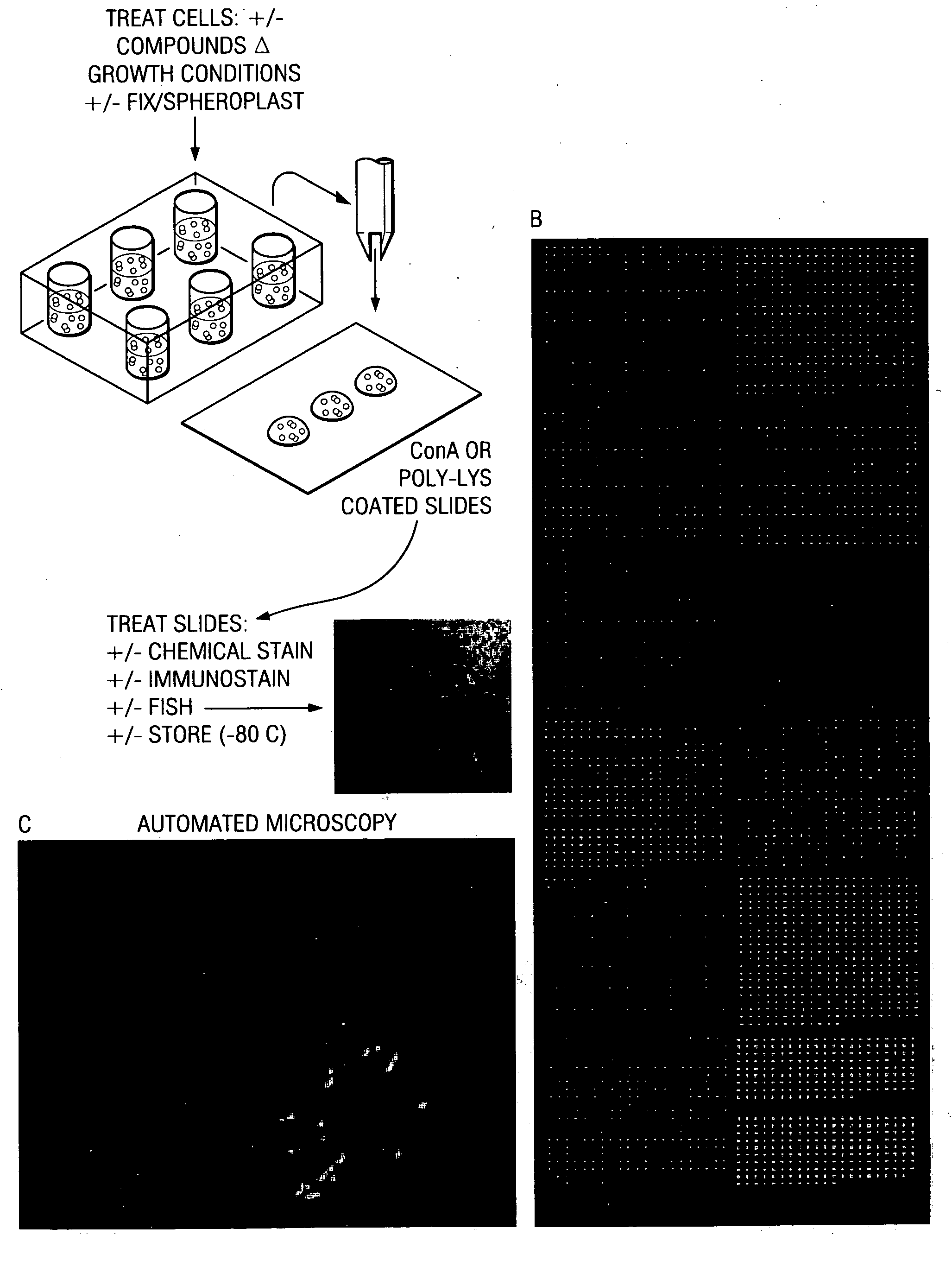
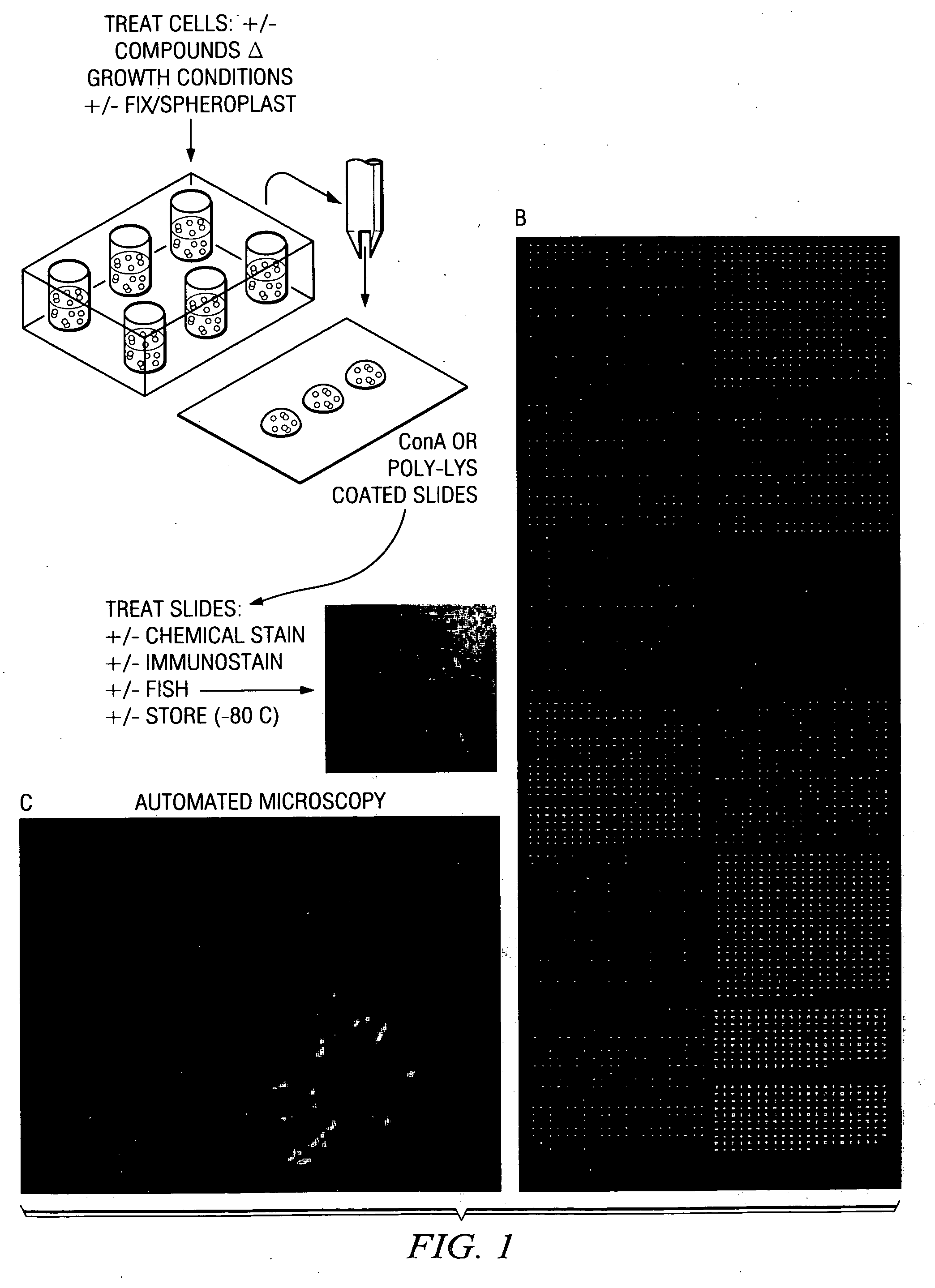
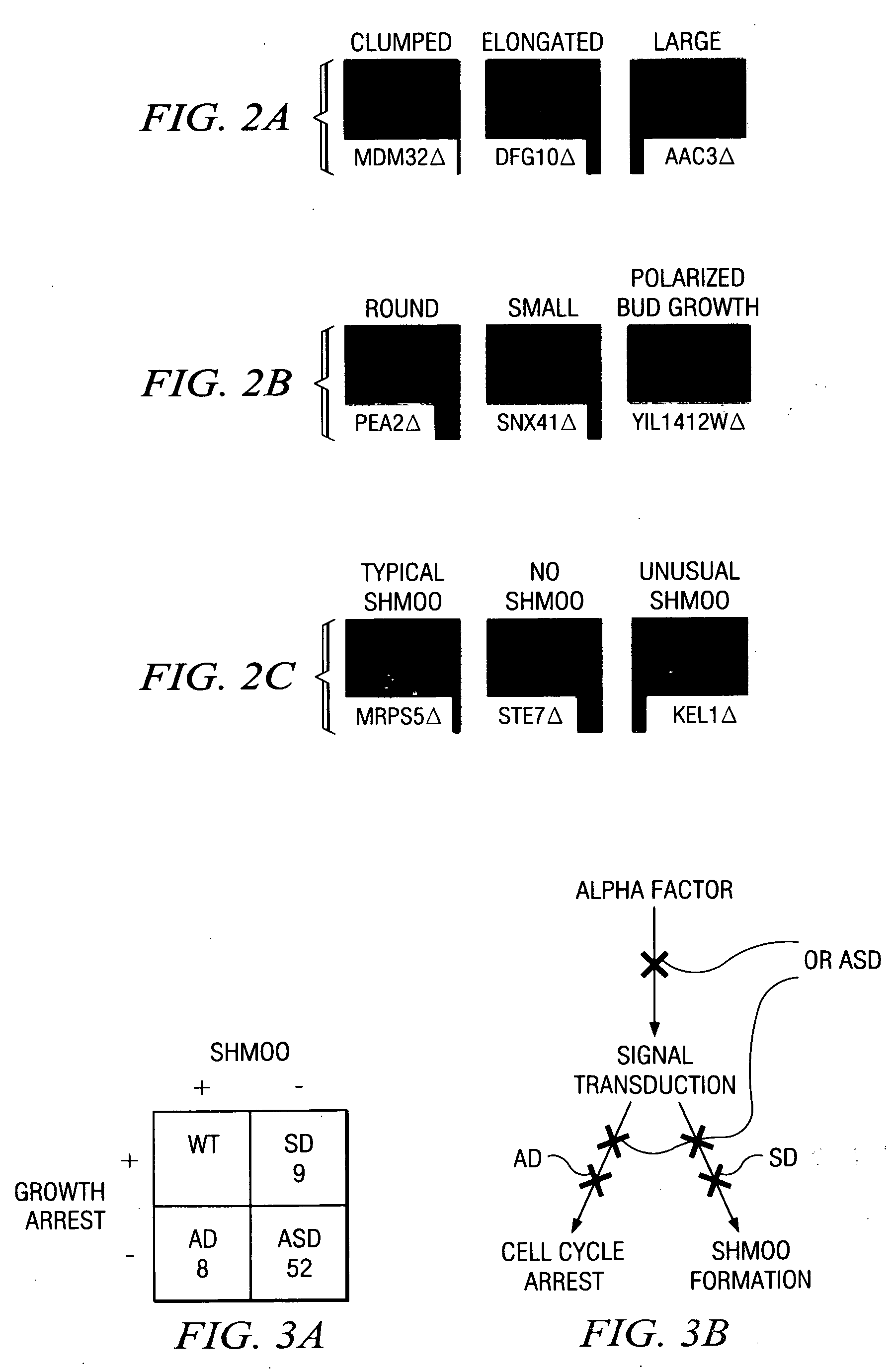
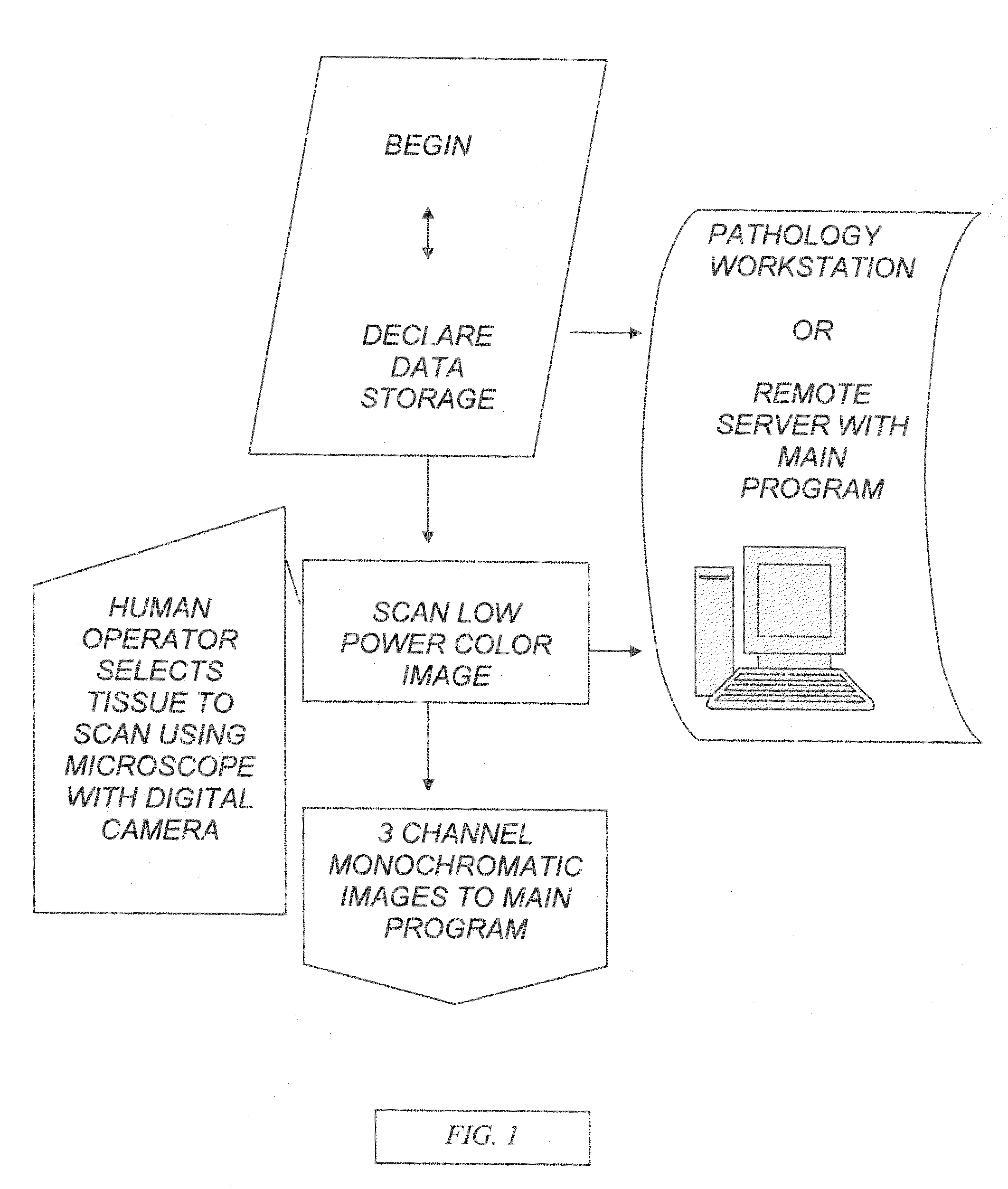
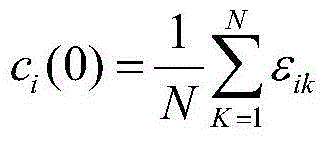Patents
Literature
150 results about "Cell feature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Human cells feature a cell membrane surrounding two compartments: the cytoplasm and the nucleus of the cell. Each cell also has several organelles, or structures with specific functions.
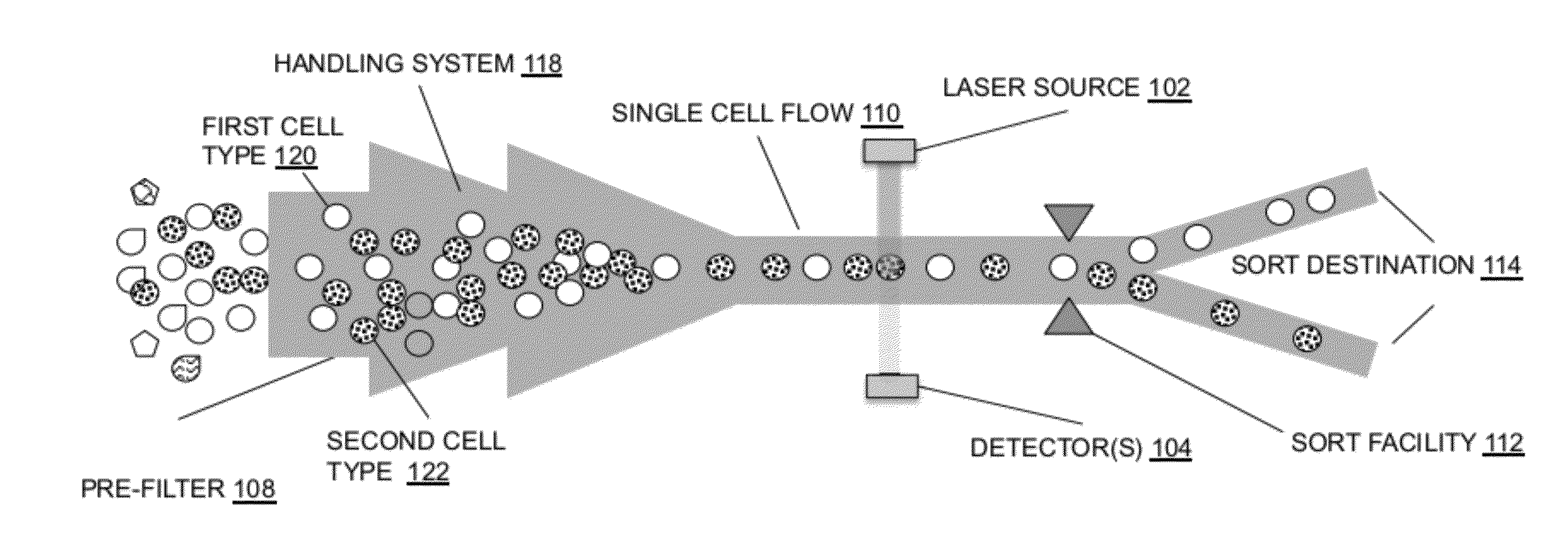
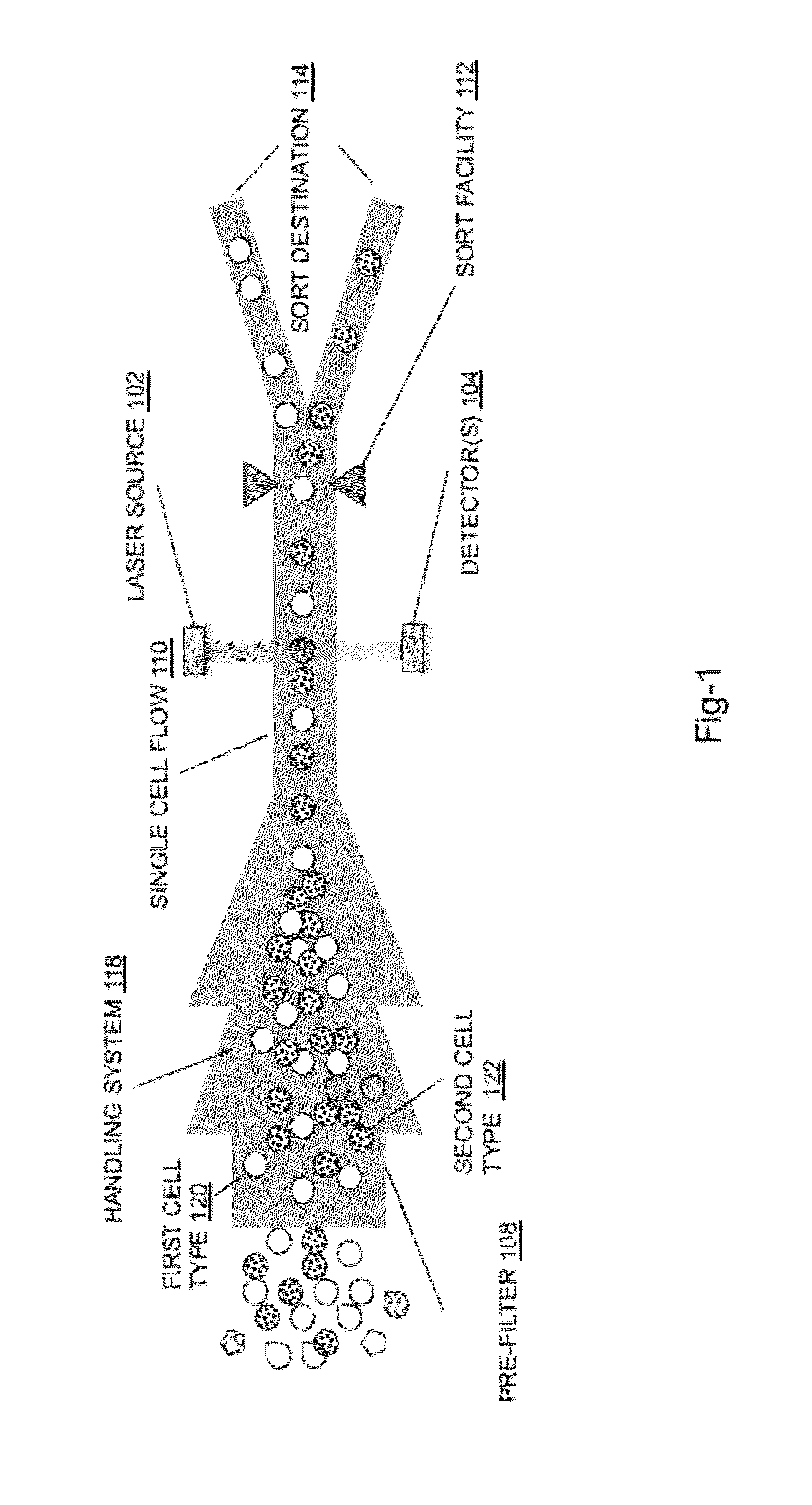
System for identifying and sorting living cells
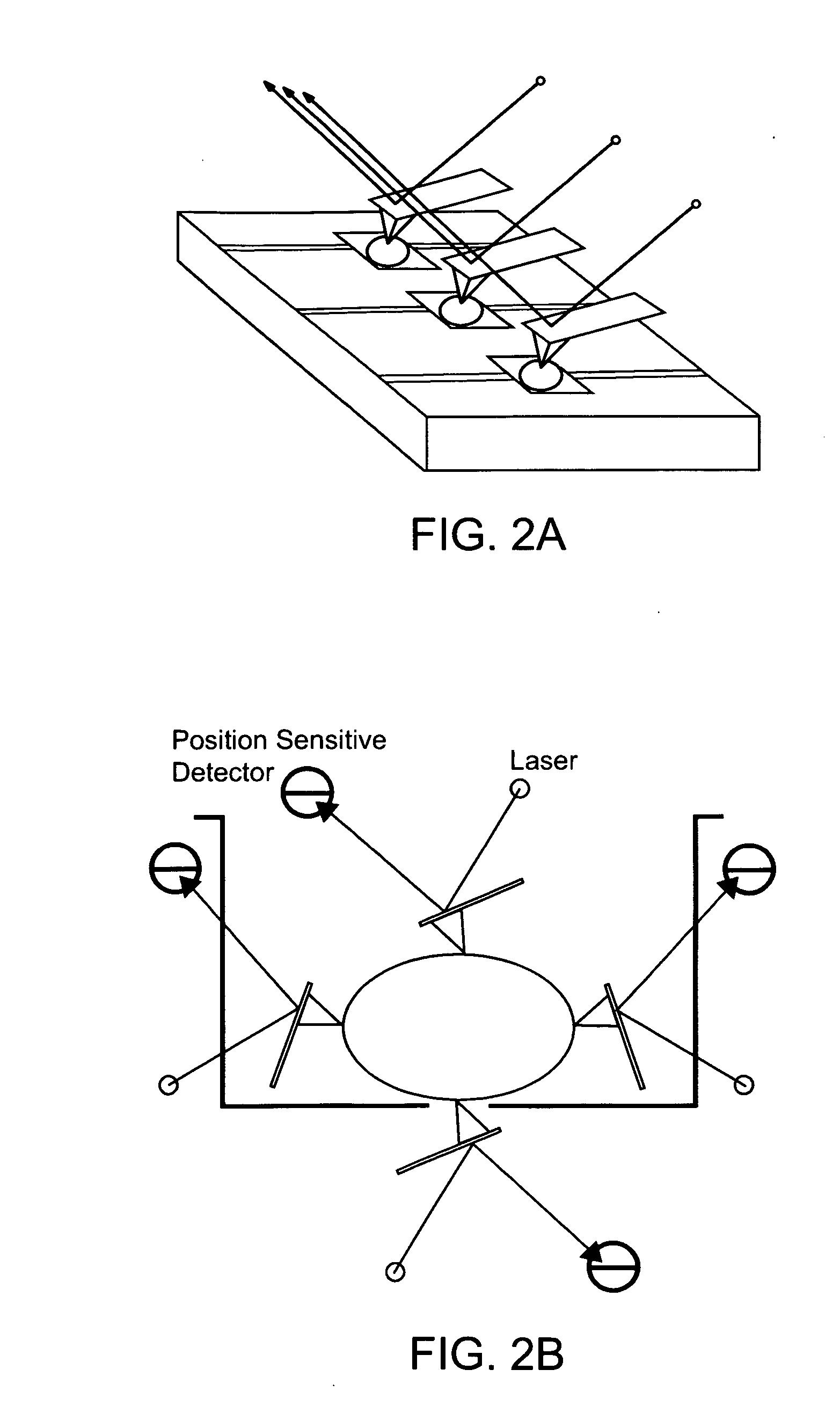
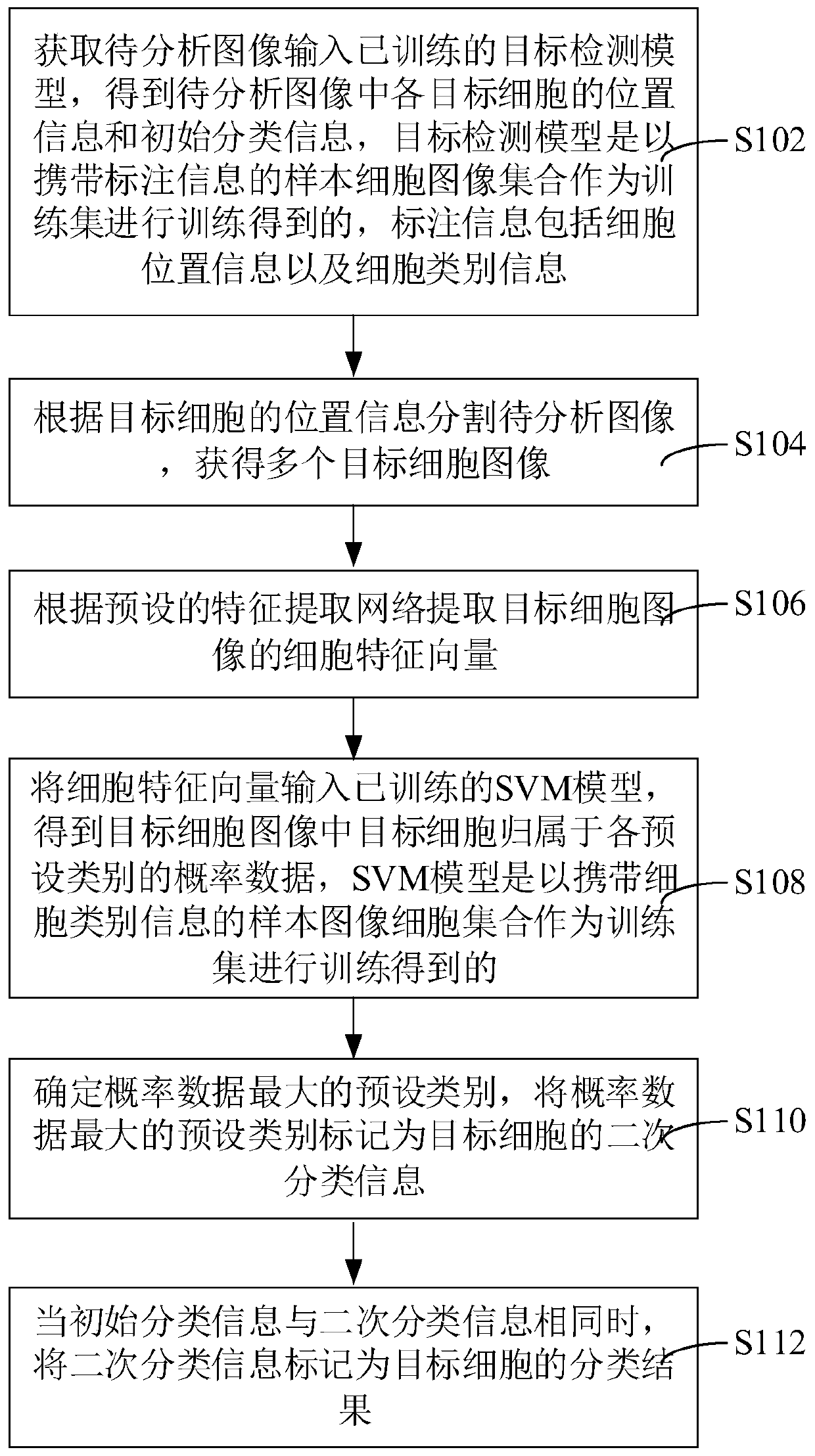
ActiveUS20120122084A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFlow cellIr absorption
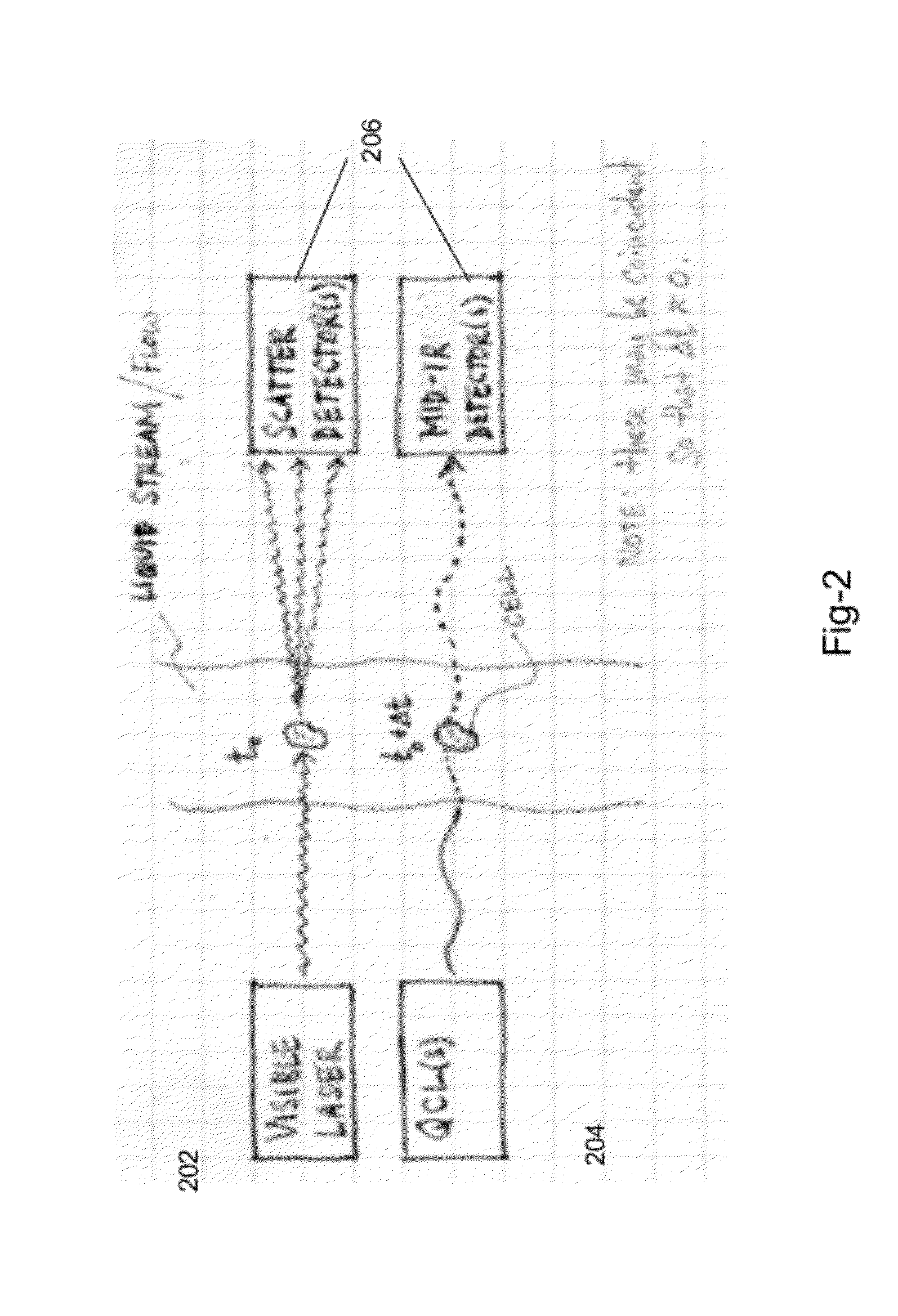
In embodiments of the present invention, a system and method of cytometry may include presenting a single sperm cell to at least one laser source configured to deliver light to the sperm cell in order to induce bond vibrations in the sperm cell DNA, and detecting the signature of the bond vibrations. The bond vibration signature is used to calculate a DNA content carried by the sperm cell which is used to identify the sperm cell as carrying an X-chromosome or Y-chromosome. Another system and method may include flowing cells past at least one QCL source one-by-one using a fluid handling system, delivering QCL light to a single cell to induce resonant mid-IR absorption by one or more analytes of the cell, and detecting, using a mid-infrared detection facility, the transmitted mid-infrared wavelength light, wherein the transmitted mid-infrared wavelength light is used to identify a cell characteristic.
Owner:1087 SYST
Adipose tissue-derived stromal cell that expresses characteristics of a neuronal cell
The invention is in the area of pleuripotent stem cells generated from adipose tissue-derived stromal cells and uses thereof. In particular, the invention includes isolated adipose tissue derived stromal cells that have been induced to express at least one phenotypic characteristic of a neuronal, astroglial, hematopoietic progenitor, or hepatic cell. The invention also includes an isolated adipocyte tissue-derived stromal cell that has been dedifferentiated such that there is an absence of adipocyte phenotypic markers.
Owner:VETSTEM BIOPHARMA INC
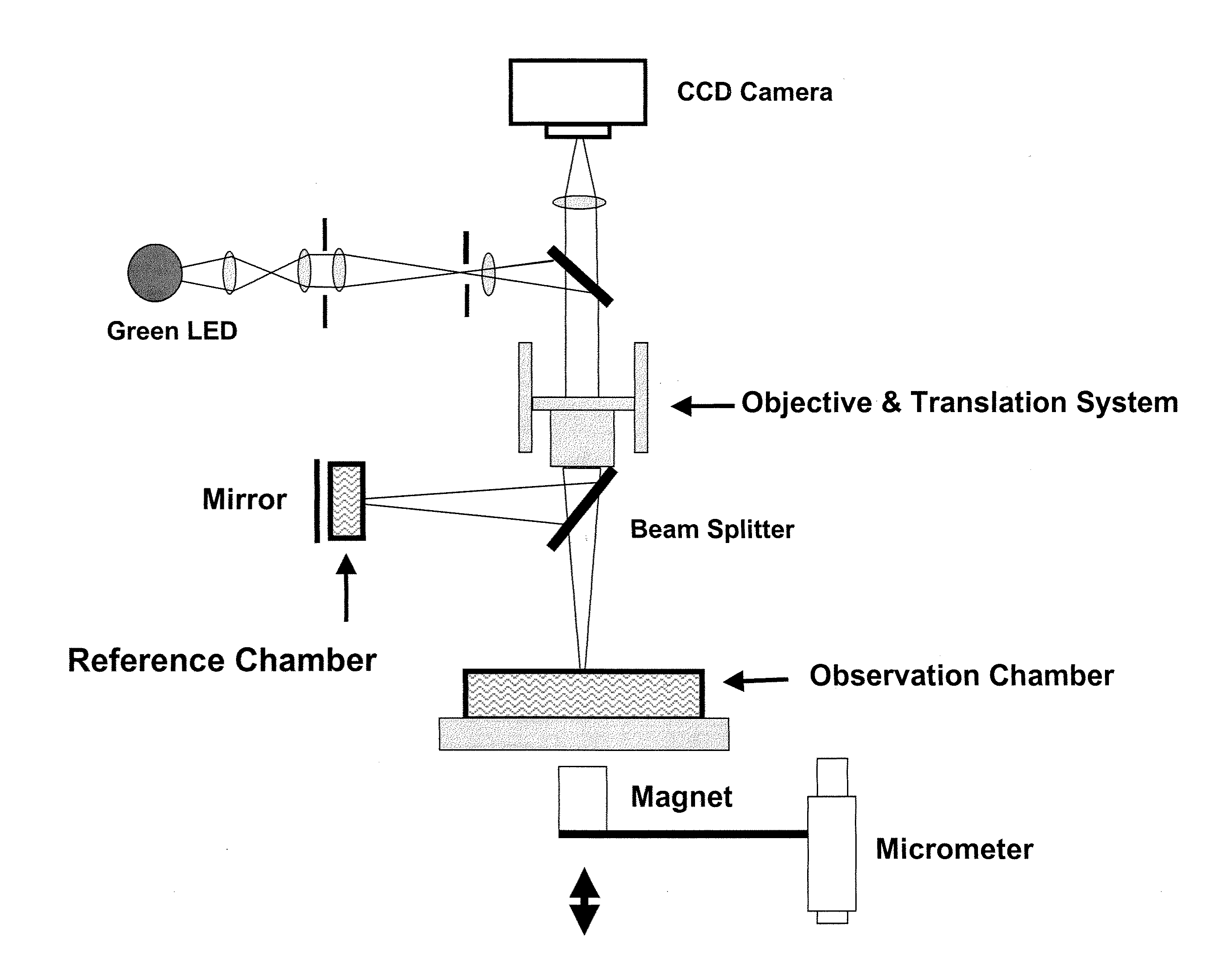
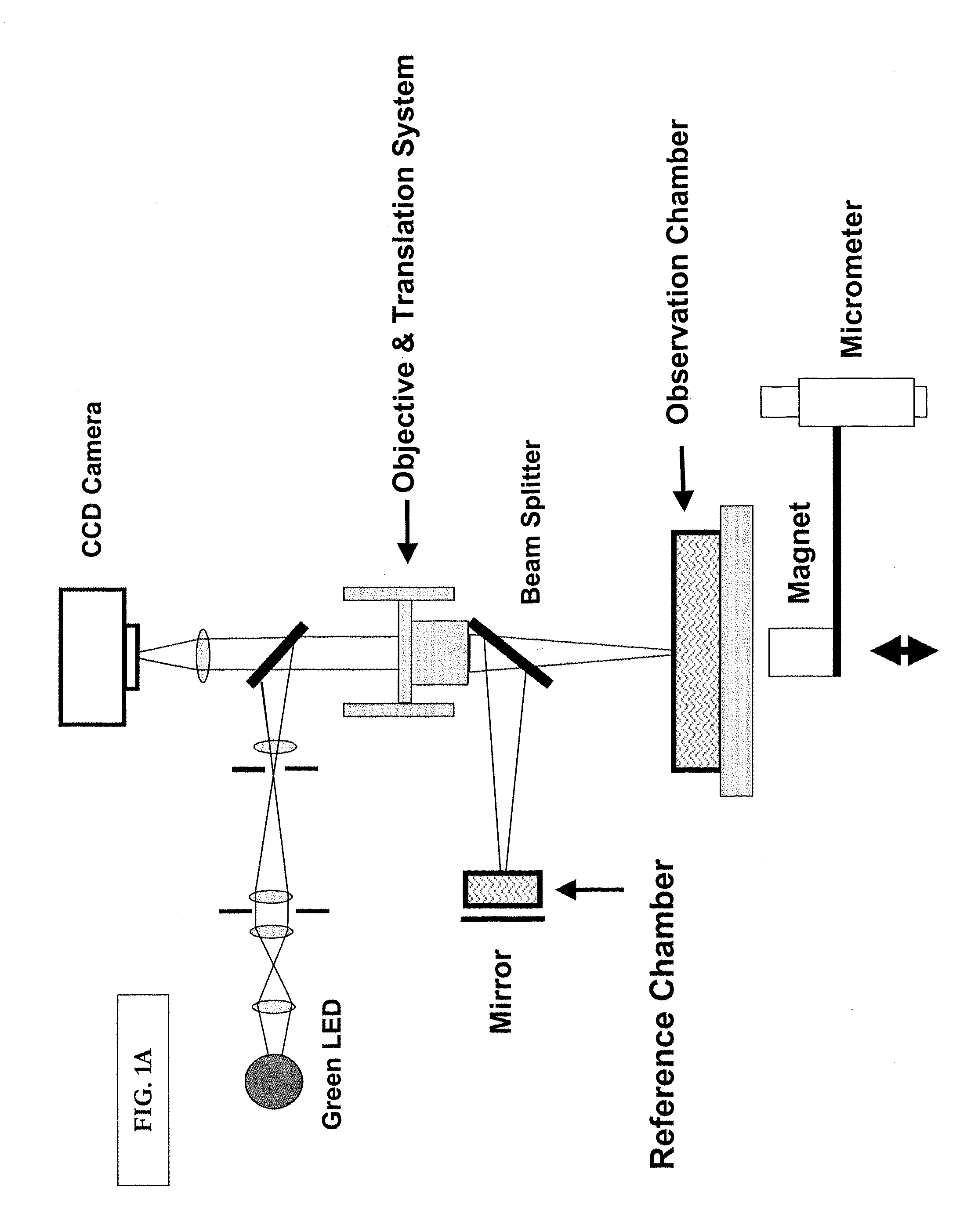
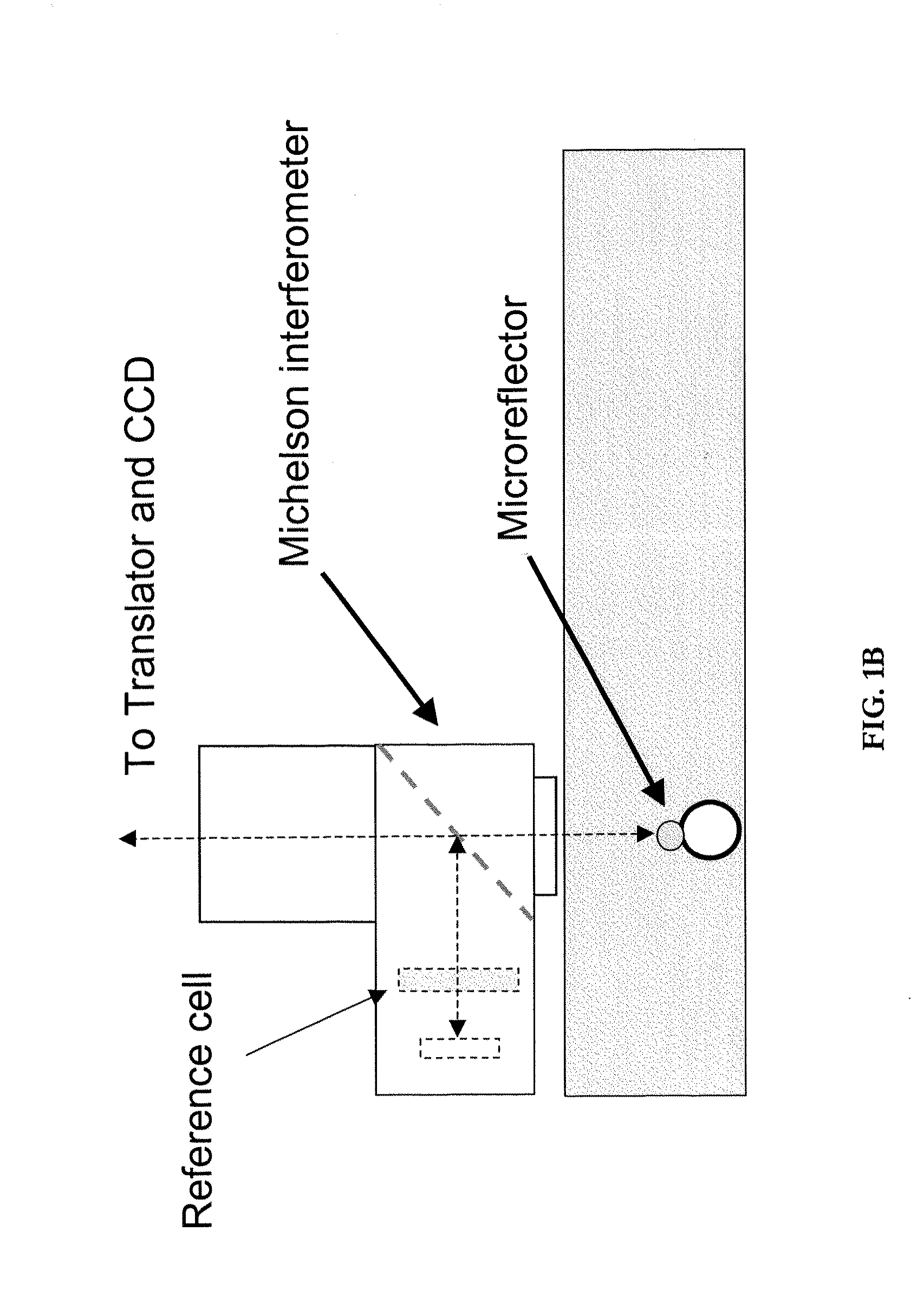
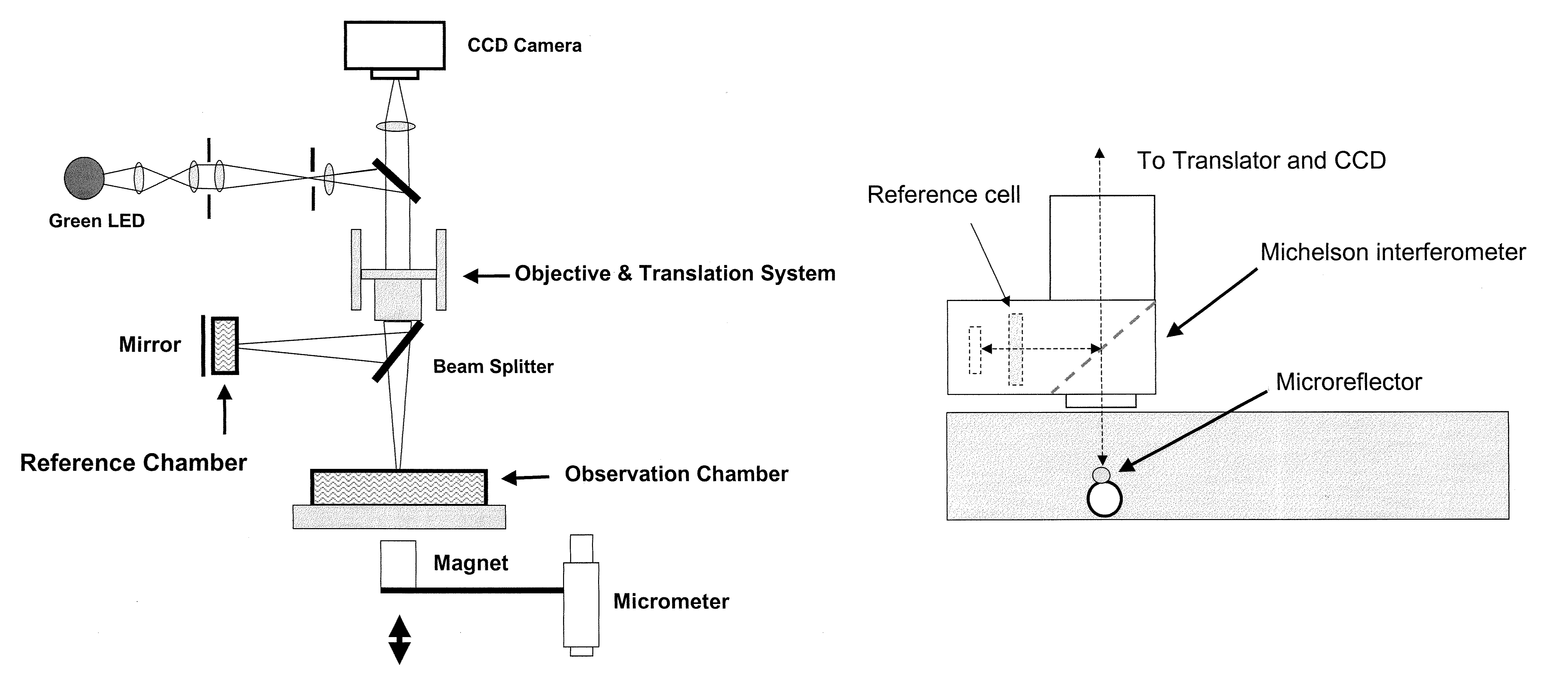
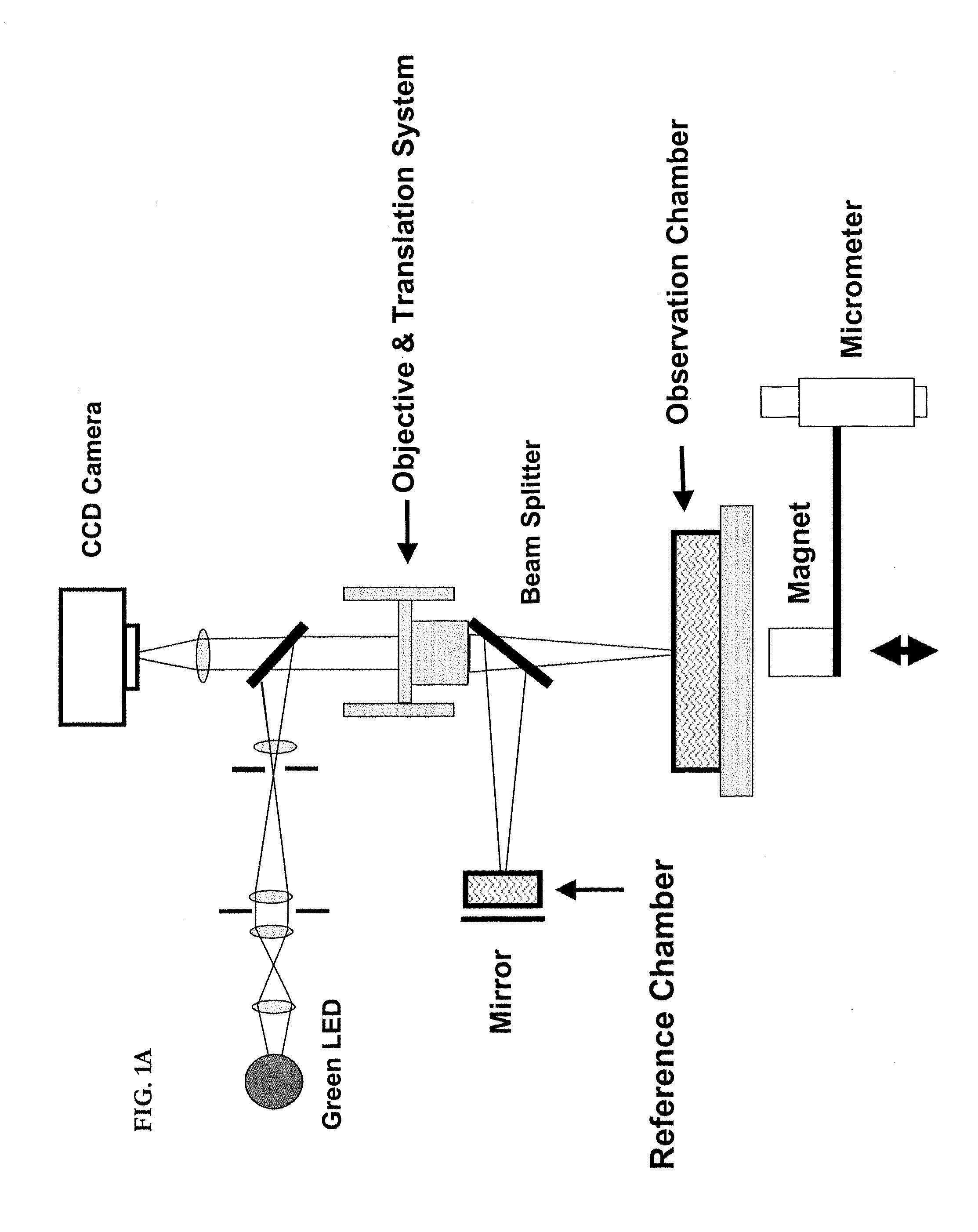
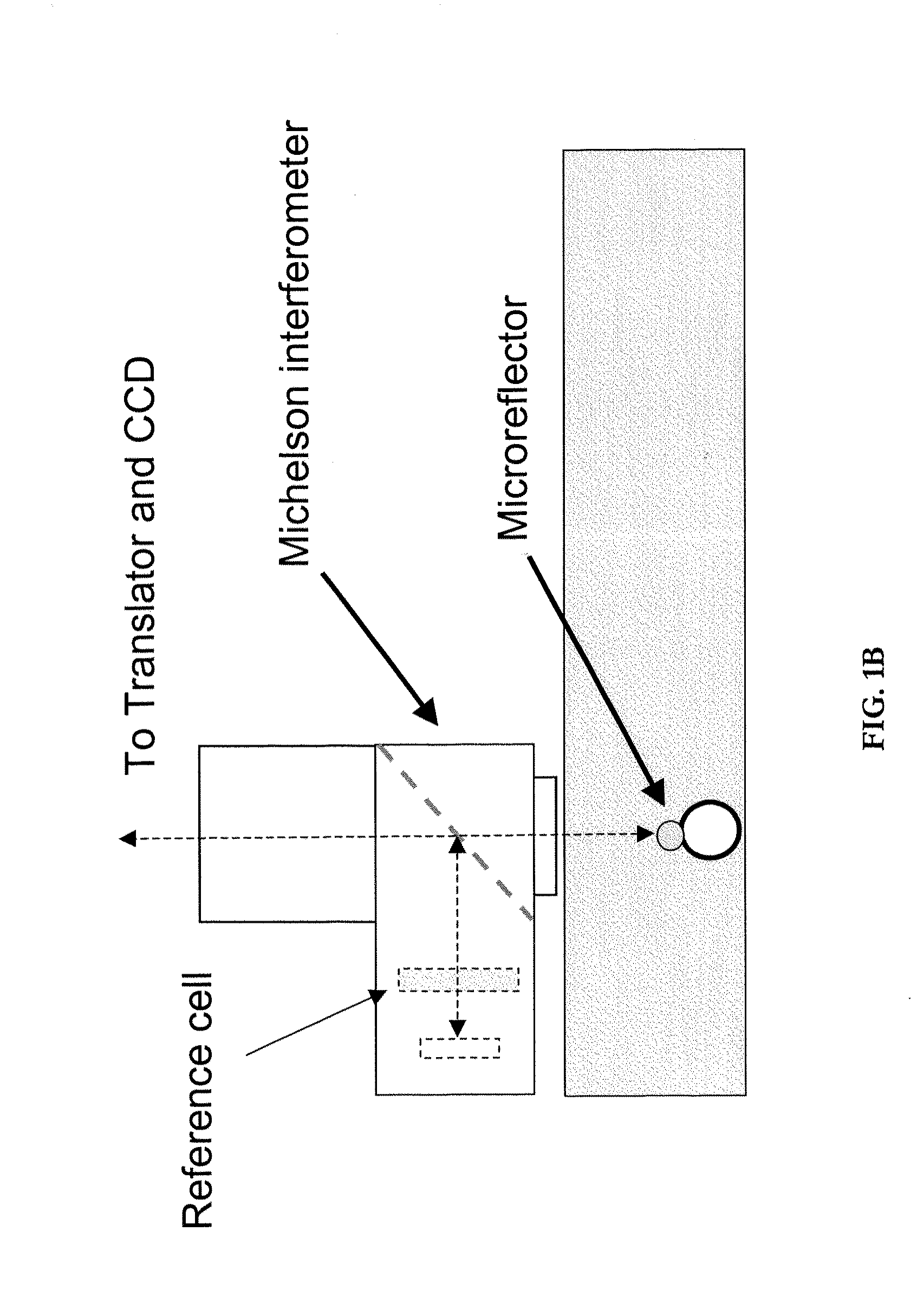
Optical cytometry
