Patents
Literature
134 results about "Opening surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
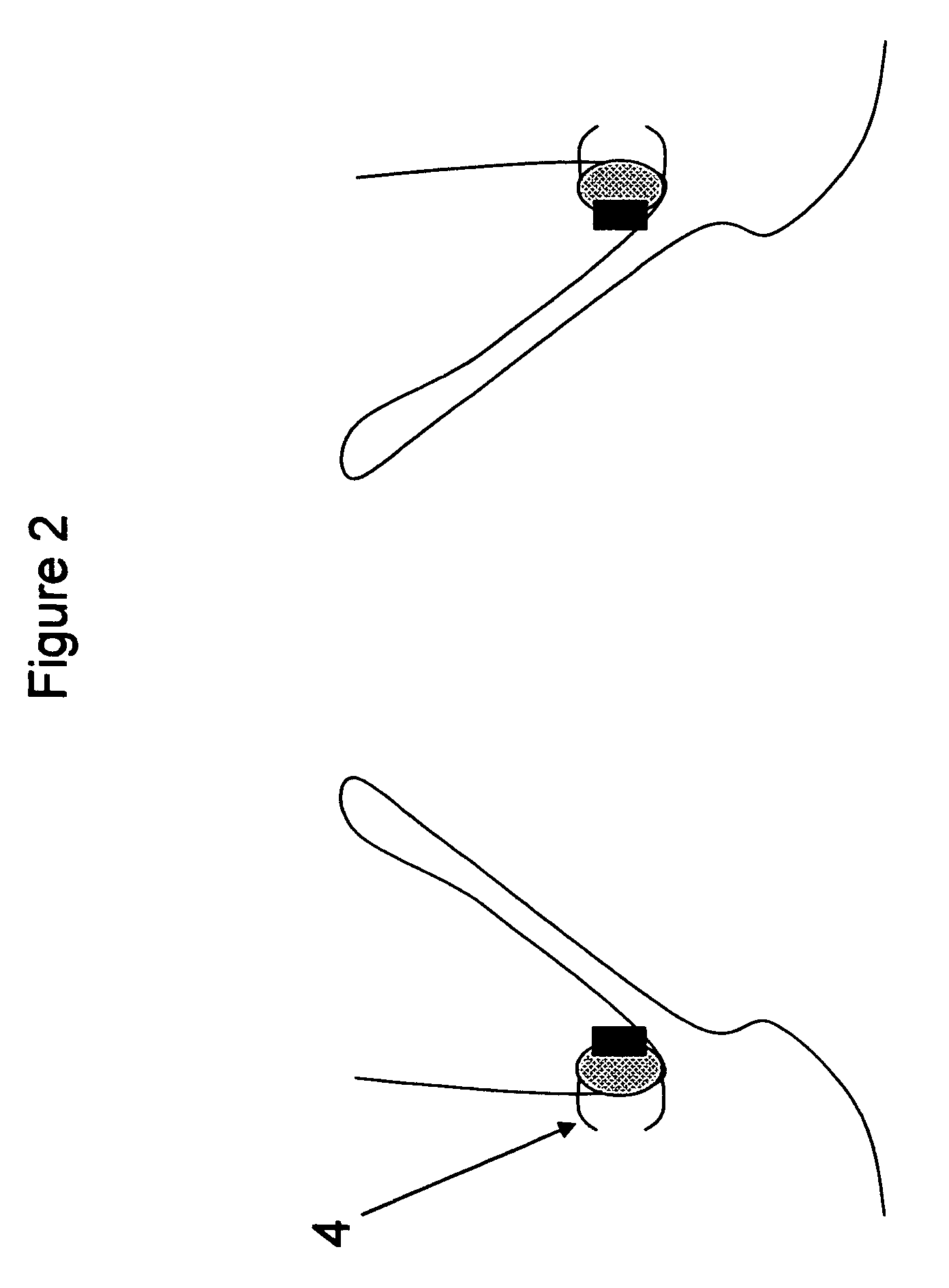
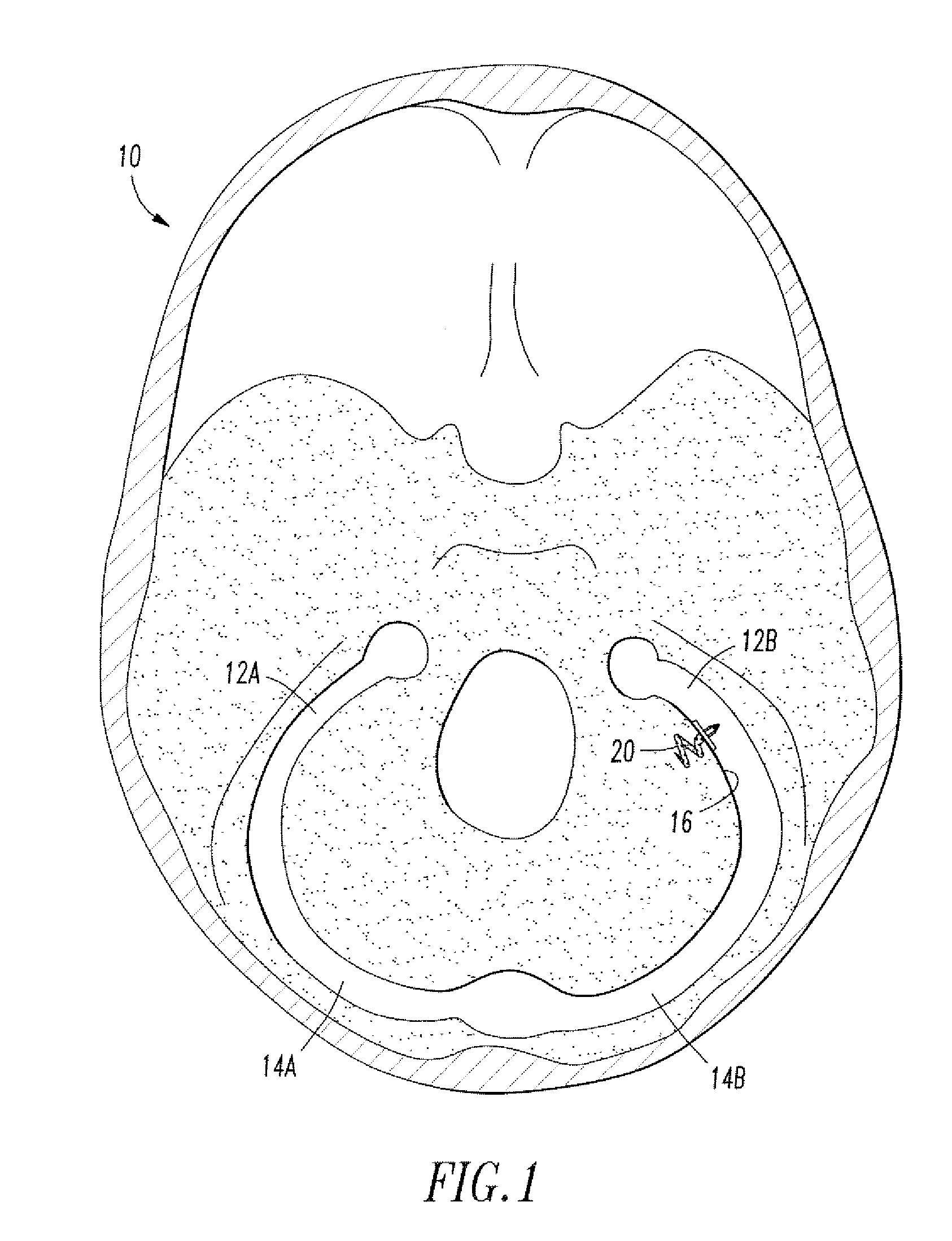
Percutaneous cardiac valve repair with adjustable artificial chordae
InactiveUS20070118151A1Reduction of mitral valve regurgitationEasy to operateSuture equipmentsHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass time
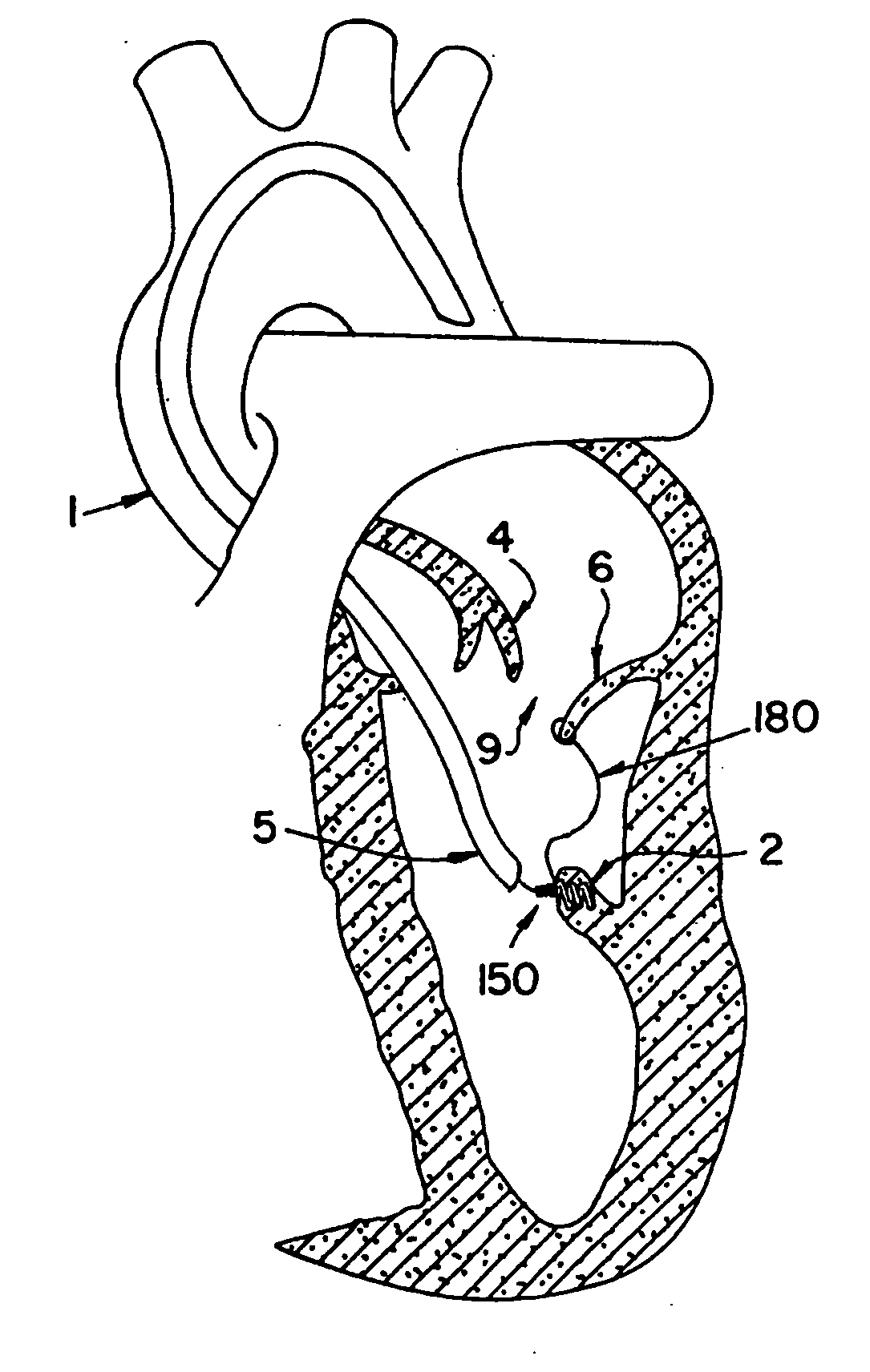
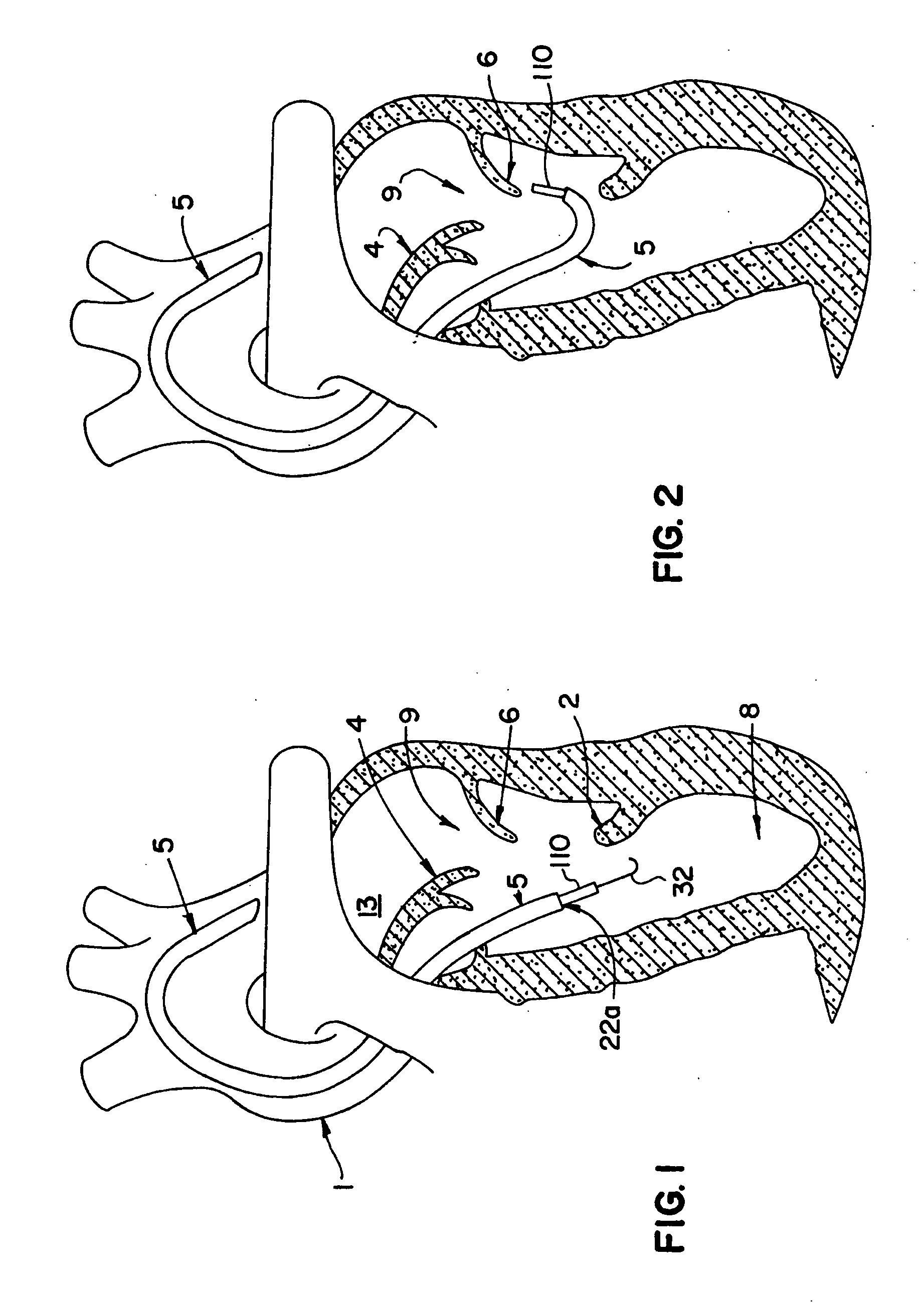
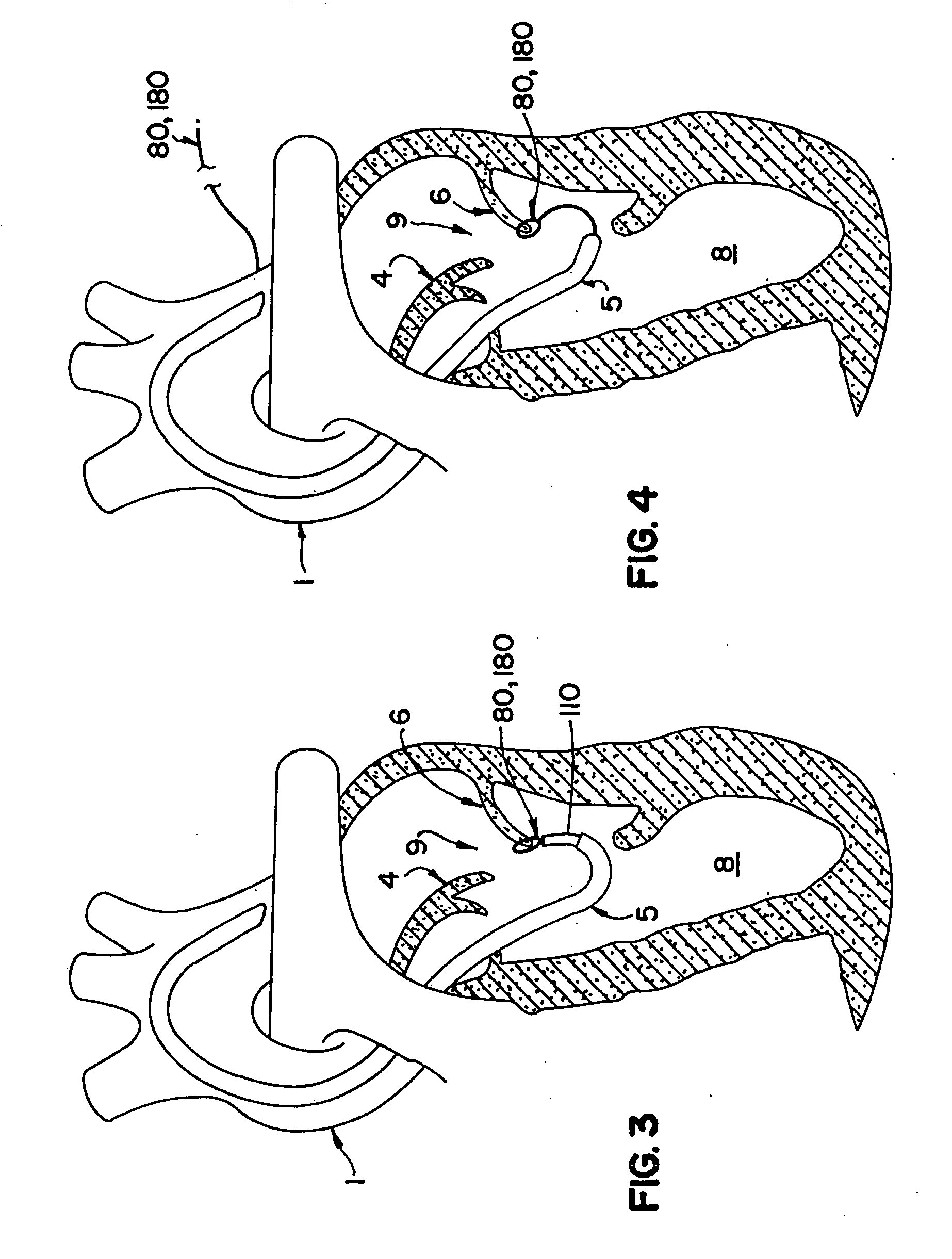
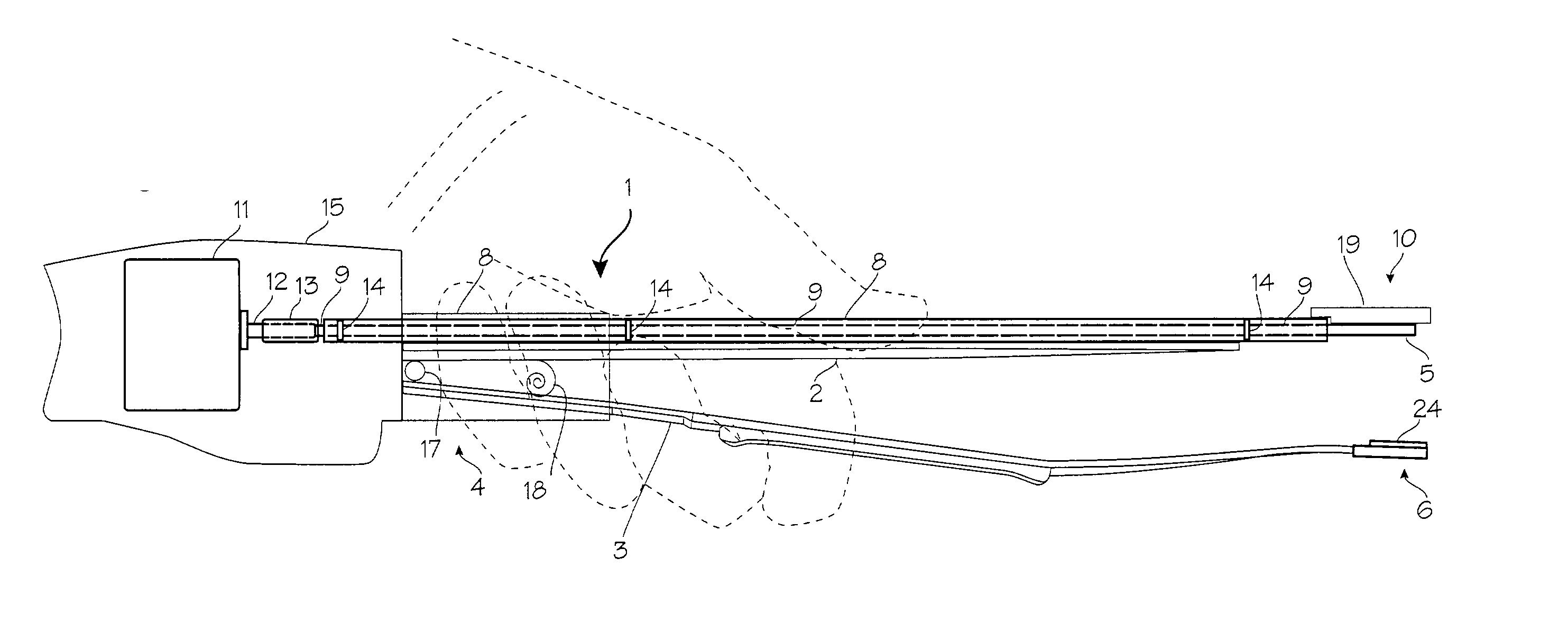
The invention includes a novel method and system to achieve leaflet coaptation in a cardiac valve percutaneously by creation of neochordae to prolapsing valve segments. This technique is especially useful in cases of ruptured chordae, but may be utilized in any segment of prolapsing leaflet. The technique described herein has the additional advantage of being adjustable in the beating heart. This allows tailoring of leaflet coaptation height under various loading conditions using image-guidance, such as echocardiography. This offers an additional distinct advantage over conventional open-surgery placement of artificial chordae. In traditional open surgical valve repair, chord length must be estimated in the arrested heart and may or may not be correct once the patient is weaned from cardiopulmonary bypass. The technique described below also allows for placement of multiple artificial chordae, as dictated by the patient's pathophysiology.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
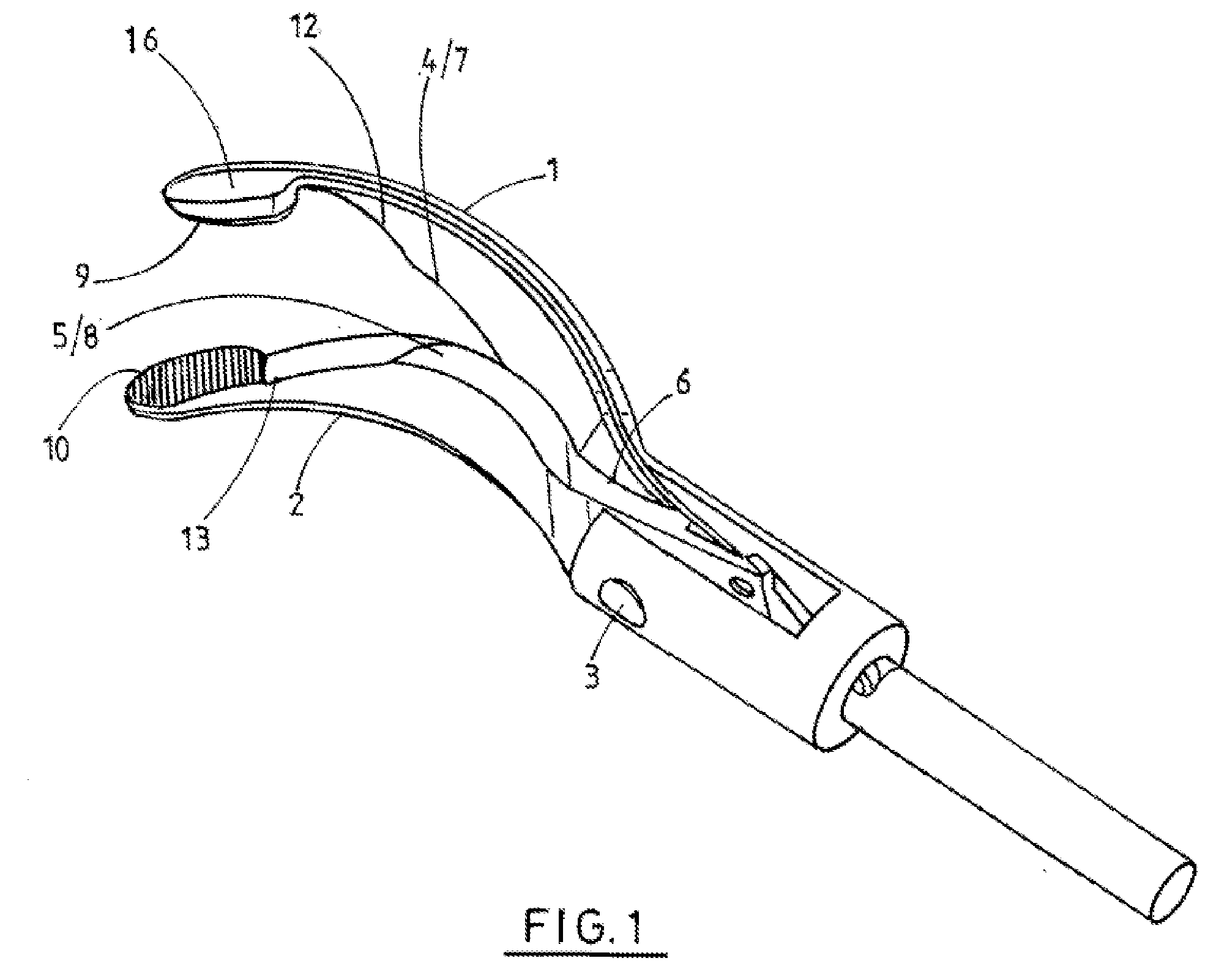
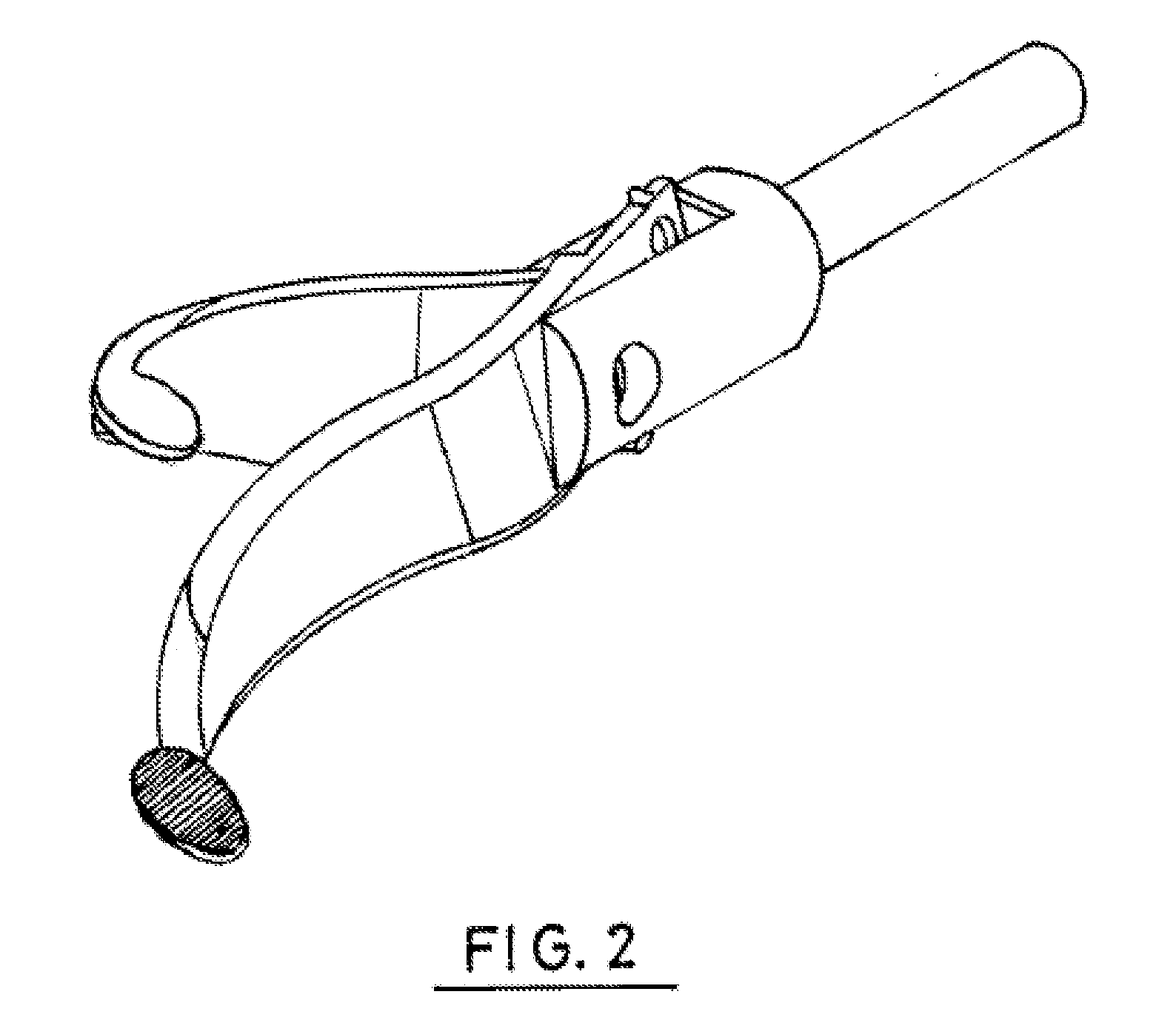
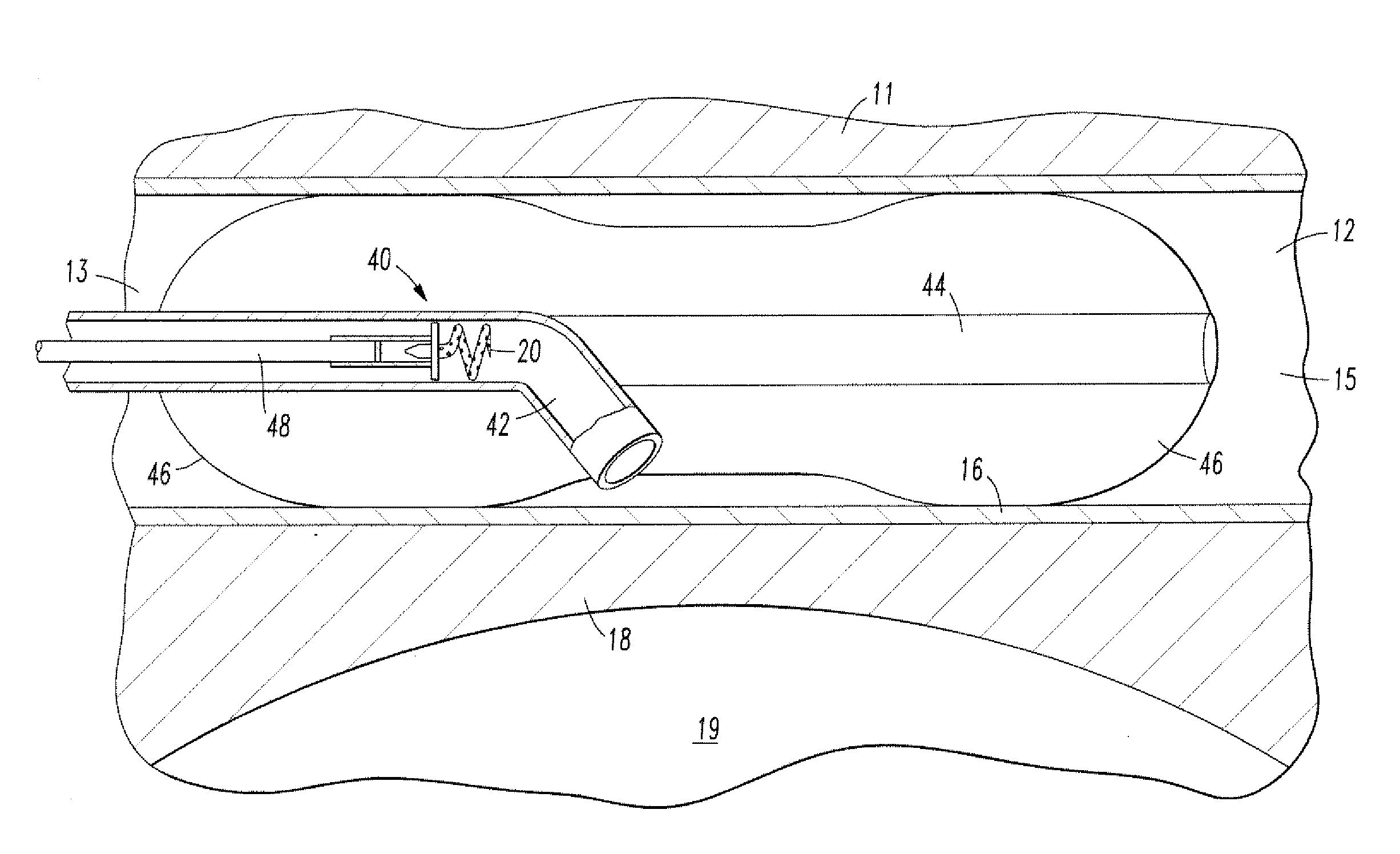
Ultrasonic forceps
Ultrasonic forceps adapted for use in open surgical forceps. The device is provided in the form of traditional open surgery forceps or tweezers, and the transmitting rod which transmits ultrasonic vibration from a proximally located transducer to the distally mounted welding horn runs through a lumen in one of the arms of the forceps.
Owner:STARION INSTR
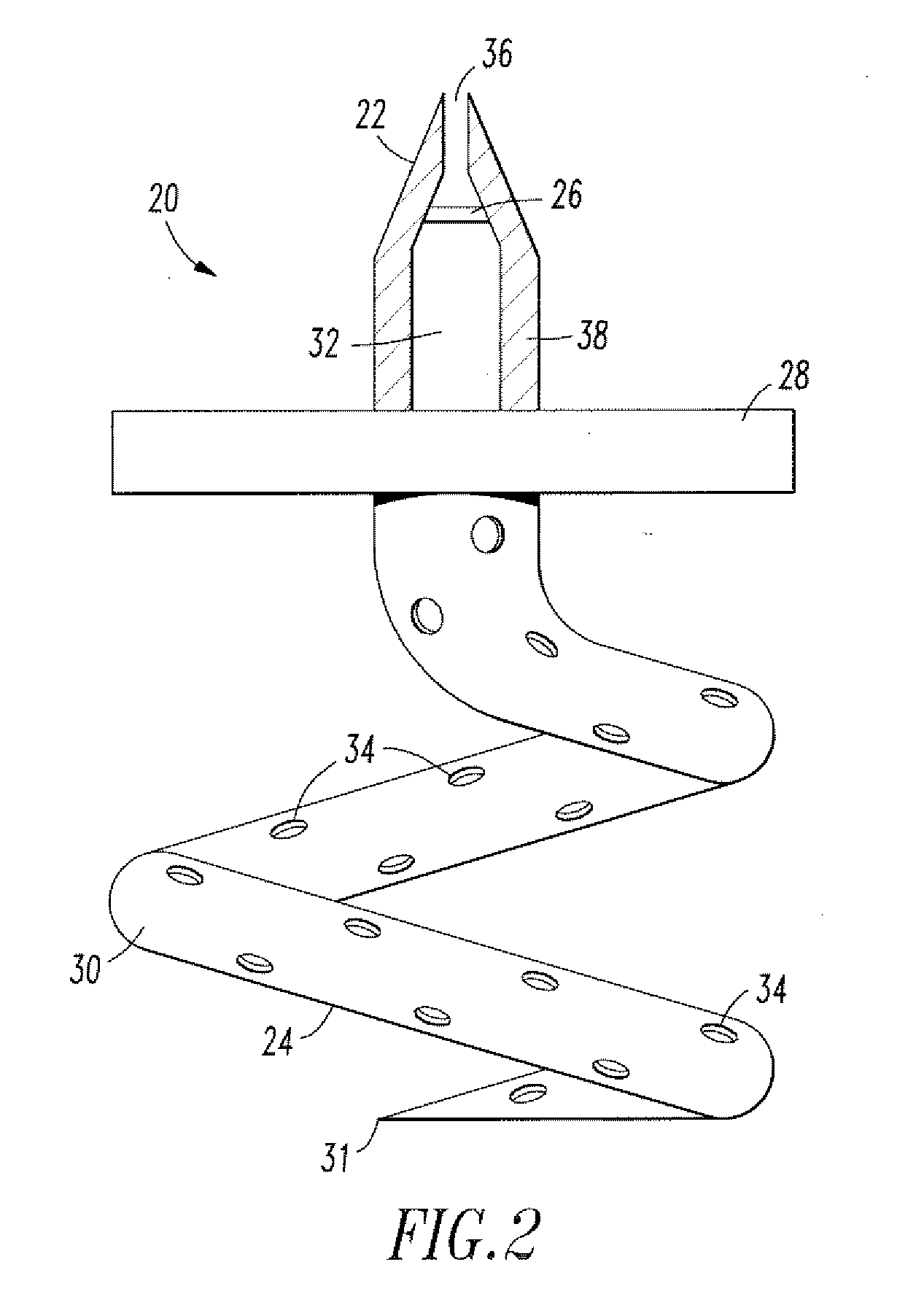
Method and apparatus for vascular and visceral clipping
InactiveUS20050251183A1Convenient treatmentMinimizing chanceSnap fastenersClothes buttonsTrauma surgeryLarge intestine
