Patents
Literature
191 results about "Fed-batch culture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
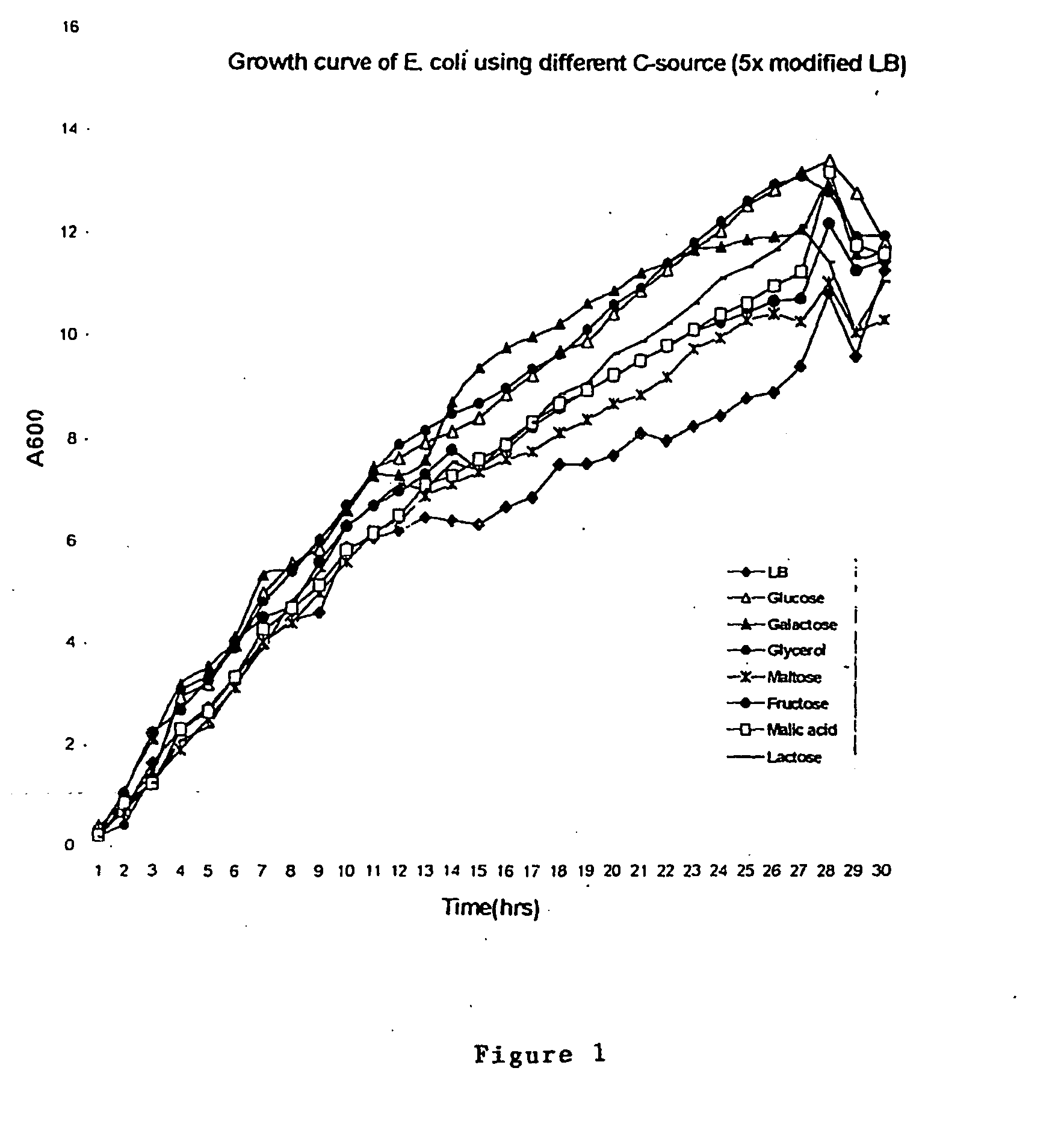
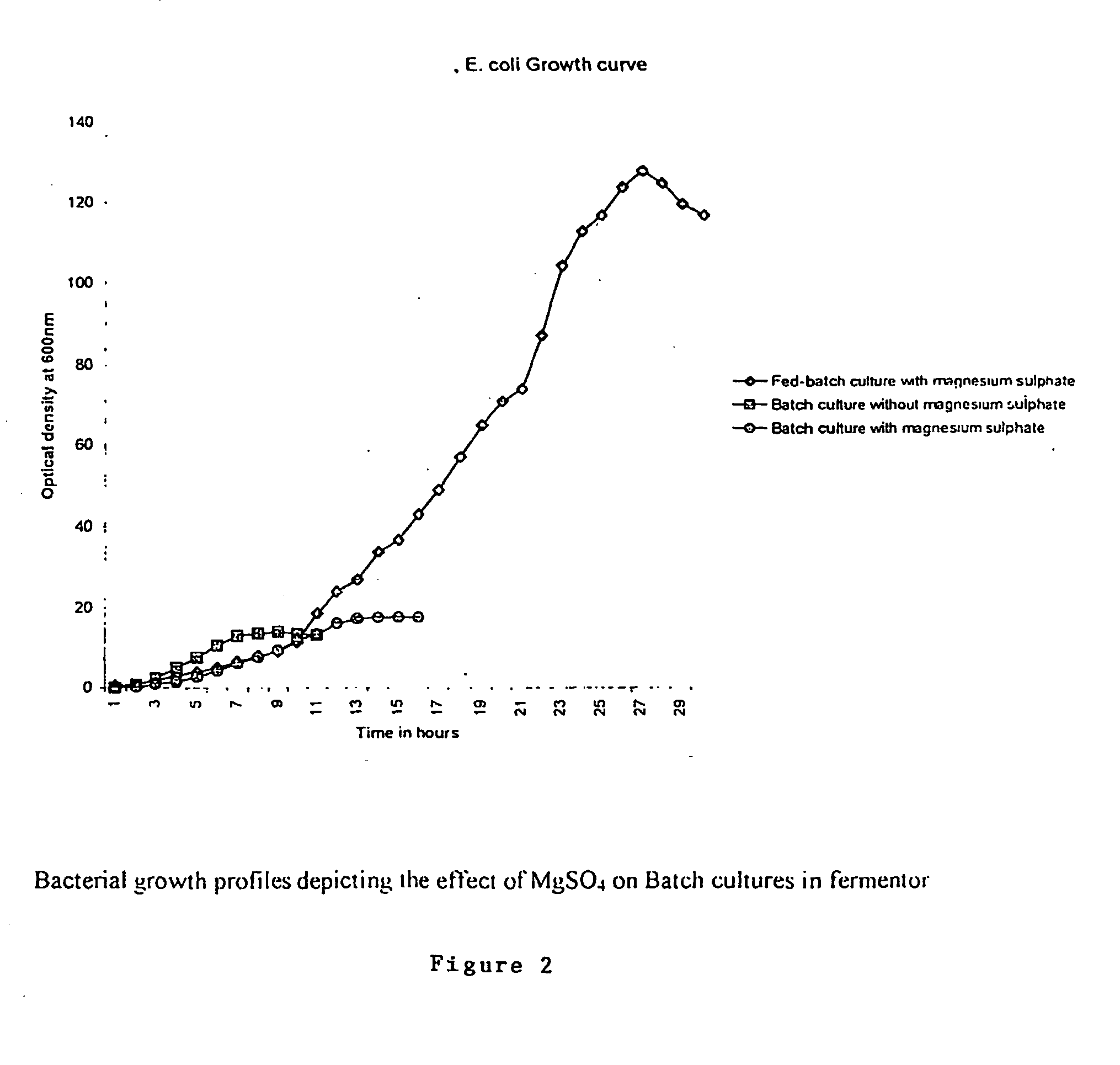
Fed-batch culture is, in the broadest sense, defined as an operational technique in biotechnological processes where one or more nutrients (substrates) are fed (supplied) to the bioreactor during cultivation and in which the product(s) remain in the bioreactor until the end of the run. An alternative description of the method is that of a culture in which "a base medium supports initial cell culture and a feed medium is added to prevent nutrient depletion". It is also a type of semi-batch culture. In some cases, all the nutrients are fed into the bioreactor. The advantage of the fed-batch culture is that one can control concentration of fed-substrate in the culture liquid at arbitrarily desired levels (in many cases, at low levels).
Use of perfusion to enhance production of fed-batch cell culture in bioreactors
InactiveUS20090042253A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFiltrationFeed pump
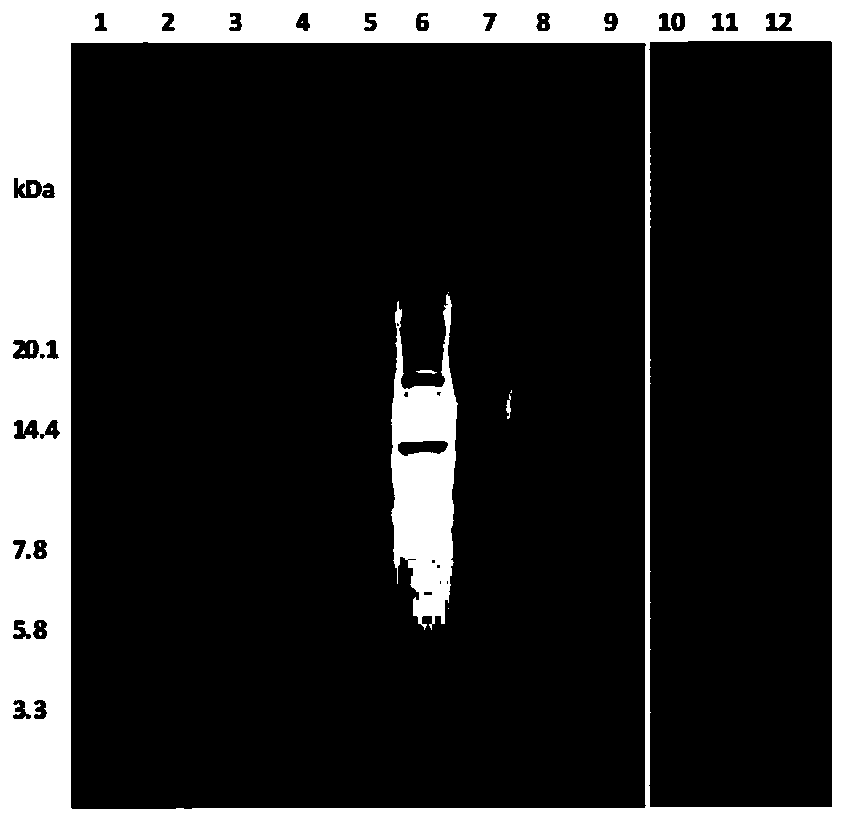
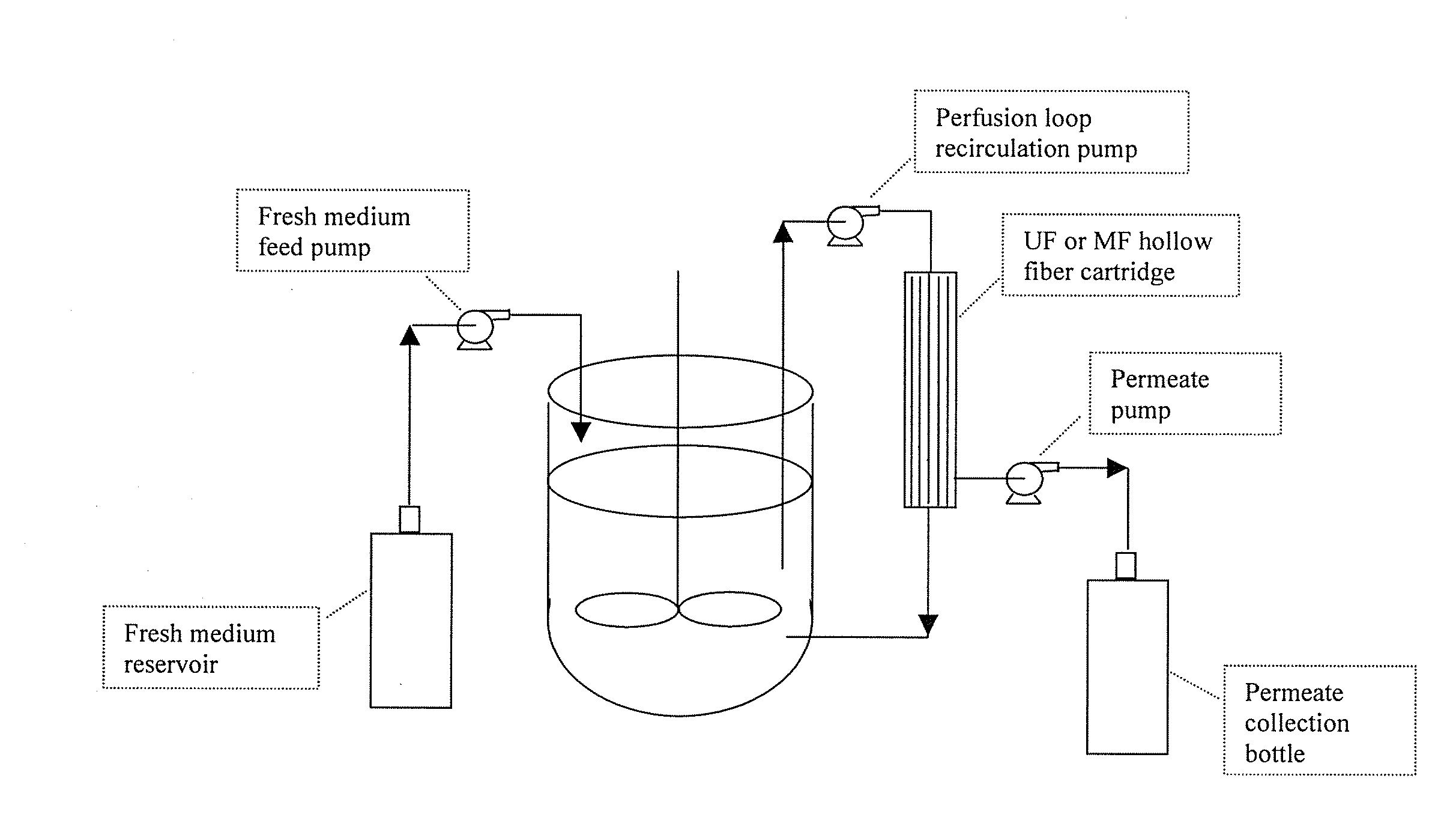
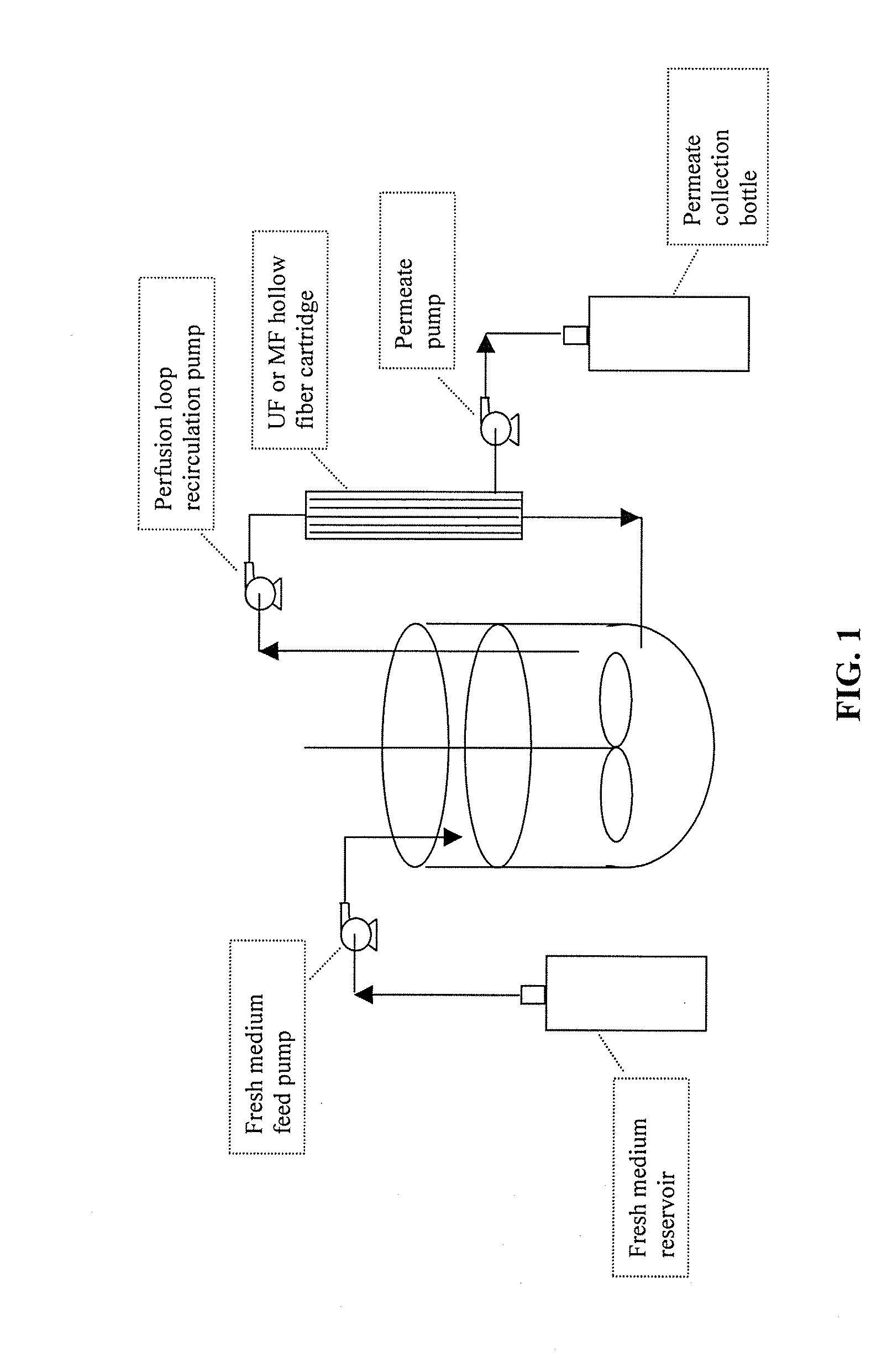
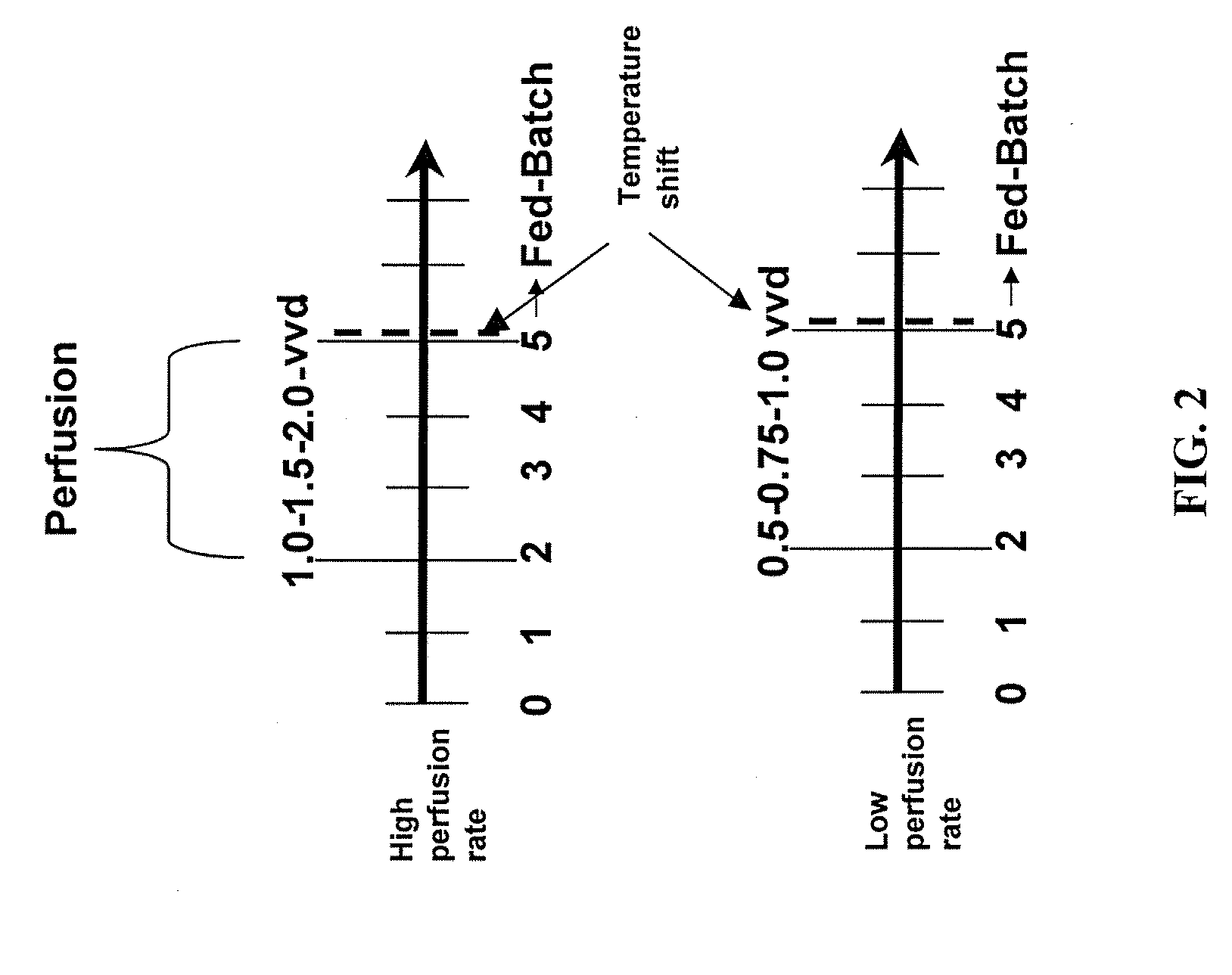
The invention relates to methods of improving protein production, e.g., large-scale commercial protein production, e.g., antibody production, utilizing a modified fed-batch cell culture method comprising a cell growth phase and a polypeptide production phase. The modified fed-batch cell culture method combines both cell culture perfusion and fed-batch methods to achieve higher titers of polypeptide products. Because the modified fed-batch cell culture method of the invention produces higher polypeptide product titers than fed-batch culture alone, it will substantially improve commercial-scale protein production. The invention also relates to a perfusion bioreactor apparatus comprising a fresh medium reservoir connected to a bioreactor by a feed pump, a recirculation loop connected to the bioreactor, wherein the recirculation loop comprises a filtration device, e.g., ultrafiltration or microfiltration, and a permeate pump connecting the filtration device to a permeate collection container.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Nonlinear Model Predictive Control of a Biofuel Fermentation Process
ActiveUS20080167852A1Maximizing yeast growthMaximize productionBiological substance pretreatmentsTemperatue controlBiotechnologyLinear control
System and method for managing batch fermentation in a biofuel production process. A nonlinear control model of yeast growth and fermentable sugar concentration for biofuel (e.g., fuel ethanol) production in a batch fermentation process (pure and / or fed-batch fermentation) of a biofuel production process is provided. Process information for the batch fermentation process is received, and the nonlinear control model executed using the process information as input to determine values of one or more fermentation process variables for the batch fermentation process, e.g., fermentation temperature and / or enzyme flow, for substantially maximizing yeast growth and achieving target fermentable sugar concentrations. The batch fermentation process is then controlled in accordance with the determined values for the one or more fermentation process variables to substantially maximize yeast growth and achieve target fermentable sugar concentrations, where substantially maximizing yeast growth and achieving target fermentable sugar concentrations substantially maximizes biofuel production in the batch fermentation process.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