The present invention provides optical systems and methods for determining a characteristic of a cell, such as cell type, cellular response to a biochemical event, biological state and the like. The methods typically involve using interferometry to observe membrane properties in a cell and then use this information to determine one or more characteristics of a cell. The methods of the invention are useful for applications such as drug screening as well as diagnostic techniques.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
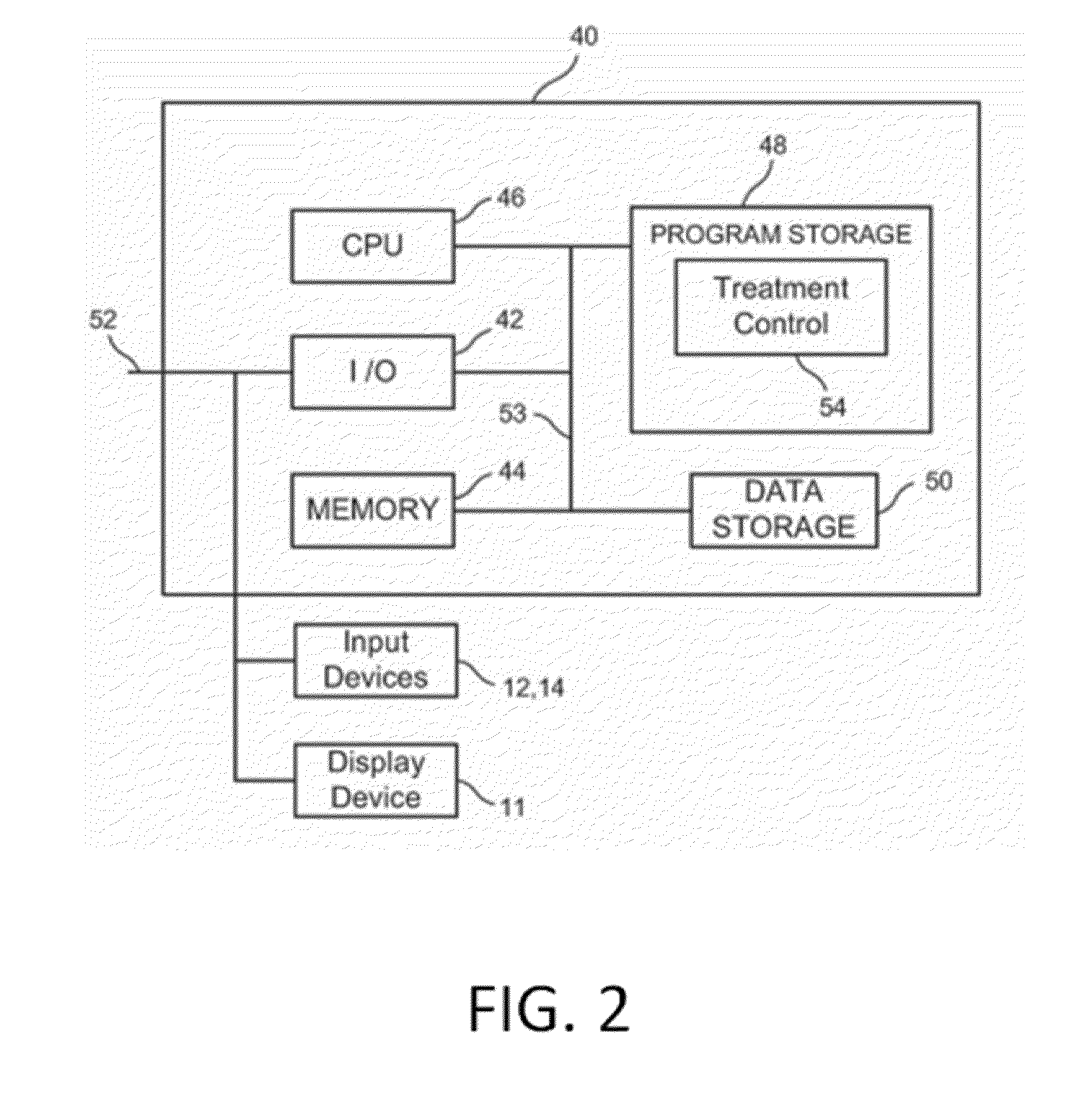
Treatment planning for electrical-energy based therapies based on cell characteristics
PendingUS20150289923A1High precisionMinimize impactSurgical instruments for heatingElectricityMedicine
A method for treating a target tissue in a patient in need thereof is provided. The method includes the steps of identifying one or more characteristics of one or more cells of a target tissue; calculating a threshold electric field for inducing IRE in the target tissue based on the one or more characteristics; constructing a treatment protocol of one or more pulse parameters, wherein the treatment protocol is capable of inducing IRE in the target tissue; and delivering the treatment protocol to the target tissue. Systems for treatment planning for medical therapies involving administering electrical treatment energy are also provided.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
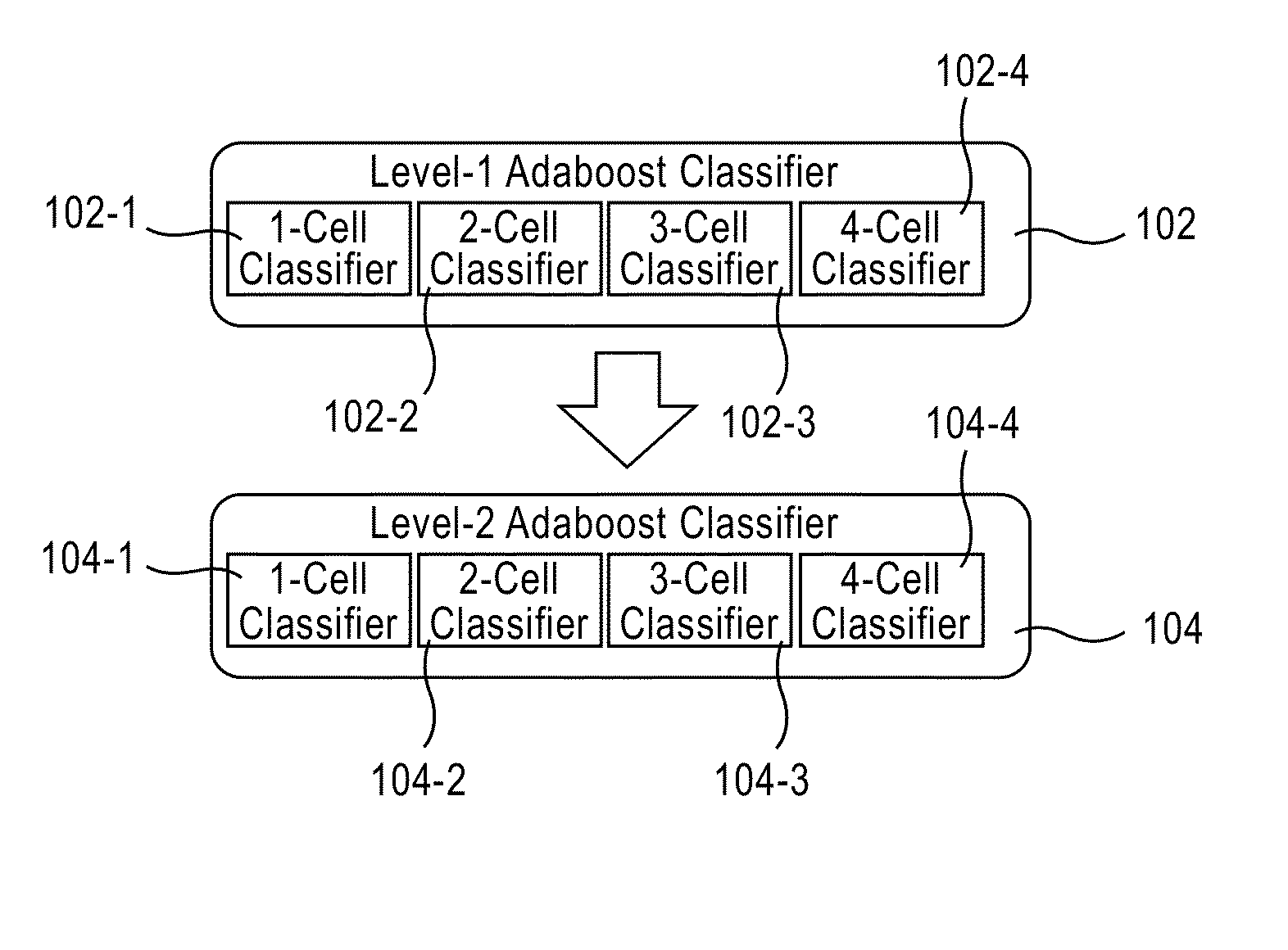
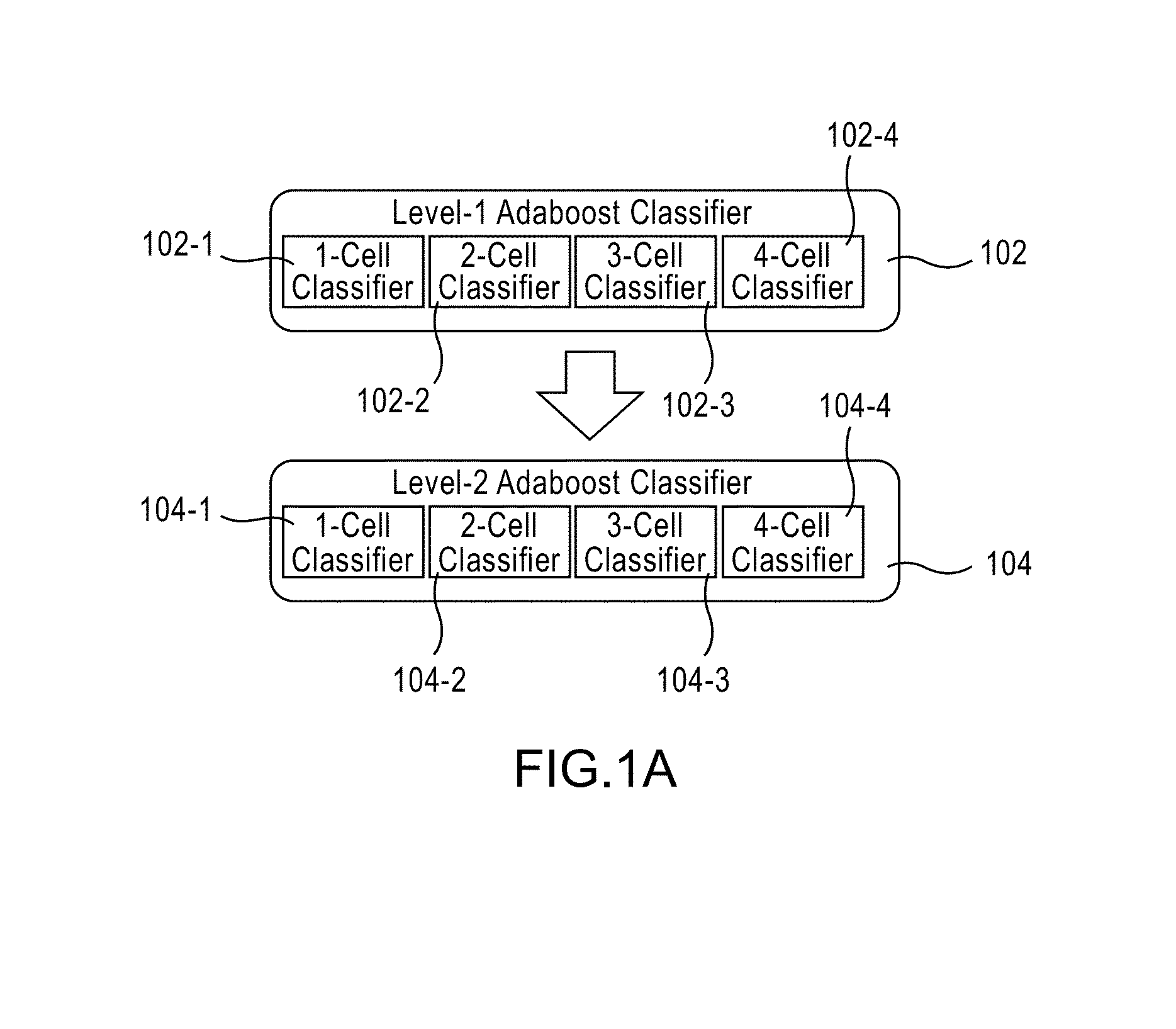
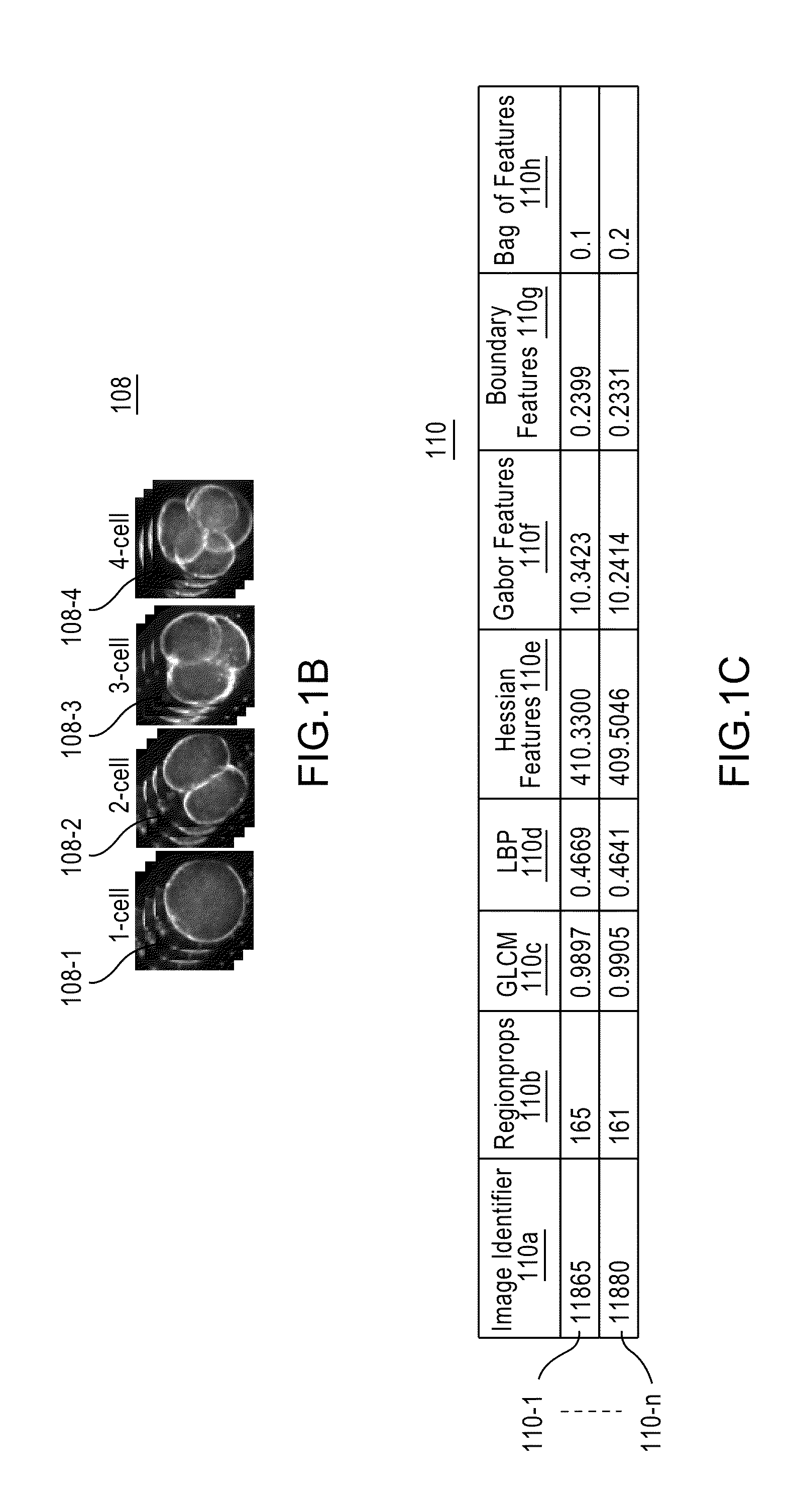
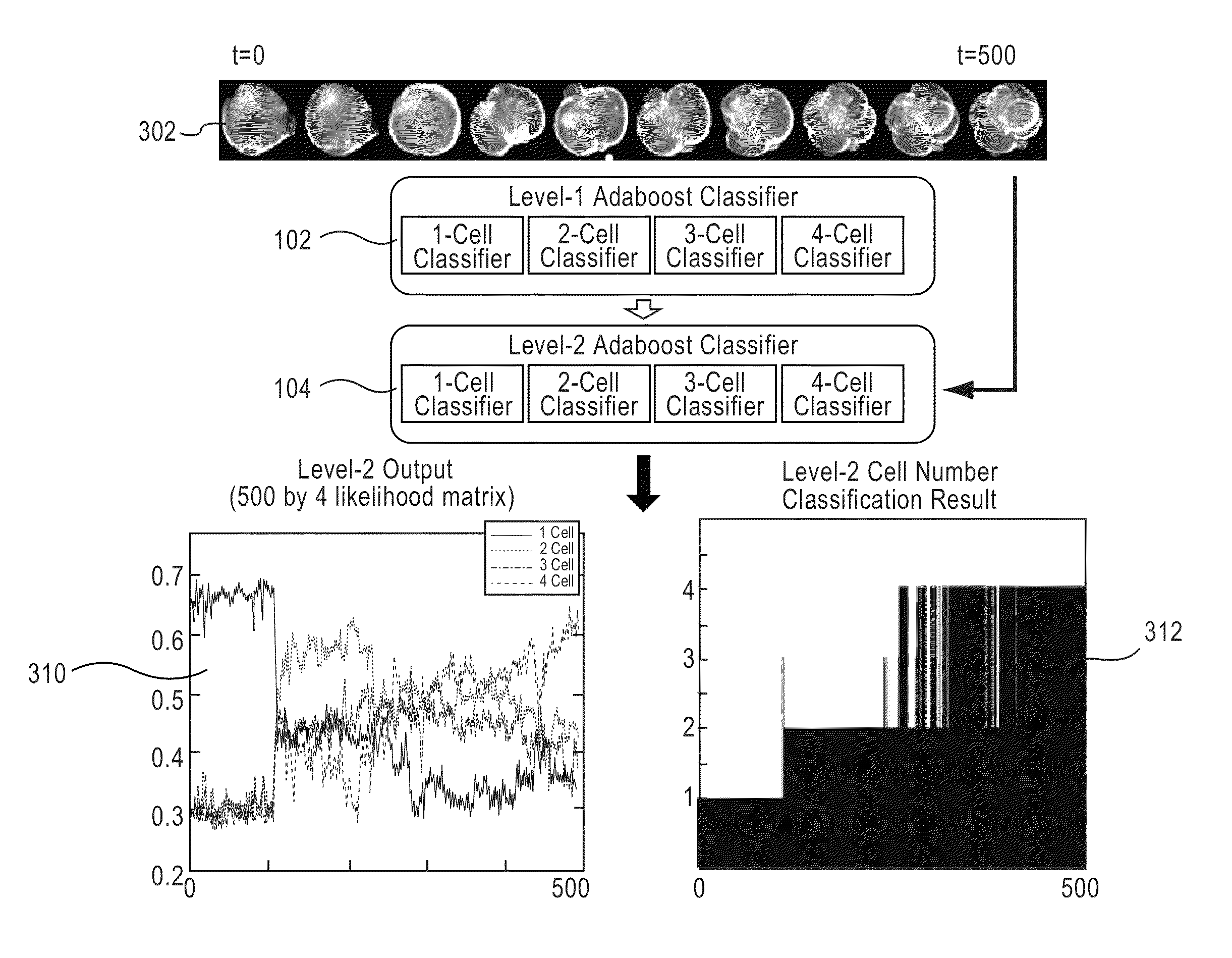
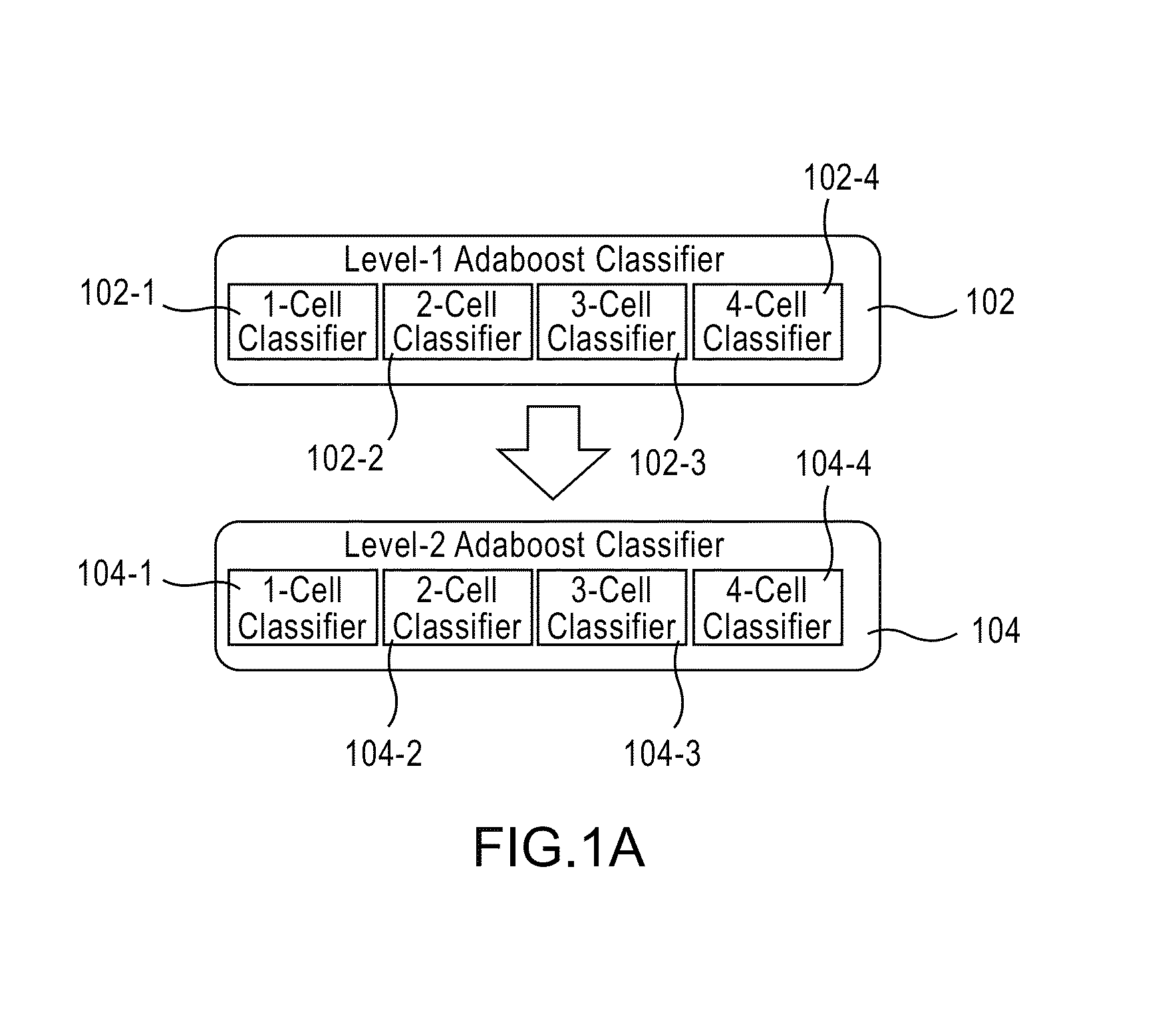
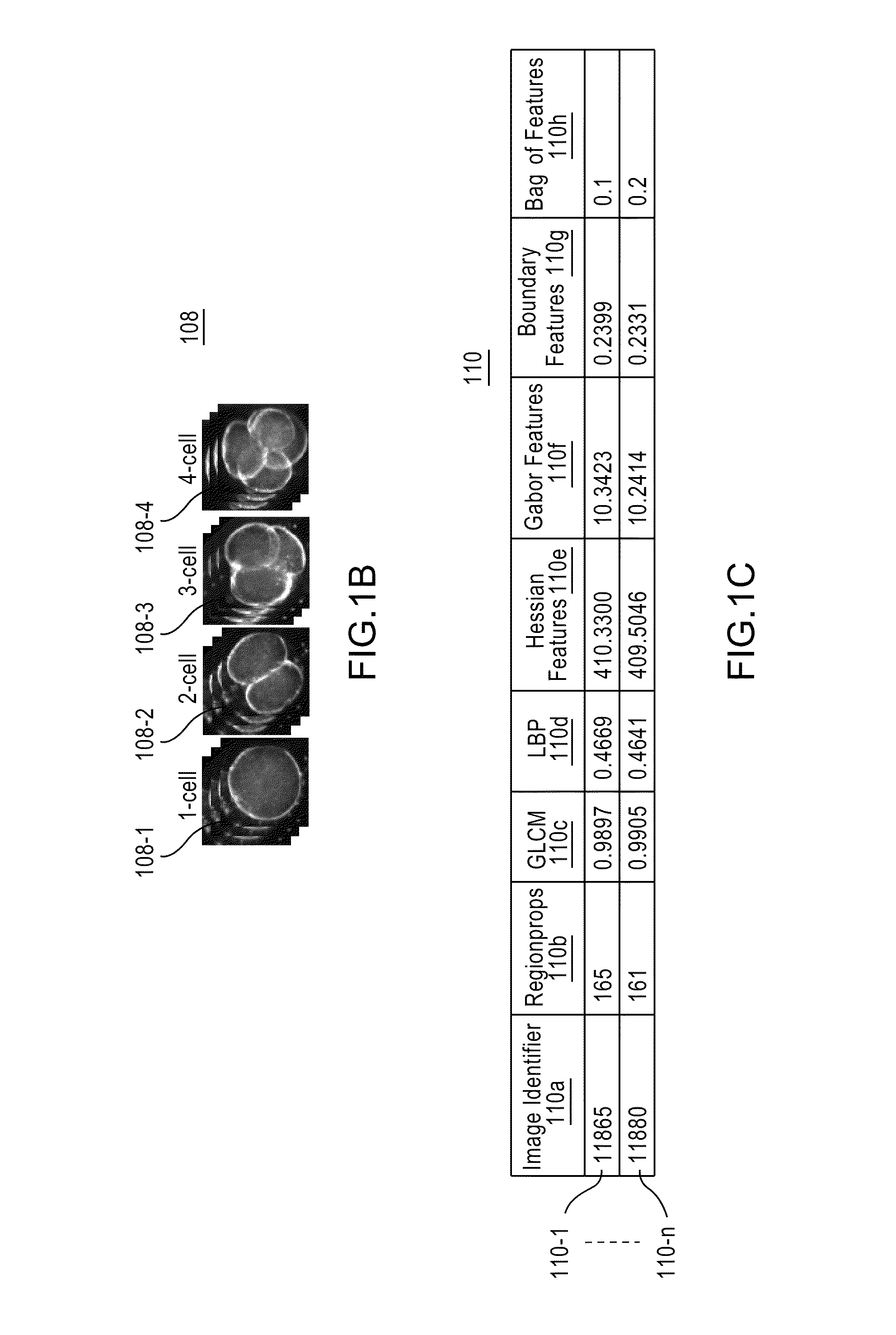
Apparatus, method, and system for image-based human embryo cell classification
Apparatuses, methods, and systems for automated cell classification, embryo ranking, and / or embryo categorization are provided. An apparatus includes a classification module configured to apply classifiers to images of one or more cells to determine, for each image, a classification probability associated with each classifier. Each classifier is associated with a distinct first number of cells, and is configured to determine the classification probability for each image based on cell features including one or more machine learned cell features. The classification probability indicates an estimated likelihood that the distinct first number of cells is shown in each image. The classification module is further configured to classify each image as showing a second number of cells based on the distinct first number of cells and the classification probabilities associated therewith. The classification module is implemented in at least one of a memory or a processing device.
Owner:ARES TRADING SA
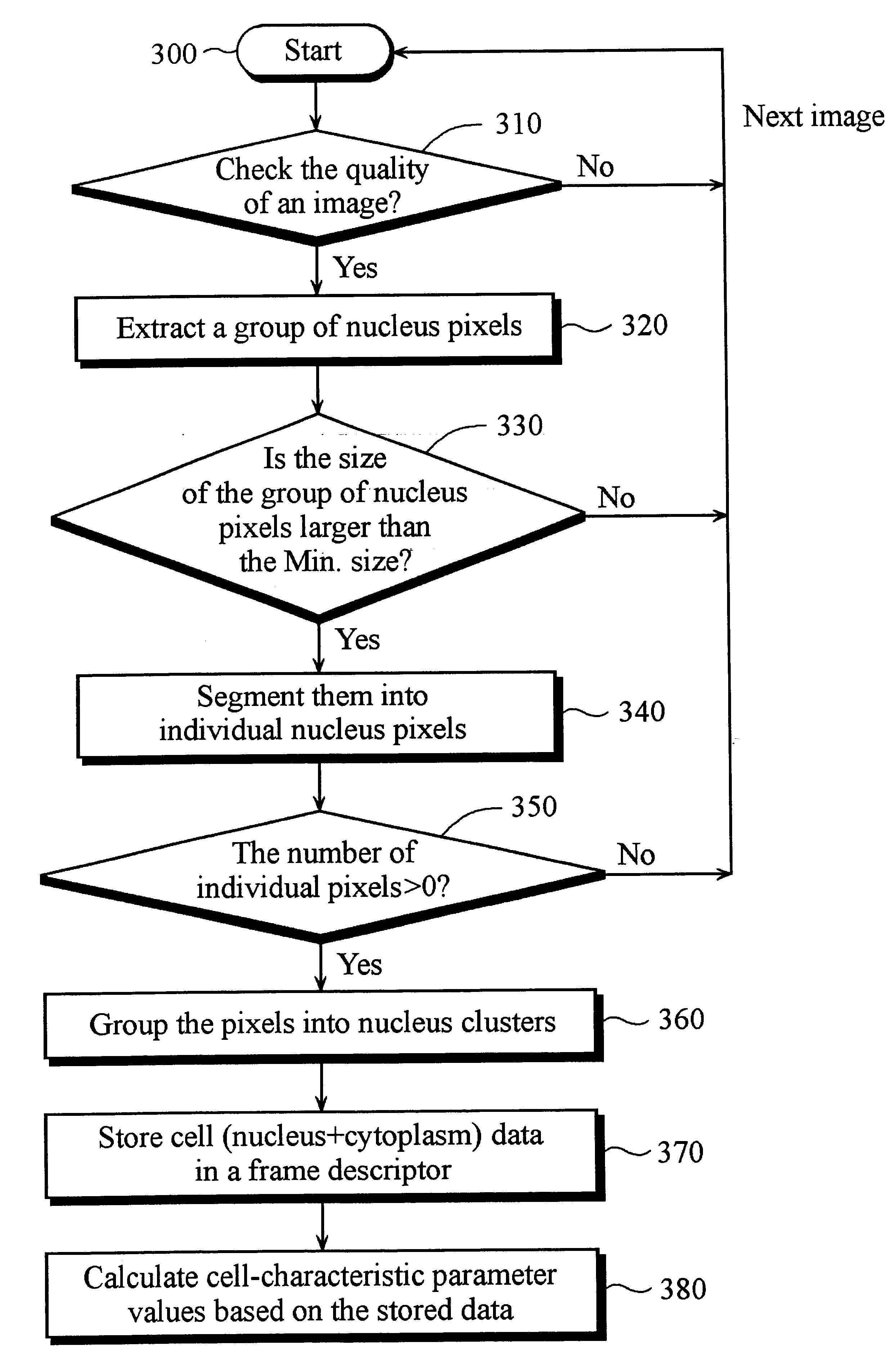
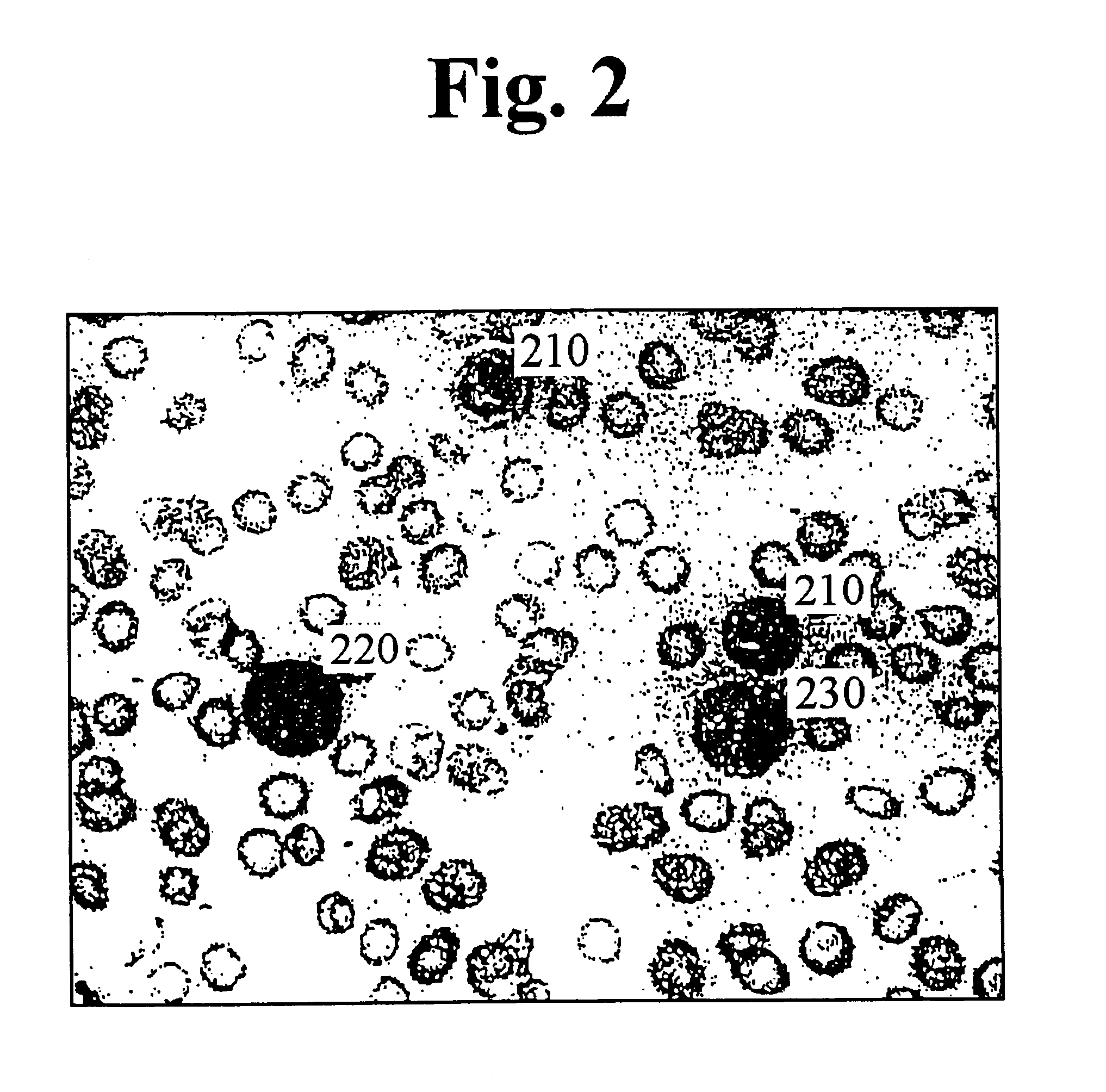
Method and apparatus for automatically recognizing blood cells
