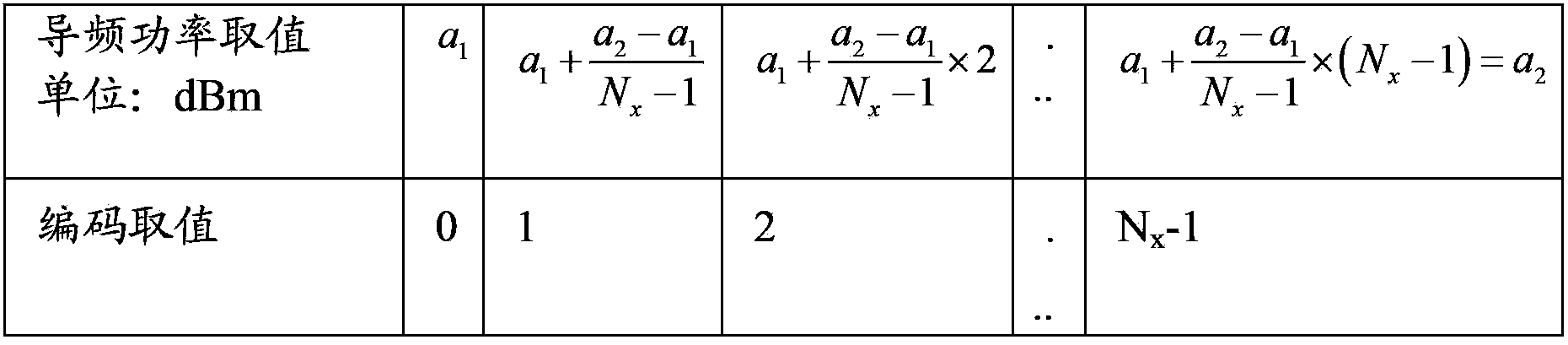Patents
Literature
67 results about "Cell regulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
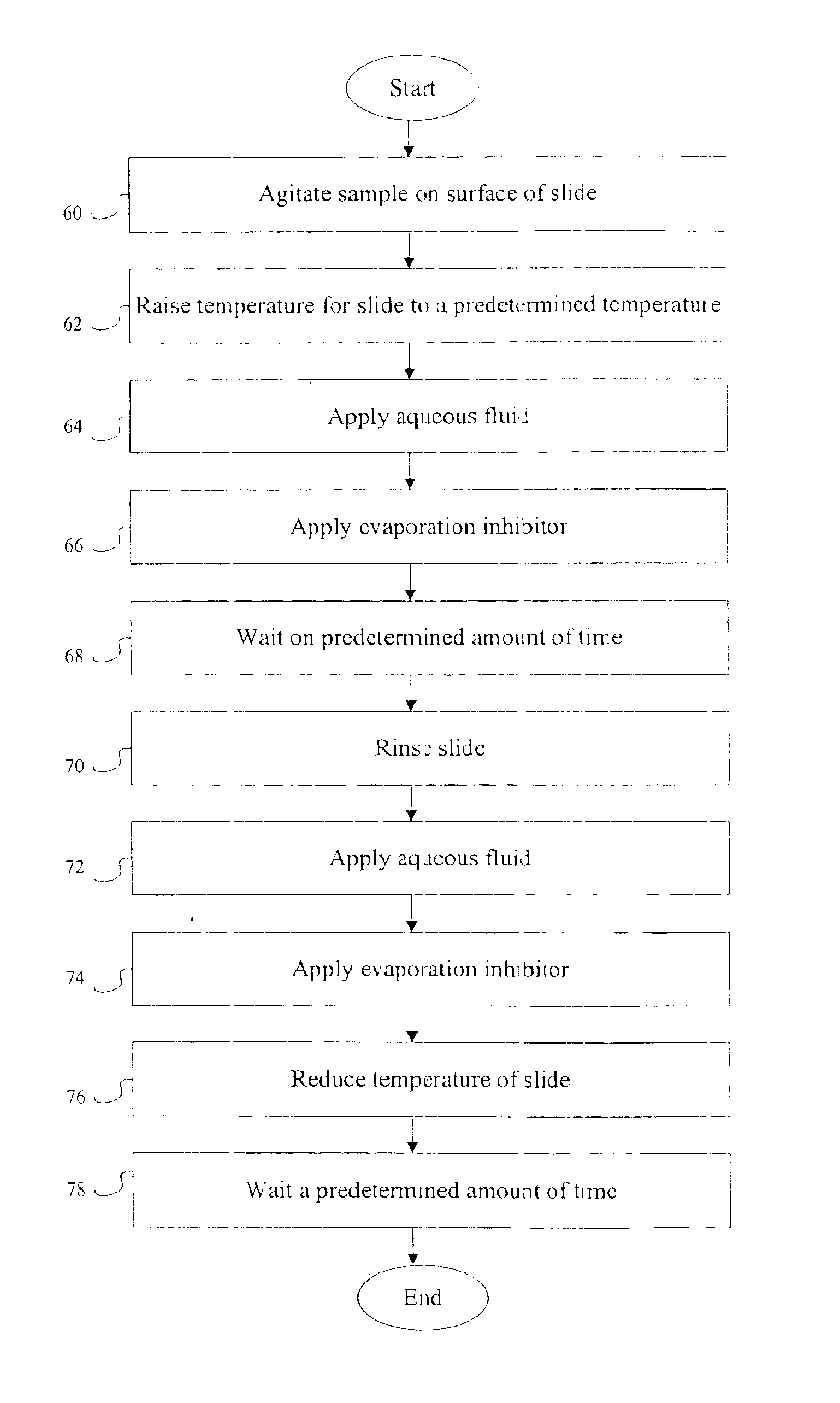
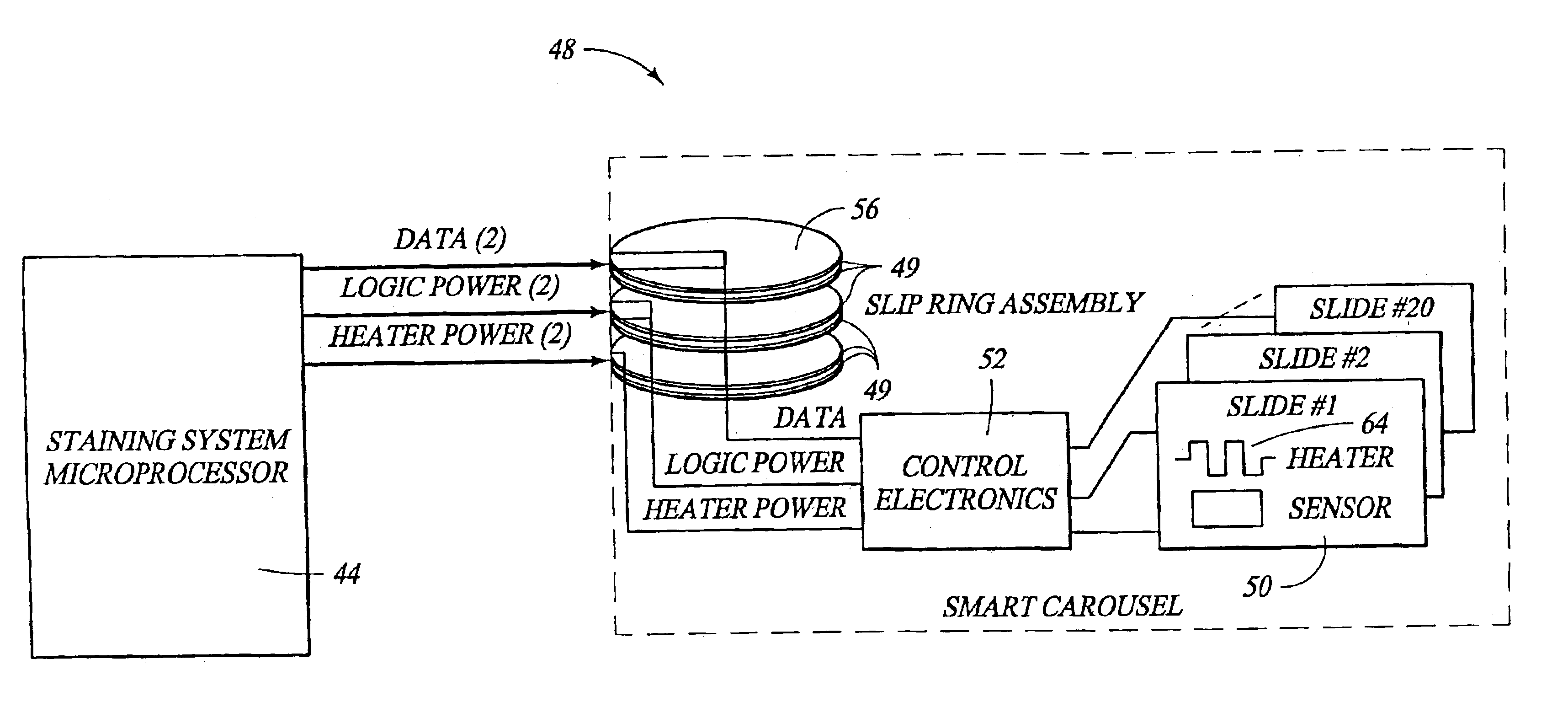
Removal of embedding media from biological samples and cell conditioning on automated staining instruments
InactiveUS6855559B1Increase semaphoreAccurate interpretationWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationCytochemistryOrganic solvent
The present invention provides reagents for use in an automated environment for removing or etching embedding media by exposing a biological sample to be stained in histochemical or cytochemical procedures without the dependence on organic solvents. The reagents comprise components optimized to facilitate removal or etching of the embedding media from the biological sample. The present invention also provides reagents for use in an automated environment for cell conditioning biological samples wherein the cells are predisposed for access by reagent molecules for histochemical and cytochemical staining procedures. The reagents comprise components optimized to facilitate molecular access to cells and cell constituents within the biological sample.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
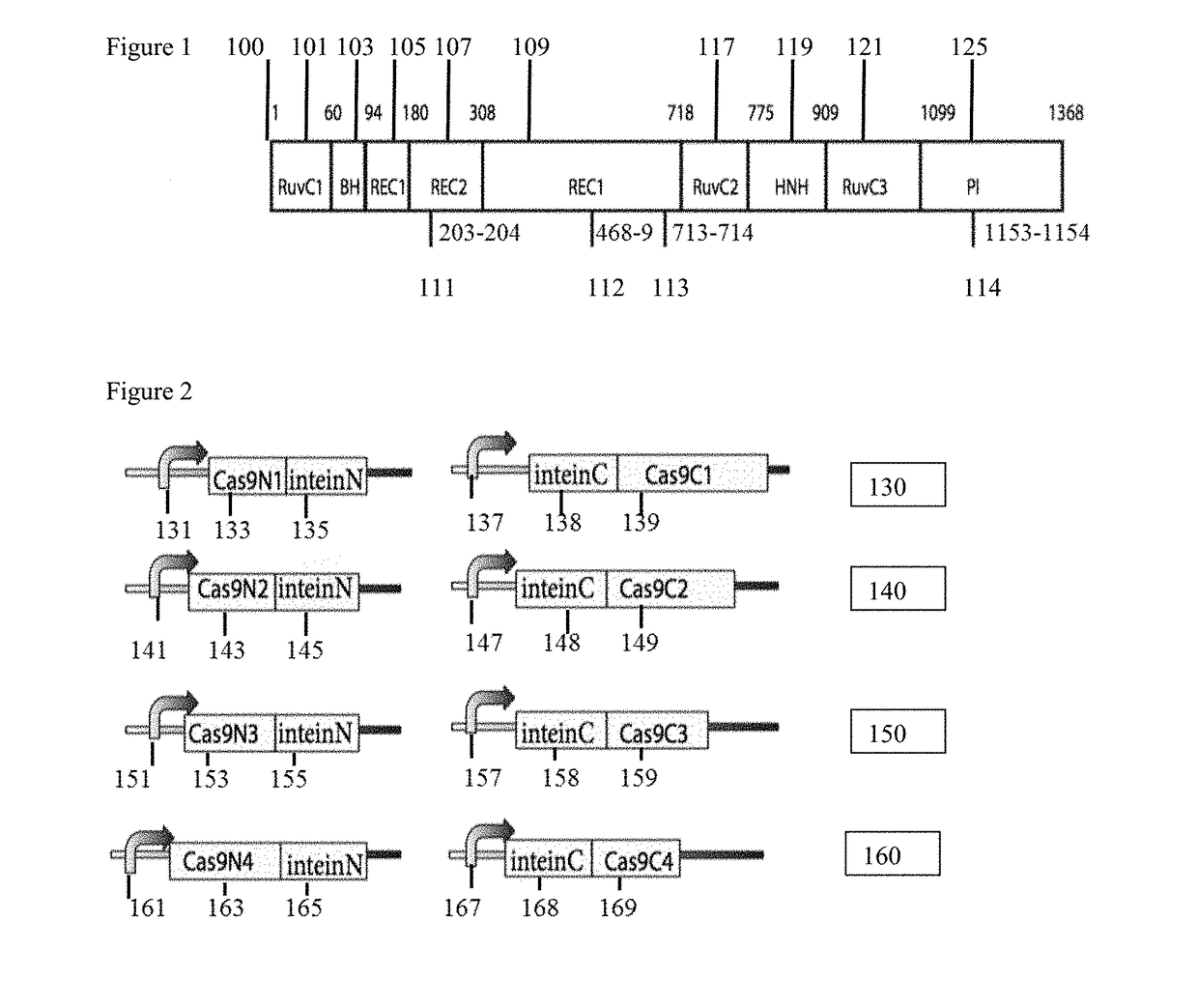
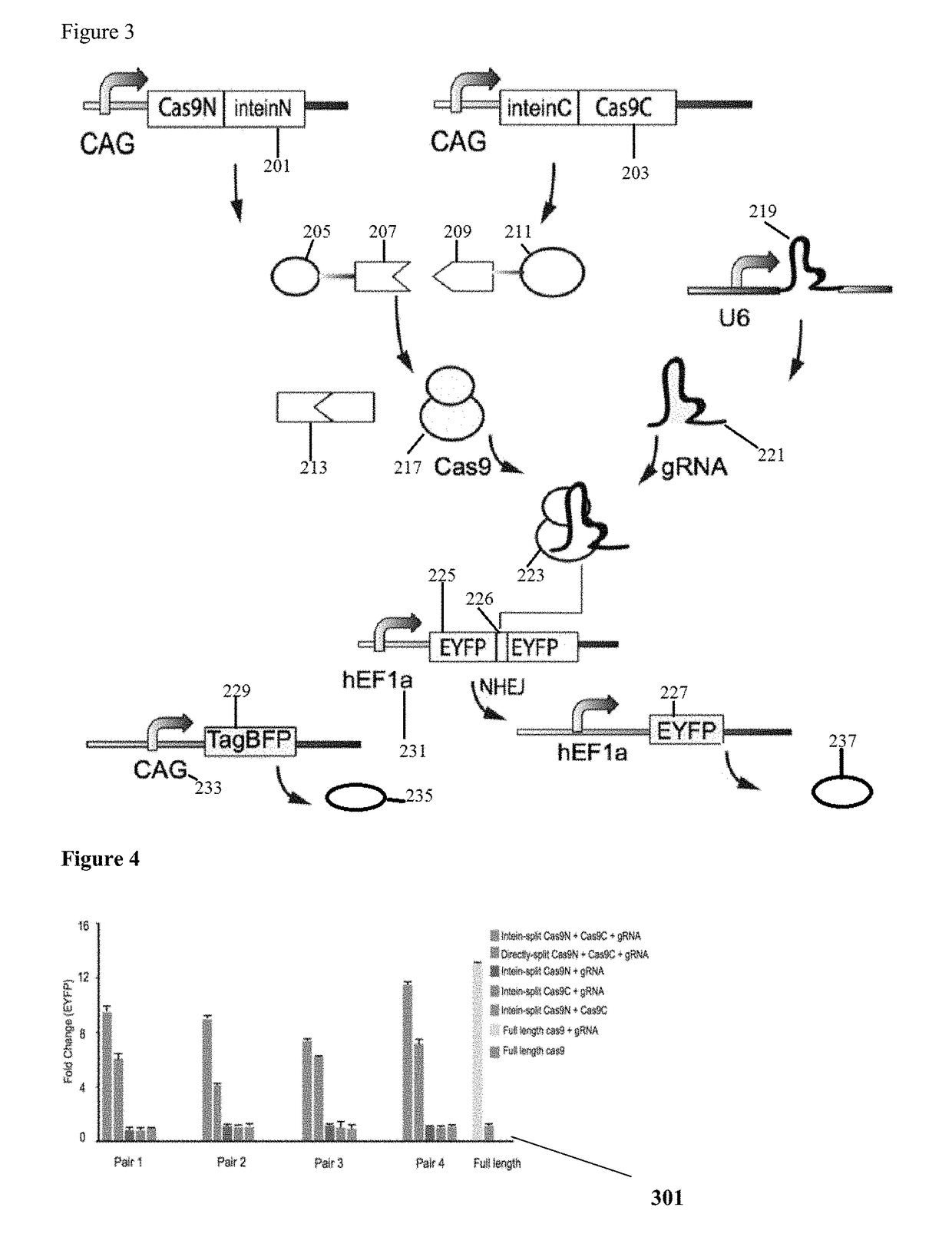
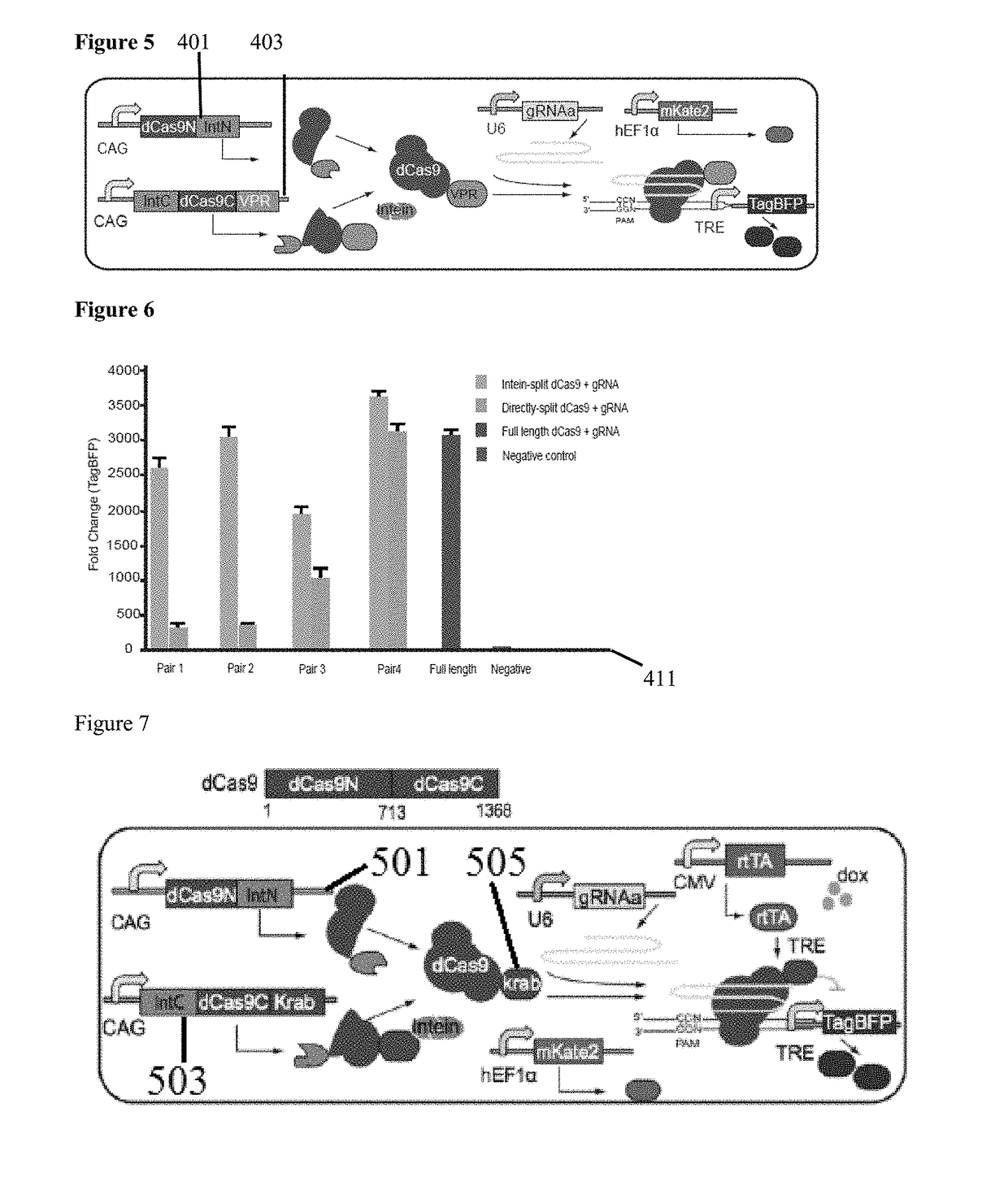
Genetic indicator and control system and method utilizing split Cas9/CRISPR domains for transcriptional control in eukaryotic cell lines
PendingUS20170233703A1Facilitated engineeringIncrease the number ofHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLiving systemsPlant cell
While genetic engineering has undergone rapid advancement with the discovery of CRISPR / Cas9, there is room for improvement for genetic circuit control, precision (reducing circuit ‘leakiness’) and delivery into living systems. The claimed invention offers programmable and precise regulation of dCas9 functions in response to multiple molecular signals by using synthetic gene circuits, greatly expanding applications. Moreover, using the system to greatest therapeutic potential has been greatly limited by the restrictive cargo size of existing viral delivery systems. By splitting dCas9 into multiple sections, the delivery size of synthetic gene circuits is greatly reduced. By exchanging split dCas9 domains, differential regulation on one gene, or activating two different genes in response to cell-type specific microRNAs is illustrated. Practical applications of the illustrative examples include engineered sensory switches including indicators for bladder cancer as well as enhanced systems for adenovirus delivery, cellular regulation, plant cell modification and potential therapeutic applications.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
