Patents
Literature
34 results about "Levoglucosan" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
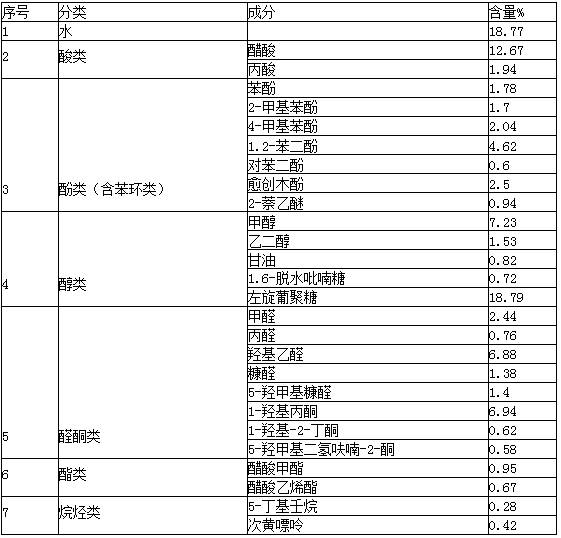
Levoglucosan (C₆H₁₀O₅) is an organic compound with a six-carbon ring structure formed from the pyrolysis of carbohydrates, such as starch and cellulose. As a result, levoglucosan is often used as a chemical tracer for biomass burning in atmospheric chemistry studies, particularly with respect to airborne particulate matter. Along with other tracers such as potassium, oxalate, and gaseous acetonitrile, levoglucosan has been shown to be highly correlated with regional fires. This is because the gas emitted by the pyrolysis of wood (biomass) contains significant amounts of levoglucosan.
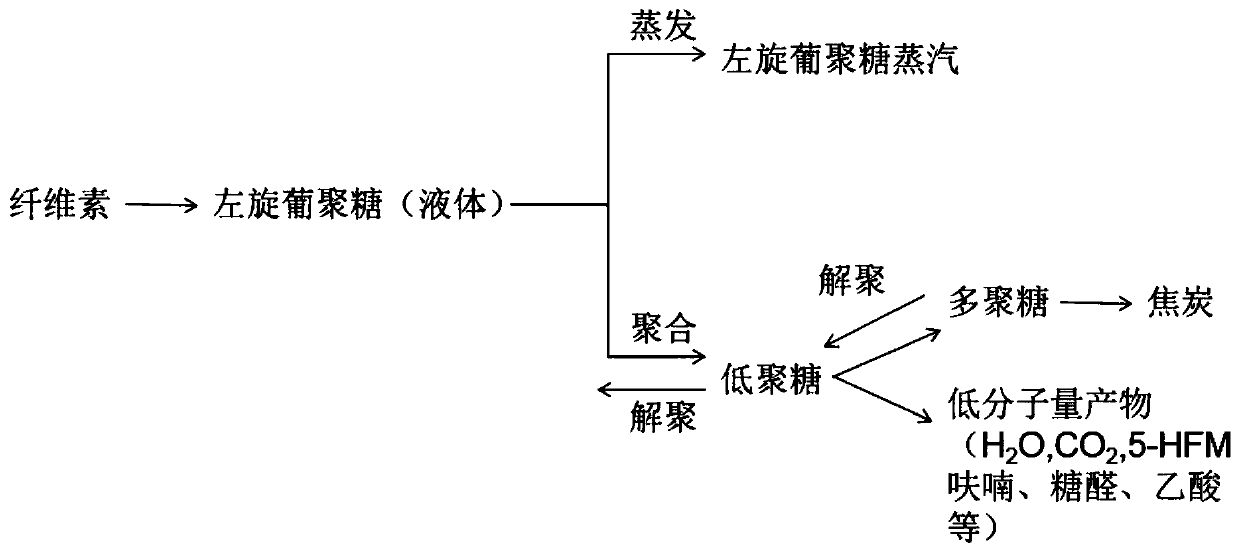
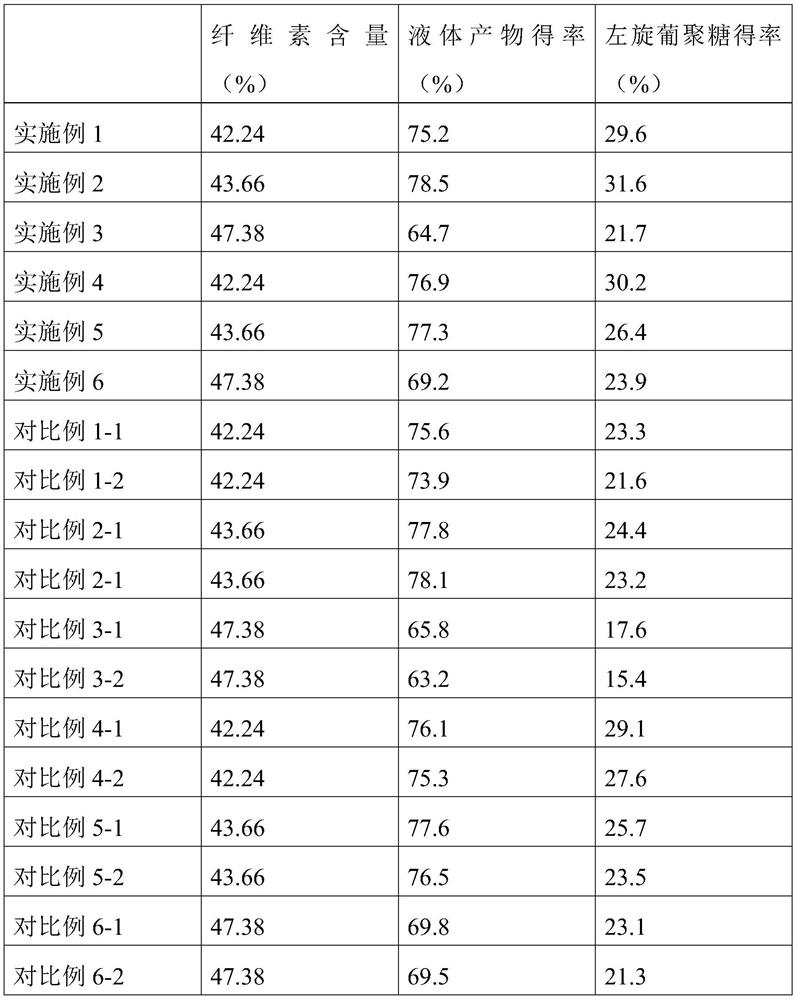
Method for directional thermal degradation of fiber biomass
The invention discloses a method for directional thermal degradation of a fiber biomass, which comprises the following steps: crushing a fiber biomass, adding a directional thermal degradation catalyst with a certain concentration for pretreatment, mixing, filtering, washing with deionized water, drying at the temperature of 80-120 DEG C, and rapidly cracking at the temperature of 250-600 DEG C, thereby obtaining liquid products which mainly comprise furfural, L-glucosene, L-glucan and the like. The method for directional thermal degradation of the fiber biomass greatly reduces the types of the liquid products and facilitates the high-value use of the liquid products.
Owner:INST OF CHEM IND OF FOREST PROD CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
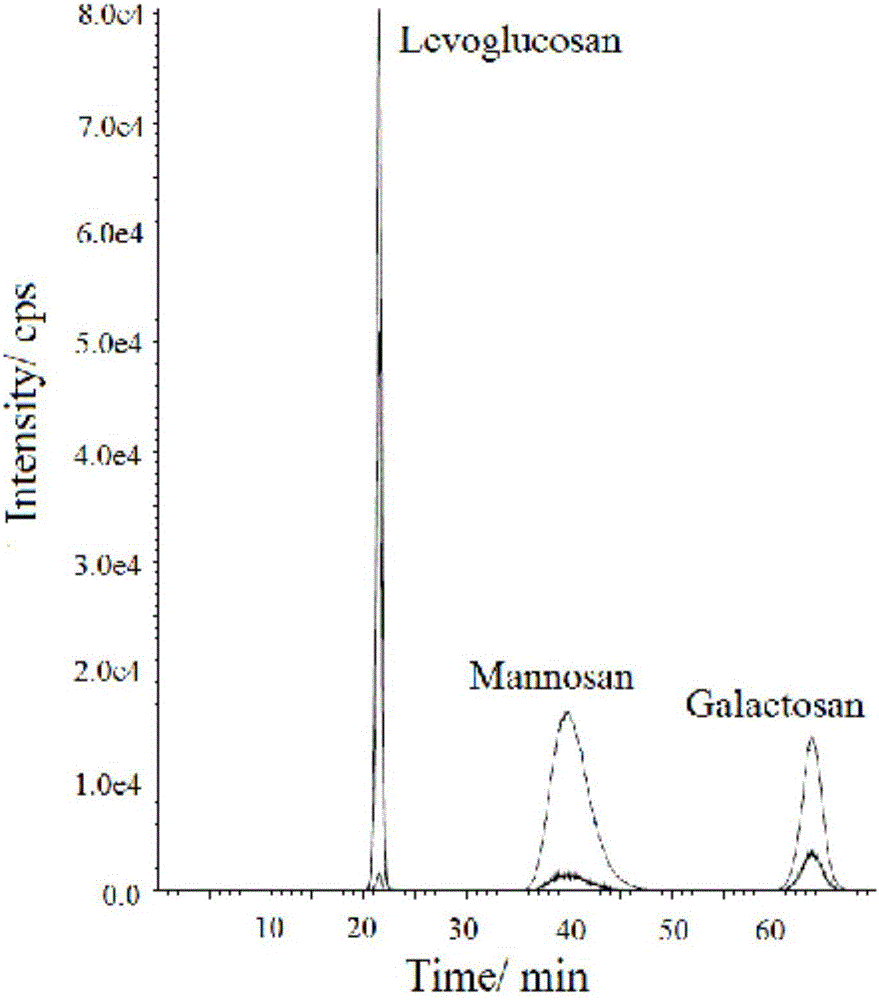
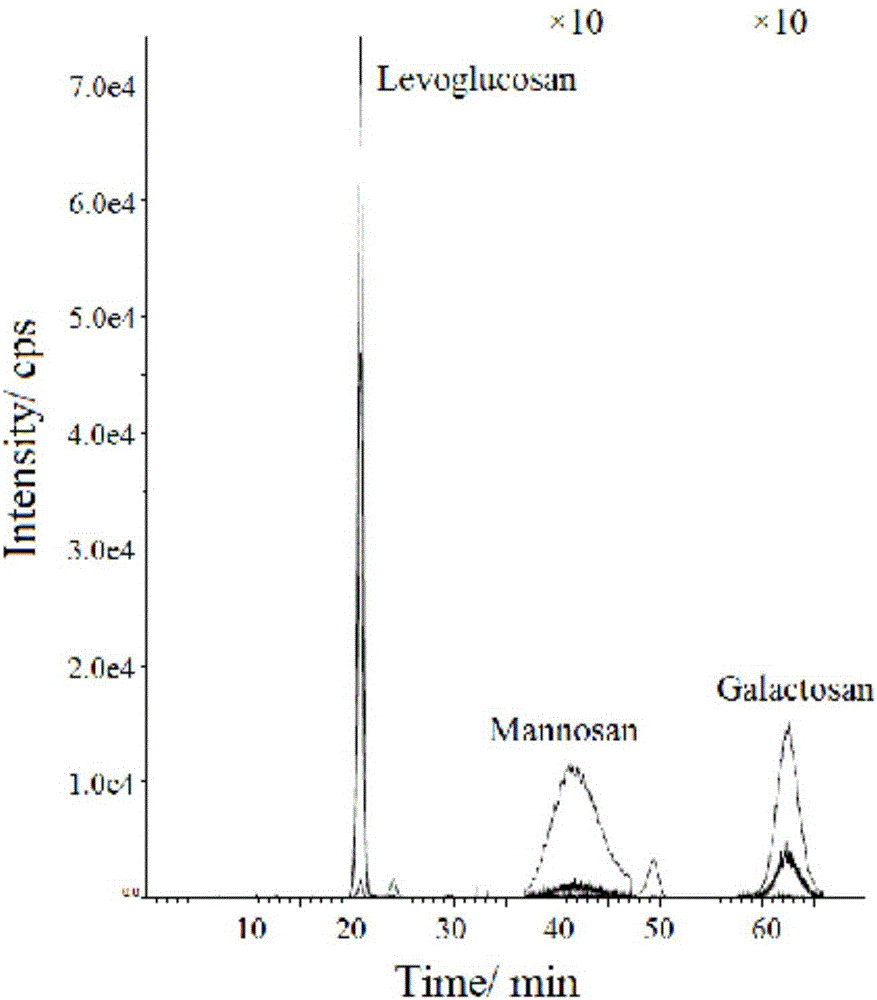
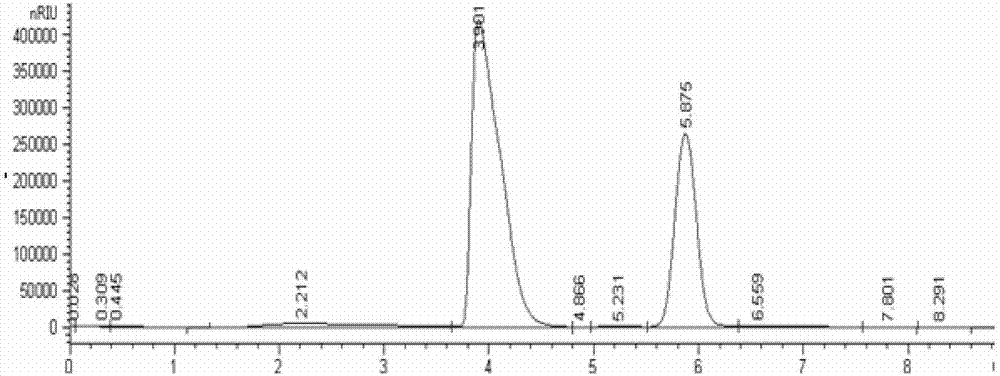
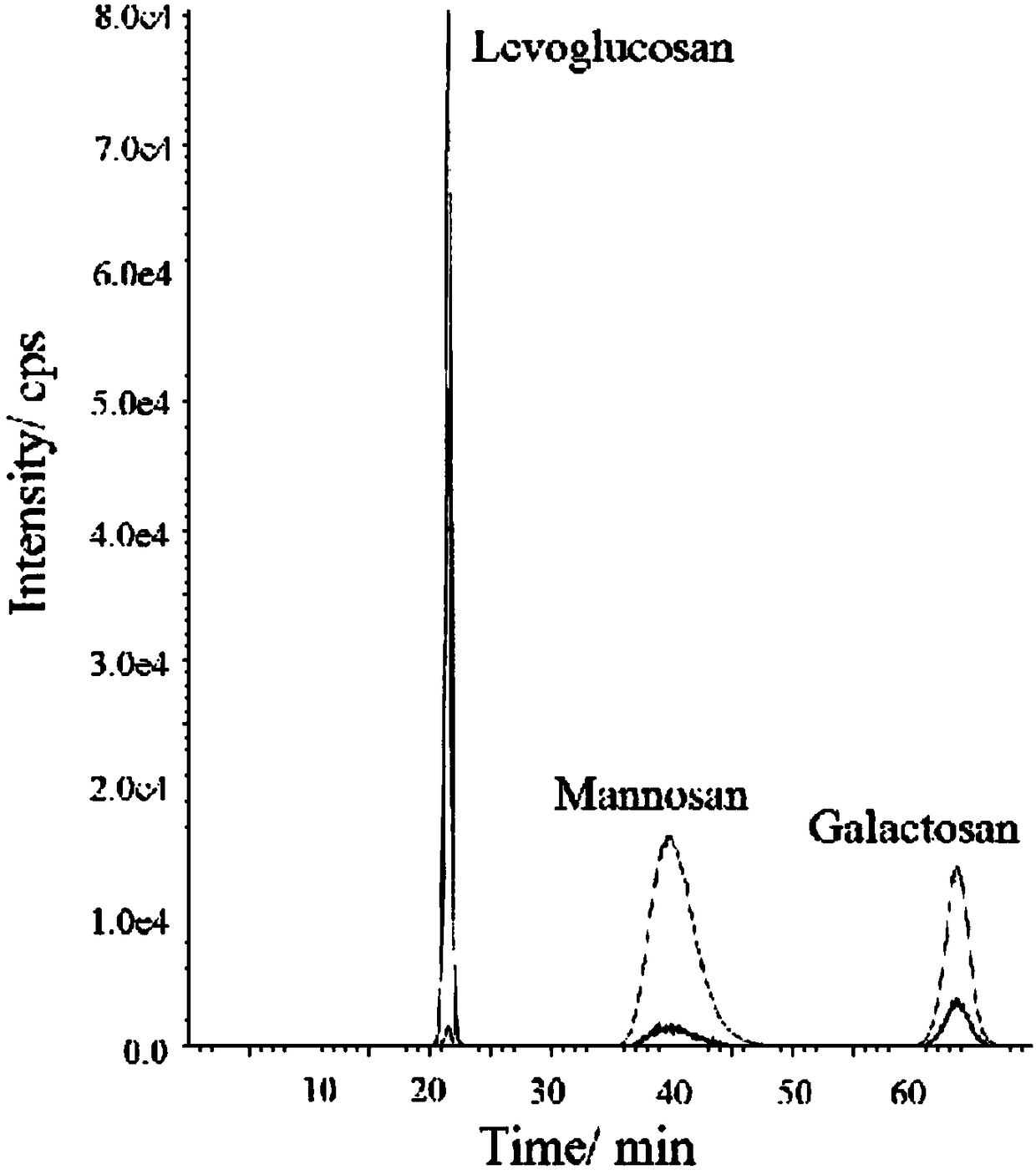
