Patents
Literature
73 results about "Cardiac Catheters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
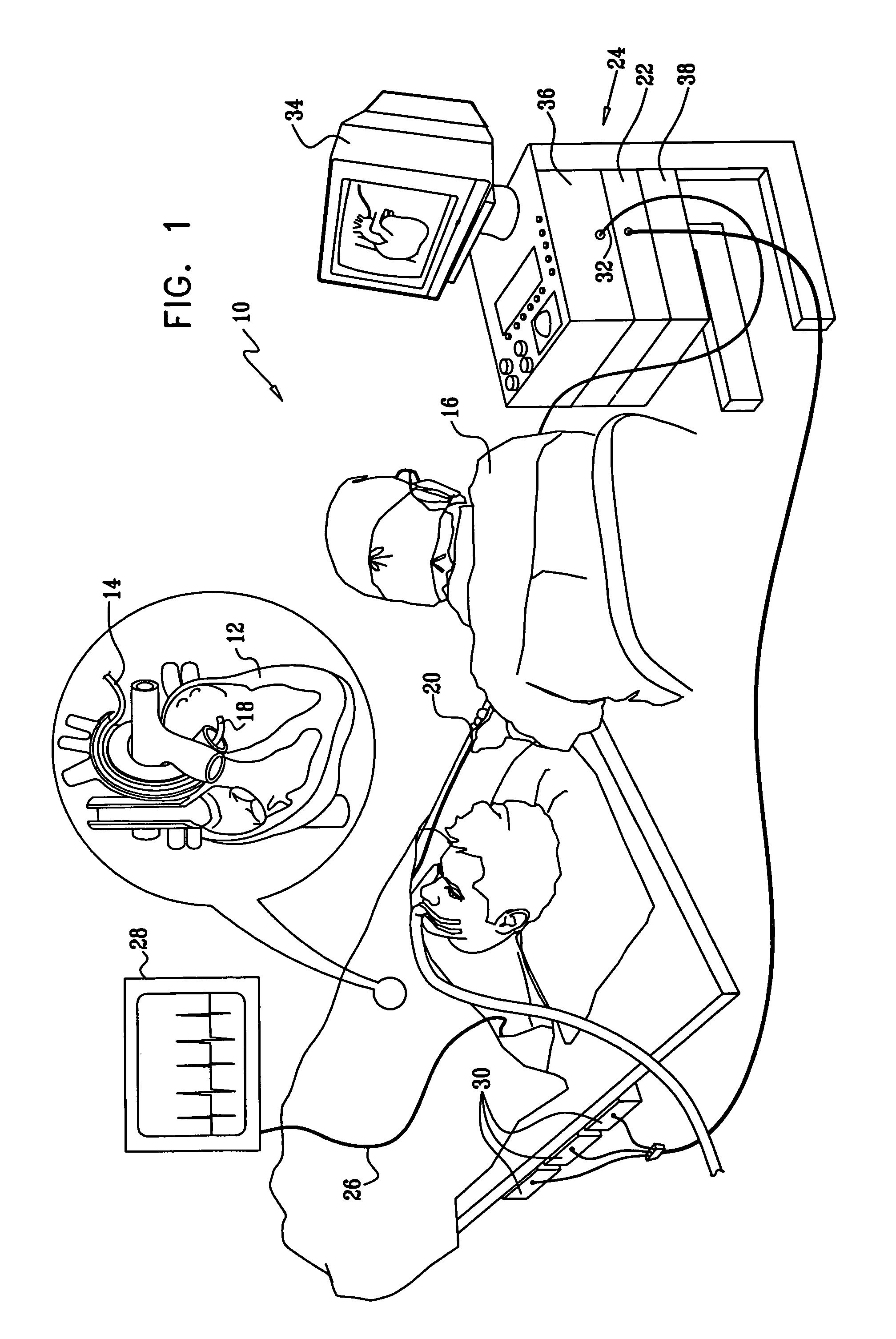
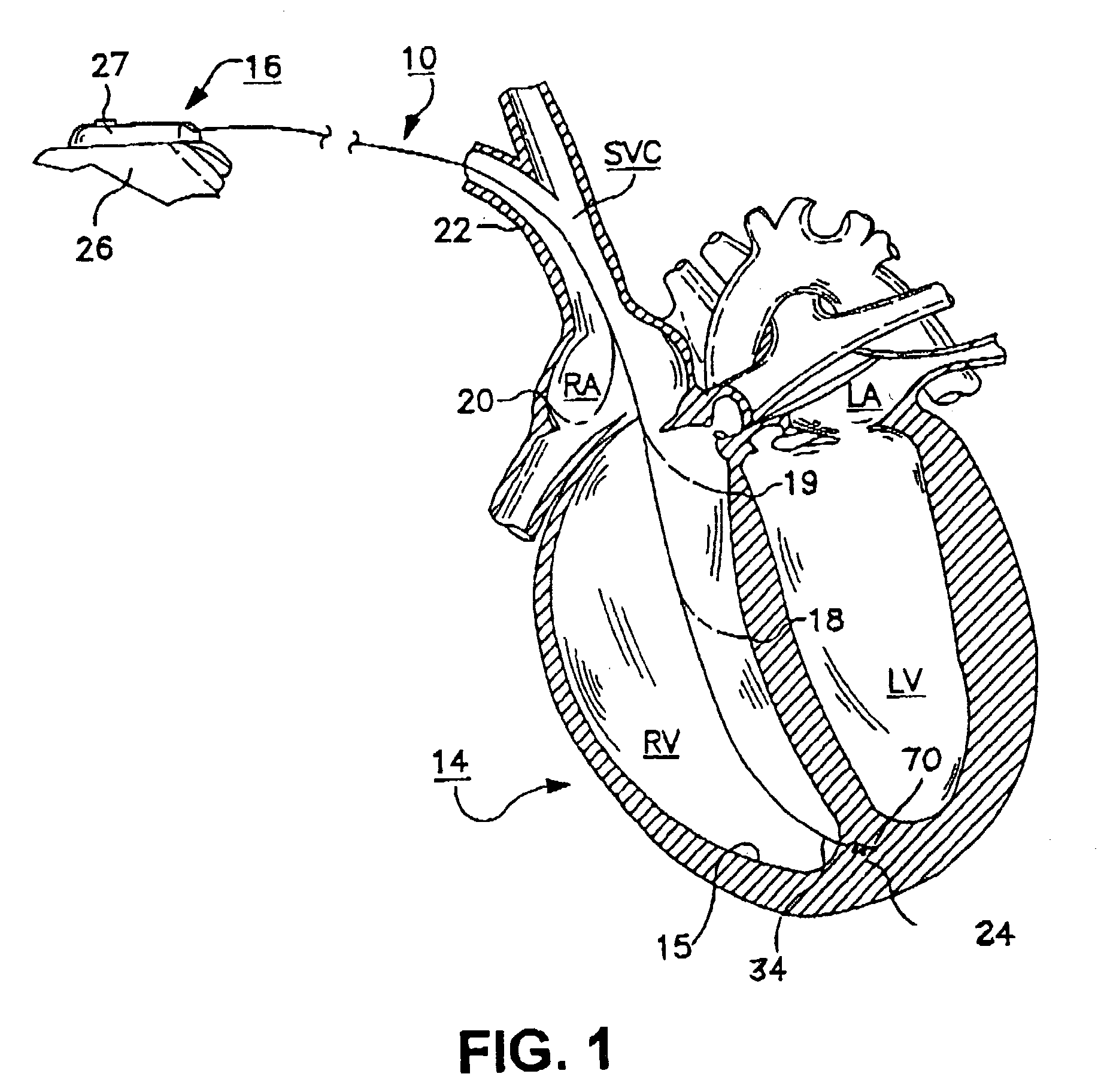
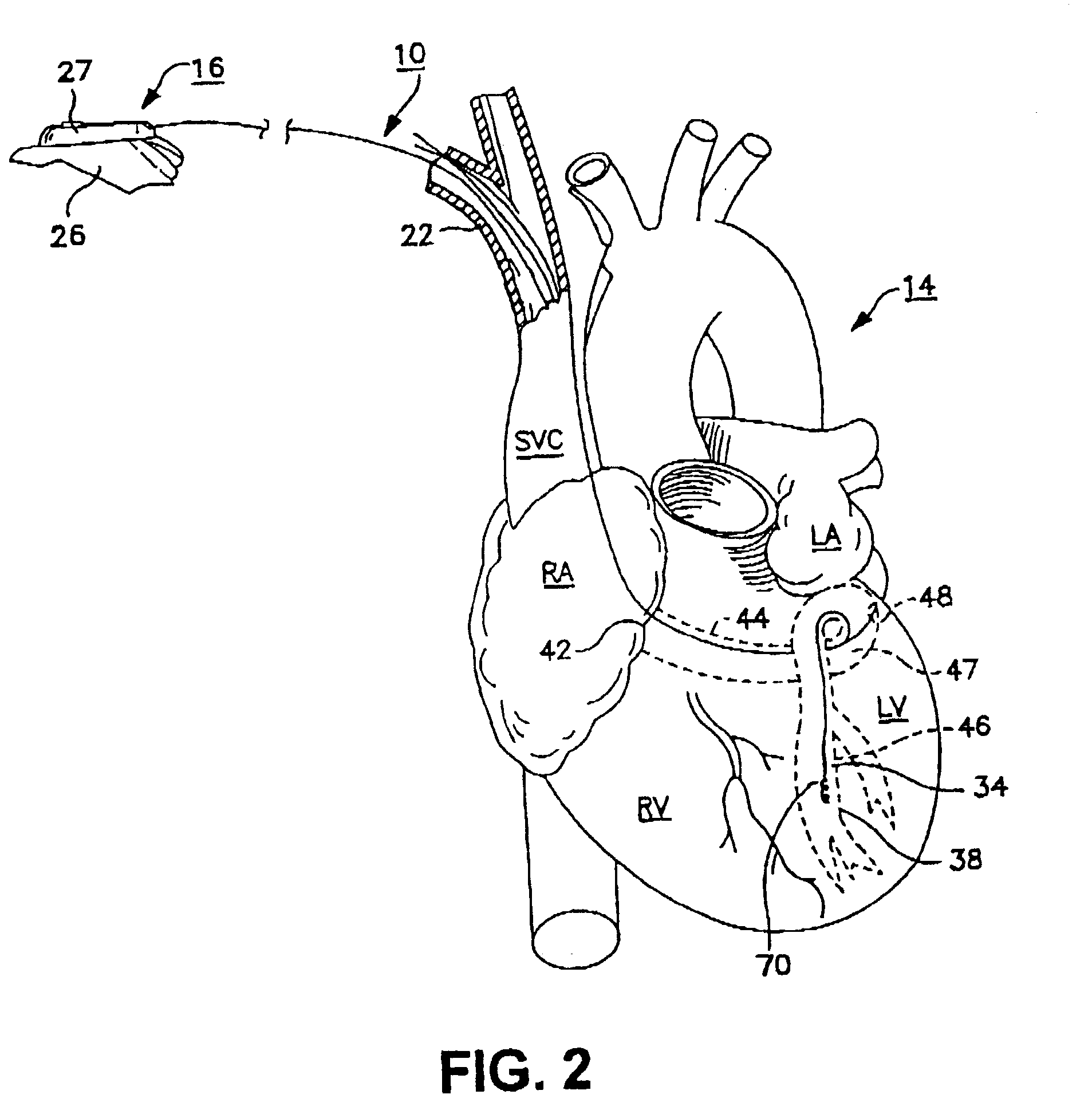
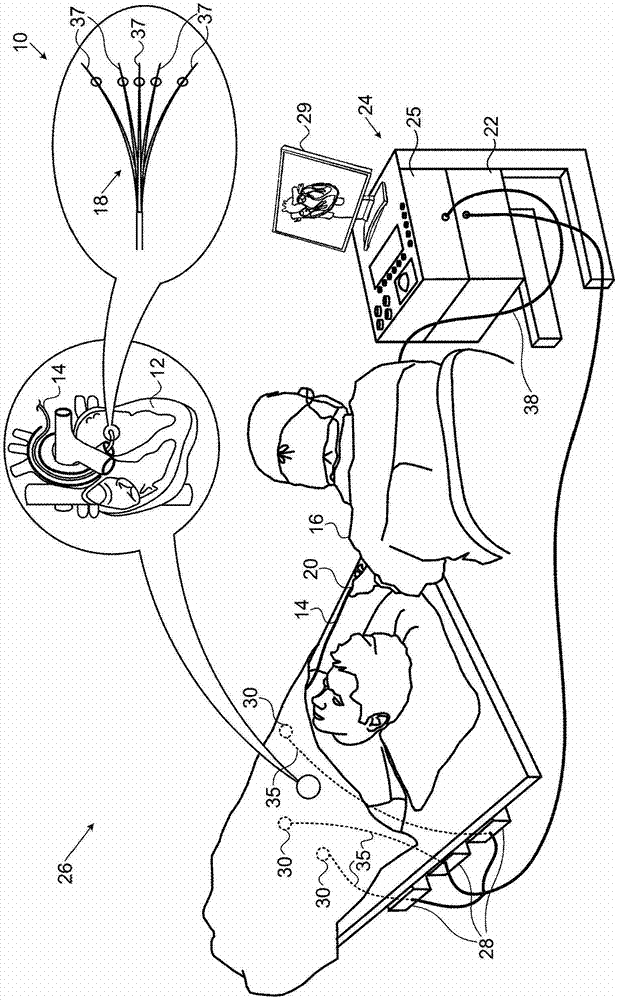
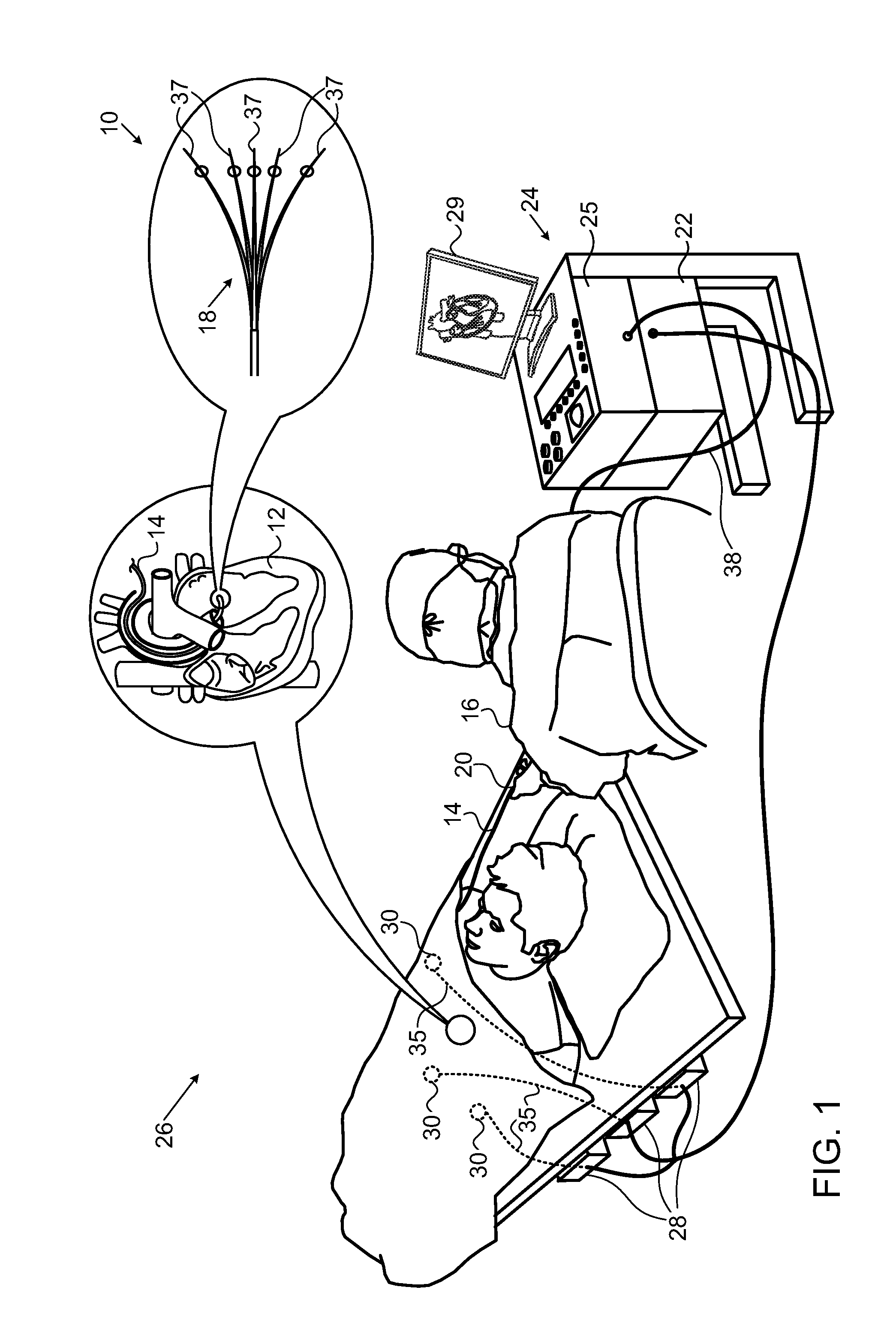
Catheters inserted into various locations within the heart for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
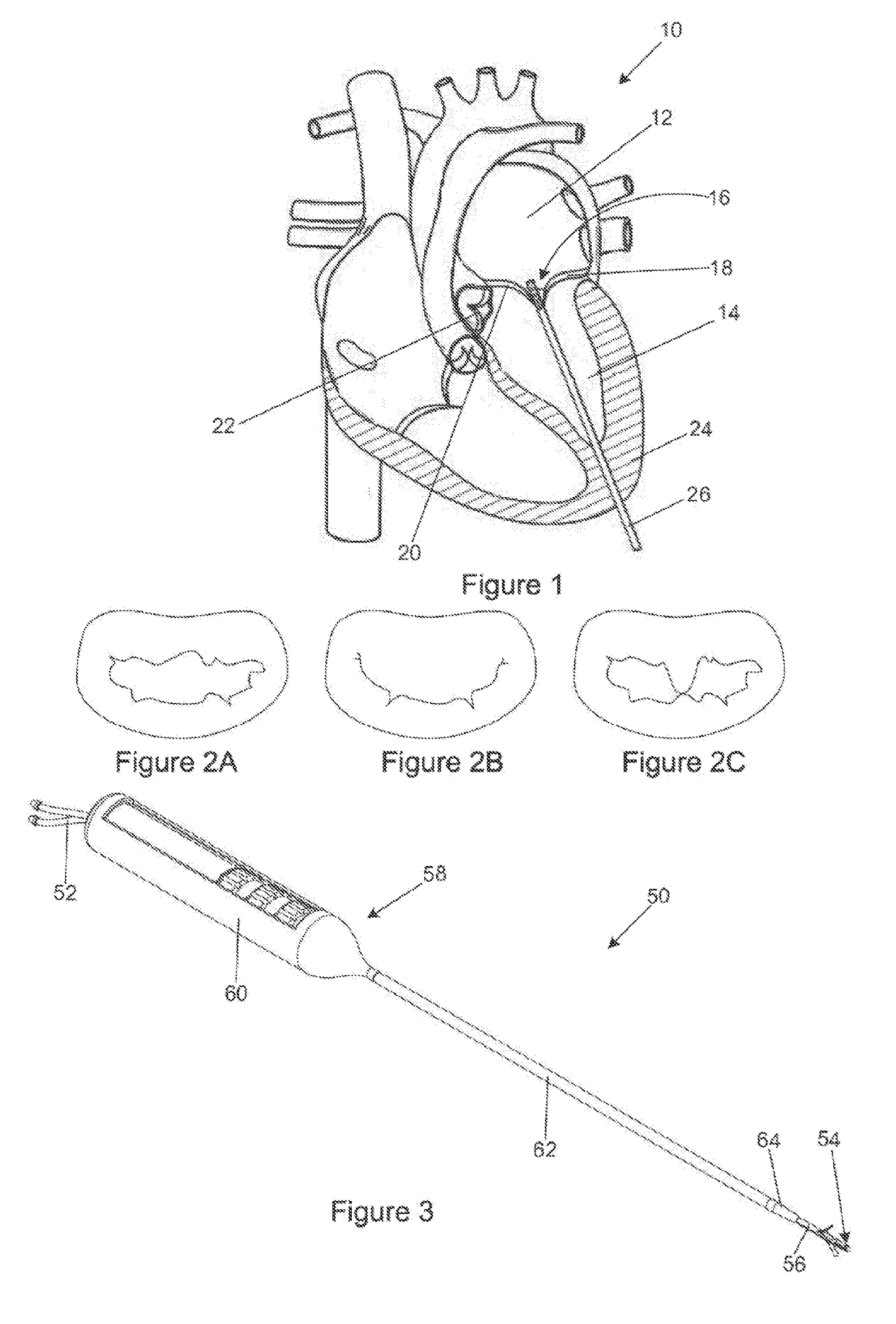
Mitral and tricuspid valve repair
A novel approach to mitral or tricuspid valve repair involves the performance of an edge-to-edge fastening / securing of opposing heart valve leaflets through a catheter entering the heart. Thus, a device is introduced including a leaflet fastener applicator through a cardiac catheter or other suitable catheter. The leaflet fastener applicator and cardiac catheter can be formed into a kit. A gripper can be used to hold the heart valve leaflets while they are fastened.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Lesion assessment by pacing
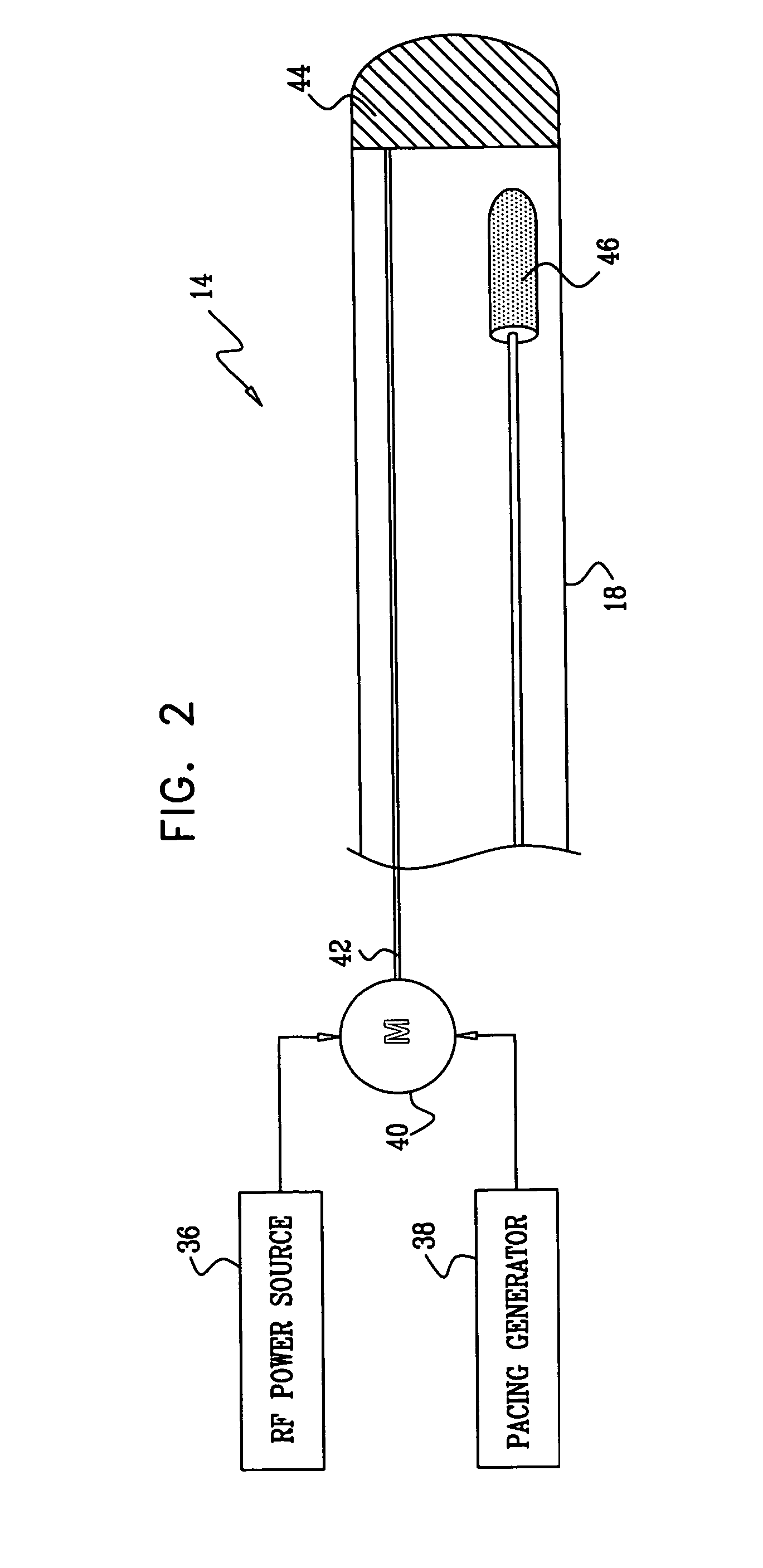
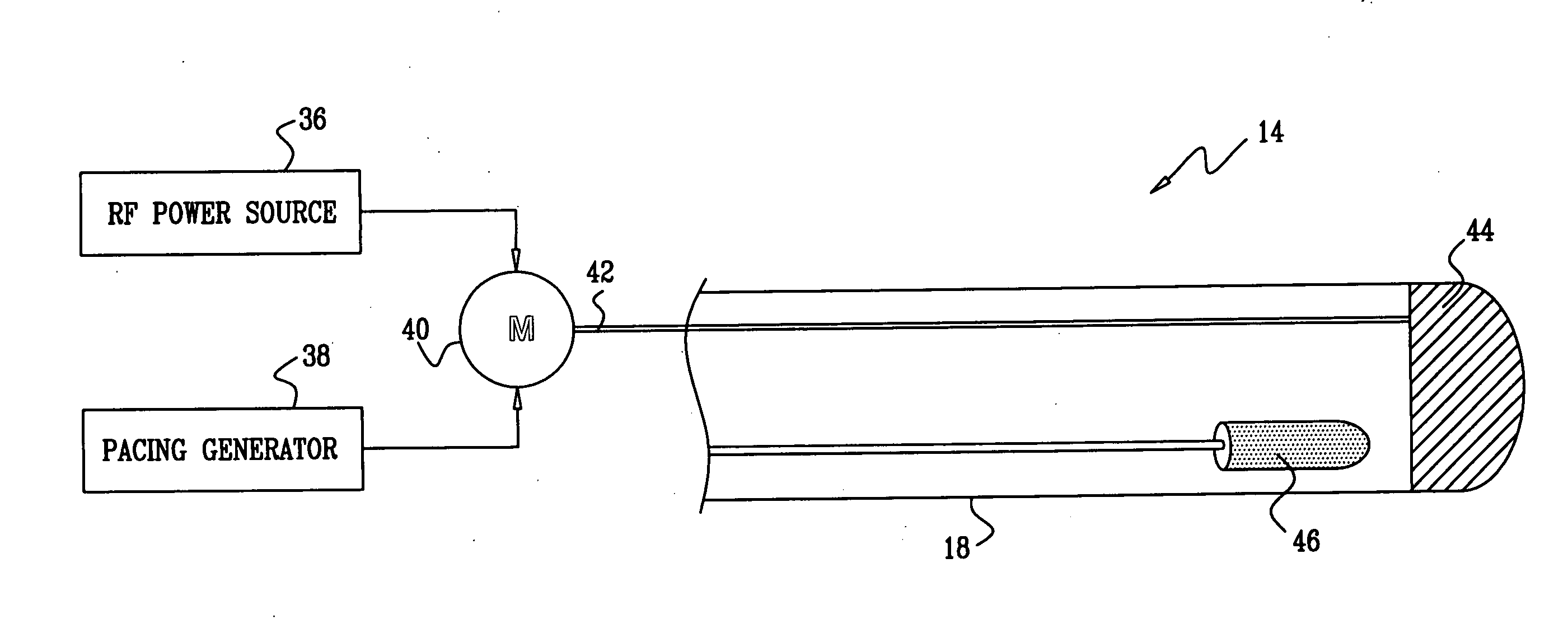
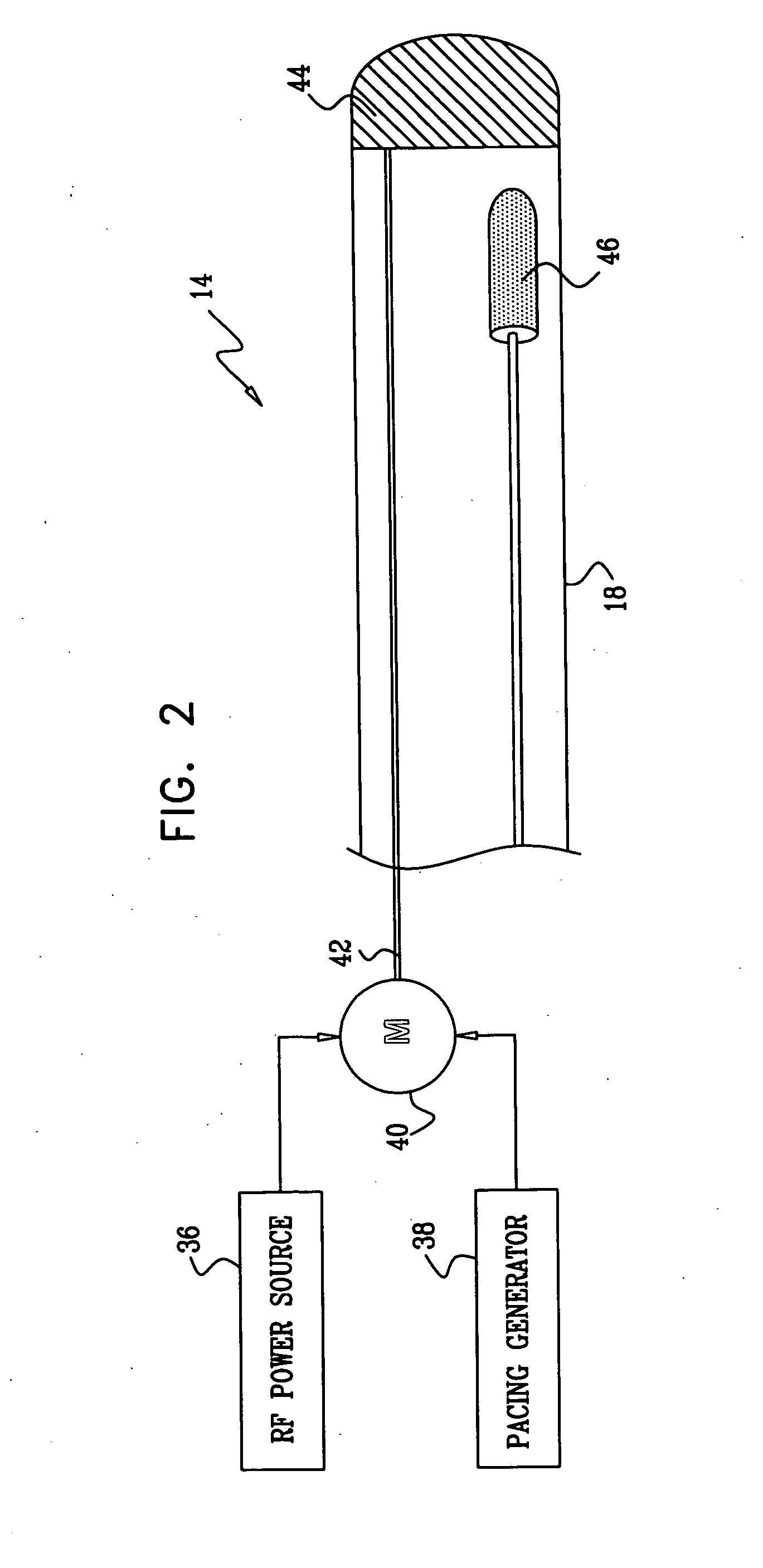
Monitoring intracardiac ablation progress in near real time is accomplished by evaluating capture of a pacing signal while ablation energy is concurrently directed to a target site. Sufficiency of ablation is indicated by failure of signal capture at a maximum predetermined pacing voltage. A common electrode in a cardiac catheter is simultaneously used to test pacing capture and to deliver ablation energy.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
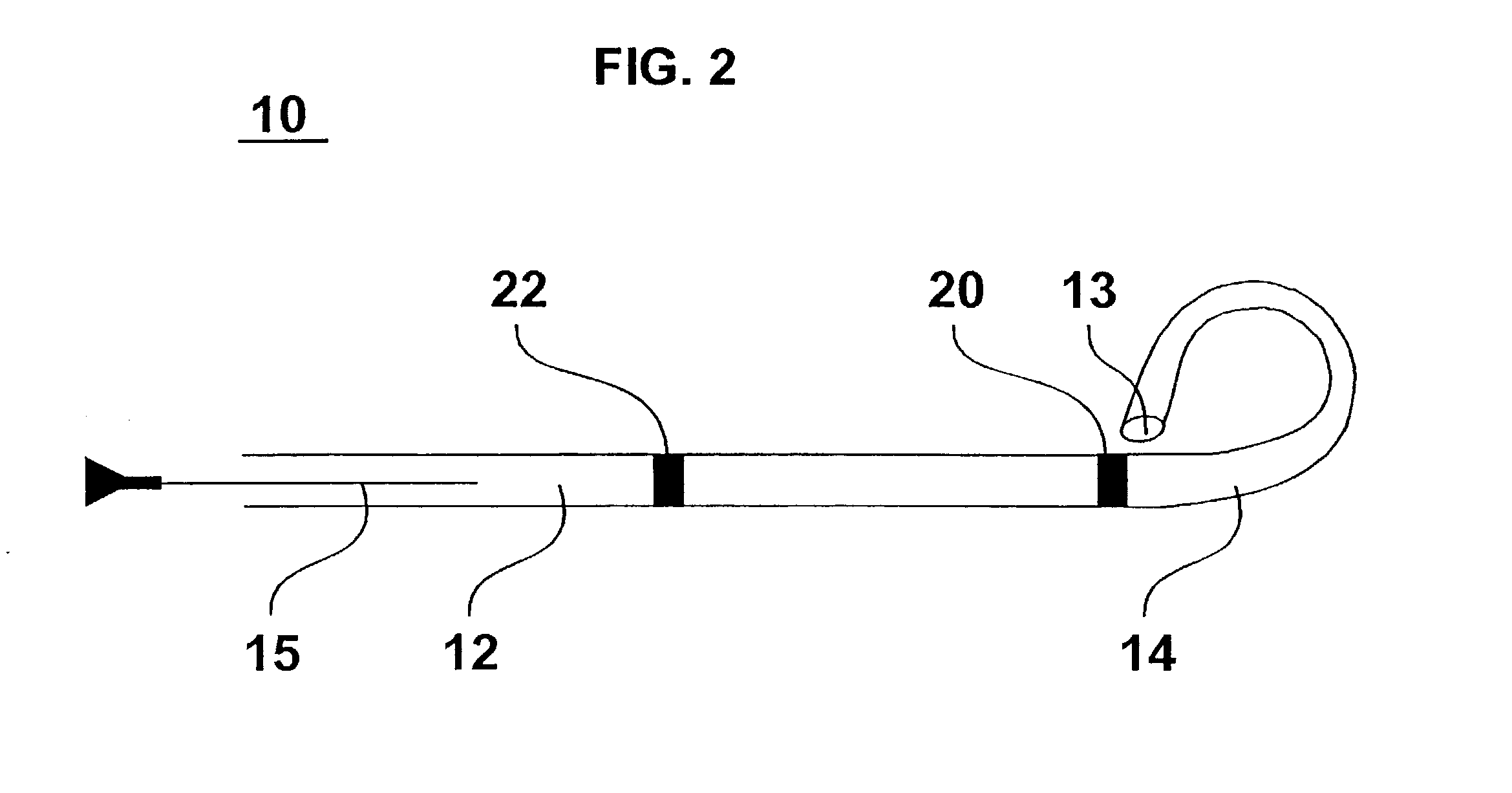
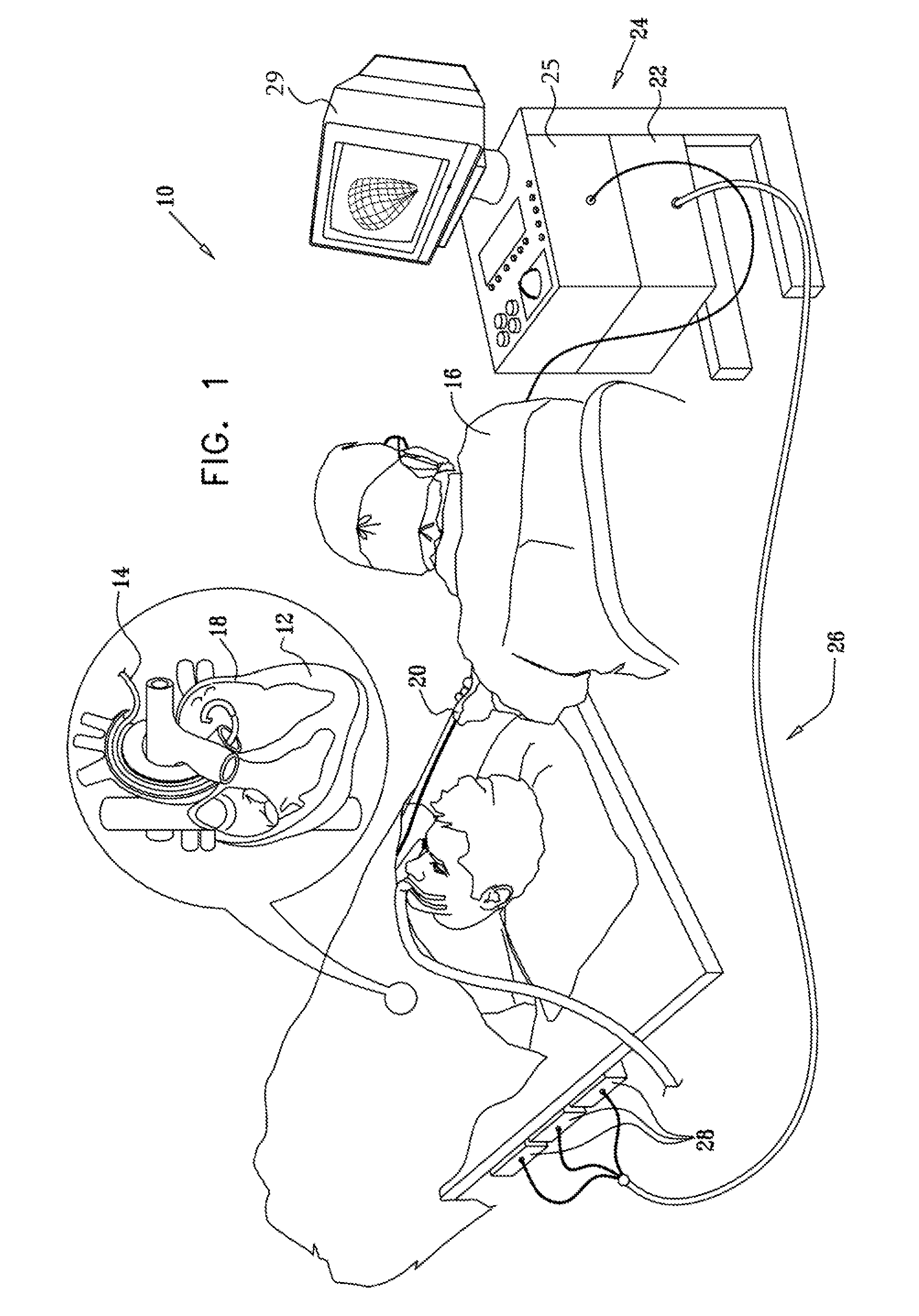
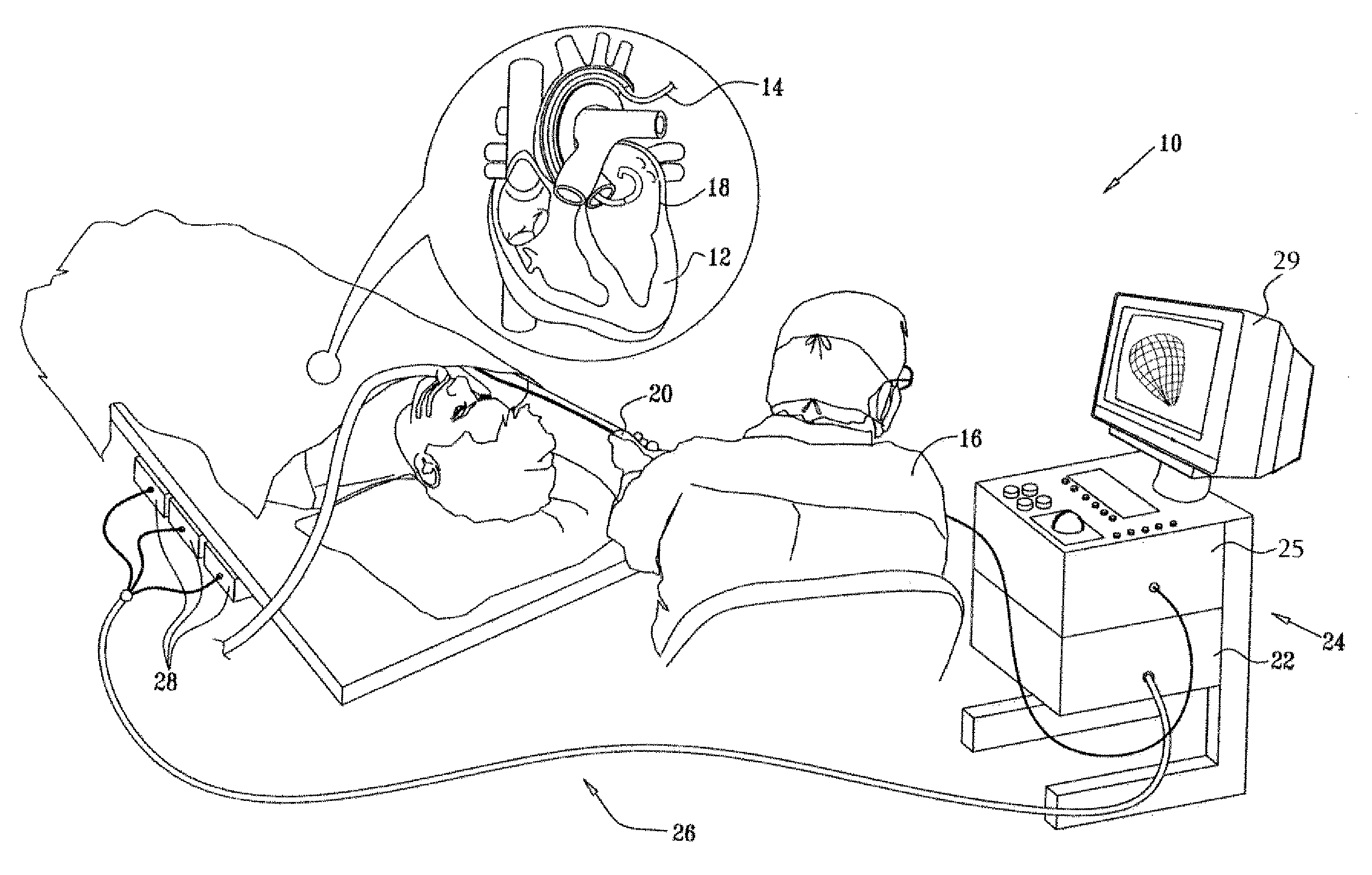
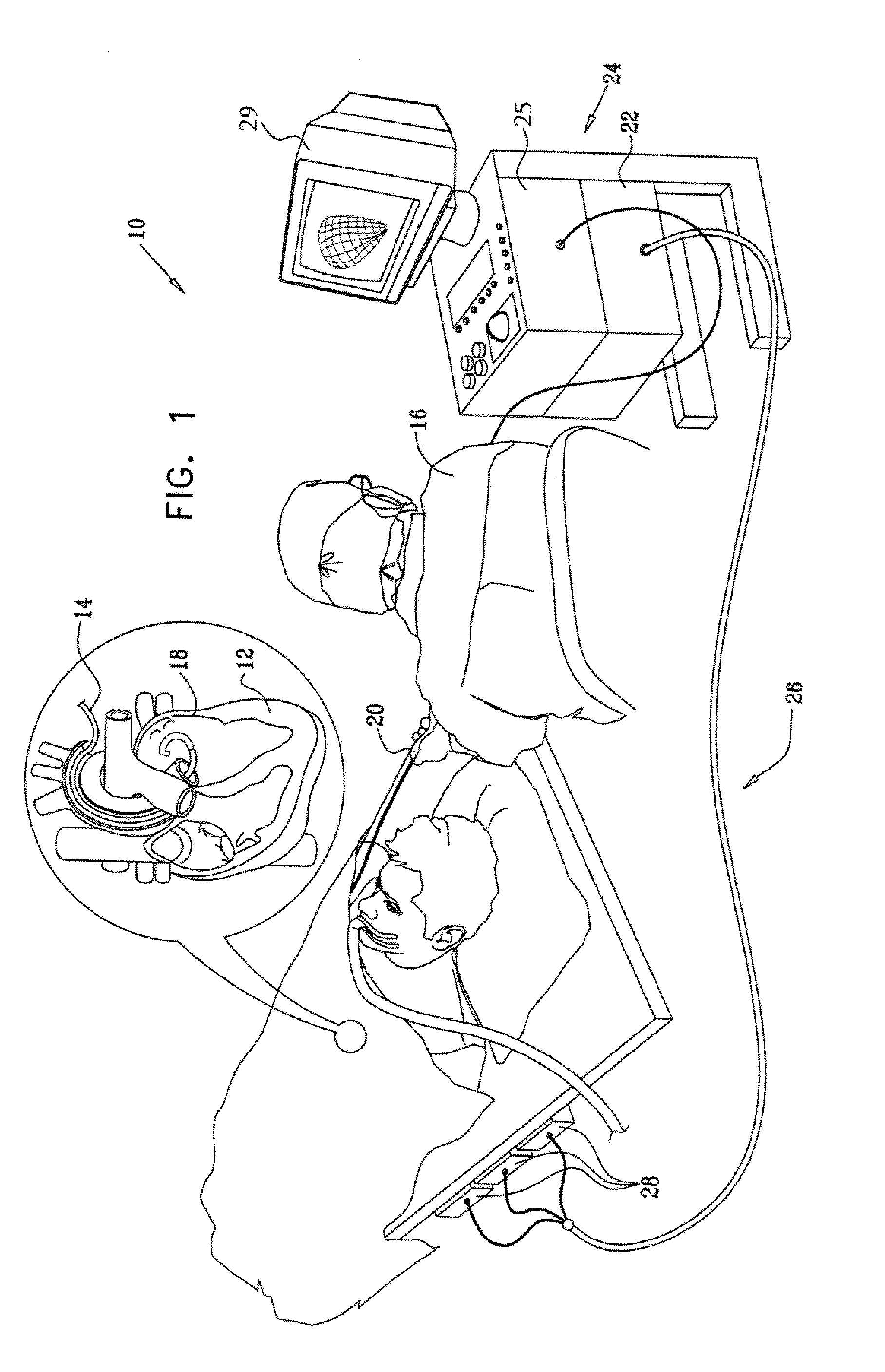