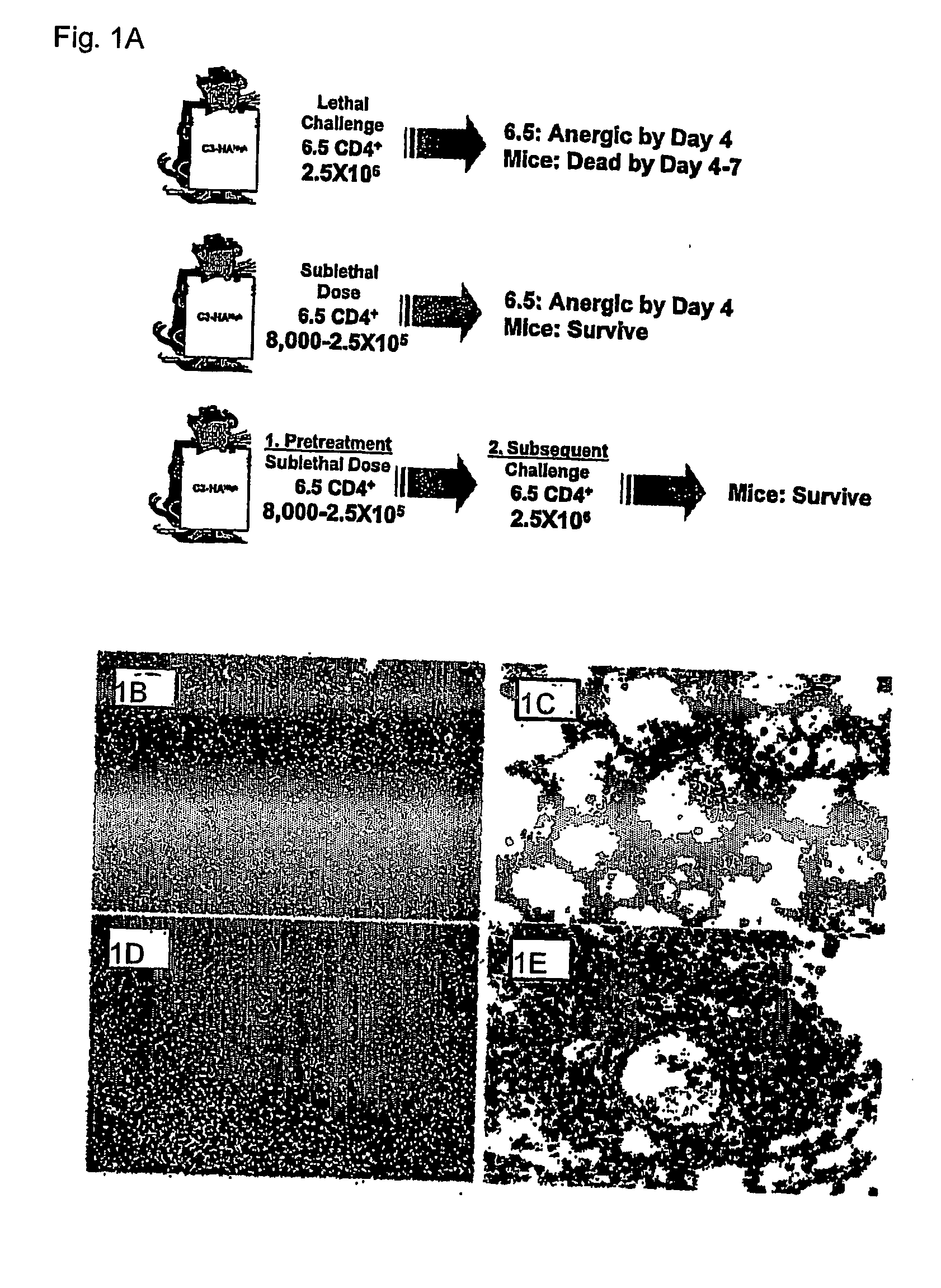
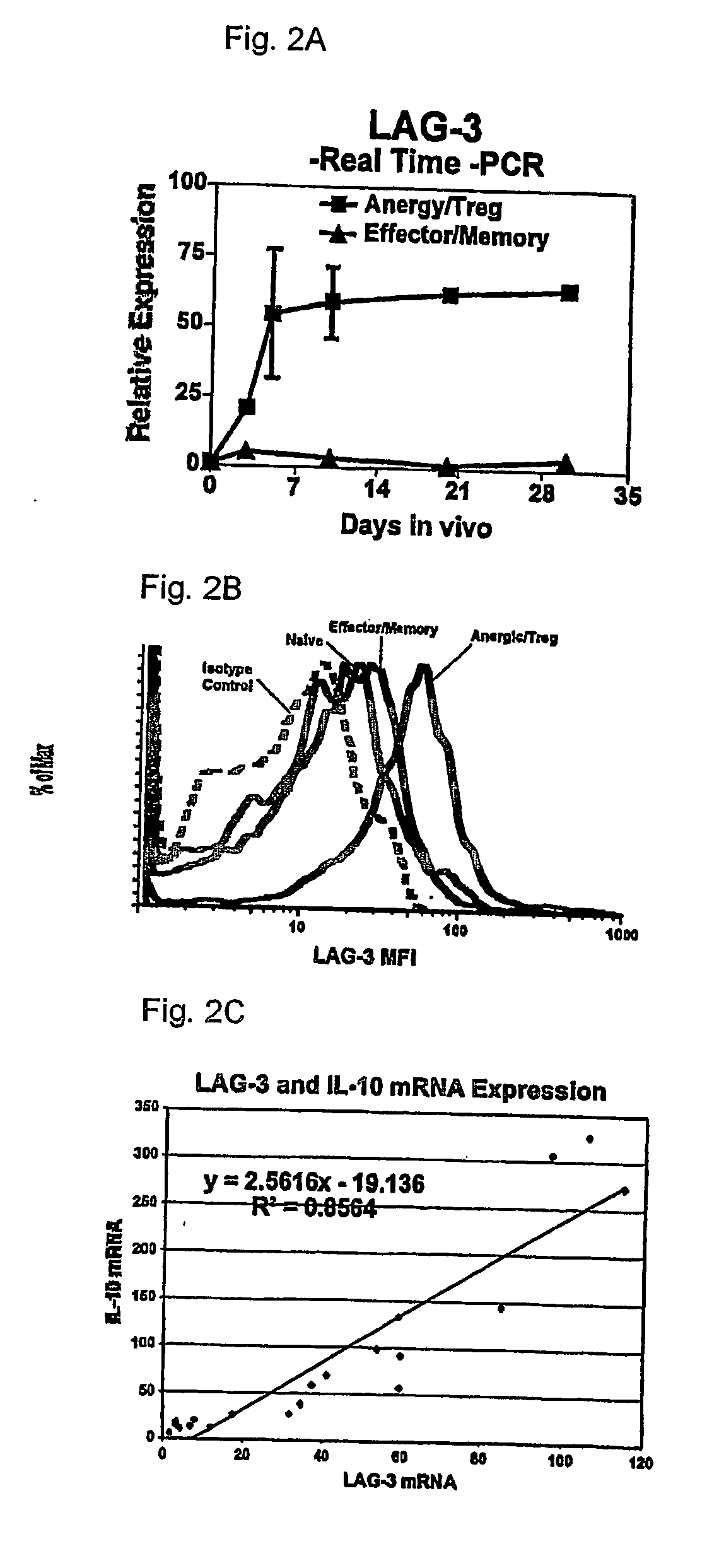
T cell regulation
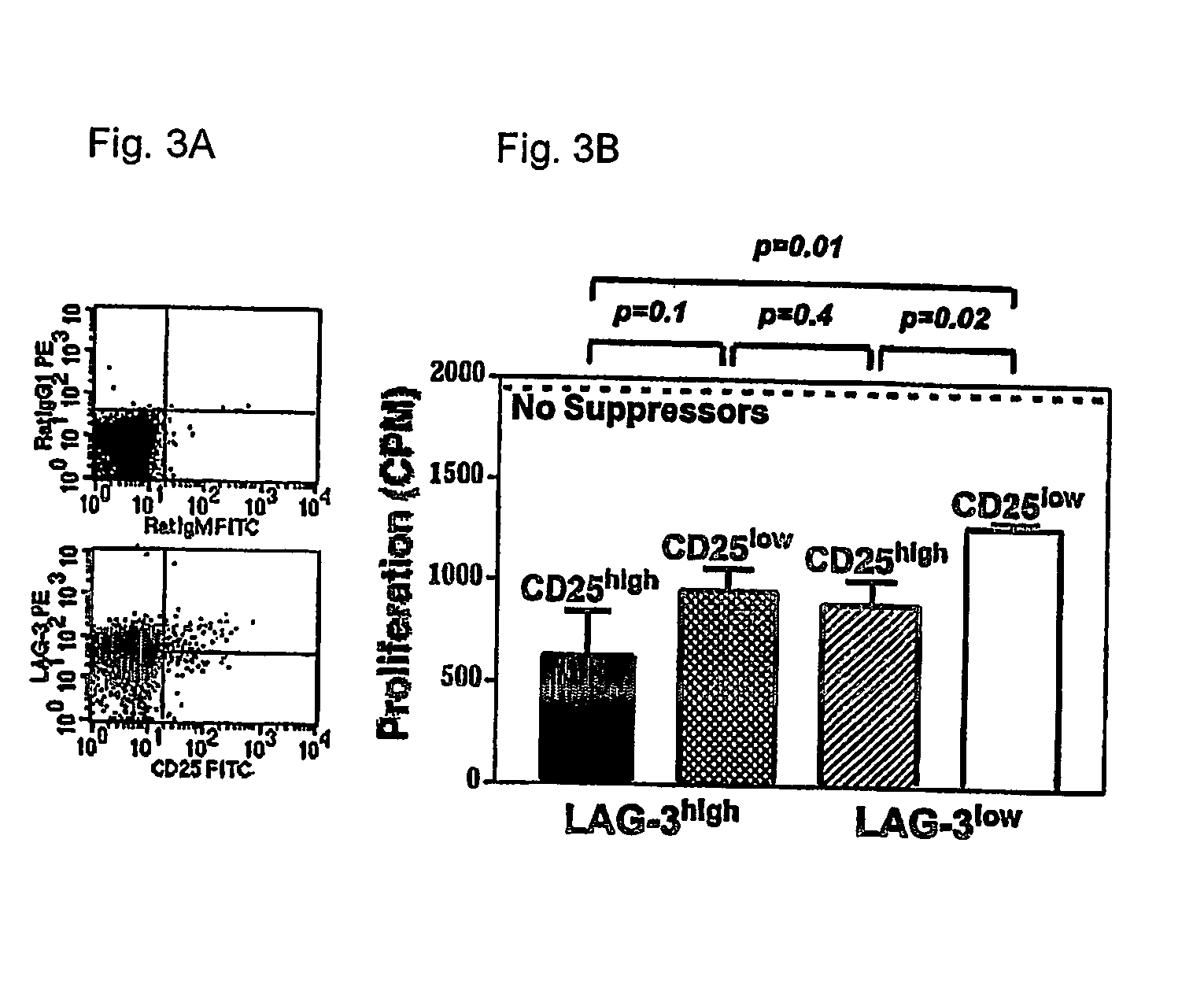
InactiveUS20060240024A1Increases magnitudeSimple methodAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderRegulatory T cellAutoimmune responses
Regulatory T cells (Treg) limit autoimmunity but can also attenuate the magnitude of anti-pathogen and anti-tumor immunity. Understanding the mechanism of Treg function and therapeutic manipulation of Treg in vivo requires identification of Treg selective receptors. A comparative analysis of gene expression arrays from antigen specific CD4+ T cells differentiating to either an effector / memory or a regulatory phenotype revealed Treg selective expression of LAG-3 (CD223), a CD4-related molecule that binds MHC class II. LAG-3 expression on CD4+ T cells correlates with the cells' in vitro suppressor activity, and ectopic expression of LAG-3 on CD4 T cells confers suppressor activity on the T cells. Antibodies to LAG-3 inhibit suppression both in vitro and in vivo. LAG-3 marks regulatory T cell populations and contributes to their suppressor activity.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC +1
Removal of embedding media from biological samples and cell conditioning on automated staining instruments
InactiveUS7067325B2Improve accessibilityPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingCytochemistryEtching
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Removal of embedding media from biological samples and cell conditioning on automated staining instruments
InactiveUS7410753B2Increase semaphoreAccurate interpretationWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationCytochemistryOrganic solvent
The present invention provides reagents for use in an automated environment for removing or etching embedding media by exposing a biological sample to be stained in histochemical or cytochemical procedures without the dependence on organic solvents. The reagents comprise components optimized to facilitate removal or etching of the embedding media from the biological sample. The present invention also provides reagents for use in an automated environment for cell conditioning biological samples wherein the cells are predisposed for access by reagent molecules for histochemical and cytochemical staining procedures. The reagents comprise components optimized to facilitate molecular access to cells and cell constituents within the biological sample.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND +1
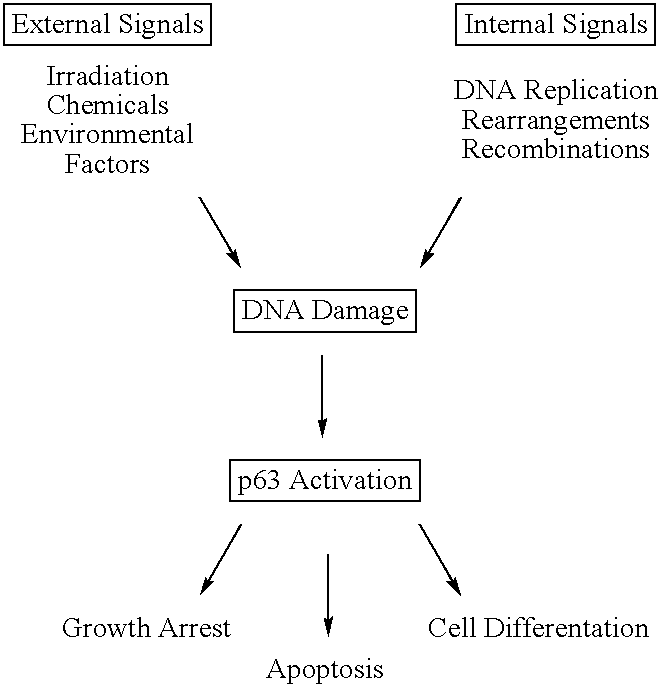
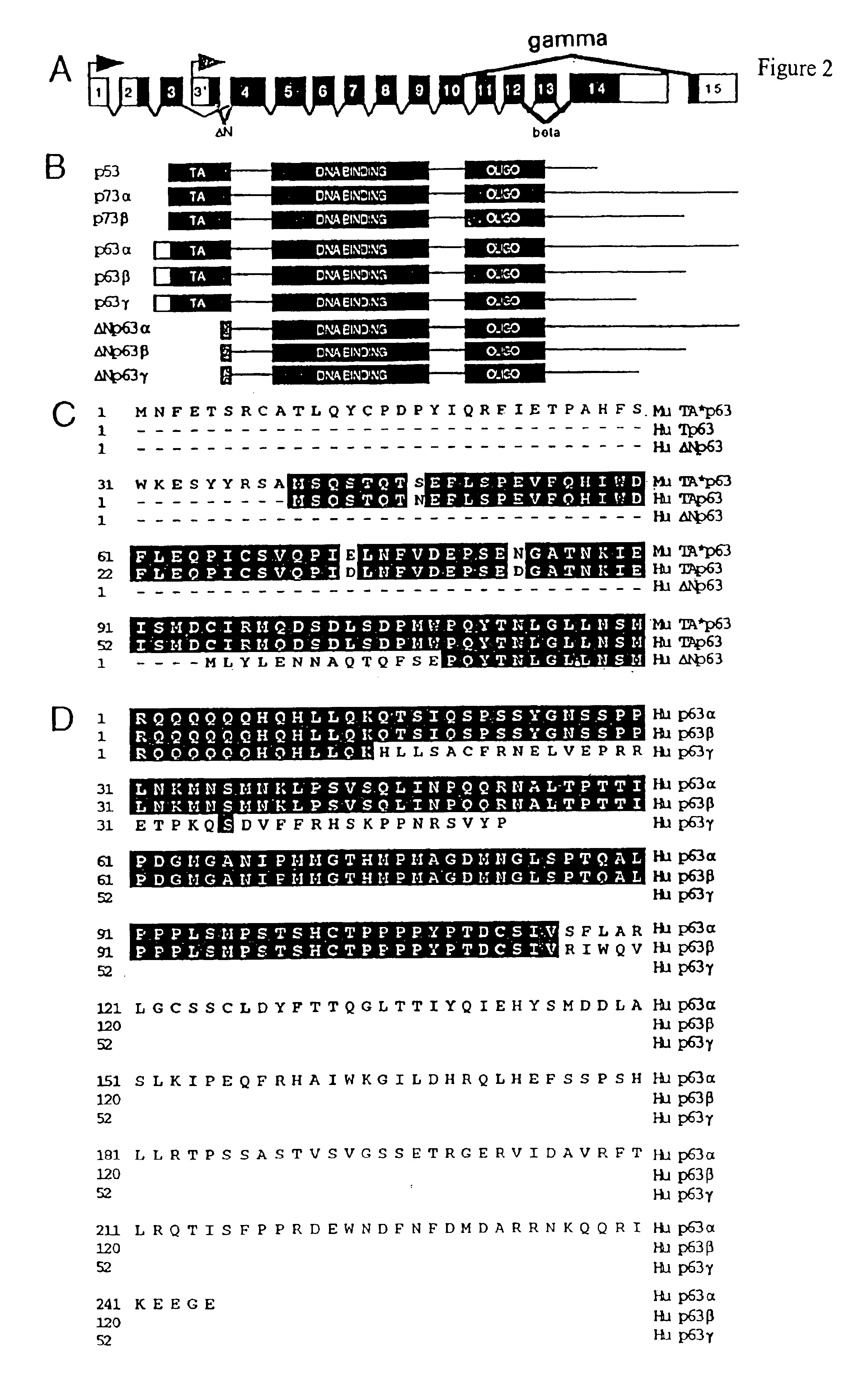
Cell regulatory genes, encoded products, and uses related thereto
