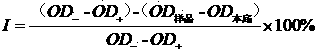Patents
Literature
173 results about "D-galactal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
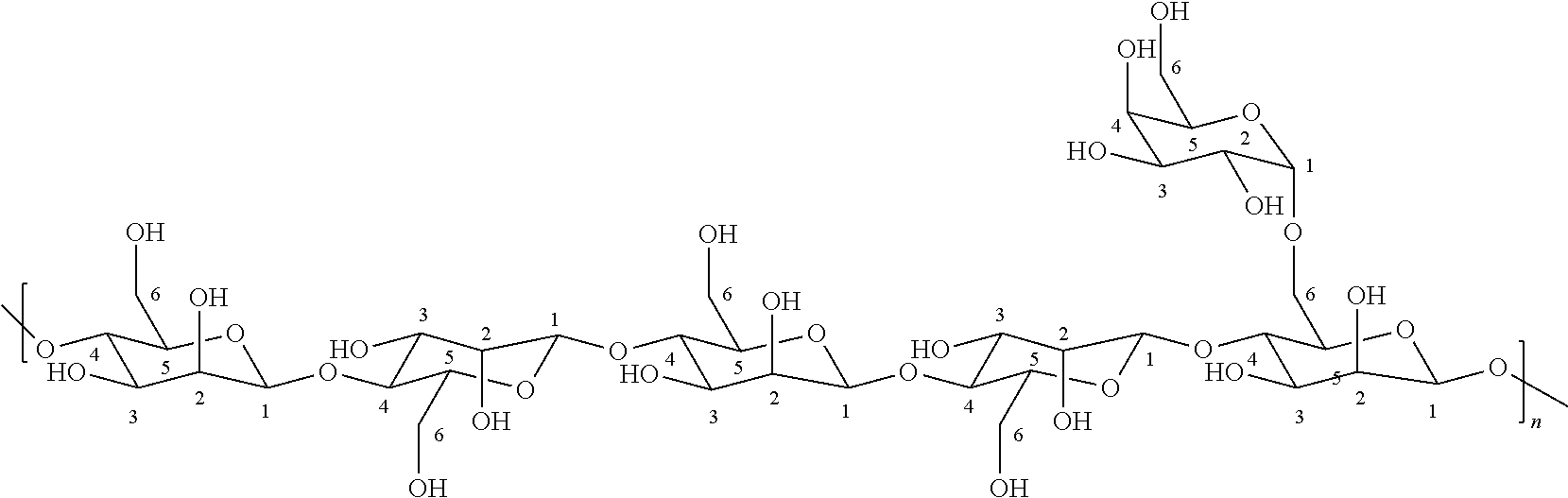
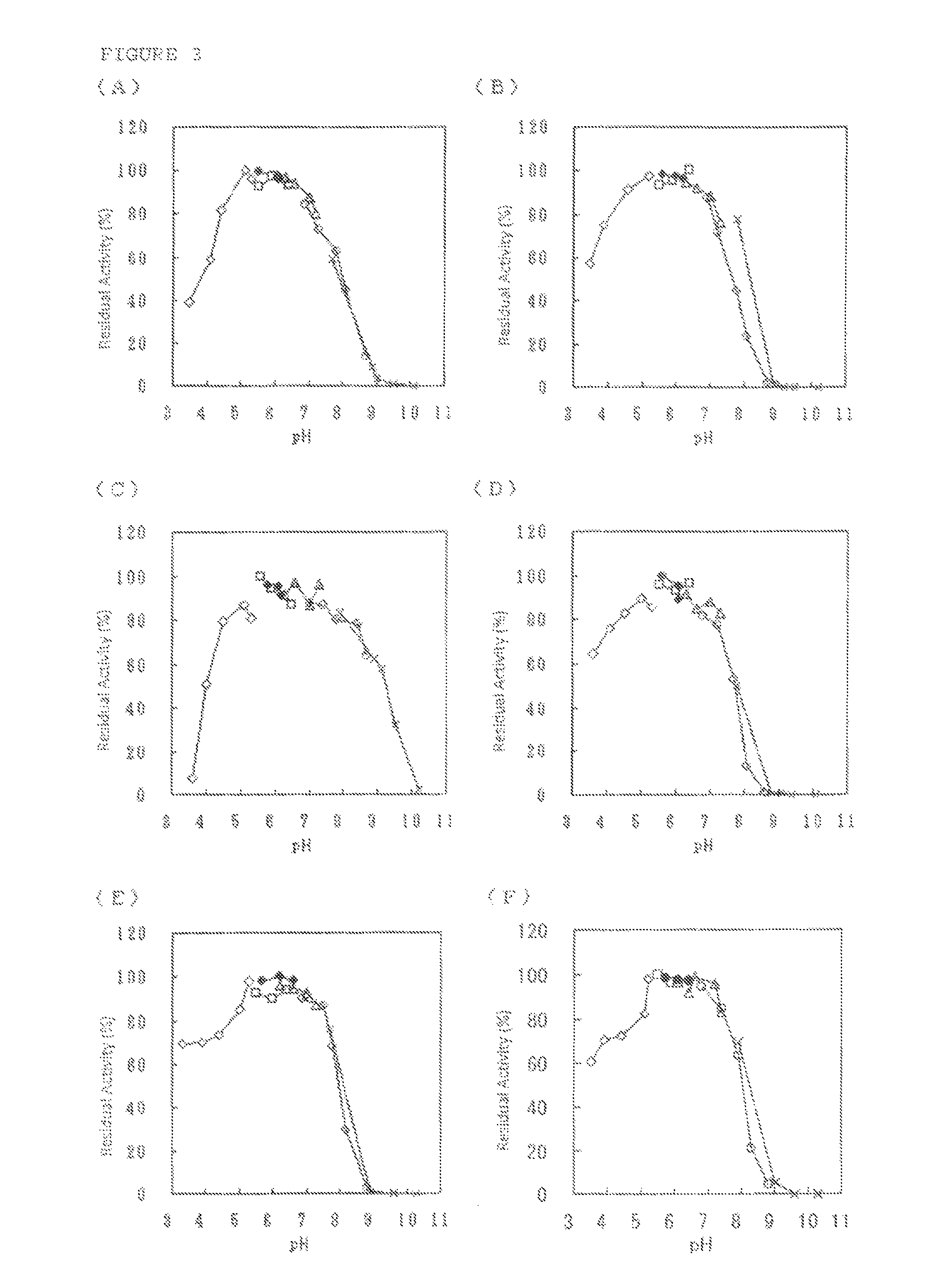
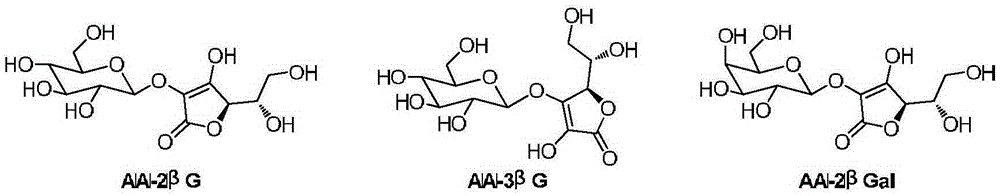
D-Galactal 95% Synonym: 1,5-Anhydro-2-deoxy-D-lyxo-hex-1-enitol CAS Number 21193-75-9. Empirical Formula (Hill Notation) C 6 H 10 O 4. Molecular Weight 146.14 . Beilstein Registry Number 81690 . EC Number 244-264-7. MDL number MFCD00038067. PubChem Substance ID 24869955
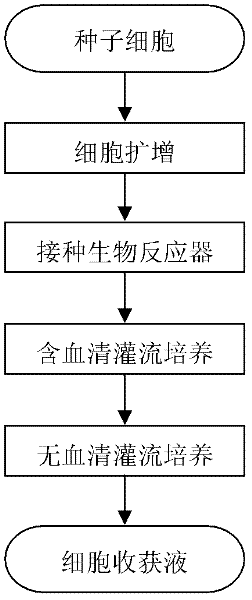
Product quality enhancement in mammalian cell culture processes for protein production
ActiveUS7332303B2Low production costQuality improvementAnimal cellsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsHigh cellBiotechnology
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Coffee plant with reduced alpha-D-galactosidase activity
InactiveUS7238858B2Lower Level RequirementsGalactose branching in the galacto-mannans is increasedOther foreign material introduction processesEnzymesPlant cellD-galactal
The present invention relates to the modification of galactomannans present in the green coffee bean by reducing the endogenous level of α-D-galactosidase activity. In particular, the present invention pertains to a plant cell with reduced α-D-galactosidase activity and to a plant harboring such a plant cell.
Owner:NESTEC SA
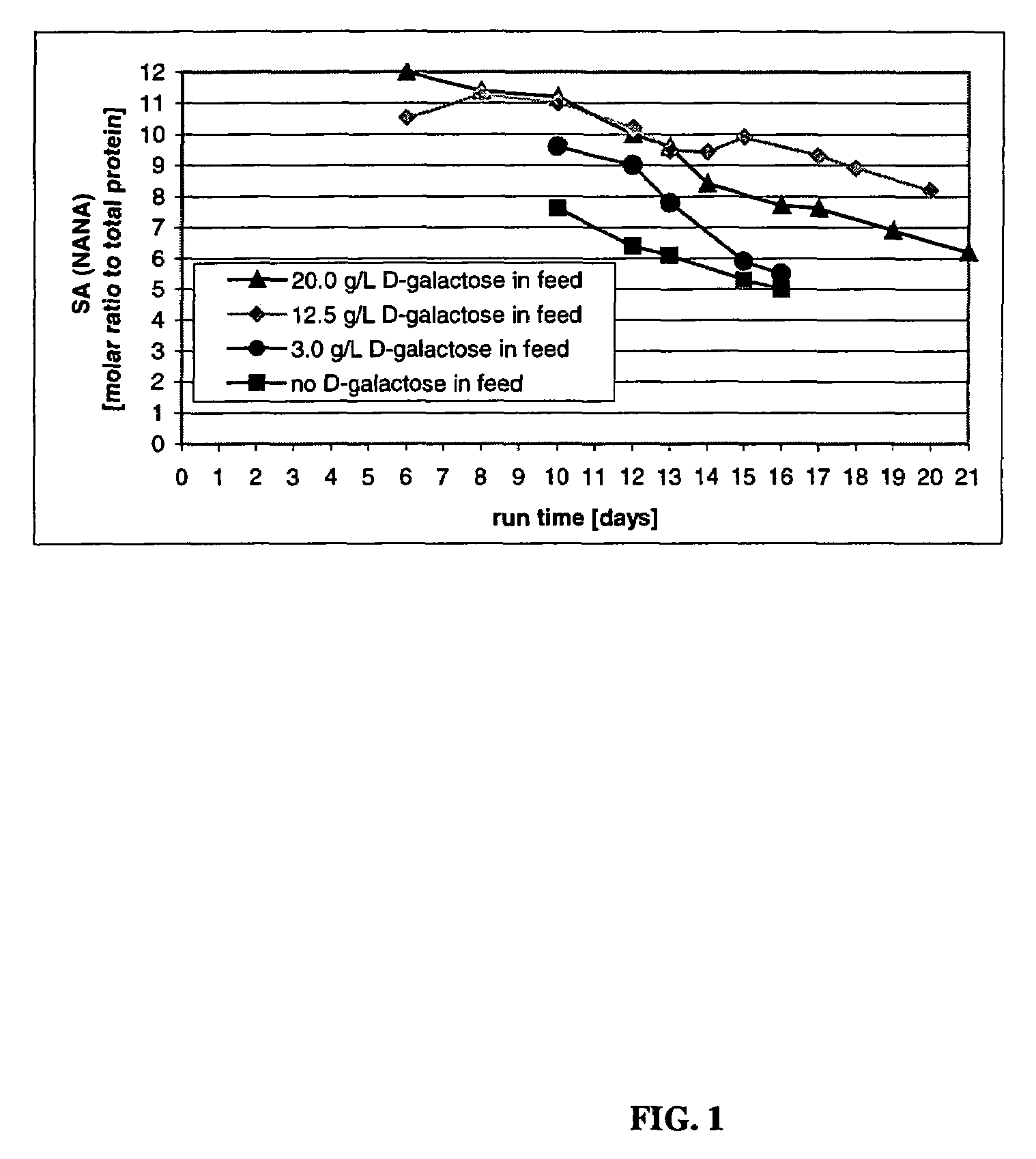
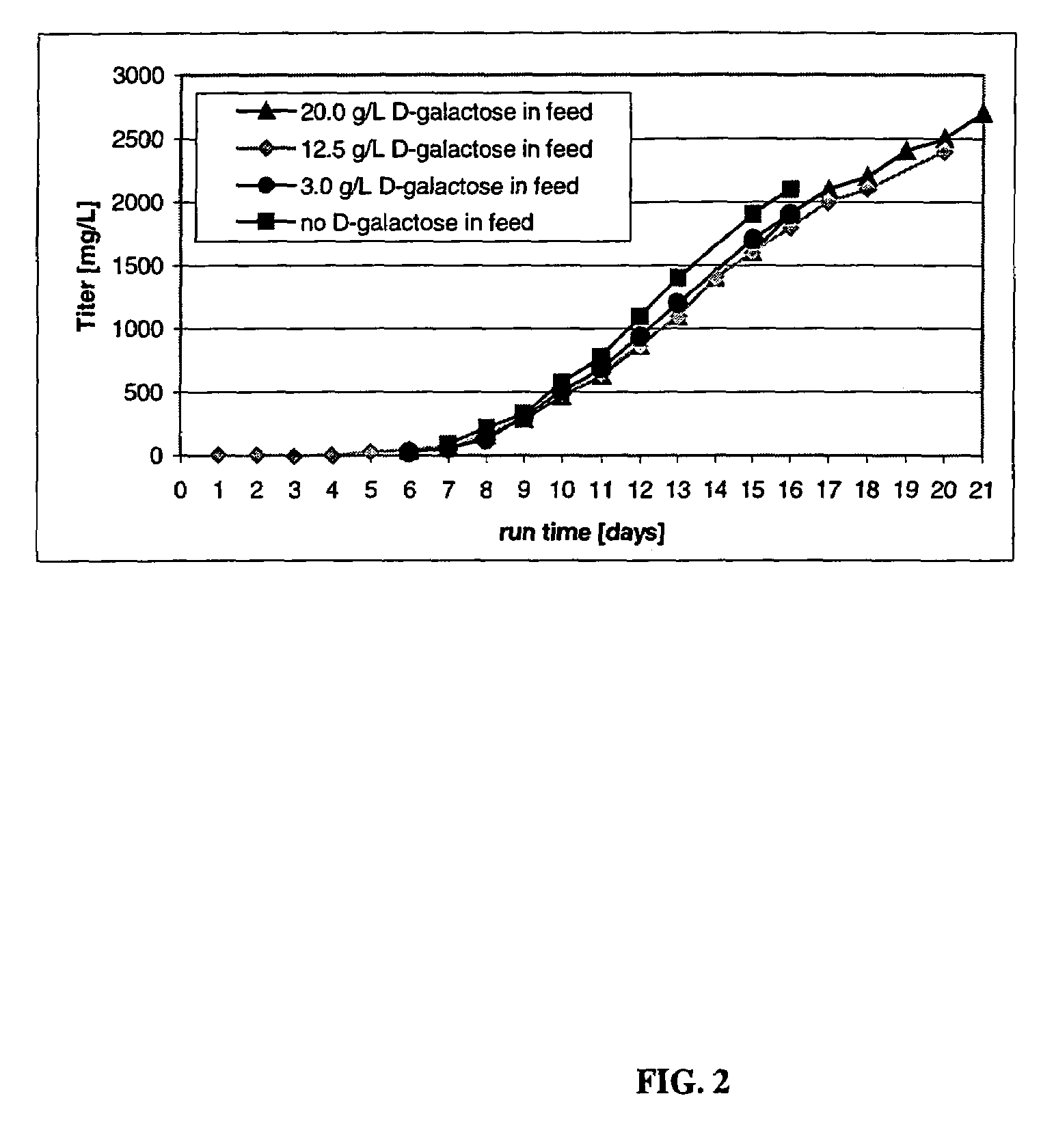
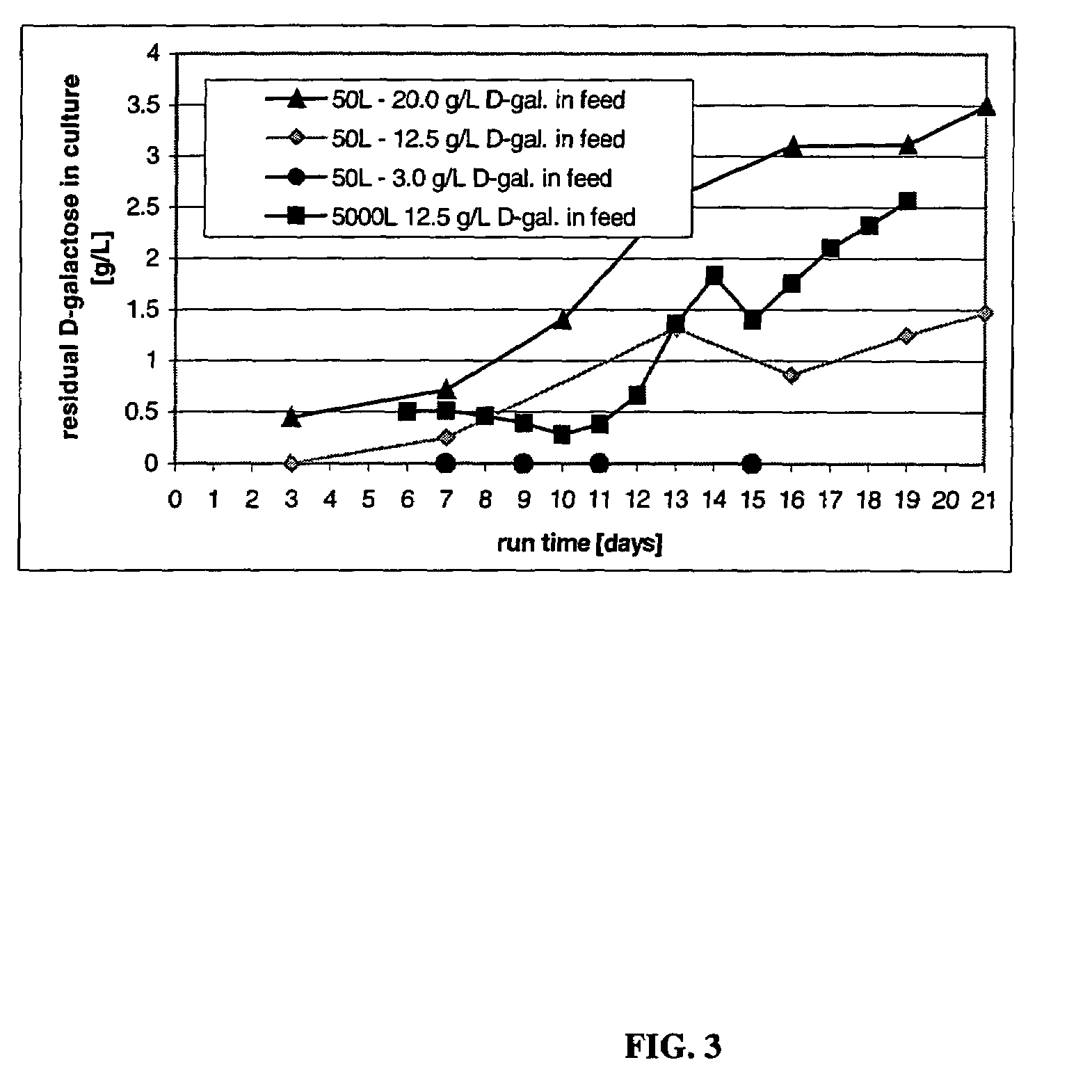
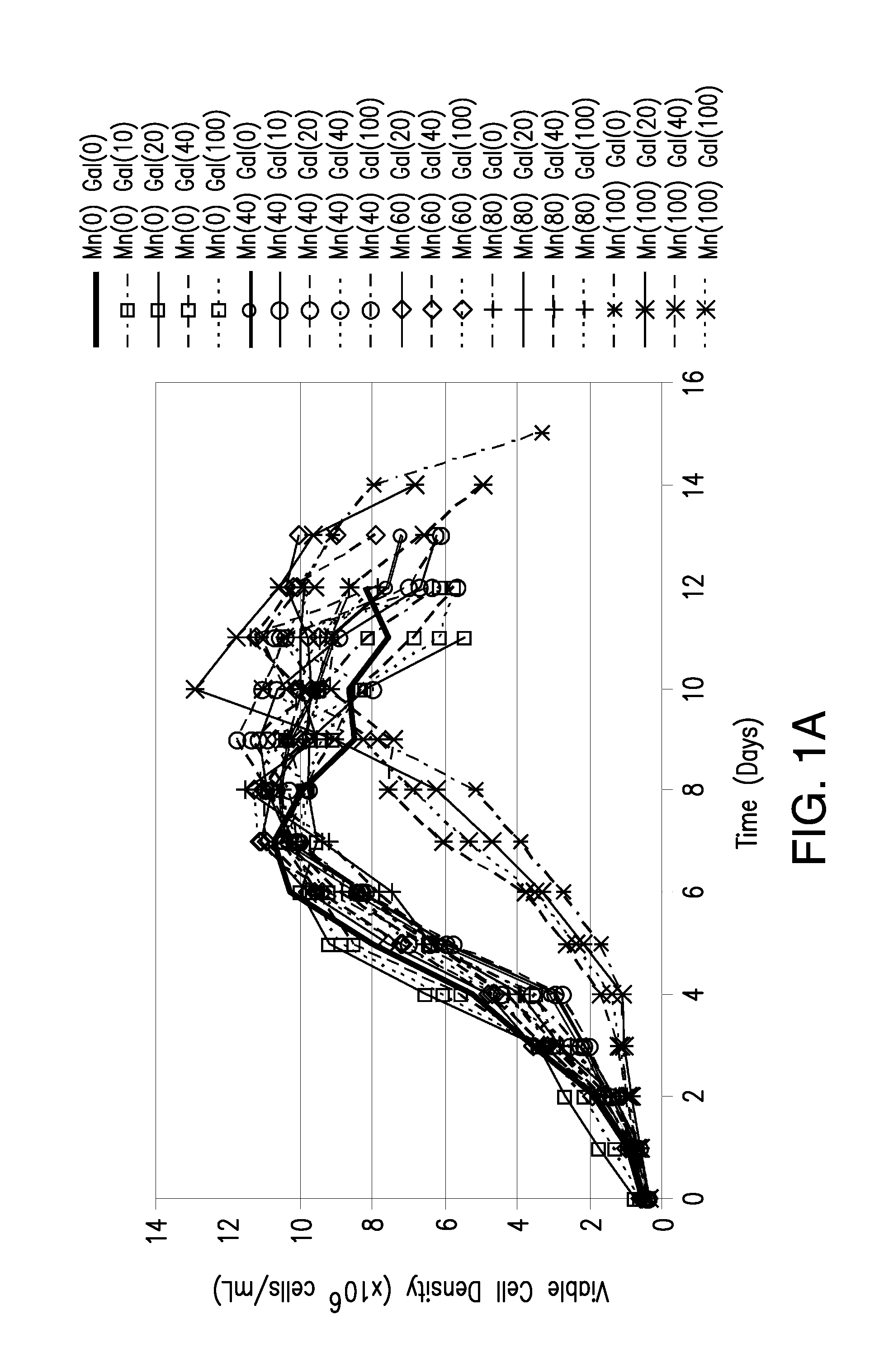
Methods for controlling the galactosylation profile of recombinantly-expressed proteins
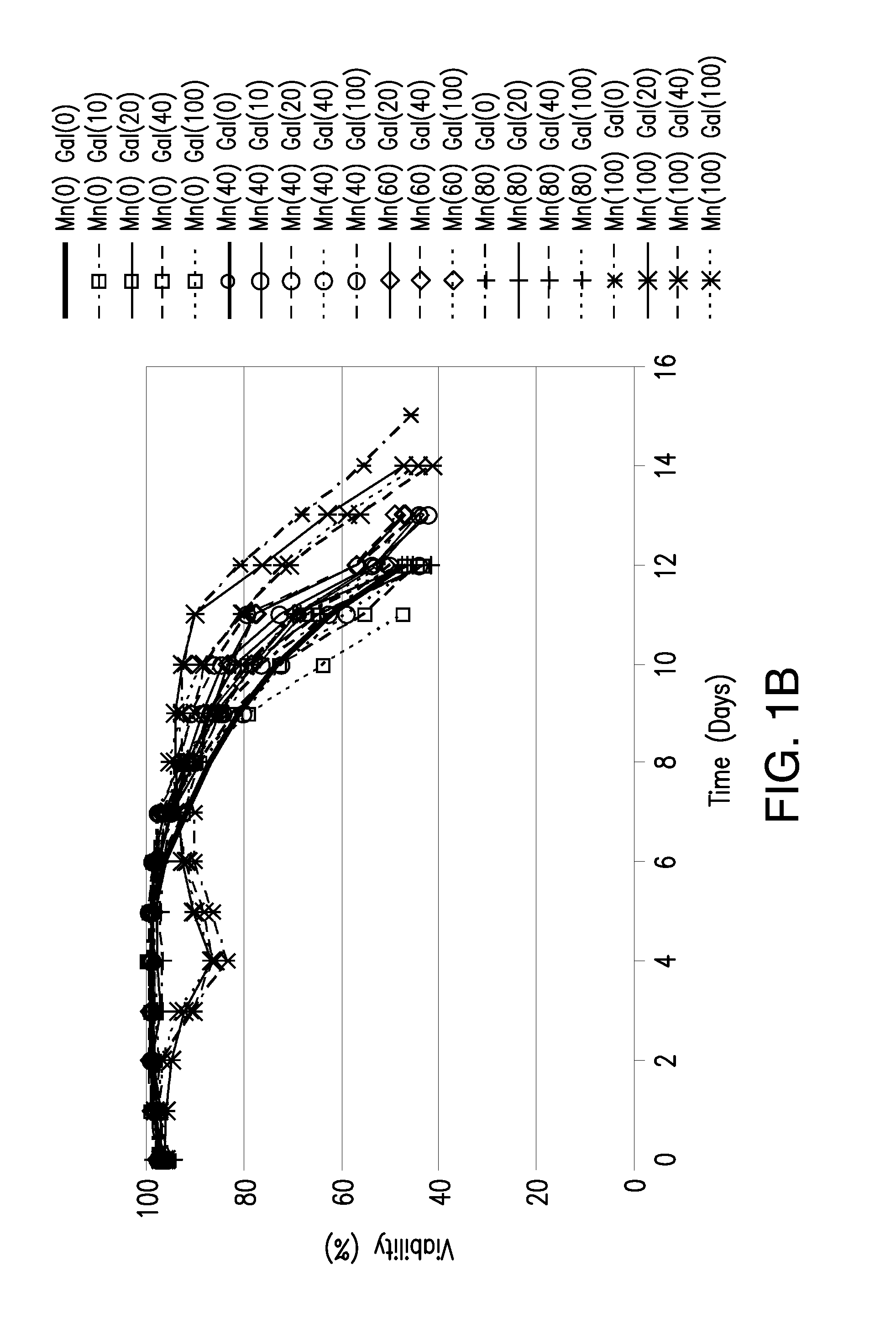
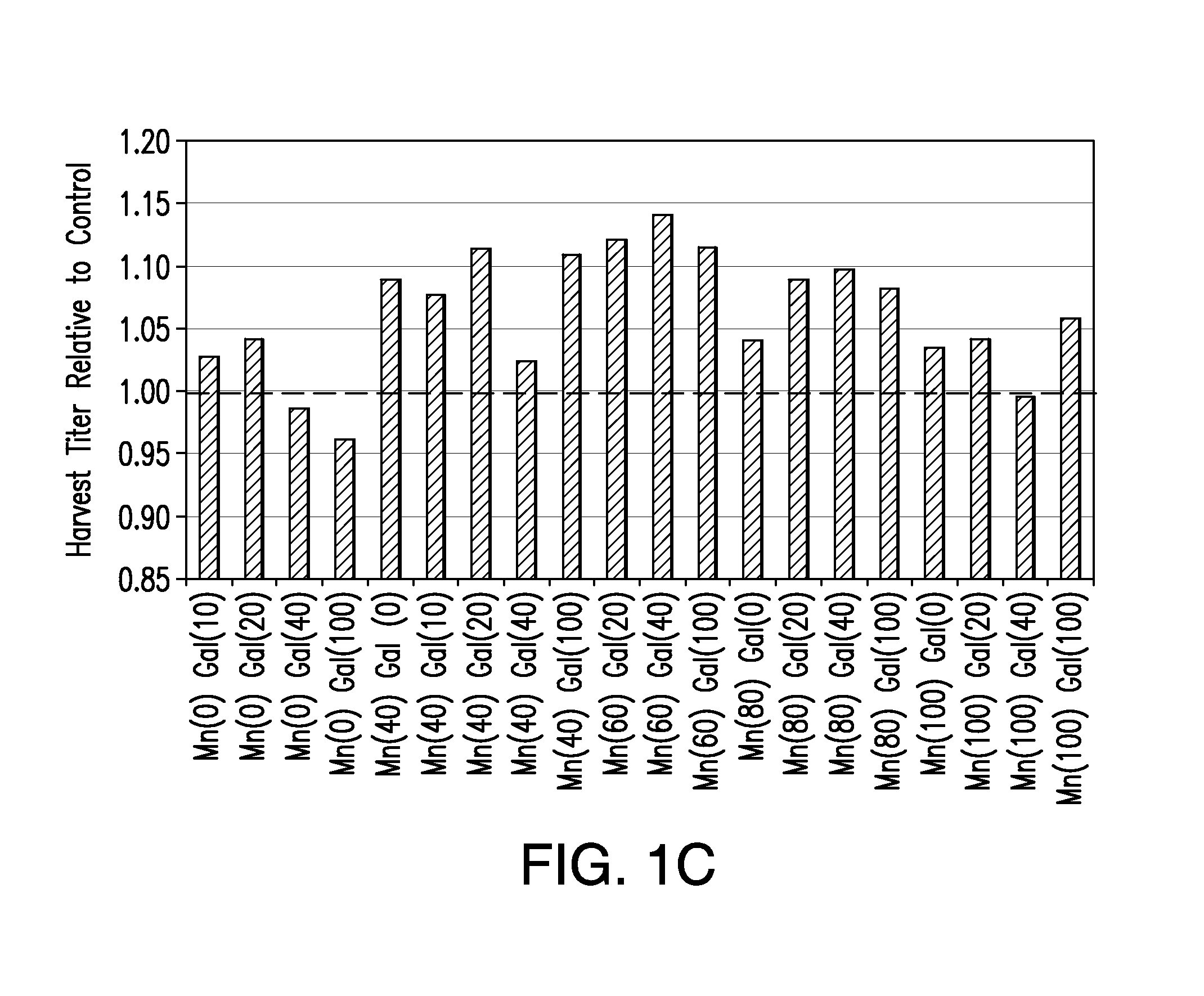
