Patents
Literature
216 results about "Broadcast encryption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
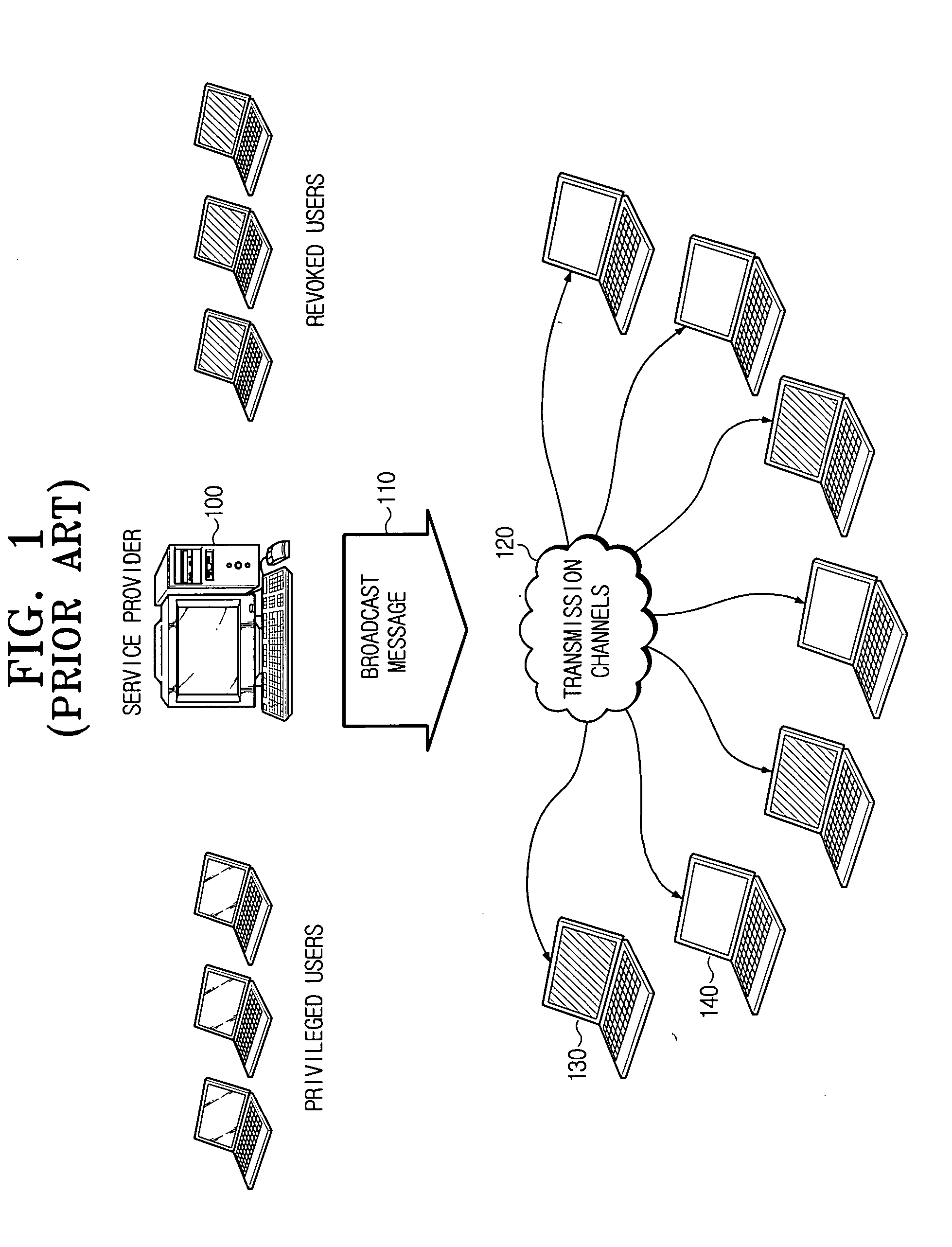
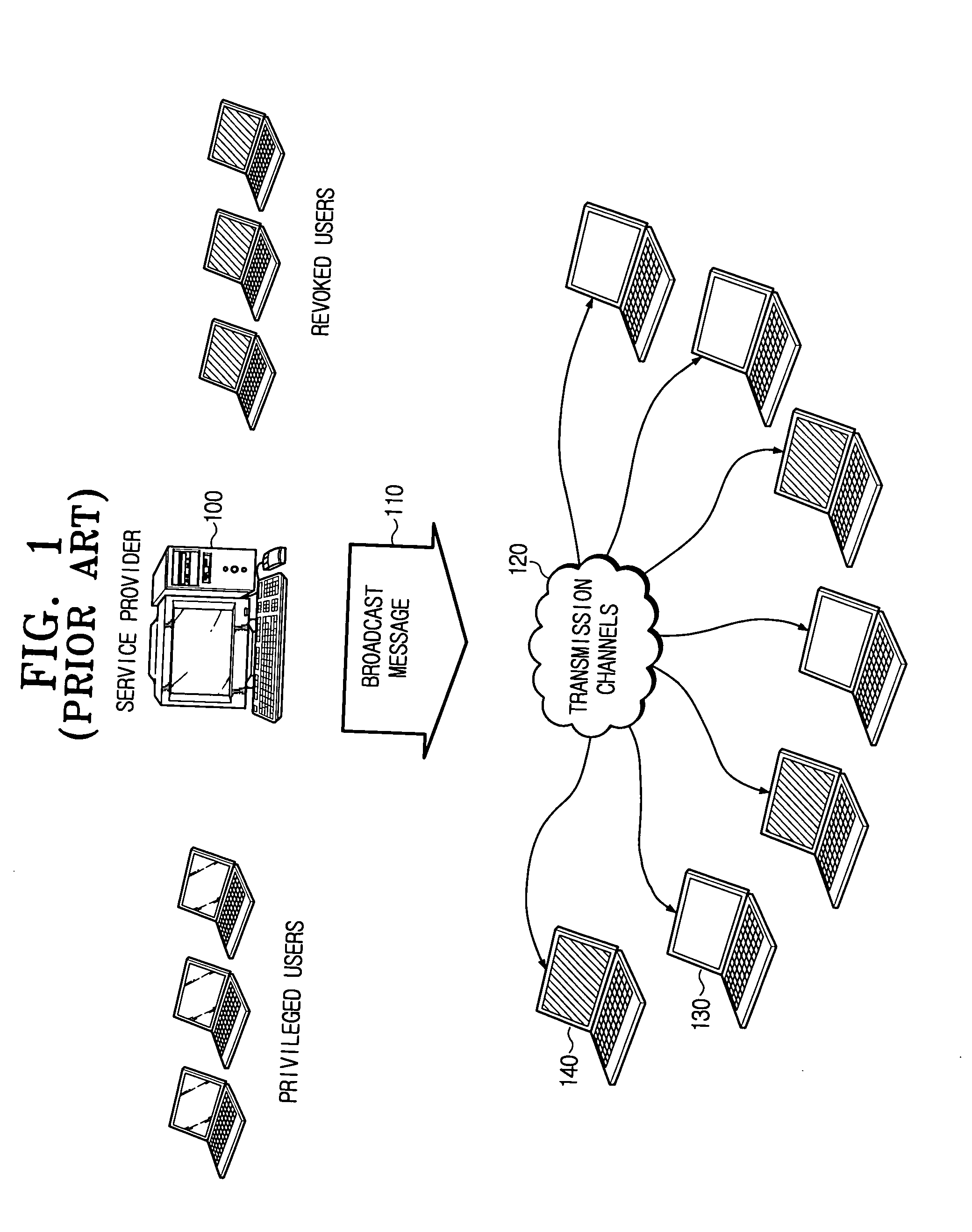
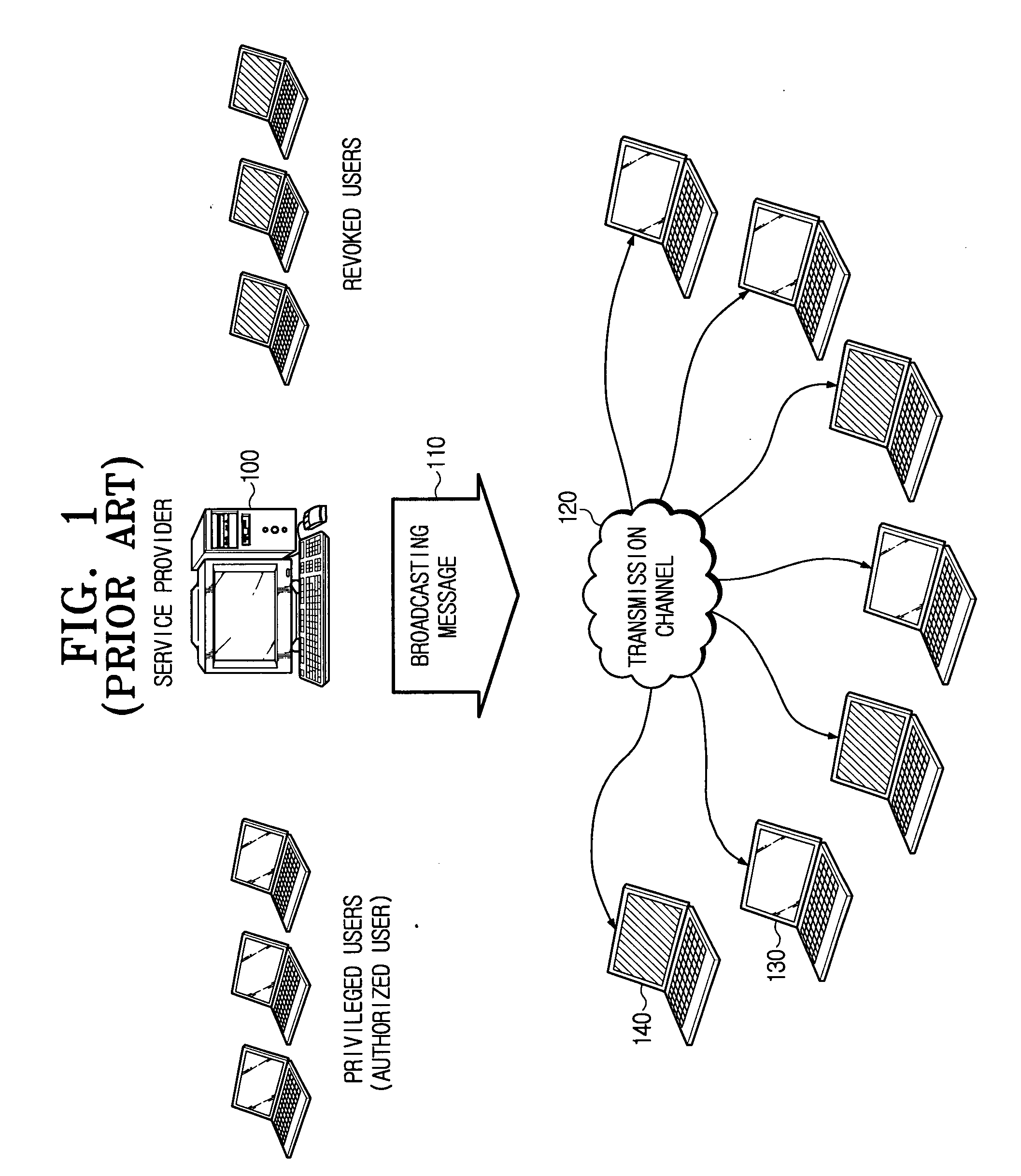
Broadcast encryption is the cryptographic problem of delivering encrypted content (e.g. TV programs or data on DVDs) over a broadcast channel in such a way that only qualified users (e.g. subscribers who have paid their fees or DVD players conforming to a specification) can decrypt the content. The challenge arises from the requirement that the set of qualified users can change in each broadcast emission, and therefore revocation of individual users or user groups should be possible using broadcast transmissions, only, and without affecting any remaining users. As efficient revocation is the primary objective of broadcast encryption, solutions are also referred to as revocation schemes.
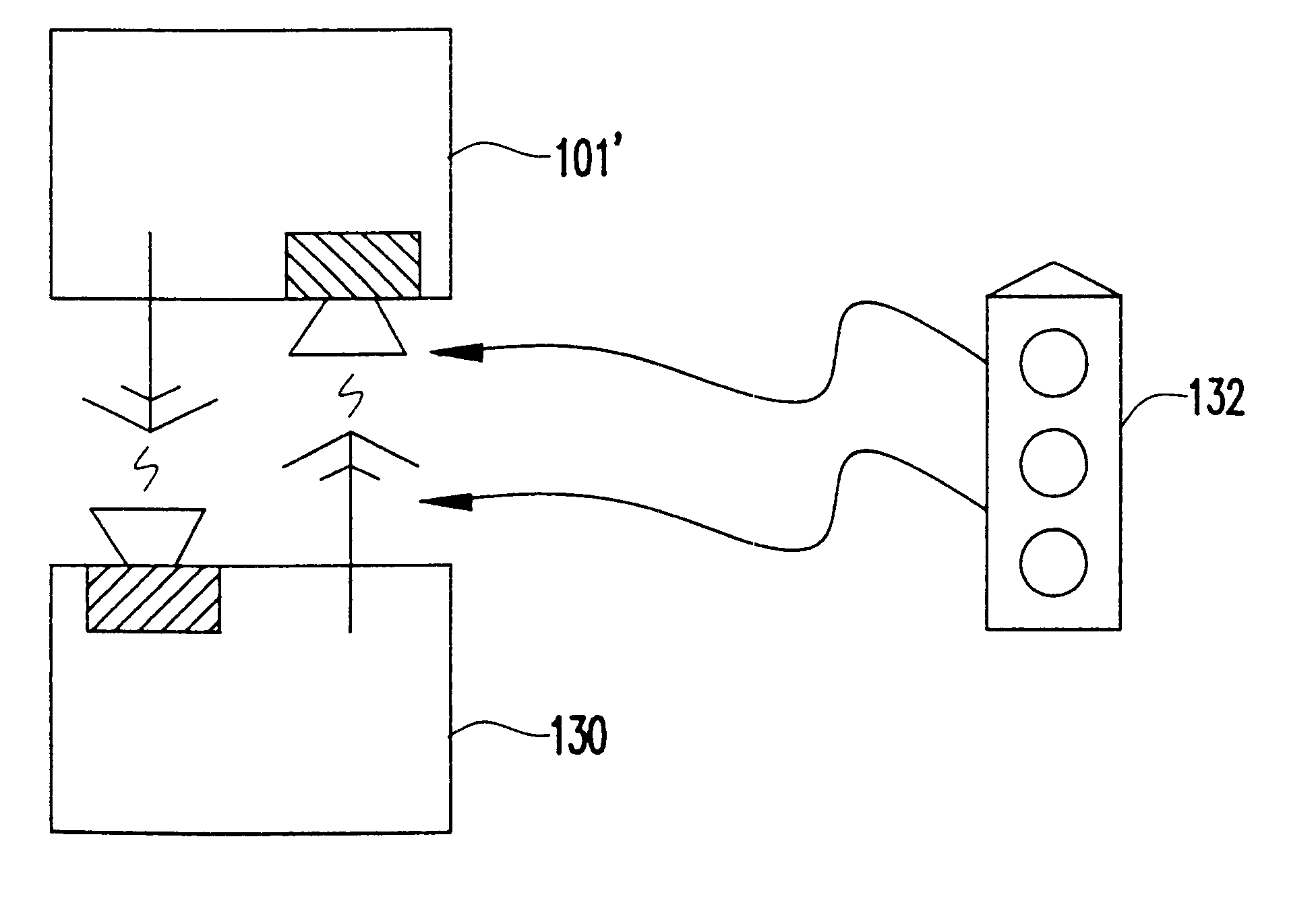
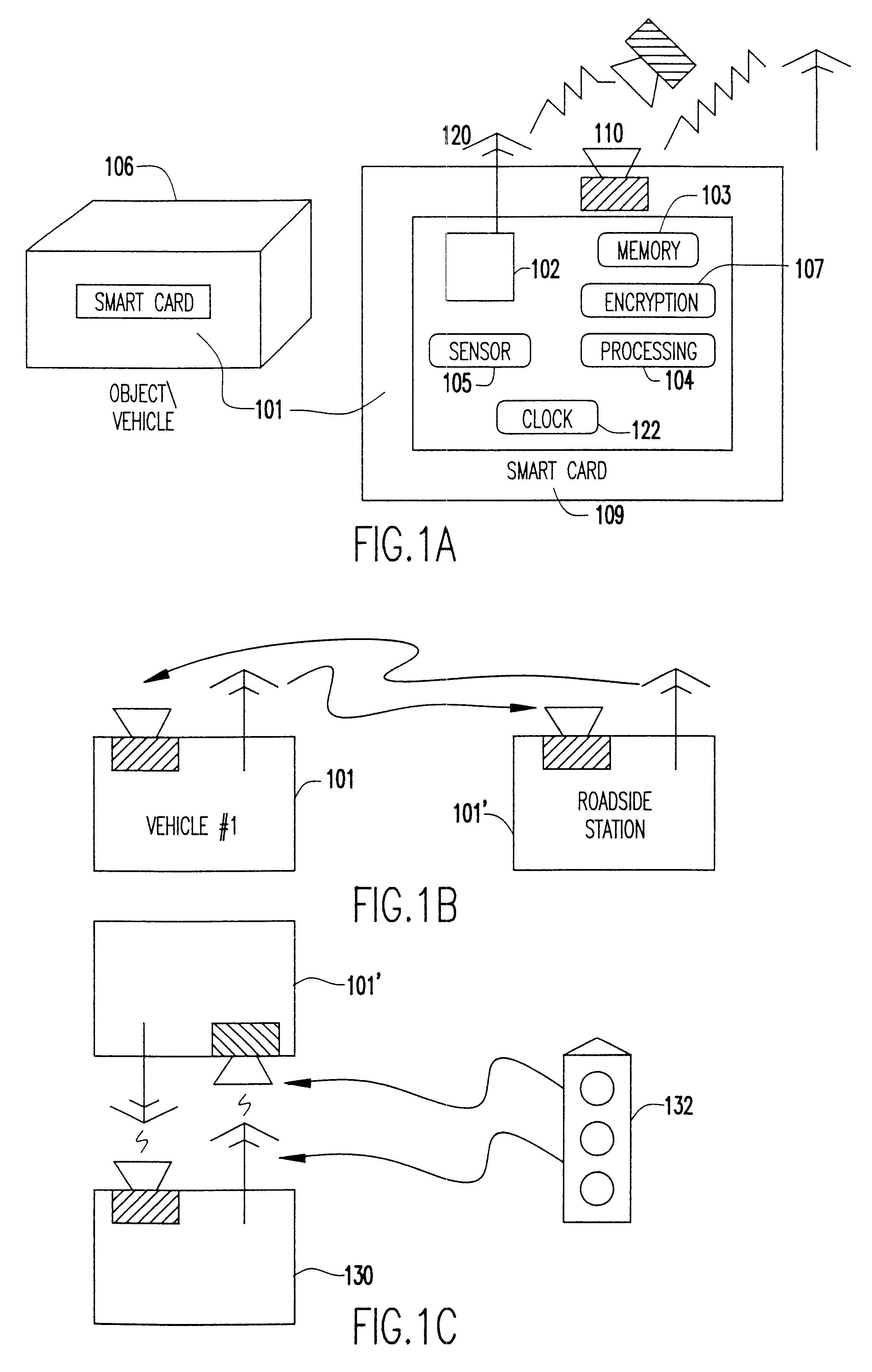
Event-recorder for transmitting and storing electronic signature data
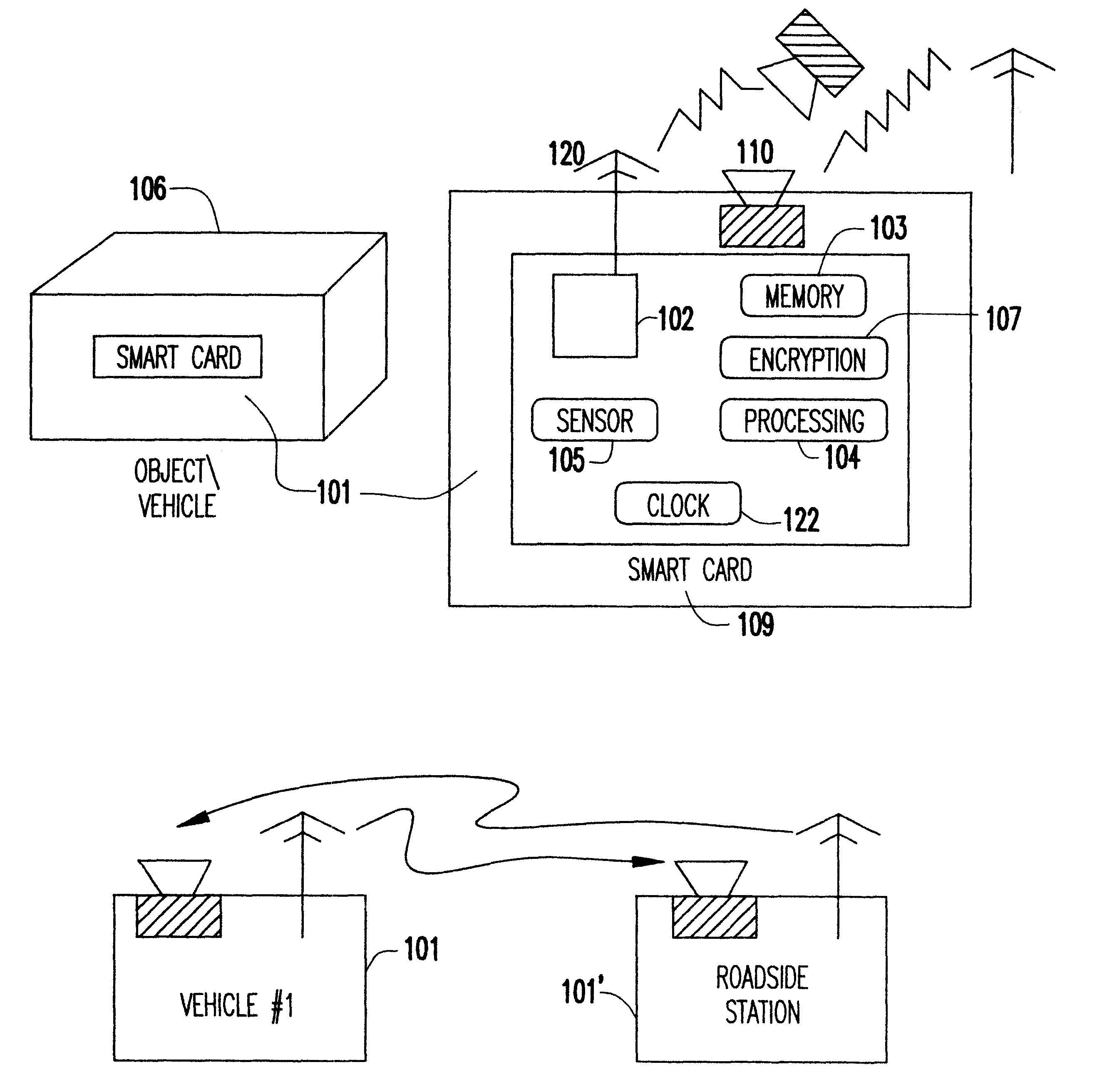
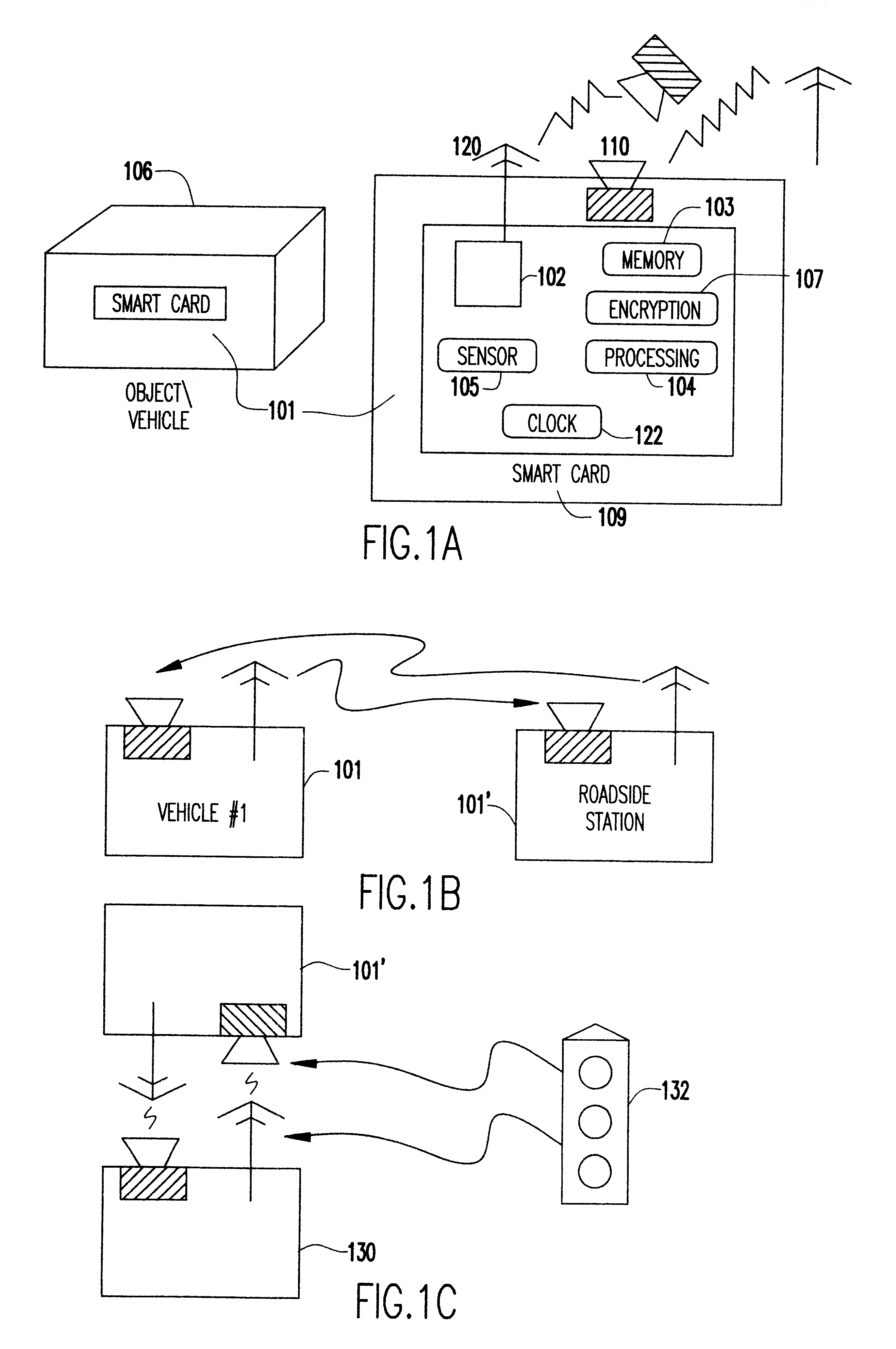
An electronic event recorder for attachment to a vehicle is provided which can broadcast encrypted signature and data, thereby leaving behind an electronic version of a "fingerprint" in the event of an accident or traffic violation. The fingerprint, captured by an external data acquisition system or another vehicle so equipped, provides a history of events related to the vehicle. The event recorder is preferably integrated on a smart card and housed in a tamper proof casing. In a first mode of operation, monitoring stations along the roadways periodically send an interrogation signal, such as when radar detects that the vehicle is speeding. Upon receiving the interrogation signal the smart card transmits the vehicle's signature information to the monitoring station where it is time and date stamped along with the speed of the vehicle. In a second mode of operation, when a sensor detects a sudden or violent acceleration or deceleration, such as occurs during a collision, a smart card mounted in each car will exchange signature information automatically. This is particularly useful when the collision occurs in a parking lot when one of the hit vehicles is typically unattended.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
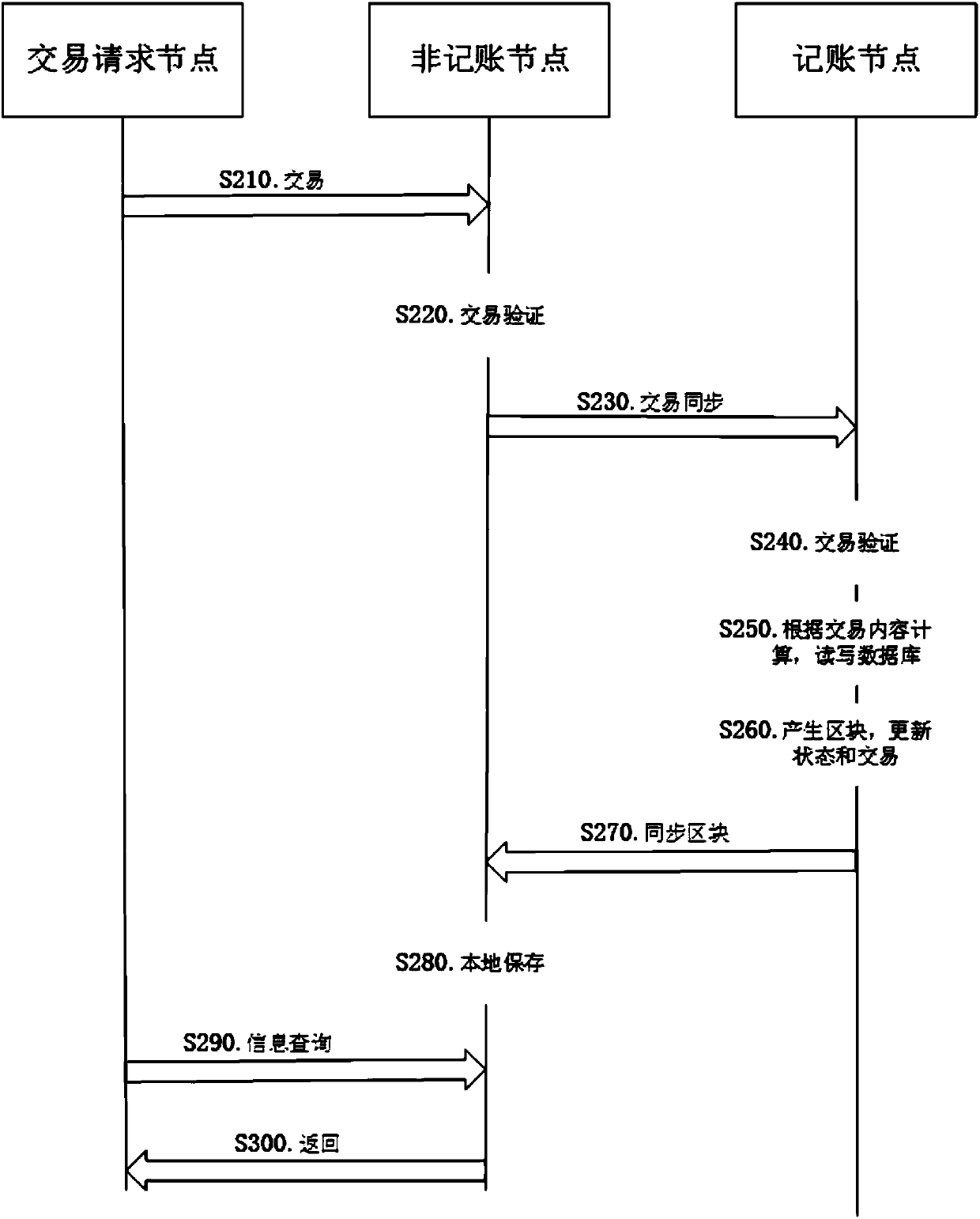
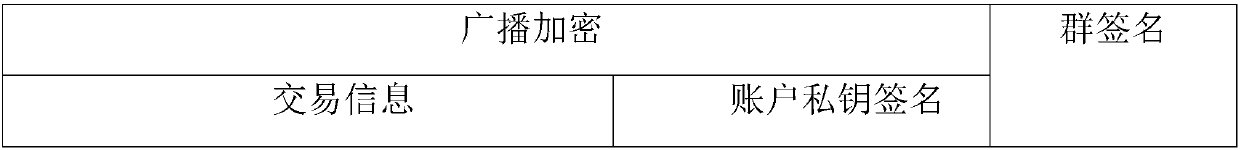
Method and system for privacy protection of block chain transaction
ActiveCN107911216ARealize regulationSupport reviewKey distribution for secure communicationFinancePublic accountPrivacy protection
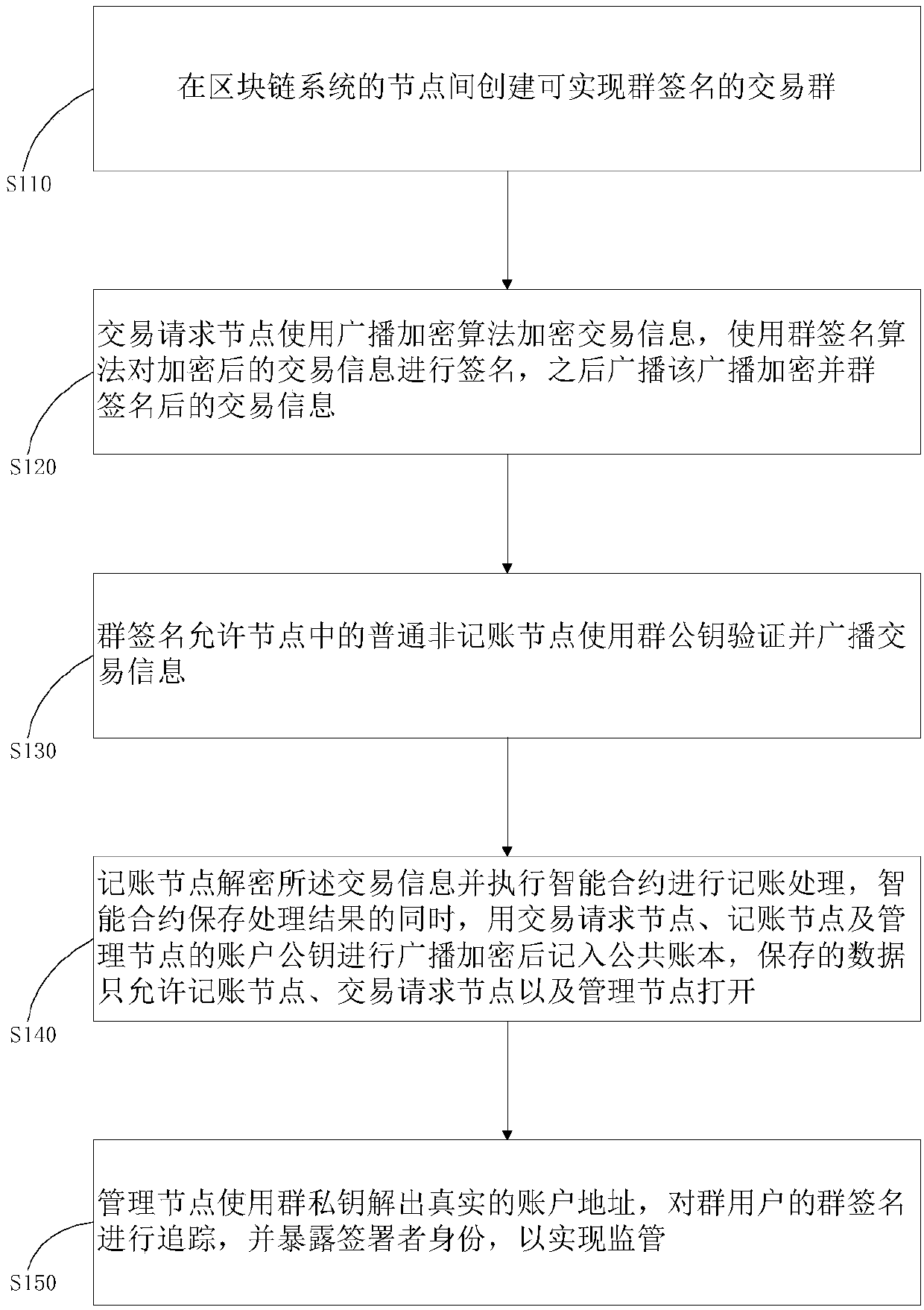
The invention provides a method and system for privacy protection of block chain transaction. The method comprises: a transaction group is established between nodes of a block chain system, a user establishes an account at a node, and the node generates public and private key information of the account and then joining of a group is carried out; a transaction request node encrypts transaction information by using a broadcast encryption algorithm, carries out group signature processing on the encrypted transaction information, and then broadcasts the transaction information after broadcast encryption and group signature processing; a common non-account-recording node verifies the transaction information and then broadcasts the transaction information, an account-recording node decrypts thetransaction information and performs an intelligent contract to carry out account recording, broadcast encryption is carried out and then the information is recorded into a public account book, wherein the stored data are only allowed to be opened by the account-recording node, the transaction request node and an administration node. With the broadcast encryption algorithm and group signature technology, a privacy protection problem in the block chain system is solved and the traceability of the transaction is ensured.
