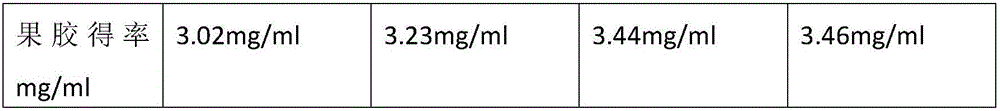
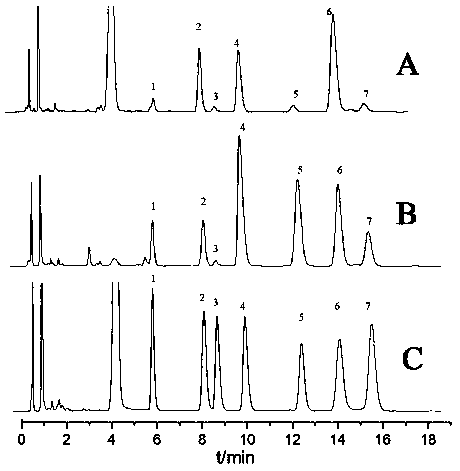
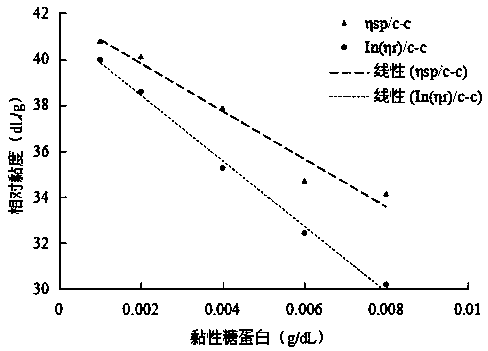
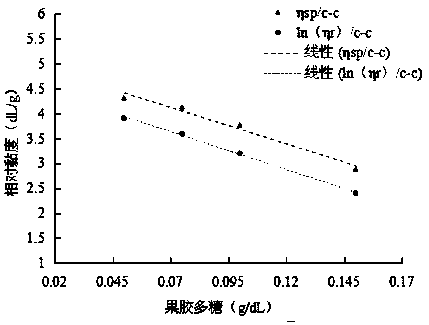
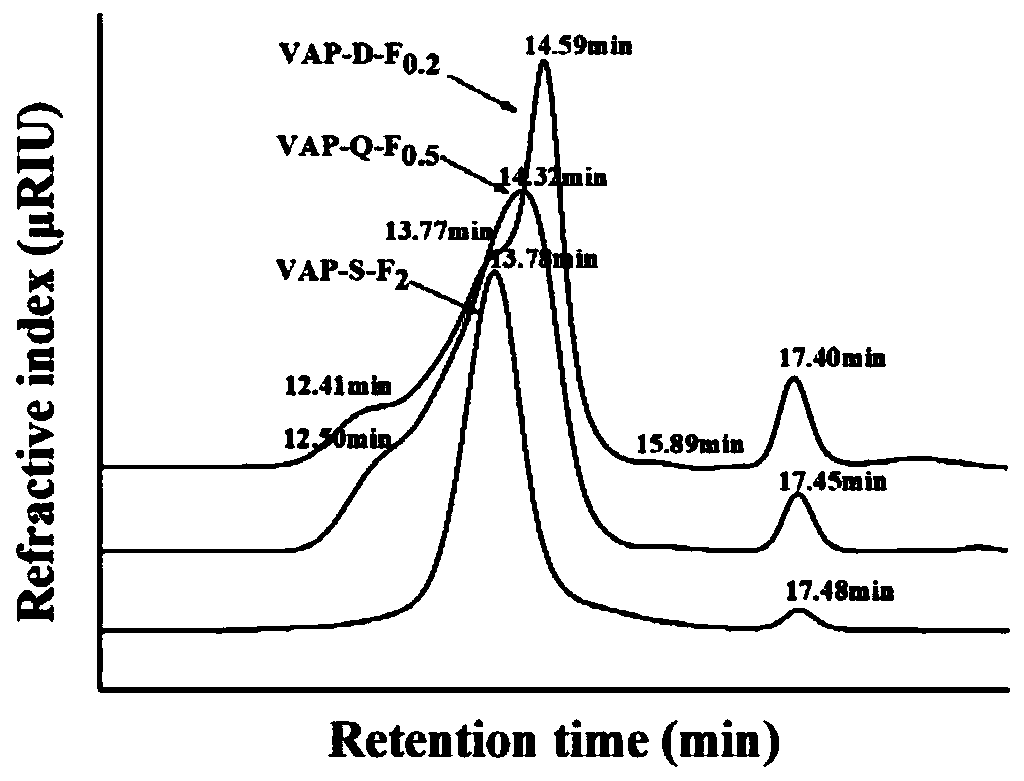
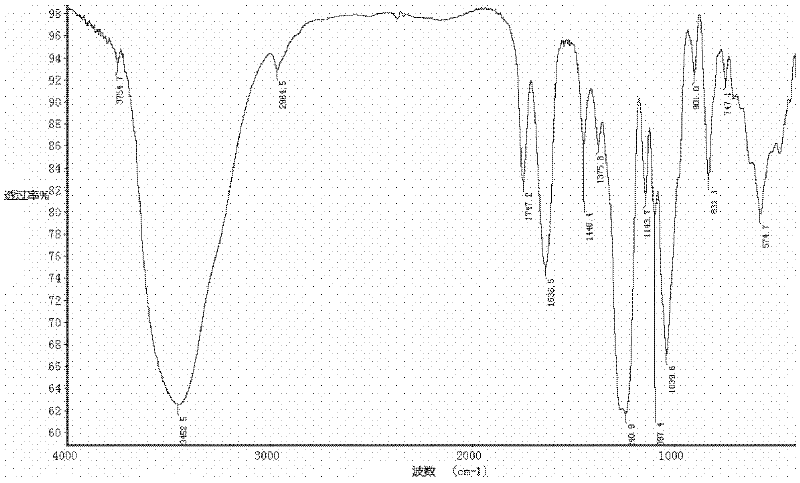
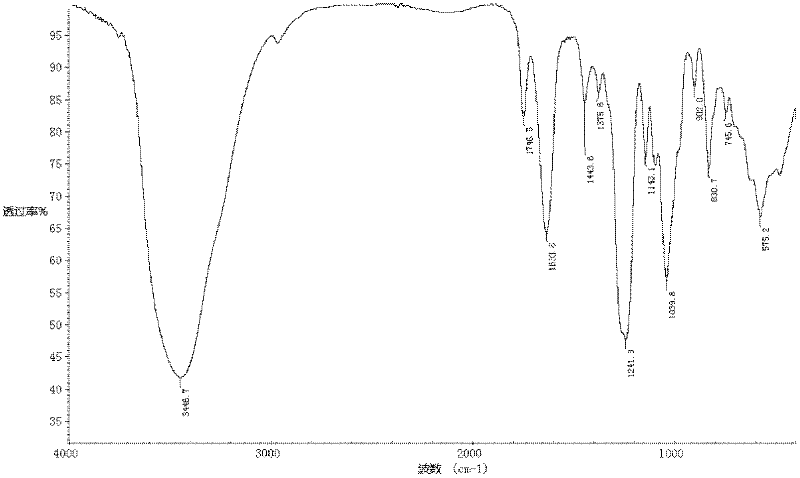
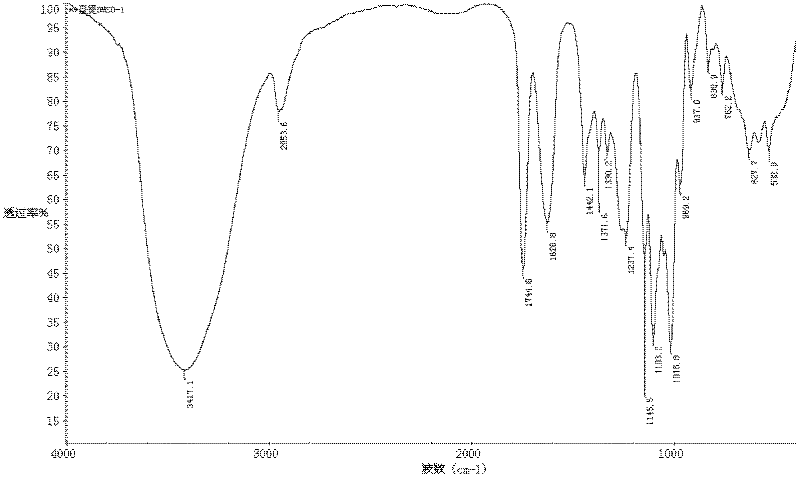
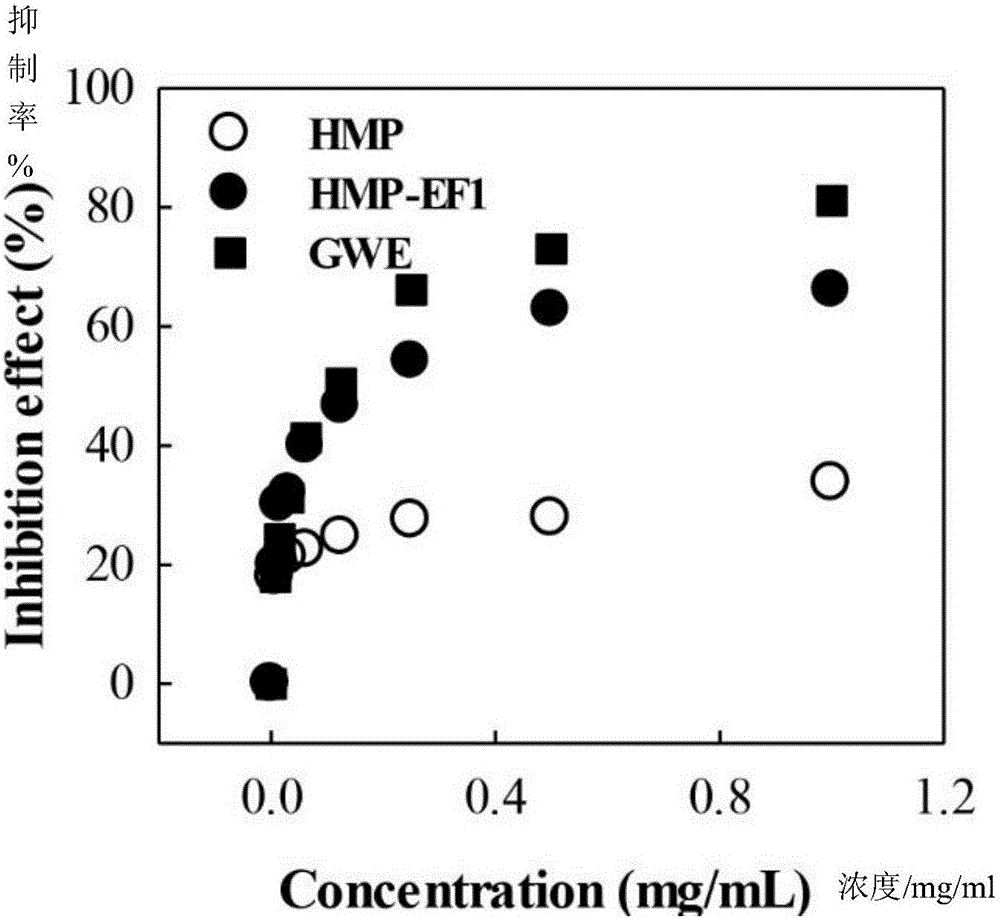
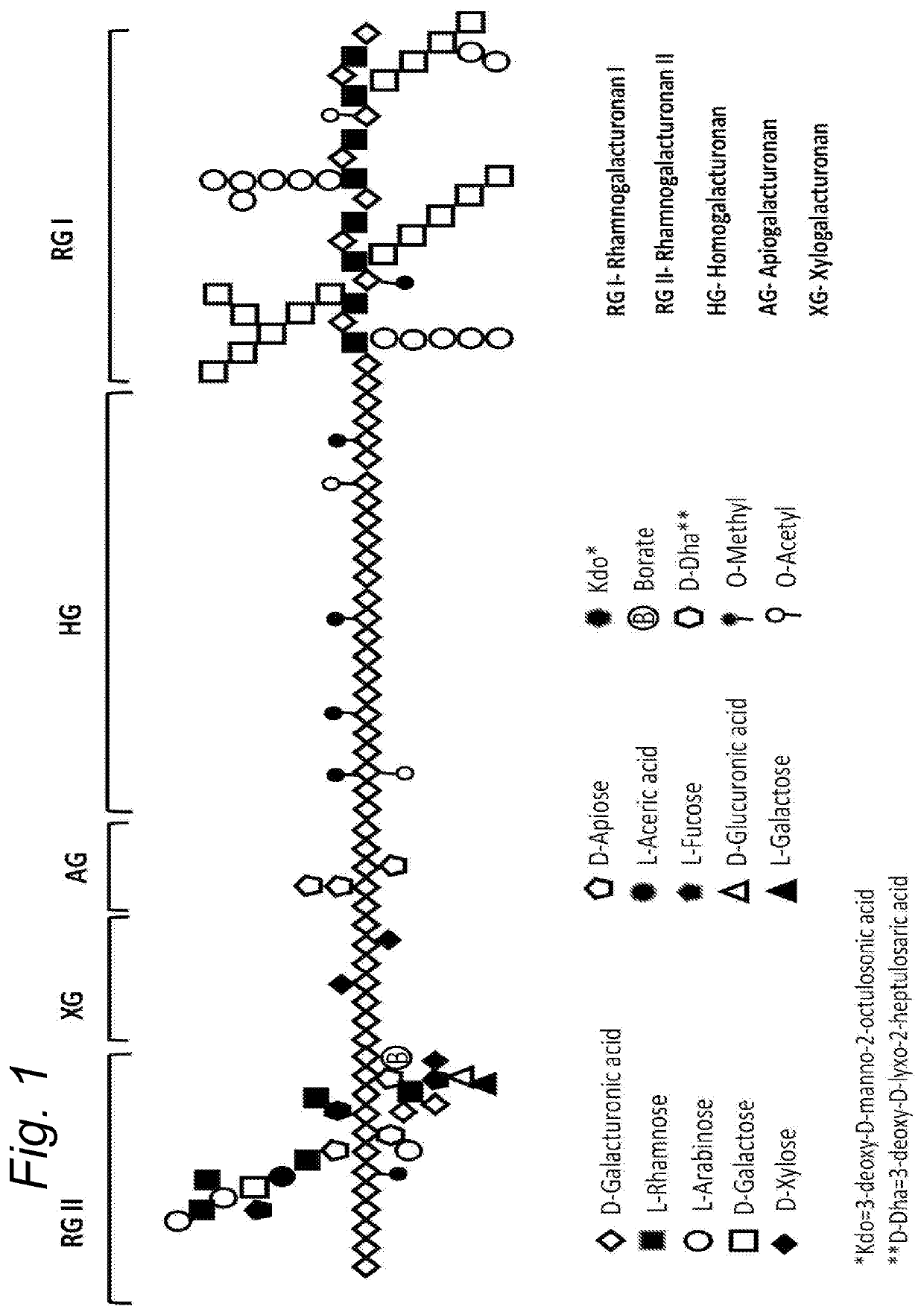
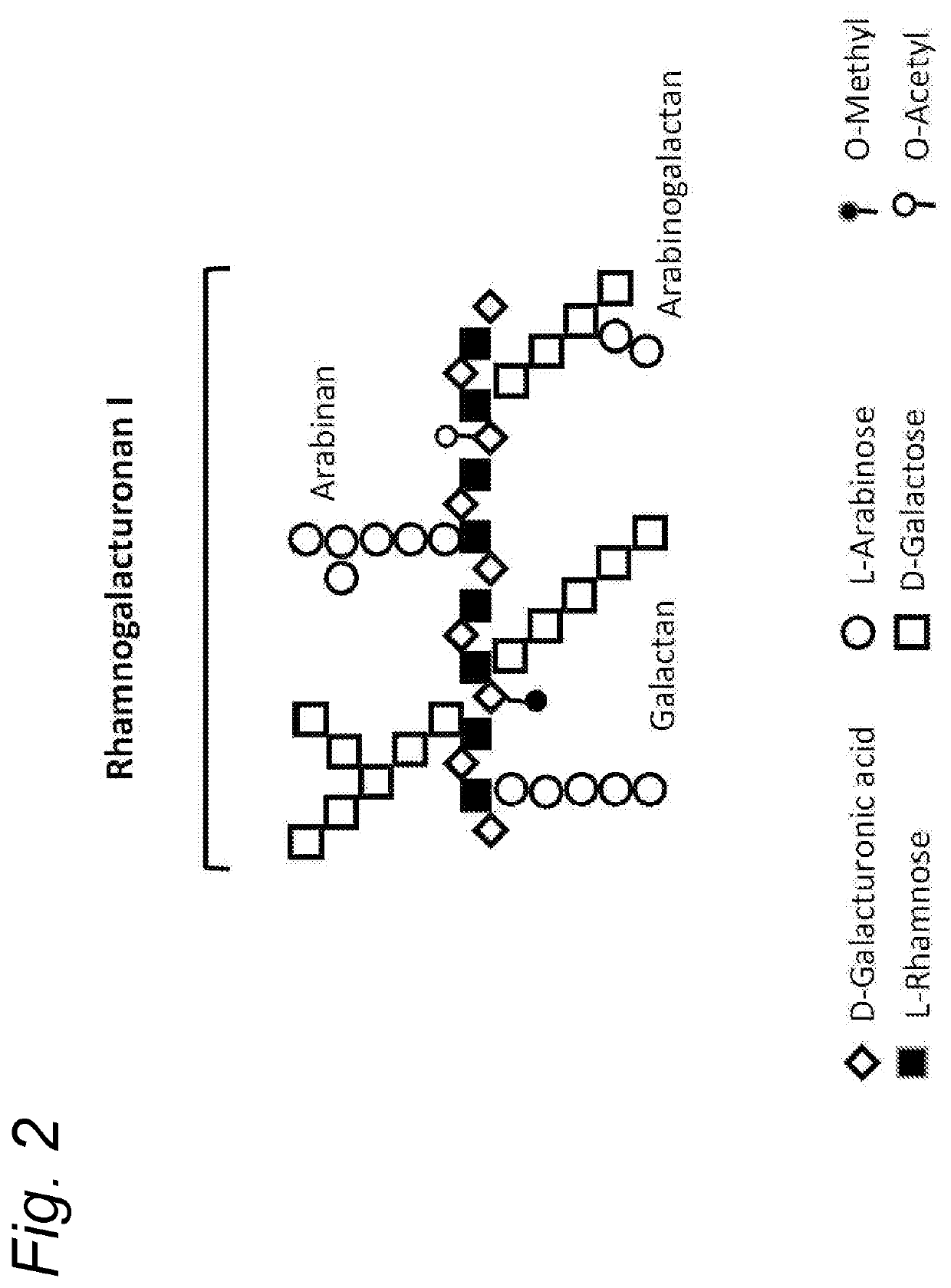
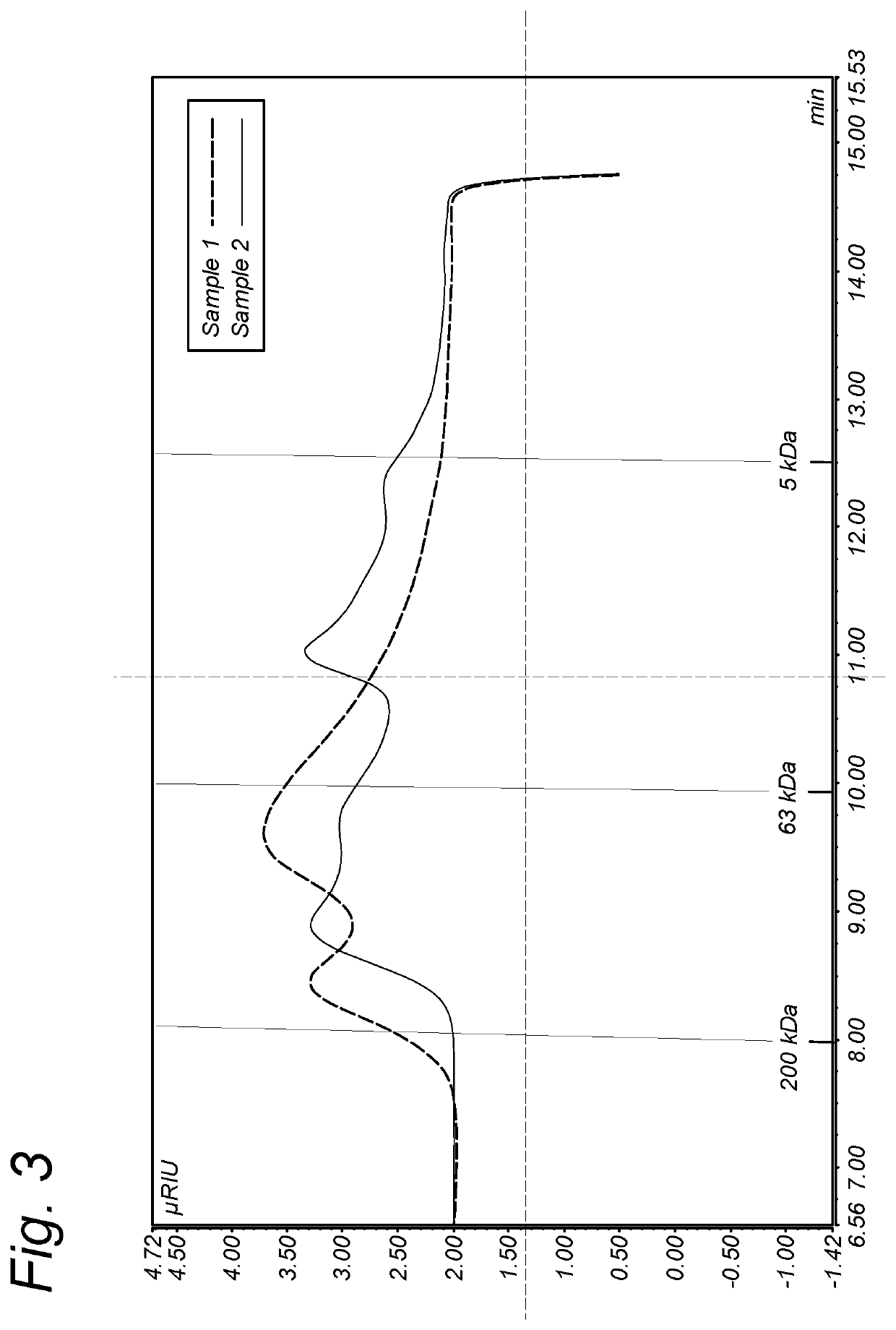
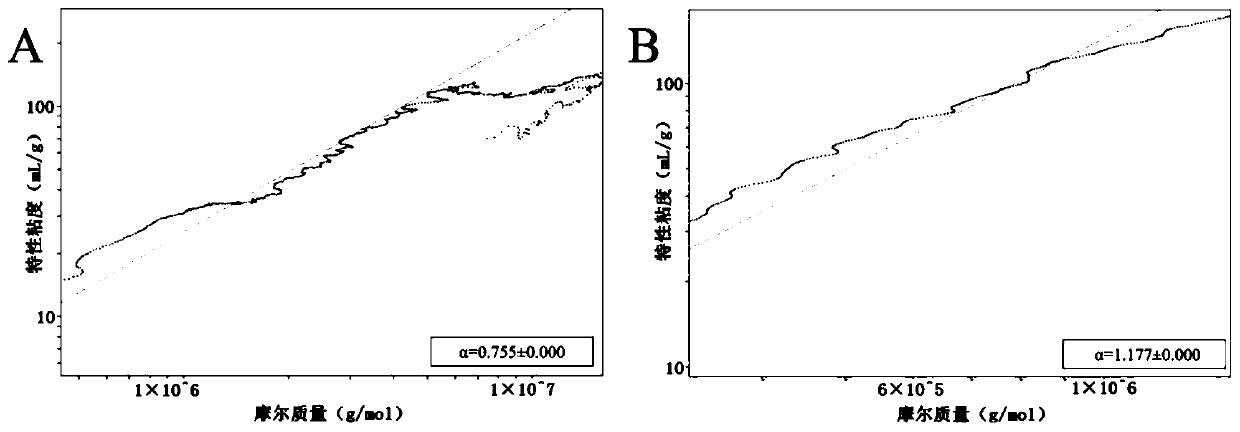
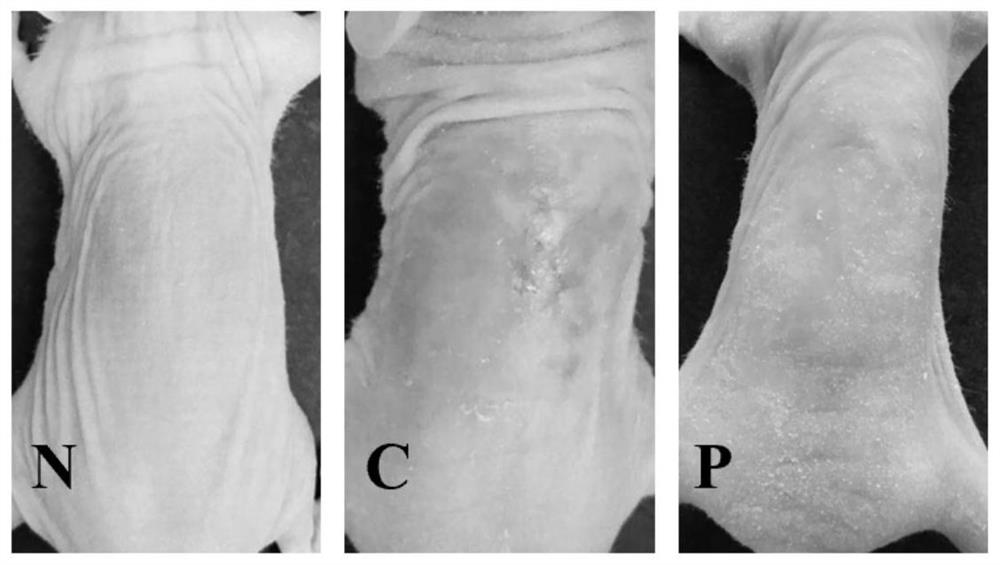
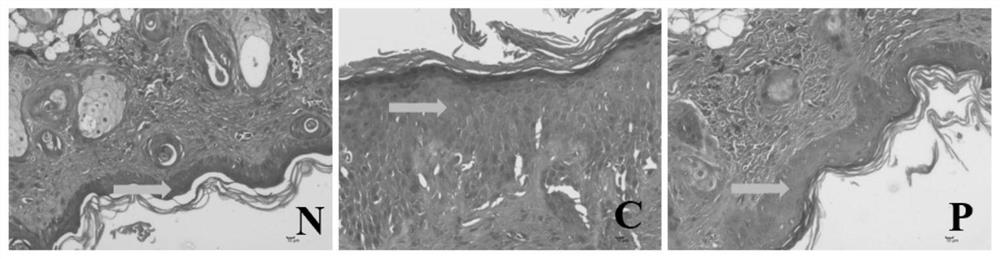
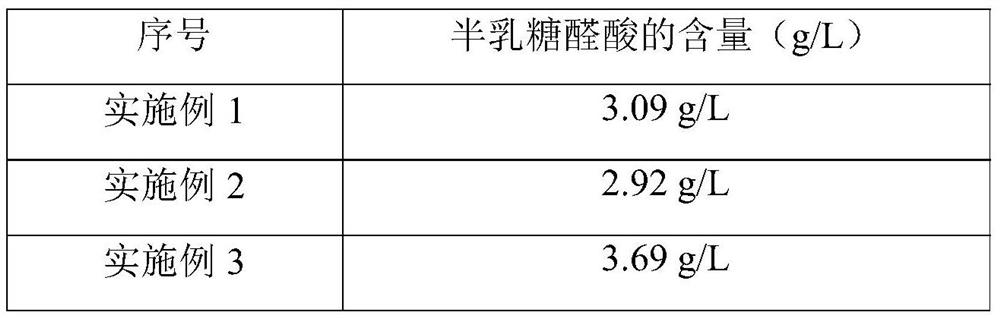
Patents
Literature
