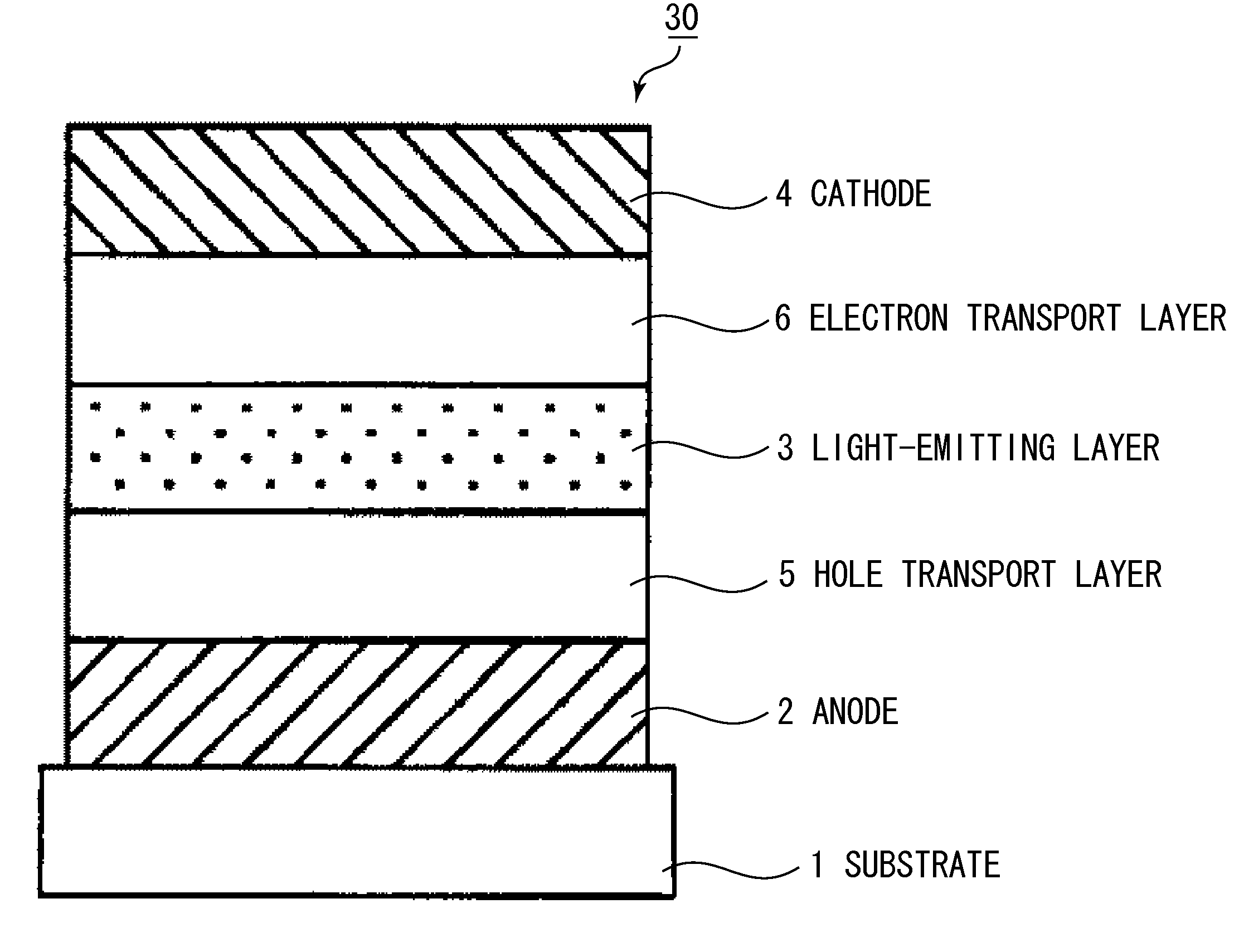
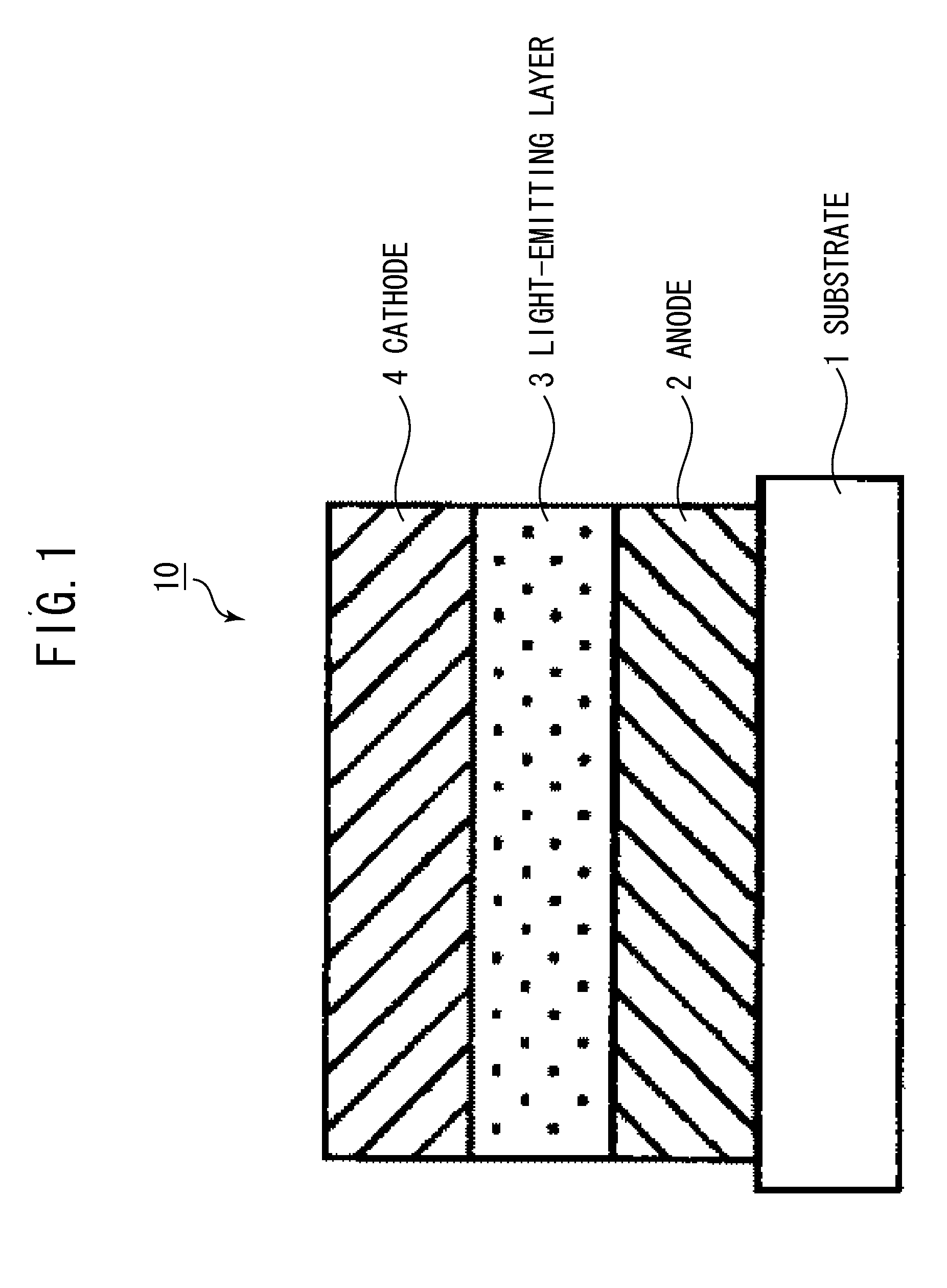
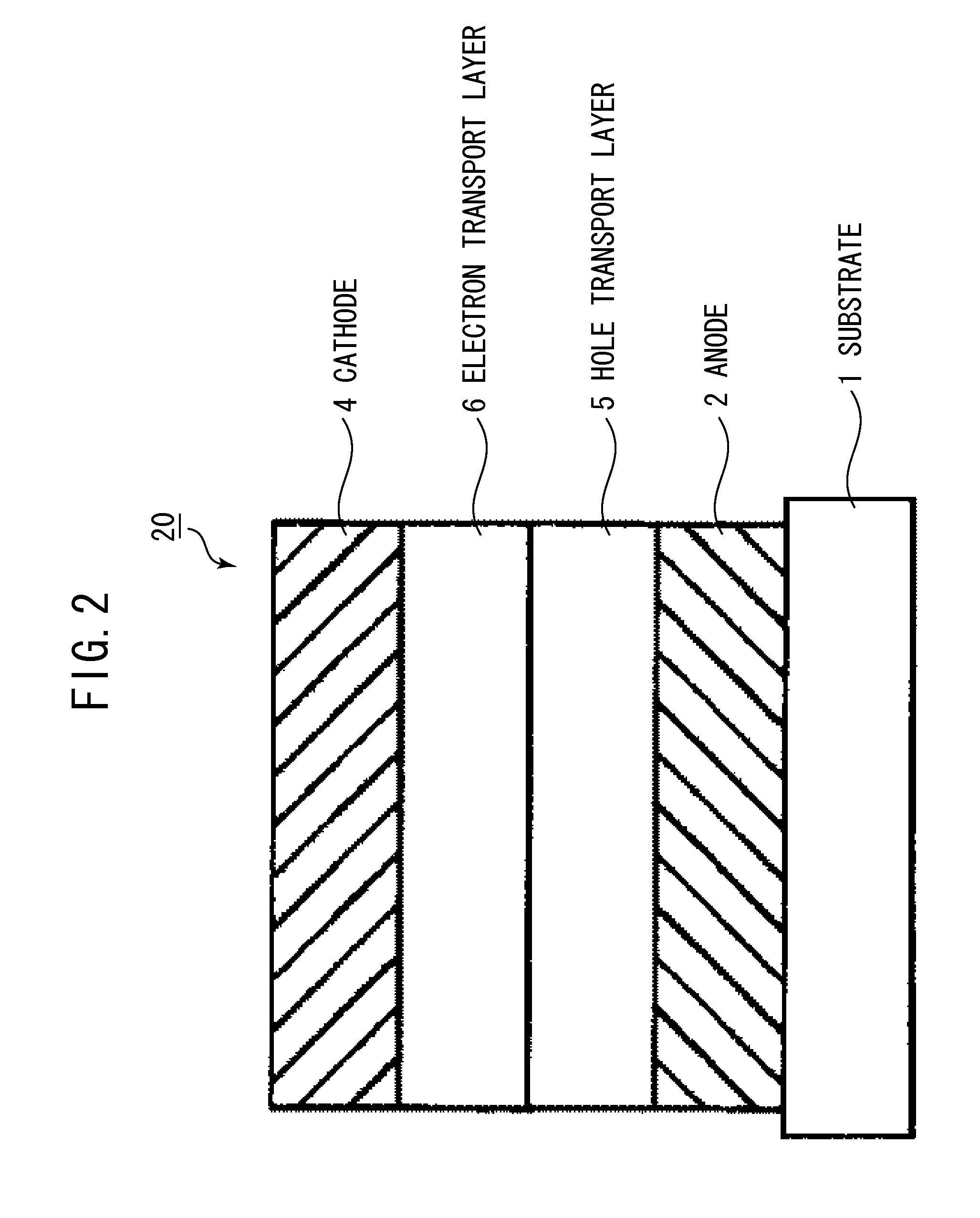
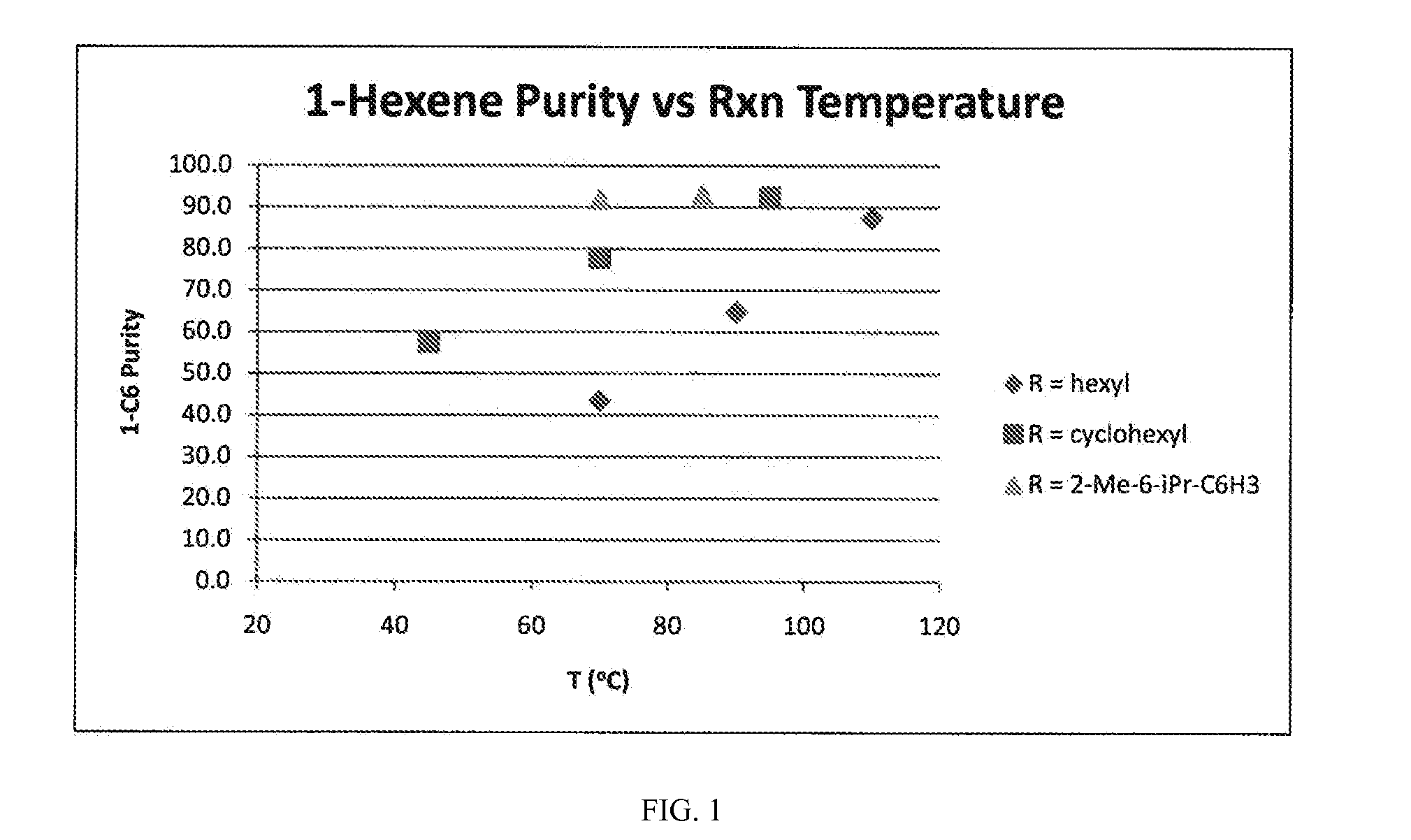
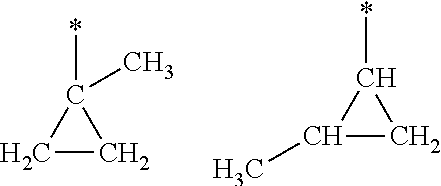
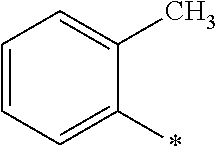
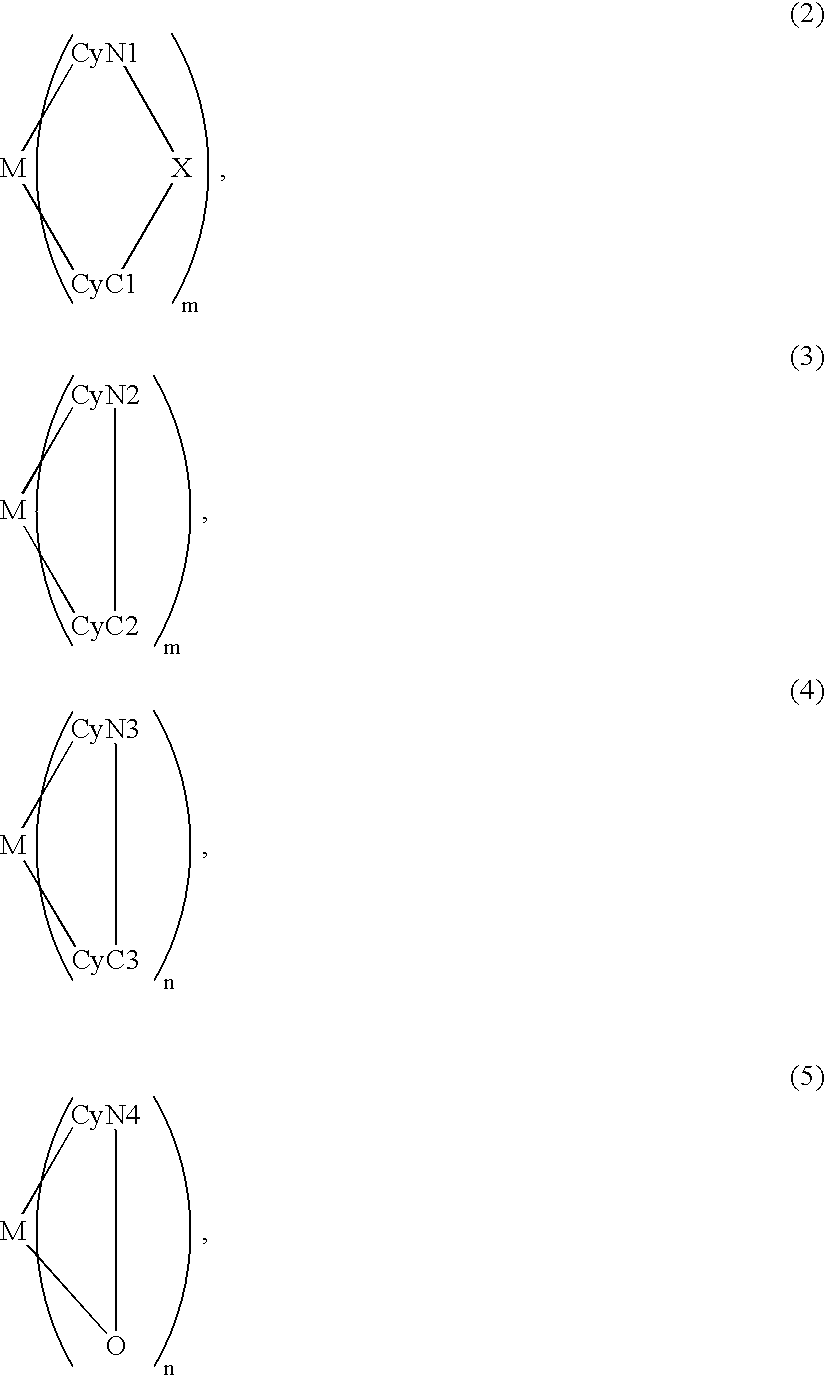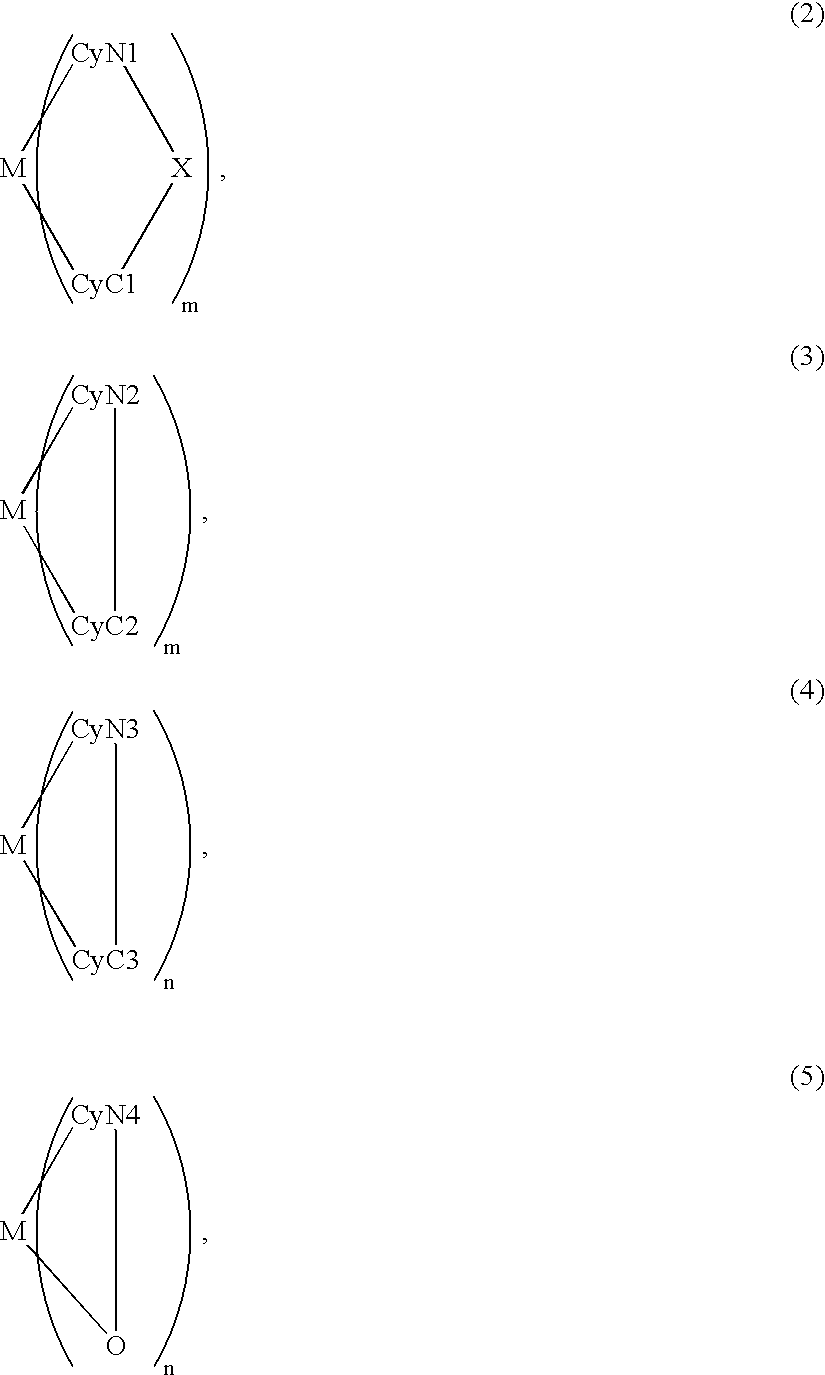Patents
Literature
827results about "Group 6/16 element organic compounds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
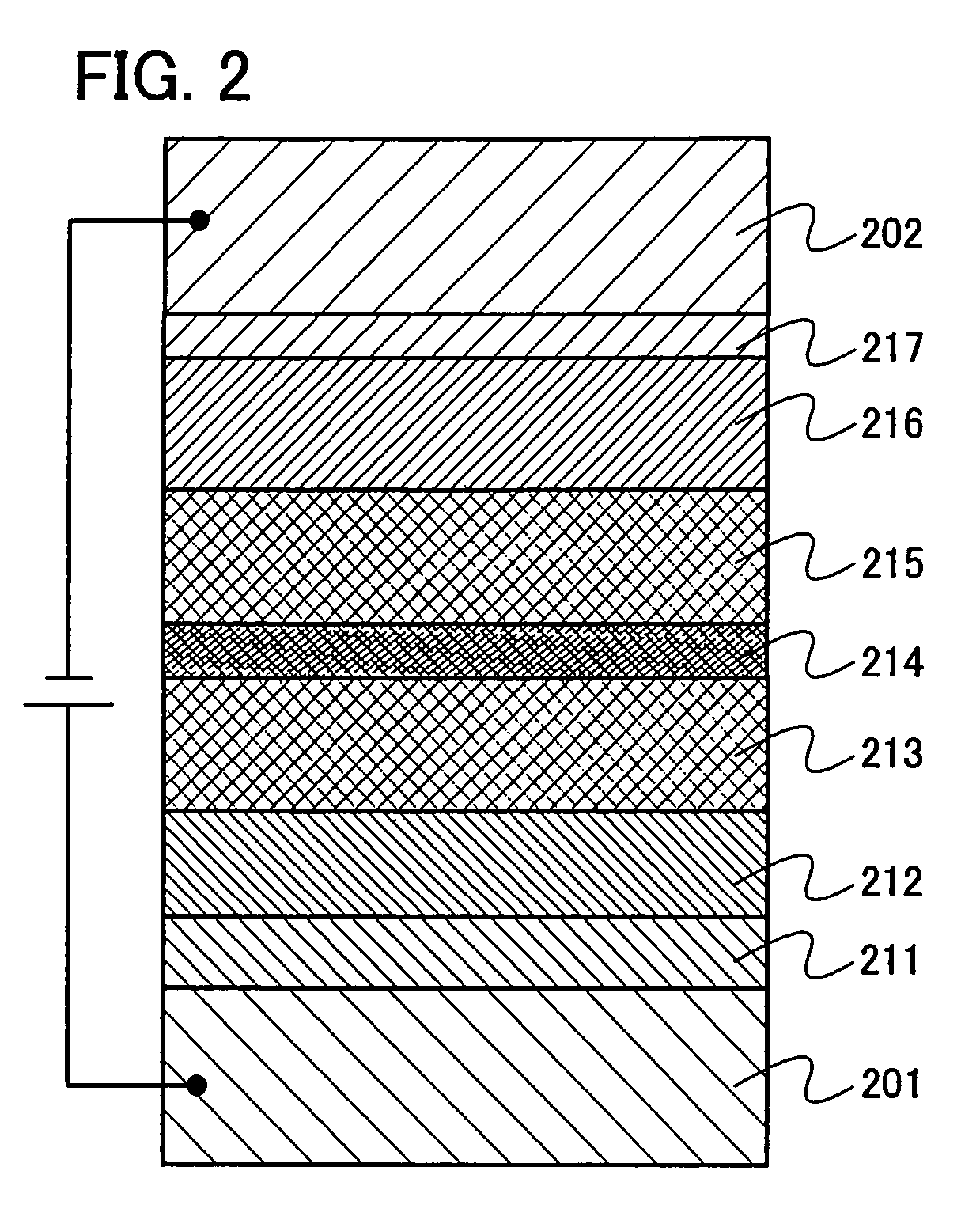