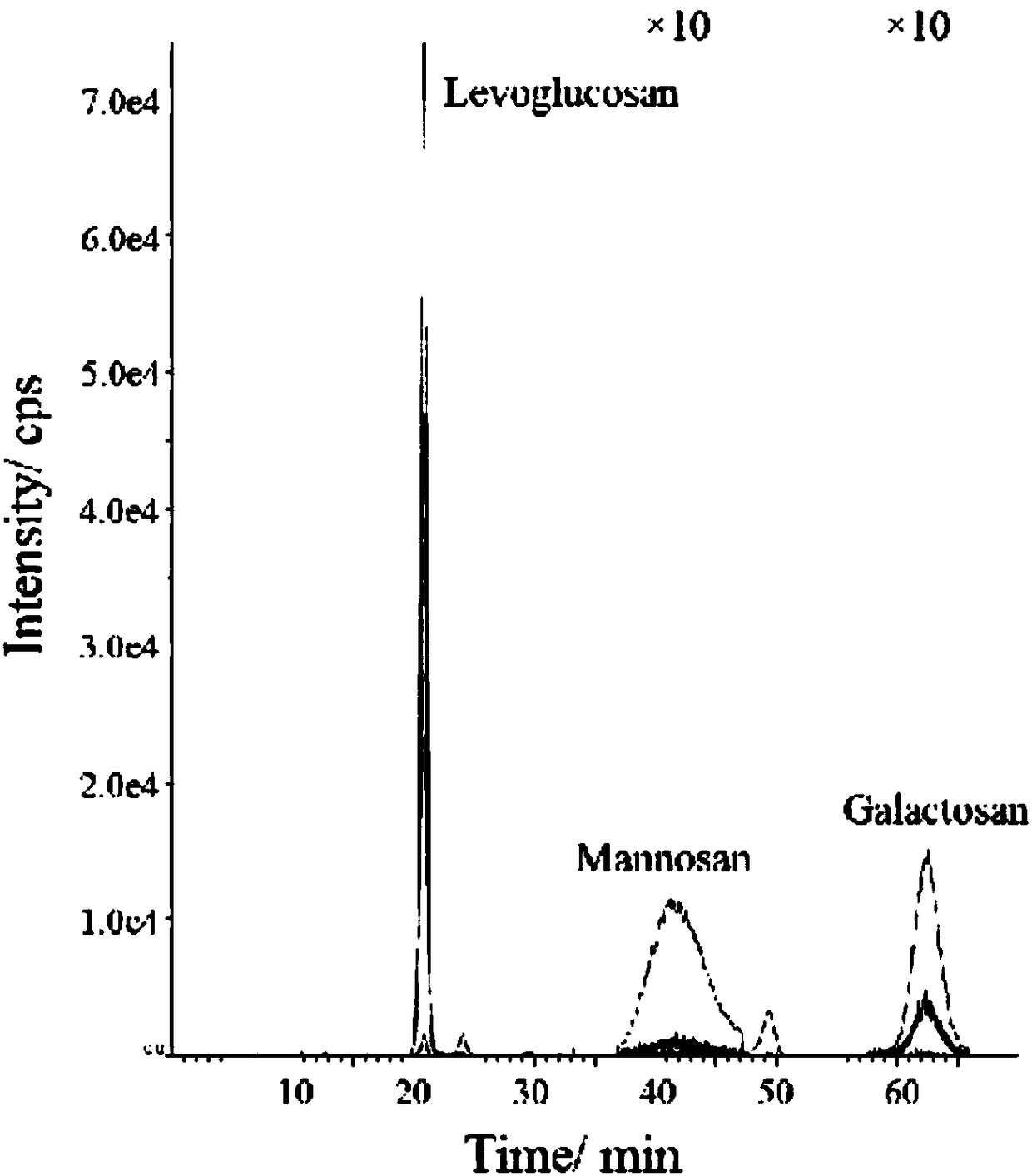
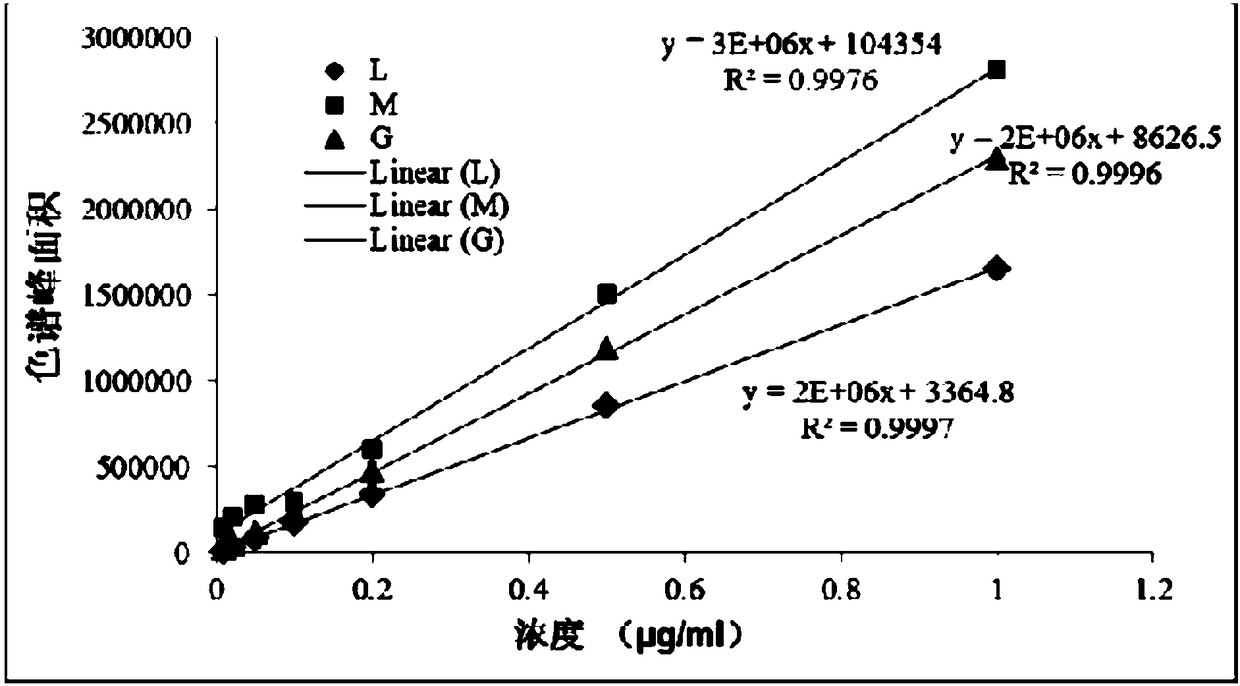
Method for synchronously measuring levoglucosan, mannan and galactosan in aerosol for high performance liquid chromatography-tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry combination
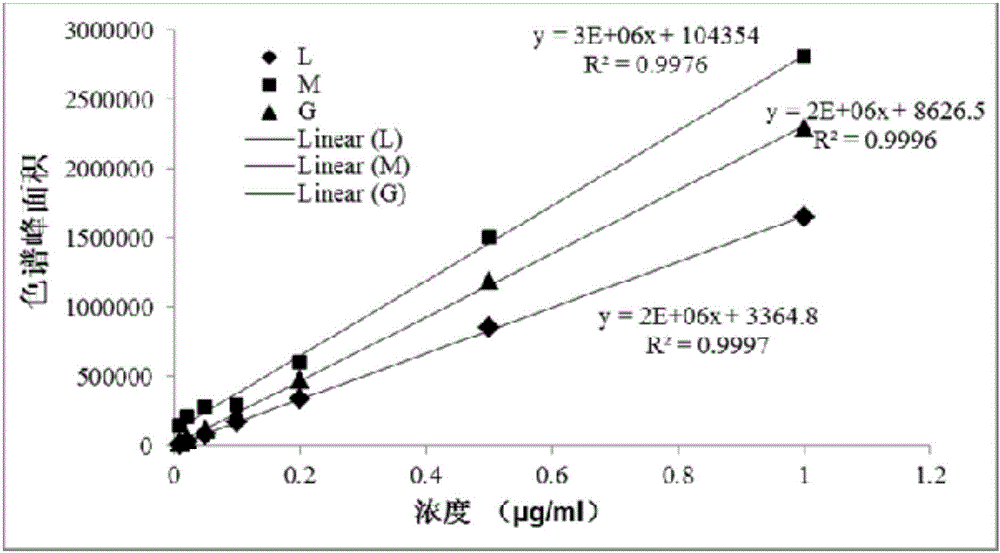
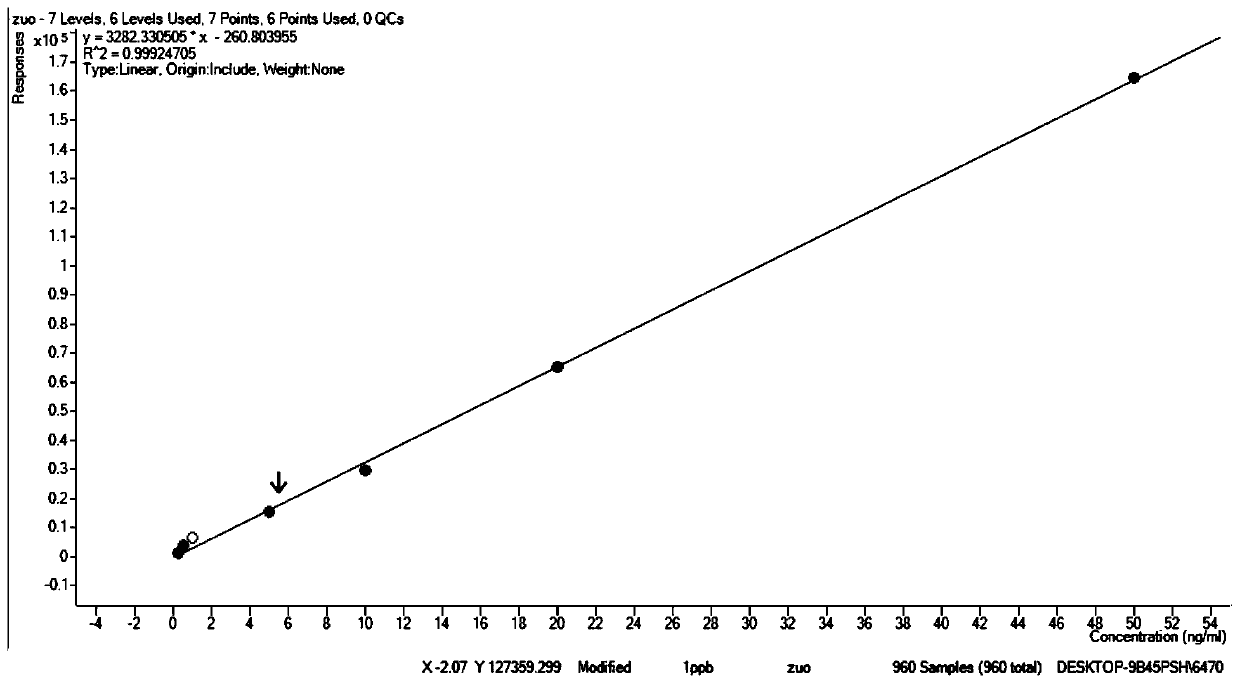
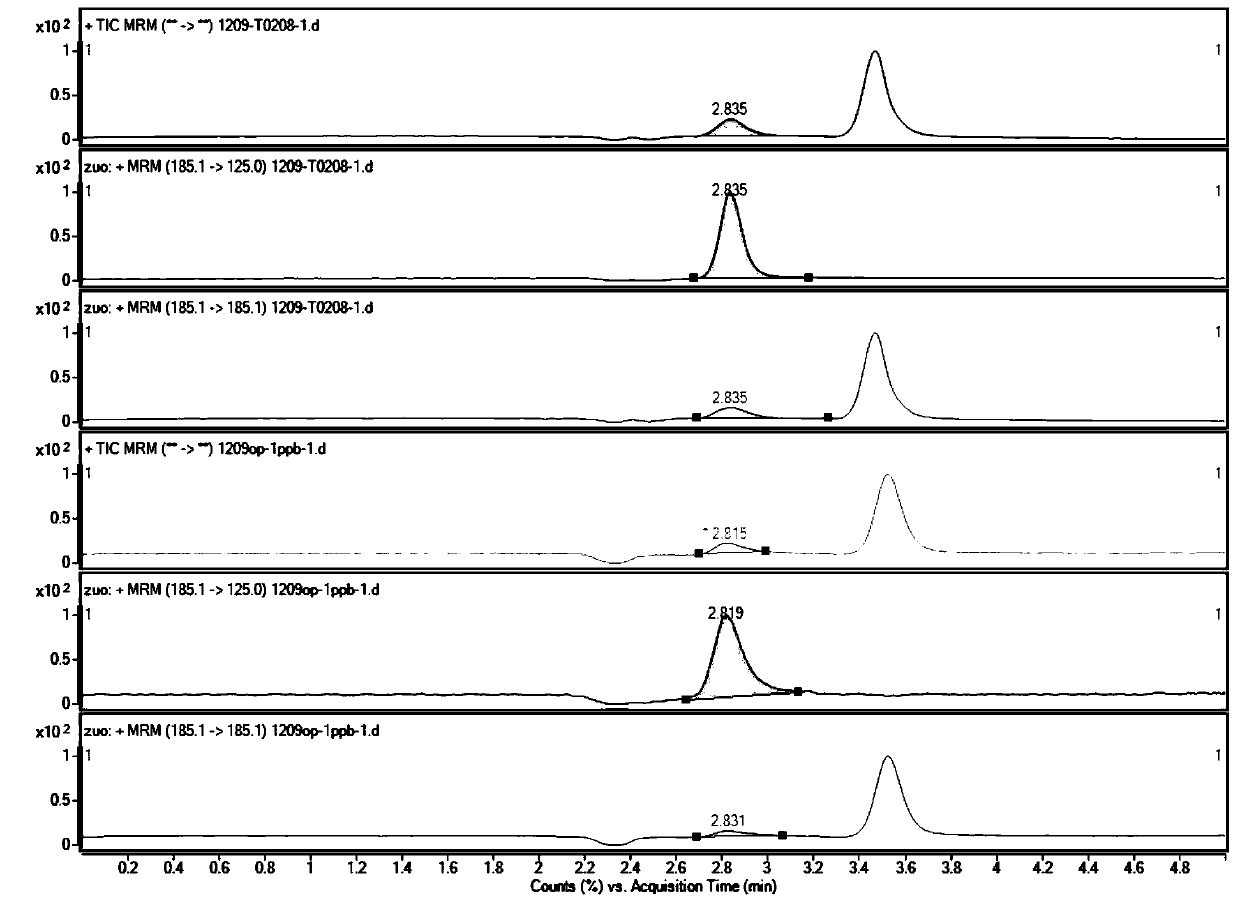
A method for synchronously measuring levoglucosan, mannan and galactosan in aerosol for high performance liquid chromatography-tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry combination includes the steps that levoglucosan, mannan and galactosan in an aerosol sample are subjected to ultrasonic extraction with ultrapure water and detected by means of a high performance liquid chromatography-tandem quadrupolemass spectrometer; ammonia water is adopted as a mobile phase; an electrospray ionization mode suitable for polar molecule analysis is adopted as an ion source of a mass spectrometry, ion source parameters and compound parameters optimized many times are adopted in a mass spectrometric method, and qualitative and quantitative analysis is conducted in an anion and multiple-reaction monitoring mode.By means of the external standard curve method, the linear relation of L, M and G is good in the range of 0.01<-1> microgramme per milliliter, the correlation coefficient is larger than 0.99, the detection limit of L is smaller than 0.005 microgramme per milliliter, the detection limits of M and G are both smaller than 0.01 microgramme per milliliter, experiment repeatability is good, relative standard deviations of repetitive experiments of L, M and G are 1.31%, 4.48% and 1.31% respectively, and the adding standard recovery rates of L, M and G all reach 97% or above.