54 results about "Pectic polysaccharide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The pectins, which are most abundant in the plant primary cell walls and the middle lamellae, are a class of molecules defined by the presence of galacturonic acid. The pectic polysaccharides include the galacturonans (homogalacturonan, substituted galacturonans,...
Unsaturated pectin oligosaccharide and compound biological preservatives
The invention relates to a preparation and application of unsaturated pectic oligosaccharide and a compound biological preservative combined with the unsaturated pectic oligosaccharides, which is characterized in that: pectin is extracted from pericarps or fruit residues, pectate lyase produced by the fermentation of aspergillus niger-wz003 is added into the pectin, and then the unsaturated pectic oligosaccharide is obtained by centrifugal separation, monosaccharide removal by yeast, decoloration by active carbon, polyether sulfone membrane and membrane separation of regenerated cellulose, and the unsaturated pectic oligosaccharide can be obtained by a further drying step. The preparation method of unsaturated pectic oligosaccharide and a compound biological preservative combined with the unsaturated pectic oligosaccharides has the advantages that: self-made pectate lyase is utilized, so the raw materials are easy to obtain and the cost is low; meanwhile, the pectic oligosaccharide and the compound biological preservative has the advantages of innocuity, high efficiency, broad spectrum and wide application range and can reduce the addition of chemical preservatives.