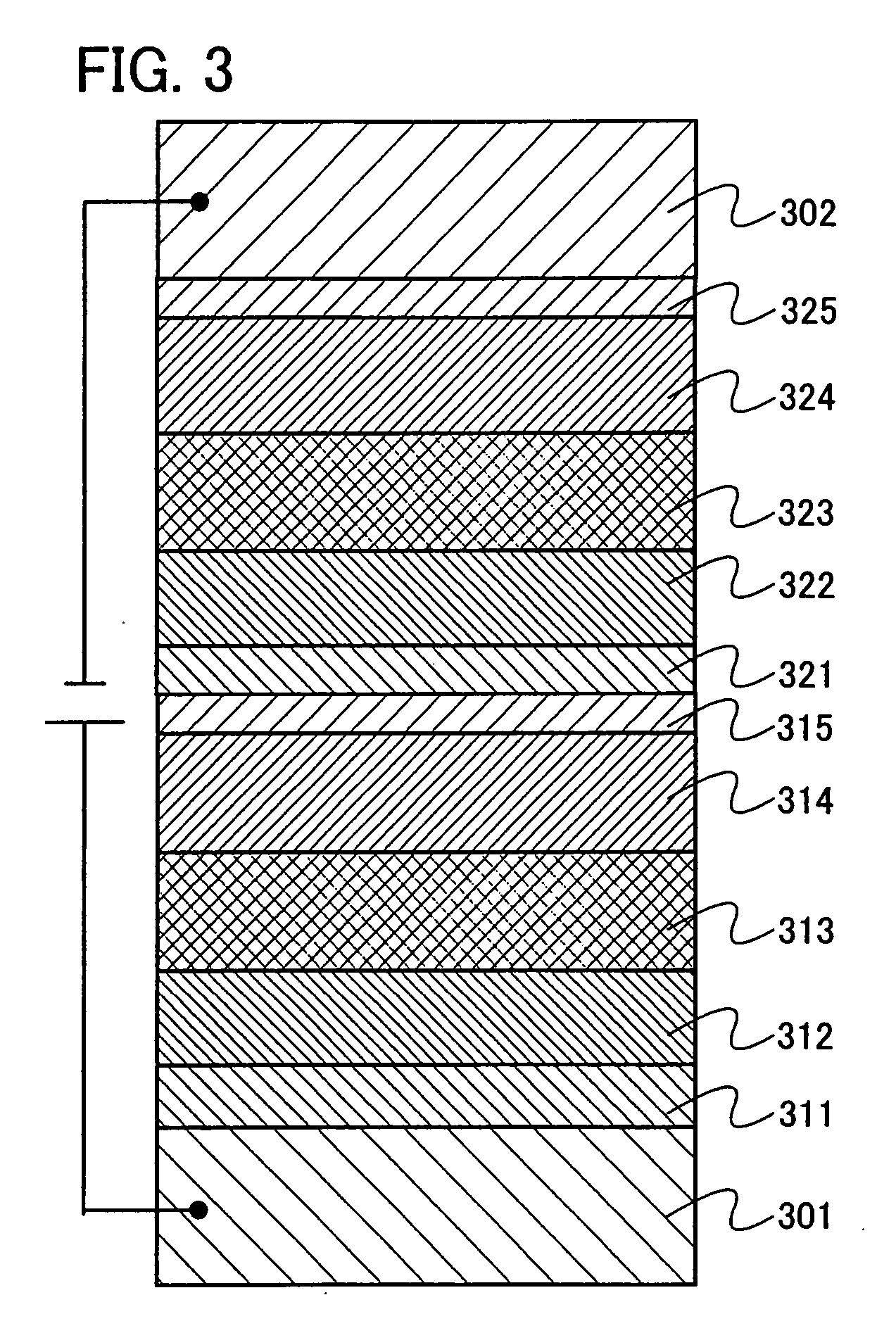
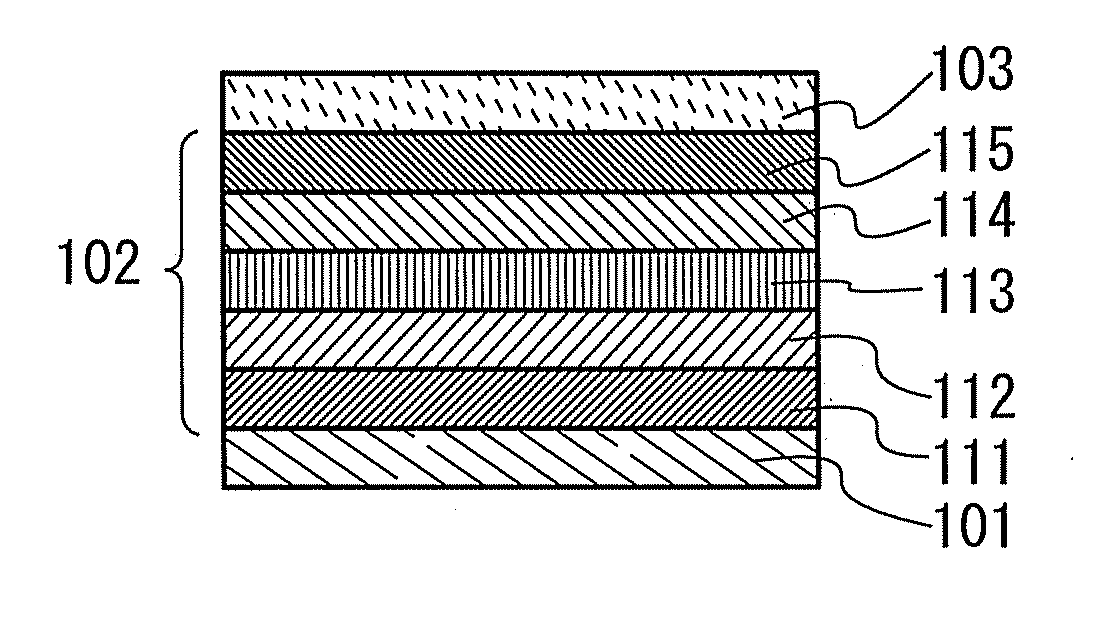
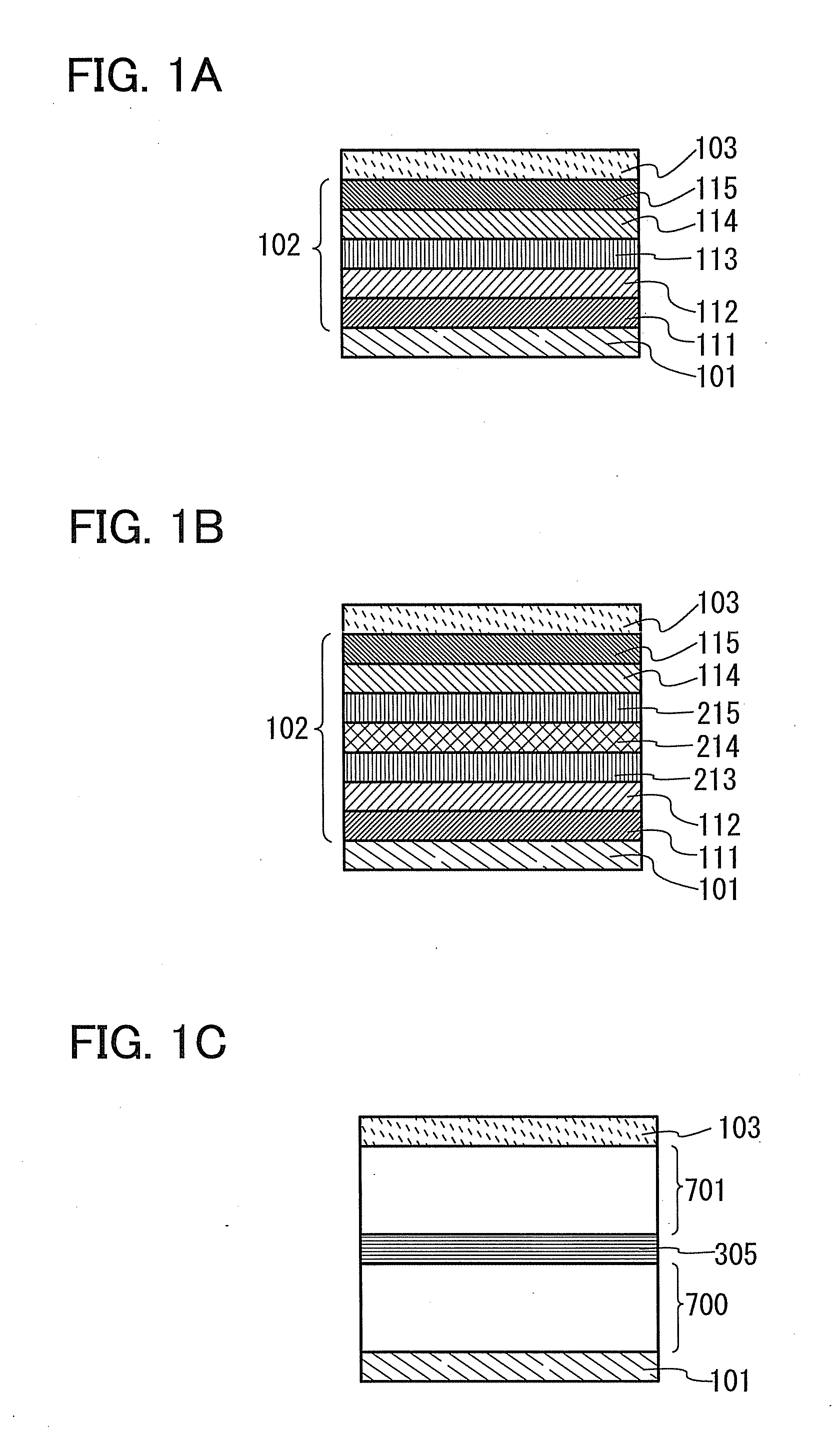
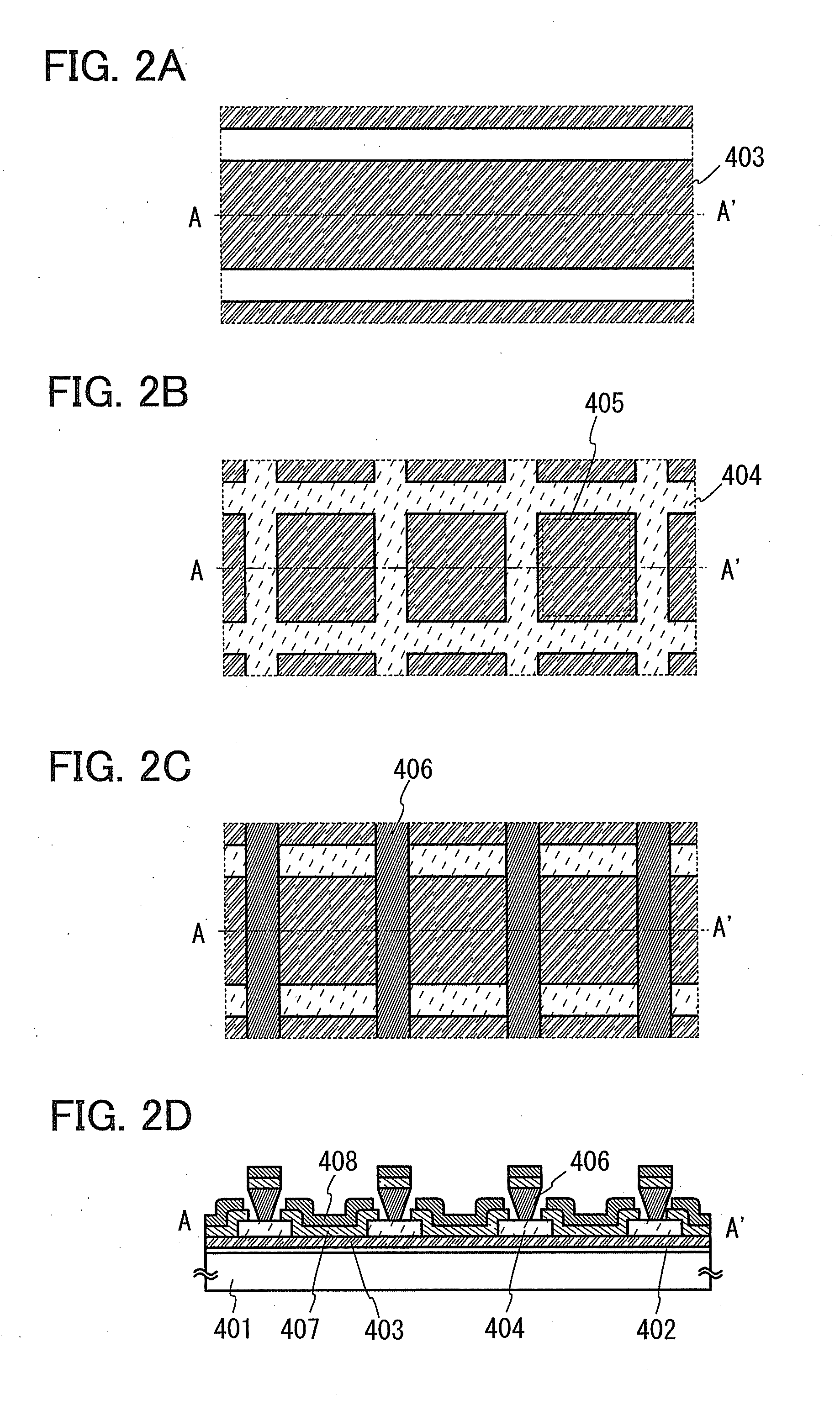
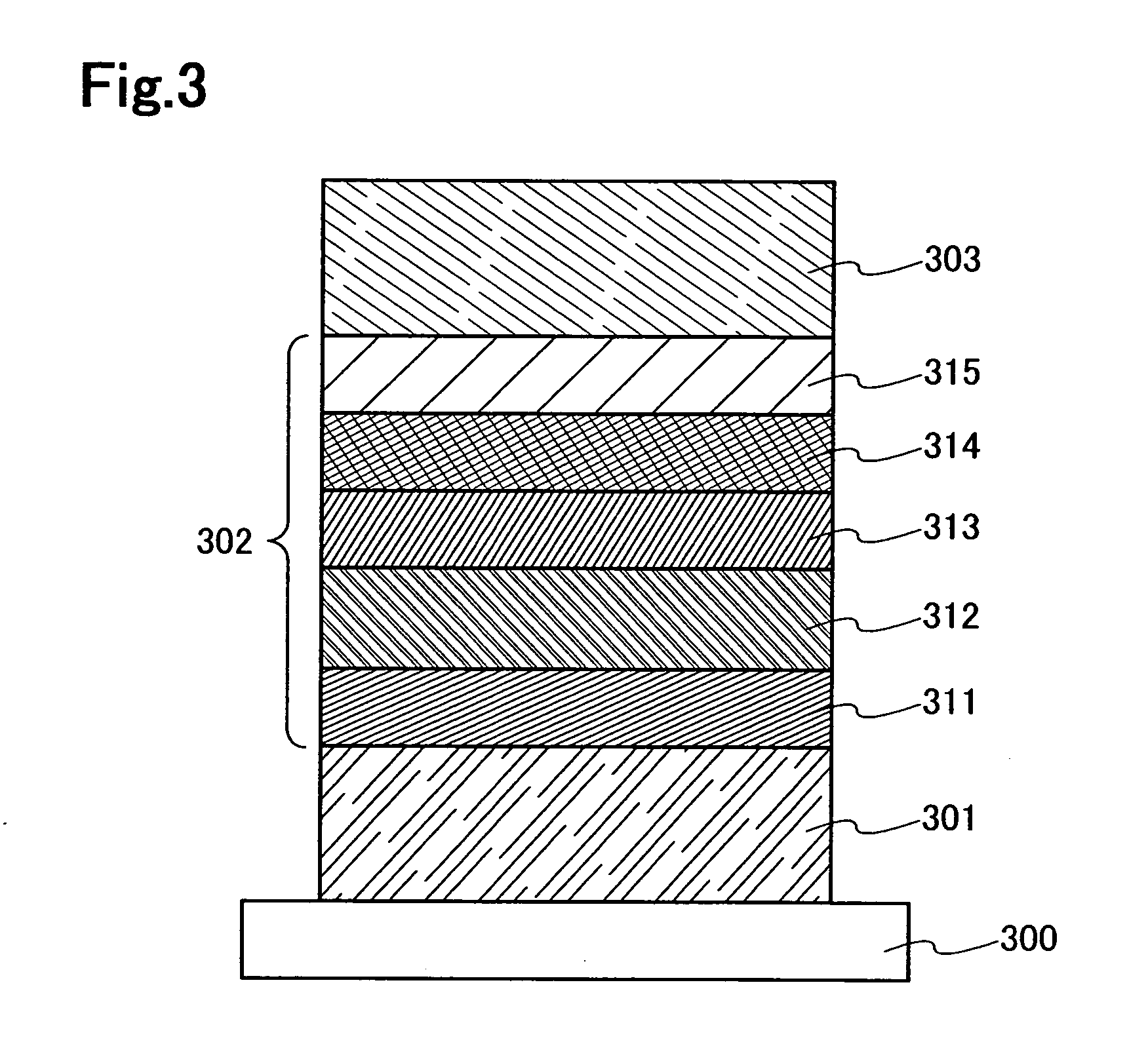
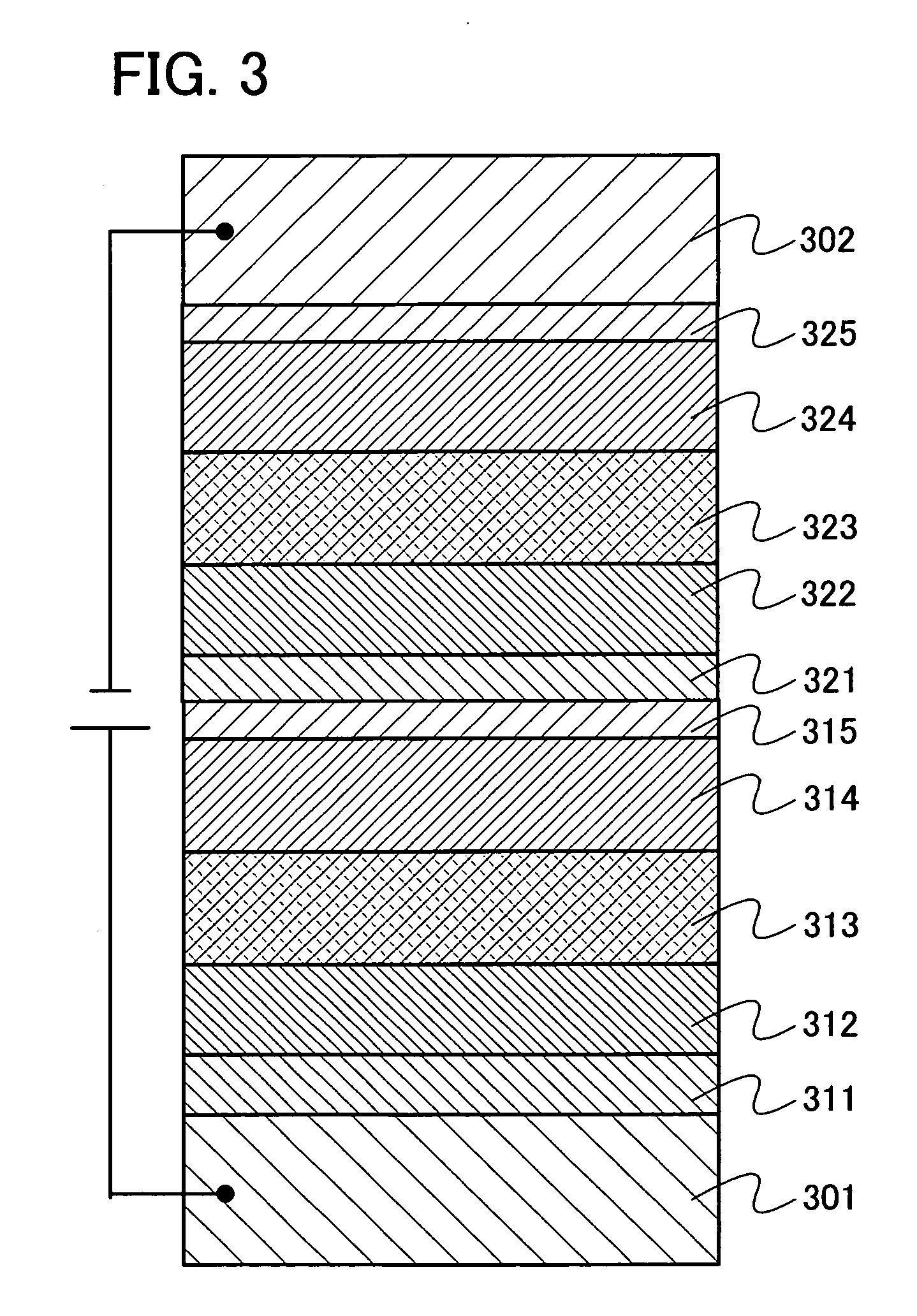
Organometallic complex and organic light-emitting element using same
InactiveUS20090039776A1Improve efficiencyIncreased durabilityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesSimple Organic CompoundsOrganic compound
