane and substrate with fluidic network, an array of membranes and an array of fluidic networks in substrate, a high throughput screen, methods for production of the membrane, substrate structure, and a method for interconnected array of substrate structures and a method for attaching membranes to structure, a method to electrically record events from the membranes and a method to screen large compound library using the array. More particularly, it relates to biological cells and artificial cell membranes adhered to the substrate with a high electrical resistivity seal, a method to manufacture array configuration of such substrates, and a method to screen compounds using the membrane receptors such as ion-channels, ion pumps, & receptors.
Owner:CYTOPLEX BIOSCI
Synthetic genomes
ActiveUS20070264688A1Complement and facilitate abilitySugar derivativesTissue cultureChemical synthesisHydrogen
Methods are provided for constructing a synthetic genome, comprising generating and assembling nucleic acid cassettes comprising portions of the genome, wherein at least one of the nucleic acid cassettes is constructed from nucleic acid components that have been chemically synthesized, or from copies of the chemically synthesized nucleic acid components. In one embodiment, the entire synthetic genome is constructed from nucleic acid components that have been chemically synthesized, or from copies of the chemically synthesized nucleic acid components. Rational methods may be used to design the synthetic genome (e.g., to establish a minimal genome and / or to optimize the function of genes within a genome, such as by mutating or rearranging the order of the genes). Synthetic genomes of the invention may be introduced into vesicles (e.g., bacterial cells from which part or all of the resident genome has been removed, or synthetic vesicles) to generate synthetic cells. Synthetic genomes or synthetic cells may be used for a variety of purposes, including the generation of synthetic fuels, such as hydrogen or ethanol.
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
Locating packet-switched mobile terminals using network initiated artificial cell hops
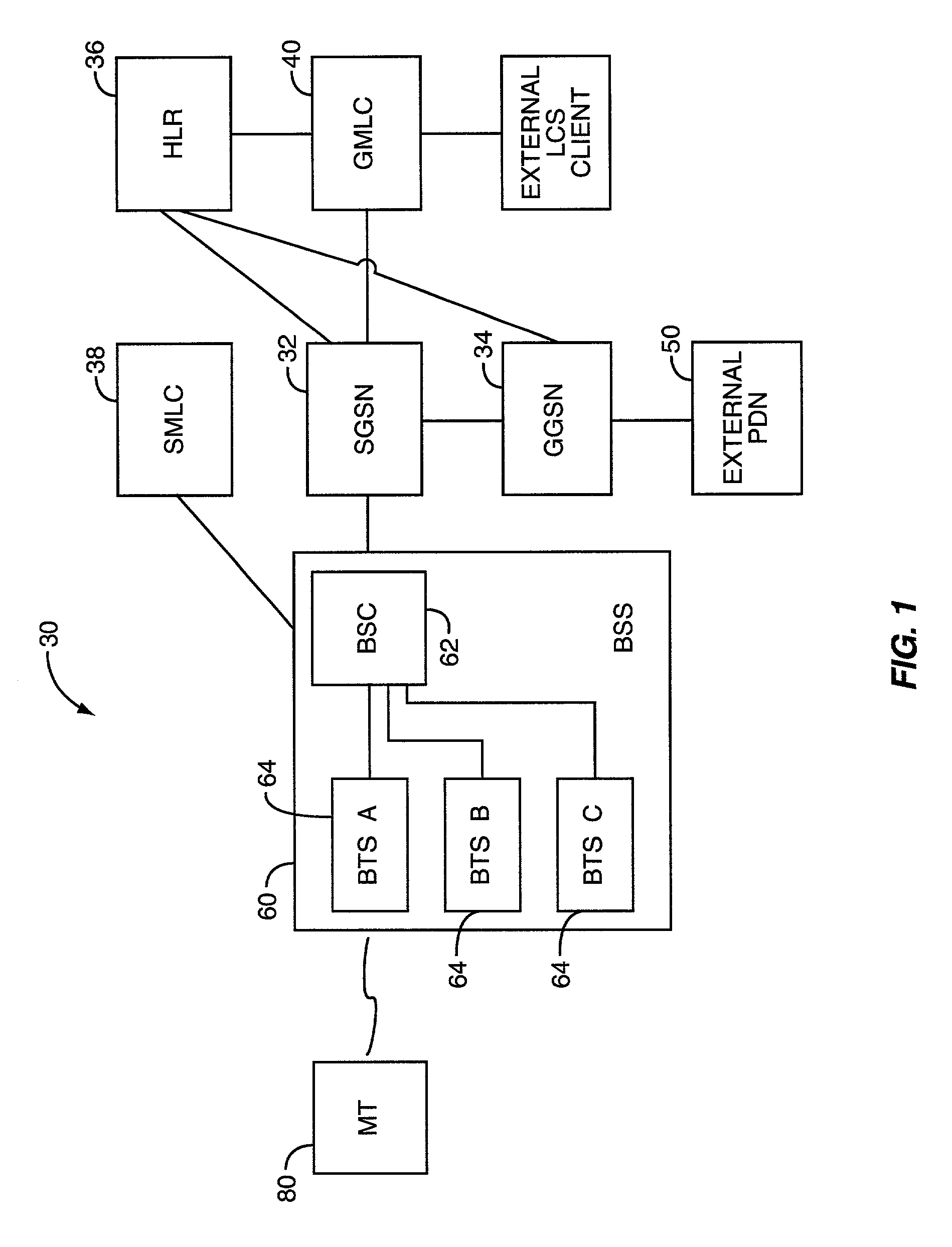
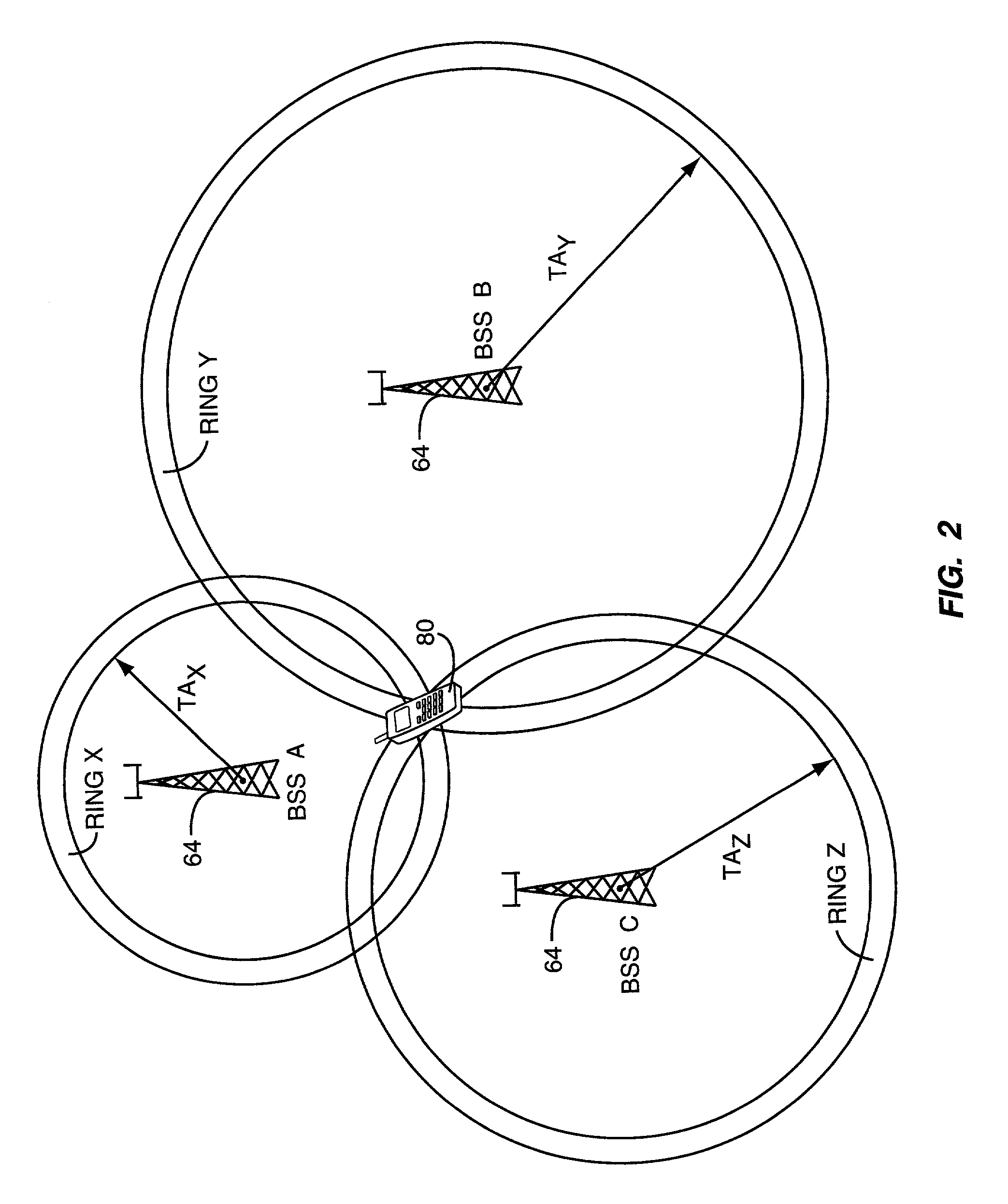
InactiveUS6987979B2Telephonic communicationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSynthetic CellsTiming advance
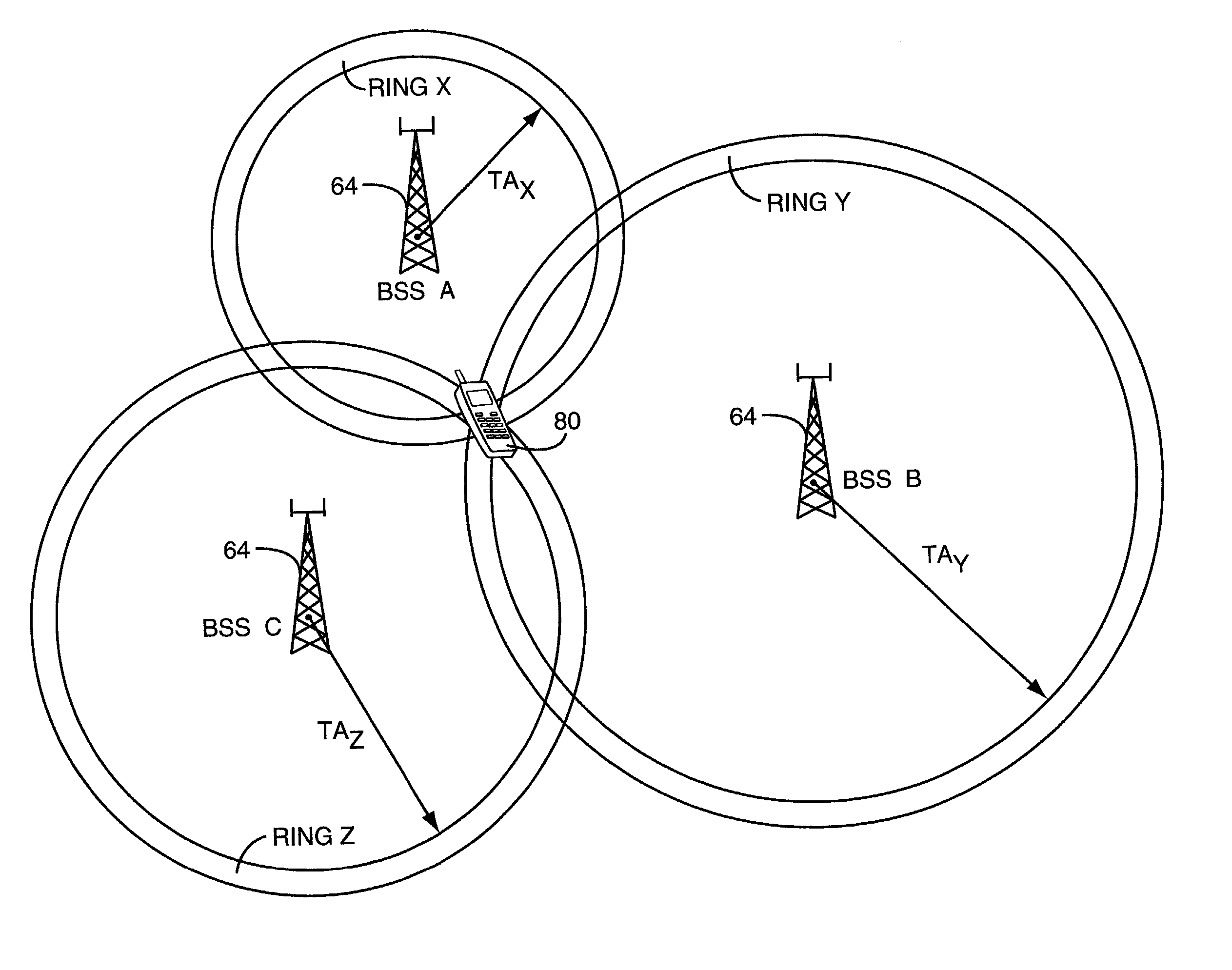
Determining the position of a mobile terminal operating in a packet-switched communications system based on timing advance values obtained through network initiated artificial cell hops. The mobile terminal may be instructed to perform a series of artificial cell changes so that timing advance values may be obtained for the mobile terminal with respect to a plurality of base stations. The position of the mobile terminal is then determined based on the timing advance values, optionally supplemented by signal strength measurements. The mobile terminal may contact a network entity via the base station in each cell before being instructed to change to the next base station. Or, the mobile terminal may be supplied with a list of base stations to contact, with the mobile terminal transmitting short access bursts to the base station in a given cell before automatically tuning to the next cell, without waiting for an acknowledgement.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
Device and method for controlled electroporation and molecular delivery into cells and tissue
InactiveUS20050170510A1Accurate measurementAccurate voltage controlGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsCell layerElectroporation
In biology and biotechnology, electroporation is an important technique for introducing entities (DNA, RNAi, peptides, proteins, antibodies, genes, small molecules, nanoparticles, etc.) into cells. Applications range widely from genetic engineering to regenerative medicine to drug delivery. It has been demonstrated that the electrical currents flowing through cells can be used to monitor and control the process of electroporation for biological and artificial cells. In this application, a device and system are disclosed which allow precise monitoring and controlling electroporation of cells and cell layers, with examples shown using adherent cells grown on porous membranes.