The present invention relates to methods for modulating the glycosylation profile of recombinantly-expressed proteins. In particular, the present invention relates to methods of controlling the galactosylation profile of recombinantly-expressed proteins by supplementing production medium, e.g., a hydrolysate-based or a chemically defined medium, with manganese and / or D-galactose.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Preparation method for fast separating flavonoid glycosides from oil-tea-cakes with medium pressure column
ActiveCN101899070ASimple processHigh product contentSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationCamellia oleiferaSolvent
The invention discloses a preparation method for fast separating flavonoid glycosides from oil-tea-cakes with a medium pressure column, which comprises the following steps of: decorticating and crushing camellia oleifera abel seeds, degreasing the camellia oleifera abel seeds with non-polar solvents, performing extraction with ethanol water, filtering and condensing the extract to obtain crude extract concrete, performing fast separation with the medium pressure column to obtain an over 90 percent flavonoid glycoside mixture, and further adopting a high performance liquid chromatography to prepare over 95 percent flavonoid glycoside monomers, wherein the flavonoid glycoside monomers are kaemplerol 3-O-[2-O-beta-D-galactose-6-O-alpha-L-rhamnose]-beta-D-glucoside (I) and kaemplerol 3-O-[2-O-beta-D-xylose-6-O-alpha-L-rhamnose]-beta-D-glucoside (II) respectively. The method can be used for batch preparation, and has the advantage of providing quality raw materials for the development of flavonoid glycoside medicaments and healthcare functional products in the oil-tea-cakes.