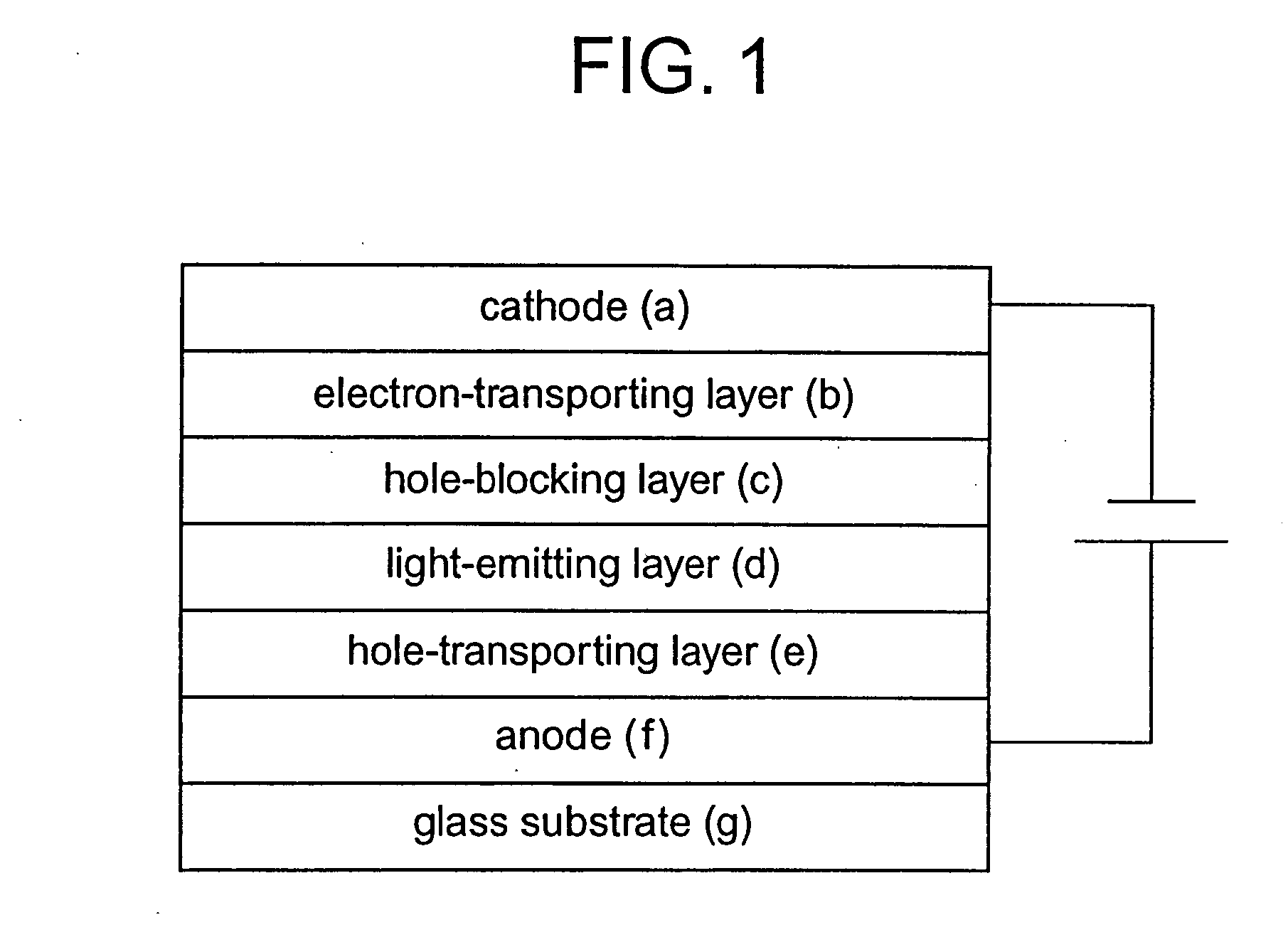
An organometallic complex and an organic light-emitting element containing the complex which has a very high efficiency, a high luminance, and durability. The organic light-emitting element has an anode, a cathode, and a layer including an organic compound sandwiched between the anode and cathode. The layer containing the organic compound includes at least one organometallic complex represented by General Formula [I] below.