High cell density process for growth of Listeria
InactiveUS20060121053A1Increase productionIncrease costAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAntigenHigh cell
The present invention relates to fed batch culture methods for high cell density growth of Listeria which produce cultures having an OD600 greater than about 2.2 or higher. In particular, the invention provides methods for high cell density growth of Listeria comprising growth in a pH controlled bioreactor and, optionally, the gradual addition of a carbon source, e.g., glucose, with or without one or more additional nutrients, e.g., vitamins, when growth in the initial culture is nearly complete or complete. In one embodiment, the methods of the invention are used to produce Listeria-based compositions, e.g., vaccines comprising Listeria that express a tumor-associated antigen, e.g., an EphA2 antigenic peptide, for eliciting an immune response against hyperproliferative cells.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
High-cell density fed-batch fermentation process for producing recombinant protein
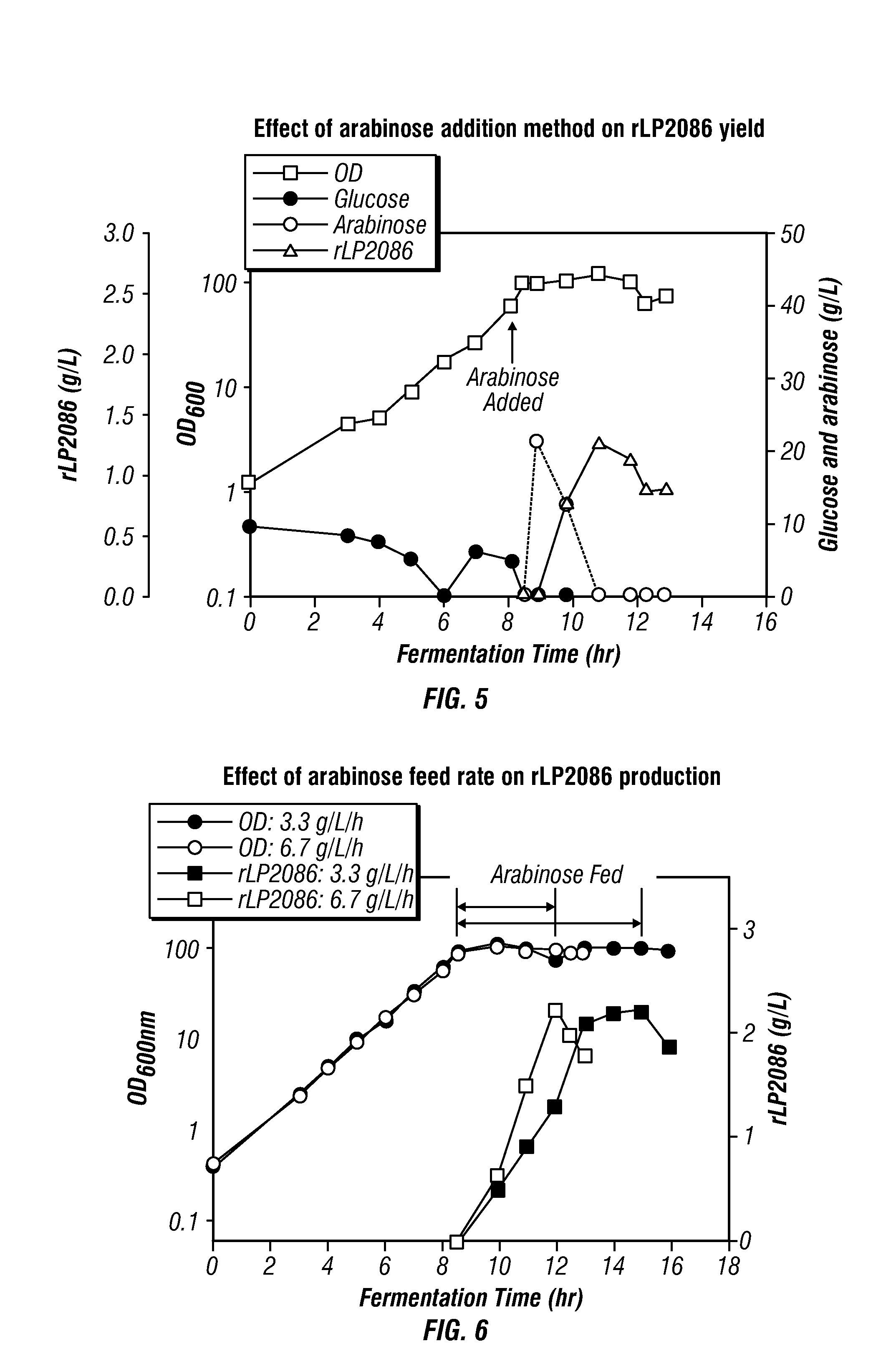
Methods for producing proteins, for example, recombinant meningococcal 2086 proteins, using fed-batch fermentation with continuous input of an inducer after achieving a threshold parameter, and optionally continuous input of a carbon source, for example, a constant rate input, to improve protein yields, as well as high density protein compositions and compositions for use in the methods of the present invention, are provided.
Owner:WYETH LLC
IL-21 production in prokaryotic hosts
The expression vectors and methods using an E. coli expression system for the large scale production of IL-21 are described. The vectors utilize the IL-21 coding sequence with specific changes in nucleotides in order to optimize codons and mRNA secondary structure for translation in E. coli. Using the expression vectors, the IL-21 gene was produced in E. coli to a level of greater than 1 g / L in fed batch fermentation. Also included are OmpT deficient E. coli strains transformed with an IL-21 expression vector.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
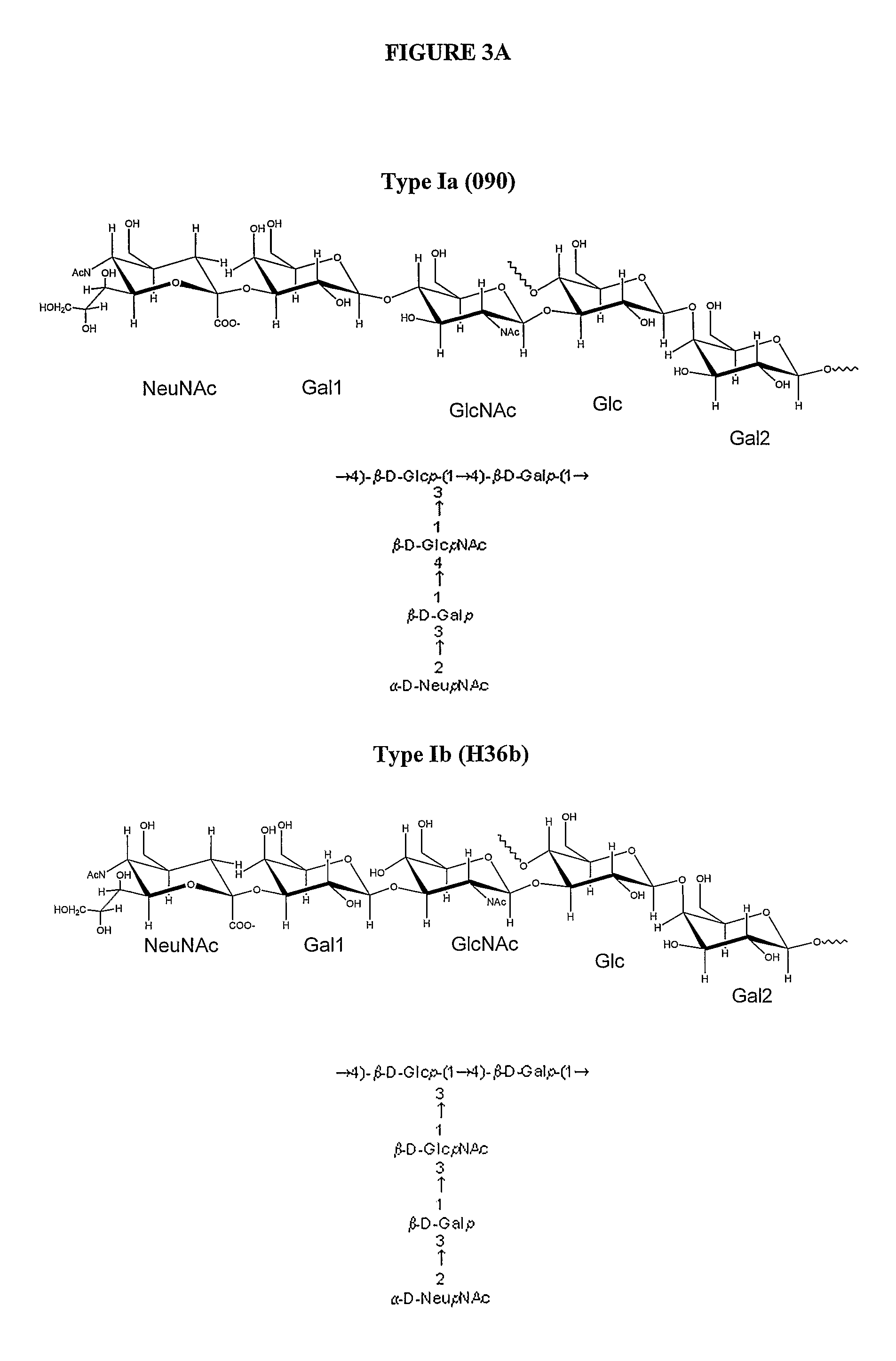
Preparation method of 3'-sialic acid lactose
InactiveCN102154163AChange the status quo of less ingredientsEfficient additionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliSialic acid
The invention provides a preparation method of 3'-sialic acid lactose, belonging to the technical field of biological engineering. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: taking colibacillus CCTCC (colibacillus China center for type culture collection) NO: M208088 as a starting strain, adding a fermentation medium into a fermentation tank, fermenting for 2-6h, then adding a fed batch culture medium, and adding lactose in a flowing way at the mid-later period of the fermentation; and centrifuging the fermentation liquid to obtain liquid supernatant 1 and a thallus, diluting the centrifuged thallus by adding water and splitting in a heating way, recentrifuging to obtain liquid supernatant 2, merging the liquid supernatant 1 and the liquid supernatant 2, and absorbing, desorbing and vacuum drying by ion exchange resin to obtain the 3'-sialic acid lactose. A mass of the 3'-sialic acid lactose can be prepared by the CCTCC NO: M208088. The 3'-sialic acid lactose can change the current situation that the sialyloligosaccharide component is less in exogenous adding substances in conventional baby milk, and can provide the guarantee to add more efficient sialic acid trophic factors into the baby milk.