InactiveUS6946256B1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansSuppressorApoptosis
This application describes the cloning of p63, a gene at chromosome 3q27-29, that bears homology to the tumor suppressor p53. The p63 gene encodes at least six different isotypes. p63 was detected in a variety of human and mouse tissue and demonstrates remarkably divergent activities, such as the ability to transactivate p53 reporter genes and induce apoptosis. Isotopes of p63 lacking a transactivation domain act as dominant negatives towards the transactivation by p53 and p63.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +2
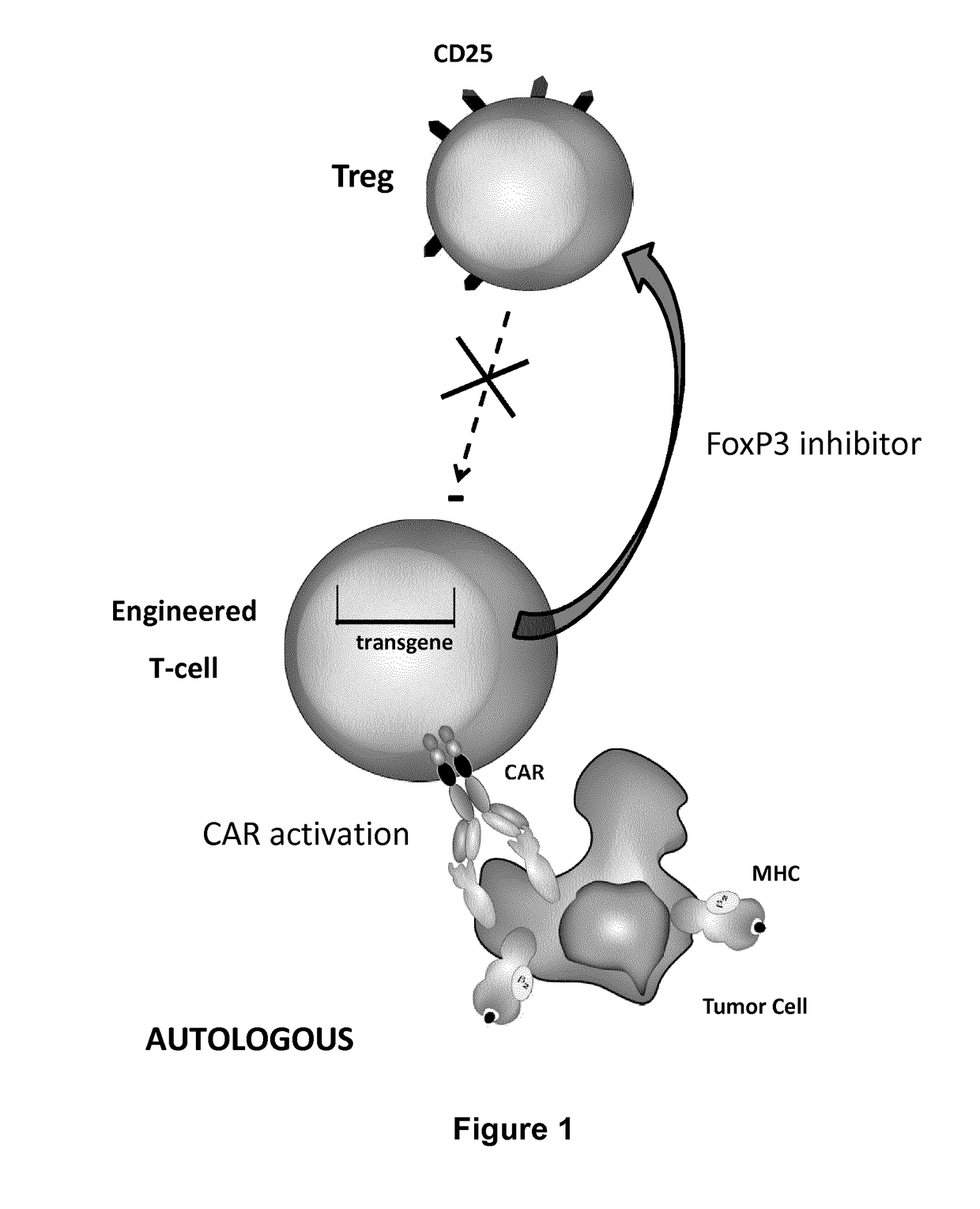
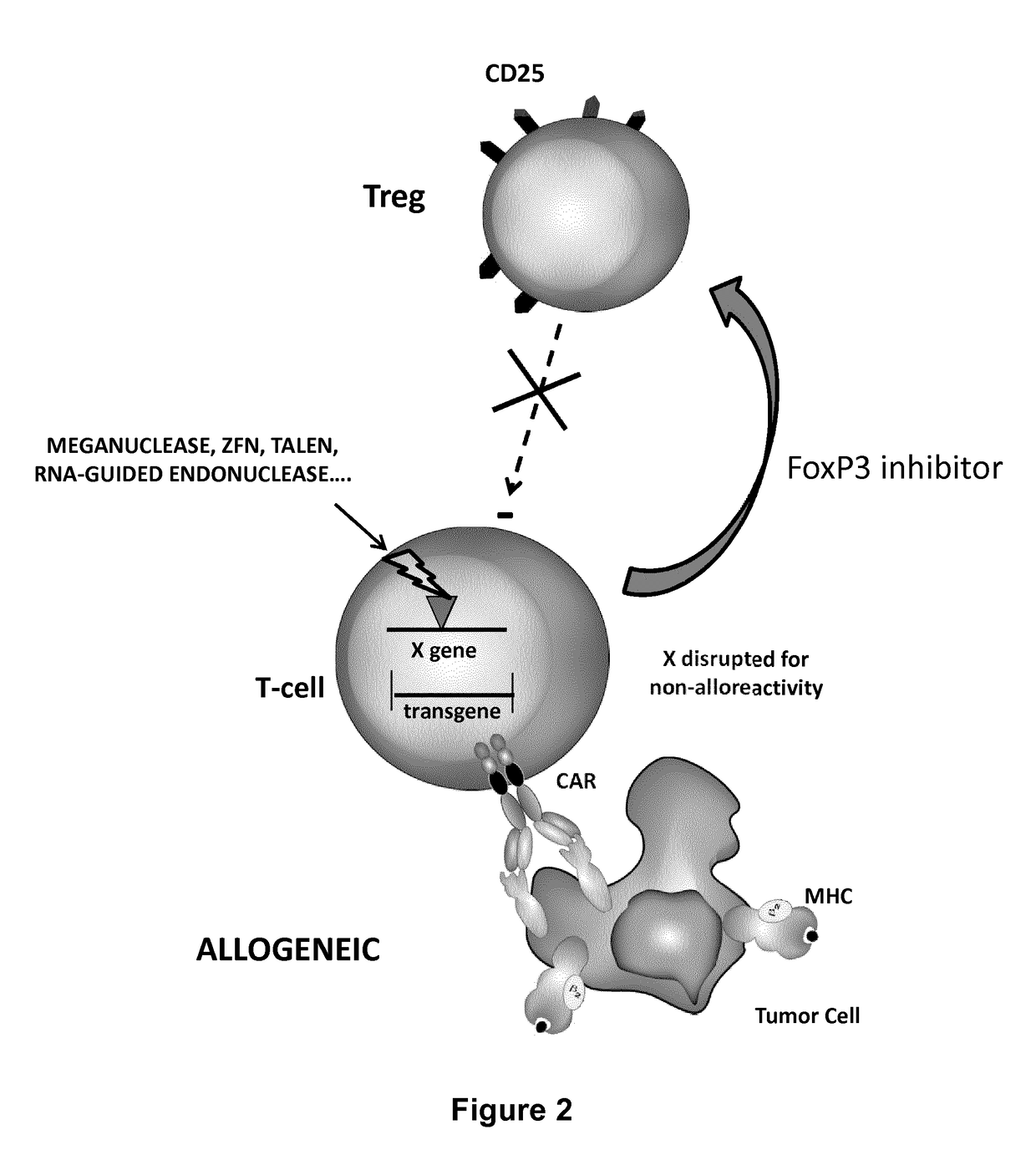
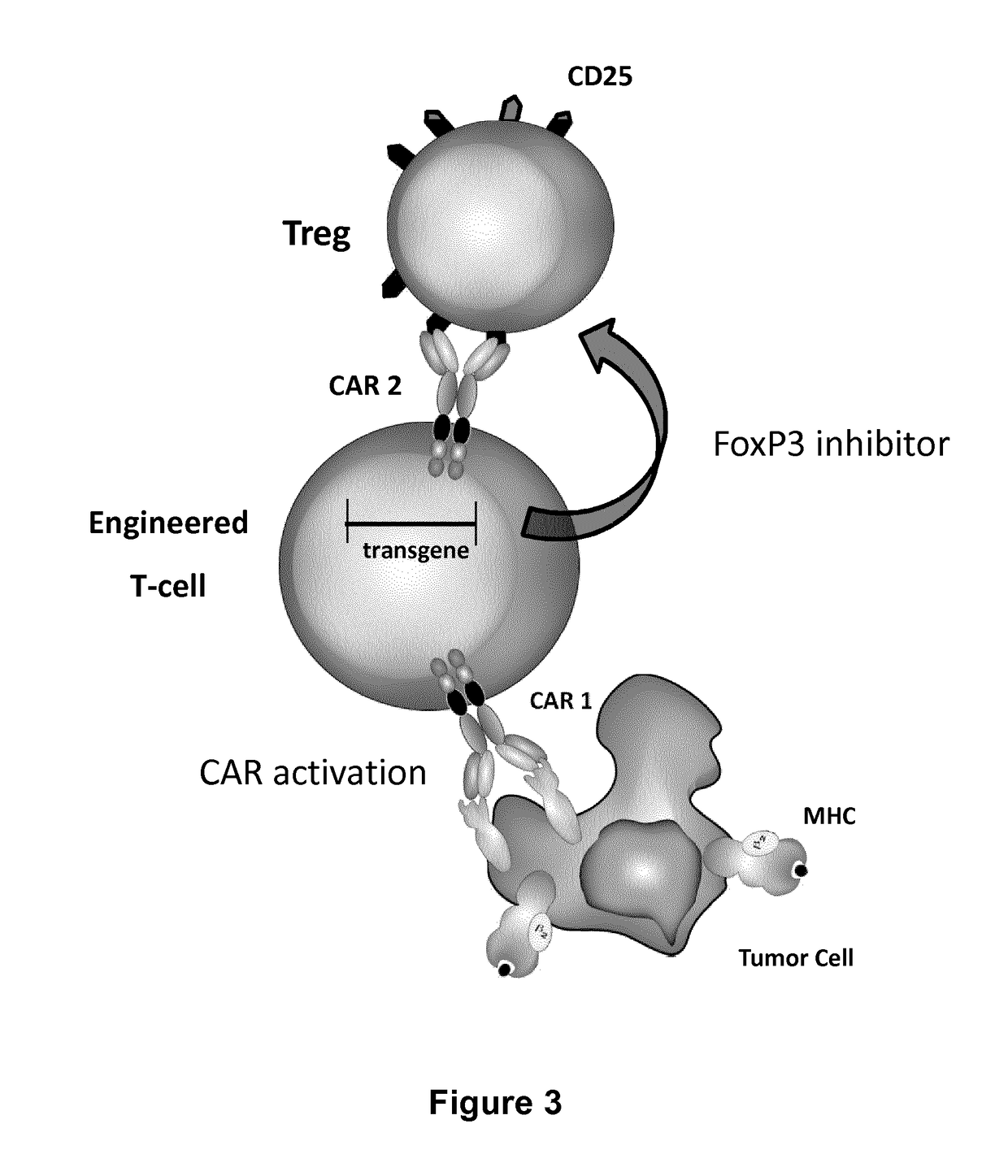
Method for in situ inhibition of regulatory t cells
ActiveUS20170067022A1Reducing FoxP transcriptional activityHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenInfected cell
The present invention pertains to engineered T-cells, method for their preparation and their use as medicament, particularly for immunotherapy. The engineered T-cells of the invention are designed to express both a Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) directed against at least one antigen expressed at the surface of a malignant or infected cell, and a secreted inhibitor of regulatory T-cells (Treg). Preferably, such secreted inhibitor is a peptide inhibitor of forkhead / winged helix transcription factor 3 (FoxP3), a specific factor involved into the differentiation of T-cells into regulatory T-cells. The engineered T-cells of the invention direct their immune activity towards specific malignant or infected cells, while at the same time will prevent neighbouring regulatory T-cells from modulating the immune response. The invention opens the way to standard and affordable adoptive immunotherapy strategies, especially for treating or preventing cancer, and bacterial or viral infections.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Esterified fatty acid composition
ActiveUS20050208162A1Improve efficacyImprove stabilityBiocideHalogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsSide effectArthritis
The invention is directed to compositions comprising lecithin, olive oil, esterified fatty acids and mixed tocophenols for use in the treatment and prevention of various types of arthritis and other inflammatory joint conditions, periodontal diseases and psoriasis, which avoid many of the side effects associated with known treatments. The compositions of the present invention have the advantage of increased stability, a reduction of arachidonic acid in cells, a reduction in eicosanoid production and enhanced cell regulation and communication. Also disclosed are methods for using the compositions for treatment and prevention.