InactiveUS6330350B1Biological particle analysisAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsRed blood cellCell feature
A method and apparatus for automatically recognizing blood cells is provided. The method comprises obtaining image data of said blood cells, storing the image data of said blood cells in a memory, analyzing the image data of said blood cells and calculating a plurality of cell-characteristic parameter values for each of said blood cells, and recognizing each of said blood cells based on said plurality of cell-characteristic parameter values. In order to analyze the image data of blood cells, a group of nucleus pixels are first extracted from said stored image data and stored in the memory. The group of nucleus pixels are then segmented into individual nucleus clusters which represent each of the blood cells, and the data of the individual nucleus clusters are stored together with the associated cytoplasm data in the memory. Cell-characteristic parameter values for each of the blood cells are calculated based on its nucleus and associated cytoplasm data. The cell-characteristic parameter values are used in recognizing the blood cells.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
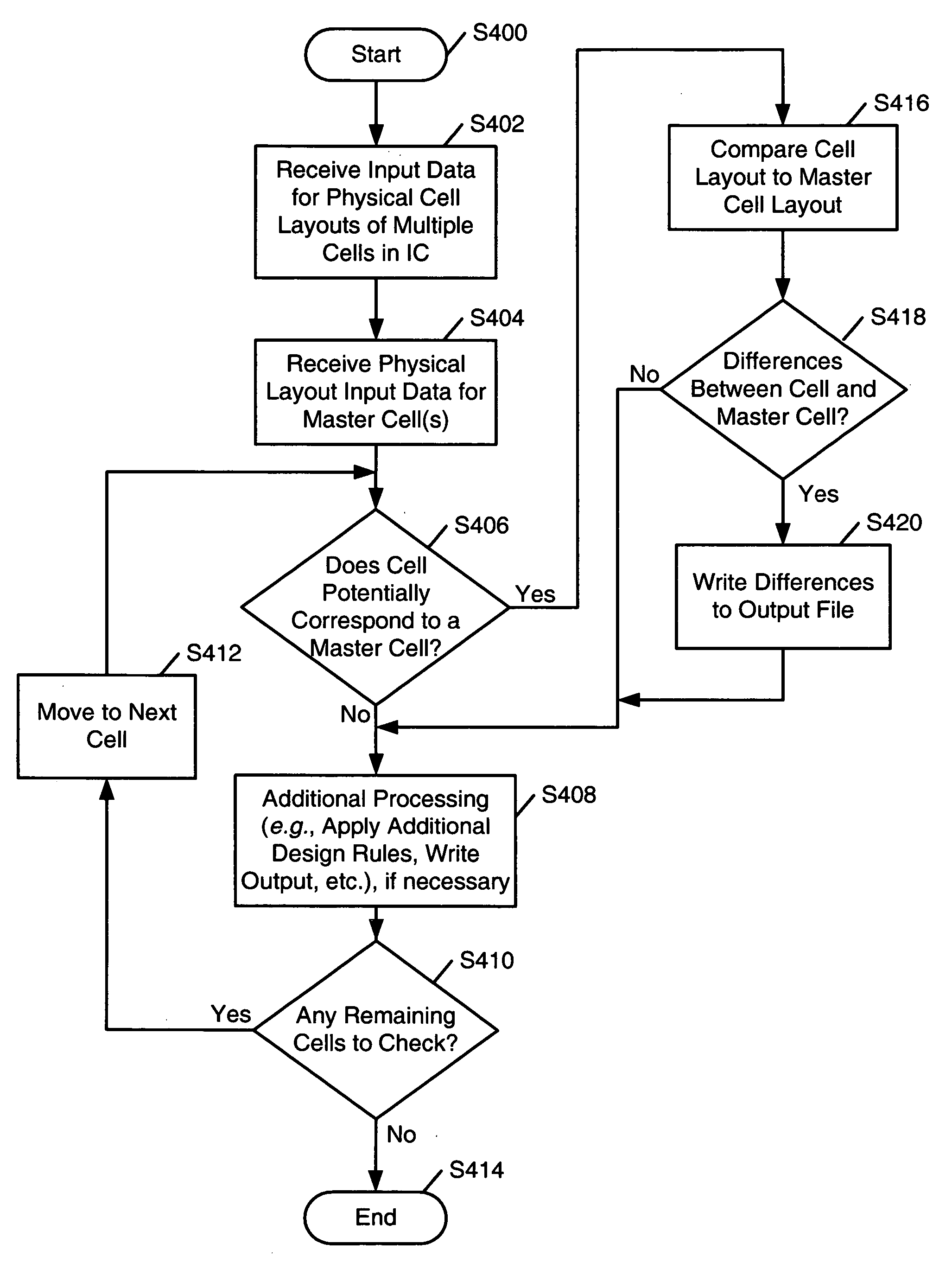
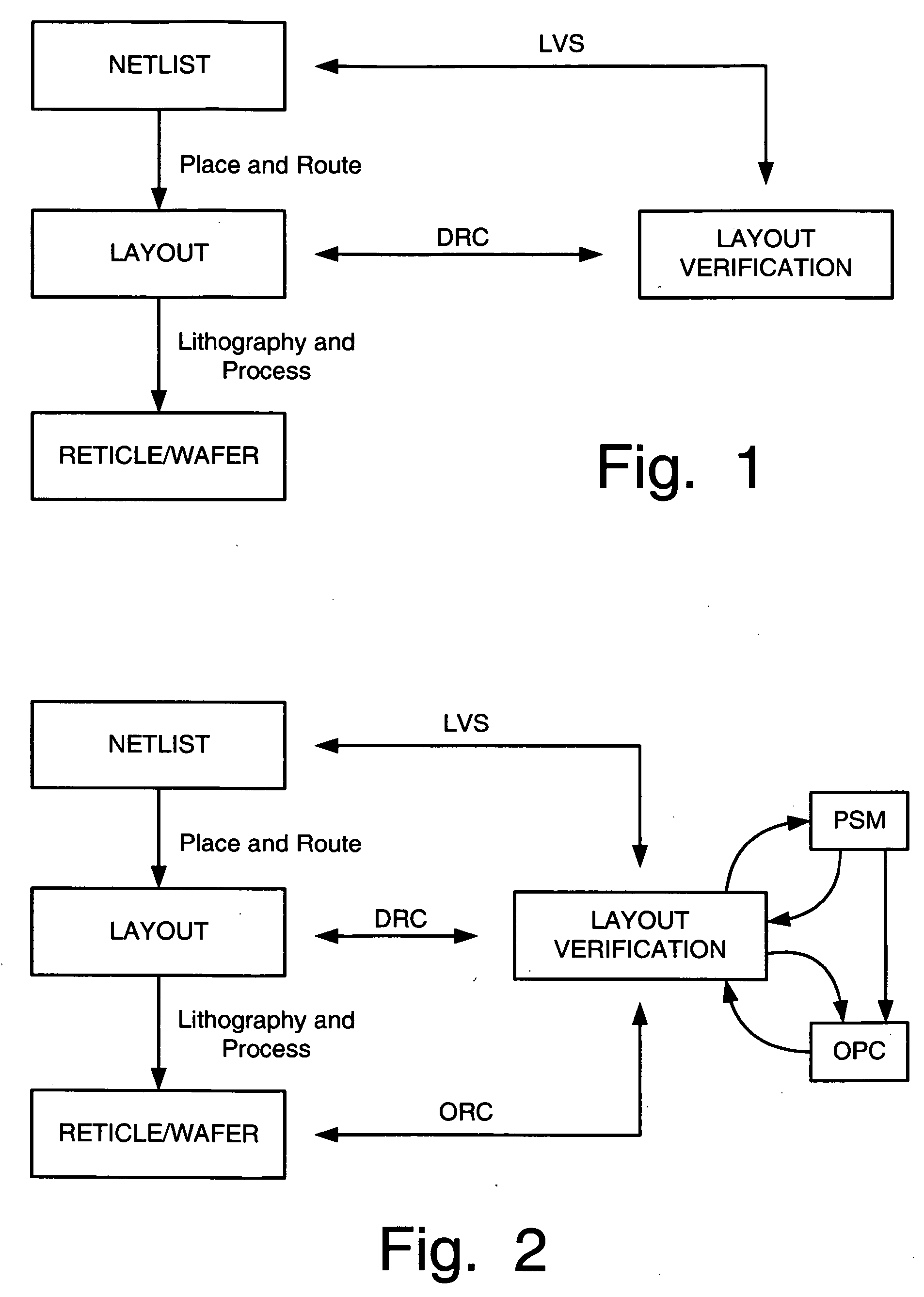
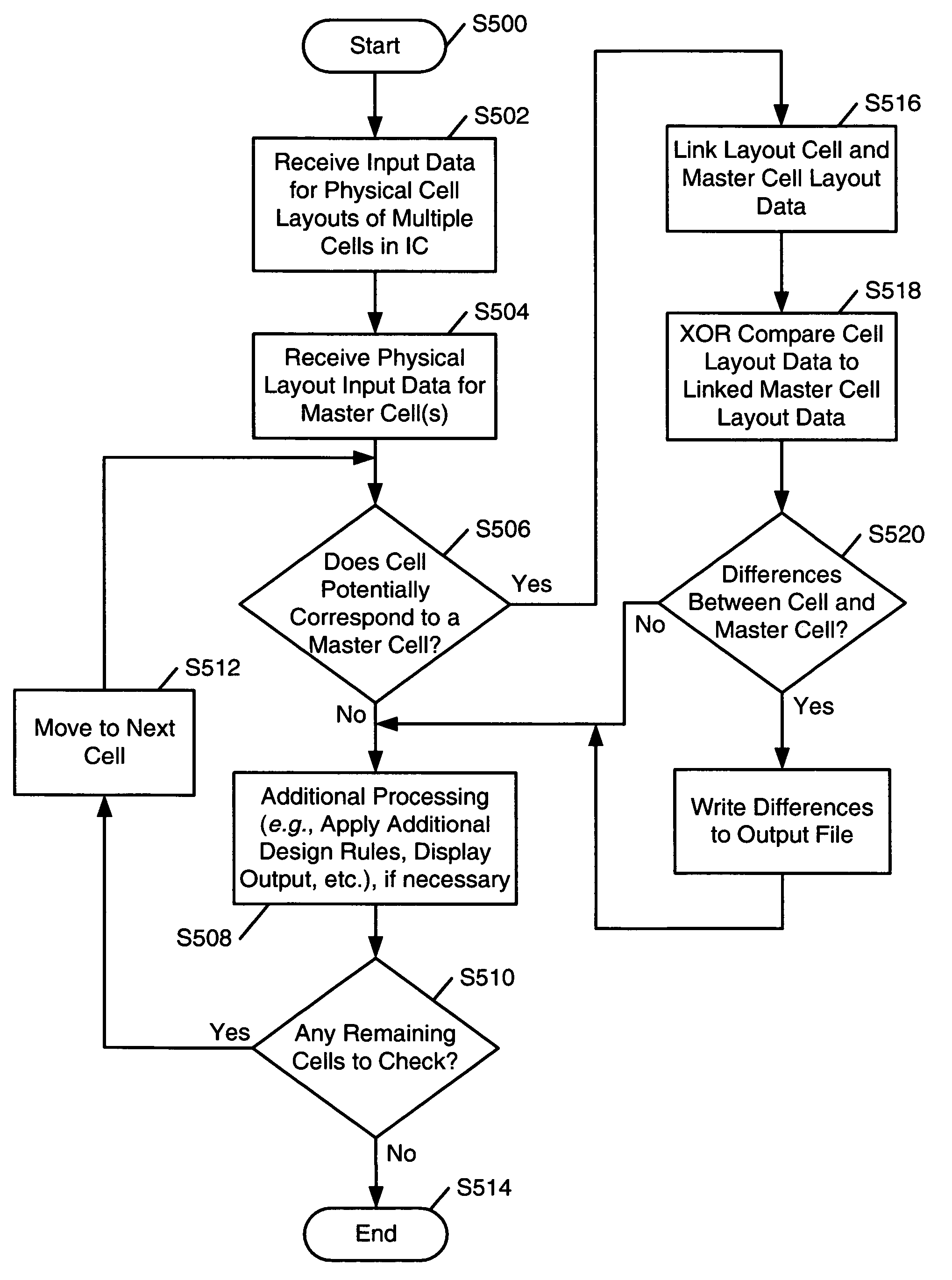
In-line XOR checking of master cells during integrated circuit design rule checking
ActiveUS20060090146A1Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsComputer hardwareComputer architecture
Systems and methods for verifying integrated circuit designs: (a) receive input corresponding to physical layouts of cells of the design and available master cells. The systems and methods then determine if the design cells are intended to correspond to one of the master cells, and if so, the systems and methods then determine if the layouts of the cells and the corresponding master cells match one another, e.g., by a layout vs. layout comparison of the design cell with the master cell to determine if the coordinates of the polygon(s) in the design cell match corresponding coordinates of the polygon(s) in the master cell. An “XOR” comparison may be used to determine if the design cell features match the corresponding master cell features. Computer-readable media may be adapted to include computer-executable instructions for performing such methods and operating such systems.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
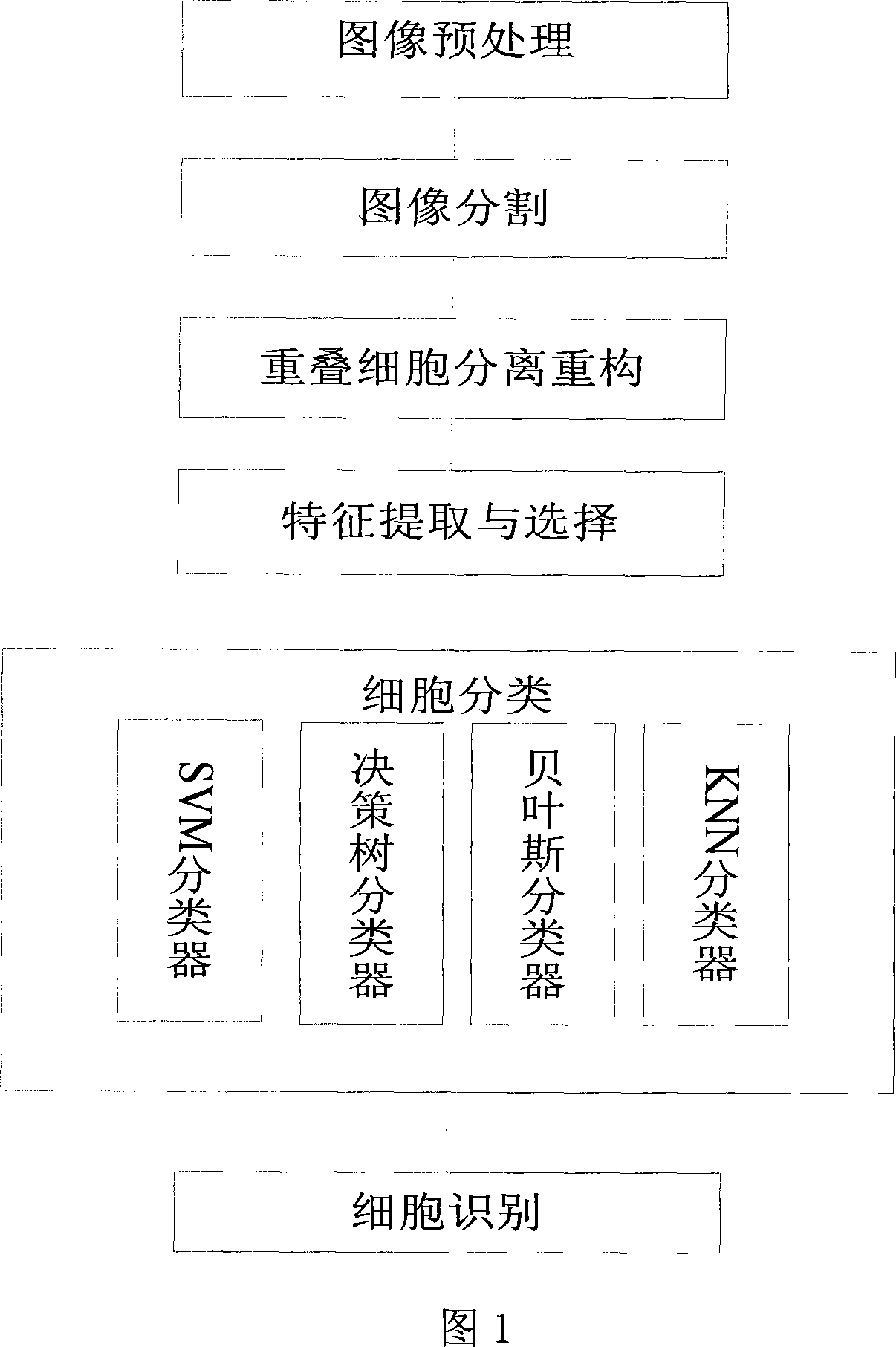
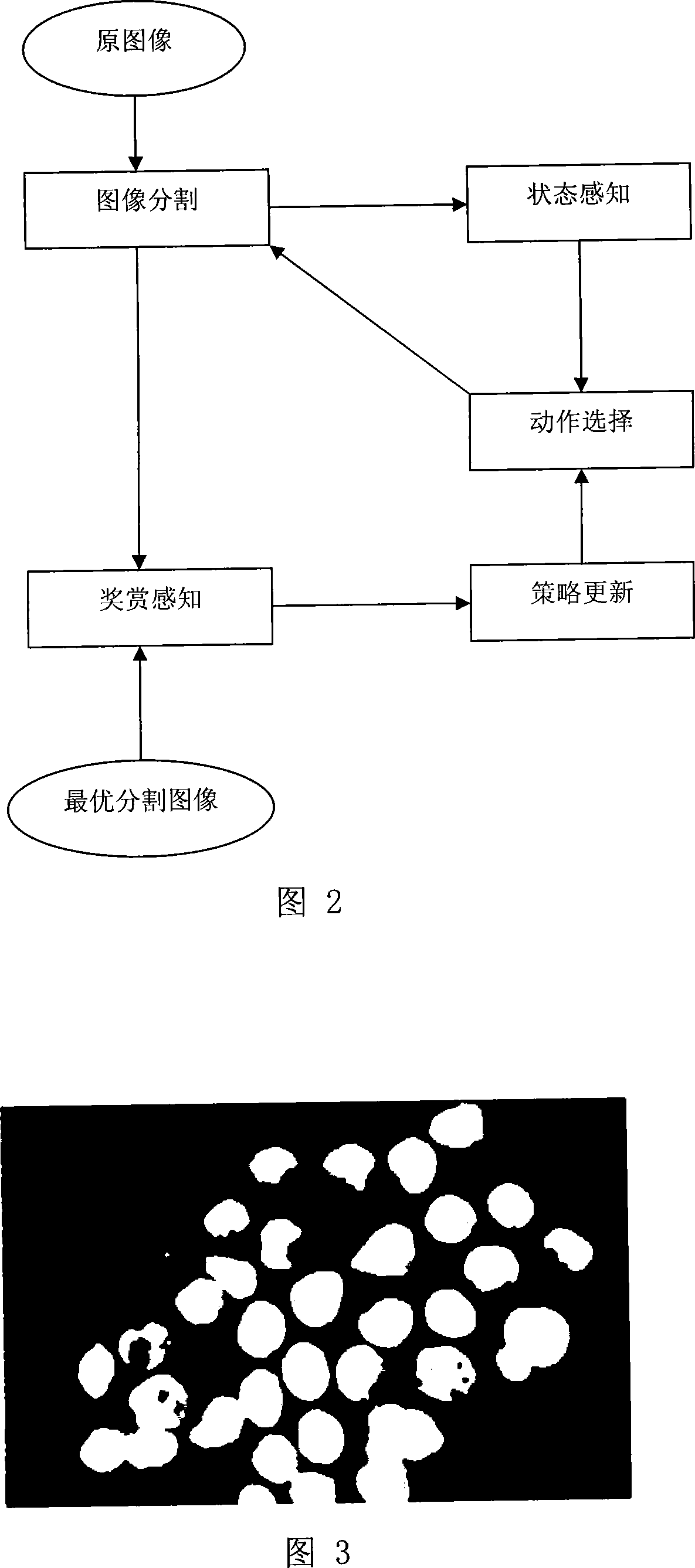
Intelligentize lung cancer early cell pathological picture recognition processing method
InactiveCN101226155AHigh simulationAvoid situations with low classification accuracyImage analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansSmall-cell carcinomaSquamous Carcinomas