Owner:INST OF CHEM IND OF FOREST PROD CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Cassia Derivatives
InactiveUS20140127149A1Enhance the imageBetter sensory profileOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsHydrogen atomD-galactal
This invention relates to a cationically and amphiphilically modified polygalactomannan having repeating units with an average D-mannosyl to D-galactosyl residue ratio of at least 5 to 1 and to compositions containing same. A portion of the hydrogen atoms of hydroxyl groups situated on the mannosyl and galactosyl residues of the galactomannan are replaced with an amphiphilic and a cationic substituent.
Owner:LUBRIZOL ADVANCED MATERIALS INC
Method for detecting monosaccharide component in rainbow conk glycopeptide
InactiveCN103018352AEfficient separationQuality assuranceComponent separationAdditive ingredientD-galactal
The invention belongs to the field of monosaccharide component analysis, and in particular relates to a method for detecting monosaccharide components in rainbow conk glycopeptide. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out a test on HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) chromatographic condition and systematic compatibility; subsequently respectively absorbing a mixed reference solution and a test solution to be injected into the HPLC chromatographic instrument so as to obtain a chromatogram, wherein the reference solution is a 1phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone derivative solution of D-glucose, D-mannose, D-xylose, L-xylose, D-galactose, D-arabinose, D-hydrochloric acid glucosamine and L-rhamnose reference solutions; and the test solution is a 1-phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone derivative solution of a rainbow conk glycopeptide acid hydrolysis product. Polysaccharide peptide products such as rainbow conk glycopeptide, rainbow conk intracellular glycopeptide, rainbow conk extracellular glycopeptides and coriolus versicolor polysaccharide are distinguished by detecting the mole ratio of eight monosaccharide ingredients in a test sample, so that the quality and the curative effect of the rainbow conk glycopeptide are ensured.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Abelmoschus manihot polysaccharide with anti-tumor activity and preparation method thereof
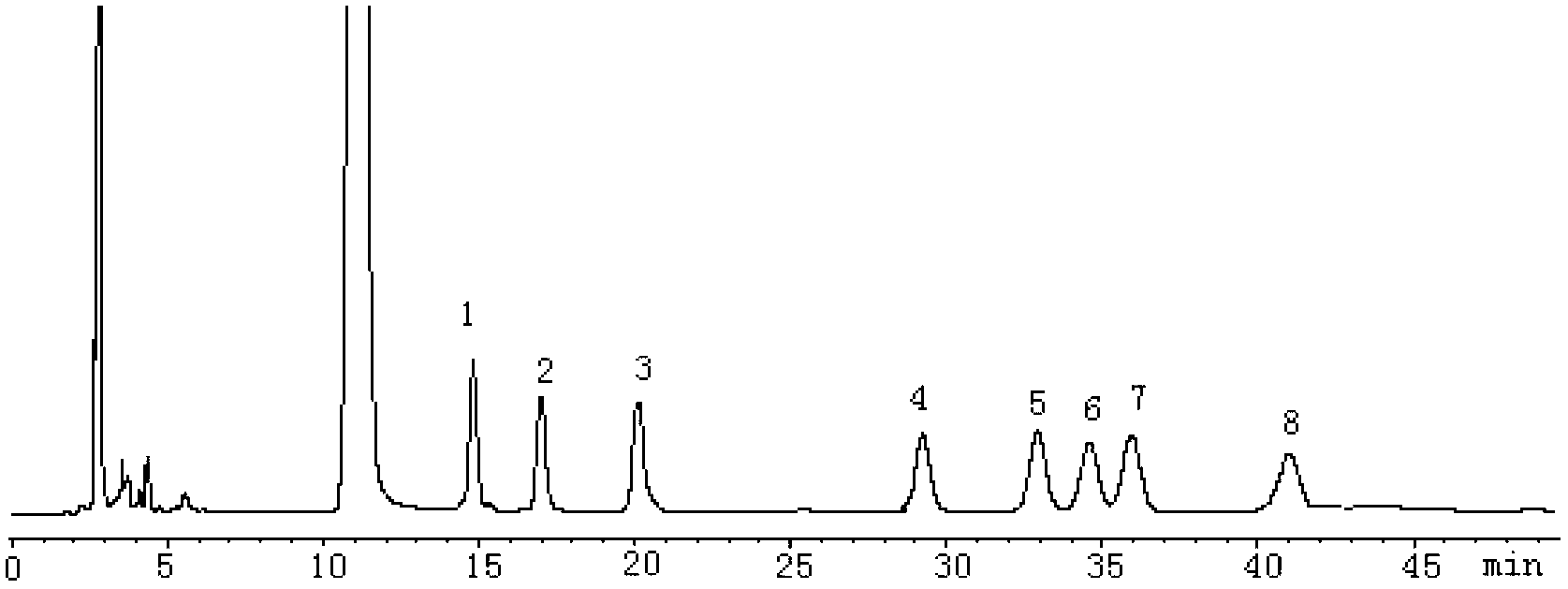
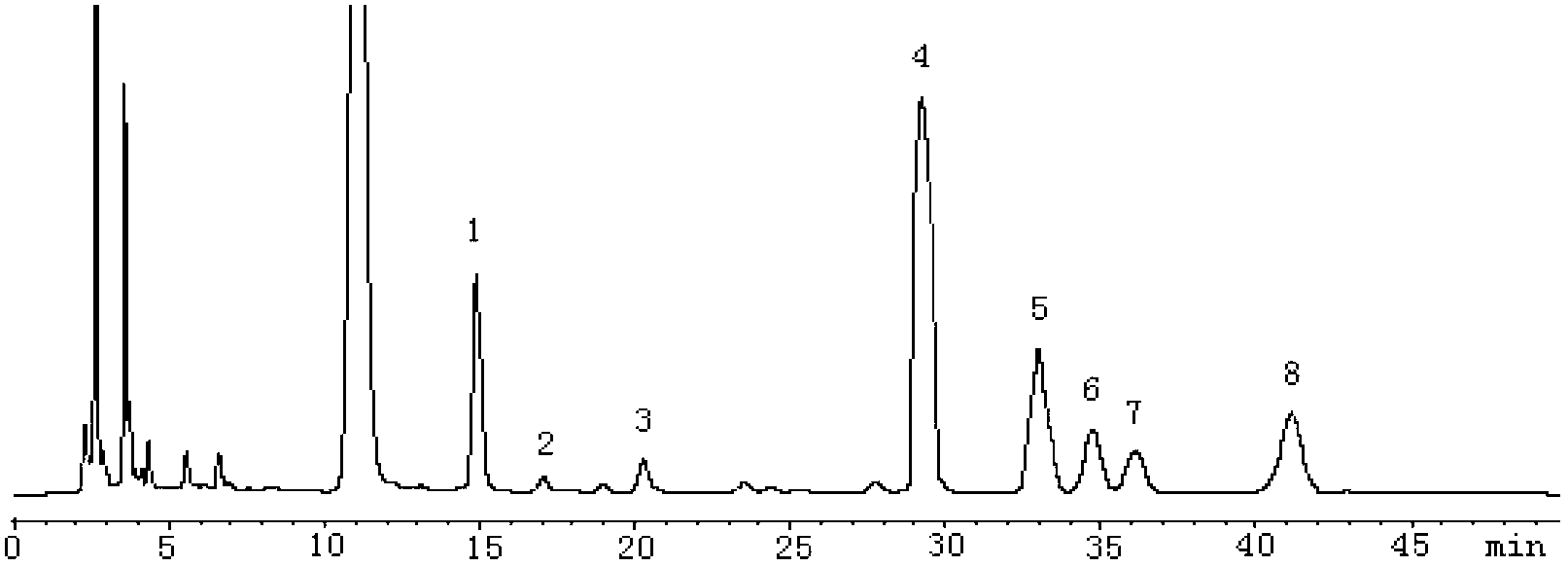
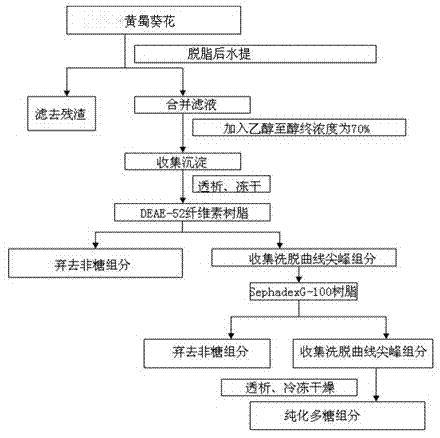
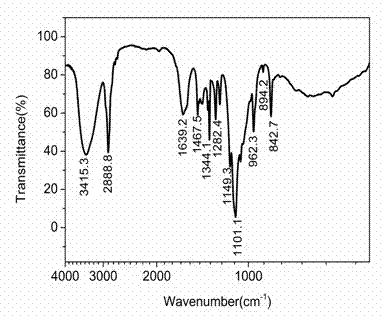
ActiveCN102964466AHas antitumor activityHigh purityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsStructural formulaPyran
The invention discloses an abelmoschus manihot polysaccharide with an anti-tumor activity and a preparation method thereof. The polysaccharide is formed by beta-D-glucopyranose, alpha-D-mannopyranose, alpha-D-galactose and alpha-L-fucopyranose in a mol ratio of 1: 0.91: 2.14: 1.0, and has the molecular weight of 8867. The structural formula of a basic unit of the polysaccharide is that alpha-D-galactose (1->6) and alpha-D-mannopyranose (2->6) are taken as main chains and mannose C-3 branches are connected with the alpha-L-fucopyranose (1->3) and connected with the beta-D-glucopyranose (->1). According to the abelmoschus manihot polysaccharide disclosed by the invention, an extraction and separation process is selected through a large number of experiments; firstly, a water extraction and alcohol precipitation method is used for obtaining a rough polysaccharide and then protein is removed; and then, a DEAE-52 (Diethyl Aminoethanol-52) cellulose resin and SephadexG-100 gel resin are combined for purifying to prepare the abelmoschus manihot polysaccharide with high purity. Anti-tumor experiment results show that the abelmoschus manihot polysaccharide has very good anti-tumor activity and has no untoward effects after being used for a long period; and the abelmoschus manihot polysaccharide can be conveniently prepared into medicines with various preparations with pharmaceutically acceptable carriers, and is convenient to take clinically.
Owner:江苏鼎泰药物研究(集团)股份有限公司
Chinese magnoliavine fruit polysaccharide extract and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102805762ASignificant antiallergic activityObvious superiorityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsMast cell degranulation testLactose
The invention discloses a Chinese magnoliavine fruit polysaccharide extract and a preparation method and an application thereof. Counted by D-glucose, the content of polysaccharides is not lower than 45 percent of the total weight of the polysaccharide extract; a monosaccharide mainly comprises D-glucose, D-galactose and D-galacturonic acid; the mass ratio of the D-glucose to the D-galactose is (3-9):1; and the D-galacturonic acid accounts for 5-40 percent of the total weight of the polysaccharide extract. As proved by mouse ear heterogeneous driven dermal sensitivity test and rat peritoneal mast cell degranulation test, the Chinese magnoliavine fruit polysaccharide extract has remarkable anti-allergic action activity, and can be used for preparing anti-allergic action medicaments, functional foods and cosmetics.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUATUO MEDICAL SCI CO LTD
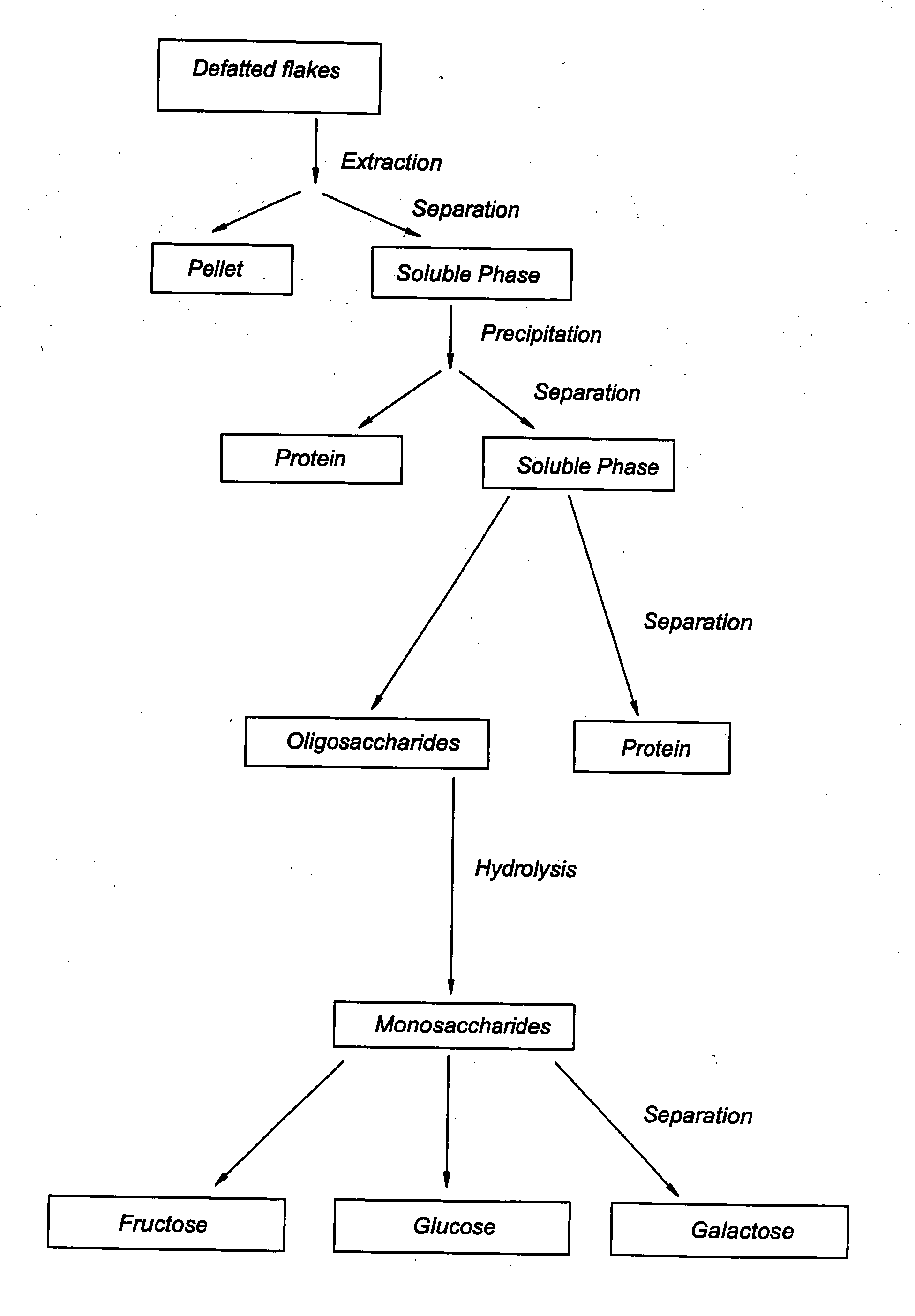
D-galactose isolation system
InactiveUS20040198965A1Suitable for useLow costSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationLactoseHydrolysis
The invention relates to procedures for the manufacturing of D-galactose and D-galactose containing compositions. More specifically, the invention provides a method for isolating D-galactose from legume material, which method comprises subjecting a legume composition containing non-homologuous soluble polysaccharide, commonly referred to as oligosaccharide, to one or more treatments, resulting in a preparation comprising at least 30% oligosaccharides, and subsequent hydrolysis of the oligosaccharides in this preparation into mainly monosaccharides.
Owner:CARGILL AMSTERDAM
Cassia Derivatives
InactiveUS20130129639A1Improve compatibilityBetter sensory profileBiocideOrganic active ingredientsHydrogen atomD-galactal
This invention relates to a cationically and hydrophobically modified polygalactomannan having repeating units with a D-mannosyl to D-galactosyl residue ratio of at least 5 to 1 and to compositions containing same. A portion of the hydrogen atoms of hydroxyl groups situated on the mannosyl and galactosyl residues of the galactomannan are replaced with a hydrophobic substituent and a cationic substituent.