Owner:TRIPHARMA LLC
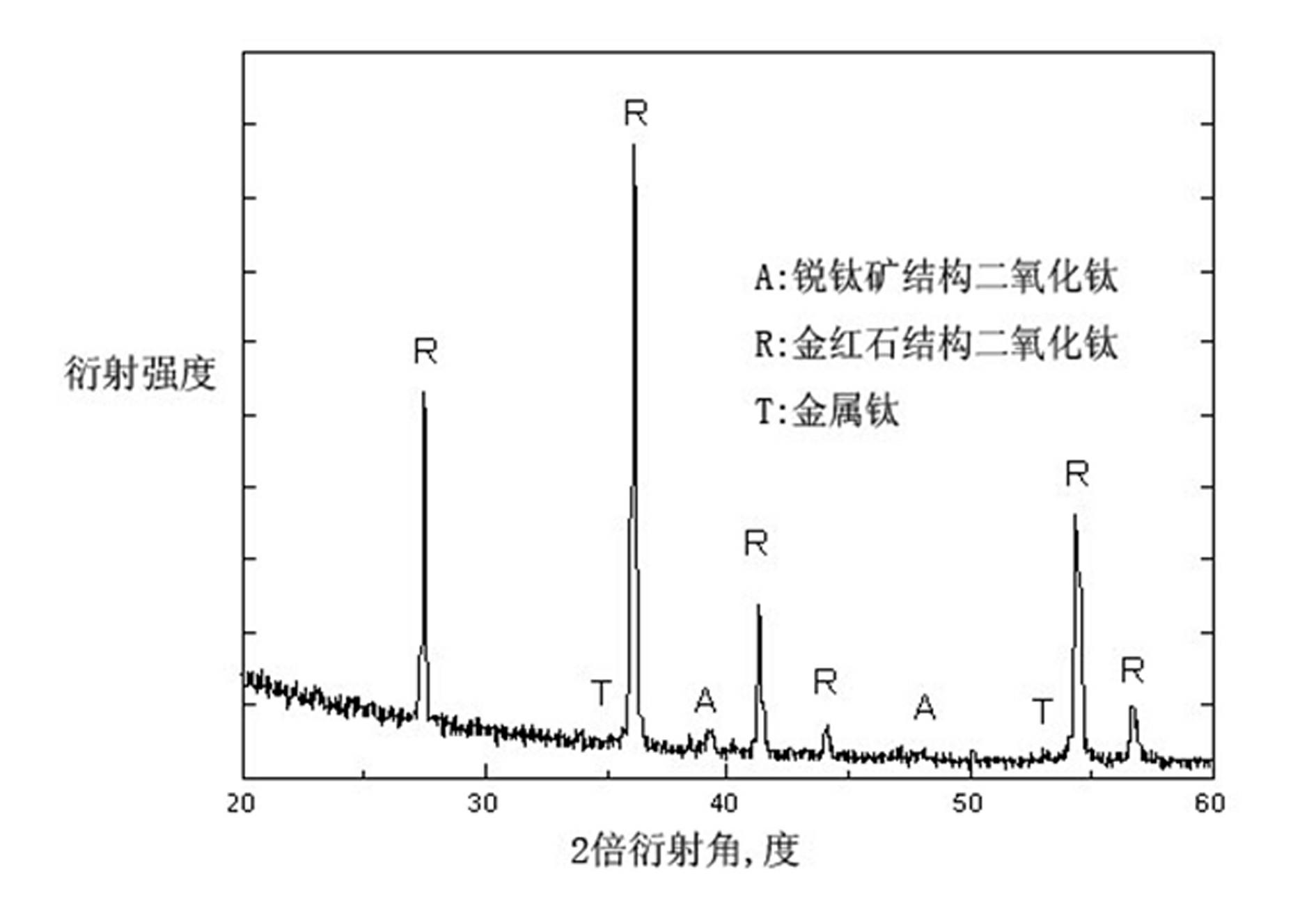
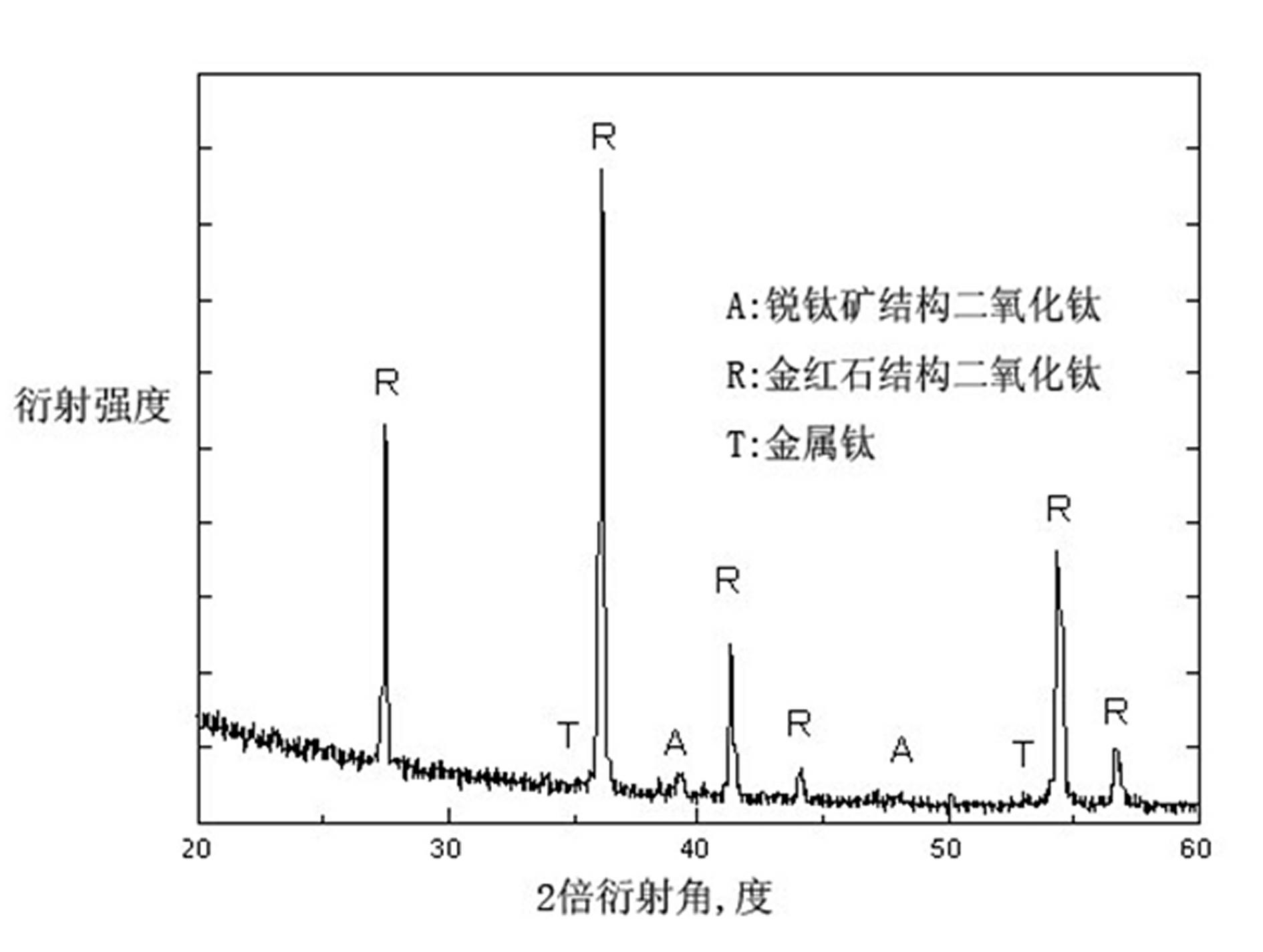
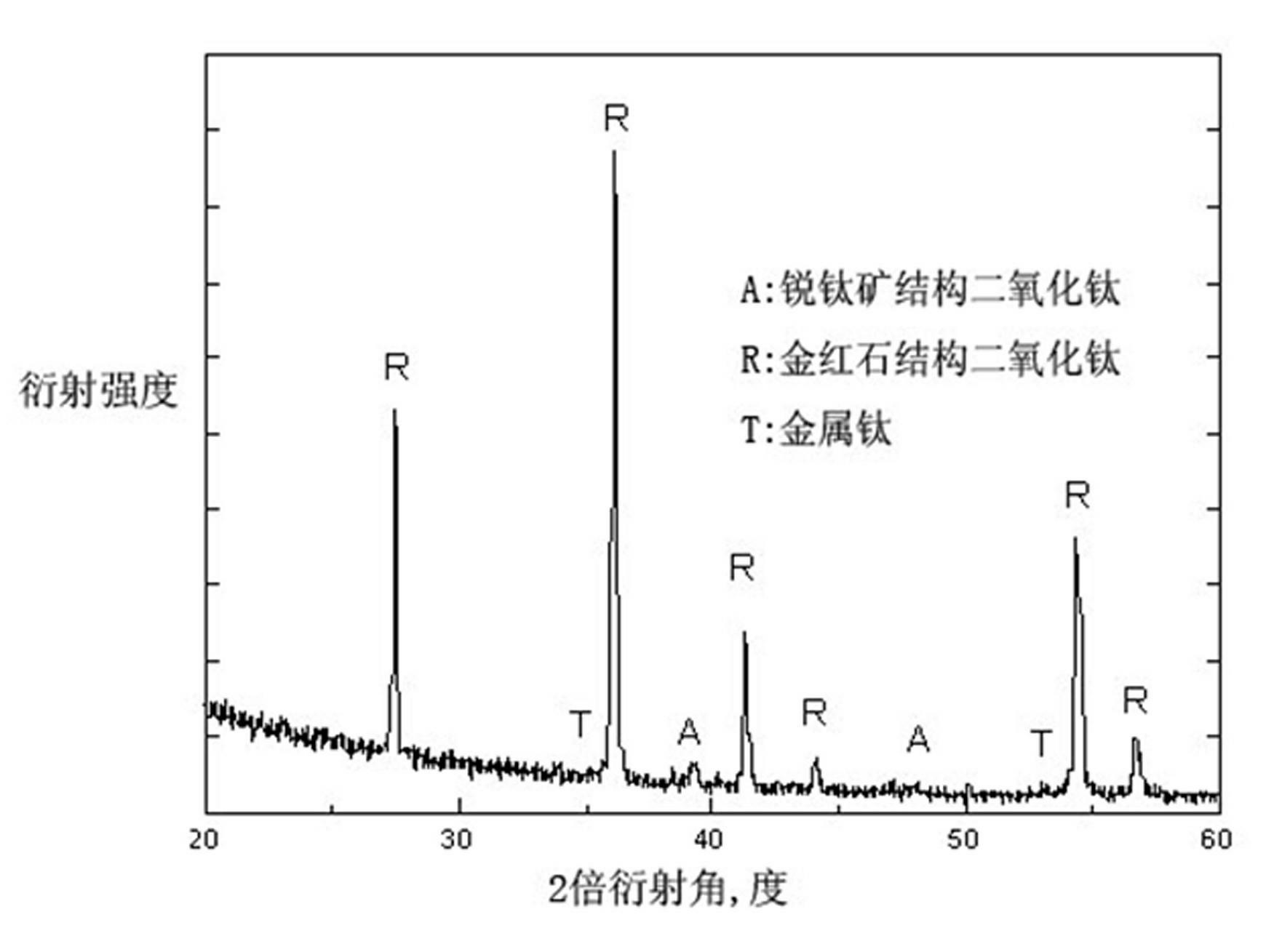
Artificial tooth root or joint material and microarc oxidation preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102090982AImprove surface antibacterial abilityImprove biological activityImpression capsSurface reaction electrolytic coatingMicro arc oxidationPlasma electrolytic oxidation
The invention discloses an artificial tooth root or joint material capable of releasing zinc and cerium trace elements and having a nano / micron porous surface structure and a microarc oxidation preparation method thereof. The artificial tooth root or joint is prepared from a pure titanium or titanium alloy matrix and a porous titanium dioxide bioactive surface layer, wherein the porous titanium dioxide bioactive surface layer is obtained on the surface of the pure titanium or titanium alloy matrix by using a microarc oxidization technology and doped with the trace zinc and cerium elements, the pore diameter of the porous titanium dioxide bioactive surface layer is changed between 50nm and 500nm, thus the surface bacteriostatic capacity, the bioactivity and the cell regulation and control capacity of the initial implanted surface can be improved remarkably, and multiple beneficial functions are obtained. The preparation method comprises the steps of: firstly processing the artificial tooth root (joint) by selecting pure titanium or titanium alloy; then obtaining the titanium dioxide bioactive surface layer with the nano-micro porous structure on the surface of the artificial tooth root (joint) by adopting a microarc oxidization technology; meanwhile adding zinc and cerium soluble salts to electrolyte and carrying out synchronous doping by utilizing a microarc oxidization process.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
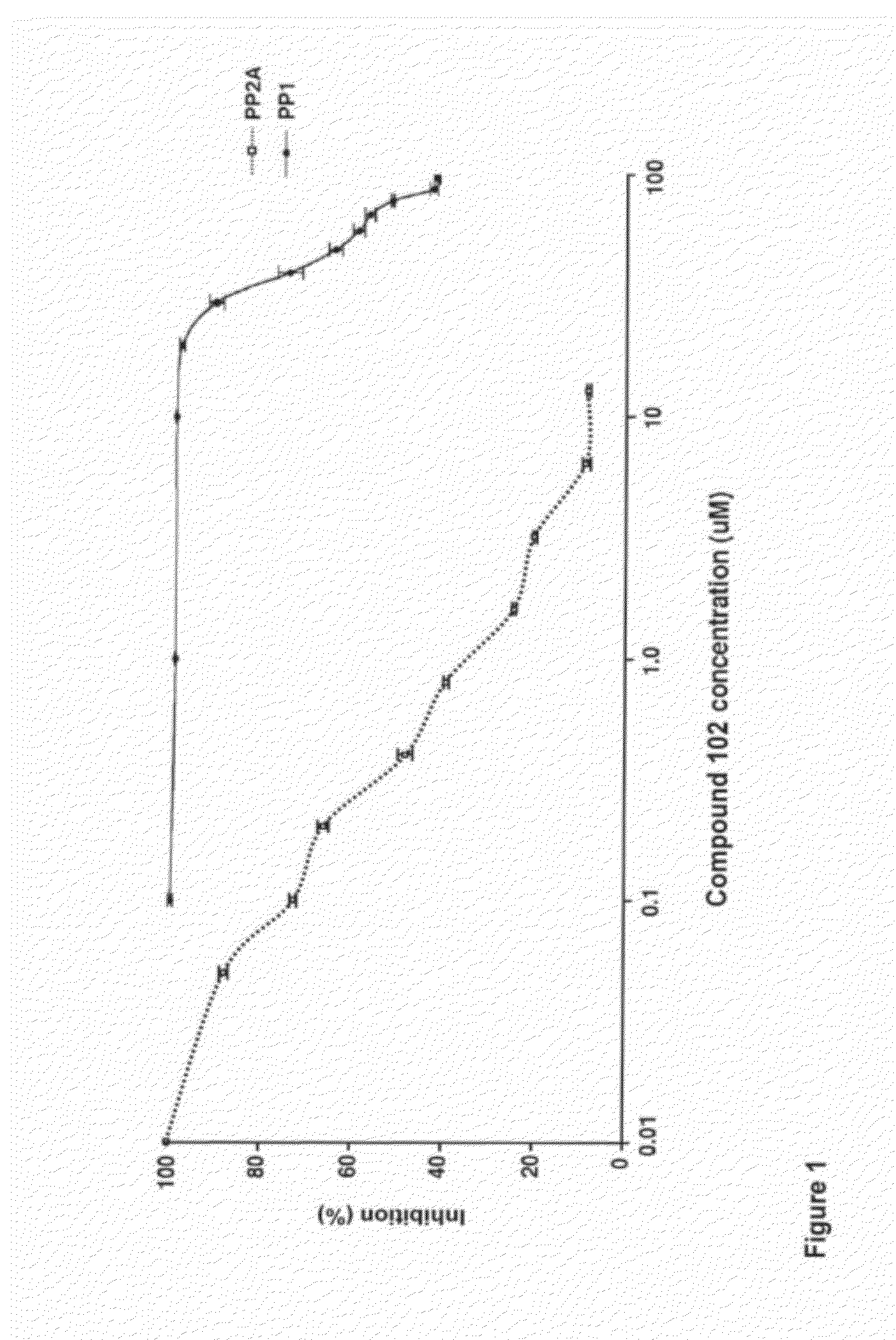
Methods of modulating cell regulation by inhibiting p53
InactiveUS20120135522A1Raise the possibilityIncrease productivityCell culture active agentsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsCellular RegulationSomatic cell
Disclosed herein are methods of inhibiting the function of p53 in a cell by contacting the cell with an effective amount of a PP2A inhibitor. Also disclosed herein are processes for producing an induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell by contacting a somatic cell expressing at least one gene that encodes a reprogramming factor with an amount of a PP2A inhibitor effective to produce the iPS cell; reversibly inhibiting p53 function during production of an iPS cell by contacting a somatic cell with an amount of a PP2A inhibitor effective to reversibly inhibit p53 function; increasing the likelihood of producing an (iPS) cell.
Owner:LIXTE BIOTECH
Ferroferric oxide/calcium phosphate nuclear shell structure nano particle and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a preparation method of a ferroferric oxide / calcium phosphate nuclear shell structure nano particle. The ferroferric oxide used as a nuclear structure is prepared by using a coprecipitation method, and magnetofluid with favorable dispersibility in water can be prepared by modifying the surface of the ferroferric oxide. A mixed solution with the molar ratio of calcium salt and phosphate of 1.0-1.6 is prepared, and the pH value of the solution is adjusted to be 1-10, and the solution is aged at low temperature to form precursor sol. The magnetofluid is uniformly dispersed into the sol to obtain the ferroferric oxide / calcium phosphate nuclear shell structure composite nano particle in the processes of drying and high-temperature sintering. The particle diameter of the composite nano particle is between 80nm and 120nm, wherein the particle diameter of the ferroferric oxide is between 8nm and 60nm. The composite particle is used for a cell regulation and bone repair project under the action of a magnetic field.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Preparation method of Chinese patent medicine particles for treating psoriasis
InactiveCN102397442AReduce manufacturing costPromote activationAnthropod material medical ingredientsGranular deliverySaposhnikoviaForsythia
The invention discloses a preparation method of Chinese patent medicine particles for treating psoriasis, and belongs to the field of pharmacy. The Chinese patent medicine particles for treating psoriasis are prepared from honeysuckle flower, weeping forsythia, divaricate saposhnikovia root, periostracum cicadae, dahurian angelica root, radix sophorae flavescentis, licorice, densefruit pittany root-bark, glabrous greenbrier rhizome, bark of Chinese corktree, raw rehmannia root, red paeony root, Chinese angelica, cane sugar, dextrin and water through processes. The Chinese patent medicine particles for treating psoriasis have small side effects, and after being taken, can fast activate a cell regulation and control system, release a cell protection enzyme, remove cells abnormally divided and thoroughly recover skin normal differentiation and metabolic functions. Practices prove that the Chinese patent medicine particles for treating psoriasis have good treatment effects.