Owner:JUZIX TECH SHENZHEN CO LTD +1
Virtual key management and isolation of data deployments in multi-tenant environments
ActiveUS20140283010A1Multiple keys/algorithms usageDigital data processing detailsVirtualizationData center
Tenants in a multi-tenant shared deployment are provided their own distinct key spaces over which they control a key management system. In this manner, virtual key management domains are created on a per-tenant (per-customer) basis so that, whenever a particular customer's data is co-tenanted, stored, transmitted or virtualized in the IT infrastructure of the provider's datacenter(s), it is secured using key management materials specific to that customer. This assures that the entirety of a tenant's data remains secure by cryptographically isolating it from other tenants' applications. The virtual key management domains are established using a broadcast encryption (BE) protocol and, in particular, a multiple management key variant scheme of that protocol. The broadcast encryption-based virtual key management system (VKMS) and protocol achieves per-tenant (as well as per-application) secured isolation of data and can be used across any combination of resources in or across all levels of a co-tenanted IT infrastructure.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method, Apparatus and System for Secure Distribution of Content
InactiveUS20090290711A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsDigital data protectionSmart cardContent security
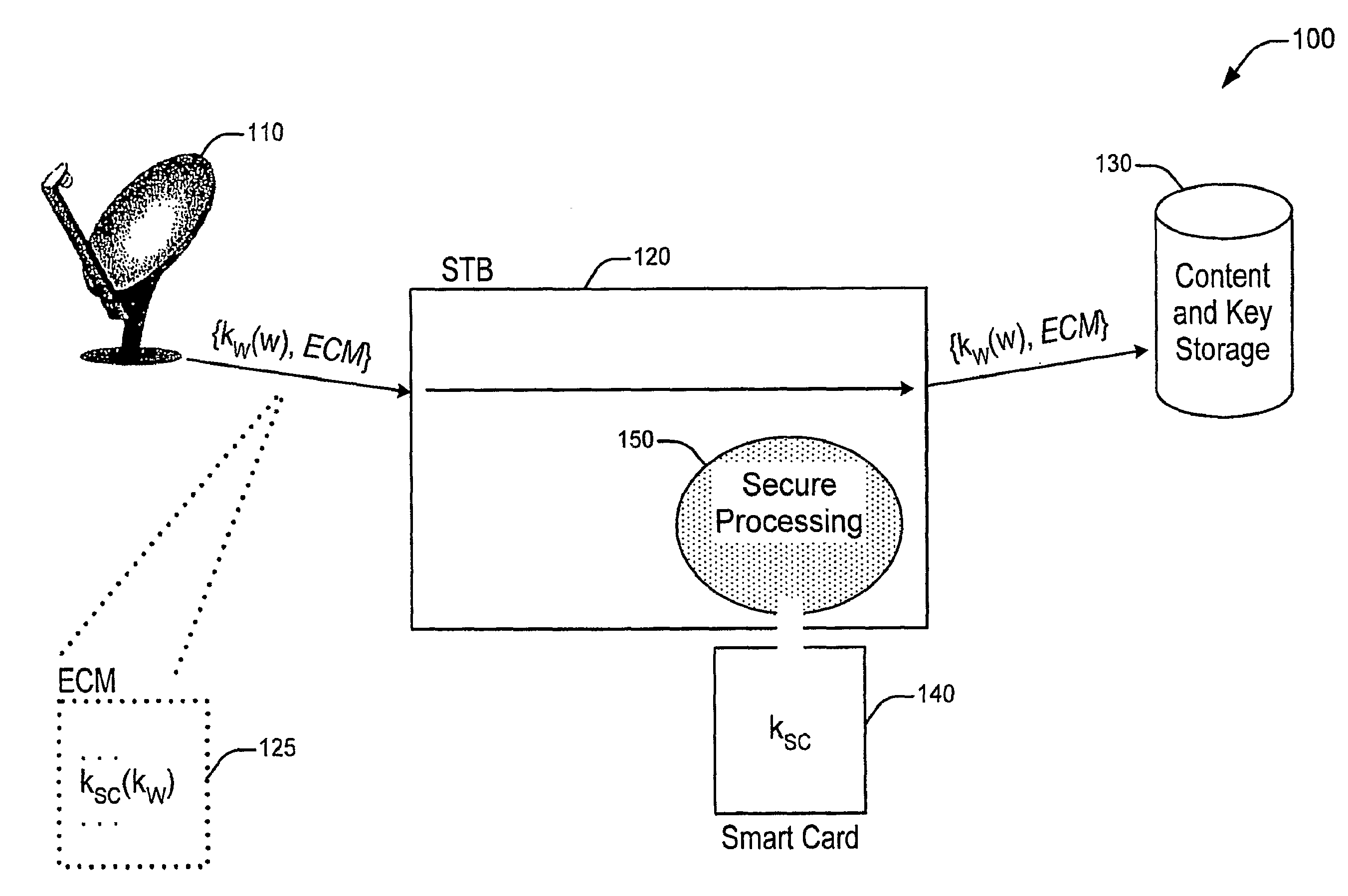
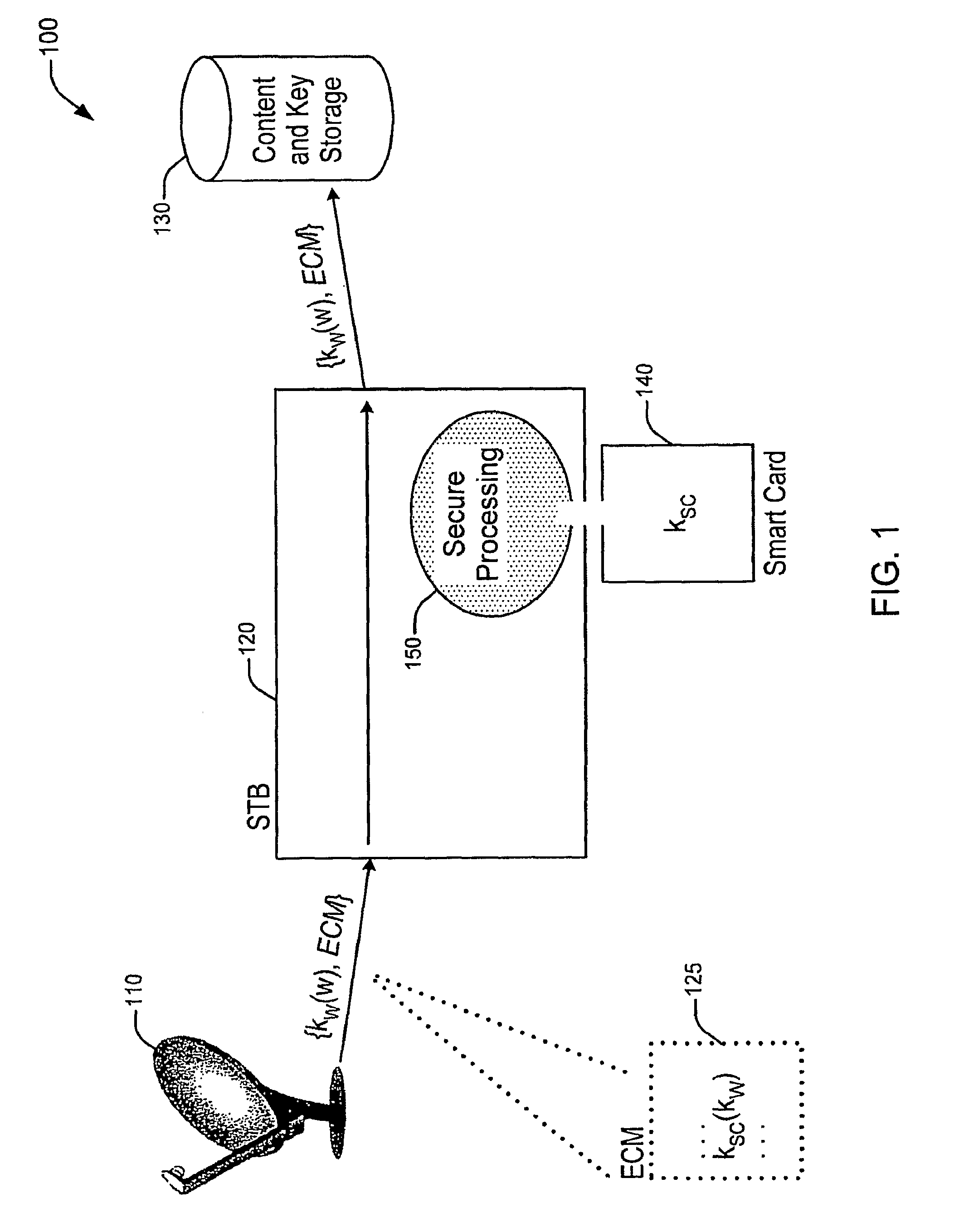
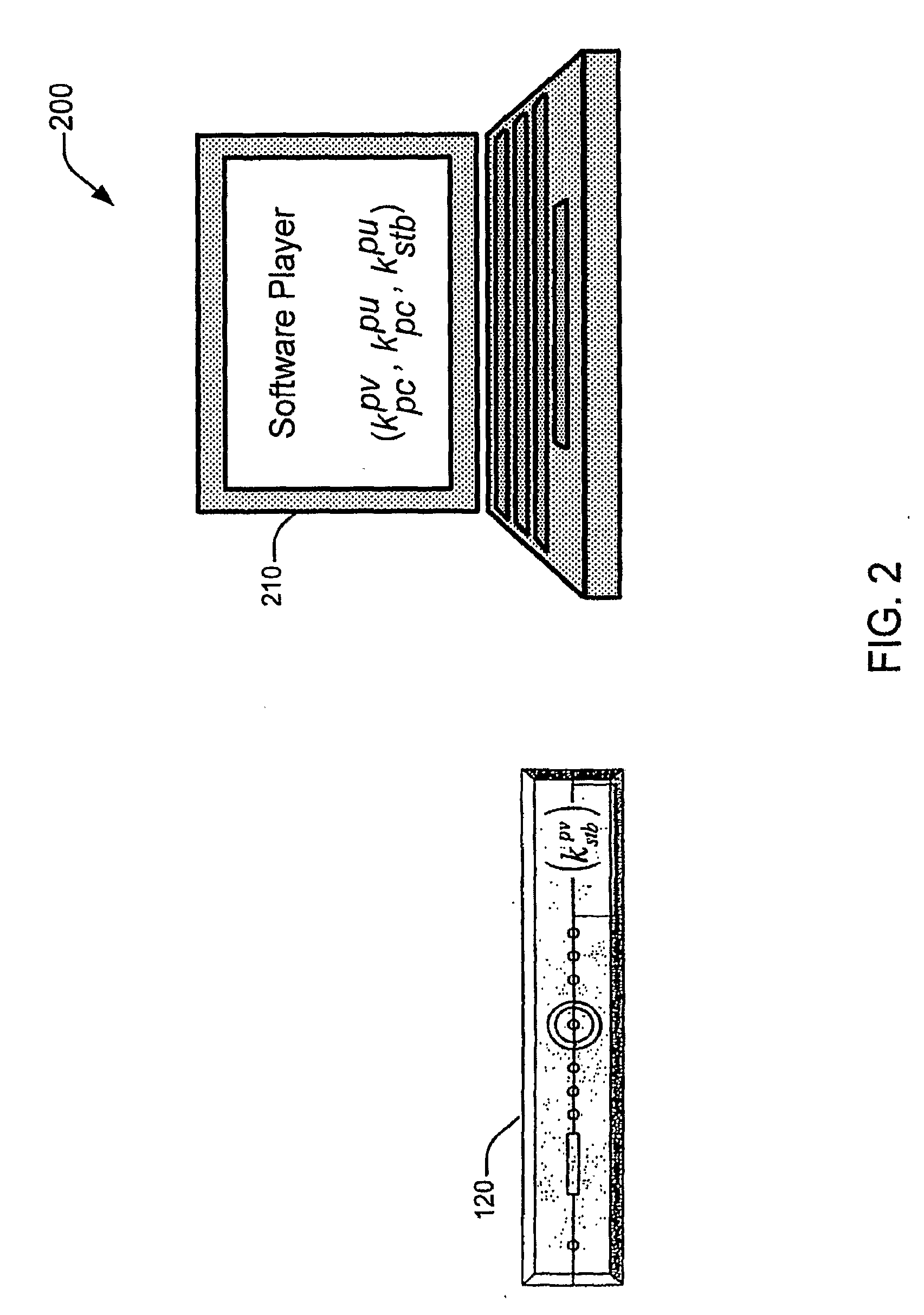
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method, apparatus and system for the secure distribution of content such as audiovisual content in a way that prevents users from misusing the content and provides a mechanism for tracking pirated material back to the original location of misappropriation. A security device, in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, incorporates encryption methods to insure the broadcast encryption key remains secure. A marking device, in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, incorporates, for example, digital watermarking methods that attach to the content information to identify a location of origin of the misappropriation, such as a Set-top Box (STB) and / or smart card.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
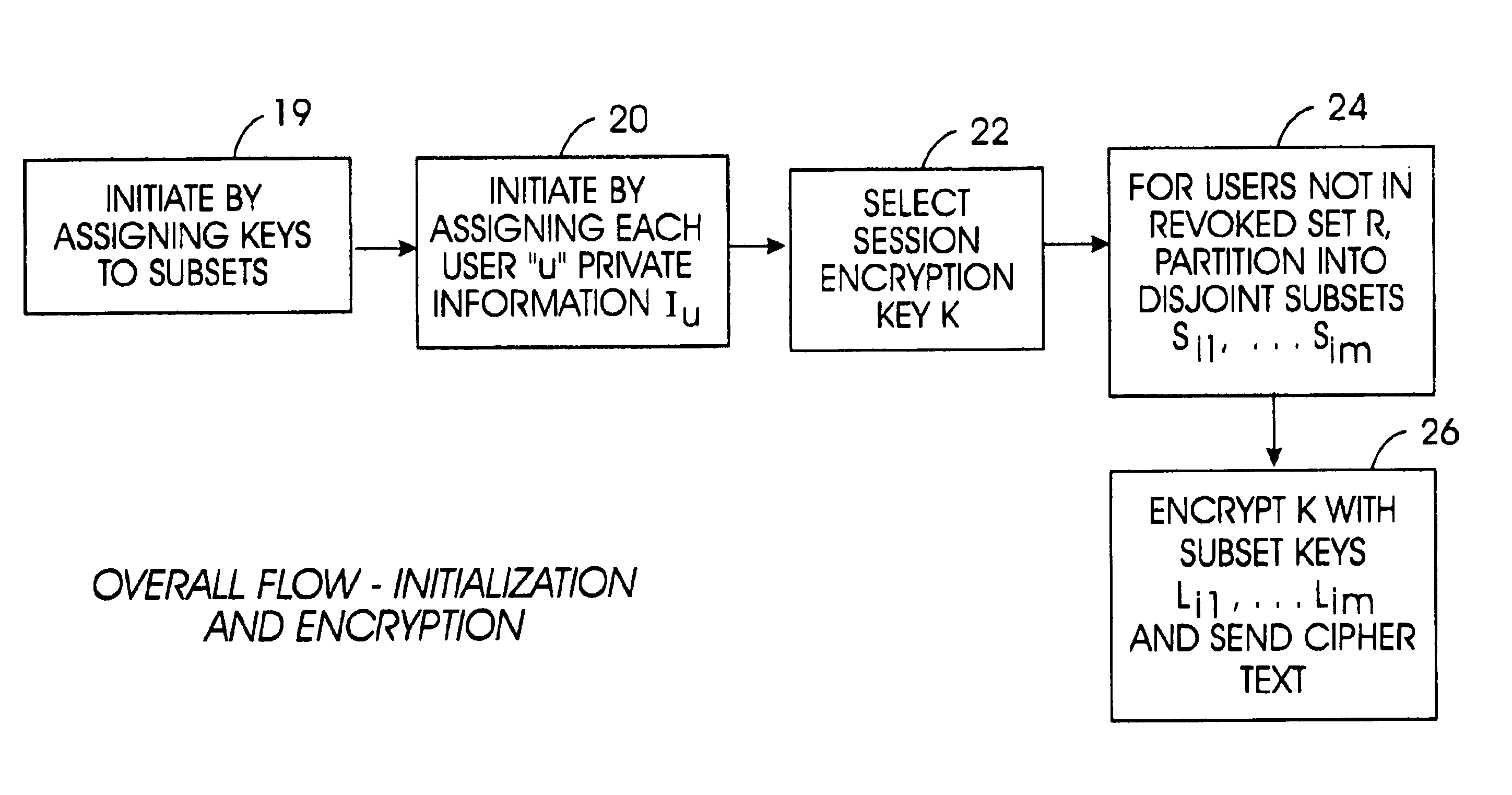
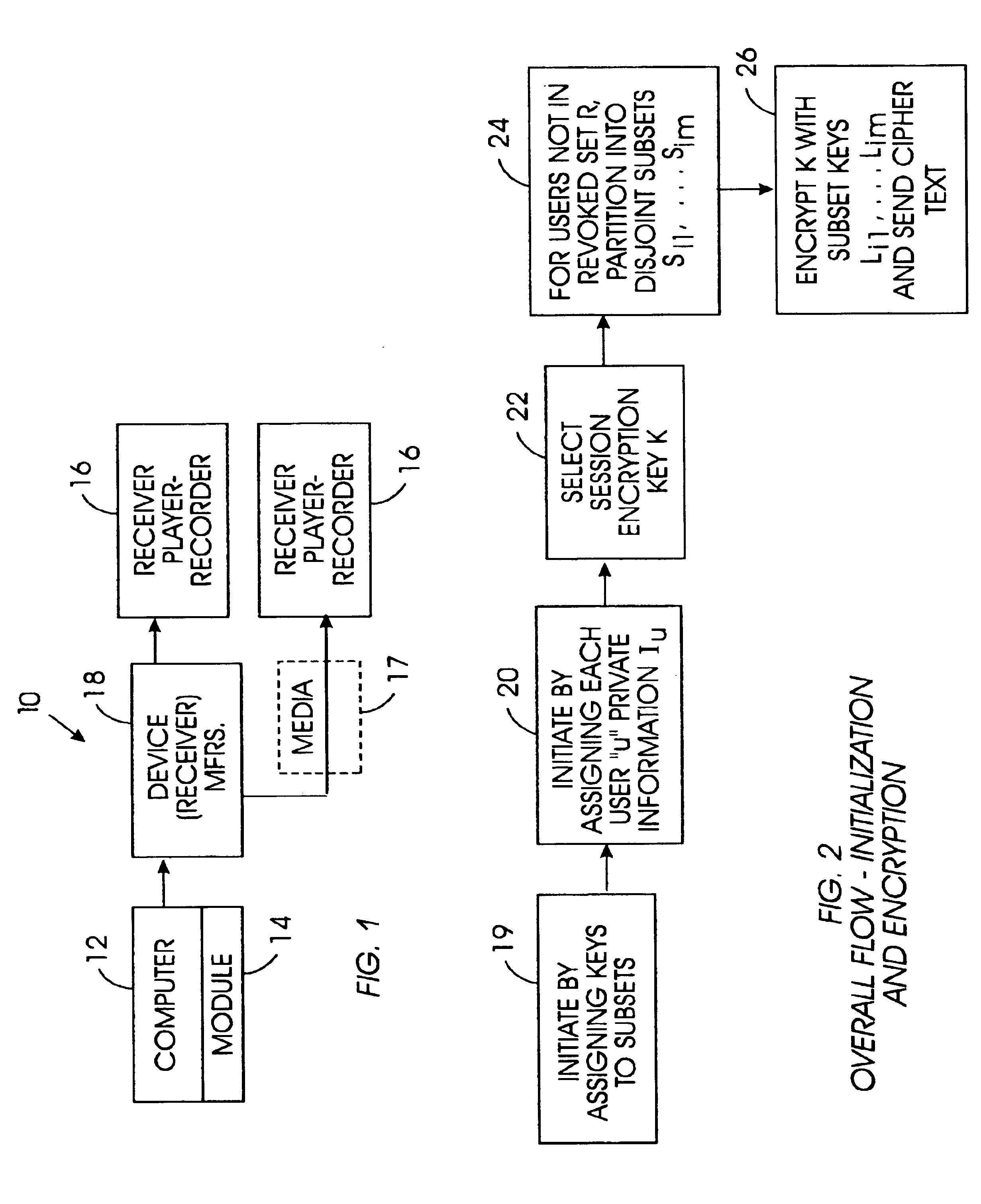
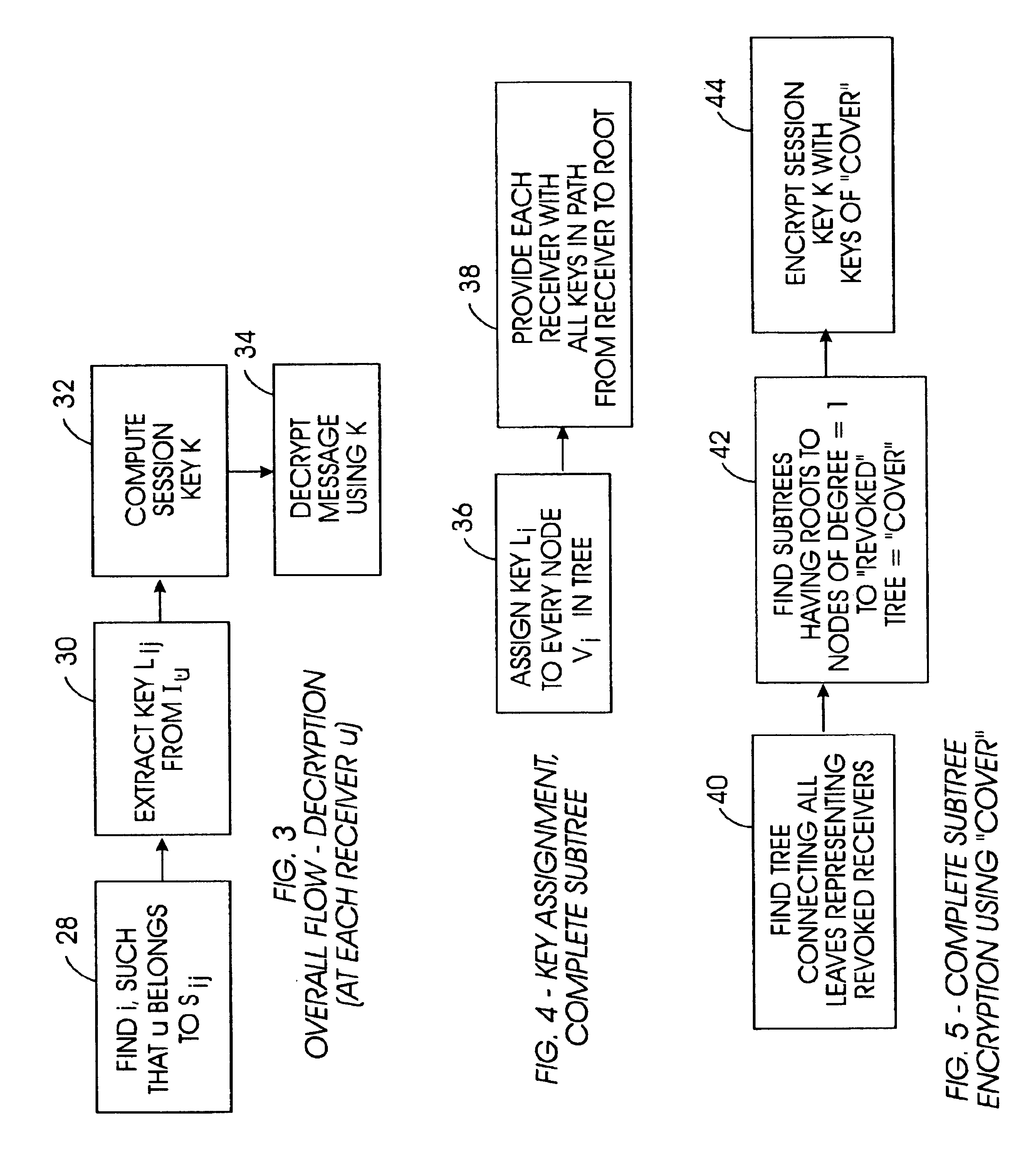
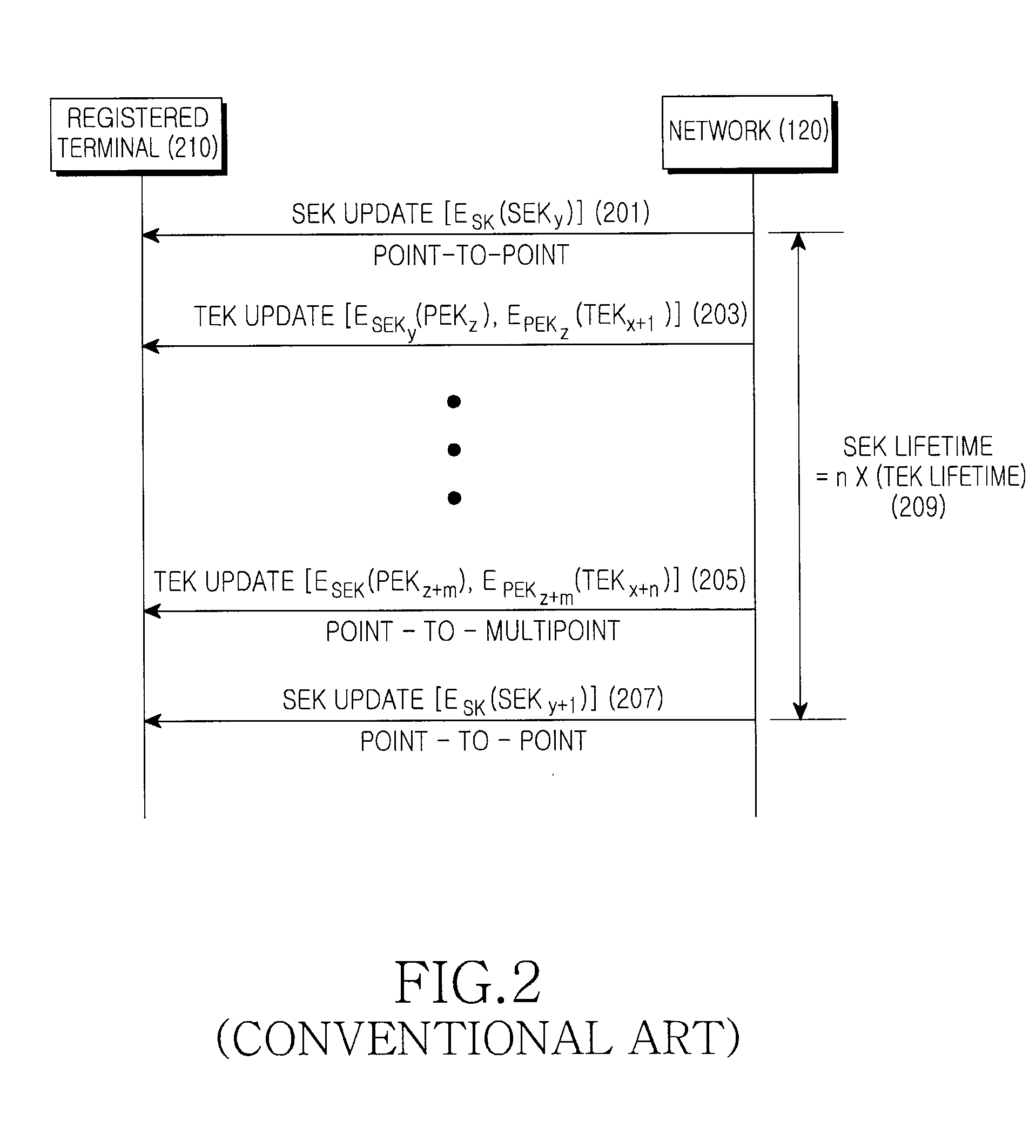
Method for broadcast encryption and key revocation of stateless receivers
InactiveUS7039803B2Special service provision for substationKey distribution for secure communicationBroadcastingSession key
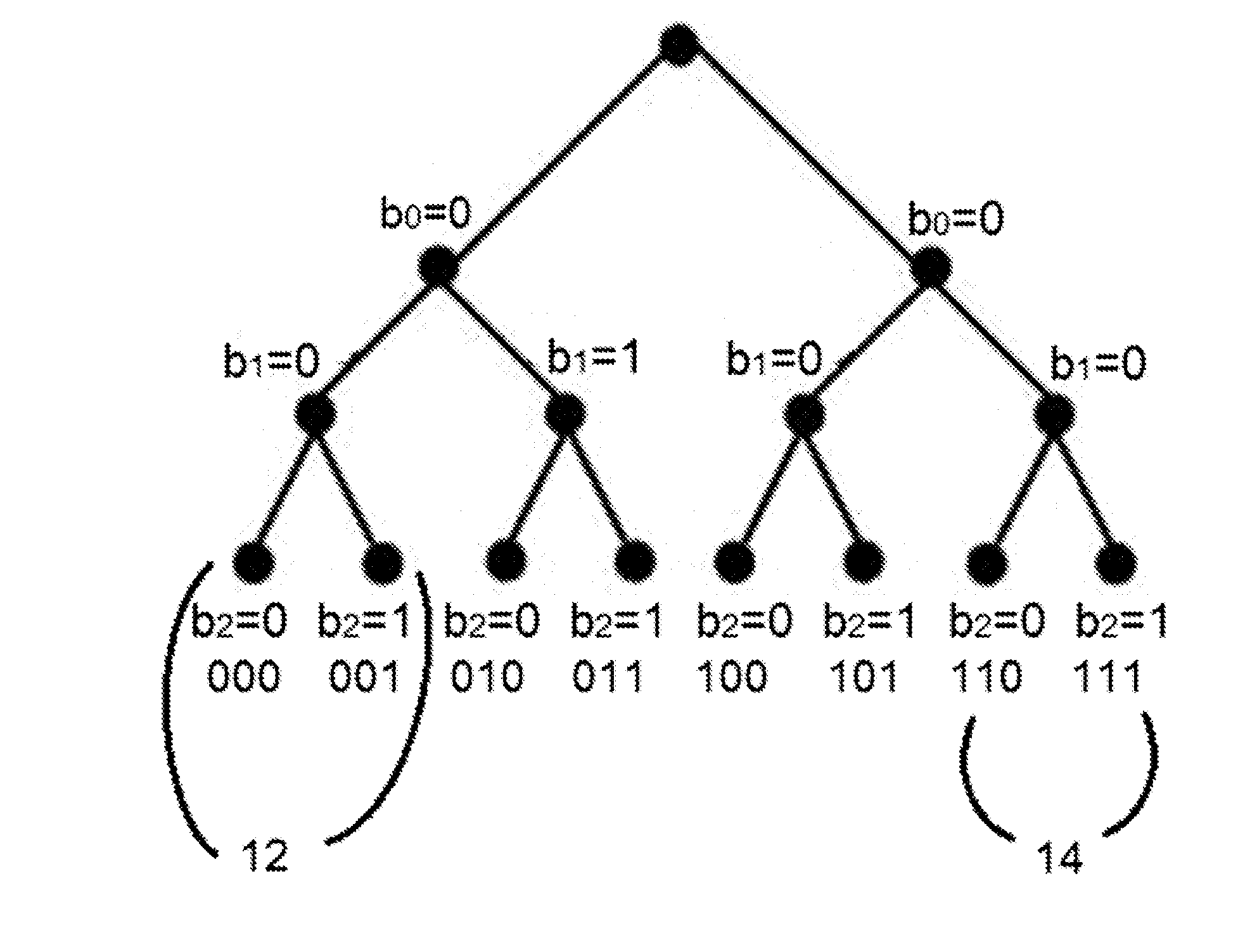
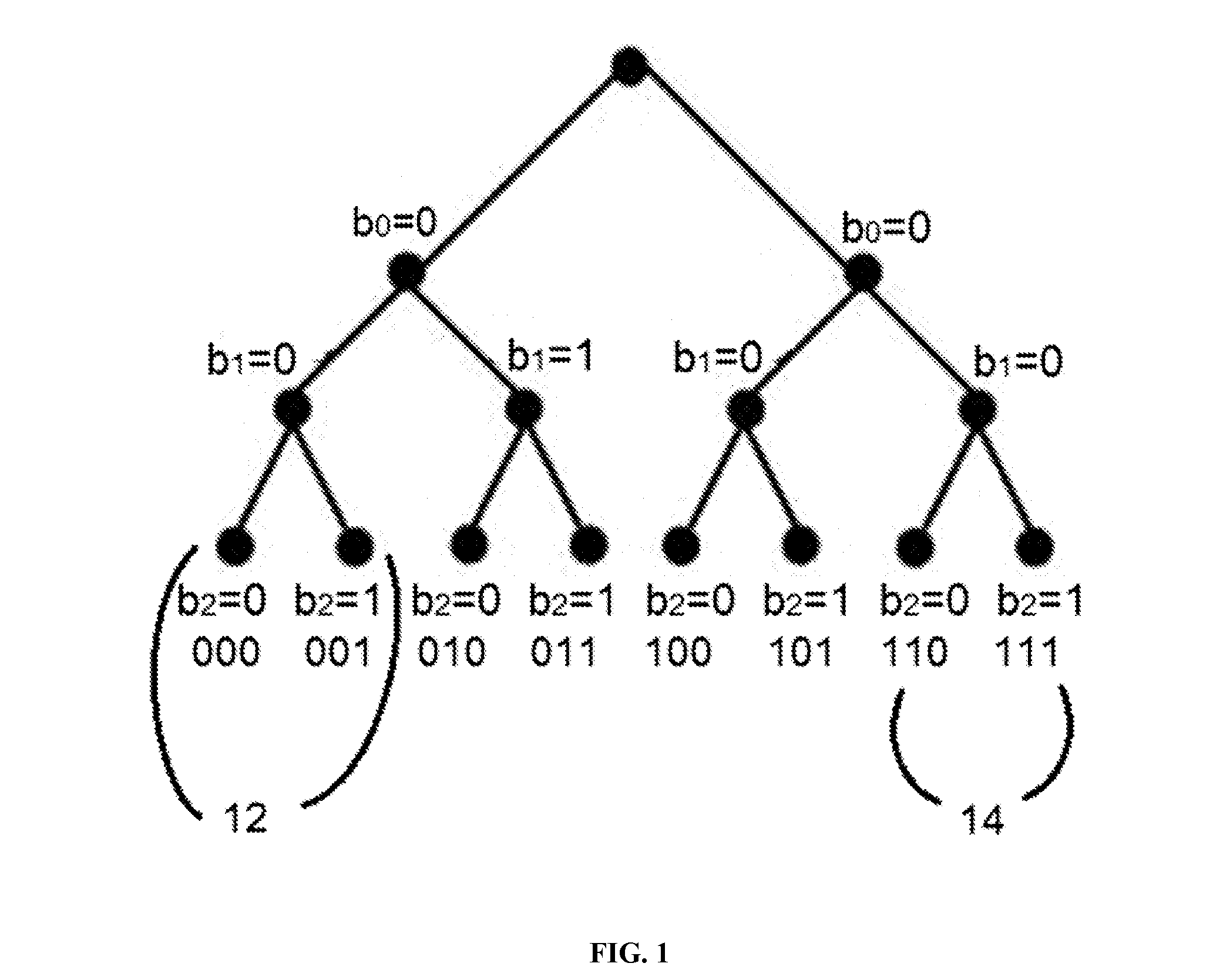
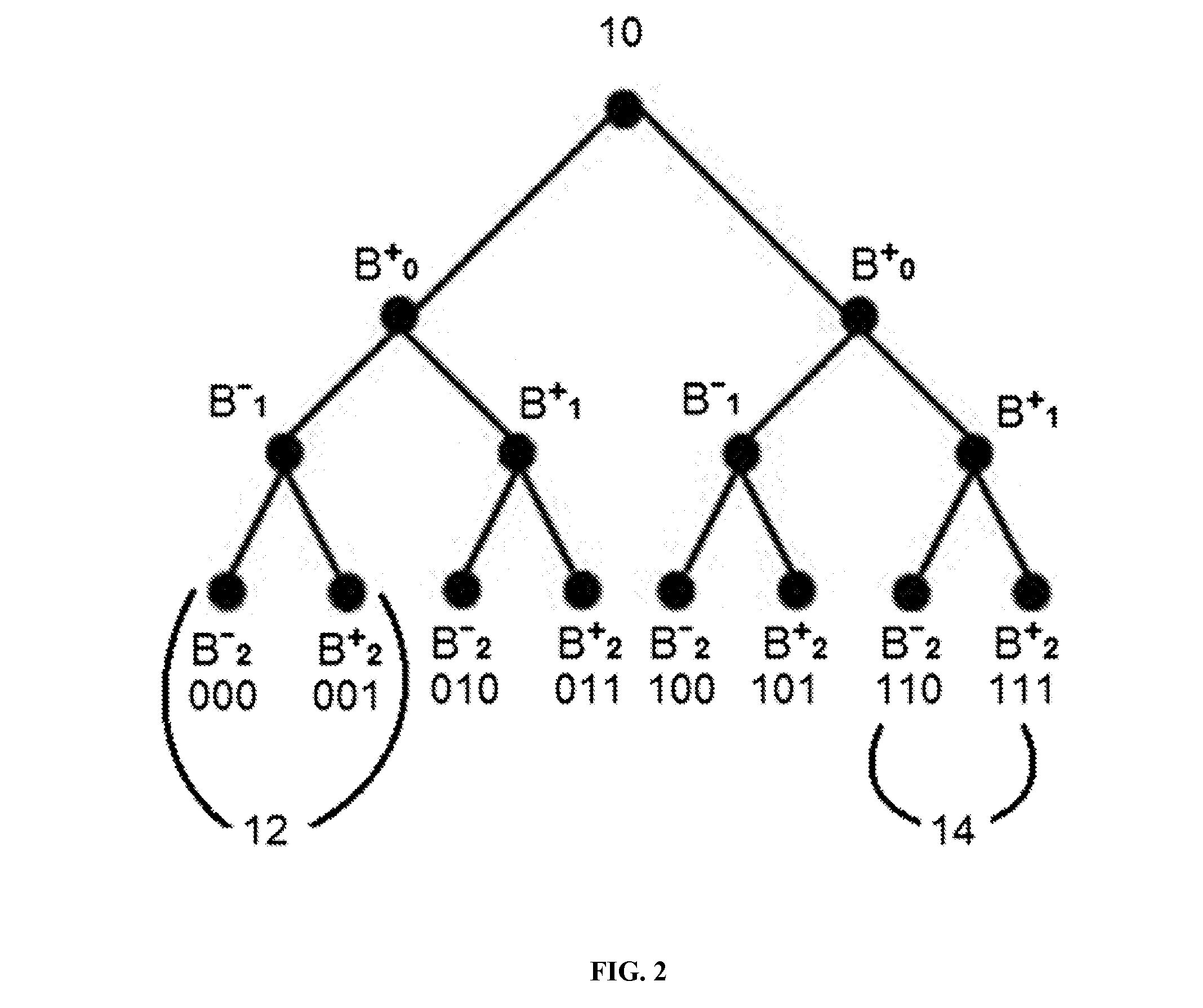
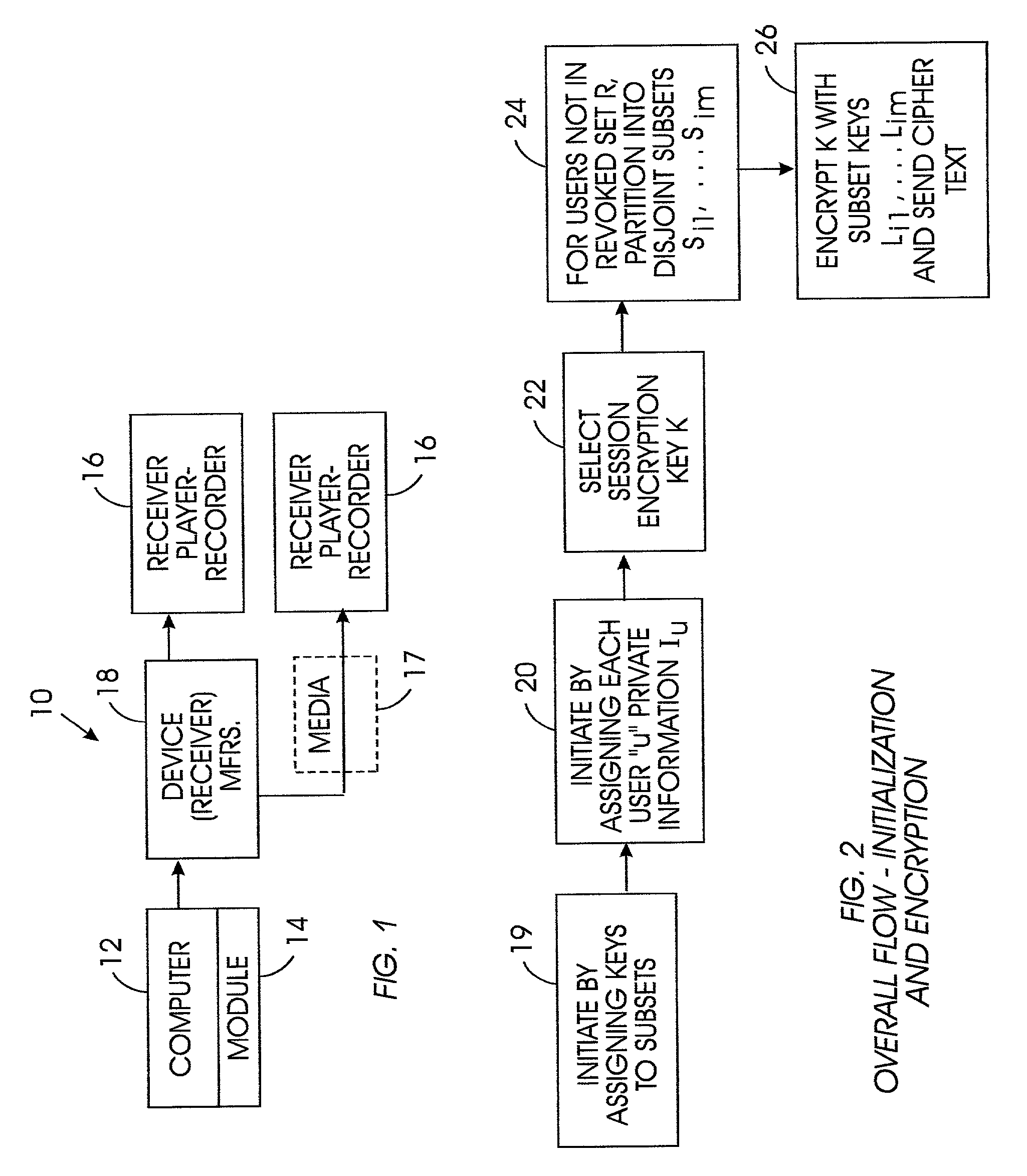
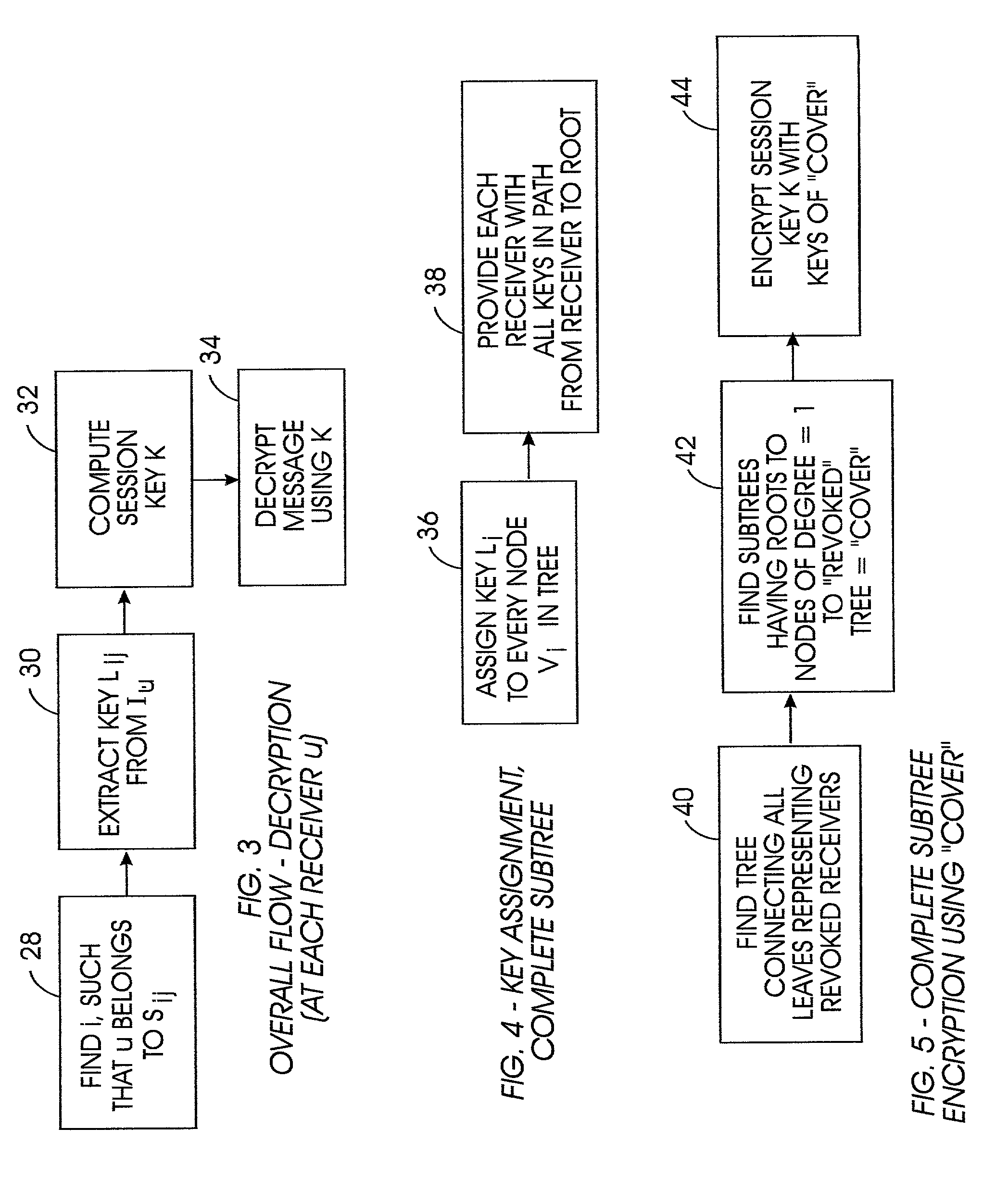
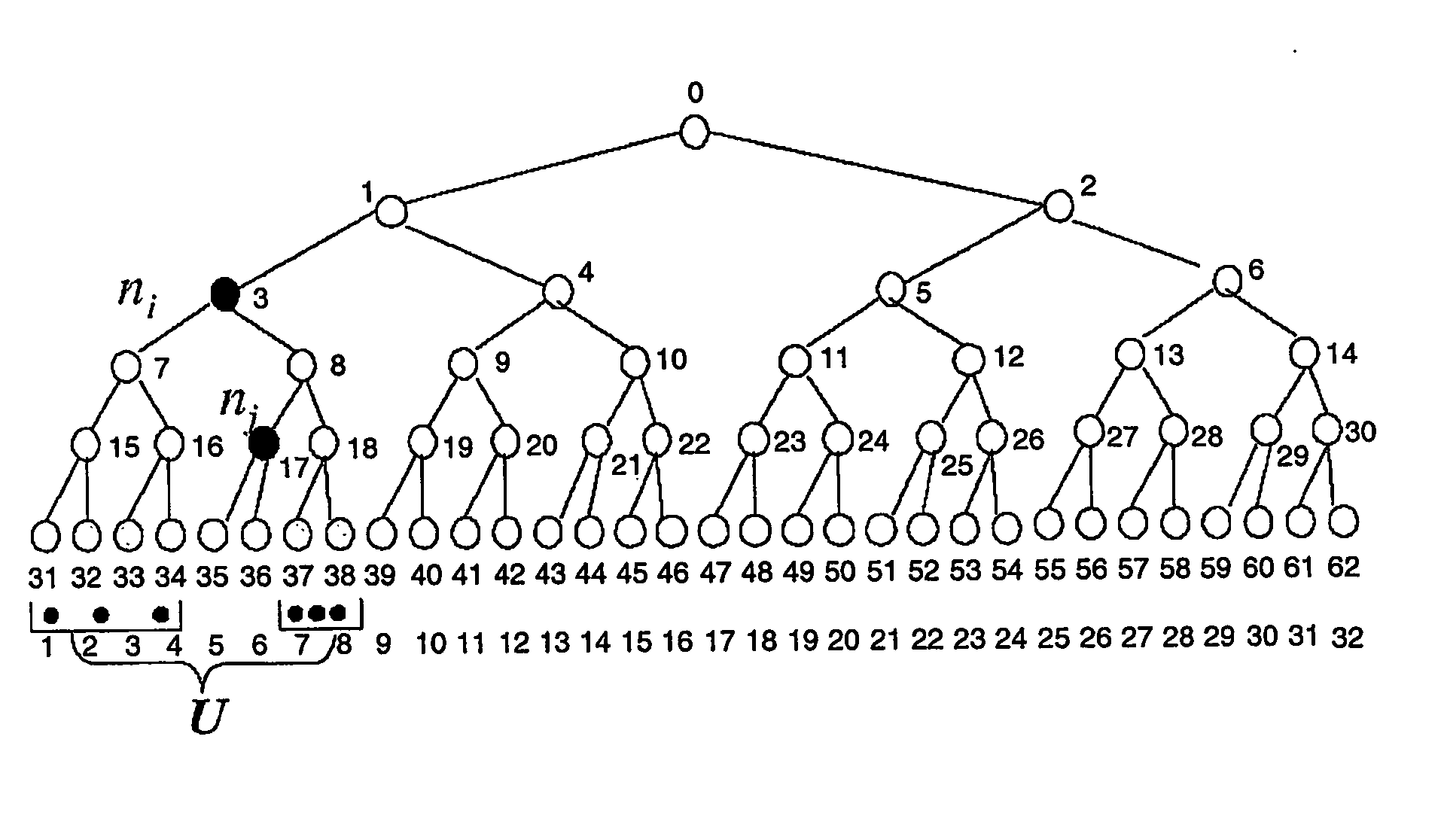
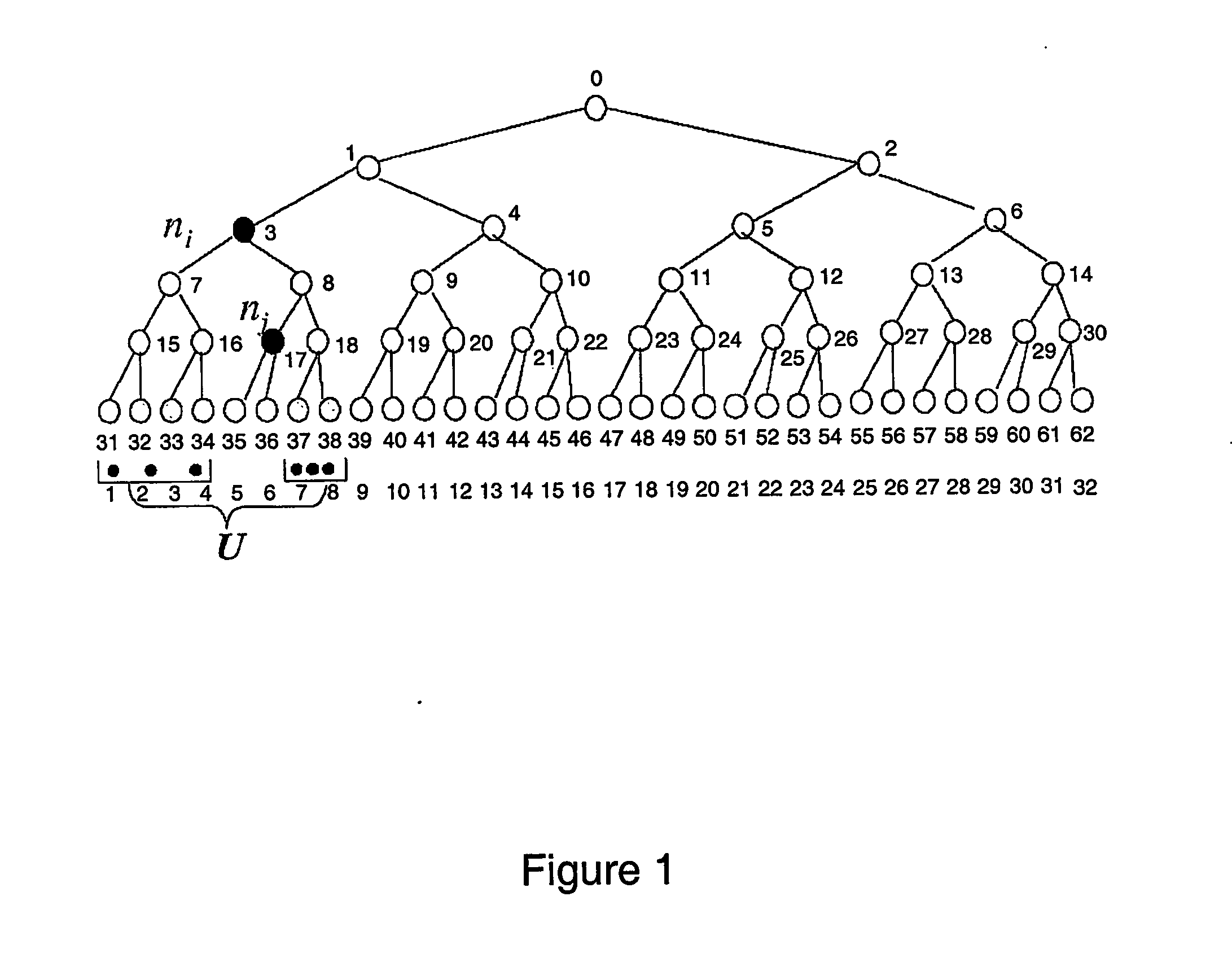
A tree is used to partition stateless receivers in a broadcast content encryption system into subsets. Two different methods of partitioning are disclosed. When a set of revoked receivers is identified, the revoked receivers define a relatively small cover of the non-revoked receivers by disjoint subsets. Subset keys associated with the subsets are then used to encrypt a session key that in turn is used to encrypt the broadcast content. Only non-revoked receivers can decrypt the session key and, hence, the content.
