Array antenna Taylor-Schelkunoff polynomial design method
An array antenna and design method technology, applied in the field of array antennas, can solve the problems of not comprehensively considering the mutual influence factors of side lobes and feeding methods, and not realizing on-demand controllability design, so as to simplify design and manufacture, and reduce radiation. Loss, the effect of a simple synthesis process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] The following embodiments will further illustrate the present invention in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0034] The design steps of the embodiment of the present invention are as follows:
[0035] Step 1: Select the array antenna aperture size, number of array elements, array element spacing and sidelobe level according to the comprehensive parameters of the pattern required by the system;
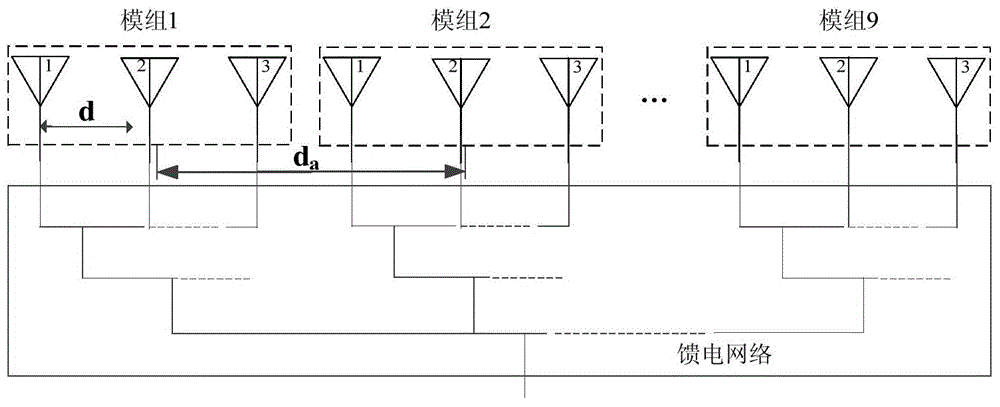
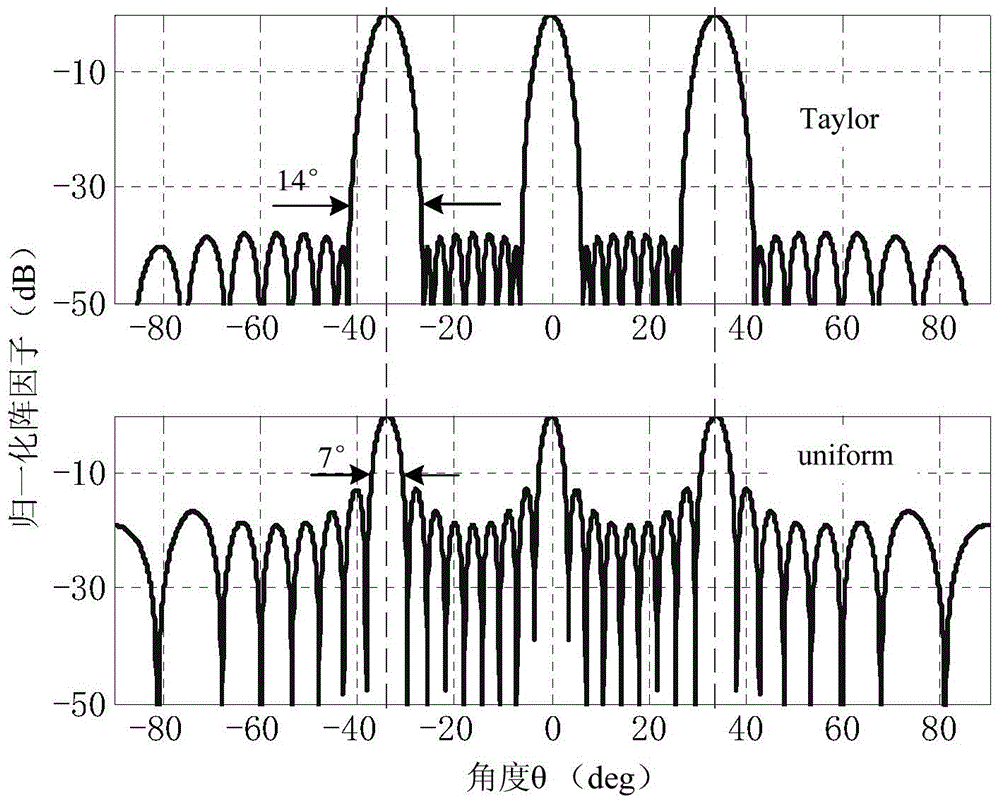
[0036] In this embodiment, the antenna aperture size l=16.2λ, and the number of array elements is 3N a =27,N a is the number of modules, the sidelobe level is SLL=-40dB, and the distance is d a =1.8λ is a periodic linear distribution, and λ is a free-space wavelength, such as figure 1 shown.
[0037] Step 2: Divide the array antenna into 9 modules according to the total number of array elements;
[0038] In order to achieve the sidelobe level SLL=-40dB required by the system, this embodiment temporarily divides the array antenna into 9 modules.
[0039] Step 3: S...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com