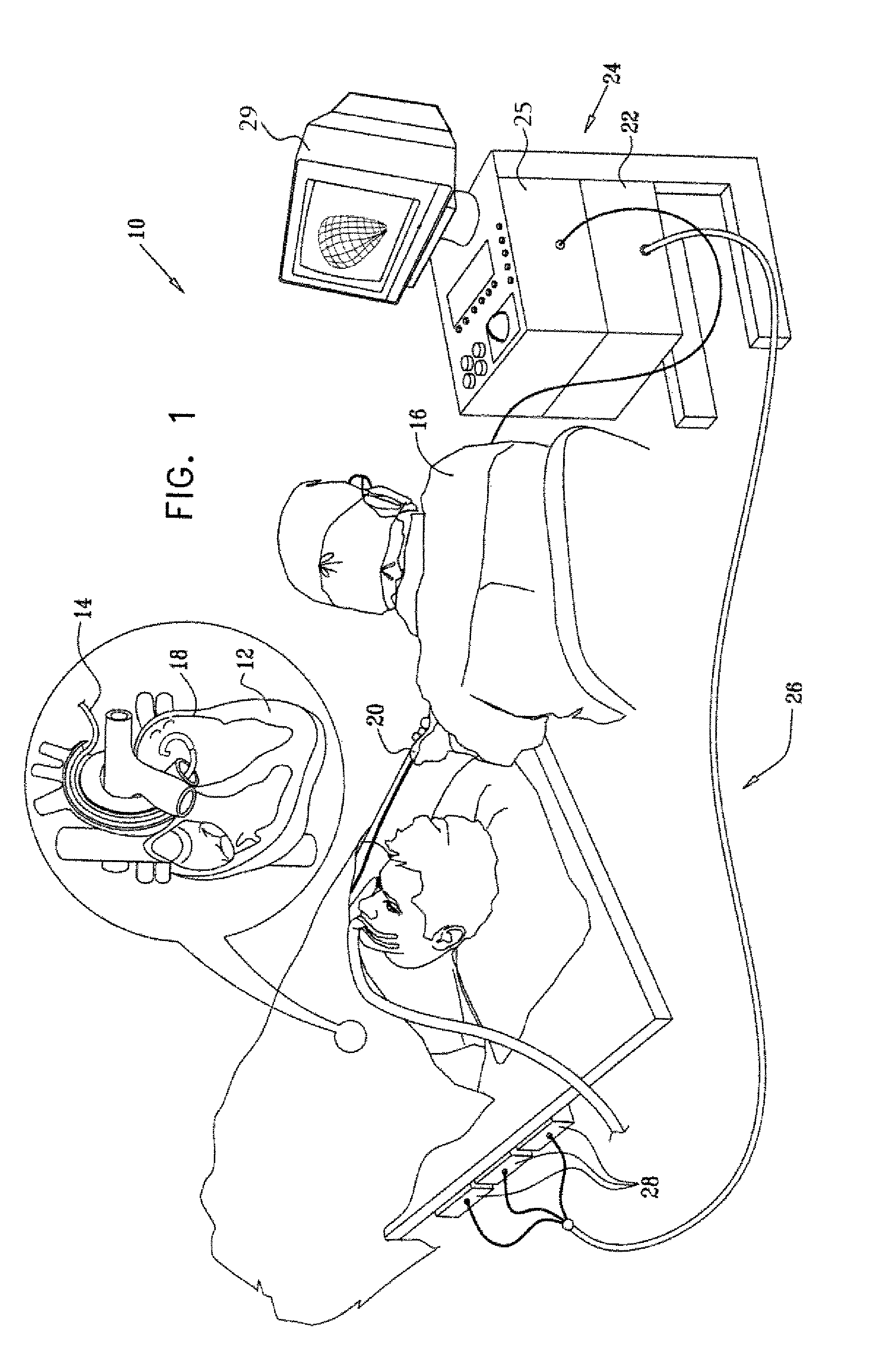
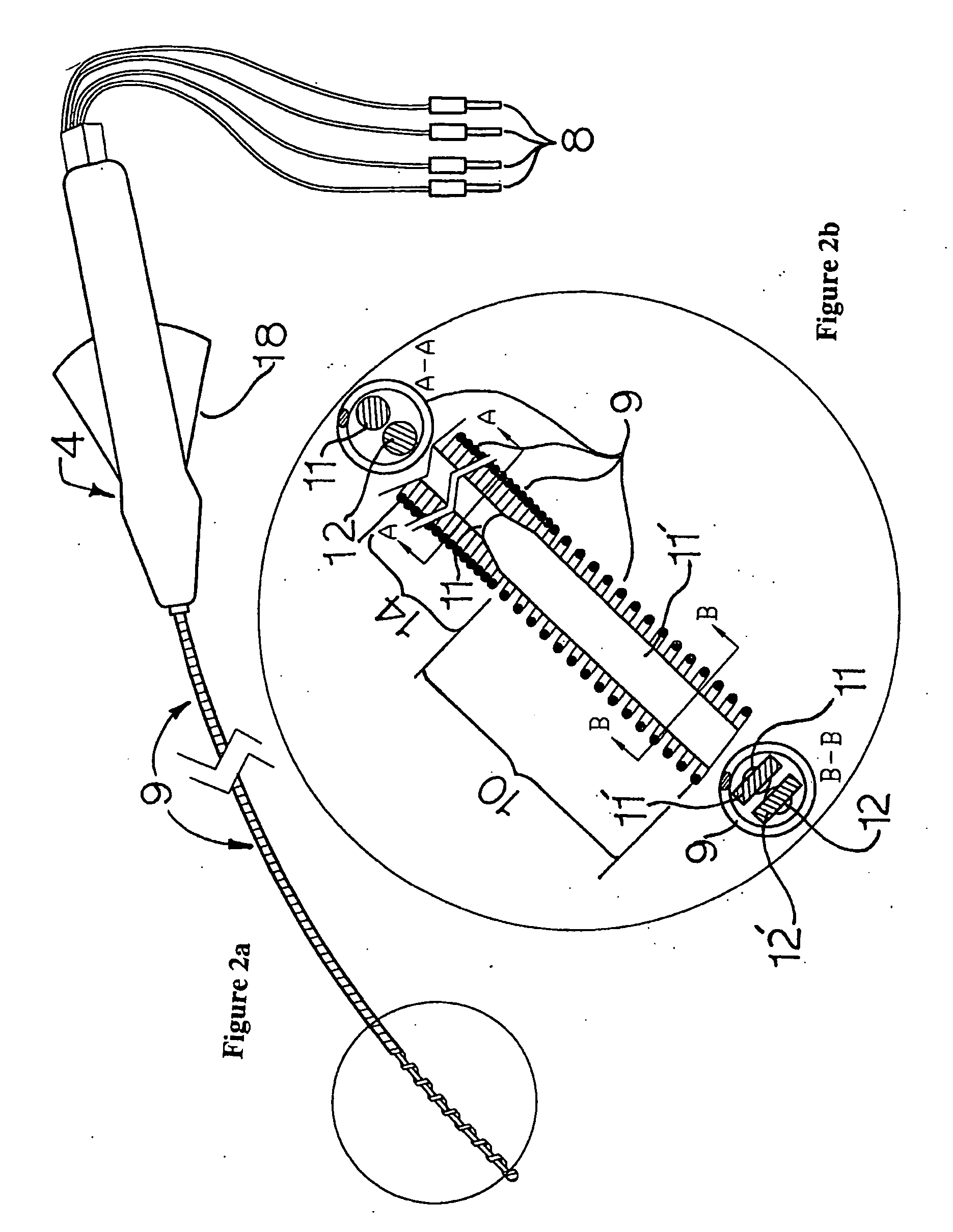
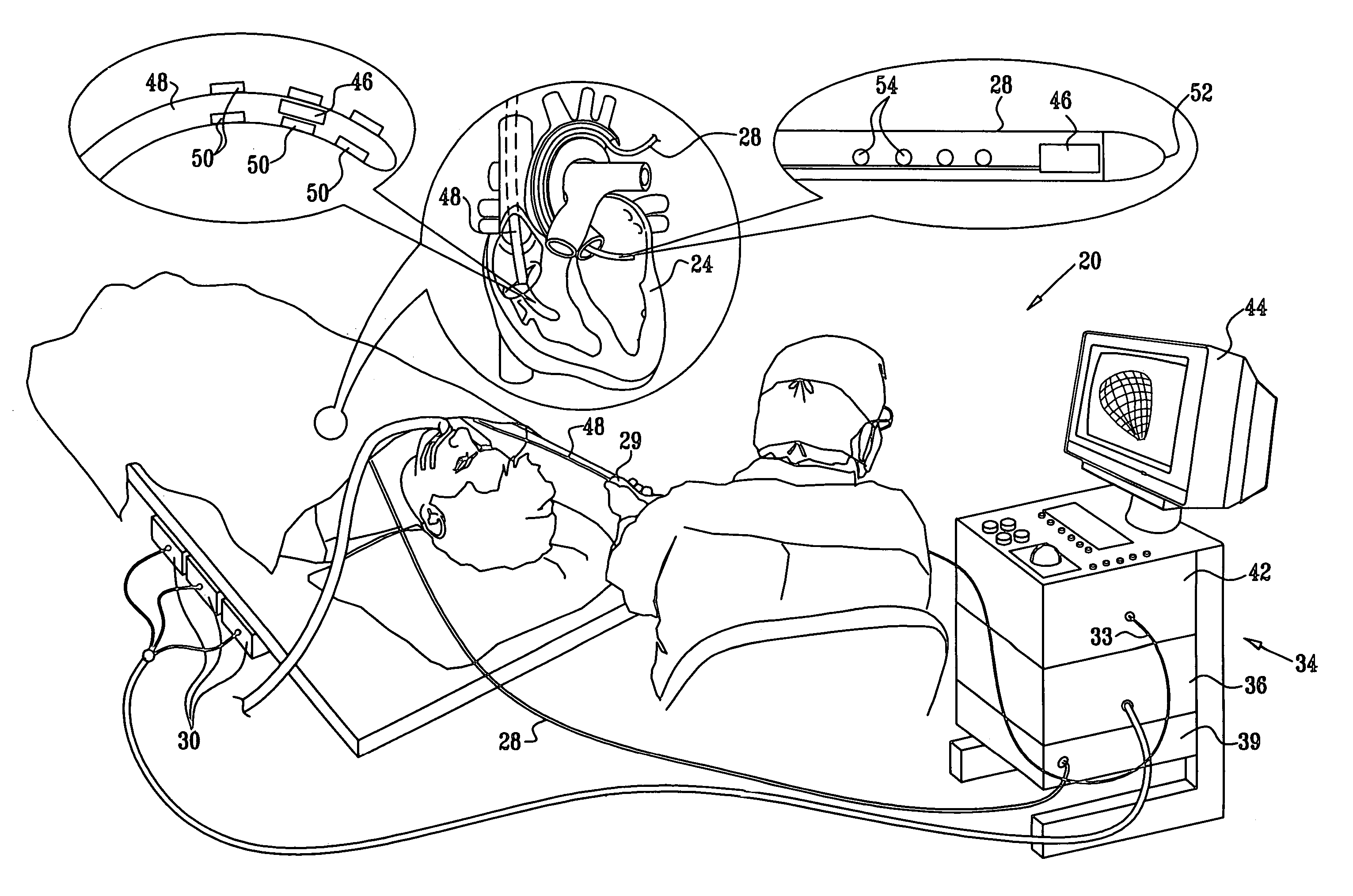
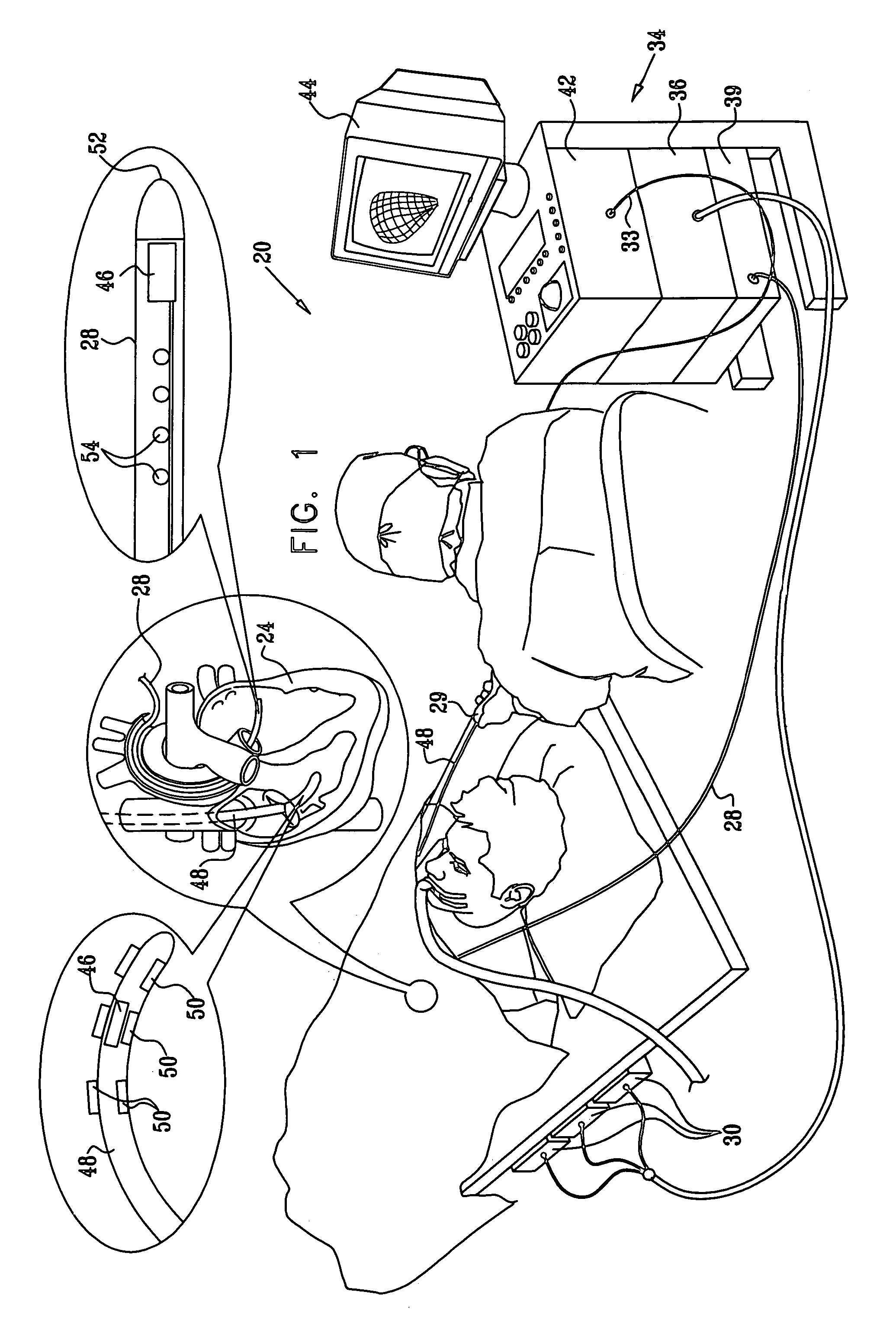
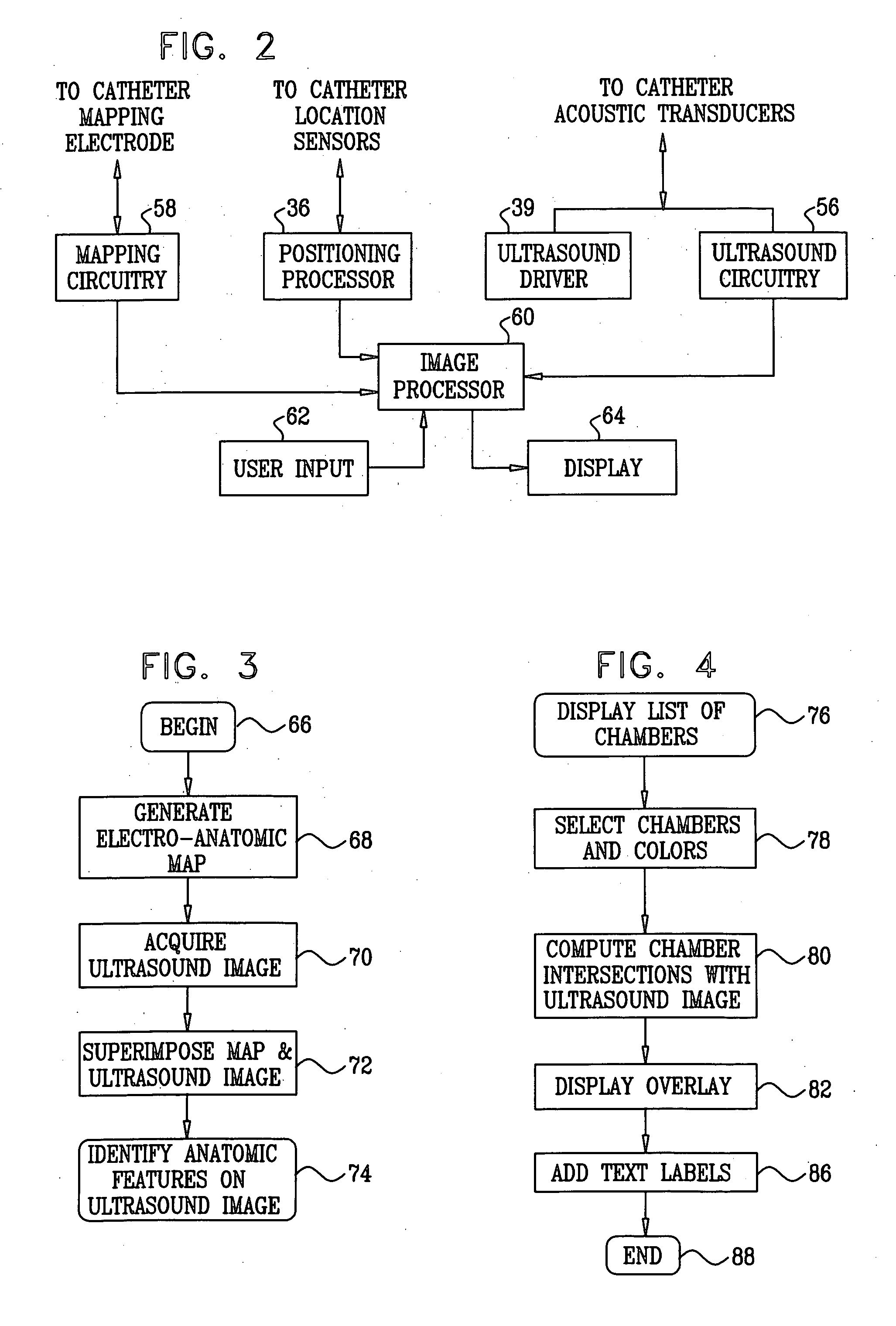
Cardiac catheter imaging system
InactiveUS7187964B2Improve understandingAccurate guideElectrocardiographyCatheterHumans tissuesCatheter device
Owner:KHOURY DIRAR S
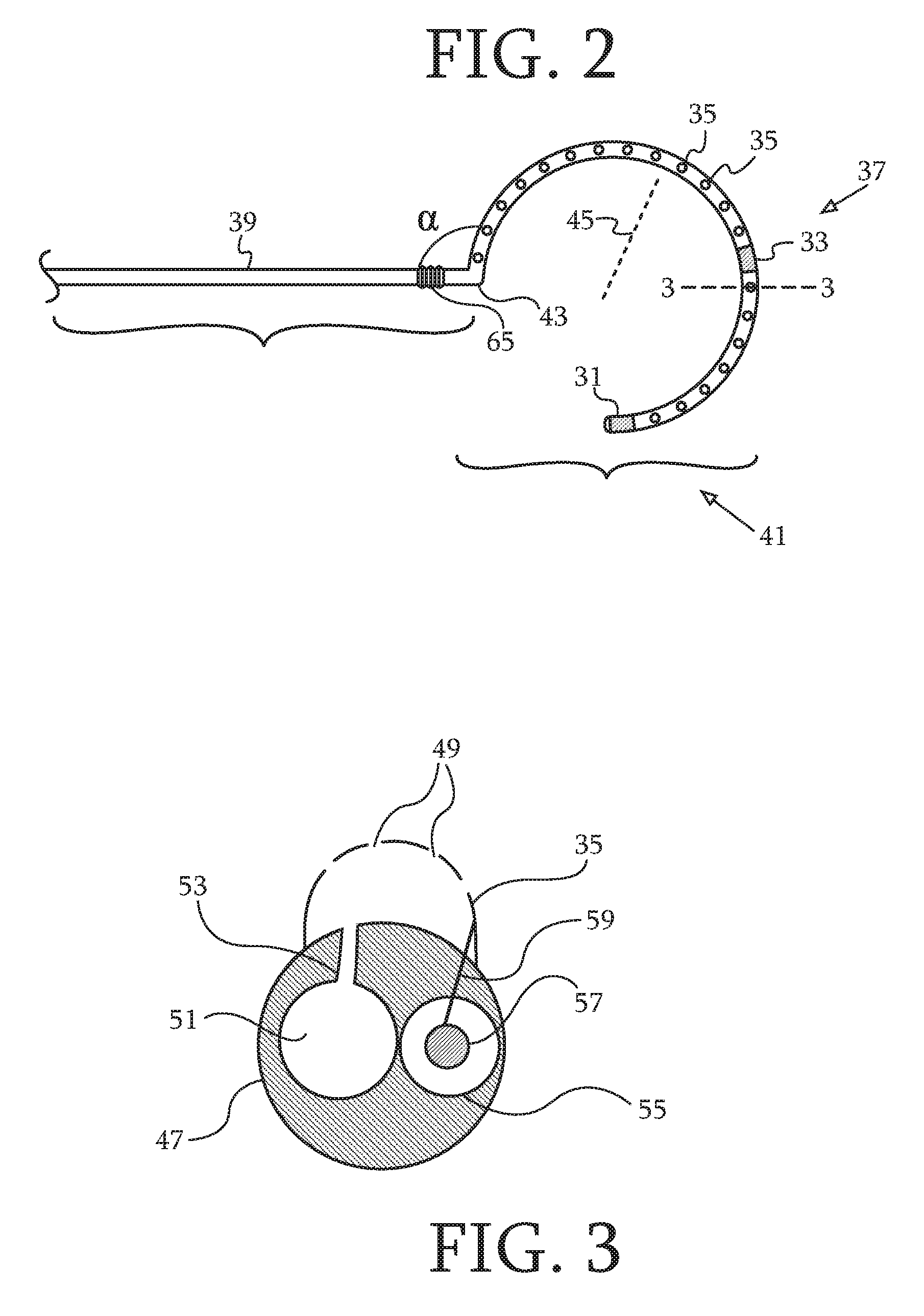
Dual-Purpose Lasso Catheter with Irrigation
ActiveUS20100168548A1Electrical resistance is minimizedDrag minimizationElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesElectrical connectionDual purpose
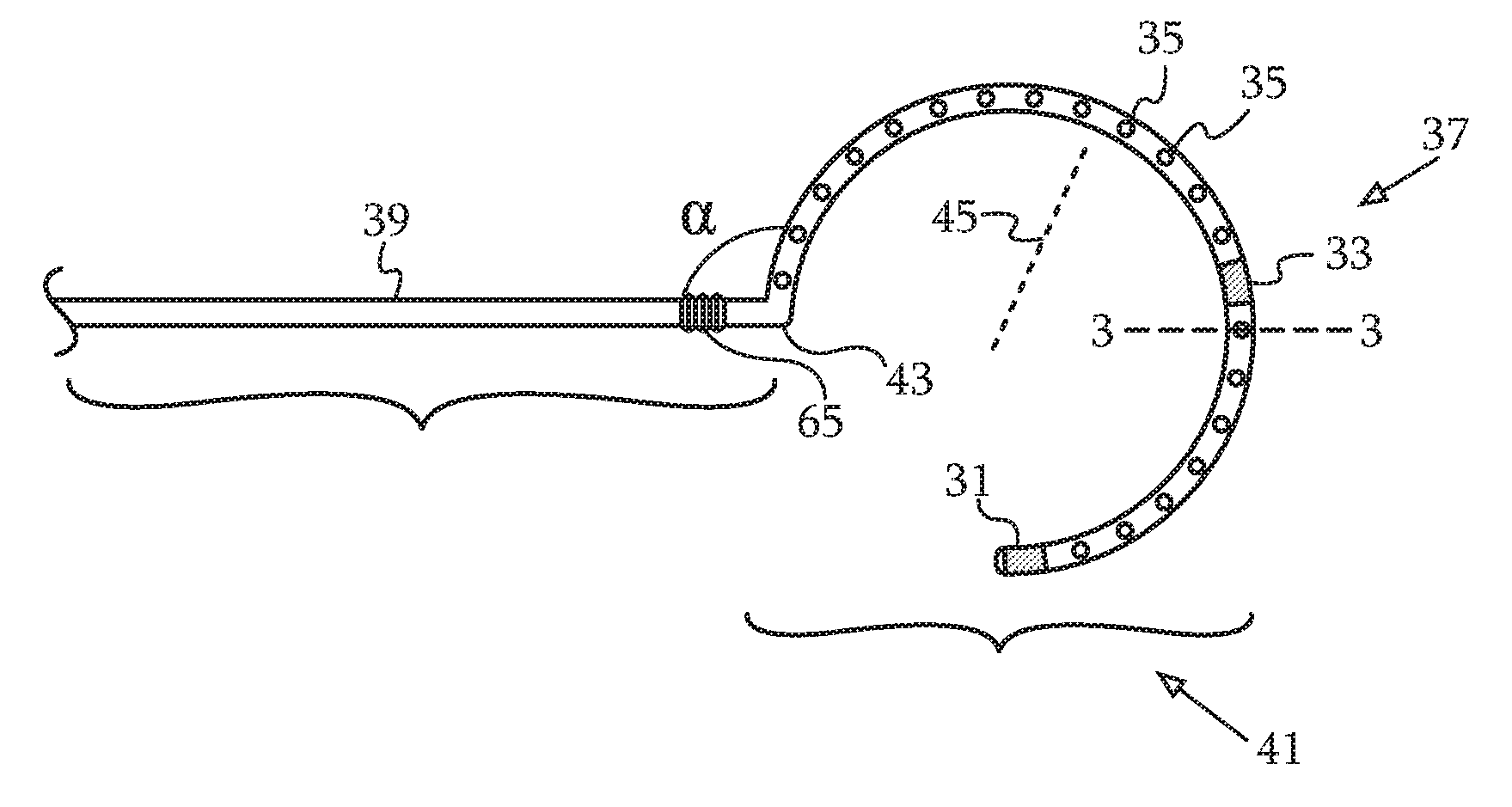
Cardiac catheters, including a lasso catheter, are provided for use in a system for electrical mapping of the heart has an array of raised, perforated electrodes, which are in fluid communication with an irrigating lumen. There are position sensors on a distal loop section and on a proximal base section of the catheter. The electrodes are sensing electrodes that may be adapted for pacing or ablation. The raised electrodes securely contact cardiac tissue, forming electrical connections having little resistance.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Bilumen guide catheters for accessing cardiac sites
ActiveUS20040116878A1Meet actual needsAdvantageously employedTransvascular endocardial electrodesCatheterHeart chamberElectrical stimulations
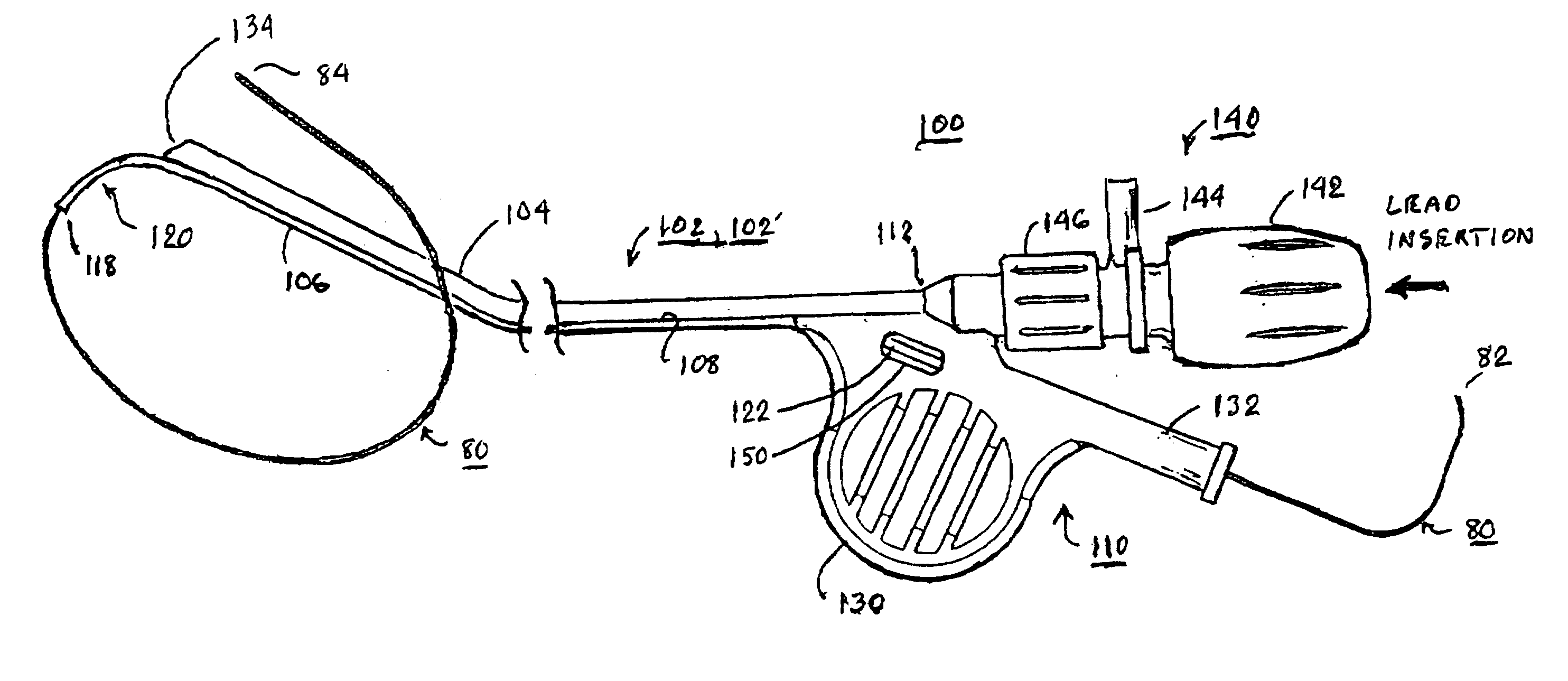
Bilumen catheters and methods of using same for facilitating implantation of cardiac leads for applying electrical stimulation to and / or sensing electrical activity of the heart through one or more electrode positioned at an implantation site within a heart chamber or cardiac vessel adjacent a heart chamber, and more particularly to a method and apparatus for introducing such