Owner:IBM CORP
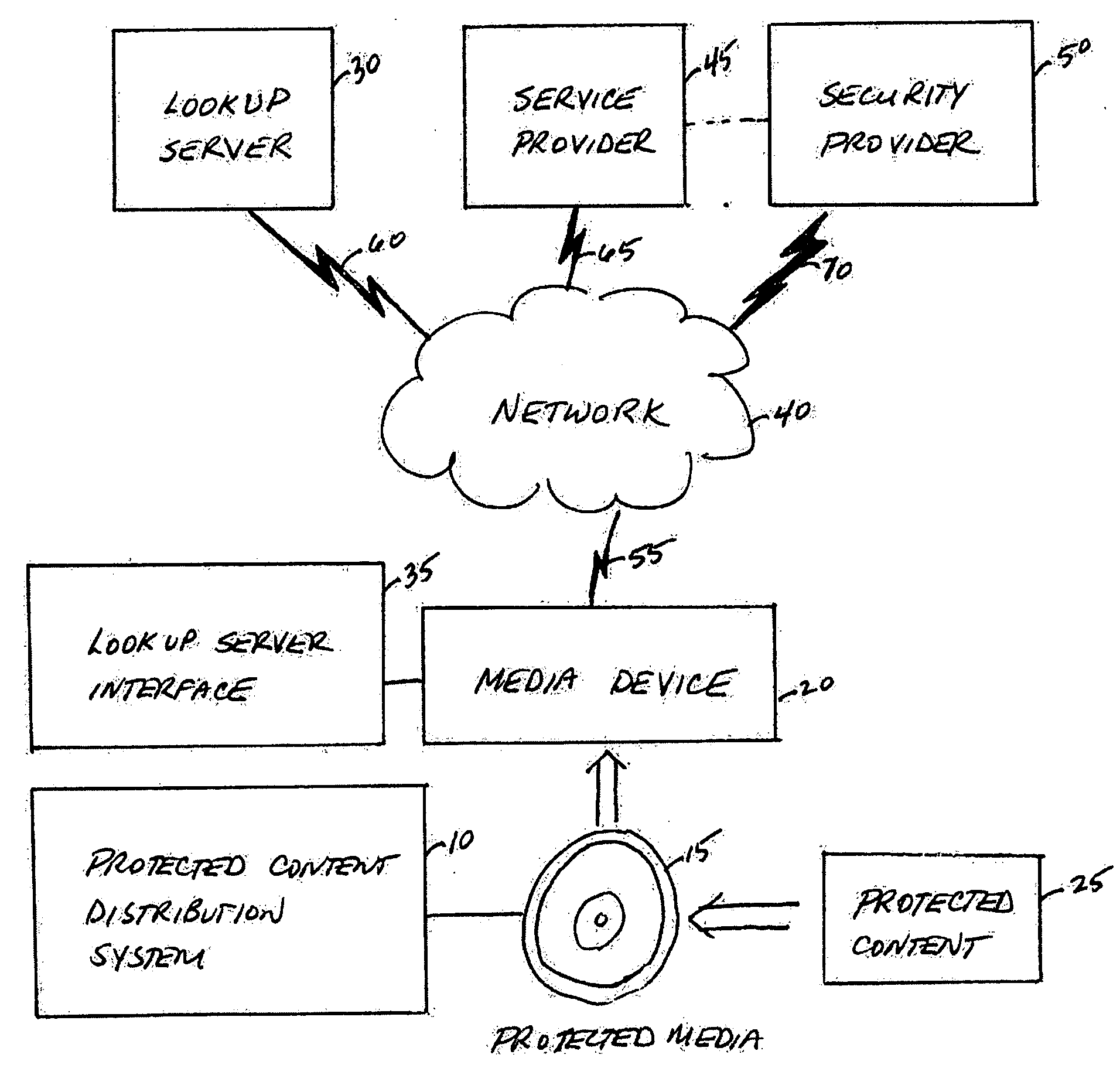
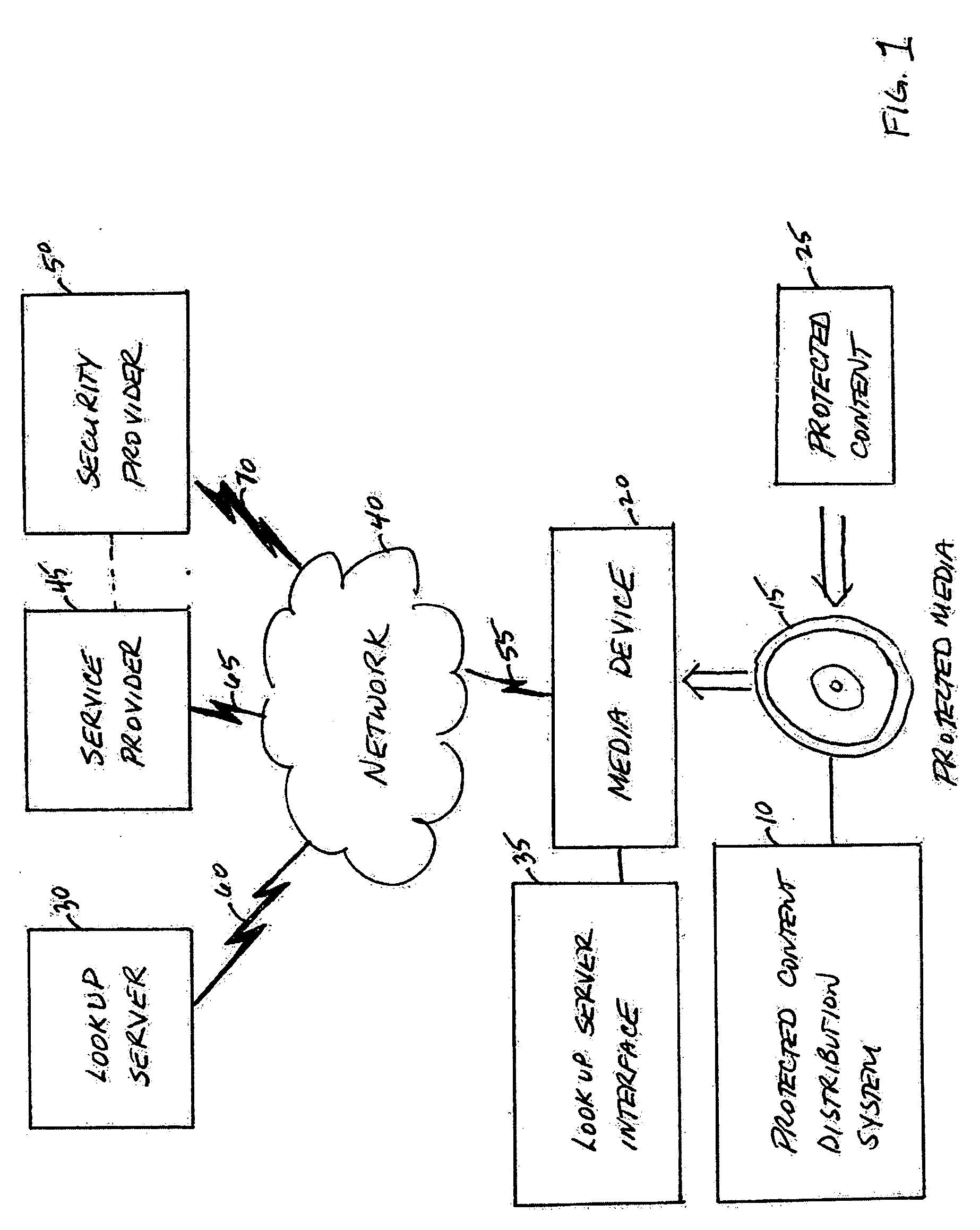
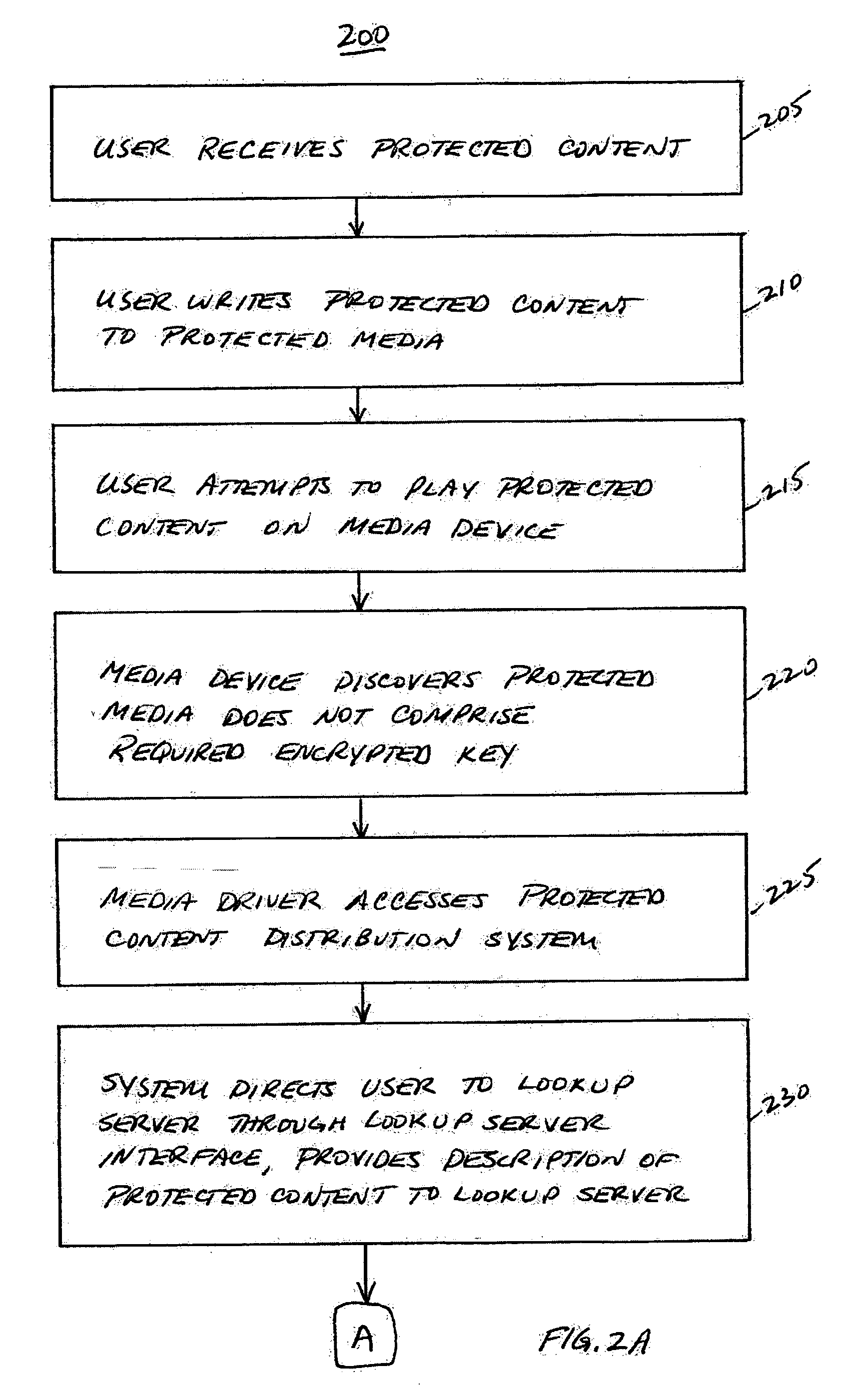
System, service, and method for enabling authorized use of distributed content on a protected media
InactiveUS20060200865A1Avoid playingEliminate needDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationContent distributionCopy protection
A protected content distribution system utilizes media-based copy protection to support online distribution of protected content in a secure and legitimate fashion. Using a media-based copy protection scheme based on broadcast encryption, the protected content distribution system realizes online distribution of protected content such as, for example audio files, movies, etc, authorizing consumption of unlicensed content by transfer of a unique encrypted key to the protected media. This transaction is fast, involving the transfer of an encrypted binding key rather than the protected content. Content is enabled through a unique encrypted key on protected media accessed through a device separate from the media driver.
Owner:IBM CORP
Event-recorder for transmitting and storing electronic signature data
InactiveUS6737954B2Data processing applicationsRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesTamper resistanceRadar
An electronic event recorder for attachment to a vehicle is provided which can broadcast encrypted signature and data, thereby leaving behind an electronic version of a "fingerprint" in the event of an accident or traffic violation. The fingerprint, captured by an external data acquisition system or another vehicle so equipped, provides a history of events related to the vehicle. The event recorder is preferably integrated on a smart card and housed in a tamper proof casing. In a first mode of operation, monitoring stations along the roadways periodically send an interrogation signal, such as when radar detects that the vehicle is speeding. Upon receiving the interrogation signal the smart card transmits the vehicle's signature information to the monitoring station where it is time and date stamped along with the speed of the vehicle. In a second mode of operation, when a sensor detects a sudden or violent acceleration or deceleration, such as occurs during a collision, a smart card mounted in each car will exchange signature information automatically. This is particularly useful when the collision occurs in a parking lot when one of the hit vehicles is typically unattended.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
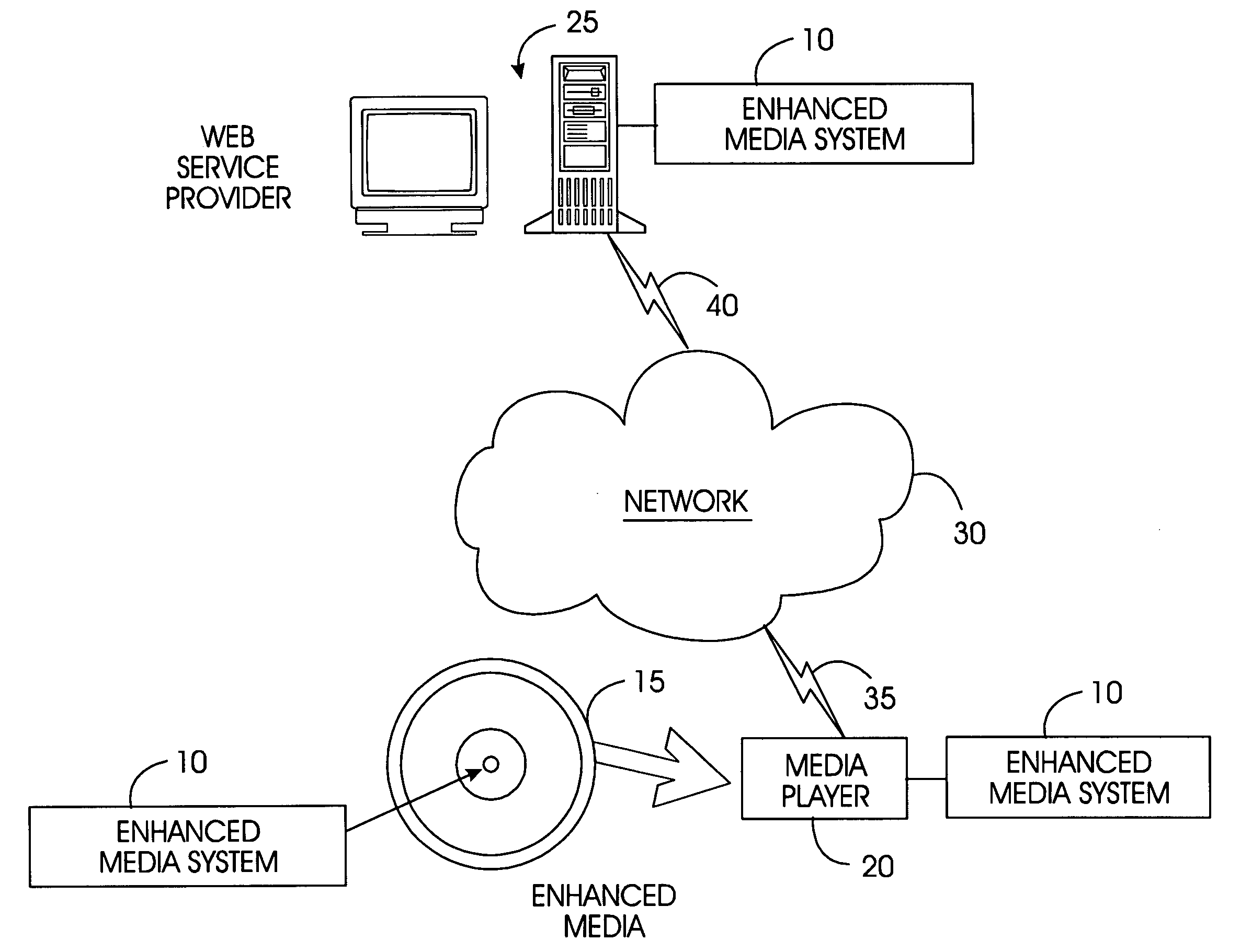
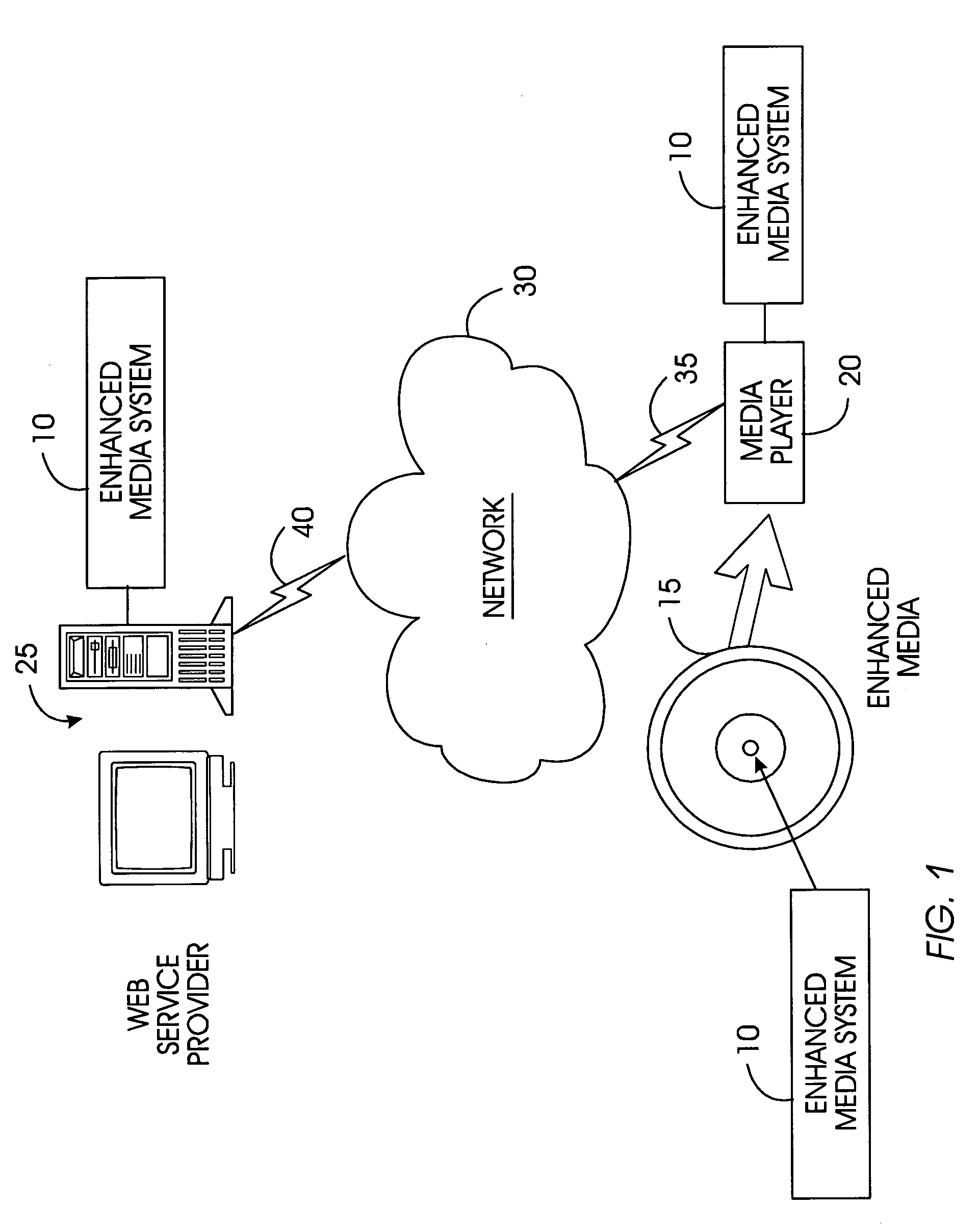
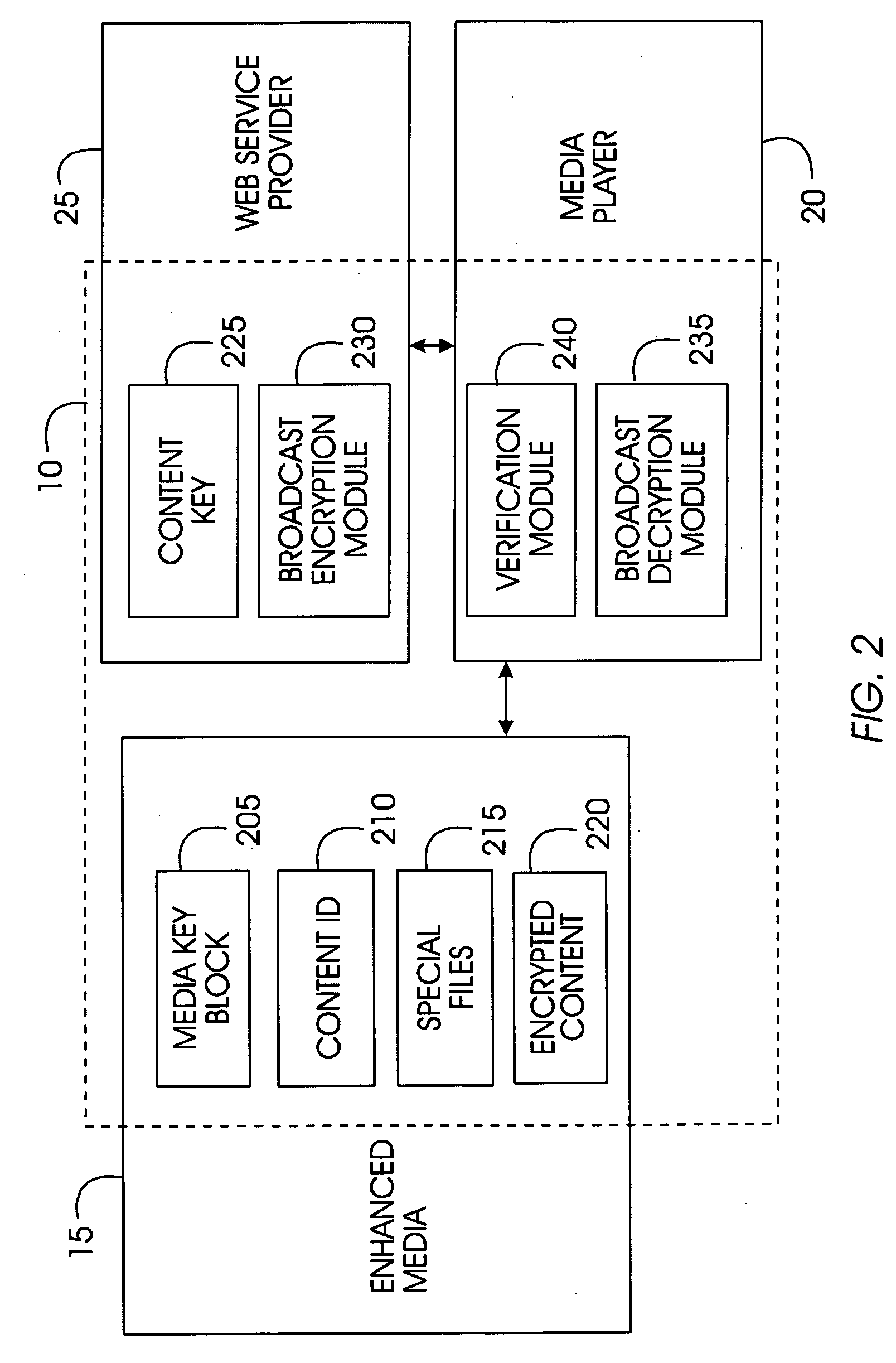
System, method, and service for delivering enhanced multimedia content on physical media
InactiveUS20050111663A1Control productionCombating fraudKey distribution for secure communicationRecord information storageThe InternetUniform resource locator
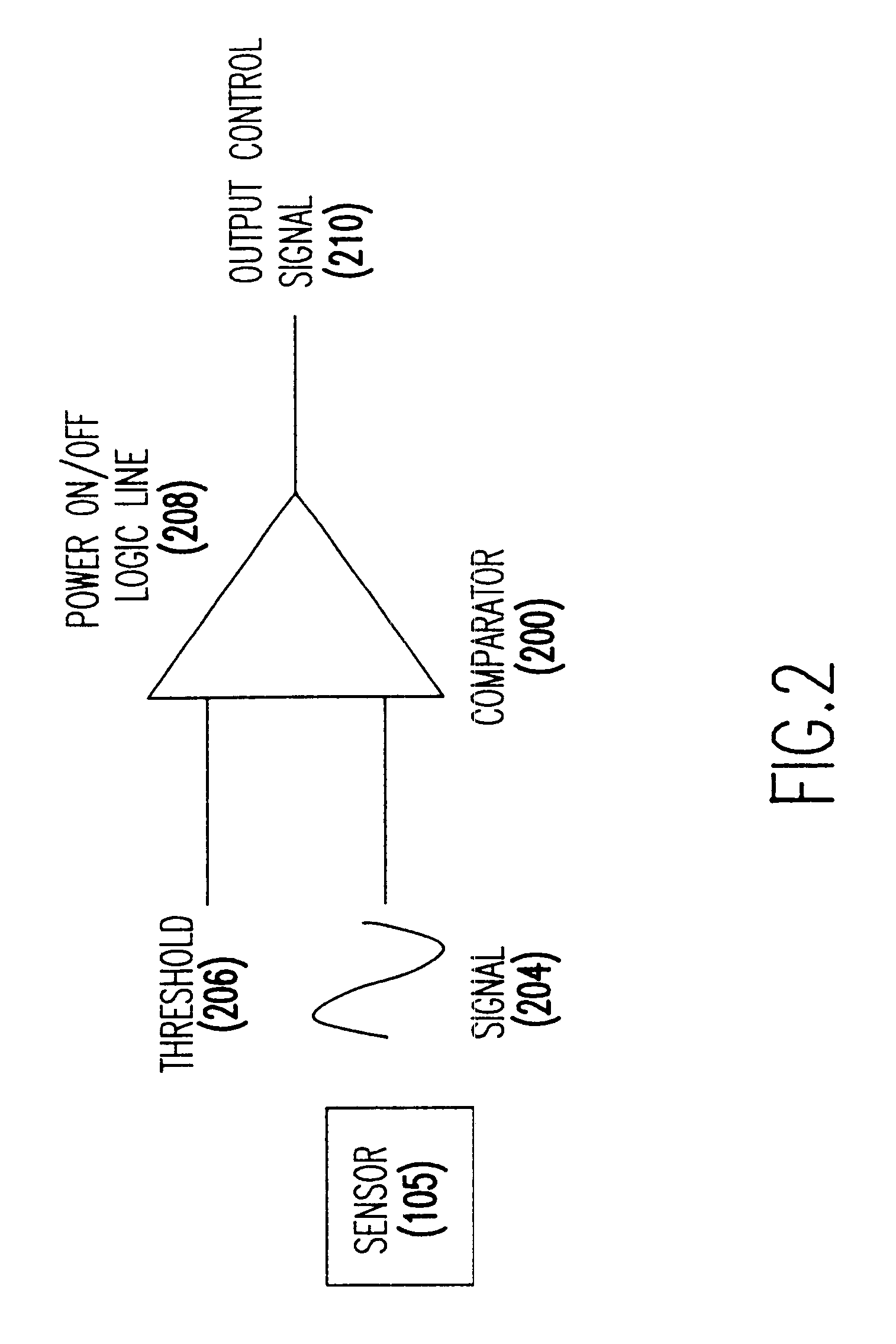
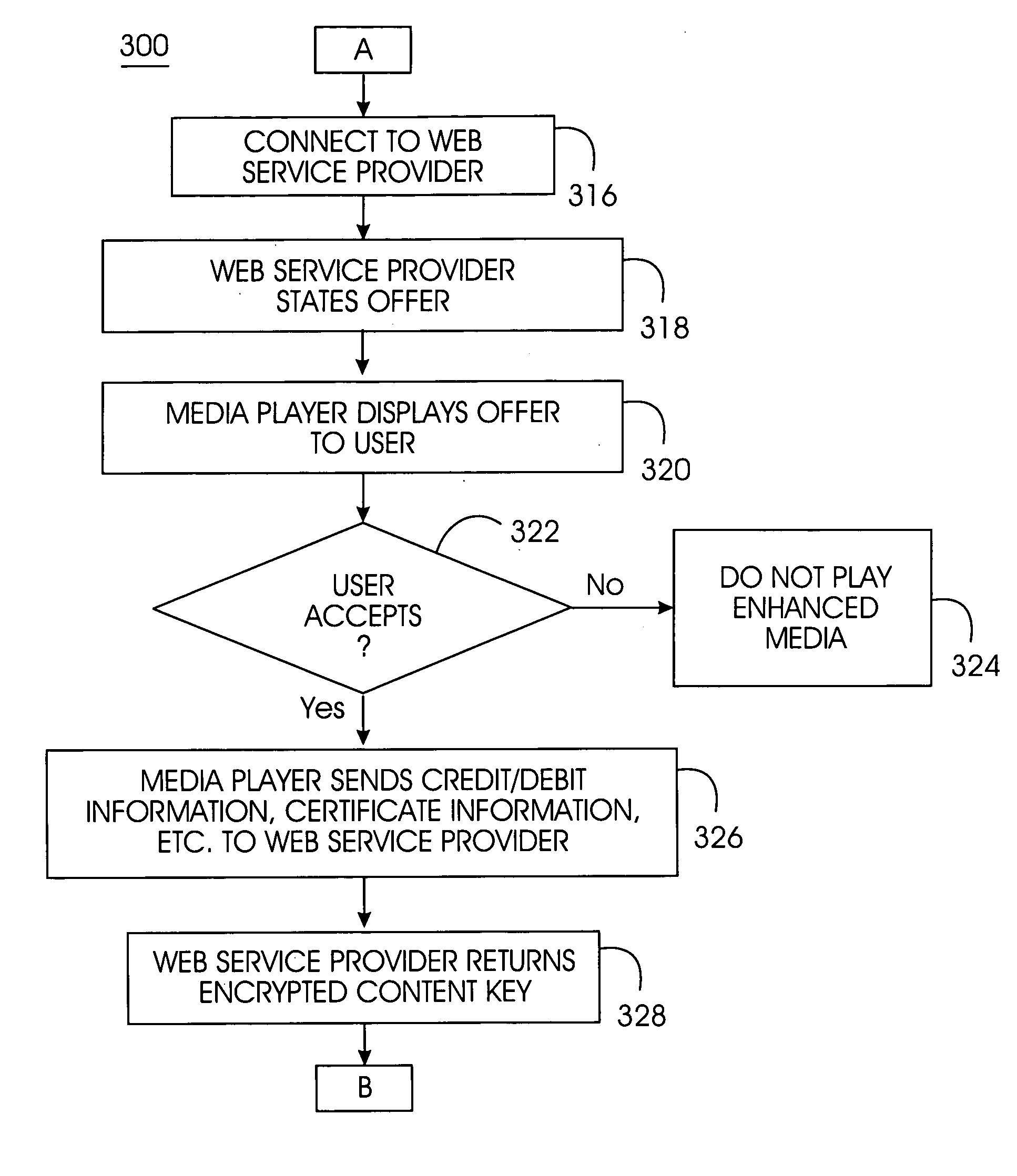
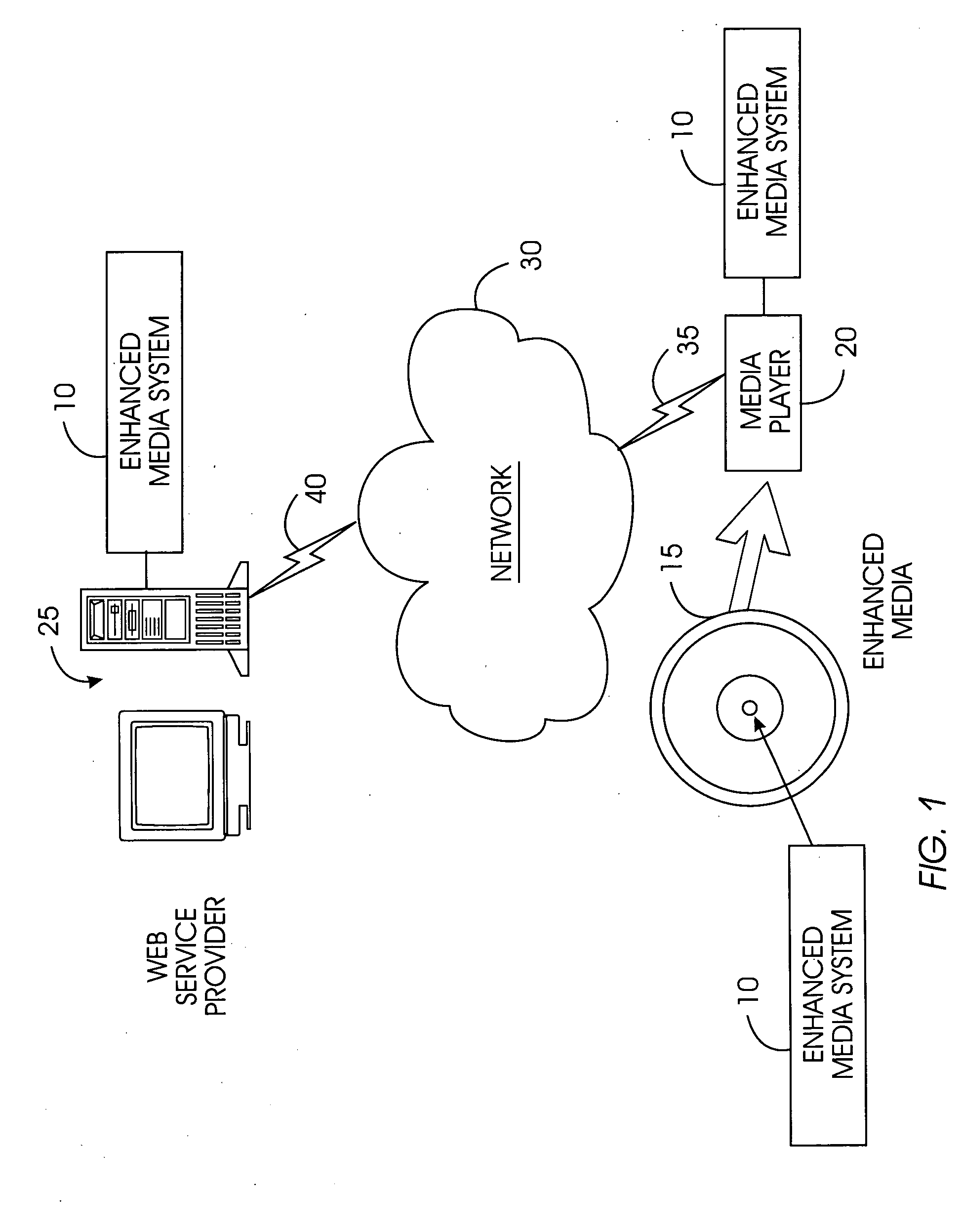
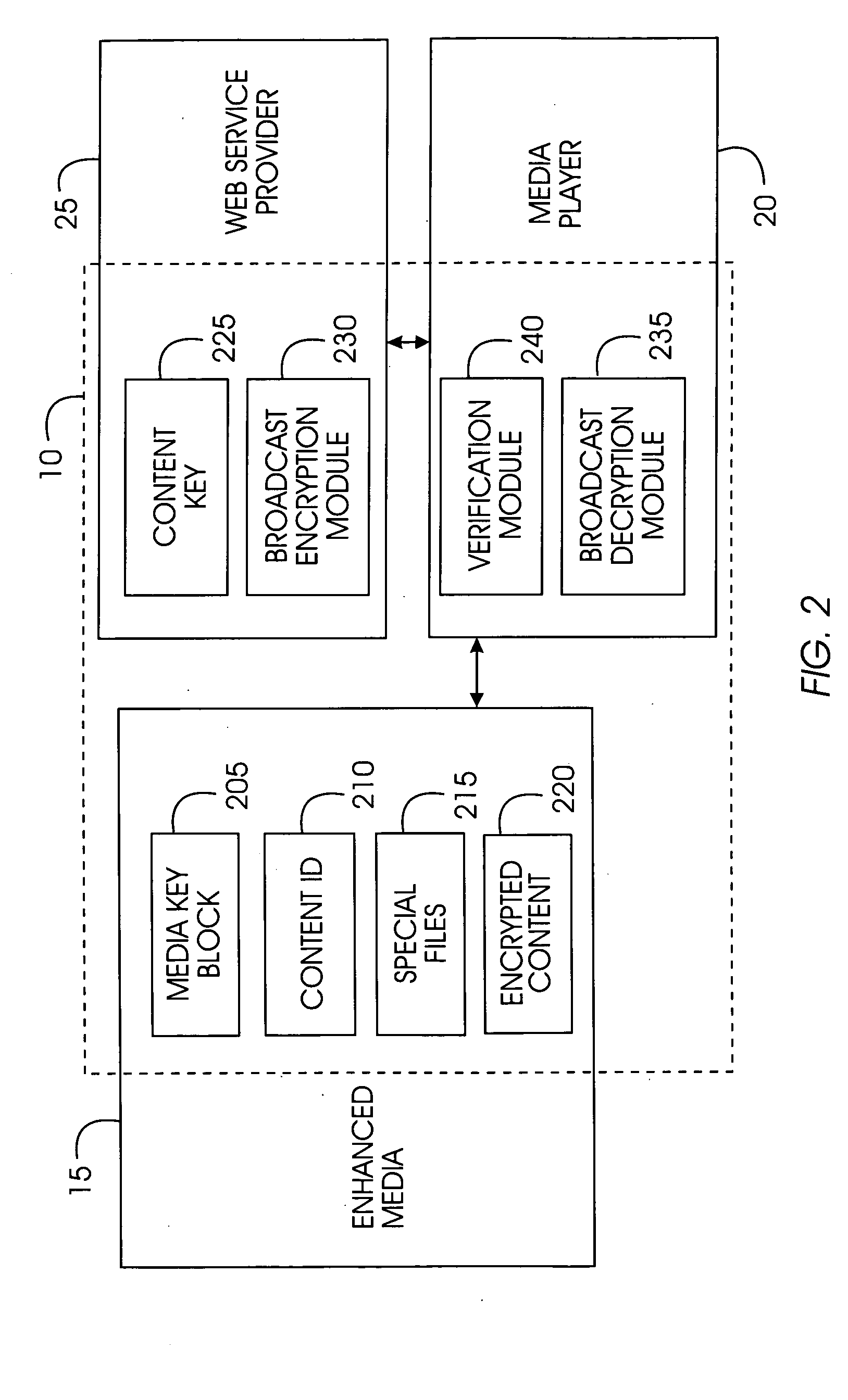
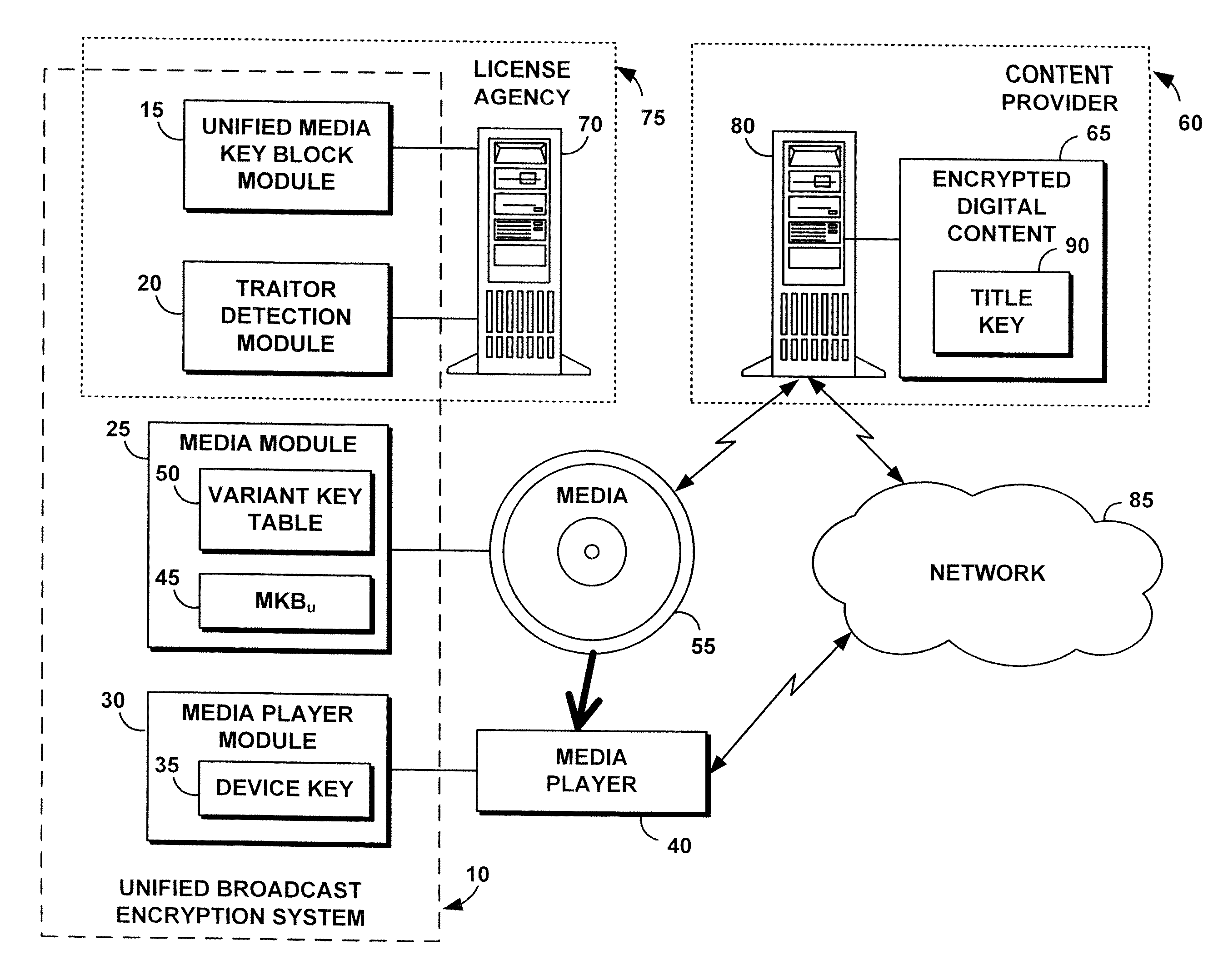