Owner:重庆檬泰生物科技有限公司
Pectic polysaccharides isolated from fruit pods of okra
The invention relates to a method for producing a high molecular weight pectin-like polysaccharide from fruit pods of okra. The high molecular weight pectin-like polysaccharide, when dissolved in a buffer, exhibit viscoelastic properties, and is very useful in applications such as ophthalmic surgery, dermatology and orthopedics.
Owner:BOHUS BIOTECH
Edible film coating fresh-keeping agent and preparation method and use method of edible film coating fresh-keeping agent
InactiveCN103653184ANo pollution in the processExtended shelf lifeEggs preservation by coatingPolysaccharide/gum food ingredientsPectic polysaccharideGlycerol
The invention relates to an edible film coating fresh-keeping agent, and a preparation method and a use method of the edible film coating fresh-keeping agent. The edible film coating fresh-keeping agent comprises the following raw materials: mucedin, chitosan, zein, glycerol, whey protein isolate, soybean protein isolate, pectic polysaccharide and glycerol. The edible film coating fresh-keeping agent has corrosion prevention, fresh preservation, sterilization and water loss prevention effects, can avoid escape of nutrients, or spoiling and deterioration of food, is edible and biodegradable, and avoids pollution to an environment.
Owner:BOHAI UNIV
Active extract of citrus peels as well as extraction process and application thereof
ActiveCN101850010ASimple extraction processReasonable process conditionsAntinoxious agentsFood preparationBlood plasmaD-galactal
The invention discloses an anti-oxidation active extract of citrus peels as well as an extraction process and application thereof. The active extract of the citrus peels mainly contains a citrus flavonoid substance and pectic polysaccharide. The extraction process of the active extract of the citrus peels comprises the steps of preprocessing raw materials, refluxing and extracting by a dipping method, decompressing and concentrating and drying in vacuum. The invention takes the in-vitro oxidation resistance of the extract to combine with the extraction yield as indexes, adopts a response surface method to optimize the extraction process, has reasonable technological conditions and good effect stability and is suitable for industrialized production. The active extract of the citrus peels, which is obtained by extraction, has an obvious effect to a model mouse with senility caused by D-galactose and can lower the content of the MDA (malondialdehyde) of the plasma, the liver and the brain obviously; the activity of the SOD (superoxide dismutase) of the plasma, the liver and the brain is obviously enhanced; the activity of the GSH-Px (glutathione peroxidase) of the plasma and the liver is obviously enhanced; and the invention can be used for preparing an anti-oxidation medicine, an anti-oxidation food or an anti-oxidation health-care product.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV +1
Application of pectin polysaccharide in preparation of antiallergic food, medicine or cosmetic
InactiveCN101623101ANot stickyImprove solubilityCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsPectic polysaccharideSide effect
The invention relates to the application of pectin polysaccharide in the preparation of antiallergic food, medicine or cosmetic. The adopted technical scheme comprises: the antiallergic food, medicine or cosmetic contains the active ingredient of pectin polysaccharide which is prepared according to the method: pectin water solution with the mass percentage concentration of 1-2% is taken, the pH value of the pectin water solution is adjusted to be 2-4, the decomposition reaction is carried out for 15-24min at 95-120 DEG C, and pectin decomposition substance can be obtained; the obtained pectin decomposition substance is separated by a hollow fiber membrane or ceramic filtering membrane, and compound with the molecular weight of 6000 daltons is recovered, so that the pectin polysaccharide can be obtained. The invention has the advantages of safe use, no toxic side effect, good antiallergic effect and easy practical operation.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
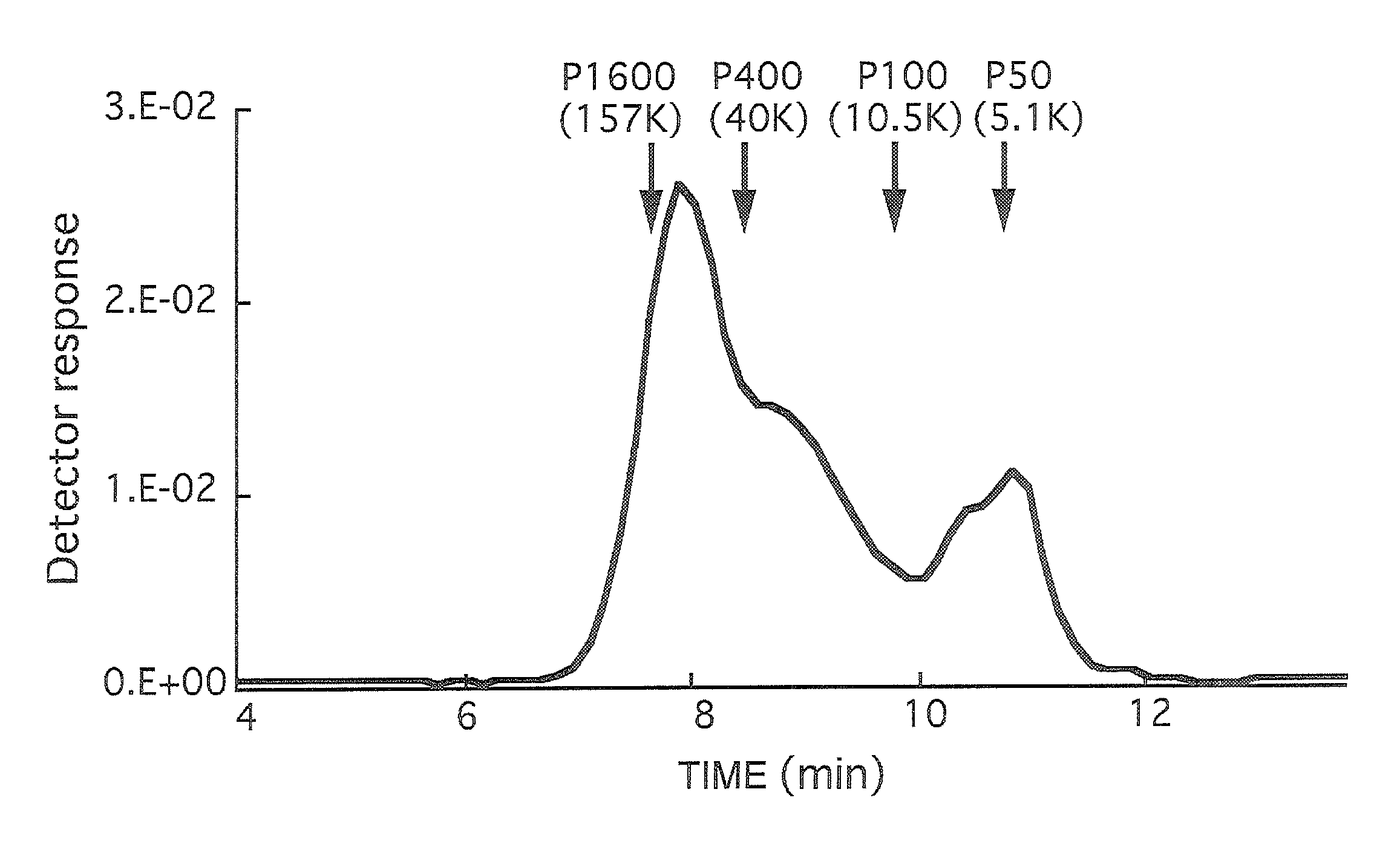
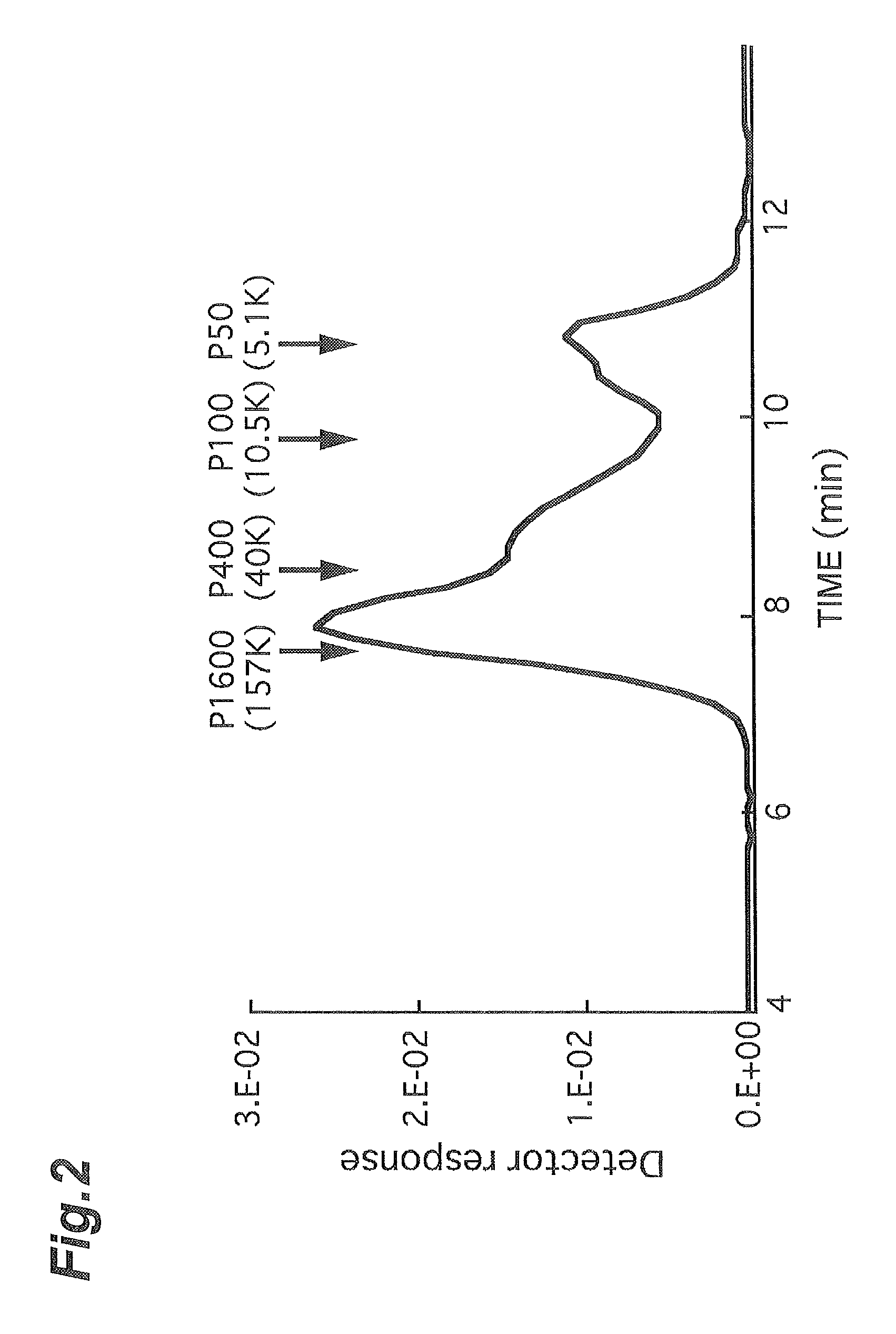
Pectic polysaccharide and method for producing same
ActiveUS20140134310A1Suppress aggregate precipitationLow viscosityMilk preparationDough treatmentPectic polysaccharideGalacturonic acid
The present invention provides a pectic polysaccharide, wherein a degree of methyl esterification of constituent galacturonic acid is 45% or less, a structure of a single molecule observed with an atomic force microscope comprises a star structure, and a diameter of the molecule is more than 100 nm and equal to or less than 200 nm.