a cardiac lead having low torqueability and pushability through a tortuous pathway to enable attachment of the cardiac lead at the implantation site employing a bilumen guide catheter are disclosed. The bilumen catheter body includes a relatively large diameter delivery lumen to introduce a small diameter cardiac lead and a small diameter guide lumen to receive a stylet or guidewire to locate the guide catheter body distal end at the implantation site. The small diameter lumen within a small diameter guide tube extends distally from the delivery exit port of the delivery lumen.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Dual-purpose lasso catheter with irrigation
ActiveUS8475450B2Drag minimizationImprove spatial resolutionElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesElectrical connectionDual purpose
Cardiac catheters, including a lasso catheter, are provided for use in a system for electrical mapping of the heart has an array of raised, perforated electrodes, which are in fluid communication with an irrigating lumen. There are position sensors on a distal loop section and on a proximal base section of the catheter. The electrodes are sensing electrodes that may be adapted for pacing or ablation. The raised electrodes securely contact cardiac tissue, forming electrical connections having little resistance.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
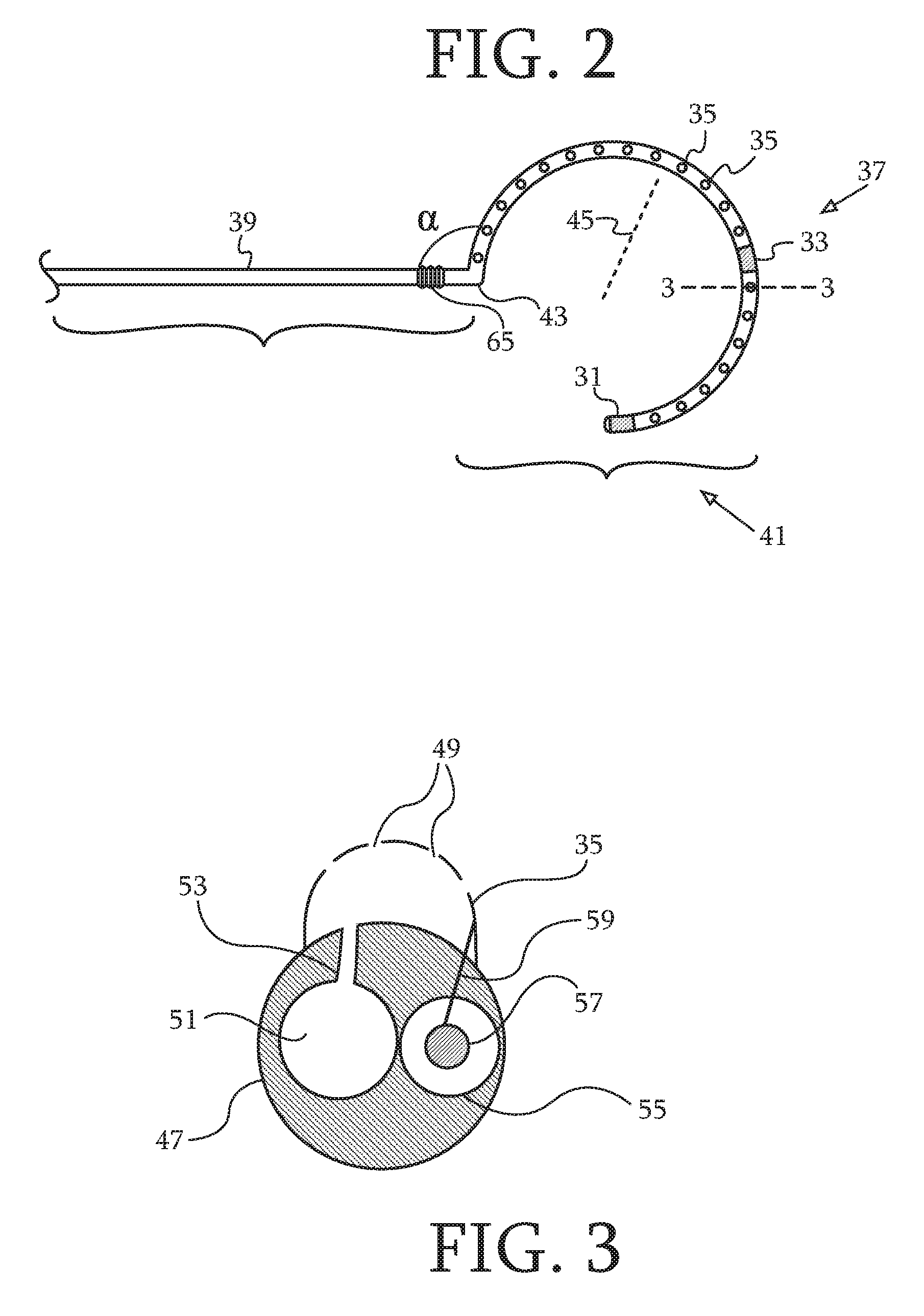
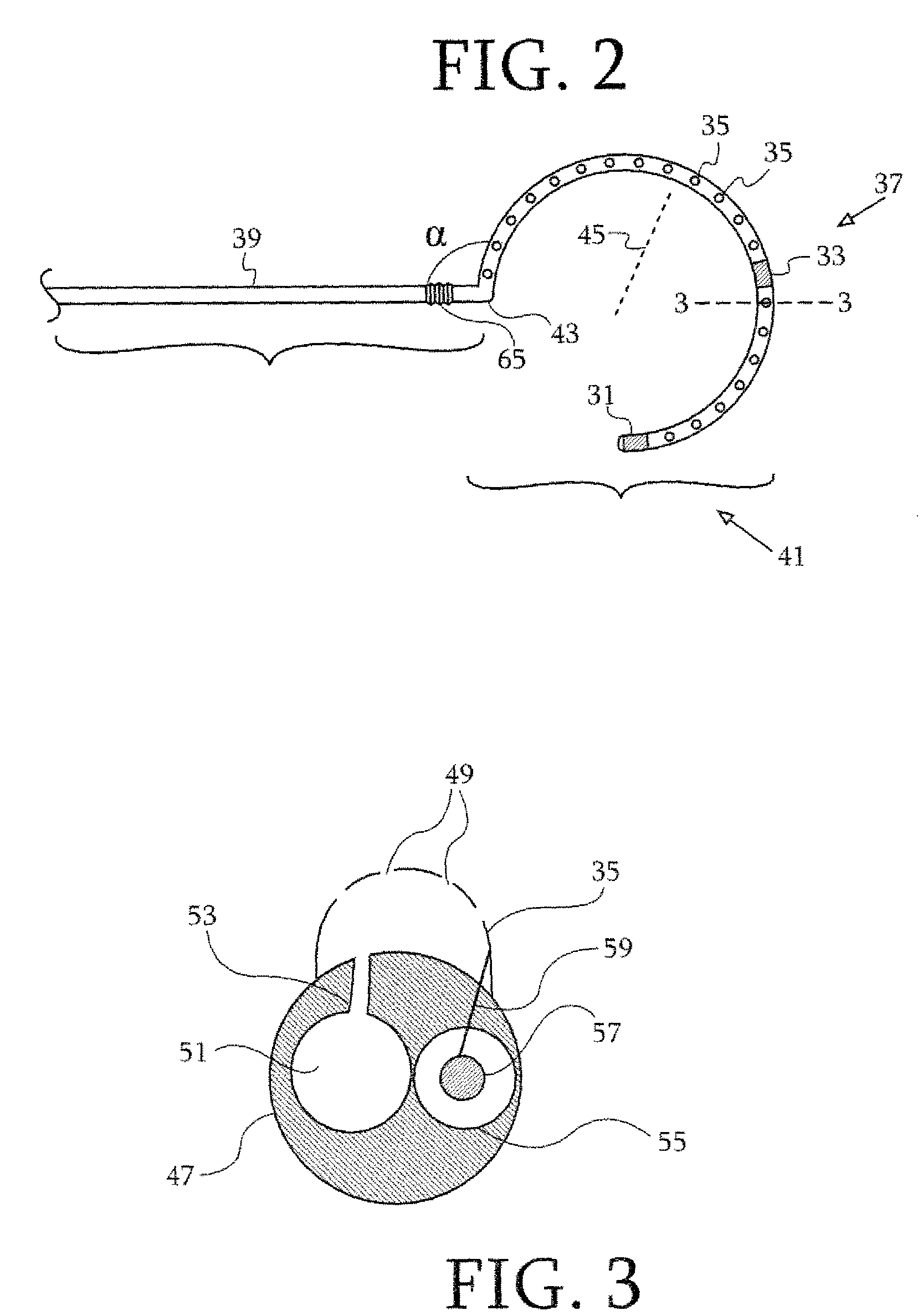
Dual-purpose lasso catheter with irrigation using circumferentially arranged ring bump electrodes
ActiveUS20100222859A1Electrical resistance is minimizedDrag minimizationUltrasound therapyElectrocardiographyUrologyCardiac Catheters
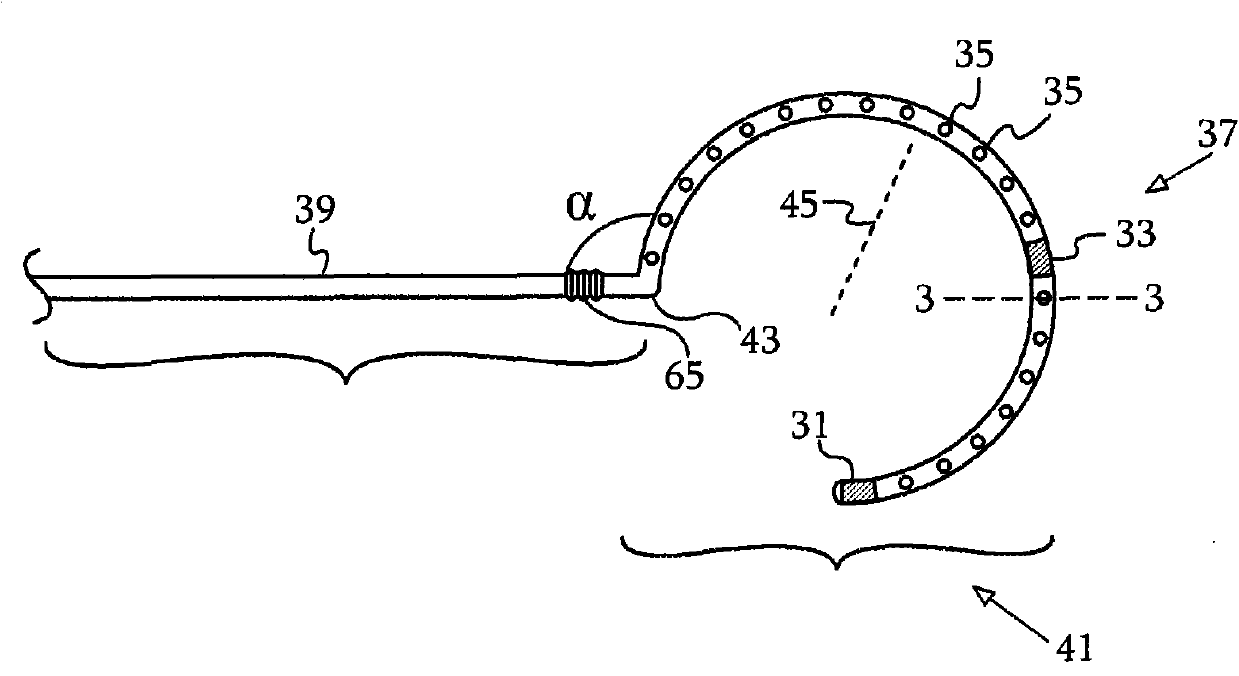