Owner:HUANG YONG +2
Synthetic Cell Platforms and Methods of Use Thereof
The present invention provides synthetic cell platforms. The synthetic cell platforms can be used for culturing cells in vitro. The synthetic cell platforms can also be implanted together with bound cells into an individual. The present invention provides methods of using the platforms to provide cells or progeny of such cells for use in various applications, including clinical applications; and methods of use of the platforms to introduce cells into an individual.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Mono-dispersed nano/micron polymer hollow microsphere resin and method for synthesizing the same
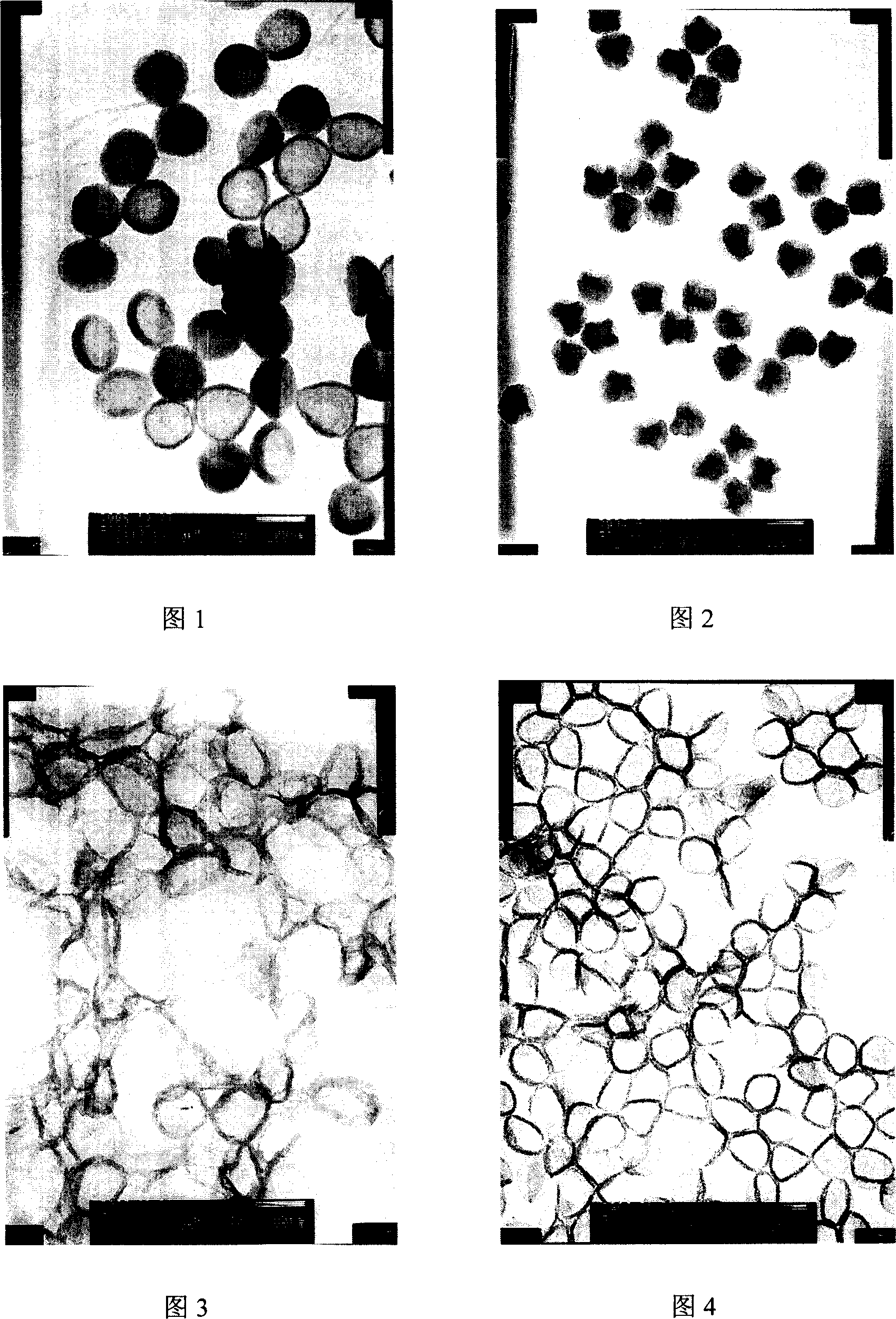
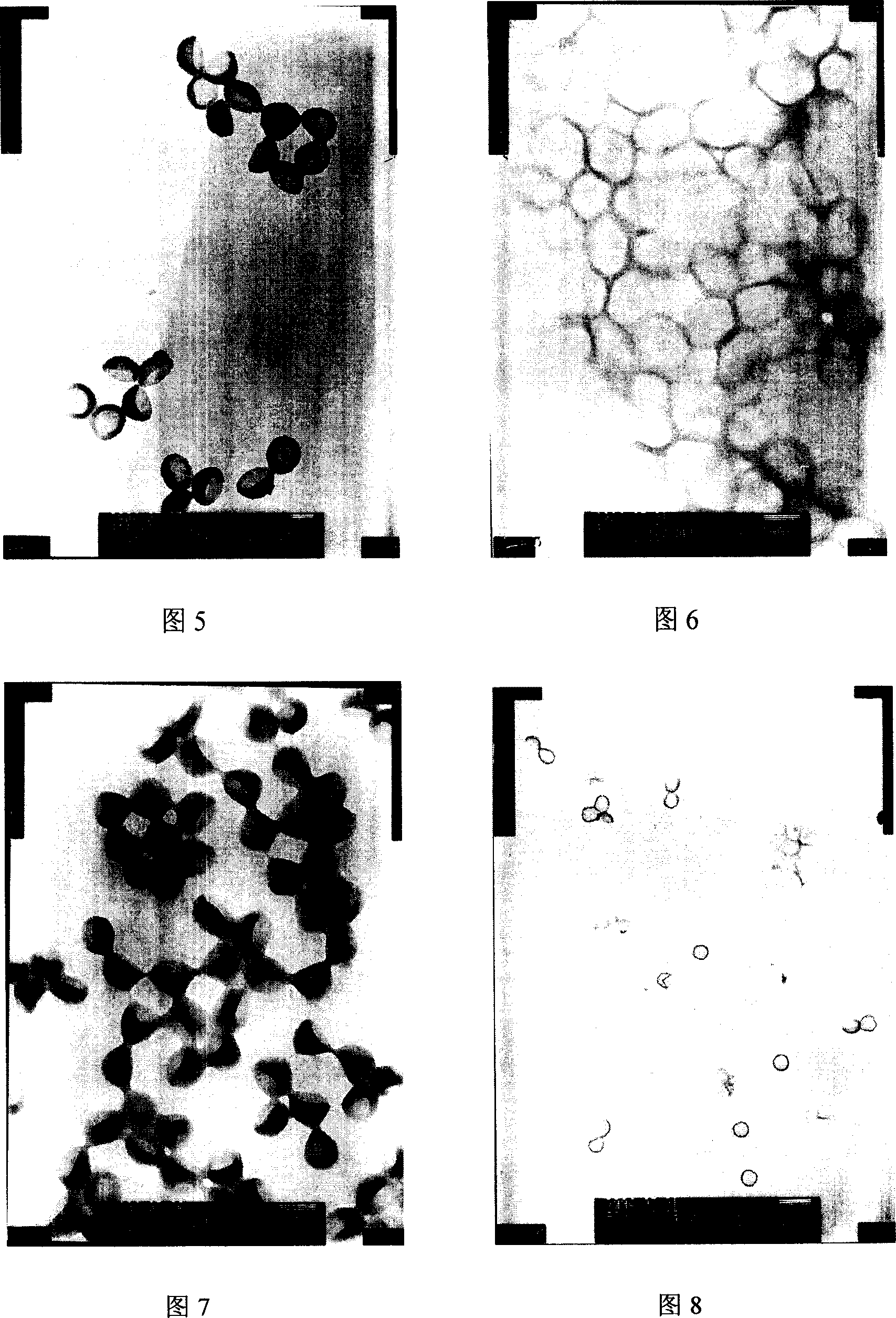
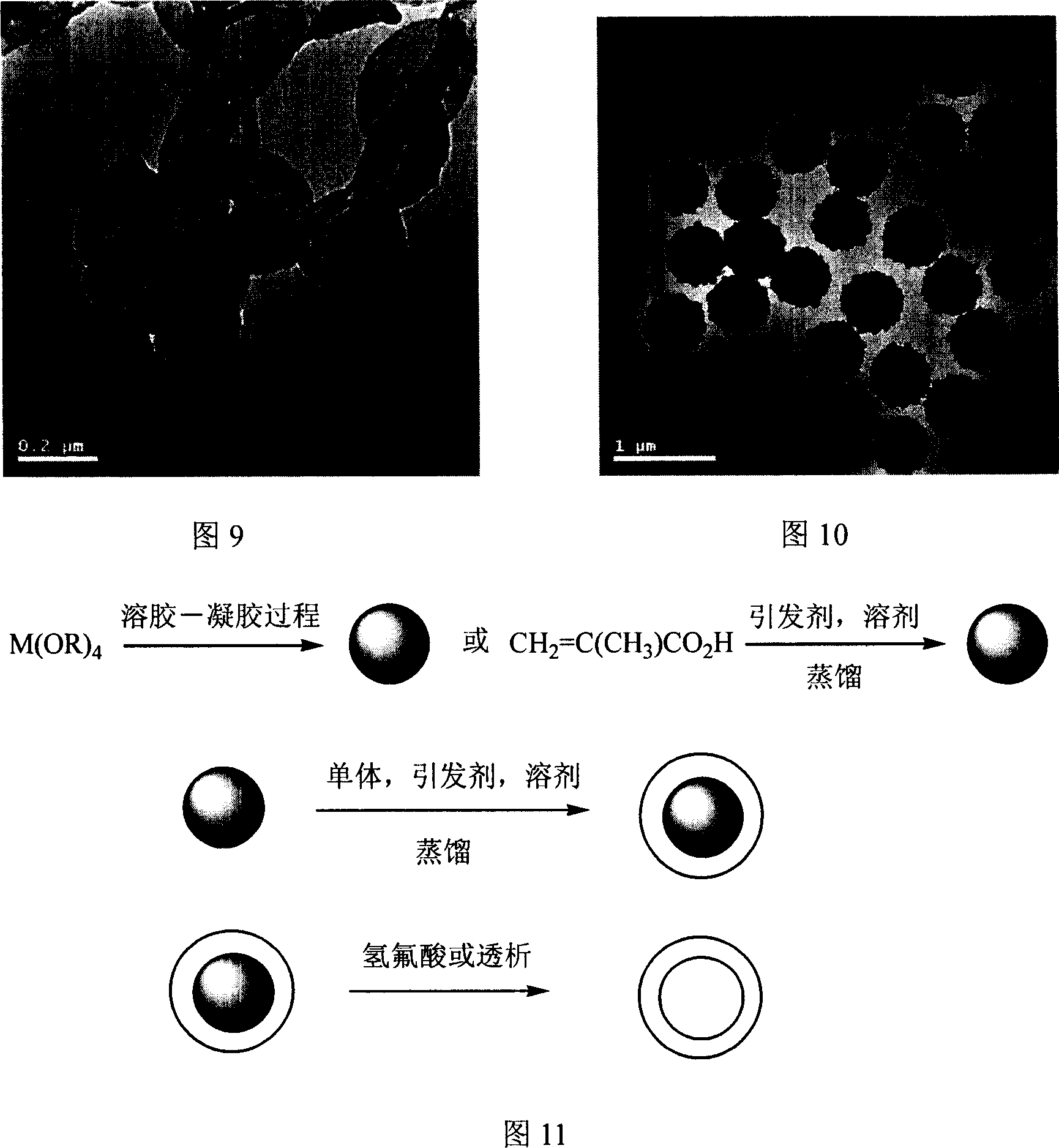
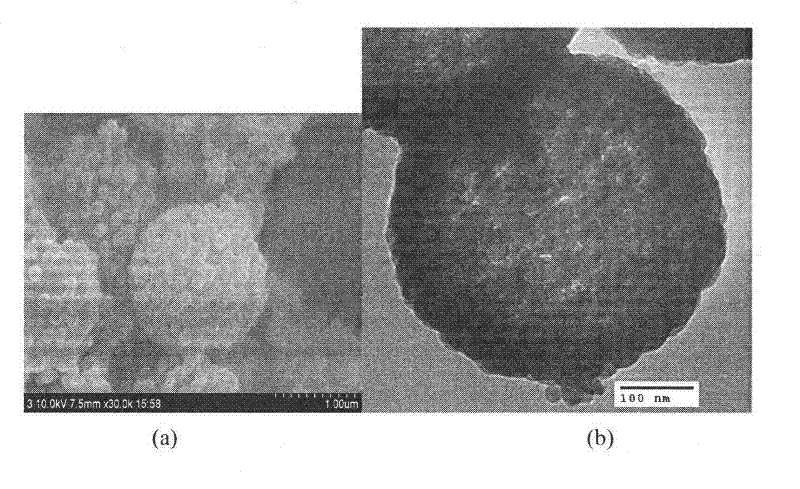
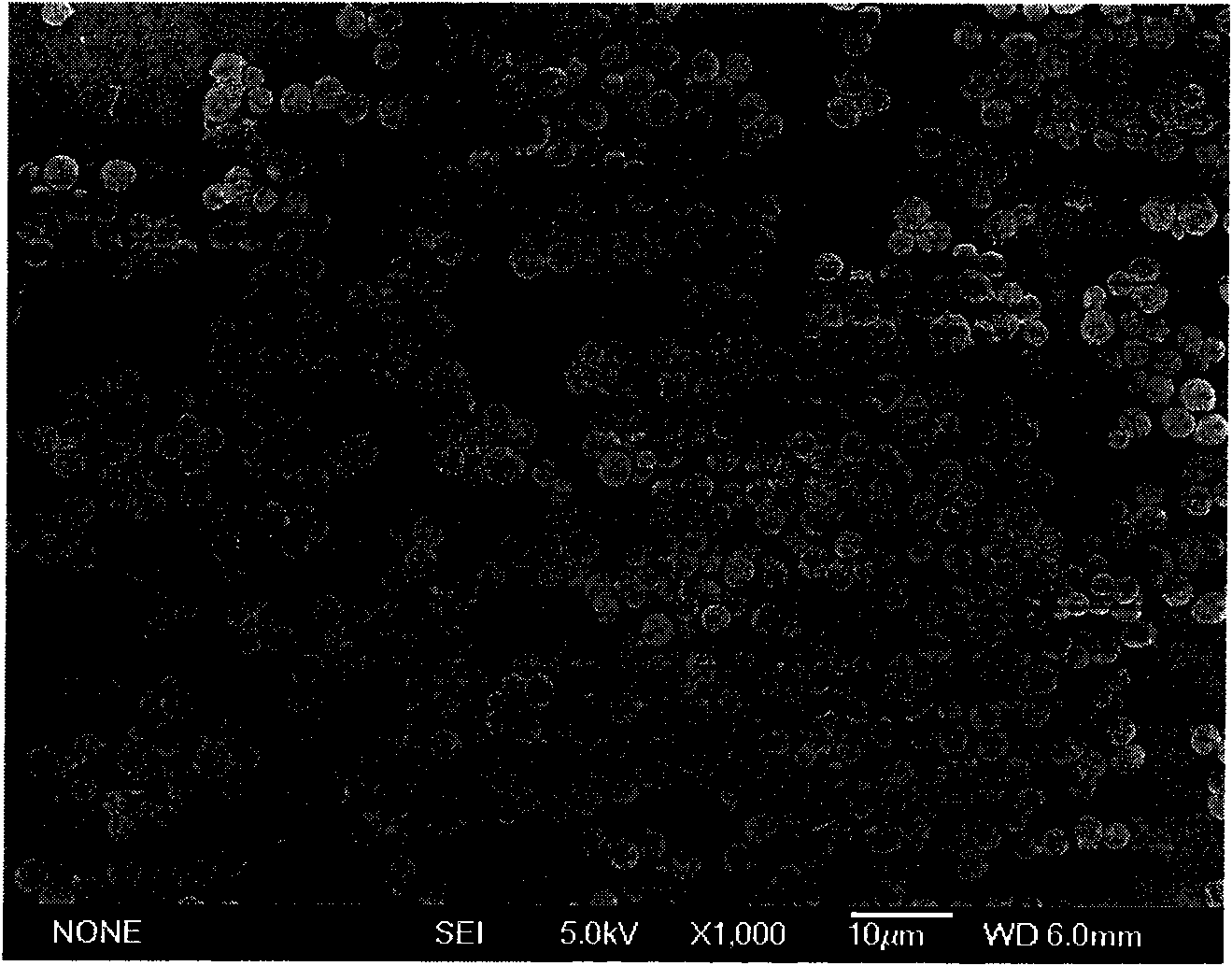
The invention relates to a preparation method of isodisperse nano / micron polymer hollow microsphere. The hollow microsphere with 10 nano-10 micron inner diameter and 10 nano-200 nano wall thickness is polyene type monomer homopolymer or copolymer (20-100 percent crosslinking) of polyene type monomer and other functional monoene type monomer. The polyene type monomer or the polyene type monomer and other functional monoene type monomer are distilled with the existence of a template to prepare a series of sodisperse sodisperse hollow microsphere with different inner diameters and wall thicknesses after precipitation polymerization. The invention has the advantages of simple conditions, easy operation, pure products and being easy to get raw materials and environment protective and so on. The nano / micron polymer hollow microsphere of the invention can be applied to systems with controllable transportation and release such as dyes, cosmetics, medicine, enzymes, proteins, etc. as well as light fillings, nano micro vessels, low dielectric constant materials, catalyst carrier and has very important application value in aspects such as artificial cell, disease diagnosis, biological material separation, etc.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
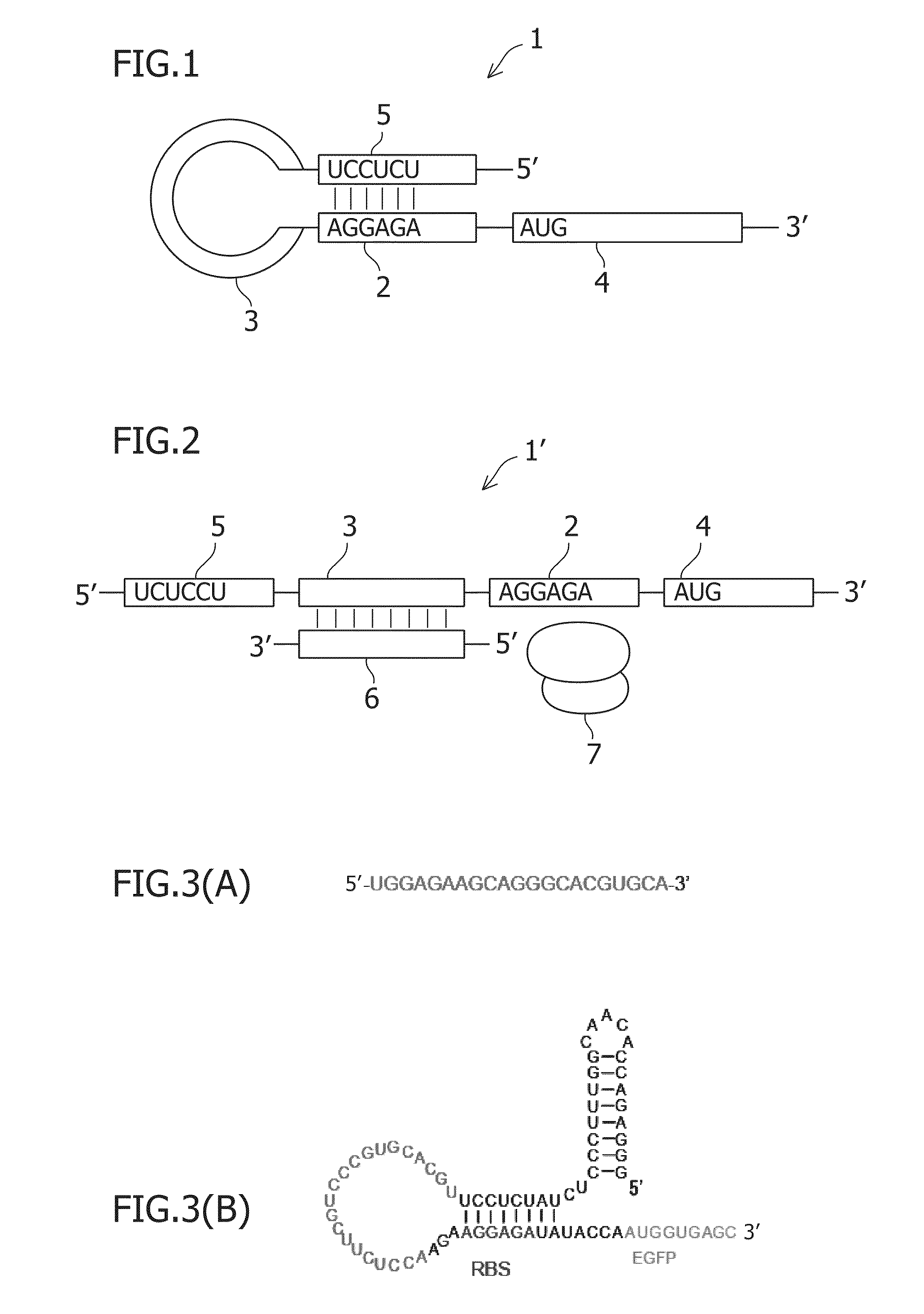
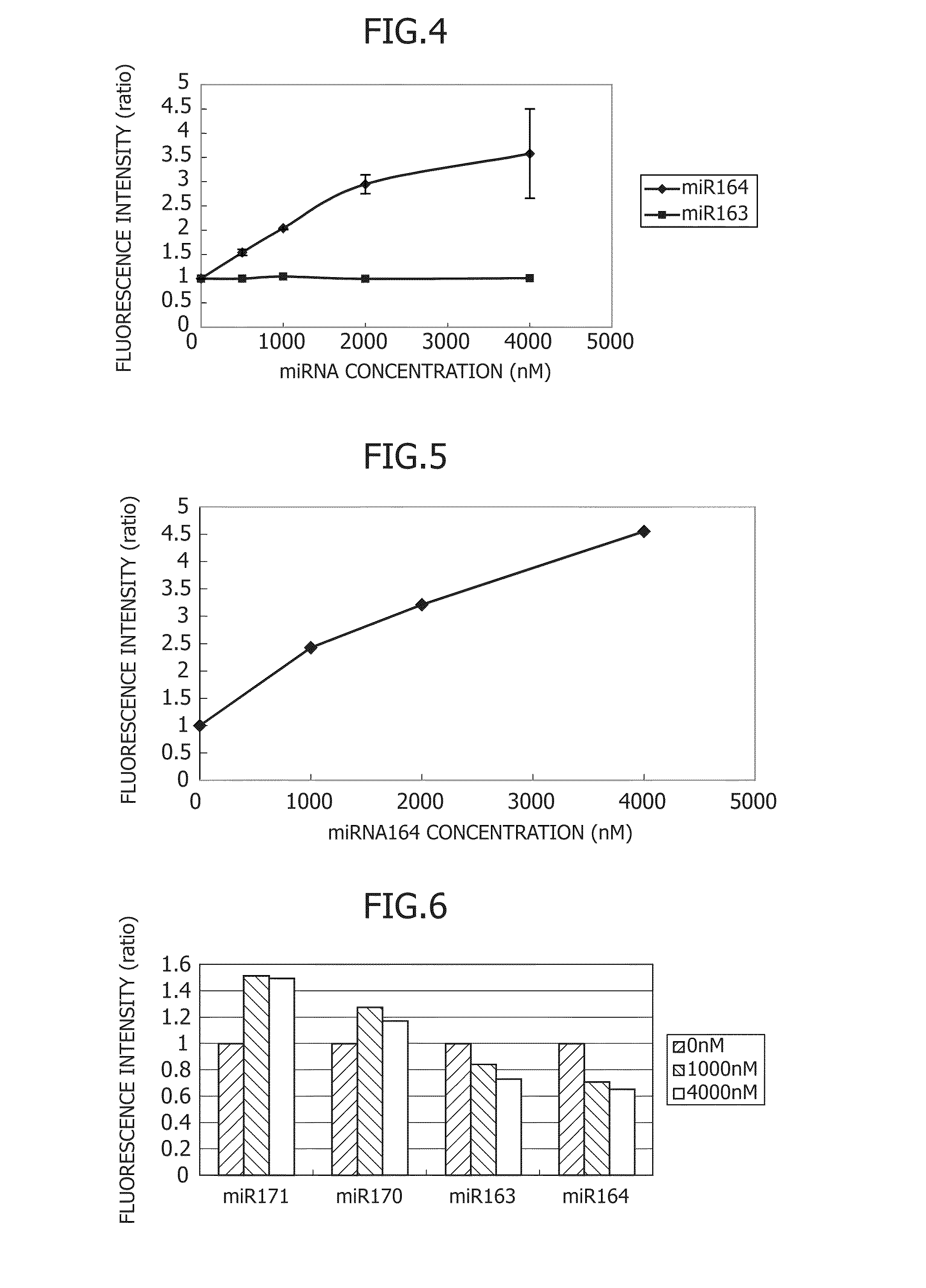
Small rna-dependent translational regulatory system in cell or artificial cell model
An object of the present invention is to construct an mRNA which specifically responds to a short RNA sequence and can activate, repress, and regulate the translation of the desired gene, and to construct an artificial cell model system using a liposome comprising the mRNA and a cell-free translational system encapsulated therein. The present invention provides: an mRNA comprising a target RNA-binding site located immediately 5′ to the ribosome-binding site, and a nucleotide sequence located 5′ to the target RNA-binding site, the nucleotide sequence being complementary to the ribosome-binding site; an mRNA comprising a small RNA-binding site located 3′ to the start codon, and a nucleotide sequence located 3′ to the small RNA-binding site, the nucleotide sequence encoding a protein; and a liposome comprising any of these mRNAs encapsulated therein.