Owner:朱云利
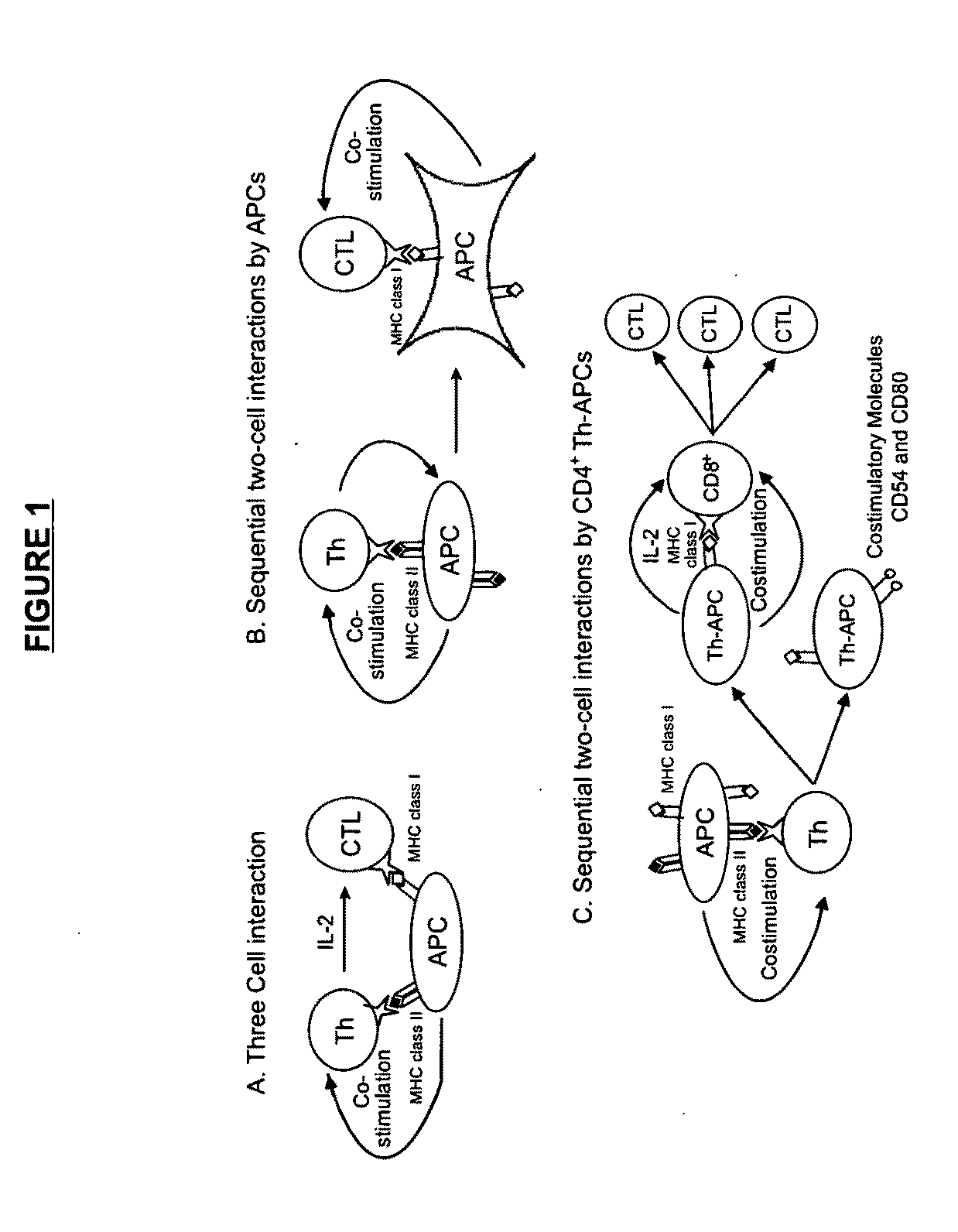
Materials and Method of Modulating the Immune Response
Methods and materials to modulate the immune response to treat or prevent a disease or to prevent transplant rejection, including methods of making T helper-antigen presenting cells and / or T regulatory-antigen specific cells and methods of using these cells. The invention also relates to methods of making exosome-absorbed dendritic cells and the uses of these cells to modulate the immune response to treat or prevent a disease or to prevent transplant rejection.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN
Automated immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization assay formulations
InactiveUS7550298B2Improve accessibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationCytochemistryOrganic solvent
Provided herein are reagents for use in an automated environment for cell conditioning of biological samples wherein the cells or tissues are predisposed for access by reagent molecules for histochemical and cytochemical staining procedures. The reagents include, but are not limited to, components optimized to facilitate molecular access to cells and cell constituents within the biological sample. Also provided herein are reagents for use in an automated environment for removing or etching embedding media by exposing a biological sample to be stained in histochemical or cytochemical procedures without the dependence on organic solvents. The reagents include, but are not limited to, components optimized to facilitate removal or etching of the embedding media from the biological sample.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Suede nap ultra-soft protein leather
InactiveCN109098008AGood moisture absorption and air permeabilityImprove appearance qualityTextiles and paperAdditive ingredientTouch Senses
Owner:FUJIAN HUAXIA SYNTHETIC LEATHER CO LTD
Combination comprising immunostimulatory oligonucleotides
ActiveUS10487333B2Organic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseCD137
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Antenna feeder optimization method
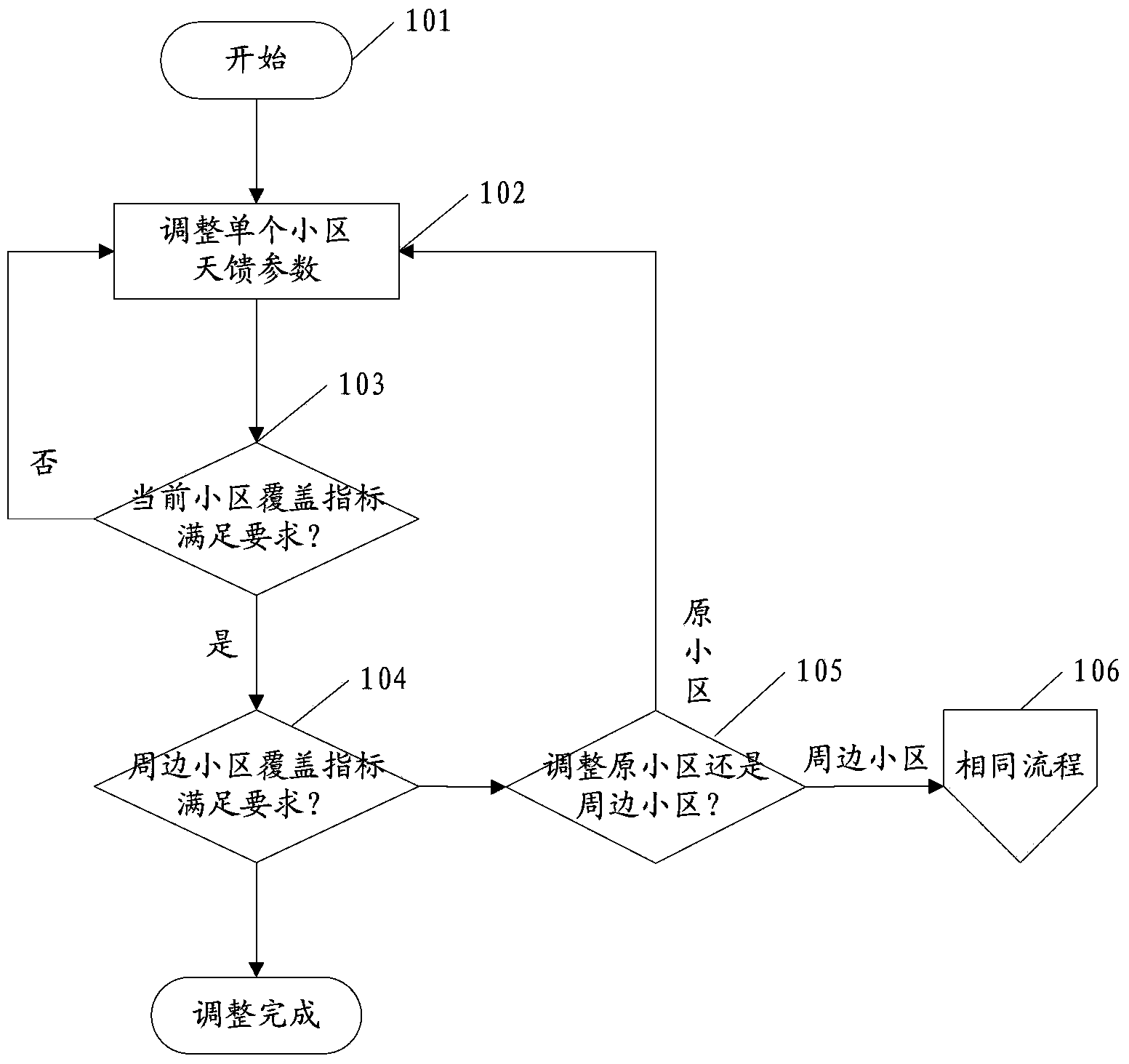
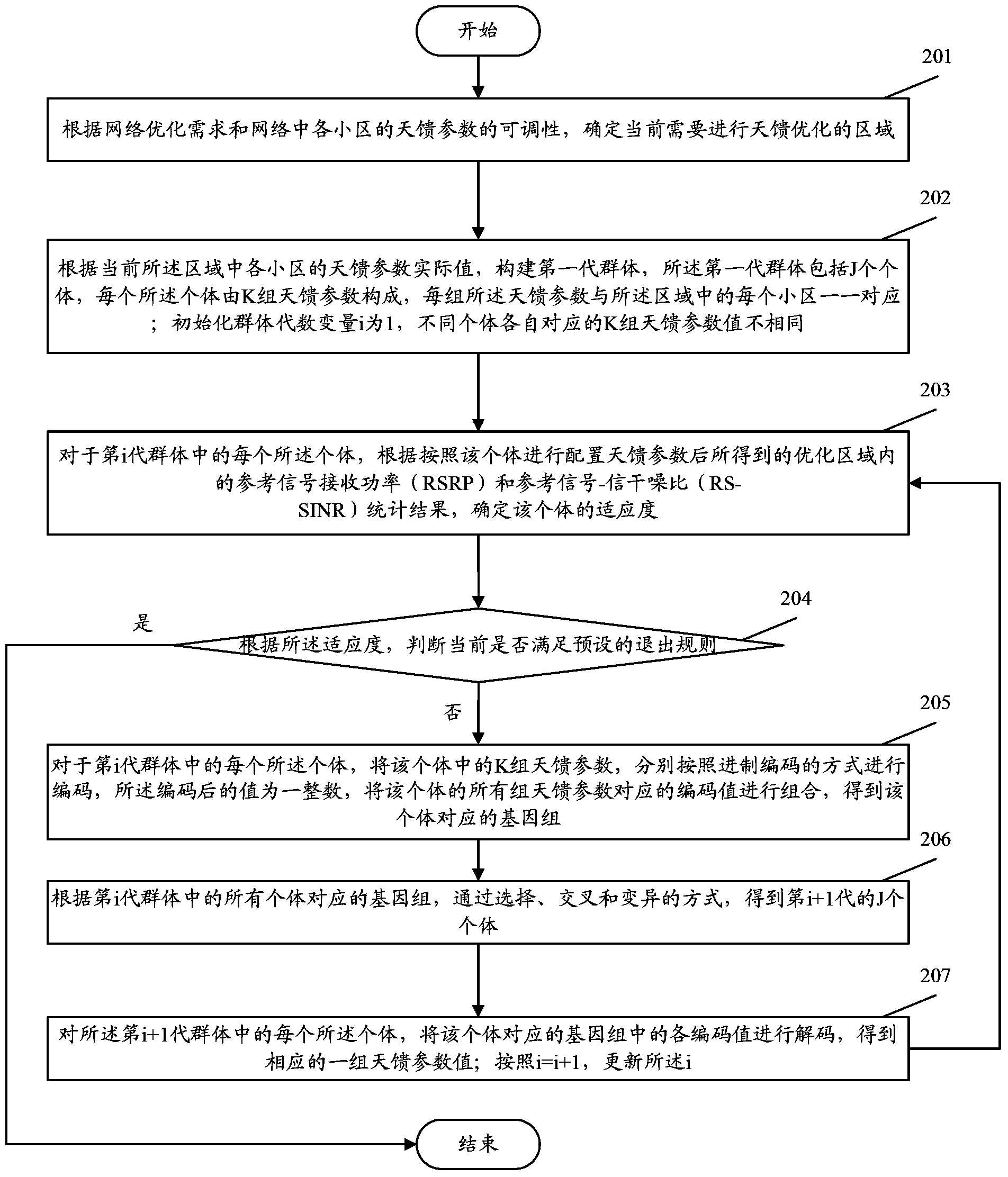
InactiveCN104349358AQuality improvementReduce the number of times to adjust antenna feed parameters by climbing towersWireless communicationGenetic algorithmEngineering
The invention provides an antenna feeder optimization method. According to the method, a genetic algorithm is used, and during the cell antenna feeder parameter optimization configuration, the relationship among the cells is sufficiently considered, so that the spread influence on the surrounding cells during the single cell regulation is avoided. When the antenna feeder optimization method is adopted, the optimization efficiency can be improved, the times for climbing a tower to regulate antenna feeder parameters by workers can be greatly reduced, the network optimization cost is reduced, and the network quality is improved.
Owner:POTEVIO INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
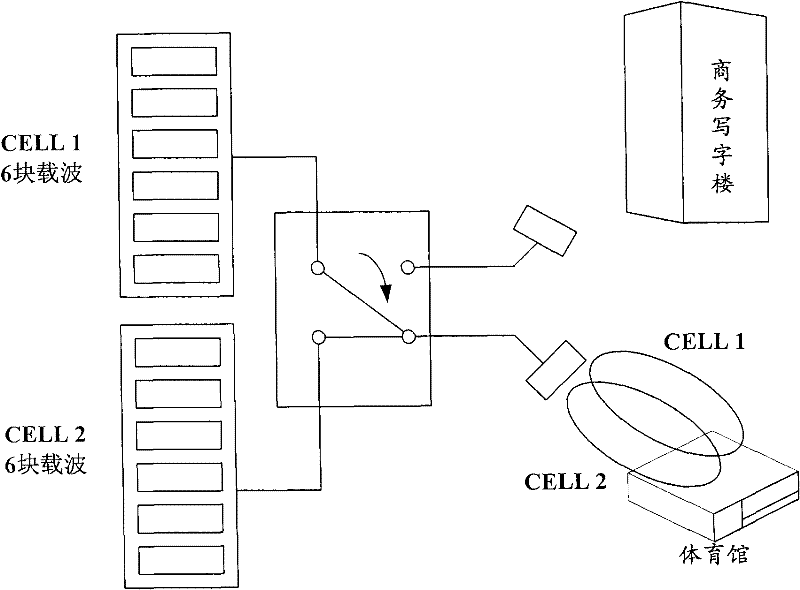
Method for dynamically allocating wireless network resources, and carrier pool base station system
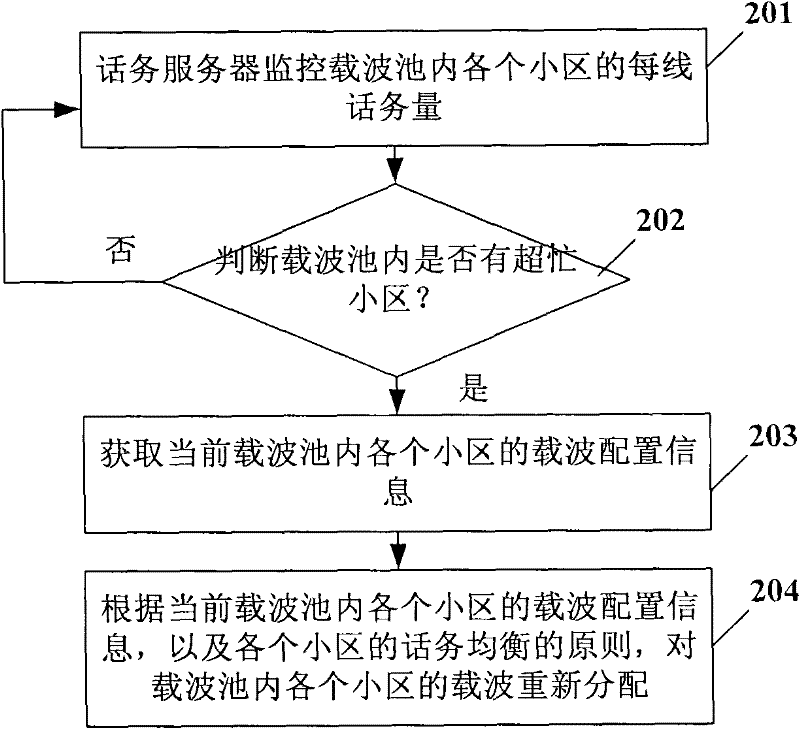
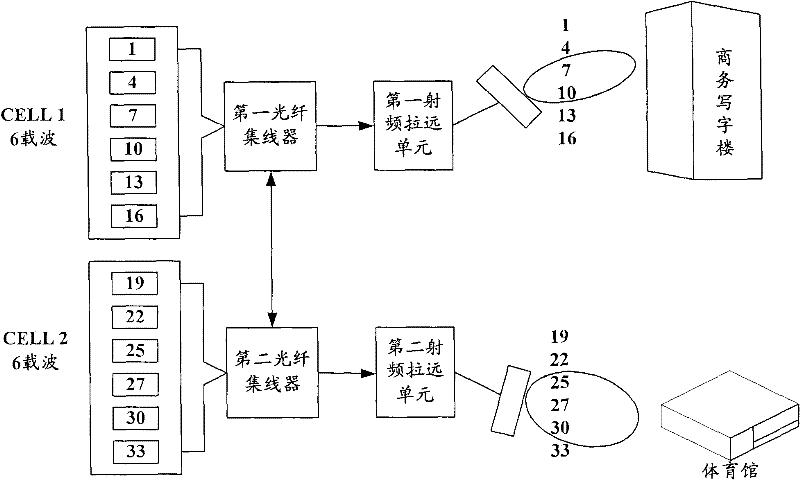
ActiveCN102547724AAvoid modificationImplement dynamic allocationNetwork planningCarrier signalCell regulation
The invention provides a method for dynamically allocating wireless network resources, and a carrier pool base station system, belonging to the technical field of communication. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, obtaining carrier wave configuration information of each cell in a current carrier pool; and secondly, re-allocating carrier waves of each cell in the carrier pool according to the carrier wave configuration information of each cell in the current carrier pool. The invention realizes dynamic allocation of the quantity of the carrier waves in the cells by using the carrier waves as units, and avoids the problem of neighbor area modification caused by the cell regulation.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GRP BEIJING