Owner:CANON KK
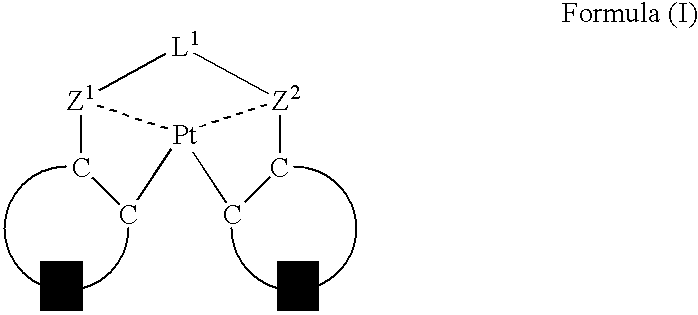
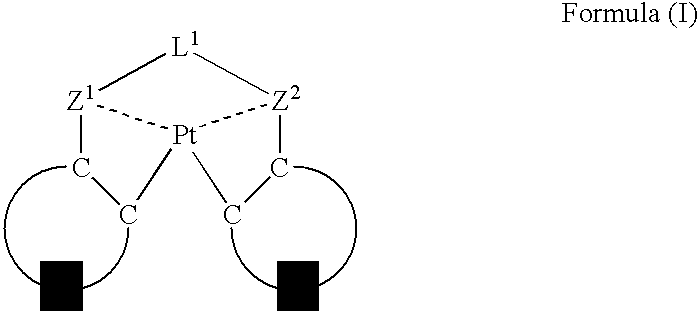
Organic electroluminescent device
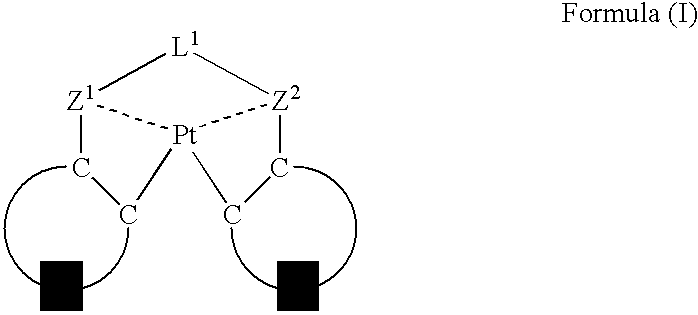
ActiveUS20060263635A1Group 5/15 element organic compoundsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsPlatinumNitrogen
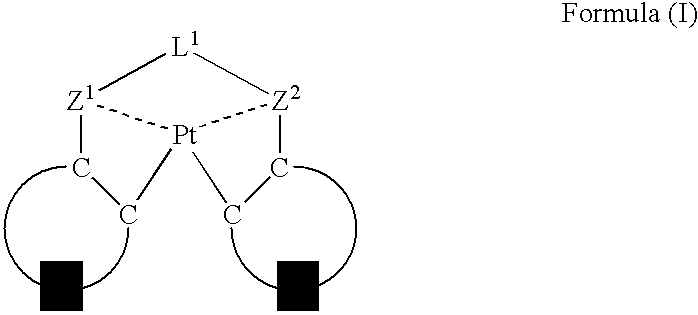
An organic electroluminescent device having a pair of electrodes and at least one organic layer interposed between the pair of electrodes, in which the at least one organic layer contains at least one compound represented by formula (I): wherein, Z1 and Z2 each independently represent a nitrogen-containing aromatic six-membered ring coordinated to the platinum through a nitrogen atom; Q1 represents a group of atoms necessary for forming, together with the —C—C—, a nitrogen-containing aromatic five-membered ring; L1 represents a single bond or a divalent linking group; and n is 0 or 1.
Owner:UDC IRELAND +1
Organometallic Complex, Light-Emitting Element, Light-Emitting Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device
InactiveUS20140246656A1Improve efficiencyHigh sublimabilityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesHydrogenEmission efficiency
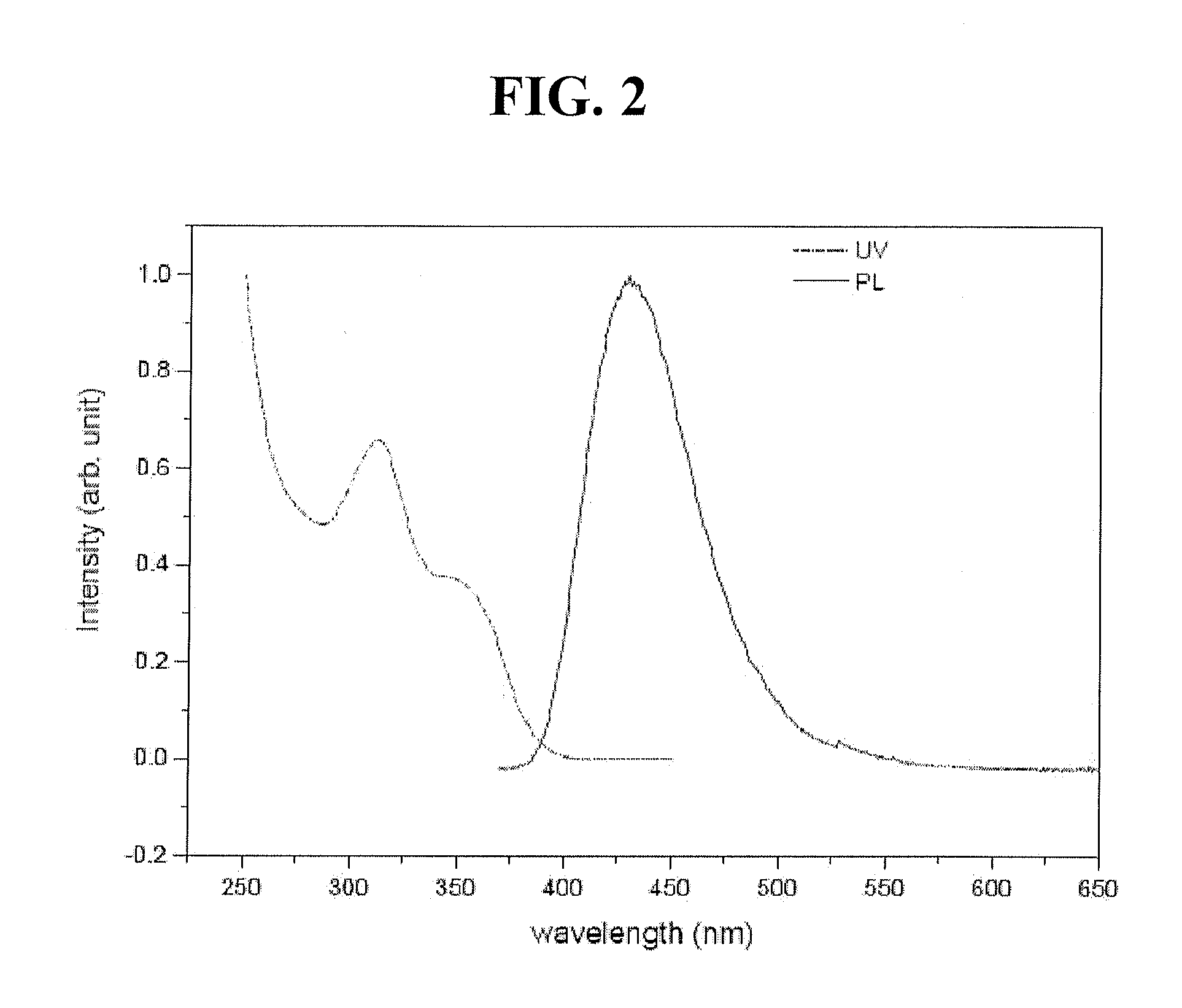
As a novel substance having a novel skeleton, an organometallic complex having high emission efficiency and improved color purity is provided. The color purity is improved by reducing the half width of an emission spectrum. The organometallic complex is represented by General Formula (G1). In General Formula (G1), at least one of R1 to R4 represents a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, and the others each independently represent hydrogen or a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms. Note that the case where all of R1 to R4 represent alkyl groups each having 1 carbon atom is excluded. Further, R5 to R9 each independently represent hydrogen or a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Organometallic Complex, Light-Emitting Element, Light-Emitting Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device
ActiveUS20130165653A1Improve emission efficiencyHigh color purityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsNitrogenKetone
As a novel substance having a novel skeleton, an organometallic complex with high emission efficiency which achieves improved color purity by a reduction of half width of an emission spectrum is provided. One embodiment of the present invention is an organometallic complex in which a β-diketone and a six-membered heteroaromatic ring including two or more nitrogen atoms inclusive of a nitrogen atom that is a coordinating atom are ligands. In General Formula (G1), X represents a substituted or unsubstituted six-membered heteroaromatic ring including two or more nitrogen atoms inclusive of a nitrogen atom that is a coordinating atom. Further, R1 to R4 each represent a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Atomic layer deposition using metal amidinates
ActiveUS20060141155A1Improve conductivityReduce the temperatureGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsHydrogenWater vapor
Metal films are deposited with uniform thickness and excellent step coverage. Copper metal films were deposited on heated substrates by the reaction of alternating doses of copper(I) NN′-diisopropylacetamidinate vapor and hydrogen gas. Cobalt metal films were deposited on heated substrates by the reaction of alternating doses of cobalt(II) bis(N,N′-diisopropylacetamidinate) vapor and hydrogen gas. Nitrides and oxides of these metals can be formed by replacing the hydrogen with ammonia or water vapor, respectively. The films have very uniform thickness and excellent step coverage in narrow holes. Suitable applications include electrical interconnects in microelectronics and magnetoresistant layers in magnetic information storage devices.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Organometallic Complex, and Light-Emitting Element, Light-Emitting Device, and Electronic Device Including the Organometallic Complex
ActiveUS20100105902A1Improve emission efficiencySolve low luminous efficiencyGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsGroup 1/11 element organic compoundsLength waveLight emitting device
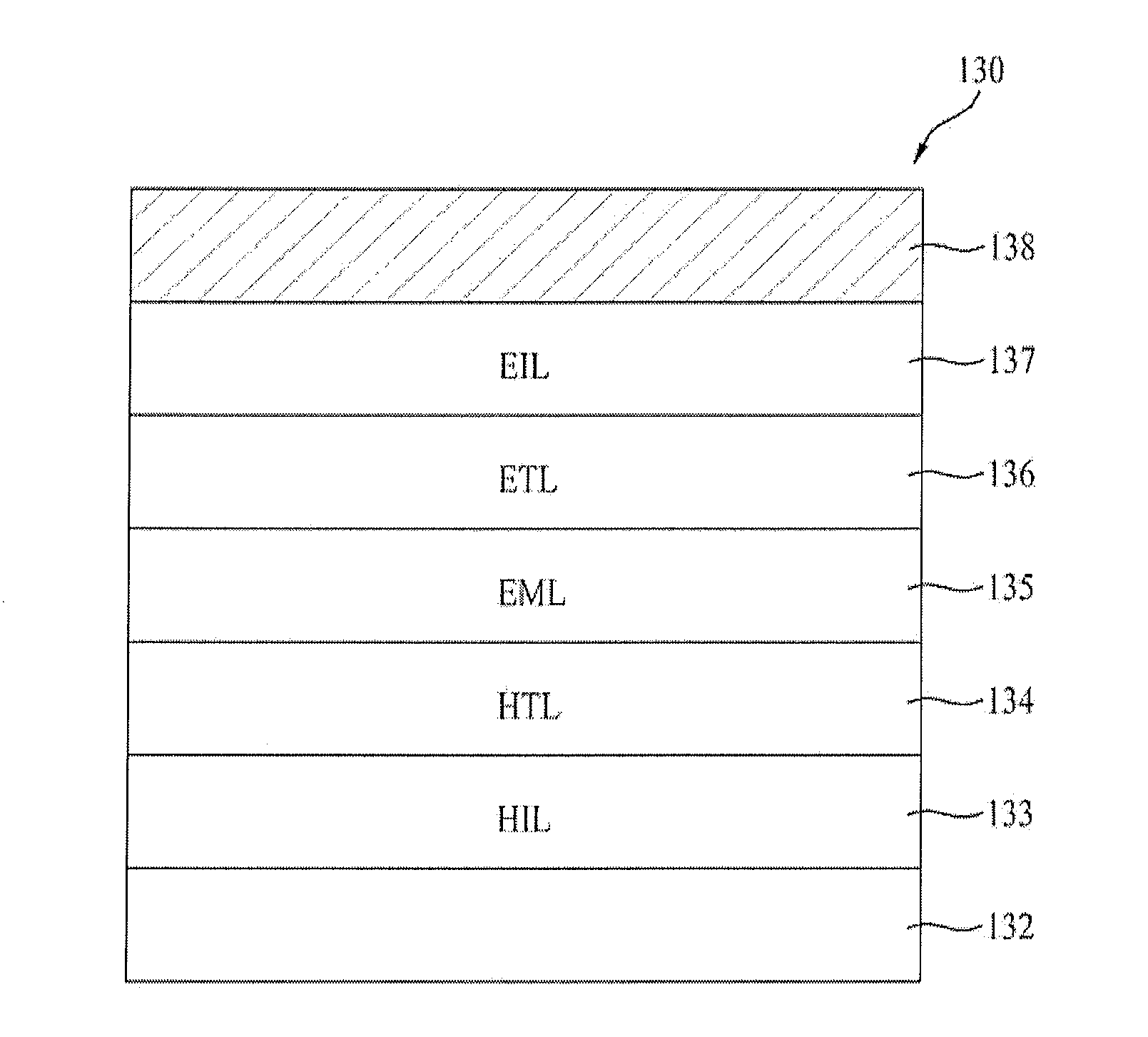
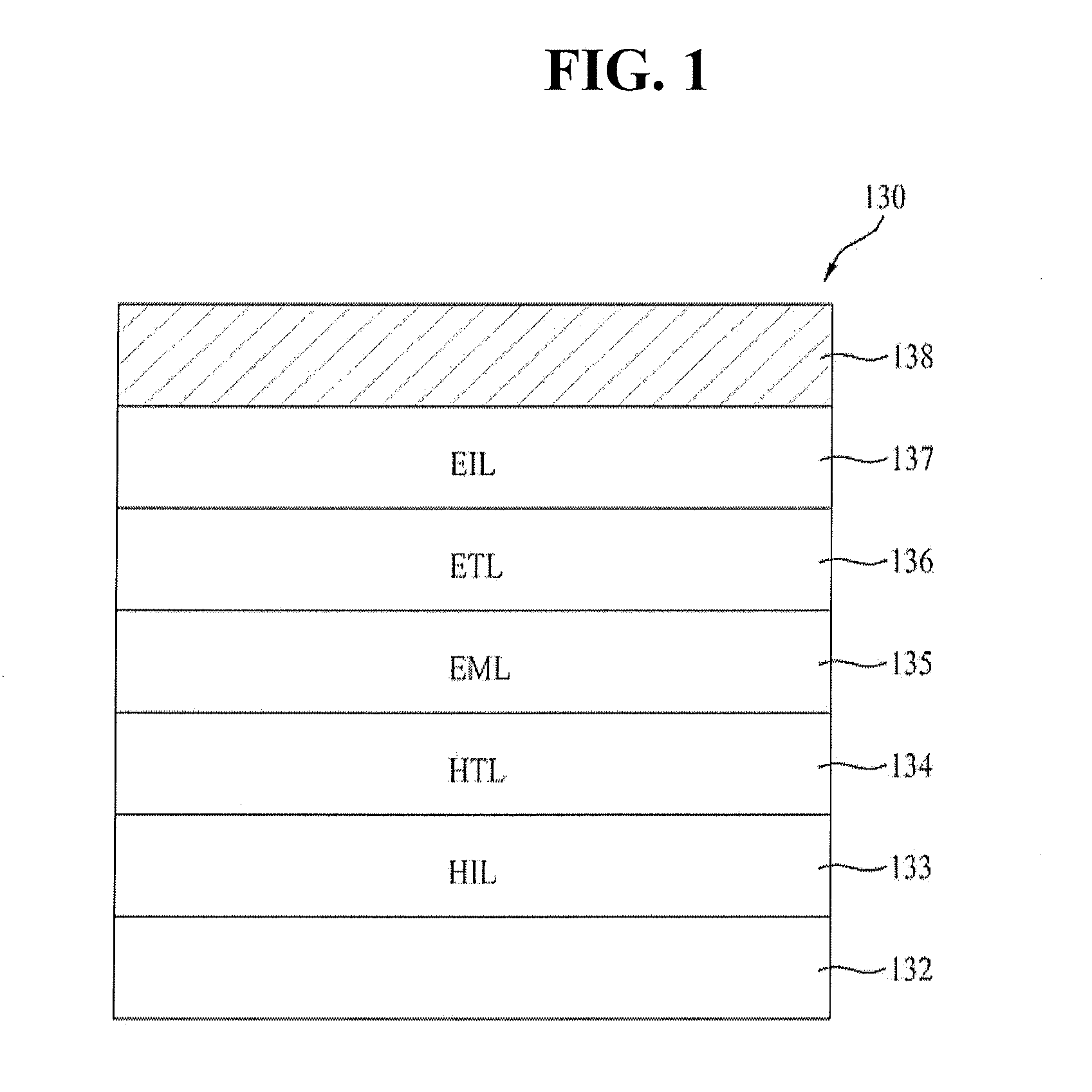
An organometallic complex is provided by which favorable red-color light emission can be obtained. Further, an organometallic complex having a peak of light emission at about 620 nm is provided because the wavelength of light which is perceived as excellent red-color light is about 620 nm. Furthermore, an organometallic complex is provided by which red-color light emission with high luminous efficiency (cd / A) can be obtained. An organometallic complex represented by the following general formula (G2) and a light-emitting element, a light-emitting device, and an electronic device including the organometallic complex represented by the following general formula (G2) are provided.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Complexes with tridentate ligands
ActiveUS20090115322A1Group 5/15 element organic compoundsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsOrganic light emitting deviceCoordination complex
The present invention relates to organic light emitting devices (OLEDs), and more specifically to phosphorescent organic materials used in such devices. More specifically, the present invention relates to emissive phosphorescent material which comprise at least one tridentate ligand bound to a metal center, wherein at least one of the bonds to the tridentate ligand is a carbon-metal bond.