Enhanced multimedia content on physical media interacts with the user through a media player and the Internet. Enhanced multimedia utilizes IDs for pieces of content on the media and a media key block. On the enhanced media is a file with a list of URLs. As the enhanced media plays a section requiring a set of keys for decryption, the media player accesses the URL for that section and obtains the decryption key. The decryption key may be purchased or provided for free. Secure encryption and transmission of these keys is accomplished by broadcast encryption using a media key block. Each media has a unique set of keys that allow the media player to process the media key block; however, each media follows a unique path through the media key block. All legitimate media players obtain the media key; circumvention devices cannot decipher the media key block.
Owner:IBM CORP
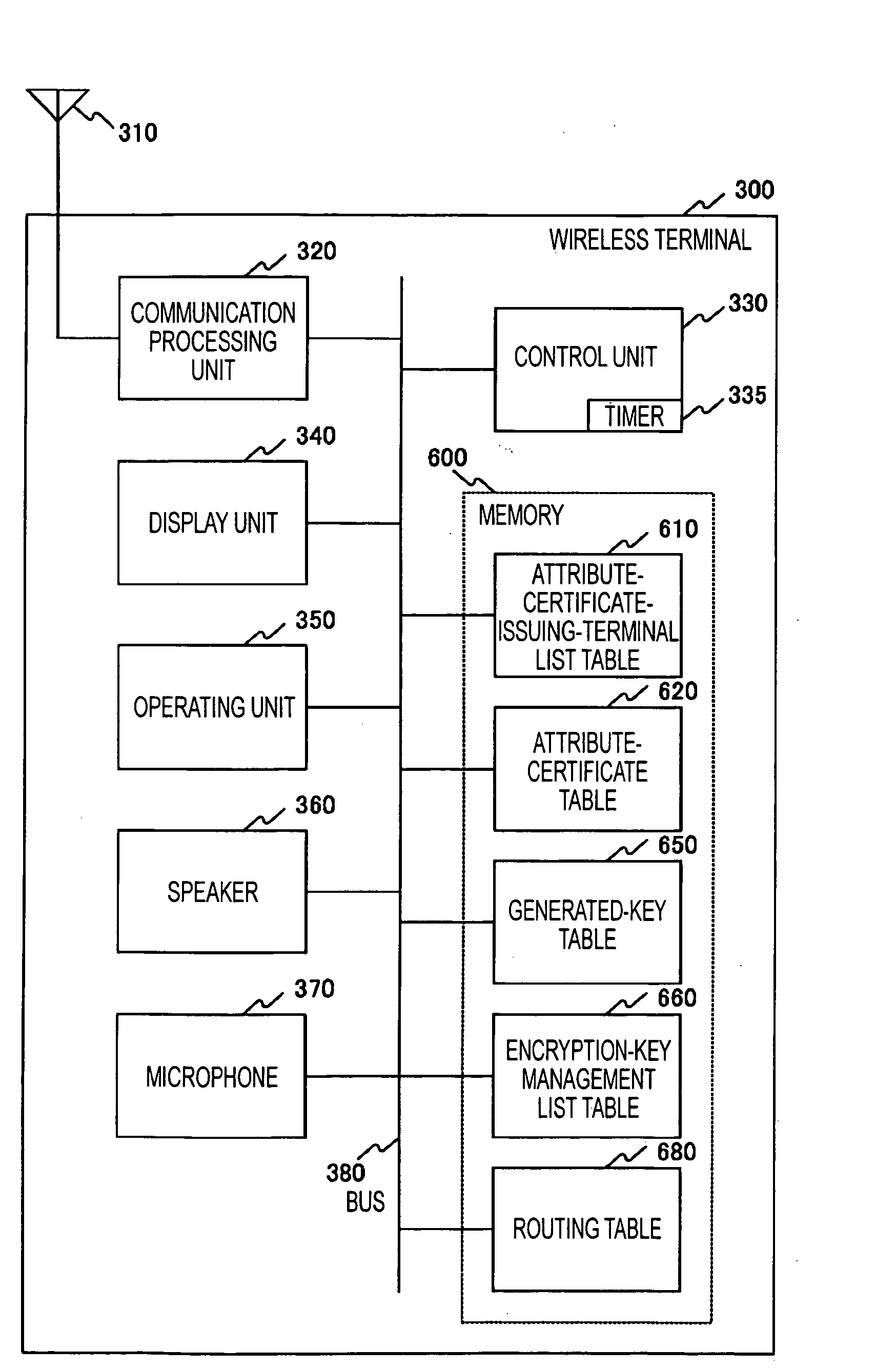
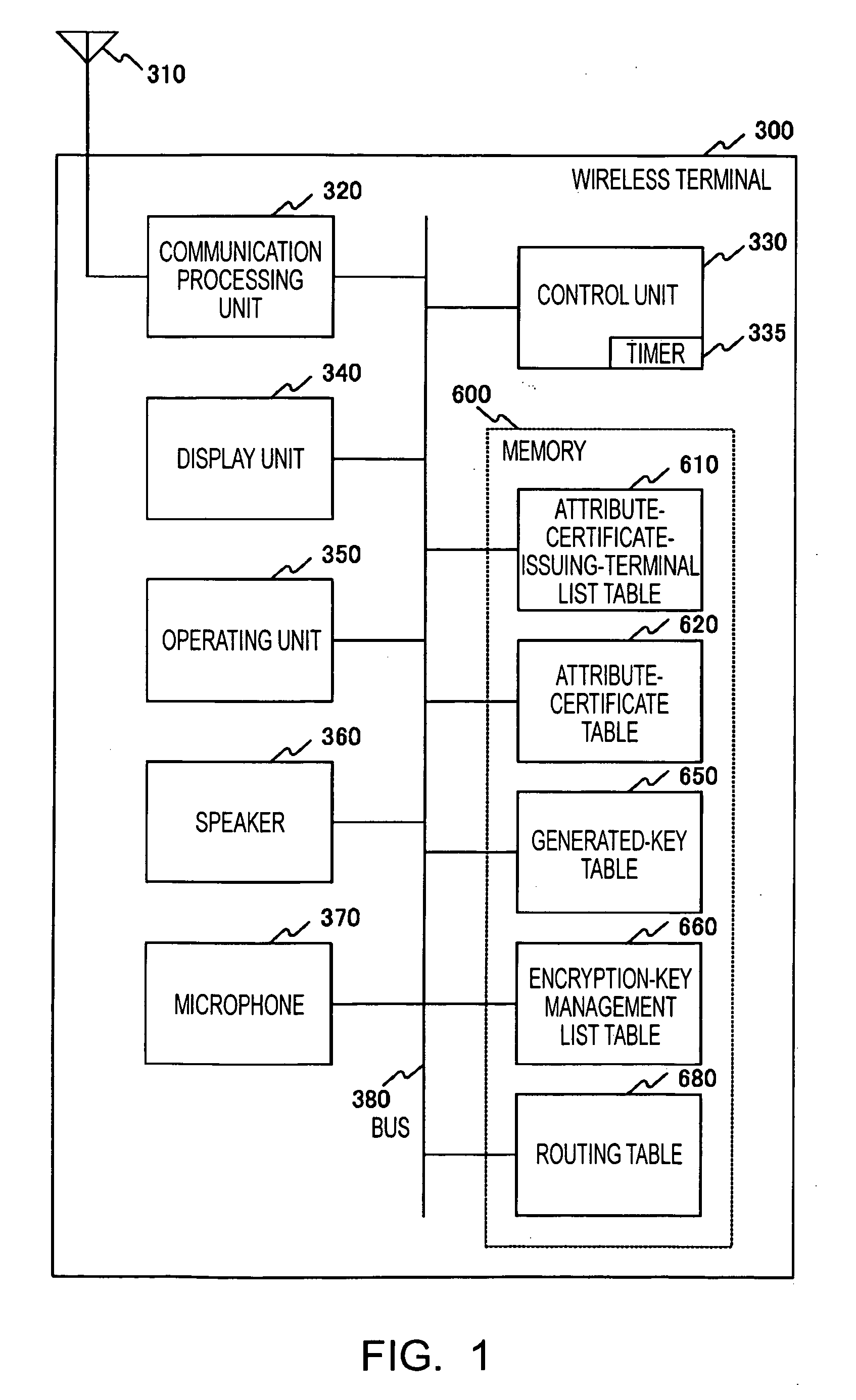
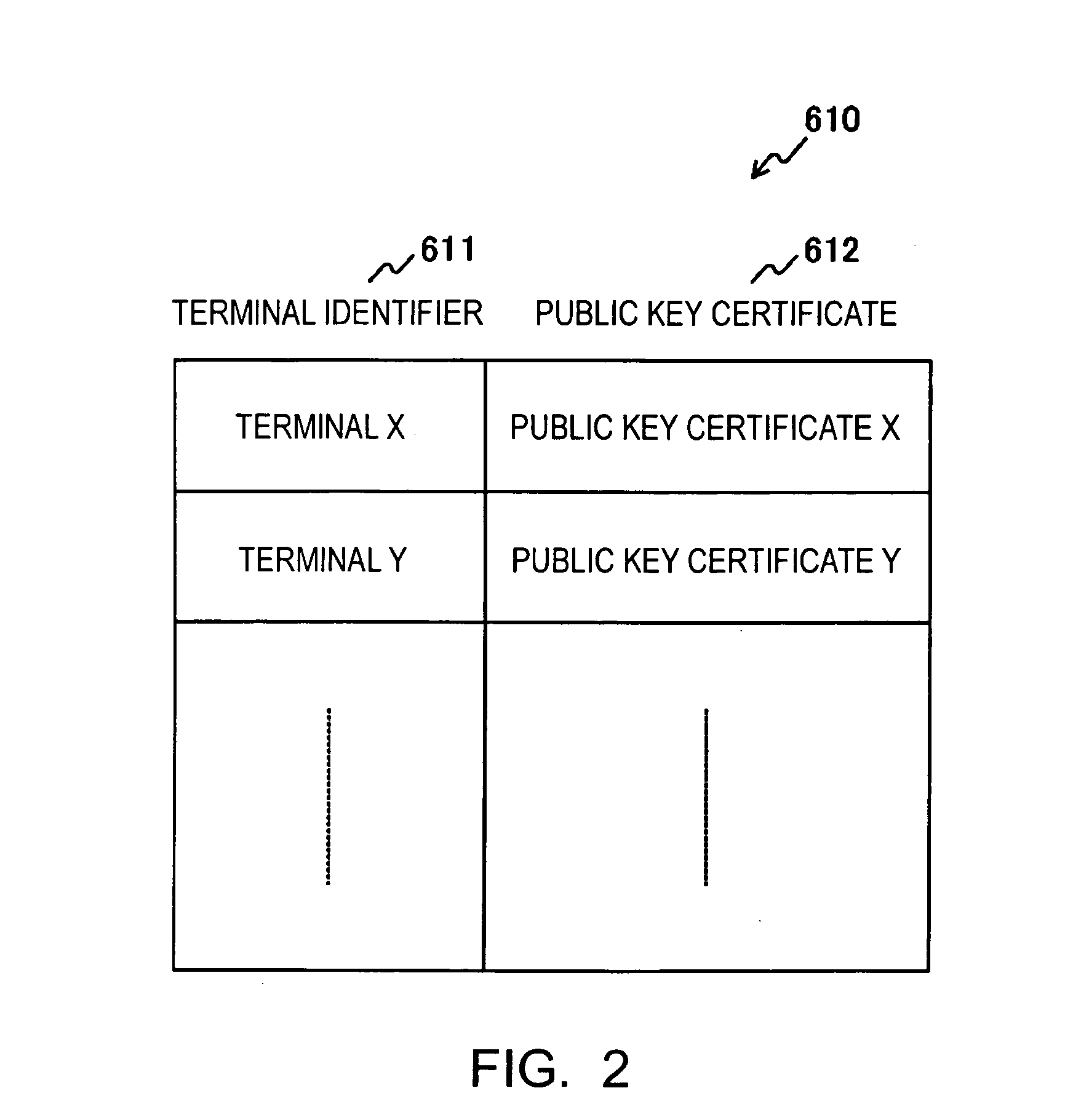
Broadcast encryption key distribution system
ActiveUS20050123141A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationKey distributionBroadcasting
Each terminal in a wireless ad-hoc communication system includes an encryption-key management list table 660. The encryption-key management list table 660 stores, in association with a terminal identifier 661 such as a MAC address, a unicast encryption key 662 for use in unicast communication with a terminal identified by the terminal identifier 661, and a broadcast encryption key 663 used when the terminal identified by the terminal identifier 661 performs broadcast communication. Therefore, a broadcast encryption key is provided for each terminal that performs broadcast communication, and the broadcast encryption keys are managed by the individual terminals in an independent and distributed manner. This allows independent and distributed management of broadcast encryption keys in a wireless ad-hoc communication system.
Owner:SONY CORP
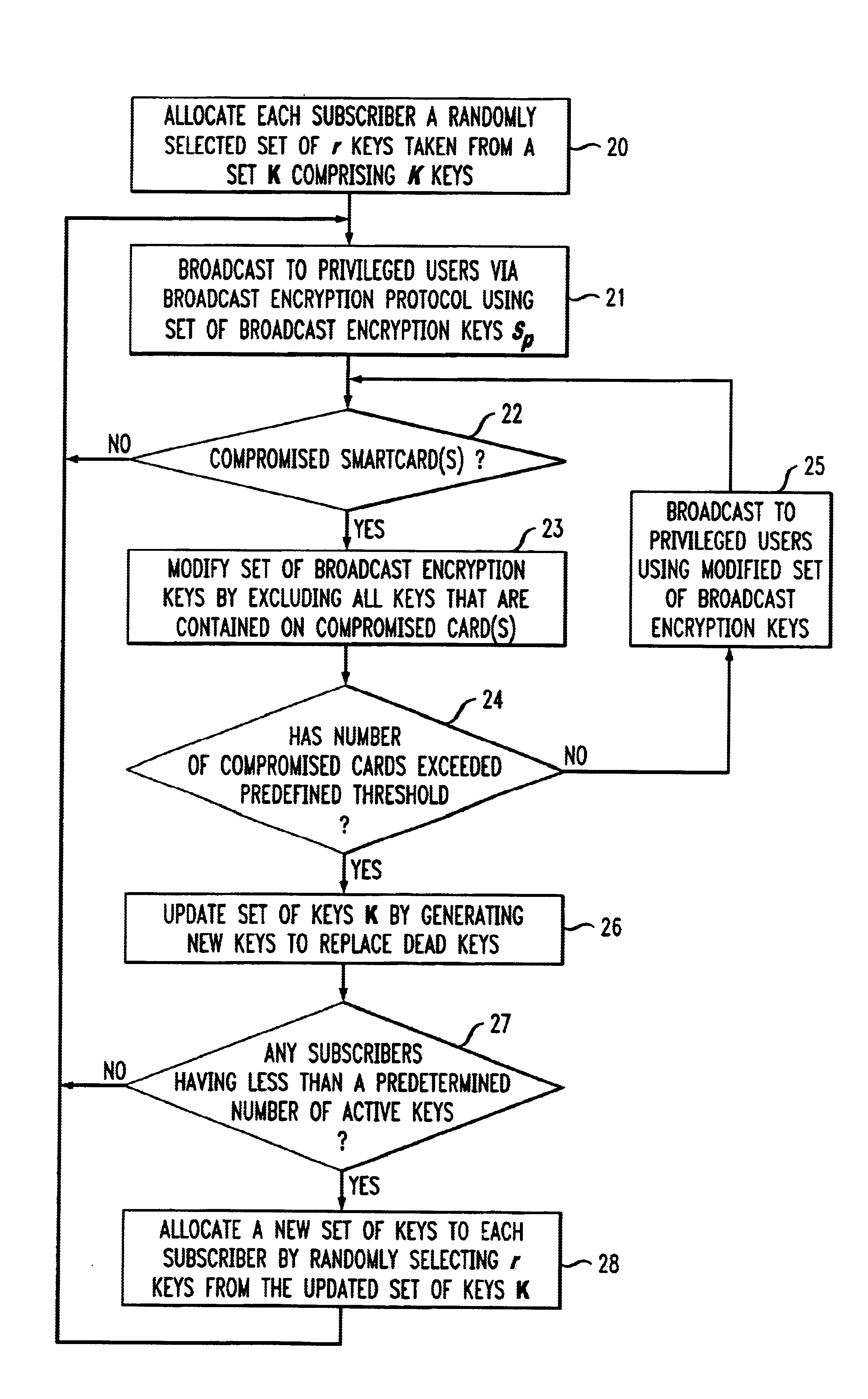
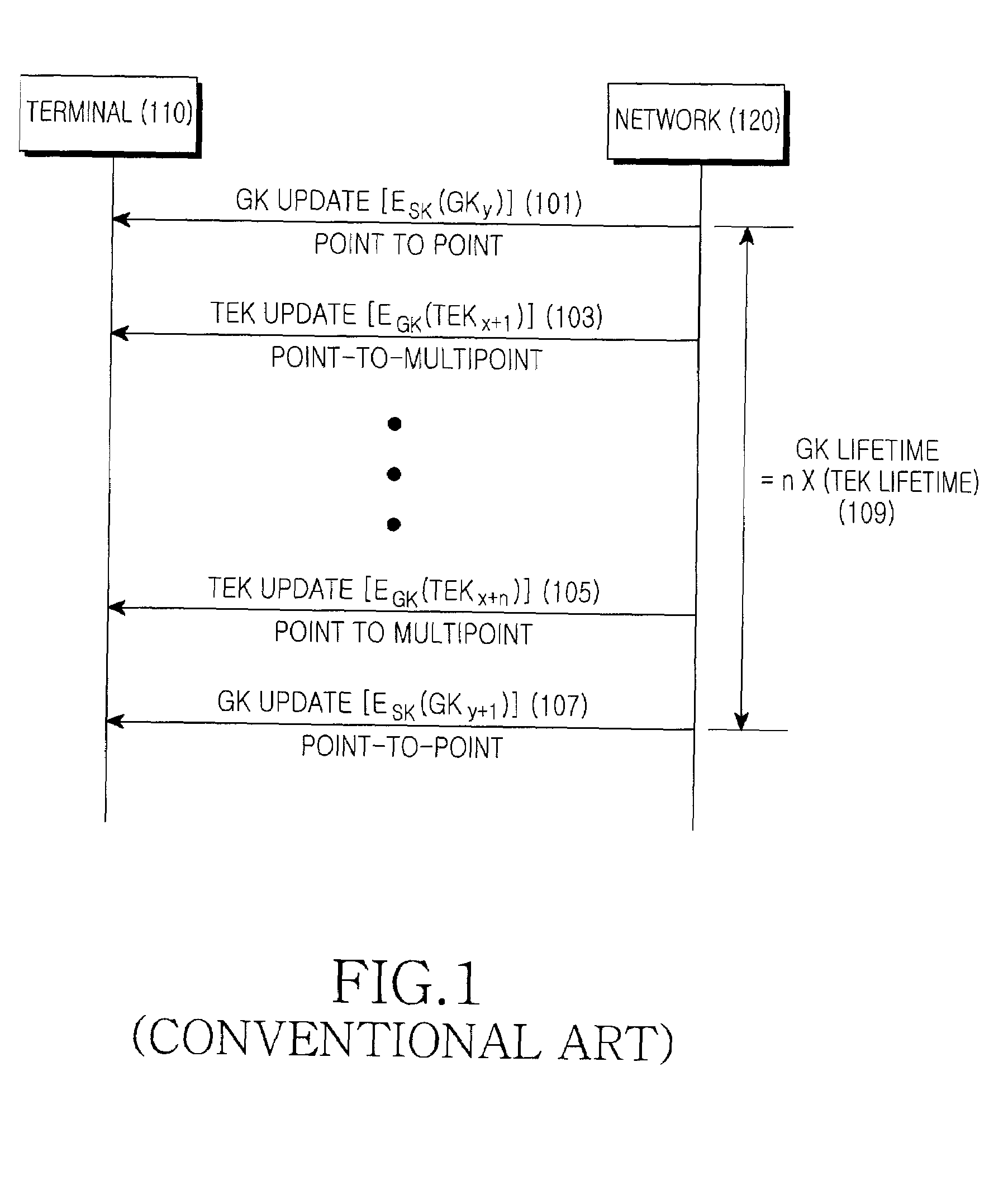
Method for providing long-lived broadcast encrypton
InactiveUS6839436B1Increase probabilityEnsure the needKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationBroadcastingPositive fraction
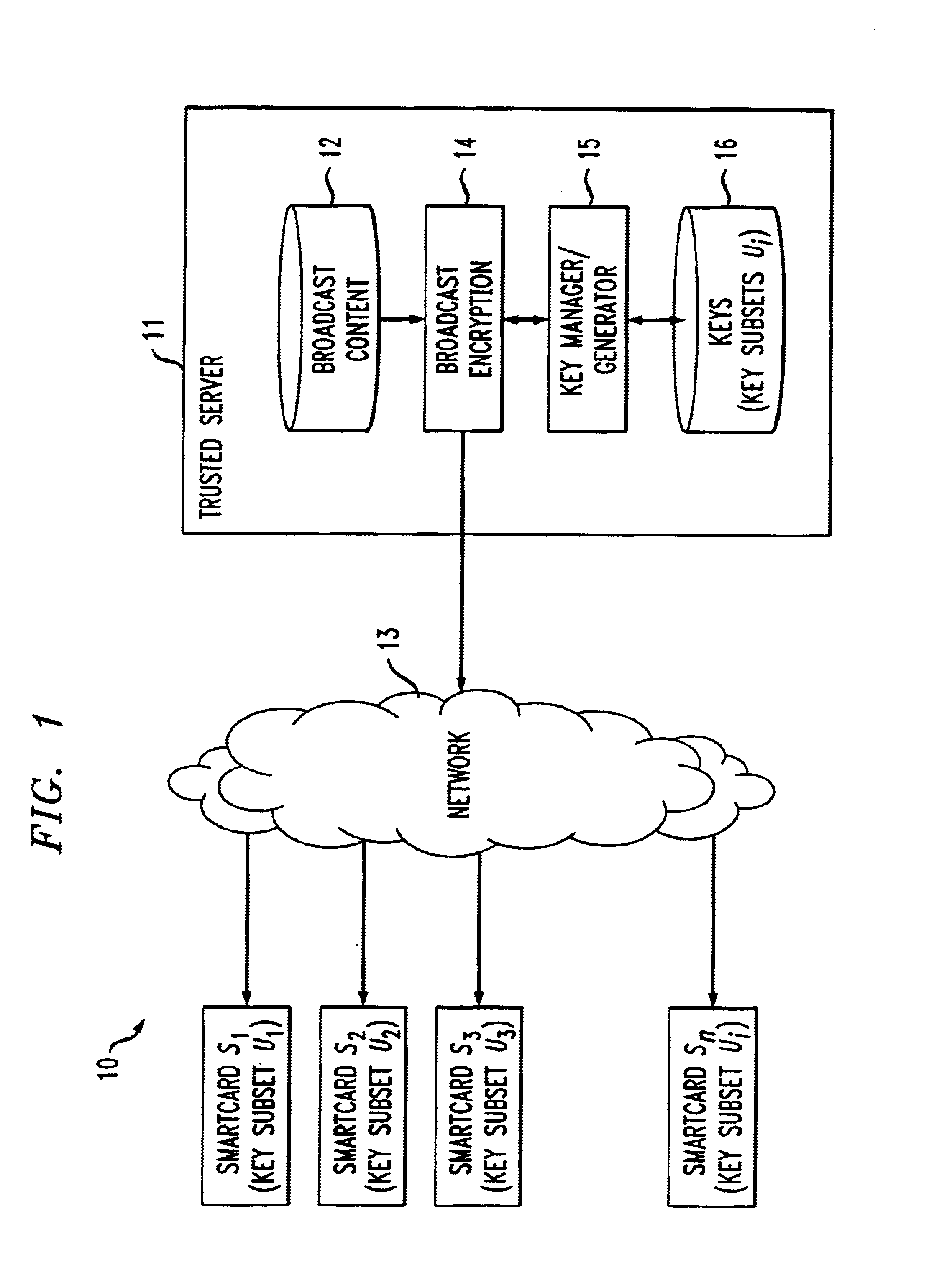
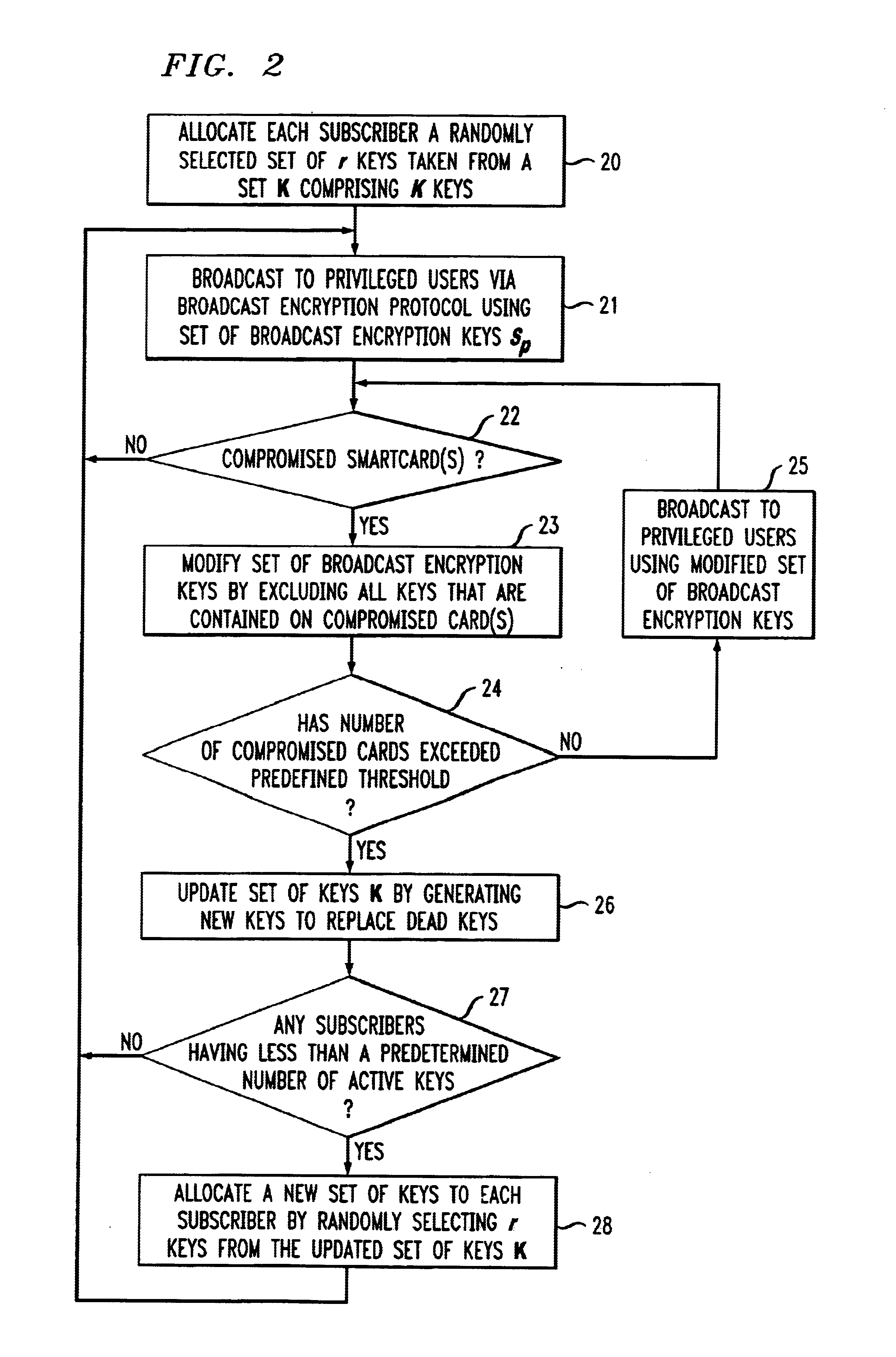
A long-lived broadcast encryption method that adapts to the presence of compromised keys and continues to broadcast securely to privileged sets of users over time. In one aspect, a method for providing long-lived broadcast encryption comprises the steps of: allocating, to each of a plurality of subscribers, a corresponding set of subscriber keys; broadcasting encrypted content to the plurality of subscribers using a set of broadcast keys, wherein the encrypted content is decoded by a given subscriber using the subscriber's corresponding set of subscriber keys; modifying the set of broadcast keys, which are used for broadcasting encrypted content, by excluding compromised subscriber keys; and updating a set of subscriber keys corresponding to at least one subscriber when the at least one subscriber's set of subscriber keys comprises an amount of active keys that falls below a first predetermined threshold. In a long-lived broadcast encryption scheme, for any positive fraction β, a plurality of parameter values may be selected, a priori, in such a way to ensure that a steady state is achieved wherein, at most β of the total number of issued cards need to be replaced in a given recarding session.