Devices and methods for achieving hemostasis and leakage control in hollow body vessels such as the small and large intestines, arteries and veins as well as ducts leading to the gall bladder and other organs. The devices and methods disclosed herein are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery or military setting, and most especially during damage control procedures. In such cases, the patient may have received trauma to the abdomen, extremities, neck or thoracic region. The devices utilize removable or permanently implanted, broad, soft, parallel jaw clips with minimal projections to maintain vessel contents without damage to the tissue comprising the vessel. These clips are applied using either standard instruments or custom devices that are subsequently removed leaving the clips implanted, on a temporary or permanent basis, to provide for hemostasis or leakage prevention, or both. These clips overcome the limitations of clips and sutures that are currently used for the same purposes. The clips come in a variety of shapes and sizes. The clips may be placed and removed by open surgery or laparoscopic access.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Ergonomic handpiece for laparoscopic and open surgery
InactiveUS20120101495A1Enhanced ergonomic featureDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingMotor driveHand movements
A surgical tool having an elongate shaft, with a directional operative element at its distal end, is provided with a mechanism to rotate the shaft and the operative element about a longitudinal axis shaft. This allows the operative element to be aligned with an element of tissue without excessive hand movement by the user. In a preferred version, the mechanism is electrically powered and is regulated to produce smooth, controlled, accurate motion between selected rotational positions. The mechanism may include a linear magnetic motor drive to move a drive element longitudinally along the tool. This drive element is engaged with a helical formation on a drive shaft, such that longitudinal motion of the drive element is converted to rotational motion of the drive shaft, and of the shaft and operative element, to which the shaft is mounted.