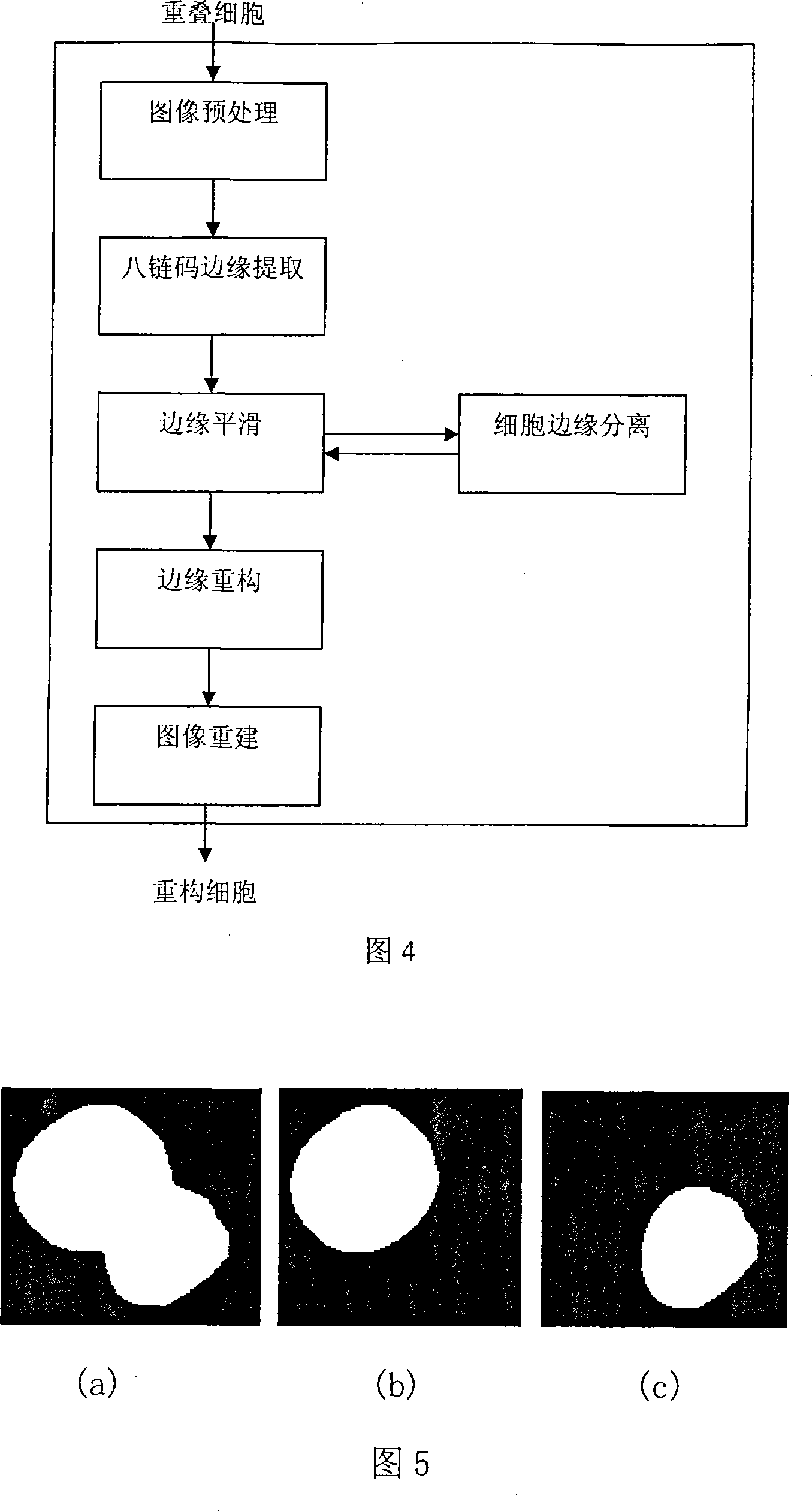
The invention relates to an intelligent lung cancer early cell pathological image recognition processing method, which comprises image pretreatment, image segmentation, laminate cell separation and reconstruction, cell character extraction and cell classification. The invention has the advantages that the image segmentation based on reinforcement learning uses incremental learning and continuous interaction with environment to search for optimized segmentation threshold value to obtain the segmentation effect which average value is 91%, the laminate cell separation and reconstruction uses B spline and modified deBoor-Cox method to simulate true cell edge better, the classifier uses general vote method to avoid low classifying accuracy of single classifier and improve total classifying accuracy, the application of two-stage classifier can reduce the possibility of false positive and false negative. Tests prove that the classifying accuracy of cancer or no cancer can average reach 93.8%, the classifying accuracy of squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma and small cell carcinoma average reaches 75%, and the false positive and negative average reach 4-6%.
Owner:中国人民解放军第八一医院 +1
Method for automatically identifying and counting white blood cells
InactiveCN103020639AImplement classificationImprove classification efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionColor/spectral properties measurementsSupport vector machineWhite blood cell
The invention provides a method for automatically identifying and counting white blood cells. The method comprises the following steps of: preprocessing, color space conversion, coarse segmentation, checking of white blood cells, fine segmentation, characteristic parameter extraction, identification and classification, result output and the like. The method can be used for automatically identifying and classifying the white blood cells in blood by extracting a group of cell characteristic parameters and utilizing a support vector machine, and has the advantages of high classification efficiency, good effect, high accuracy, high stability and high robustness.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Computer-assisted cell analysis
InactiveUS20060050946A1High throughput screeningReduce the number of cellsImage enhancementImage analysisStainingComputer-aided