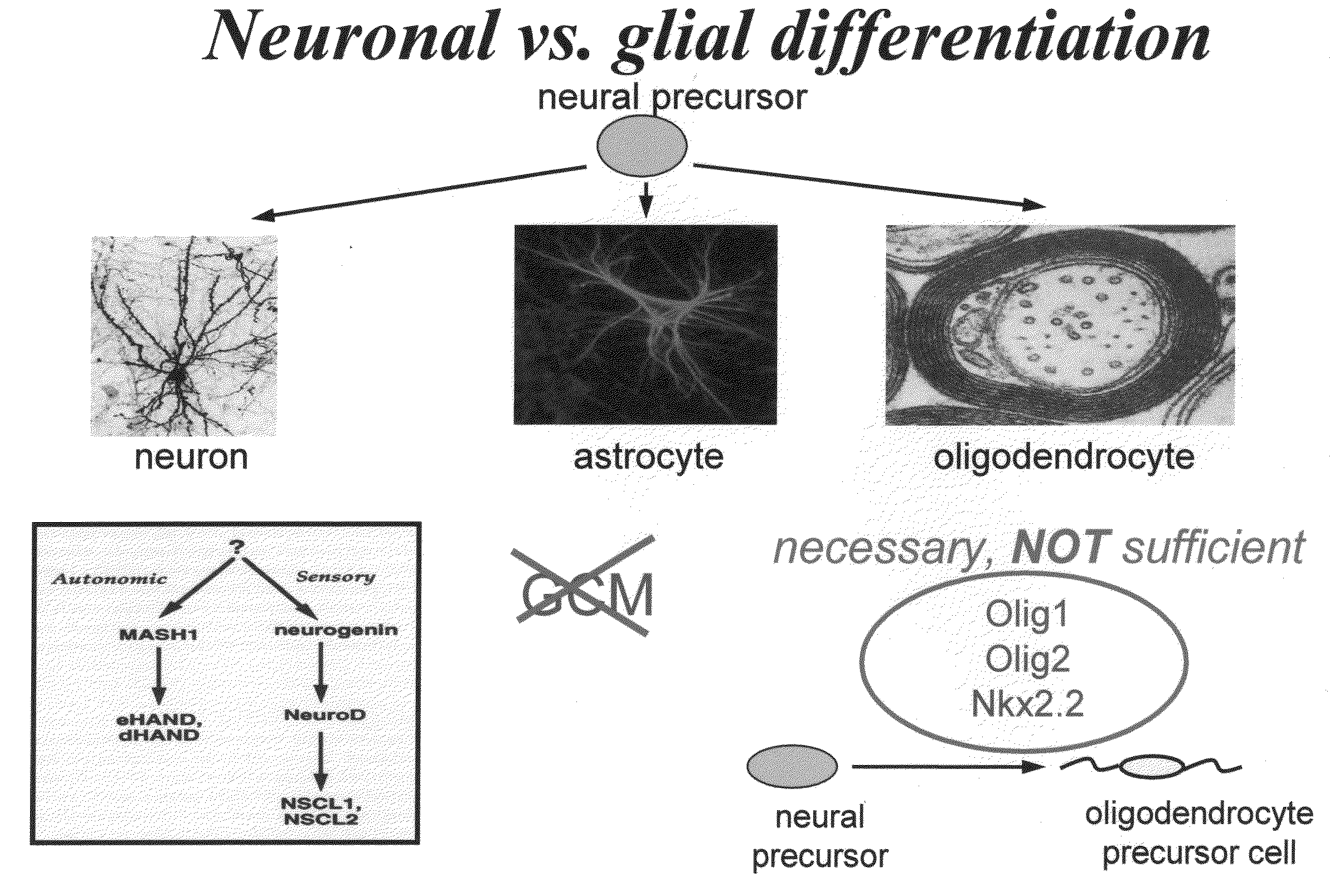
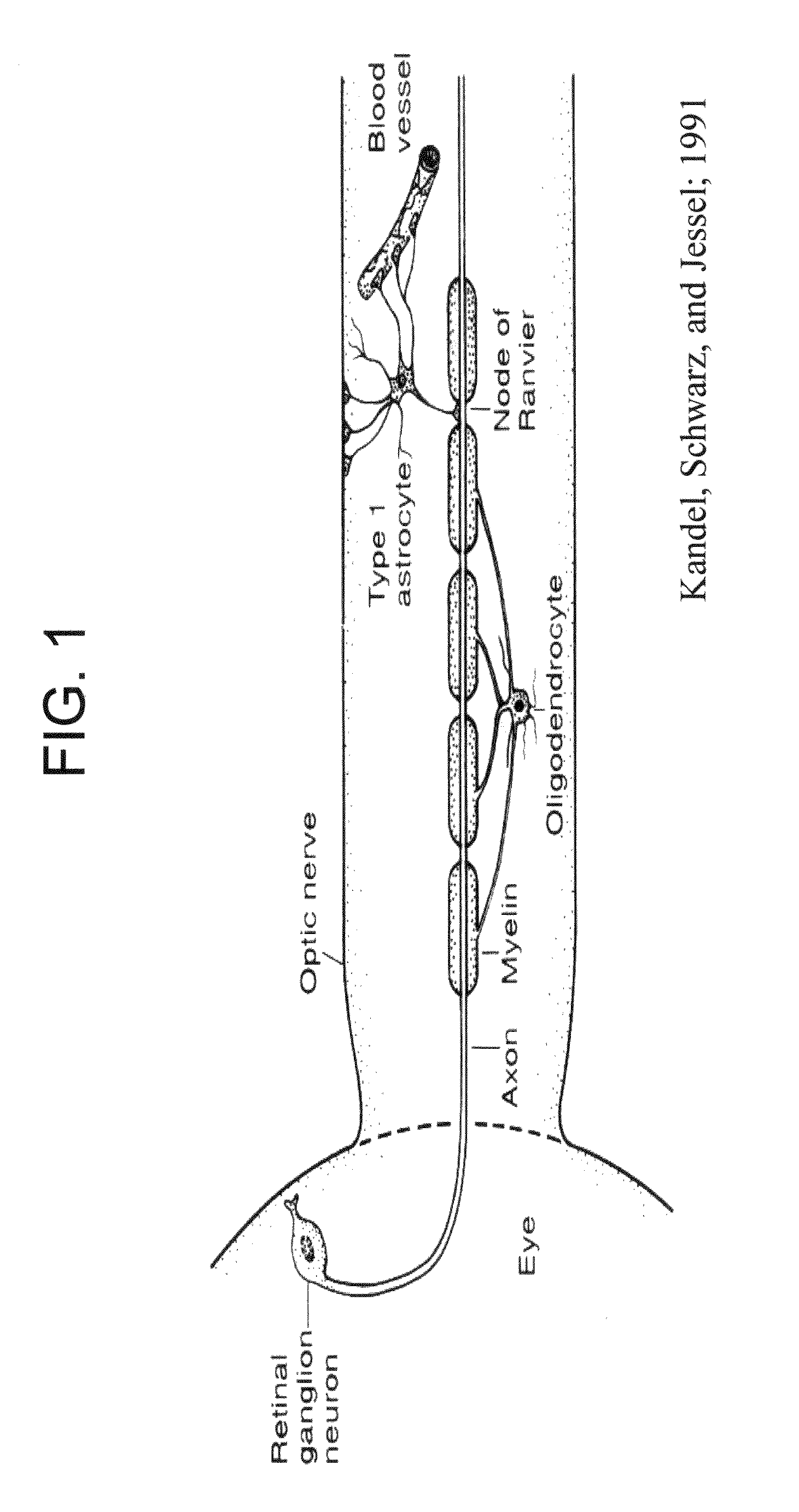
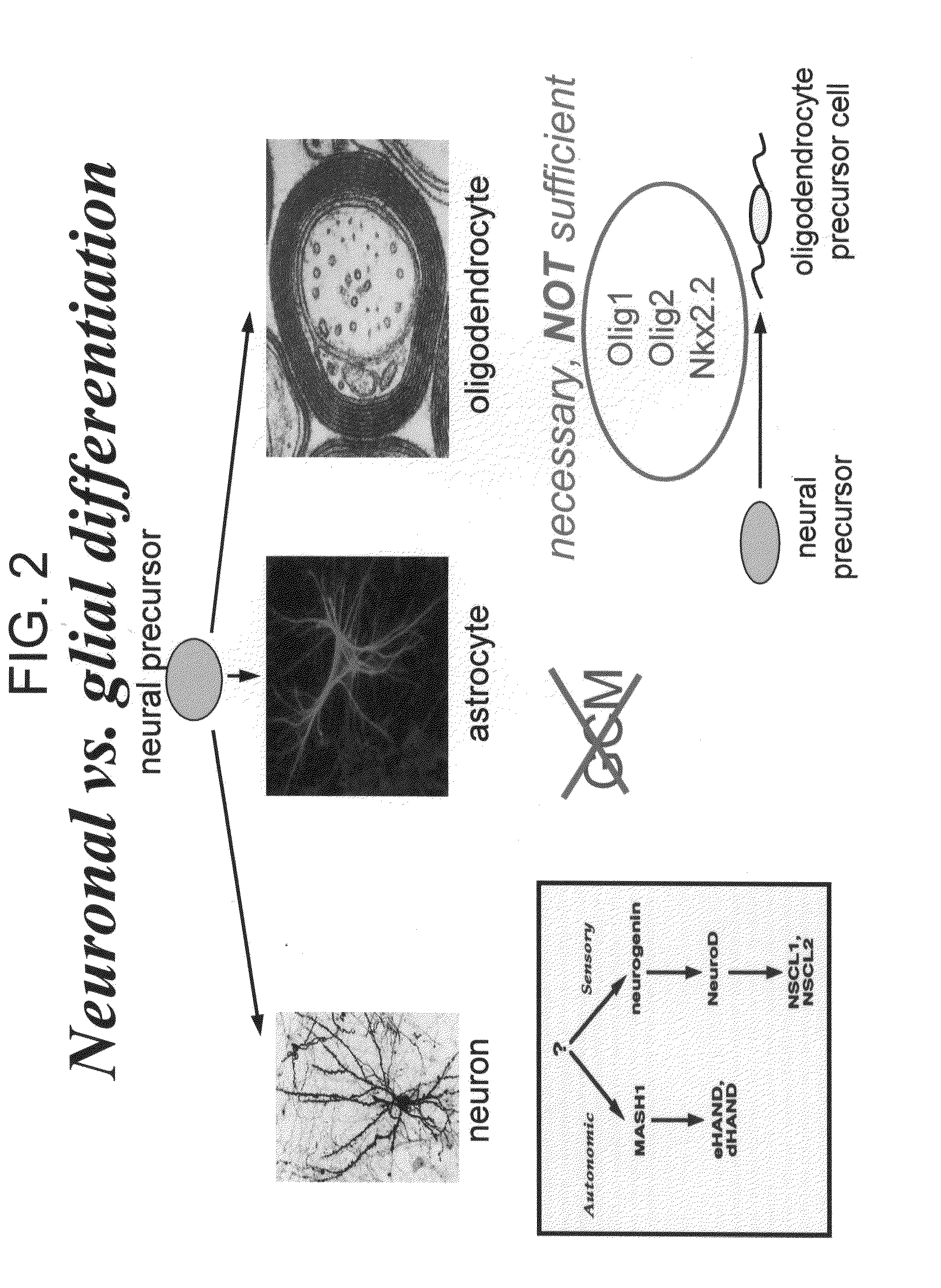
Cell cycle regulation and differentiation
InactiveUS20090258423A1Promote differentiationPromotes differentiationNervous disorderBiological material analysisNeural cellCell cycle
The present invention provides compositions and methods for regulating neural cell proliferation or differentiation. The present invention also provides methods for selecting for bioactive agents effective in regulating proliferation or differentiation.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
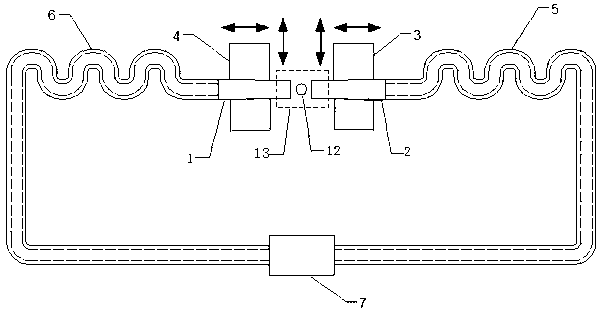
Single-cell clamping method and single-cell position regulating device
InactiveCN103131664ARealize position controlRealize the clamping effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluid viscosityControl cell
The invention provides a single-cell clamping method and a single-cell position regulating device. The method is that in the regulating operation process of cells, fluid pressure and fluid viscosity force between clamping tubes are used for clamping the cells, the cells are wrapped and clamped to move in a non-contacting mode through the movement of the clamping tubes, and so that the position regulation of the cells is achieved. The device comprises two cell clamping tubes, two soft micro tubes, a control unit and a micropump unit which supplies the needed flow to the cell clamping tubes. Each cell clamping tube is connected with the micropump unit through the soft micro tubes, and the two cell clamping tubes are installed on the control unit and are distributed on two sides of the cells. The single-cell clamping method and the single-cell position regulating device can be suitable for the cells with different shapes and different sizes, the three-dimensional position regulation of the cells is achieved, mechanical damage to the cells can be avoided, and the single-cell clamping method and the single-cell position regulating device are beneficial to improving the success rate of cell experiment operation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
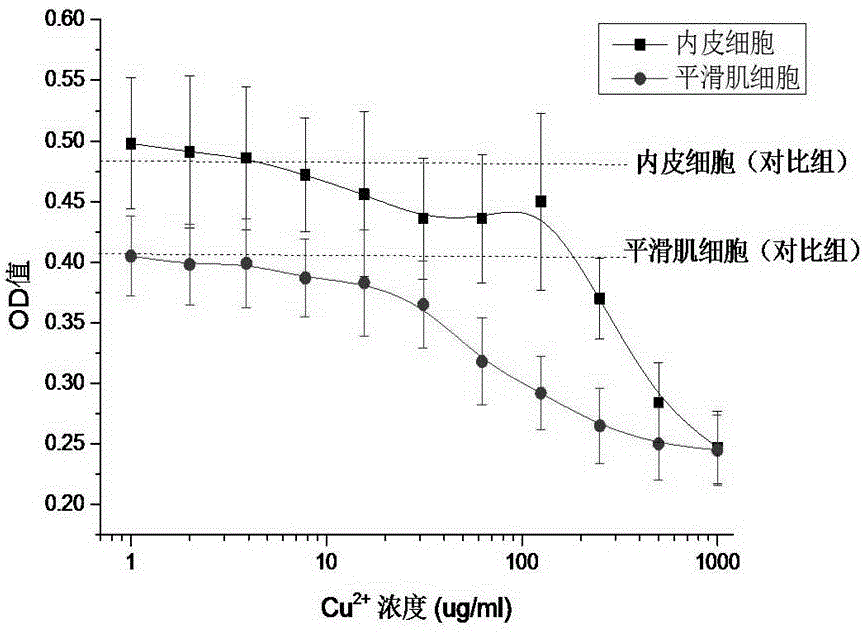
Inorganic nano-coating capable of regulating and controlling cell response and preparation method of inorganic nano-coating
InactiveCN106310390AControllable ratioChange side effectsSurgeryVacuum evaporation coatingComposite filmControl cell
The invention discloses inorganic nano-coating capable of regulating and controlling cell response and a preparation method of the inorganic nano-coating. The invention mainly aims to prepare a degradable metal composite film on the surface of a metal vascular stent; in particular, the film can regulate and control different response behaviors of smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells. The film adopts copper as a basic component and realizes high blood compatibility, cell regulation and control mechanism, degradation behaviors and physical properties by regulating and controlling the proportion of other components and a composite structure of the copper and other components. The coating is a metal nano-film, has high ductility and a good binding force, and is suitable for the mechanical requirements of machines in the using process. The invention also relates to a method for regulating and controlling different cell response behaviors by ions generated in the degradation process of the film.