Cardiac catheters, including a lasso catheter, are provided for use in a system for electrical mapping and ablation of the heart has an array of raised, circumferential ring bump electrodes wherein each circumferential electrode has multiple perforations, which are in fluid communication with a cavity or chamber formed under the surface of the circumferential ring. The cavity is formed 360° around the outer surface or loop lumen of the lasso segment of the catheter which is in fluid communication with a breach hole (or holes) drilled through loop lumen and in fluid communication with an irrigating lumen. Each circumferential ring has a breach hole (or holes) that range from smaller to larger from the proximal end of the loop segment to the distal end of the loop segment in one embodiment.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
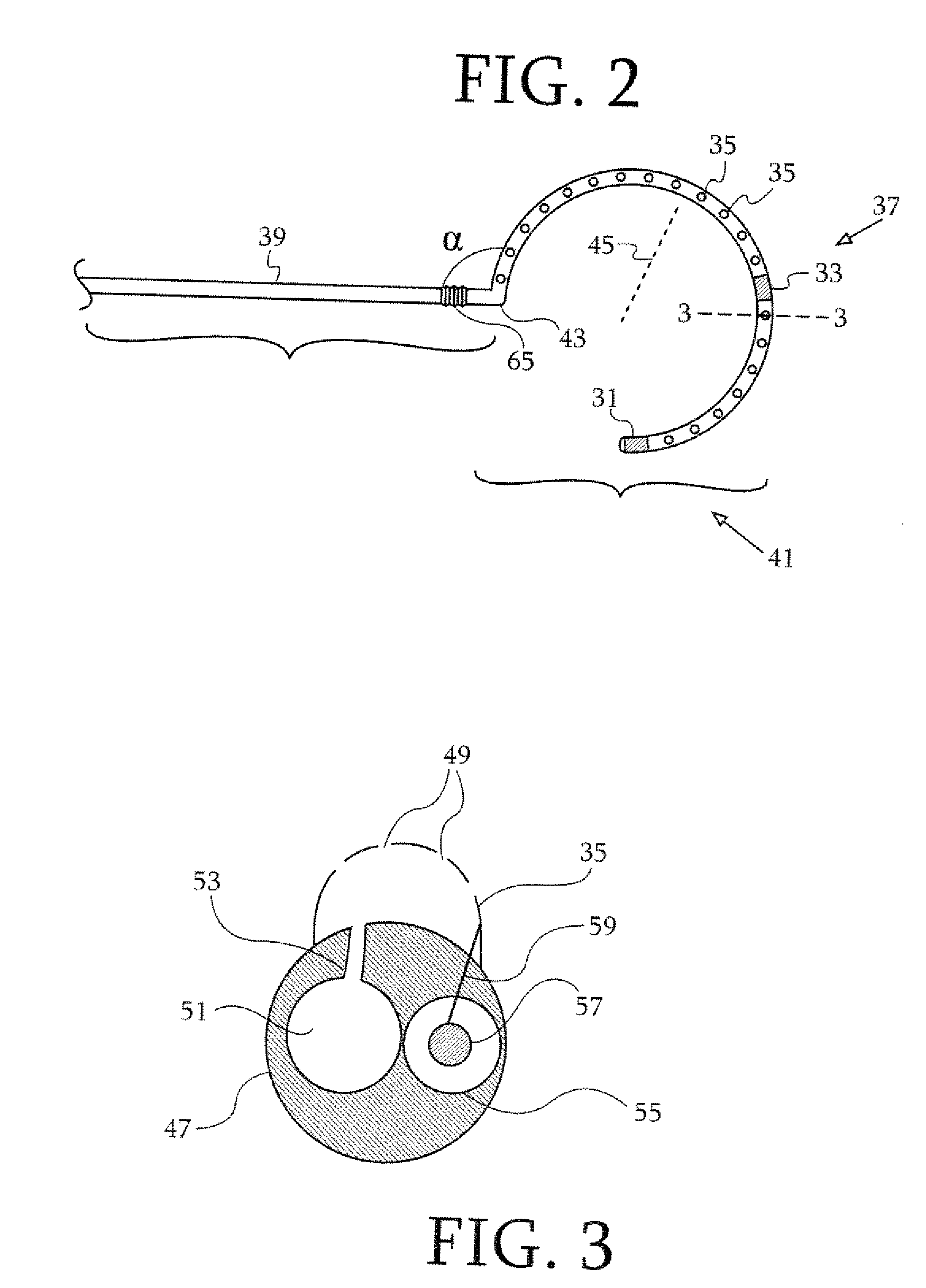
Heart valve leaflet capture device
ActiveUS20170348102A1Efficient captureHeart valvesEvaluation of blood vesselsAcute angleValve leaflet
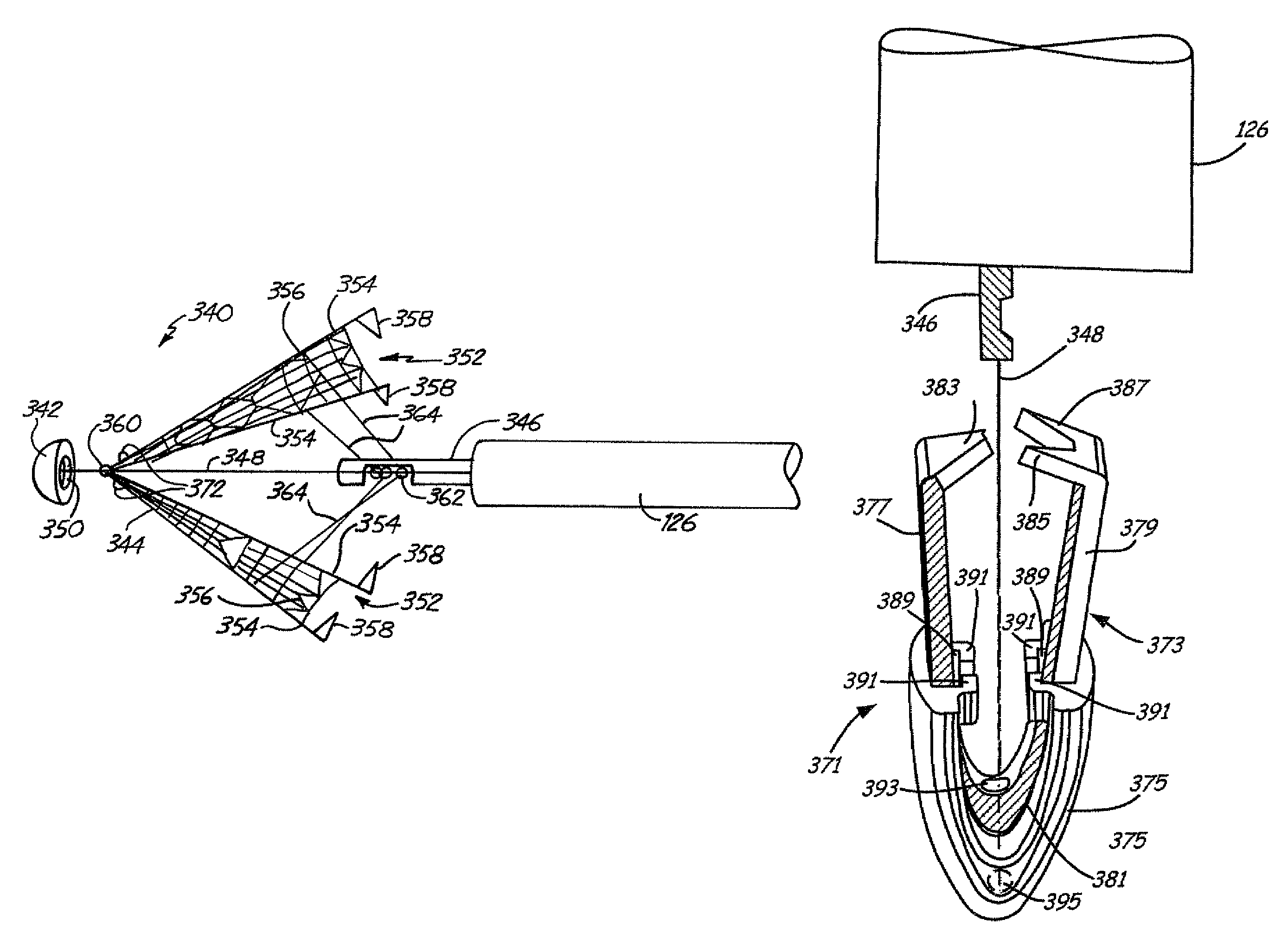
The invention provides a heart valve leaflet capture device (250) comprising a cardiac catheter probe having a proximal end for manipulating the device (250) and a distal end terminating in a transvalve element (256). The transvalve element (256) is configured to pass through a heart valve generally parallel to a longitudinal axis of the catheter and includes two or three leaflet gripping elements (252). The leaflet gripping elements (252) are individually movable by operation of an associated actuating mechanism (260) between a radially retracted position, in which they are withdrawn with respect to the transvalve element (256), and a capture position, in which they diverge outwardly at an acute angle from the transvalve element (256). In the capture position, each leaflet gripping element (252) defines a convergent capture zone that is directed towards the edges of a target valve leaflet and in which the target valve leaflet may be captured.