Owner:何俊
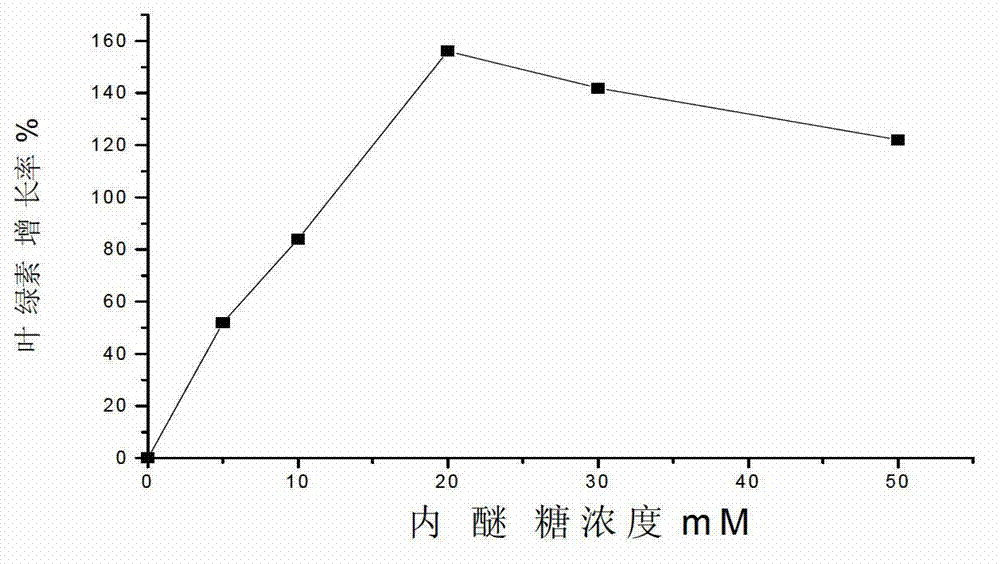
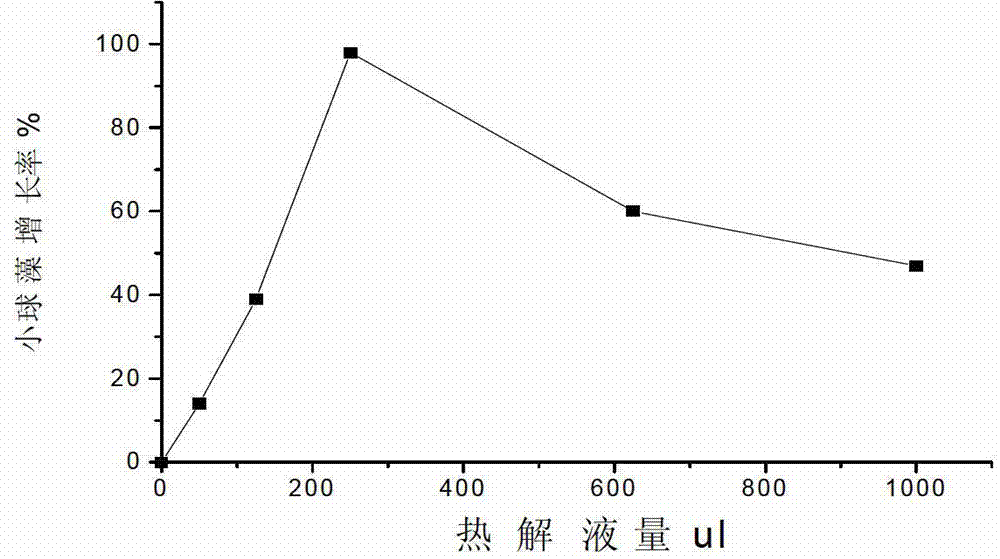
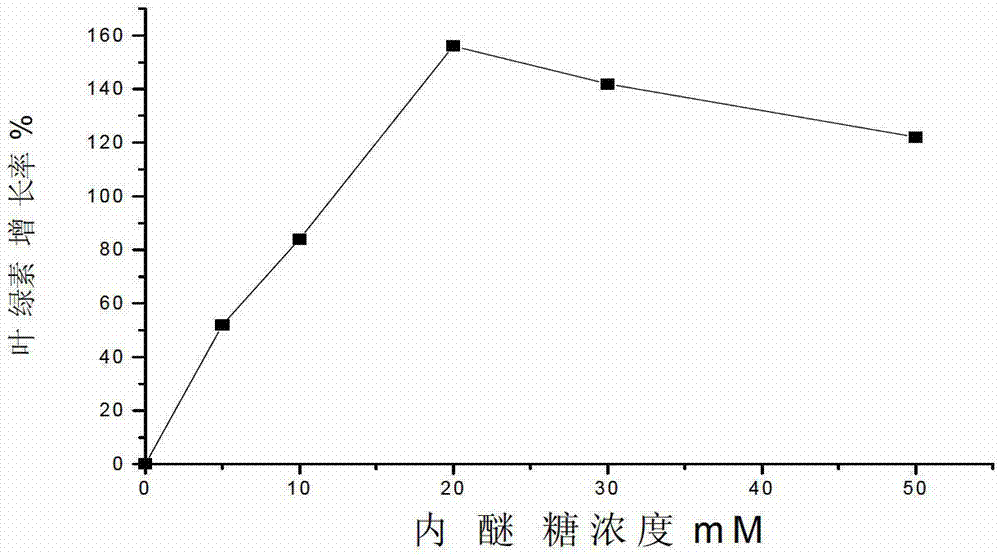
Method for promoting growth of Nannochlorisoculata and increasing contents of chlorophyll and mycoprotein of Nannochlorisoculata
ActiveCN103045481AReduce use costUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesMycoproteinFungus protein
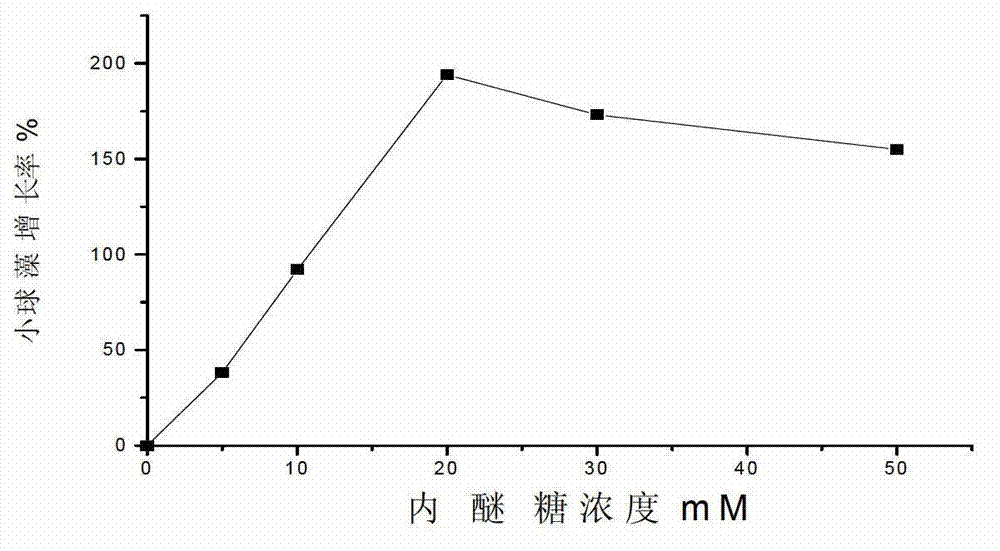
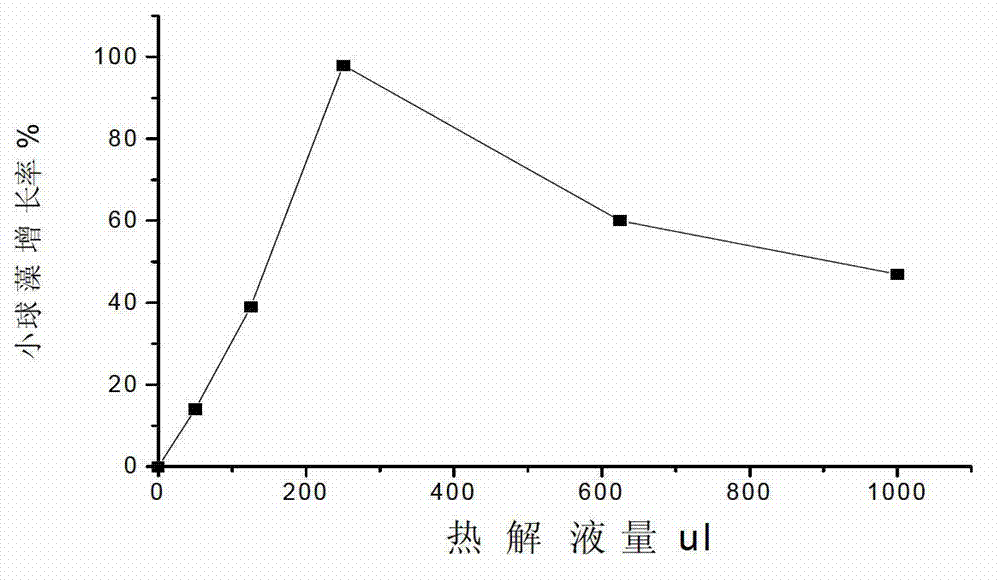
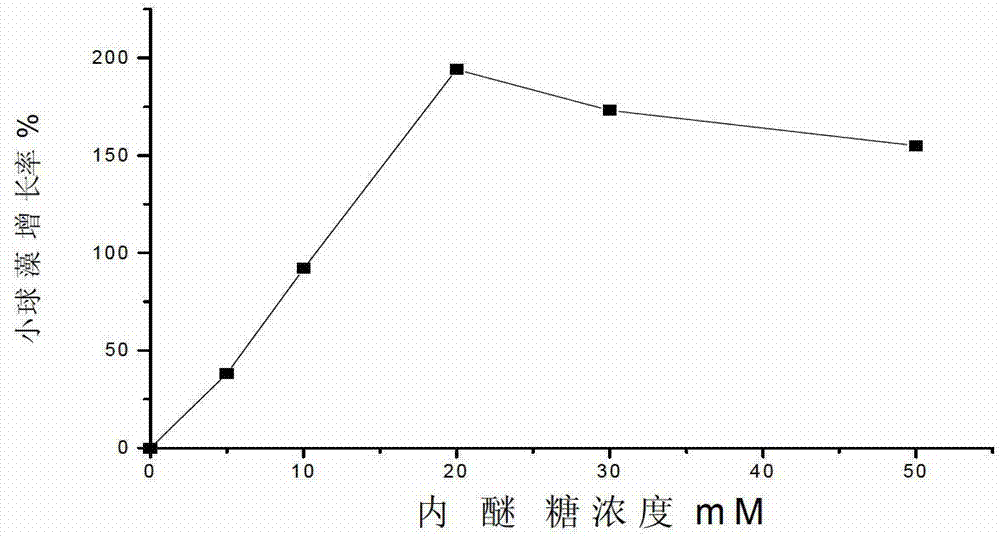
The invention relates to a method for promoting growth of Nannochlorisoculata and increasing contents of chlorophyll and single-cell protein of the Nannochlorisoculata. The method comprises the step that levoglucosan from biomass pyrolysis or cellulose pyrolysis liquid subjected to detoxification treatment is added to a Nannochlorisoculata culture solution, wherein the additive amount of levoglucosan is 5-50mM, and the additive amount of the cellulose pyrolysis liquid is 0.25-2% by weight. By taking a cellulosic biomass high-temperature pyrolysis product, namely levoglucosan or the pyrolysis liquid as an accelerant, a result shows that levoglucosan or the pyrolysis liquid can promote the growth of the Nannochlorisoculata obviously; a promoting rate reaches up to 194%; and the contents of chlorophyll and mycoprotein can be increased significantly, so that a use value of a cellulosic biomass can be increased.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
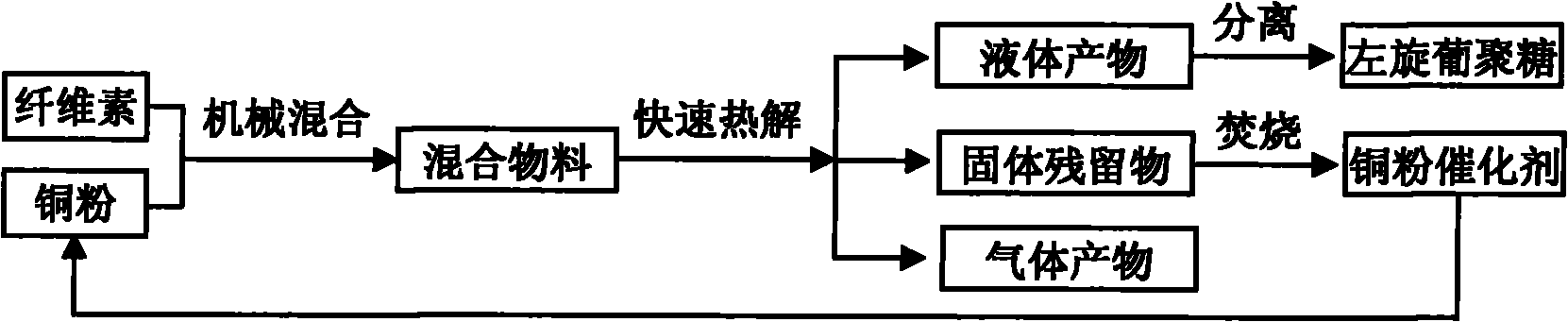
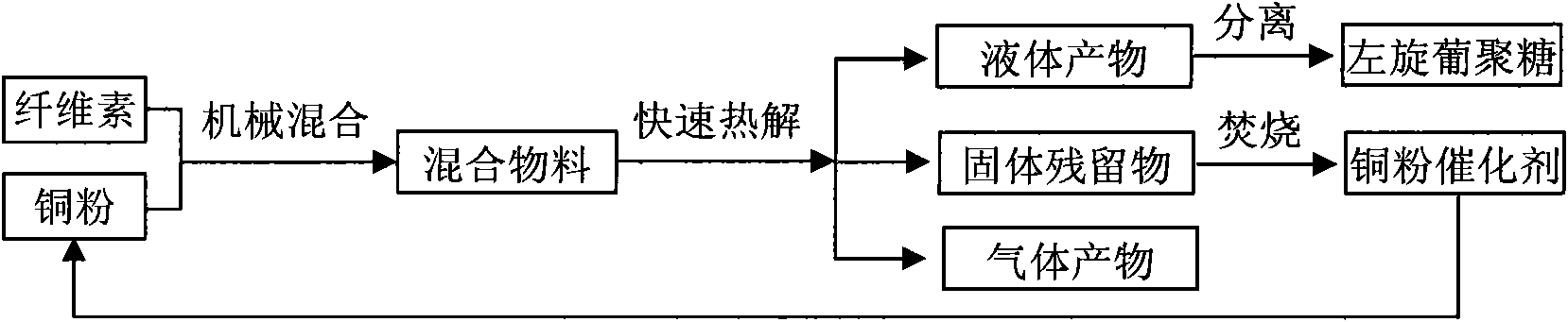
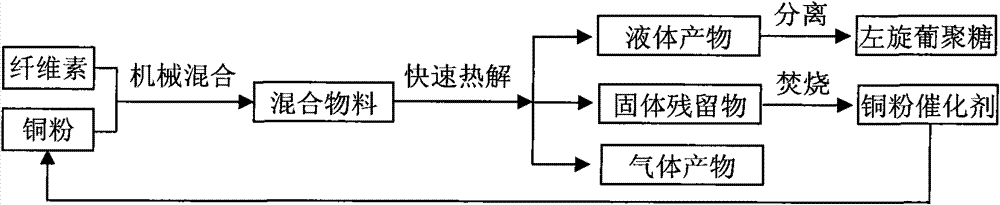
Method for preparing levoglucosan from cellulose by catalytic pyrolysis
ActiveCN102020722AInhibition of ring-opening fragmentationEasy to passChemical recyclingCatalytic pyrolysisLiquid product
The invention belongs to the field of utilization of biomass energy, and in particular relates to a method for preparing levoglucosan from cellulose by catalytic pyrolysis. The method comprises the following steps of: mechanically mixing copper powder serving as a catalyst and cellulose powder; performing fast pyrolysis under an oxygen-free condition at the temperature of between 280 and 450 DEG C; condensing pyrolysis gas to obtain a levoglucosan-rich liquid product; and burning solid residues to recover the copper powder catalyst. In the product prepared from the cellulose by the catalytic pyrolysis of the copper powder, the levoglucosan has high yield and purity and is convenient to subsequently separate and extract; in addition, the solid copper powder is used as the catalyst, is veryconvenient to recover, does not substantially have the problem such as inactivation and the like and can be repeatedly recycled.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Method for producing melanin by eurotium cristatum utilizing levoglucosan as well as cellulose pyrolysis solution and so on
The invention relates to the utilization of eurotium cristatum onto melanin produced by carbon sources including a cellulose biomass high-temperature pyrolysis product pyrolysis solution, levoglucosan and the like. The eurotium cristatum is grown by using levoglucosan, maltose, glucose, sucrose, lactose, molasses, stevia rebaudiana, pyrolysis solution and the like as carbon sources, and can be used for producing melanin.