Owner:FUJI OIL CO LTD
Method for degrading pectic polysaccharides with high efficiency
InactiveCN102191298AAvoid introducingSimple post-processingFermentationPectic polysaccharideAcid hydrolysis
The invention provides a method for degrading pectic polysaccharides with high efficiency, which comprises the following steps: 1) subjecting part of pectic polysaccharides to acid hydrolysis; and 2) performing enzymolysis of a product obtained by the step 1). The invention provides the method for degrading pectic polysaccharides, which have high oligogalacturonide content and high degree of polymerization, with high efficiency.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Pectic Polysaccharides Isolated from Fruit Pods of Okra
InactiveUS20090170809A1More expensiveLow yieldOrganic active ingredientsBiocidePectic polysaccharideHibiscus esculentus
The invention relates to a method for producing a high molecular weight pectin-like polysaccharide from fruit pods of okra. The high molecular weight pectin-like polysaccharide, when dissolved in a buffer, exhibit viscoelastic properties, and is very useful in applications such as ophthalmic surgery, dermatology and orthopedics.
Owner:BOHUS BIOTECH
Homogeneous pectic polysaccharides and method for obtaining same from tea polysaccharides
The invention discloses homogeneous pectic polysaccharides and a method for obtaining the same from tea polysaccharides. In particular, the invention relates to polygalacturonic acid homogeneous pectic polysaccharides and a method for obtaining the same from tea polysaccharides or tea leaf polysaccharides. The homogeneous pectic polysaccharides and the method have the following beneficial effects: 1,4-connected polygalacturonic acid pectic polysaccharides are obtained from tea polysaccharides through separation and purification for the first time; the preparation method is simple and is high in yield; acids, alkalies and other toxic and harmful reagents are not used in the whole preparation process, thus the stability of the activity structures of tea polysaccharides can be fully ensured and the preparation method is suitable for large-scale production; in particular, the tea leaves obtained after extracting tea polyphenols can be effectively utilized by using the method, thus the resources can be saved and the refuses can be reclaimed; and the method has great significance in study and production of polygalacturonic acid homogeneous pectic polysaccharides.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
Method for recycling pectin in orange can acid treatment water
ActiveCN105820269AReduce the cost of trainingReduce purchasing costsHigh concentrationPectic polysaccharide
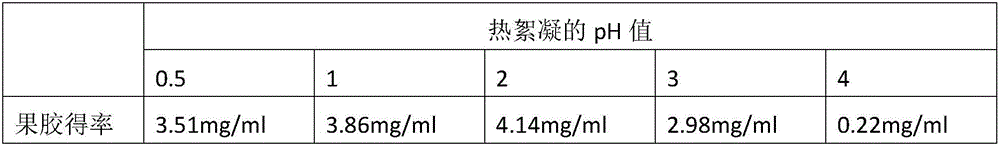
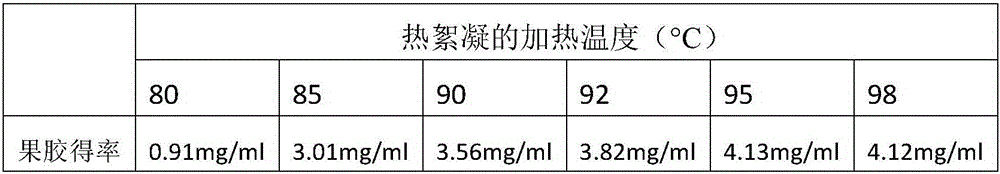
The invention discloses a method for recycling pectin in orange can acid treatment water .The method comprises the steps that the orange can acid treatment water is filtered, and then the pH is regulated to be neutral; then, the orange can acid treatment water is subjected to vacuum concentration until the mass fraction of total solids ranges from 1.1% to 1.6%, the pH is regulated to be 0.5-3 with a mixed solution of citric acid monohydrate and hydrochloric acid, uniform heating is carried out at 85-98 DEG C, and flocculent precipitate is generated; the precipitate is filtered and then washed 1-2 times with a high-concentration ethanol aqueous solution, drying and grinding are carried out, and pectin polysaccharide is obtained .According to the method, conventional simple equipment is used, manual operation is simple, the technological cost is low, industrial production can be easily achieved, the method can be effectively used for treating and recycling the orange can acid processing water and is environmentally friendly, and the additional value of orange processing is increased .
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for simultaneously preparing pectic polysaccharide and viscous glycoprotein by utilizing okra fermented wine dregs
InactiveCN110916198AImprove use valueEasy to acceptUltrafiltrationPeptide preparation methodsLeesPectic polysaccharide
The invention belongs to the technical field of separation and purification, and particularly relates to a method for simultaneously preparing pectic polysaccharide and viscous glycoprotein by utilizing okra fermented wine dregs. The method comprises the following steps: by taking okra fermented wine dregs as a raw material, carrying out two-stage enzymolysis treatment by adopting different enzymesystems, carrying out step-by-step extracting by using three extracting solutions, extracting a target object in the raw material to the maximum extent, and separating out a mixture of crude pectic polysaccharide and viscous glycoprotein by utilizing an ultrafiltration membrane, performing separation, purification and preparation of the okra pectin polysaccharide and the viscous glycoprotein through a DEAE-Sepharose F.F ion exchange column and a Sephadex G-100 glucan gel column, the prepared okra fermented wine lees pectin polysaccharide is light yellow brown, and the viscous glycoprotein islight yellow. Through the co-production method, the main components such as pectin polysaccharide and viscous glycoprotein in the okra fermented wine dregs can be prepared in a combined manner, so that the emission of wastes in the extraction process is reduced, the production cost is reduced, and the utilization value of raw material is improved.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Method for recovering pectin from canned citrus alkali treatment water
The invention discloses a method for recovering pectin from canned citrus alkali treatment water. The method comprises the following steps: after filtering the canned citrus alkali treatment water, regulating the pH value to neutrality; carrying out vacuum concentration at 50 DEG C until the mass percent of total solids is 1.3-1.8%, regulating the pH value to 0.5-3 by using a citric acid monohydrate-hydrochloric acid mixed solution, and uniformly heating at 85-98 DEG C to generate a flocculent precipitate; and after filtering the precipitate, washing with a high-concentration ethanol water solution 1-2 times, drying and pulverizing to obtain the pectin polysaccharides. The method is simple to operate and technically easy to implement, is suitable for industrialized application to canned citrus processing industry, and implements green processing of citrus, less discharge and more utilization.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Anti-fatigue compound preparation and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104274568AHigh activityInhibition formationAntinoxious agentsPill deliveryNutrientCompounded preparations
The invention discloses an anti-fatigue compound preparation and a preparation method thereof, wherein the preparation comprises the following components in percentages by weight: 10-65% of salvia miltiorrhiza, 15-35% of astragalus, 15-35% of herba epimedii and 5-20% of Chinese wampee fruit. In the invention, the salvia miltiorrhiza, astragalus, herba epimedii and Chinese wampee fruit are adopted, which contain phenolic acids, flavonoids, pectin, polysaccharides and saponin compounds, have the functions of increasing coronary blood flow, reducing blood lipid, inhibiting thrombosis, improving microcirculation, eliminating free radicals, preventing oxidization and the like, and can be used for preventing body fatigue and movement injuries, enhancing the body immunity and protecting the organs and tissues from being damaged. A variety of nutrients in the present invention activate the immune systems at different levels and generate a comprehensive anti-fatigue effect, the traditional Chinese medicine with an immunity enhancement function is prepared into a novel compound preparation by means of modern extraction separation and preparation formation process, to improve the activity of the drug.