Owner:LUBRIZOL ADVANCED MATERIALS INC
Culture method for highly expressing erythropoietin in serum-free medium and cho cells
ActiveCN102268402AIncreased glycosylationIncrease the proportionMicroorganism based processesArtificial cell constructsCulture fluidChinese hamster
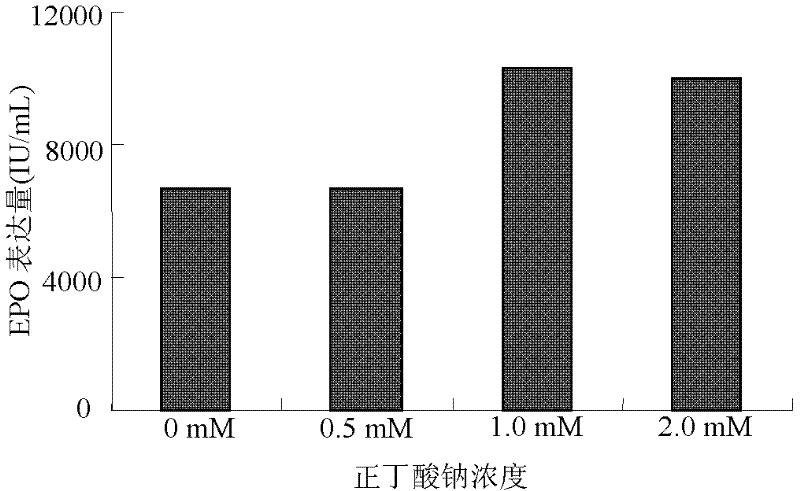
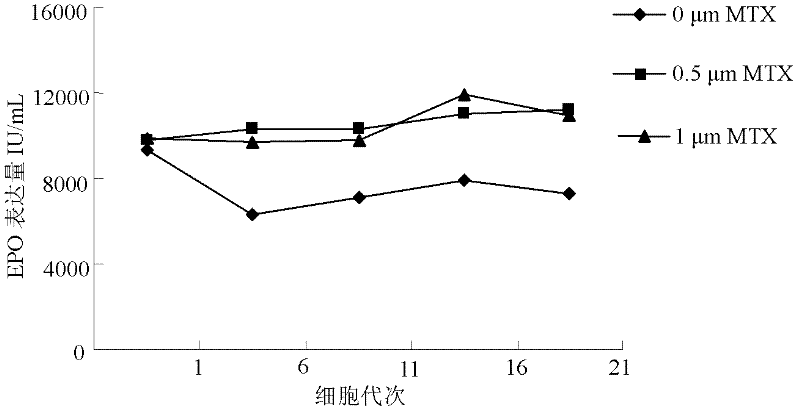
The invention discloses a serum free medium for expressing erythropoietin in CHO (Chinese hamster ovary) cells, and a culture method for high expression of erythropoietin in CHO cells. The serum free medium contains additives D-glucose and sodium butyrate, and also contains one or more of D-galactose, D-mannitose and N-acetylglucosamine. The culture method comprises the steps of: performing serumculture on activated seed cells by using a serum medium, and then performing serum free culture by the serum free medium. By adopting the medium and culture method disclosed by the invention, recombinant human erythropoietin protein of high and stable expression can be obtained, and the glycosylation degree of erythropoietin is improved, i.e. the specific gravity of EPO (erythropoietin) sialic acid is improved. As high as 1.0*107IU recombinant human erythropoietin can be obtained from one liter of culture fluid by the culture method provided by the invention, the expression is stable, and theculture method is simple and suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:SHENZHEN SCIPROGEN BIO PHARMA
Active extract of citrus peels as well as extraction process and application thereof
ActiveCN101850010ASimple extraction processReasonable process conditionsAntinoxious agentsFood preparationBlood plasmaD-galactal
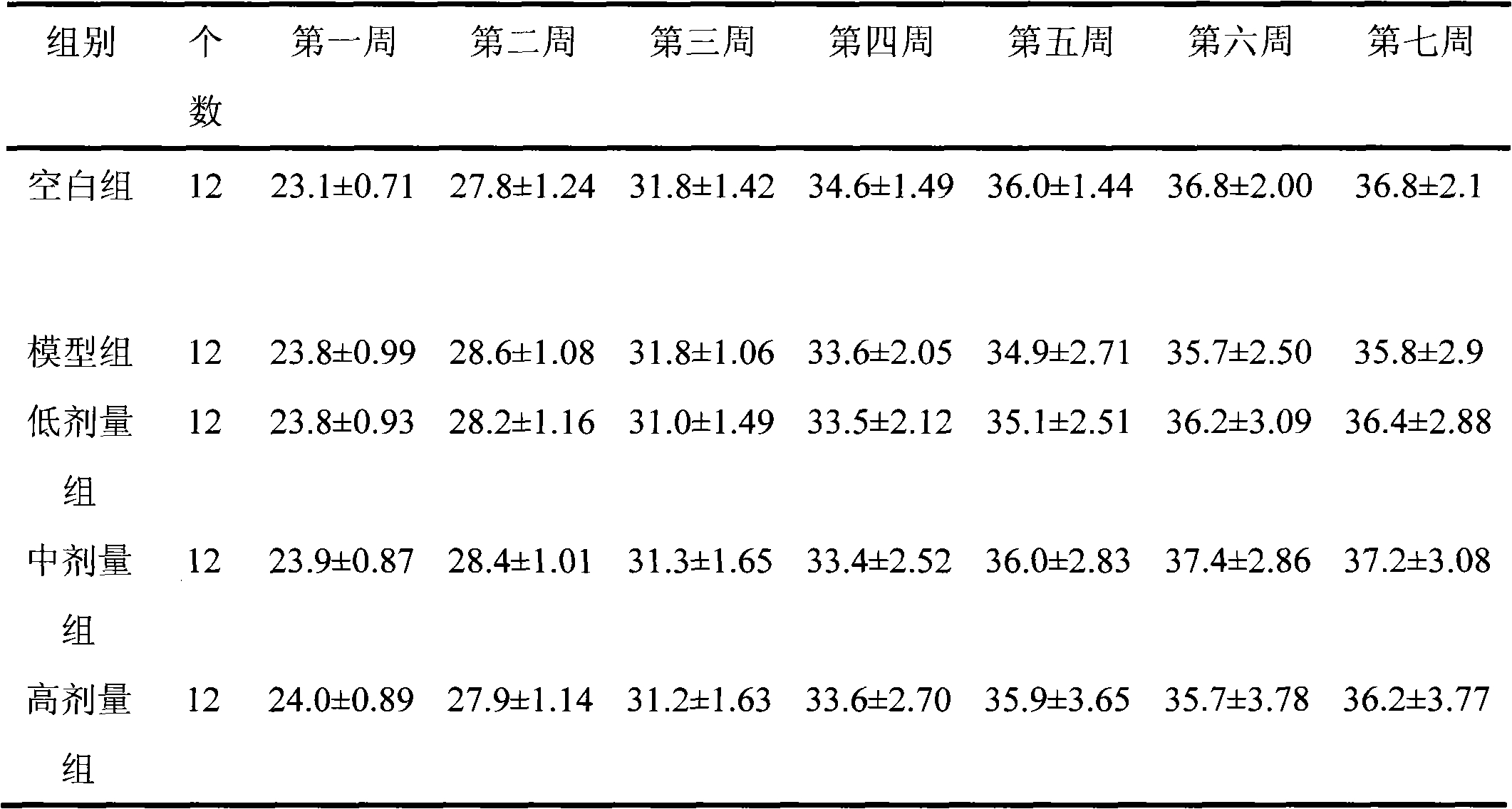
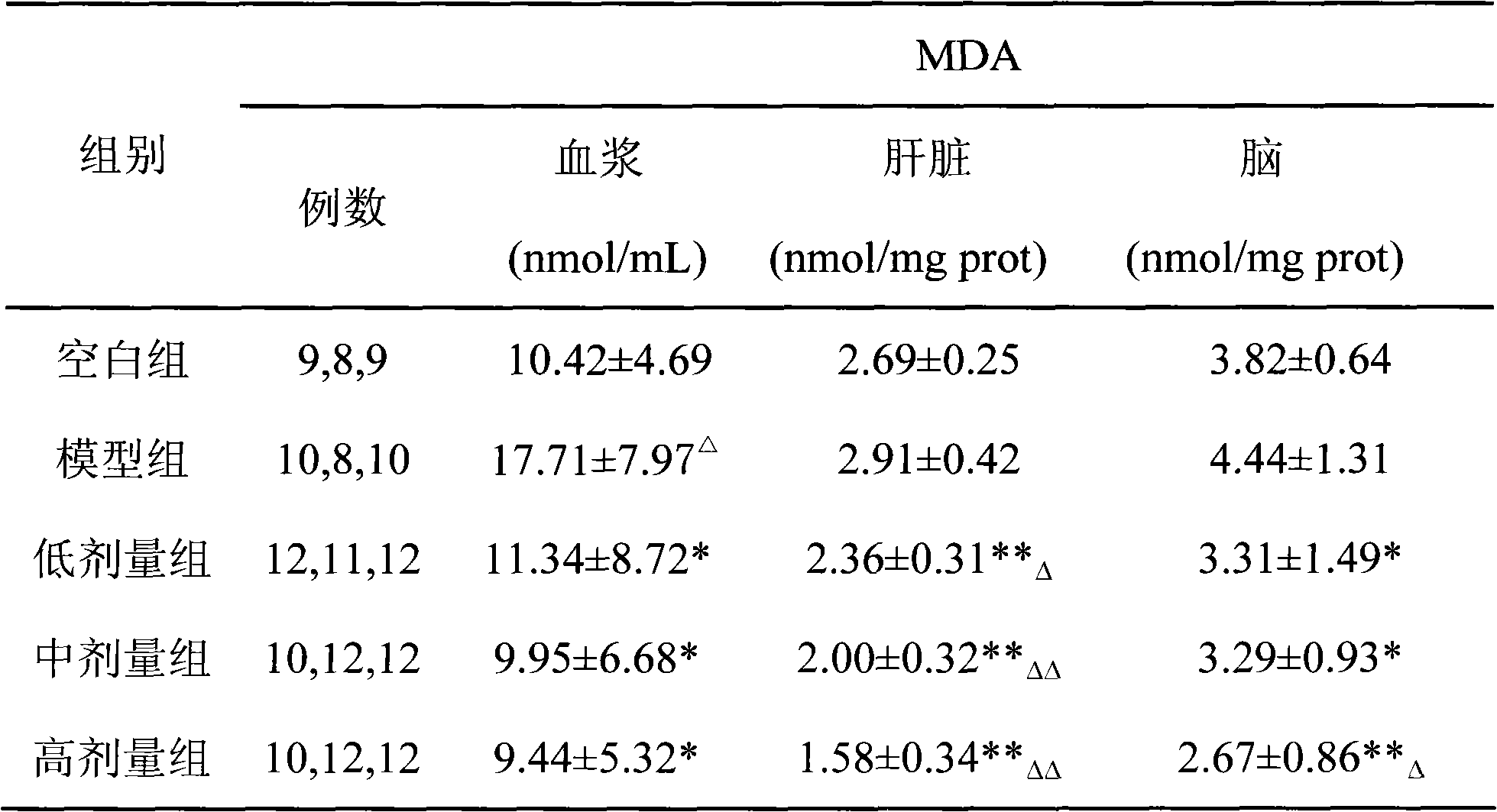
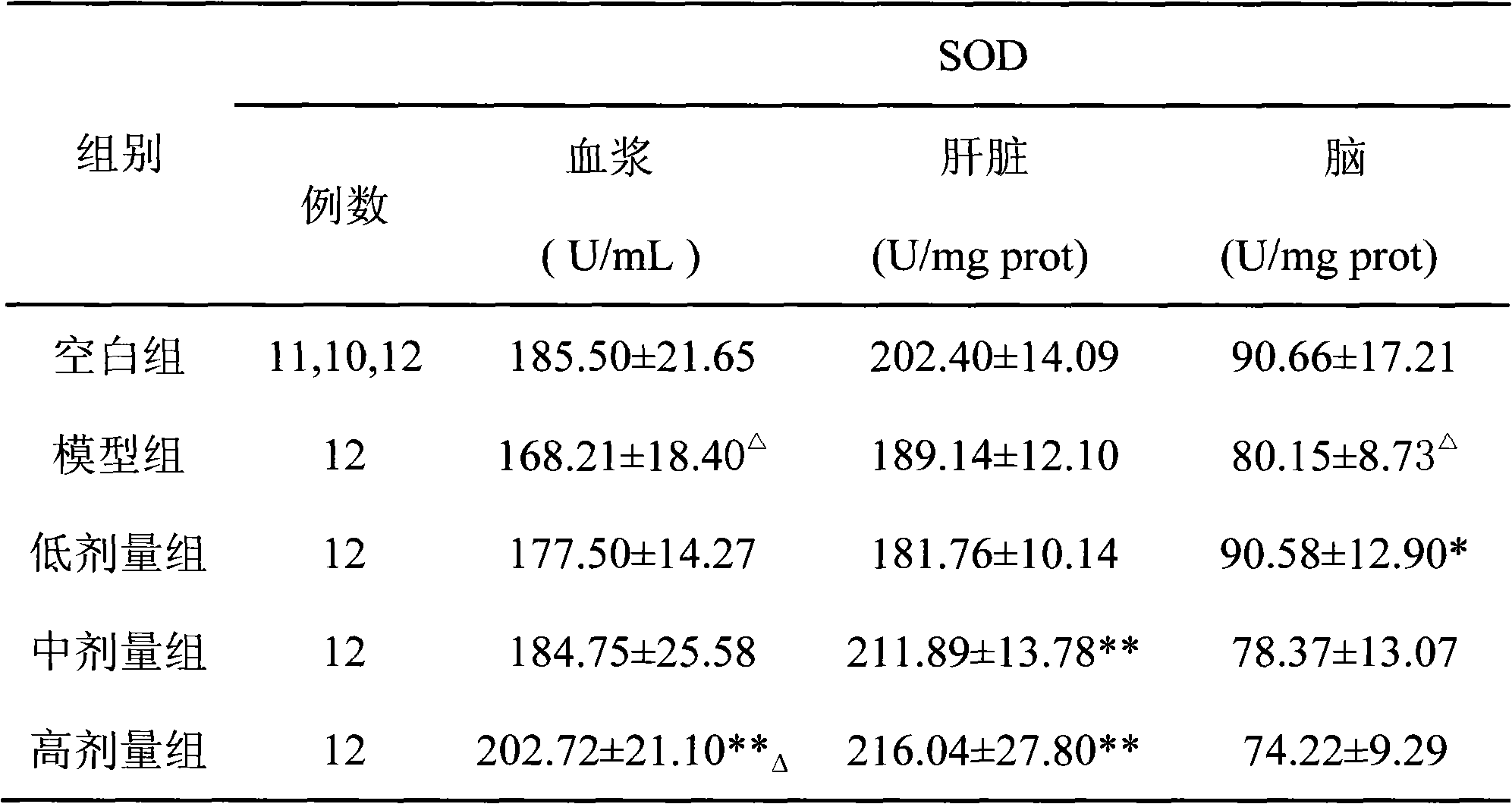
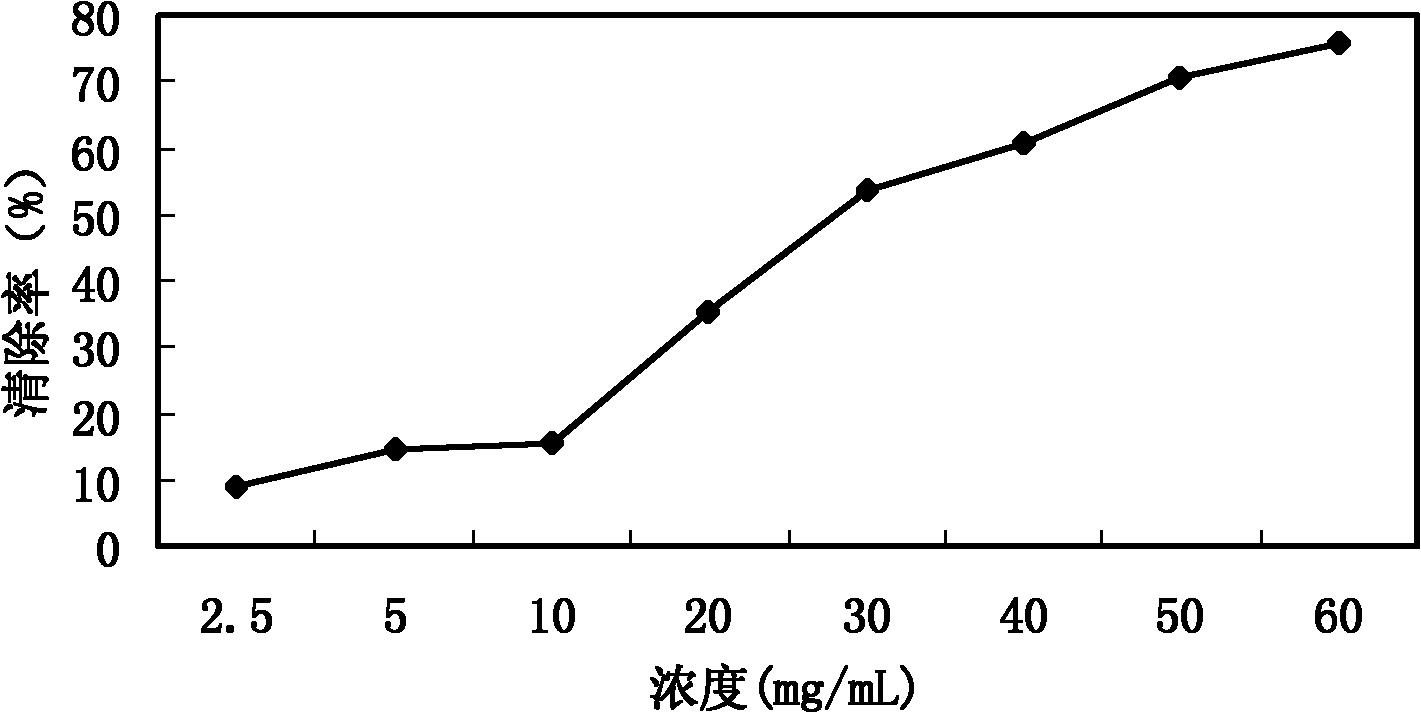
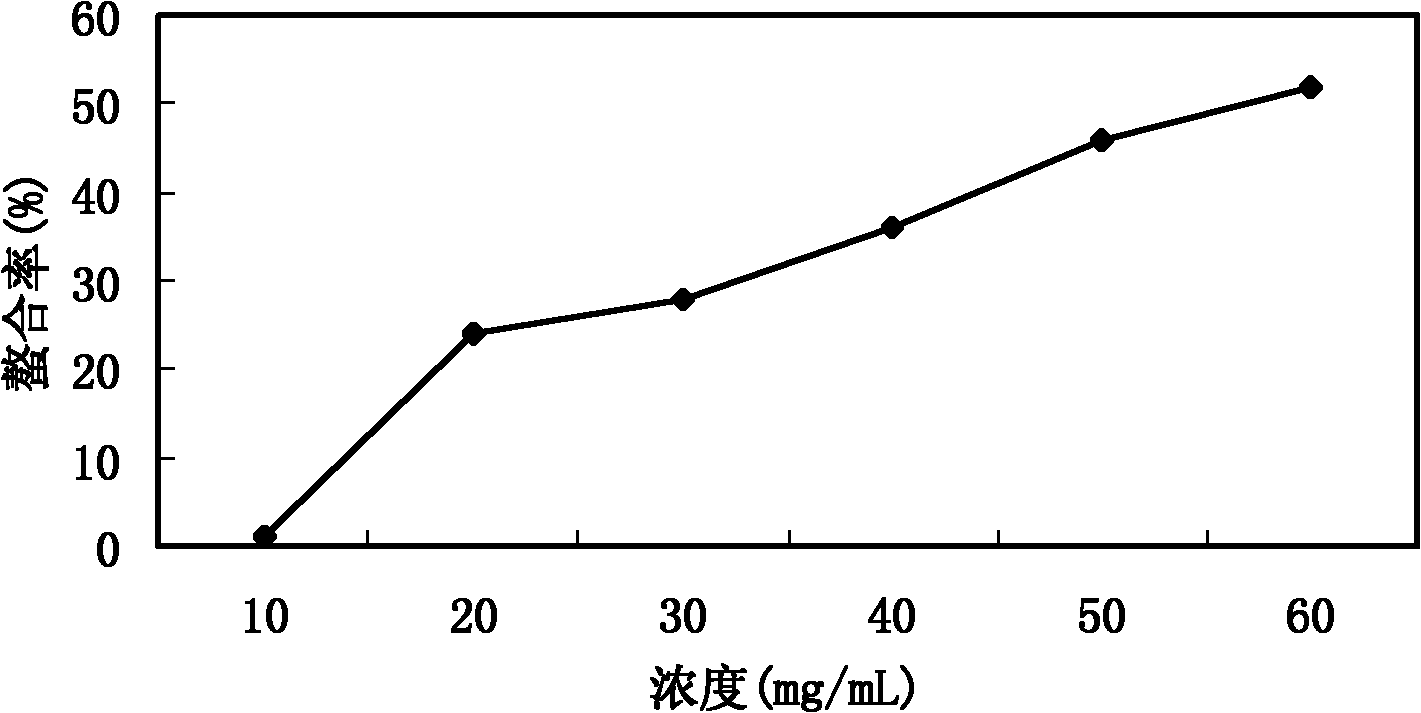
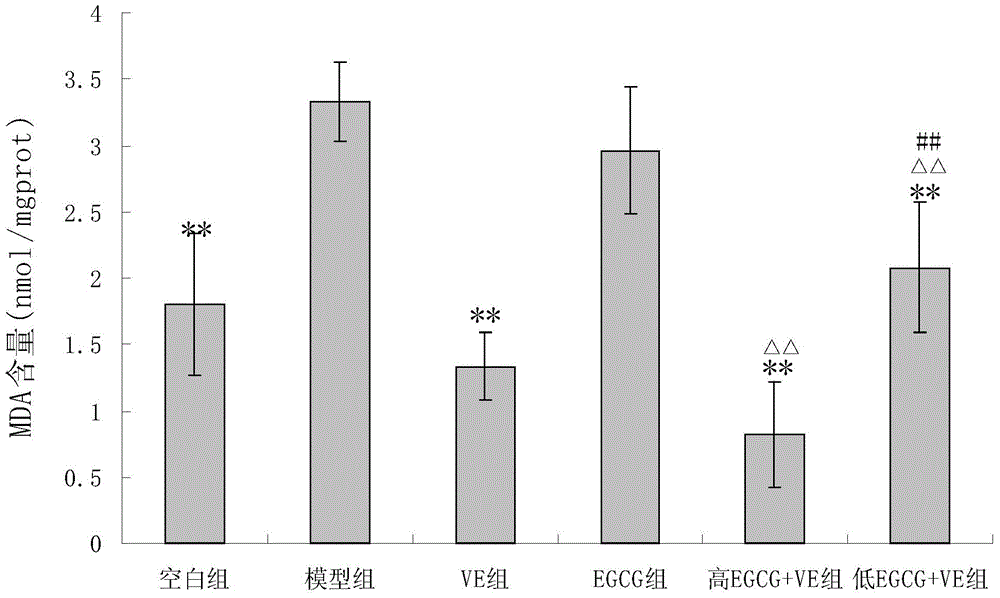
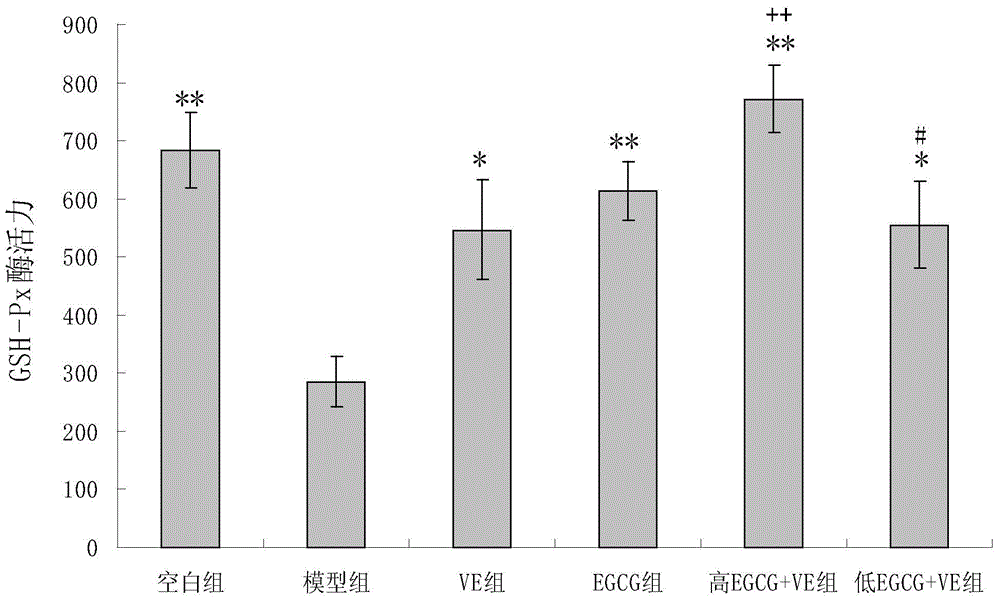
The invention discloses an anti-oxidation active extract of citrus peels as well as an extraction process and application thereof. The active extract of the citrus peels mainly contains a citrus flavonoid substance and pectic polysaccharide. The extraction process of the active extract of the citrus peels comprises the steps of preprocessing raw materials, refluxing and extracting by a dipping method, decompressing and concentrating and drying in vacuum. The invention takes the in-vitro oxidation resistance of the extract to combine with the extraction yield as indexes, adopts a response surface method to optimize the extraction process, has reasonable technological conditions and good effect stability and is suitable for industrialized production. The active extract of the citrus peels, which is obtained by extraction, has an obvious effect to a model mouse with senility caused by D-galactose and can lower the content of the MDA (malondialdehyde) of the plasma, the liver and the brain obviously; the activity of the SOD (superoxide dismutase) of the plasma, the liver and the brain is obviously enhanced; the activity of the GSH-Px (glutathione peroxidase) of the plasma and the liver is obviously enhanced; and the invention can be used for preparing an anti-oxidation medicine, an anti-oxidation food or an anti-oxidation health-care product.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV +1
Preparation method of polysaccharide in pine cone from Pinus koraiensis
InactiveCN102020721ARemove weak polarityRemoves moderately polar chemicalsPinus koraiensisD-galactal
The invention discloses a preparation method of polysaccharide in pine cone from Pinus koraiensis, relating to a preparation method of polysaccharide in pine cone from Pinus koraiensis. The invention solves the problems that the traditional preparation method of the polysaccharide in pine cone from Pinus koraiensis cannot completely remove chemical components with weak polarity and medium polarity in the pine cone from Pinus koraiensis and the protein removal rate is relatively lower. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1. degreasing; 2. extracting; 3. preparing coarse polysaccharide; 4. deproteinizing; and 5. decoloring, collecting precipitates, freezing and drying to obtain the refined polysaccharide in pine cone from Pinus koraiensis. The extraction rate of the neutral polysaccharide in pine cone from Pinus koraiensis prepared by the invention can reach 1.15-1.52 percent, the protein removal rate is up to over 70 percent and the pigment removal rate is up to over 95 percent. The chromatography test shows that the neutral polysaccharide mainly comprises seven monosaccharides, namely D-ribose, L-rhamnose, L-arabinose, D-xylose, D-mannose, D-glucose and D-galactose, and the preparation method of polysaccharide in pine cone from Pinus koraiensis is applied to the field of preparation of neutral polysaccharide pine cone from Pinus koraiensis.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for extracting L-arabinose and D-galactose from Arabic gum