Owner:朱莉
Method for efficiently producing cellulase
InactiveCN101735993AIncrease vitalityPromote formationMicroorganism based processesEnzymesMetaboliteSugar
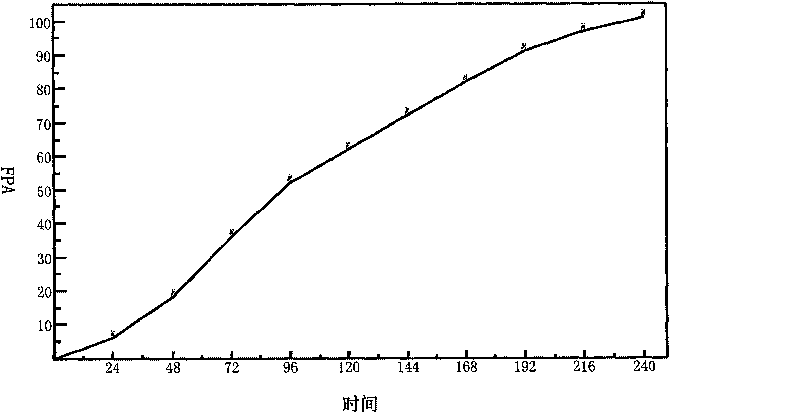
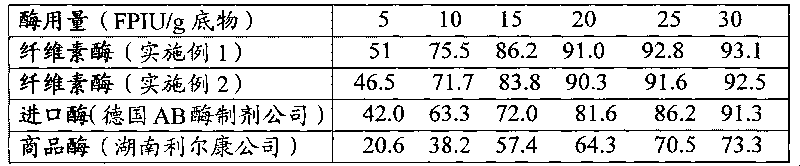
The invention provides a method for producing cellulase, which comprises the following steps of: inoculating Trichoderma reesei to a fermentation medium; fermenting for 60 to 90 hours, and then starting feed-batch culture; feeding a culture medium when a pH value of a fermentation liquor is more than 4.8 in the process of the feed-batch culture; stopping feeding the culture medium when the pH value of the fermentation liquor is less than 4.5; and stopping fermenting when the total fermentation time reaches 192 to 240 hours. The method integrates an insoluble carbon source and a soluble carbon source to collaboratively induce expression of cellulase genes. The method achieves coordinated balance in the process of growing strains and forming a target metabolic product through the feed-batch culture, solves the problems existing in the process for producing the cellulase by merely taking cellulose or soluble sugar as an inducer, effectively improves fermentation level of the cellulase; and the obtained cellulase has high degradation performance to cellulose substrates.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
FQ15 enterococcus faecalis and method for producing somatotrophic feed additive with the bacteria
The invention discloses an FQ15 enterococcus faecalis and a method of a feed additive which uses the bacteria production for promoting the growth: an MRS culture medium is taken as a seed culture medium, and the FQ15 enterococcus faecalis is cultured under the aerobic or facultative condition at 30 to 45 DEG C for 4 to 24 hours, so as to become a grade one seed; the grade one seed liquid is inoculated in a seed tank for amplification culture, the MRS culture medium is adopted as the seed culture medium, and the culture is carried out for 4 to 24 hours under the aerobic or the facultative condition at 30 to 45 DEG C to become a grade two seed; the grade two seed liquid is inoculated in a fermentation tank for fermentation culture, an improved MRS culture medium is adopted as the fermentation culture medium, and the culture is carried out for 8 to 36 hours by using timing or continuous fed-batch fermentation mode under the aerobic or the facultative condition at 30 to 45 DEG C; the obtained fermentation liquid is sub-packaged or the fermentation liquid which is obtained by step c is separated, 1 to 25 percent drying protector is added in the bacterial sludge, and the granulation at 20 - 80 DEG C, freeze-drying or spray drying are adopted. The invention has the advantages that the invention can substitute the feed antibiotics and improve the high efficient weight increase of livestock and poultry; the production process is simple; the cost is low, etc.
Owner:DALIAN SANYI ANIMAL MEDICINE CO LTD +2
Il-21 production in prokaryotic hosts
The expression vectors and methods using an E. coli expression system for the large scale production of IL-21 are described. The vectors utilize the IL-21 coding sequence with specific changes in nucleotides in order to optimize codons and mRNA secondary structure for translation in E. coli. Using the expression vectors, the IL-21 gene was produced in E. coli to a level of greater than 1 g / L in fed batch fermentation. Also included are OmpT deficient E. coli strains transformed with an IL-2 1 expression vector.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
Il-21 production in prokaryotic hosts
The expression vectors and methods using an E. coli expression system for the large scale production of IL-21 are described. The vectors utilize the IL-21 coding sequence with specific changes in nucleotides in order to optimize codons and mRNA secondary structure for translation in E. coli. Using the expression vectors, the IL-21 gene was produced in E. coli to a level of greater than 1 g / L in fed batch fermentation. Also included are OmpT deficient E. coli strains transformed with an IL-21 expression vector.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
Il-21 production in prokaryotic hosts
The expression vectors and methods using an E. coli expression system for the large scale production of IL-21 are described. The vectors utilize the IL-21 coding sequence with specific changes in nucleotides in order to optimize codons and mRNA secondary structure for translation in E. coli. Using the expression vectors, the IL-21 gene was produced in E. coli to a level of greater than 1 g / L in fed batch fermentation. Also included are OmpT deficient E. coli strains transformed with an IL-21 expression vector.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
FGF18 production in prokaryotic hosts
The expression vectors and methods using an E. coli expression system for the large scale production of FGF18 are described. The vectors utilize the FGF18 coding sequence with specific changes in nucleotides in order to optimize codons and mRNA secondary structure for translation in E. coli. Using the expression vectors, the FGF18 gene was produced in E. coli to a level of greater than 1 g / L in fed batch fermentation. Also included are OmpT deficient E. coli strains, as well as OmpT and fhuA negative strains transformed with an FGF18 expression vector.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
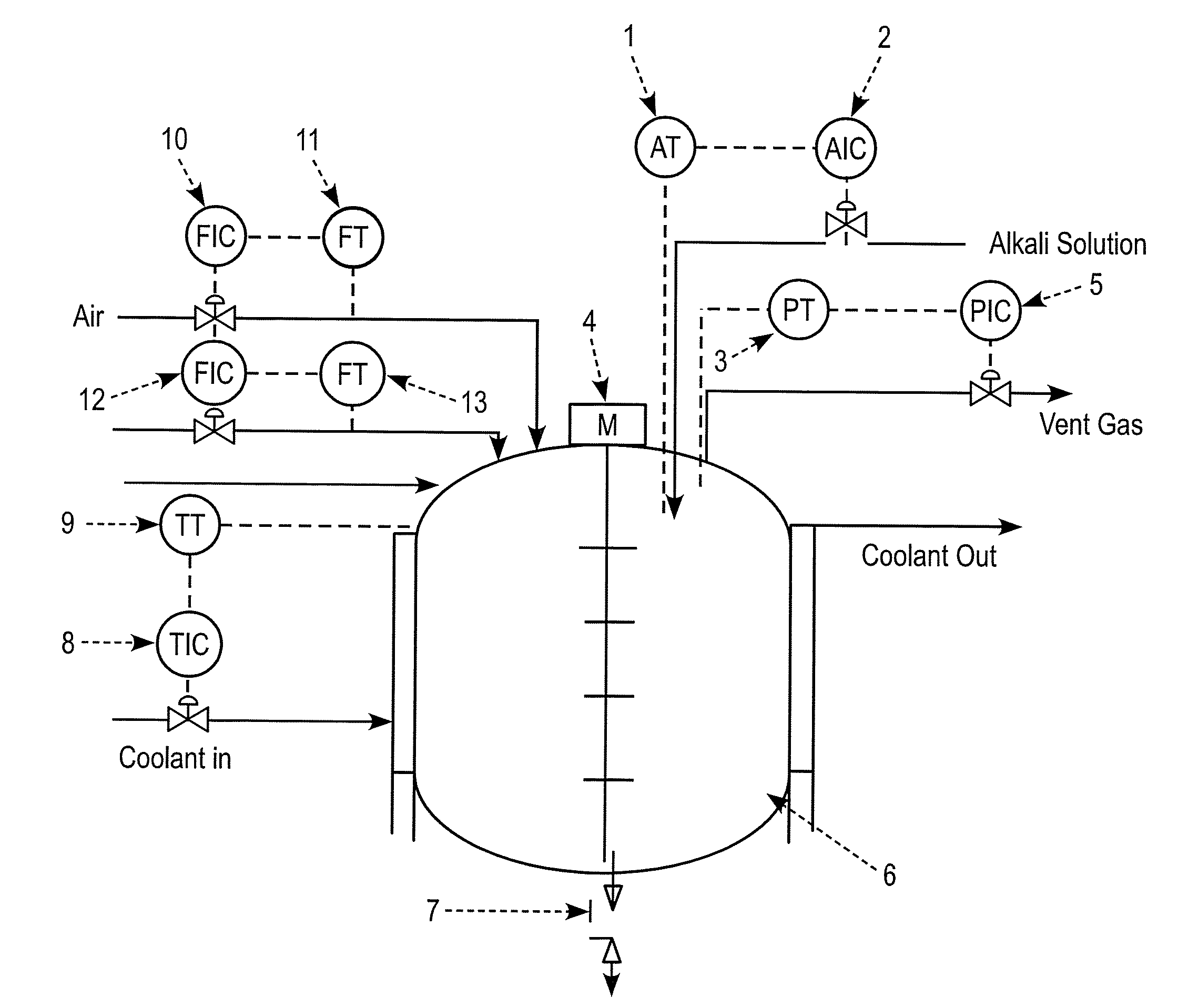
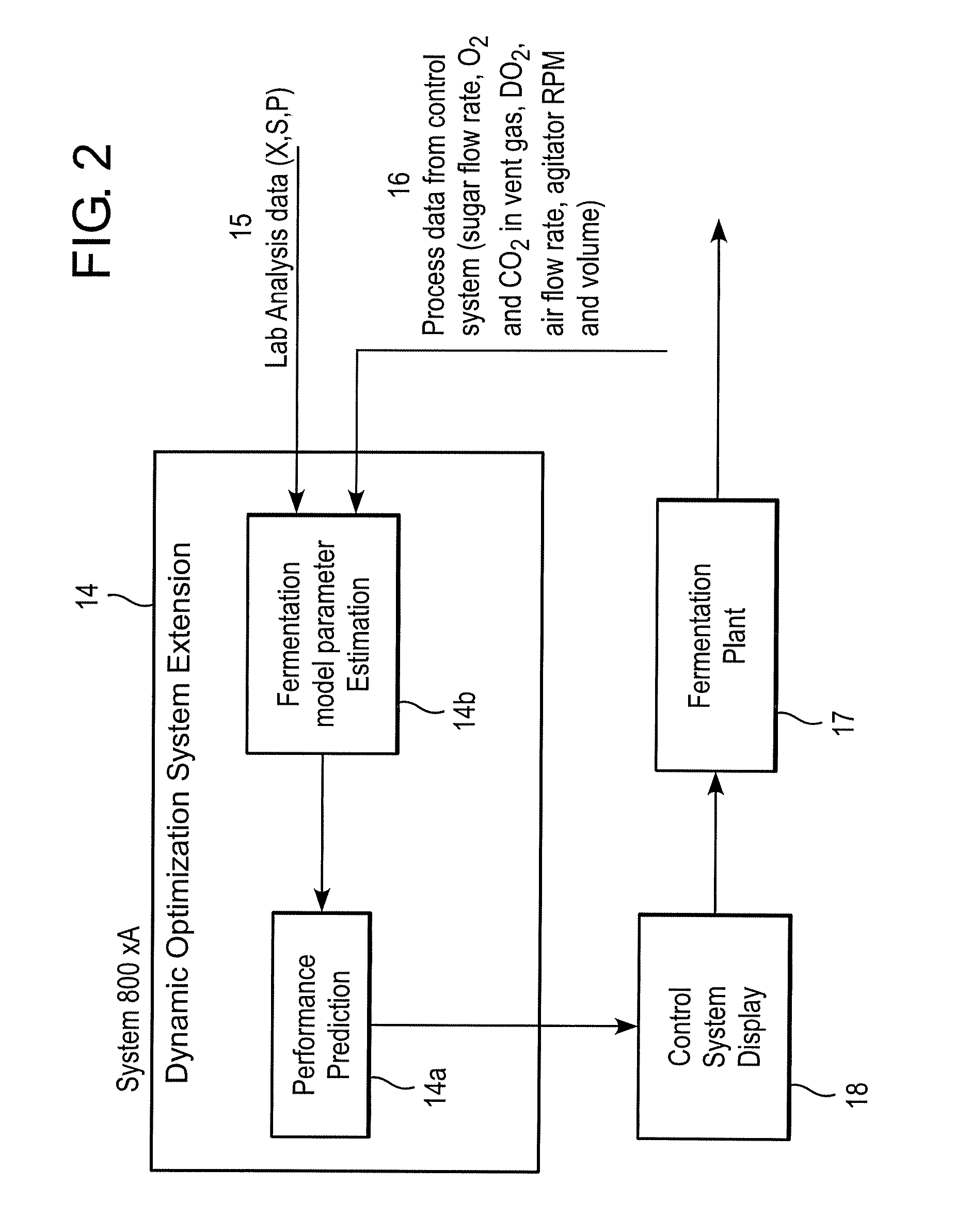
Method for on-line prediction of future performance of a fermentation unit
InactiveUS20090048816A1Minimize plant model mismatchImprove business performanceBiochemistry apparatusAnalogue computers for chemical processesControl systemBatch fermentation