Owner:STRAIT ACCESS TECH HLDG
Lesion assessment by pacing
Monitoring intracardiac ablation progress in near real time is accomplished by evaluating capture of a pacing signal while ablation energy is concurrently directed to a target site. Sufficiency of ablation is indicated by failure of signal capture at a maximum predetermined pacing voltage. A common electrode in a cardiac catheter is simultaneously used to test pacing capture and to deliver ablation energy.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
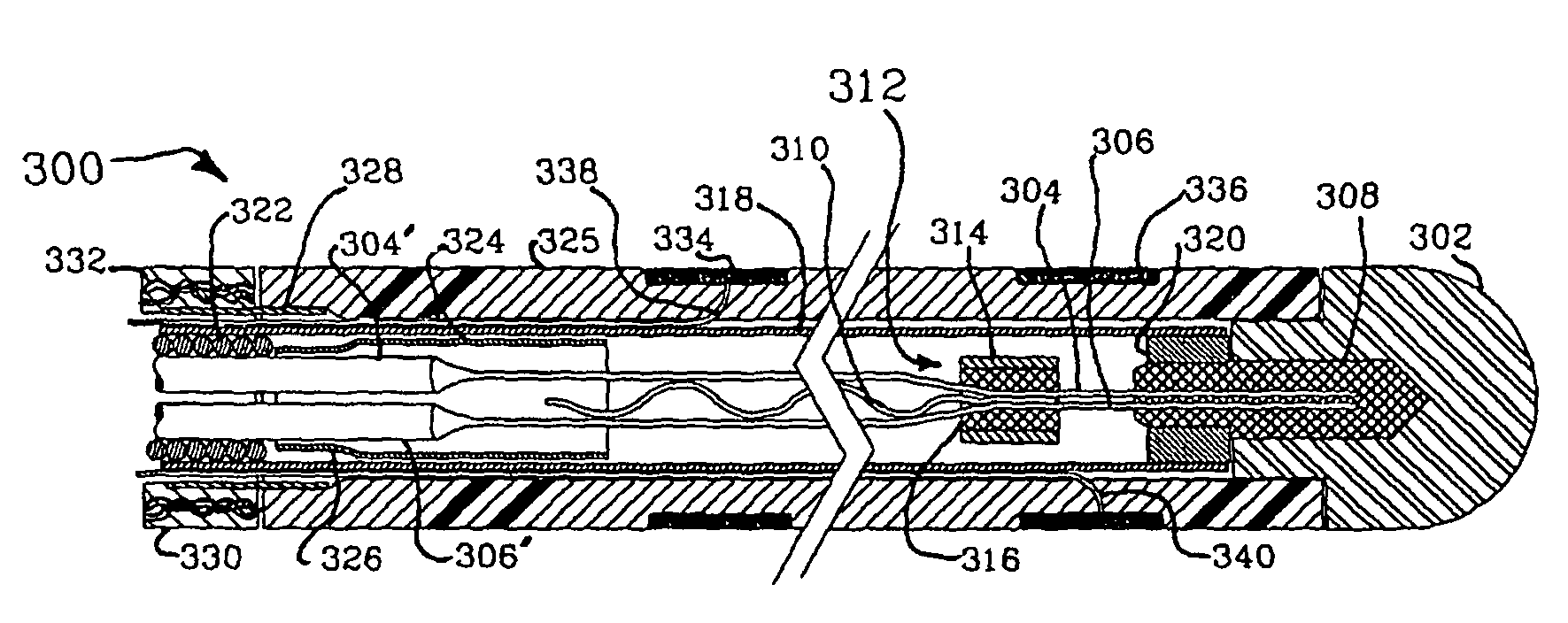
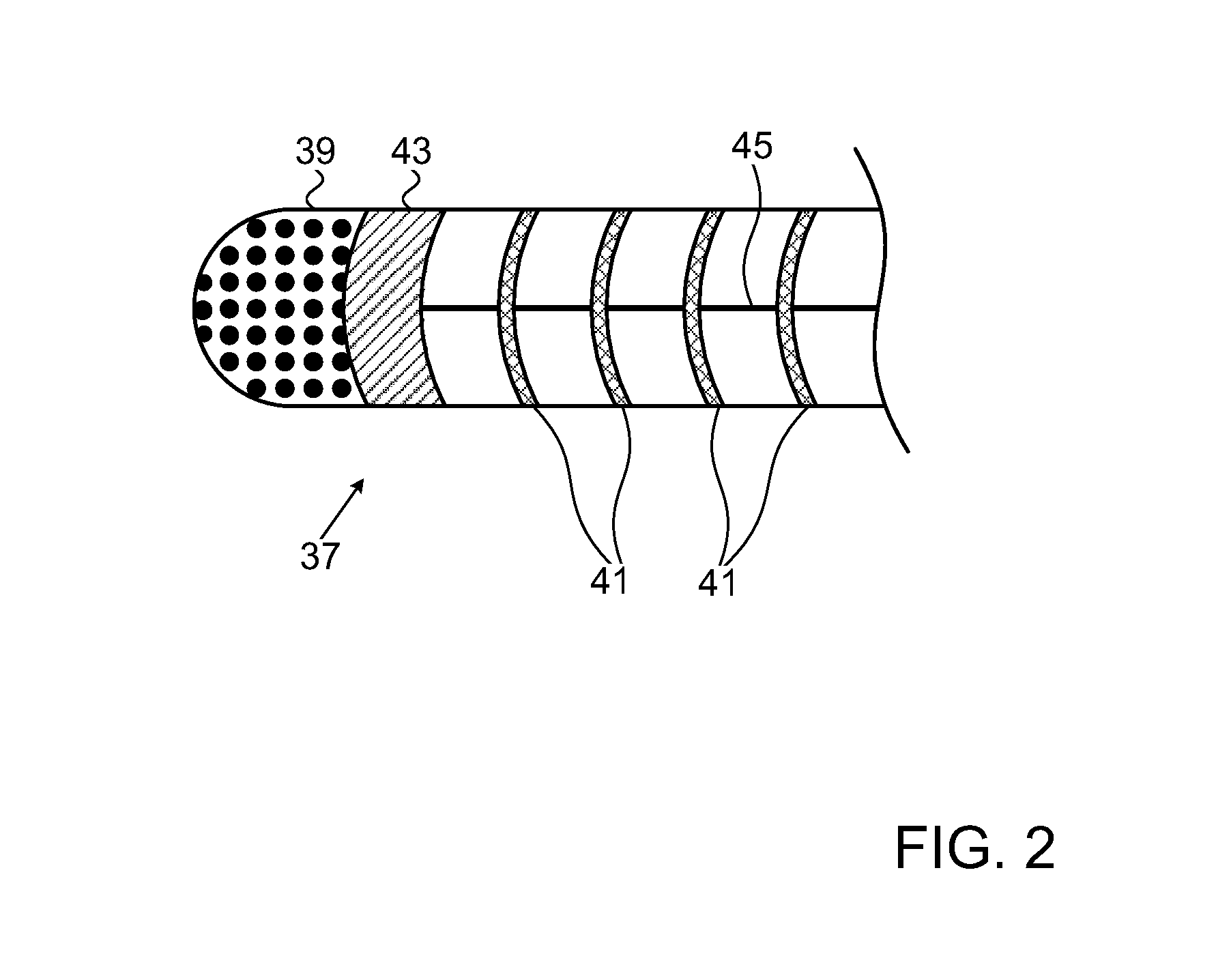
Composite flexible and conductive catheter electrode
InactiveUS20070249923A1Meet functional requirementsAllow flexibilityEnvelopes/bags making machineryEar treatmentContinuous/uninterruptedElectricity
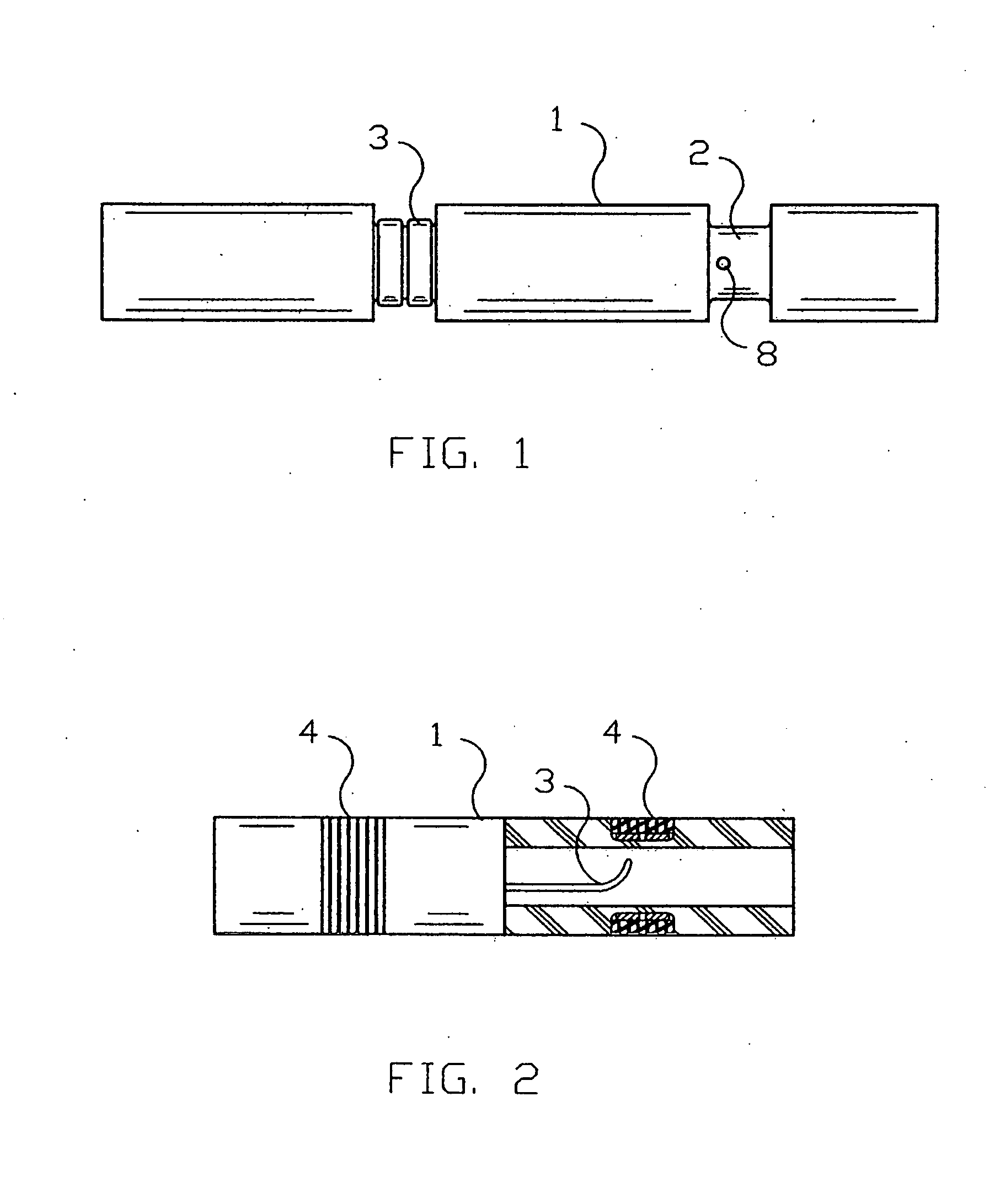
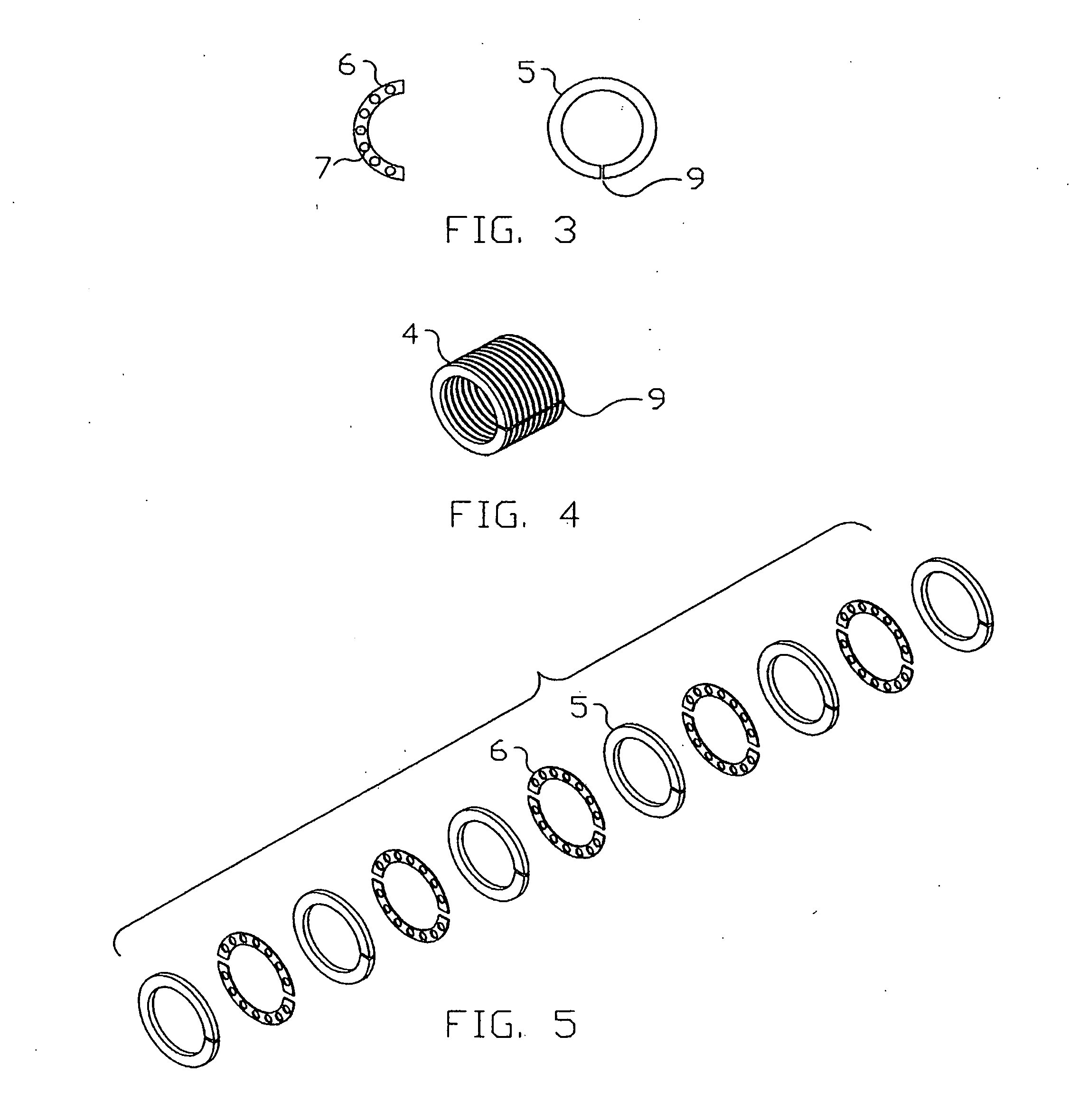
A flexible cardiac catheter for sensing electrical activity within and administering therapy to a patients' heart has a series of flexible, conductive electrode bands positioned in grooves in the catheter's tubular body. The bands consist of alternating flexible and conductive elements, providing flexibility and overall versatility to the catheter. The electrode bands have controllable flexibility due to the elastic properties of the flexible elements and continuous uninterrupted electrical current conductance from the one-piece design of the conductive element. The synergy of the components of the composite flexible and conductive bands will help solve problems current electrode bands have and will allow for a freedom in the design of catheter electrode band configurations in the future.