Owner:UNIVERSAL DISPLAY
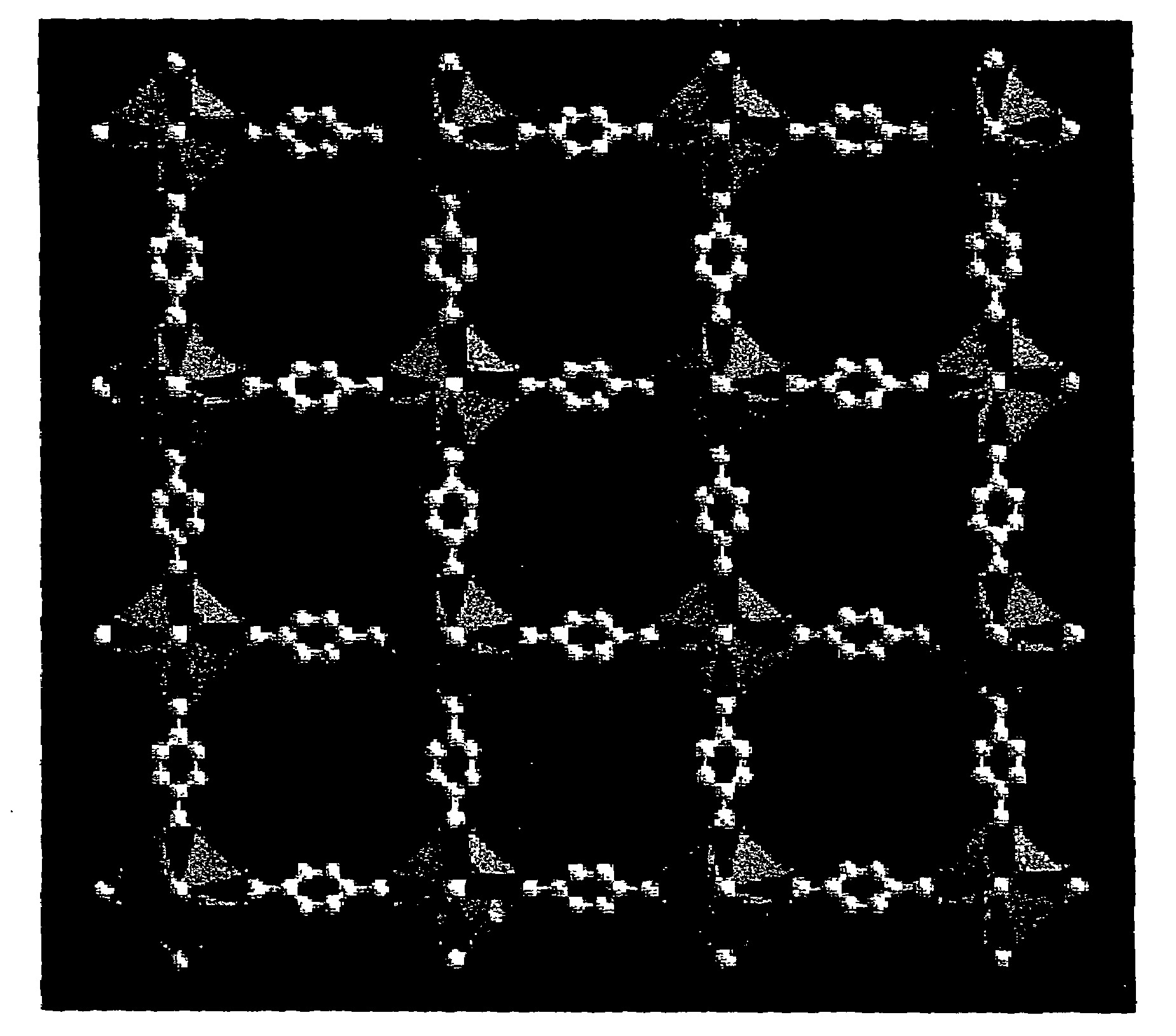
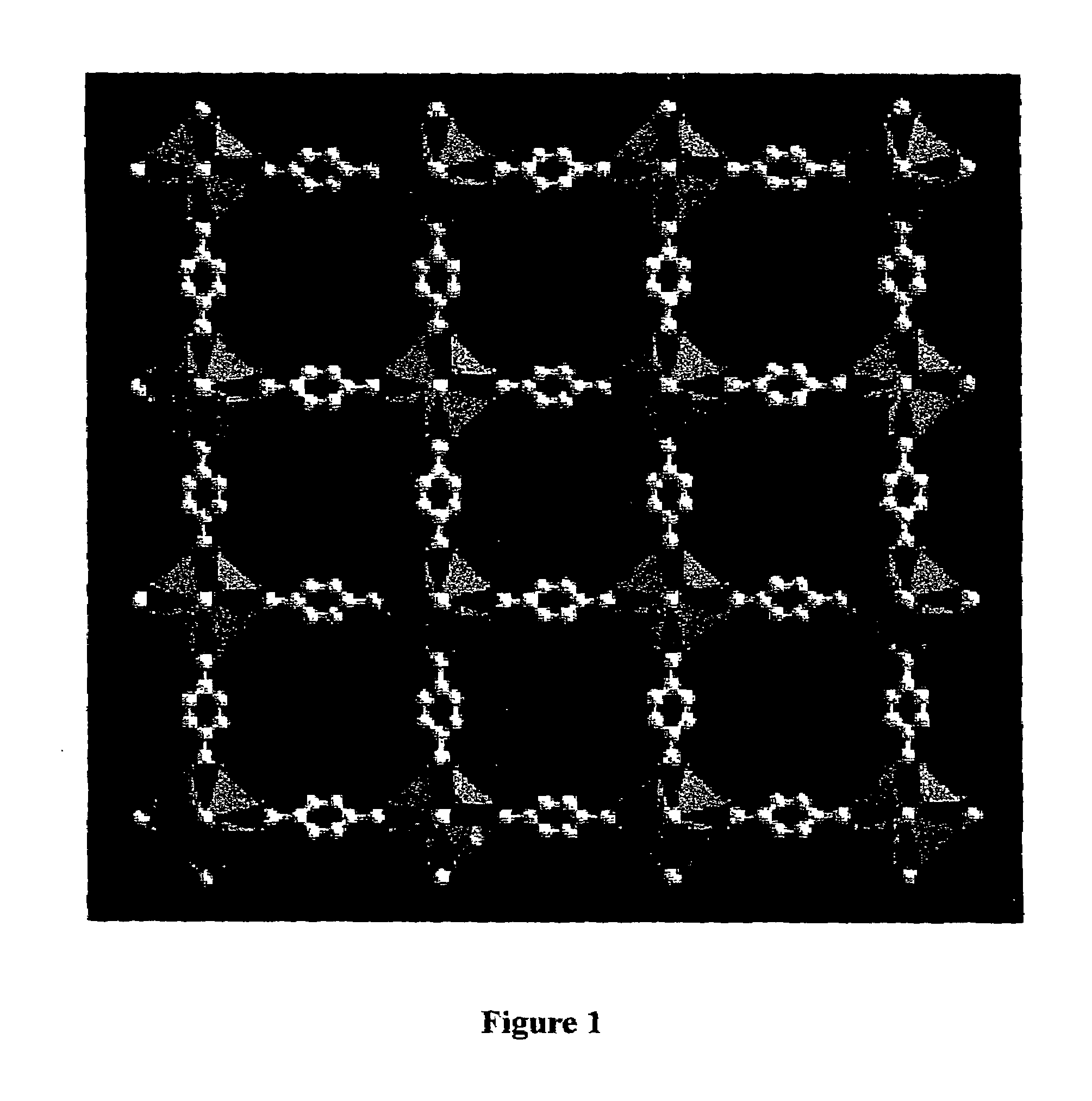
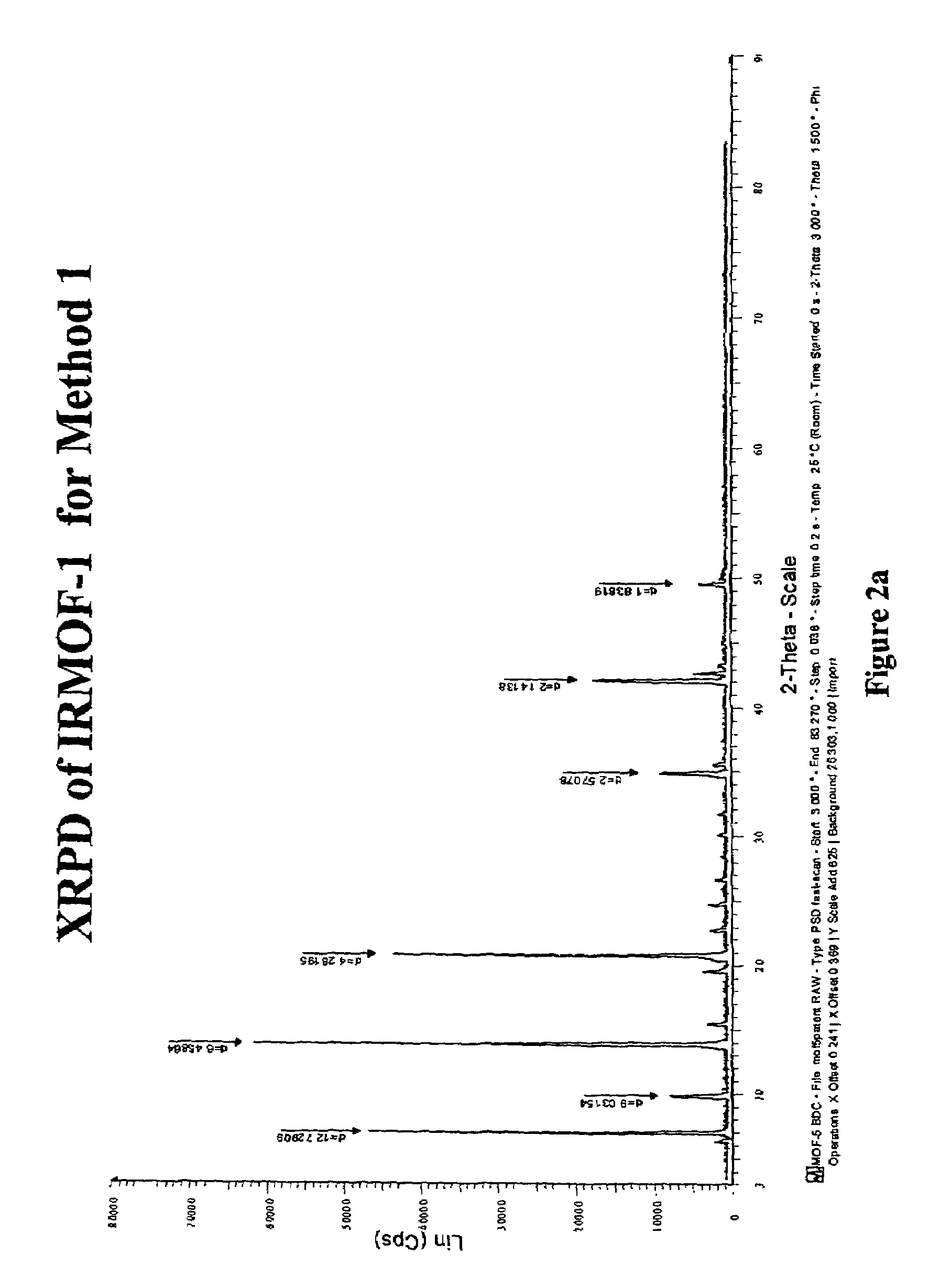
Isoreticular metal-organic frameworks, process for forming the same, and systematic design of pore size and functionality therein, with application for gas storage
InactiveUS6930193B2High methane storage capacityIncrease storage capacityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsOrganic linkingSystems design
An isoreticular metal-organic framework (IRMOF) and method for systematically forming the same. The method comprises the steps of dissolving at least one source of metal cations and at least one organic linking compound in a solvent to form a solution; and crystallizing the solution under predetermined conditions to form a predetermined IRMOF. At least one of functionality, dimension, pore size and free volume of the IRMOF is substantially determined by the organic linking compound.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Metal coordination compound, luminescence device and display apparatus
InactiveUS20030054198A1Group 5/15 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesQuinolinePerylene derivatives
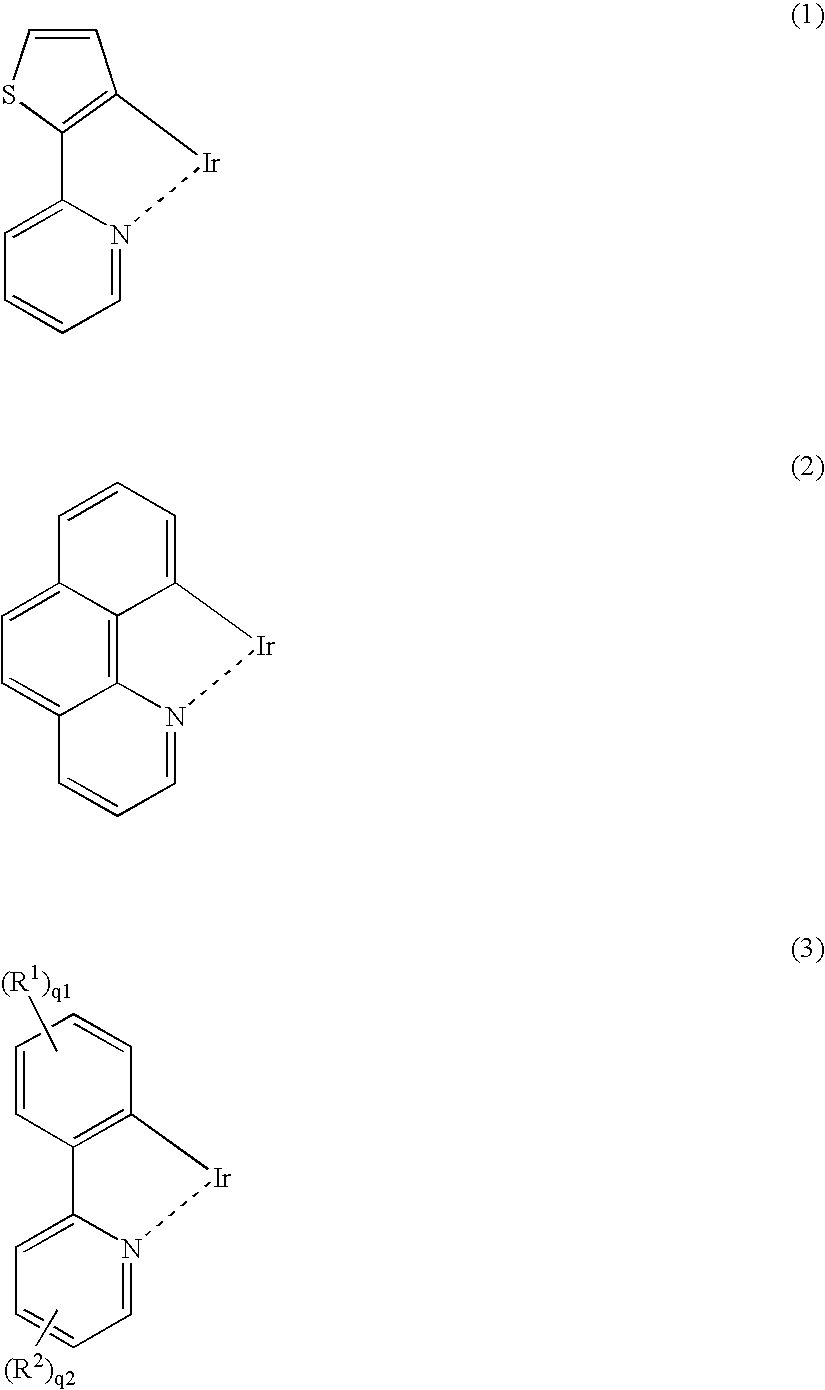
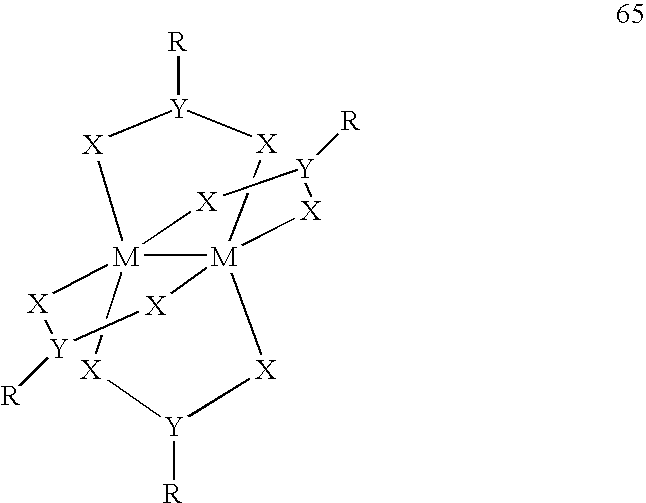
An organic EL device includes a luminescence layer containing, as a luminescent material allowing a high-luminescence and high-efficiency luminescence for a long period of time, a metal coordination compound represented by the following formula (1): LmML'n, wherein M denotes Ir, Pt, Ph or Pd; L denotes a bidentate ligand; L' denotes a bidentate ligand different from L; m is an integer of 1, 2 or 3; and n is an integer of 0, 1 or 2 with the proviso that the sum of m and n is 2 or 3. The partial structure MLm is represented by a formula (2) or a formula (3) shown below, and the partial structure ML'n is represented by a formula (4) or a formula (5) shown below: wherein CyN1, CyN2 and CyN3 independently denote a substituted or unsubstituted cyclic group containing a nitrogen atom connected to M; CyN4 denotes a cyclic group containing 8-quinoline or its derivative having a nitrogen atom connected to M; CyC1, CyC2 and CyC3 independently denote a substituted or unsubstituted cyclic group containing a carbon atom connected to M, with the proviso that the metal coordination compound is represented by the formula (2) when n is 0.