A method is disclosed for on-line prediction of performance of a fermentation unit, such as prediction of performance parameters like concentration of product, biomass, or sugar in the broth of a batch / fed-batch fermentation unit containing bacteria and nutrients. A computer model predicts a future product concentration based on current plant data. While a batch is in progress, model parameters are adjusted on-line based on plant data to reduce a mismatch between the plant data and model data. A method / fermenter model can be implemented as a software program in a PC that can be interfaced to a plant control system for on-line deployment in an actual plant environment. An on-line performance monitoring system can be used by plant operating personnel, to know the performance of the batch in advance for implementing corrective measures in advance to improve / maintain performance at desired level.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
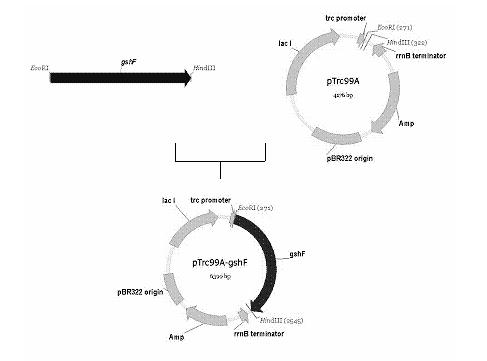
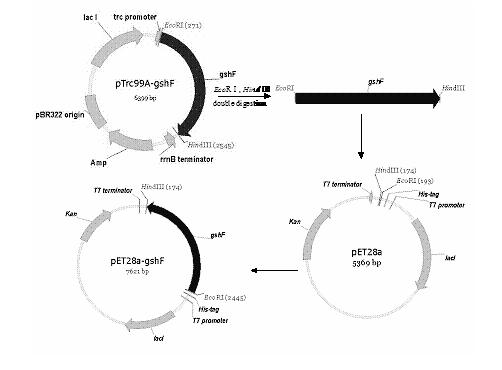
Method for producing glutathione by fermentation of recombinant Escherichia coli
ActiveCN102586369AIncrease productionHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesFermentationGamma-Glutamylcysteine synthetaseEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a method for producing glutathione by fermentation of recombinant Escherichia coli. The method comprises the following stages of: (1) carrying out batch culture or fed-batch culture to obtain a great deal of recombinant Escherichia coli cells expressing exogenous bifunctional glutathione synthetase, wherein the bifunctional glutathione synthetase is protein which simultaneously has activities of gamma-glutamyl cysteine synthetase and glutathione synthetase; (2) carrying out over-expression on the bifunctional glutathione synthetase obtained in the stage (1); and (3) adding L-glutamic acid, L-cysteine and glycine precursor amino acids to realize high-efficiency production of glutathione by fermentation. According to the invention, the recombinant Escherichia coli strain expressing the exogenous bifunctional glutathione synthetase is used for producing glutathione by fermentation, so that the method not only has high GSH (Glutathione) synthesizing capability, but also is free from GSH feedback inhibition, and has the advantages of rapid reaction, high glutathione yield and short production period.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
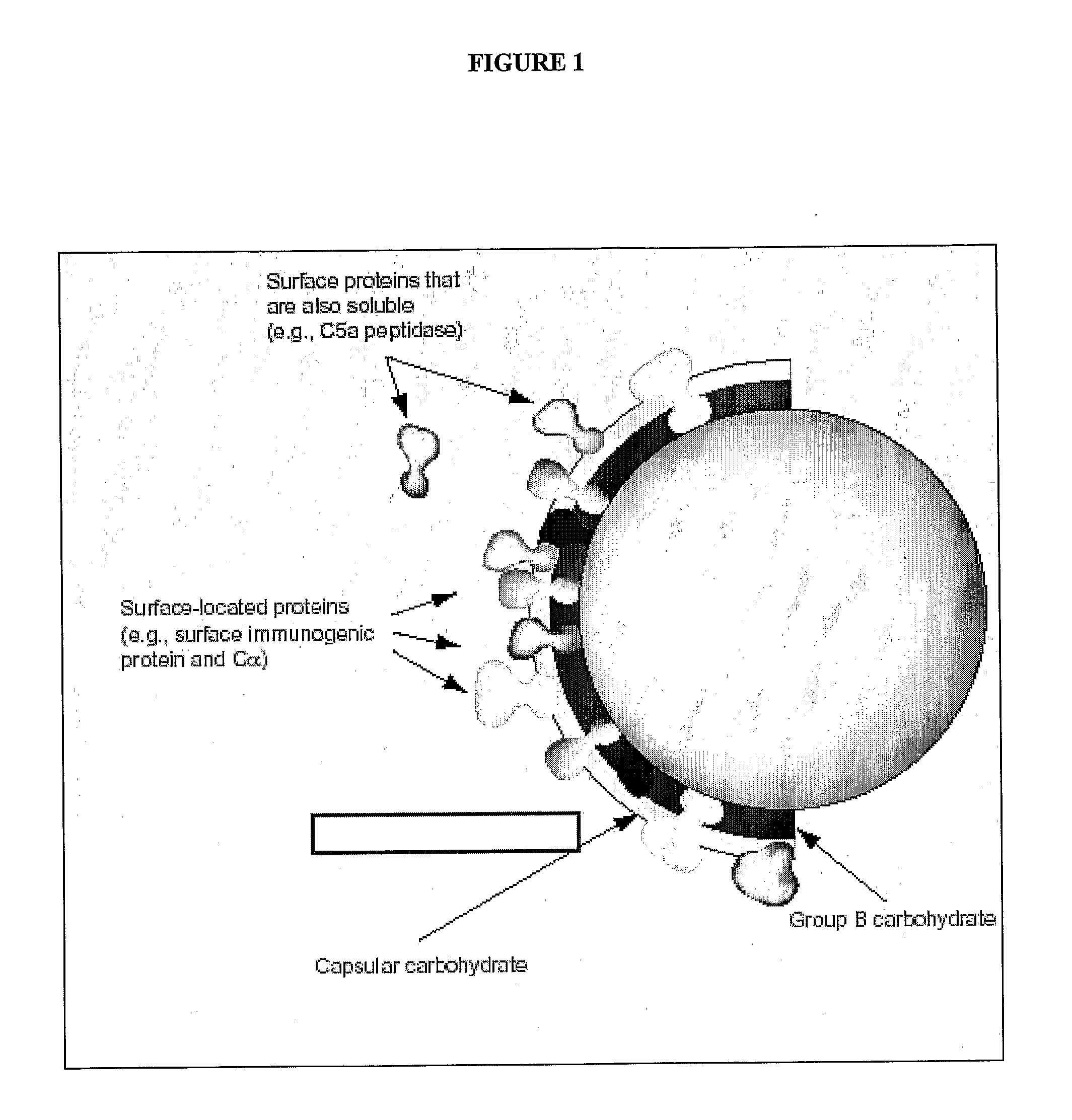
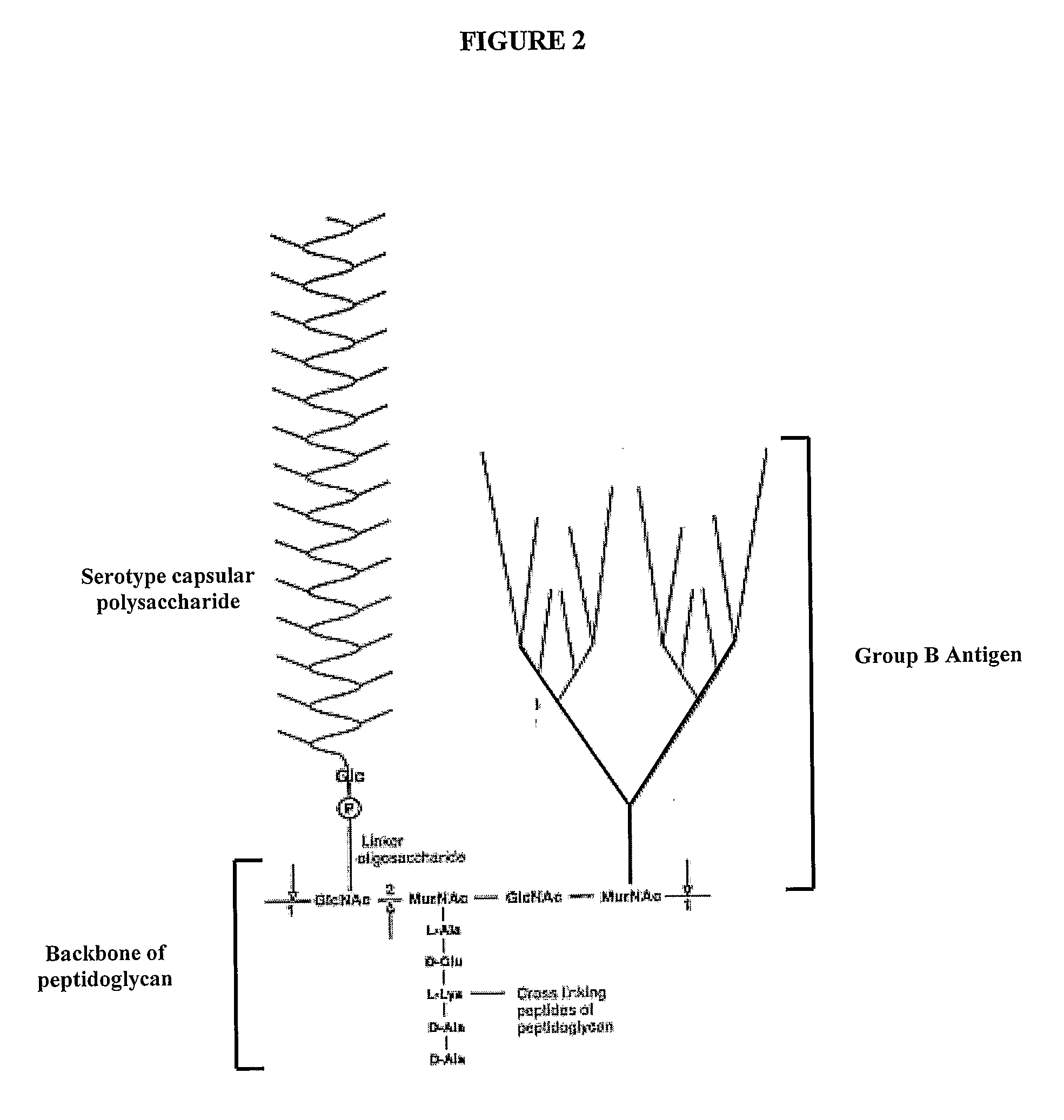
Fermentation processes for cultivating streptococci and purification processes for obtaining cps therefrom
ActiveUS20100272755A1Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesPurification methods
This invention is in the field of bacterial cultures and specifically relates to the optimization of culture conditions to improve the production of bacterial capsular polysaccharides from Streptococcus strains in fed batch culture and to novel purification methods suitable for production scale purification of bacterial capsular polysaccharides from Streptococcus strains resulting in higher levels of purity than previously obtained for production scale.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
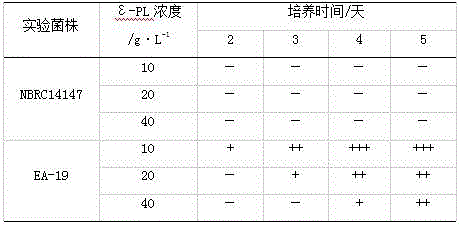
Epsilon-polylysine high-yielding strain and epsilon-polylysine production method
ActiveCN106434421AIncrease concentrationHigh ability to produce ε-polylysineBacteriaMutant preparationEpsilon-PolylysineWastewater
The invention relates to an epsilon-polylysine high-yielding strain and an epsilon-polylysine production method, and belongs to the biotechnical field. The epsilon-polylysine high-yielding strain EA-19 is named as Streptomyces albus, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.10156. The strain EA-19 is used to carry out fed batch fermentation culture, and the concentration of epsilon-polylysine in a fermentation liquid reaches 38.5-39 g / L. The epsilon-polylysine production method comprises is characterized in that the strain EA-19 is adopted to carry out fermentation culture. A bubbling technology is adopted, ventilation is carried out in and after the fermentation culture process, so epsilon-polylysine generated after fermentation exists in foams, and is separated from the fermentation liquid, so the technical problem of difficulty separation of epsilon-polylysine in present preparation methods is solved, a step of ion exchange which causes generation of a large amount of wastewater is omitted, and the product yield is improved by 50% or above. The method has the advantages of simple process, easiness in amplification, low energy consumption, small device investment, and easiness in realization of large-scale production.
Owner:SHANDONG ACADEMY OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES
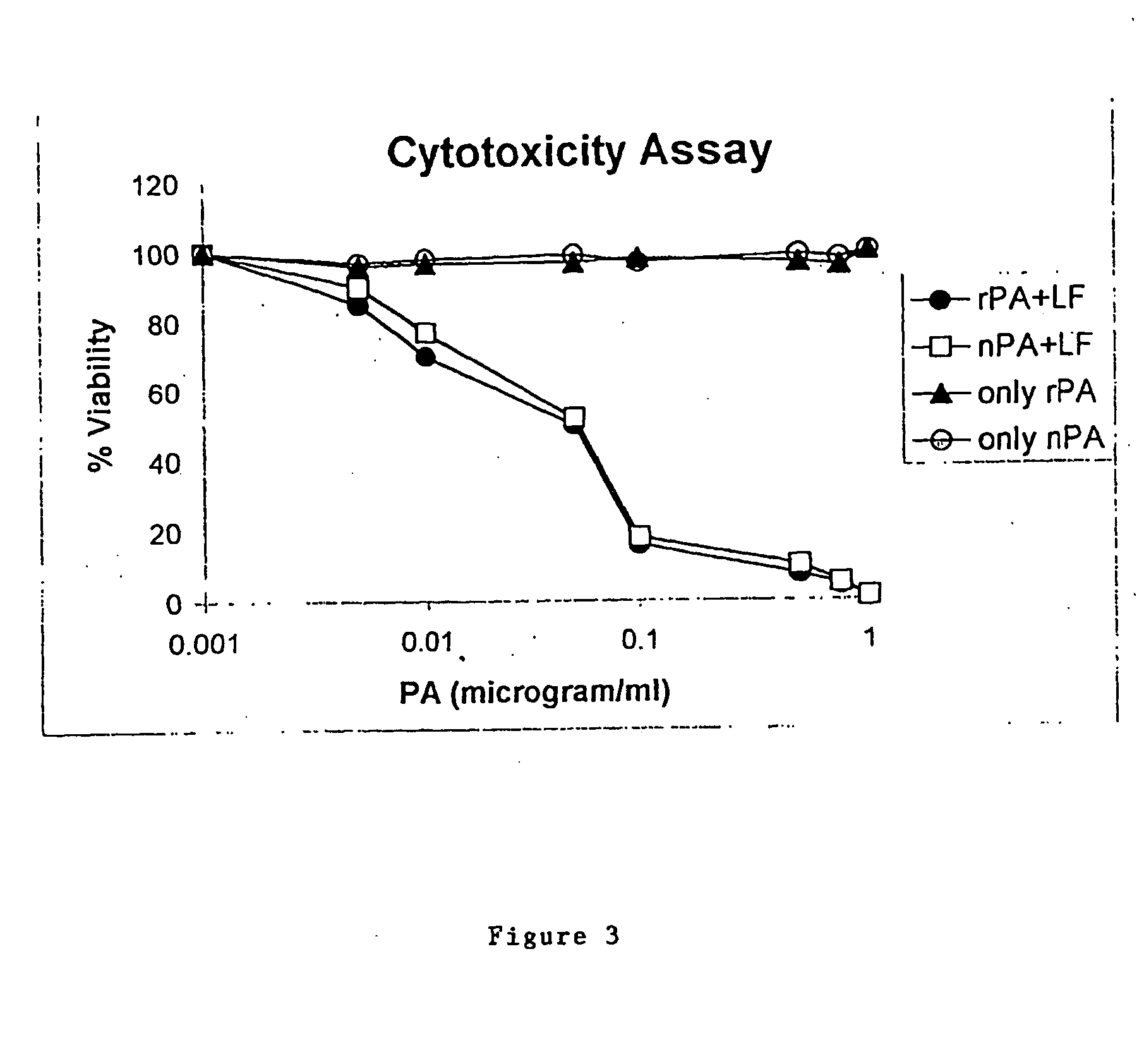
High level constitutive production of anthrax protective antigen
InactiveUS20050054038A1Maximizing harvestingMinimized volumeAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsEscherichia coliAntigen
The present invention relates to a process for preparing anthrax protective antigen protein from E. coli using fed batch culture. This process creates a constitutively expressing system for rapid, efficient, cost-effective and high-level production of anthrax PA from E. coli. The steps of the process involves, transforming E. coli DH5α cells with the recombinant constitutive expression plasmid containing the PA gene to obtain recombinant DH5α cells and testing the PA expression by lysis of said cells followed by denaturing gel electrophoresis and Western Blotting technique using PA antibodies. This is followed by fermentation and harvesting of the high cell density cells. The said cells are solubilized using 6-8 Molar Urea and separated by centrifugation. The urea denatured PA is isolated from said supernatant and purified and thereafter eluted.