Owner:GEMPLU
Efficient Privacy-Preserving Ciphertext-Policy Attribute Based Encryption and Broadcast Encryption
InactiveUS20160241399A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationCommunications systemAttribute-based encryption
A new construction of CP-ABE, named Privacy Preserving Constant CP-ABE (PPC-CP-ABE) that significantly reduces the ciphertext to a constant size with any given number of attributes is disclosed. PPCCP-ABE leverages a hidden policy construction such that the recipients' privacy is preserved efficiently. A Privacy Preserving Attribute Based Broadcast Encryption (PP-AB-BE) scheme is disclosed. PP-AB-BE is flexible because a broadcasted message can be encrypted by an expressive hidden access policy, either with or without explicit specifying the receivers. PP-AB-BE significantly reduces the storage and communication overhead. Also, PP-AB-BE attains minimal bound on storage overhead for each user to cover all possible subgroups in the communication system.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Method for tracing traitor receivers in a broadcast encryption system
InactiveUS7010125B2Key distribution for secure communicationOptical discsCovering systemComputer security
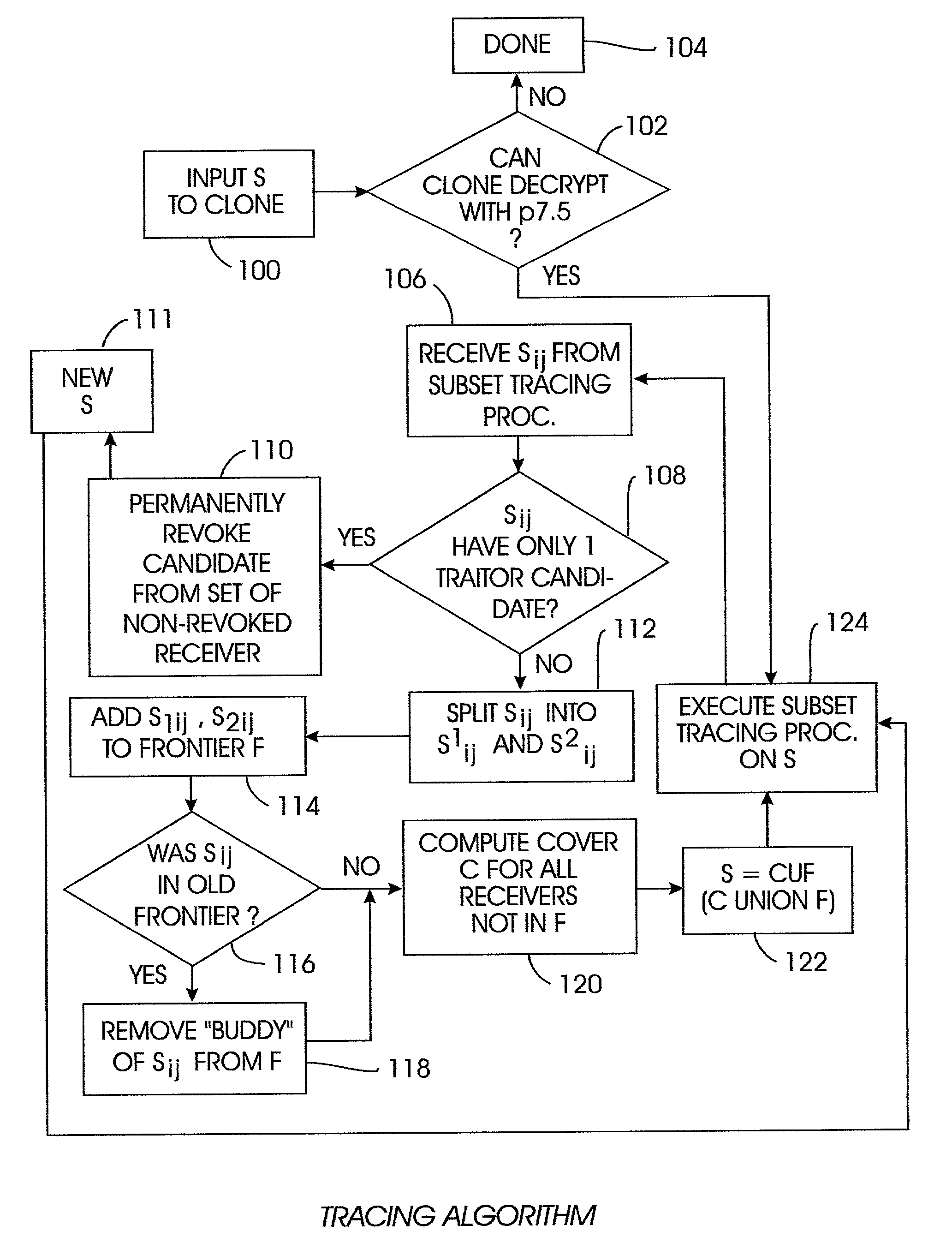
A method for tracing traitor receivers in a broadcast encryption system. The method includes using a false key to encode plural subsets representing receivers in the system. The subsets are derived from a tree using a Subset-Cover system, and the traitor receiver is associated with one or more compromised keys that have been obtained by a potentially cloned pirate receiver. Using a clone of the pirate receiver, the identity of the traitor receiver is determined, or the pirate receiver clones are rendered useless for decrypting data using the compromised key by generating an appropriate set of subsets.
Owner:IBM CORP
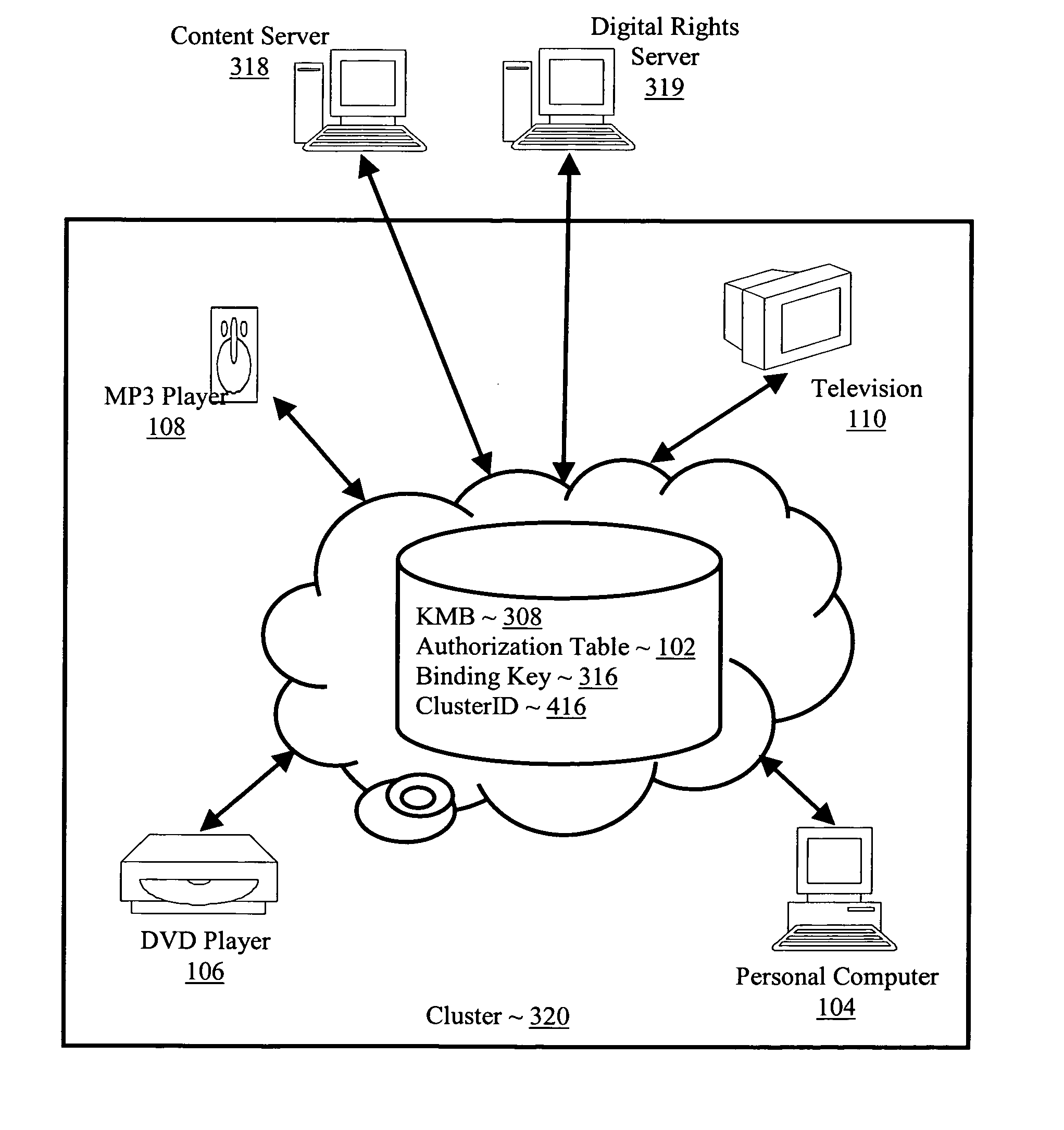
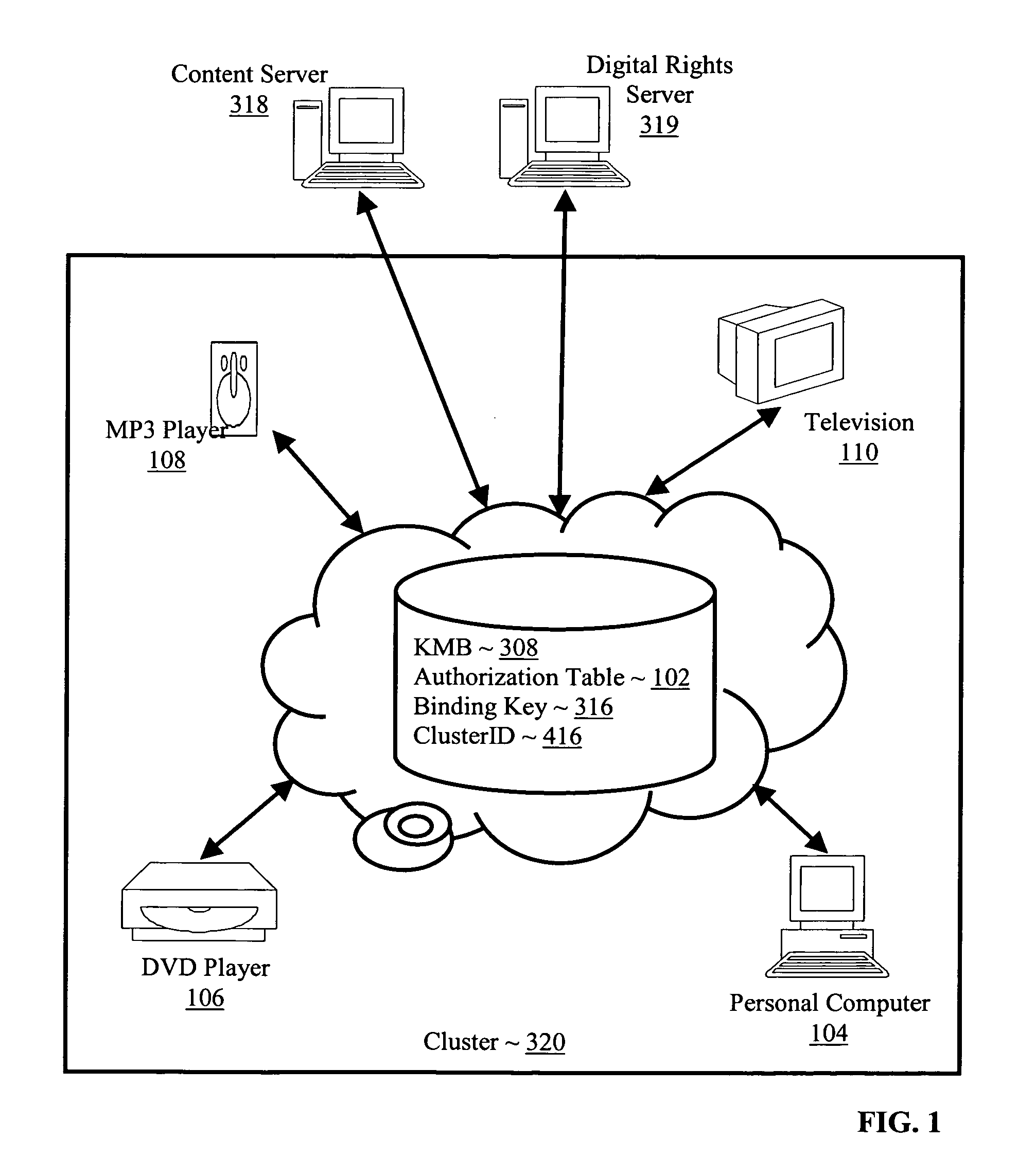
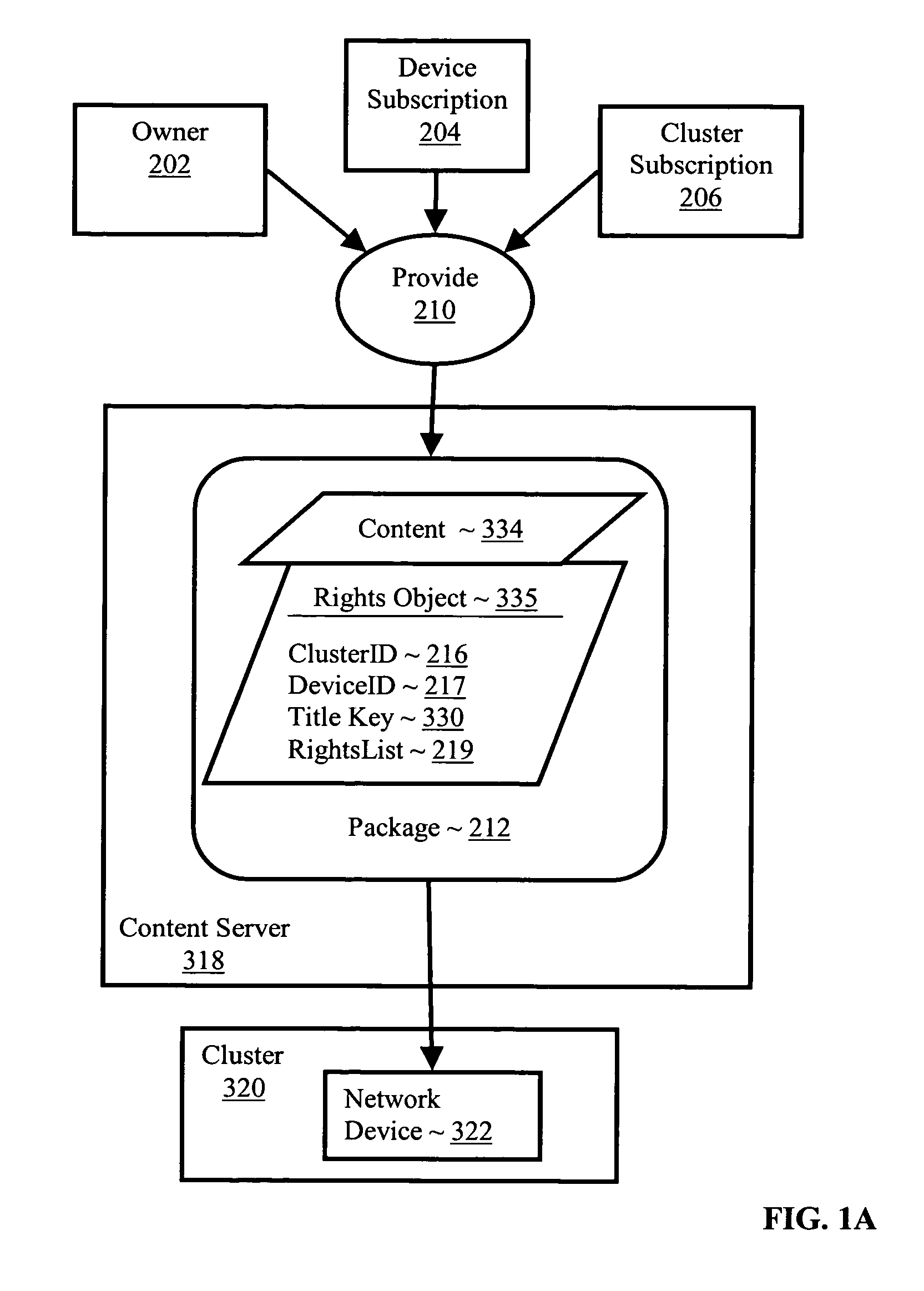
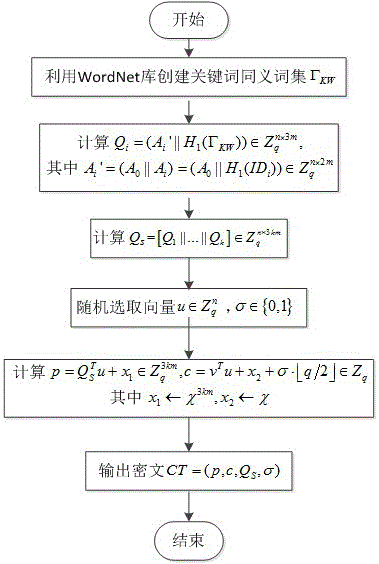
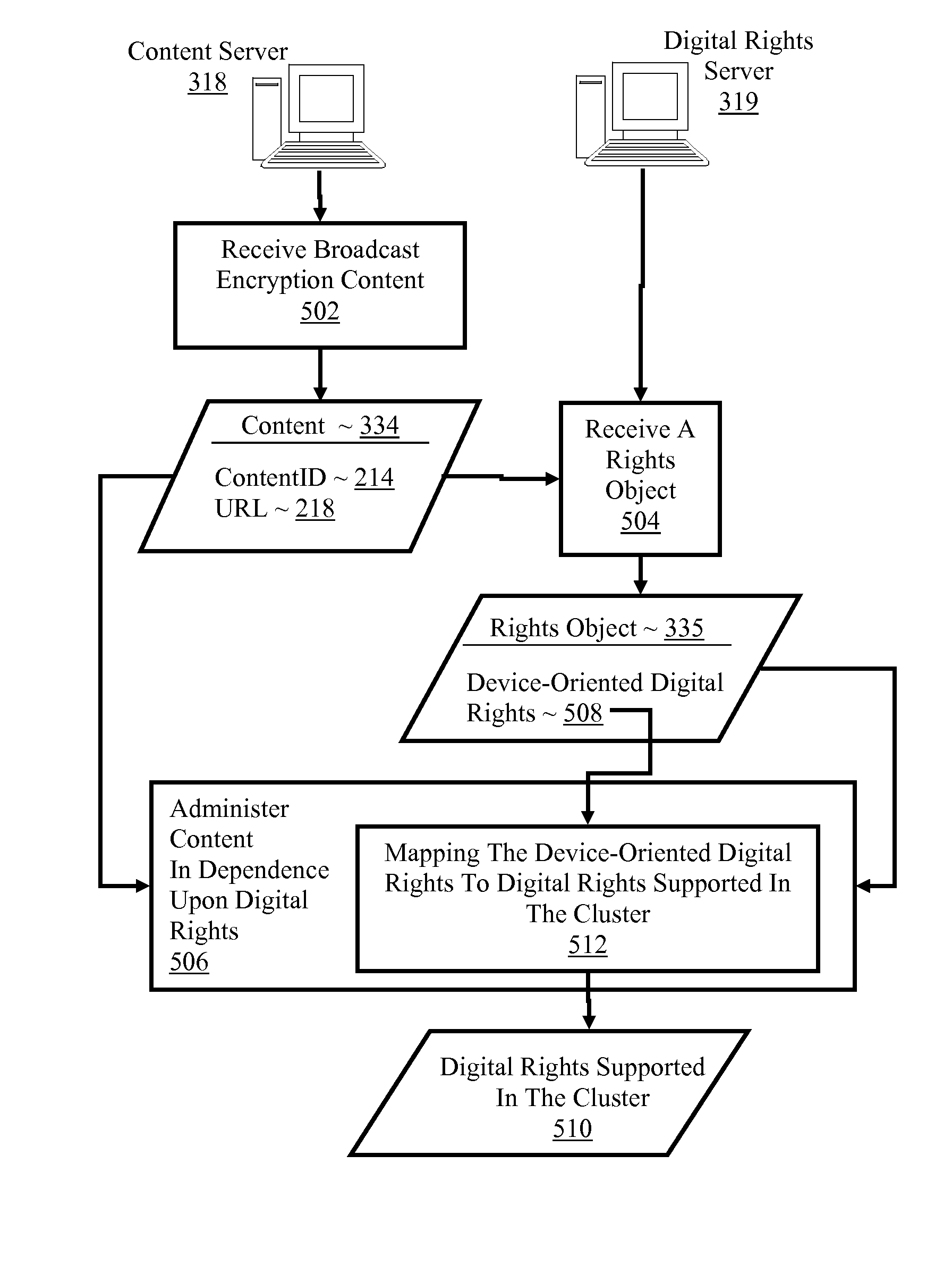
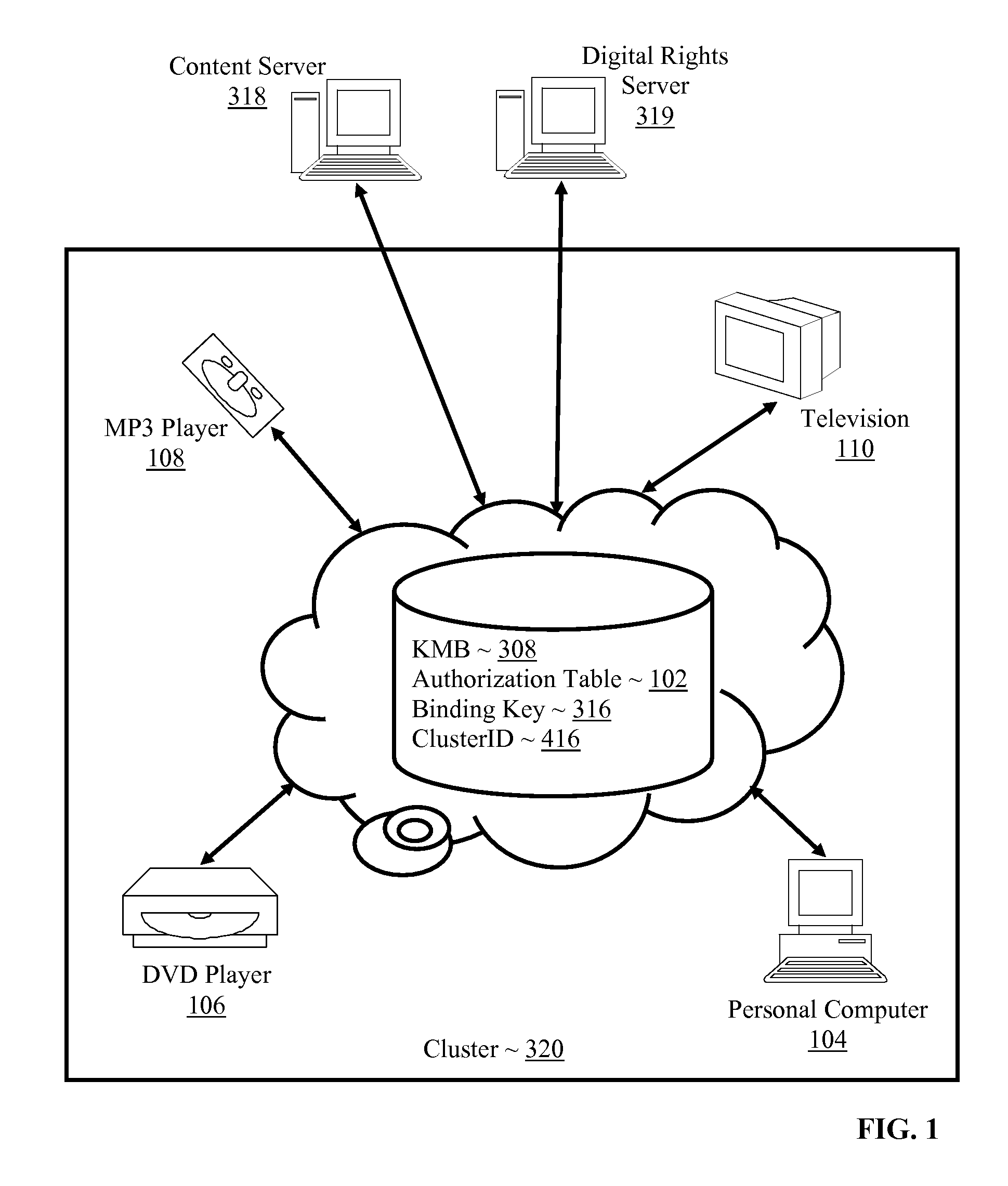
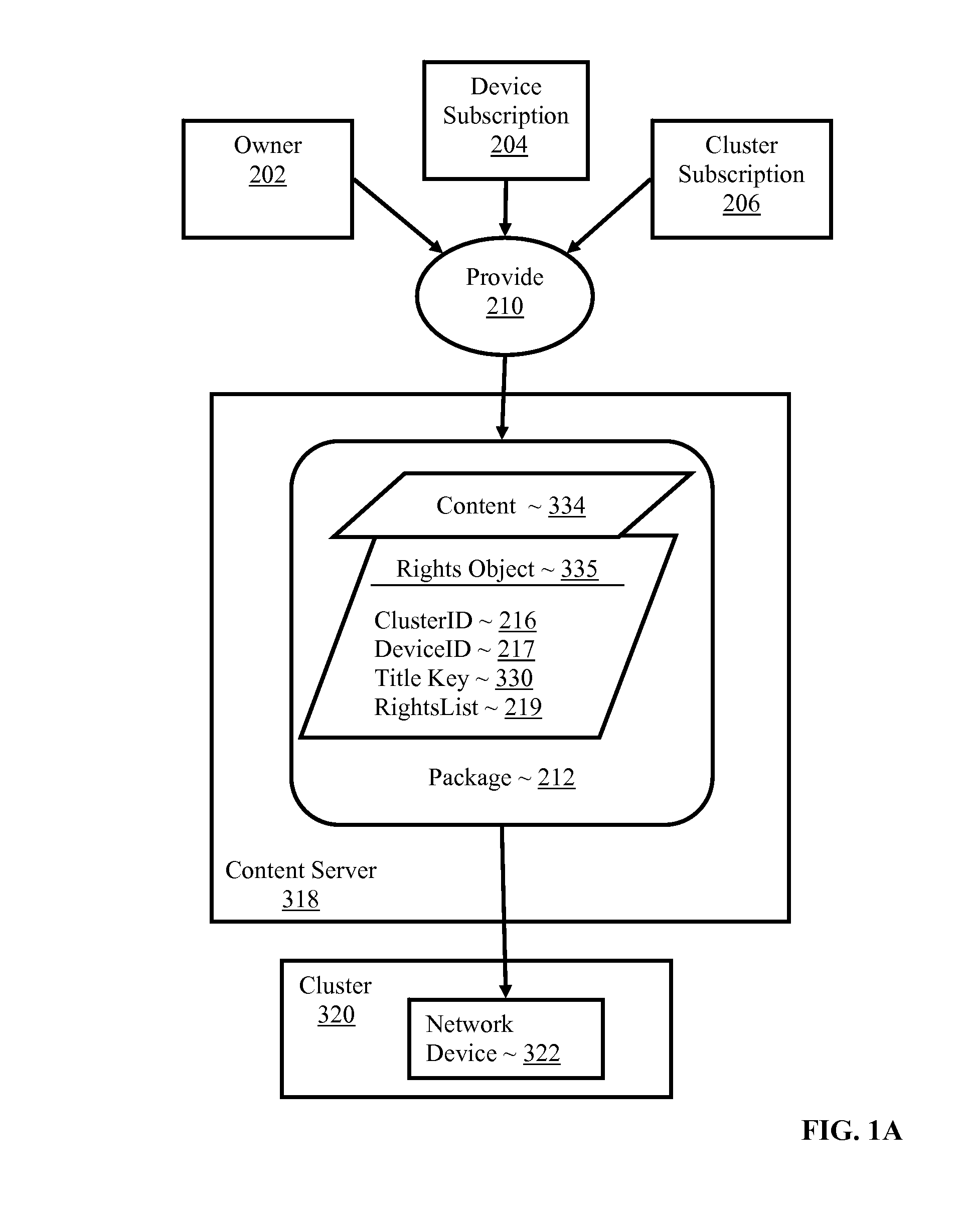
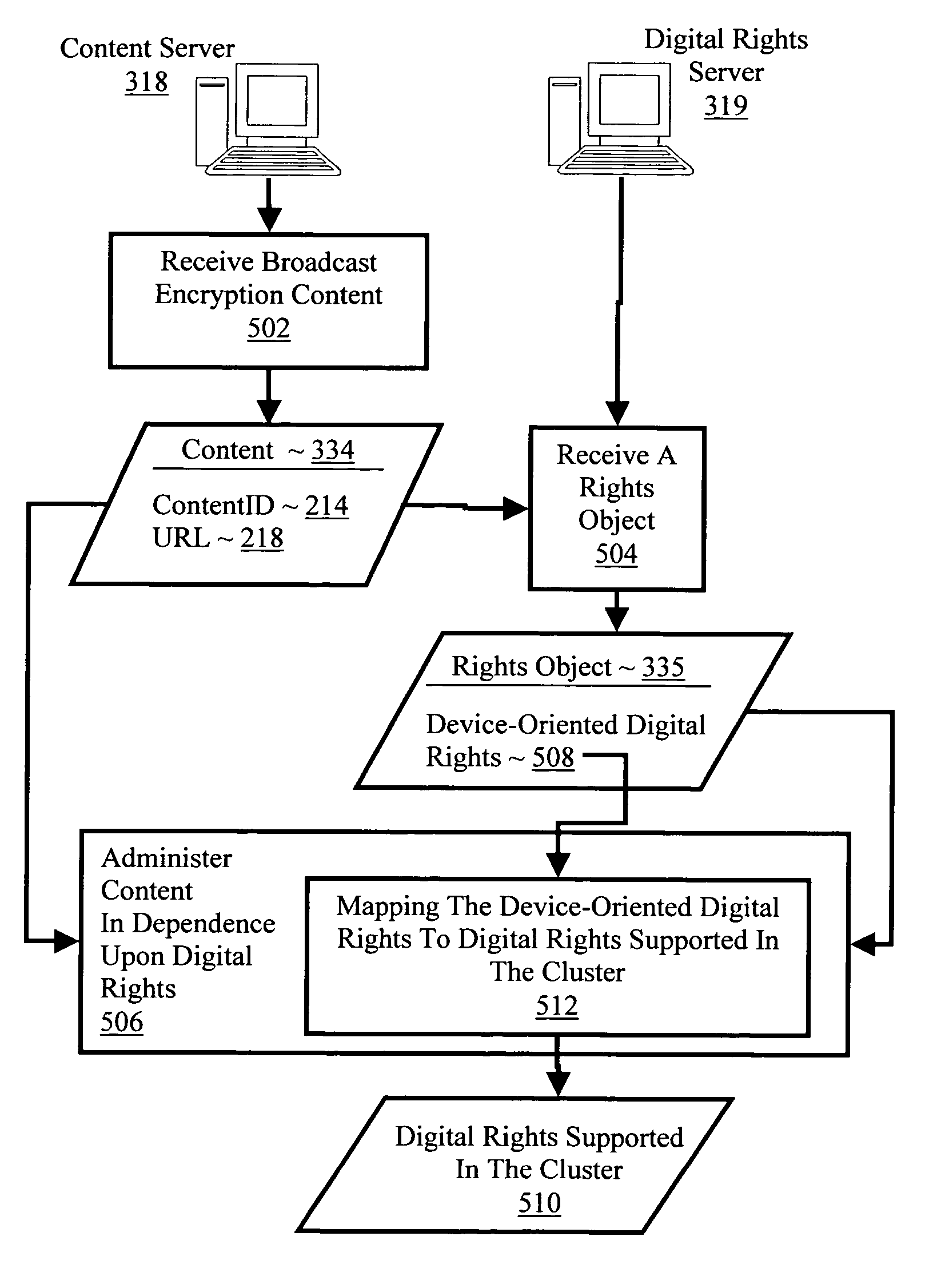
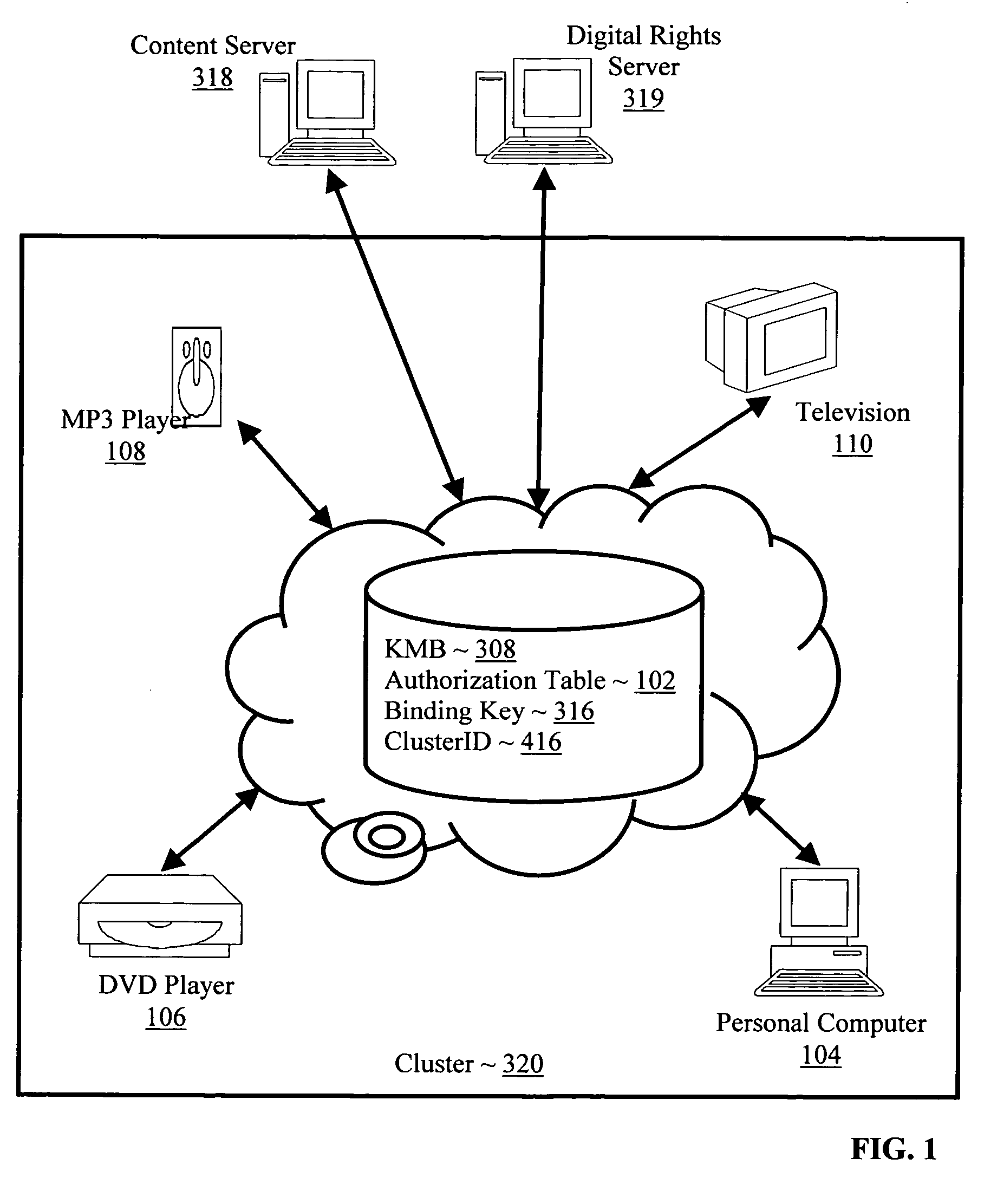
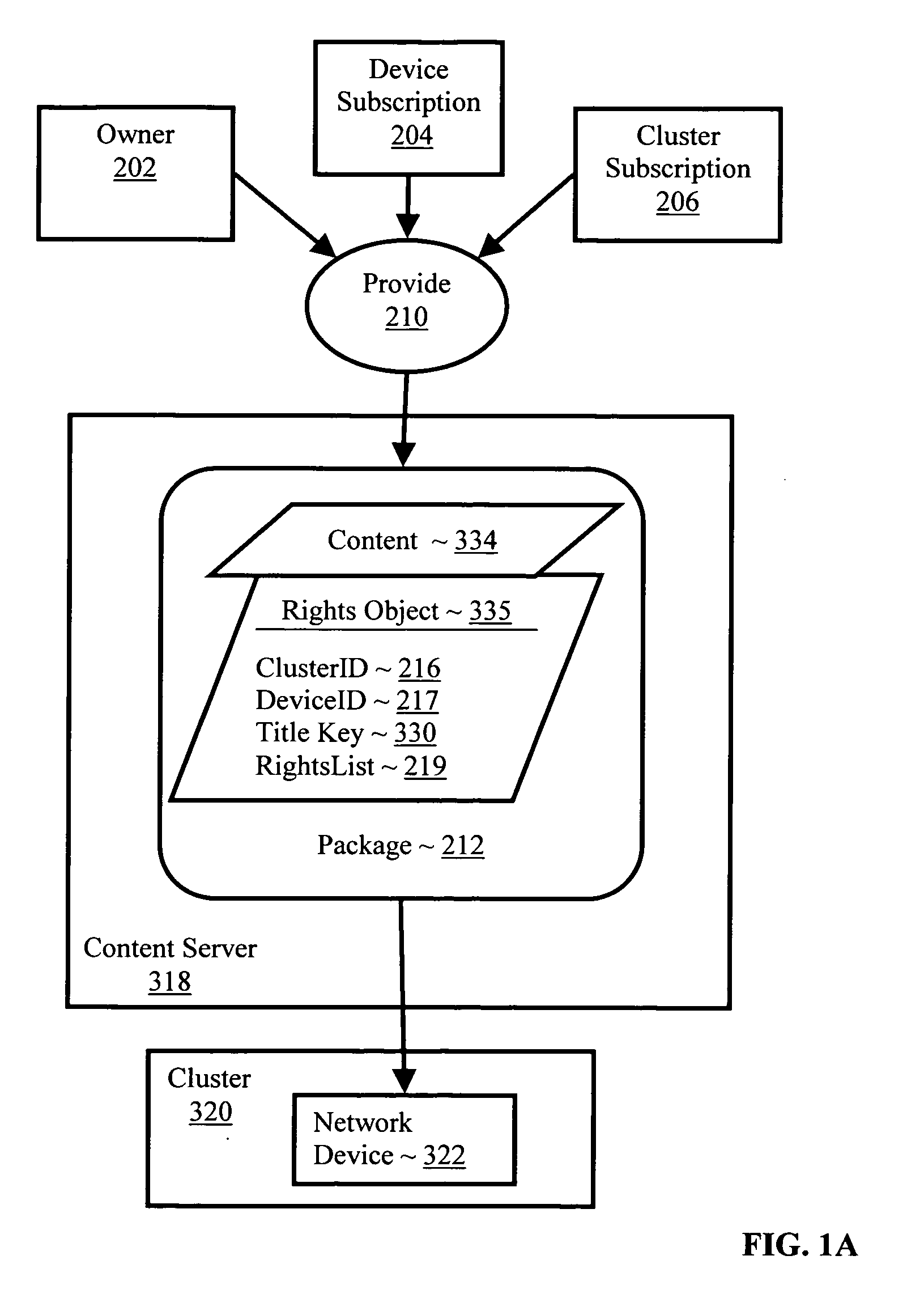
Controlling with rights objects delivery of broadcast encryption content for a network cluster from a content server outside the cluster
InactiveUS20060059573A1Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsAuthorizationNetwork clustering
Methods, systems, and products are disclosed for controlling with rights objects delivery of broadcast encryption content for a network cluster from a content server outside the cluster that include receiving in the content server from a network device a key management block for the cluster, a unique data token for the cluster, and an encrypted cluster id; calculating a binding key for the cluster in dependence upon the key management block for the cluster, the unique data token for the cluster, and the encrypted cluster id; inserting a title key into a rights object defining rights for the broadcast encryption content; and sending the rights object to the cluster. In typical embodiments, the rights for content include an authorization for a play period and an authorized number of copies of the broadcast encryption content to devices outside the cluster.