Owner:GUANGDONG MEDICAL UNIV
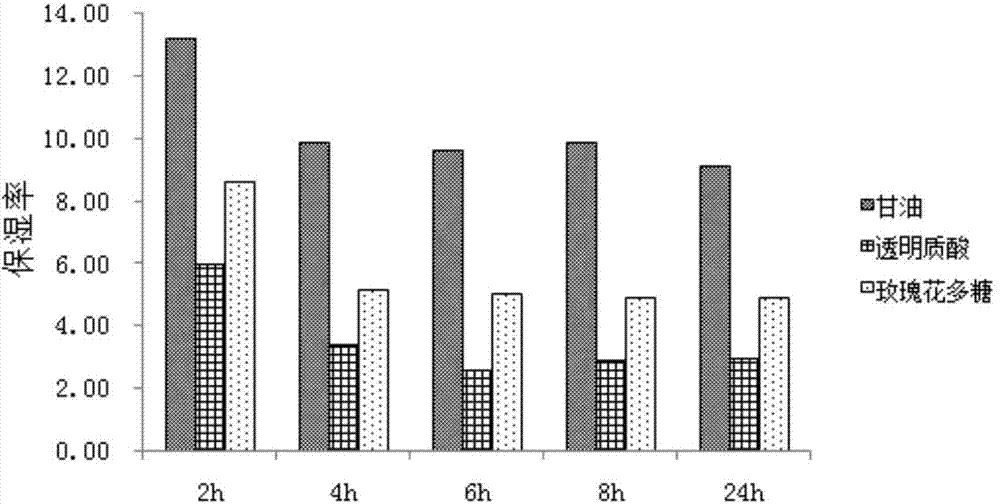
Rose acidic pectic polysaccharide and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a preparation method and moisturizing application of acidic pectic polysaccharide from roses. Moisturizing experiments show that the rose acidic pectic polysaccharide has a remarkable moisturizing effect, and has market application values in medical supplies and cosmetics, which have moisturizing efficacies.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
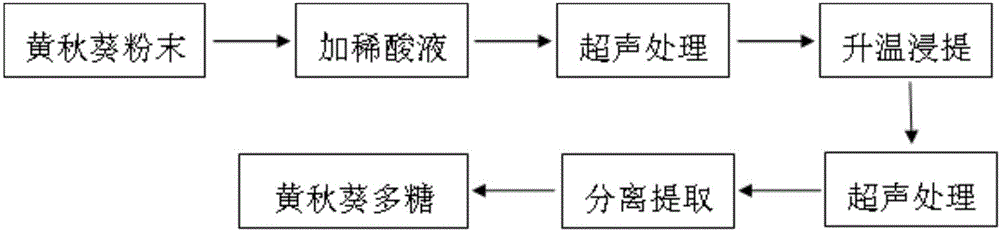
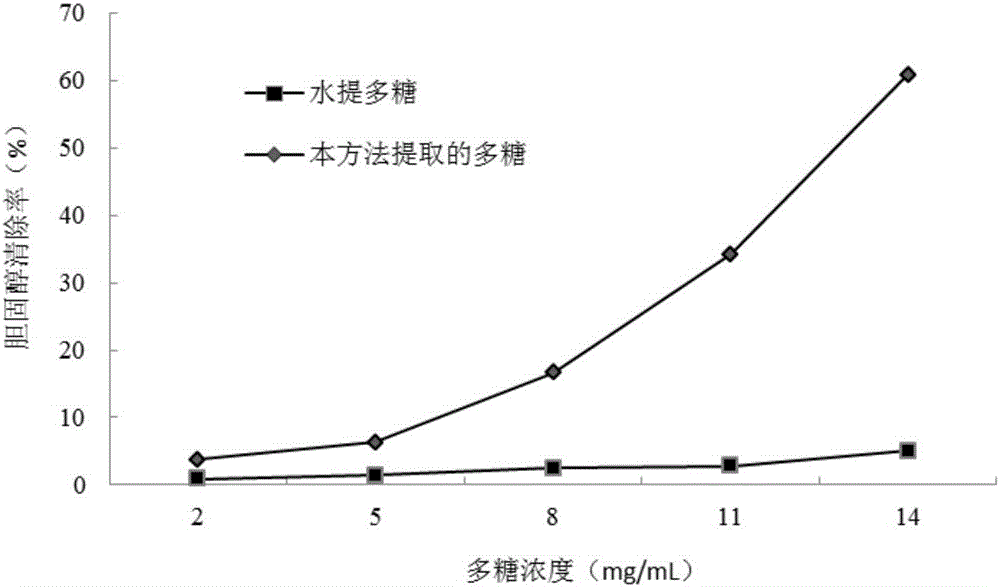
Preparation method of okra pectic polysaccharides with high cholesterol removal activity
InactiveCN106496353AHas antioxidant activityHigh ability to clear cholesterolMetabolism disorderAntinoxious agentsPectic polysaccharideAlcohol
The invention discloses a preparation method of okra pectic polysaccharides with high cholesterol removal activity. The method comprises the following steps: preparing okra powder, extracting okra pectic polysaccharides, separating crude okra polysaccharides, purifying the okra pectic polysaccharides, carrying out reduced pressure concentration on obtained extract liquid, carrying out alcohol precipitation, removing proteins, and carrying out freeze drying to obtain the okra pectic polysaccharides. The okra pectic polysaccharides obtained through the method have certain anti-oxidation activity, and also have high cholesterol removal ability.
Owner:WUHU INST OF TECH
Identification method for fast-growing milkvetch root and wild milkvetch root
The invention discloses an identification method for fast-growing milkvetch root and wild milkvetch root. The identification method comprises: drying milkvetch root, and crushing; sequentially removing water-soluble components, fat-soluble components and starch from the milkvetch root powder by using a PBS buffer liquid, 80% ethanol, acetone and amylase; carrying out graded mixing on the treated milkvetch root powder sequentially by using a EPG solution, a NaCO3 solution, a 1 M KOH solution and a 4 M KOH solution to extract milkvetch root pectin polysaccharides and hemicellulose polysaccharides; sequentially washing the extracted pectin polysaccharides and the extracted hemicellulose polysaccharides, removing impurities, and carrying out free drying to obtain polysaccharide powder; and carrying out acid hydrolysis, acetylation and GC-MS analysis, and treating the data by using SMICA13 and SPSS software to obtain the molar ratio of the arabinose in the hemicellulose polysaccharide to the arabinose in the pectin polysaccharide, wherein the identified milkvetch root is the fast-growing milkvetch root when the ratio is more than 0.5, and the identified milkvetch root is the wild milkvetch root when the ratio is less than 0.5. According to the present invention, the detection sensitivity of the method is high, the polysaccharide component ratio identification is simple and is easy to operate, and the basis is provided for the identification of the milkvetch root herb source.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Pectic oligosaccharide, preparation method thereof and application of AGEs
InactiveCN109221892AWide variety of sourcesHigh inhibition rateFermentationFood ingredient functionsPectinasePolysulfone membrane
The invention discloses pectic oligosaccharide, a preparation method thereof and application of an AGEs inhibitor. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adequately stirring the raw material, namely haw powder at 90 DEG C for 4 hours by virtue of a hot-water method, and separating to extract haw pectin; degrading pectin by virtue of pectinase, and collecting products with molecularweights of 1kDa-3kDa from enzymatic hydrolysate respectively through 1kDa-3kDa polysulfone membranes. The pectic oligosaccharide with a medium molecular weight has the advantages that the raw materialis easily available, the operation is simple, the inhibition rate to the generation of AGEs is high, and the pectic oligosaccharide is safe and non-toxic and low in cost; and the pectic oligosaccharide, as a dietary fiber has probiotics activity and multiple biological activities of resisting oxidation activity, reducing blood fat and the like.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Method for separating and purifying mixed-bean pectic polysaccharides
The invention discloses a method for separating and purifying mixed-bean pectic polysaccharides. According to the method, three different species of mixed beans comprising small red beans, white hyacinth beans and red kidney beans are used as raw materials. Through superfine grinding, hot water extraction, homogeneous-pore strongly-acidic styrene filler column adsorption and ethanol precipitation,mixed-bean refined polysaccharides with a pectic polysaccharide content of about 90% are quickly and efficiently prepared from the mixed beans, and gel column separation and purification are carriedout on the mixed-bean refined polysaccharides to finally prepare the mixed-bean pectic polysaccharides with good uniformity. The whole method is rapid and is good in stability from extraction to separation, and the obtained mixed-bean pectic polysaccharides are high in purity and good in quality.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
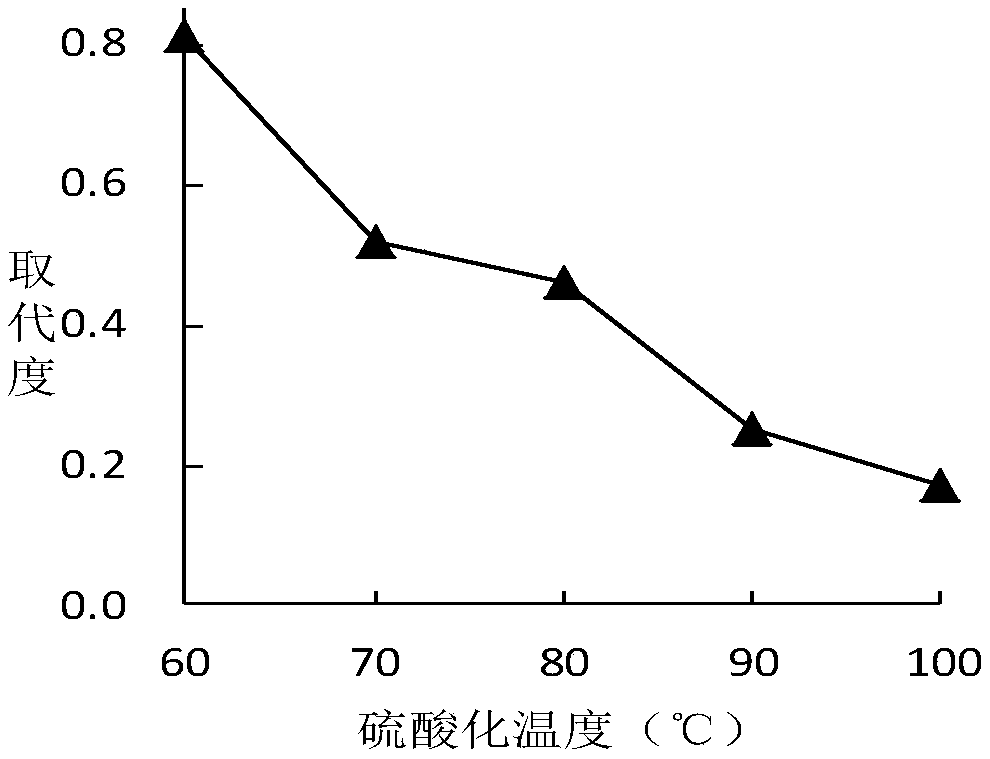
Method for sulfonating pectin
InactiveCN102585034AImprove anticoagulationGood antitumor activityAntiviralsAntineoplastic agentsAnti virusPectic polysaccharide
The invention discloses a method for sulfonating pectin, which comprises the step of sulfonating pectin or triethylamine pectin salt by using sulfur trioxide-pyridine complex in a dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) environment so as to obtain sulfonated pectin polysaccharide. The method adopts the following two systems: a trioxide-pyridine complex-DMSO system, and a TBA-trioxide-pyridine complex-DMSO system. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in operation and good in sulfonating effect. The sulfonated pectin polysaccharide prepared by the method is small in degradation in the reaction process, small in side reaction, has good anticoagulation, anti-tumor and anti-virus actives and a wide application range.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Orange peel radish cake, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107319425AGreat tasteHigh nutritional valueFood ingredient as mouthfeel improving agentPectic polysaccharideSugar
The invention discloses orange peel radish cake. The orange peel radish cake is prepared from, by weight, 2 to 4 parts of white radish, 0.5 to 1 part of orange peel, 1 to 2 parts of glutinous rice flour, and 1 to 2 parts of white granulated sugar. According to the preparation method, orange peel is added into radish cake, so that the obtained orange peel radish cake is rich in nutrients and physiologically active ingredients in orange peel, is higher in nutritional value, and possesses health care functions; and pectic polysaccharides in orange peel possess excellent gelation properties, so that the mouthfeel of radish cake is improved further.