Owner:BHATNAGAR RAKESH
Streptomyces and multi-antibiotics metabolic regulation fermentation process
ActiveCN102643764AImprove fermentation titerGood control effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesStreptomyces aureochromogenesInorganic salts
The invention discloses a streptomyces and a multi-antibiotics metabolic regulation fermentation process. According to the method, nutrient media components are optimized, inorganic salt is added to disturb a metabolic network of streptomyces aureochromogenes, and a target production way is strengthened, so that the generation of products is promoted. Meanwhile, the multi-antibiotics fermentationprocess is optimized, and a method of flowing-feeding glucose is adopted for a feed supplement batch fermentation method, so that the fermentation unit and the production output are greatly improved,and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
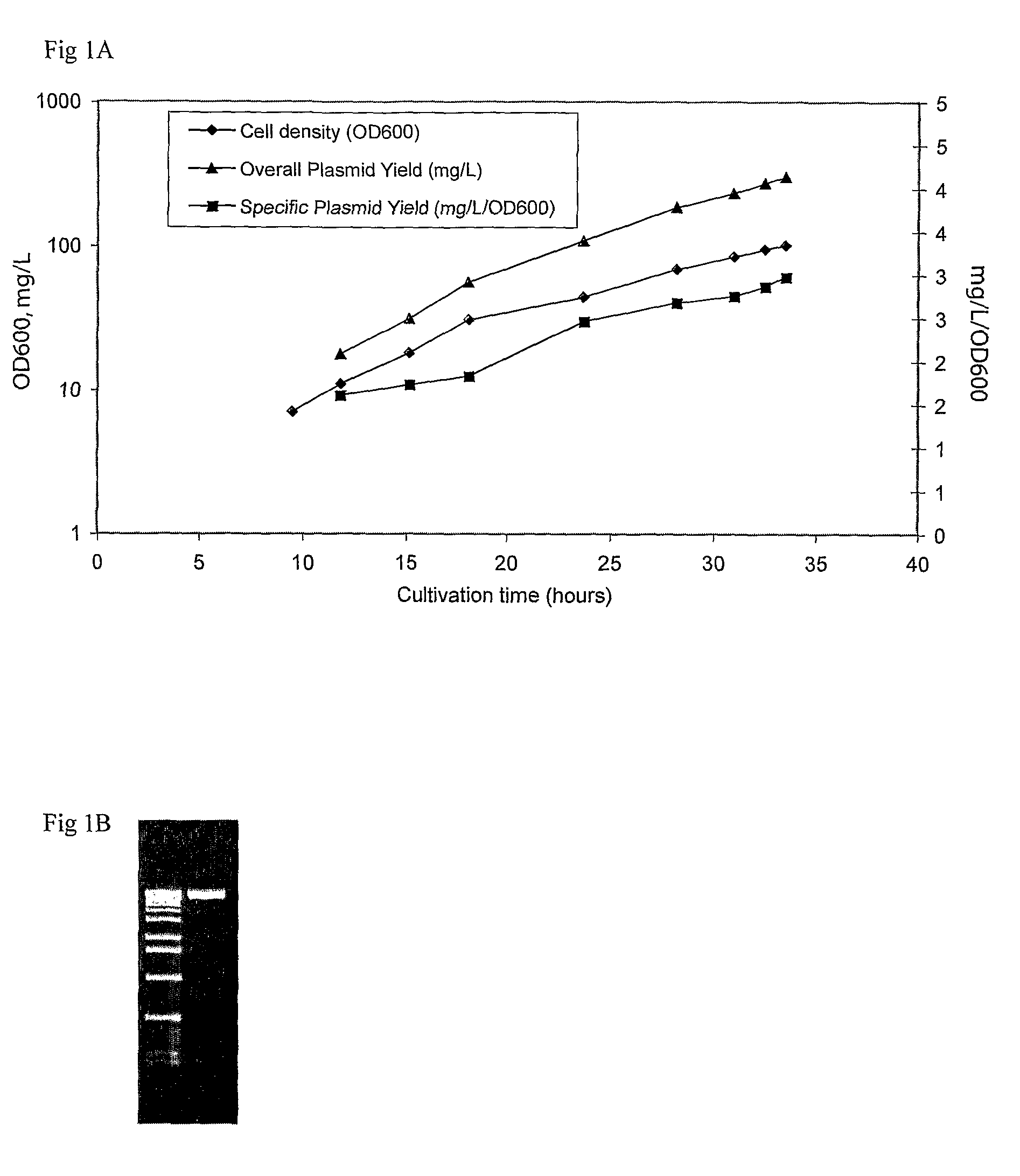
Process for plasmid DNA fermentation
ActiveUS7943377B2Improve plasmid DNA production yieldImprove plasmid DNA qualityGenetic therapy composition manufactureTissue cultureBatch fermentationPlasmid dna
Improvements in plasmid DNA production technology are needed to insure the economic feasibility of future DNA vaccines and DNA therapeutics. General methods are described, by means of which it is possible to dramatically increase plasmid DNA productivity in a fermentor. These processes feature Fed-batch fermentation strategies, combined with novel growth and induction phase temperature shifts.
Owner:ALDEVRON LLC
Method for restructuring/breeding Actinobacillus succinogenes strain, and method for producing succinic acid by fermenting Actinobacillus succinogenes strain
InactiveCN101531972AImproved sodium toleranceImprove fermentation characteristicsBacteriaMutant preparationGenome shufflingX-ray
The invention relates to an Actinobacillus succinogenes strain CGMCC 2653 (namely F3-10) with better sodium-ion tolerance and acid-producing performance, a method for breeding the strain and a method for producing succinic acid by fermenting the strain. Actinobacillus succinogenes CGMCC 1593 is taken as an original strain and then subjected to X-ray mutation, ultraviolet mutation, diethyl sulfate (EMS) chemical mutation and nitrosoguanidine (NTG) chemical mutation respectively; three strains X-8, UV-17 and SE-6 with improved fermentative acid-producing performance and particularly improved sodium-ion tolerance, as well as a high-yield strain SF-9 with fluoroacetate resistance, are obtained by screening the obtained product; and a genome restructuring method is used for breeding the strains so as to obtain the strain F3-10 with high yield, sodium tolerance and fluoroacetate resistance. The strain F3-10 takes sugarcane molasses as raw material, adopts Na2CO3 to control fermentation pH, and performs fed-batch fermentation in a 5L fermenter, and produces 53.96 grams of succinic acid per liter in 48 hours; the yield of consumed sugar is 89.2 percent; the utilization rate of sugar is 94.0 percent; and the ratio of succinic acid to heteroacid is 6.58:1. Therefore, the strain F3-10 is remarkably improved as compared with the original strain CGMCC 1593.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