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
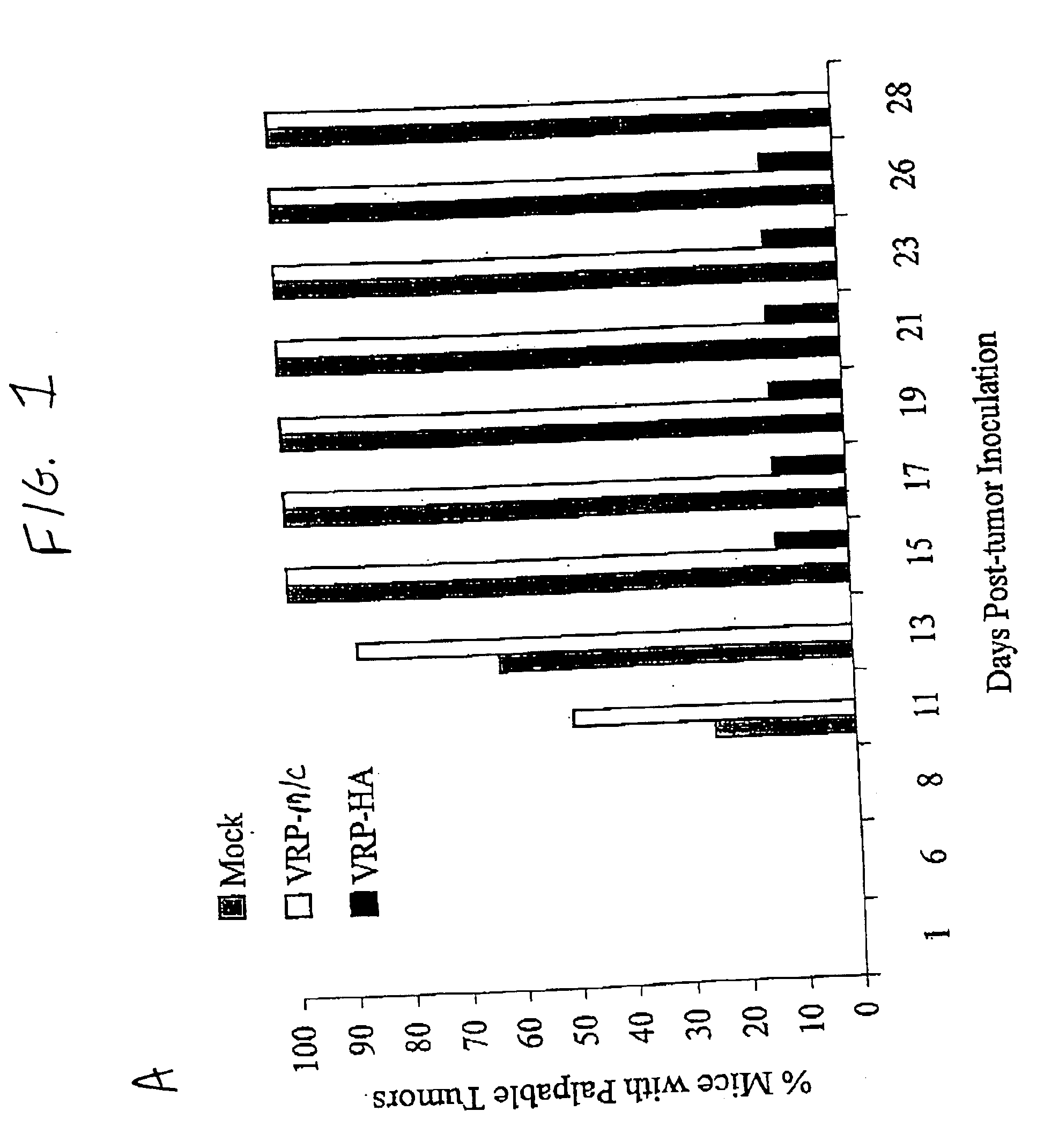
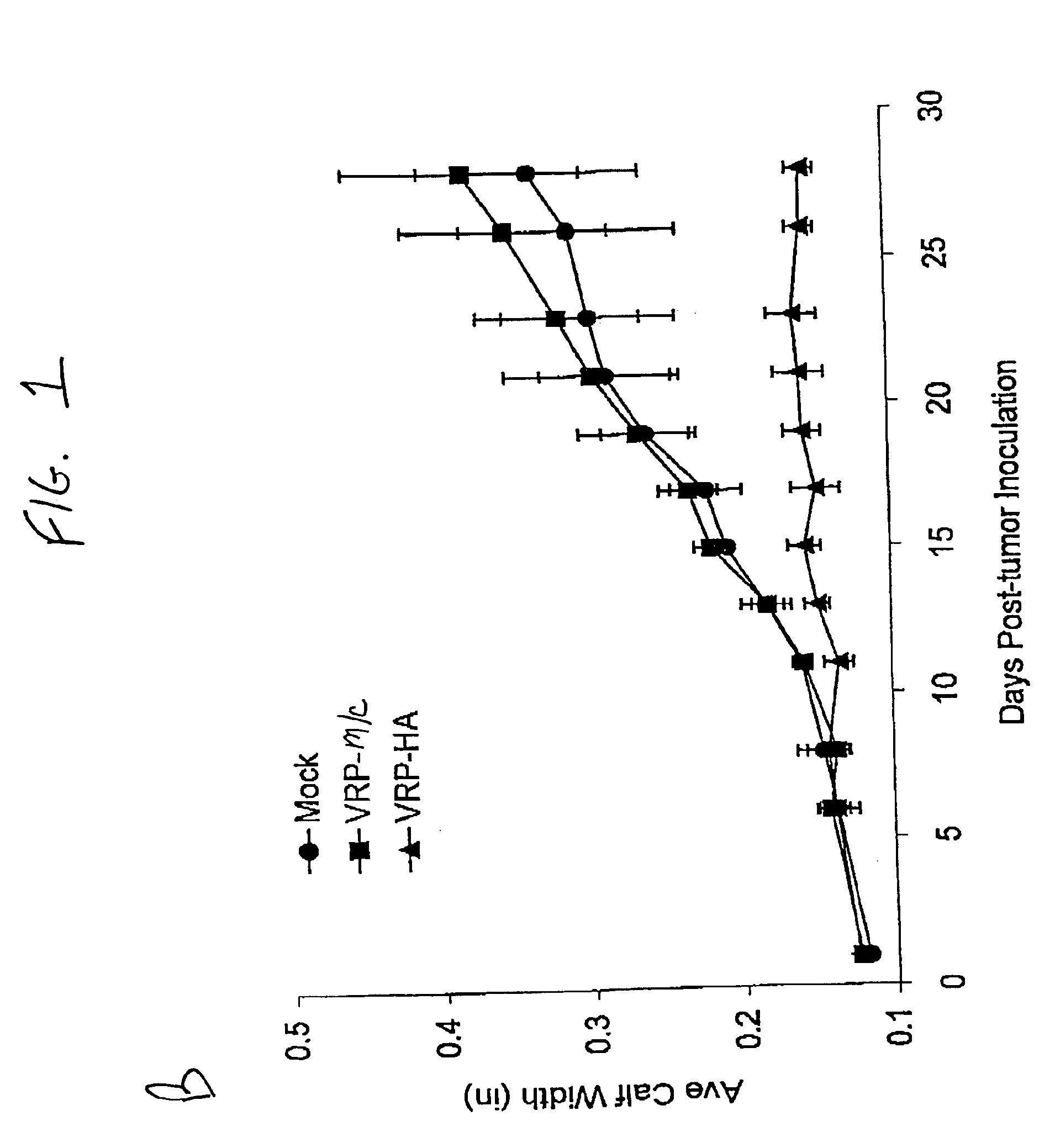
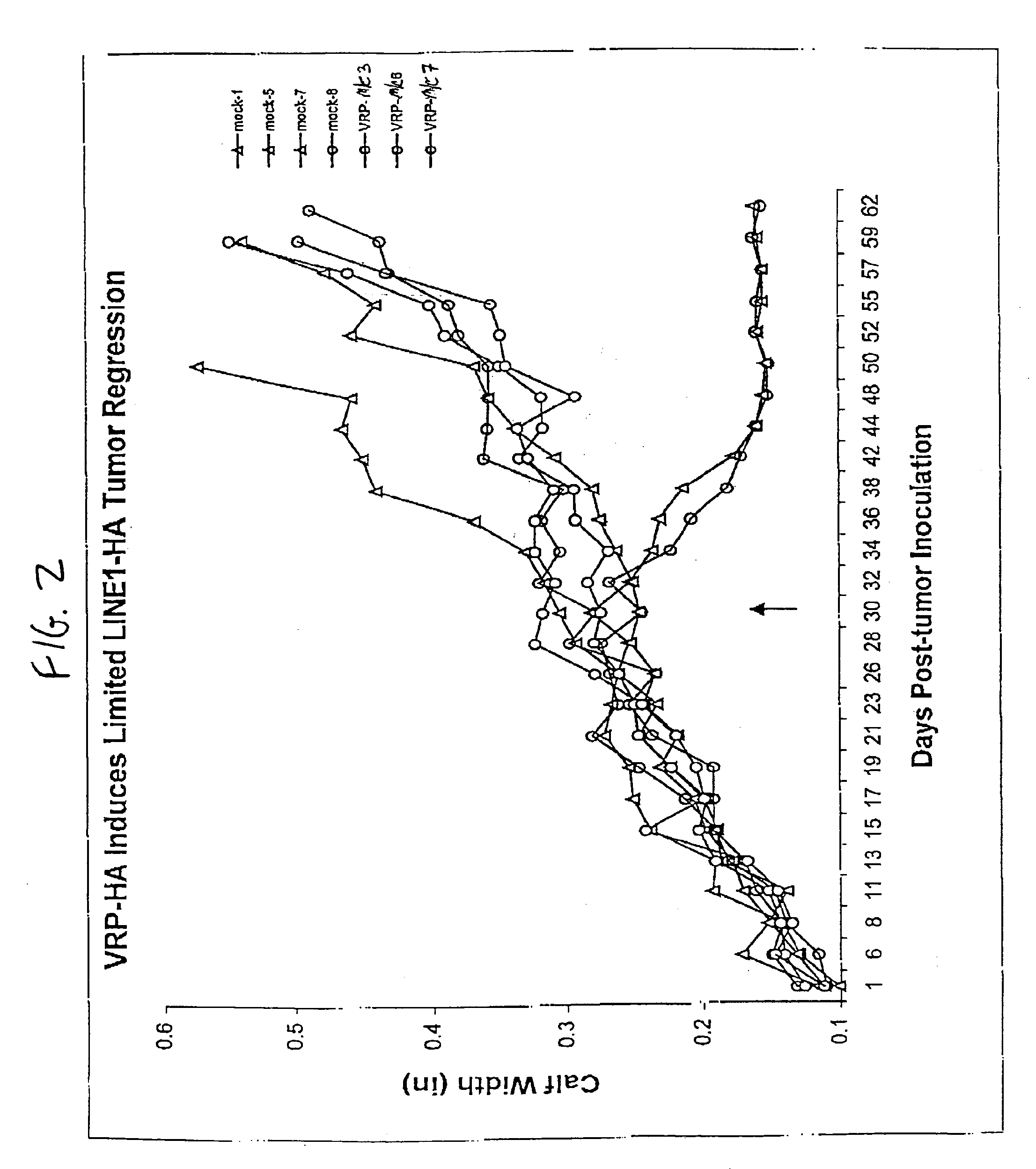
Methods and modified cells for the treatment of cancer
InactiveUS6844188B1Improve securityImproving immunogenicityBiocideSugar derivativesAbnormal tissue growthLymphatic Spread
The present invention provides methods of preventing and / or treating cancers (including tumors). In one preferred embodiment, the invention is practiced to induce regression of an existing cancer or tumor and / or to prevent metastasis and / or to prevent growth of metastatic nodules. In other preferred embodiments, the invention may be used as a prophylaxis to prevent the development of primary cancers through a childhood or adult vaccination program against specific tumor antigens for cancers with high incidences. In an alternate preferred embodiment, the present invention provides methods of establishing an immune response against a universal artificial tumor antigen through a childhood or adult vaccine program, thus providing a long-term immune response that can be utilized at any point to treat any cancer which develops later in life. The present invention also provides cancer and tumor cells stably expressing an artificial antigen, preferably an artificial cell-surface antigen.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL UNIVERSTIY OF THE
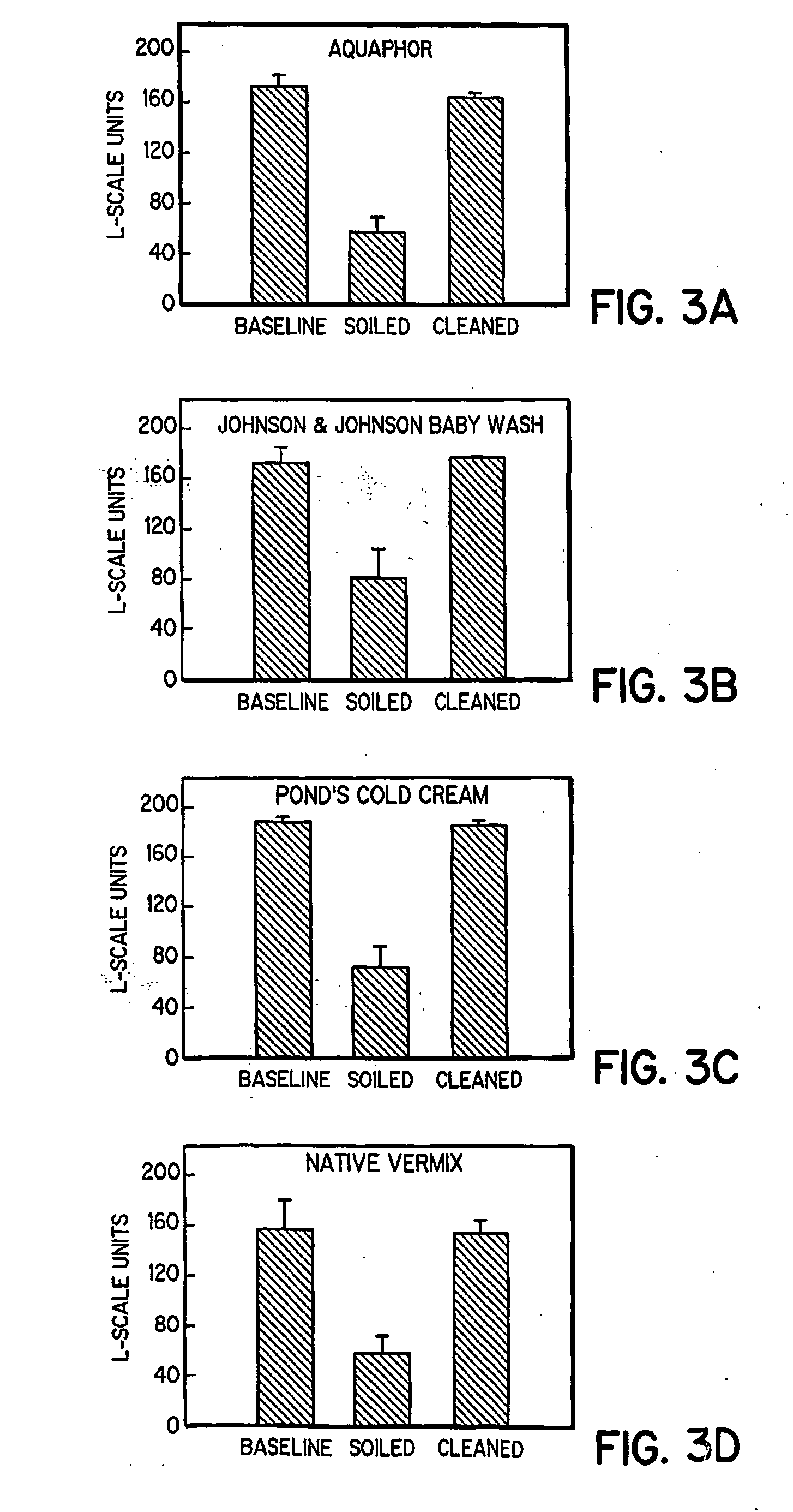
Simulated vernix compositions for skin cleansing and other applications
InactiveUS20050163812A1Effective treatmentCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSkin surfaceWater vapor
A composition and a method of producing a composition which simulates hydration, cleansing and other properties of native vernix. The composition contains, in one embodiment, hydrated synthetic cells in a lipid matrix to provide properties which are substantially similar to those of native vernix, and may also contain proteins. In one embodiment, the composition contains water-in-oil emulsified particles providing water vapor transport and evaporative water loss properties simulating native vernix. In one embodiment, the composition contains cubosomes / water with up to 30% protein and about 5% lipid to about 30% lipid. The composition may be used to cleanse newborn skin, compromised skin surfaces, as well as normal skin, to provide hydration / barrier function, and other applications.