InactiveCN102146102ASimple and fast operationImprove product qualitySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationAlcoholDistillation
The invention discloses a method for extracting L-arabinose and D-galactose from Arabic gum, which comprises the following steps of: (1) performing catalytic hydrolysis on the Arabic gum by using an acid catalyst A1, neutralizing, and evaporating out moisture from the obtained reaction liquid to obtain mixed thick syrup; (2) adding an acid catalyst A2 and ketone compounds into the mixed thick syrup for etherification reaction, and after the reaction is finished, neutralizing, distilling to recover the ketone compounds, dissolving the residue by using a mixture of alcohol compounds and water, and performing extraction treatment to respectively obtain arabinose etherate and galactose etherate; and (3) dehydrating and de-etherizing the obtained arabinose etherate and galactose etherate under the catalysis of an acid catalyst A3, neutralizing, and performing decoloration, drying by distillation and crystallization on the obtained solution to obtain the L-arabinose and the D-galactose. The method has the advantages of simple operation, high quality and yield of products, low production cost, capacity of recycling a solvent, suitability for large-scale industrial production and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
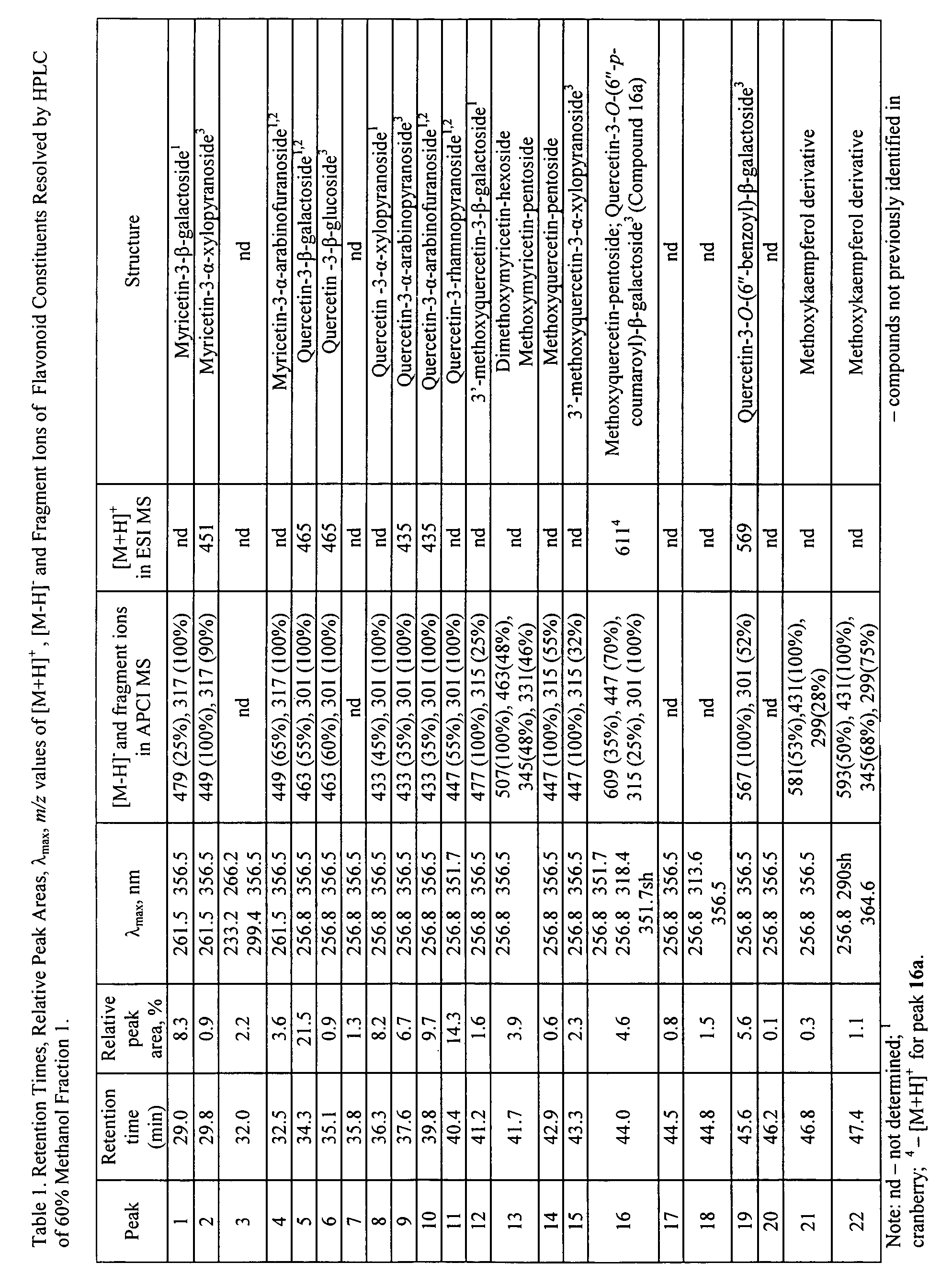
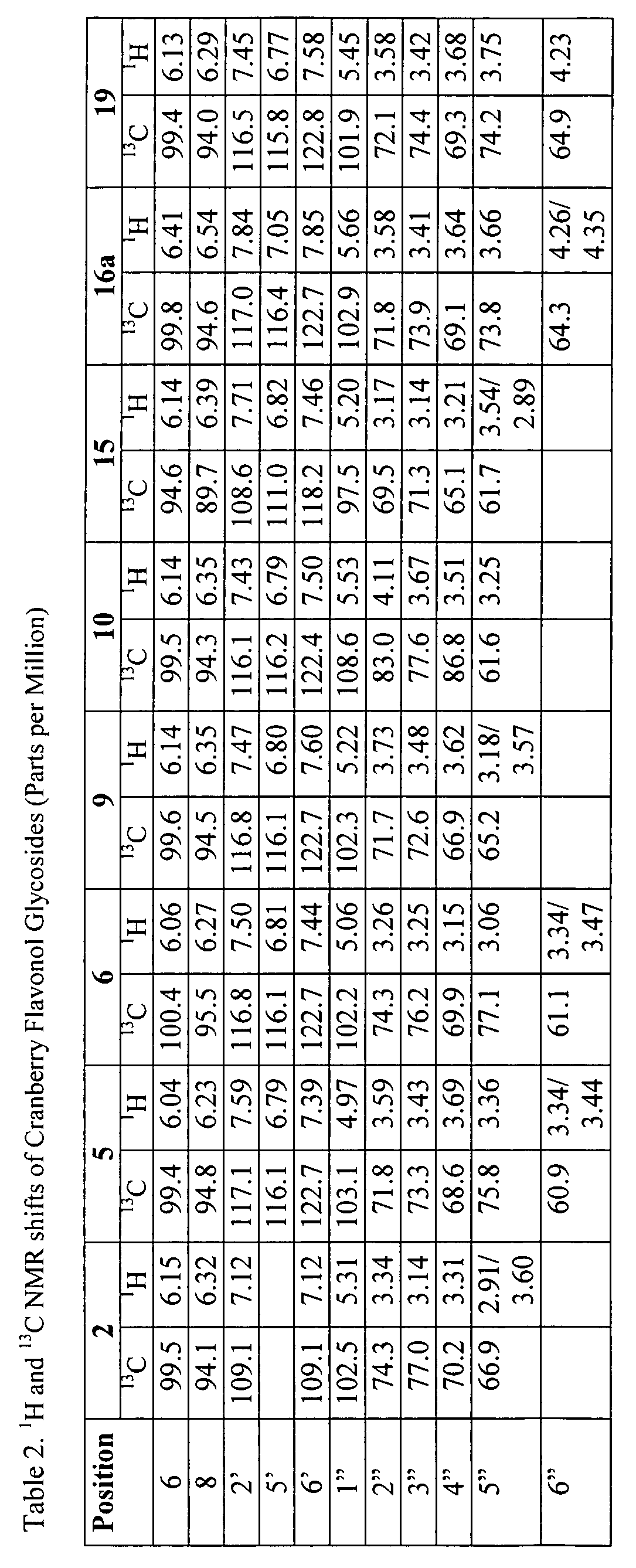
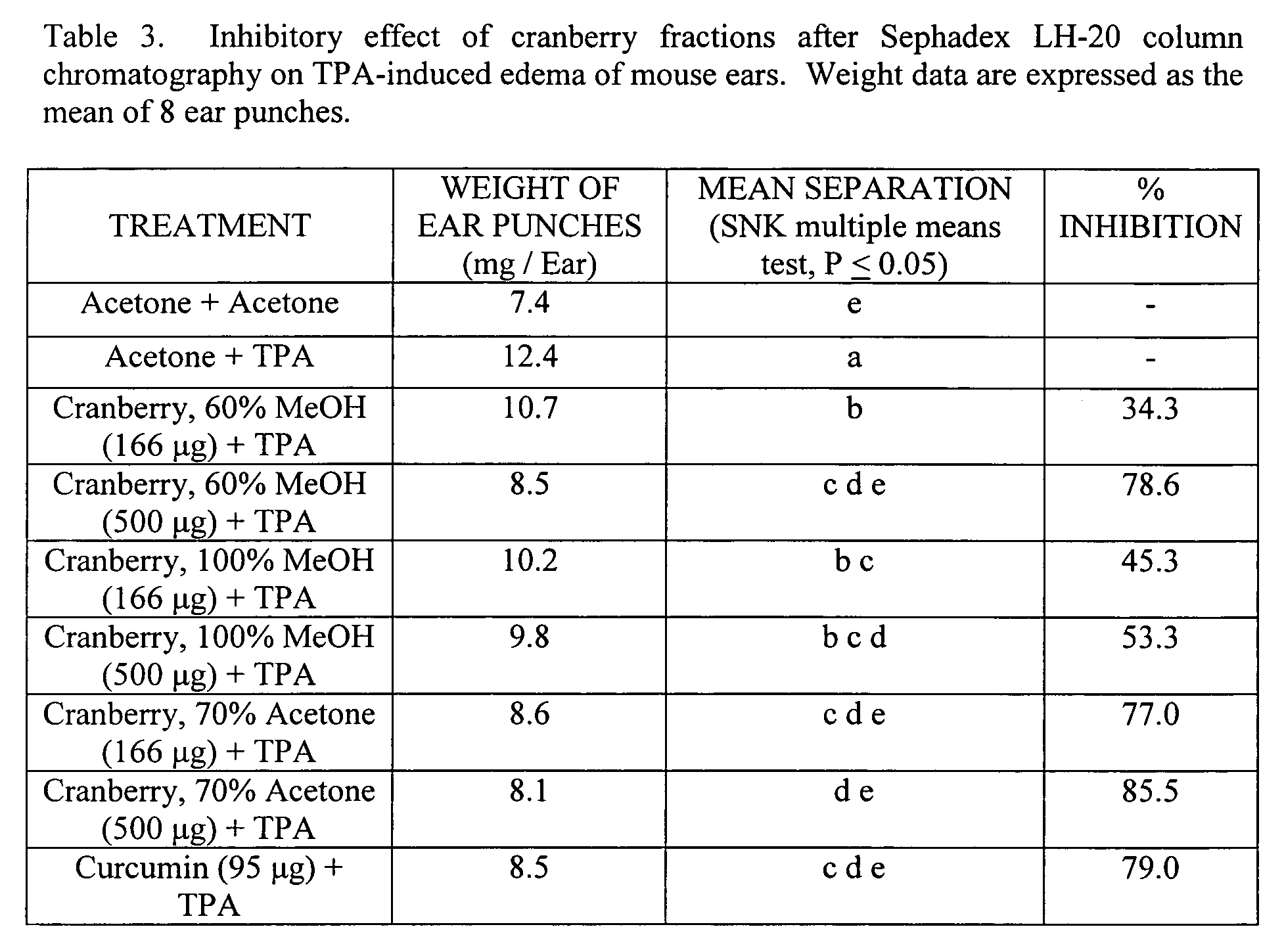
Anti-inflammatory cranberry flavonol extract preparations
The present invention is directed to extracts of cranberries (Vaccinium macrocarpon) comprising either mixed flavonols that are substantially free of anthocyanins and proanthocyanidins or a purified cranberry flavonol compound, including myricetin-3-β-xylopyranoside, quercetin-3-β-glucoside, quercetin-3-α-arabinopyranoside, 3′-methoxyquercetin-3-α-xylopyranoside, quercetin-3-O-(6″-p-coumaroyl)-β-galactoside, and quercetin-3-O-(6″-benzoyl)-β-galactoside. The present invention also embodies the use of those extracts, as well as extracts comprising the cranberry flavonol compound quercetin-3-α-arabinofuranoside, for the treatment of inflammatory disorders. Pharmaceutical, food, dietary supplement, and cosmetic compositions utilizing the extracts or compounds of the present invention are also recited.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
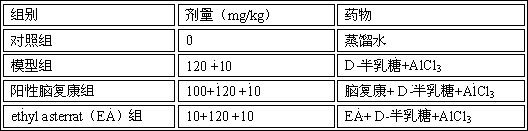
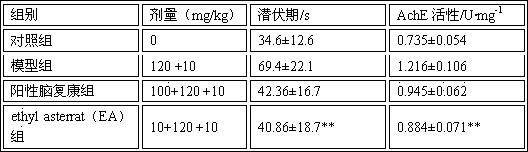
Application of ethyl asterrate in preparation of anti-alzheimer medicine
InactiveCN103768075AEnhance memorySignificant anti-senile dementia effectSalicyclic acid active ingredientsNervous disorderStructural formulaRat model
The invention discloses application of ethyl asterrate in preparation of an anti-alzheimer medicine, and in particular relates to application of diphenyl ether compound ethyl asterrate shown in the structural formula (I) in inhibition of the activity of acetylcholine esterase and preparation of an anti-alzheimer medicine. Experiments prove that the ethyl asterrate can remarkably inhibit the activity of acetylcholine esterase, can remarkably improve the memory and space exploration capability of an alzheimer rat model caused by D-galactose and AlCl3, can be applied to preparation of the anti-alzheimer medicine, and indicates an excellent market application prospect.
Owner:YICHUN UNIVERSITY
Monosaccharide production system
A monosaccharide production system is disclosed. The production system can be directed to processes for producing a D-galactose preparation, a D-galactose preparation and an isoflavones preparation, a tagatose preparation, and a tagatose preparation and an isoflavones preparation.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Method for identifying stigma maydis polysaccharide by utilizing thin layer chromatography