Owner:SRA DEV LTD
Method and apparatus for vascular and visceral clipping
InactiveUS7322995B2Convenient treatmentMinimizing chanceSnap fastenersClothes buttonsTrauma surgeryChest region
Devices and methods for achieving hemostasis and leakage control in hollow body vessels such as the small and large intestines, arteries and veins as well as ducts leading to the gall bladder and other organs. The devices and methods disclosed herein are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery or military setting, and most especially during damage control procedures. In such cases, the patient may have received trauma to the abdomen, extremities, neck or thoracic region. The devices utilize removable or permanently implanted, broad, soft, parallel jaw clips with minimal projections to maintain vessel contents without damage to the tissue comprising the vessel. These clips are applied using either standard instruments or custom devices that are subsequently removed leaving the clips implanted, on a temporary or permanent basis, to provide for hemostasis or leakage prevention, or both. These clips overcome the limitations of clips and sutures that are currently used for the same purposes. The clips come in a variety of shapes and sizes. The clips may be placed and removed by open surgery or laparoscopic access.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
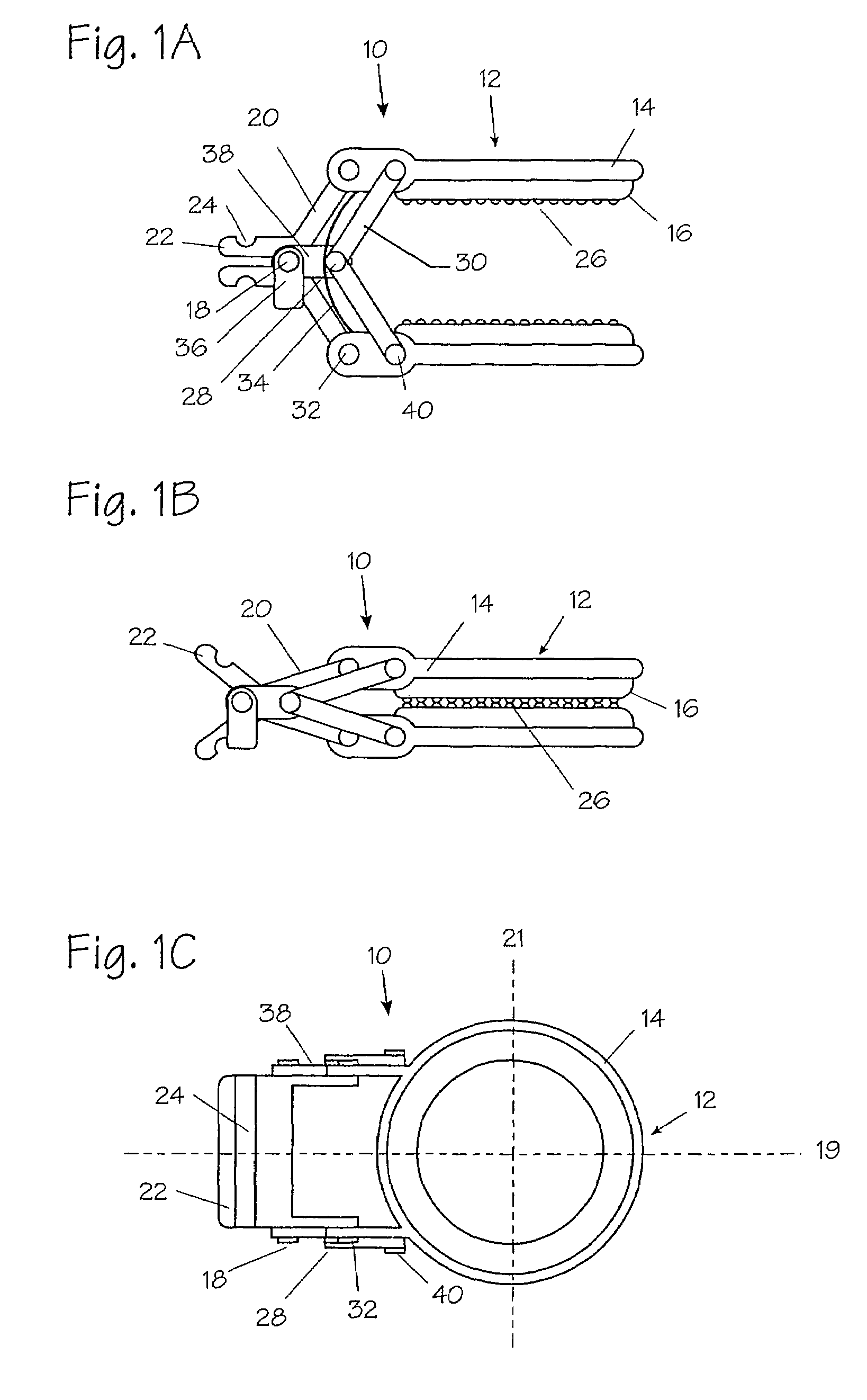
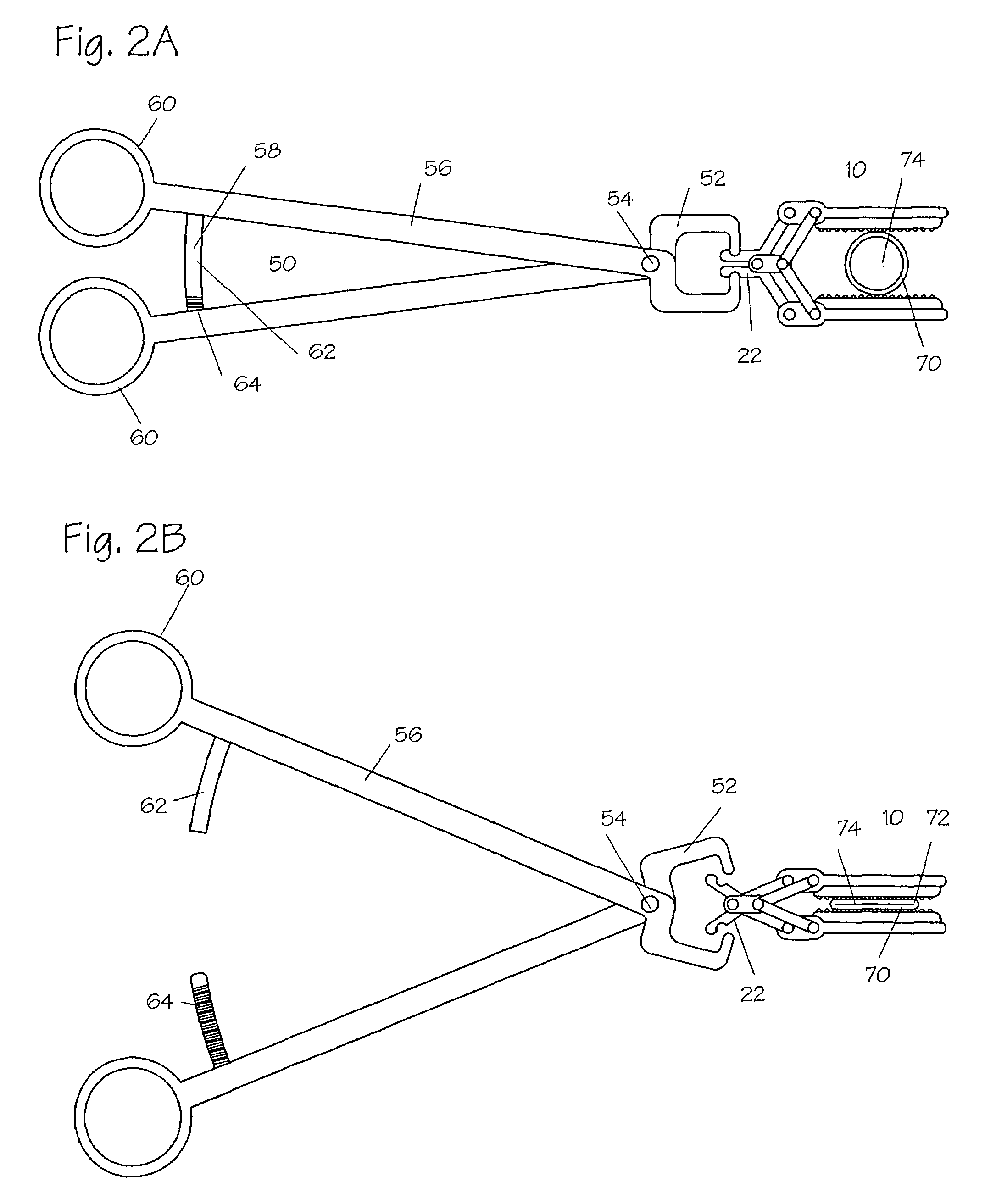
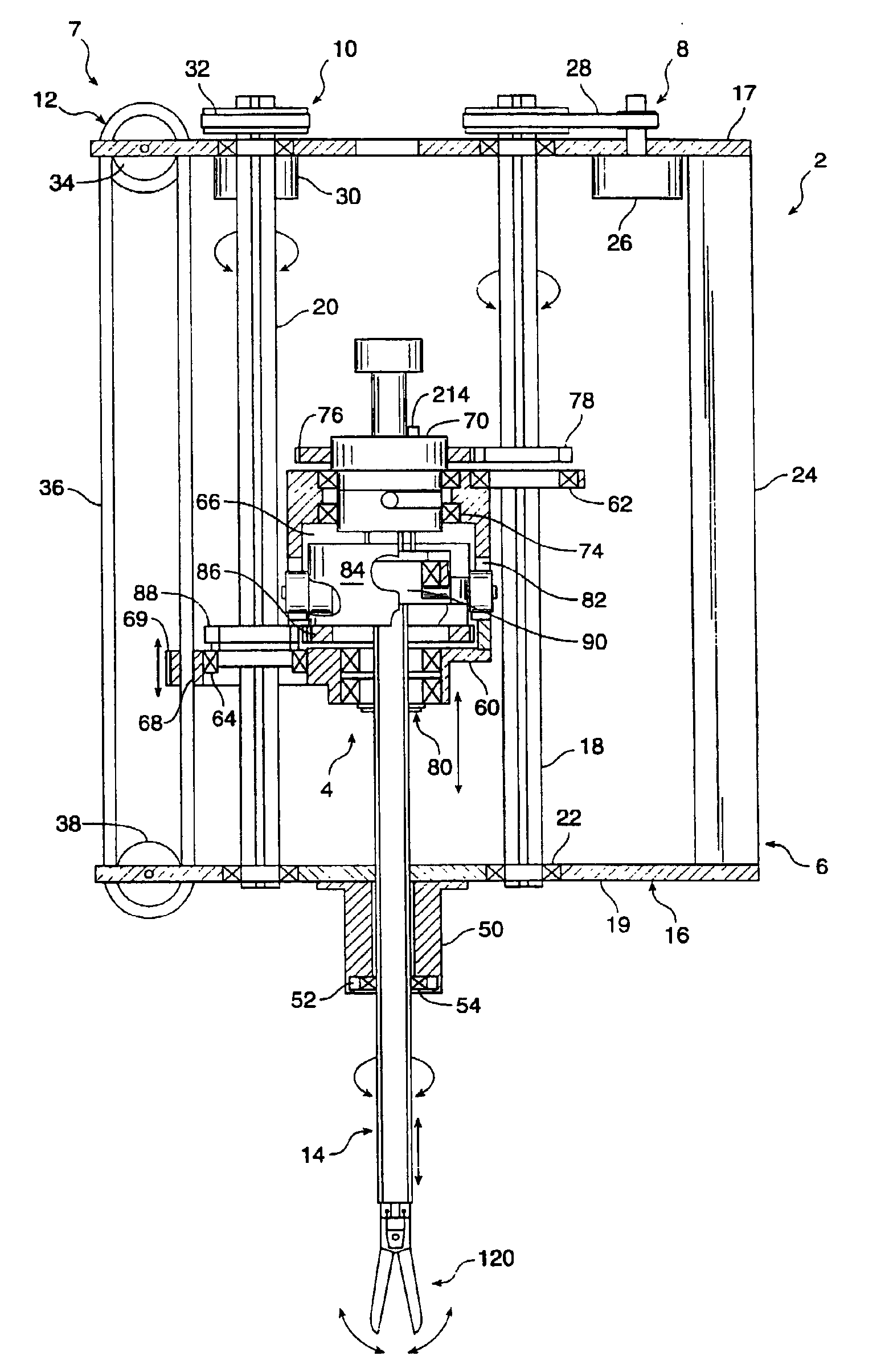
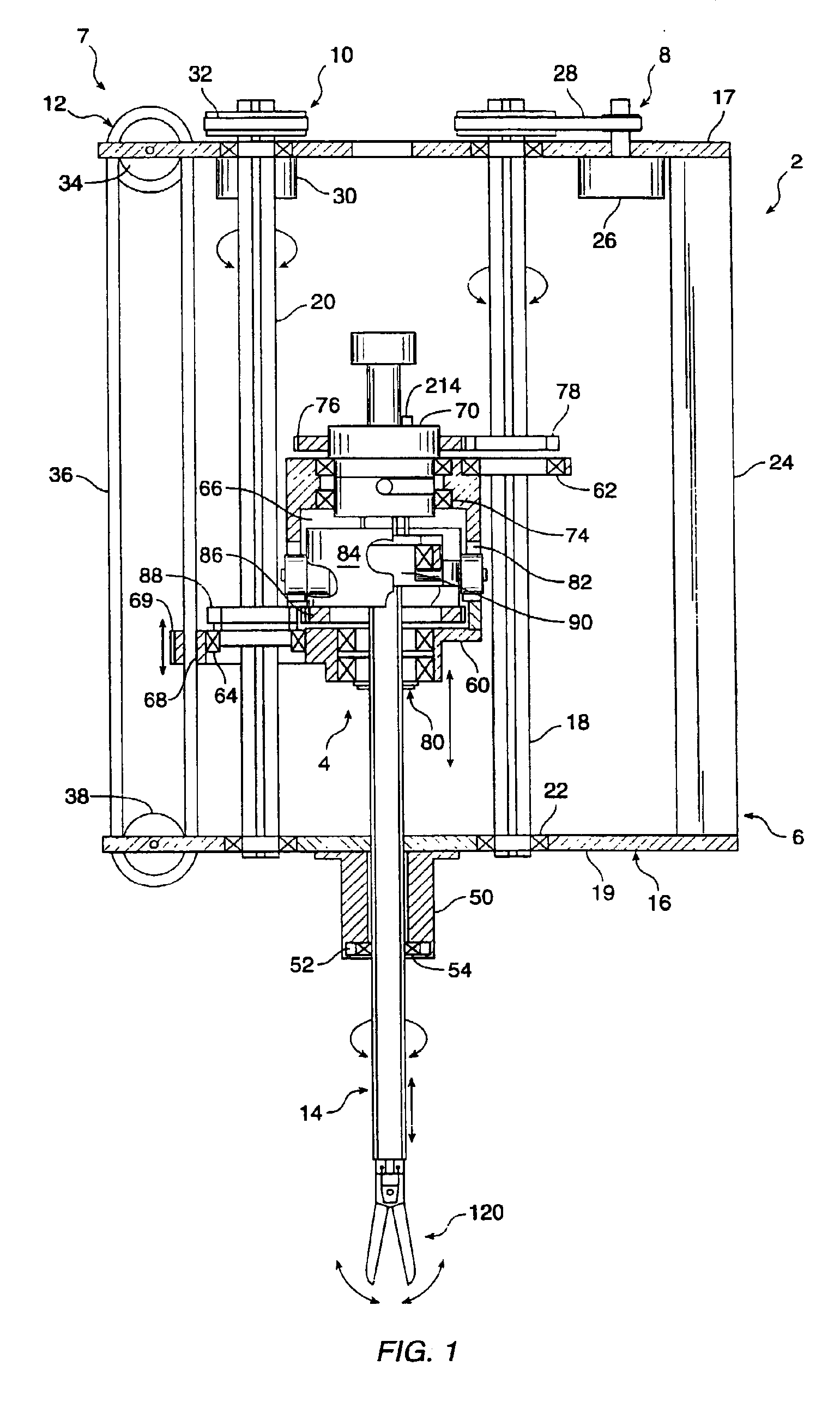
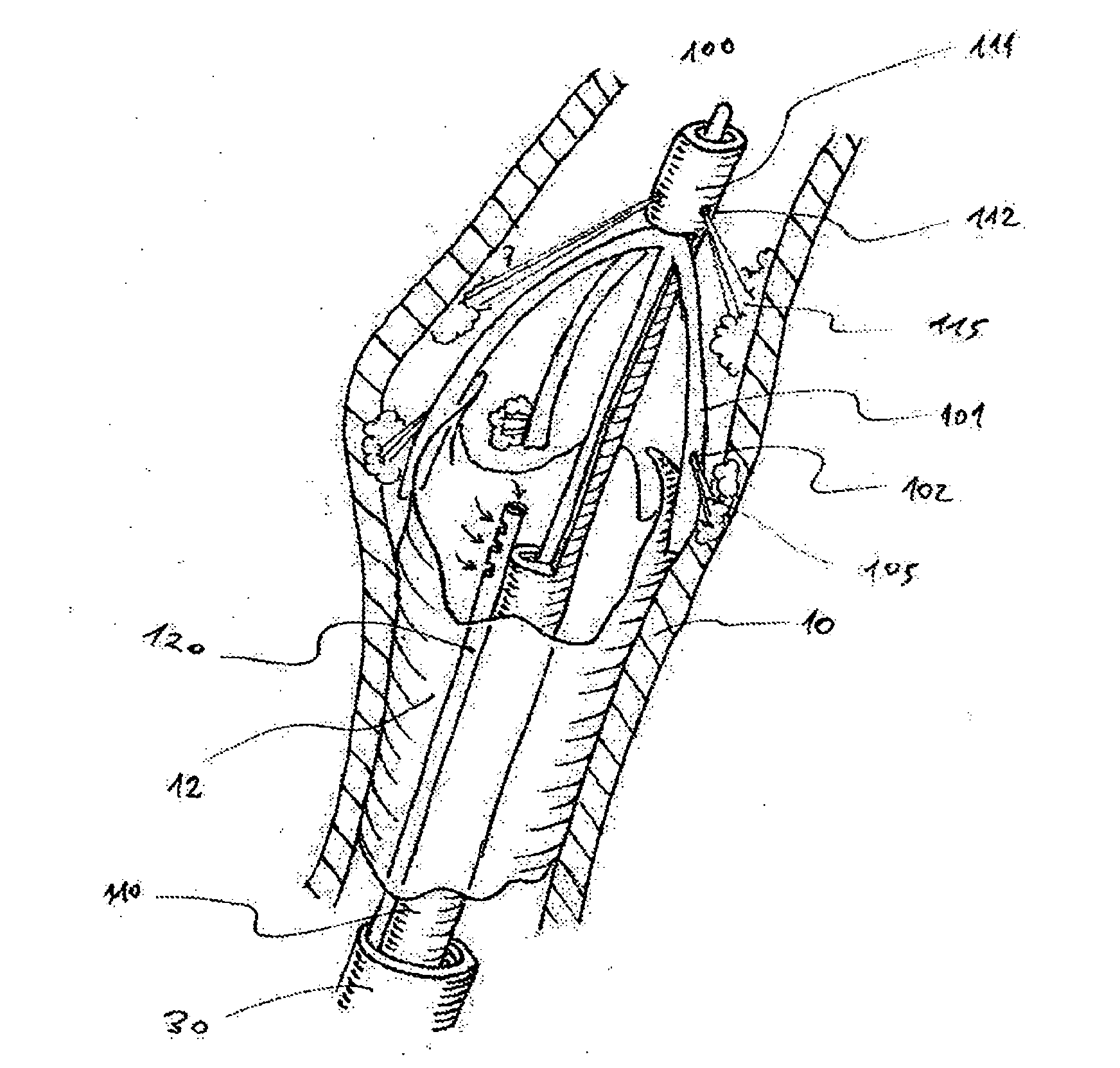
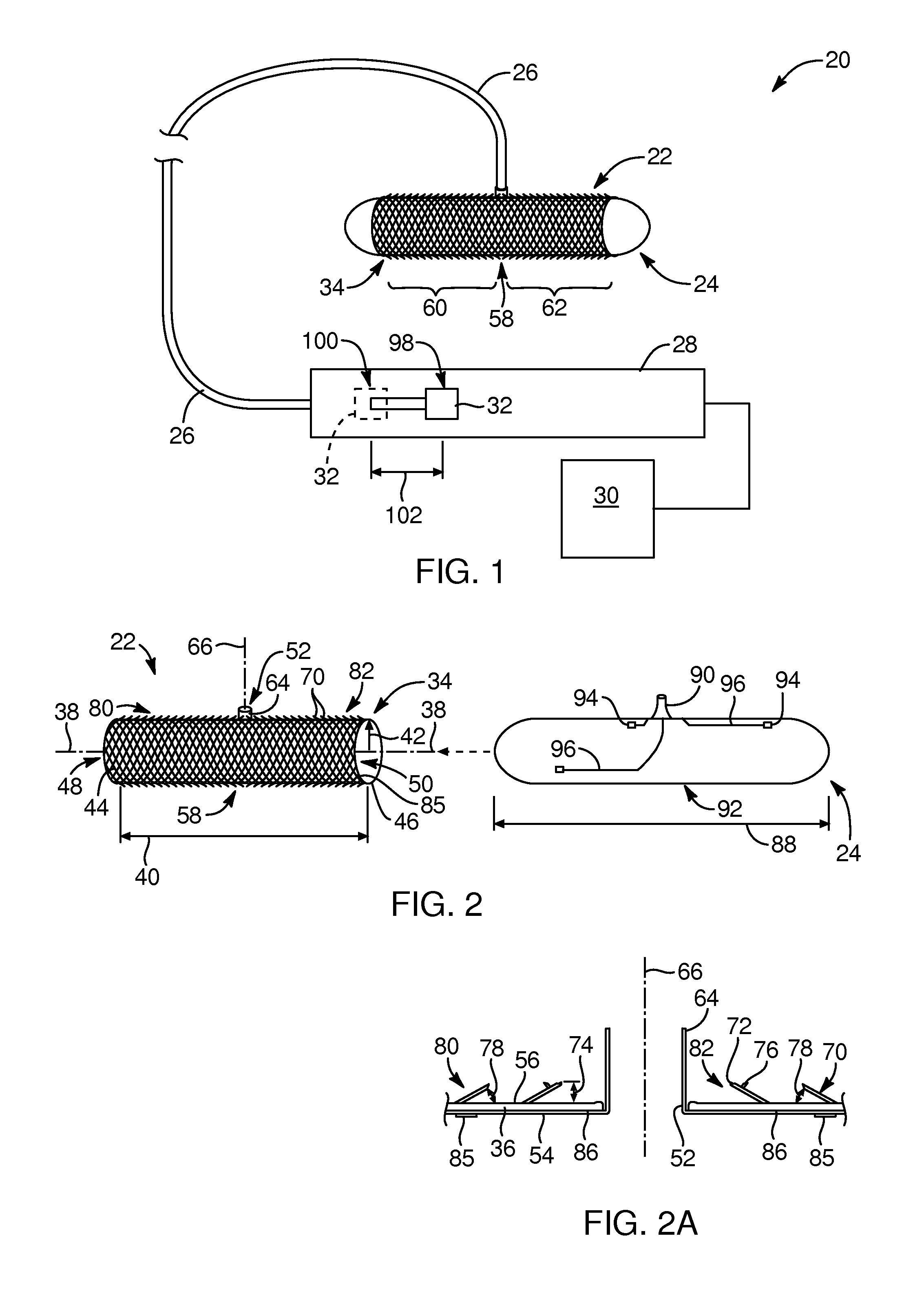
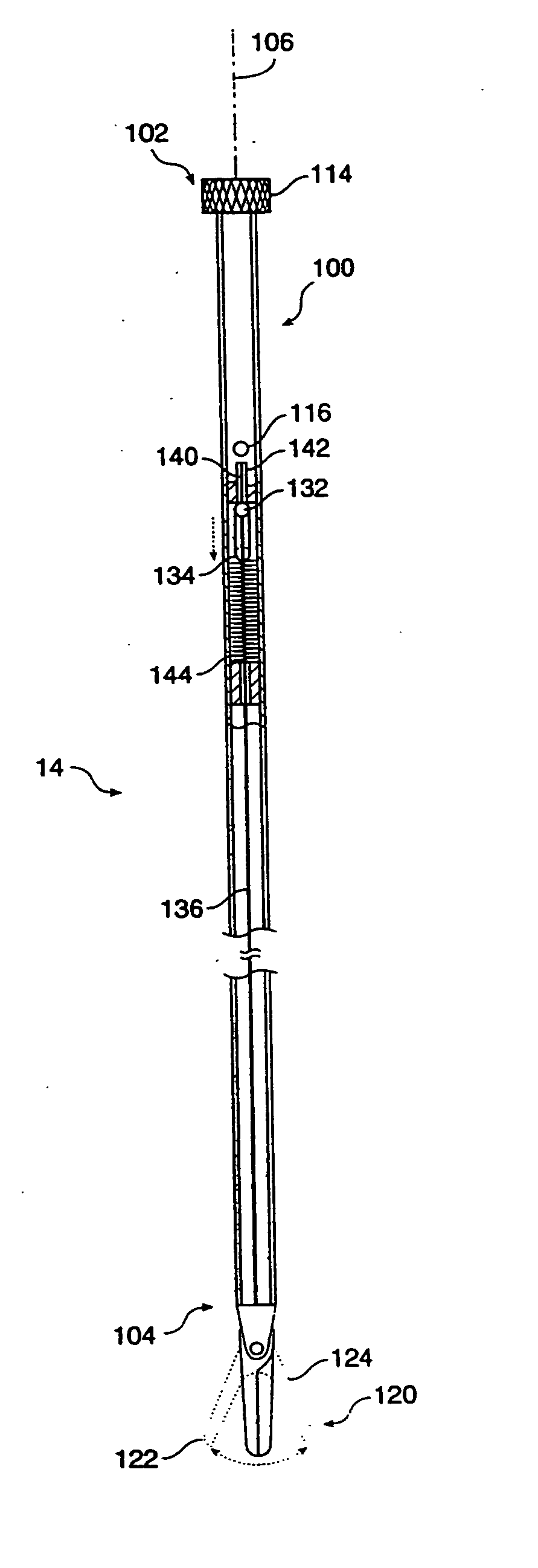
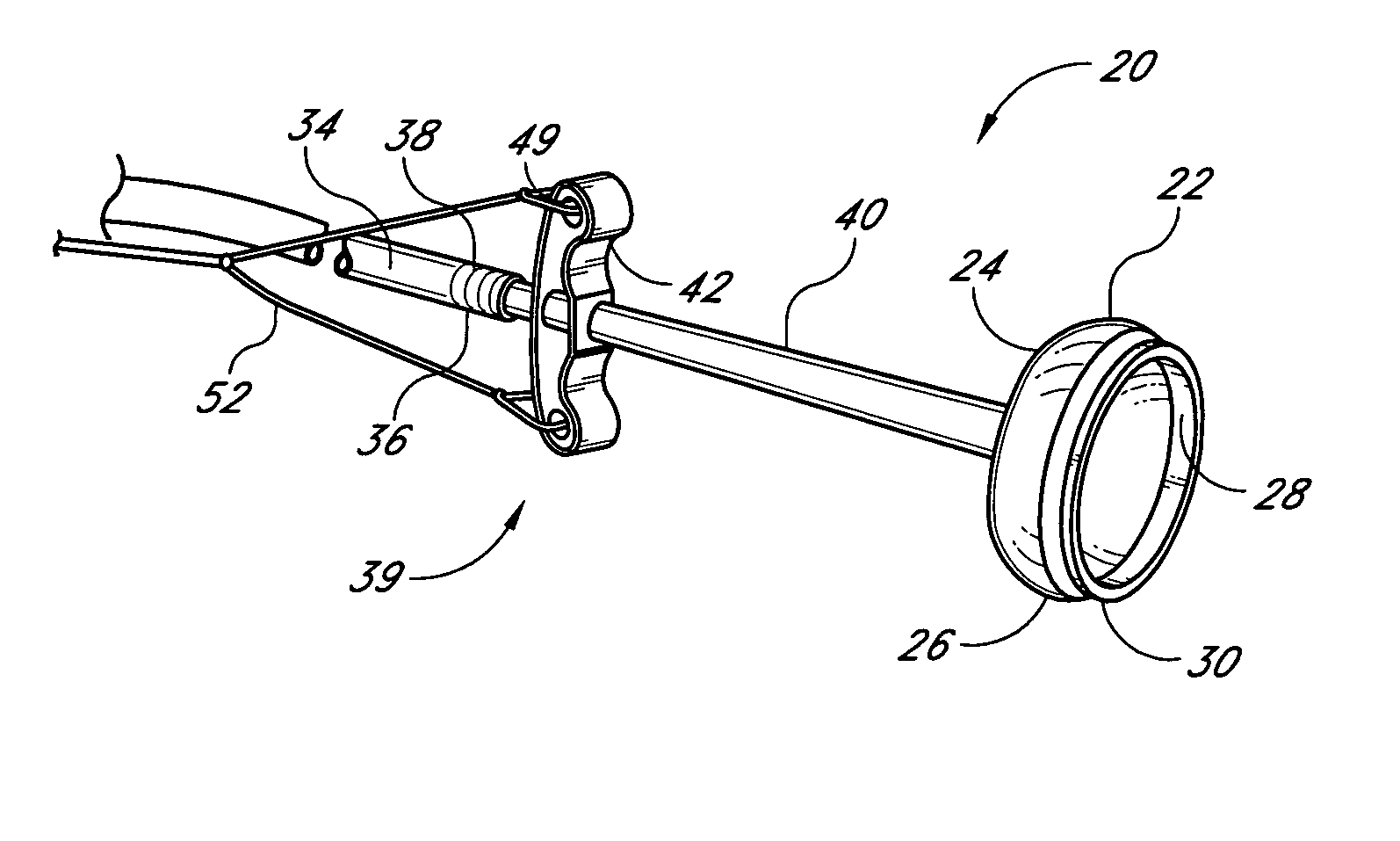
System and method for releasably holding a surgical instrument
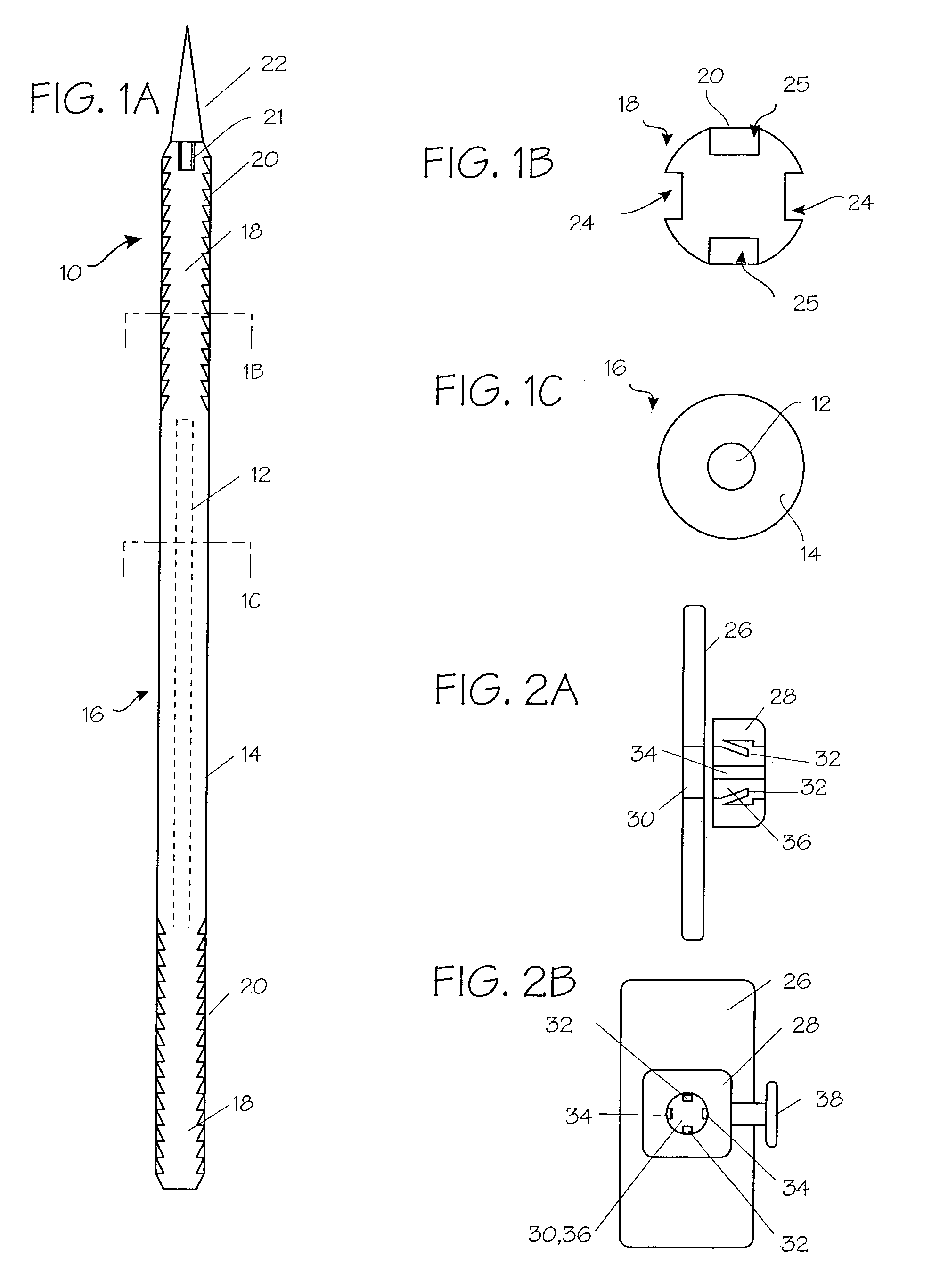
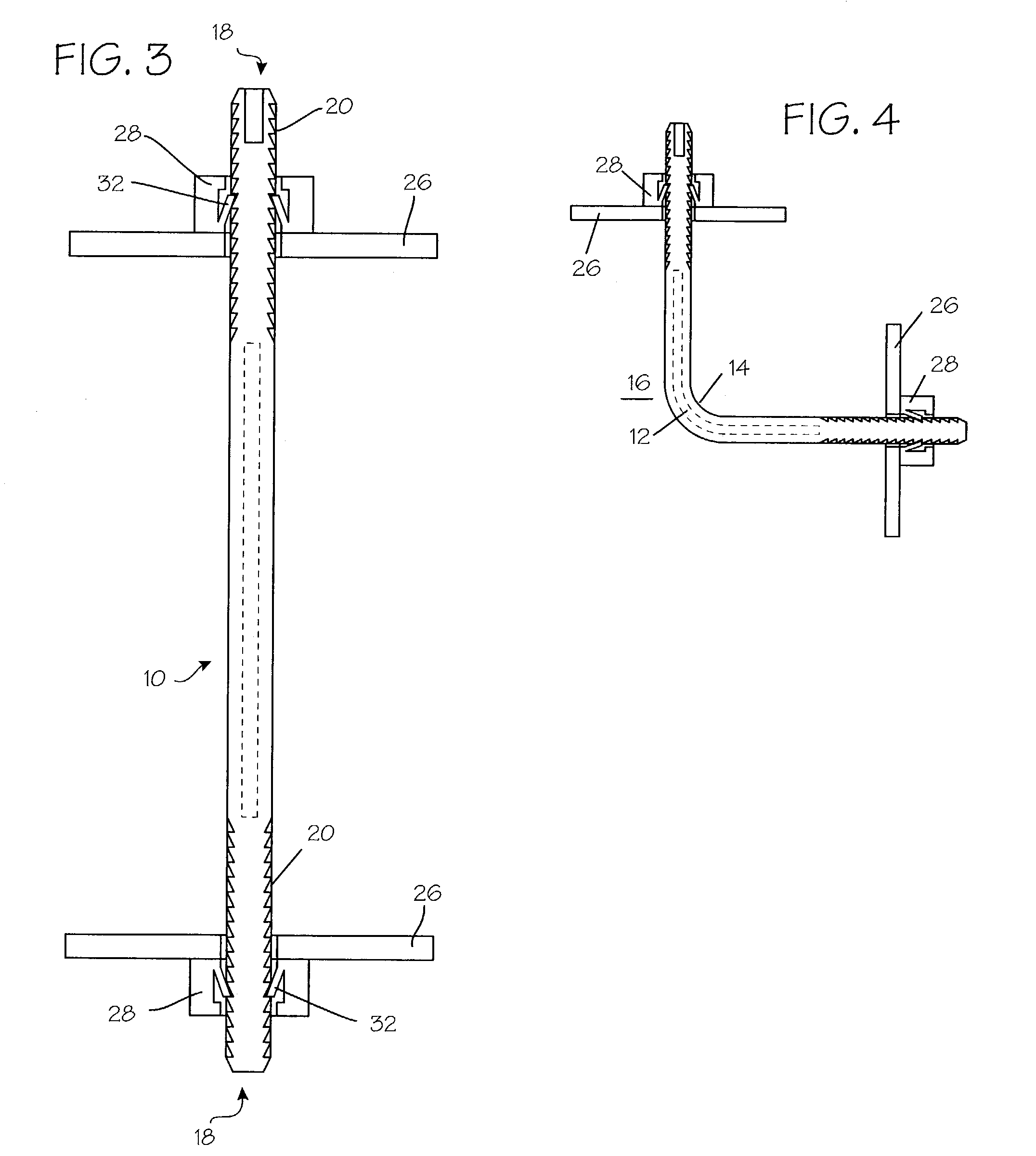
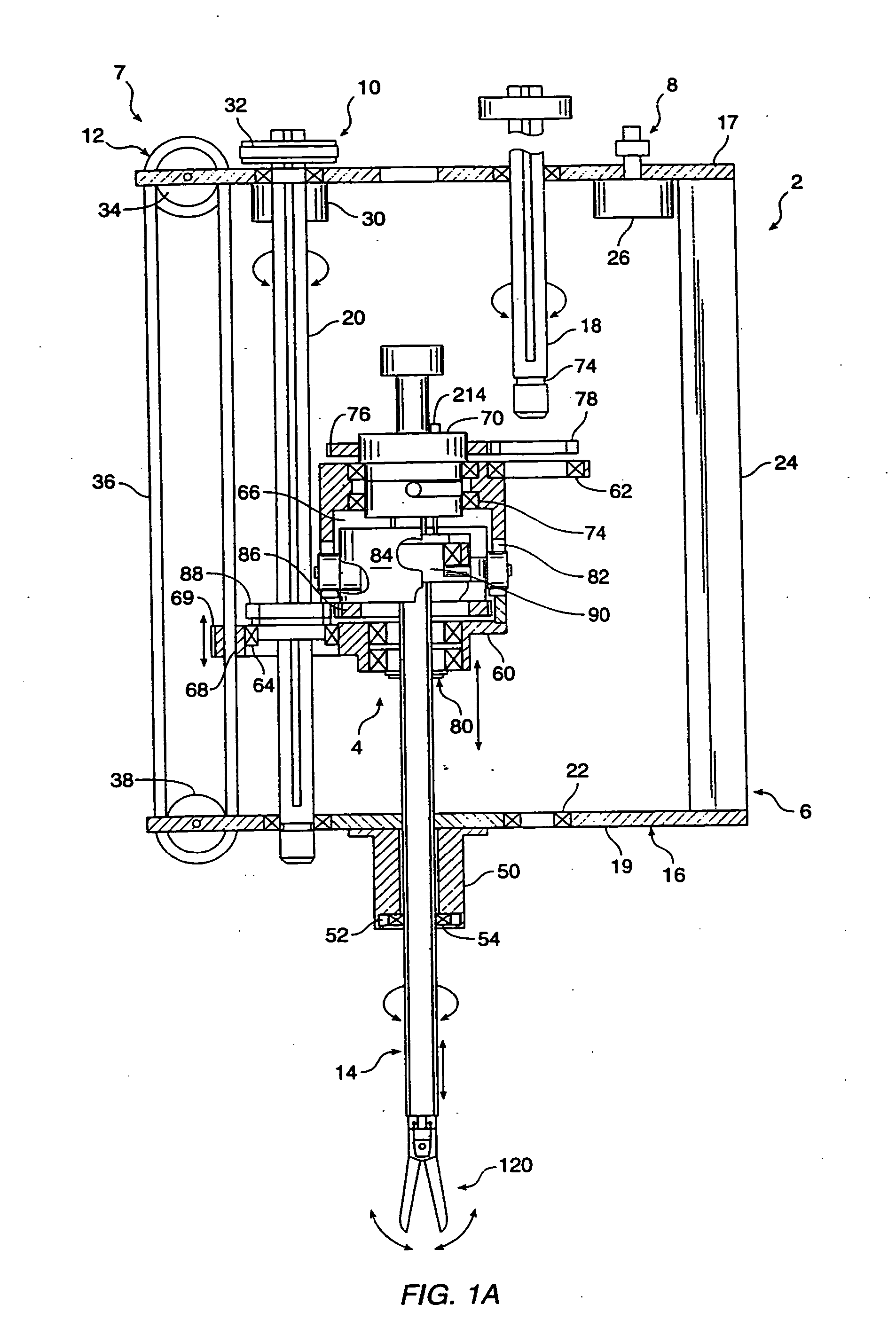
The invention is directed to a system and method for releasably holding a surgical instrument (14), such as an endoscopic instrument configured for delivery through a small percutaneous penetration in a patient. The instrument comprises an elongate shaft (100) with a pair of mounting pins (116) laterally extending from the shaft between its proximal and distal ends. An instrument holder comprises a support having a central bore (202) and an axially extending slot (204) for receiving the instrument shaft and the mounting pins. A pair of locking slots (206) are cut into the support transversely to and in communication with the axial slot so that the mounting pins can be rotated within the locking slots. The instrument support further includes a latch assembly for automatically locking the mounting pins within the locking slots to releasably couple the instrument to the instrument holder. With this twist-lock motion, the surgeon can rapidly engage and disengage various instruments from the holder during a surgical procedure, such as open surgery, laparoscopy or thoracoscopy.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Forward deploying suturing device and methods of use