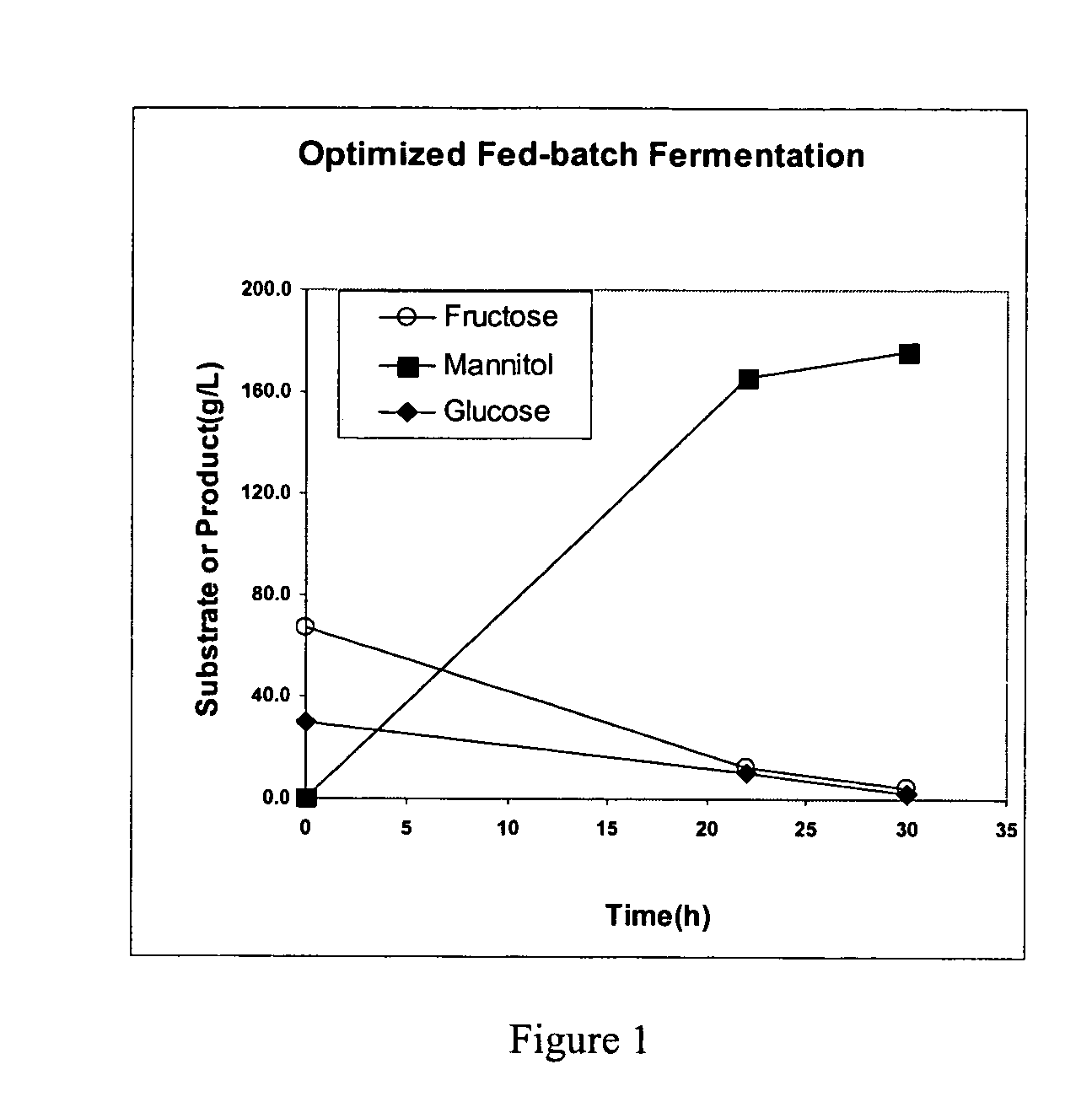
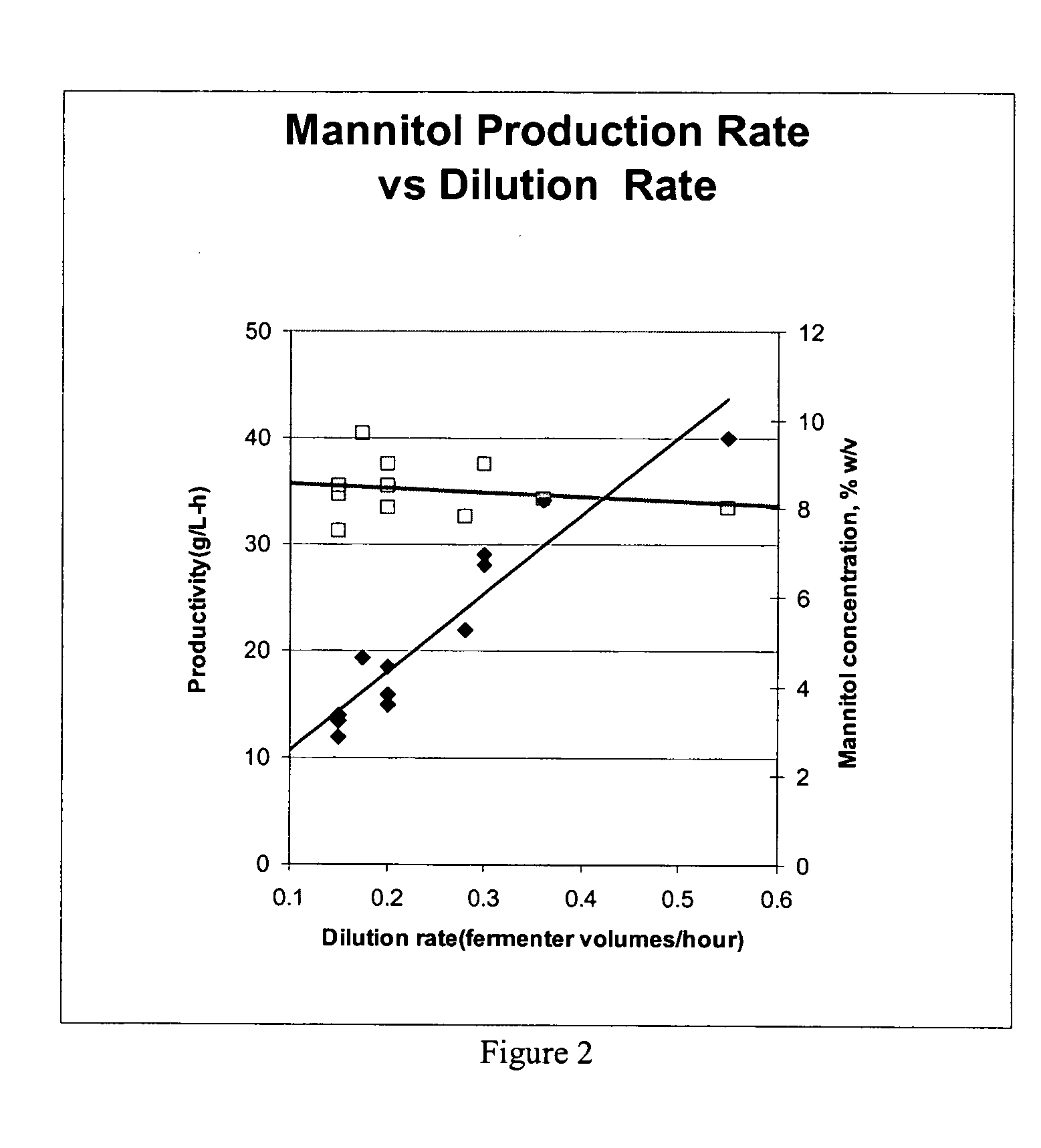
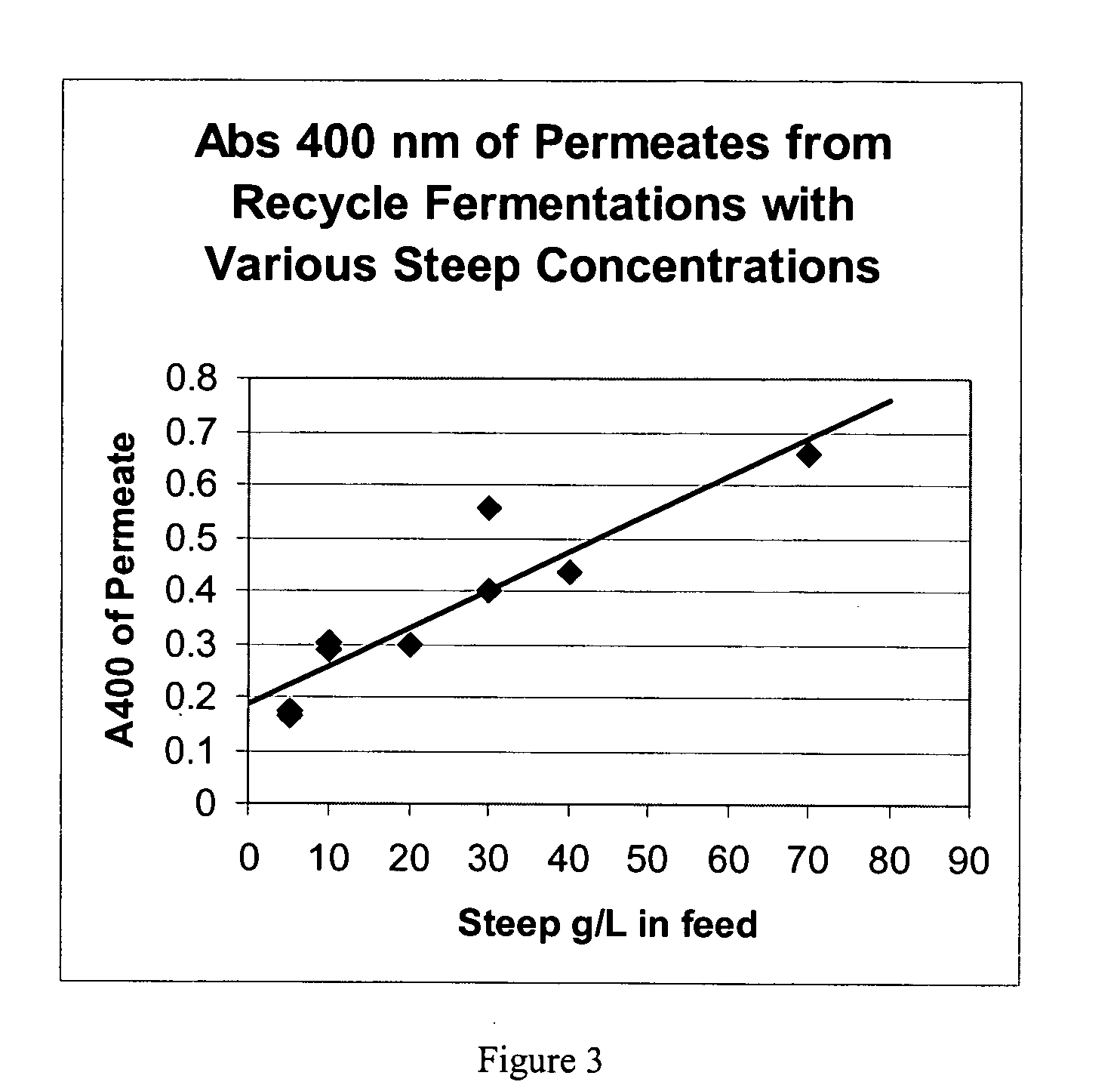
Fermentative production of mannitol
InactiveUS20060134765A1Accelerate the accumulation processLow costFermentationMANNITOL/SORBITOLFed-batch culture
The invention provides processes for continuous fed-batch fermentative production and continuous recycle fermentative production of mannitol.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Bacillus velezensis LfF-1 strain and application thereof in protease production
ActiveCN110551661AIncrease vitalityHigh recovery rate of enzyme activityBacteriaHydrolasesProtease preparationBatch fermentation
The invention discloses a Bacillus velezensis LfF-1 strain and application thereof in protease production. The Bacillus velezensis LfF-1 strain is separated for a first time, the strain is preserved in the Guangdong Microbiological Culture Collection Center in August 16, 2019, and the preservation number is GDMCC NO: 60741. The strain has a remarkable capability for producing protease through fermentation, and types of cultures produced through protease fermentation can be enriched; a protease preparation can be produced by using the strain through a fermentation tank replenishing on-batch fermentation process, the activity of the protease is as high as 17.84 ten thousand U / g, the enzyme activity recovery rate is as high as 96.8%, types of conventional commercial protease can be greatly enriched, and the production efficiency of the protease preparation can be improved; and in addition, the method for producing the protease from the strain through fermentation is simple and feasible, and has wide application prospects in producing protein foods, functional peptide products or feed additives.
Owner:LINGNAN NORMAL UNIV
Cutinase producing gene engineering bacteria and use thereof
The invention discloses a cutinase producing gene engineering bacteria and use thereof and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. Recombinant plasmid Tfu-0883-hlyAs / pET20b(+) is constructed, Escherichia coli E.coliBL21(DE3) is converted to obtain recombinant Escherichia coli Tfu-0883-hlyAs / pET20b(+) / E.coliBL21(DE3). A certain specific growth speed is controlled in a feed supplement batch fermentation manner, fermentation culture is performed for 30 to 34 hours, and the enzyme survival rate in fermentation supernate reaches 700 to 750U / Ml. In the invention, glycerol is used as a main raw material, a semisynthetic culture medium is adopted, and the cutinase producing gene engineering bacteria have the advantages of stability, convenient regulation and the like and are suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
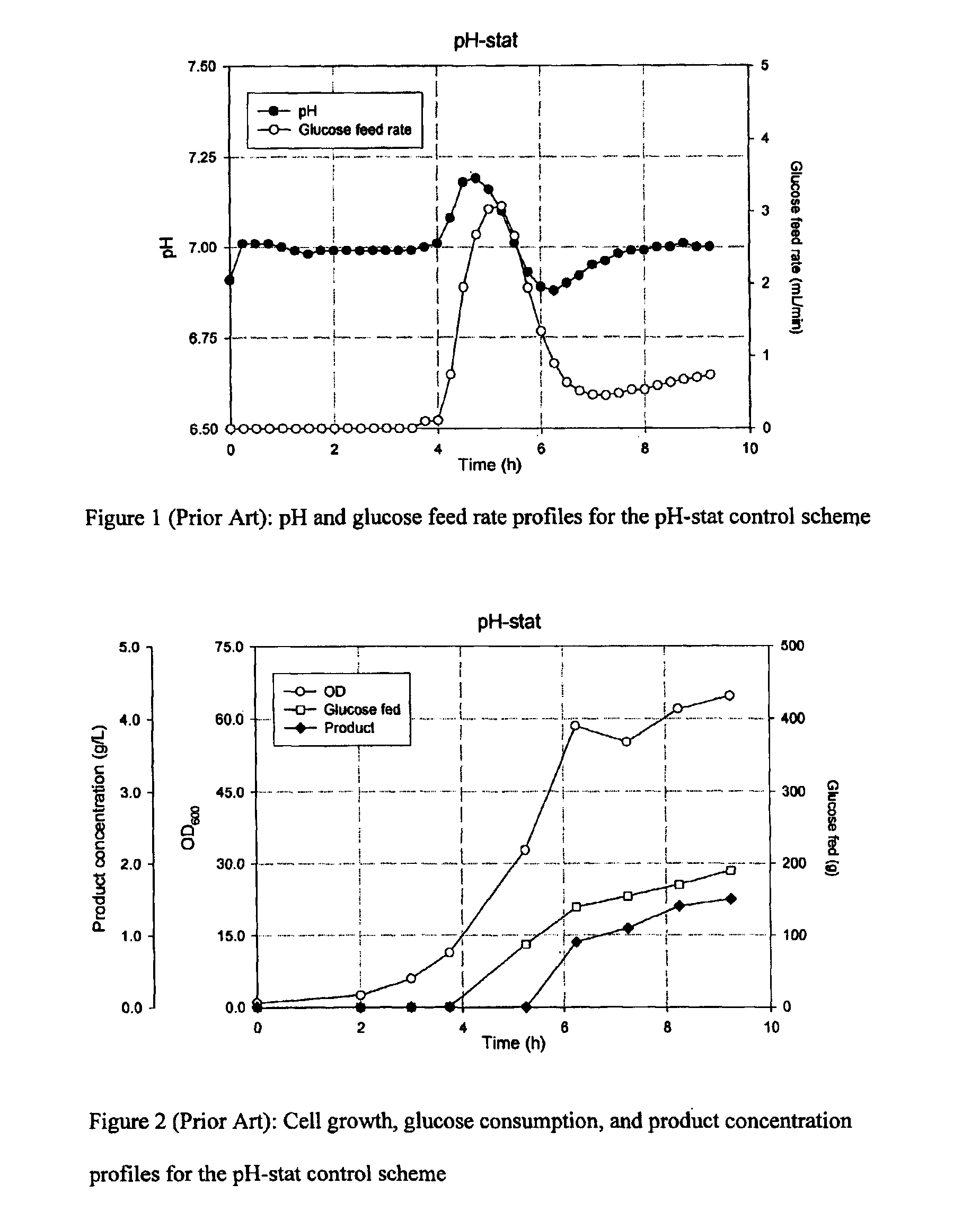
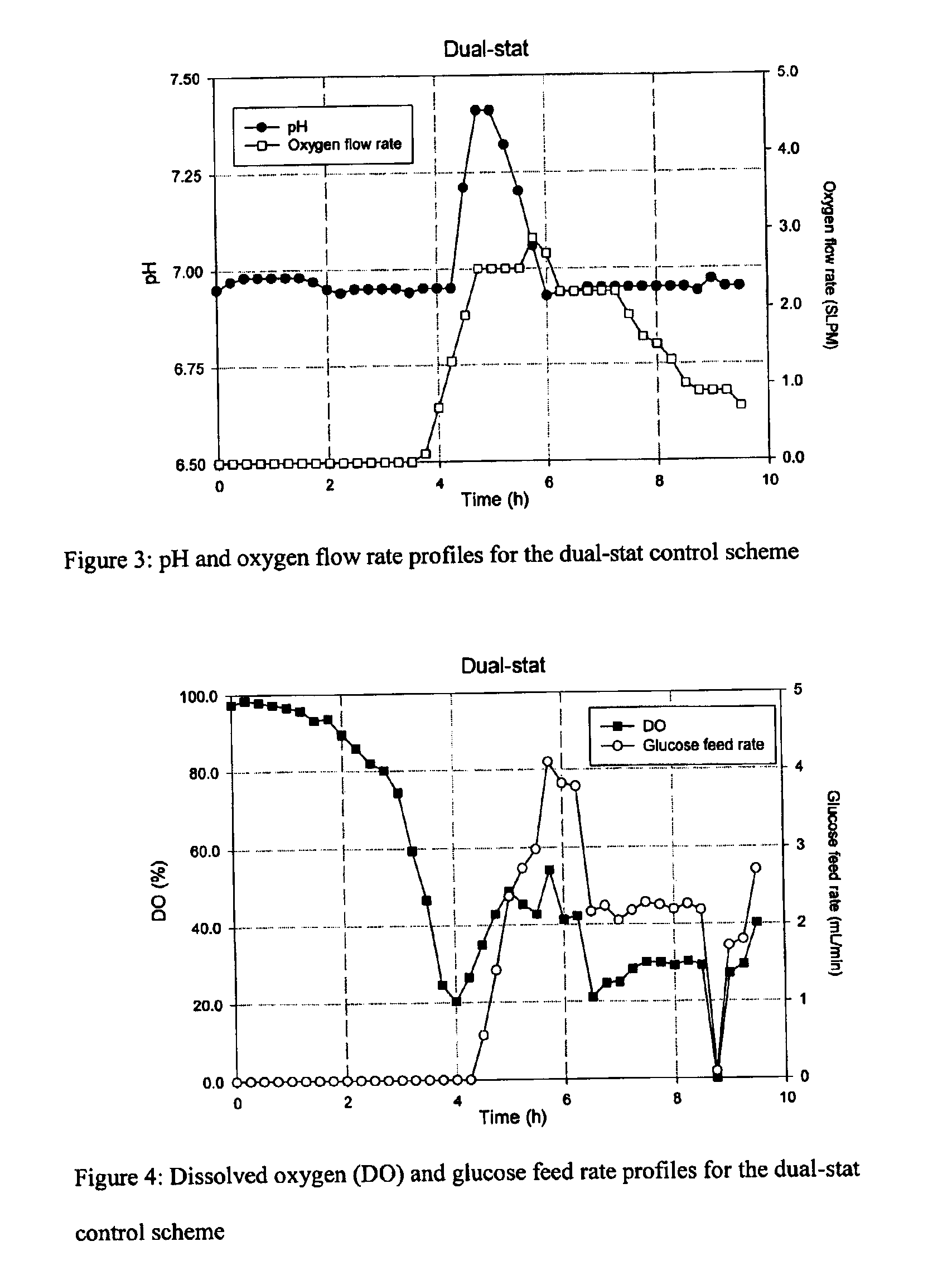
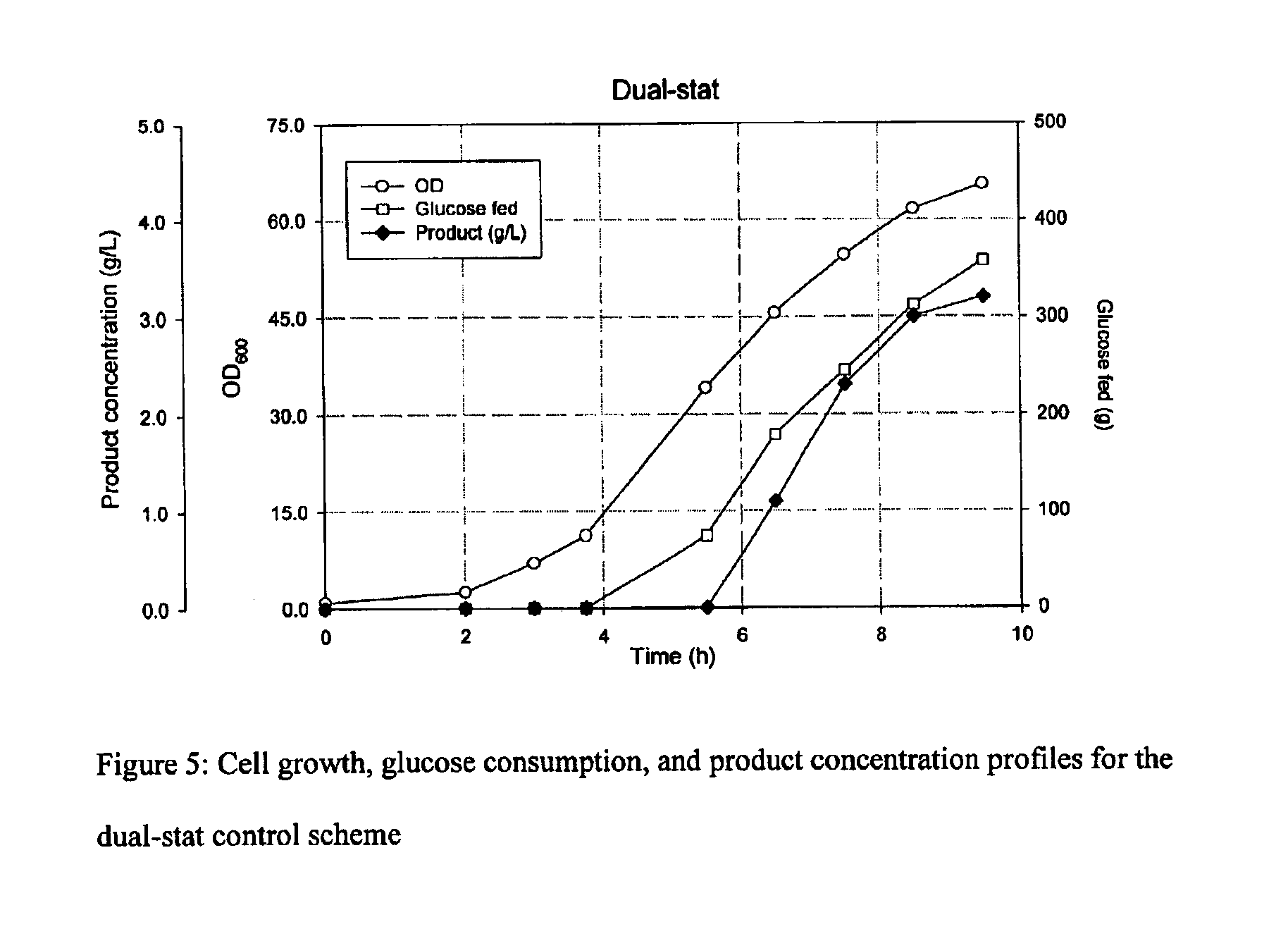
Feeding processes for fermentation
InactiveUS6955892B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnimal scienceBatch fermentation
Embodiments of the present invention generally relate to novel fed-batch fermentations wherein processes of DO-stat and pH-stat are combined for nutrient feeding control.