The invention relates to a method for identifying stigma maydis polysaccharide by utilizing thin layer chromatography and belongs to the technical field of medicine authentication. The method comprises the following steps that: a thin layer plate is prepared by silica gel G and sodium carboxymethylcellulose (CMC-Na); D-glucose, D-xylose, D-mannose, L-Arabinose, Alfa-rhamnose, D-galactose and D-galacturonic acid are used as reference substances; corn stigma polysaccharide crude product extracted by water extraction and alcohol precipitation is used as a sample, the sample is dissolved by 50% ethanol, trifluoroacetic acid is utilized to carry out hydrolysis, hydrogen peroxide is used for decoloration, normal butanol methanol, chloroform, glacial acetic acid and water are used as developing solvents, and aniline, diphenylamine, phosphoric acid and water solution are used for color development. The spot position and color of the sample and the reference substances are consistent, so that the type of saccharine contained in the corn stigma can be judged. The method has high specificity, is simple to operate and can be used for accurately identifying the type of monosaccharide in the stigma maydis polysaccharide.
Owner:JILIN INST OF CHEM TECH
Preparation method for fast separating flavonoid glycosides from oil-tea-cakes with medium pressure column
ActiveCN101899070BSimple processHigh product contentSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationCamellia oleiferaSolvent
The invention discloses a preparation method for fast separating flavonoid glycosides from oil-tea-cakes with a medium pressure column, which comprises the following steps of: decorticating and crushing camellia oleifera abel seeds, degreasing the camellia oleifera abel seeds with non-polar solvents, performing extraction with ethanol water, filtering and condensing the extract to obtain crude extract concrete, performing fast separation with the medium pressure column to obtain an over 90 percent flavonoid glycoside mixture, and further adopting a high performance liquid chromatography to prepare over 95 percent flavonoid glycoside monomers, wherein the flavonoid glycoside monomers are kaemplerol 3-O-[2-O-beta-D-galactose-6-O-alpha-L-rhamnose]-beta-D-glucoside (I) and kaemplerol 3-O-[2-O-beta-D-xylose-6-O-alpha-L-rhamnose]-beta-D-glucoside (II) respectively. The method can be used for batch preparation, and has the advantage of providing quality raw materials for the development of flavonoid glycoside medicaments and healthcare functional products in the oil-tea-cakes.
Owner:INST OF CHEM IND OF FOREST PROD CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Preparation method of nanometer fiber immobilization beta-D-galactosidase
InactiveCN101864408AHigh vitality maintenance rateMild immobilization conditionsFilament/thread formingOn/in organic carrierFiberGalactooligosaccharide
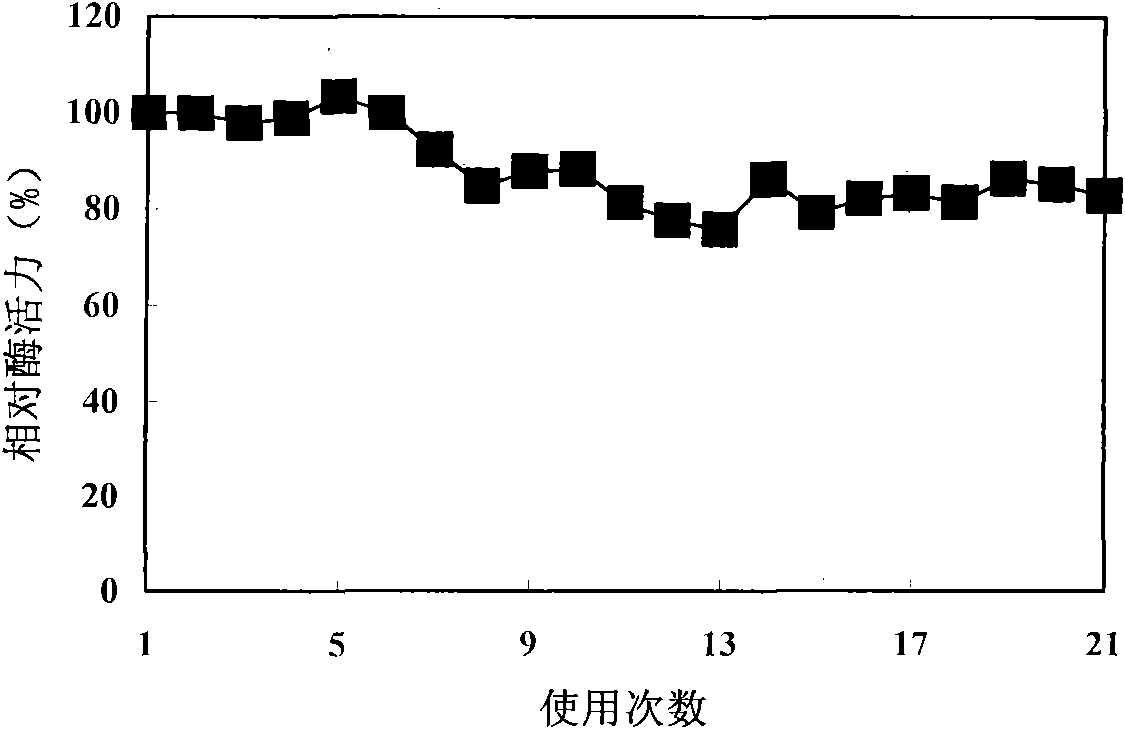
The invention relates to a preparation method of nanometer fiber immobilization beta-D-galactosidase, which belongs to the technical field of enzyme immobilization and application thereof. The method comprises the following processes: using phenylethylene-maleic anhydride copolymers for preparing nanometer fiber by a static electric spinning method; carrying out pretreatment on an ethanol water solution; and then, using anhydride groups on the surface of the fiber for carrying out covalence coupling on beta-D-galactosidase to obtain immobilization beta-D-galactosidase. The enzyme load capacity can reach 20 to 30 mg enzyme / g nanometer fiber, the enzyme activity recovery rate is between 45 and 60 percent, and 85 percent catalysis activity of the immobilization enzyme can still be maintained after the immobilization enzyme is repeatedly used for 21 times. The method has the advantages of simplicity, convenience and easy implementation. The obtained immobilization enzyme can be easily recovered and repeatedly used, and can be used in the fields of the synthesis of alkyl galactoside and functional oligomate, the production of low lactose milk and the like.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Neoagarobiose hydrolase and application thereof
ActiveCN103468661AAvoid pollutionConvenient whiteningBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliTotal protein
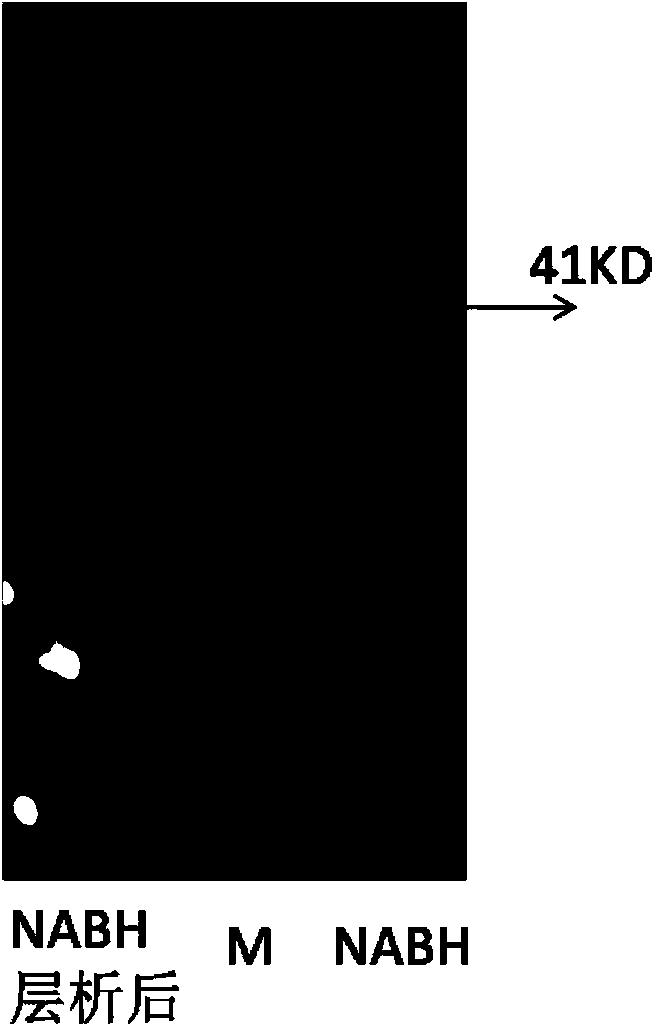
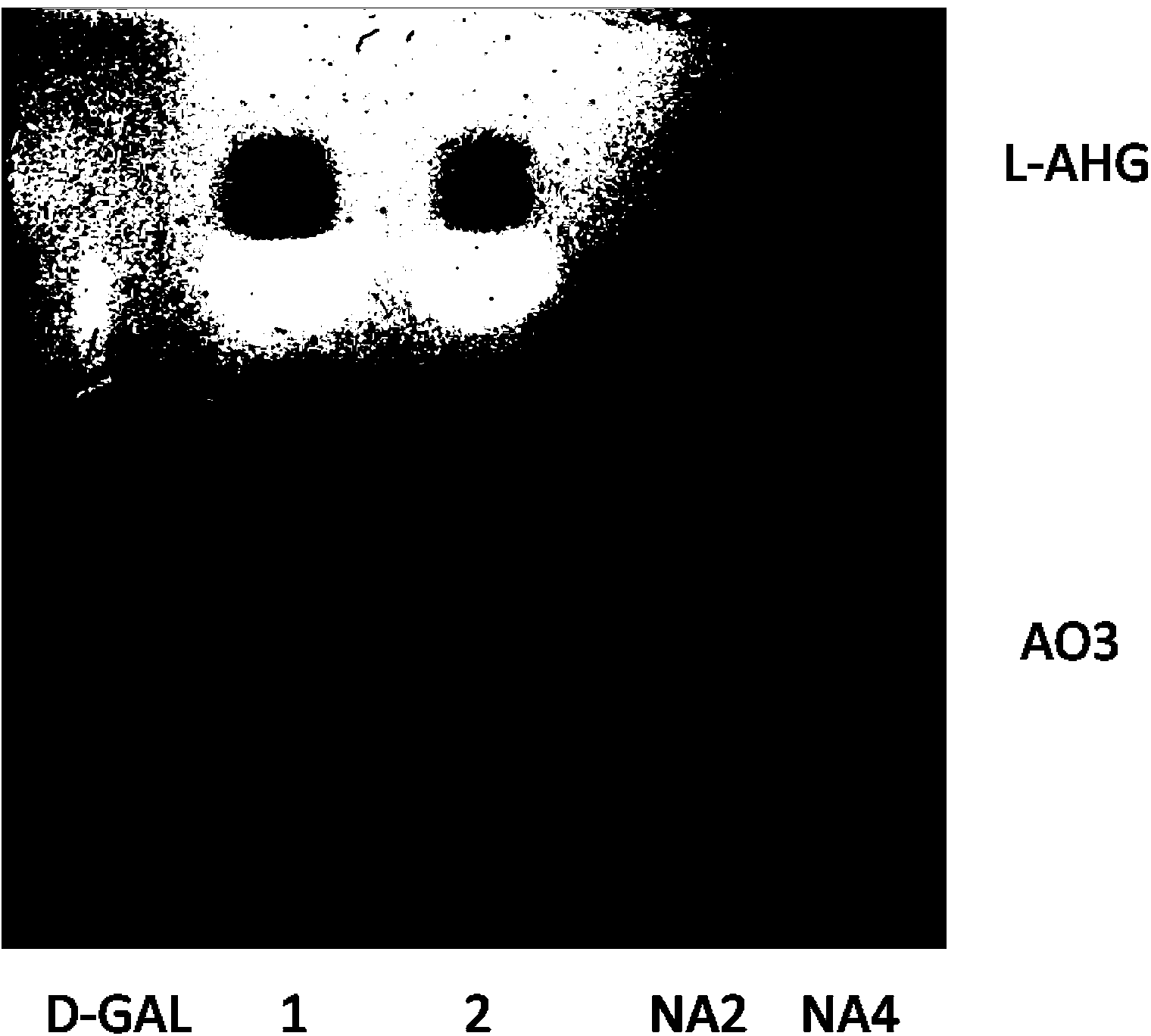
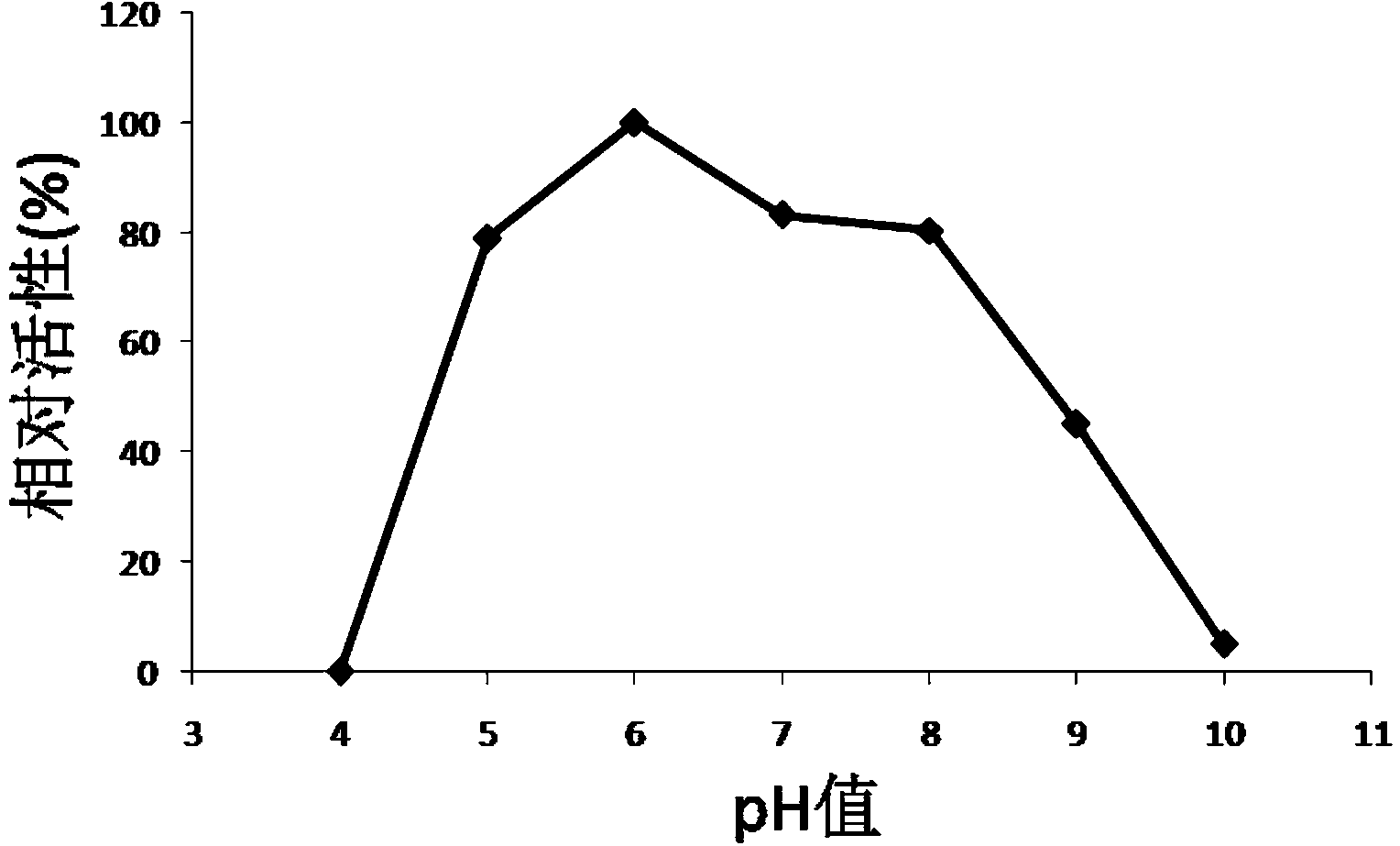