InactiveUS7582096B2Improve performanceSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSurgical operationOpen surgery
Sutures can be placed in difficult to access areas of the human body with devices, and related methods, utilizing a needle carrier. The devices and methods can be used in conjunction with both endosurgical and traditional open surgery procedures.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method and apparatus for improved hemostasis and damage control operations
InactiveUS6998510B2Improved hemostatic packing in trauma careGood hemostasisPlastersBaby linensTamponadePERITONEOSCOPE
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in traumatized patients. The devices utilize fluid impermeable outer surfaces and distributed pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of pressure. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for throabogenic or antipathogenic agents. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to cover the entire wound area over the hemostatic pack. The hemostatic packing devices may be placed and removed by open surgery or laparoscopic access without generating excessive re-bleeding, and may further comprise antimicrobial or thrombogenic regions.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Method and apparatus for anchoring implants
InactiveUS20060069400A1Reduce risk of migrationReduce intrusionStentsHeart valvesLaparoscopyTherapeutic Devices
Methods, devices and systems facilitate retention of a variety of therapeutic devices. Devices generally include an anchoring element, which has been designed to promote fibrotic ingrowth, and an anchored device, which has been designed to firmly engage the complementary region of the anchoring element. The anchoring element may be placed in a minimally invasive procedure temporally separated from the deployment of the anchored device. Once enough time has passed to ensure appropriate fixation of the anchoring element by tissue and cellular ingrowth at the site of placement, the anchored device may then be deployed during which it firmly engages the complementary region of the anchoring element. In this manner, a firm attachment to the implantation site may be made with a minimum of required hardware. Some embodiments are delivered through a delivery tube or catheter and while some embodiments may require laparoscopy or open surgery for one or more of the placement procedures. Some embodiments anchor devices within the cardiovascular tree while others may anchor devices within the gastrointestinal, peritoneal, pleural, pulmonary, urogynecologic, nasopharyngeal or dermatologic regions of the body.