Owner:成都迈德克科技有限公司
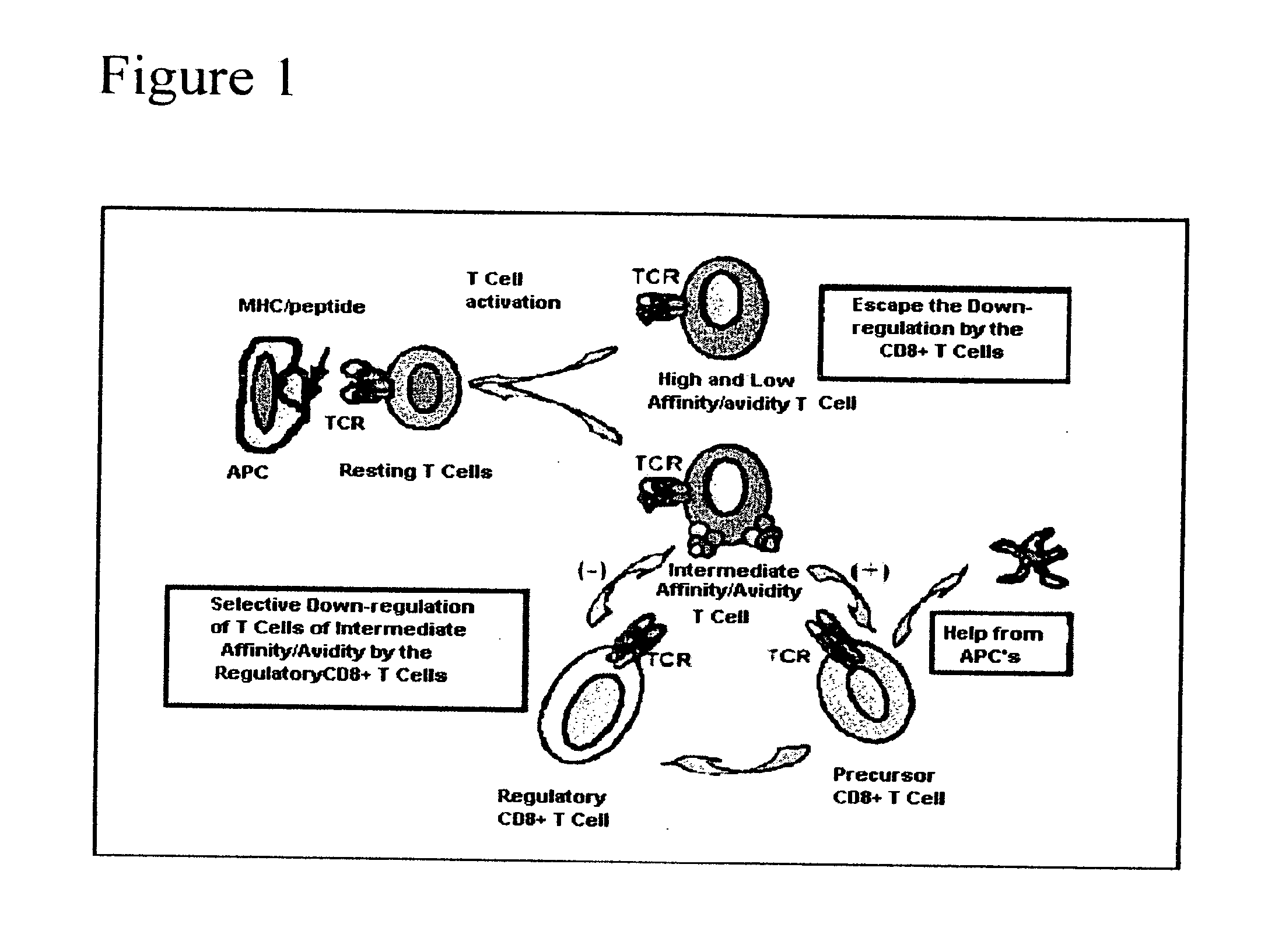
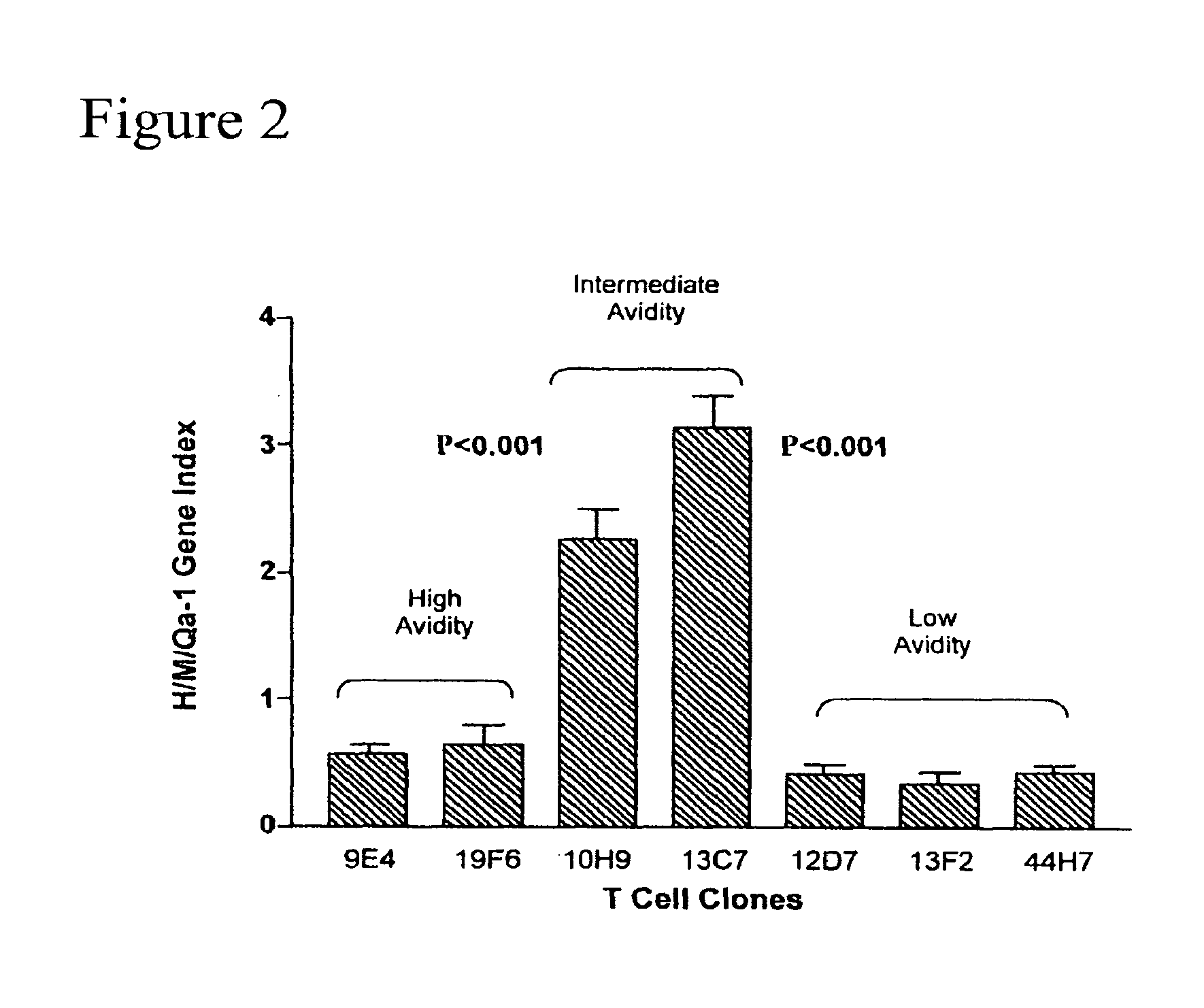
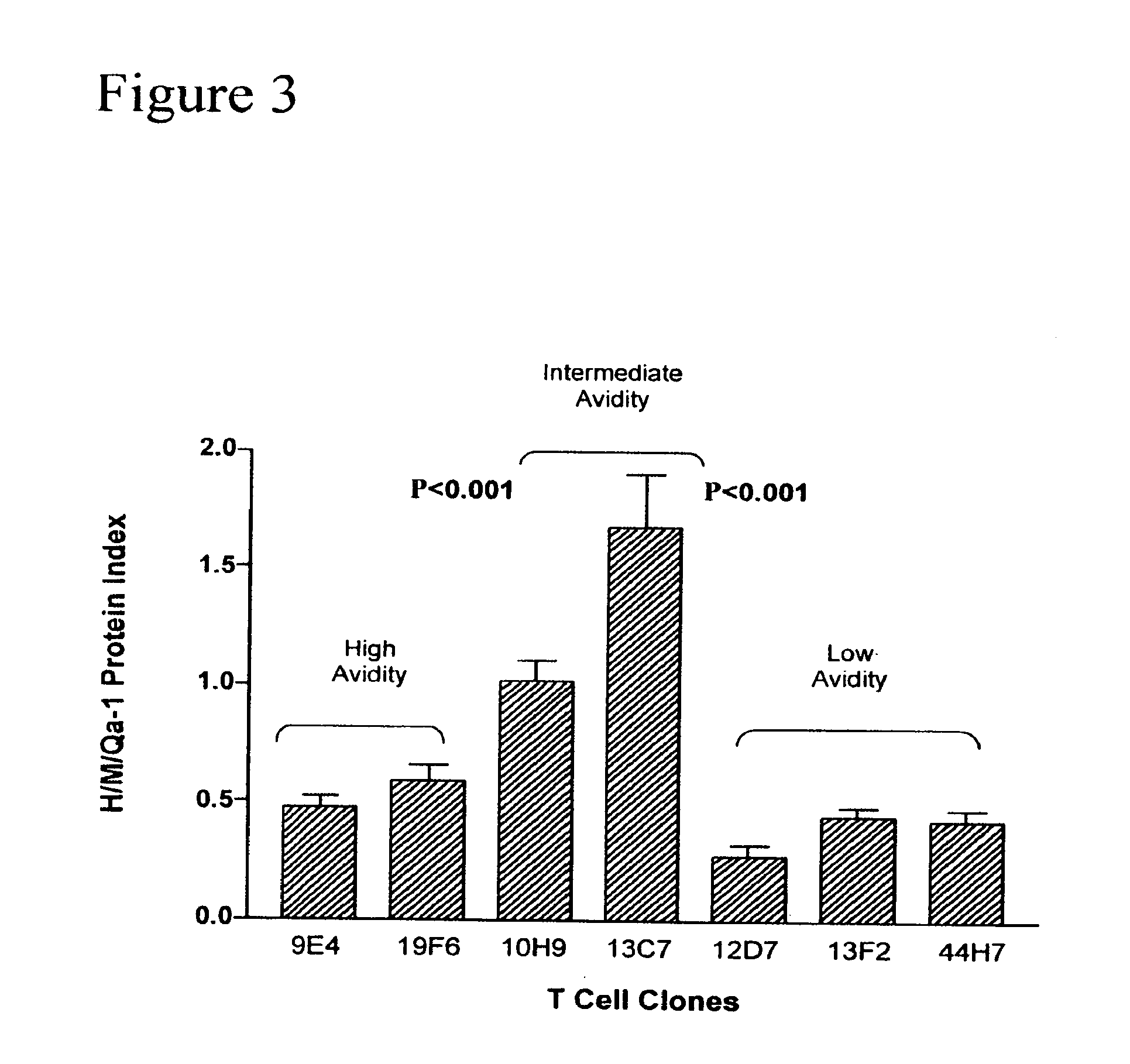
Methods to activate or block the HLA-E/Qa-1 restricted CD8+ T cell regulatory pathway to treat immunological disease
ActiveUS20130209498A1Control and/or amelioration of autoimmune diseasesEnhancing down-regulation of an antigen-activated HLA-EAntibacterial agentsBiocideAntigenDisease
Methods are provided for inhibiting or enhancing down-regulation of an antigen-activated HLA-E+ T cell by an HLA-E-restricted CD8+ T cell comprising contacting the HLA-E+ T cell and CD8+ T cell with an agent which inhibits or enhances, respectively, binding between (i) T cell receptor (TCR) on the surface of the CD8+ T cell and (ii) a self peptide presented by HLA-E on the surface of the HLA-E+ T cell, thereby inhibiting or enhancing, respectively, down-regulation of the antigen-activated HLA-E+ T cell. Compositions comprising agents which inhibit or enhance / activate, respectively, binding between (i) T cell receptor (TCR) on the surface of a CD8+ T cell and (ii) a self peptide presented by HLA-E on the surface of a HLA-E+ T cell, and assays for identifying such agents, are provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Light sheet fluorescence microscopic imaging method and device based on double-core optical fiber light control
ActiveCN112834410ACompact structureEasy to operateMicroscopesIndividual particle analysisMicro imagingFluorescence
The invention provides a light sheet fluorescence microscopic imaging method and system based on double-core optical fiber light control. The system is characterized in that a light control part of the device is formed by oppositely installing two two-core optical fibers of which the output end surfaces are processed into specific angles, wherein a focused light field formed near the output end face of one two-core optical fiber stably captures a cell to be detected and adjusts the output power of each fiber core of the other two-core optical fiber, so that the cell rotates around a specific axis. And when the cells rotate to a certain angle and reach a stable state every time, a structure image of a certain layer of cells is obtained by using a light sheet fluorescence microscopy technology, and finally a three-dimensional structure image of the cells is obtained. The system constructed by the invention can be used for obtaining high-time and high-spatial resolution three-dimensional structure images of living single cells, and has the characteristics of small light damage, simple structure, low cost, simplicity and convenience in operation and the like. The system can be applied to many research fields such as biology, medicine and life science.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Apparatus and method for early diagnosis of cell death
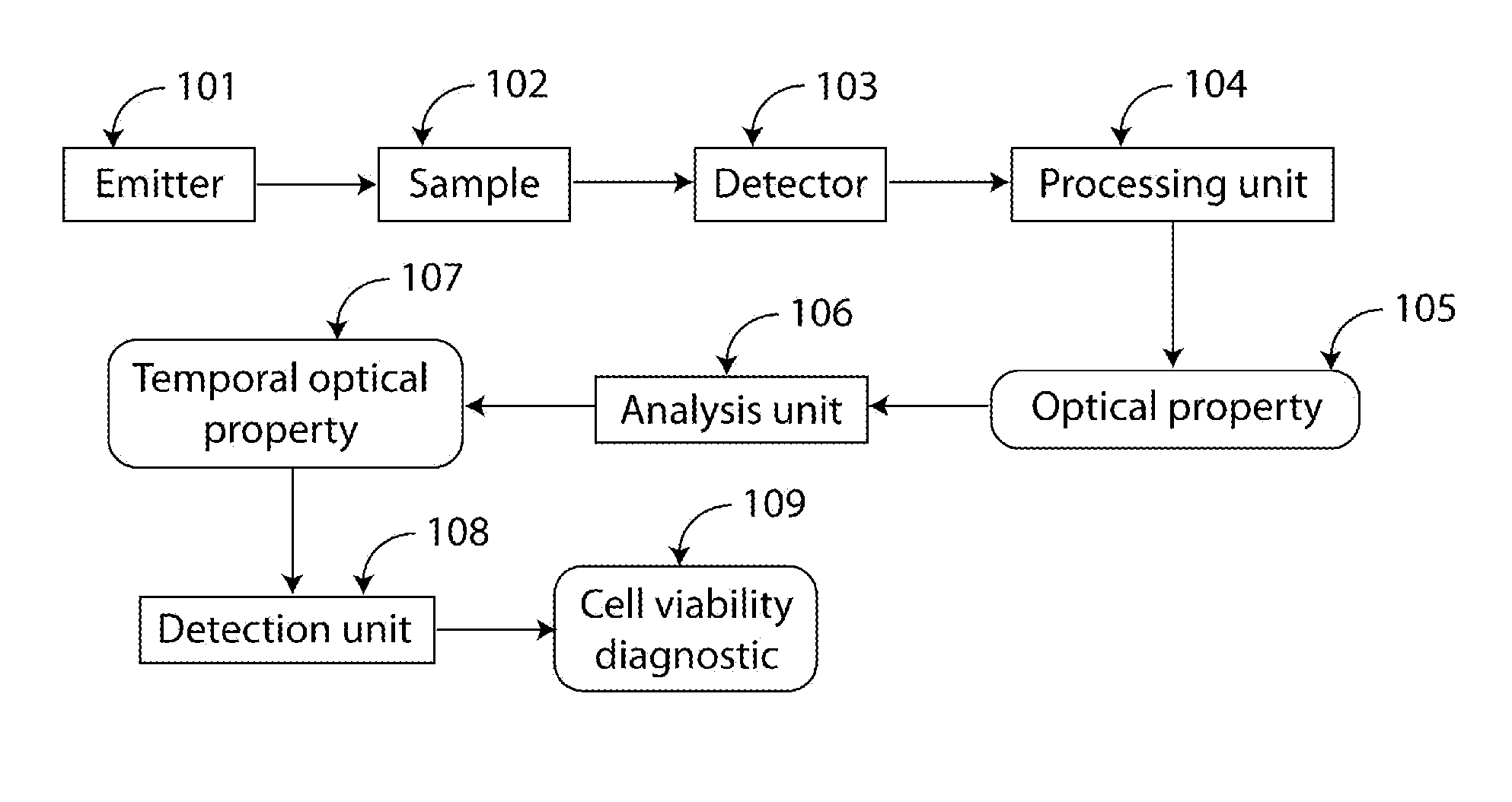
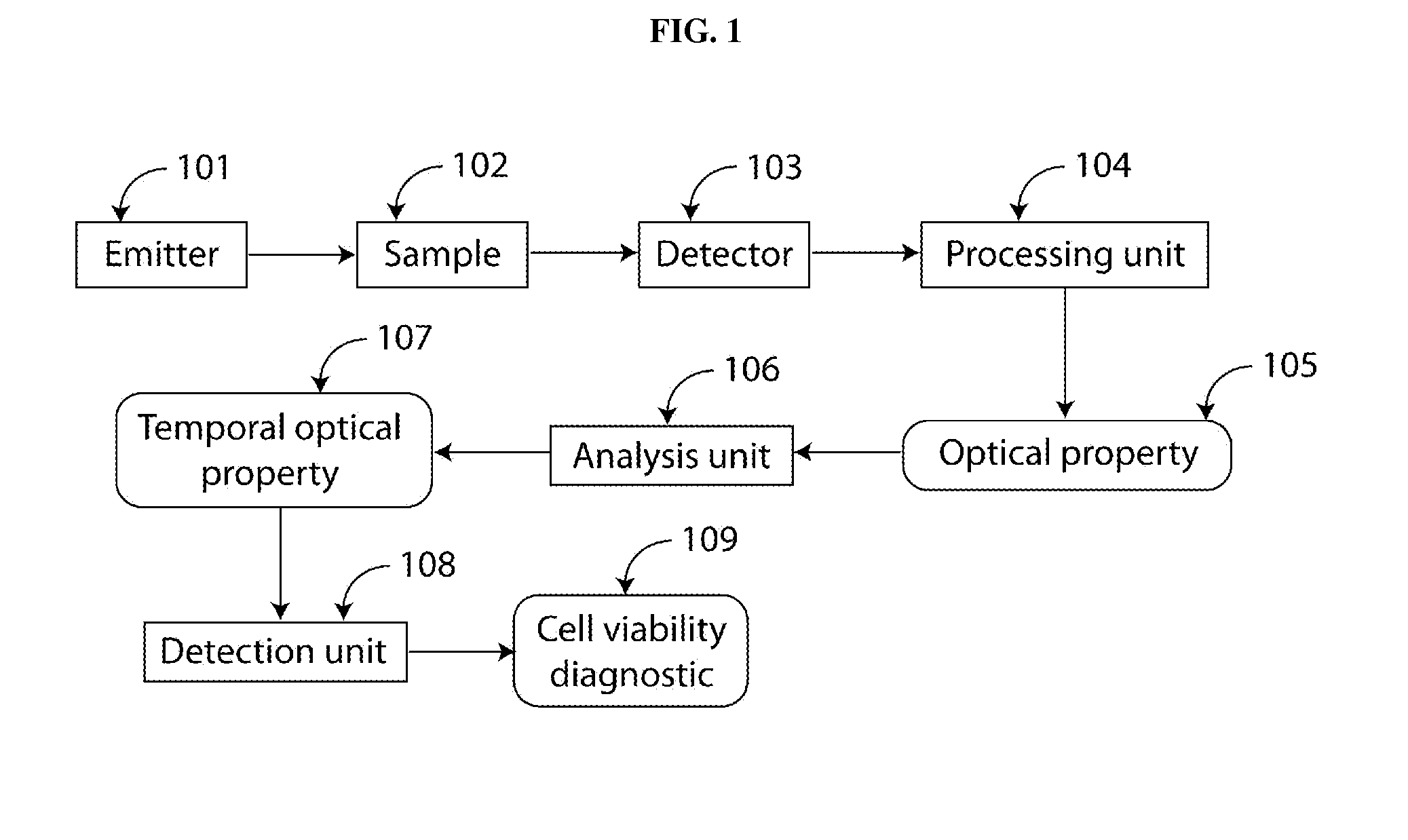
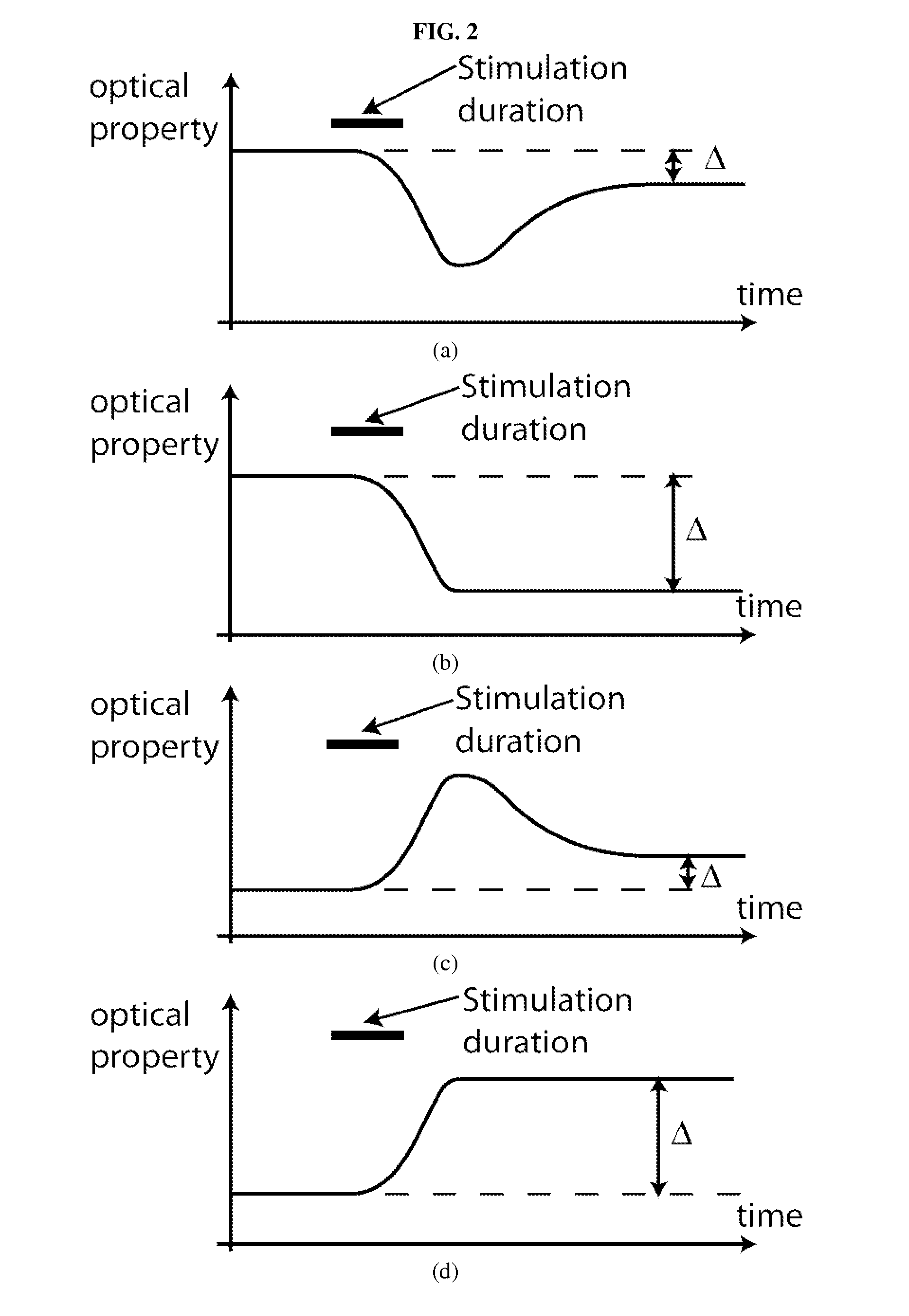
ActiveUS20130210066A1Ability to monitorEarly diagnosisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiagnosis earlyCellular homeostasis
An apparatus for measuring through optical means temporally resolved, optical properties, and / or phenotypes, linked to cellular homeostasis. Those temporal measurements enable the detection of cell regulation through various channels linked to homeostasis, in order to assess cell viability or early cell death through rapid diagnostic.