Owner:GUANGXI WEIZHIFANG FOOD TECH CO LTD
Method for extracting pectin polysaccharides from soybean hulls
InactiveCN106317252APromote precipitationPromote flocculation and sedimentationLactariusSoybean hulls
Owner:邵玉华
Pectic polysaccharide and method for producing same
ActiveUS9107450B2Suppress aggregate precipitationLow viscosityMilk preparationFood preparationPectic polysaccharideGalacturonic acid
The present invention provides a pectic polysaccharide, wherein a degree of methyl esterification of constituent galacturonic acid is 45% or less, a structure of a single molecule observed with an atomic force microscope comprises a star structure, and a diameter of the molecule is more than 100 nm and equal to or less than 200 nm.
Owner:FUJI OIL CO LTD
Pectin composition, preparation method, and application thereof
ActiveCN106692257AHigh activityOvercome physical chemistryOrganic active ingredientsAntinoxious agentsPectic polysaccharideChemical reaction
The invention discloses a pectin composition with activity capable of highly inhibiting human enteraden cancer cells, and a preparation technology, a drug and food thereof. The pectin composition provided by the invention comprises food pectic polysaccharide and a crassulaceae plant extract, wherein the crassulaceae plant extract is a water extract or an extract of a water / alcohol mixed solvent. Pectin and the crassulaceae plant extract are subjected to esterification reaction at a food in-situ state, and finally the pectic polysaccharide composition with high activity is prepared. The prepared composition has the activity capable of highly inhibiting the human enteraden cancer cells, and is relatively stable. The composition overcomes the defects in physical chemistry and functionality of the original pectic polysaccharide and the plant extract, and is more suitable to be used. The preparation method of the pectin composition provided by the invention overcomes the defects of a traditional organic chemical reaction technology, and has the advantages that a preparation process is safe and non-toxic, a product is a food-grade food, the preparation cost is lower, a food processing process can be applied, and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Enzymatically hydrolysed pectic polysaccharides for treating or preventing infections
PendingUS20200246373A1Modulate responsivenessImprove the immunityOrganic active ingredientsTransferasesMonosaccharide compositionDietary supplement
The invention relates to a product for use in the therapeutic or prophylactic treatment of infections, said treatment comprising oral administration of the product, wherein the product is selected from a nutritional formulation, a food product, a dietary supplement, a beverage and a pharmaceutical product, said product containing carrot RG-I polysaccharides having the following combination features:a molecular weight in the range 10-300 kDa;a backbone consisting of galacturonic acid residues and rhamnose residues, said rhamnose residues being contained in alpha(1→4)-galacturonic-alpha(1→2)-rhamnose residues;the following monosaccharide composition:20-60 mol. % galacturonic acid residues, wherein the individual galacturonic acids can be methylated and / or acetyl-esterified;8-50 mol. % rhamnose residues;0-40 mol. % arabinose residues;0-40 mol. % galactose residues;molar ratio of galacturonic acid residues to rhamnose residues in the range of 5:1 to 1:1;galacturonic acid residues, rhamnose residues, arabinose residues and galactose residues together constitute at least 85 mol. % of the monosaccharide residues in the carrot RG-I polysaccharides.These carrot RG-I polysaccharides can be produced by partially hydrolysing pectic polysaccharides present in a carrot pectin isolate. The effectiveness of carrot RG-I polysaccharides against infections is substantially improved by enzymatically hydrolysing the RG-I polysaccharides to remove at least part of the homogalacturonan component.
Owner:NUTRILEADS
A polysaccharide of Rubus oleifera is used to inhibit blood coagulation
InactiveCN105030810BApplication has a long historyHigh effective/safety factorOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderPectic polysaccharideRosaceae
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
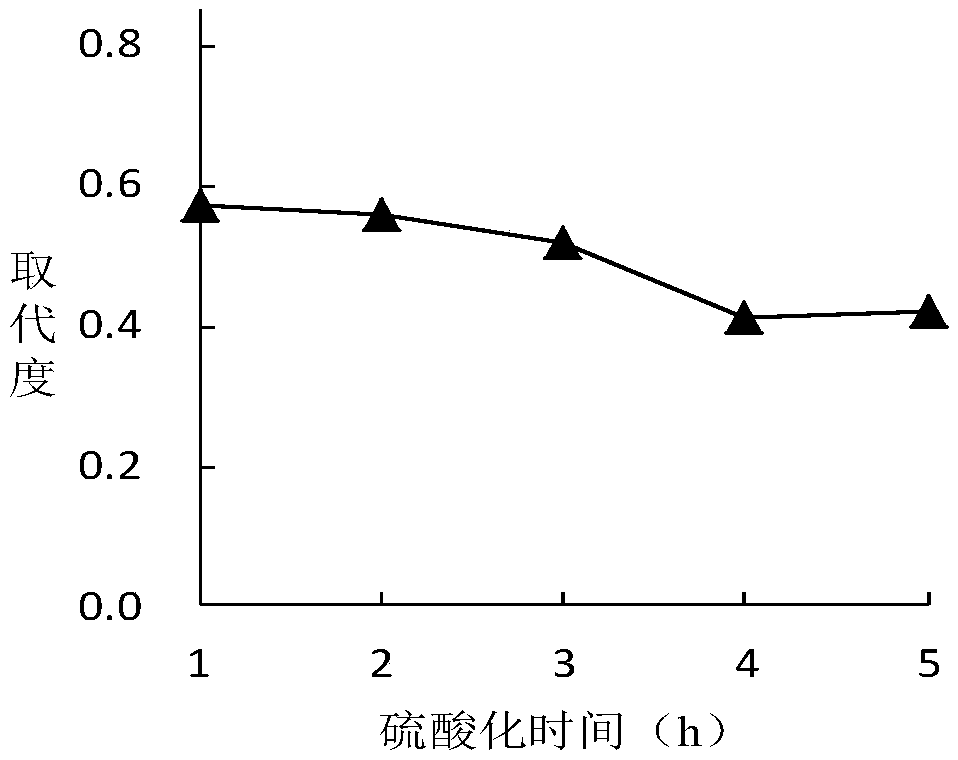
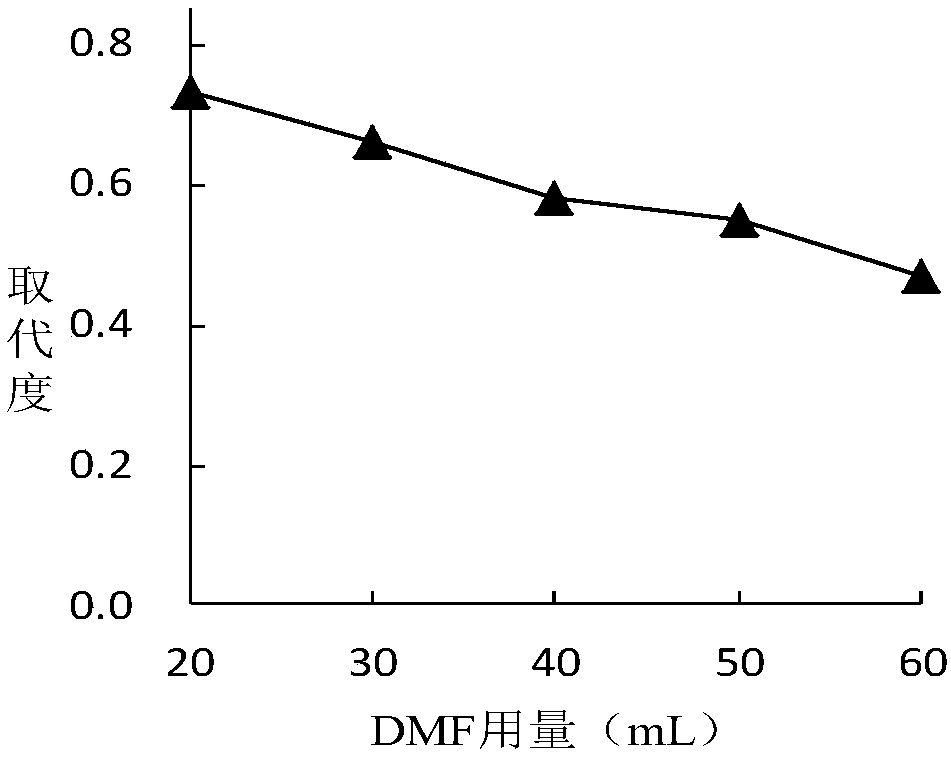
Pectin polysaccharide sulfated modified product with effect of improving antioxidant activity and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a sulfated modification method for reinforcing the anti-oxidation activity by pectin polysaccharides. The sulfated modification method comprises the following steps: carryingout sulfated modification by adopting an N,N-DMF (Dimethyl Formamide)sulfamate, taking the sulfated substitution degree as an index, and investigating the sulfurization temperature, the sulfurizationtime, the DMF using amount and sulfamic acid using amount by a single factor, thus obtaining sulfated pectin polysaccharides in different substitution degrees. The invention also relates to application of the sulfated pectin polysaccharides in medicine preparation, and particularly in antioxidant drug preparation. The application is characterized by preparing drugs for removing hydroxyl radicals,super-oxide anions and Fe<3+> reducing capacity. According to the sulfated modification method disclosed by the invention, the artificially synthesized sulfated pectin polysaccharides in different substitution degrees are used for in-vitro antioxidant activity tests, and reference basis is provided for the application of the sulfated pectin polysaccharides in the field of medicine.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Lycium barbarum polysaccharide and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111040042ALow binding constantGood effectOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsMonosaccharide compositionPectic polysaccharide