Owner:THERANOVA LLC
See-through abdomen display for minimally invasive surgery
This invention is in the domain of minimally invasive surgery and is a method and apparatus that transforms and displays images of internal organs and tissues taken from internally located imaging devices on external skin. The image displayed on the skin aligns with the actual physical location, orientation, and size of the internal organs and tissues in a way that viewers have the perception that the skin is transparent. This method and apparatus enables surgeons to have the same hand-eye coordination as in an open surgery during a minimally invasive surgery.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Replaceable Tip Suturing Devices, System, and Methods for Use with Differing Needles
Medical suturing devices, systems, and methods will be useful for endoscopic or open surgeries, including ear, nose, and throat procedures. Articulation motions may be transferred from a handle to needle grasping jaws using an axial movement of a shaft. Portions of the devices may be disposable, replaceable, and / or reusable, with different needle-grasping jaws and / or different elongate extension bodies having different configurations optionally being selectably coupleably to an articulatable handle and housing so as to allow the user to configure the device for a particular procedure.
Owner:BOSS INSTR
Medical device and method for human tissue and foreign body extraction
A coaxial tube assembly, a bag, a bag-translating assembly, a de-bulking tool, and a drive assembly. The bag is delivered into a cavity in a patient's body either manually for open surgery or through the coaxial tube assembly by operation of the drive assembly for minimally invasive surgery. After a mass of tissue is placed in the bag, which is now secured to the bag-translating assembly, the drive assembly is operated to activate the bag-translation assembly to retract the bag into the annular space of the coaxial tube assembly. As the bag is being retracted, the mass in the bag is pulled into engagement with the de-bulking tool, which extends through the lumen of the coaxial tube assembly. The drive assembly activates the de-bulking tool to morcellate the mass in the bag and convey the morcellated bits of the mass through the lumen of the coaxial tube assembly.
Owner:DAI Z
Method and apparatus for solid organ tissue approximation
InactiveUS7235090B2Improved haemostatic tissue appositionEasy and fast applicationIntravenous devicesSurgical veterinaryTrauma surgeryParenchyma
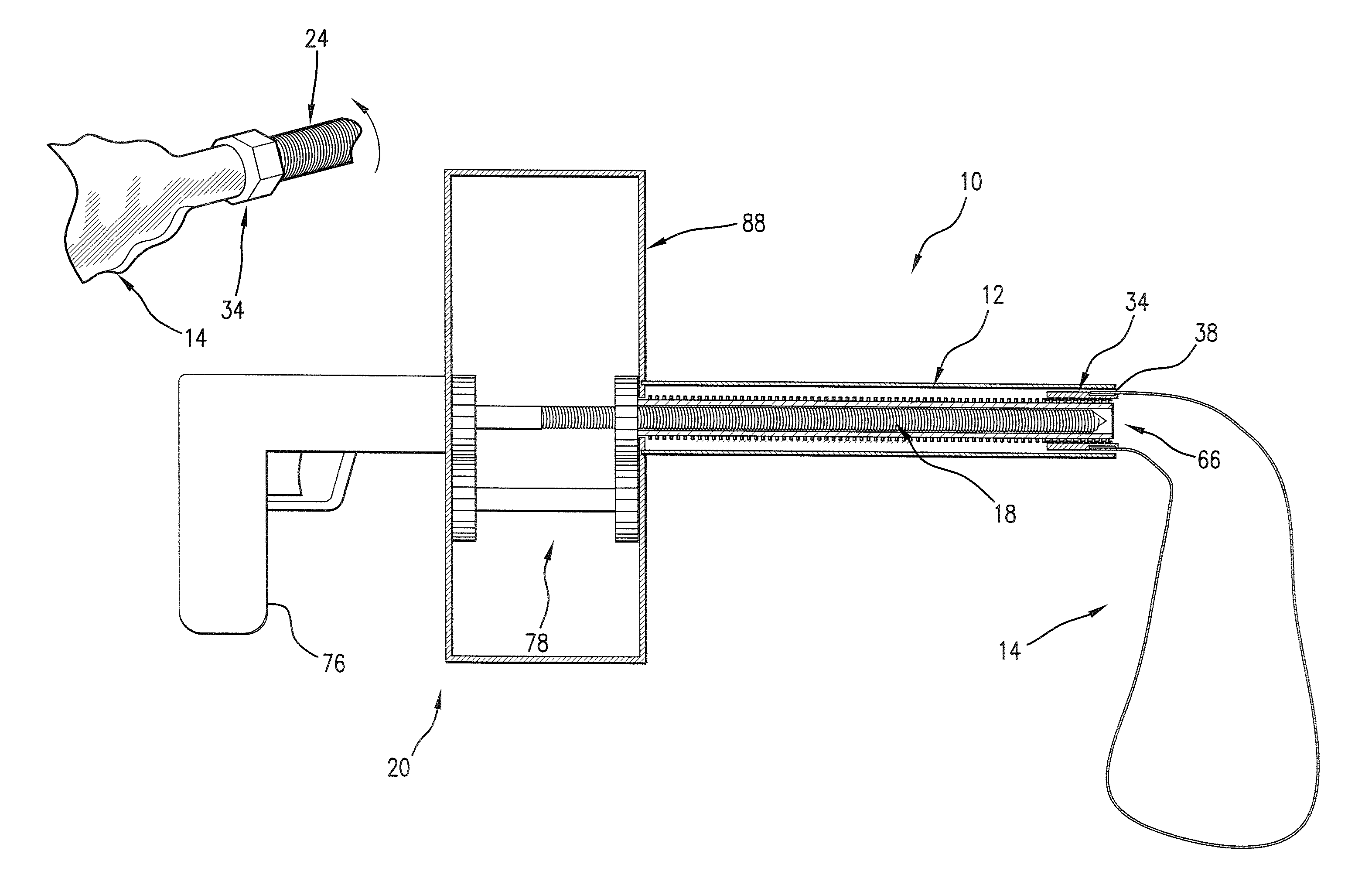
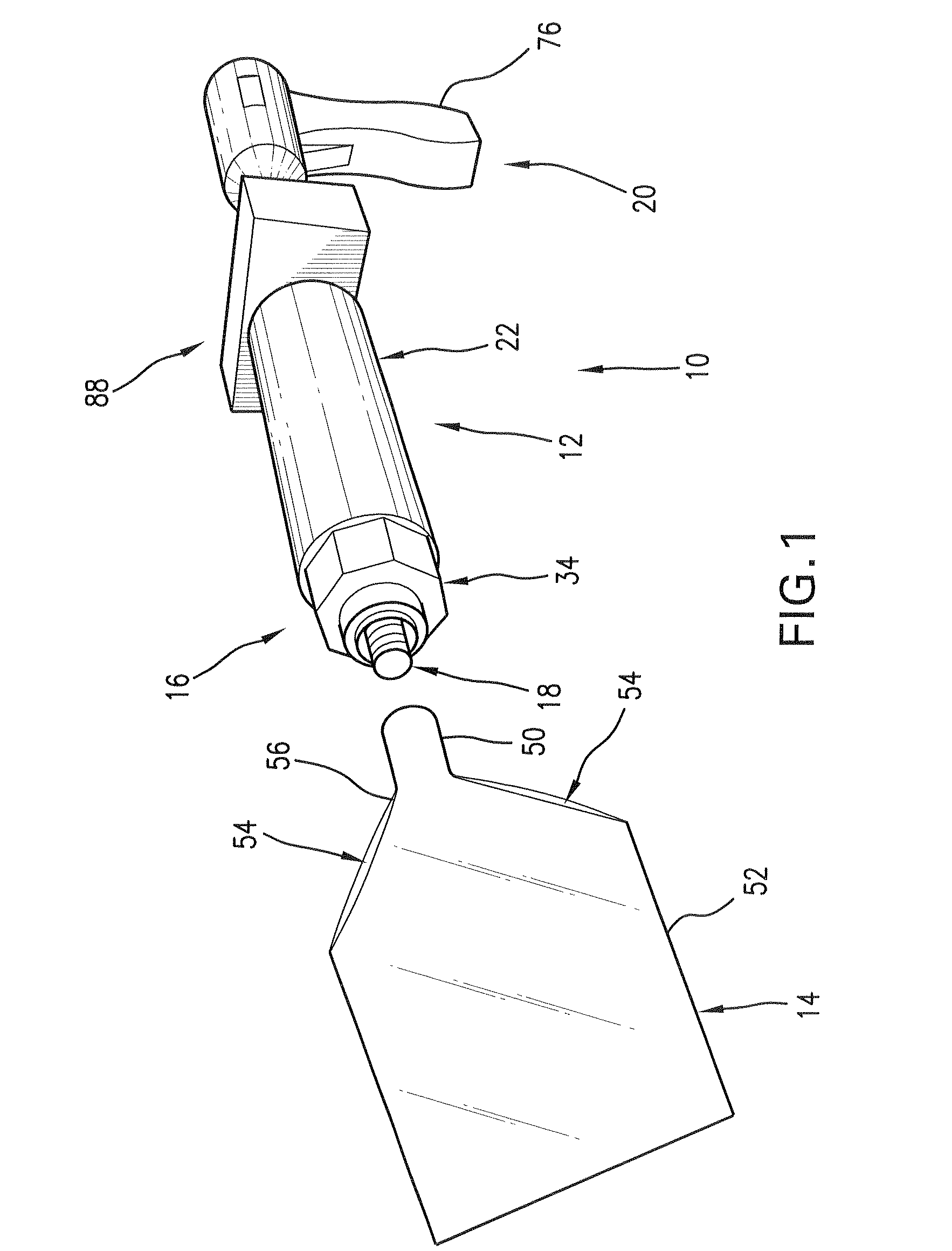
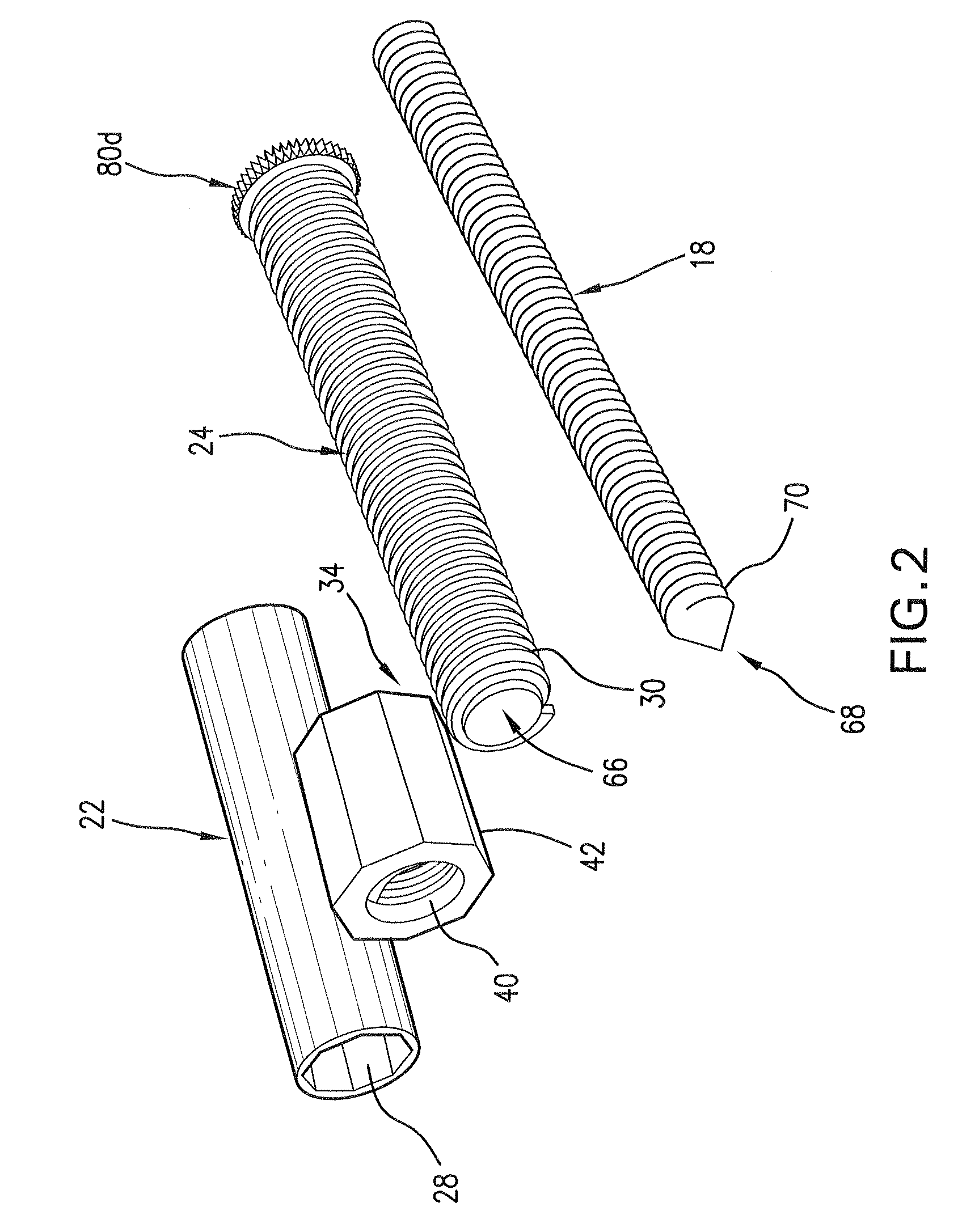
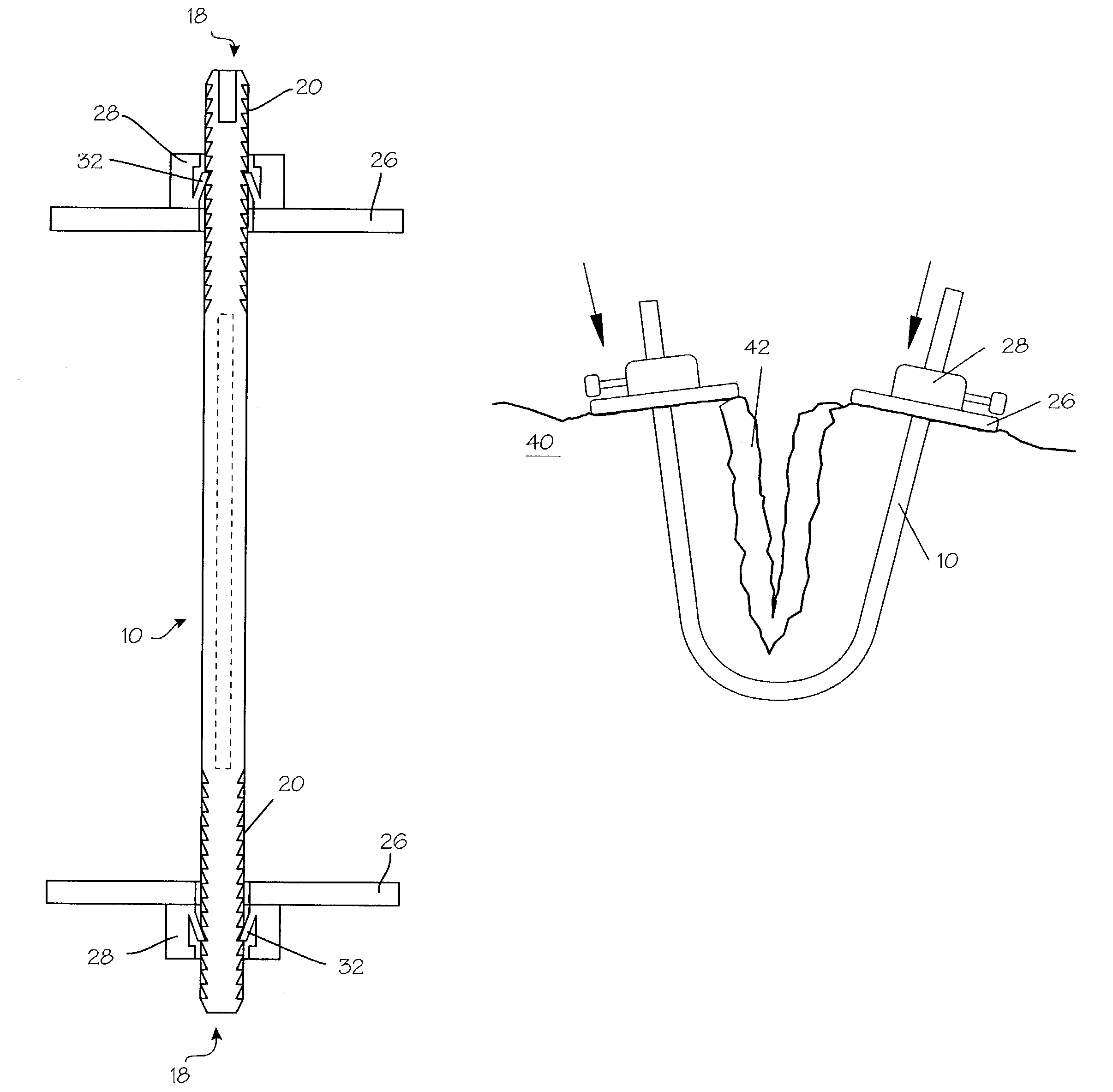
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in solid visceral wounds. Such devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery or military setting. In such cases, the patient may have received trauma to the abdominal viscera. The devices utilize flexible, variable depth transfixing bolts that penetrate the viscera. These bolts are pulled tight to bring the tissue into apposition and hold said tissue in apposition while the wound heals. These bolts overcome the limitations of sutures that are currently used for the same purposes. The bolts come in a variety of lengths and diameters. Since the bolts are flexible, the curvature may be adjusted by the surgeon. The devices are flexible, bendable, and conformable in their wet or dry state. They can be used either straight or through a broad range of curvatures to suit the needs of various pathologies. The bolts include pressure plates that are capable of exerting compressive pressure over broad areas of visceral wounds without causing tearing of the friable parenchyma. The bolts may be placed and removed by open surgery or laparoscopic access.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Method and apparatus for anchoring implants
InactiveUS7850704B2Low mechanical strengthReliable anchoringStentsHeart valvesSufficient timeTherapeutic Devices
Methods, devices and systems facilitate retention of a variety of therapeutic devices. Devices generally include an anchoring element, which has been designed to promote fibrotic ingrowth, and an anchored device, which has been designed to firmly engage the complementary region of the anchoring element. The anchoring element may be placed in a minimally invasive procedure temporally separated from the deployment of the anchored device. Once enough time has passed to ensure appropriate fixation of the anchoring element by tissue and cellular ingrowth at the site of placement, the anchored device may then be deployed during which it firmly engages the complementary region of the anchoring element. In this manner, a firm attachment to the implantation site may be made with a minimum of required hardware. Some embodiments are delivered through a delivery tube or catheter and while some embodiments may require laparoscopy or open surgery for one or more of the placement procedures. Some embodiments anchor devices within the cardiovascular tree while others may anchor devices within the gastrointestinal, peritoneal, pleural, pulmonary, urogynecologic, nasopharyngeal or dermatologic regions of the body.
Owner:THERANOVA LLC
Devices and methods for percutaneous endarterectomy
Devices and methods are provided for percutaneously treating atherosclerotic plaques within blood vessels. Atherosclerotic plaques cause significant morbidity and mortality by narrowing the arteries, which adversely affects blood flow, and by acting as a source for thrombi and emboli thus causing acute organ ischemia. Current treatments include open surgery with its inherent drawbacks, and stenting, which is less invasive but leaves the plaque material in the artery, which promotes restenosis. The present invention combines the advantages of both approaches. In general, the invention provides tools that enable percutaneously dissecting the plaque from the arterial wall and removing it from the body.