Owner:CINCINNATI UNIV OF +1
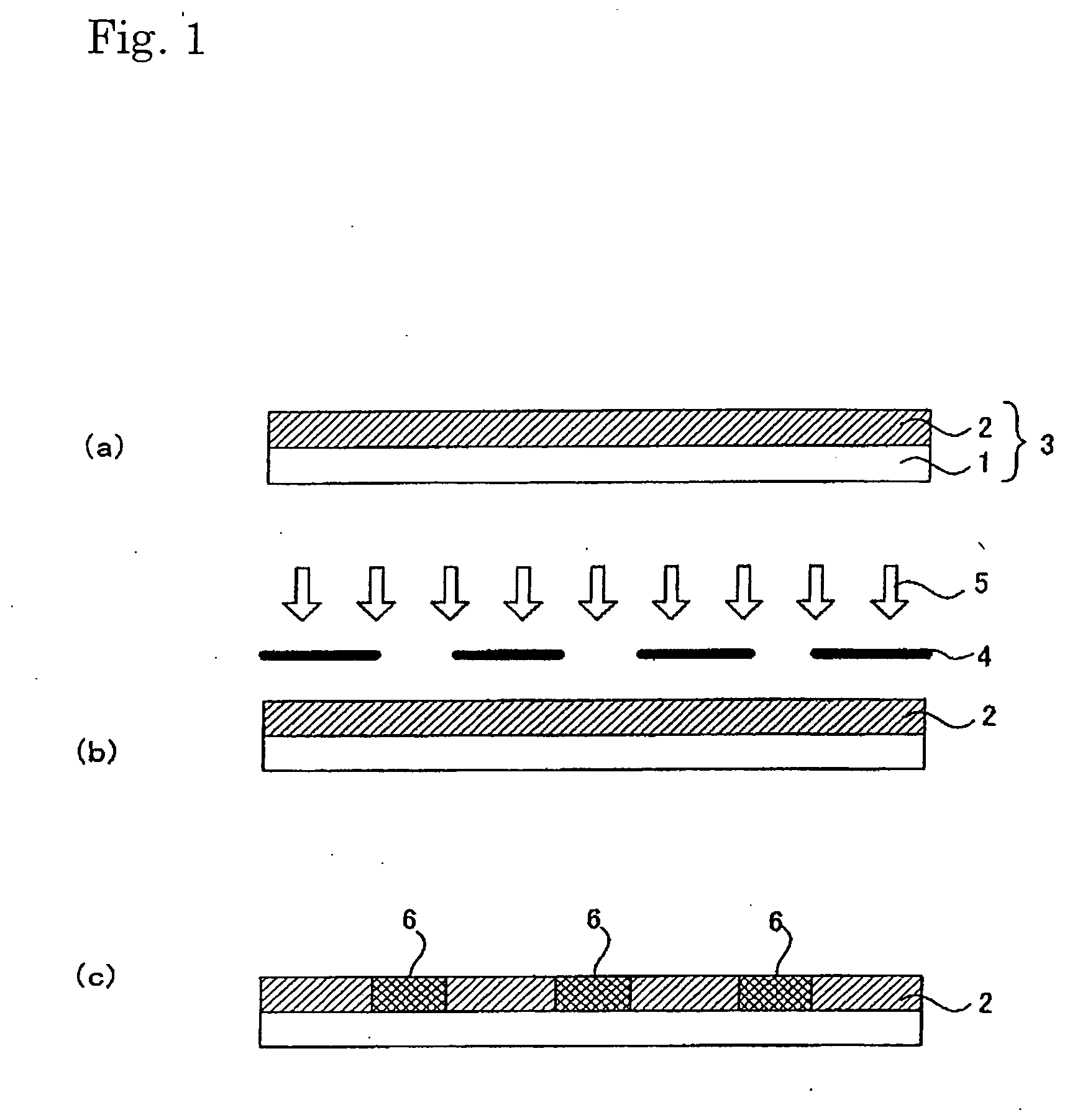
Method of constructing artificial cell tissue and base material therefor
InactiveUS20070122901A1Promote cell adhesionExact strengthArtificial cell constructsCell culture supports/coatingTransfer cellCell adhesion
The present invention relates to a method for culturing cells, which comprises the steps of: causing cells to adhere to the surface of a cell array substrate having a cell adhesiveness variation pattern that comprises regions having good cell adhesiveness and regions having inhibited cell adhesiveness patterned on a substrate; transferring the adhered cells to a cell culture substrate in such patterned state; and culturing the transferred cells.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Treatment of diabetes with synthetic beta cells
InactiveUS6933133B2Reduce formationReduce expressionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGlucose polymersActrapid insulin
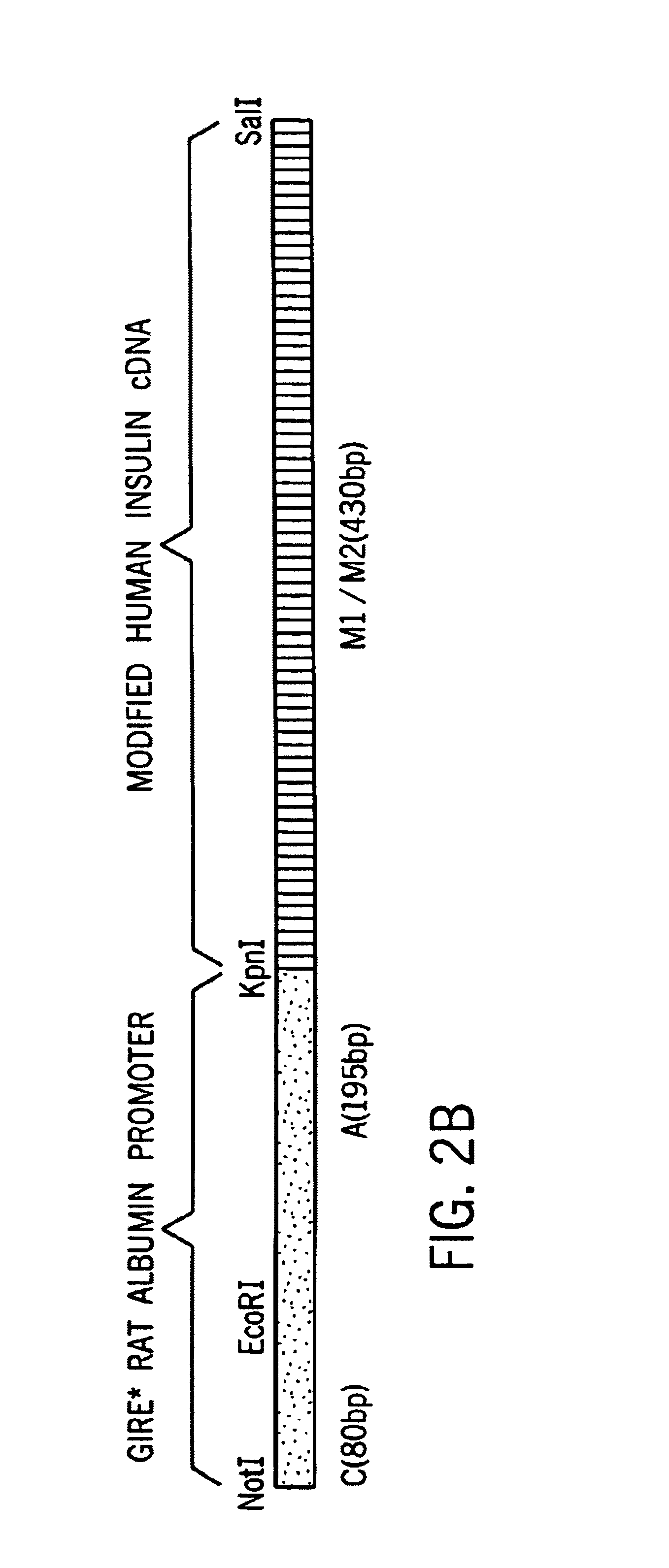
Disclosed is a method for obtaining glucose-regulated expression of active insulin in the cells of a mammalian subject. The method involves delivering into the subject a genetic construct comprising a coding sequence for a human proinsulin operably connected a promoter functional in the host cells. The construct includes a glucose responsive regulatory module having at least one glucose inducible regulatory element comprising a pair of CACGTG motifs linked by a five base nucleotide sequence, which confers glucose inducible expression of the proinsulin coding sequence. To ensure proper processing of the proinsulin to active insulin, the coding sequence was modified to direct the synthesis of a mutant proinsulin polypeptide having amino acid sequences that can be cleaved to mature insulin in suitable host cells, such as hepatocytes.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Top-emitting white organic light-emitting diodes having improved efficiency and stability
ActiveUS20130153871A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSomatotropic hormoneRadioactive agent
Treatment for Cancer Using A Preparation containing a combination of one or more Natural or Synthetic or a Combination of Natural and Synthetic Boswellic Acids and one or more Natural or Synthetic or a Combination of Natural and Synthetic Cytokinins such as Kinetin, Kinetin Riboside and other Cytokinins and (the Preparation) could also contain one or more Natural or Synthetic or a Combination of Natural and Synthetic plant growth hormones such as Auxins in any percentage Ratio and could Optionally include Pharmaceutically Suitable Radioactive Agent (Radio Therapy) in any percentage ratio as a “Stand Alone” Treatment for Cancer or to Be used in Conjunction with other Pharmaceutically Suitable Therapy and Treatment(s) in any percentage ratio as a Treatment for Treating Cancer.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Preparation technology of PCL/GE (polycaprolactone/gelatin) electrospinning composite stent
InactiveCN105688274AHigh biosecurityGood biocompatibilityElectro-spinningTissue regenerationFiberNormal bone
The invention discloses a preparation technology of a PCL / GE (polycaprolactone / gelatin) electrospinning composite stent, and belongs to the technical field of biological tissue engineering stents. The preparation technology sequentially comprises a preparation technology of a PCL / GE nanometer fiber electrospinning film which is made of an artificial cell extracellular matrix (ECM) stent material, a preparation method of an electrospinning film coated with hydroxyapatite crystals, and a building method of the electrospinning composite stent. The preparation technology has the advantages that the electrospinning film coated with the hydroxyapatite crystals and the PCL / GE electrospinning film are combined to form an ECM structure which is similar to natural bone tissues; the prepared electrospinning composite stent has no obvious cell toxicity, the internal stent structure is similar to the ECM of the natural bone tissues, and the outer layer structure can block the invasion of peripheral connective tissues; the biocompatibility is good, and the regeneration of bone tissues can be effectively promoted; a stable environment is provided for the regeneration of new bones, and the structure and function of the ECM of the normal bone tissues can be simulated.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE HOSPITAL
Macroporous/mesoporous hollow silica microballoon and its preparation method
The invention relates to a macroporous / mesoporous hollow silica microballoon and its preparation method. The macroporous / mesoporous hollow microballoon is prepared by the following steps of: carrying out self assembly on organic polymer microballoons with different particle sizes to obtain a template, generating a silica outer layer by in situ method, and calcining to remove the internal organic matter. The internal cavity of the microballon obtained is 500-2000nm controllable and the pore diameter of the microballoon surface is 10-100nm controllable, so as to form the macroporous / mesoporous hollow structure. The preparation method provided by the invention has characteristics of simple condition, convenient operation, easily obtained raw materials, pure product, environmental protection and the like. The silica hollow microballoon provided by the invention can be widely applied in a controllable transport and delivery system of medicament, dye, cosmetic and sensitive reagents such as enzyme and protein as a carrier material, can be used as a lightweight filling material, a high selectivity catalyst or a catalyst carrier, and has a very important value in the aspects of artificial cells, disease diagnosis and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Amphiphilic porous hollow carbon microsphere as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102070135AEasy to separateEasy to recycleCatalyst carriersPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPtru catalystMicrosphere
The invention discloses an amphiphilic porous hollow carbon microsphere, a preparation method thereof, applications of the amphiphilic porous hollow carbon microsphere as a carrier in enriching and loading of active molecules or a catalyst, and a method for separating and recovering the porous hollow carbon microsphere from a dispersion system by utilizing the amphipathy. The method comprises thefollowing steps of: dispersing microzyme in an aqueous solution of a cytoderm surface protectant; and then, carrying out carbonation treatment to obtain the amphiphilic porous hollow carbon microsphere. The prepared hollow carbon microsphere has a pore size capable of being controlled in the mesoporous and macroporous range as required, and can be suitable for the loading, the storage and the transmission of guest molecules in different sizes; by utilizing the characteristic of the amphiphilic porous hollow carbon microsphere capable of spontaneously transferring to a two-phase interface froma polar or non-polar dispersion system, the microsphere can be conveniently separated and recovered from a reaction mixing system. The easy and low-cost synthesis method and the special properties ofthe hollow carbon microsphere are favorable to the applications of the hollow carbon microsphere to the fields, such as energy storage, medicament transmission, artificial cells, catalytic carriers, and the like.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Simulated vernix compositions for skin cleansing and other applications
InactiveUS20050232890A1Effective treatmentCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsLipid formationSkin surface
A composition and a method of producing a composition which simulates hydration, cleansing and other properties of native vernix. The composition contains hydrated synthetic cells in a lipid matrix to provide rheological properties which are substantially similar to those of native vernix, and may also contain proteins. In one embodiment, the composition contains cubosomes / water with up to 30% protein and about 5% lipid to about 30% lipid. The composition may be used to cleanse newborn skin, compromised skin surfaces, as well as normal skin, to provide hydration / barrier function, and other applications.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Method for treatment of spider silk-filament for use as thread or a composition in the manufacture of cosmetic, medical, textile or industrial applications such as bio-artificial cell tissue or skin based on (recombinant) spider silk
InactiveUS20150056256A1Reduced pathological immune responseImprove scalabilityCosmetic preparationsElectric discharge heatingAntioxidantMagnetite Nanoparticles
A method for the treatment of spider silk filament for use as a thread or composition in the manufacture of cosmetic, medical, textile, and industrial applications, wherein the spider silk filament, derived from genetically modified organisms, is treated with at least one component selected from the group consisting of vitamins, hormones, antioxidants, chelating agents, antibiotics, preserving agents, fragrances, dyes, pigments, magnetic nanoparticles, nanocrystals, cell adhesion enhancers, thermal insulators, shrinkage agents and cosmetic, medical or dermatological active substances. Textile fabrics obtained by this method are stronger, bio-compatible, bio-degradable and have a higher thermal conductivity. Treated spider silk filament can also be applied in an oil-in-water or water-in-oil protective cream that is hypoallergenic and ensures a firmer skin.