Owner:NV ORGANON
Production and fermentation process for citric acid
The invention provides a production and fermentation process for citric acid. The process is characterized in that feeding liquid is refilled into a fermentation tank during the fermentation process of citric acid. According to the invention, through fed batch of the feeding liquid with high concentration of sugar during fed batch fermentation, the concentration of the acid through fermentative production is improved, and inhibition of high initial sugar concentration on fermentation of the citric acid is avoided. With the production and fermentation process provided by the invention, the concentration of the acid through fermentative production is improved, fermentative production intensity is enhanced, the conversion ratio of sugar to the acid during fermentation and the utilization rate of equipment are increased, and thus, economic benefits of an enterprise are increased and competitiveness of the enterprise is improved.
Owner:RIZHAO JINHE BOYUAN BIOCHEM
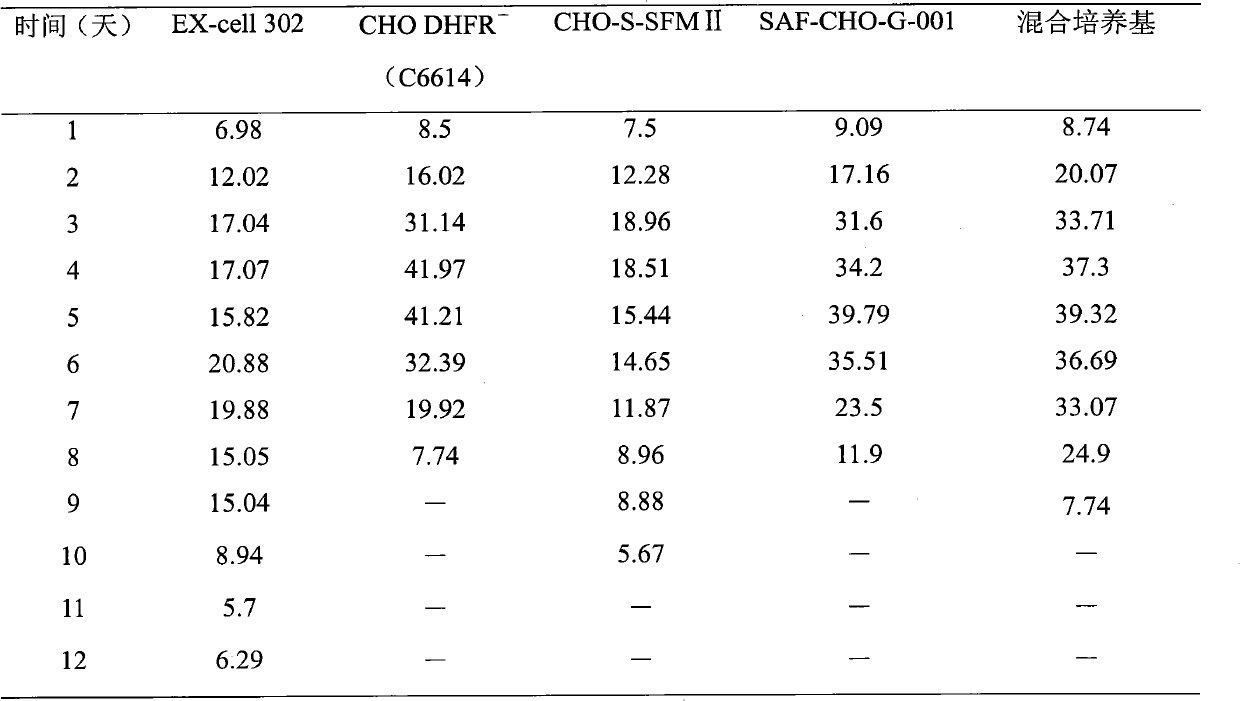
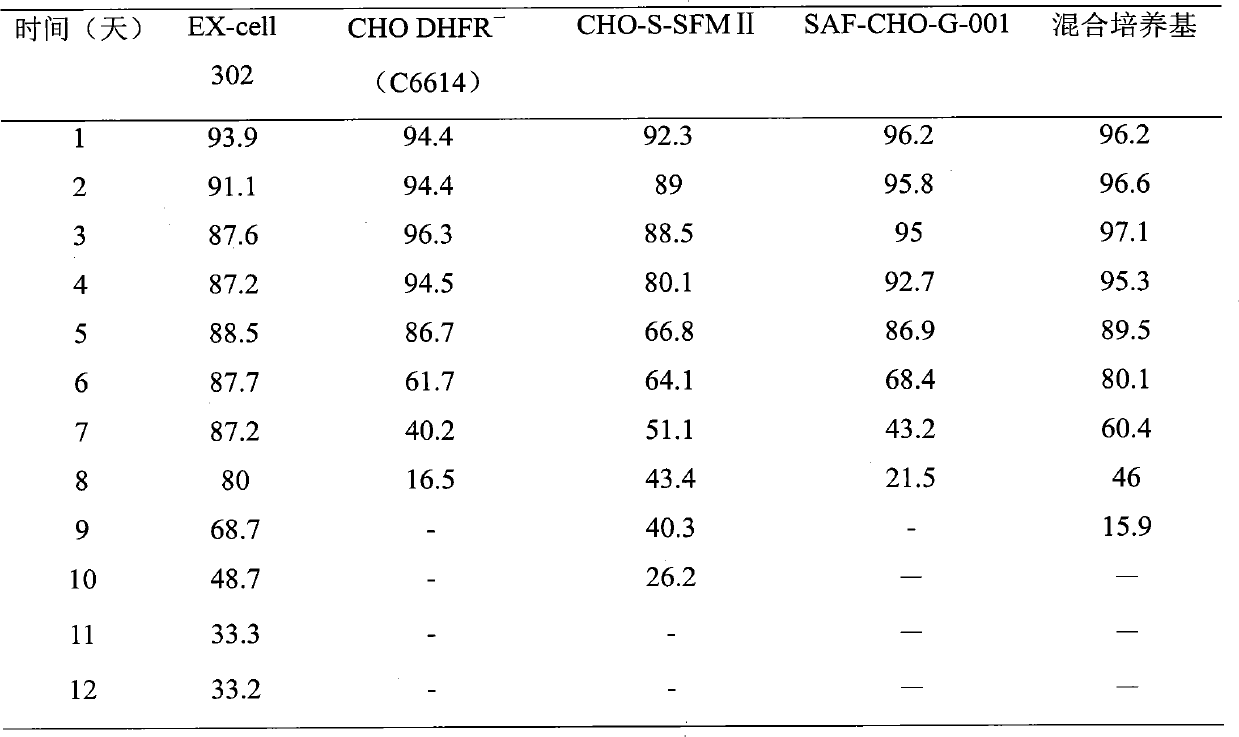
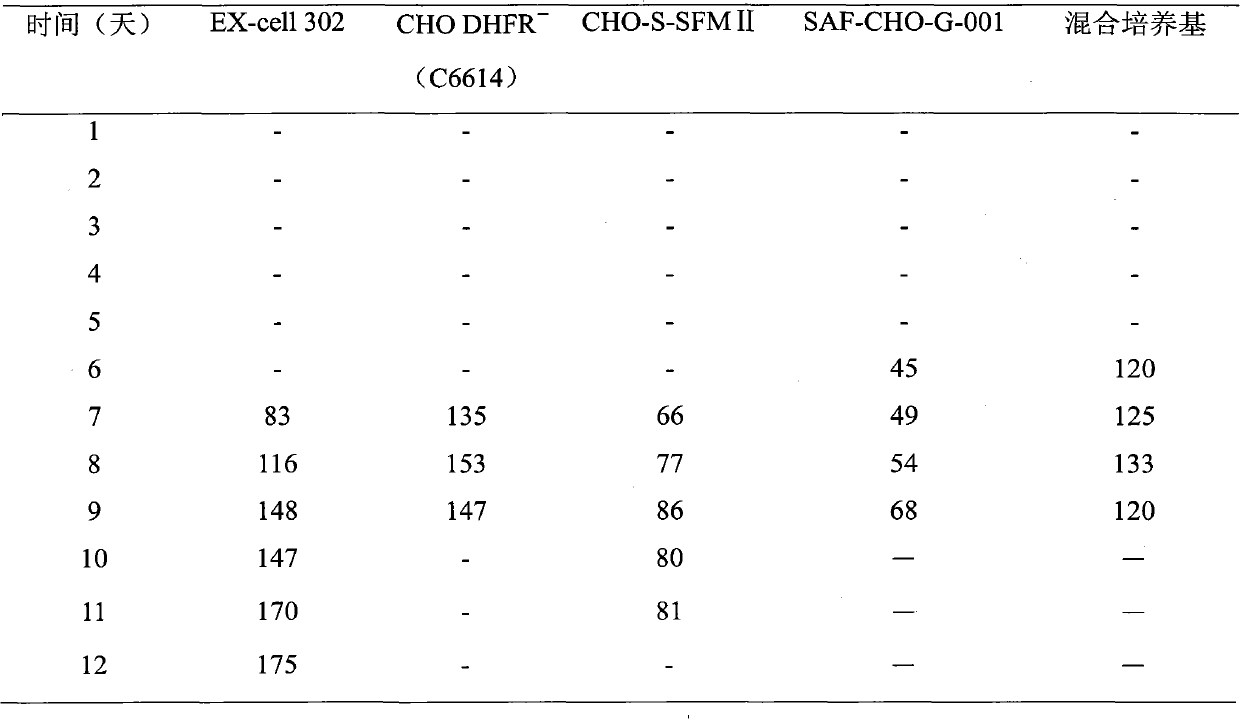
Medium suitable for cultivating CHO cell and cultivation technology thereof
The invention discloses a medium suitable for cultivating CHO cell and cultivation technology thereof, relates to a basic medium with C6614 and fed-batch medium with EX-Cell 302. The whole cultivation technology is to use the fed-batch concentration medium to process the fed-batch culture and the cooling culture, and combine with the perfusion basic medium method. The technology has excellent effects; the technology has the characteristics of good stability, strong operability, little difference in the batch result; and the yield of recombinant protein is largely improved.
Owner:CHENGDU KANGHONG BIOTECH
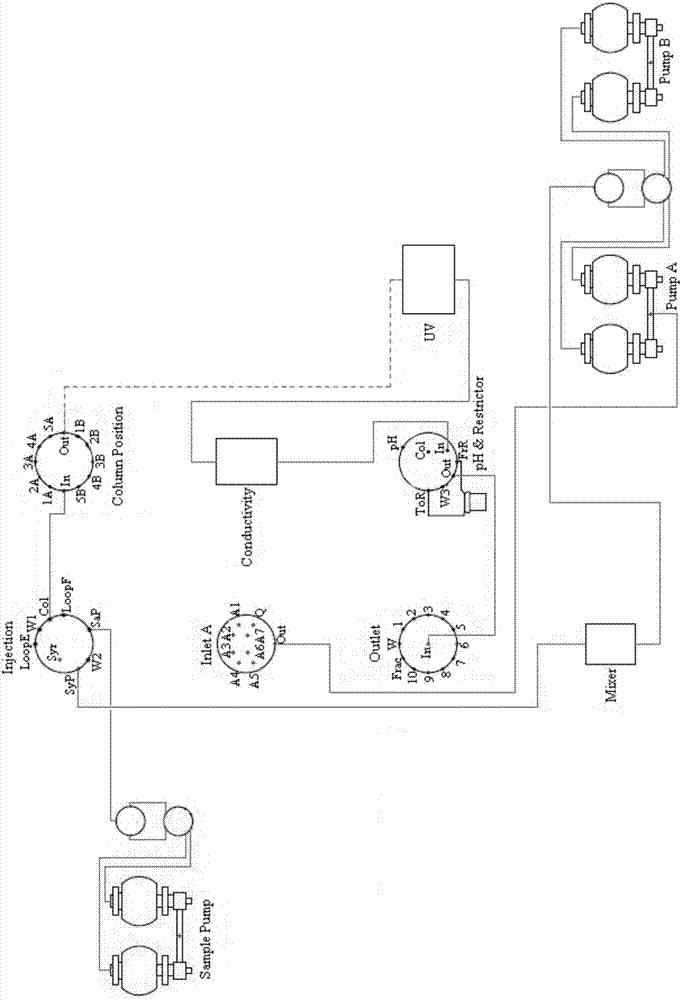
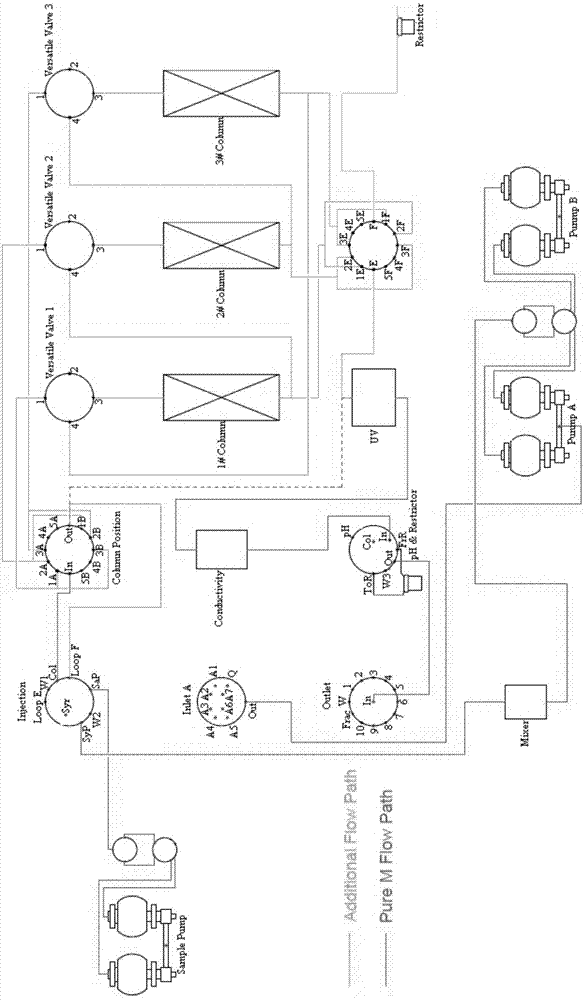
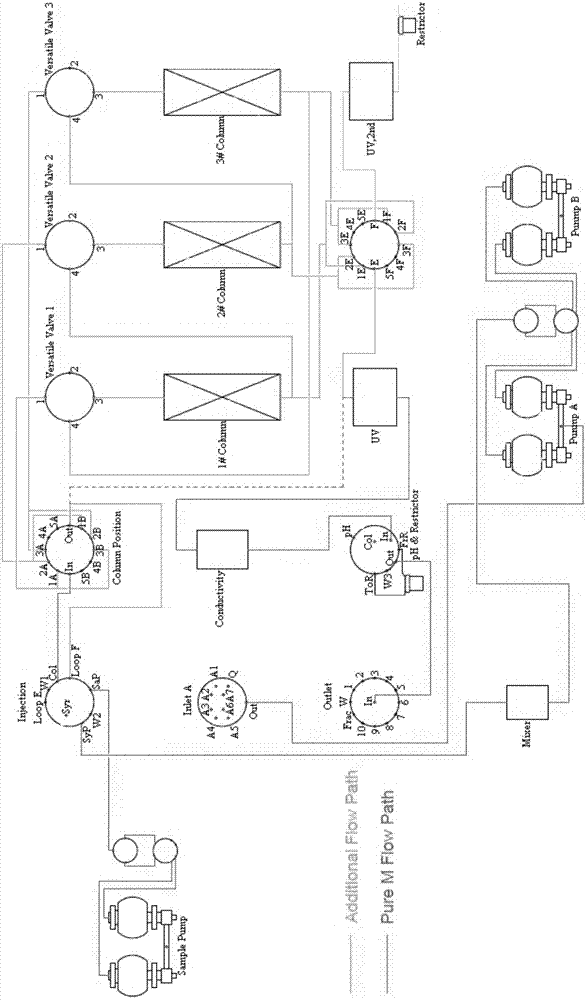
Modified chromatographic apparatus and method of using same in continuous-flow chromatography
ActiveCN107485891AEnables continuous purificationLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChromatographic separationPerfusion Culture
The invention discloses a modified AKTA pure chromatographic apparatus. On the basis of the structure of original standard AKTA pure, three multifunctional valves, as well as a second column position valve or a Loop ring valve, are added, so that two flow paths, which work simultaneously, are formed by three columns; one flow path is used for continuously loading a sample, while the other one flow path is used for pretreatment before and post-treatment after sample loading, so that continuous purification of a perfusion culture material solution is achieved. The modified apparatus can achieve low-cost, multi-cycle and automated purification of fed-batch culture solutions, avoids accumulation and degradation of the sample, can maintain the stability of the sample, is free of an extra large-volume buffer container, and is high in purification efficiency.