Owner:ANGIOWORKS MEDICAL
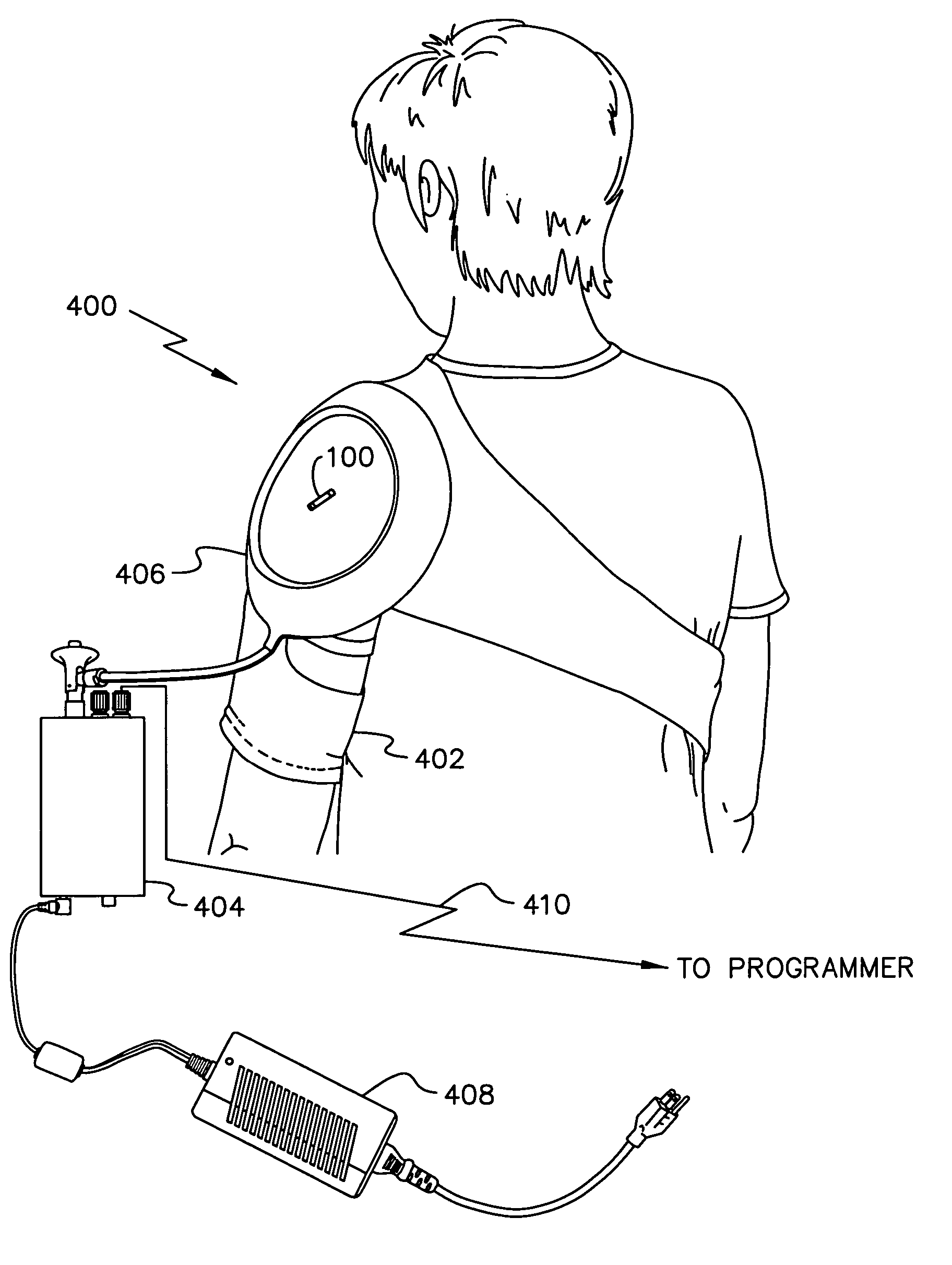
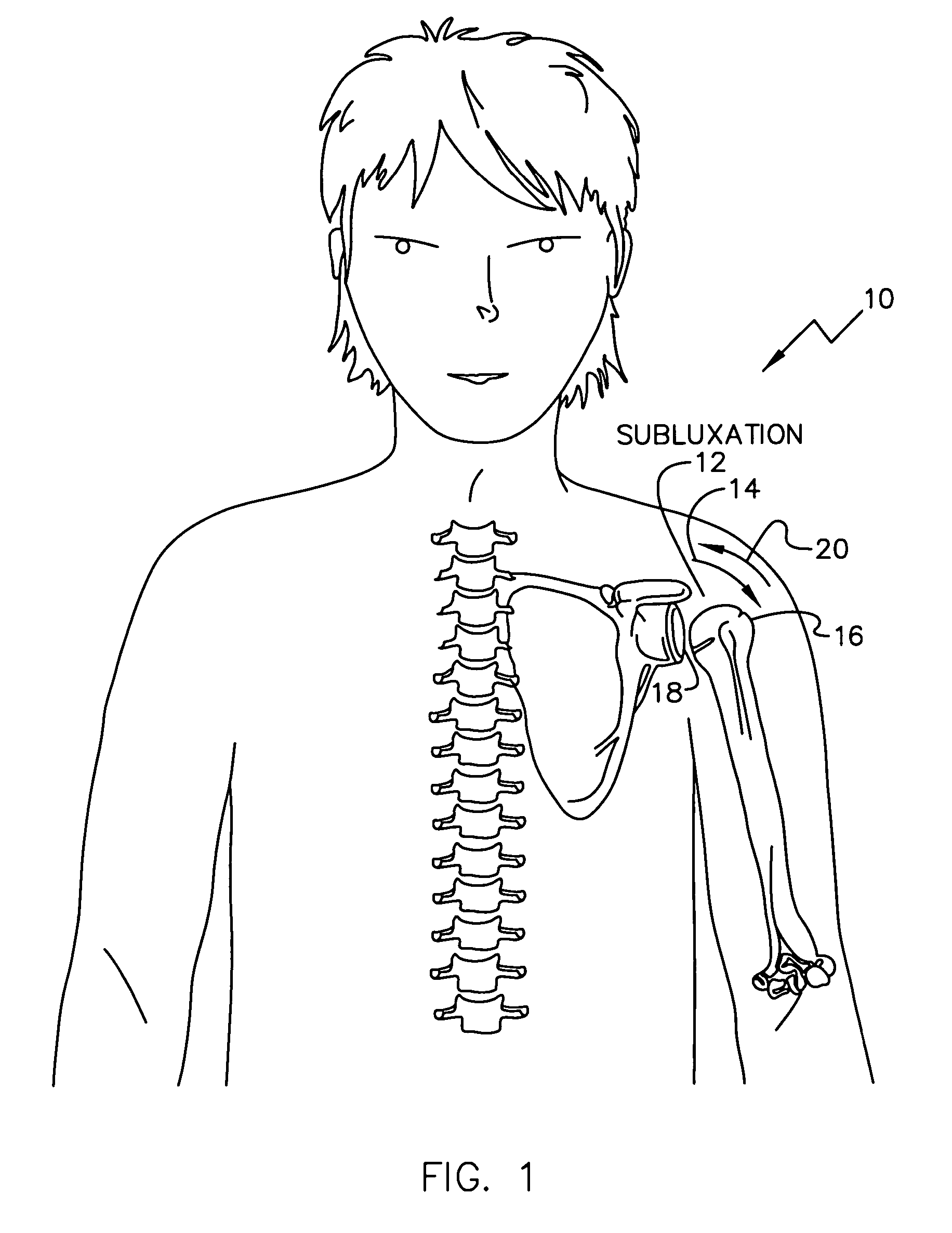
Electrical treatment to treat shoulder subluxation
A method for treating shoulder subluxation using an implantable device to stimulate the axillary nerve which in turn activates sensory fibers to relieve shoulder pain and activates deltoid muscle to treat disuse atrophy and possibly augment any weakened voluntary movements. Known stimulation devices are either (1) external requiring surface electrodes or (2) implantable located directly into the deltoid muscle allowing stimulation of the proximate motor-points; each requiring relatively large stimulus currents and neither directly dealing with the pain resulting from the shoulder subluxation. In the present invention, a device is implanted via injection or open surgery proximate to the axillary nerve. Advantageously, the nerve branches into portions that stimulate the deltoid muscle and pass sensory signals. By stimulating the axillary nerve (1) a lower stimulus signal level can be used and (2) pain may be blocked while treating the atrophied deltoid muscle and augmenting weakened voluntary movements.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
Multipurpose Surgical Tool
InactiveUS20070244515A1Overcome limitationsIncrease awarenessSurgical scissorsSurgical instrument detailsOpen surgeryEndoscope
The invention relates to a surgical tool. In particular, the invention relates to a multi-functional surgical tool that has a cutting means, and a grasping means, with a buffer region between the cutting and grasping means. The invention particularly relates to a multi-functional surgical tool that is suitable for use in endoscopic or laparoscopic surgery, but may also be used in open surgery.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
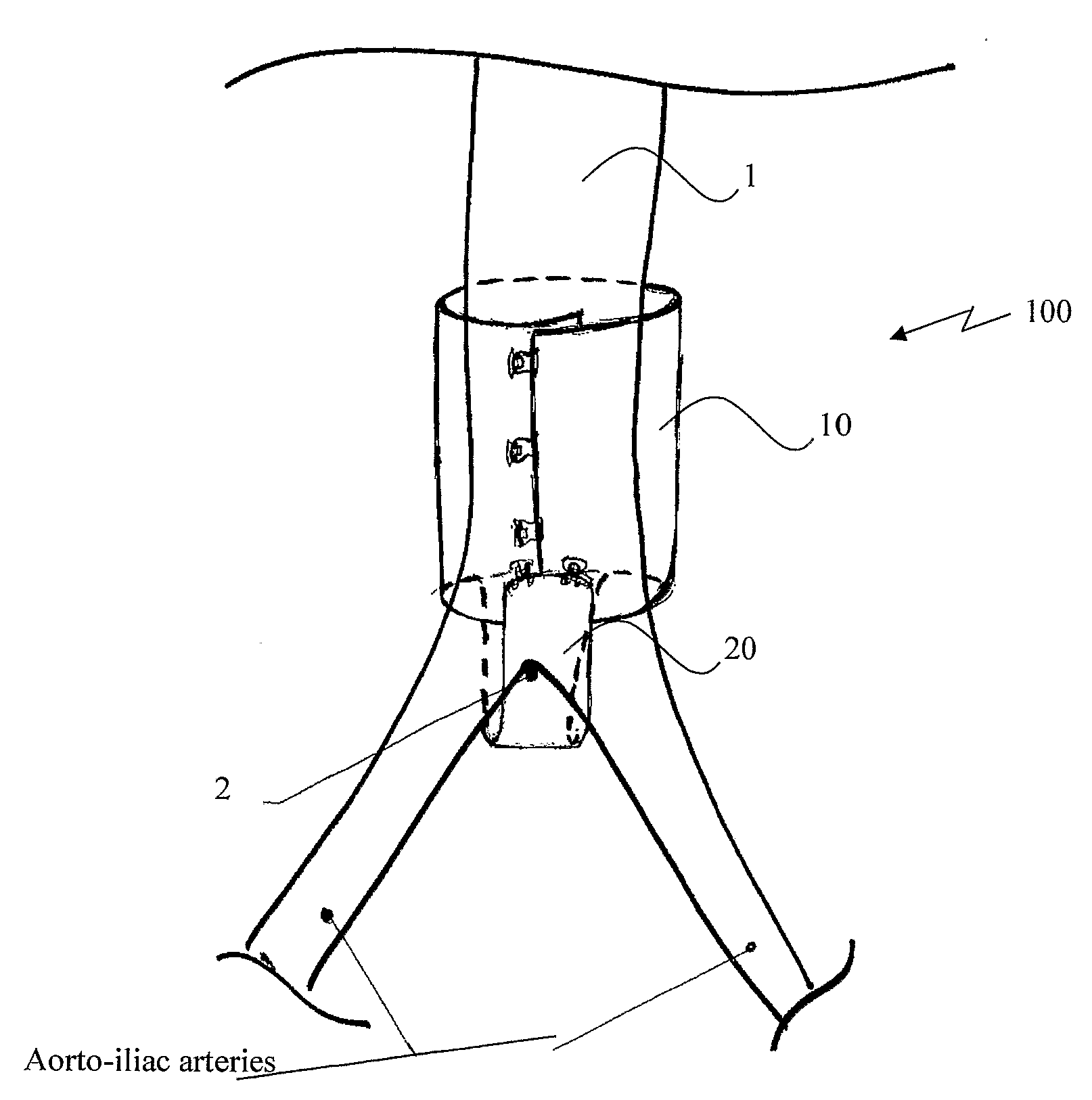
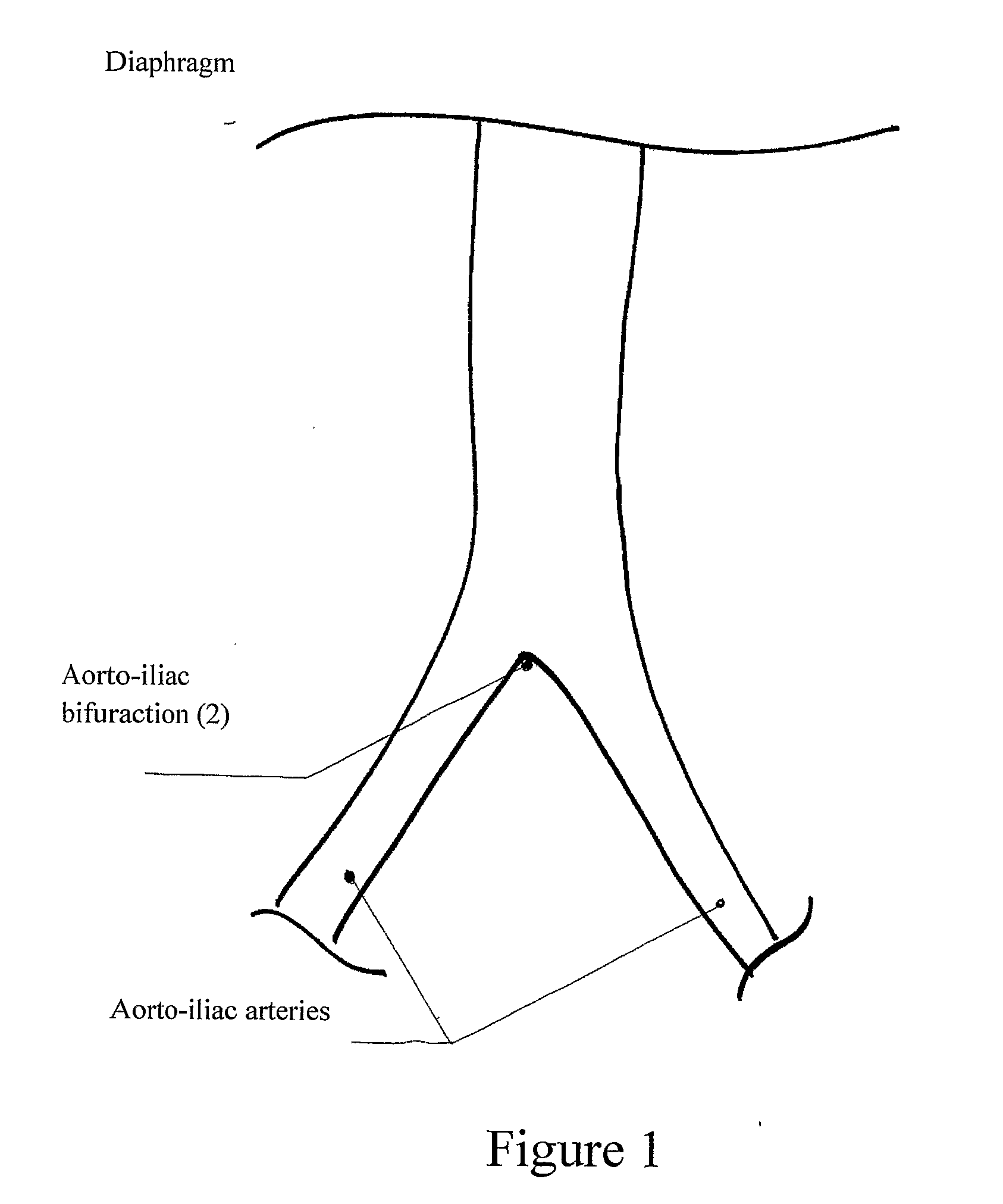
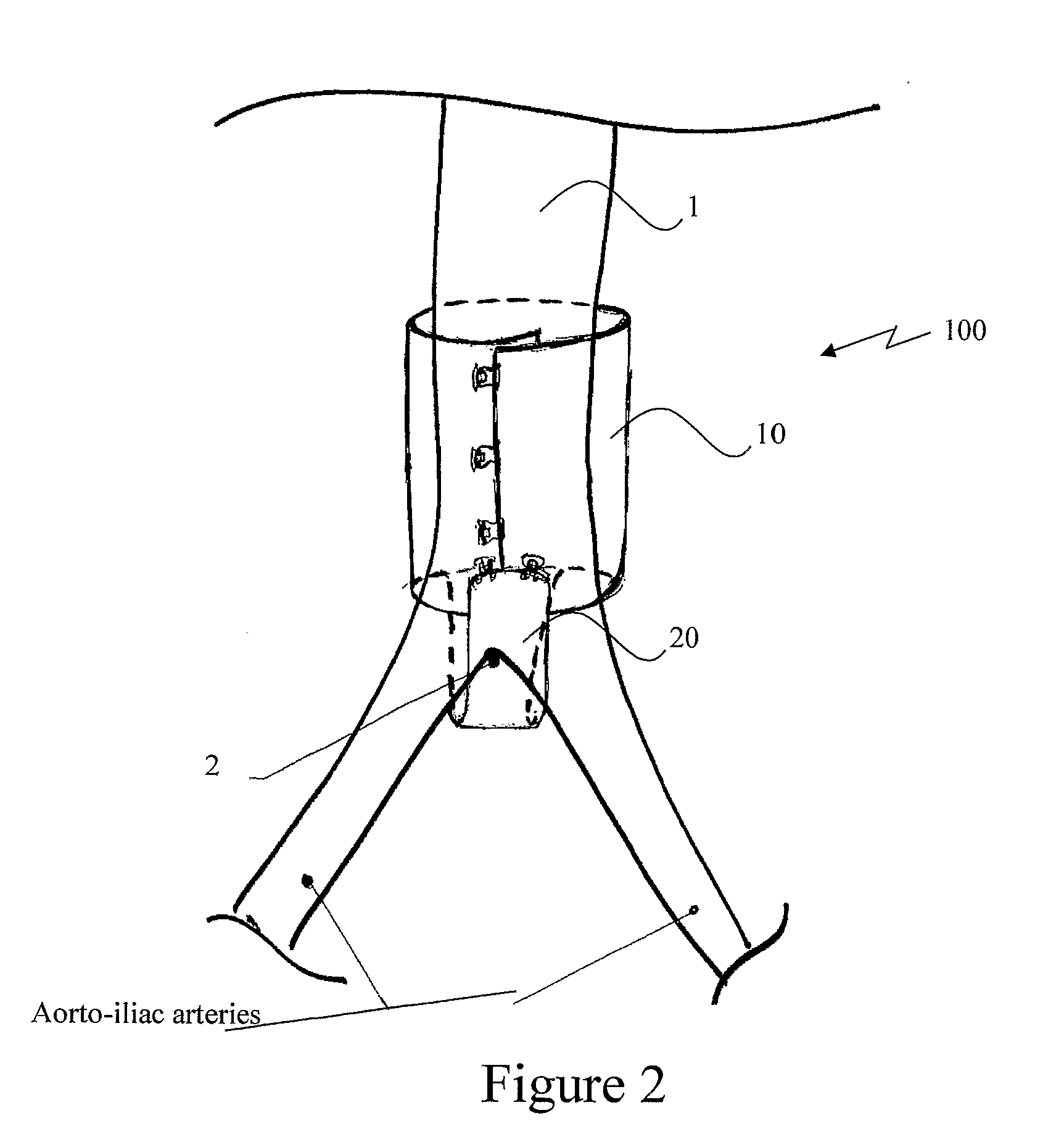
Extra-vascular wrapping for treating aneurysmatic aorta and methods thereof
InactiveUS20100070019A1Inhibiting scar tissue formationInhibition formationStentsSurgeryDistal portionIliac Aneurysm
A new extra-vascular wrapping (EVW) is disclosed. The EVW comprises of a (i) wrapping adapted to at least partially encircle at least a segment of an aorta, especially an aneurysmatic aorta, and (ii) anchoring means located at the distal portion of the wrapping adapted to immobilize the wrapping to the aorto-iliac bifurcation via engagement of the aorto-iliac junction, wherein the bifurcation-anchored wrapping is applied external to the aorta and further wherein the wrapping is collapse-resistant in the proximal-to-distal direction of the aorta. The EVW is presented with its various embodiments, such as gusset-like structured EVW, Sustained drug delivery EVW, supported EVW and ringed EVW. Methods for treating aneurysmatic aorta in an open-surgery procedure by utilizing the EVWs and by applying step of positioning a macroporous medical textile externally adjacent to the aorta are also disclosed.