The present invention provides methods and systems for automated morphological analysis of cells. The inventive methods are particularly useful in the rapid analysis of cells required in a biological screen. Agents which cause a particular phenotype in the cells can be identified using the inventive quantitative morphometric analysis of cells. The data gathered using the inventive method can also be quantified and analyzed later for various trends and classifications. Characteristics of cells which can be determined using this method include number of nuclei, size of cell, size of nuclei, number of the centrosomes, shape of cells, size of centrosomes, perimeter of nucleus, shape of nucleus, pattern of staining, and degree of staining.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods and devices for determining a cell characteristic, and applications employing the same
InactiveUS20050239047A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell featureCell type
The present invention provides methods of determining a characteristic of a cell, such as cell type, cellular response to a biochemical event, and biological state. The method generally involves detecting membrane movement in a cell to determine a characteristic of a cell. The methods of the invention are useful for applications such as drug screening and diagnostics. The invention further provides databases of cell characteristics, as determined by the instant methods. The invention further provides systems for determining the characteristic of a cell
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
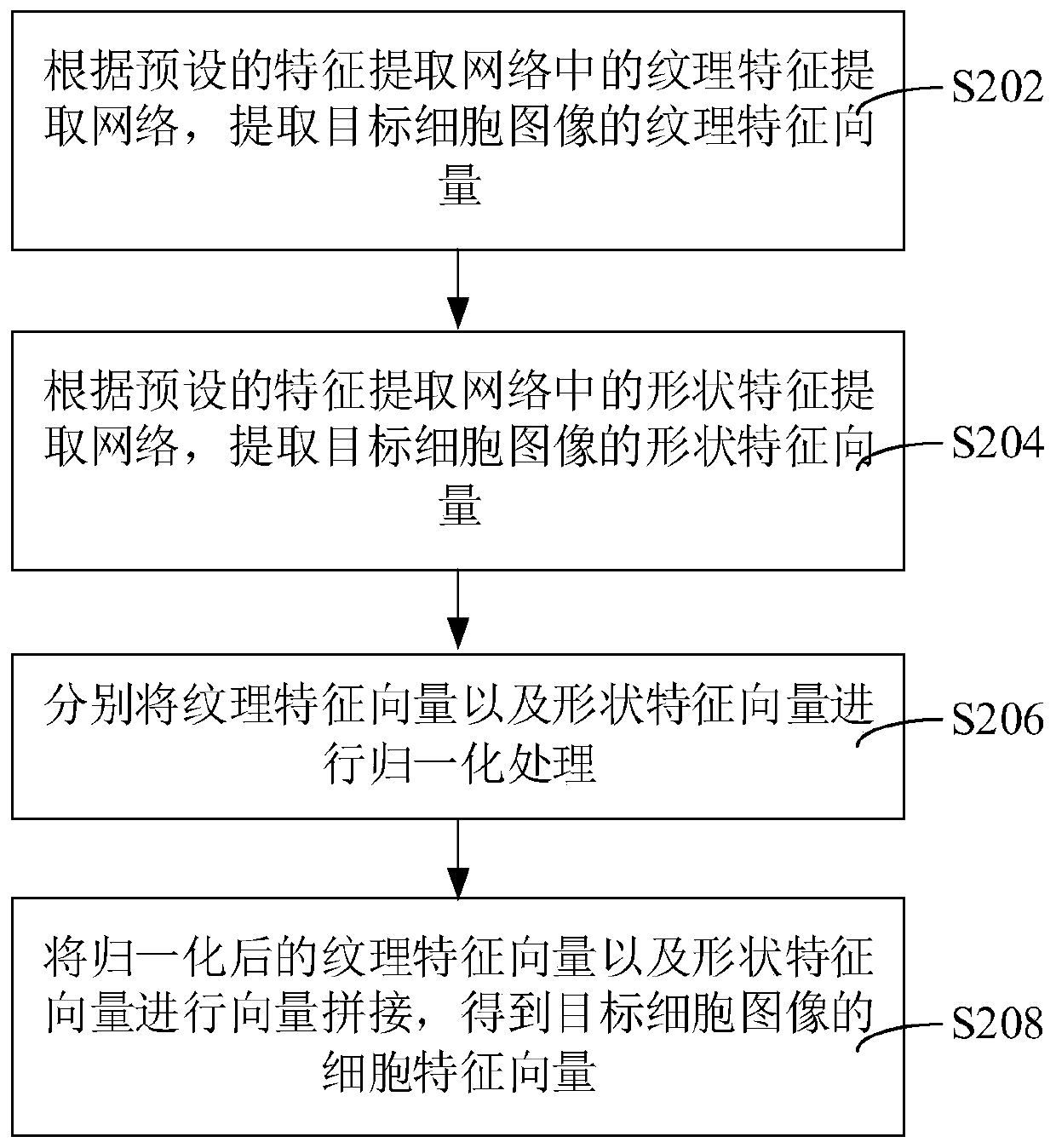
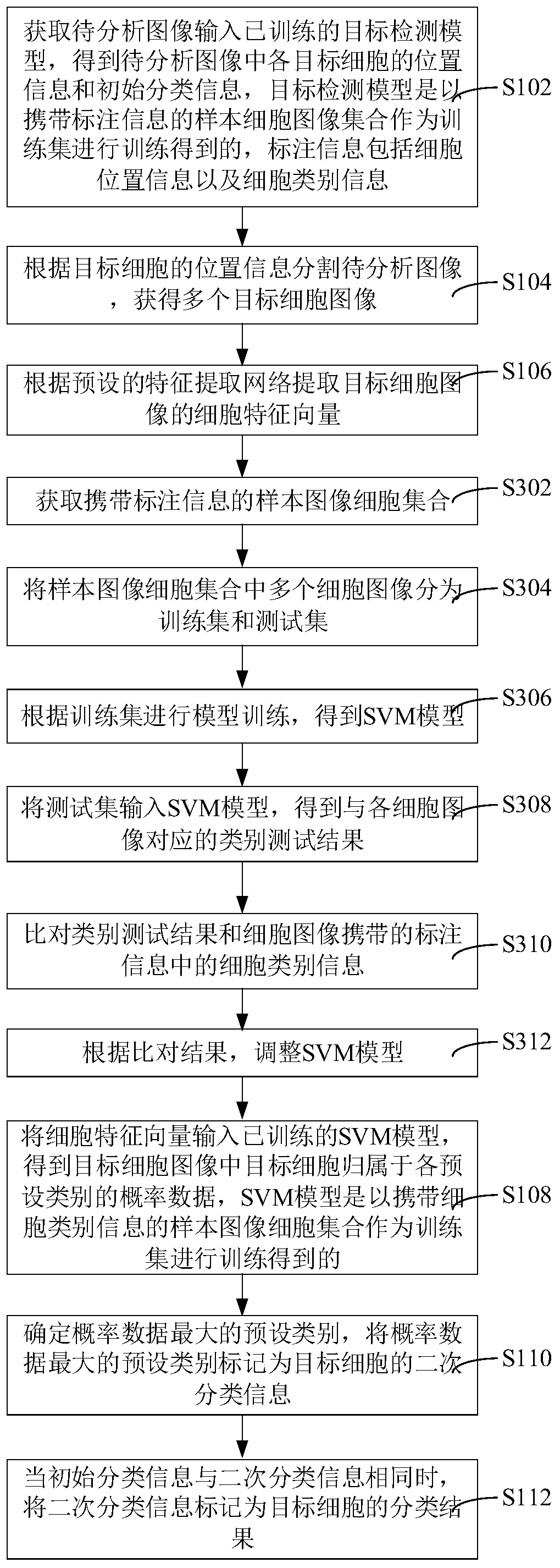
Cell classification method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN110110799AImprove accuracyAccurately determineCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionClassification methods
The invention relates to a cell classification method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining a to-be-analyzed image and inputting the to-be-analyzed image into a trained target detection model, obtaining position information and initial classification information of each target cell in the to-be-analyzed image; wherein the labeling information comprises cell position information and cell type information; segmenting a to-be-analyzed image according to the position information of the target cell; obtaining a plurality of target cell images, extracting a cell feature vector of the target cell image according to a preset feature extraction network; inputting the cell feature vectors into a trained SVM model; and obtaining probability data of the target cell belonging to each preset category in the target cell image, marking the preset category with the maximum probability data as secondary classification information of the target cell, and marking the secondary classification information as a classification result of the target cell when the initial classification information is the same as the secondary classification information. By adopting the method, the cell category can be accurately determined, and the cell recognition accuracy is improved.