The invention provides a neoagarobiose hydrolase. The amino acid sequence of the neoagarobiose hydrolase is SEQ IDNO:1. The neoagarobiose hydrolase can degrade neoagarobiose to generate 3,6-anhydro-L-galactose (L-AHG) and D-galactose, and therefore the neoagarobiose hydrolase can be used for preparing pure L-3,6-inner ether galactose. Serving as a biocatalyst used for producing the L-AHG, the neoagarobiose hydrolase has a user-friendly reaction environment, high catalytic activity, a certain advantage over a chemical method and good application potential and prospects. The L-AHG is a kind of levoglucosan, has good skin whitening performance and anti-inflammatory activity and has very good potential application value in the aspects of medicine and cosmetics. According to recombined escherichia coli strains, recombined agarase expressed by pETNA / BL21 accounts for 28% of total protein. The expression level is high, the recombined agarase is easily purified and expression quantity is not reduced after continuous passage is carried out. The neoagarobiose hydrolase is adopted for preparing recombined neoagarobiose hydrolase and the L-AHG in a mass mode.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for preparing beta-D-galactoside galactose hydrolase preparation
ActiveCN101845424AHigh extraction rateSolve the problem of slow flowMicroorganism based processesEnzymesFiltration membraneGram
The invention discloses a method for preparing a beta-D-galactoside galactose hydrolase preparation. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) performing microporous membrane filtration on fermentation solution containing target enzyme to obtain clarified solution containing the target enzyme; 2) introducing the clarified solution containing the target enzyme into an ultra-filtration columnarray 1 and an ultra-filtration column array 2 in turn, and collecting the target enzyme solution; and 3) adding an aid into the target enzyme solution, and drying the mixture to obtain a target enzyme preparation, wherein the step 1) and the step 2) are performed under closed conditions. In the method, the sterile enzyme-containing classified solution filtered by a microporous membrane only needs to flow through an ultra-filtration membrane passage at one time during ultra-filtration and a circulating step is saved; therefore, compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of avoiding the contact of the liquid and the environment, thereby ensuring that the product is not polluted during extracting and saving a re-sterilizing step. Experiments prove that the number of bacteriain the enzyme preparation finished product obtained by the method is less than 100 in every gram, and the number of bacteria in the enzyme preparation produced by the prior art is generally 1,000 in every gram.
Owner:中诺生物科技发展江苏有限公司
Method for extracting xylitol and D-galactitol from xylose mother solution
The invention discloses a method for extracting xylitol and D-galactitol from xylose mother solution, which adopts a homologous exchange method to construct a bacillus subtilis 168 xylose isomerase gene (xylA) deficient strain Bsxyl, utilizes the engineering strain Bsxyl to purify xylose mother solution to obtain xylose and D-galactose and further carries out catalytic hydrogenation and crystallization separation to obtain xylitol and galactitol. The Bsxyl strain is already stored in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on March 25, 2010, the strain accession number of the Bsxyl strain is CGMCC No.3692, and the strain can purify xylose mother solution to obtain xylose and D-galactose. The strain can purify fermentation culture solution containing xylose mother solution, so that the total purity of xylose and galactose can reach more than 88.8 percent, and after further catalytic hydrogenation and crystallization separation, obtaining xylitol and D-galactitol the purity of which is more than 98 percent.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV FOR NATITIES
Hawthorn fruit cyanidin-3-hydroxyl glycosyl transferase and encoding genes and application thereof
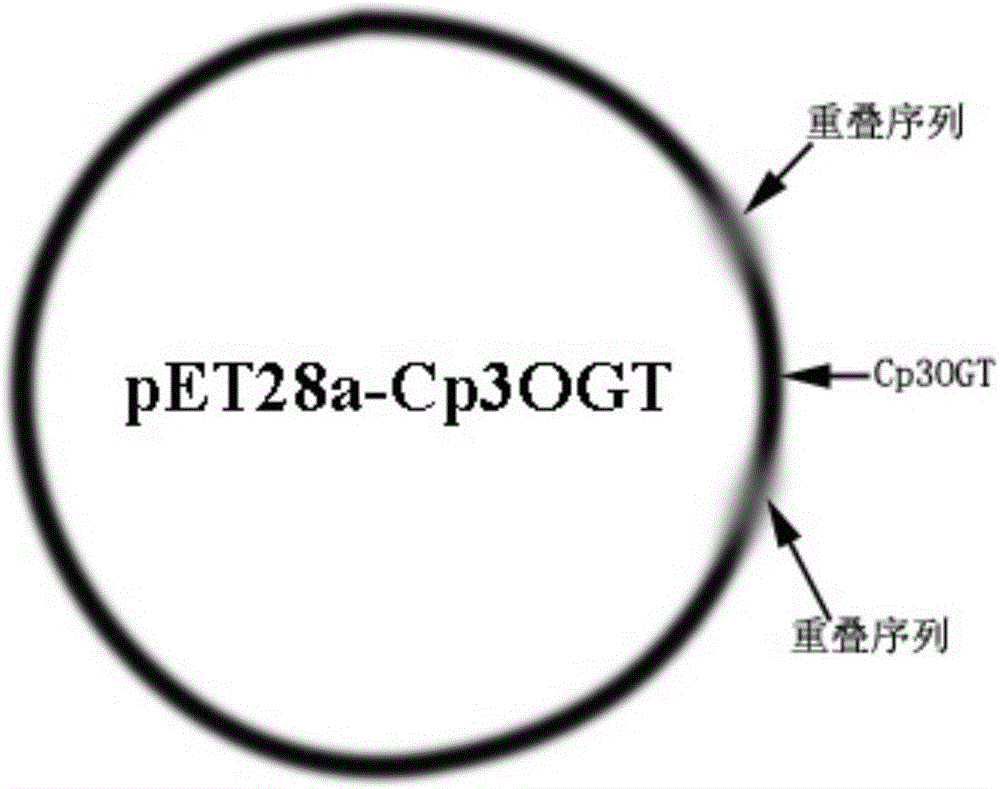
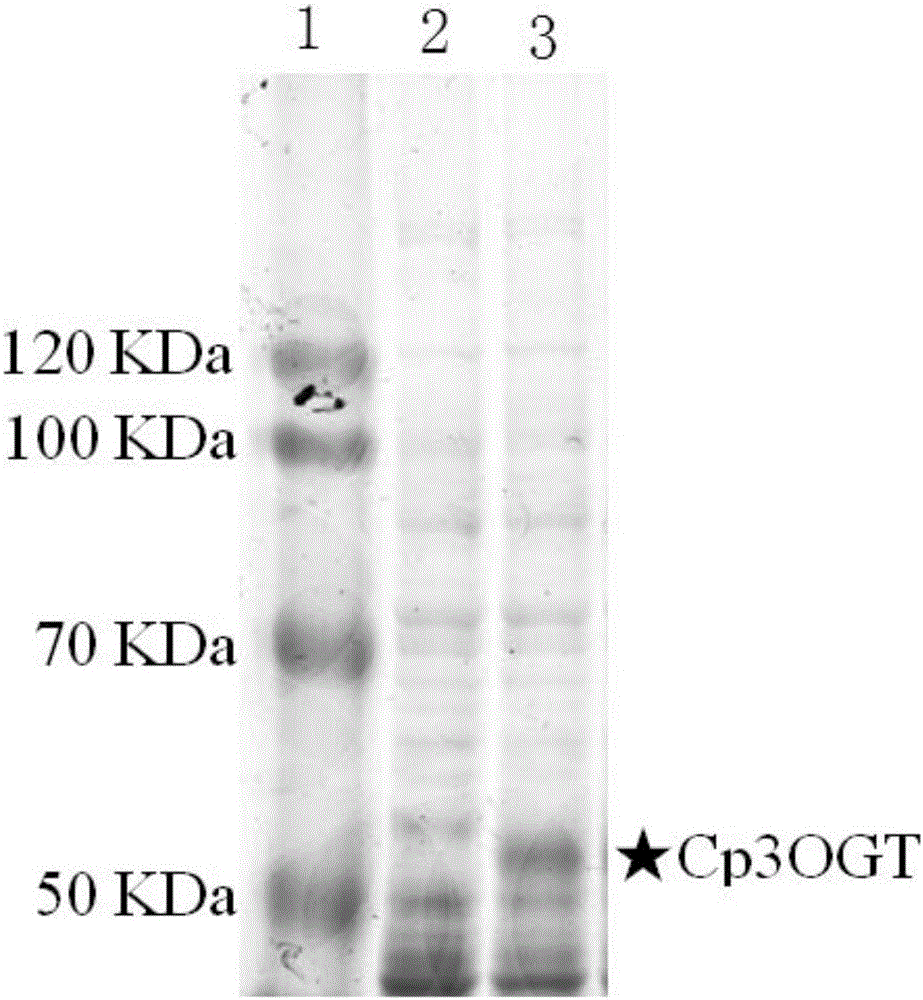
The invention discloses hawthorn fruit cyanidin-3-hydroxyl glycosyl transferase and encoding genes and application thereof. The invention provides protein. The protein is protein as shown in sequence 2 in a sequence table or protein derived from the sequence 2. The protein derived from the sequence 2 has the same function of the protein as shown in the sequence 2 and is obtained by subjecting the amino acid sequence as shown in the sequence 2 in the sequence table to one or more amino acid residue substitution and / or loss and / or adding. Hawthorn fruit cyanidin-3-O-galactoside transferase (Cp3OGT) genes are cloned from hawthorn fruit for the first time. In-vitro experiments show that Cp3OGT has the activity for catalyzing cyanidin and UDP-D-galactose to generate cyanidin-3-O-galactoside.