Owner:LYNCEE TEC
Method for preparing microvesicular adam15
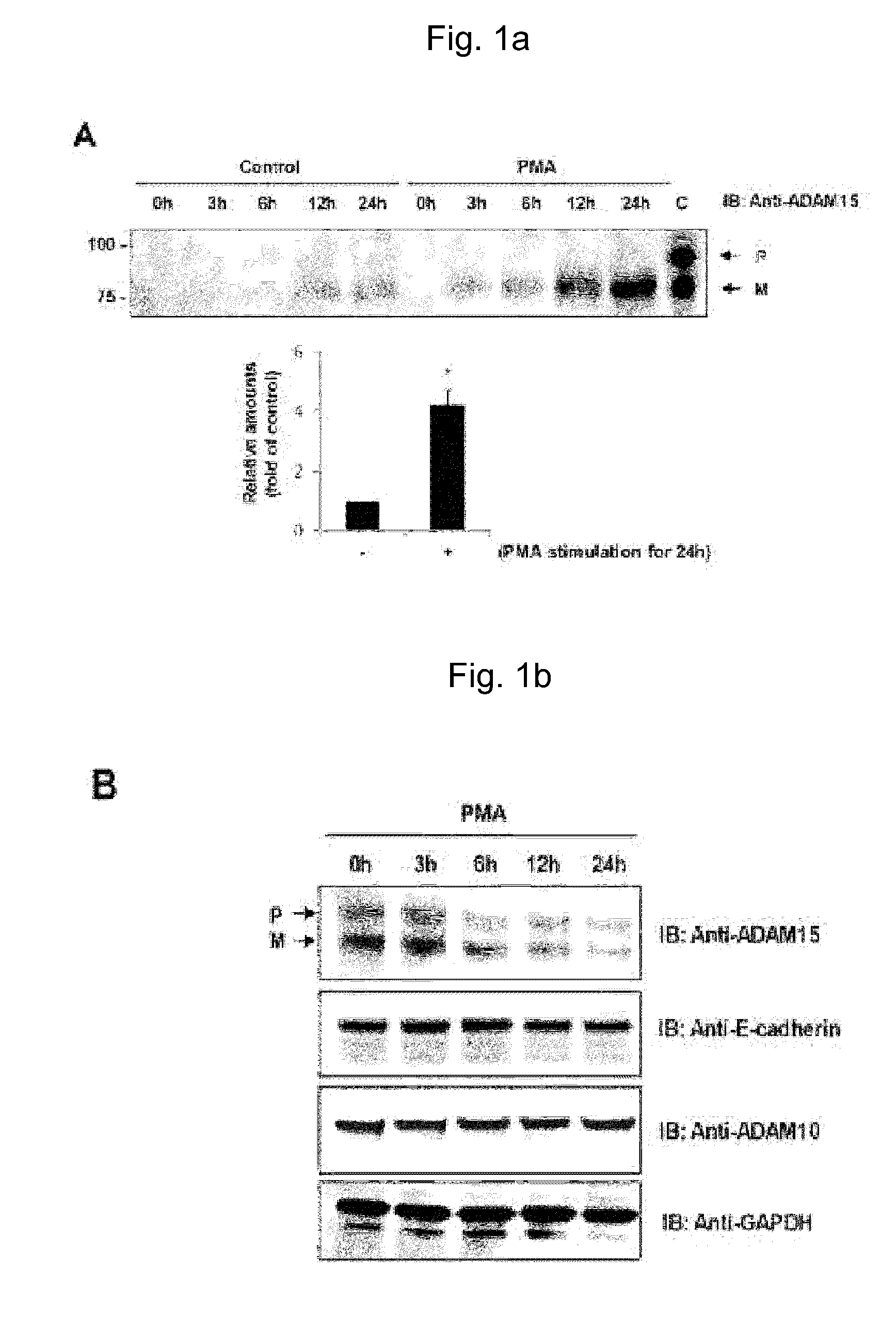
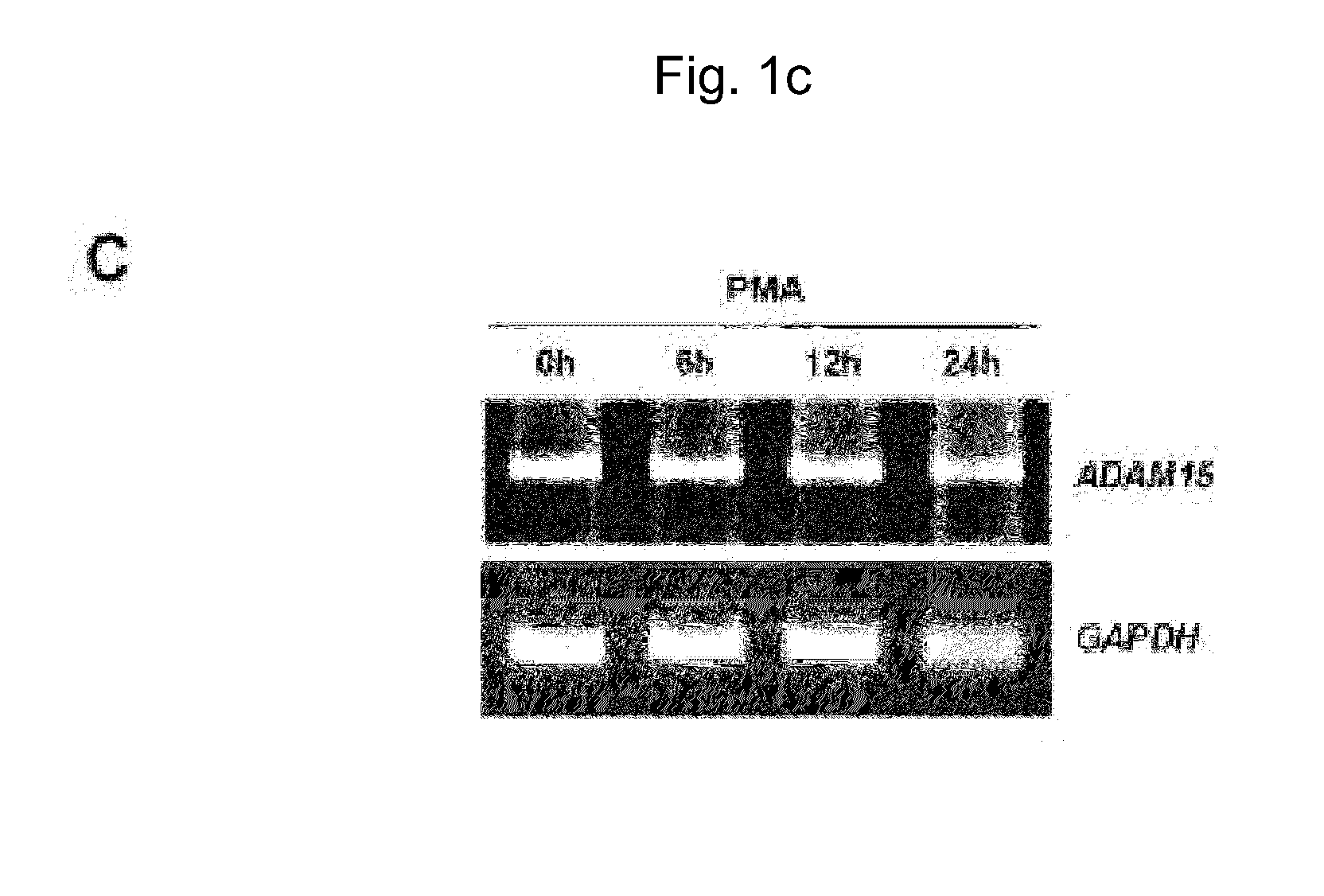
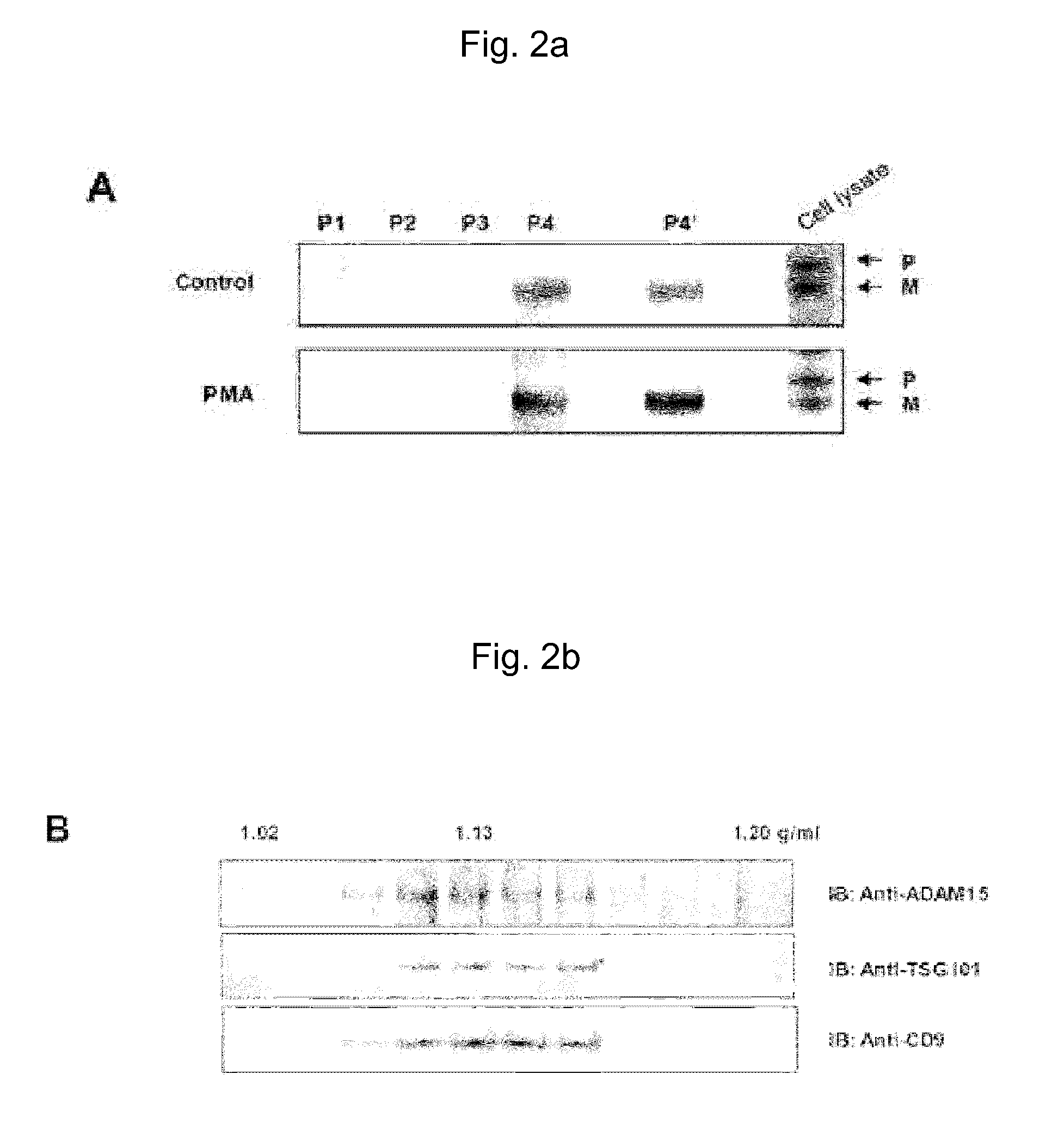
InactiveUS20140212949A1Suppresses adhesionSuppresses proliferationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMammalian cellCell regulation
The present invention relates to a method for preparing microvesicular ADAM15, comprising: (a) a step of activating protein kinase C (PKC) of separated mammalian cells; and (b) a step of separating microvesicle-containing ADAM15 from the mammalian cells. According to the present invention, a method for preparing microvesicular ADAM15 from mammalian cells is provided, and a novel cell regulation mechanism mediated by ADAM proteins is provided by the study of the function of the microvesicular ADAM15. Further, the present invention may provide a novel anti-cancer drug using microvesicular ADAM15, which inhibits adhesion, proliferation and migration of tumor cells.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
Esterified fatty acid composition
ActiveUS7776914B2Avoid certain side effectImprove efficacyBiocideCosmetic preparationsSide effectMedicine
Owner:IMAGENETIX
Primer set, application, product and method for detecting related SNP sites of drug metabolism ability of rheumatic immune diseases
ActiveCN110551813BImprove accuracyShort detection cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationIMMUNE SUPPRESSANTSImmunomodulating Agent
Owner:JIANGSU SIMCERE MEDICAL DEVICE CO LTD +2
Hybrid cells
A rapid, simple-to-use method for preparing hybrid cells, applicable to fully differentiated, non-dividing cells, entails bringing at least two different cells into contact under conditions that promote cell fusion and then purifying the resultant hybrid without antibiotic or metabolic selection. This approach yields hybrid cells useful in a variety of applications, including clinical treatment regimens, as cellular modulators of the immune system.
Owner:GHC RES DEV CORP
Esterified fatty acid composition
ActiveUS7612111B2Avoid certain side effectImprove efficacyHalogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsBiocideSide effectMedicine
The invention is directed to compositions comprising lecithin, olive oil, esterified fatty acids and mixed tocophenols for use in the treatment and prevention of various types of arthritis and other inflammatory joint conditions, periodontal diseases and psoriasis, which avoid many of the side effects associated with known treatments. The compositions of the present invention have the advantage of increased stability, a reduction of arachidonic acid in cells, a reduction in eicosanoid production and enhanced cell regulation and communication. Also disclosed are methods for using the compositions for treatment and prevention.
Owner:THINGS OF THAT NATURE INC
Method for dynamic communication in wireless coverage area
ActiveCN101631314AFast and efficient dynamic programmingEasy to handleNetwork planningIslandingDynamic planning
The invention relates to a method for dynamic communication in a wireless coverage area, which comprises the steps of detecting communicating neighbors and gateway degree information of nodes, setting an initial transmission power and a transmission velocity, adjusting the coverage area and processing isolated cells, wherein the communicating nodes refers to nodes A and B which can receive detection reports mutually; and the isolated cells refers to cells which have the maximum gateway degree and no route to a gateway. Compared with the prior art, the method has the following advantages of realizing quick and effective dynamic planning of a wireless coverage range, introducing gateway information to aim the planning at increasing the total bandwidth of the system, increasing the processing of the isolated cells to reduce communication islands in a dynamic process, performing passive broadcast detection to reduce signaling interaction and acquire equivalent information and optimally ensuring the transmission velocity and high bandwidth in cell regulation.
Owner:上海寰创网络科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com