Owner:ESSAIDI JALILA
Pipettes, methods of use, and methods of stimulating an object of interest
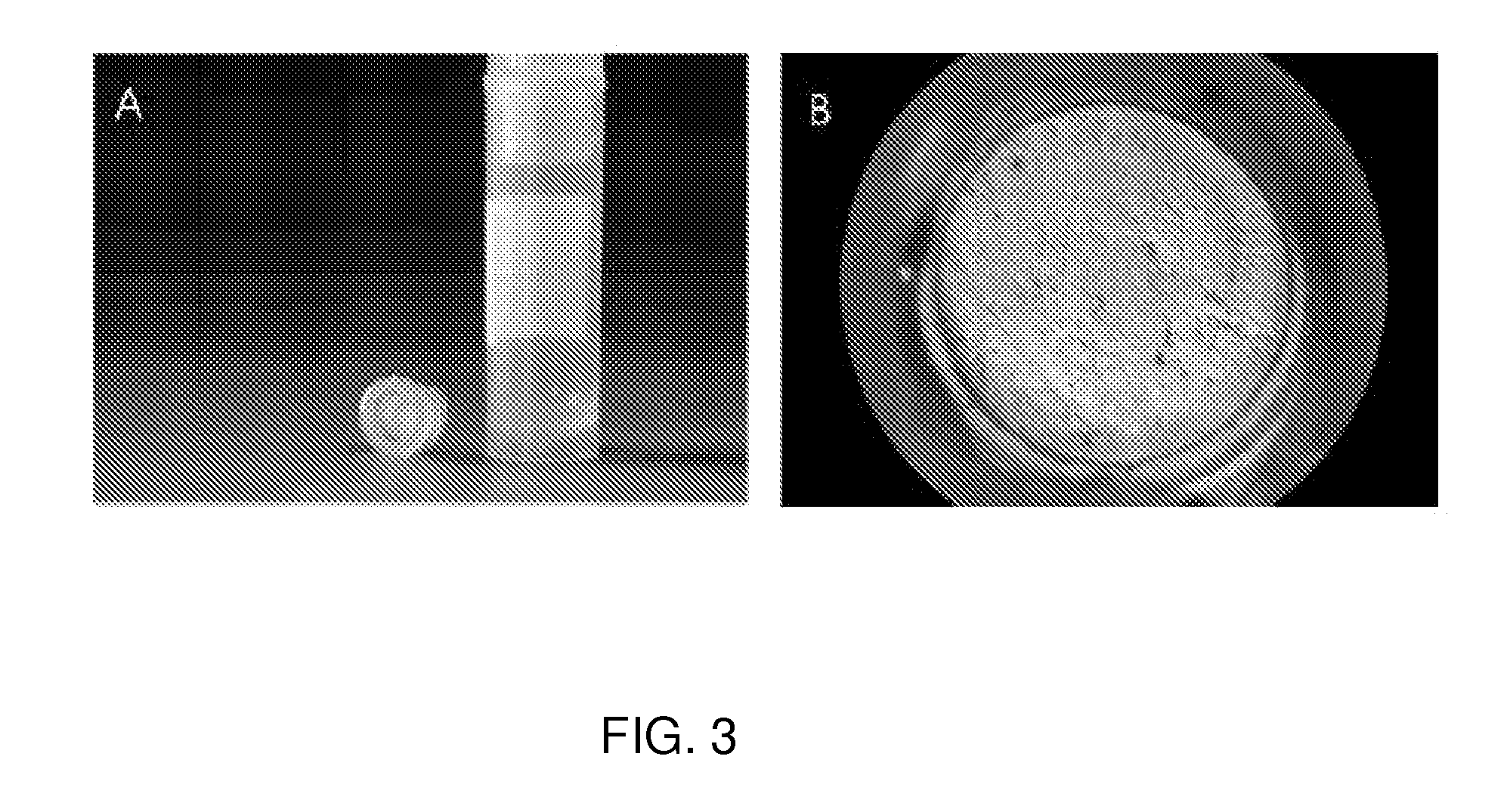
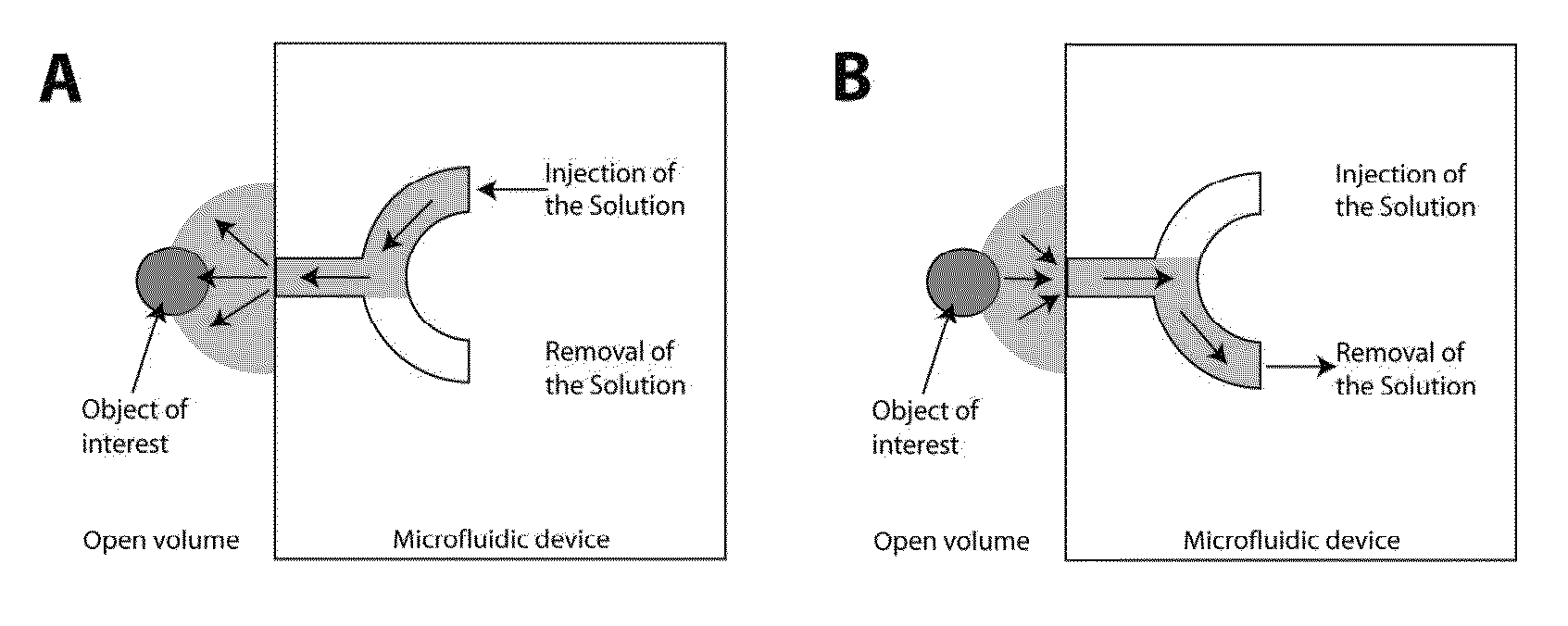
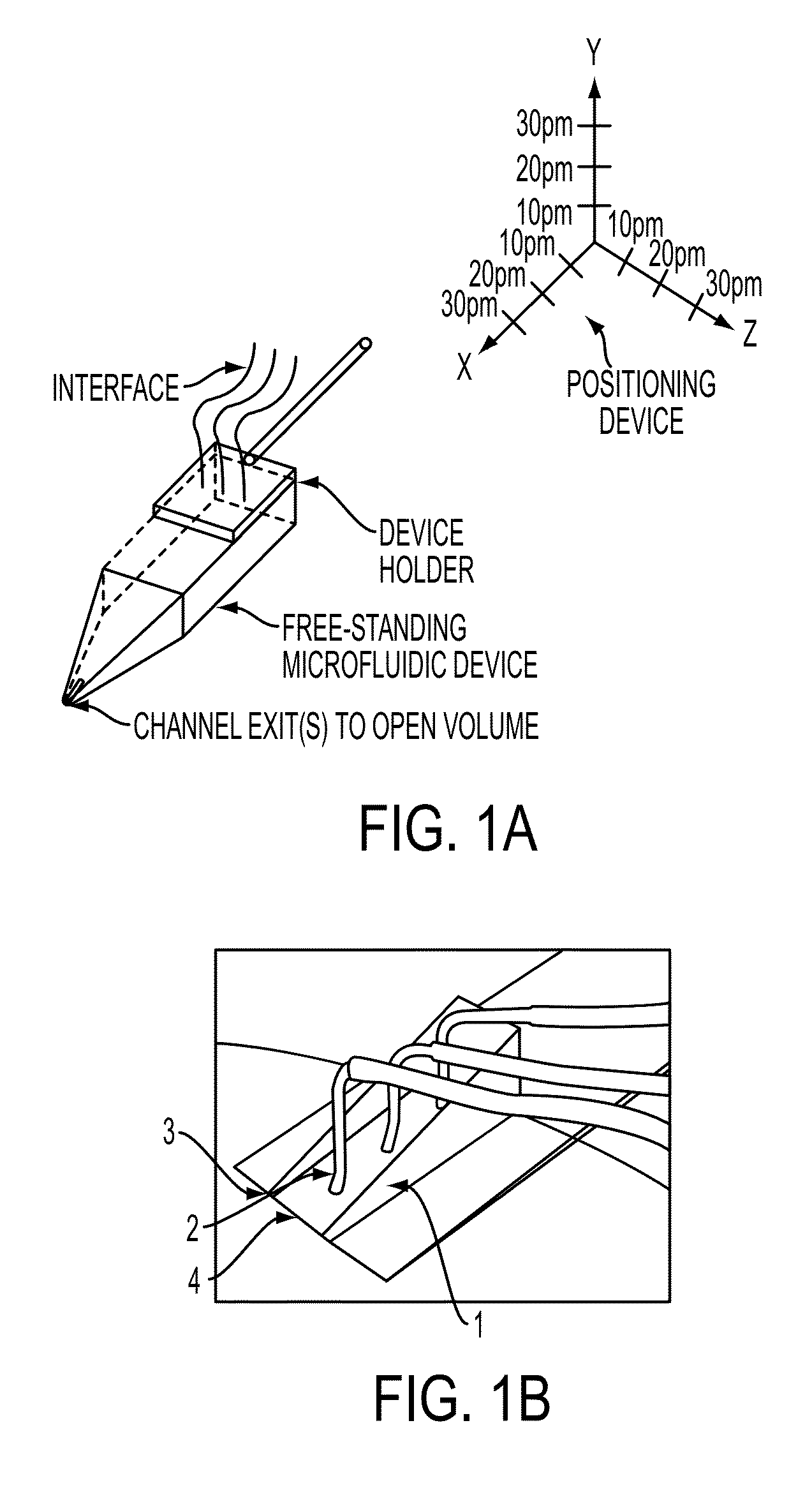
ActiveUS9126197B2Highly localized and contamination-free fluid deliveryImproved vibration stabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysis componentsPipetteHorizontal axis
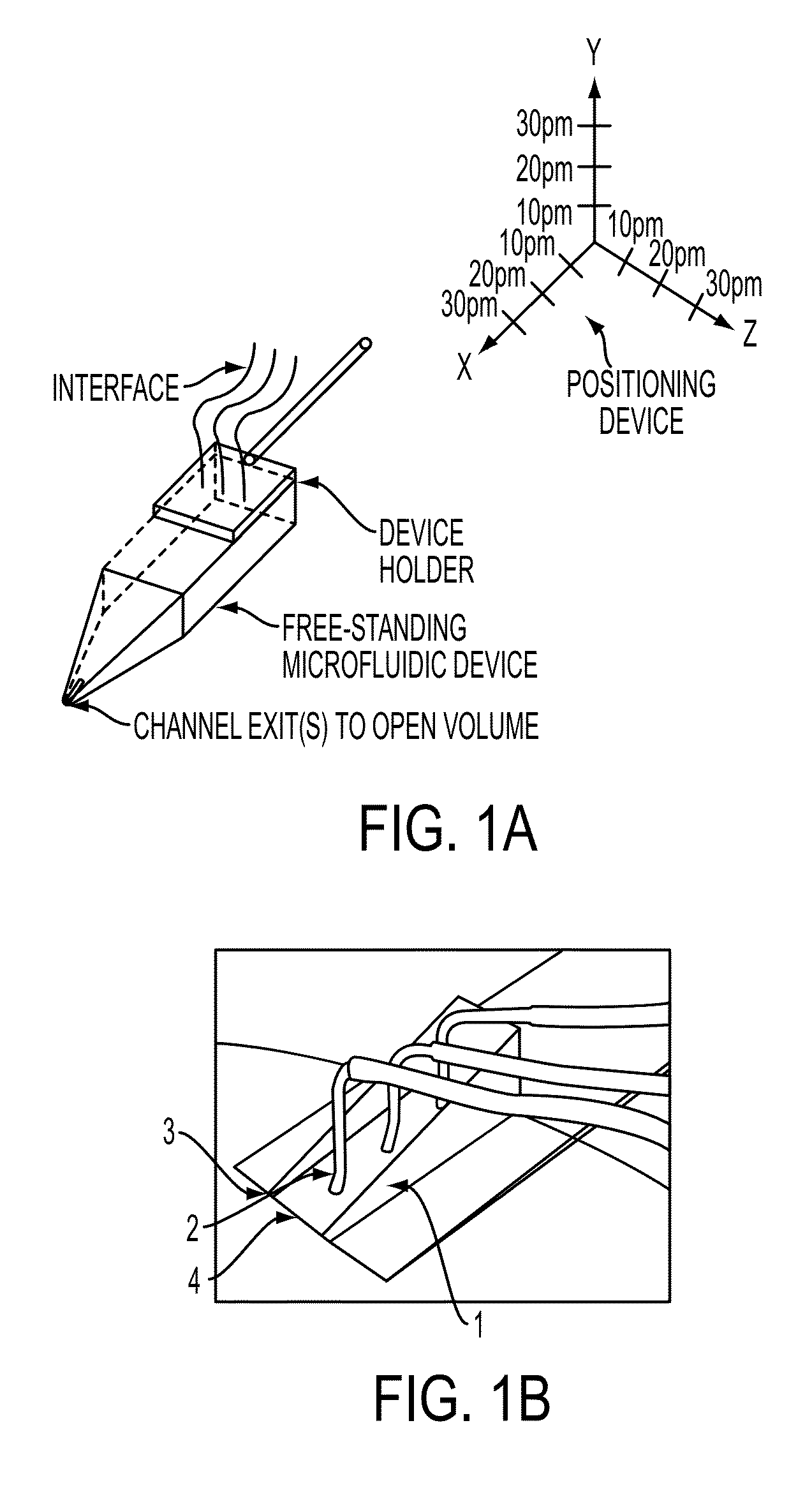
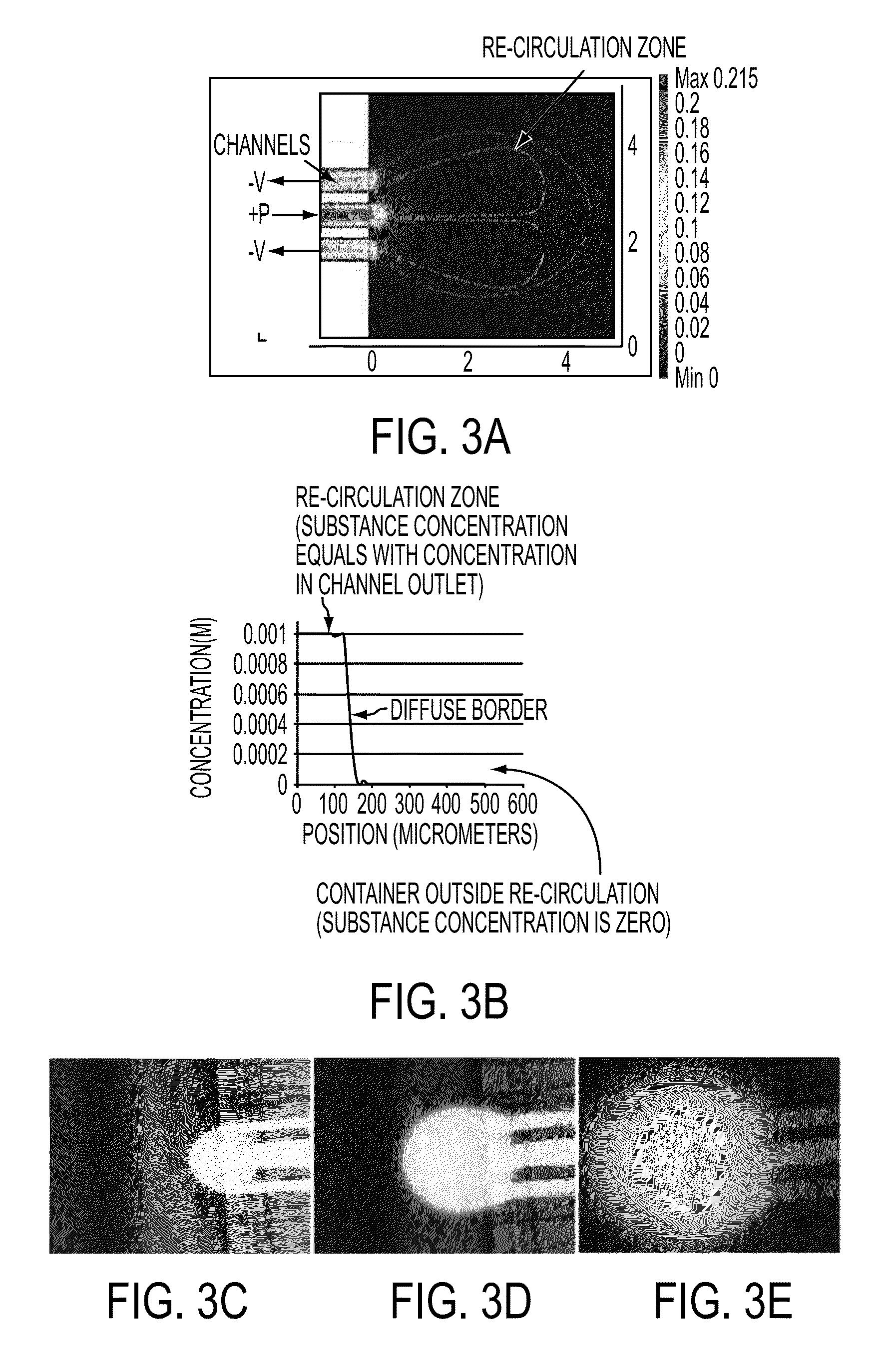
The present invention features a freestanding microfluidic pipette with both solution exchange capability and fluid re-circulation, enabling highly localized and contamination- free fluid delivery within a confined volume in the vicinity of the pipette exit. Preferably, the device features direct positioning, so the pipette can be directed at a point or object of interest, such as a biological or artificial cell, a defined surface area or a sensor element within an open volume, using micro- or nanopositioning techniques. One aspect of the invention provides a free-standing pipette. The free-standing pipette includes a microfluidic device comprising one or more channels with exits leading into an open-volume and a positioning device programmed to hold the microfluidic device at an angle from a horizontal axis.