Owner:广州锟元方青医疗科技有限公司
Cell microarray for profiling of cellular phenotypes and gene function
InactiveUS20060160169A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell featureCellular phenotype
The present invention includes compositions, methods and systems for analyzing one or more cell characteristics including the steps of depositing one or more spots on a substrate that include one or more cells from a strain collection, contacting the one or more cells with one or more agents and evaluating optically effect of the agent on the one or more cells.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Virtual flow cytometry on immunostained tissue-tissue cytometer
InactiveUS7899624B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsColor imageCytometry
Owner:CUALING HERNANI D
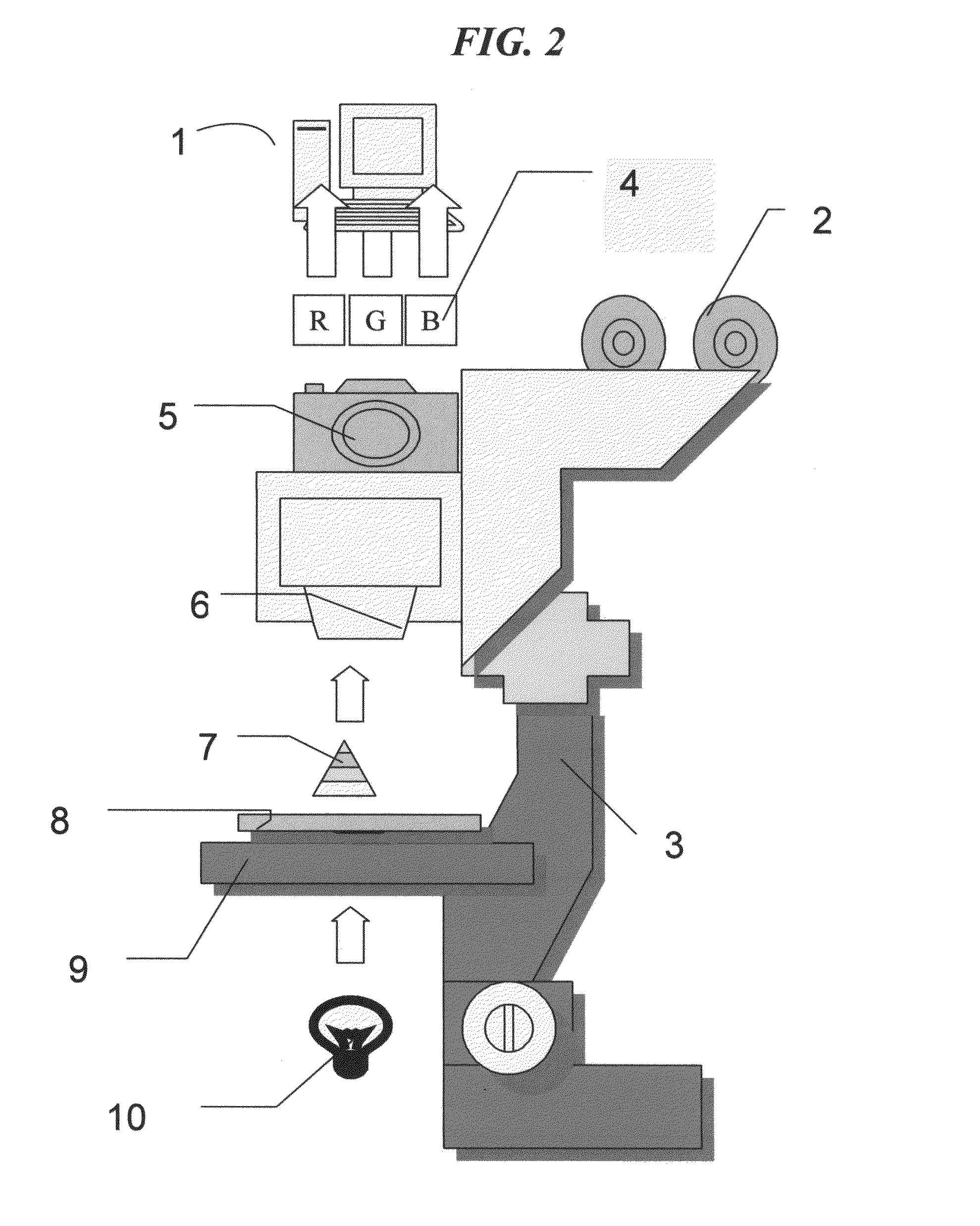
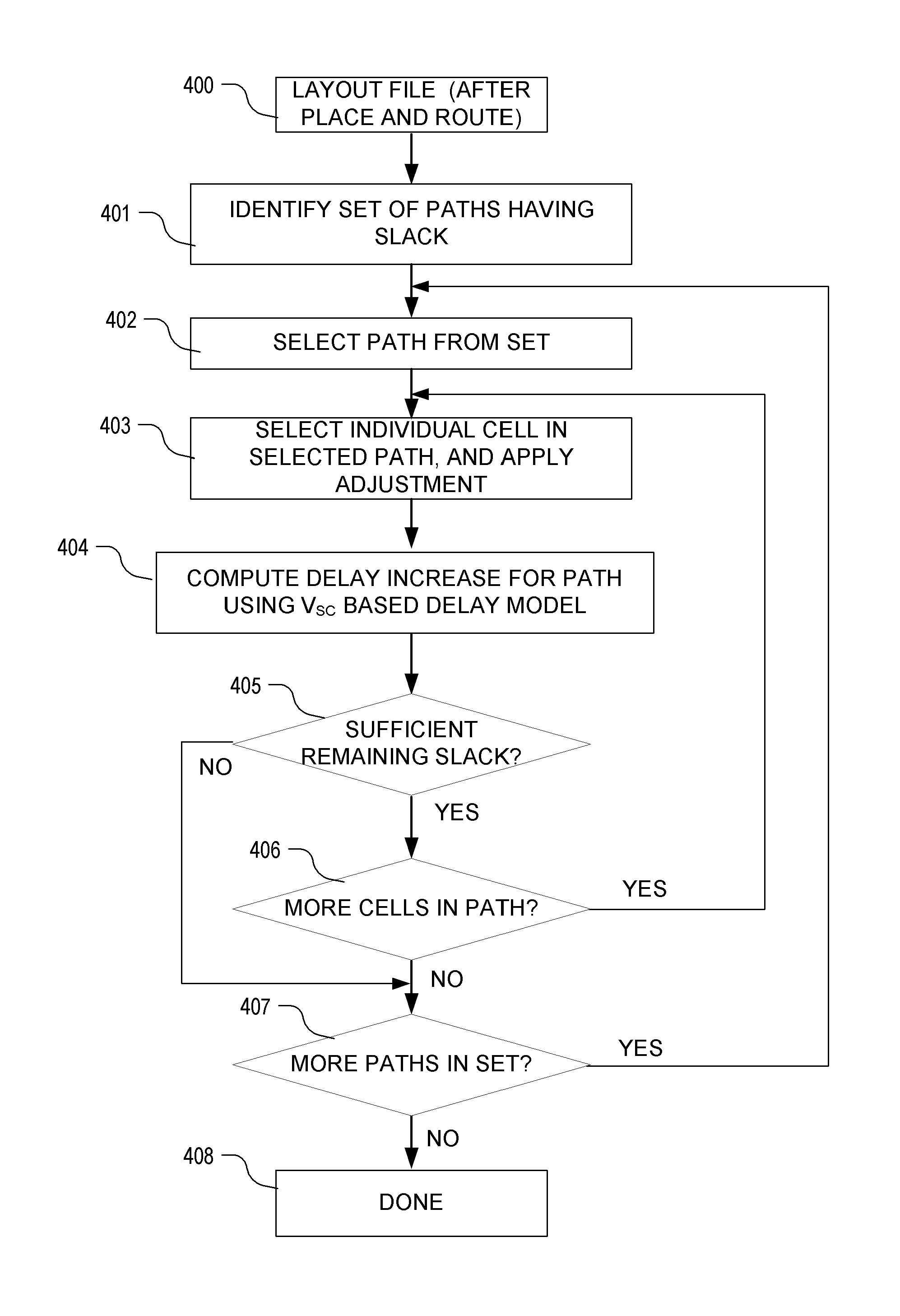
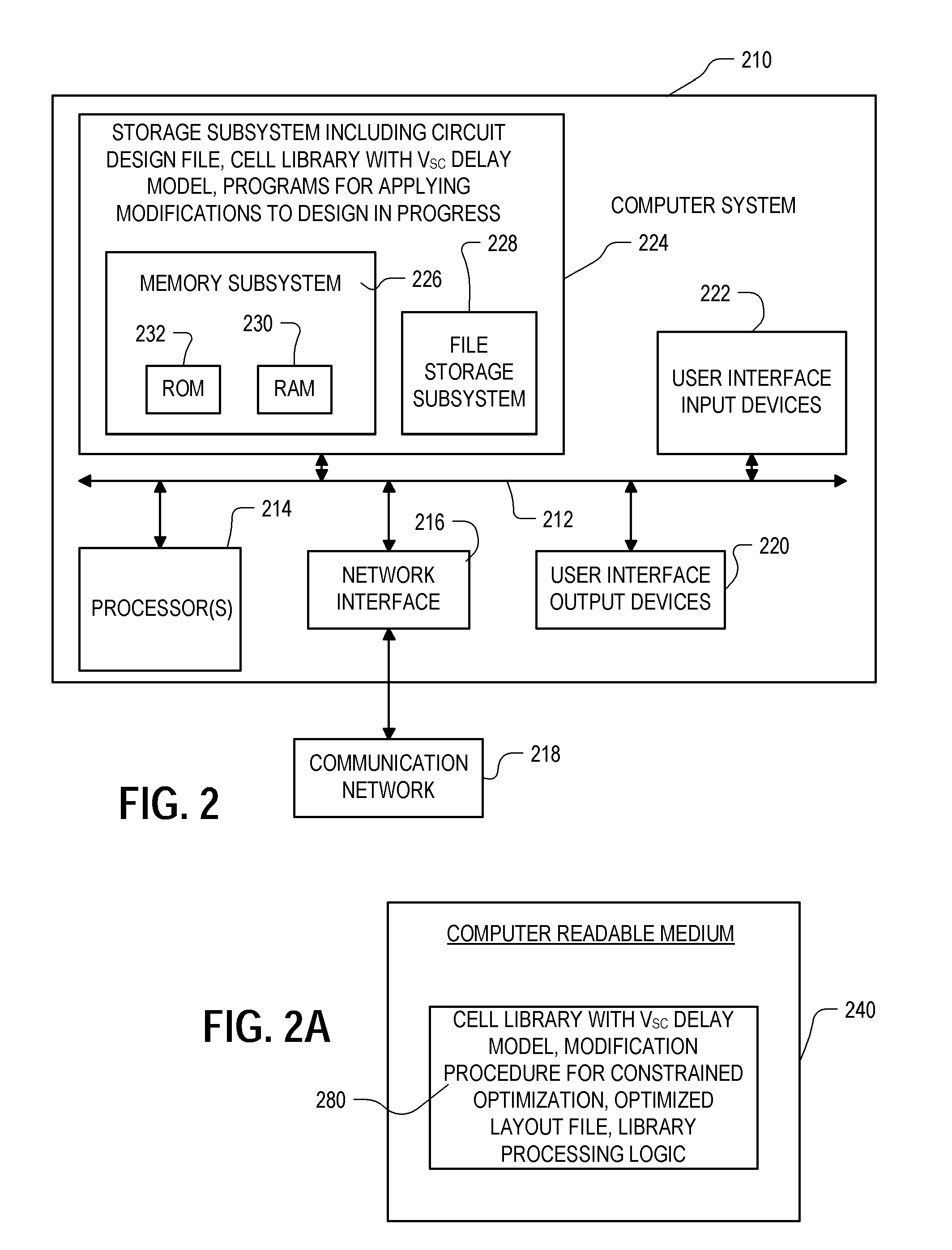
Modeling of cell delay change for electronic design automation
ActiveUS20110231811A1Reduce the required powerDesign optimisation/simulationCAD circuit designCell featureLeakage power
An integrated circuit design optimization procedure to modify a cell feature, such as gate length, models changes in delay as a result of the modification. In the delay change calculation, a characteristic of an event in cell switching behavior, such as the output short-circuit voltage VSC, is determined for the modified cell, where changes in the determined characteristic correlate with changes in delay of the cell due to the modification. Next, a value for delay of the modified cell is determined as a function of the determined characteristic of the event. The procedure can be applied after placement and routing. A timing-constrained, leakage power reduction is described using the delay change model.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Cells exhibiting neuronal cell progenitor characteristics and methods of making them
Disclosed are cells exhibiting neuronal progenitor cell characteristics, and methods of making them from marrow adherent stem cells by regulating cellular pathways in the marrow adherent stem cells that are associated with glial transdifferentiation of the marrow adherent stem cells.
Owner:SANBIO
Nano coating of negative electrode materials and preparation method of secondary aluminium cell using negative electrode materials
InactiveCN101662022AIncrease energy densityRich in aluminum resourcesElectrode manufacturing processesSecondary cellsSemimetalHigh energy
The invention discloses a novel high-energy secondary aluminium cell and a preparation method. The aim is to provide a method for preparing nano material-coated negative electrode active materials, by coating the negative electrode active materials with the nano materials, it is possible to subject the negative electrode active materials to nano treatment; therefore, the high-energy secondary aluminium cell features obviously improved properties, simple material composition, low cost, simple technology, environmentally friendly synthesis path, relatively high charge-discharge capacity and relatively good cycle property and market prospect. The aluminium cell comprises the positive and negative electrodes in the modified positive and negative electrode active materials coated by the nano material surfaces or any one electrode in the singly coated positive or negative electrode active materials, polyelectrolyte (ionic liquid) and a diaphragm. The coating materials are semimetals, oxides, salts or conductive polymers. The invention uses the nano materials in the secondary aluminium cell for the first time; therefore, the cell has higher open circuit voltage and reversible capacity and better cycle property, can be applied to such fields as portable power sources like mobile telephones, notebooks and portable electronic components, and as electric vehicles, hybrid electric vehicles and the like, and has broad application and development prospects.
Owner:无锡欧力达新能源电力科技有限公司
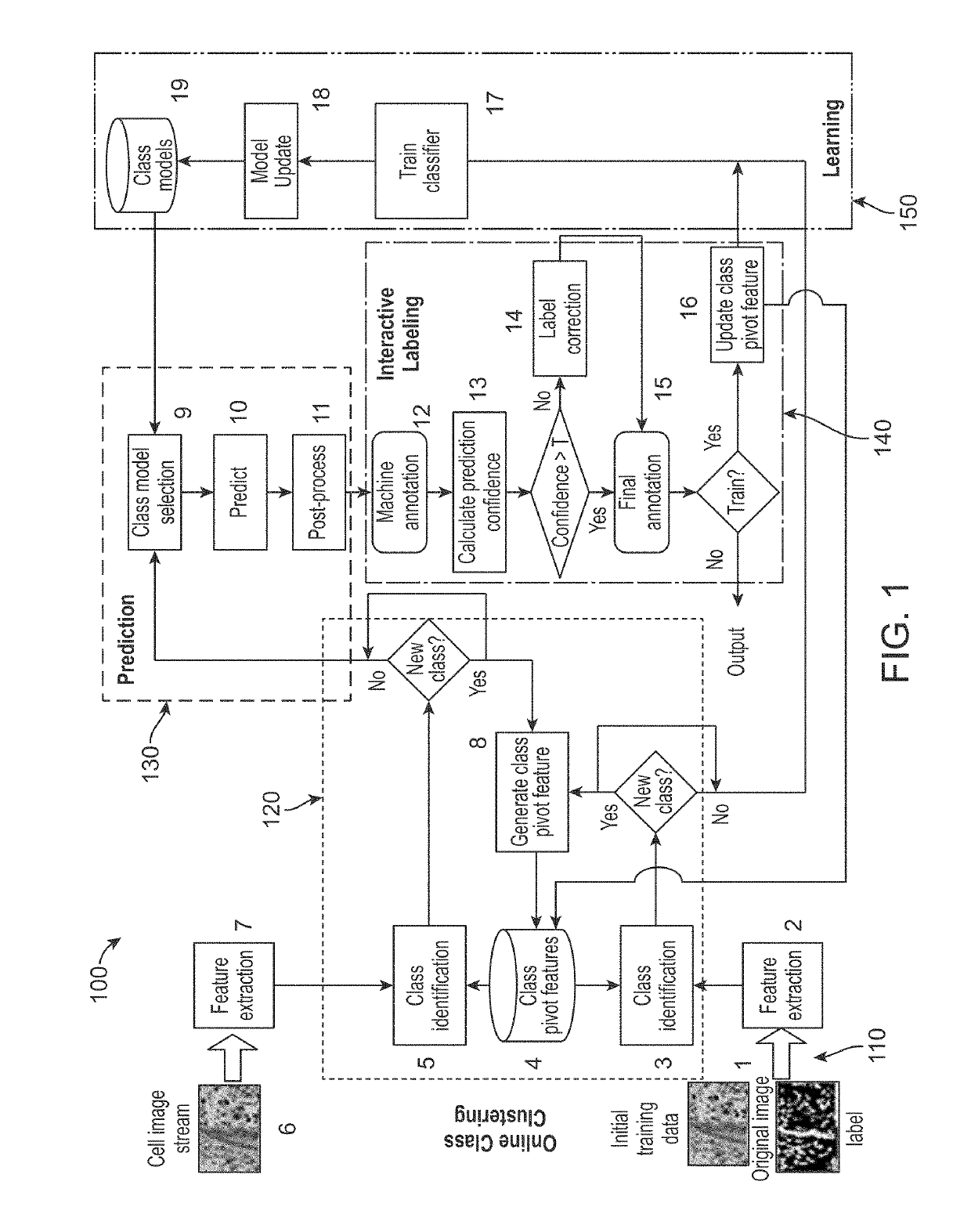
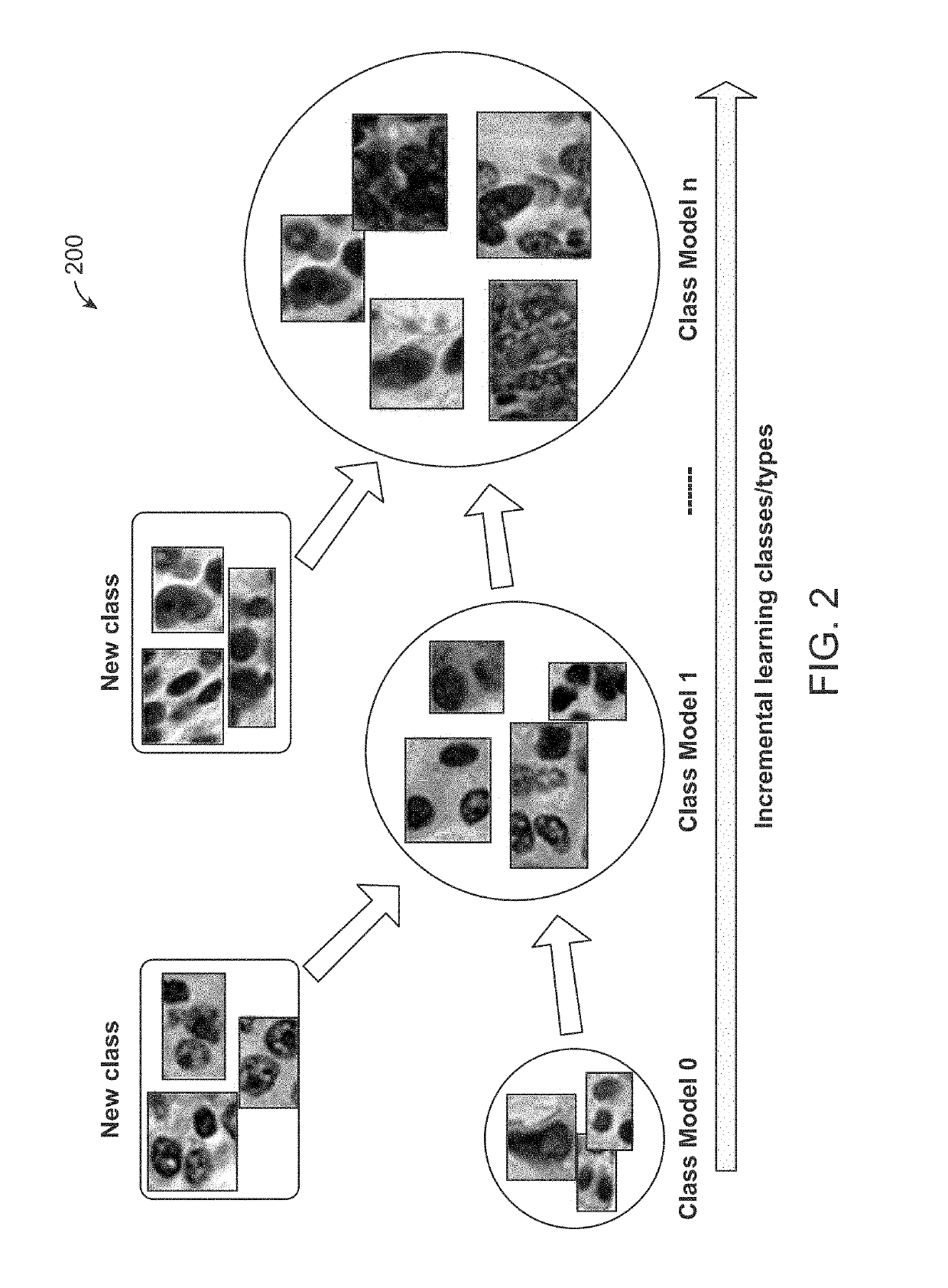
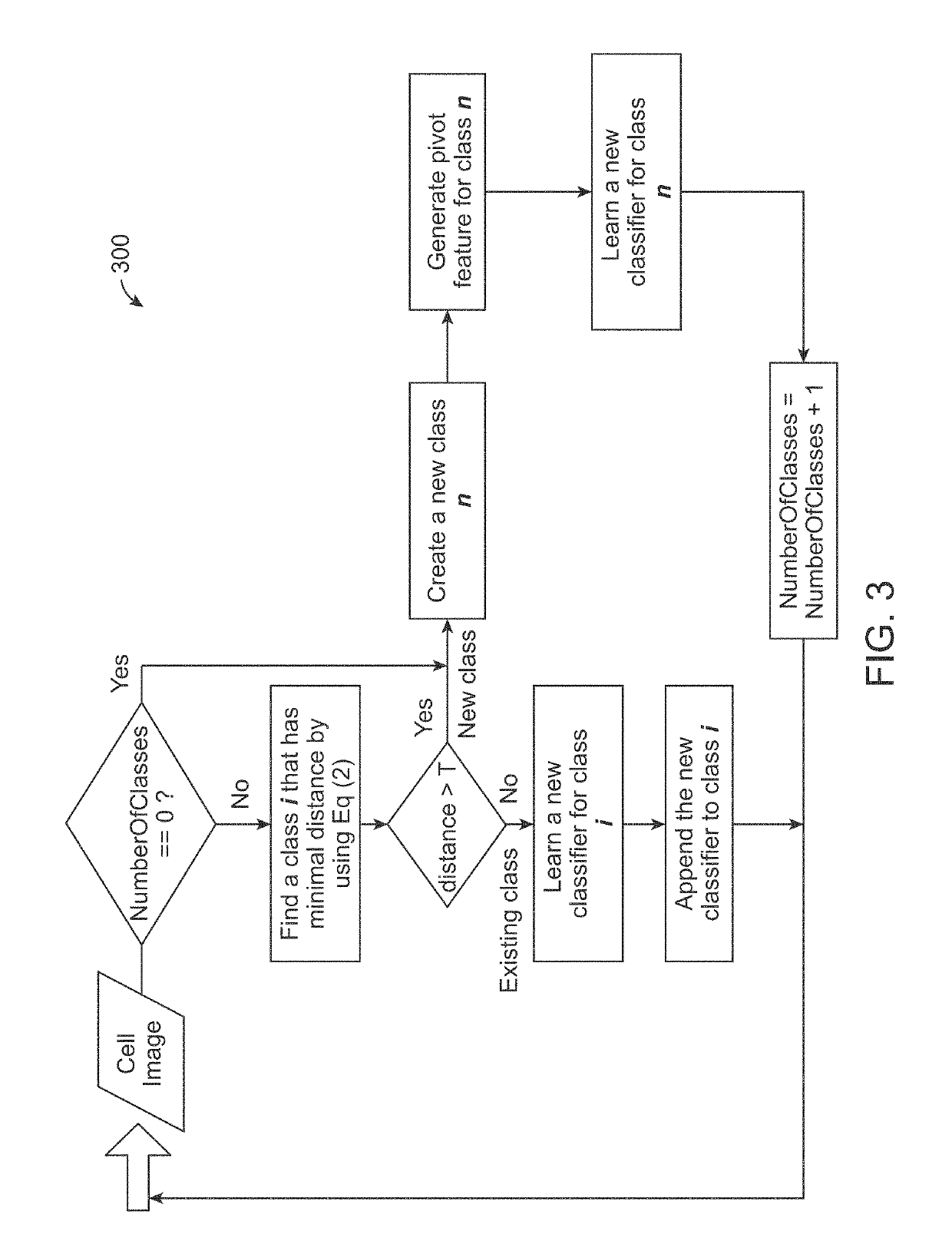
Method and system for cell annotation with adaptive incremental learning
ActiveUS20190180147A1Increase capacityImage enhancementImage analysisIncremental learningComputer vision