Owner:IBM CORP
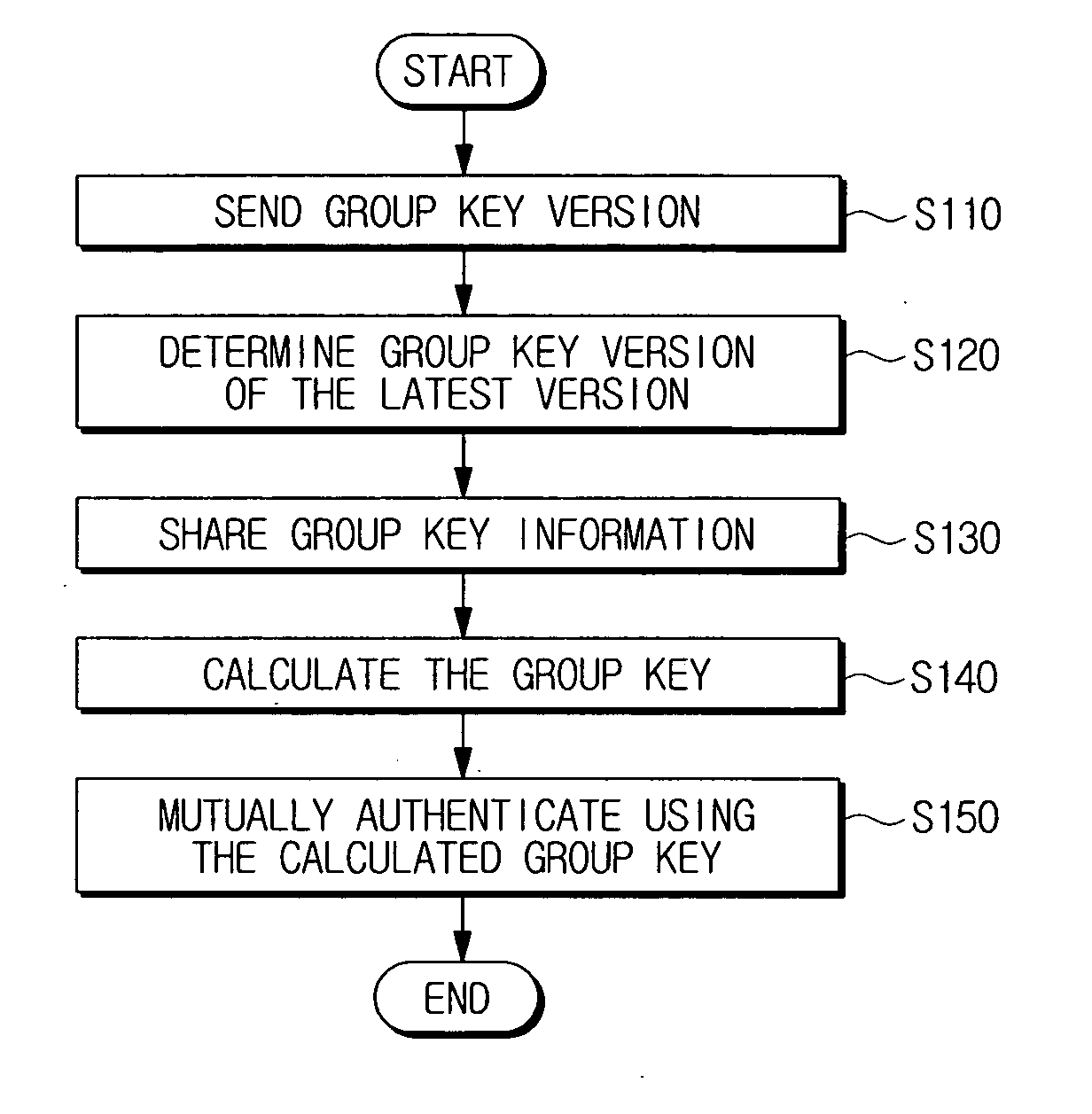
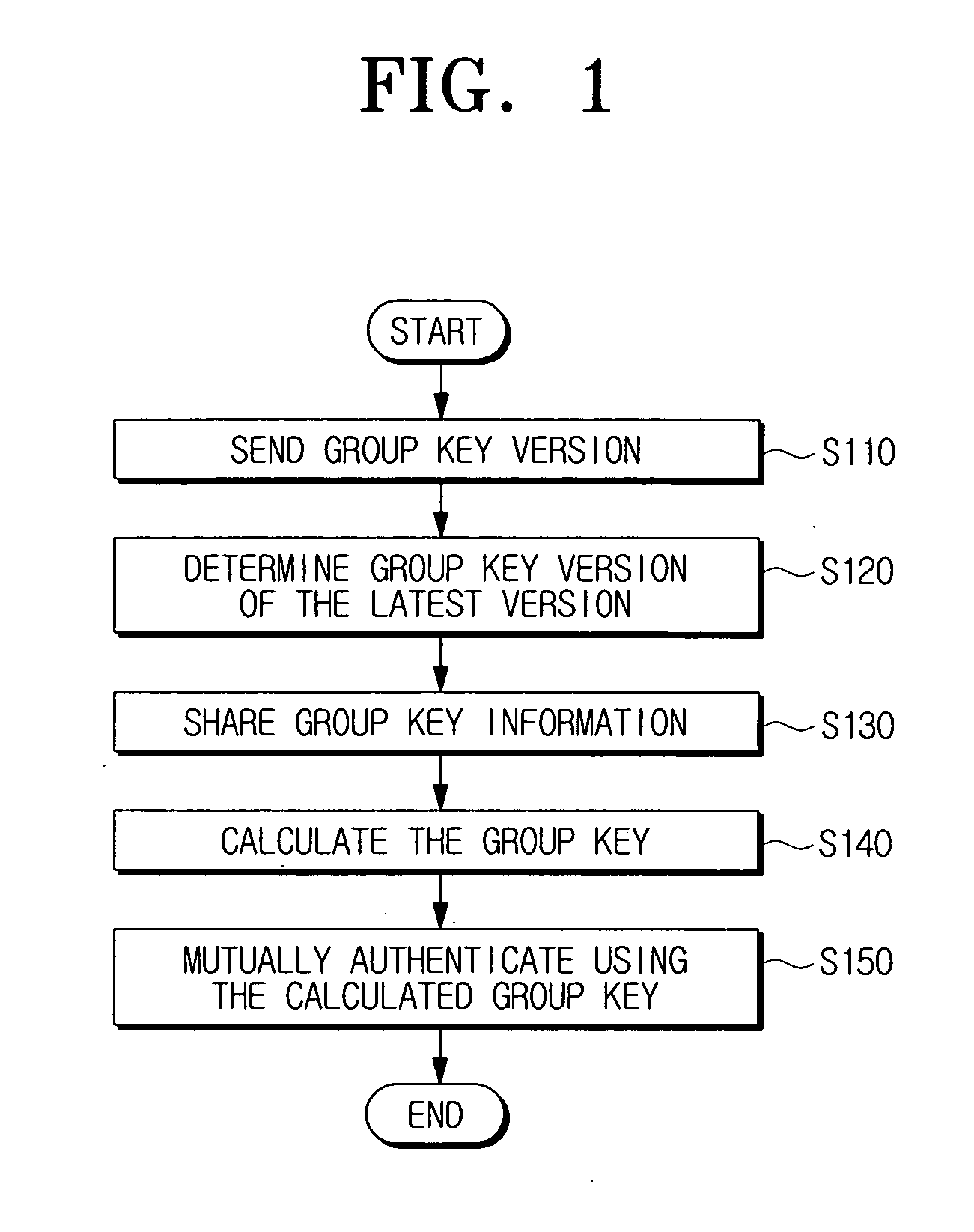
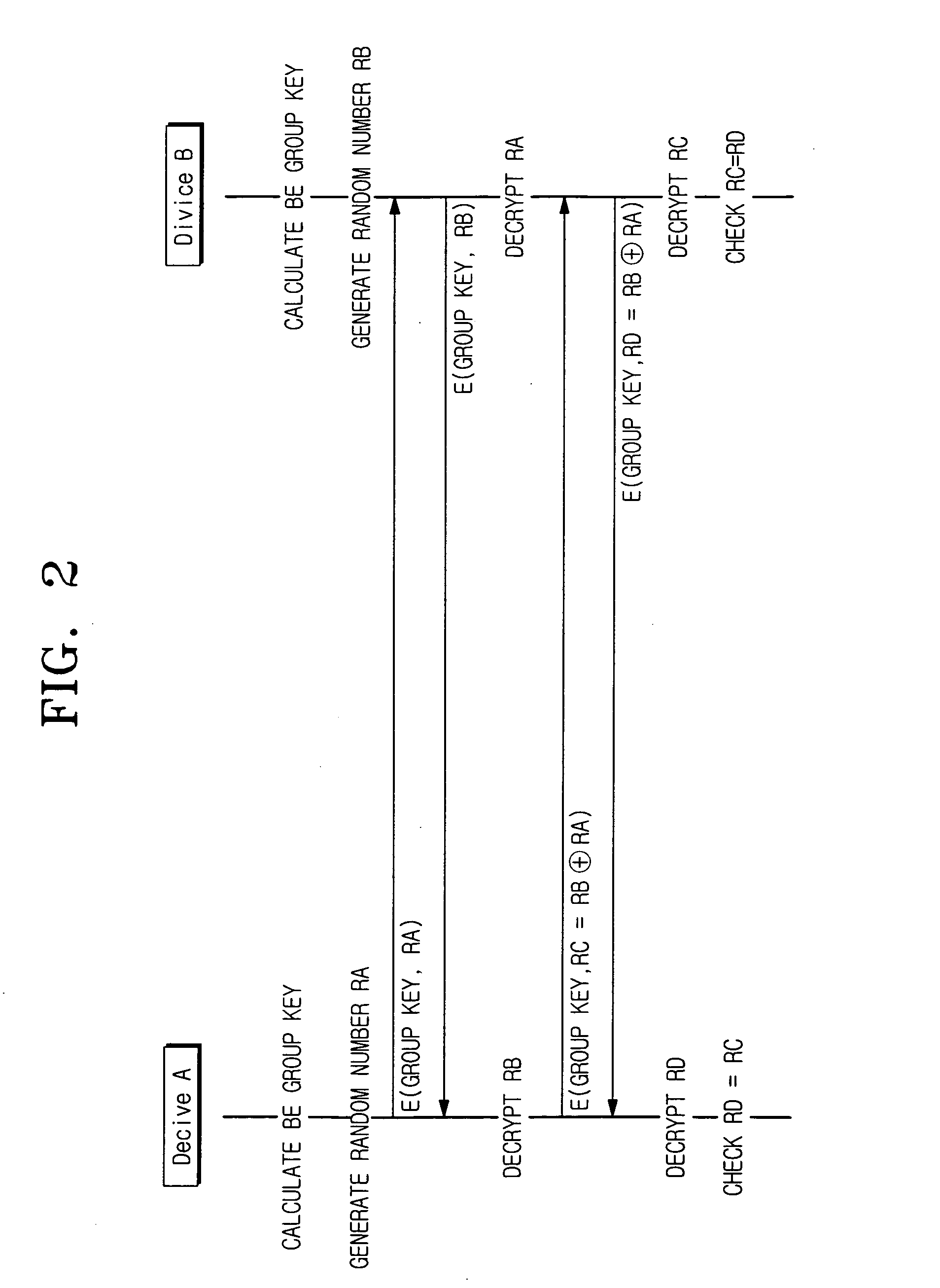
Device authentication method using broadcast encryption (BE)
InactiveUS20080010242A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationAuthentication serverBroadcasting
A device authentication method using broadcast encryption is provided, in which, a hash value corresponding to a group key version is generated, the generated hash value is encrypted with a group key, group key information comprising the encrypted hash value is generated, and the generated group key information including a signature of an authentication server for the group key information is transmitted. Accordingly, mutual authentication is accomplished by using the group key version including in the group key information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Hybrid broadcast encryption method
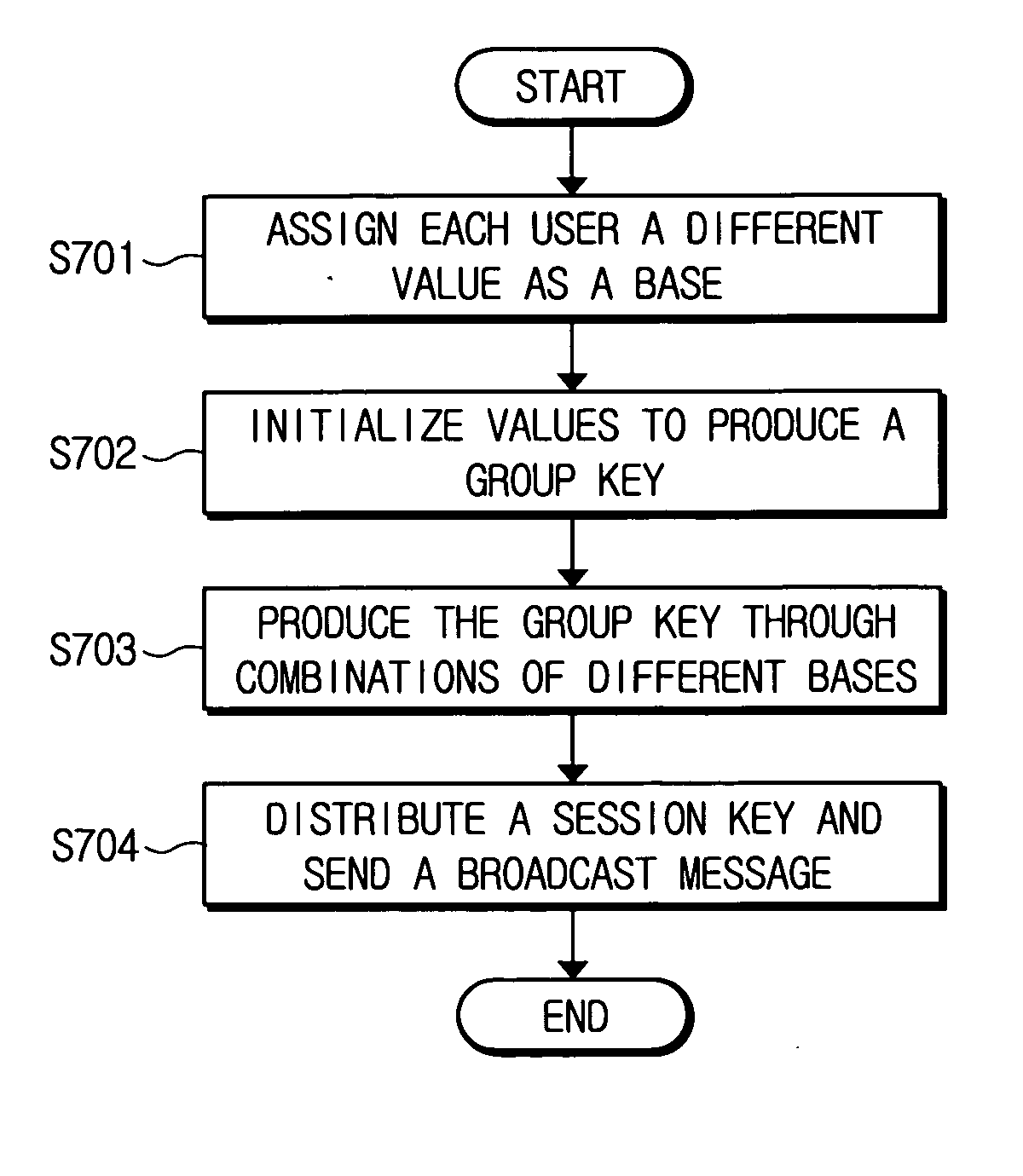
InactiveUS20060177067A1Reduce overheadSleeve/socket jointsKey distribution for secure communicationBroadcastingSession key
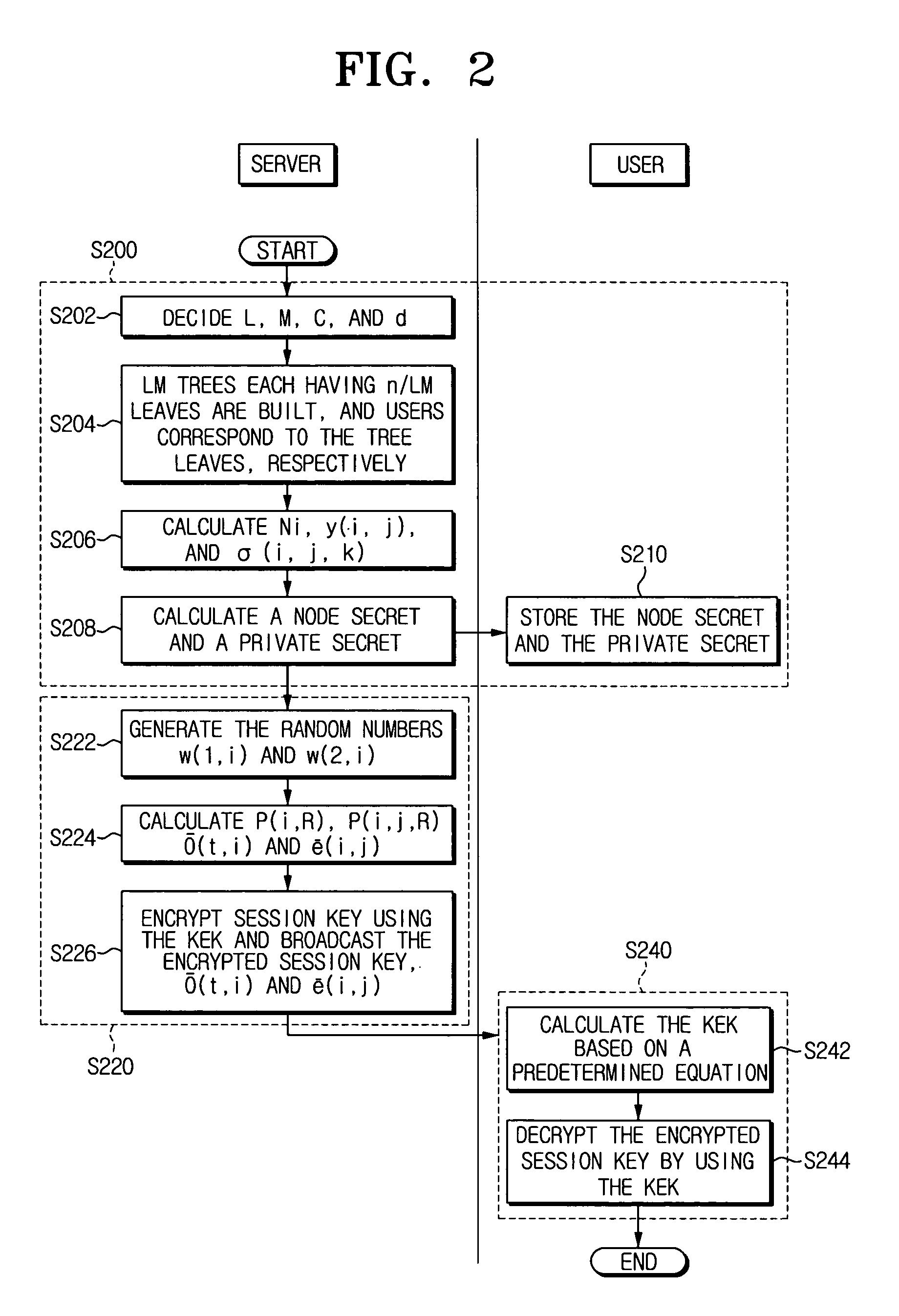
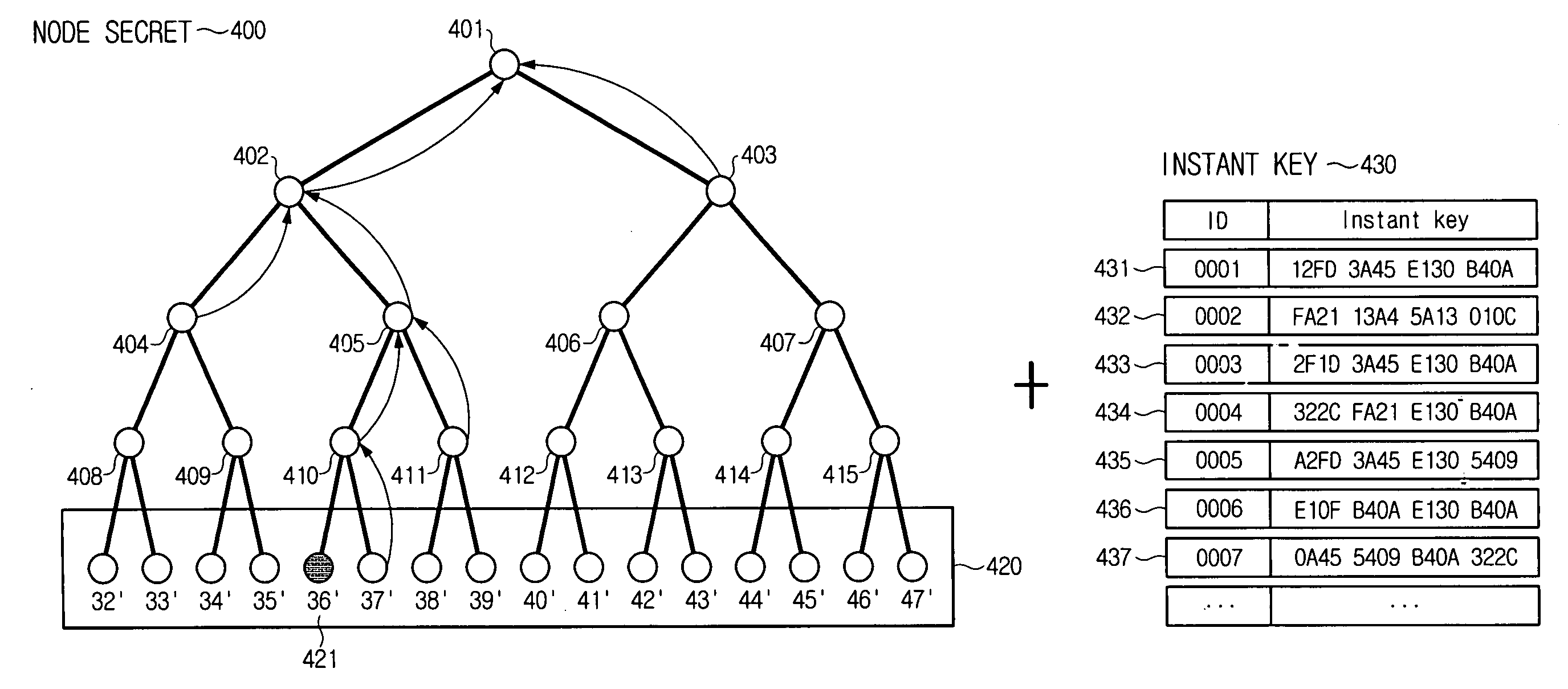
A hybrid broadcast encryption method is provided. The hybrid broadcast encryption method includes setting initialization values, generating a node secret using the initialization values; generating a private secret using the node secret; sending the node secret and the private secret; generating a broadcast message based on a revoked group; encrypting a session key using a key encryption key (KEK) which is allocated to every user group and the broadcast message; and broadcasting to every user the encrypted session key and the broadcast message.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for controlling access to encrypted content using multiple broadcast encryption based control blocks
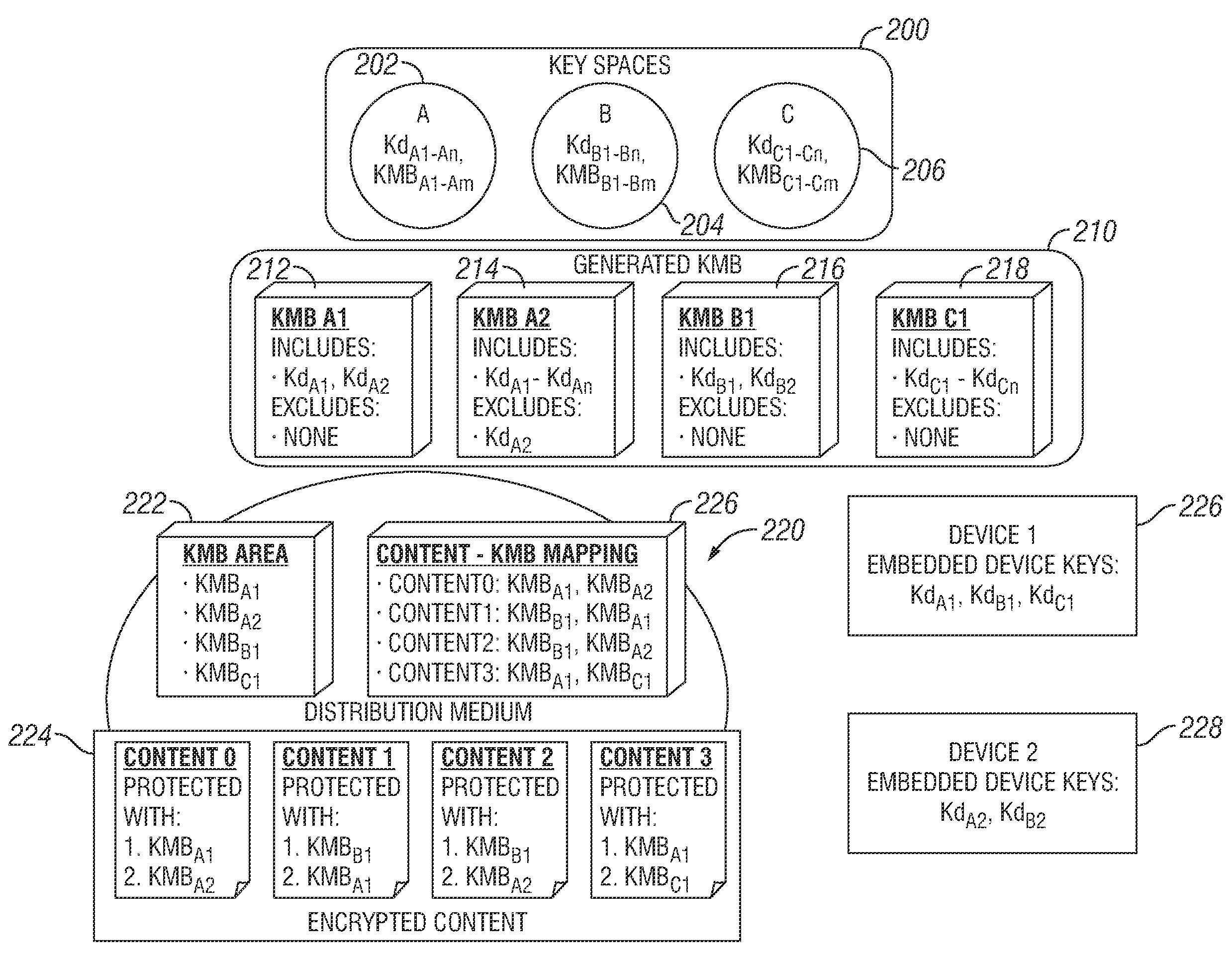
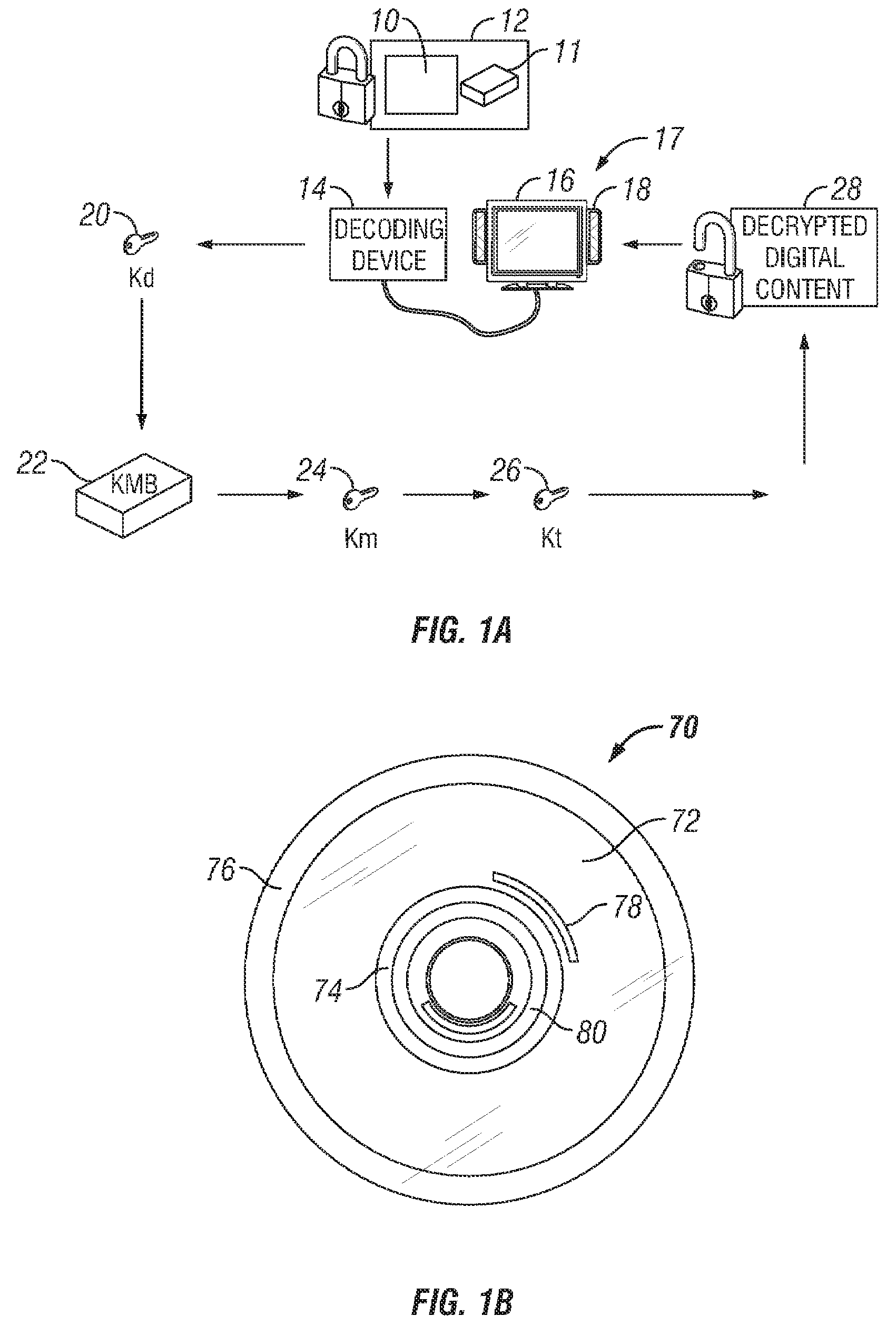
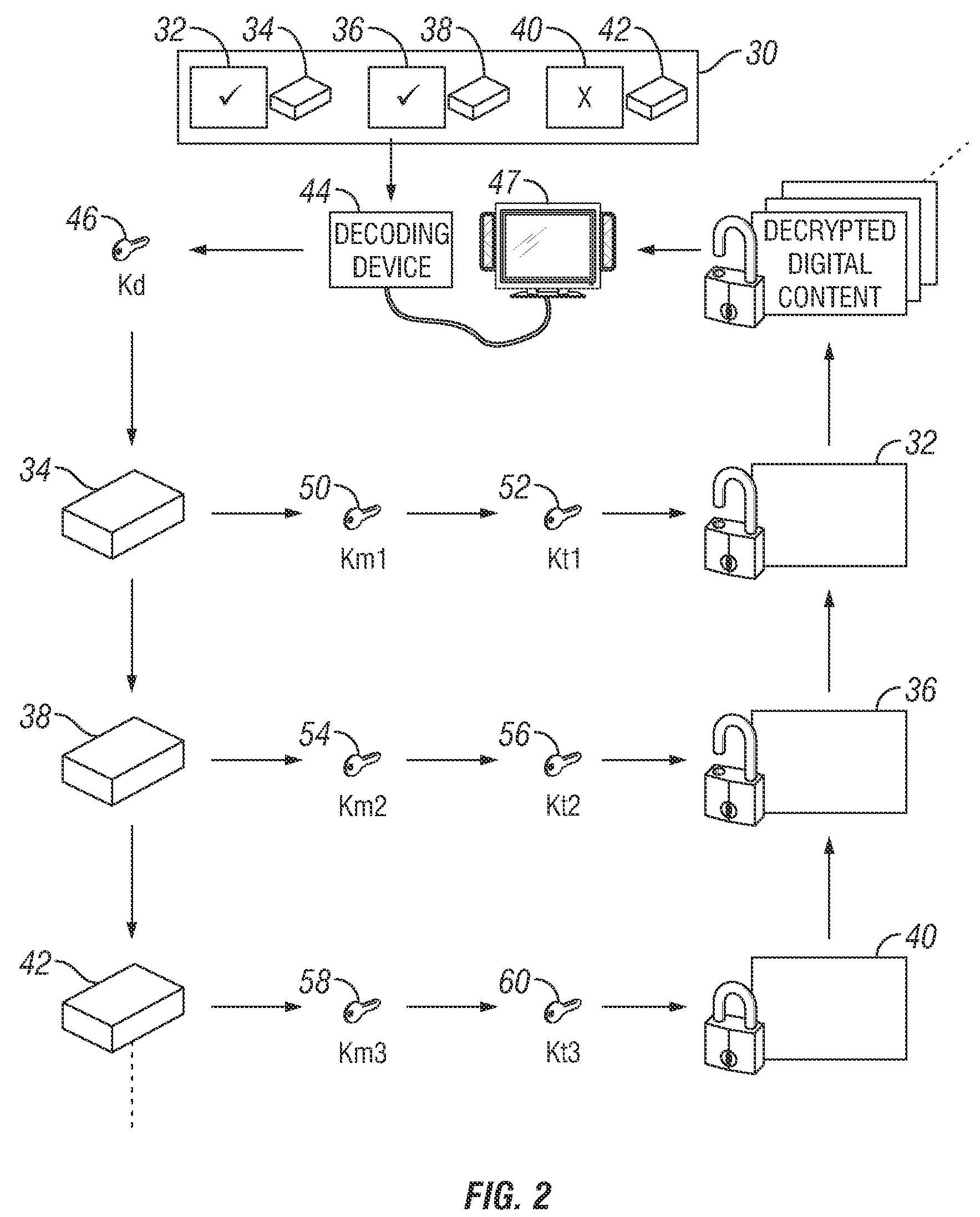
An apparatus and a method are provided for selectively accessing digital content carried on a distribution medium such as a physical medium or a broadcast medium. In one embodiment, a plurality of digital content items are encrypted under a plurality of different key management blocks, wherein each key management block is associated with a different set of device keys. The plurality of content items may be provided together on a single distribution medium to devices having assigned device keys, so that devices may selectively access content as determined by the different key management block used to encrypt the various content items and by the device keys assigned to the devices. Depending on the association between the device key and the key management blocks, the decoding device may decode all of the content items, some of the content items, or none of the content items. To provide greater security, each content item may be multiple encrypted using multiple key management blocks per content item.