Owner:巴州正达绿源生物科技有限公司
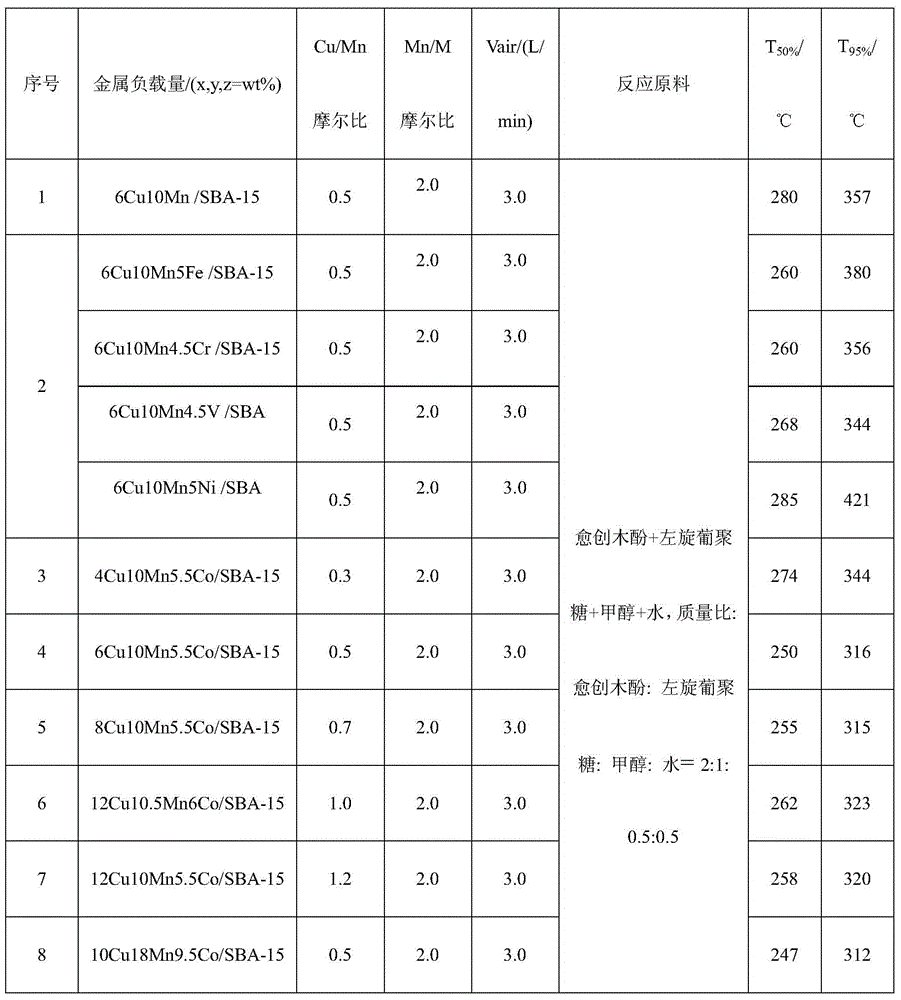
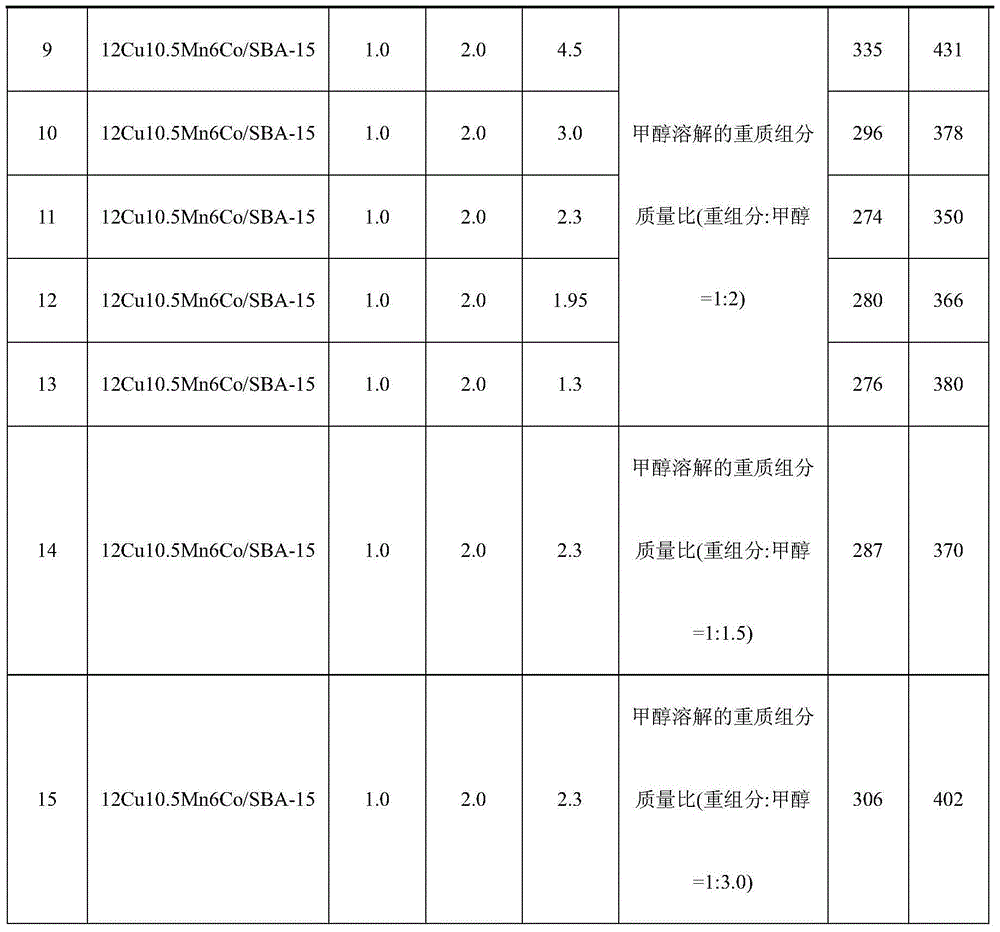
Method for low-temperature complete combustion of bio-oil heavy components by use of Cu-Mn base supported monolithic catalyst
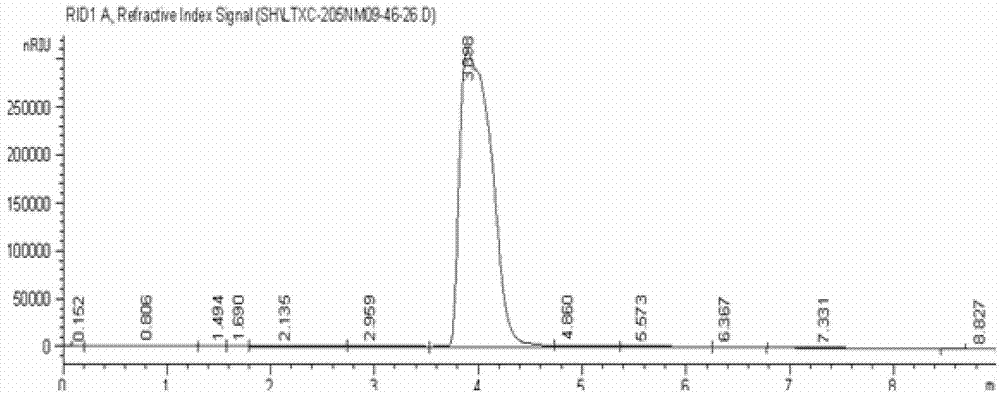
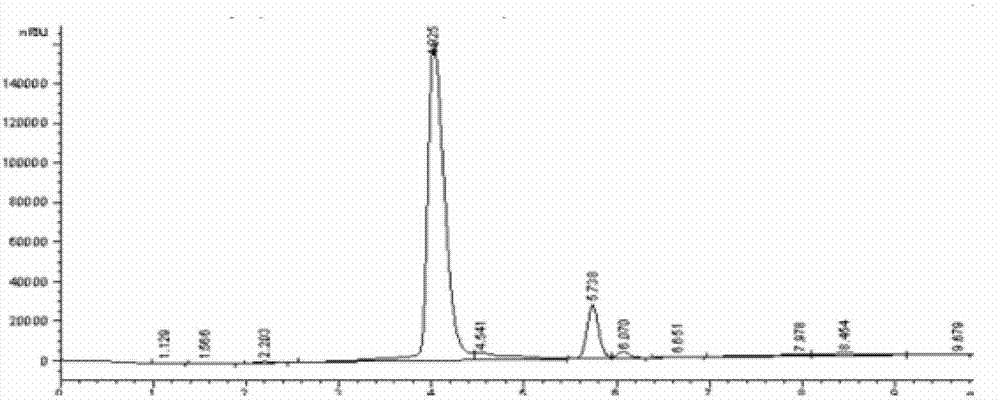
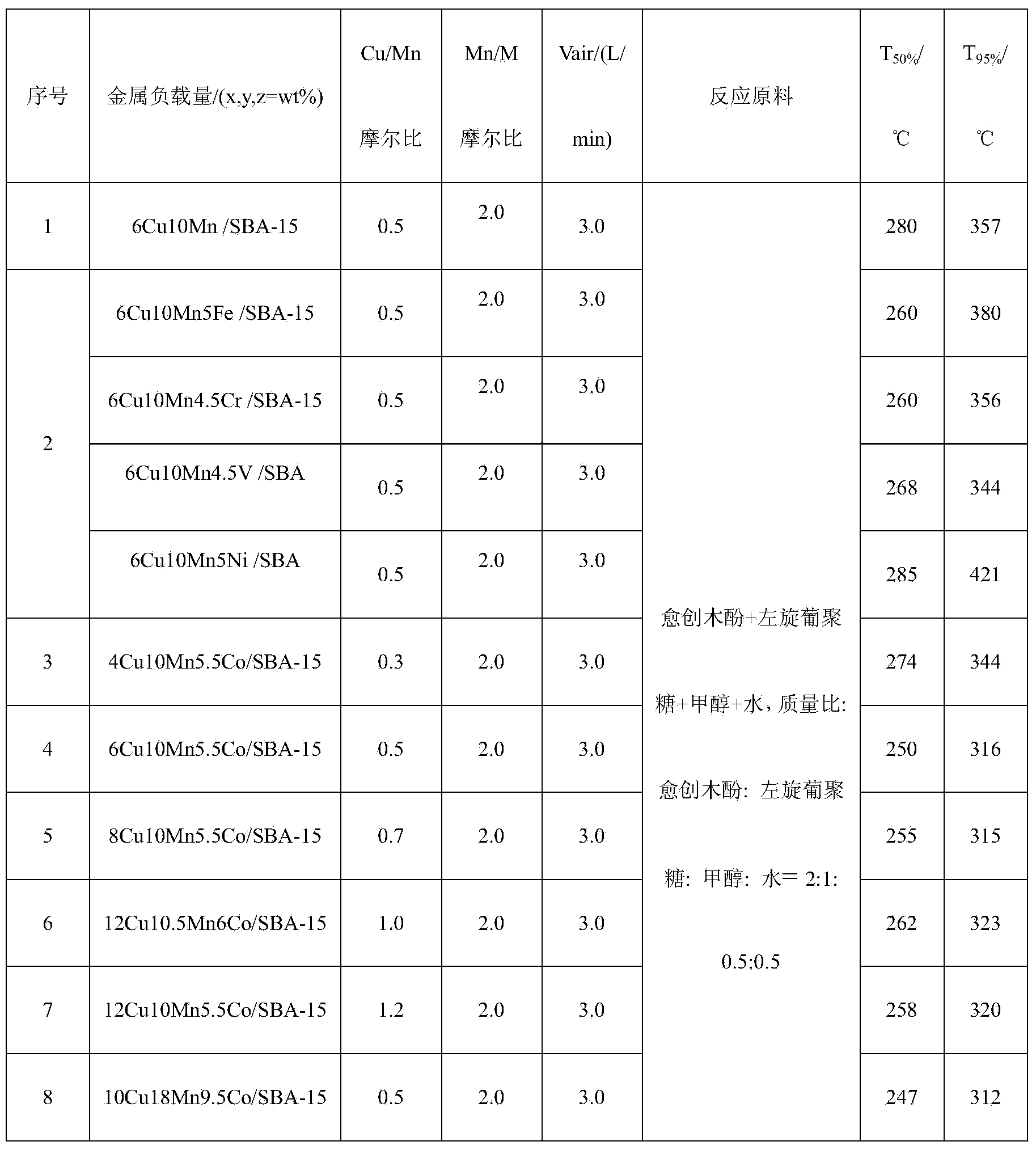
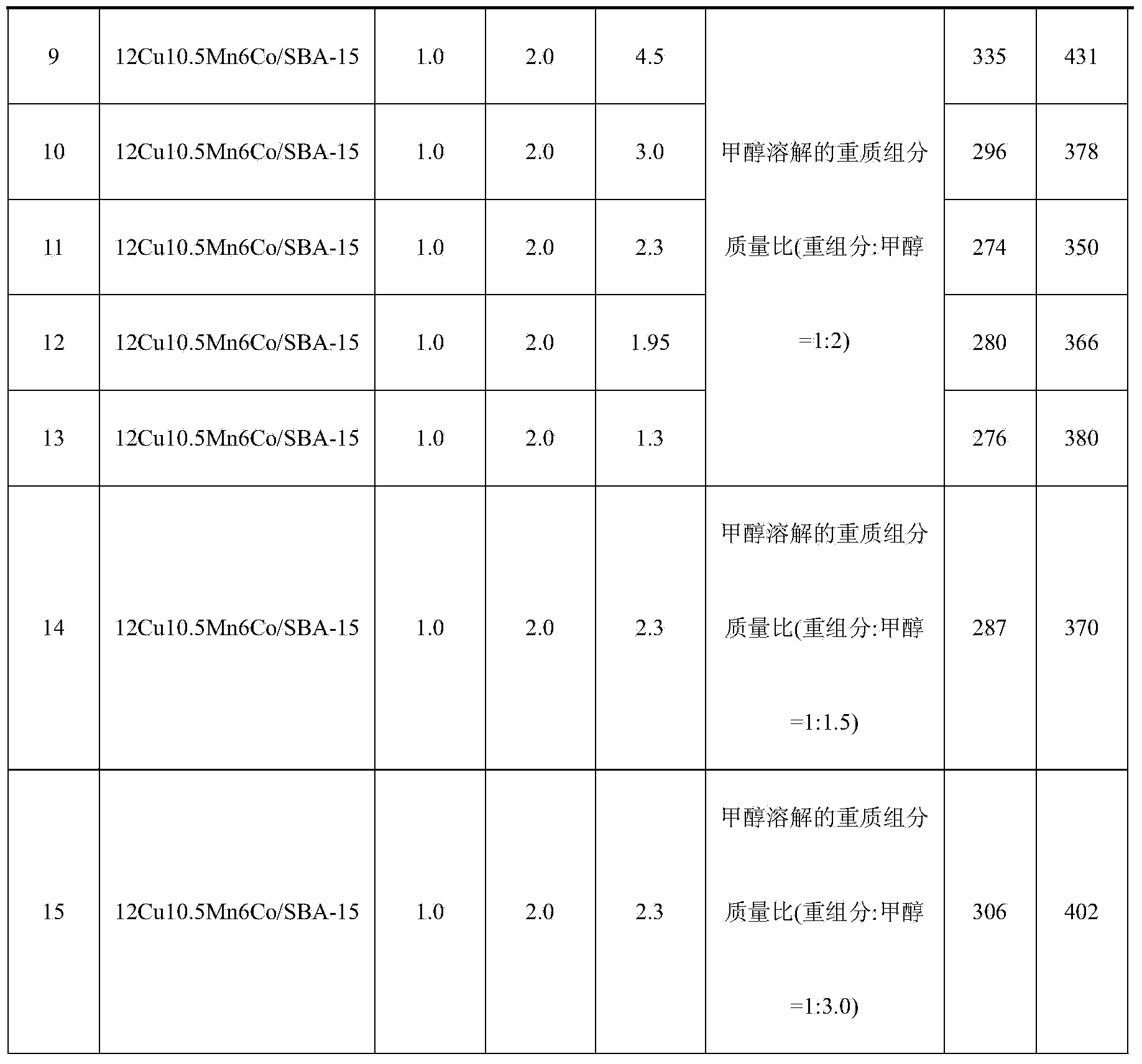
The invention discloses a method for low-temperature complete combustion of bio-oil heavy components by the use of a Cu-Mn base supported monolithic catalyst. By a technological condition that an xCuyMnzM / SBA-15 composite oxide cordierite ceramic monolithic catalyst with a low-temperature activity is used to catalyze a model of a bio-oil heavy components mixture including guaiacol, levoglucosan, methanol and water mixed solution (guaiacol represents benzene oxygenate in the heavy components, levoglucosan represents carbohydrate in the heavy components, and methanol and water are used as solvents for homogeneous mixing of two model compounds), exploration and research are performed to obtain a catalyst system and technological conditions suitable for low-temperature oriented conversion of methanol-soluble viscous real bio-oil heavy components to CO2 and H2O, and low-temperature complete conversion of bio-oil heavy components is realized.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
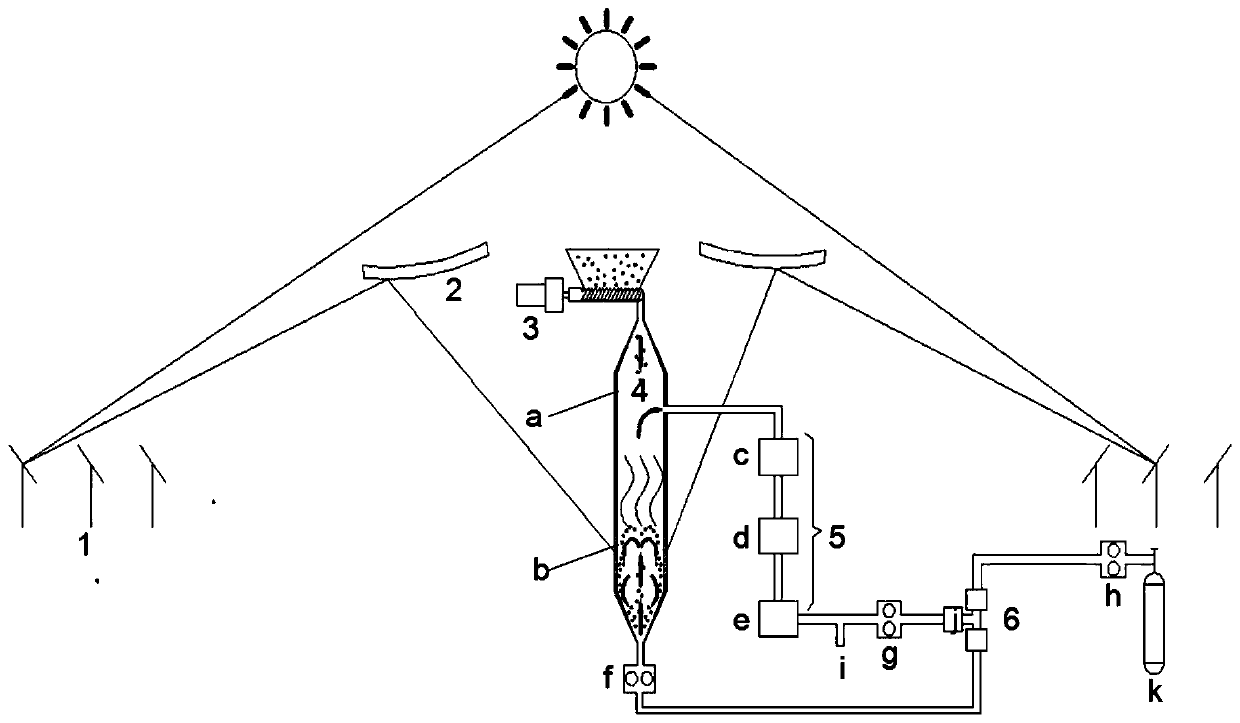
System and method for preparing bio-oil rich in levoglucosan
ActiveCN109943353AIncrease productionAvoid secondary reactionsBiofuelsEnergy inputThermal energyHyperboloid
The invention belongs to the biomass pyrolysis field and particularly discloses a system and method for preparing bio-oil rich in levoglucosan. The system comprises a heliostat field, a hyperboloid reflection mirror, a spiral feeder, a solar fluidized bed pyrolysis reactor, a biological oil grading, condensing and collecting device and a tail gas circular utilization device. By utilizing the system, the bio-oil rich in levoglucosan can be prepared by virtue of a concentrating solar power double-temperature region effect. Cellulose is pyrolyzed in a high-temperature region of the reactor so asto generate primary tar through the efficient utilization of heat produced by solar radiation, and the primary tar rapidly enters a low-temperature region, so that the secondary region is avoided; bycarrying out timed condensation and collection, the bio-oil rich in levoglucosan is obtained; and the system has the characteristics that the structure is compact, the operation process is simple, themaintenance cost of equipment is low, the utilization rate of solar power is high, the purity of levoglucosan in the prepared bio-oil is high, the quality of the bio-oil is good, and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
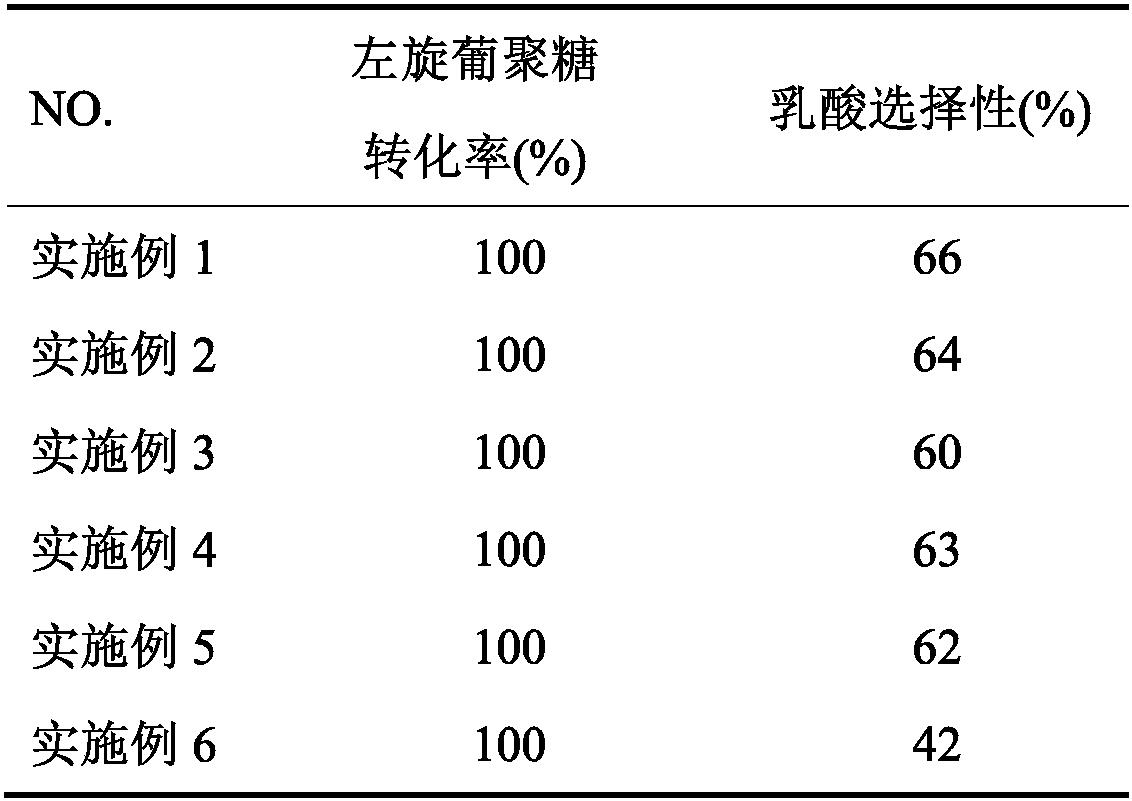
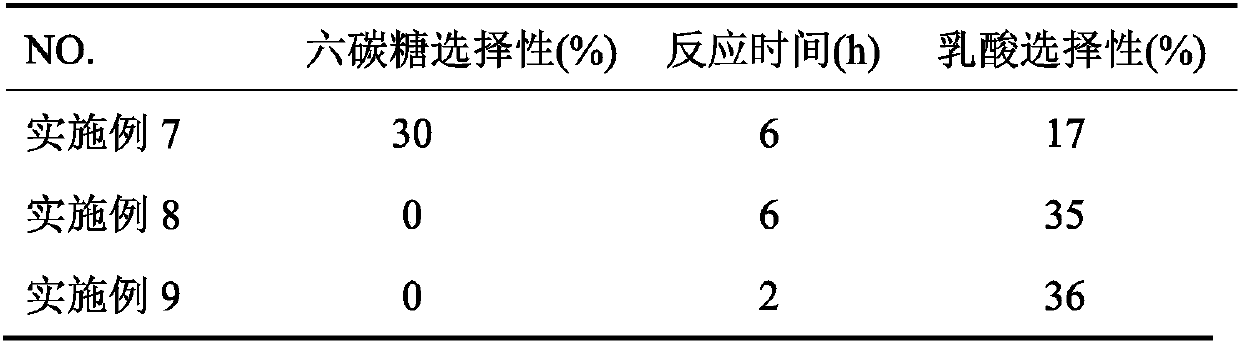
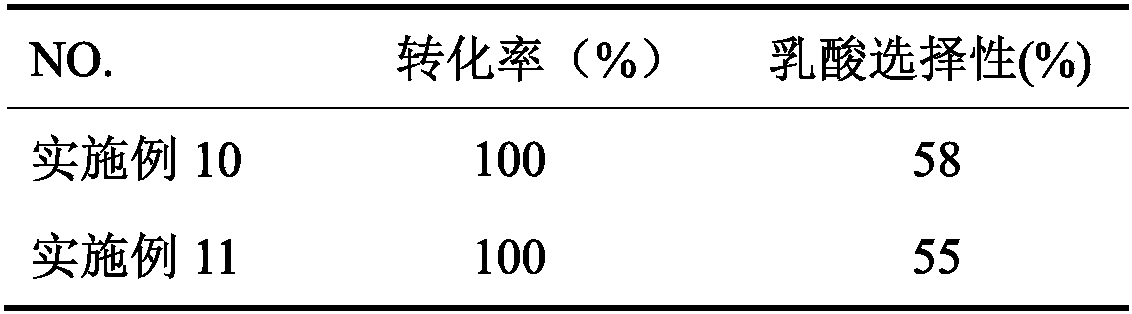
Method for preparing lactic acid by using alkaline-earth metal modified Sn-beta catalyst
InactiveCN110575844AWide variety of sourcesNo pollution in the processMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic compound preparationAlkaline earth metalCatalytic method
The invention discloses a method for preparing lactic acid by using an alkaline-earth metal modified Sn-beta catalyst. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out ion exchange reaction on an Sn-beta catalyst and an alkaline-earth metal solution to prepare the alkaline-earth metal modified catalyst; and mixing the catalyst, a saccharide substrate and a solvent, adding lactic acid, and carrying out lactic acid preparation reaction. In the catalytic reaction process, hydrolysis of levoglucosan and the polysaccharide substrate can be promoted by externally adding lactic acid, Sn is taken as an L acid active site in the reaction, alkaline earth metal ions and adjacent skeleton oxygen are taken as Lewis acid-base pair active sites, and generation of a trans-aldol reaction can be promoted through the synergistic effect of Sn, the alkaline earth metal ions and the adjacent skeleton oxygen, so that the selectivity of lactic acid is improved. Compared with other methods, the method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple catalyst preparation, short reaction time, good catalytic effect, easy industrialization and the like. The substrate used in the catalytic method is suitable for biomass thermal cracking product levoglucosan which can be obtained on a large scale, and has a good effect on high-molecular polysaccharides such as cellulose and inulin.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Recombinant bacteria capable of synthesizing 3-hydracrylic acid by using glucan as well as construction method and application of recombinant bacteria