Owner:KEENAN ERICK
Dual-purpose lasso catheter with irrigation
ActiveCN101766502AElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesCardiac muscle tissueRat heart
The invention relates to a dual-purpose lasso catheter with irrigation. Cardiac catheters, including a lasso catheter, are provided for use in a system for electrical mapping of the heart has an array of raised, perforated electrodes, which are in fluid communication with an irrigating lumen. There are position sensors on a distal loop section and on a proximal base section of the catheter. The electrodes are sensing electrodes that may be adapted for pacing or ablation. The raised electrodes securely contact cardiac tissue, forming electrical connections having little resistance.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
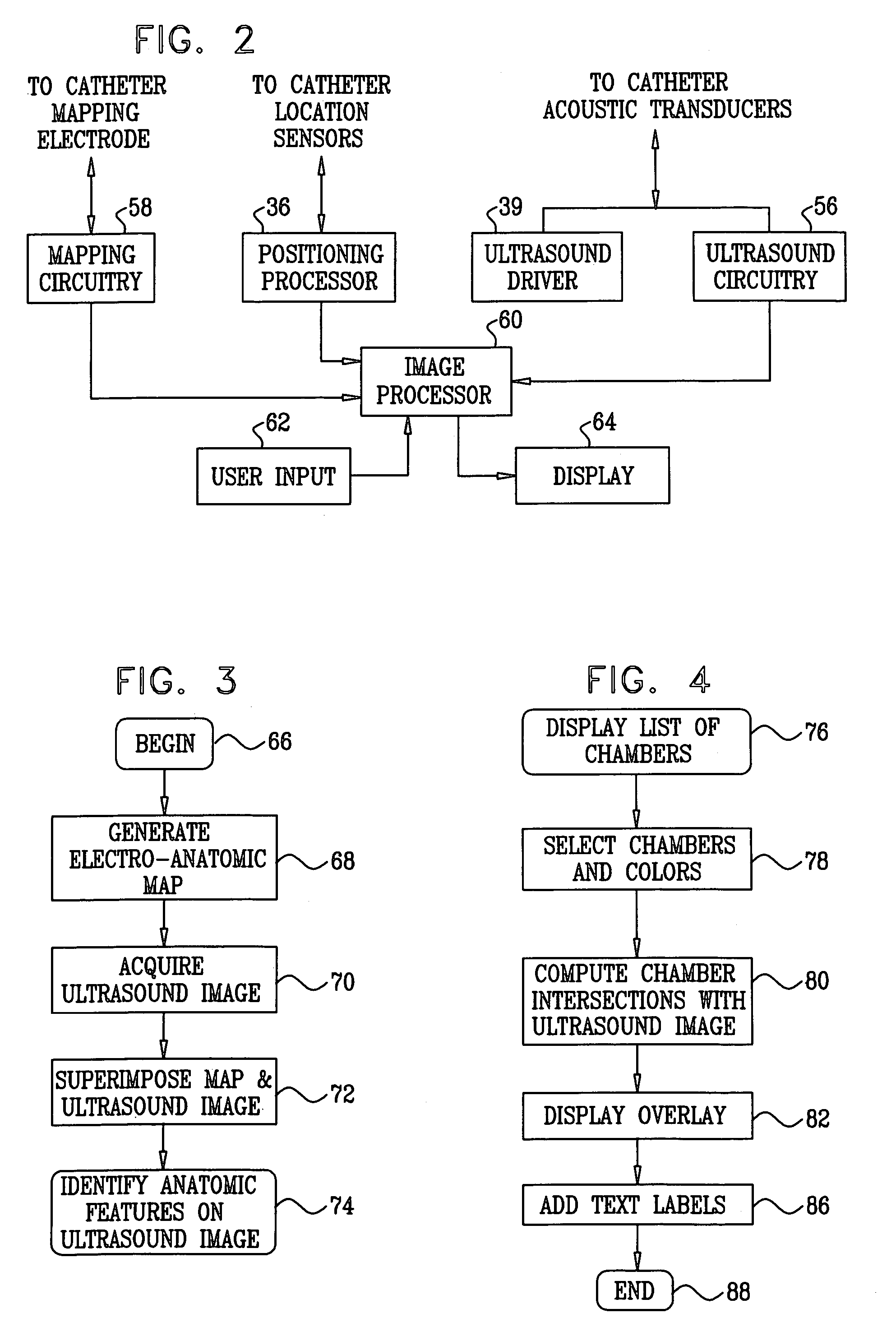
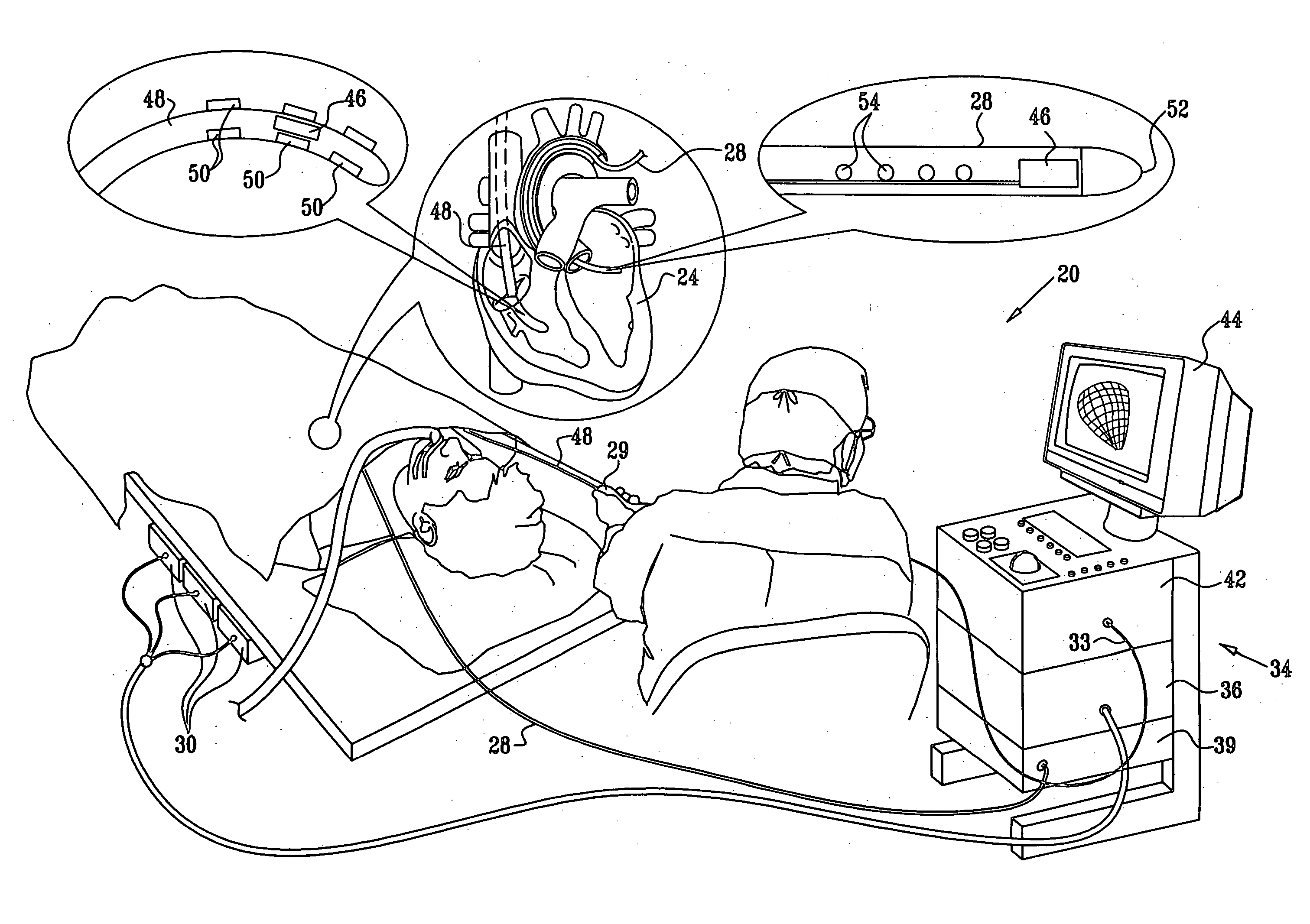
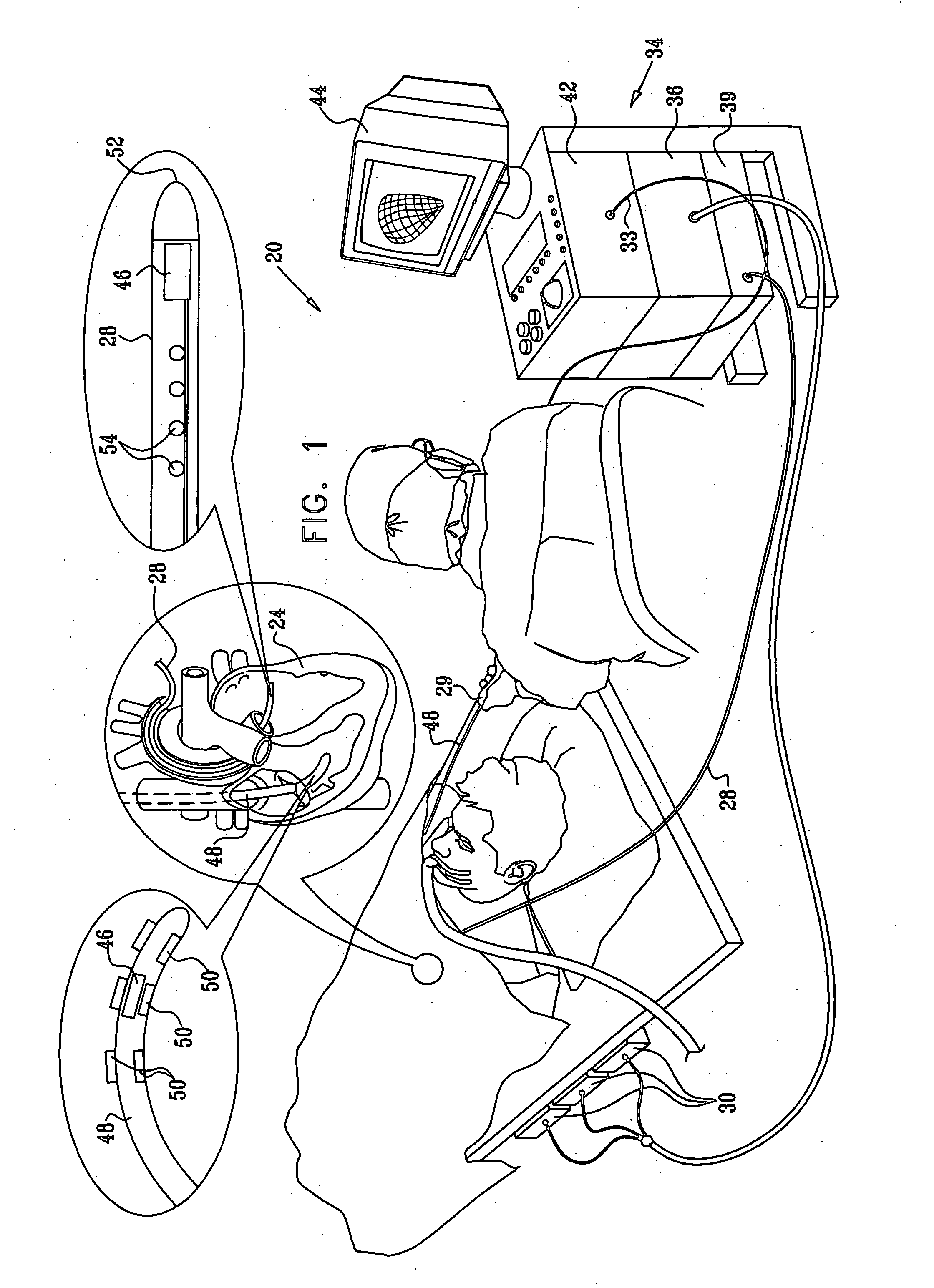
System For Continuous Cardiac Imaging And Mapping
InactiveUS20110118590A1Improve precisionImprove reliabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectricityCardiac imaging
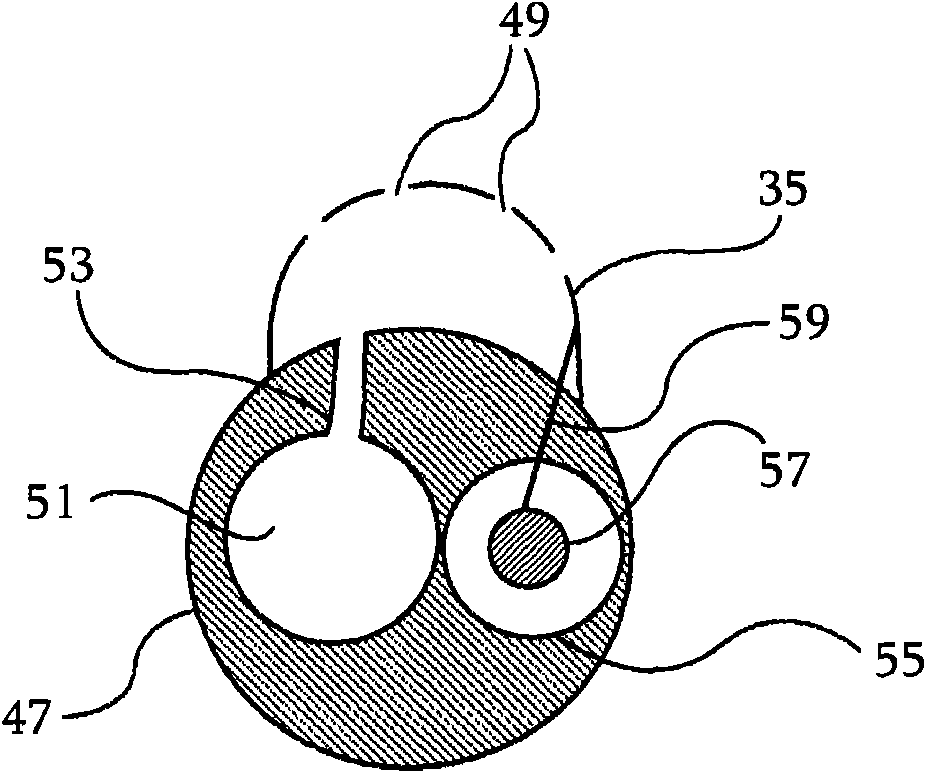
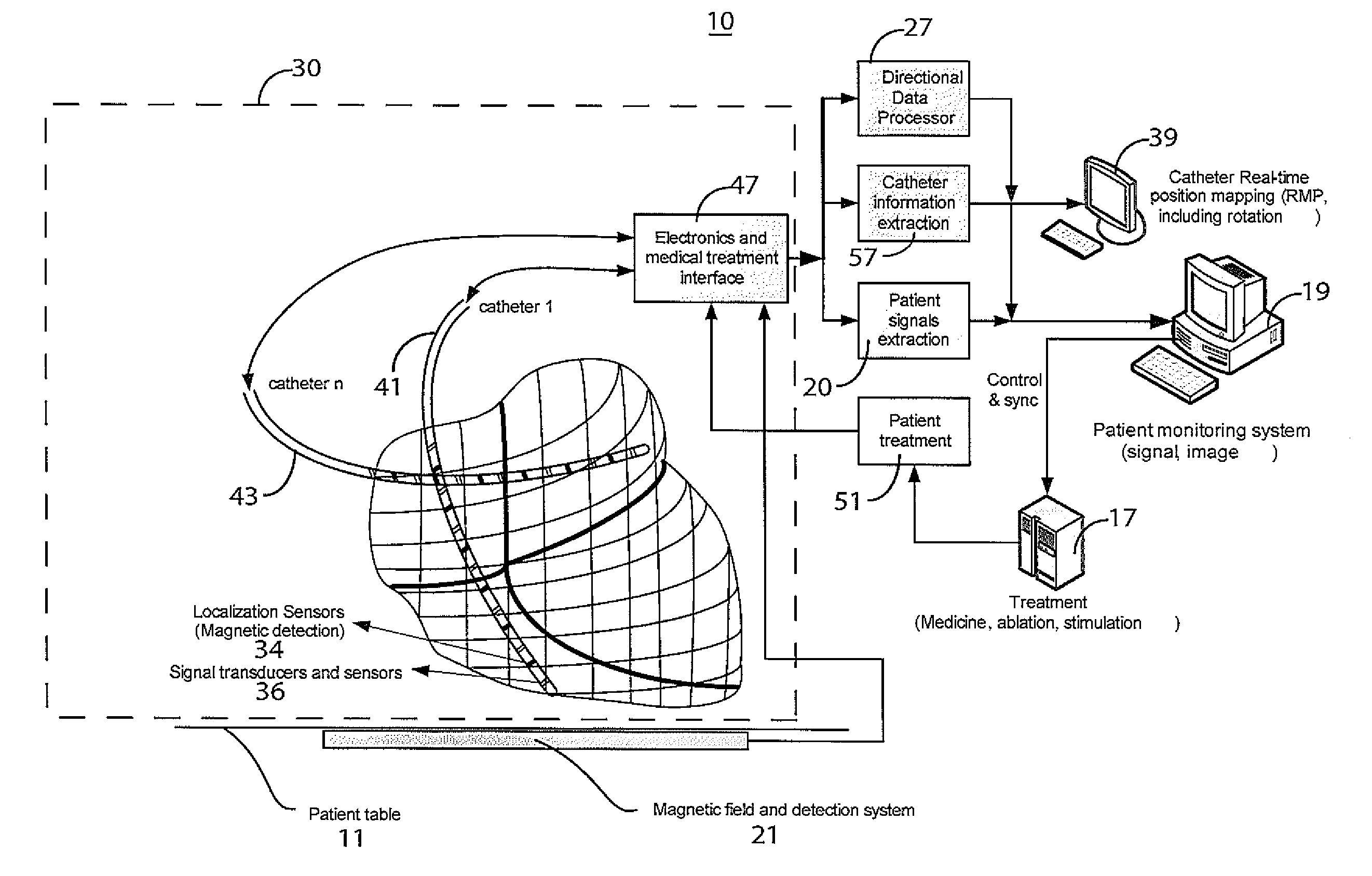
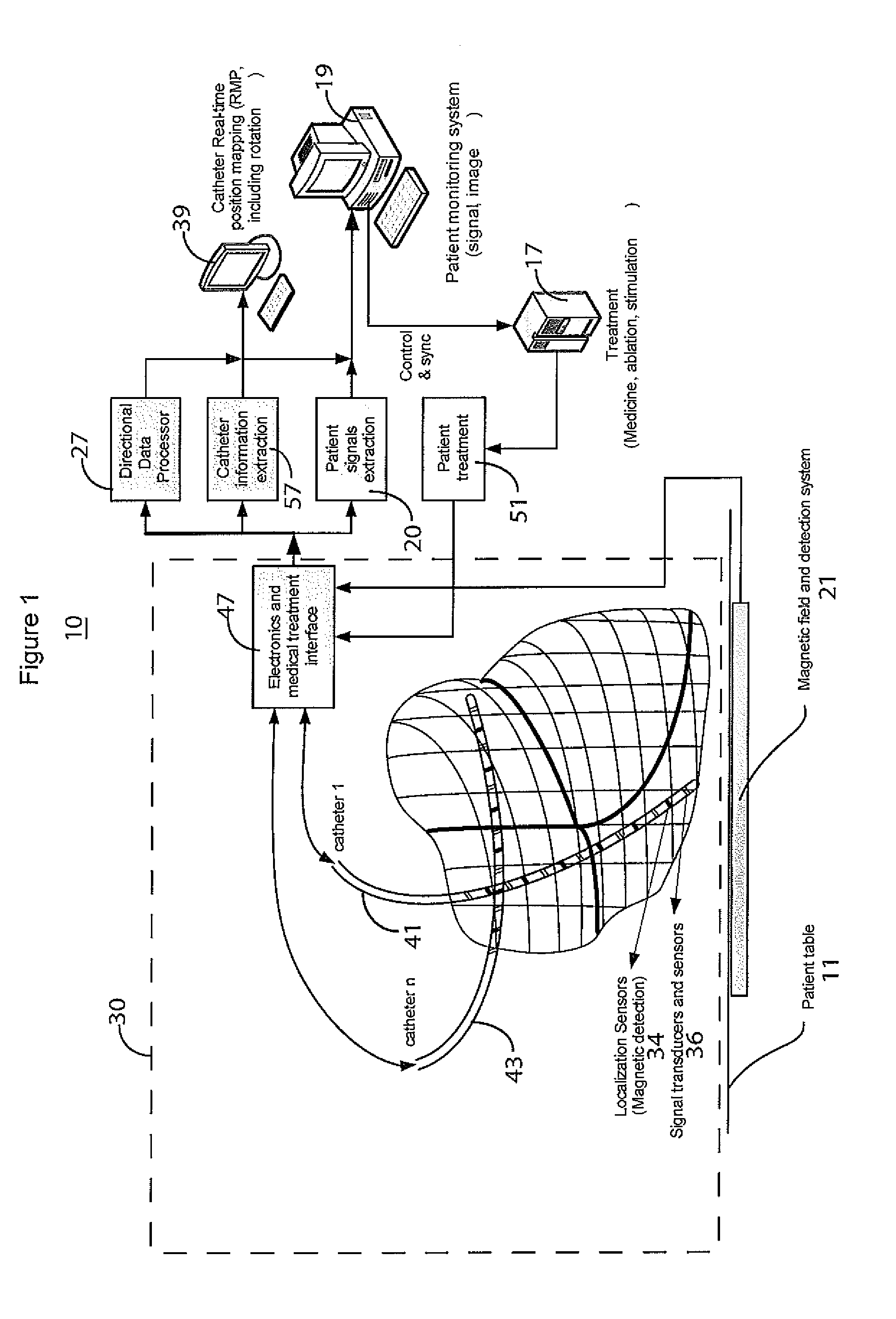
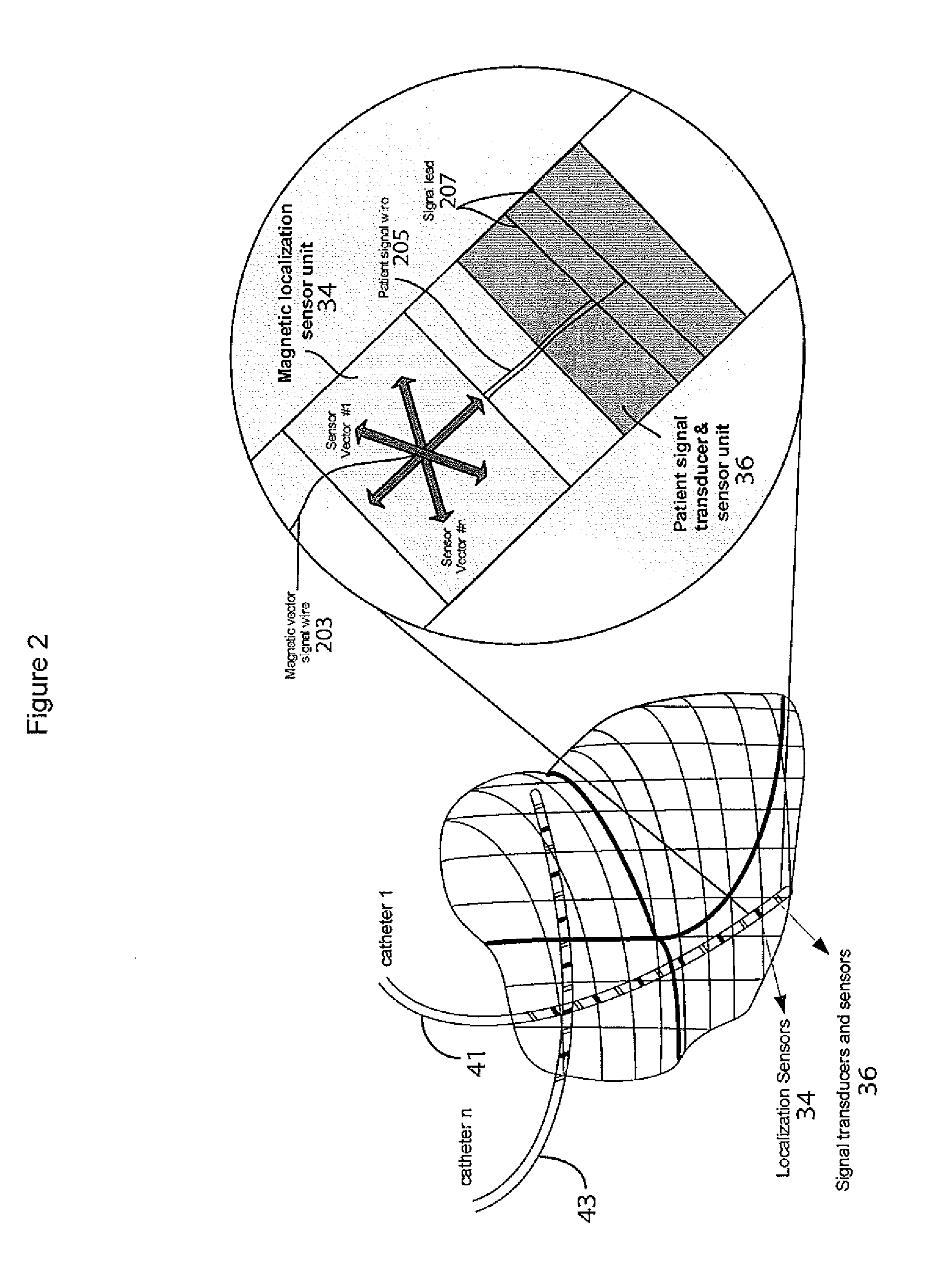
A system improves precision and reliability of intra-cardiac catheter position tracking and monitoring. An interventional system for internal anatomical examination includes a catheterization device for internal anatomical insertion. The catheterization device includes, at least one magnetic field sensor for generating an electrical signal in response to rotational movement of the at least one sensor about an axis through the catheterization device within a magnetic field applied externally to patient anatomy and a signal interface for buffering the electrical signal for further processing. A signal processor processes the buffered electrical signal to derive a signal indicative of angle of rotation of the catheterization device relative to a reference. The angle of rotation is about an axis through the catheterization device. A reproduction device presents a user with data indicating the angle of rotation of the catheterization device.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDIAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Robotically controlled catheter and method of its calibration
ActiveUS20080033284A1ElectrocardiographySurgical needlesMotion vectorFourier transform on finite groups