Owner:IBM CORP
Combination-based broadcast encryption method
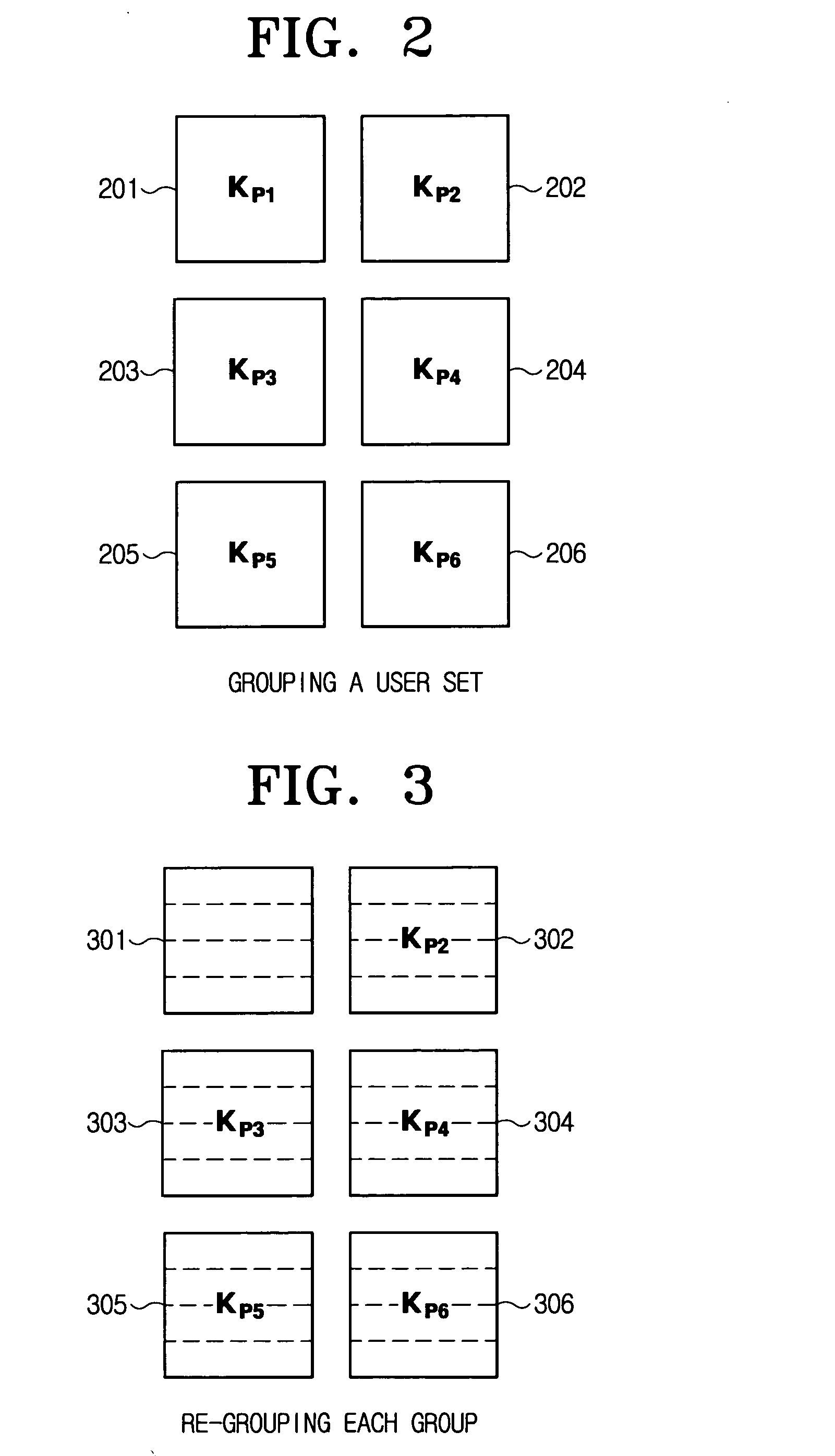
ActiveUS20070140483A1Easy to calculateKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsBase NumberSession key
A combination-based broadcast encryption method includes: assigning by a server a base group of different combinations to each user; producing and sending secret information for each user by using as a base the base group allocated to each user; producing and sending an inverse-base parameter value through calculations with integers used to produce the base group and key value information of one or more privileged users; and deriving a group key by using the key value information of the privileged users, encrypting a session key by using the derived group key, and sending the encrypted session key to each user. Accordingly, each user is assigned a different base through a combination, thereby having security against collusion attacks.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Renewable traitor tracing
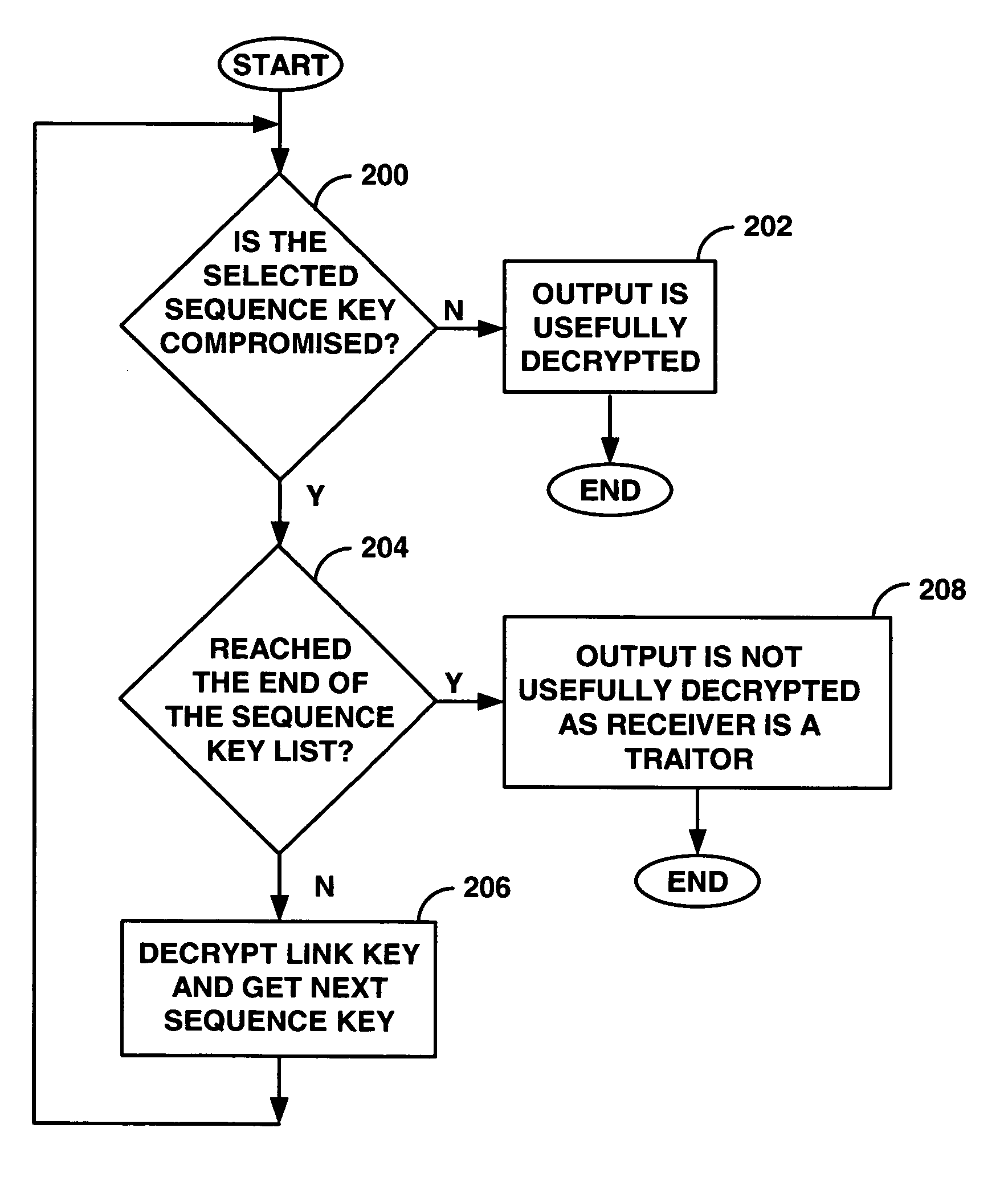
ActiveUS20070067244A1Efficient use ofData processing applicationsComputer security arrangementsTraitor tracingLicense
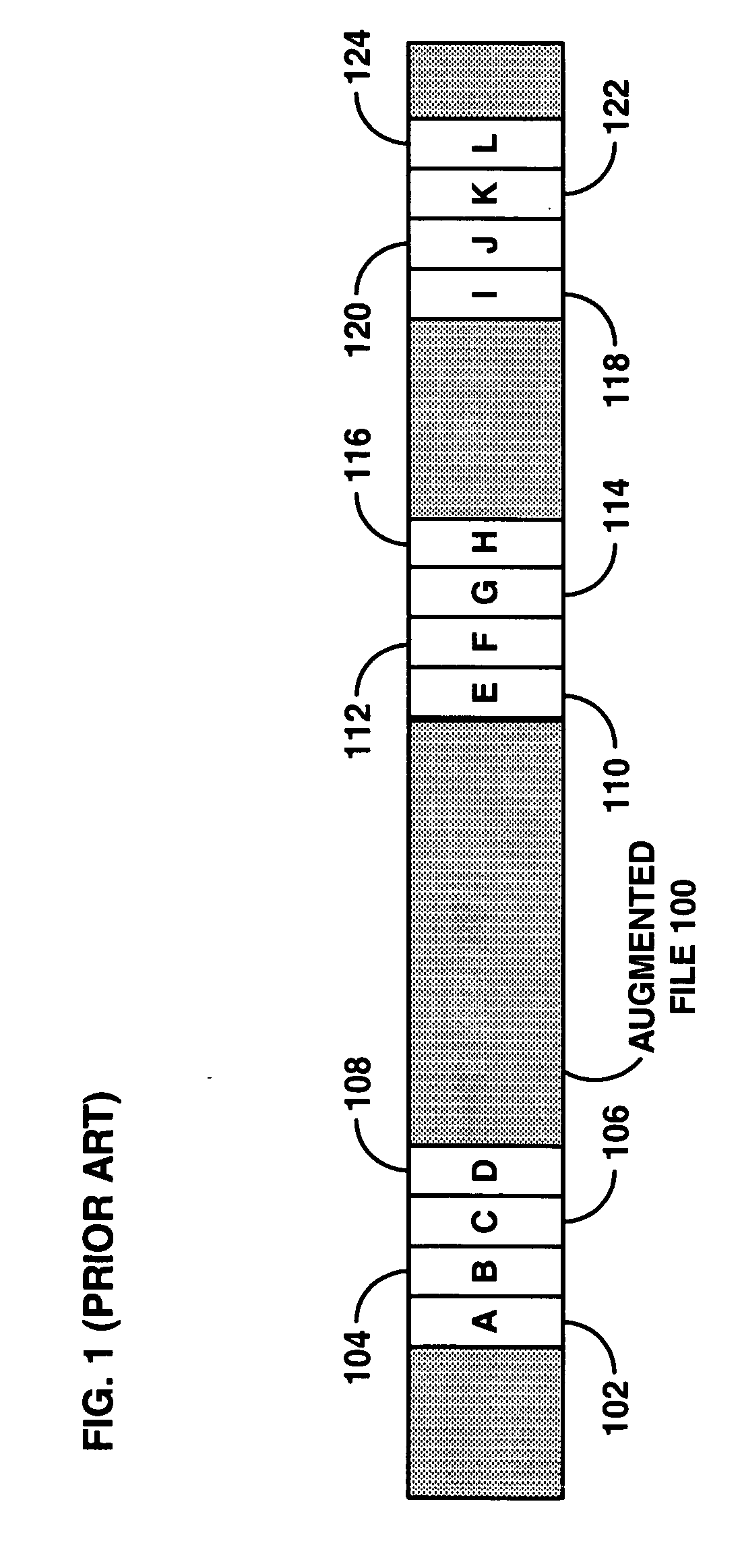
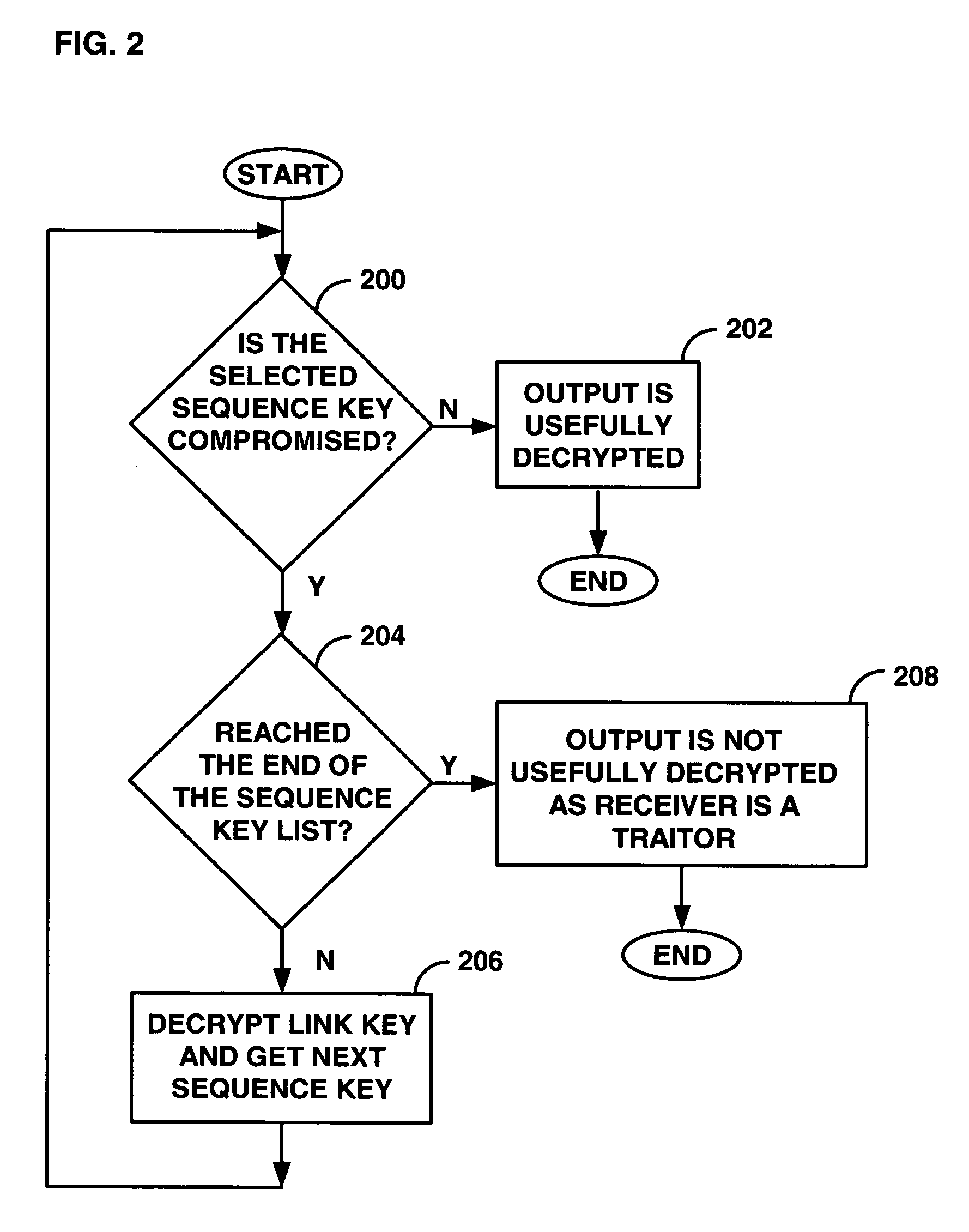
A system, method, and computer program product to renewably prevent traitors in a broadcast encryption system from re-using compromised keys. A license agency assigns individual receivers a set of Sequence Keys preferably at manufacture, and assigns Sequence Key Blocks (SKBs) to protected content files to be distributed. The files may be distributed on prerecorded media and typically include several file modifications. The particular modifications in a pirated version of a file can help identify which traitors contributed to its theft. SKBs assigned to new files distributed after traitors have been identified cannot be usefully processed using the compromised keys employed in previous content piracy. Innocent receivers that happen to have compromised key(s) in common with traitors can use a replacement uncompromised Sequence Key from the set to usefully decrypt content. Traitors will however step through all their Sequence Keys without reaching one that will work.
Owner:IBM CORP
Grid-based multi-user fuzzy searchable encryption method in secure multimedia cloud storage
ActiveCN106803784AImplement searchKey distribution for secure communicationSpecial data processing applicationsGrid basedCloud storage
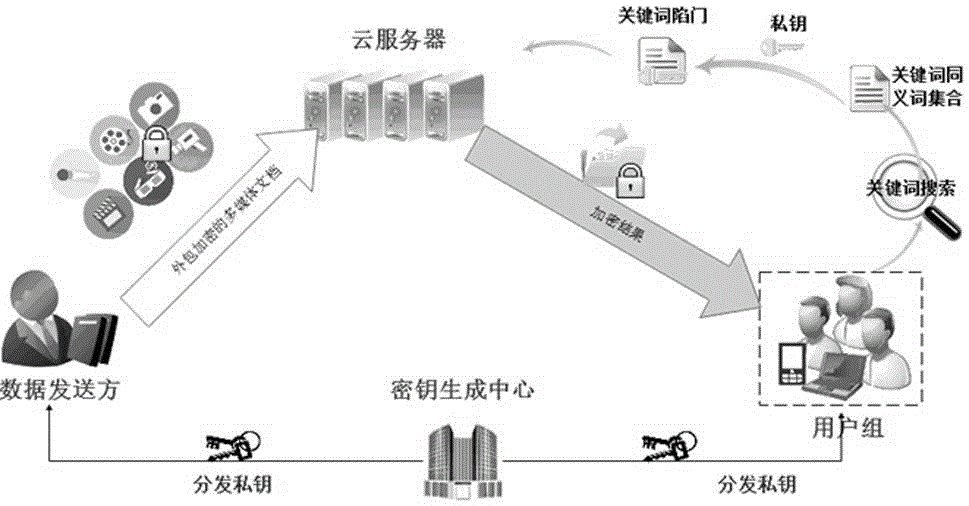
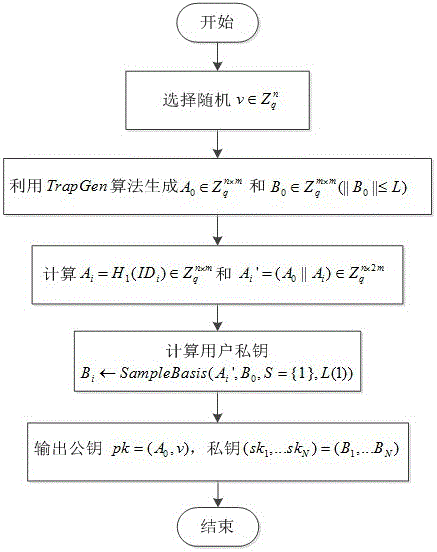
The invention relates to a grid-based multi-user fuzzy searchable encryption method in secure multimedia cloud storage. The semantic information is used to realize the privacy semantic search of encrypted data. The user-selected search keywords do not need to be exactly the same as the keywords in the outsourced encrypted multimedia data. in view of the shortcomings of the existing scheme that only supports single-user application, the scheme introduces the searchable broadcast encryption method; encrypted multimedia files can be shared by a group of users without sharing their own private keys; each authorized user can use his / her unique private key to generate his / her own keyword trap door; and the user can also upload the encrypted multimedia files as a data sender using the group public key. The scheme introduces the concept of post-quantum security and designs a searchable broadcast encryption scheme that supports semantic keyword search, and the scheme is constructed by means of grid-based cryptography and grid-based proxy methods. Based on the difficulty of LWE (error learning) problem, the security of resisting quantum attack can be realized.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Controlling With Rights Objects Delivery Of Broadcast Encryption Content For A Network Cluster From A Content Server Outside The Cluster
InactiveUS20090016533A1Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsAuthorizationNetwork clustering
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Management of encryption keys for broadcast encryption and transmission of messages using broadcast encryption
InactiveUS20140064490A1Improve system performanceReduce data volumeKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageBroadcastingComputer science
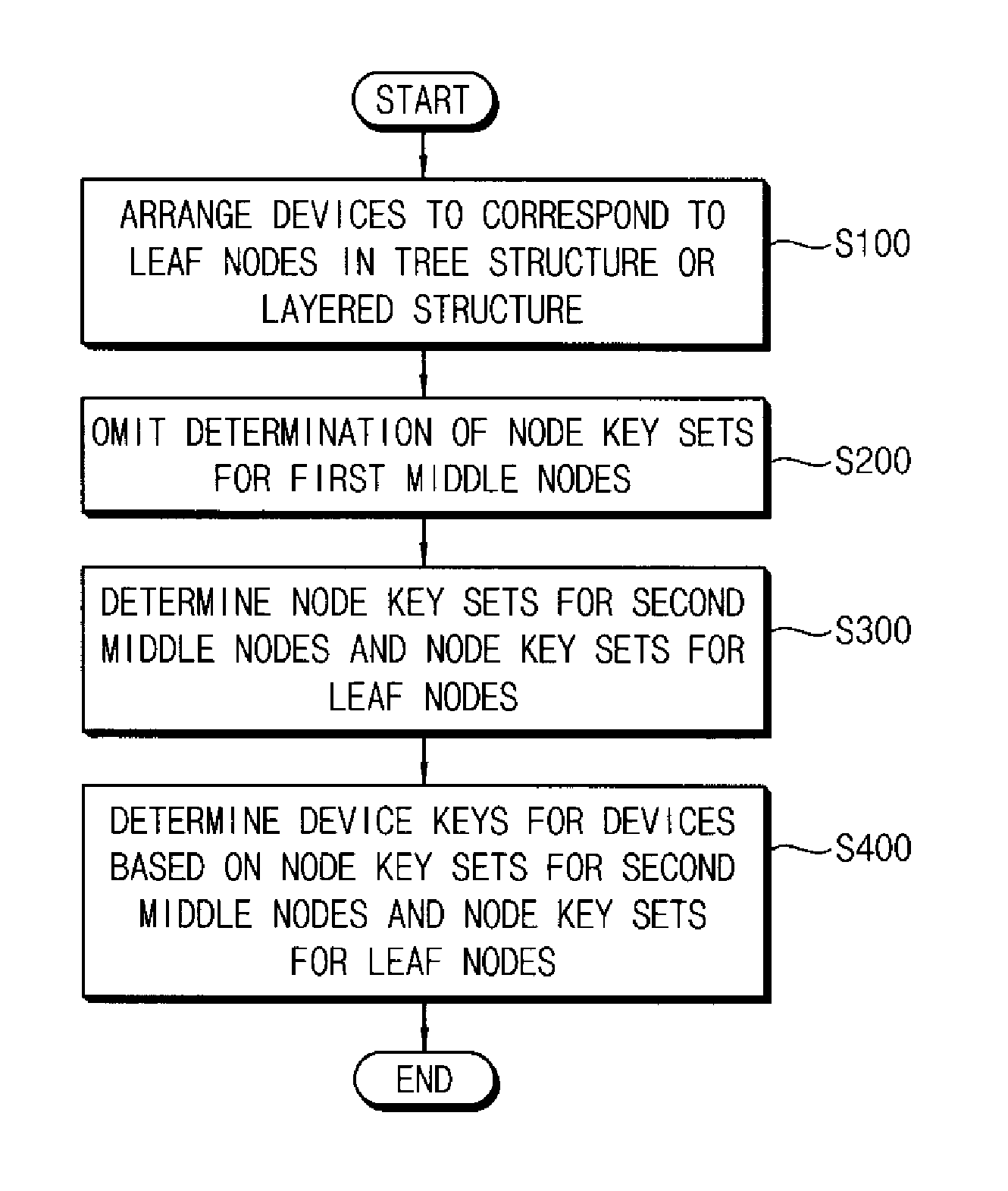
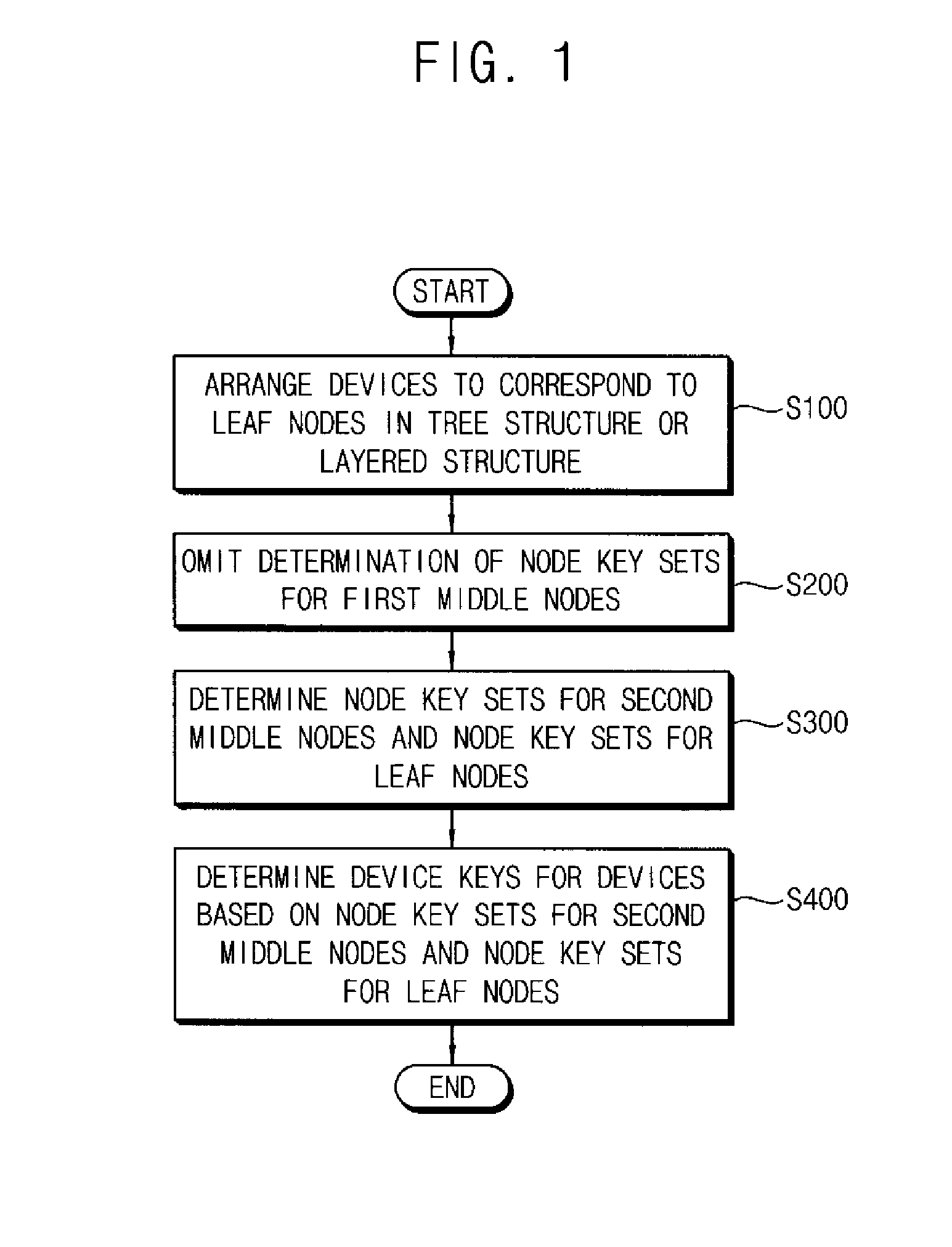
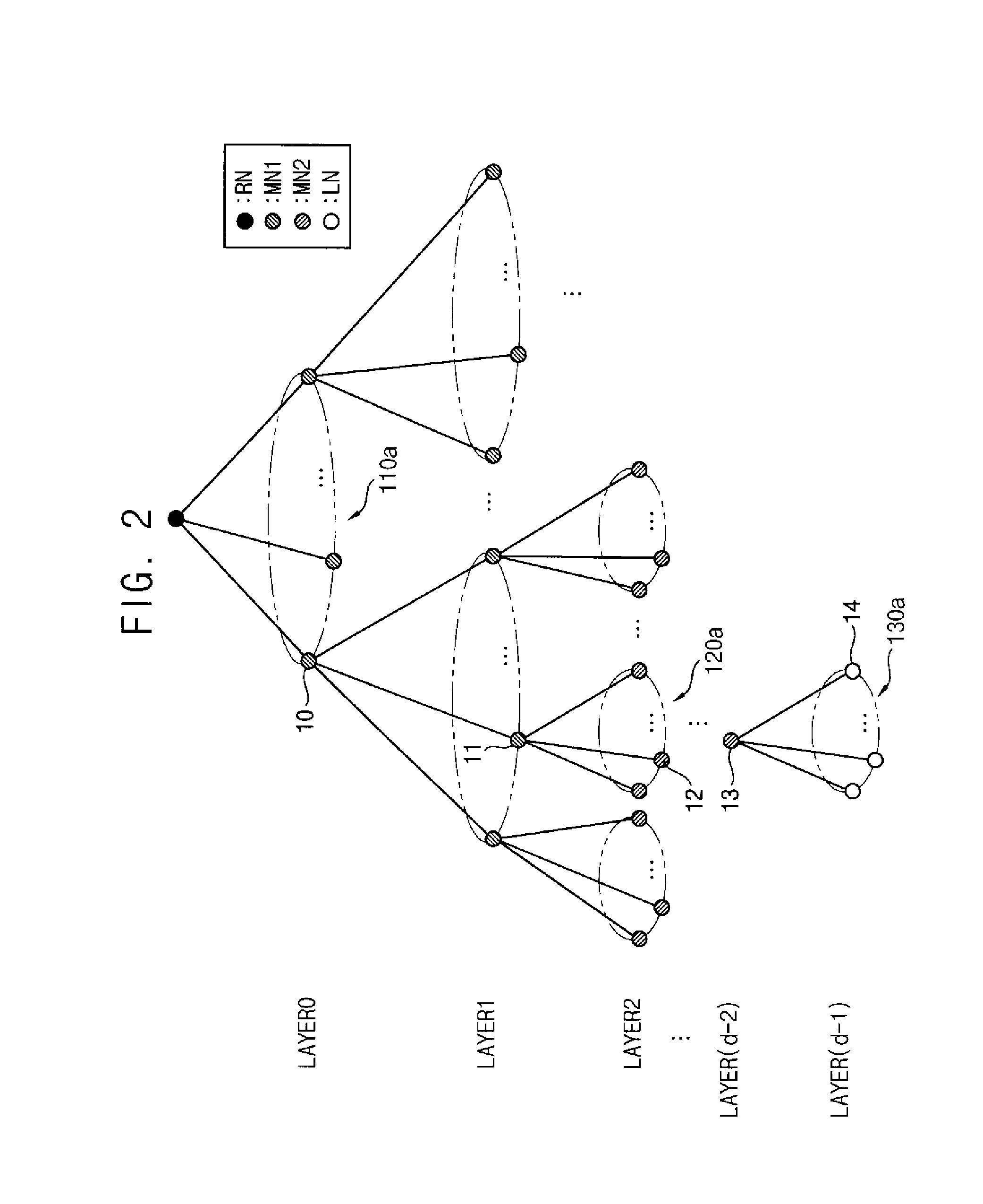
A method of managing keys for broadcast encryption comprises identifying a plurality of devices as corresponding to a plurality of leaf nodes in a tree structure comprising a plurality of nodes having a root node, a plurality of middle nodes, and the leaf nodes, the plurality of middle nodes comprising first middle nodes and second middle nodes, determining node key sets for the second middle nodes and for the leaf nodes and omitting a determination of node key sets for first middle nodes of the middle nodes, and determining device keys for the plurality of devices based on the node key sets for the second middle nodes and the node key sets for the leaf nodes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Privacy protection system based on broadcast and attribute encryption technology
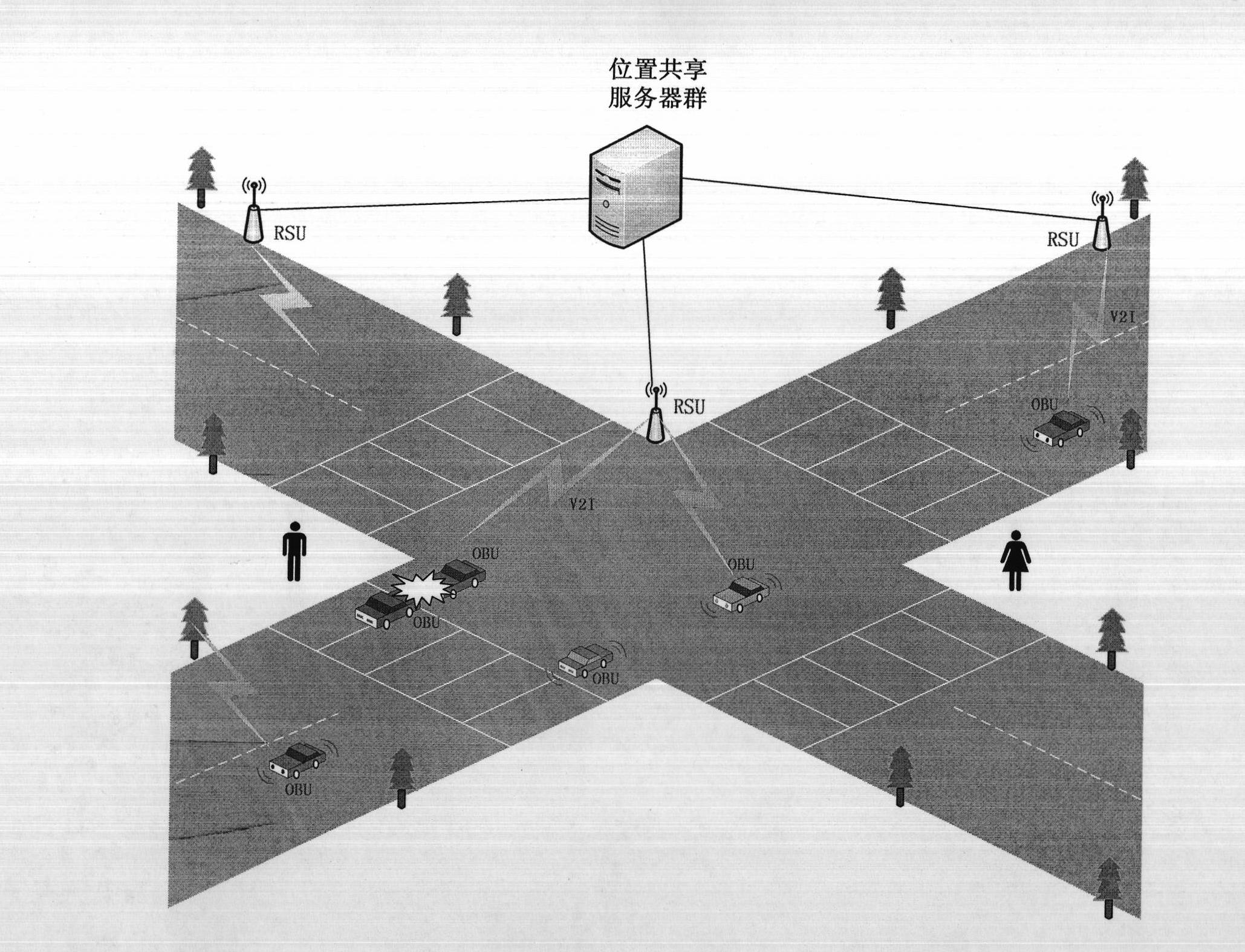
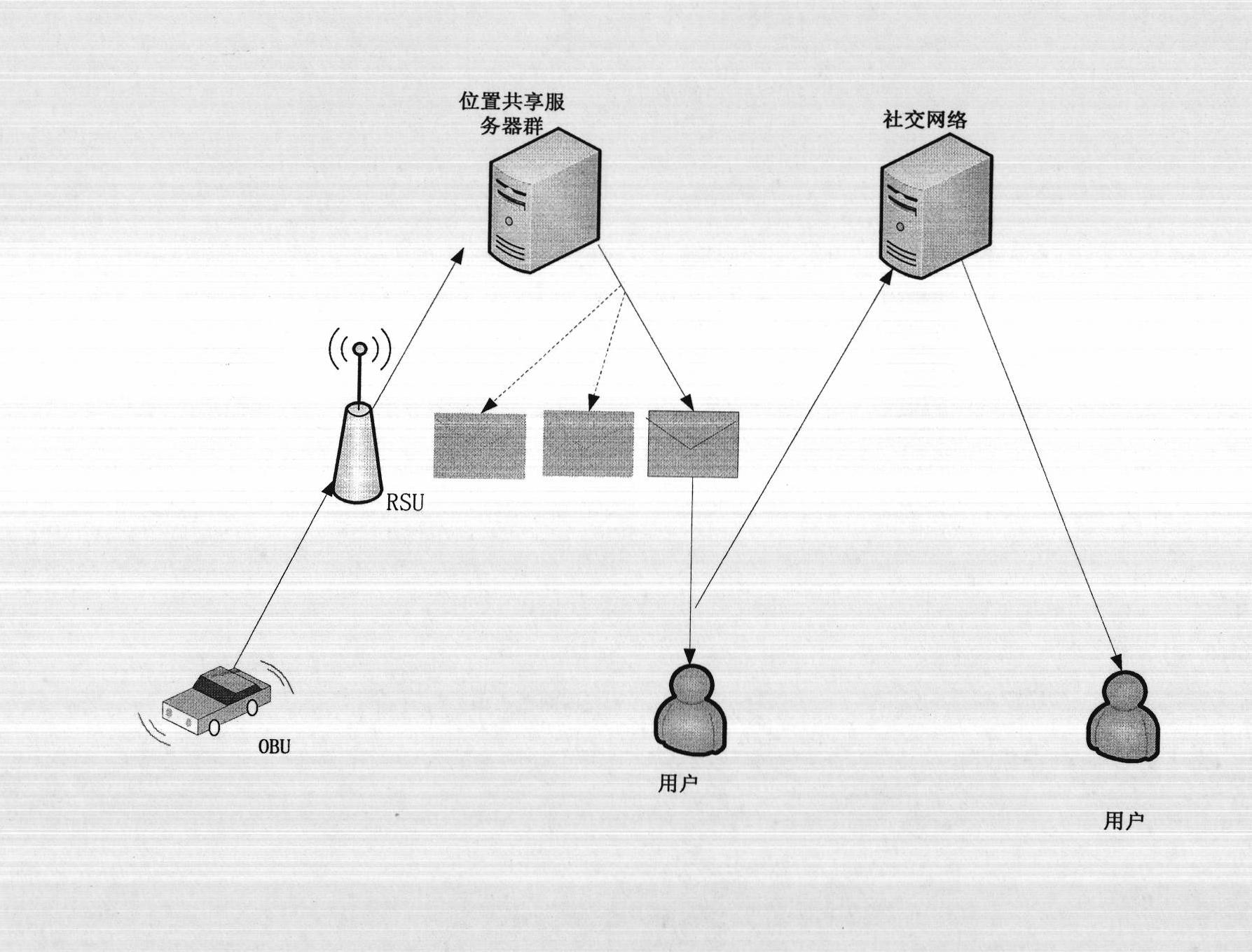
InactiveCN102624917ALimit readReduce the probability of guessing hitsTransmissionLocation sharingOn board
A privacy protection system based on the broadcast and attribute encryption technology comprises a location sharing server group, road-side units (RSU) and an on board unit (OBU) which are all interconnected through wireless networks. The privacy protection system based on the broadcast and attribute encryption technology has the advantages that by utilizing two mechanisms of broadcast encryption location information and anonymization OBU identification, the location sharing server group cannot obtain accurate user information; by utilizing the mechanism based on the attribute encryption, the identification of a user is ensured to be only deciphered by the real RSU; the mechanism based on the attribute encryption is utilized during the location sharing of the user, and persons reading the location information can be effectively and flexibly limited through the mechanism.