The invention provides recombinant bacteria capable of synthesizing 3-hydracrylic acid by using glucan as well as a construction method and application of the recombinant bacteria, and belongs to the field of gene engineering and fermentation engineering. Klebsiella pneumoniae is host bacteria for expressing a gene lgk capable of encoding levodextran kinase and a gene aldH capable of encoding aldehyde dehydrogenase. The construction method comprises the following steps: obtaining a recombinant carrier puC18-lgk-aldH, converting the recombinant carrier puC18-lgk-aldH into a competent cell of the host Klebsiella pneumoniae, and obtaining the recombinant bacteria. By use of the levodextran kinase gene lgk and the aldehyde dehydrogenase gene aldH which are optimized through a codon, in combination with the whole scheme, the substrate use rate is increased, and the yield is increased.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Method for preparing levorodextrone based on pyrolytic carbon-catalyzed cellulose
InactiveCN106622203AEasy to prepareQuick breakPhysical/chemical process catalystsSugar derivativesCatalytic pyrolysisActivated carbon
The invention belongs to the field of biomass energy utilization and particularly relates to a preparation method of a pyrolytic carbon-modified catalyst, and a method for preparing levorodextrone by catalyzing pyrolytic cellulose by using the catalyst. The pyrolytic carbon-modified catalyst is a composite catalyst formed by activating activated carbon generated by pyrolyzation of the cellulose as a carrier by using a sulfuric acid; and the pyrolytic carbon-modified catalyst and the cellulose are quickly catalyzed and pyrolyzed at 300-400 DEG C in an oxygen-free environment in a fixed bed reactor to obtain a liquid product containing levorodextrone. Levorodextrone is high in yield and high in purity. In addition, the catalyst is cheap and easy to prepare, does not need to be separated from a pyrolytic residue of the cellulose, and can be further processed for further use.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
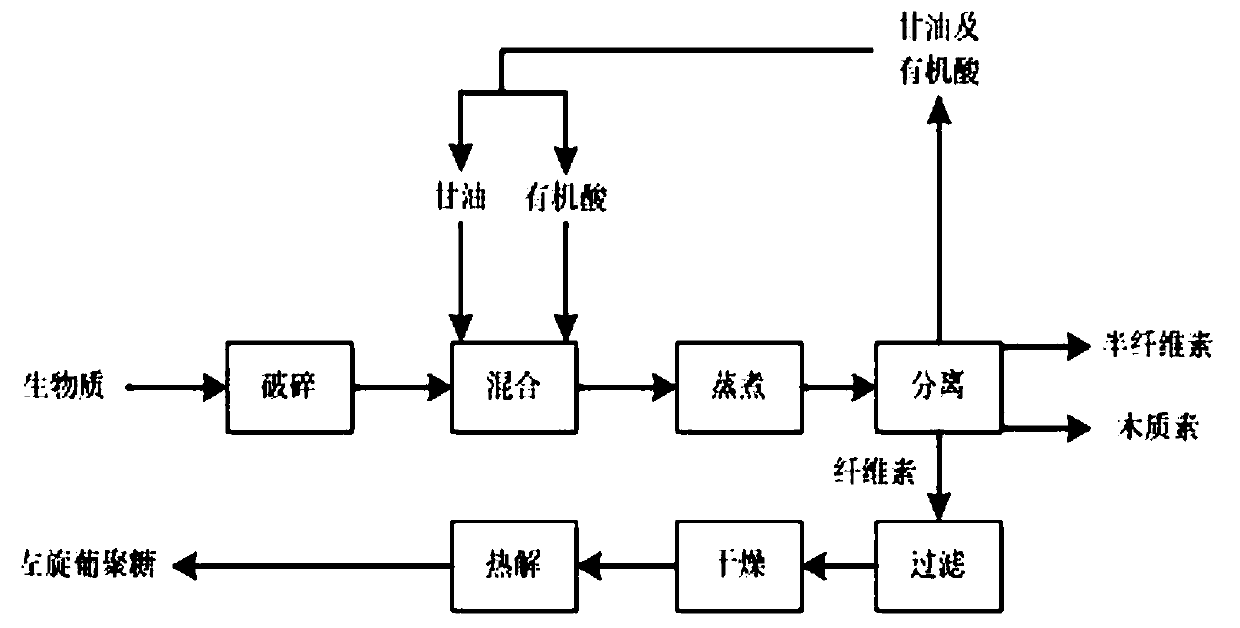
Method for preparing L-glucan by utilizing lignocellulose biomass
The invention discloses a method for preparing L-glucan by utilizing lignocellulose biomass. The method comprises the following steps: crushing lignocellulose biomass, mixing the lignocellulose biomass with glycerol and organic acid amine, carrying out a reaction at 100-200 DEG C for 0.5-3 hours, carrying out liquid-solid separation on the reaction product, drying the solid product at 60-110 DEG C for 0.5-5 hours, and treating the product at 300-600 DEG C for 1-2 seconds for quick pyrolysis, thereby obtaining the L-glucan. According to the method, the raw material source is wide, the lignocellulose biomass with low price is used as the raw material, and the lignin, the hemicellulose, the cellulose and the alkali metal are synchronously separated by adopting the mixed solvent of the glycerol and the organic acid to prepare the L-glucan with high additional value; the method is high in yield, and the utilization value of forestry and agricultural residues is improved; meanwhile, the content of acid in cellulose is adjusted by controlling the drying temperature and time, water washing is unnecessary and generation of waste water is avoided.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Antibiotic-free fragrant feed additive composition for animals
InactiveCN109997966AEnhance physical fitnessPromote growth and developmentAccessory food factorsPropanoic acidLinalool
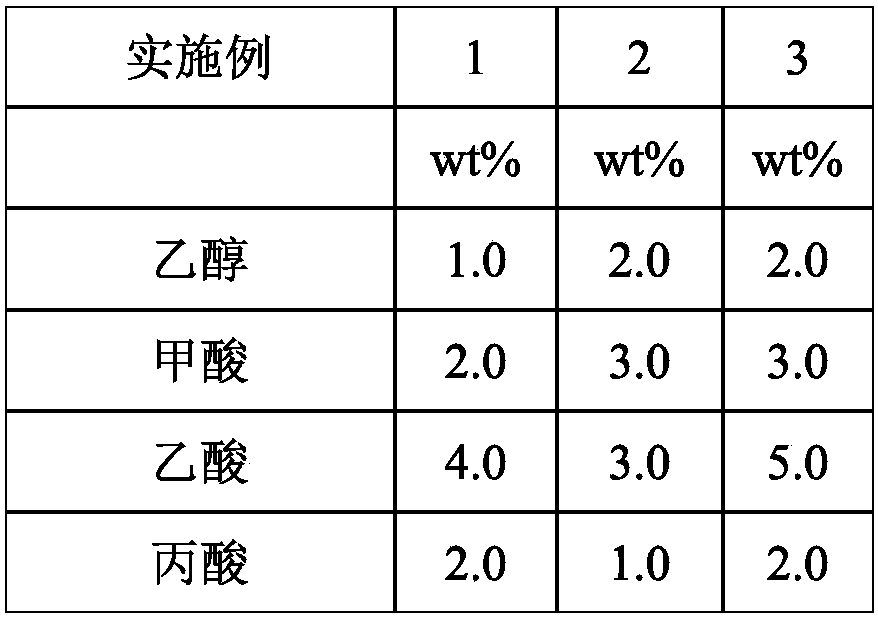
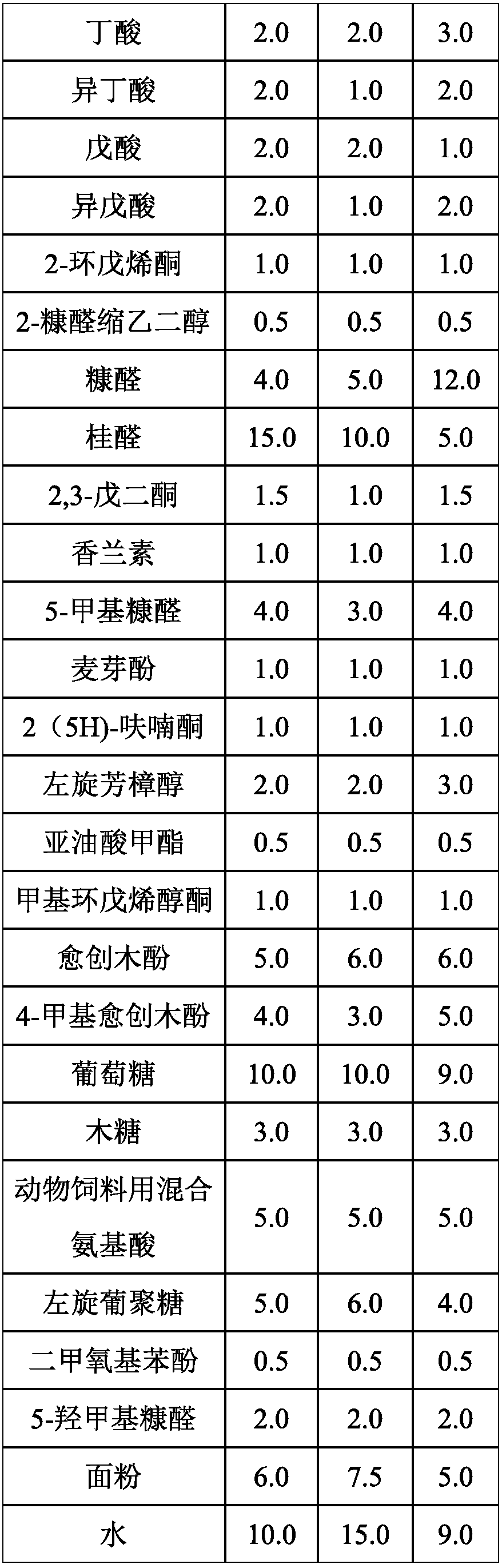
The invention discloses an antibiotic-free fragrant feed additive composition for animals; the composition is cooperatively used with a common daily diet, and the daily consumption accounts for 0.2-1.5% of the weight of the common daily diet, wherein the composition includes the following components: ethanol, formic acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid, isobutyric acid, valeric acid, isovaleric acid, furfural, 5-methyl furfural, 5-hydroxymethyl furfural, vanillin, maltol, guaiacol, 4-methyl guaiacol, dimethoxyphenol, carvacrol, thymol, carvacrol, cinnamaldehyde, 2,3-pentanedione, methyl cyclopentenolone, 2-cyclopentenone, 2(5H) furanone, furfural ethylene glycol, L-linalool, methyl linoleate, glucose, xylose, mixed amino acids for animal feeds, L-dextran, natural excipients andwater. The antibiotic-free fragrant feed additive composition for animals is suitable for raising pigs, chickens, ducks, quails, pigeons, rabbits, sheep, cattle, fishes, shrimps and other animals.