Owner:ENDOSPAN
Needle device
ActiveUS8277411B2Reduce riskLimit insertionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesBody organsVisual inspection
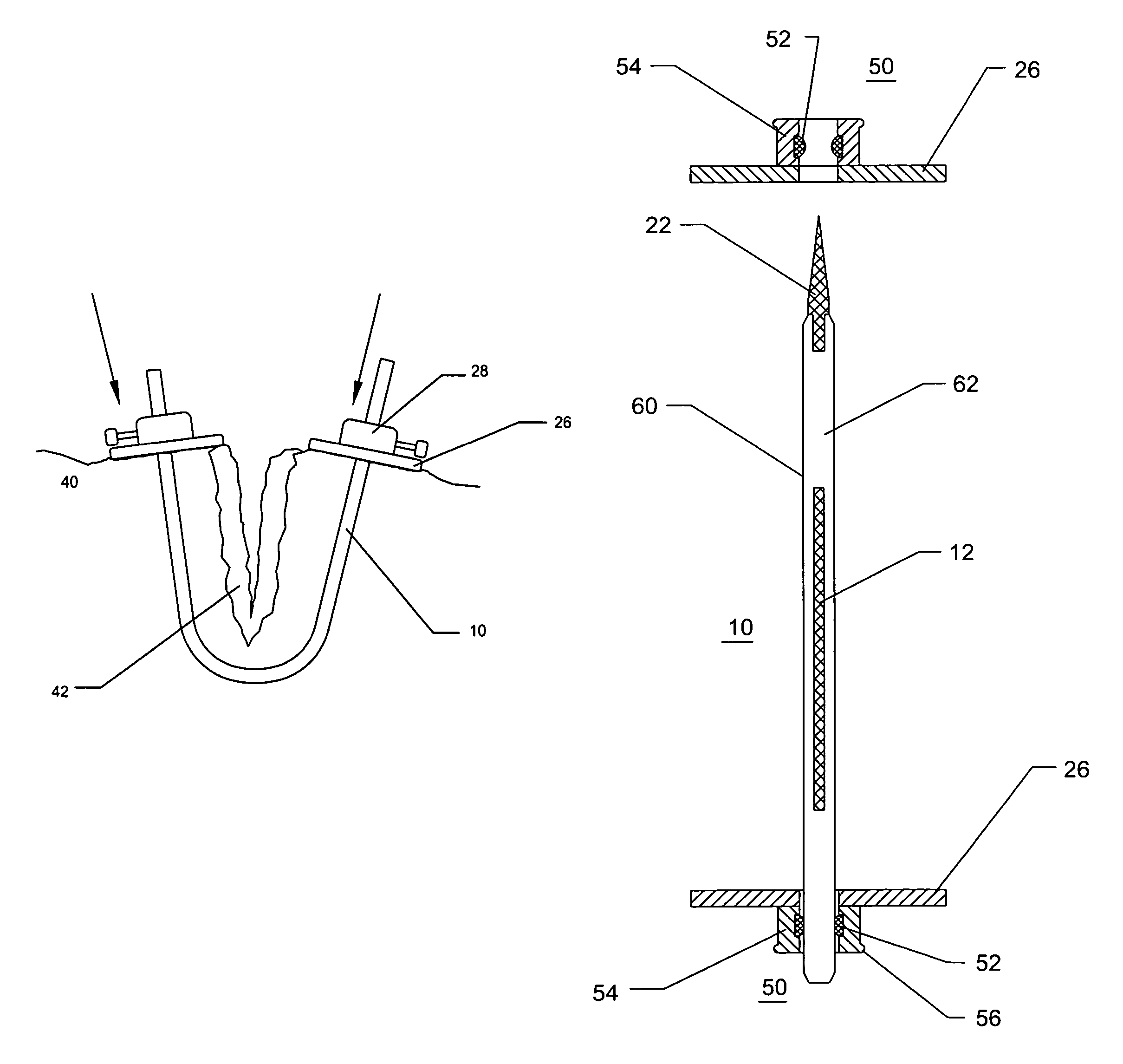
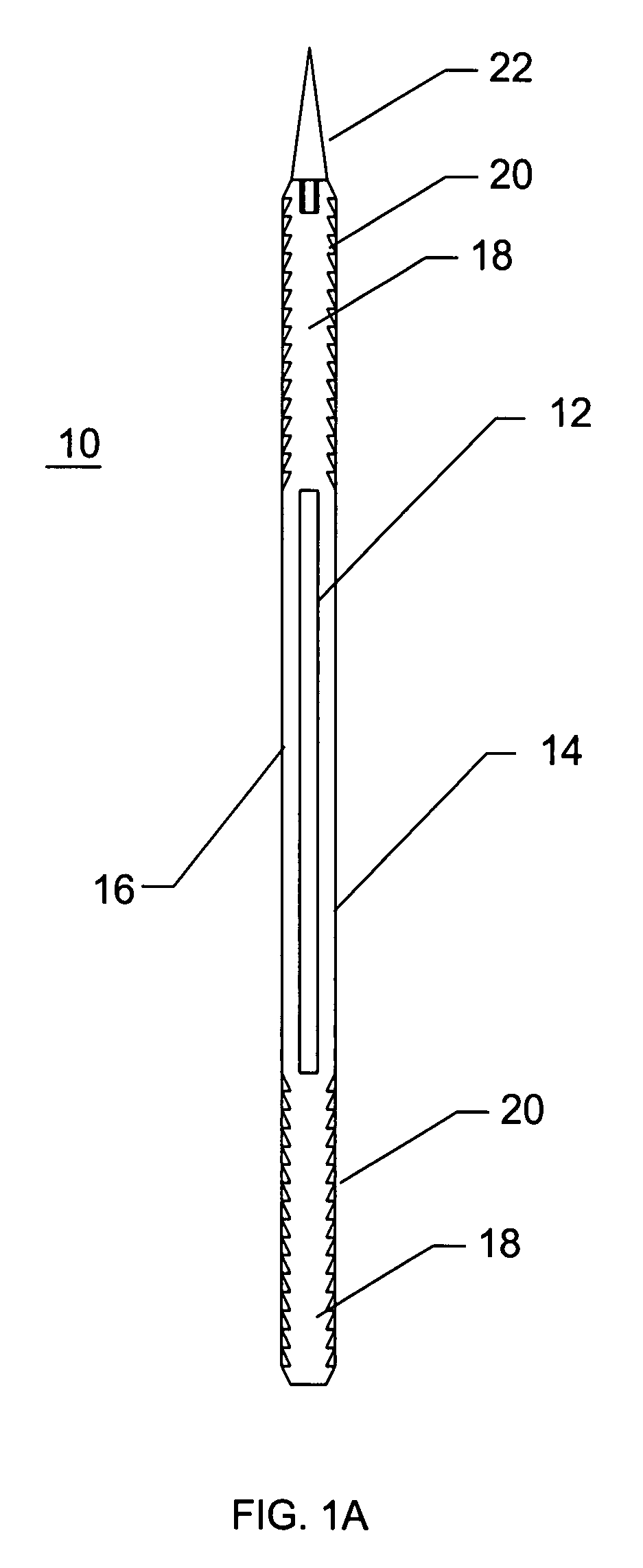
A needle device for penetrating body tissues while substantially reducing the risk of damage to blood vessels and body organs by using visual control of the operative tip during insertion and the procedure, is disclosed herein. The needle device of the present invention has a large and diverse applicability to a number of medical procedures by enabling internal visual inspection of body tissues and cavities during treatment without open surgery or supplemental penetrating or visualization devices.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Endovascular cerebrospinal fluid shunt
InactiveUS20100191168A1More physiologic drainageWound drainsMedical devicesShunt DeviceSubarachnoid space
An implantable shunt device for draining cerebrospinal fluid from a patient's subarachnoid space. The device includes a shunt having opposed first and second ends. A one-way valve is located at the first end of the shunt. A helical tip is disposed at the second end. The helical tip is constructed to penetrate a sinus wall of the patient. Upon implantation, a hollow passageway extends between the helical tip and one-way valve such that fluid can be drained through the helical tip and out through the valve. The endovascular cerebrospinal fluid shunt of the present invention can be placed into a patient percutaneously via a catheter inserted into the venous system of the body through a needle hole, without the need for open surgery and the skin incisions required with current shunt devices. The device also allows for more physiologic drainage of cerebrospinal fluid since the device is shunting cerebrospinal fluid into the same cerebral venous system that occurs naturally in normal people.
Owner:TUFTS MEDICAL CENTER INC
Method and apparatus for anchoring cardiovascular implants
InactiveUS20090030435A1Reduce risk of migrationReduce intrusionSuture equipmentsStentsVascular implantTherapeutic Devices
Methods, devices and systems facilitate retention of a variety of therapeutic devices. Devices generally include an anchoring element, which has been designed to promote fibrotic ingrowth, and an anchored device, which has been designed to firmly engage the complementary region of the anchoring element. The anchoring element may be placed in a minimally invasive procedure temporally separated from the deployment of the anchored device. Once enough time has passed to ensure appropriate fixation of the anchoring element by tissue and cellular ingrowth at the site of placement, the anchored device may then be deployed during which it firmly engages the complementary region of the anchoring element. In this manner, a firm attachment to the implantation site may be made with a minimum of required hardware. Some embodiments are delivered through a delivery tube or catheter and while some embodiments may require laparoscopy or open surgery for one or more of the placement procedures. Some embodiments anchor devices within the cardiovascular tree while others may anchor devices within the gastrointestinal, peritoneal, pleural, pulmonary, urogynecologic, nasopharyngeal or dermatologic regions of the body. An alternative embodiment provides for the placement of the anchoring element and anchored device simultaneously, but allows for their removal separately. This embodiment allows the device, which may be placed only temporarily and be designed to be removed, to experience significant fibrotic ingrowth, but then to be easily detached from the ingrowth-anchored region to allow for simple and quick device removal.
Owner:THERANOVA LLC
Medical device and method for human tissue and foreign body extraction
ActiveUS20090326546A1Additional drawbackEndoscopic cutting instrumentsSuction devicesHuman fetus tissueEngineering
A coaxial tube assembly, a bag, a bag-translating assembly, a de-bulking tool, and a drive assembly. The bag is delivered into a cavity in a patient's body either manually for open surgery or through the coaxial tube assembly by operation of the drive assembly for minimally invasive surgery. After a mass of tissue is placed in the bag, which is now secured to the bag-translating assembly, the drive assembly is operated to activate the bag-translation assembly to retract the bag into the annular space of the coaxial tube assembly. As the bag is being retracted, the mass in the bag is pulled into engagement with the de-bulking tool, which extends through the lumen of the coaxial tube assembly. The drive assembly activates the de-bulking tool to morcellate the mass in the bag and convey the morcellated bits of the mass through the lumen of the coaxial tube assembly.
Owner:DAI Z
Spinal rod and screw securing apparatus and method
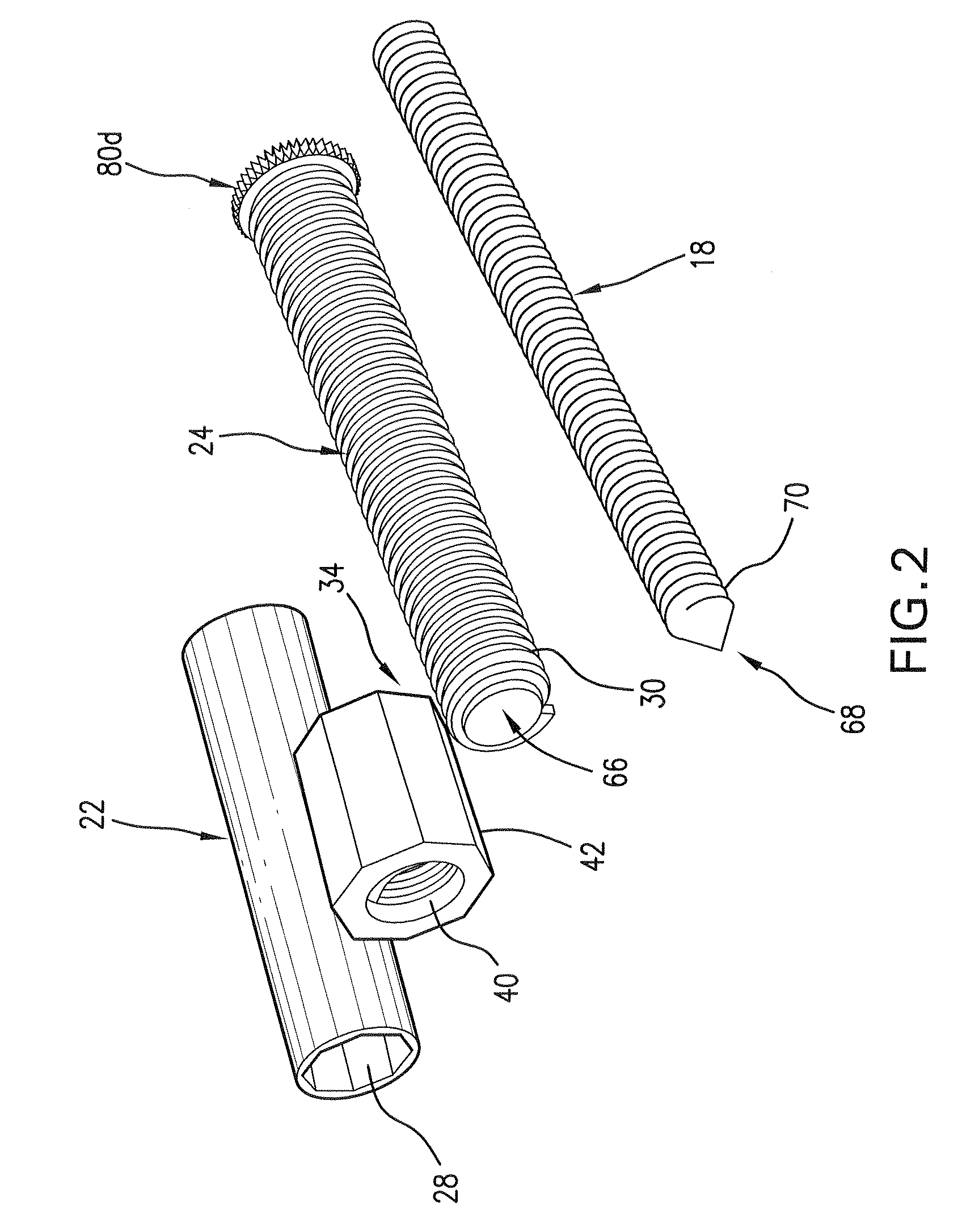
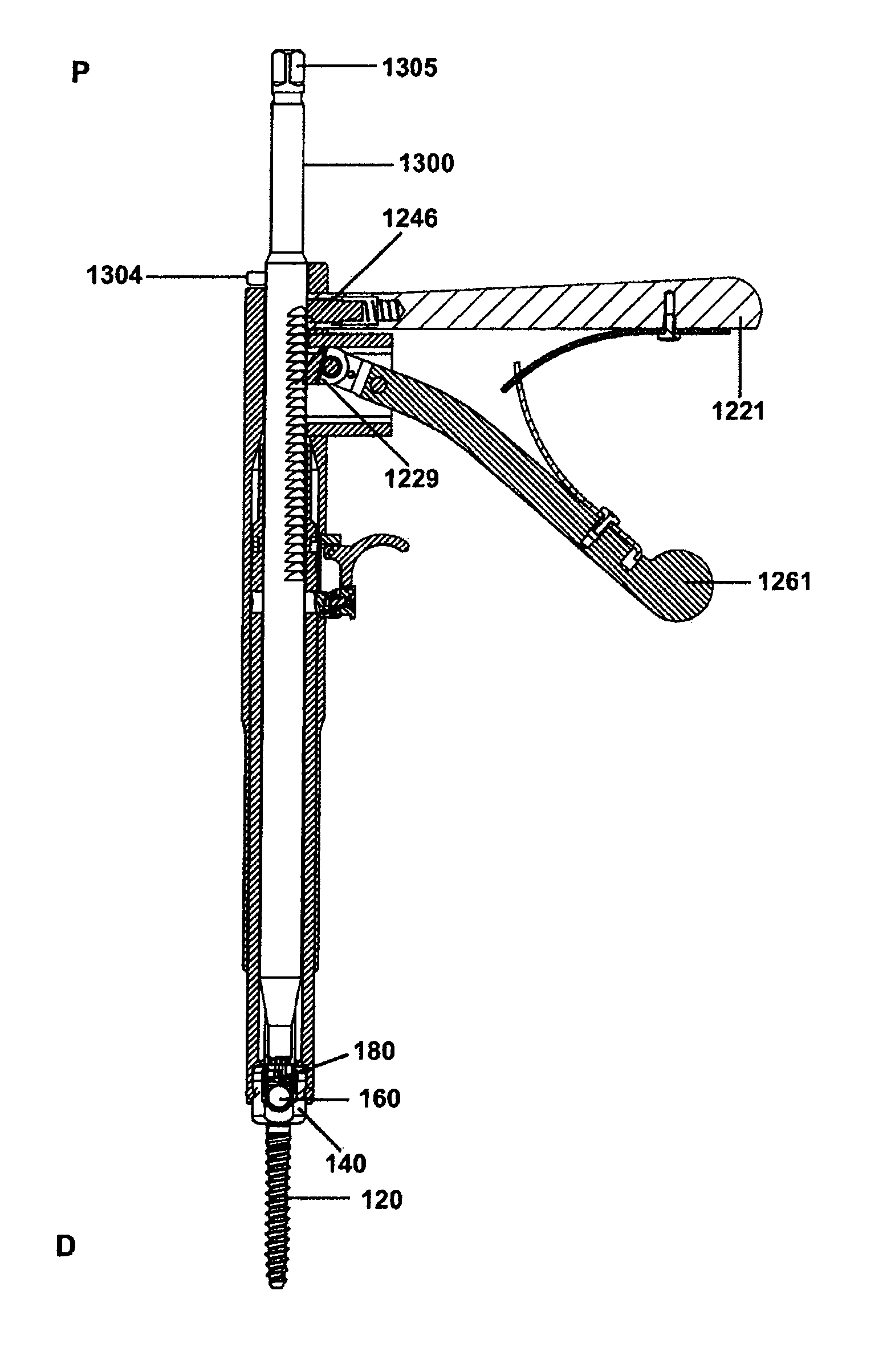
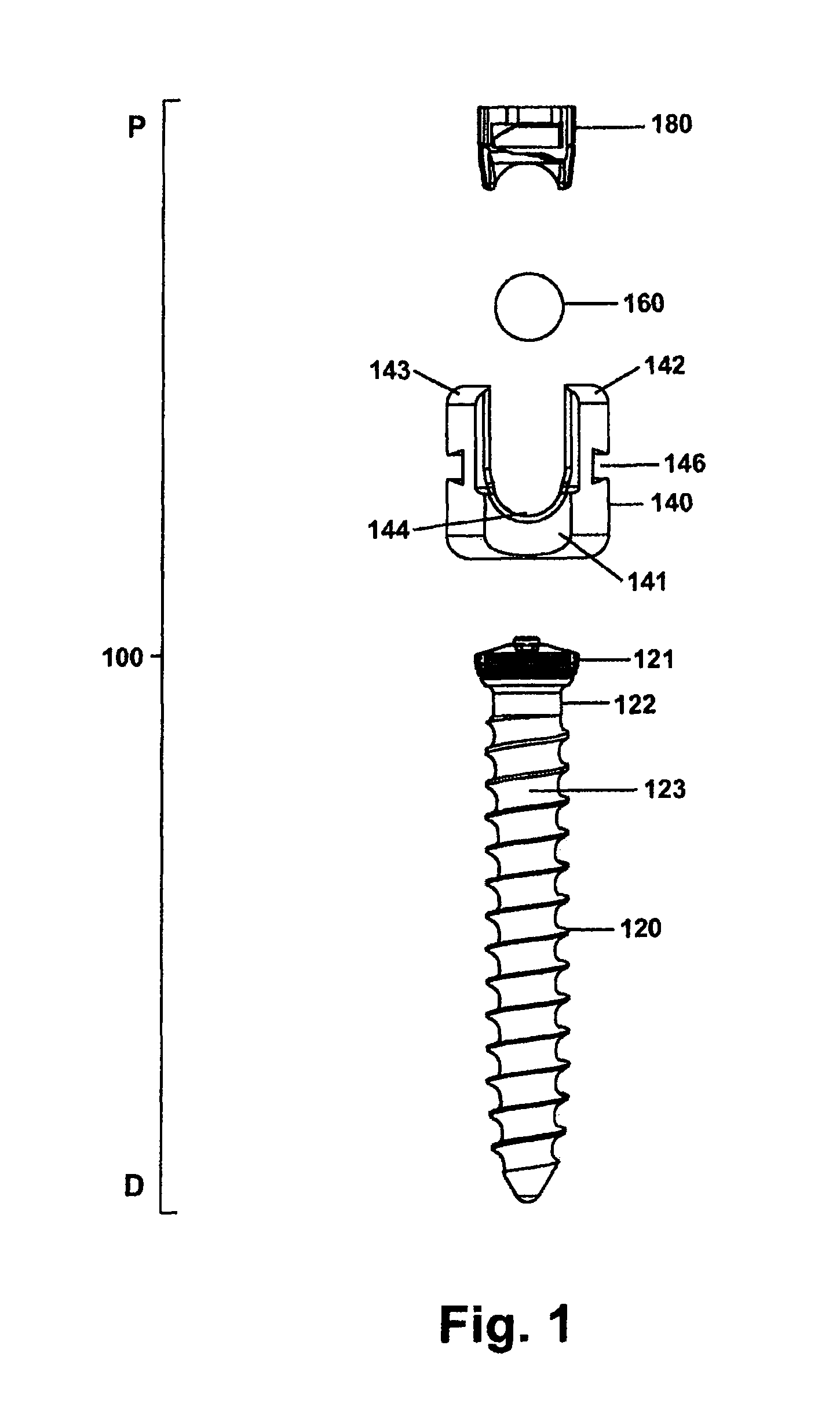
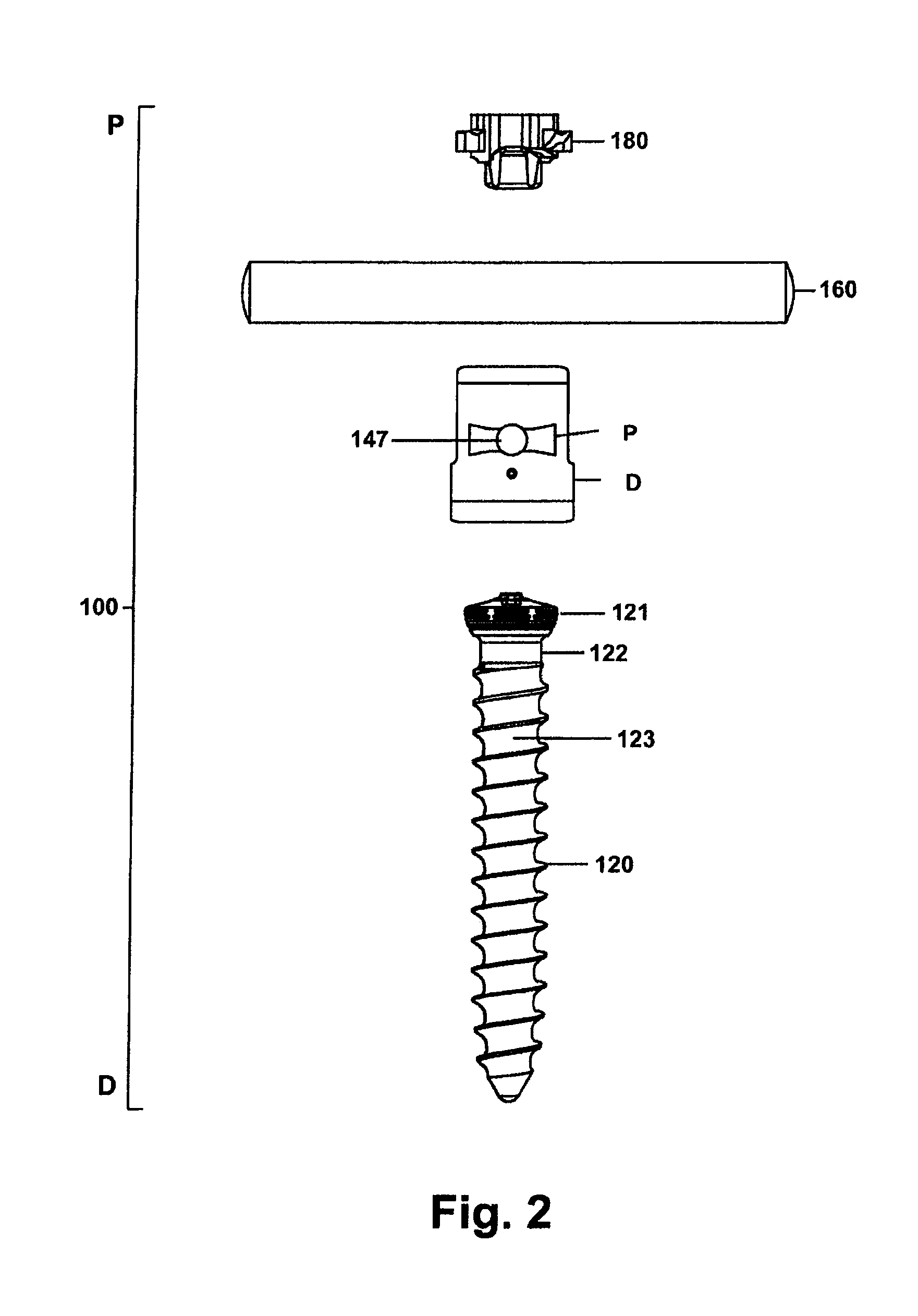
ActiveUS8900240B2Shorten operation timeSimple stationary gripInternal osteosythesisFastenersSpinal columnVia incision
Owner:XTANT MEDICAL HLDG INC
Forward deploying suturing device and methods of use
InactiveUS20090287226A1Improve performanceSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSurgical operationHuman body
Sutures can be placed in difficult to access areas of the human body with devices, and related methods, utilizing a needle carrier. The devices and methods can be used in conjunction with both endosurgical and traditional open surgery procedures.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Open surgery anastomosis device, system, and method
InactiveUS20140052160A1Prevent potential leak and migrationInhibit migrationStentsBlood vesselsAnatomical structuresSurgical department
A medical device, system and method tor an open surgical procedure configured to couple, for example, open ends of anatomical structures. The system includes an expandable tubular structure and inflatable balloon positioned within the tubular structure. The tubular structure includes a lateral opening defined in a wall of the tubular structure through which the balloon is inflated to radially expand the tubular structure, after which the balloon is deflated, and then removed from the tubular structure to, thereby, provide a fluid flow path through the tubular structure.