Owner:FLUICELL AB
Simulated vernix compositions for skin cleansing and other applications
InactiveUS7807188B2Effective treatmentCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsLipid formationSkin surface
A composition and a method of producing a composition which simulates hydration, cleansing and other properties of native vernix. The composition contains hydrated synthetic cells in a lipid matrix to provide rheological properties which are substantially similar to those of native vernix, and may also contain proteins. In one embodiment, the composition contains cubosomes / water with up to 30% protein and about 5% lipid to about 30% lipid. The composition may be used to cleanse newborn skin, compromised skin surfaces, as well as normal skin, to provide hydration / barrier function, and other applications.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Artificial cell membrane materials applied to photoinduction stem grafting and synthesis method thereof
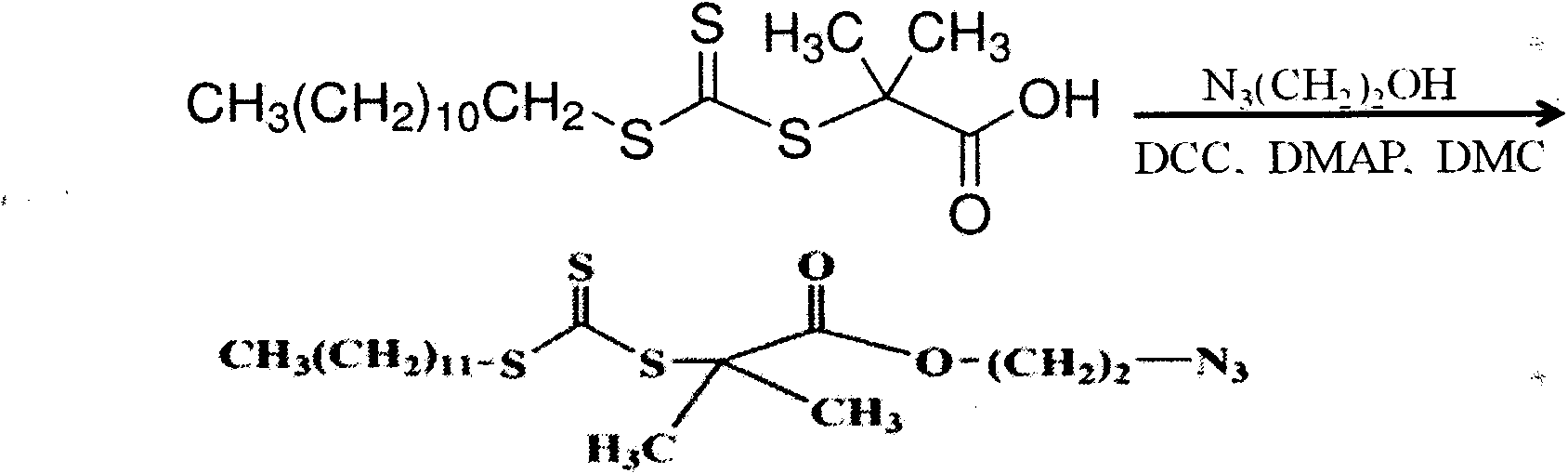
InactiveCN103483480ADoes not affect mechanical propertiesDoes not affect structural propertiesCoatingsPropanoic acidBiocompatibility Testing
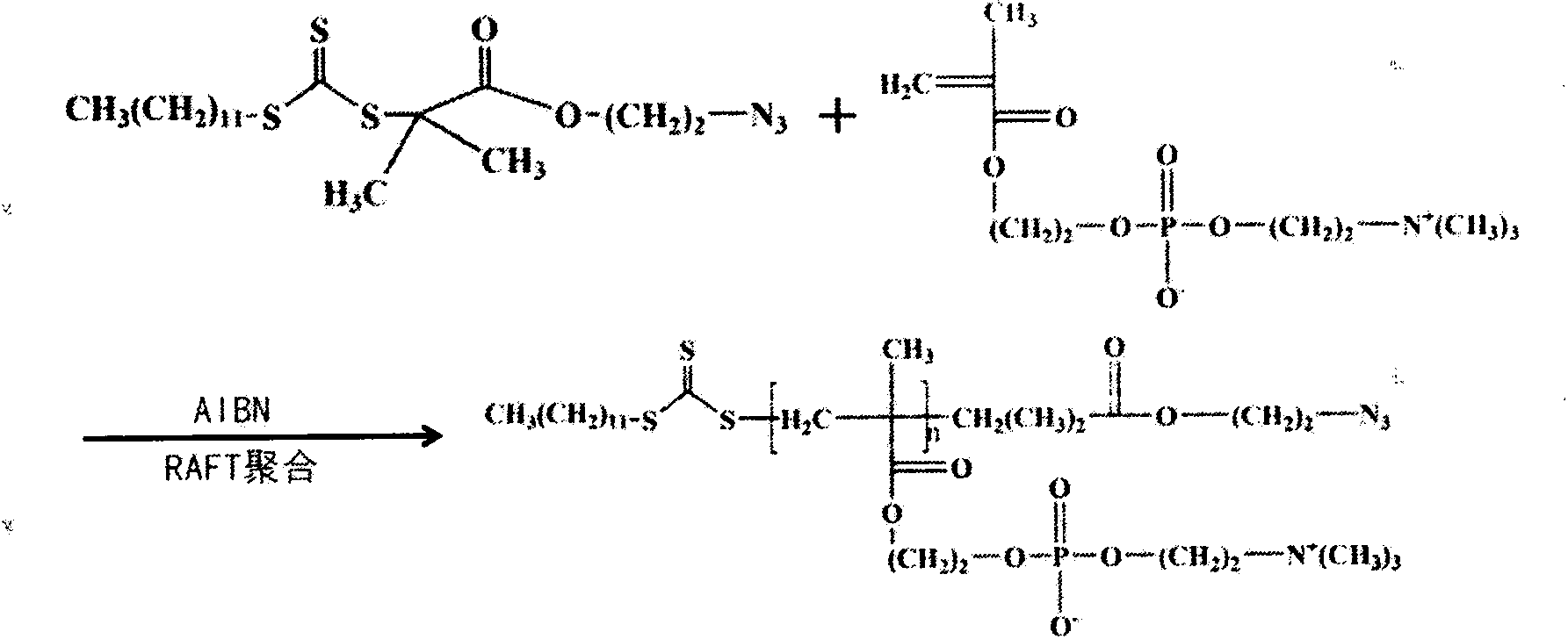
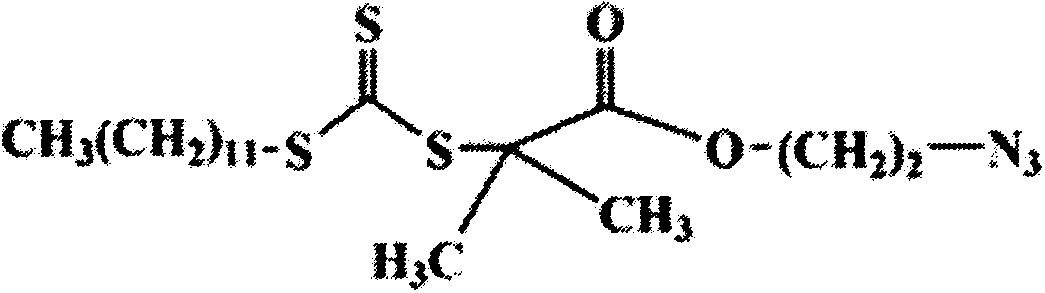
The invention discloses artificial cell membrane materials applied to photoinduction stem grafting and a synthesis method of the artificial cell membrane materials. The synthesis method of the artificial cell membrane materials comprises the following steps that 2-(dodecyl trithiocarbonate)-2- methyl propionic acid, dicyclohexyl carbodiimide, 4- dimethylamino pyridine and dichloromethane are added into a flask, all the components are stirred and dissolved under the protection of nitrogen, azide ethanol is dropwise added and stirred, washing is carried out through diluted hydrochloric acid and distilled water, solvents are removed through a reduced pressure distillation method, and a yellow oily liquid a is obtained; MPC, a midbody a, azo different nitrile and absolute ethyl alcohol are added into a boiling tube and are evenly dissolved, then after the nitrogen is removed through three times of 'vacuumizing-induction of highly pure nitorgen' operations on the boiling tube, and reaction away from light is carried out on the boiling tube in a sealed mode under the protection of highly pure nitrogen; the reaction liquid is precipitated through trichloromethane / diethyl ether mixed solvents, and solid products are collected. By means of the technical scheme, the artificial cell membrane materials have good biocompatibility, achieve the various effects of restraining of protein adsorption, anticoagulation, surface lubrication and the like, and have good medical prospects.
Owner:西安维萃禾生物科技有限公司 +1
Method for the cryopreservation of cells, artificial cell constructs or three-dimensional complex tissues assemblies
InactiveUS20120077181A1Increase ratingsIncrease vitalityFungiBacteriaArtificial cellCryopreservation
The cryopreservation of cells and tissue cultures for long term storage of cells, cell constructs or three-dimensional complex tissues assemblies is based on the use of a collagen cell carrier (CCC) having a specific composition and thickness and appropriate mechanical properties which are maintained after thawing. The collagen cell carrier provides a suitable support for the cryopreservation resulting in high survival rates after thawing and providing cells and tissue assemblies already adhered to a mechanically stable and biocompatible support. Frozen collagen carrier-cells assemblies, the frozen artificial cell constructs or three-dimensional complex tissue assemblies obtainable by the method and the use thereof after thawing are also disclosed.
Owner:NATURIN GMBH & CO
Pipettes, methods of use, and methods of stimulating an object of interest
ActiveUS20130017553A1Improved vibration stabilityHighly localized and contamination-free fluid deliveryBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysis componentsPipetteHorizontal axis
The present invention features a freestanding microfluidic pipette with both solution exchange capability and fluid re-circulation, enabling highly localized and contamination- free fluid delivery within a confined volume in the vicinity of the pipette exit. Preferably, the device features direct positioning, so the pipette can be directed at a point or object of interest, such as a biological or artificial cell, a defined surface area or a sensor element within an open volume, using micro- or nanopositioning techniques. One aspect of the invention provides a free-standing pipette. The free-standing pipette includes a microfluidic device comprising one or more channels with exits leading into an open-volume and a positioning device programmed to hold the microfluidic device at an angle from a horizontal axis.