Owner:CANON KK
Organometallic complex and light emitting element, light emitting device, and electronic device using the organometallic complex
InactiveUS20070244320A1High light emitting efficiencyReduce power consumptionGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesArylHydrogen
An organometallic complex having a structure represented by the following general formula (G1) is provided. (In the formula, A represents an aromatic hydrocarbon group having 6 to 25 carbon atoms. Further, Z represents any one of hydrogen, an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, or an aryl group having 6 to 25 carbon atoms. In addition, Ar1 represents an aryl group having 6 to 25 carbon atoms. R1 represents any one of hydrogen, an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, or an alkoxy group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms. Further, M is a central metal and represents an element belonging to Group 9 or Group 10.)
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Organometallic Complex, Light-Emitting Element, Light-Emitting Device, Electronic Device and Lighting Device
ActiveUS20120098417A1Improve emission efficiencyReduce power consumptionGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesIridiumHydrogen
Provided is a novel substance that can emit phosphorescence. Alternatively, provided is a novel substance with high emission efficiency. An organometallic complex in which a 4-arylpyrimidine derivative is a ligand and iridium is a central metal is provided. Specifically, an organometallic complex having a structure represented by a general formula (G1) is provided. In the general formula (G1), R1 represents a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms or a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group having 6 to 10 carbon atoms, R2 represents any of hydrogen, a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, and a substituted or unsubstituted phenyl group, R3 represents hydrogen or a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, and Ar1 represents a substituted or unsubstituted arylene group having 6 to 10 carbon atoms.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Blue phosphorescent compound and organic electroluminescent device using the same
Disclosed are a blue phosphorescent compound with a high color purity and a high efficiency, and an organic electroluminescent device using the same. The blue phosphorescent compound is represented by the following Formula:wherein R1 to R5 are each independently hydrogen (H), fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), a cyano group, a C1 to C6 alkyl group, a C1 to C6 alkoxy group, a C6 to C20 substituted or unsubstituted aromatic group, a C5 to C20 substituted or unsubstituted heterocyclic group, a C1 to C6 amine group, a C6 to C20 aromatic-substituted amine group, or a C5 to C20 heterocycle-substituted amine group, X is selected from nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), phosphorous (P) and sulfur (S) atoms, at least one of A1, A2, A3 and A4 is nitrogen (N), and the remaining are selected from hydrogen (H)-substituted carbon, and alkyl or alkoxy-substituted carbon, L is a monodentate or bidentate ligand and n is 1 to 3.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Isoreticular metal-organic frameworks, process for forming the same, and systematic design of pore size and functionality therein, with application for gas storage
InactiveUS7196210B2Group 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSystems designMetal-organic framework
The ability to design and construct solid-state materials with pre-determined structures is a grand challenge in chemistry. An inventive strategy based on reticulating metal ions and organic carboxylate links into extended networks has been advanced to a point that has allowed the design of porous structures in which pore size and functionality can be varied systematically. MOF-5, a prototype of a new class of porous materials and one that is constructed from octahedral Zn—O—C clusters and benzene links, was used to demonstrate that its 3-D porous system can be functionalized with the organic groups, —Br, —NH2, —OC3H7, —OC5H11, —H4C2, and —H4C4, and its pore size expanded with the long molecular struts biphenyl, tetrahydropyrene, pyrene, and terphenyl. The ability to direct the formation of the octahedral clusters in the presence of a desired carboxylate link is an essential feature of this strategy, which resulted in the design of an isoreticular (having the same framework topology) series of sixteen well-defined materials whose crystals have open space representing up to 91.1% of the crystal volume, and homogeneous periodic pores that can be incrementally varied from 3.8 to 28.8 angstroms. Unlike the unpredictable nature of zeolite and other molecular sieve syntheses, the deliberate control exercised at the molecular level in the design of these crystals is expected to have tremendous implications on materials properties and future technologies. Indeed, data indicate that members of this series represent the first monocrystalline mesoporous organic / inorganic frameworks, and exhibit the highest capacity for methane storage (155 cm3 / cm3 at 36 atm) and the lowest densities (0.41 to 0.21 g / cm3) attained to date for any crystalline material at room temperature.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Light-emitting material comprising orthometalated iridium complex, light-emitting device, high efficiency red light-emitting device, and novel iridium complex
InactiveUS7238437B2Group 5/15 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesIridiumLight emitting device
Owner:UDC IRELAND
Volatile dihydropyrazinly and dihydropyrazine metal complexes
ActiveUS20150030782A1Improve responseHighly effectiveGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsVacuum evaporation coatingProtonationRuthenium
A composition comprising dihydropyrazinyl anions that can be coordinated as 6 electron ligands to a broad range of different metals to yield volatile metal complexes for ALD and CVD depositions are described herein. Also described herein are undeprotonated dihydropyrazines that can coordinate to metals as stabilizing neutral ligands. In one embodiment, the composition is used for the direct liquid injection delivery of the metal dihydropyrazinyl complex precursor to the chamber of an ALD or CVD chamber for the deposition of metal-containing thin films such as, for example, ruthenium or cobalt metal films.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Platinum complex and light-emitting device
InactiveUS20060202197A1Superior in light-emitting characteristicSolve low luminous efficiencyGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesPlatinum complexAtomic group
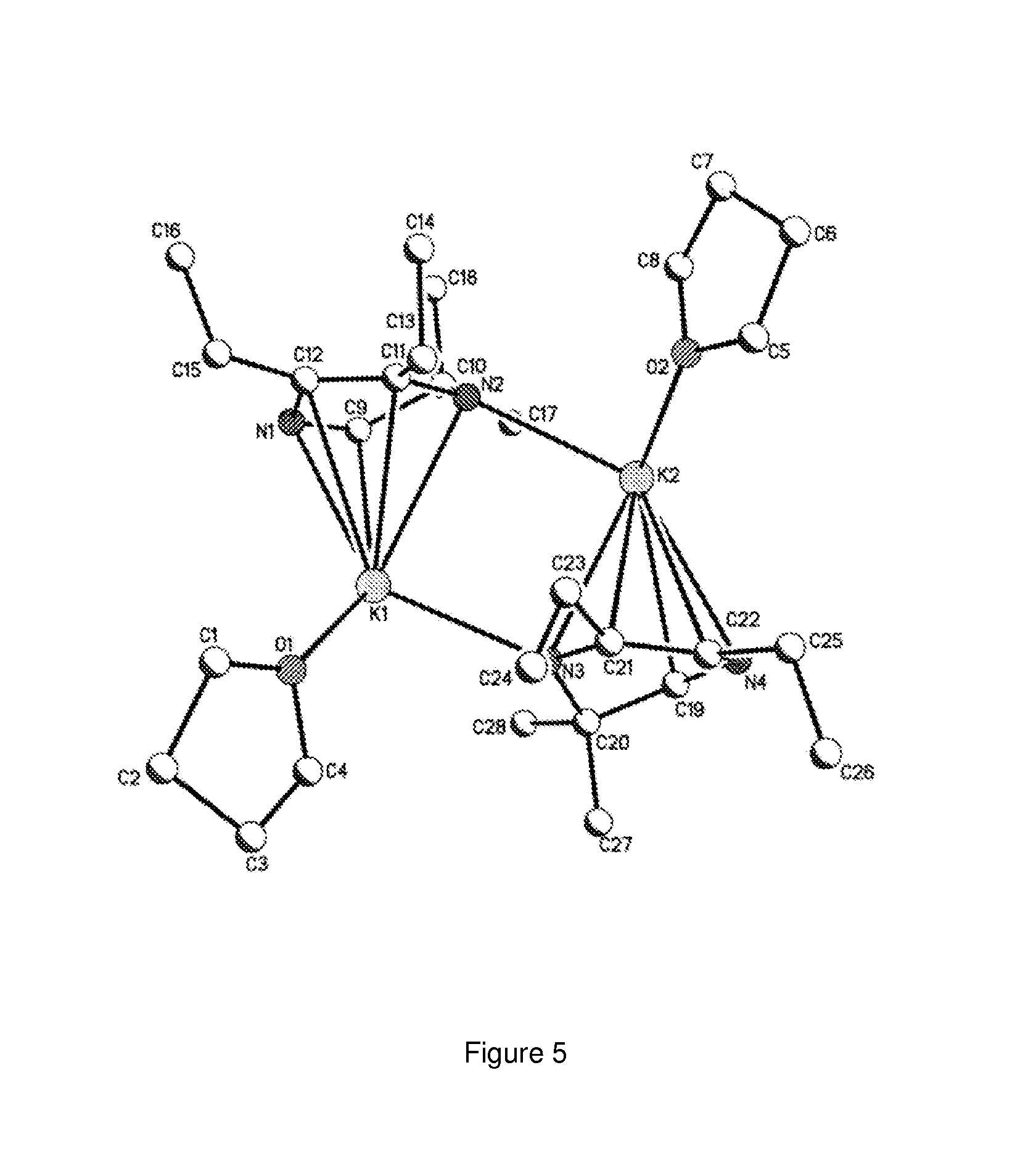
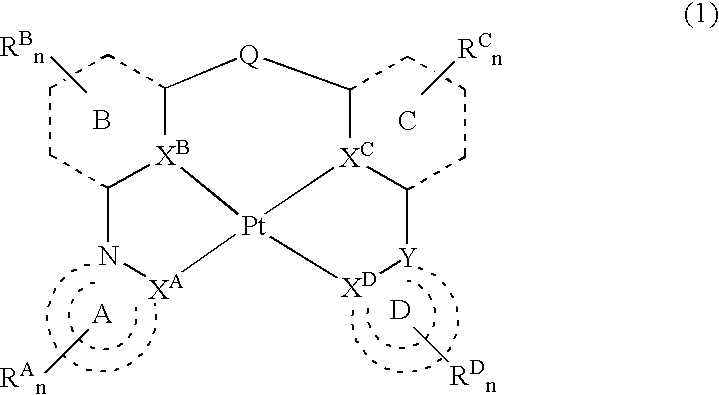
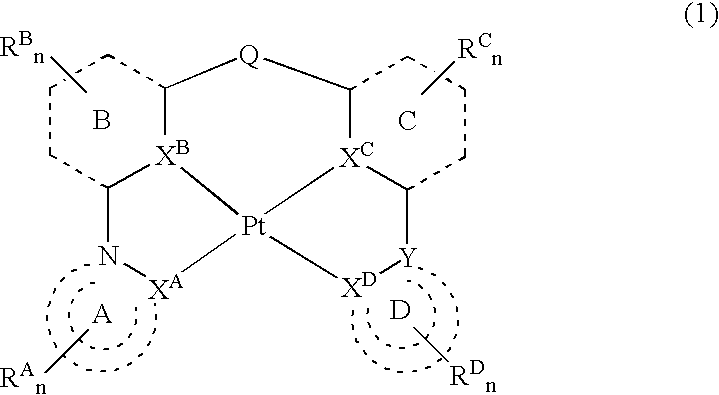
A platinum complex represented by the general formula 1, useful as a phosphorescence emission material, a tetradentate ligand useful for synthesizing the platinum complex, and a light-emitting device containing at least one of the platinum complex. In the general formula 1, two of the rings A, B, C, and D each independently represent an aromatic ring or an aromatic heterocyclic ring, while the other two rings each represent a nitrogen-containing heterocyclic ring; RA-D represent the substituents; each the rings A and B, the rings B and C, and the rings C and D may be bound to each other to form a fused ring independently via the substituent RA-D; XA-D each represent a carbon atom or nitrogen atom; Q represents a bivalent atom or atomic group; Y represents a carbon or nitrogen atom; and n is an integer of 0 to 3.