Owner:杨涛
System, method, and service for delivering multimedia content by means of a permission to decrypt titles on a physical media
InactiveUS20060129490A1Control productionCombating fraudData processing applicationsTelevision systemsThe InternetUniform resource locator
Enhanced multimedia content on physical media interacts with the user through a media player and the Internet. Enhanced multimedia utilizes IDs for pieces of content on the media and a media key block. On the enhanced media is a file with a list of URLs. As the enhanced media plays a title requiring an external permission for decryption, the media player accesses the URL for that title and obtains the permission. The permission may be purchased or provided for free. Secure encryption and transmission of permission is accomplished by broadcast encryption using a media key block. Each media has a unique set of keys that allow the media player to process the media key block; however, each media follows a unique path through the media key block. All legitimate media players obtain the media key; circumvention devices cannot decipher the media key block.
Owner:WARNER BROS ENTERTAINMENT INC +2
Controlling with rights objects delivery of broadcast encryption content for a network cluster from a content server outside the cluster
InactiveUS20060048232A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationNetsniff-ngNetwork clustering
Methods, systems, and products are disclosed for delivering broadcast encryption content. Embodiments of the present invention typically include receiving in a cluster broadcast encryption content; receiving in a cluster a rights object defining device-oriented digital rights for broadcast encryption content; and administering the broadcast encryption content on one or more network devices in the cluster in dependence upon the digital rights. In some embodiments, administering the broadcast encryption content on one or more network devices in the cluster in dependence upon the digital rights include mapping the device-oriented digital rights to digital rights supported in the cluster, excluding device-oriented rights not supported in the cluster. In some embodiments, mapping the device-oriented digital rights to digital rights supported in the cluster includes supporting in the cluster only those device-oriented digital rights having direct analogs in the cluster.
Owner:IBM CORP
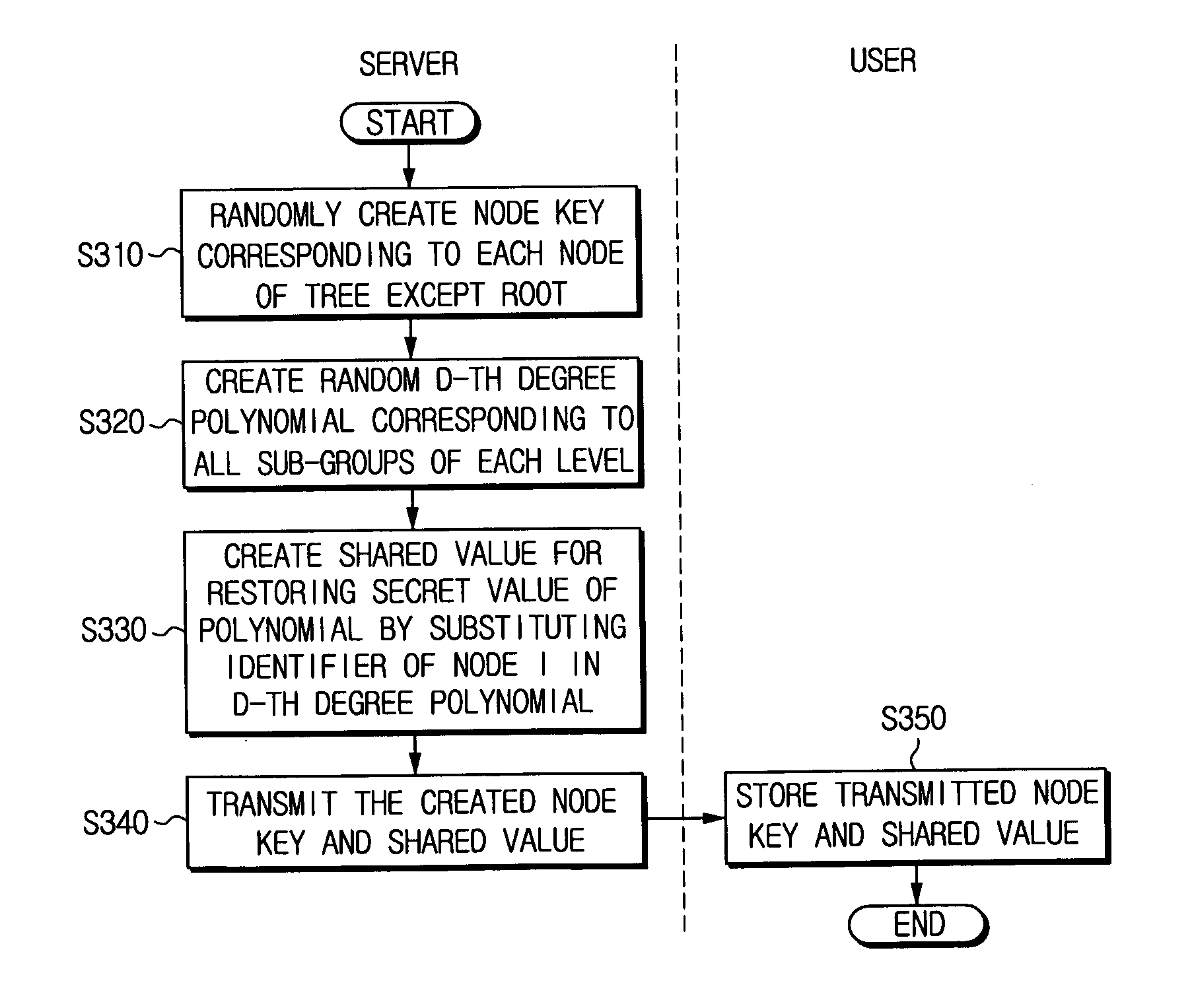
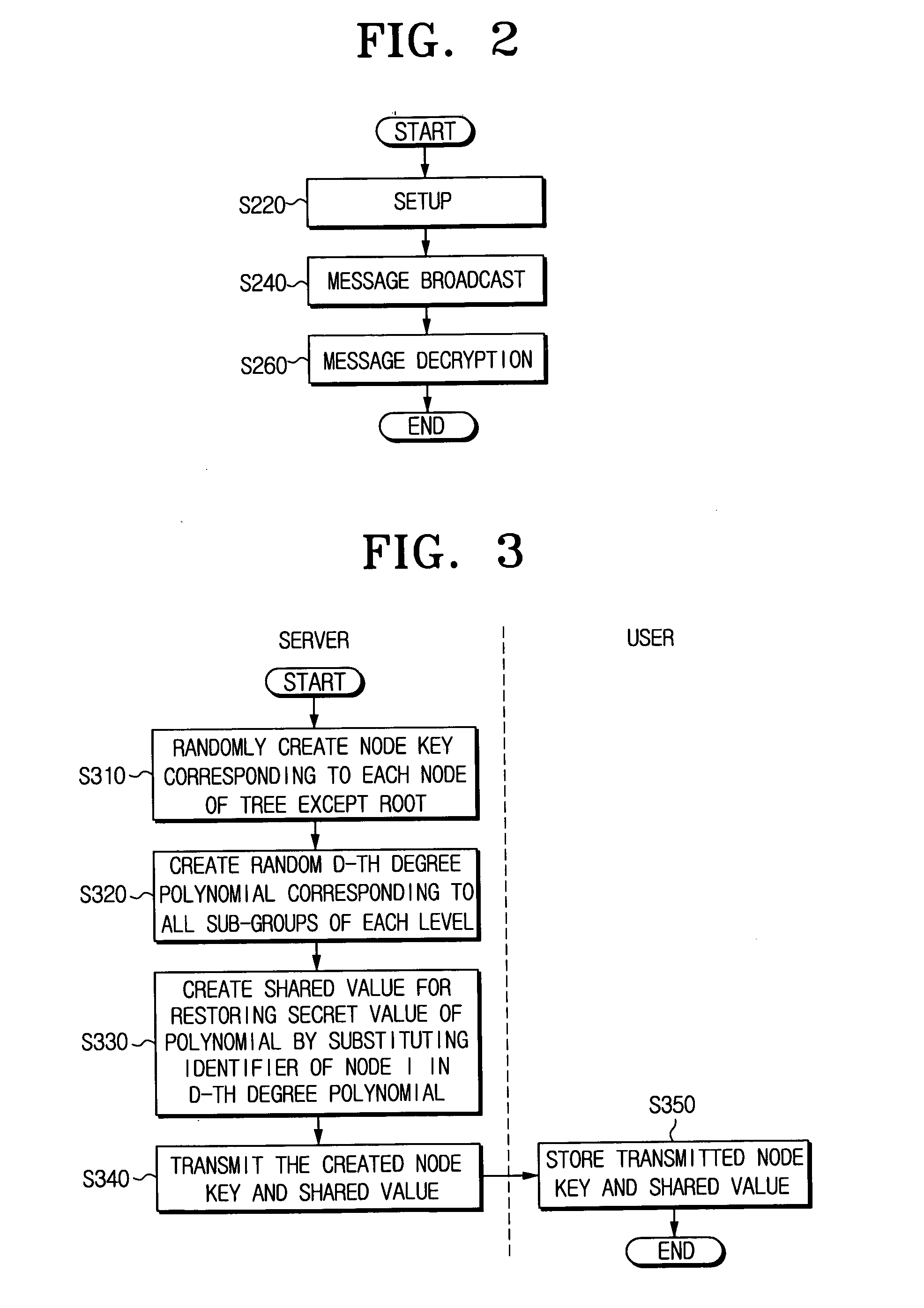
Hierarchical threshold tree-based broadcast encryption method
ActiveUS20070189539A1Reduce loadKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationGroup keyTree based
A hierarchical threshold tree-based broadcast encryption method includes a first step for a server initialization and a user subscription, a second step of distributing a message to enable a privileged user (authorized user) to decrypt a group key, and a third step of the privileged user (authorized user) decrypting the message using the group key. According to the method, it is possible to prevent any group of revocators from obtaining the group key using their secret information and information being broadcast by the server.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
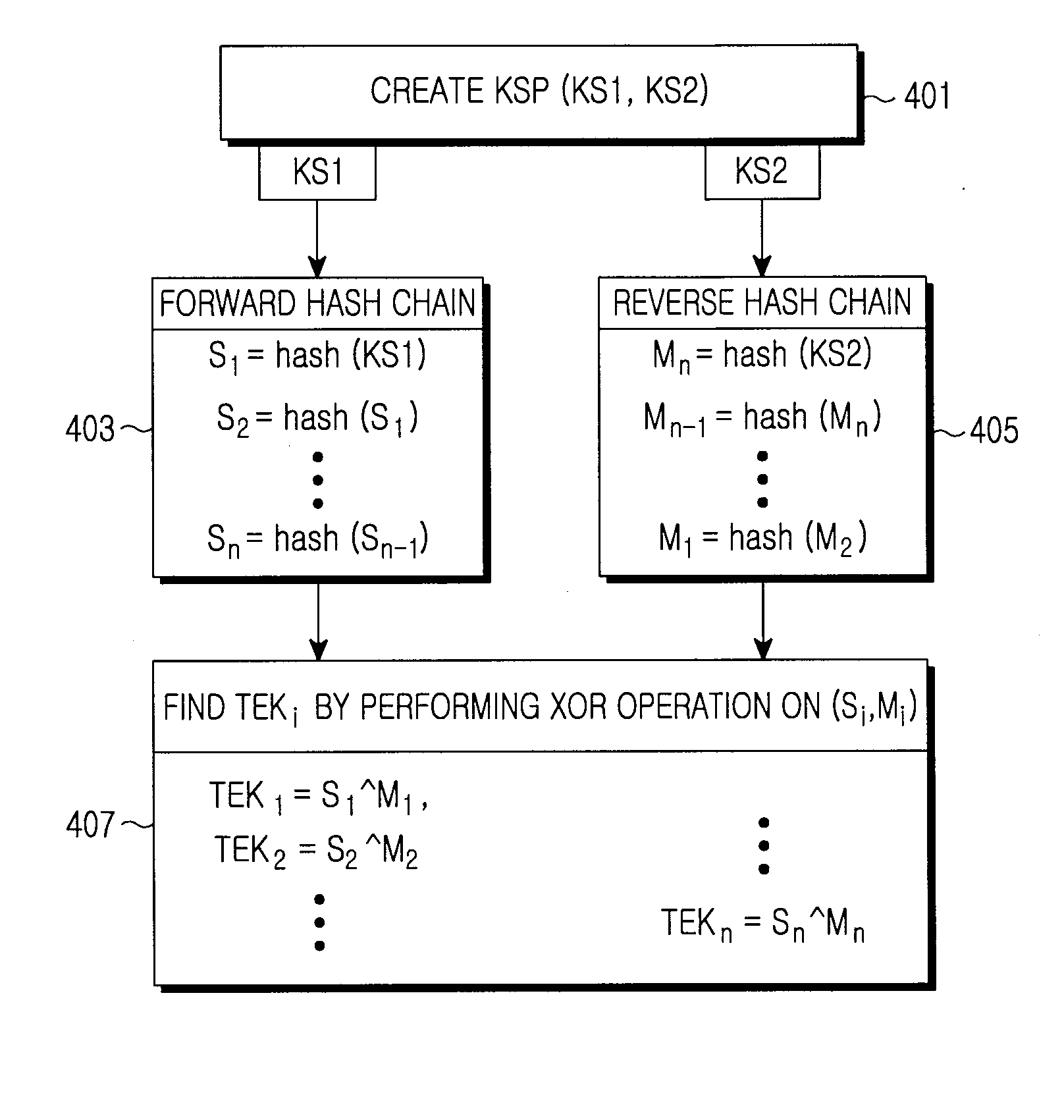
Method and apparatus for providing broadcast service using encryption key in a communication system
ActiveUS20090252324A1Reduce in quantityReduced resourceKey distribution for secure communicationMemory loss protectionCommunications systemBroadcast service
A method and apparatus for providing a broadcast service in a communication system is provided. The method includes creating a seed key pair including a first key and a second key, transmitting the seed key pair to a terminal to which the broadcast service is to be provided, creating a certain number of encryption keys using the seed key pair, the certain number corresponding to a lifetime of the seed key pair, encrypting broadcast service data for the lifetime using the encryption keys, and broadcasting the encrypted broadcast service data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
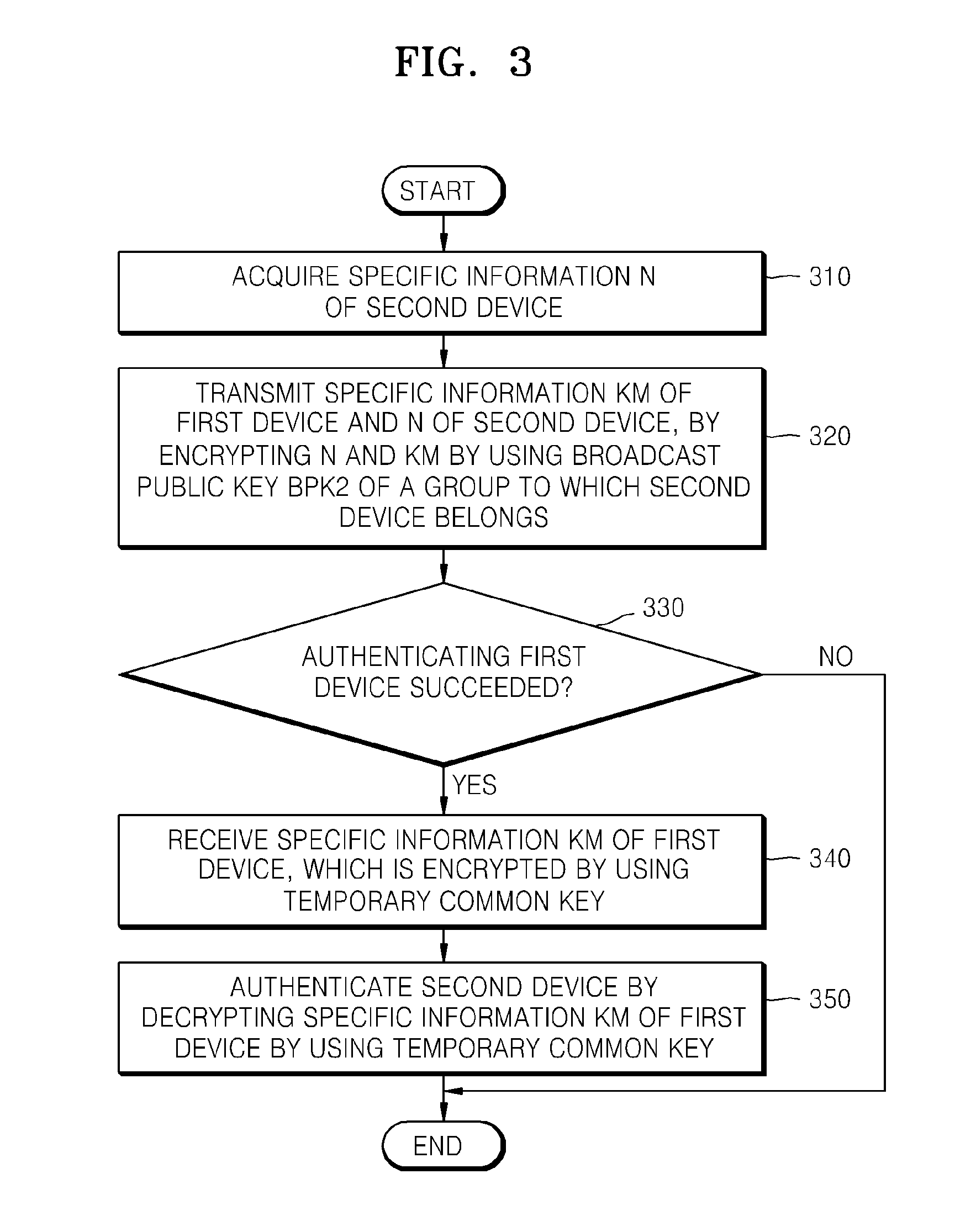
Method of authenticating and reproducing content using public broadcast encryption and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20090016537A1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital computer detailsPublic broadcastingDatacasting
Provided are a method and apparatus for mutually authenticating devices in a group and reproducing content using public broadcast encryption. The method of authenticating a first device and a second device includes acquiring specific information of the second device from the second device, transmitting data, containing the acquired specific information of the second device and specific information of the first device, by encrypting the data using a broadcast public key of a group to which the second device belongs, and determining whether authentication of the first device succeeds by decrypting the encrypted data by using a private key of the second device. If authentication succeeds, receiving the specific information of the first device, which is encrypted by using a temporary common key by using the decrypted data, and authenticating the second device by decrypting the encrypted specific information of the first device by using the temporary common key.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
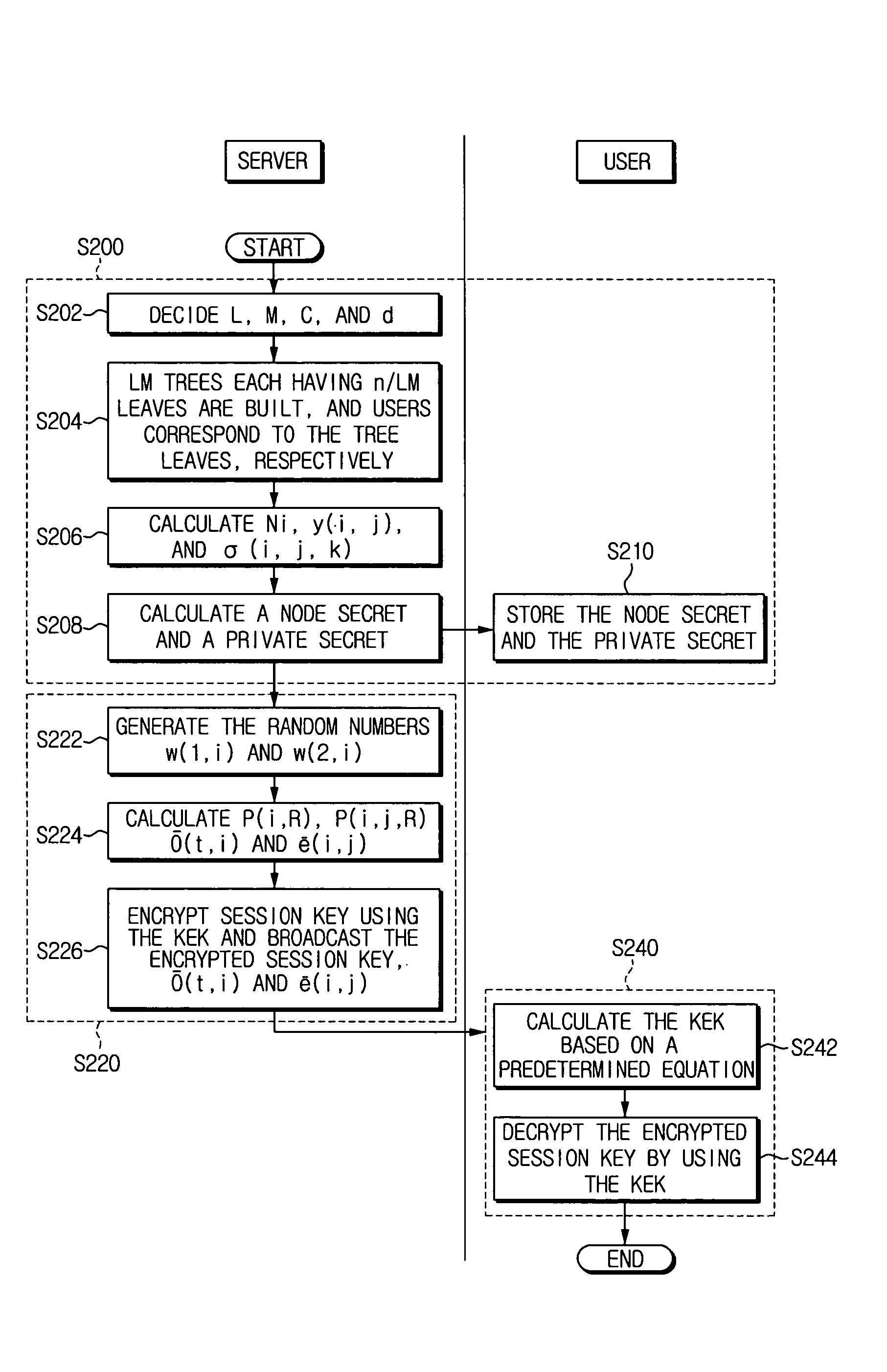
Apparatus and method for generating a key for broadcast encryption
ActiveUS20060078110A1Generate efficientlyFacilitates key updateKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationBroadcast dataKey generator
An apparatus and method for generating a key for a broadcast encryption. The apparatus includes a node secret generator for managing a user that receives broadcast data in a tree structure and for generating a unique node secret for each node in the tree structure. The apparatus also includes an instant key generator for temporarily generating an instant key used at all nodes in common in the tree structure, and a node key generator for generating a node key for each node by operating the node secret generated at the node secret generator and the instant key generated at the instant key generator. Thus, key update can be efficiently achieved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System, method, and service for performing unified broadcast encryption and traitor tracing for digital content
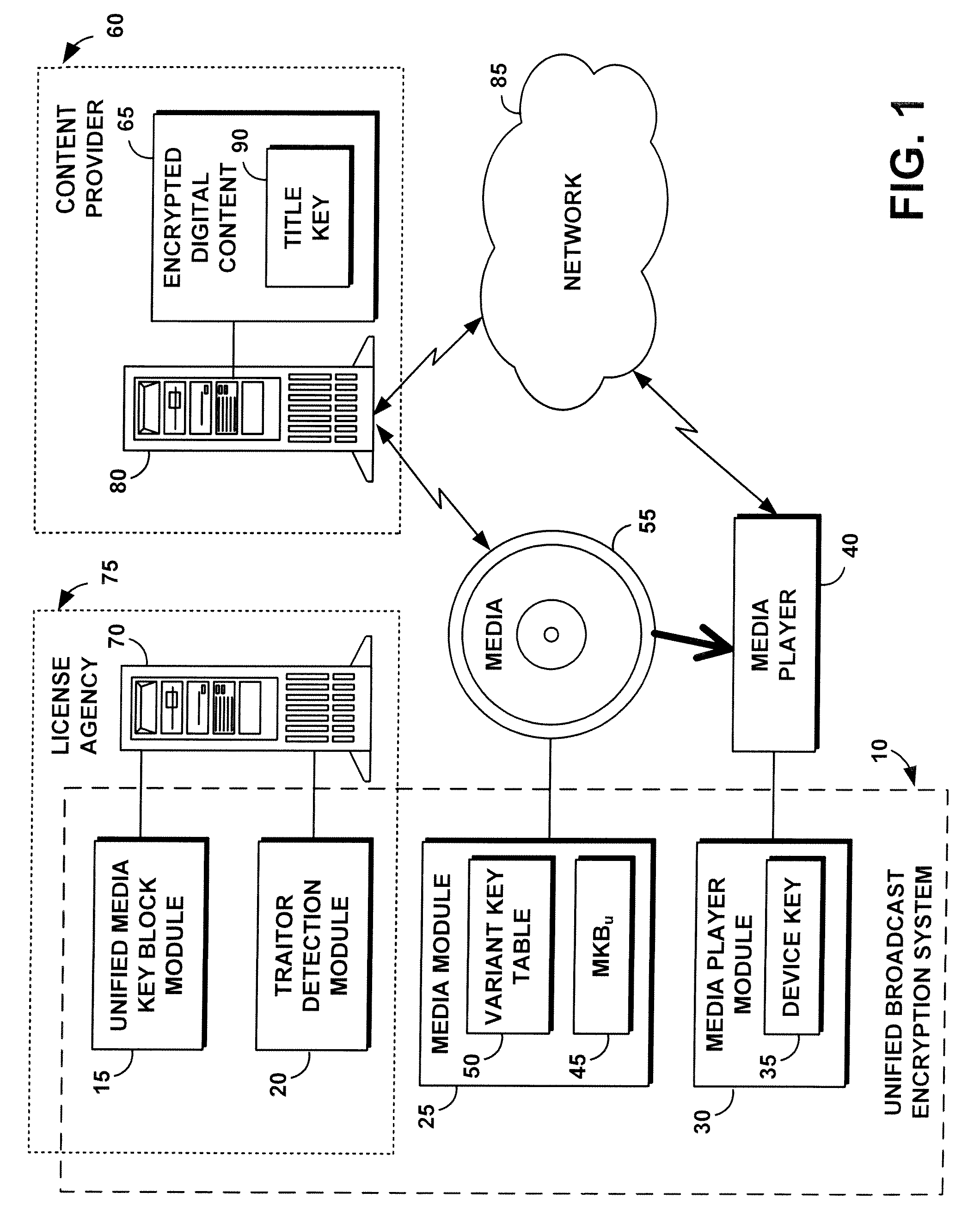
InactiveUS20080279376A1Preventing future piracyImprove abilitiesUser identity/authority verificationRecord information storageComputer hardwareDigital content
A unified broadcast encryption system divides a media key tree into S subtrees, divides digital content into segments, and converts some of the segments into variations; the number of segments and variations is q. The system subdivides each of the subtrees into q / |S| subdivided subtrees, assigns a key media variant to each of the subdivided subtrees, and generates a unified media key block (MKBu). The system decrypts digital content by obtaining required key media variants from the MKBu, using the key media variant to find an entry in a variant key table, decrypt a title key, and locate a variant number from the variant key table. The system uses the variant number to identify which of the variations may be decrypted by the title key and uses the title key to decrypt segments and variations.
Owner:IBM CORP
Broadcast encryption using rsa
ActiveUS20070016769A1Improve efficiencyKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsCiphertextEngineering
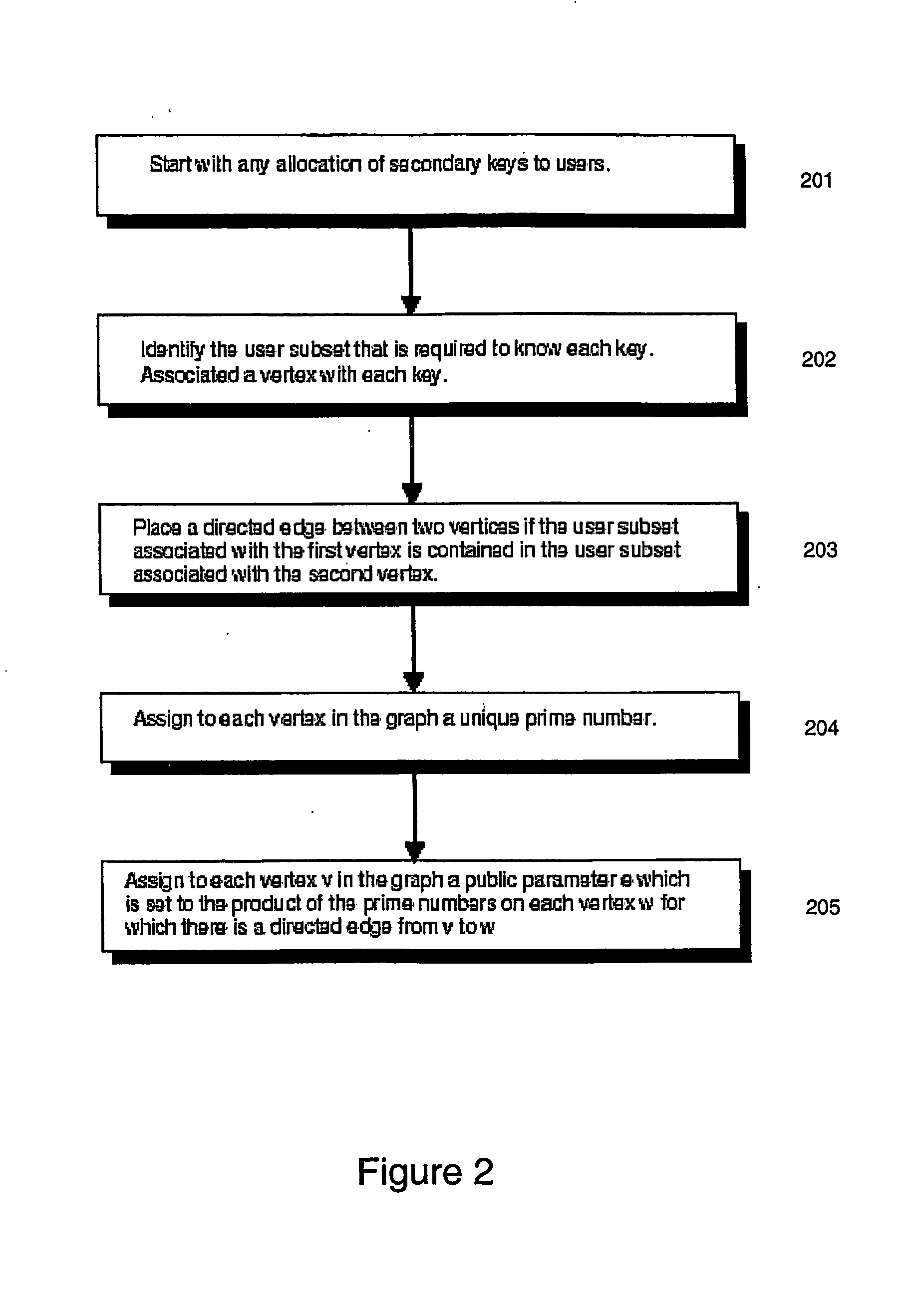
Methods, components and systems for implementing secure and efficient broadcast encryption schemes with configurable and practical tradeoffs among a pre-broadcast transmission bandwidth t, a key storage cost k, and a key derivation cost c, in which the schemes use subtree difference and key decomposition to generate secondary keys, use the secondary keys to encrypt the broadcast and generate ciphertexts, and use the RSA encryption scheme to implement derivability between the primary keys and the secondary keys. To decrypt the broadcast, a privileged user uses one of its primary keys to derive a secondary key, which is used to decrypt the broadcast. The product of key derivation costc and the key storage cost k is at most (2a−log a−2)loga n, when n is the number of users, 1≦b≦log n, a=2b, and revoked users r<n / 3.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com