Owner:厦门牡丹香化实业有限公司
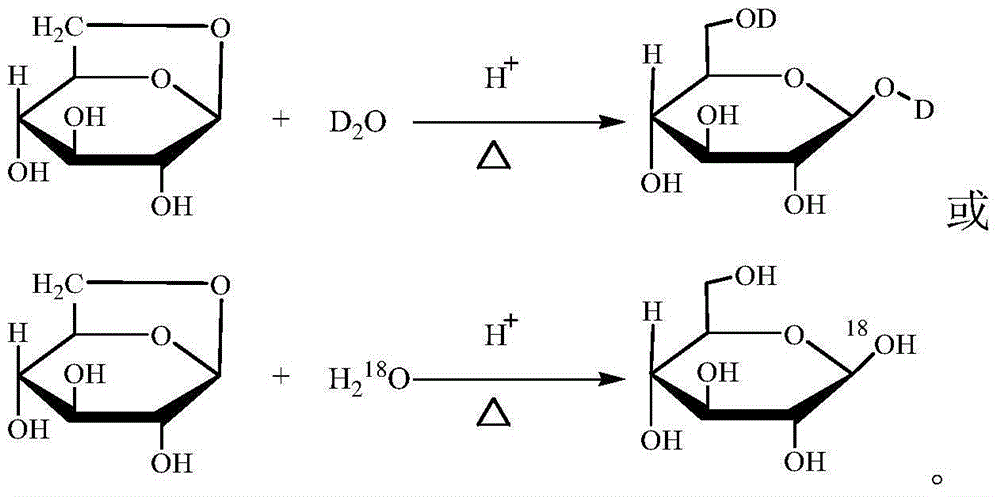
Preparation method of 1, 6-II-D or 1-<18>O stable isotope labeling glucose
InactiveCN105037446AEasy to manufactureEasy to prepareSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationStable Isotope LabelingD-Glucopyranose
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF URBAN CONSTR
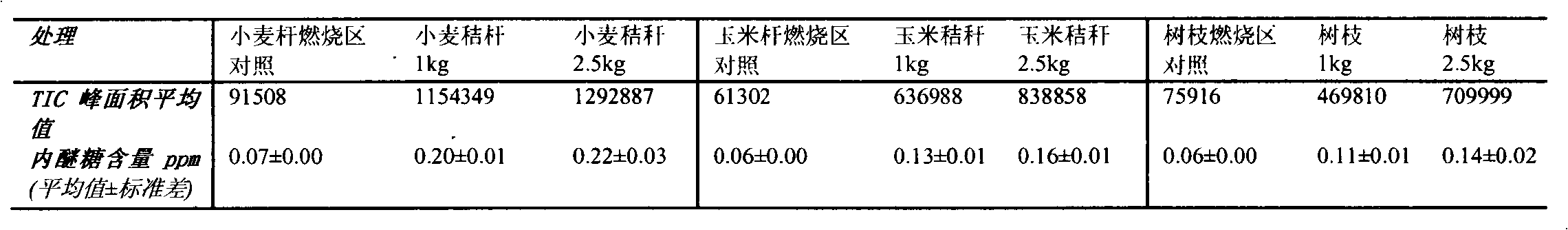
Method for measuring combustion quantity of cellulosic biomass
The invention relates to a quantitative method for combustion quantity of cellulosic biomass during combustion, belonging to the field of environmental monitoring. According to the invention, a specific tracer molecule 1,6-anhydro-beta-D-glucopyranose (hereinafter referred to as levoglucosan) for combustion of the cellulosic biomass is utilized to reflect the quantity of combusted biomass based on the content of levoglucosan in soil. The method comprises selection of the specific tracer molecule for combustion of the cellulosic biomass, acquisition of a soil sample, pretreatment of the sample, extraction and purification of the tracer molecule in soil and trace detection of levoglucosan. With the method provided by the invention, combustion quantity of cellulose in a specific cellulose combustion process (e.g., a mountain fire, a forest fire and burning of residual crops in a farmland) can be conveniently estimated, and the method has application prospects in aspects like environmental monitoring, criminal investigation and archaeology.
Owner:GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI GSCAS
Device for transforming cellulose into levodextron
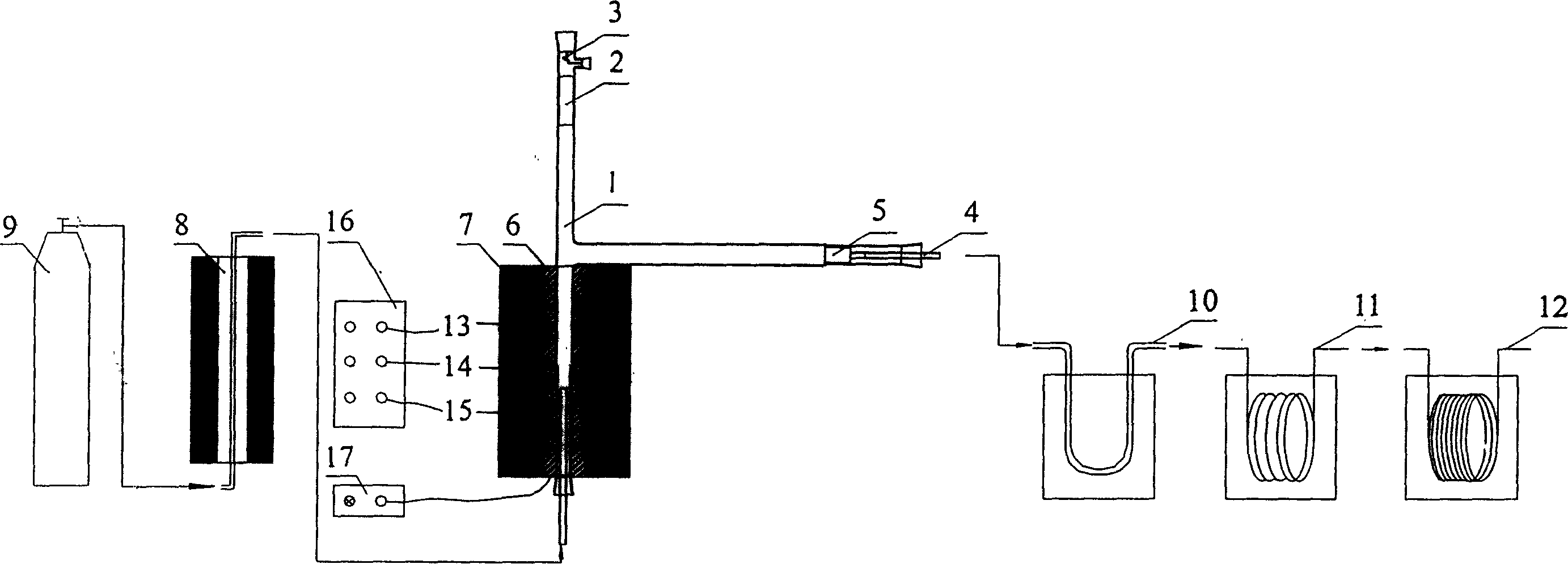
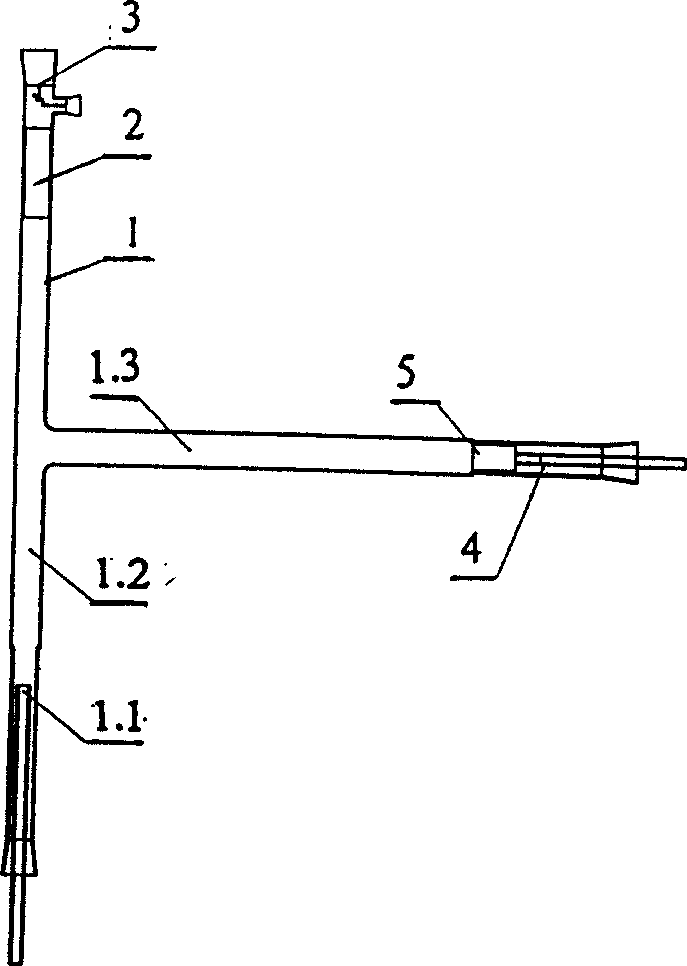
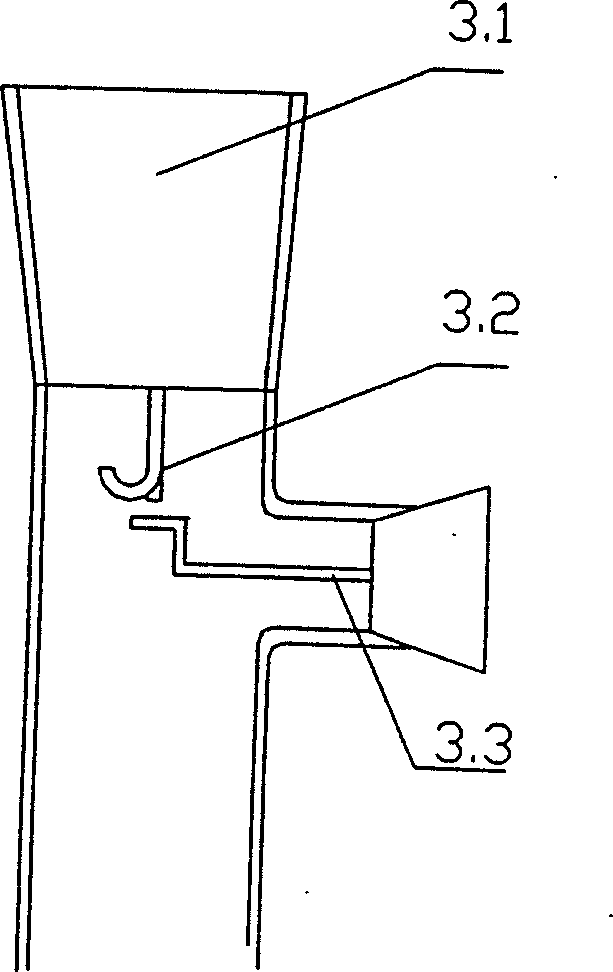
The invention discloses a fibrin transforming laevoglucose device. A nitrogen gas interface, which connects to high purification nitrogen gas through fluid bed pre-heating unit, is connected in the bottom of quartz glass cell. A filter is set in the horizontal branch of the reactor, and the outlet connects to multi-step condensing unit. The top of the quartz glass cell reactor is set a sealed cover. The material inlet of the up sealed cover is set a pothook used to fill cylinder material, and the silicon carbon tube is set outside the quartz glass cell. And the two ends of the silicon carbon tube are cool ends that connect to power supply. One end of the thermocouple connects to the heating zone in the middle of the silicon carbon tube, and the other end connects to control panel. Asbestos blanket is set outside the silicon carbon tube. Under the best reaction condition, the output of laevoglucose could reach 54.5%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing levoglucosan through rapid pyrolysis of coupling pretreatment biomass
The invention provides a method for preparing levoglucosan through rapid pyrolysis of coupling pretreatment biomass, which comprises the following steps: mixing a biomass raw material with alkali liquor, and carrying out alkali pretreatment to obtain an alkali pretreatment product; carrying out solid-liquid separation on the alkali pretreatment product to obtain solid filter residues, mixing the solid filter residues with a Fenton reagent, and carrying out Fenton pretreatment to obtain a Fenton pretreatment product; carrying out solid-liquid separation on the Fenton pretreatment product to obtain filter residues, washing the filter residues to be neutral, and drying the filter residues to obtain a coupling pretreatment product; and quickly pyrolyzing the coupling pretreatment product, and condensing and pyrolyzing the volatile product to obtain bio-oil containing levodextran. According to the method disclosed by the invention, alkali liquor pretreatment is firstly carried out to mainly remove a large amount of lignin in the biomass, then Fenton pretreatment is carried out to mainly break cellulose and hemicellulose as well as glucosidic bonds between the cellulose and degrade part of hemicellulose, and finally a porous short-chain cellulose enriched substrate is formed, so that higher levoglucosan yield can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for promoting growth of Nannochlorisoculata and increasing contents of chlorophyll and mycoprotein of Nannochlorisoculata
ActiveCN103045481BReduce use costUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesMycoproteinFungus protein
The invention relates to a method for promoting growth of Nannochlorisoculata and increasing contents of chlorophyll and single-cell protein of the Nannochlorisoculata. The method comprises the step that levoglucosan from biomass pyrolysis or cellulose pyrolysis liquid subjected to detoxification treatment is added to a Nannochlorisoculata culture solution, wherein the additive amount of levoglucosan is 5-50mM, and the additive amount of the cellulose pyrolysis liquid is 0.25-2% by weight. By taking a cellulosic biomass high-temperature pyrolysis product, namely levoglucosan or the pyrolysis liquid as an accelerant, a result shows that levoglucosan or the pyrolysis liquid can promote the growth of the Nannochlorisoculata obviously; a promoting rate reaches up to 194%; and the contents of chlorophyll and mycoprotein can be increased significantly, so that a use value of a cellulosic biomass can be increased.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
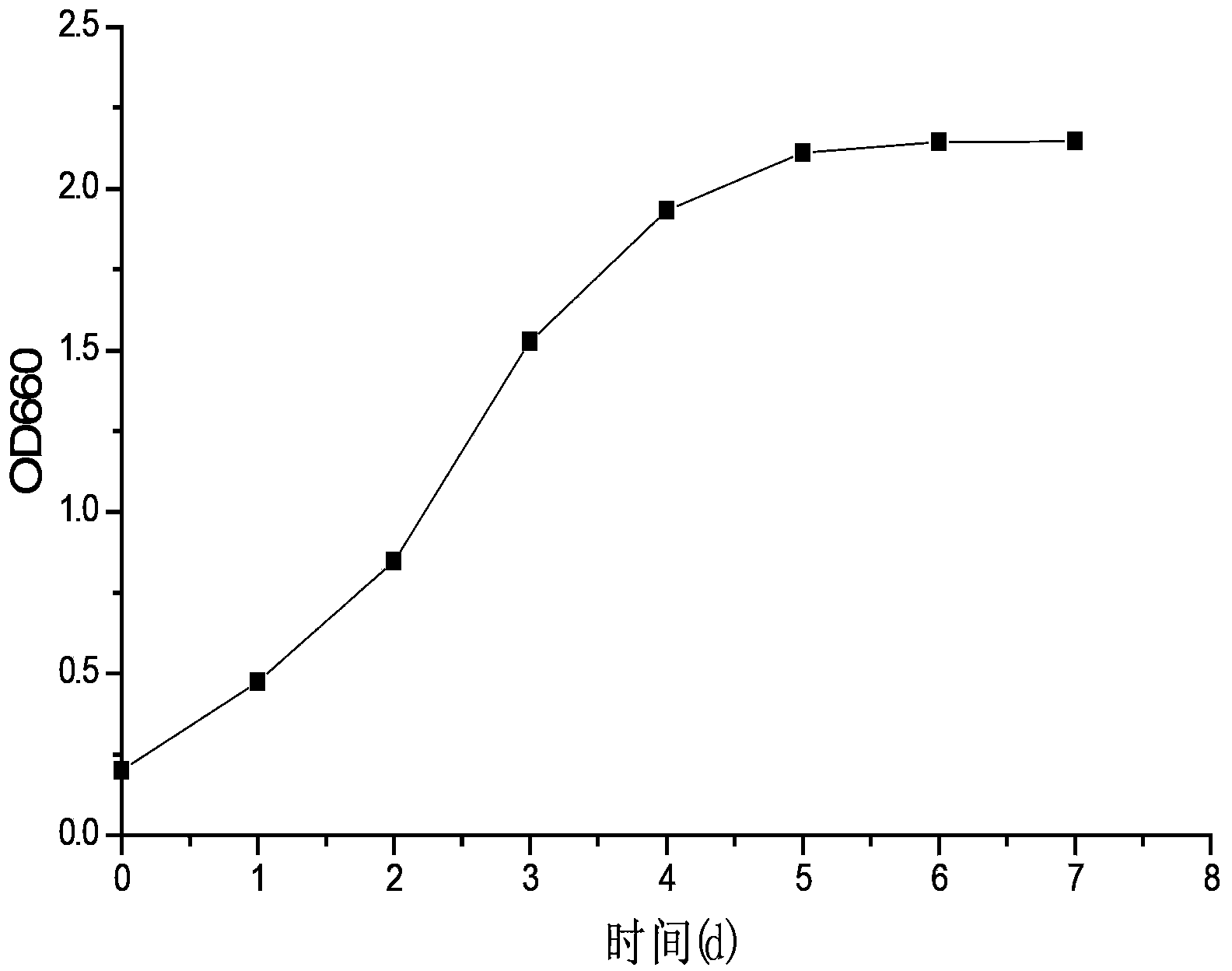
Method for producing carotinoid and single-cell protein via transforming cellulose pyrolytical liquid and levoglucosan through photosynthetic bacteria
The invention relates to photosynthetic bacteria and applications thereof. Cellulose pyrolytical liquid and levoglucosan are utilized to culture the photosynthetic bacteria, and the obtained photosynthetic bacteria can be used for producing carotinoid and single-cell protein and also can be used as a water quality improving agent for aquaculture and sewage treatment or can be used as a leaf fertilizer and the like. The levoglucosan or the cellulose pyrolytical liquid is prepared to form a culture solution, under the conditions of certain loading volume and transformation temperature, the culture solution is cultured for certain time to obtain carotinoid-rich photosynthetic bacteria thallus, and the thallus which is subjected to carotinoid extraction can be used as a single-cell protein feed. The photosynthetic bacteria are utilized to effectively use the high-temperature pyrolysis products of cellulose biomass and the levoglucosan to prepare the carotinoid and the photosynthetic bacteria single-cell protein, the cellulose biomass is effectively utilized, the cellulose biomass with rich sources can be transformed into products with high additional values, wastes are turned into wealth, and the method has good economic and environmental application potentials and a social benefit.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