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
Drug compound preparation for treating Alzheimer's disease
ActiveCN103948584AReduce depositionSimple ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseAdditive ingredient
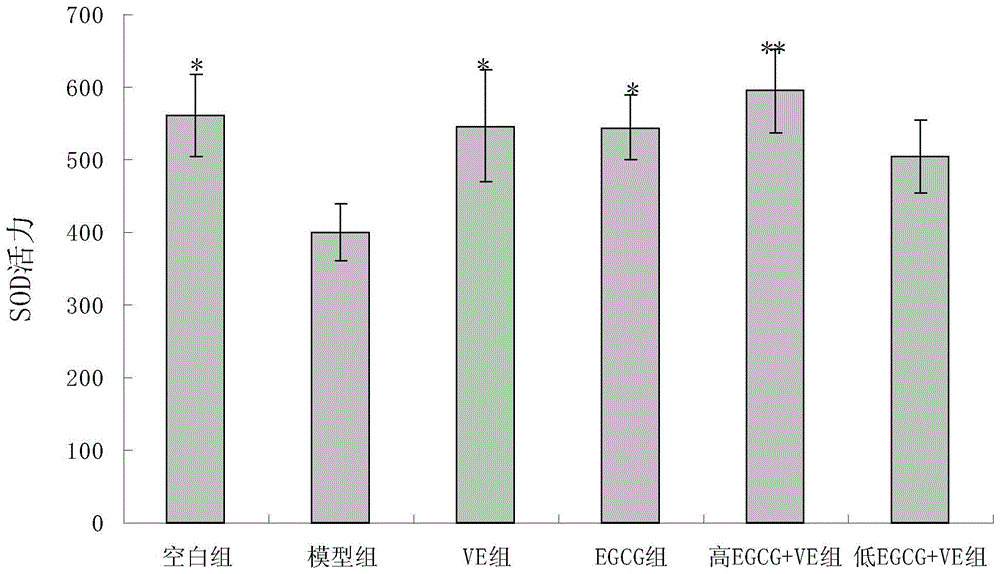
A drug compound preparation for treating Alzheimer's disease includes the main components of epigallocatechin gallate and vitamin E. Oil-soluble vitamin E is mixed with 1 part by volume of edible oil solution, and water-soluble EGCG is mixed with 2 parts by volume of distilled water; the two liquids are mixed and then added with an emulsifier in the weigh 10% of the edible oil, so as to form an oil-water suspension with mass fraction of EGCG of 0.02-0.1% and mass fraction of vitamin E of 0.3%. The invention has the advantage that the drug compound preparation has significant improvement on learning and memory impairment in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model induced by D-galactose, and can reduce the deposition of A beat 1-40 in the brain; and the drug compound preparation reduces antioxidation stress effect, anti-apoptosis effect and anti-inflammatory effect by increasing antioxidant enzymes, so as to exert the effect in resisting Alzheimer's disease. The drug compound preparation has simple composition, clear efficacy and easy preparation, can effectively play the roles of improving the behavior and learning and memory functions of patients, and does not generate other adverse reactions in large dose application.
Owner:沈阳百岁生物科技发展有限公司
Development culture medium for separating and identifying pathogens in urogenital tract
ActiveCN102206697AFacilitate early diagnosisGood treatment effectMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliBacteroides
The invention discloses a development culture medium for separating and identifying pathogens in a urogenital tract, which at least comprises three development substrates, namely a hexosaminidase substrate, a beta-D-galactosidase substrate, a beta-D-glucuroide substrate. The development culture medium added with the three development substrates is prepared into a microbial culture medium agar plate, a sample or a bacterial colony subjected to separate culture is inoculated into the development plate and is incubated, and a result can be directly observed. In the development culture medium, various pathogens including bacteria and fungi in a genital tract can be simultaneously cultured and identified on the same development plate, namely bacterial pathogens such as Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, enterococcus, pseudomonas aeruginosa, proteus mirabilis, staphylococcus aureus and the like and fungal pathogens such as candida albicans, candida tropicalis and the like can be simultaneously identified, and judgment can be performed through visual inspection; and the development culture medium is quick and convenient to use, and easy to operate.
Owner:AUTOBIO DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase
ActiveUS8945359B2Good reproducibilityImprove accuracyImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsConcentrations glucoseMaltose
The invention provides a flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase exhibiting reduced fluctuation of activity depending on temperature environment, and a method for measuring glucose concentration using the flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase has the following properties (1) to (3): (1) activity: which exhibits glucose dehydrogenase activity in the presence of an electron acceptor; (2) substrate specificity: which exhibits an activity of 10% or less against maltose, D-galactose, D-fructose, sorbitol, lactose and sucrose when the activity against D-glucose is defined as 100%; and (3) temperature characteristics: which exhibits lower fluctuation of activity in a wide temperature range of 10 to 50° C.
Owner:IKEDA SHOKKEN KK
Application of L-ascorbyl glycoside compounds to preparation of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
ActiveCN105267231AEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAlgluceraseGlycosidase inhibitor
The invention relates to application of L-ascorbyl glycoside compounds, such as 2-O-beta-D-glucosyl-L-ascorbic acid, 3-O-beta-D-glucosyl-L-ascorbic acid and 2-O-beta-D-galactosyl-L-ascorbic acid, to preparation of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors. The L-ascorbyl glycoside compounds are remarkable in alpha-glucosidase inhibition activity and have the inhibition effect approximate to that of voglibose, thereby being developed and applied as the alpha-glucosidase inhibitors.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for establishing animal model of Alzheimer's disease
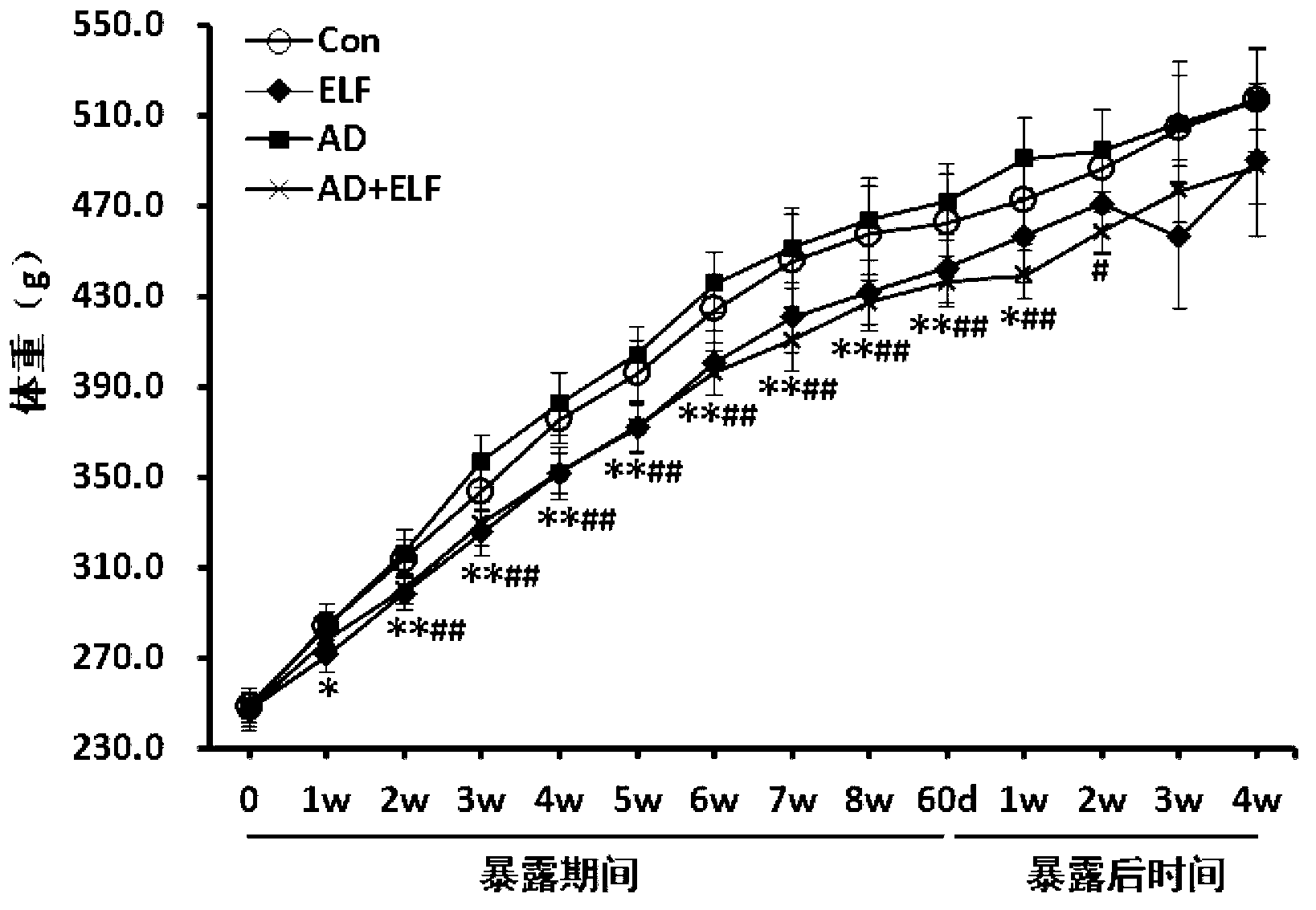
The invention provides a method for establishing an animal model of an Alzheimer's disease. The method includes feeding a rat for at least 60 days under the condition of exposing to a power-frequency magnetic field; feeding the rat with drug D of galactose and beta of amyloid protein liquid during the process of feeding, and accordingly obtaining the animal model of the Alzheimer's disease. Thus, the method can be a useful supplement of a single-factor-induced animal model of the Alzheimer's disease. According to an embodiment of the method, characteristic pathological changes of the animal of the Alzheimer's disease can be expressed; the method has a characteristic of learning and memory impairment, is consistent with the environmental requirements of long-time and lasting exposure to the power-frequency magnetic field, and has the advantages of stable performance, good reproducibility, and low cost.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
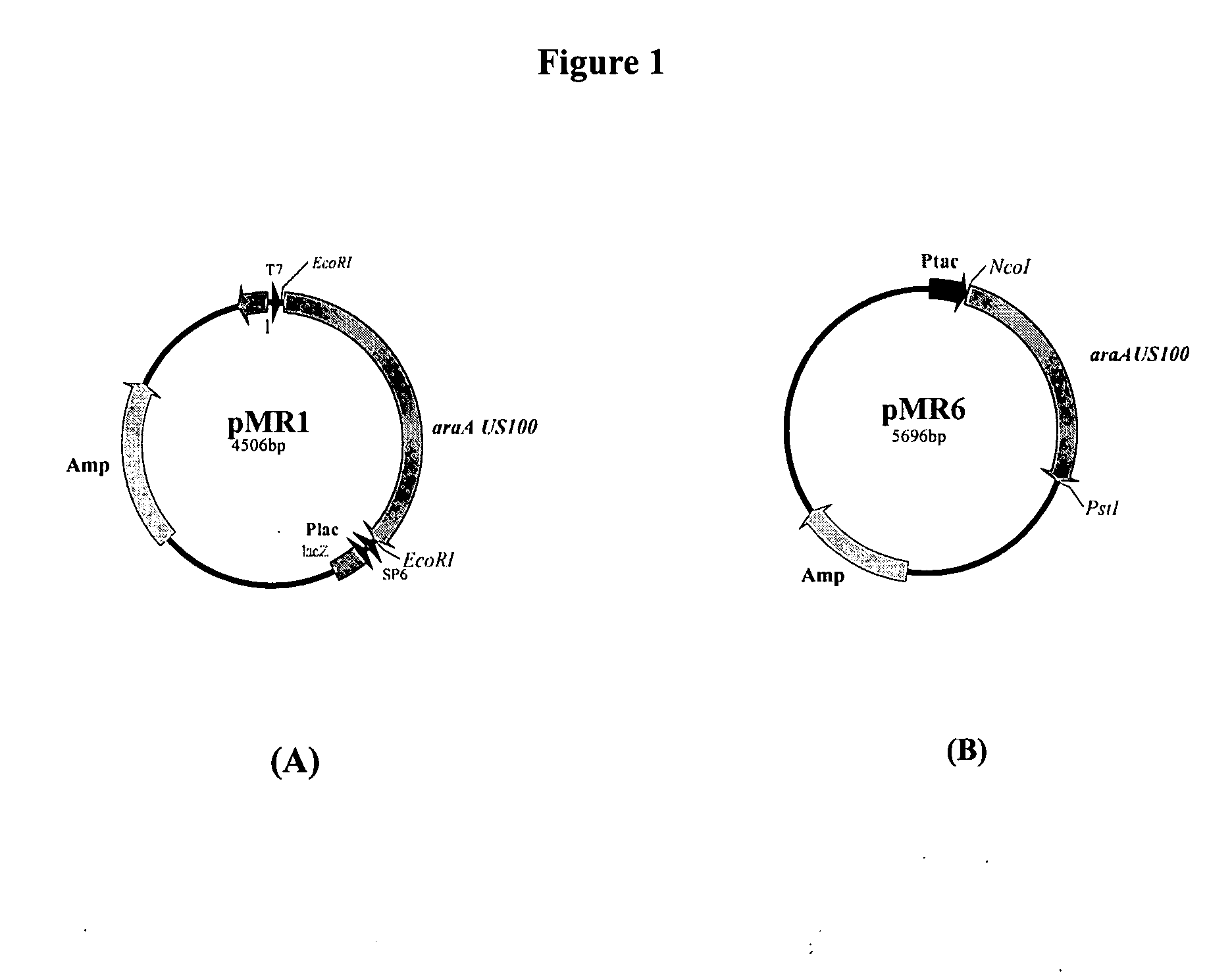
Polypeptides Having L-Arabinose Isomerase Activity Exhibiting Minimum Dependence on Metal Ions for Its Activity and for Thermostability and Nucleic Acids Encoding the Same
The invention concerns identification of a gene encoding a novel L-arabinose isomerase of the Bacillus stearothernivphilus strain US 100 (L-AI US 100), a L-arabinose isomerase expressed from said gene, recombinant vectors harbouring said gene, microorganisms transformed with said vector, a protocol for preparing and purifying said recombinant protein, biochemical and kinetic characterization of said recombinant enzyme and a method for bioconversion of a D-galactose solution into a solution rich in D-tagatose using said polypeptide. This novel protein has original characteristics, in particular its independence from metal ions for its activity and its low need for such ions for its thermostability, as well as its potential for isomerizing D-galactose into D-tagatose with great efficacy of about 48% after 7 hours at 70° C.
Owner:CENT DE BIOTECH DE SFAX - CBS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com