A method, a computer readable medium, and a system for cell annotation are disclosed. The method includes receiving at least one new cell image for cell detection; extracting cell features from the at least one new cell image; comparing the extracted cell features to a matrix of cell features of each class to predict a closest class, wherein the matrix of cell features has been generated from at least initial training data comprising at least one cell image; detecting cell pixels from the extracted cell features of the at least one new cell image using the predicted closest class to generate a likelihood map; extracting individual cells from the at least one cell image by segmenting the individual cells from the likelihood map; and performing a machine annotation on the extracted individual cells from the at least one new cell image to identify cells, non-cell pixels, and / or cell boundaries.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA LAB U S A INC
In-line XOR checking of master cells during integrated circuit design rule checking
Systems and methods for verifying integrated circuit designs: (a) receive input corresponding to physical layouts of cells of the design and available master cells. The systems and methods then determine if the design cells are intended to correspond to one of the master cells, and if so, the systems and methods then determine if the layouts of the cells and the corresponding master cells match one another, e.g., by a layout vs. layout comparison of the design cell with the master cell to determine if the coordinates of the polygon(s) in the design cell match corresponding coordinates of the polygon(s) in the master cell. An “XOR” comparison may be used to determine if the design cell features match the corresponding master cell features. Computer-readable media may be adapted to include computer-executable instructions for performing such methods and operating such systems.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
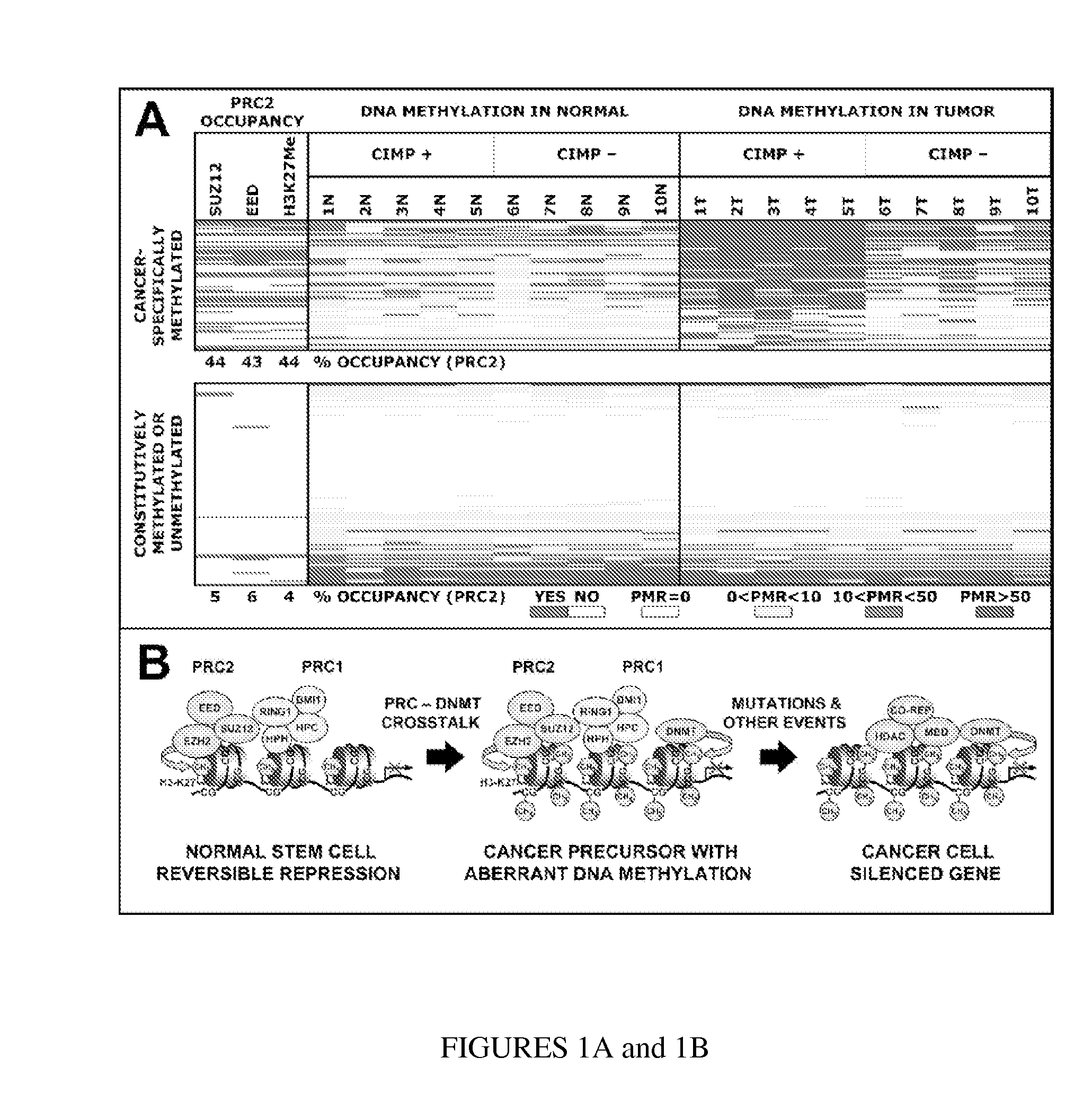
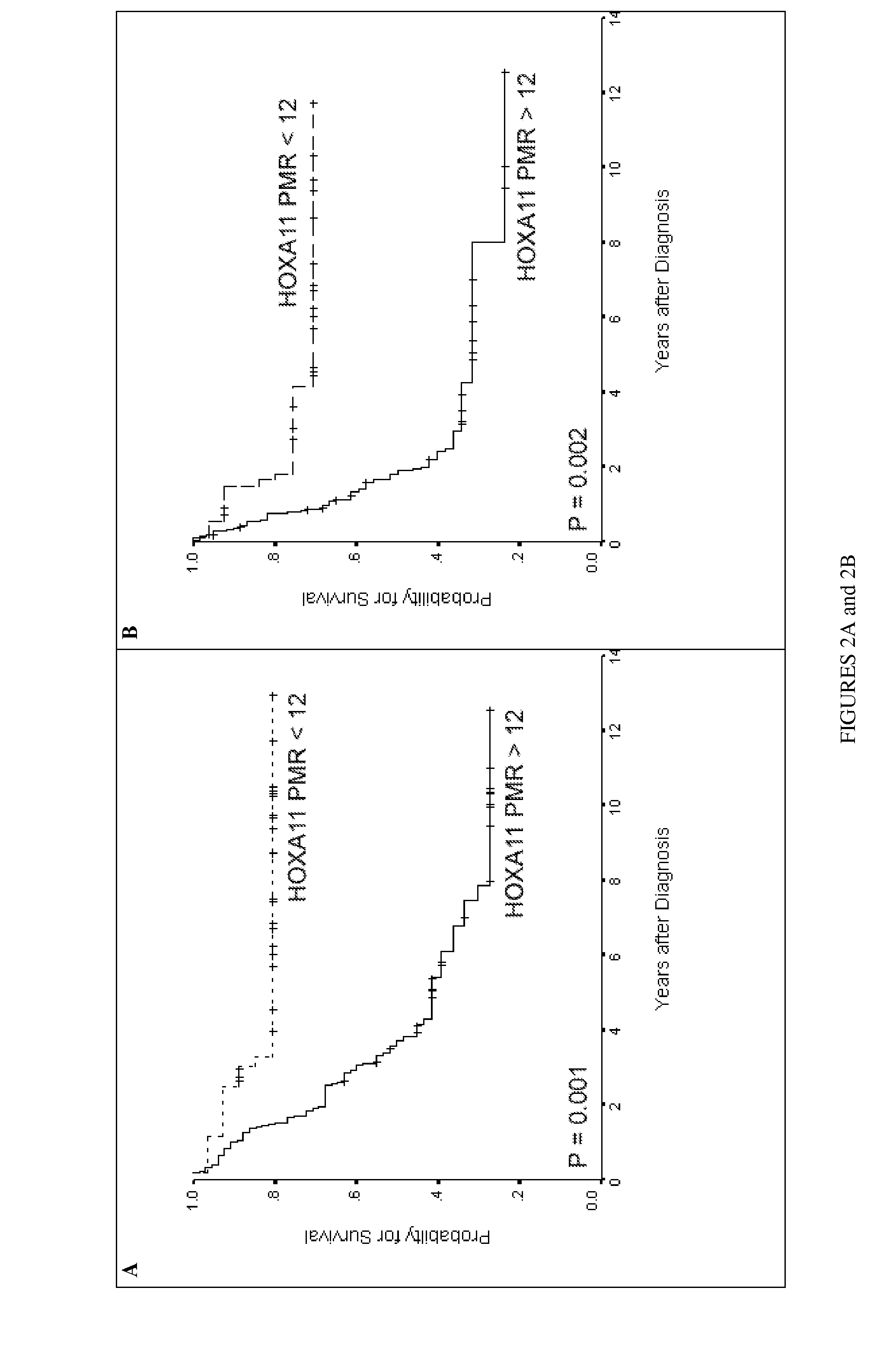
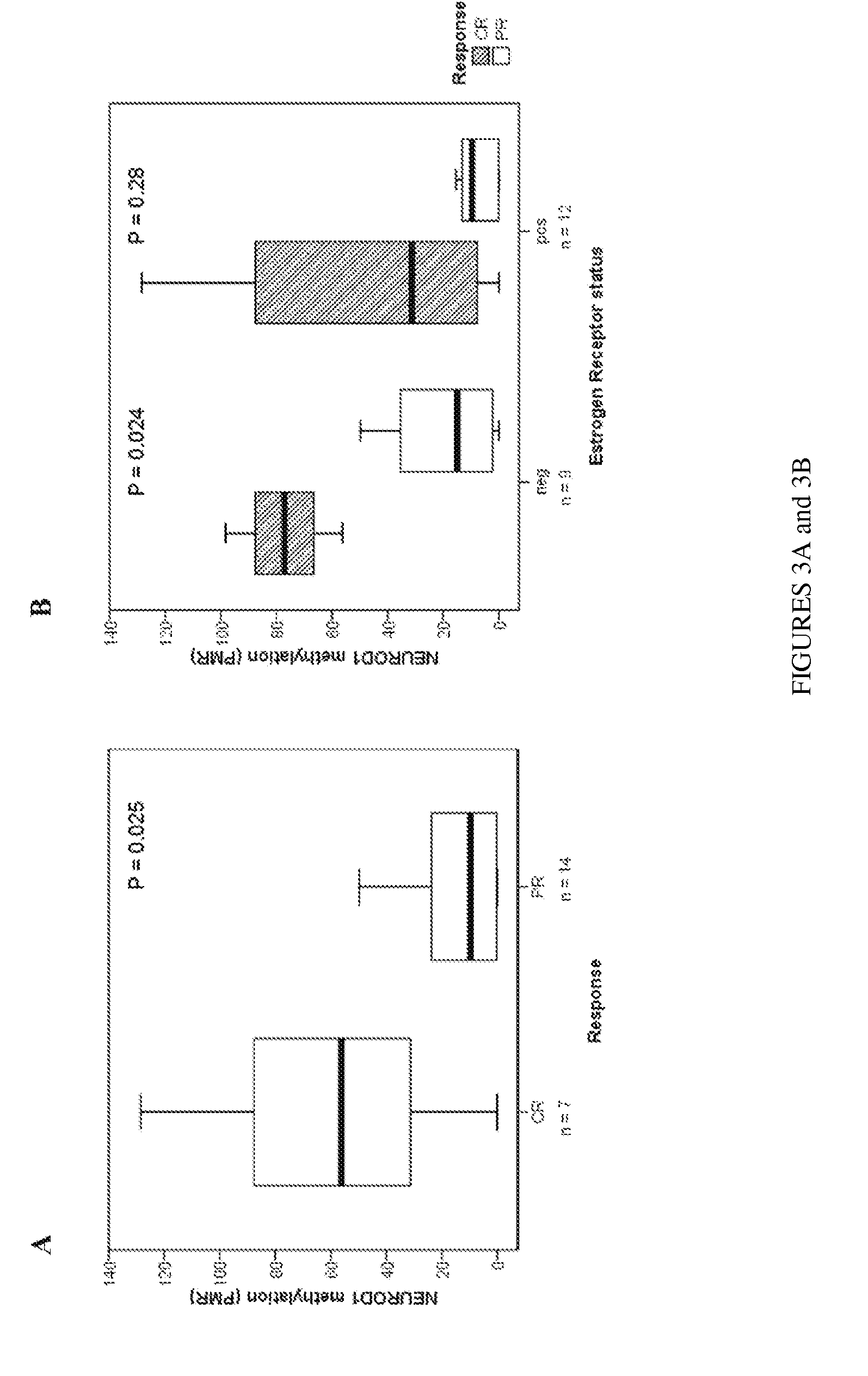
DNA methylation markers based on epigenetic stem cell signatures in cancer
ActiveUS20100172880A1Guaranteed maximum utilizationPoor outcomeBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationNon targeted
In particular aspects, stem-cell polycomb group (PcG) targets are more likely to have cancer-specific promoter DNA methylation than non-targets, indicating a stem-cell origin of cancer, where reversible gene repression is replaced by permanent silencing, locking the cell into a perpetual state of self-renewal and predisposition to subsequent malignant transformation. Exemplary aspects provide methods for identifying preferred DNA methylation markers for a cellular proliferative disorder and / or cancer and markers for developmental lineages and / or stages, based on identifying PcG protein or PcG repressive complex genomic target loci within a precursor cell (e.g., stem or progenitor cell) population, and determining, in cells of the proliferative disorder and / or cancer or cell of the particular developmental lineages and / or stages, a characteristic methylation status of the PcG target loci. Additional aspects provide methods for validating and / or monitoring a precursor cell (e.g., stem cell) population. Diagnostic and prognostic methods for ovarian and breast cancer are provided.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
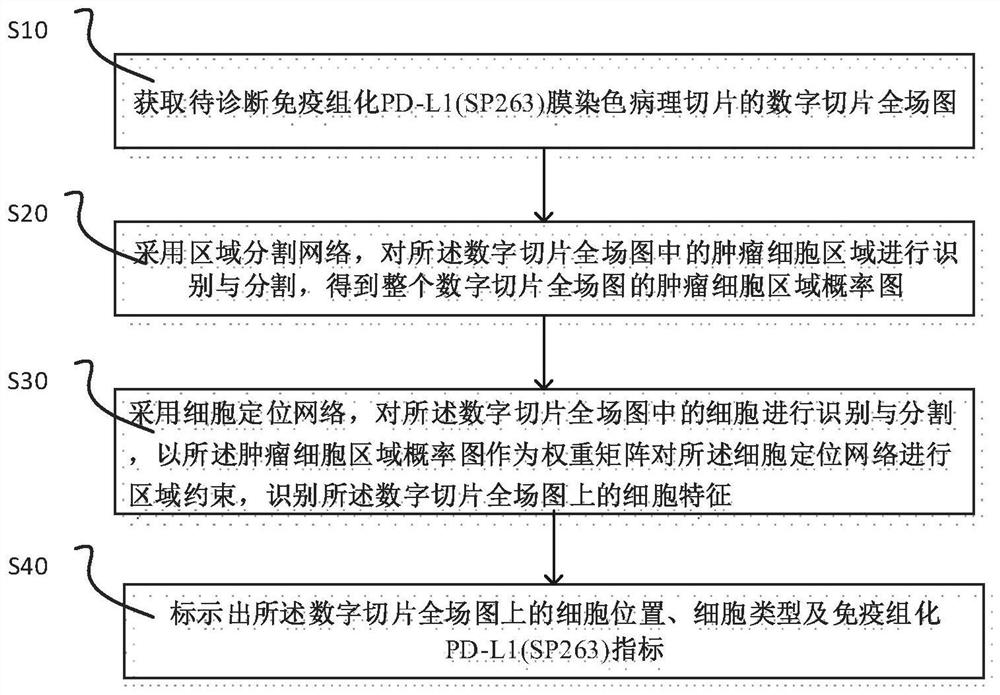
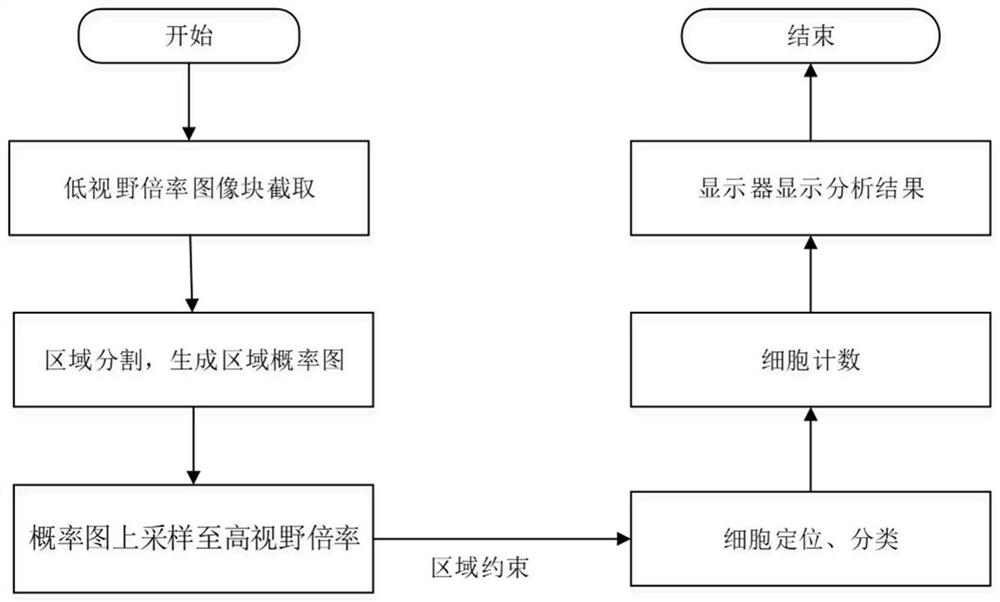
Immunohistochemical PD-L1 membrane staining pathological section image processing method, device and equipment
The invention relates to an immunohistochemical PD-L1 membrane staining pathological section image processing method, device and equipment. The image processing method comprises the following steps: acquiring a digital section full-field image of a to-be-diagnosed immunohistochemical PD-L1 (SP263) membrane staining pathological section; adopting a region segmentation network to identify and segment a tumor cell region in the digital slice full-field image under the first visual field multiplying power to obtain a tumor cell region probability graph of the whole digital slice full-field image;identifying and segmenting cells in each digital slice full-field graph, taking the tumor cell region probability graph as a weight matrix to carry out region constraint on the cell positioning network, identifying cell characteristics on the digital slice full-field graph, and positioning and classifying various cells on the digital slice full-field graph; and marking the cell position, the celltype and the immunohistochemical PD-L1 (SP263) index on the full-field diagram of the digital slice. By designing a multi-level feature collaborative diagnosis strategy, the tumor proportion score isaccurately evaluated in a mode of constraining cell features by using regional features.