Owner:SUZHOU YAOMING KANGDE INSPECTION TESTING
Genetically engineered bacterium capable of generating polyhydroxybutyrate hydroxyvalerate and application method of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN106119181AReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBatch fermentation
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium capable of generating polyhydroxybutyrate hydroxyvalerate and an application method of the genetically engineered bacterium, belonging to the fields of gene engineering and fermentation engineering. The constructed genetically engineered bacterium can be used for producing poly(3-hydrobutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) by utilizing a single carbon source, and the mole fraction of 3HV is 66%. With the adoption of the genetically engineered bacterium and the application method, the problem of high cost caused by adding of the auxiliary carbon source, namely, propionate during the production of PHBV is solved. Through the 130h fed batch fermentation by adopting a 3L fermentation tank, the corynebacterium glutamicum genetically engineered bacterium provided by the invention can generate PHBV with the weight accounting for 20% of the dry cell weight in the cells, the ratio of 3HV is 66%, and the corynebacterium glutamicum genetically engineered bacterium also can generate isoleucine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
High-efficiency preparation method of Iturin A and homologue of Iturin A
InactiveCN104694601AIncrease productionIncrease concentrationMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicrobiological TechniquesAmino acid
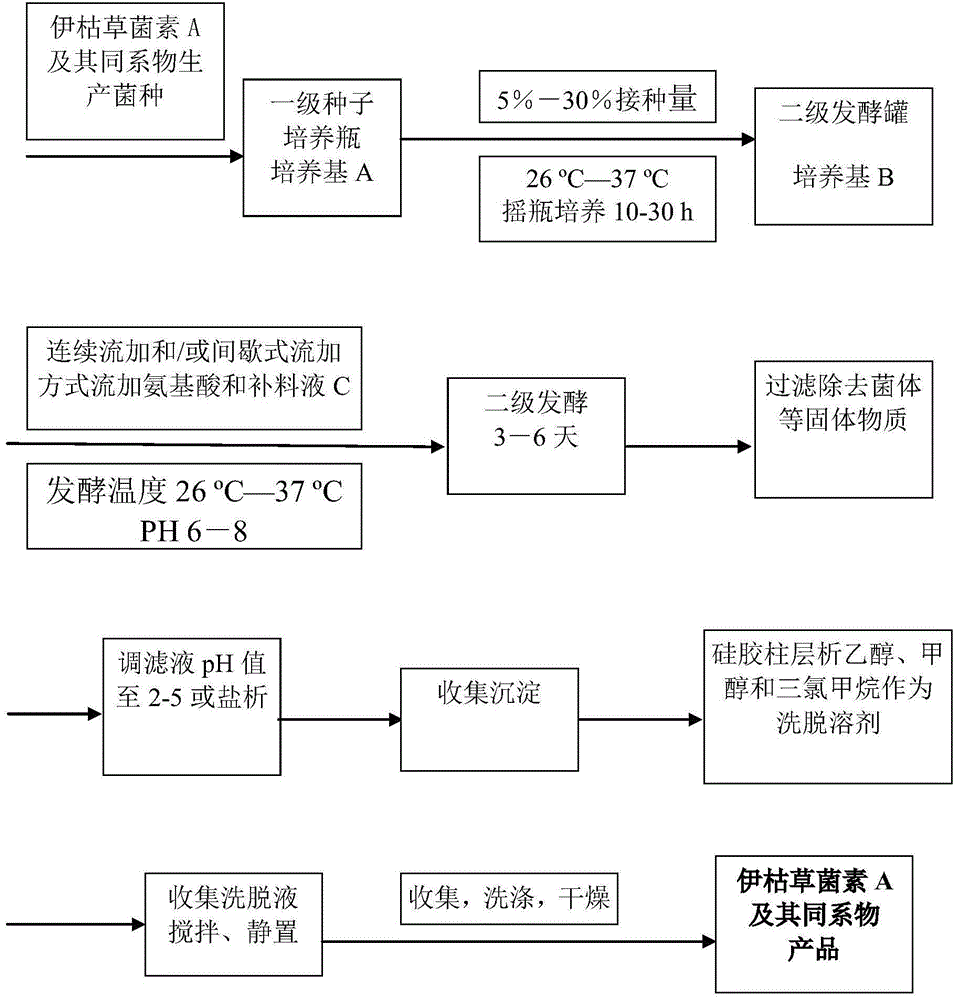
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbes and particularly relates to a high-efficiency preparation method of Iturin A and a homologue of Iturin A. The method comprises the following steps: culturing a Bacillus strain and a genetically modified bacterium thereof in a primary fluid medium, and then inoculating a secondary fluid medium with the primary fluid medium as a seed solution, wherein the strain can generate Iturin A and the homologue of Iturin A; after inoculating the secondary fluid medium with the seed solution, performing fermentation culture and the feed-batch culture of amino acid and the like; and collecting Iturin A and the homologue thereof from a fermentation culture solution after fermentation is over. The method provided by the invention has the characteristics of high production efficiency, easy industrialization and the like.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
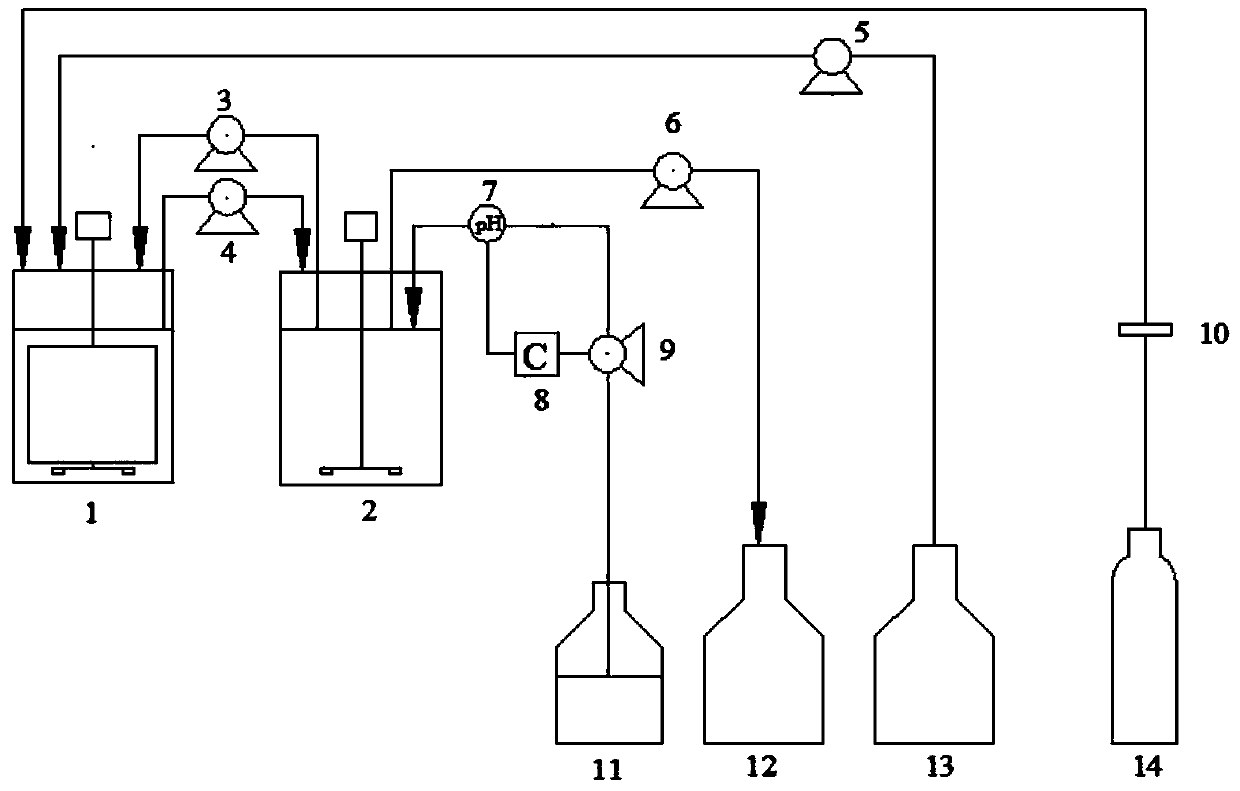
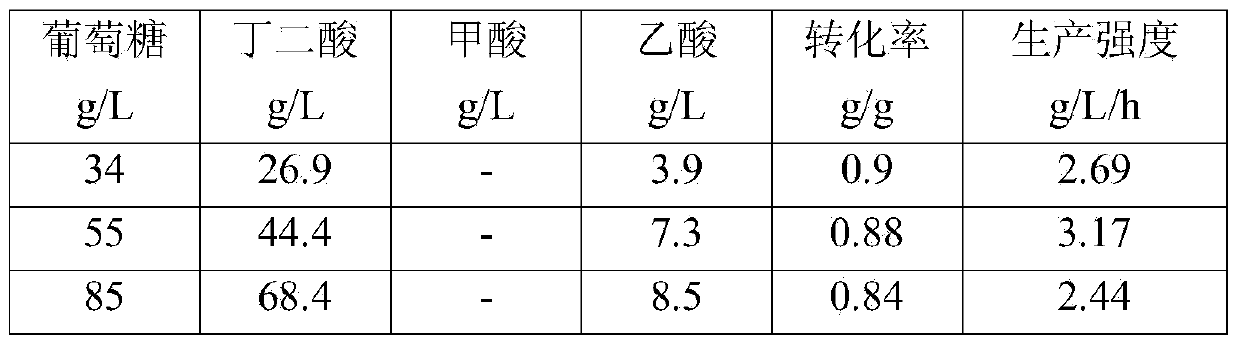
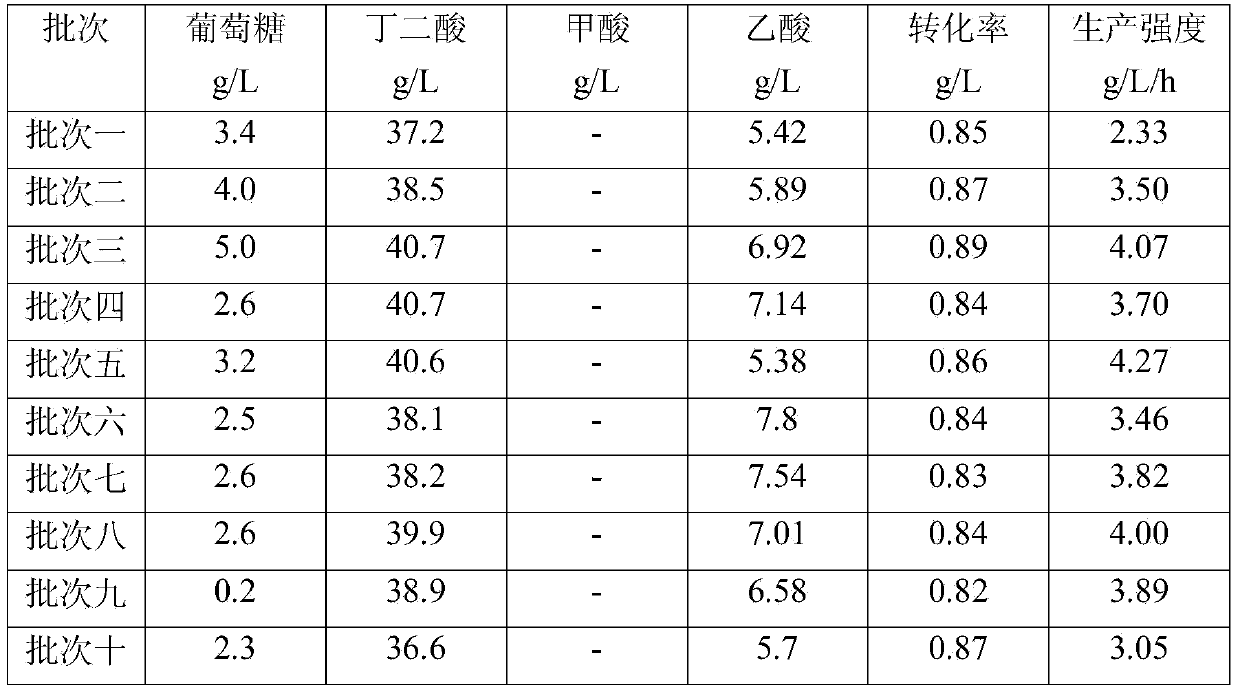
Method for fermentation production of succinic acid by using cotton fiber material to fix actinobacillus succinogenes
The invention discloses a method for fermentation production of succinic acid by using a cotton fiber material to fix actinobacillus succinogenes, belonging to the fermentation engineering field. The actinobacillus succinogenes is placed in a fermentation tank which contains a cotton fiber carrier for culturing, adsorbing and fixing; the fermentation cell concentration is improved through a repeated batch fermentation process, a repeated fed-batch fermentation process, a continuous fermentation process or a double-tank circulating continuous fermentation process; meanwhile, high acid production concentration, high production strength and high conversation rate are obtained. The conversation rate is 90% to a maximum, the production strength is 4.27g / L / h to a maximum, and the butyric acid yield is 98.7g / L to a maximum.
Owner:SHANDONG XINGQIANG CHEM IND TECH RES INST CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com