A method of calibrating a robotic device, such as a cardiac catheter, includes oscillating the device on an actuation axis by applying an oscillation vector at an oscillation frequency. While oscillating, a location of the device is periodically measured to generate a plurality of location data points, which may express the location of the device relative to a plurality of measurement axes. The location data points are then processed using a signal processing algorithm, such as a Fourier transform algorithm, to derive a transfer function relating a position of the device to a movement vector for the actuation axis. The transfer function may be resolved into and expressed as a calibration vector for the actuation axis, which may include one or more components, including zero components, directed along each of the measurement axes. The process may be repeated for any actuation axes on which calibration is desired.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Dual-purpose lasso catheter with irrigation using circumferentially arranged ring bump electrodes
ActiveUS8600472B2Drag minimizationImprove spatial resolutionUltrasound therapyElectrocardiographyDual purposeMaterial Perforation
Cardiac catheters, including a lasso catheter, are provided for use in a system for electrical mapping and ablation of the heart has an array of raised, circumferential ring bump electrodes wherein each circumferential electrode has multiple perforations, which are in fluid communication with a cavity or chamber formed under the surface of the circumferential ring. The cavity is formed 360° around the outer surface or loop lumen of the lasso segment of the catheter which is in fluid communication with a breach hole (or holes) drilled through loop lumen and in fluid communication with an irrigating lumen. Each circumferential ring has a breach hole (or holes) that range from smaller to larger from the proximal end of the loop segment to the distal end of the loop segment in one embodiment.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
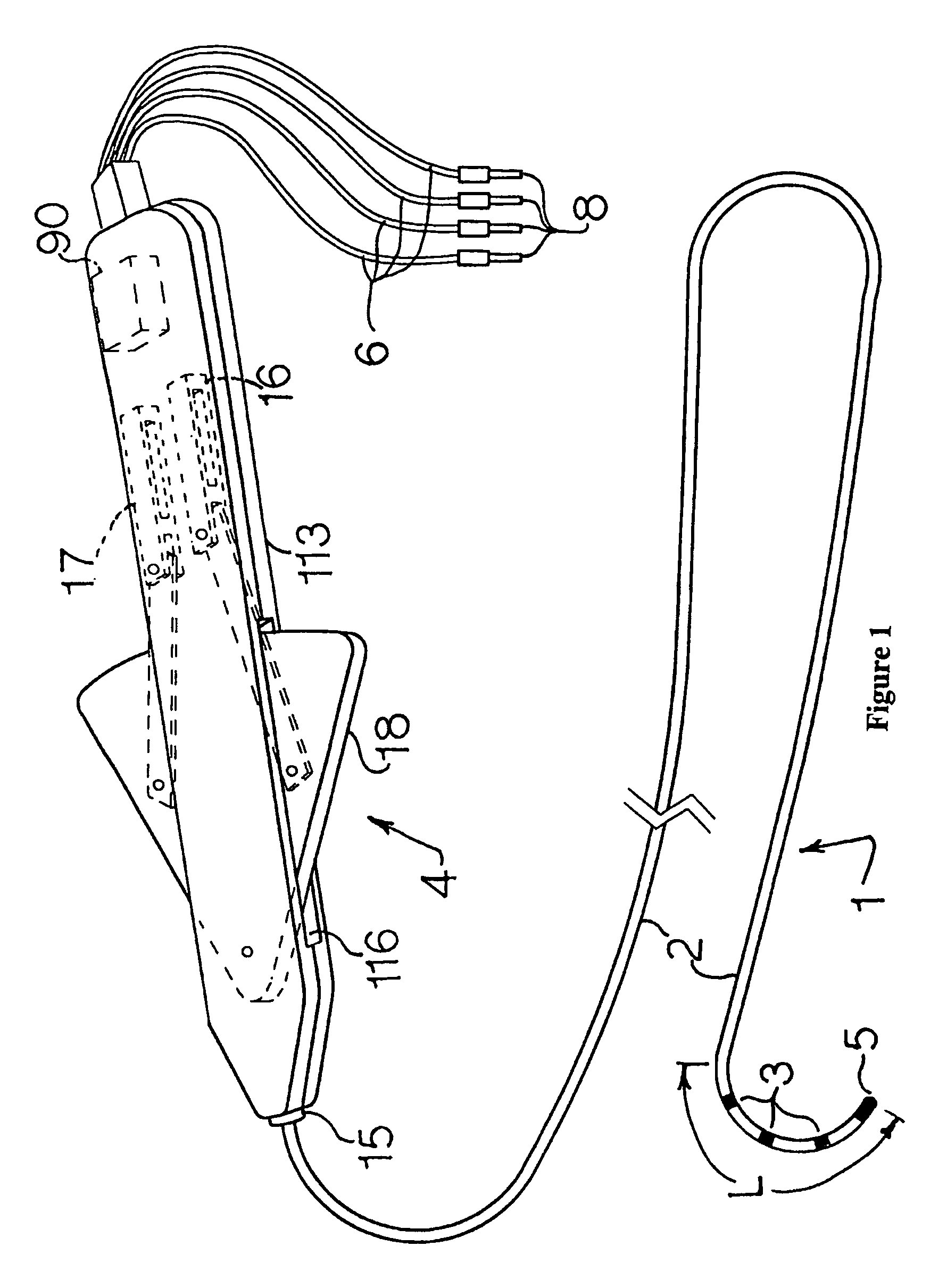
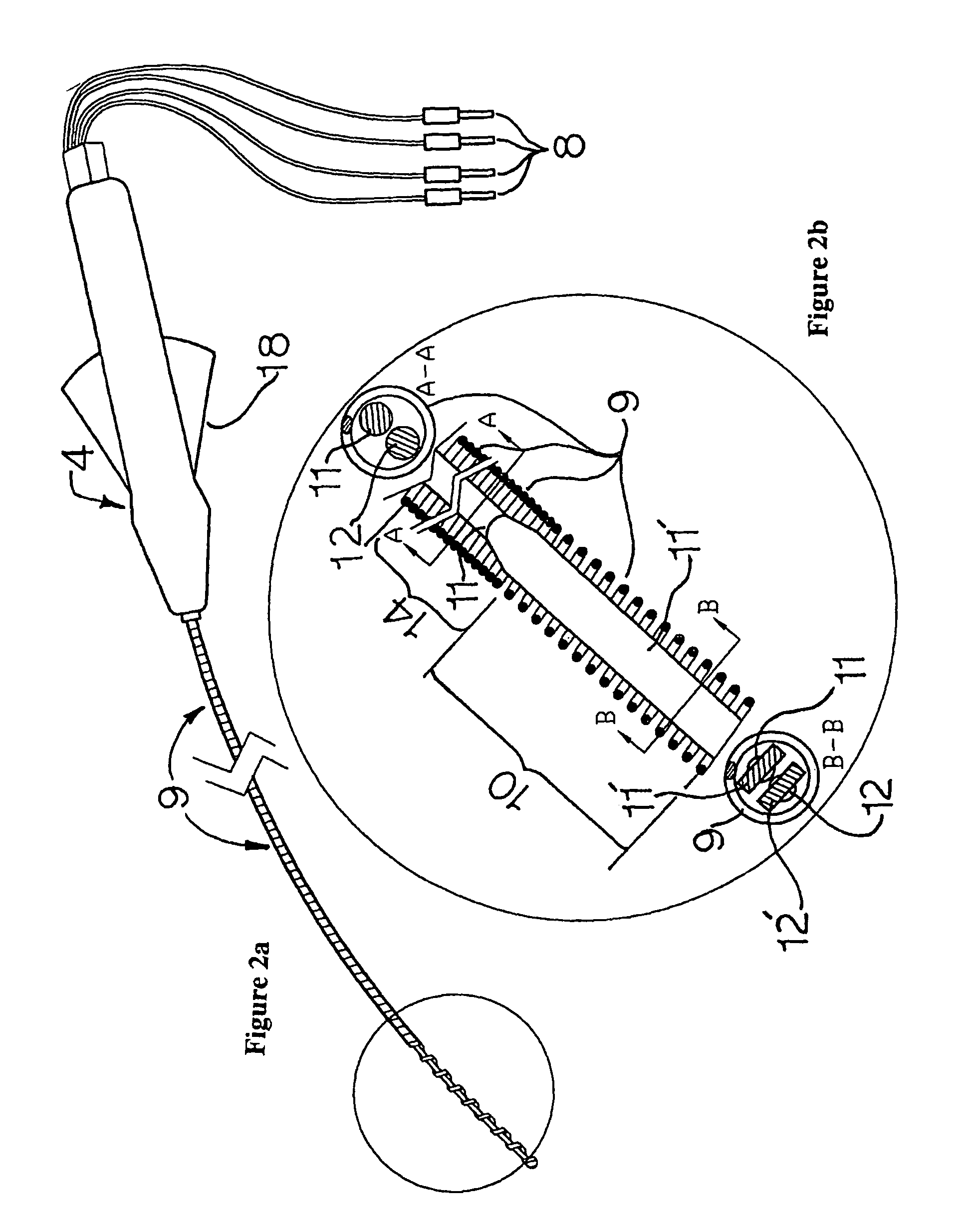
Electrophysiology/ablation catheter and remote actuator therefor
InactiveUS20070078455A1Eliminates compression loadingOverall design flexibilityInternal electrodesCatheterHand graspActuator
A cardiac catheter for minimally invasive diagnostic and / or ablation procedures includes an elongated cylindrical, electrically non-conductive exterior tube with surface electrodes disposed on its distal portion and a handle on its proximal end. The distal portion can be curved into a curvature retained by a single action on a manual actuator. An electromechanical drive system may be incorporated into the handle. An electrical heating element may be incorporated within the distal electrode for ablation procedures. A removable, disposable blood contacting segment may be provided. The non-blood contacting actuator is thus reusable. The catheter includes two tension / compression members, which are wires with circular cross-sections that are integrally formed into ribbon-like configurations at their distal portions, for curvature formation. The handle includes a pivoted member movable in one direction by the thumb of the user's hand grasping the handle and in the opposite direction by the other fingers of the same hand.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