Owner:杭州迪英加科技有限公司 +1
Methods and products for biasing cellular development
Methods are described that bias cells, such as potent and multipotent stem cells, by transfection with a nucleic acid sequence, to differentiate to a desired end-stage cell or a cell having characteristics of a desired end-stage cell. In particular embodiments, human neural stem cells are transfected with vectors comprising genes in the homeobox family of transcription factor developmental control genes, and this results in a greater percentage of resultant transformed cells, or their progeny, differentiating into a desired end-stage cell or a cell having characteristics of a desired end-stage cell.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Optical cytometry
The present invention provides optical systems and methods for determining a characteristic of a cell, such as cell type, cellular response to a biochemical event, biological state and the like. The methods typically involve using interferometry to observe membrane properties in a cell and then use this information to determine one or more characteristics of a cell. The methods of the invention are useful for applications such as drug screening as well as diagnostic techniques.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
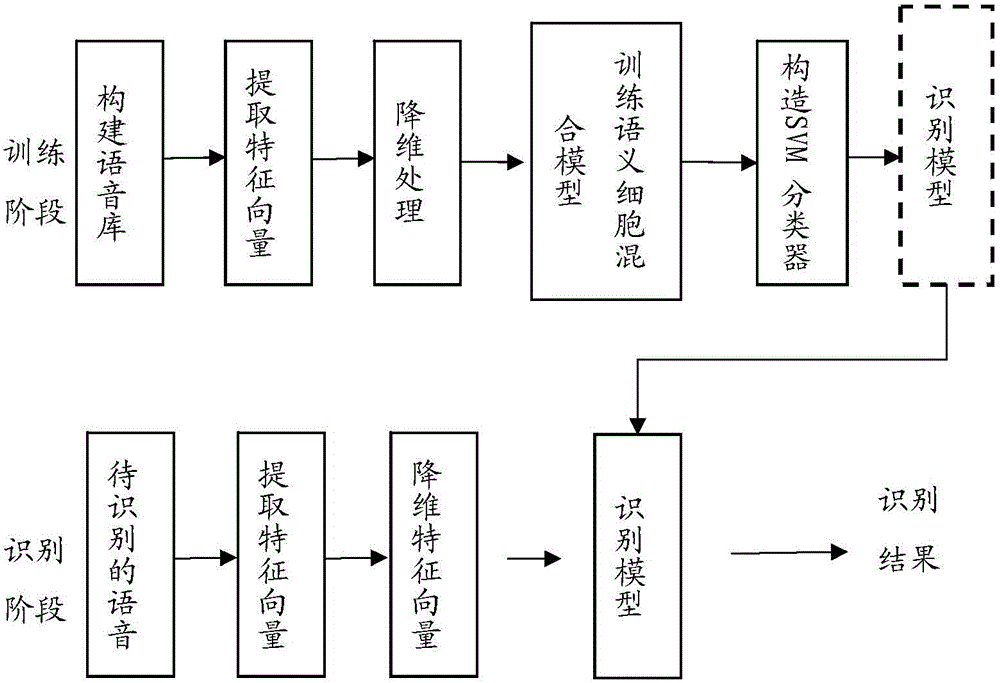
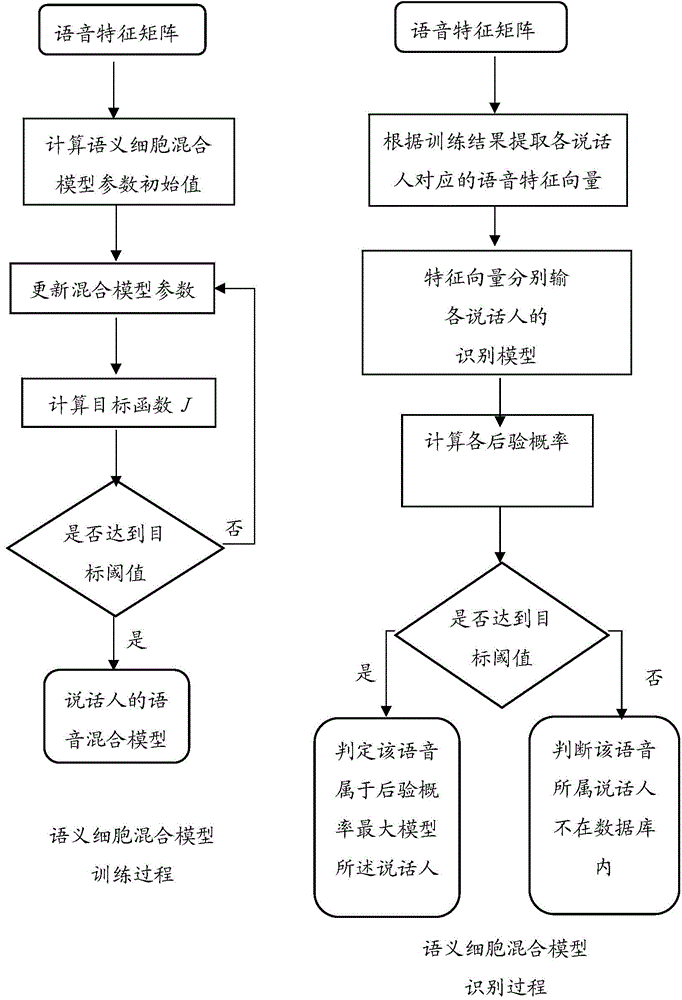
Speaker recognition method based on semantic cell mixing model
InactiveCN104538036ASolve the problem of untargeted optimizationSave spaceSpeech analysisFeature vectorDimensionality reduction
The invention discloses a speaker recognition method based on a semantic cell mixing model. The method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a voice library, wherein the voice library comprises multiple voice signals of multiple speakers; (2) preprocessing each voice signal in the voice library, extracting the voice characteristics, thereby obtaining each feature vector of each person; (3) performing dimensionality reduction on the feature vector so as to obtain a dimensionality reduction feature vector based on a semantic cell feature selection method, and training the semantic cell mixing model; (4) constructing an SVM classifier of each speaker by using a kernel function based on the semantic cell mixing model, and training a recognition model of the SVM classifier; and (5) recognizing the unknown speaker by utilizing the recognition model. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the problem that the kernel function of the conventional SVM model does not perform targeted optimization on a specific speaker, and when voice features used for a training classifier are selected, the method has high targeting property compared with the conventional common method, and the needed space for storing the model can be reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
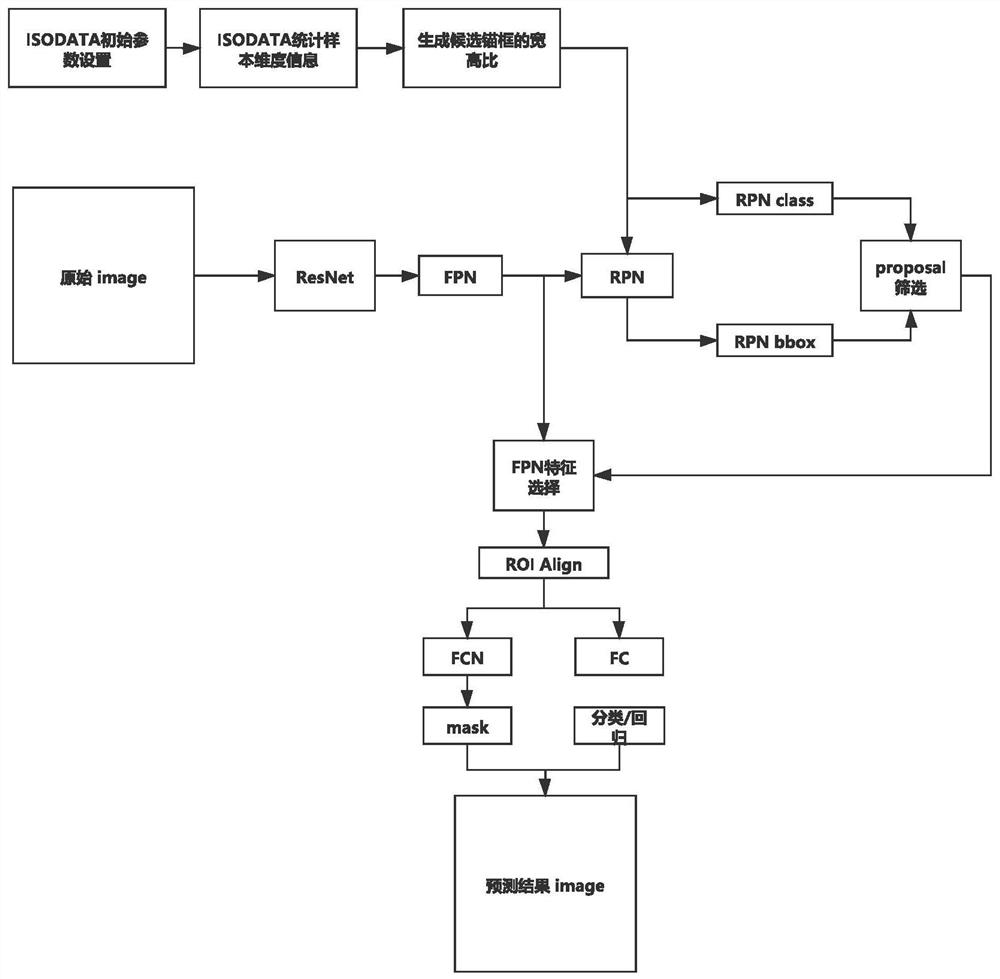
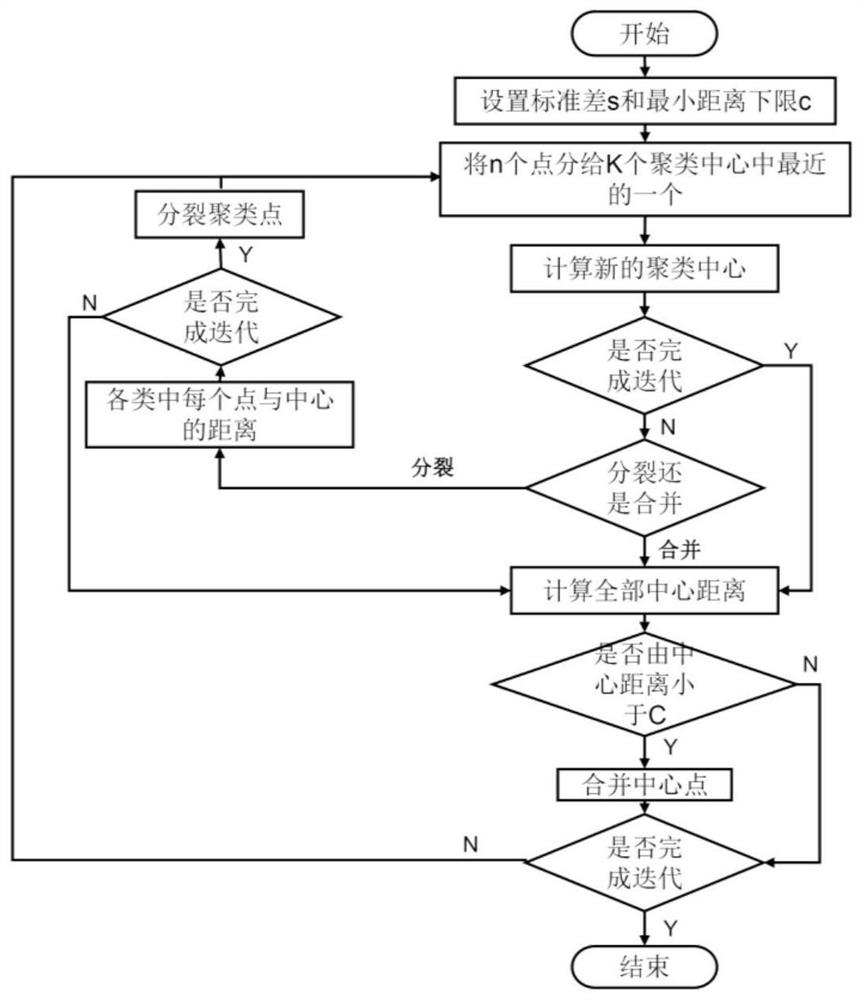
Cell image detection and segmentation method for generating candidate anchor boxes based on clustering
PendingCN111666850AAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsNeural architecturesCluster algorithmCancer cell
The invention discloses a cell image detection and segmentation method for generating candidate anchor boxes based on clustering. The cell image detection and segmentation method comprises the following steps: step 1, making a data set; step 2, data set sample dimension feature statistics: setting ISODATA clustering algorithm initial parameters, performing statistics on sample dimension information through a clustering algorithm, and generating a sample dimension proportion; step 3, cell feature extraction and fusion, including the following steps: 3.1, building a feature extraction network; 3.2, performing feature multi-scale fusion; step 4, generating a cancer cell target area candidate box, and sending the fused features and the target sample dimension proportion into an RPN network togenerate a target area; step 5, refining a detection target result of the cancer cell image; and step 6, segmentation Mask generation of the cancer cell image. According to the cell image detection and segmentation method, the generated candidate anchor boxes are enabled to better fit a real sample dimension rule; the difficulty of candidate box regression is reduced; the algorithm regression speed is improved; and the detection and segmentation performance is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Electroporative flow cytometry
InactiveUS20100221769A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiomechanicsElectroporation
Novel devices and methods are provided, which include electroporative flow cytometry, where electroporation is combined with flow cytometry. The devices and methods can be used for the detection a variety of cellular features, including protein translocation, and for monitoring biomechanics at single cell level. Using the novel devices methods it is possible to observe the release of proteins such as intracellular kinases out of the cells during electroporation. Using the novel devices methods it is possible to study cytoskeleton dynamics and deformability at a single cell level, and to correlate these to diseases such as cancers.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
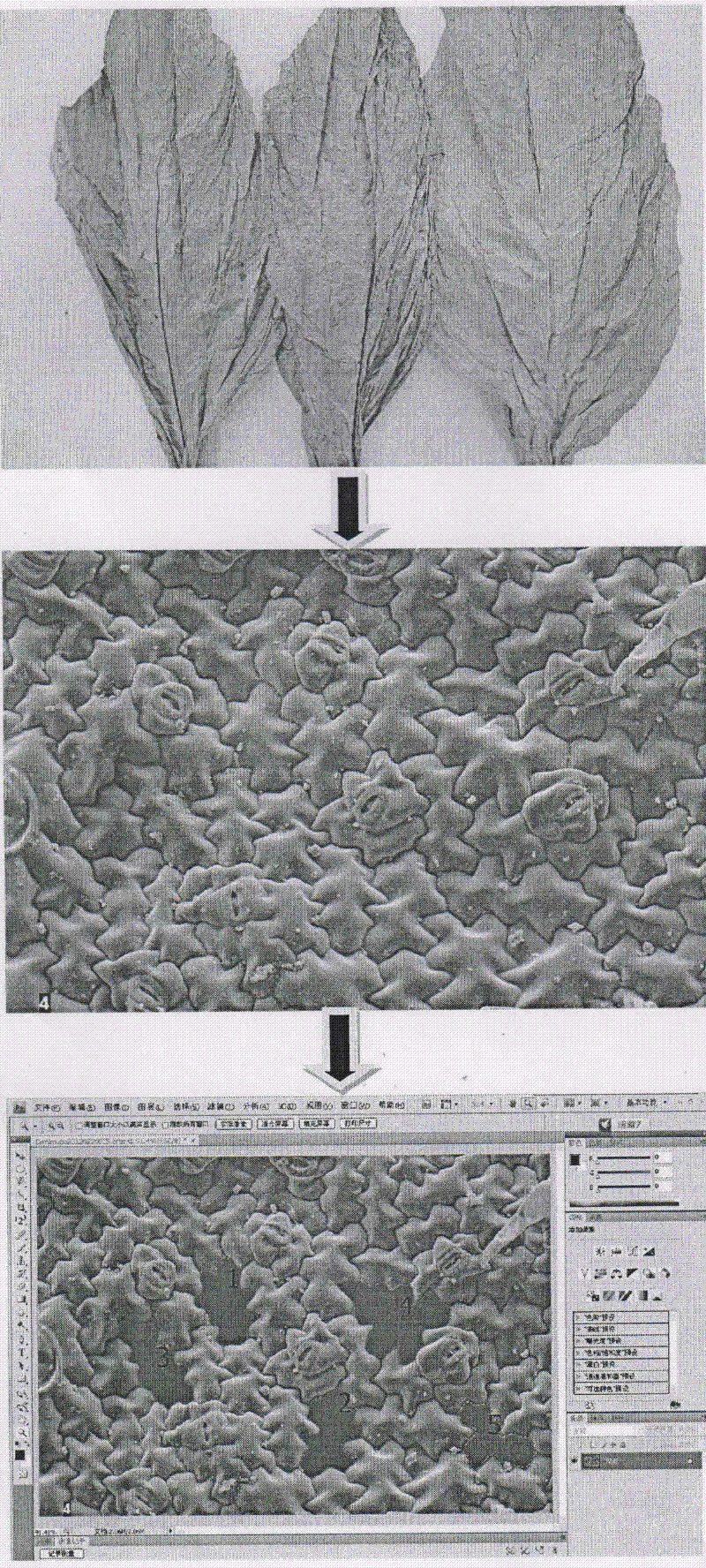
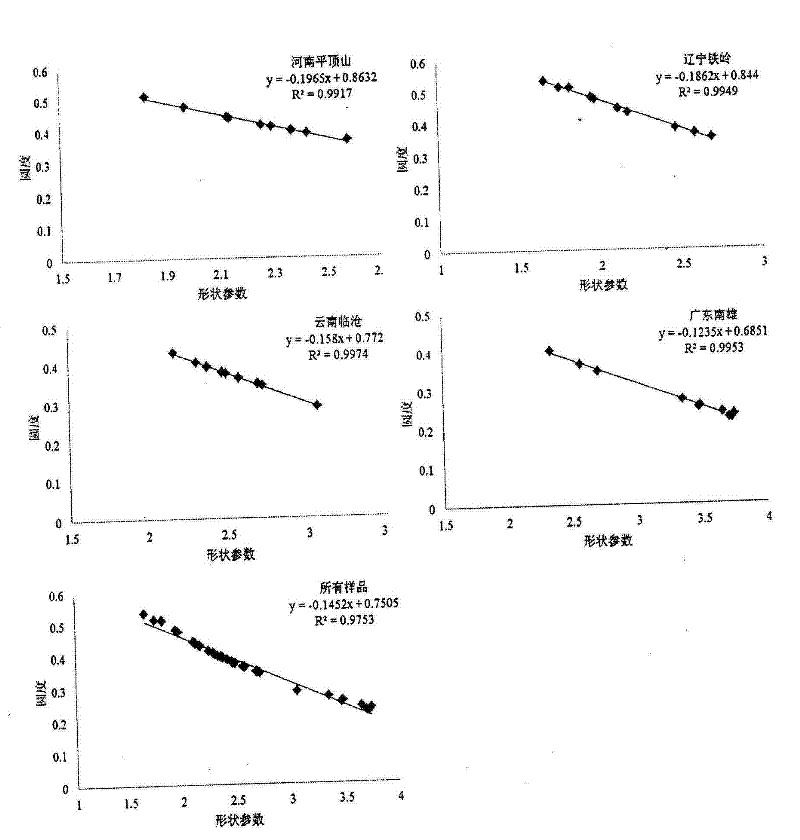
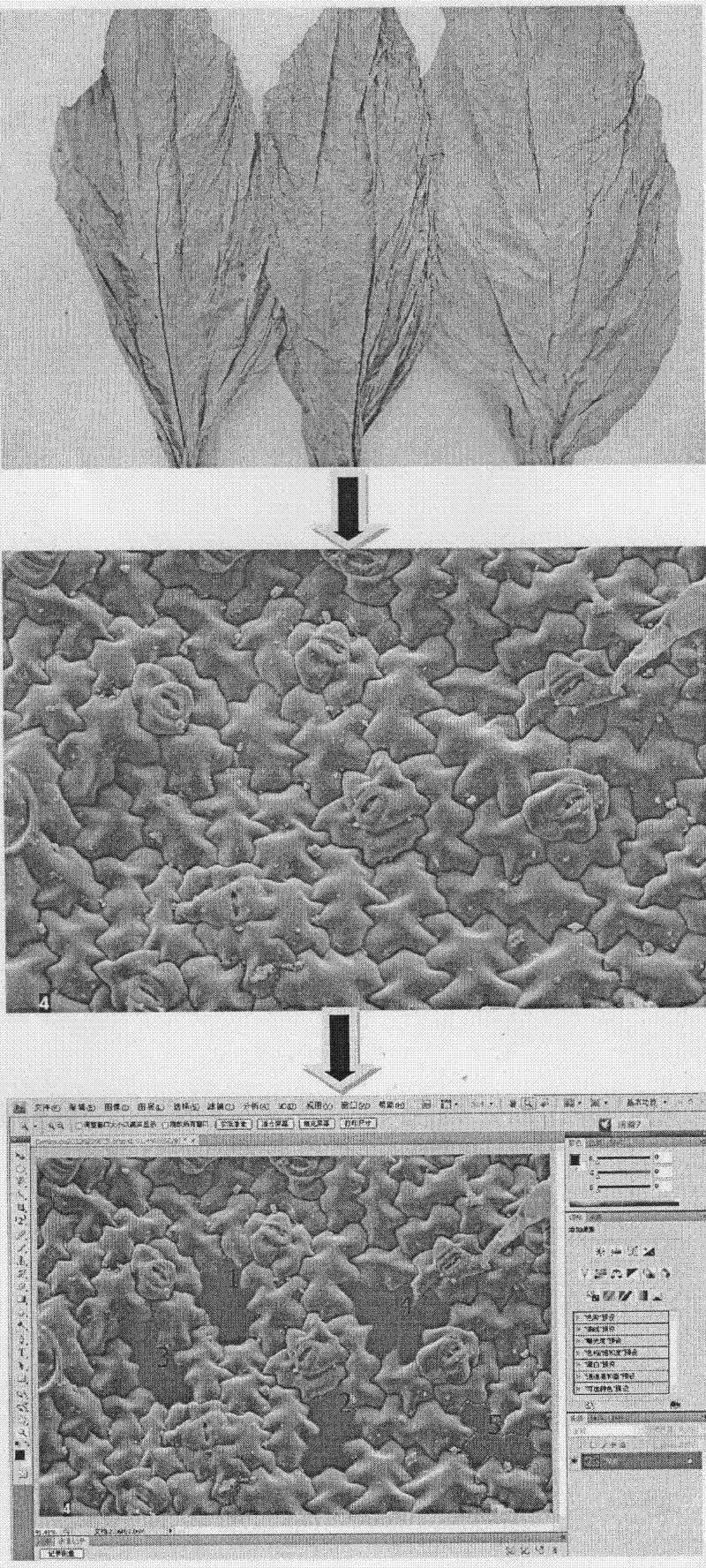
Method for quantificationally characterizing cell shape features of flue-cured tobacco leaves by utilizing Photoshop software
ActiveCN102645444AImprove Quantitative AccuracyImage analysisMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionScanning electron microscopePaintbrush
The invention relates to a method for quantificationally characterizing cell shape features of flue-cured tobacco leaves by utilizing Photoshop software, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: obtaining a surface cell feature image of the preliminarily-flue-cured tobacco leaves through a scanning electron microscope, accurately selecting cells by utilizing a magnetic lasso, a matte, a paintbrush, an eraser and other tools, respectively and quantificationally obtaining the cell circumference and the cell area by using a unit pixel length*number of pixels and pixel percentage*image area method, calculating shape feature parameters through taking the circumference and the area as variables by utilizing a formula to provide a method for objectively evaluating the cell development situations of the tobacco leaves and researching the quality features of the tobacco leaves from the microscopic field. Measurement results of a plurality of cells randomly selected from different places of origin show that the method is high in accuracy and high in fitting degree of the calculated cell shape feature parameters with software-defined roundness values (R2 is equal to 0.98-0.99), and meanwhile, the cell shape features (quality features) of the tobacco leaves from the different places of origin can be better distinguished.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Apparatus, method, and system for image-based human embryo cell classification
Apparatuses, methods, and systems for automated cell classification, embryo ranking, and / or embryo categorization are provided. An apparatus includes a classification module configured to apply classifiers to images of one or more cells to determine, for each image, a classification probability associated with each classifier. Each classifier is associated with a distinct first number of cells, and is configured to determine the classification probability for each image based on cell features including one or more machine learned cell features. The classification probability indicates an estimated likelihood that the distinct first number of cells is shown in each image. The classification module is further configured to classify each image as showing a second number of cells based on the distinct first number of cells and the classification probabilities associated therewith. The classification module is implemented in at least one of a memory or a processing device.
Owner:ARES TRADING SA
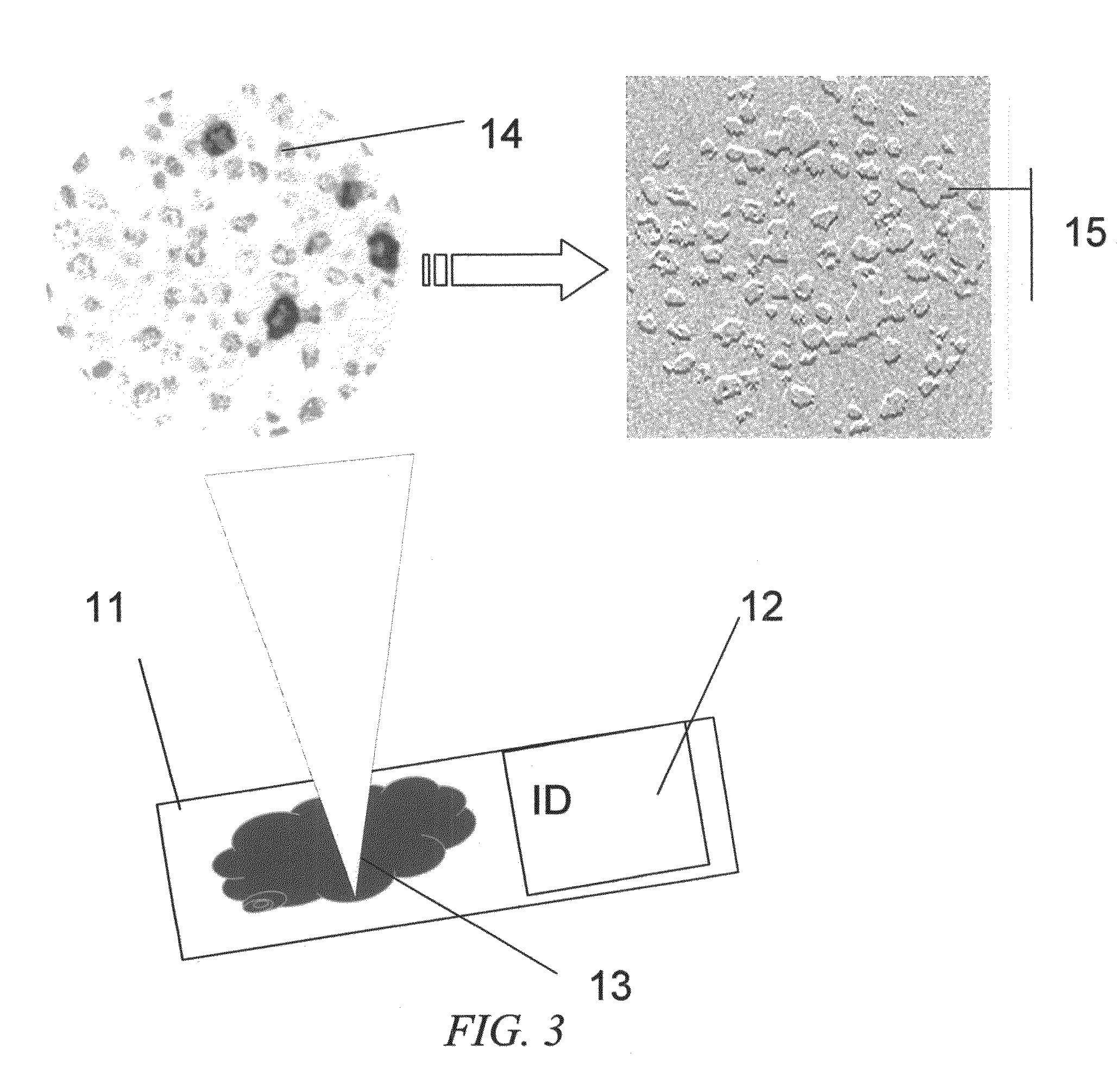
Cell Feature Extraction and Labeling Thereof
ActiveUS20100329538A1Reduce loadEstimation process is improvedImage enhancementImage analysisMeasurement pointCell feature
Owner:TWIN COAST METROLOGY
Slow characteristic based cell division recognition method and recognition device thereof
ActiveCN105303169AAccurate descriptionReduce difficultyCharacter and pattern recognitionCell divisionIdentification device
The invention discloses a slow characteristic based cell division recognition method and a recognition device thereof. The method comprises the steps of extracting cell data by adopting a mode of unsupervised slow characteristic analysis so as to acquire a slow characteristic function; solving an accumulative square offset characteristic of the cell slow characteristic, and acquiring arrangement of variation rates of the slow characteristic from small to large; carrying out detection on the final accumulative square offset characteristic by using a method of model learning, and acquiring the probability of containing mitosis in the variation process of the cell data along with the time, wherein the test data contains mitosis if an output category label is 1, and the test data does not contain mitosis if the output category label is 0. The device comprises a first acquisition module, a second acquisition module, a third acquisition module and an output module. According to the invention, the difficulty of cell characteristic extraction is reduced, and the accuracy of cell characteristic extraction is improved, thereby providing good conditions for subsequent recognition and classification for dividing cells, and being convenient for recognition tracking and processing of the cells.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com