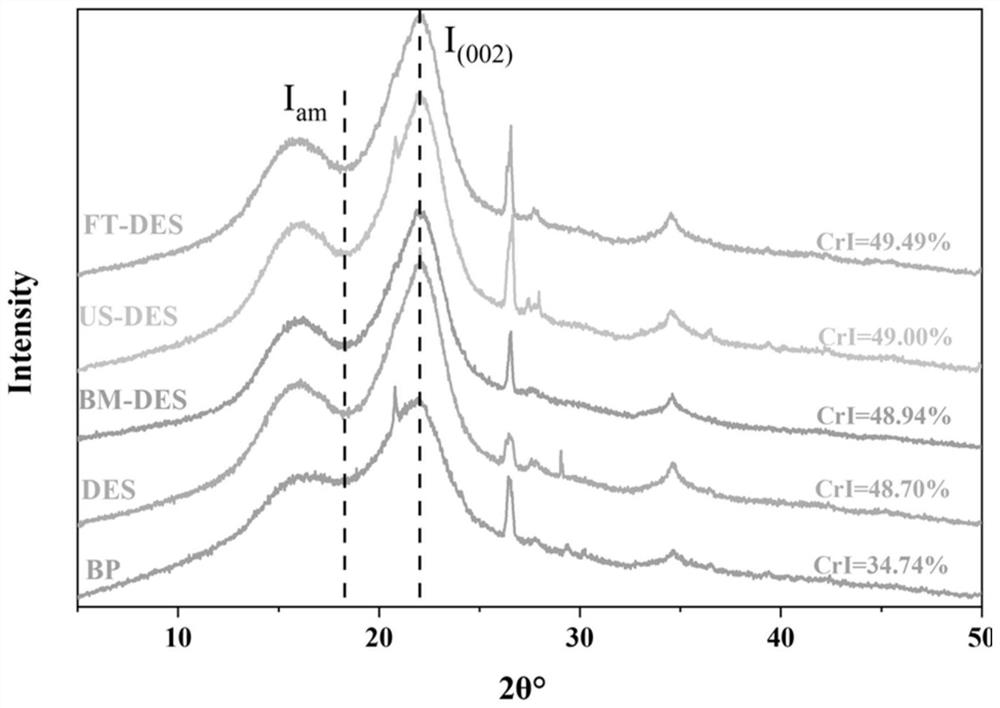
Method for improving quality of pyrolytic oil by pretreating biomass raw material by using freeze-thaw assisted low cosolvent and application of method
ActiveCN114806616AReduce usageEasy to operateBiofuelsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionEngineeringLevoglucosan
The invention discloses a method for improving the quality of pyrolytic oil by pretreating a biomass raw material by using a freezing-thawing-assisted low cosolvent and application of the method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding a biomass raw material into water, uniformly stirring and mixing, freezing in a liquid nitrogen environment at-196 DEG C for 1-4 hours, taking out, recovering to room temperature, melting, repeating the freezing and thawing operation for 0-4 times, separating solids, washing and drying to obtain a biomass raw material subjected to freezing and thawing pretreatment; (2) mixing imidazole and choline chloride, heating, stirring and dissolving to obtain an imidazole-eutectic solvent system, then adding the freeze-thaw pretreated biomass raw material, stirring and reacting, separating solids after the reaction, washing and drying to obtain solid residues; and (3) pyrolyzing the solid residues in a protective gas atmosphere at 450-600 DEG C to obtain pyrolyzed bio-oil. According to the method, the content of levoglucan in the pyrolysis bio-oil can be remarkably increased, and the quality of the pyrolysis oil is improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
A recombinant bacterium utilizing dextran to synthesize 3-hydroxypropionic acid and its construction method and application
The invention provides recombinant bacteria capable of synthesizing 3-hydracrylic acid by using glucan as well as a construction method and application of the recombinant bacteria, and belongs to the field of gene engineering and fermentation engineering. Klebsiella pneumoniae is host bacteria for expressing a gene lgk capable of encoding levodextran kinase and a gene aldH capable of encoding aldehyde dehydrogenase. The construction method comprises the following steps: obtaining a recombinant carrier puC18-lgk-aldH, converting the recombinant carrier puC18-lgk-aldH into a competent cell of the host Klebsiella pneumoniae, and obtaining the recombinant bacteria. By use of the levodextran kinase gene lgk and the aldehyde dehydrogenase gene aldH which are optimized through a codon, in combination with the whole scheme, the substrate use rate is increased, and the yield is increased.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
A kind of mxene base catalyst and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN113457701BImprove hydrophilicityImprove thermal stabilityPhysical/chemical process catalystsBio-feedstockPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
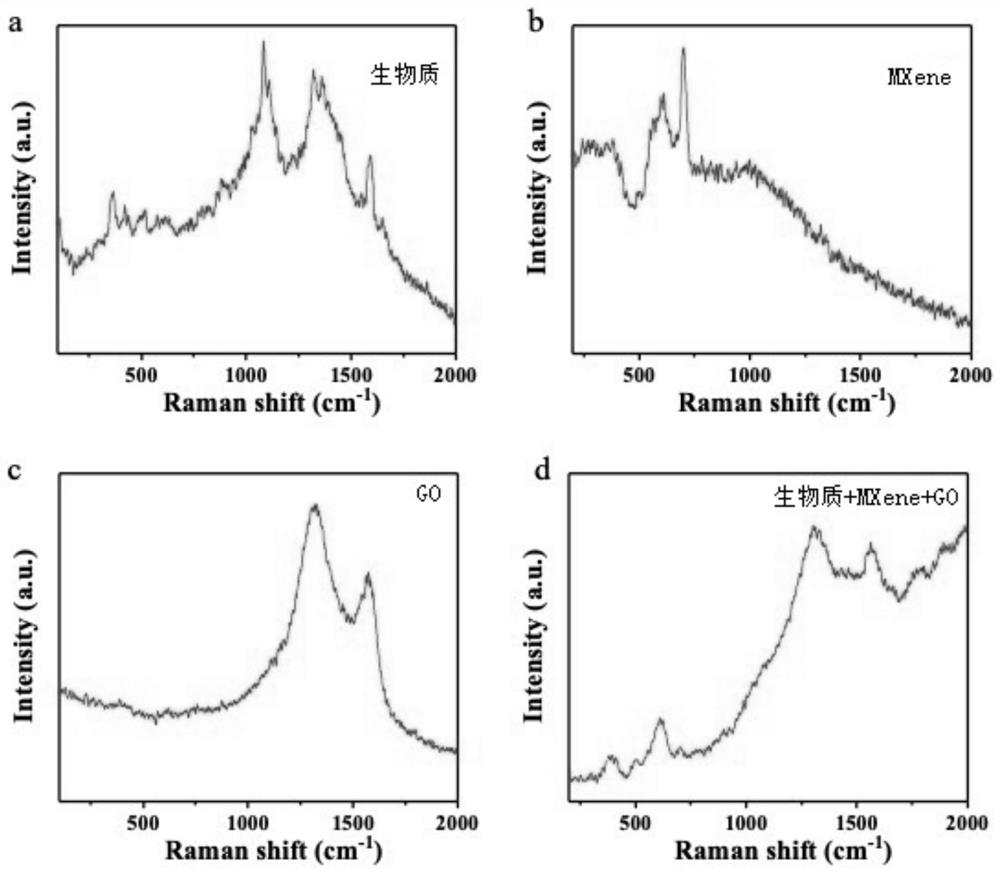
The invention provides an MXene-based catalyst and its preparation method and application. The MXene-based catalyst includes MXene and graphene oxide, and the mass ratio of MXene and graphene oxide is (0.5-5):1. Add graphene oxide dispersion liquid into MXene dispersion liquid, mix uniformly to obtain mixed liquid A, and freeze-dry mixed liquid A to obtain MXene-based catalyst. As a catalyst, it has good selectivity for the generation of levoglucosan, and can overcome the existing problems of poor selectivity of the catalyst, corrosion of equipment, difficult recovery, environmental pollution and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
A kind of method for separating levo-glucan from wood vinegar
The invention discloses a method for separating levoglucosan from wood vinegar. The method uses wood vinegar as a raw material. The separation process includes: adding an alkaline compound to adjust the wood vinegar to alkaline, and adding flocculation After flocculation, the liquid is filtered to remove the precipitate; after filtration, the clear liquid is added with a decolorizing agent for heat preservation and decolorization; after decolorization, the clear liquid is separated by ion exchange resin, and pure water is selected as the eluent for elution, and the levoglucosan The eluate was concentrated and precipitated with methanol to obtain the product levoglucosan. The invention can remove a large amount of impurities in the stock solution of the wood vinegar through pretreatment, and effectively separate the levoglucosan component in the wood vinegar.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
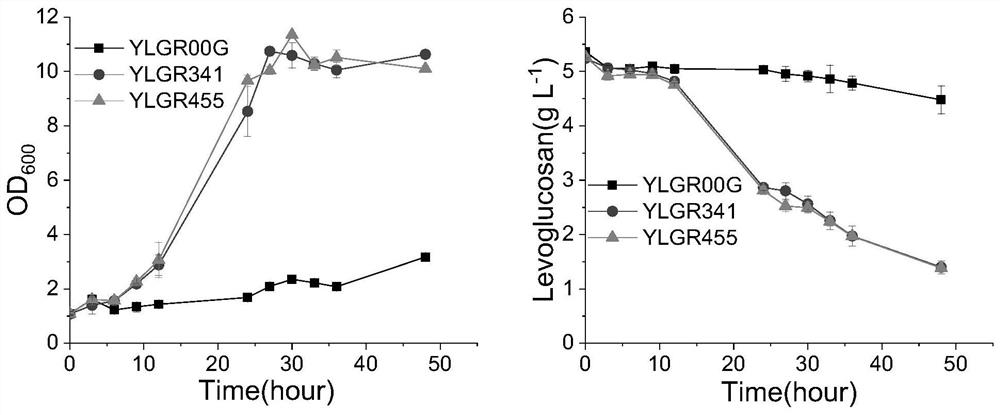
Method for improving transport capacity and utilization capacity of levodextran in saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
ActiveCN113373073AImprove transportation capacityImprove utilizationFungiTransferasesHexose TransporterKinase activity
The invention discloses a method for improving transport capacity and utilization capacity of levoglucosan in a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. The method comprises the following steps of expressing protein with levoglucosan kinase activity in saccharomyces cerevisiae, and establishing a levoglucosan metabolic pathway in the saccharomyces cerevisiae; the method is realized by utilizing a mutant for expressing the transporter Gal2p in a hexose transporter complete-deficiency saccharomyces cerevisiae recombinant strain in which the levodextran metabolic pathway is established, meanwhile, the invention also provides a recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain YLGR341 and a recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain YLGR455 which are used for related expression of the levodextran transporter Gal2pQ341A or Gal2pW455A and the levodextran kinase, Experiments prove that when the method for improving the transport capacity and the utilization capacity of the levoglucosan in the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain is applied to levodextran fermentation, compared with a non-point-mutation strain, the growth of the Gal2p point-mutation strain has obvious advantages, the levodextran utilization capacity is obviously higher than that of the non-point-mutation strain, wherein the point mutation strains YLGR341 and YLGR455 are 3.70 times and 3.72 times of the non-point-mutation strain YLGR00G correspondingly.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
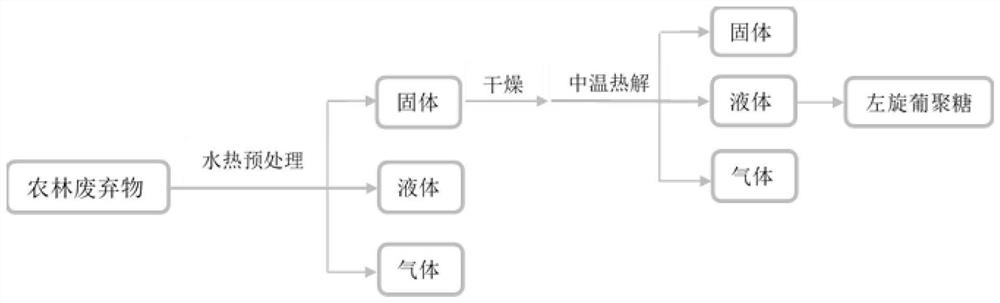
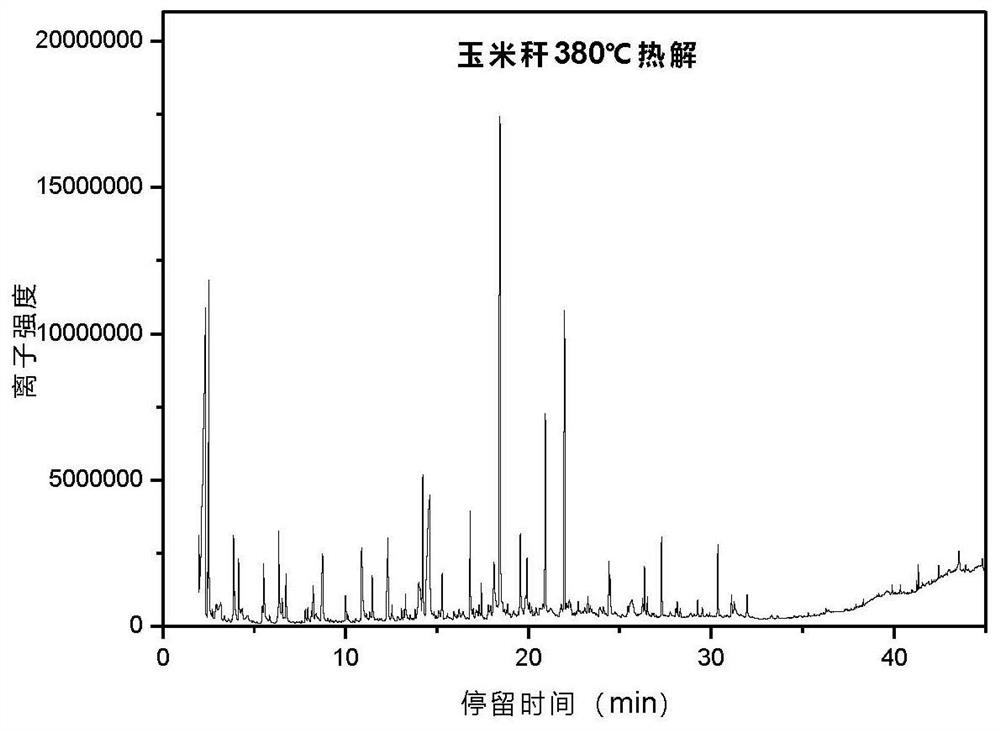
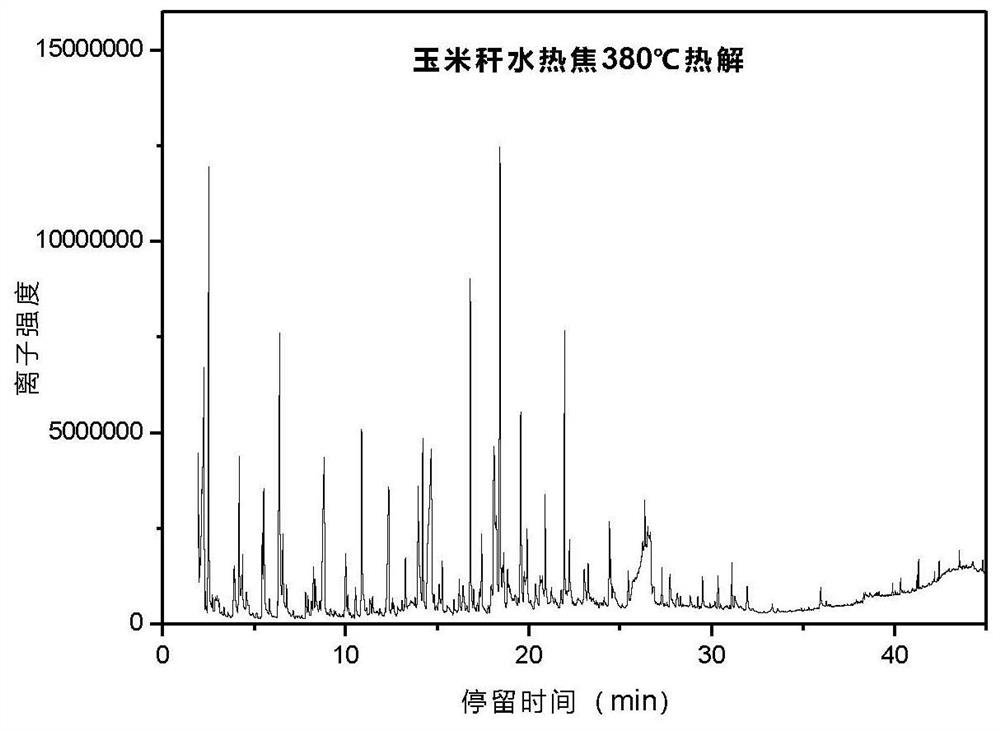
A method for preparing levoglucosan from agricultural and forestry waste