Owner:FLUICELL AB
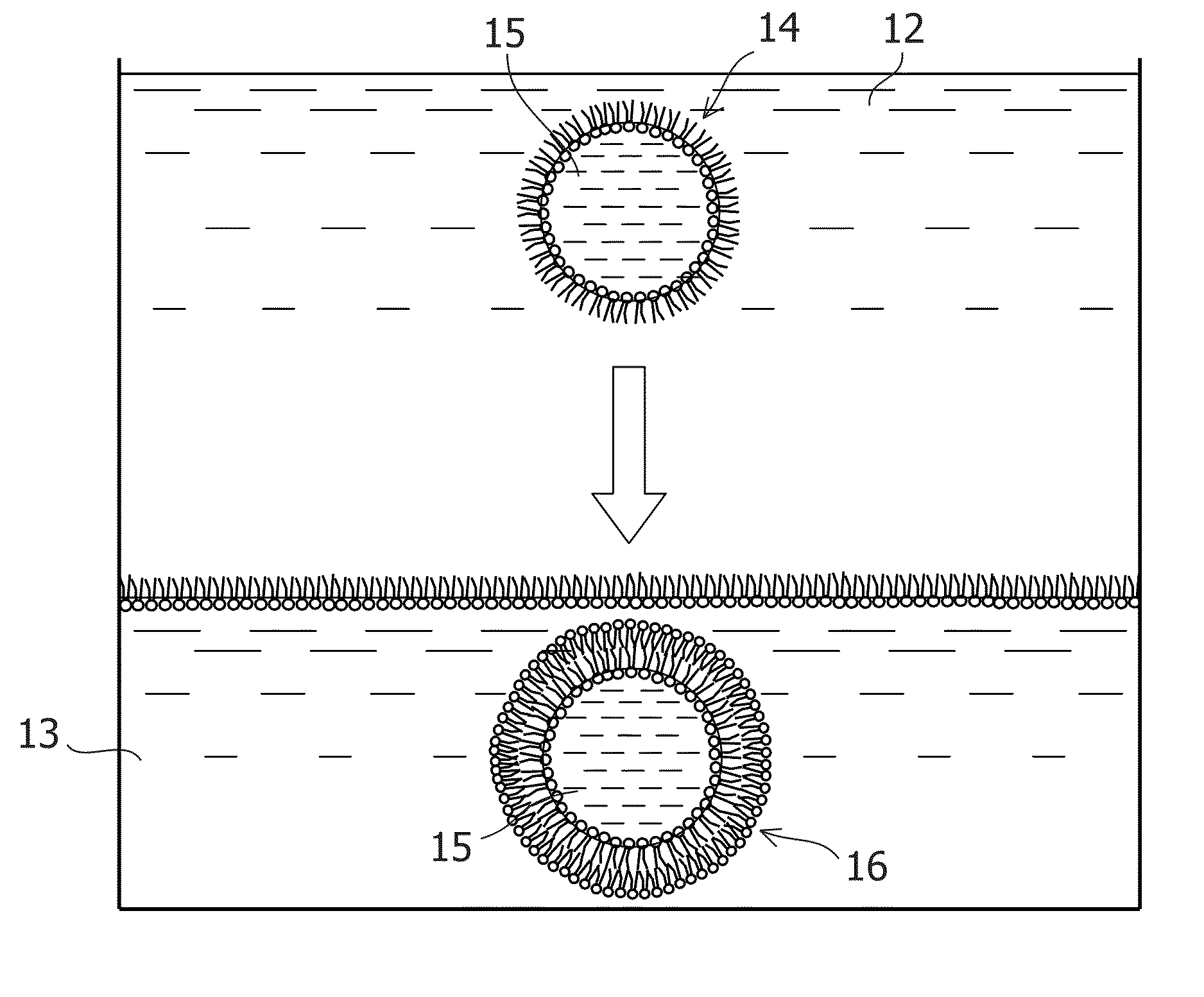
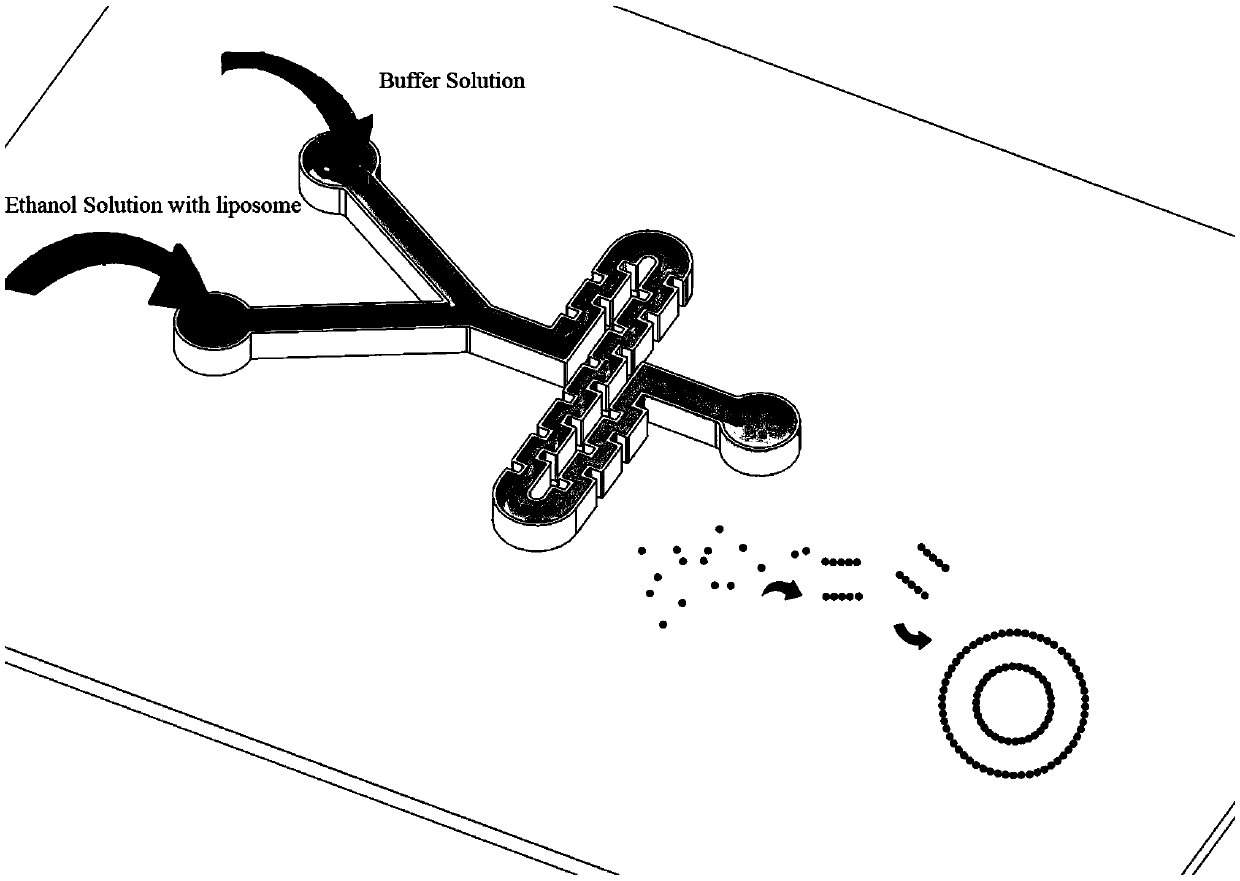
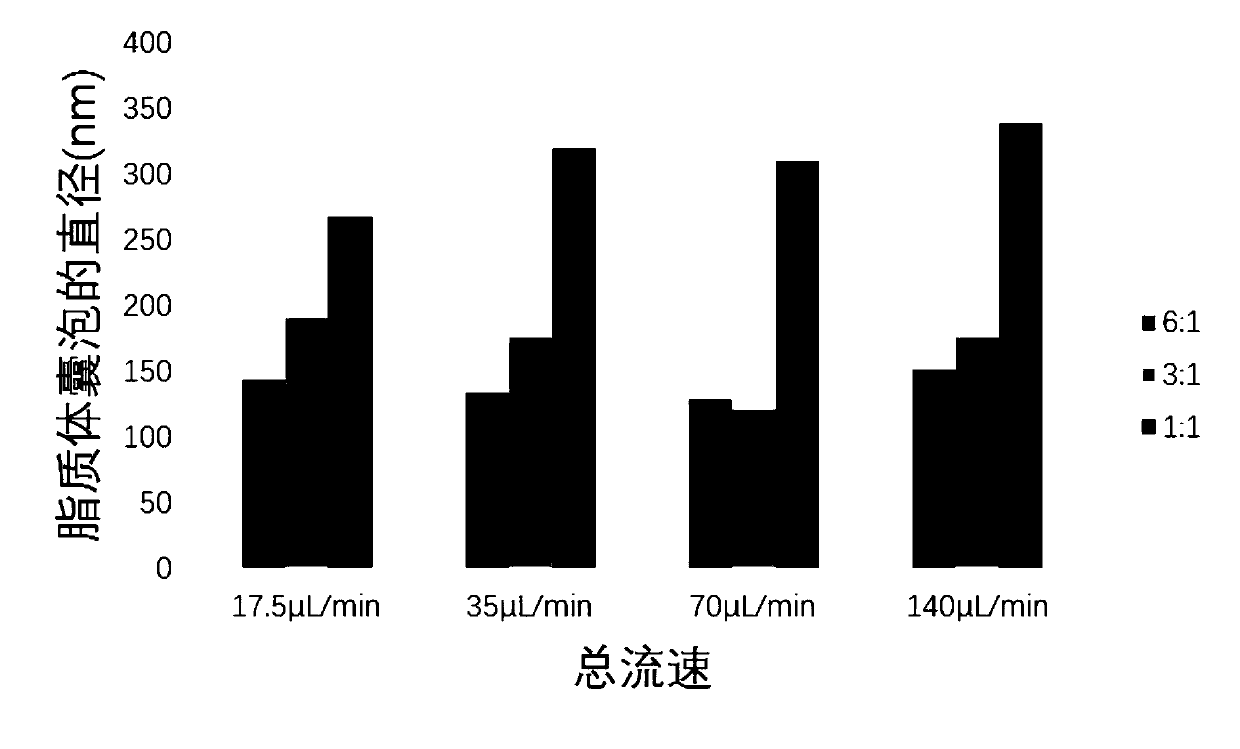
Controllable preparation method of liposome vesicle based on microfluidic device
InactiveCN109603930ALow costPrecisely control the amount addedLaboratory glasswaresPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsLiposome VesicleFlow ratio
The invention provides a preparation method of a liposome vesicle based on a microfluidic device. The preparation method comprises the steps of: preparing a microfluidic chip by a soft lithography method; preparing a precursor solution for preparing the liposome vesicle; and using a constant-pressure injection pump to inject the precursor solution into a ''Y''-shaped chip through different injection ports, setting a total flow rate, adjusting the flow ratio of a buffer solution to a phospholipid molecular alcohol solution, and collecting a product at an outlet, wherein the product is the prepared liposome vesicle. The microfluidic chip selected by the invention is a ''Y''-shaped microfluidic chip with a serpentine mixing channel of a square structure, and the chip is prepared by the soft lithography method. By using the chip, based on the principle of self-assembly on an interface, by adjusting the total flow rate and the flow rate ratio of the aqueous buffer solution to the phospholipid molecule ethanol solution, regulation of the size of the liposome vesicle and control on the dimensional uniformity are achieved, and an efficient low-cost method is provided for preparation of artificial cells with uniform properties as well as drug carriers.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
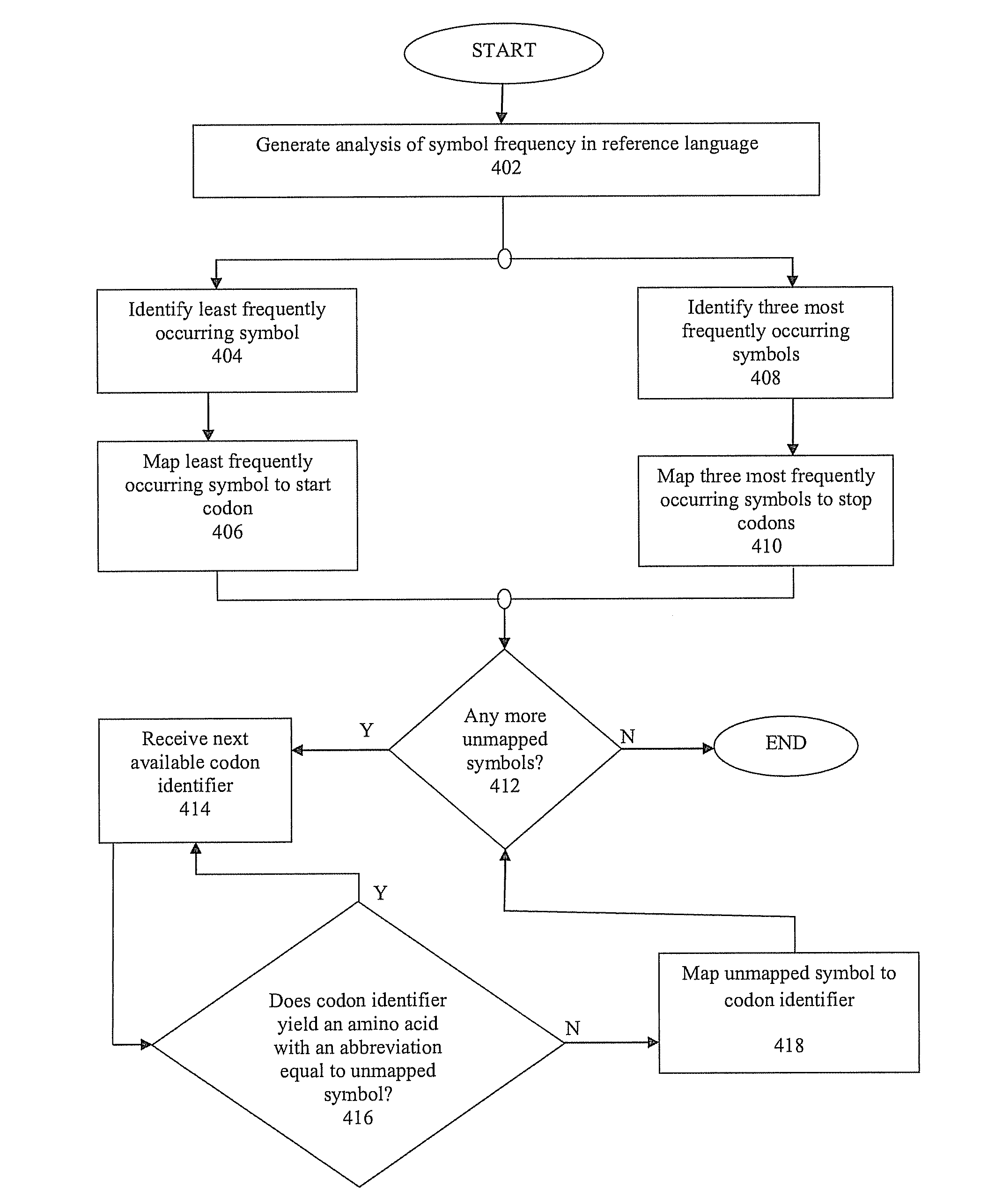
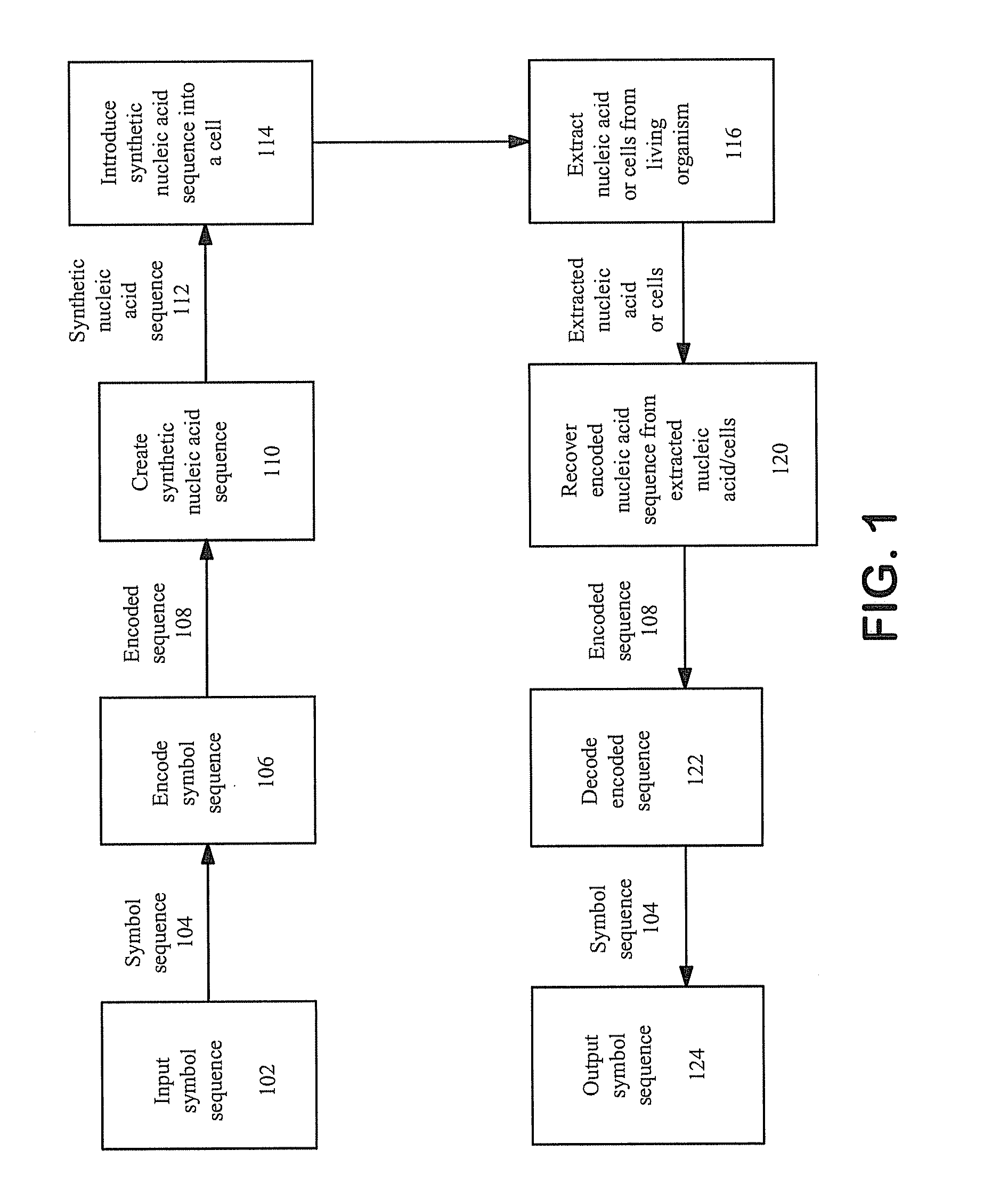
Encoding text into nucleic acid
ActiveUS20160168579A1Reduce probabilityThe decoding process is simpleBacteriaUnicellular algaeNucleic acid sequencingOrganism
Methods and apparatus are disclosed herein for encoding human readable text conveying a non-genetic message into nucleic acid sequences with a substantially reduced probability of biological impact and decoding such text from nucleic acid sequences. In one embodiment, each symbol of a symbol set of human readable symbols uniquely maps to a respective codon identifier. Mapping may ensure that each symbol will not map to a codon identifier that generates an amino acid residue which has a single-letter abbreviation that is the equivalent to the respective symbol. Synthetic nucleic acid sequences comprising such human readable text, and recombinant or synthetic cells comprising such sequences are provided, as well as methods of identifying cells, organisms, or samples containing such sequences.