The invention discloses lycium barbarum polysaccharide and a preparation method and application thereof. The lycium barbarum polysaccharide is prepared by an alkali extraction method. Monosaccharide composition of lycium barbarum polysaccharide LALP comprises arabinose, galactose, galacturonic acid, rhamnose, mannose, glucuronic acid, glucose and fucose according to a ratio of the arabinose to thegalactose to the galacturonic acid to the rhamnose to the mannose to the glucuronic acid to the glucose to the fucose is 37.26 to 22.23 to 14.53 to 7.66 to 4.11 to 1.61 to 6.18 to 6.43. The polysaccharide LALP contains two main components, the molecular weights of the two components are 183.9 kDa and 316 kDa respectively, the polydispersity coefficients of the two components are 2.793 and 1.411 respectively, and the molecular rotation radiuses of the two components are 17.5 nm and 37.3 nm respectively. Structural analysis finds that the polysaccharide is mainly composed of pectic polysaccharide of an RG-I structure, experiments show that the polysaccharide can be well combined with a molecular target Gal-3 for anti-cancer treatment, the binding constant is lower than those of other typesof plant polysaccharides, the effect is extremely good, and the polysaccharide can be developed into carbohydrate drugs for treating cancer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Premna microphylla pectin mask liquid and preparation method thereof
PendingCN112754955AImprove securityGood anti-inflammatory effectCosmetic preparationsAntipyreticAloinBiology
The invention discloses premna microphylla pectin mask liquid and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of skin care products. The premna microphylla pectin mask liquid comprises the following components: premna microphylla pectin polysaccharide, premna microphylla flavone, bioactive peptide, green tea essence, pearl powder, an aloe extract, sodium hyaluronate, nipagin and the balance of water. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing and stirring the water with the premna microphylla pectin polysaccharide and the sodium hyaluronate, performing cooling, performing mixing with an aqueous solution of other raw materials in proportion, and performing uniform stirring to obtain the premna microphylla pectin mask liquid. The premna microphylla pectin mask liquid disclosed by the invention has the advantages of oxidation resistance, safety, anti-inflammation effect and collagen repair promotion, can comprehensively deal with skin aging caused by ultraviolet rays by integrating various bioactive components, and effectively relieves damage symptoms such as redness, pruritus, desquamation, collagen loss, pigmentation and the like after the skin is dried in the sun. The preparation method is simple and mild in condition, and has popularization and practical values in the technical field of skin care products.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Transeliminase encoding gene and enzyme and preparation and application
InactiveCN111254154AEfficient degradationHigh activityFermentationGenetic engineeringHeterologousPentagalacturonic acid
The invention discloses a preparation and application of a transeliminase encoding gene derived from Aspergillus parasiticus, and an enzyme of the transeliminase encoding gene, that is, a gene of transeliminase is cloned to a pichia pastoris expression vector by using a technical method of gene engineering, then a pichia pastoris recombinant strain for heterologous expression of the enzyme can beobtained, the strain is capable of heterologously expressing the prepared transeliminase and efficiently degrading pectin polysaccharides and polygalacturonic acid (PGA). The transeliminase disclosedby the invention can be widely applied to fields such as agriculture, industry, foods, feed additives, medicines and pectin oligosaccharide preparation.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
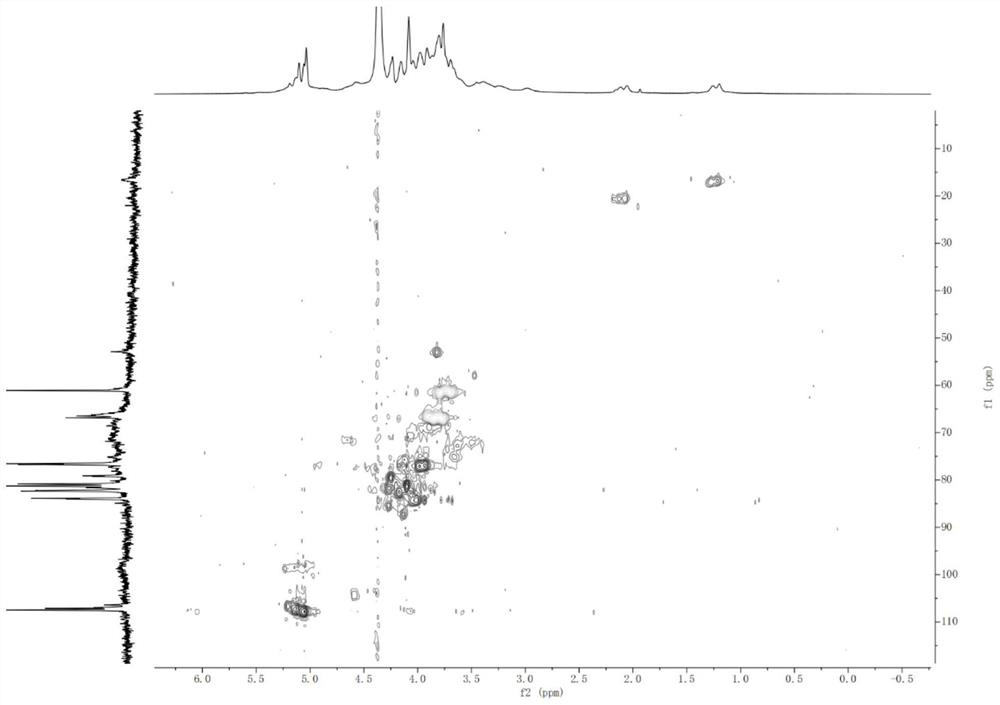
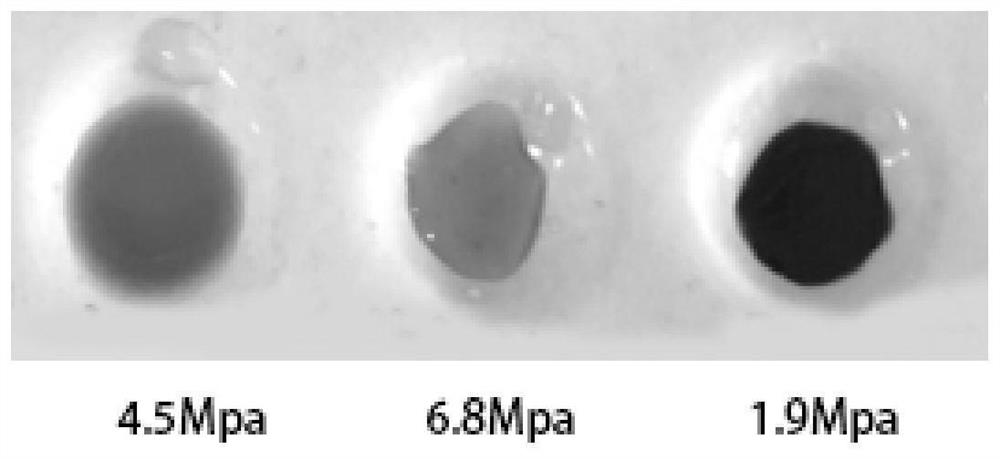
Method for preparing RG-I pectic polysaccharide rich in arabinose side chains
The invention discloses a method for preparing RG-I pectic polysaccharide rich in arabinose side chains, and belongs to the technical field of pectin extraction. The method comprises the following steps: by taking peanut meal as a raw material, carrying out medium-temperature and high-pressure treatment in an acidic and nitrogen environment, and centrifugally filtering to obtain pectic polysaccharide rich in RG-I; wherein the peanut meal is a by-product generated in the processing process of extracting oil from peanut oil by a water medium method; and the medium-temperature and high-pressure treatment conditions are as follows: the temperature is 90-105 DEG C, and the pressure is 2-7Mpa. The pectic polysaccharide rich in arabinose side chain RG-I is extracted from the peanut meal by adopting the method, the extraction rate reaches 35-40%, and the purity reaches 85-92%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com