A kind of method for separating levo-glucan from wood vinegar
A technology of levoglucosan and wood vinegar, which is applied in the field of separation of levoglucosan components in wood vinegar, can solve problems such as separation influence, separation difficulty, and removal of impurities, and achieve good industrial application prospects, technology The effect of simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1: Using different bases to adjust alkalinity
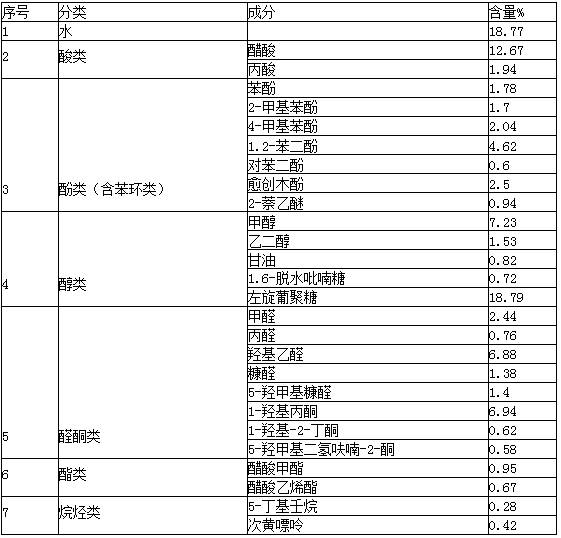
[0026] The wood vinegar obtained by pyrolysis of wood is black, with a pH of 3-4, and is completely opaque. In addition to levoglucosan, other soluble parts mainly contain phenol, hydroquinone, hydroxyacetone, acetic acid and furfural One or more of them, wherein the content of levoglucosan is about 2%. The specific ingredients are shown in Table 1:
[0027] Table 1 Composition list in wood vinegar
[0028]
[0029] In addition to soluble components, wood vinegar also contains some tiny carbon black particles that can be suspended in the solution, mixed wood tar and other components. These components exist in the form of colloids, which affect the subsequent levoglucosan. Extraction needs to be removed by pretreatment.
[0030] Take 3 parts of 100mL wood vinegar stock solution, add sodium hydroxide, magnesium oxide, sodium carbonate and triethylamine to it respectively at room temperature, let it stand for 1 ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2: use calcium hydroxide to adjust different pH
[0035] The damage to the colloidal ionosphere is different with different amounts of alkali. Take 5 parts of 100mL wood vinegar stock solution, add alkaline substance calcium hydroxide to it at room temperature, the amount is 3.0g, 3.4g, 3.8g, 4.2g, 4.6g, after standing for 1h, centrifuge at 10000rpm for 10min, and measure the precipitation The results are shown in Table 3.
[0036] Table 3 The amount of precipitation after adjusting different pH
[0037] Dosage pH Sedimentation 3.0g 6.6 4.824g 3.4g 8.2 4.976g 3.8g 9.3 5.175g 4.2g 10.0 5.333g 4.6g 10.5 5.709g
[0038]It can be seen from Table 3 that as the pH continues to increase, the ionosphere damage to the colloid is more obvious, and more precipitation is produced. But when the pH is above 10, some colloids are resuspended in the solution, causing the wood vinegar to become too viscous, which is not condu...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3: Flocculation by adding different flocculants
[0040] Although the addition of alkaline substances can destroy the colloidal ionization layer, so that it can be precipitated and removed, there are still a small amount of colloidal substances that need to be enhanced by adding flocculants to form larger particles to facilitate separation. Take 3 parts of 100mL stock solution of wood vinegar, add polyaluminum chloride, cetyltrimethylammonium bromide and sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate to it at room temperature, let stand for 1h, centrifuge at 10000rpm for 10min, The amount of precipitation was measured, and the results are shown in Table 4.
[0041] Table 4 The amount of sediment after flocculation with different flocculants
[0042] flocculant Dosage Sedimentation PAC 0.6g 0.795g cetyltrimethylammonium bromide 0.6g 0.726g Sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate 0.6g 0.769g
[0043] It can be seen from Table 4 that after adding ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| aspect ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com