Owner:TAKASAGO INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
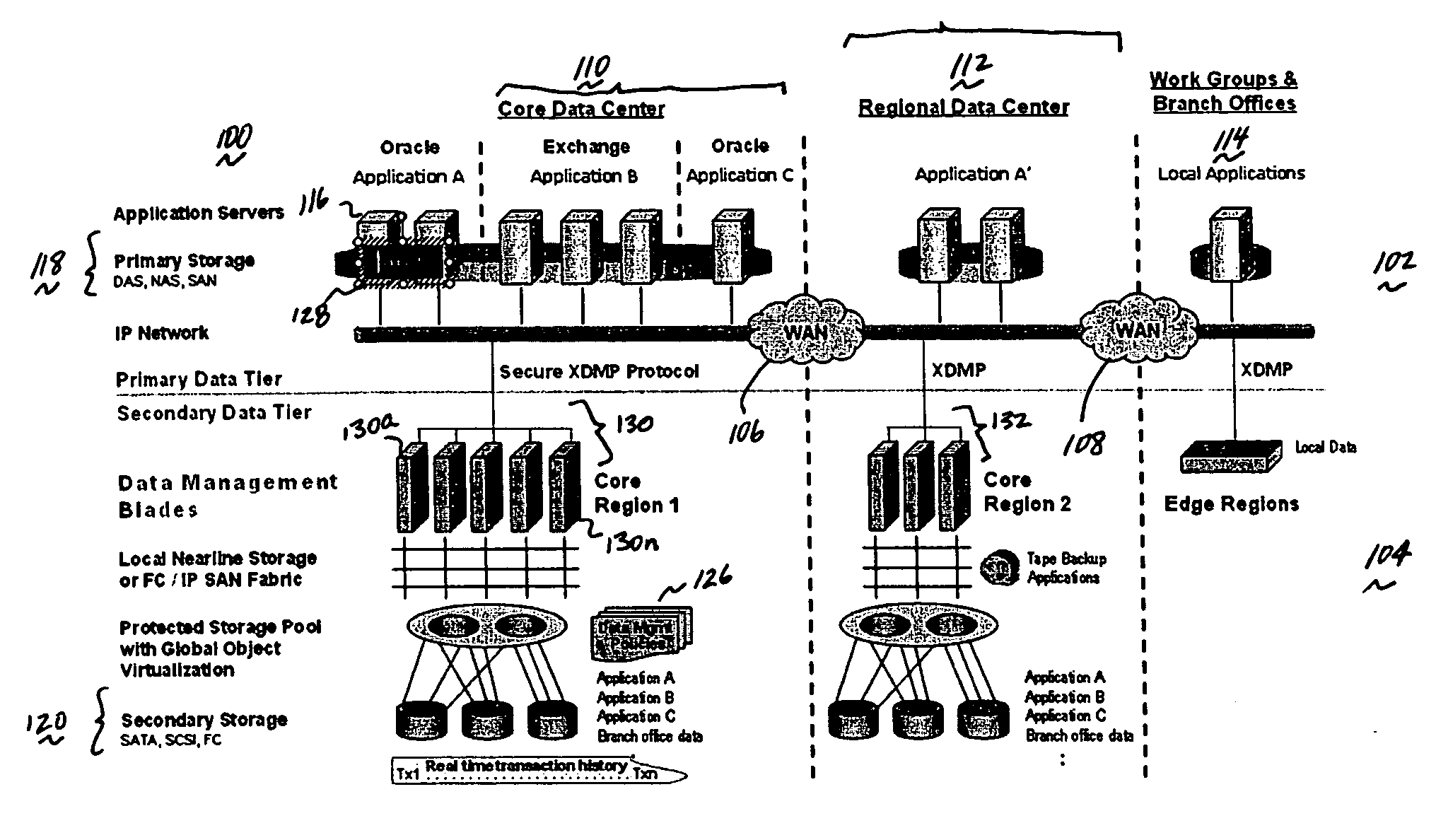
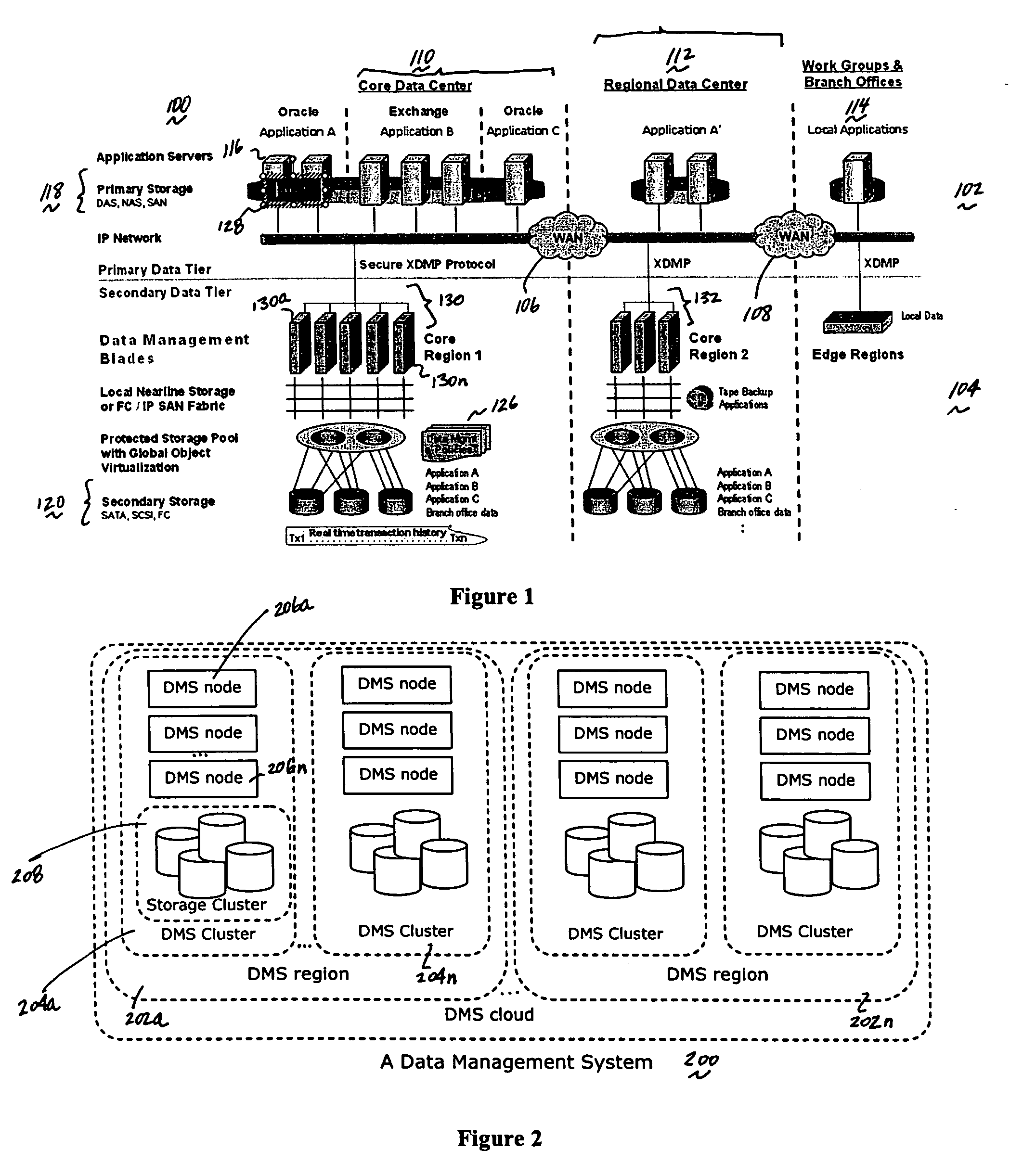
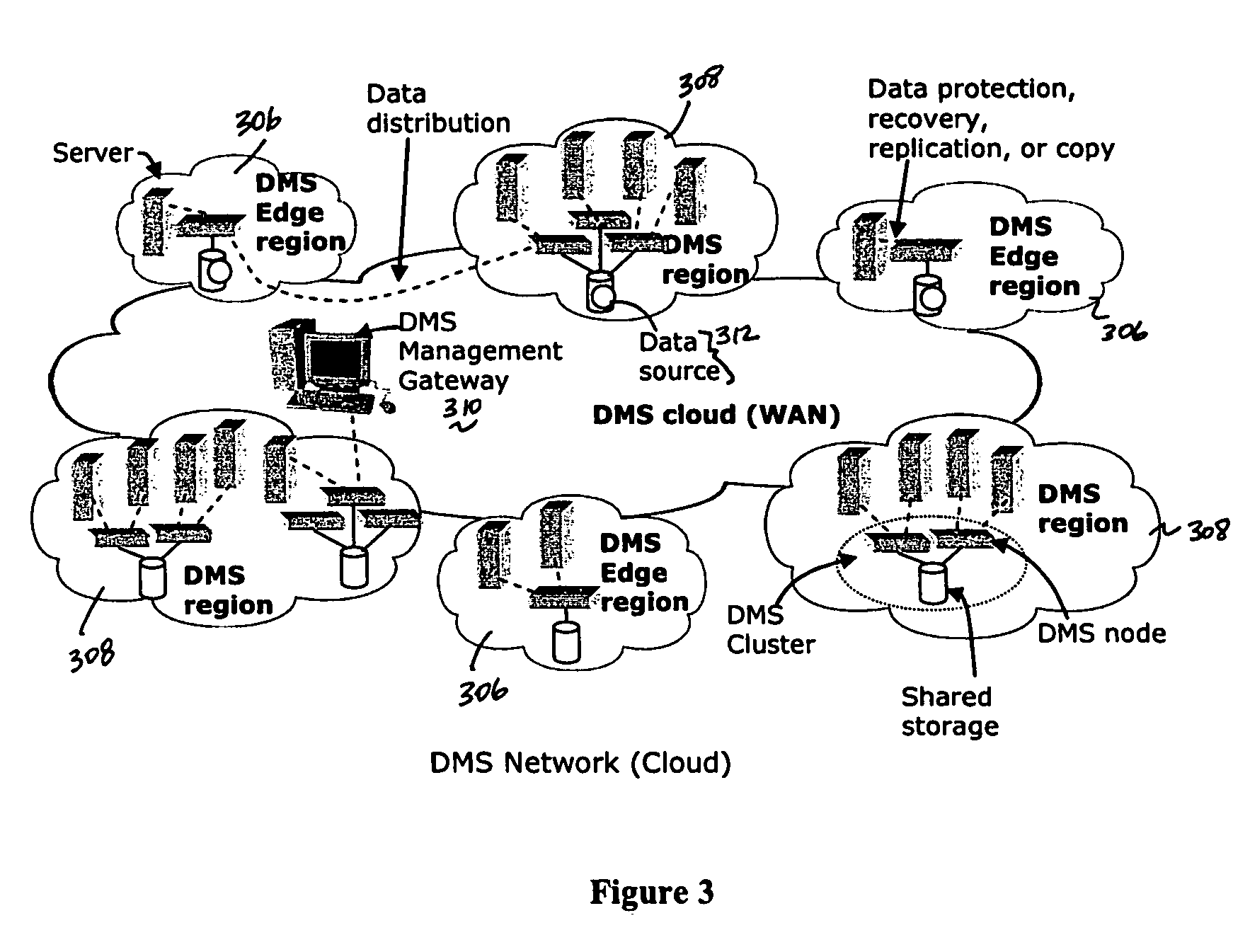
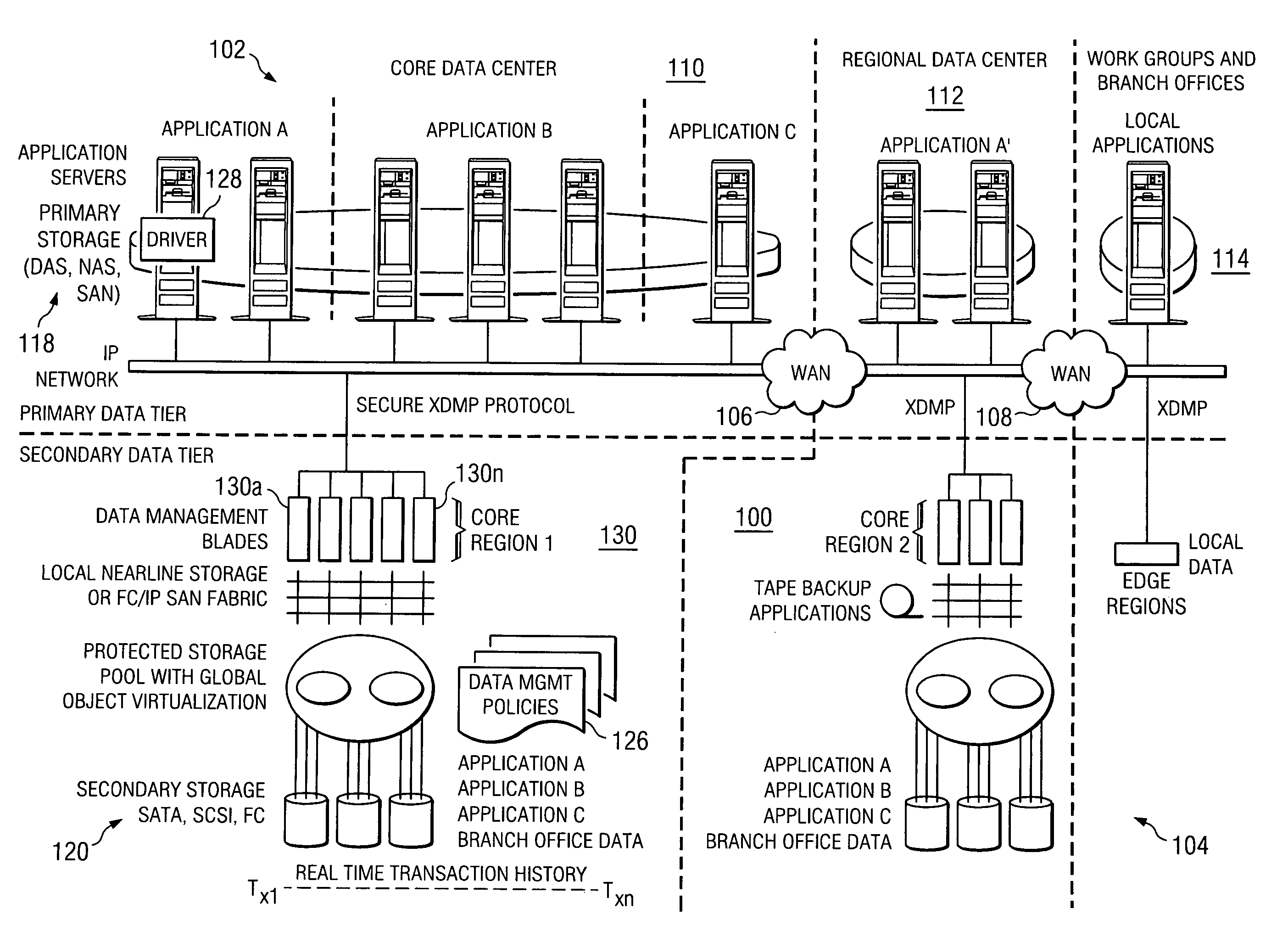
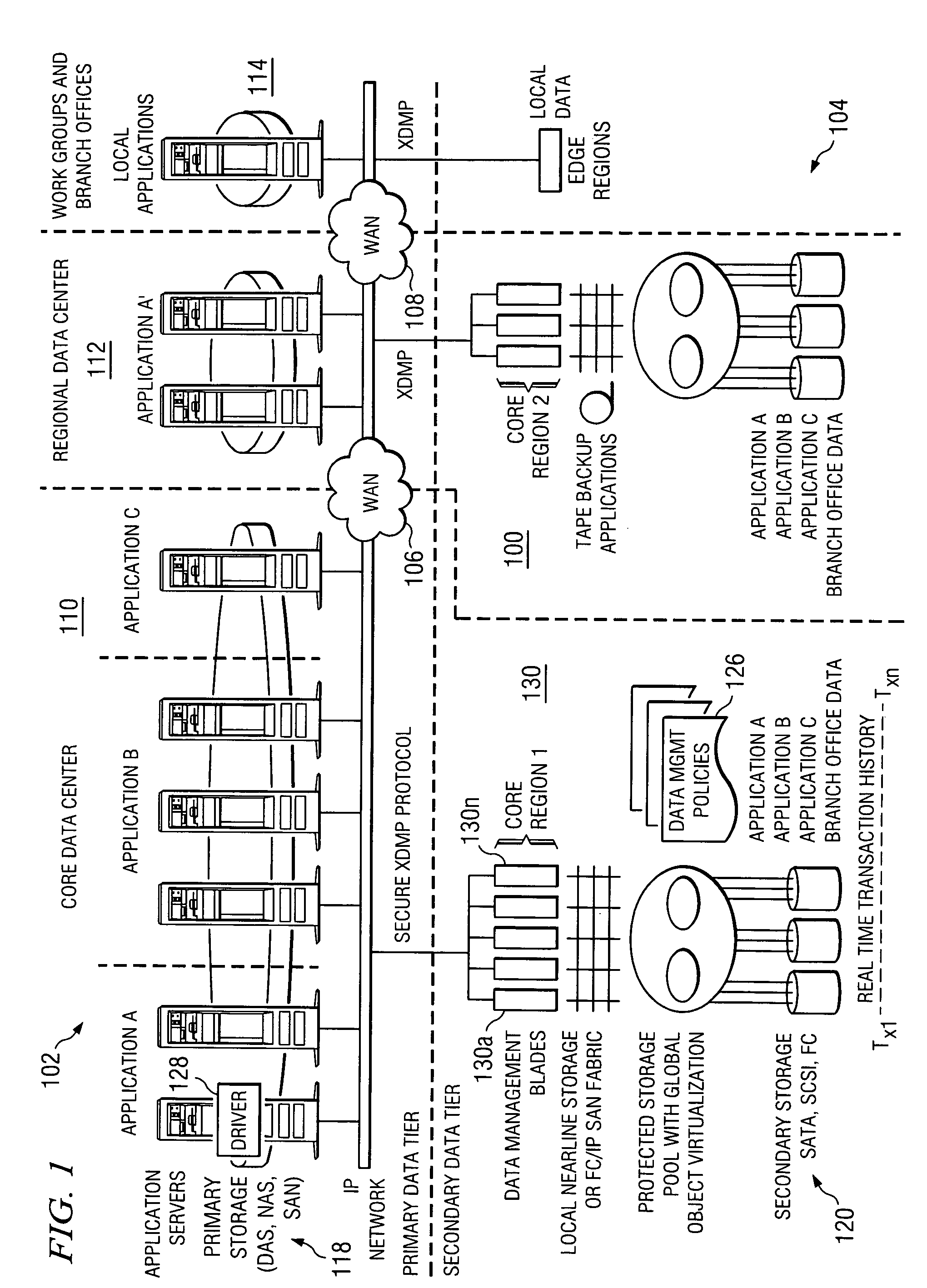
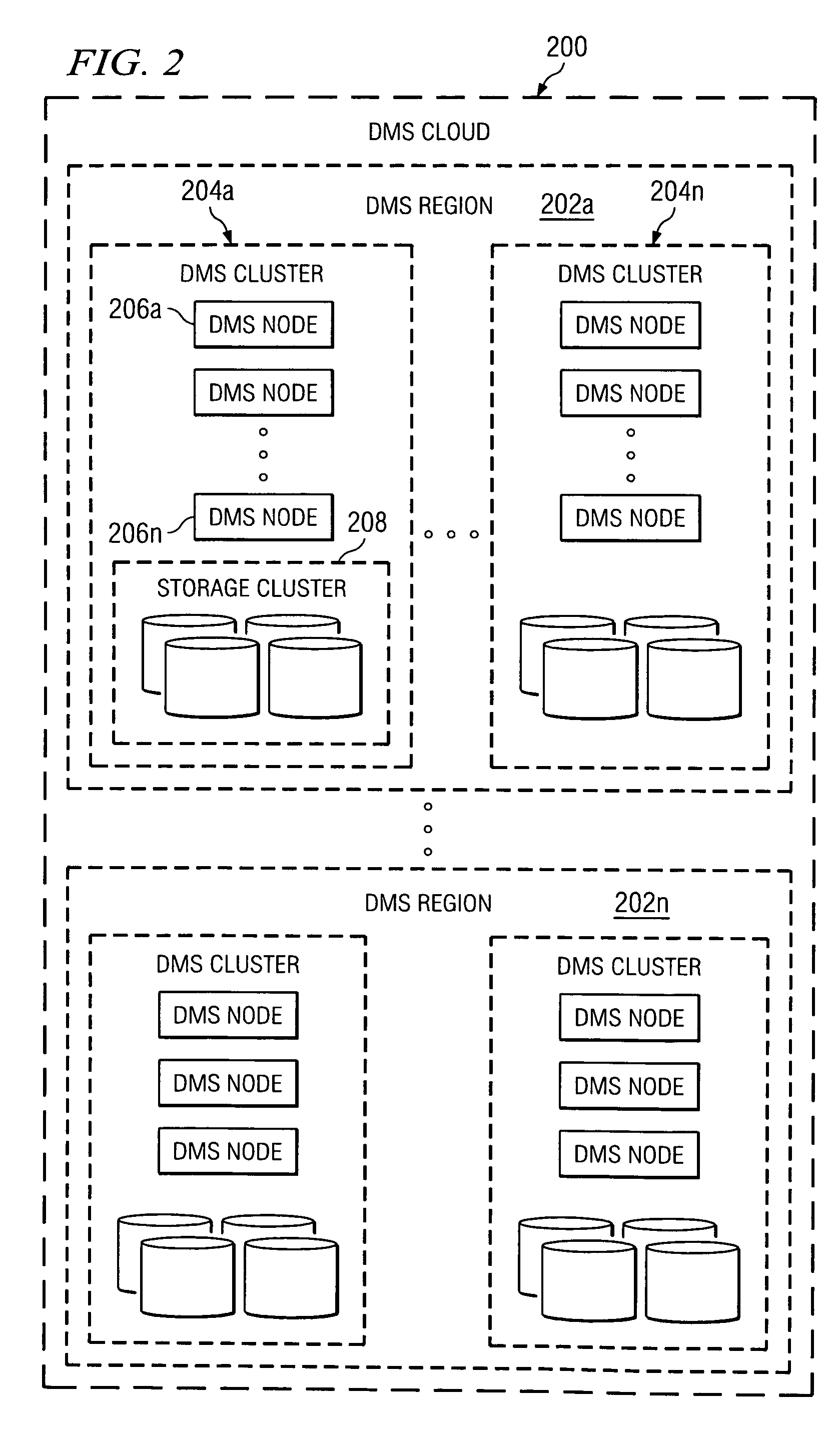
Method and system for automated, no downtime, real-time, continuous data protection
ActiveUS20050262377A1Easy to optimizeError detection/correctionGroup 6/16 element organic compoundsData streamFinite-state machine
A data management system or “DMS” provides an automated, continuous, real-time, substantially no downtime data protection service to one or more data sources associated with a set of application host servers. To facilitate the data protection service, a host driver embedded in an application server captures real-time data transactions, preferably in the form of an event journal that is provided to other DMS components. The driver functions to translate traditional file / database / block I / O and the like into a continuous, application-aware, output data stream. The host driver includes an event processor that provides the data protection service, preferably by implementing a finite state machine (FSM). In particular, the data protection is provided to a given data source in the host server by taking advantage of the continuous, real-time data that the host driver is capturing and providing to other DMS components. The state of the most current data in DMS matches the state of the data in the host server; as a consequence, the data protection is provided under the control of the finite state machine as a set of interconnected phases or “states.” The otherwise separate processes (initial data upload, continuous backup, blackout and data resynchronization, and recovery) are simply phases of the overall data protection cycle. As implemented by the finite state machine, this data protection cycle preferably loops around indefinitely until, for example, a user terminates the service. A given data protection phase (a given state) changes only as the state of the data and the environment change (a given incident).
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Organometallic complex, and light-emitting element, light-emitting device and electronic device including the organometallic compex
ActiveUS20080160345A1Improve emission efficiencySolve low luminous efficiencyGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesArylHalogen
An object is to provide an organometallic complex that can emit red light. Another object is to provide an organometallic complex having high emission efficiency. Still another object is to provide an organometallic complex that can emit red light with high luminous efficiency. The present invention provides an organometallic complex having a structure represented by the following general formula (G1′).In the formula, Ar represents an aryl group having 6 to 25 carbon atoms; R1 represents any one of hydrogen, an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, and an alkoxy group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms; R2 to R8 each represent any one of hydrogen, an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, and a halogen group; at least one of pairs R3 and R4, R4 and R5, and R5 and R6 may be bound to each other to form a ring; and M represents a central metal of Group 9 elements and Group 10 elements.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Use of a Metal Complex as an N-Dopant for an Organic Semiconducting Matrix Material, Organic of Semiconducting Material and Electronic Component, and also a Dopant and Ligand and Process for Producing same
ActiveUS20090212280A1Low oxidation potentialEasy to chargeGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsCarbanionValence electron
A method of using a metal complex as an n-dopant for doping an organic semiconducting matrix material in order to alter the latter's electrical characteristics is provided. In order to provide n-doped organic semiconductors with matrix materials having a low reduction potential, while achieving high conductivities, the n-dopant is a neutral electron-rich metal complex with a neutral or charged transition metal atom as a central atom and having at least 16 valence electrons. The complex can be polynuclear and can possess at least one metal-metal bond. At least one ligand can form a π complex with the central atom, which can be a bridge ligand, or it can contain at least one carbanion-carbon atom or a divalent atom. Methods for providing the novel n-dopants are provided.
Owner:NOVALED GMBH
Organometallic Complex and Light-Emitting Element, Light-Emitting Device, and Electronic Device Using the Same
InactiveUS20100145044A1Easy to synthesizeSharp emission spectrumGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesHydrogenAlkoxy group
An organometallic complex having a structure represented by the general formula (G1) is synthesized and applied to a light-emitting element.In the formula, R3 represents either an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, or an alkoxycarbonyl group having 1 to 5 carbon atoms; R2 and R3 each show either hydrogen or an alkyl group 1 to 4 carbon atoms; Ar represents an arylene group having 6 to 25 carbon atoms; M is a center metal selected from Group 9 element and Group 10 element.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Pt complexes as phosphorescent emitters in the fabrication of organic light emitting diodes
ActiveUS7002013B1Inhibit aggregationReduction of phosphorescence radiative lifetimeGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsGroup 1/11 element organic compoundsLight-emitting diodeCoordination complex
A series of Pt(II) complexes having the following formula are disclosed: X1 and X2 independently are C or N, X1 can also locate at another position of the hexagonal ring, when X1 is N;R1 is H, C1–C8 alkyl, or C1–C4 perfluoroalkyl, R2 is H, R1 and R2 together are C4–C8 alkylene, or R1 and R2 together are bridged carbocyclic C4–C12 alkylene, when X2 is C;R1 is H, C1–C8 alkyl, or C1–C4 perfluoroalkyl, and R2 is omitted, when X2 is N;R7 is H or methyl, and R8 is omitted, when X1 is N;R7 is H or methyl, R8 is H or methyl, or R7 and R8 together are when X1 is C.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Organometallic compounds and emission-shifting organic electrophosphorescence
InactiveUS7381479B2Group 5/15 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesExcited stateOrganic light emitting device
Emissive phosphorescent organometallic compounds are described that produce improved electroluminescence, particularly in the blue region of the visible spectrum. Organic light emitting devices employing such emissive phosphorescent organometallic compounds are also described. Also described is an organic light emitting layer including a host material having a lowest triplet excited state having a decay rate of less than about 1 per second; a guest material dispersed in the host material, the guest material having a lowest triplet excited state having a radiative decay rate of greater than about 1×105 or about 1×106 per second and wherein the energy level of the lowest triplet excited state of the host material is lower than the energy level of the lowest triplet excited state of the guest material.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +2
Organometallic complex, light emitting element using the complex, light emitting device using the element, and electric apparatus using the device
ActiveUS20050221123A1Reduce power consumptionGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesArylHydrogen
It is an object of the present invention to obtain a phosphorescent compound to be used for a light-emitting element, a light-emitting element that uses the phosphorescent compound and has a higher luminous efficiency, and a light-emitting device that uses the light-emitting element and has poser consumption reduced. The present invention provides an organometallic complex comprising a moiety represented by the following general formula (1). The organometallic complex is applied to a light-emitting element, and a light-emitting device reduced in power consumption is manufactured by using the light-emitting element. (where R1 to R4 are individually any one of hydrogen, a halogen atom, an acyl group, an alkyl group, an alkoxyl group, an aryl group, a cyano group, and a heterocyclic group, Ar is one of an aryl group having an electron-withdrawing group and a heterocyclic group having electron-withdrawing group, and M is one of an element of Group 9 and an element of Group 10)
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Luminescence device, display apparatus and metal coordination compound
A luminescence device that has an organic compound layer disposed between a pair of electrodes. This organic compound layer contains a metal coordination compound represented by the following formula (1)wherein M is Ir, Rh or Pd; n is 2 or 3; CyN is a substituted or unsubstituted cyclic group containing a nitrogen atom connected to M and capable of containing another nitrogen atom and / or sulfur atom; and CyC is a substituted or unsubstituted cyclic group containing a carbon atom connected to M and capable of containing a nitrogen atom and / or a sulfur atom.
Owner:CANON KK
Method and system for automated, no downtime, real-time, continuous data protection
ActiveUS7096392B2Error detection/correctionGroup 6/16 element organic compoundsData streamFinite-state machine
A data management system or “DMS” provides an automated, continuous, real-time, substantially no downtime data protection service to one or more data sources associated with a set of application host servers. To facilitate the data protection service, a host driver embedded in an application server captures real-time data transactions, preferably in the form of an event journal that is provided to other DMS components. The driver functions to translate traditional file / database / block I / O and the like into a continuous, application-aware, output data stream. The host driver includes an event processor that provides the data protection service, preferably by implementing a finite state machine (FSM). In particular, the data protection is provided to a given data source in the host server by taking advantage of the continuous, real-time data that the host driver is capturing and providing to other DMS components. The state of the most current data in DMS matches the state of the data in the host server; as a consequence, the data protection is provided under the control of the finite state machine as a set of interconnected phases or “states.” The otherwise separate processes (initial data upload, continuous backup, blackout and data resynchronization, and recovery) are simply phases of the overall data protection cycle. As implemented by the finite state machine, this data protection cycle preferably loops around indefinitely until, for example, a user terminates the service. A given data protection phase (a given state) changes only as the state of the data and the environment change (a given incident).
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Organometallic complex and light-emitting element, light-emitting device and electronic device using the same
ActiveUS20070129545A1Solve low luminous efficiencyHigh color purityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesHydrogenAlkoxy group
An organometallic complex having a structure represented by the general formula (G1) is synthesized and applied to a light-emitting element. In the formula, R1 represents either an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, or an alkoxycarbonyl group having 1 to 5 carbon atoms; R2 and R3 each show either hydrogen or an alkyl group 1 to 4 carbon atoms; Ar represents an arylene group having 6 to 25 carbon atoms; M is a center metal selected from Group 9 element and Group 10 element.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
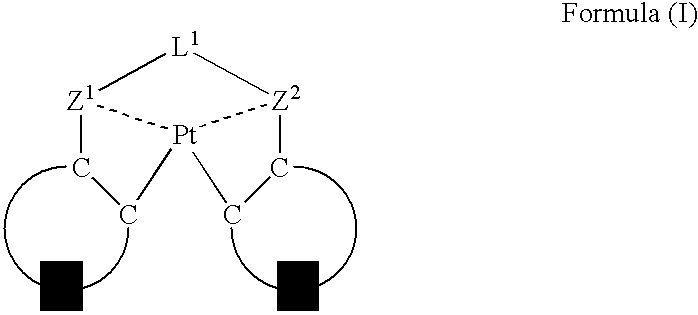
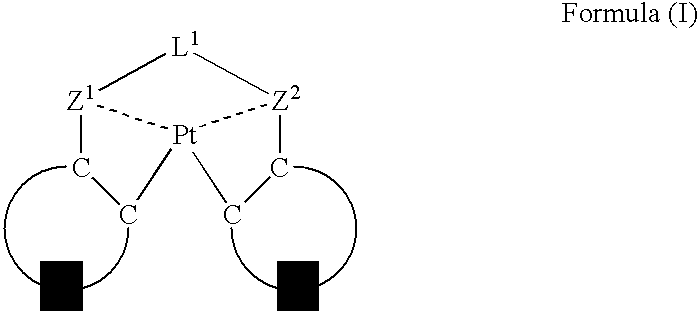
Organic electroluminescent device
ActiveUS7501190B2Group 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPlatinumOrganic layer
An organic electroluminescent device having a pair of electrodes and at least one organic layer interposed between the pair of electrodes, in which the at least one organic layer contains at least one compound represented by formula (I):wherein, Z1 and Z2 each independently represent a nitrogen-containing aromatic six-membered ring coordinated to the platinum through a nitrogen atom; Q1 represents a group of atoms necessary for forming, together with the —C—C—, a nitrogen-containing aromatic five-membered ring; and L1 represents a single bond or a divalent linking group.
Owner:UDC IRELAND +1
Bioavailable chelates of creatine and essential metals
InactiveUS6114379AImprove bioavailabilityPromote recoveryBiocideGroup 1/11 element organic compoundsMetal chelateActive transport
A chelate comprised of creatine bonded to an essential mineral selected from the group consisting of Mg, Ca, Cu, Zn, Fe, Cr, Co, Mo, Se and Mn to form a heterocyclic ring. Preferably, the metal is Mg, but Ca, Zn, Fe, Cr and Mn are also preferred. The creatine chelates of the present invention are capable of being absorbed in the stomach or intestines via active transport without substantial metabolism of the chelate. In other words, the creatine ligand is protected by the metal from undergoing cyclization in the acidic environment of the stomach and the metal is made more bioavailable due to the presence of the creatine ligand.
Owner:ALBION LAB
Olefin Oligomerization catalysts and Methods of Making and Using Same
InactiveUS20120172645A1Reduce polymer formationReduce the amount requiredGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolymer scienceOligomer
This disclosure provides for a process for preparing a catalyst system comprising a) contacting a metal compound, a diphosphino aminyl ligand metal complex, and a metal alkyl for a time period to form a mixture; and b) aging the mixture. The disclosure also provides for olefin oligomerization process comprising: a) contacting i) a metal compound, ii) a diphosphino aminyl ligand, and iii) a metal alkyl to form a mixture; b) aging the mixture; c) contacting the aged mixture with an olefin monomer; and d) forming an olefin oligomer product.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
Organofunctional silanes and their mixtures
ActiveUS20070197812A1Improve performanceLong scorch timeSilicon organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsElastomerOligomer
Organofunctional silanes, inclusive of dimers and oligomers, are provided in which individual silanes possess both free and blocked mercaptan functionality or particular mixtures of the organofunctional silanes possess both free and blocked mercaptan functionality. The organofunctional silanes and silane mixtures are useful, inter alia, as coupling agents for elastomeric compositions, e.g., rubber formulations employed in the manufacture of tires, where they exhibit a desirable balance of low scorch and good performance properties.
Owner:MOMENTIVE PERFORMANCE MATERIALS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com