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
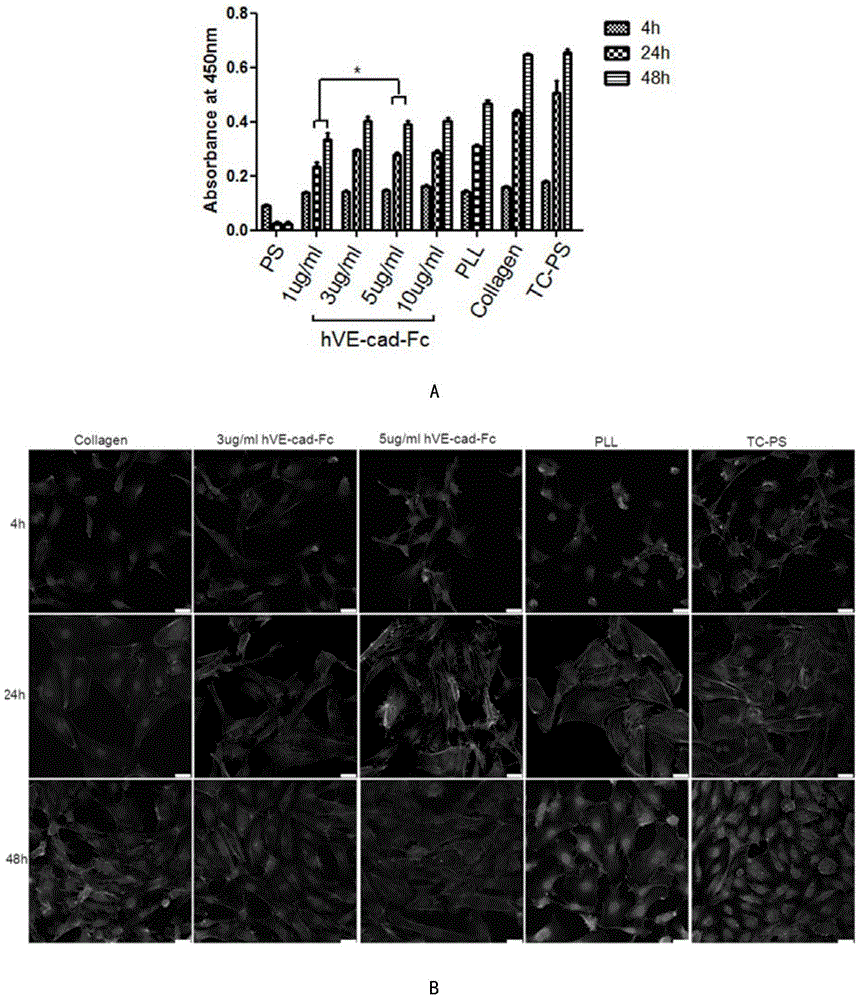
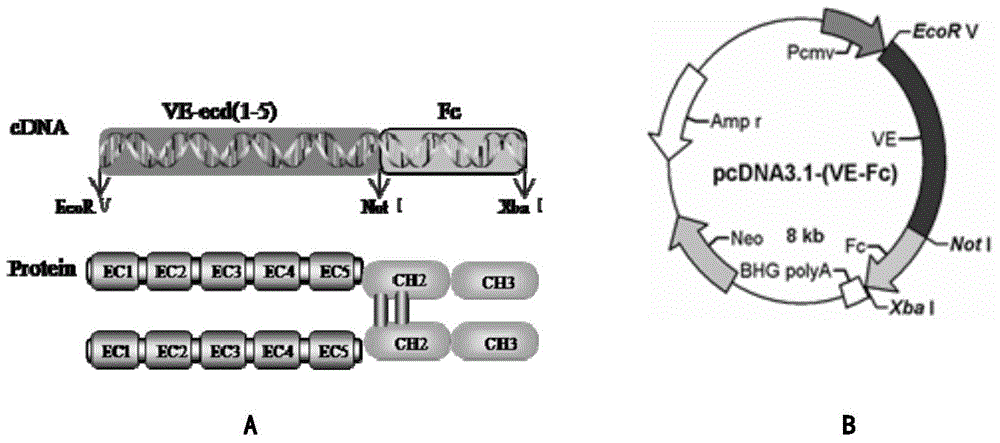
Human endothelial cell cadherins fusion protein, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104804098APromotes rapid endothelializationImproved vascularization of tissue engineeringArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsProtein CGrowth cell
The invention aims to build an expression plasmid of a fusion protein hVE-cad-Fc of an extracellular structural domain segment of human blood vessel endothelium cadherins protein and an Fc segment of immunoglobulin G by utilizing a genetic engineering technology for the first time, and realize biosynthesis of hVE-cad-Fc fusion protein using eukaryotic cells. The fusion protein forms a stable hVE-cadhrin functional protein layer matrix on the material surface via Fc mediation, so that not only is the hydrophilia of hydrophobic materials improved, but also the property of the endothelial cell selective adhesion to the material surface is greatly improved; in addition, the expression of the endothelial cell proliferation and differentiation functions is improved. According to the invention, the isologous association of the hVE-cad-Fc fusion protein matrix and VE-cadherin positively expressed on the cell surface activates the intercellular adhesion link signal path, and through the synergistic effect with the blood vessel endothelium cell growth factors, the expression of the adhesion, proliferation, anti-apoptosis and differentiation functions of the blood vessel endothelium cells are regulated and controlled; the hVE-cad-Fc fusion protein provided by the invention can be used to improve the affinity of the material endothelium cells, promote the functional modification of artificial extracellular matrix subjected to tissue engineering vascularization / endothelialization and biomedical materials.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Modified and fusion enhanced erythrocytes, cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20110091973A1Short half-lifeGenetically modified cellsBlood/immune system cellsADAMTS ProteinsChemokine receptor CCR5
Modified fusion enhanced erythrocytes (or other cell types and synthetic cells) including human viral receptor proteins, human viral coreceptor proteins and viral derived proteins capable of mediating entry of respective viruses into the modified erythrocytes, cells or pseudo-cells and the method of using the fusion enhanced modified erythrocytes, cells or pseudo-cells for the treatment or prevention of viral infections. The fusion enhanced modified erythrocytes comprises CD4 and at least one HIV coreceptor, such as CXCR4 or CCR5 and as well, at least one of cholesterol rafts, fusin, actin, a viral derived protein such as fusion peptide derived from HIV GP120 or HIV GP41 or a shorter protein derived from a long viral protein, such as a portion of HIV derived GP120, or HIV GP41 such as the 23 N-terminal peptide of the HIV-1 gp 41 protein (AVGIGALFLGFLGAAGSTMGARS) called FP23 (Fusion Peptide). These viral-fusion enhanced cells may also be electrostatic charge enhanced through further additions named in this invention. The modified erythrocytes, when administered to an HIV patient, bind to the plasma virus and induce the injection of the HIV ribonucleoprotein complex into the cells. The entrapped viral content is sequestered within said cell for at least the period of time that the cell maintains its outer membrane integrity. The virus is thereafter either degraded or deactivated within the erythrocytes, cells or pseudo-cells, or destroyed by erythrophagocytosis.
Owner:GLASER LARRY F
Implantable neuroendoprosthetic system, a method of production thereof and a method of reconstructive neurosurgical operation
Intended for the use in neurosurgery and organ tissue engineering to replace defects of nervous tissue of a mammal brain and spinal cord (B&SC) in reconstructive neurosurgical operations, a tissue-replaceable artificial cell-biopolymer neuroendoprosthetic system (ACBP NEPS) for surgical plasty of defects of nervous tissue of B&SC, stimulating regeneration and growth of damaged axons of neural cells, comprises an elastic cell-biopolymer biologically active mass, produced from a heterogeneous collagen-containing matrix for implantation, and a biocomposition of cell preparations of various types of autologous cells of a patient. Also disclosed are a method of producing the ACBP NEPS, which provides for perfusion of the biocomposition of the cell preparations of various types of autologous cells of a patient into a heterogeneous collagen-containing matrix for implantation, and a method of reconstructive neurosurgical operation comprising implantation of the ACBP NEPS into a defect of neural tissue.
Owner:BRYUKHOVETSKIY ANDREY S +1
Polypeptide nano-material containing double-pyrene groups as well as preparation method and application of polypeptide nano-material
ActiveCN106749518APrevent invasionInhibit transferPeptide preparation methodsNanotechnologyCrystallographyCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention provides a polypeptide nano-material containing double-pyrene groups as well as a preparation method and an application of polypeptide nano-material. The polypeptide nano-material containing the double-pyrene groups has a structure represented as a formula I; the polypeptide nano-material containing the double-pyrene groups can be deformed for self-assembly and can be self-assembled to form a nanofiber network structure in a tumor area and construct an artificial cell extracellular matrix in situ, and the artificial cell extracellular matrix selectively adheres to the tumor area to form a migration barrier, so that tumor invasion and metastasis can be effectively inhibited, and the polypeptide nano-material has board medical application prospect.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Preparation method of thylakoid-containing artificial cells and photosynthesis simulating method
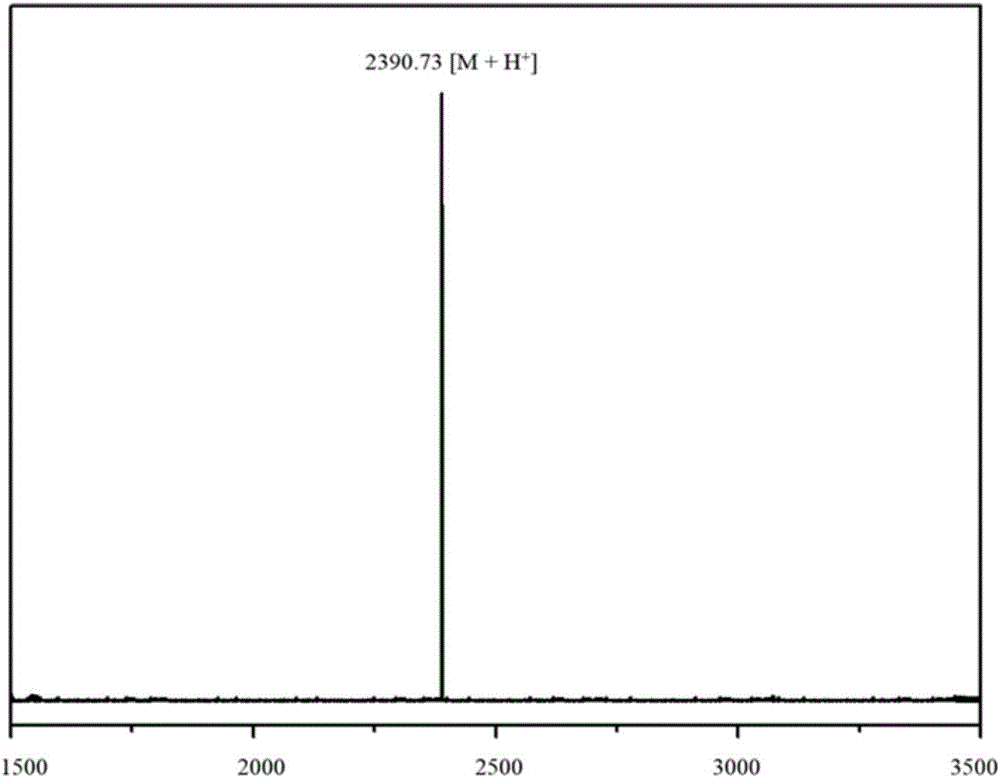
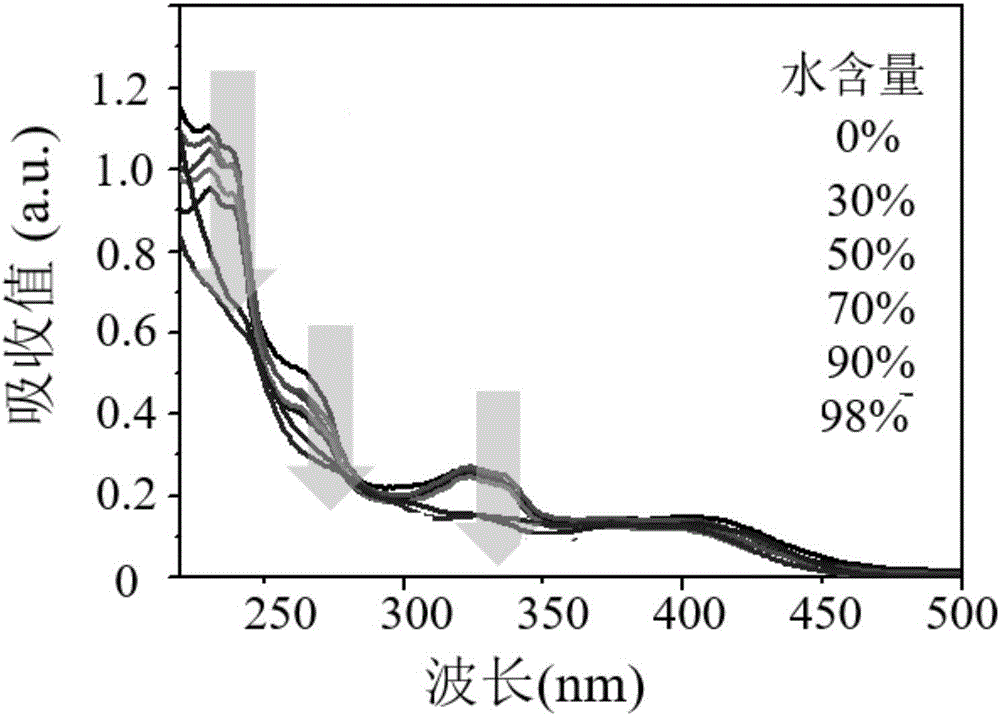
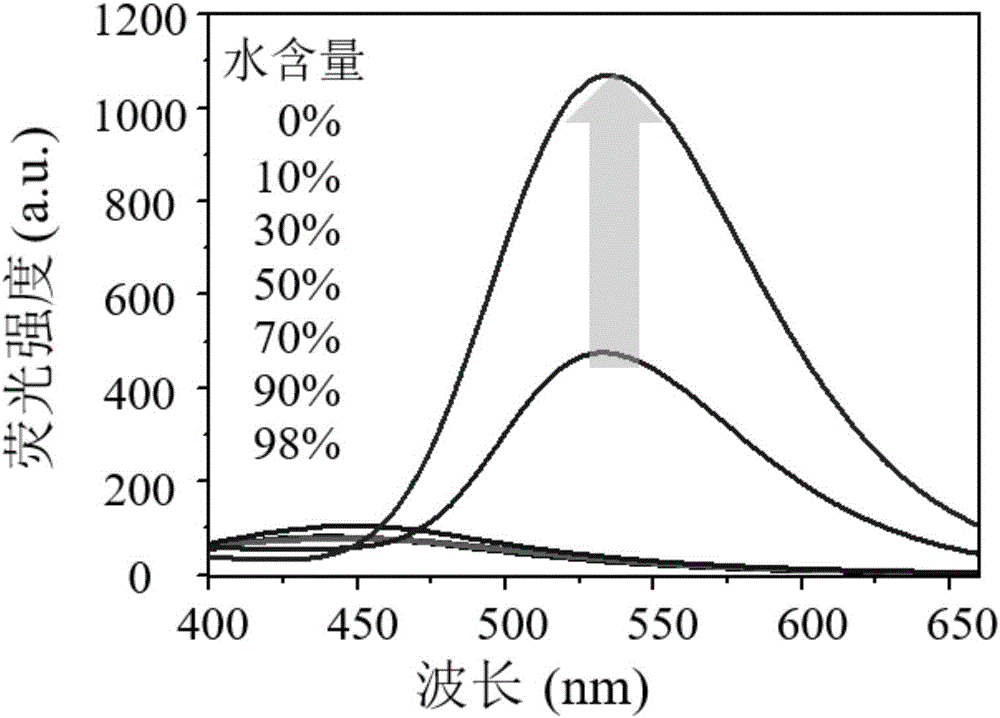
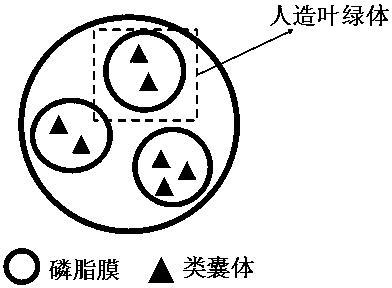
The invention relates to a preparation method of thylakoid-containing artificial cells and a photosynthesis simulating method, and belongs to the fields of biotechnology, biochemistry and synthetic biology. The method comprises the following steps of extracting thylakoid particles from fresh spinach leaves, and storing the thylakoid particles in a buffer solution for use; smearing a phospholipid solution onto an ITO glass electrode; after the solvent volatilization, forming a layer of phospholipid membrane; fixing a polytetrafluoroethylene framework by vacuum grease; adding liquid phases intothe polytetrafluoroethylene framework; applying alternating current onto the ITO glass electrode for preparing a GUV solution; mixing the GUV solution and a thylakoid solution; preparing the thylakoid-containing artificial cells. The thylakoid-containing artificial cells are prepared through the enlightenment of the natural plant cell structure and function; the model can realize the optical driveelectron transfer process under the artificial sunlight irradiation. Through the model building, the attributes of chloroplasts in nature are doubly simulated from the structure and the function. Thecomplicated cells realize simplified research, so that the development and the progress of the biomimetic chemistry are promoted.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Novel activating agent for immune cell amplification and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108384742APromote amplificationIncrease receptor activityCulture processBlood/immune system cellsFiberCell membrane
The invention discloses a novel activating agent for immune cell amplification and a preparation method thereof. The novel activating agent is prepared from the following ingredients in parts by weight: 20 to 26 percent of biological conductive nanometer fiber, 1 to 3 percent of power generation cells, 3 to 4 percent of gel mixed solution, 9 to 11 percent of composite agonists, 12 to 14 percent ofartificial cell membranes, 0.3 to 0.8 percent of cell membrane activators, 8 to 10 percent of specific antibodies and the balance of culture base solution. A great part of biological conductive nanometer fiber is used for performing loading on the composite agonists; then, the artificial cell membranes are used for coating; finally, after the treatment and activation by cell membrane activating materials, a specific antibody is combined; the power generation cells and the gel mixed solution are planted on the other small part of biological conductive nanometer fiber; then, the two parts of biological conductive nanometer fiber are put into a culture base solution to form the novel activating agent for immune cell amplification. Generally, the novel activating agent can improve the in vitro proliferation rate of immune cells by 10 to 15 times.
Owner:大连金玛健康产业发展有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com