The invention discloses a method for producing levoglucosan by using agricultural and forest waste. The method for producing the levoglucosan by using the agricultural and forest waste comprises the following steps of (1) adding the crushed agricultural and forest waste and water into a hydrothermal reaction kettle according to a mass volume ratio of (1 to 1) to (5 to 20); (2) filling the hydrothermal reaction kettle with CO2, sealing the hydrothermal reaction kettle to make the hydrothermal reaction kettle heated to 150-250 DEG C with stirring, and maintaining the temperature for 10-50 minutes; (3) cooling the hydrothermal reaction kettle, collecting a reaction product, and conducting vacuum filtration, separation and drying on the reaction product to obtain a solid product subjected to hydrothermal pre-treatment; (4) placing the solid product in a pyrolysis reactor to make the solid product subjected to pyrolysis in a CO2 atmosphere; and (5) obtaining a liquid product with a high levoglucosan concentration after conducting fractional condensation on the solid product. According to the method for producing the levoglucosan by using the agricultural and forest waste, hydrothermal pre-treatment under the CO2 atmosphere and pyrolysis under the CO2 atmosphere are combined to promote maximum conversion from the agricultural and forest waste to the levoglucosan, and the defect of alow yield of levoglucosan in bio-oil obtained by directly conducting pyrolysis on biomass is overcome.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing levoglucosan from cellulose by catalytic pyrolysis
ActiveCN102020722BInhibition of ring-opening fragmentationEasy to passChemical recyclingCatalytic pyrolysisLiquid product
The invention belongs to the field of utilization of biomass energy, and in particular relates to a method for preparing levoglucosan from cellulose by catalytic pyrolysis. The method comprises the following steps of: mechanically mixing copper powder serving as a catalyst and cellulose powder; performing fast pyrolysis under an oxygen-free condition at the temperature of between 280 and 450 DEG C; condensing pyrolysis gas to obtain a levoglucosan-rich liquid product; and burning solid residues to recover the copper powder catalyst. In the product prepared from the cellulose by the catalytic pyrolysis of the copper powder, the levoglucosan has high yield and purity and is convenient to subsequently separate and extract; in addition, the solid copper powder is used as the catalyst, is veryconvenient to recover, does not substantially have the problem such as inactivation and the like and can be repeatedly recycled.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Method for preparing levoglucosan by coupling pretreated biomass with fast pyrolysis
The invention provides a method for preparing levoglucosan by rapid pyrolysis of coupled pretreatment biomass, comprising: mixing biomass raw materials with alkali solution, performing alkali pretreatment to obtain alkali pretreatment products; solidifying the alkali pretreatment products liquid separation to obtain a solid filter residue, mix the solid filter residue with Fenton's reagent, and perform Fenton pretreatment to obtain a Fenton pretreated product; perform solid-liquid separation on the Fenton pretreated product to obtain a filter residue, wash the filter residue with water until neutral, The coupling pretreatment product is obtained after drying; the coupling pretreatment product is quickly pyrolyzed, and the pyrolysis volatile product is condensed to obtain bio-oil containing levoglucosan. The method of the present invention firstly carries out lye pretreatment, mainly removes a large amount of lignin in biomass, and then carries out Fenton pretreatment, mainly interrupts cellulose and hemicellulose, and the glucosidic bond between cellulose and cellulose, Degrading part of the hemicellulose and finally forming a porous short-chain cellulose-rich substrate can result in a higher yield of levoglucosan.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
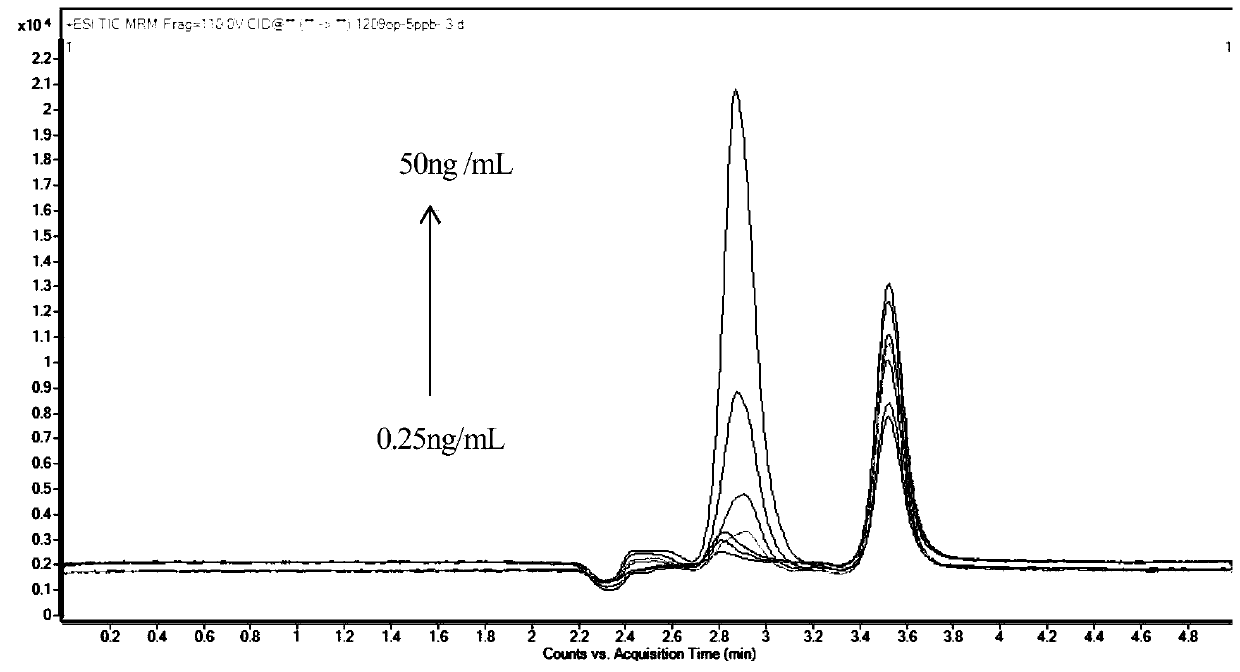
Method for detecting levoglucosan in water sample by using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometer
The invention discloses a method for detecting levoglucosan in a water sample by using an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometer. According to the method, parent ions are used as quantitative ions, daughter ions are used as qualitative ions, and the method has good sensitivity and accuracy. Compared with an existing method, the method adopts an external standard method for quantification, pollution caused by the environment, sample treatment, utensils and the like in the detection process can be detected and eliminated in time, and the reliability of adetection result is greatly improved; meanwhile, the method does not perform complex treatment on the sample, so that the accuracy and the reliable recovery rate of sample detection are ensured; moreover, the sample size of the method is only 2 [mu] L, so that the method is very suitable for detecting limited samples. Through calculation, the detection limit of the method is about 0.05 ng / mL, andthe quantification limit is about 0.2 ng / mL.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
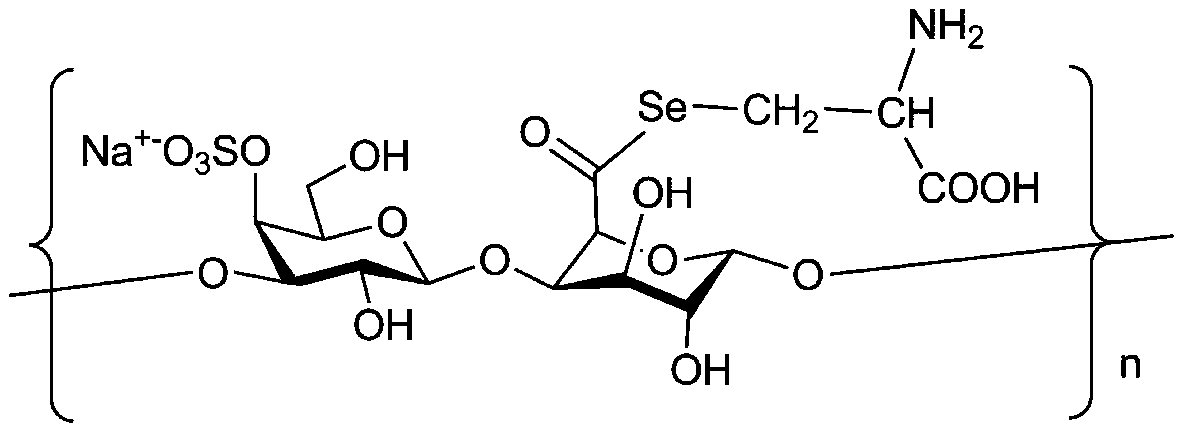
Bonded selenium polysaccharide and its preparation method and application
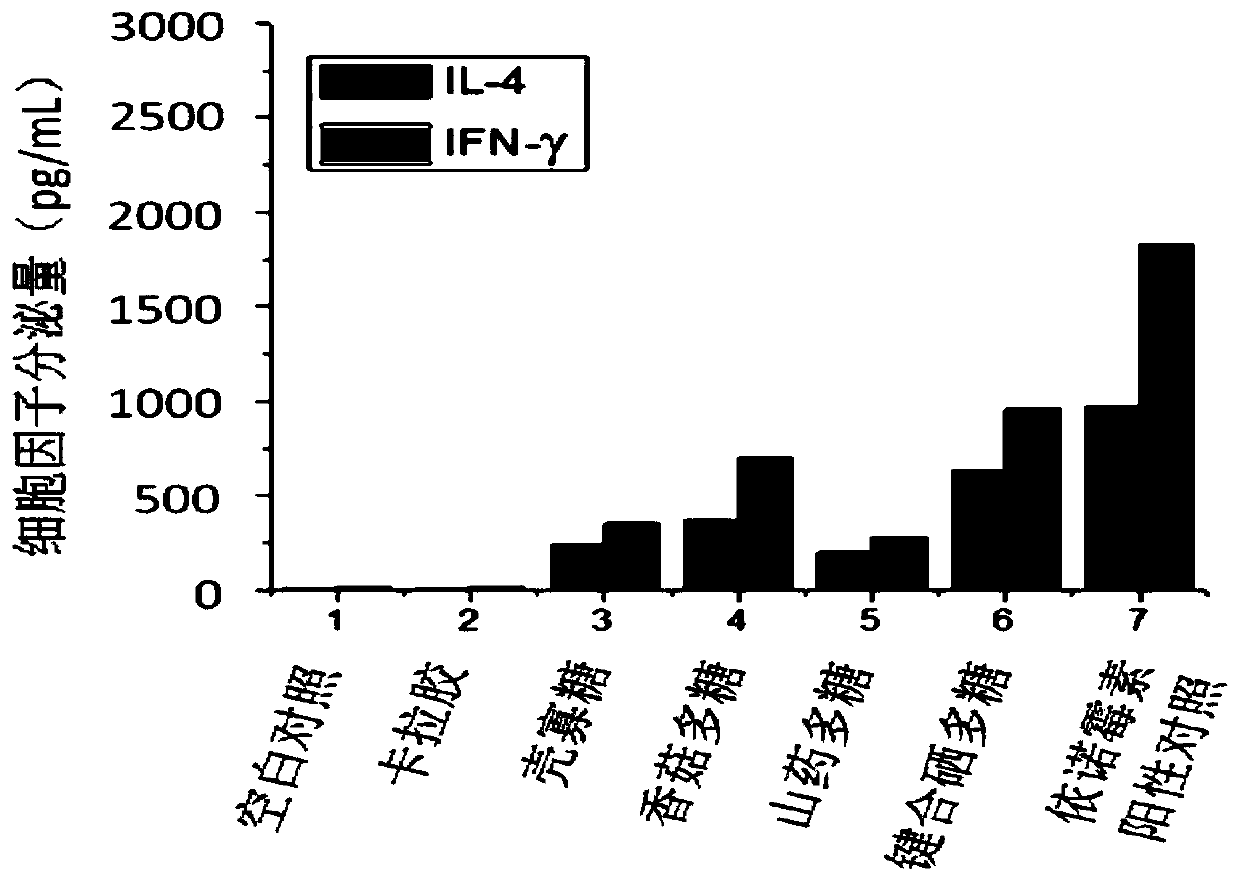
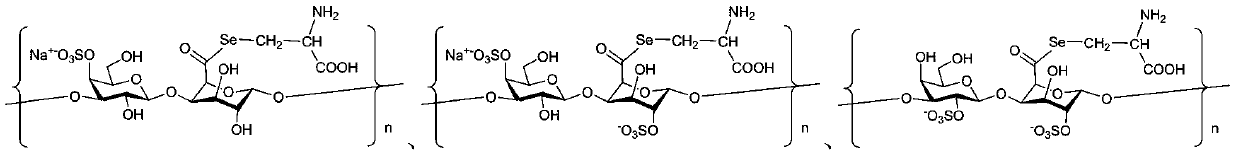
ActiveCN111087484BControllable selenium contentThe binding site is well definedOrganic active ingredientsAntinoxious agentsPolymer scienceImmunocompetence
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUHEYUAN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
A method for complete combustion of heavy components of bio-oil at low temperature using cu-mn-based supported monolithic catalysts
The invention discloses a method for low-temperature complete combustion of bio-oil heavy components by the use of a Cu-Mn base supported monolithic catalyst. By a technological condition that an xCuyMnzM / SBA-15 composite oxide cordierite ceramic monolithic catalyst with a low-temperature activity is used to catalyze a model of a bio-oil heavy components mixture including guaiacol, levoglucosan, methanol and water mixed solution (guaiacol represents benzene oxygenate in the heavy components, levoglucosan represents carbohydrate in the heavy components, and methanol and water are used as solvents for homogeneous mixing of two model compounds), exploration and research are performed to obtain a catalyst system and technological conditions suitable for low-temperature oriented conversion of methanol-soluble viscous real bio-oil heavy components to CO2 and H2O, and low-temperature complete conversion of bio-oil heavy components is realized.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com