Owner:SINGH DEVINDER +1
System and method for releasably holding a surgical instrument
The invention is directed to a system and method for releasably holding a surgical instrument (14), such as an endoscopic instrument configured for delivery through a small percutaneous penetration in a patient. The instrument comprises an elongate shaft (100) with a pair of mounting pins (116) laterally extending from the shaft between its proximal and distal ends. An instrument holder comprises a support having a central bore (202) and an axially extending slot (204) for receiving the instrument shaft and the mounting pins. A pair of locking slots (206) are cut into the support transversely to and in communication with the axial slot so that the mounting pins can be rotated within the locking slots. The instrument support further includes a latch assembly for automatically locking the mounting pins within the locking slots to releasably couple the instrument to the instrument holder. With this twist-lock motion, the surgeon can rapidly engage and disengage various instruments from the holder during a surgical procedure, such as open surgery, laparoscopy or thoracoscopy.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Ventricular assist device and related methods
ActiveUS20110130619A1Simplify the viewing processCannulasControl devicesRadiologyVentricular assistance
A method and system are provided for percutaneously gaining access to oxygenated blood with one or more anastomosis devices and pumping such oxygenated blood directly to the aorta adjacent to the right atrium or left atrium via a VAD system. In one embodiment, a VAD system can be implanted with open surgery.
Owner:COHEREX MEDICAL
Device especially useful for hernia repair surgeries and methods thereof
The present invention discloses an inflatable contour-balloon useful in minimal invasive and / or open surgery. The inflatable contour-balloon positioned in the contour of a mesh and / or a patch and / or a net. The inflatable contour-balloon is adapted to spread and / or deploy the mesh and / or the patch and / or the net in the abdominal cavity and / or pre-peritoneal and / or space and / or hollow body organs and / or natural and / or artificial orifices and / or spaces and / or post operative spaces. The present invention also discloses an elongate open-bored applicator (EOBP) adapted to spread and / or deploy a mesh and / or a patch and / or a net. The EOBP is useful in minimal invasive surgery. The EOBP has a distal portion that is insertable into the abdominal cavity and / or pre-peritoneal and / or space arid / or hollow body organs and / or natural and / or artificial orifices and / or spaces and / or post operative spaces; and a proximal portion that remains outside the body. The EOBP comprises: (a) at least one inflatable contour-balloon; (b) at least one inflatable dissection balloon. The inflatable contour-balloon and the inflatable dissection balloon are adjustable and located at the distal portion; and, (c) at least one actuating means located at the proximal portion. The actuating means is in communication with the inflatable contour-balloon and the inflatable dissection balloon. The actuating means is adapted to provide the inflatable contour-balloon and the inflatable dissection balloon with independent activation and / or de-activation.
Owner:DAVOL
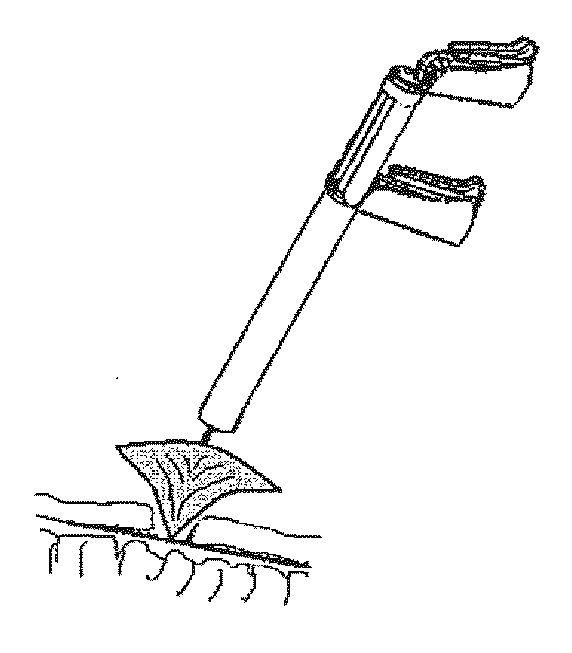
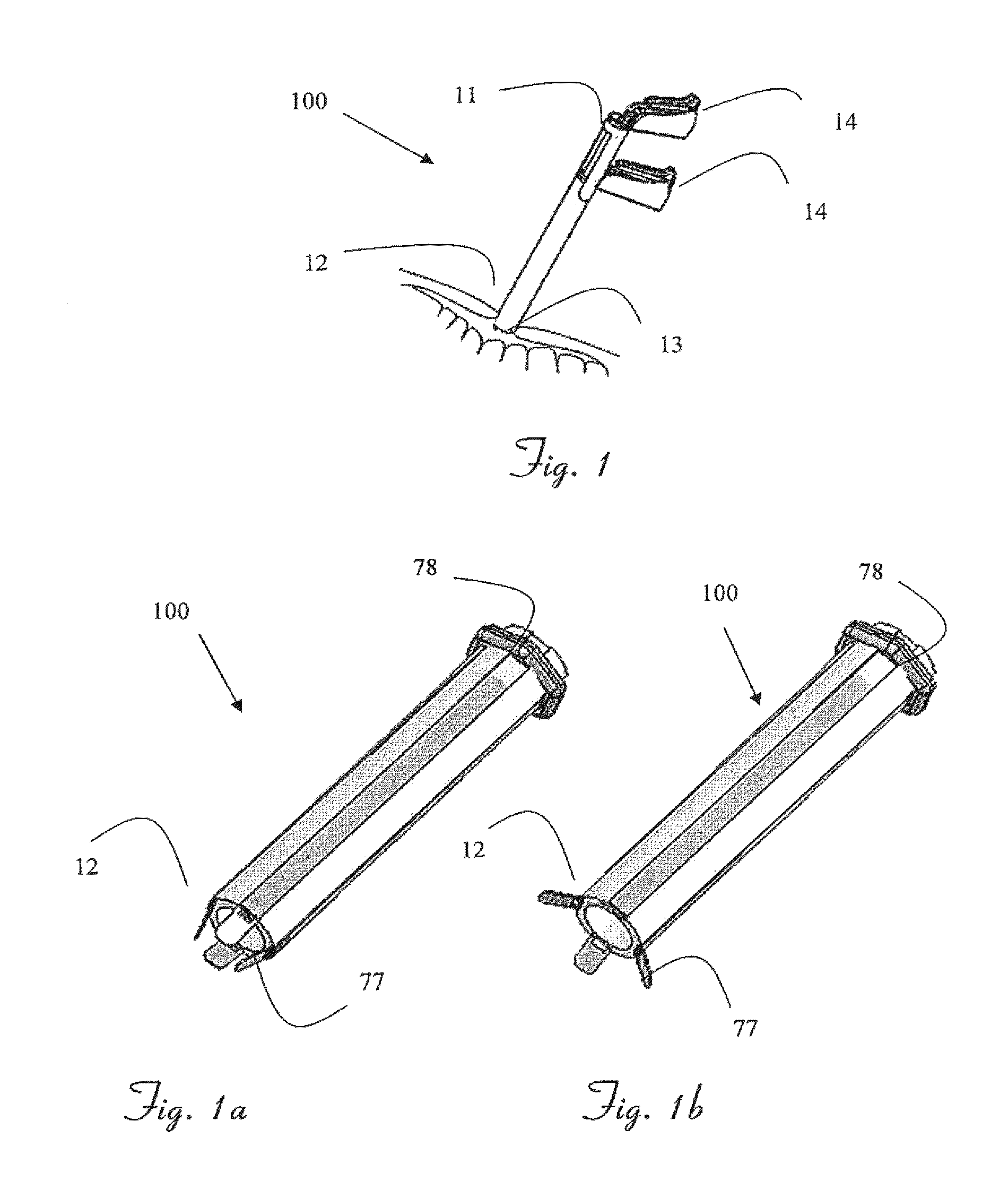
Vacuum instrument for laparotomy procedures
InactiveUS20050203334A1Efficient use ofLess traumaDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSurgical incisionAcute angle
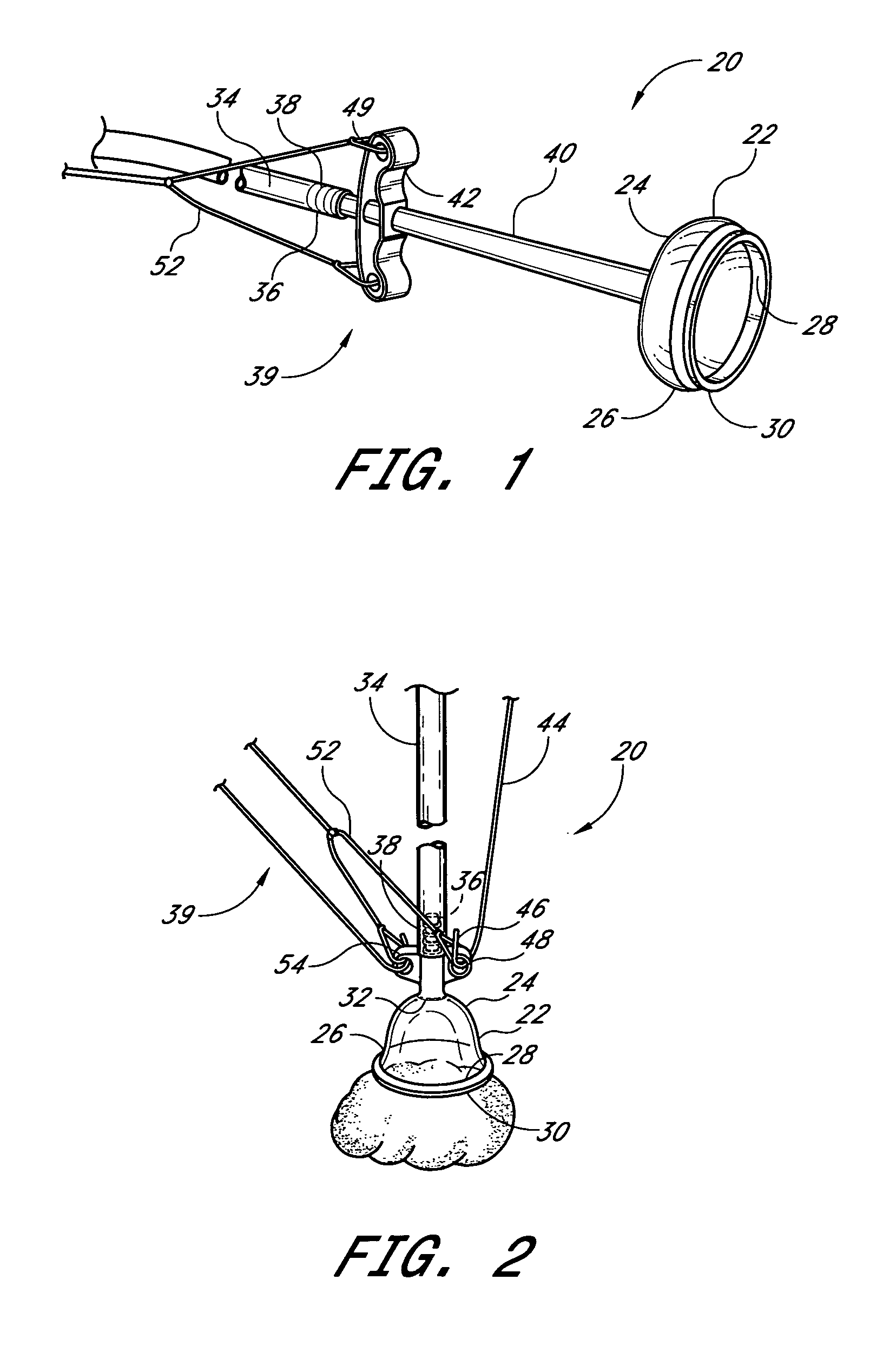
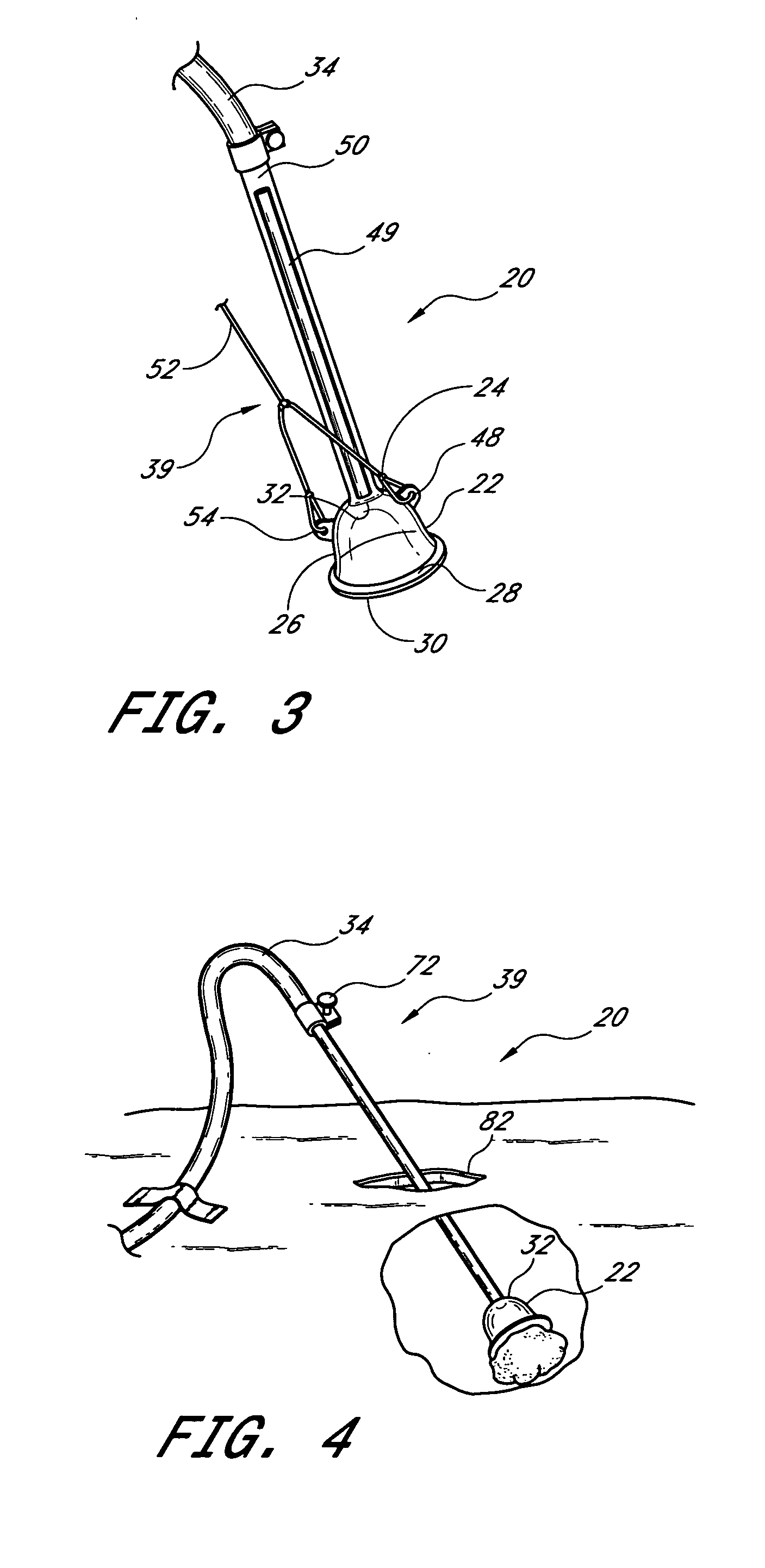
The present invention relates to a vacuum retractor that can be utilized to retract, extract and manipulate a target tissue during an open surgery. The retractor includes a vacuum cup sized for attachment to and manipulation of a target tissue. The device further includes a vacuum hose for applying a vacuum to the interior of the cup. The vacuum hose is attached to the vacuum cup at an acute angle allowing the cup to be easily inserted into and removed from a surgical incision without occlusion of the air flow through the vacuum hose. The vacuum device may be utilized with minimal or no trauma to the target tissue or surrounding tissues.
Owner:CLINICAL INNOVATIONS LTD
Method and apparatus for solid organ tissue approximation
InactiveUS8114124B2Easy and fast applicationCompression of tissueForeign body detectionSurgical veterinaryWound healingParenchyma
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com