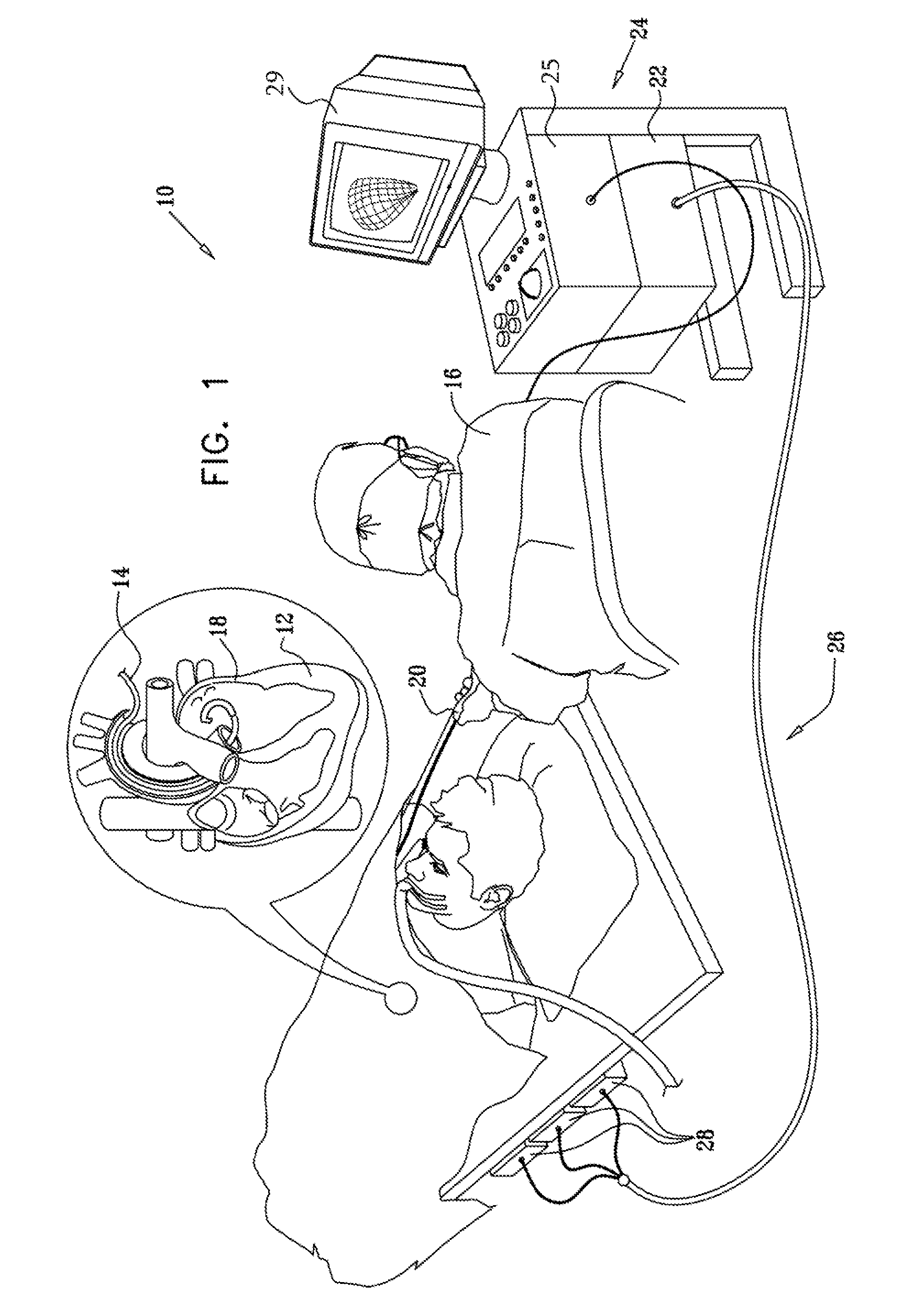
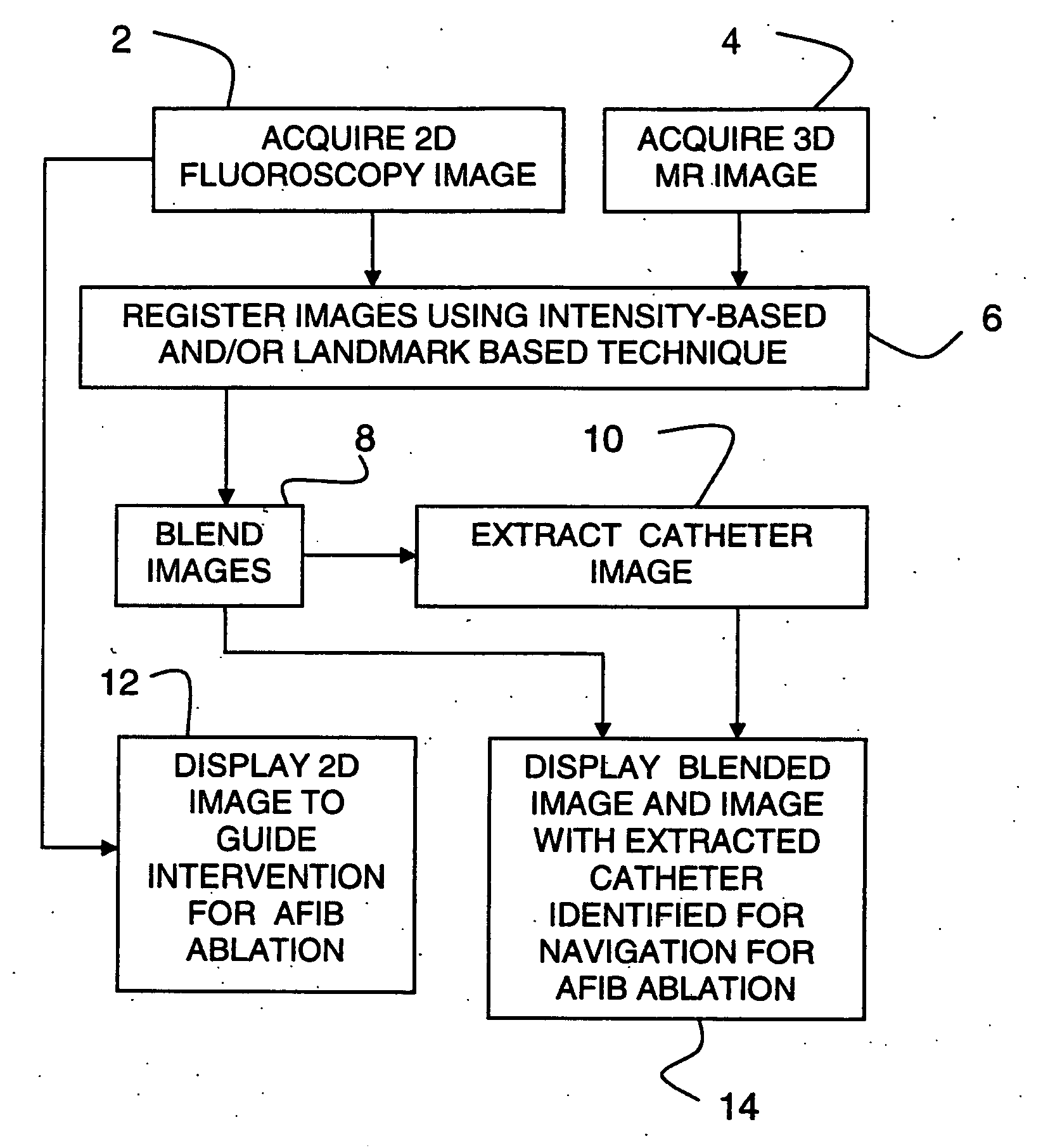
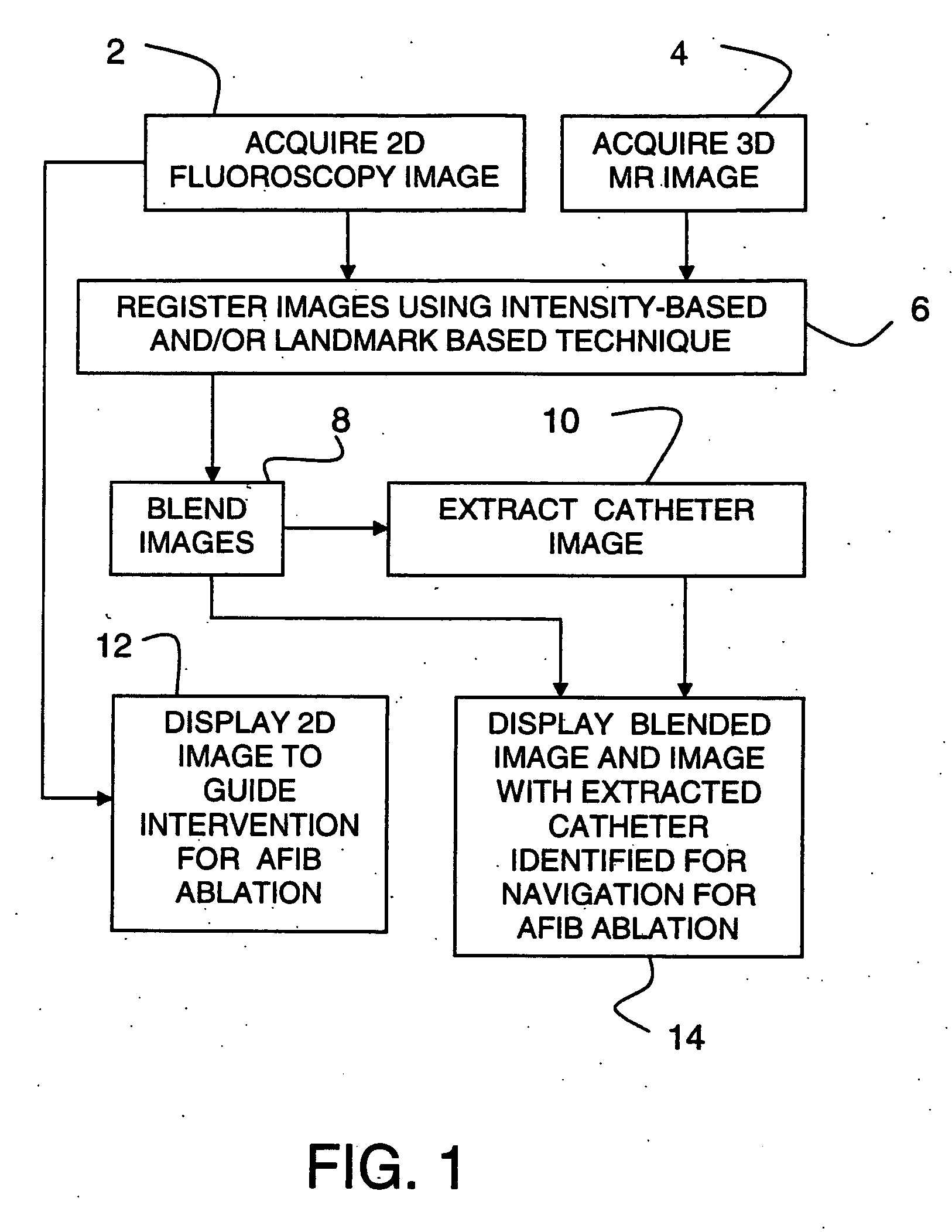
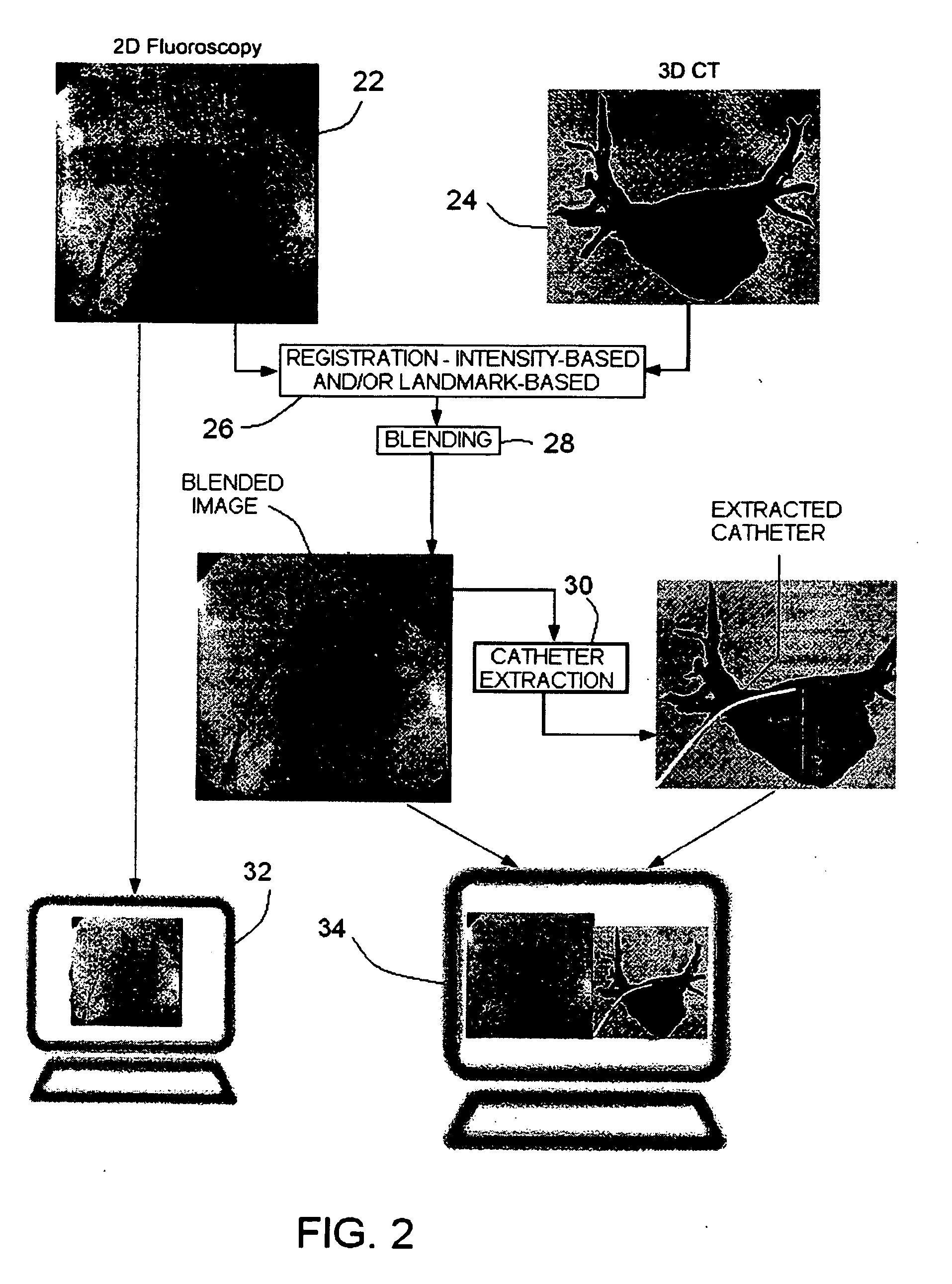
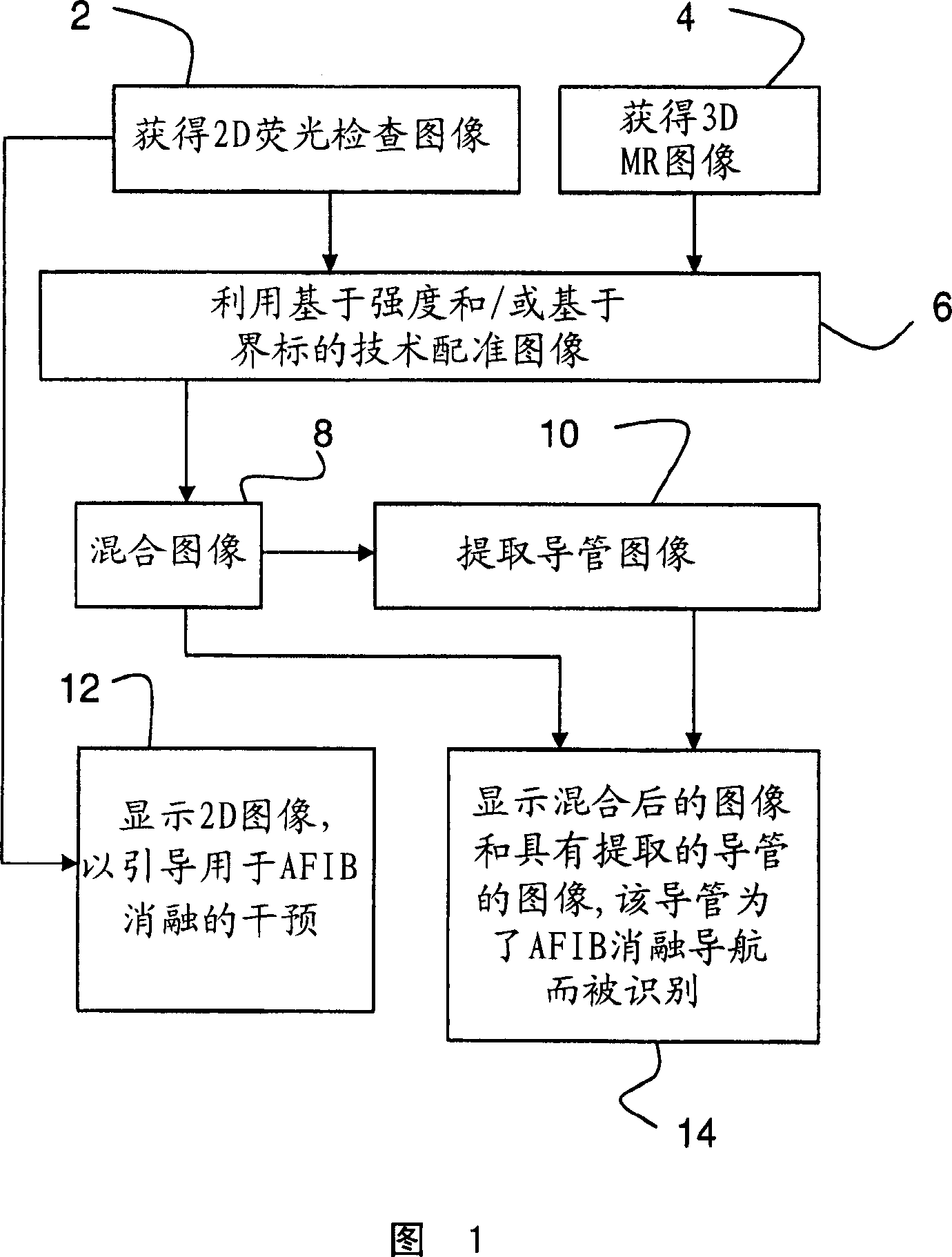
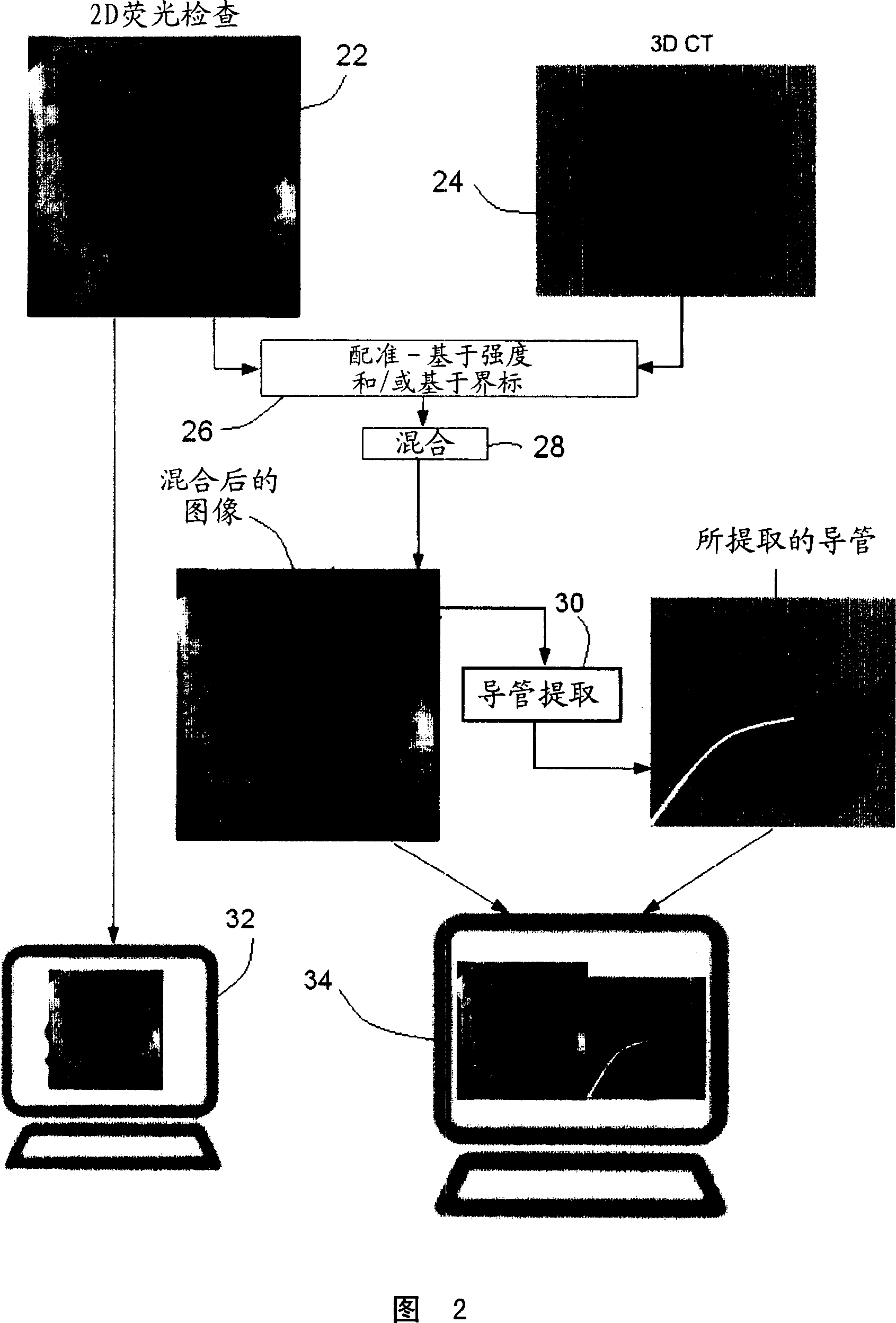
Method and system for cardiac imaging and catheter guidance for radio frequency (RF) ablation
InactiveUS20070100223A1Improve registration accuracyImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionImage extractionRf ablation
A method for imaging for cardiac catheter guidance comprises displaying a two-dimensional (2D) image of a heart, including a catheter; registering and blending the 2D image and a three-dimensional (3D) image of the heart to derive a blended image; displaying the blended image and the 3D image; and extracting an image of the catheter and inserting it into the 3D image.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Ablation electrodes with capacitive sensors for resolving magnitude and direction of forces imparted to a distal portion of a cardiac catheter
InactiveUS20110022045A1Less complicatedReduce manufacturing costCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurement deviceContact sensor
A catheter assembly for assessing contact between the catheter assembly and tissue is disclosed. In an exemplary embodiment the assembly includes a catheter shaft and a trio of pressure sensitive capacitive members each of whose electrical resistance varies with a pressure vector applied to the catheter assembly. The assembly also includes at least one measurement terminal to permit the measurement of changes in the electrical characteristics of the pressure sensitive capacitive members. The assembly may optionally include a measurement device to measure resistance, impedance and / or other electrical characteristics. The assembly may utilize a reference electrode secured to the patient's tissue, which permits the measurement device to measure changes between the reference electrode and the at least one measurement terminal. Optionally, the assembly may include a conductive outer layer. Also disclosed are sensor assemblies, contact sensor, methods of contact sensing, and methods of manufacturing relating to the use of pressure sensitive capacitors.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
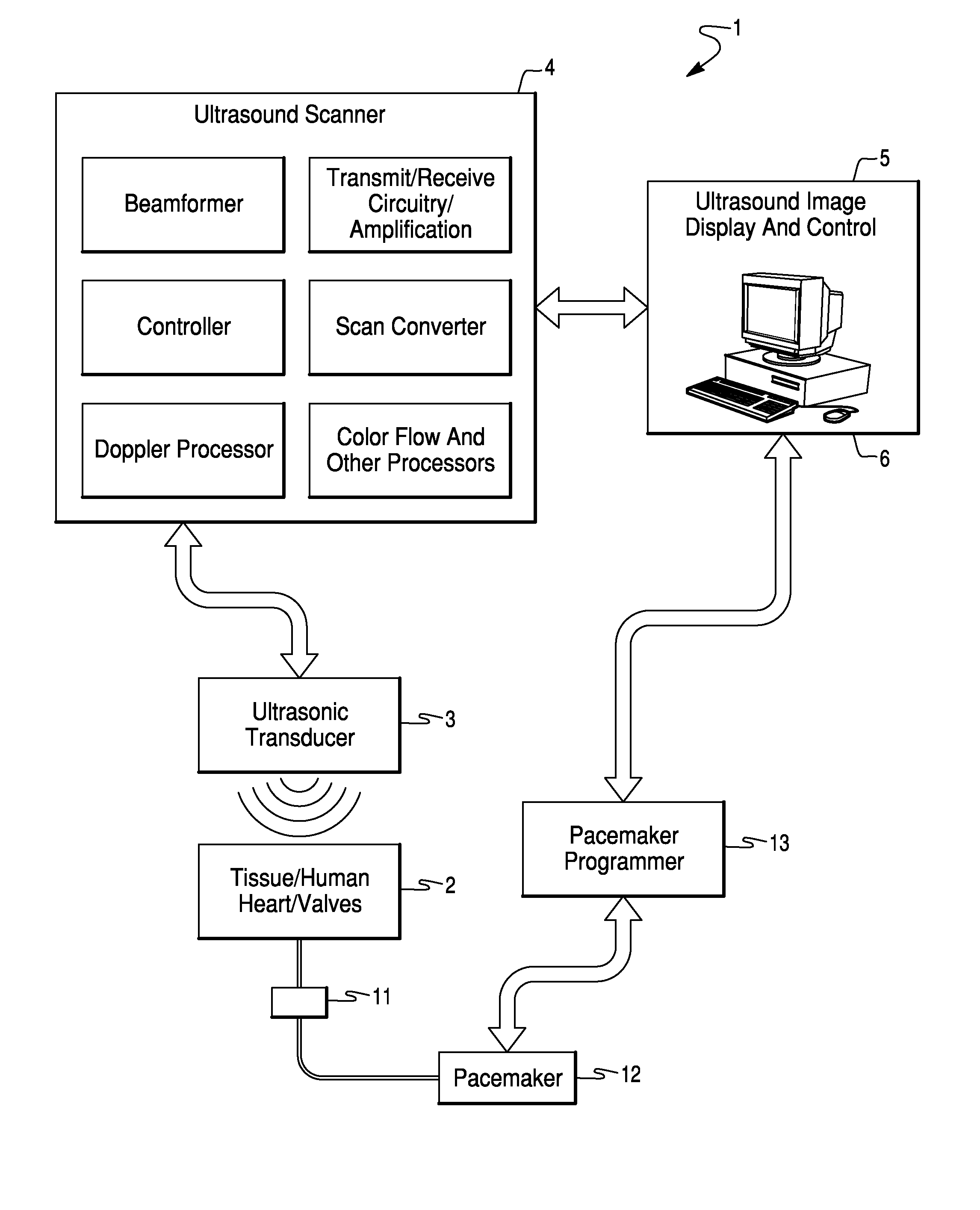
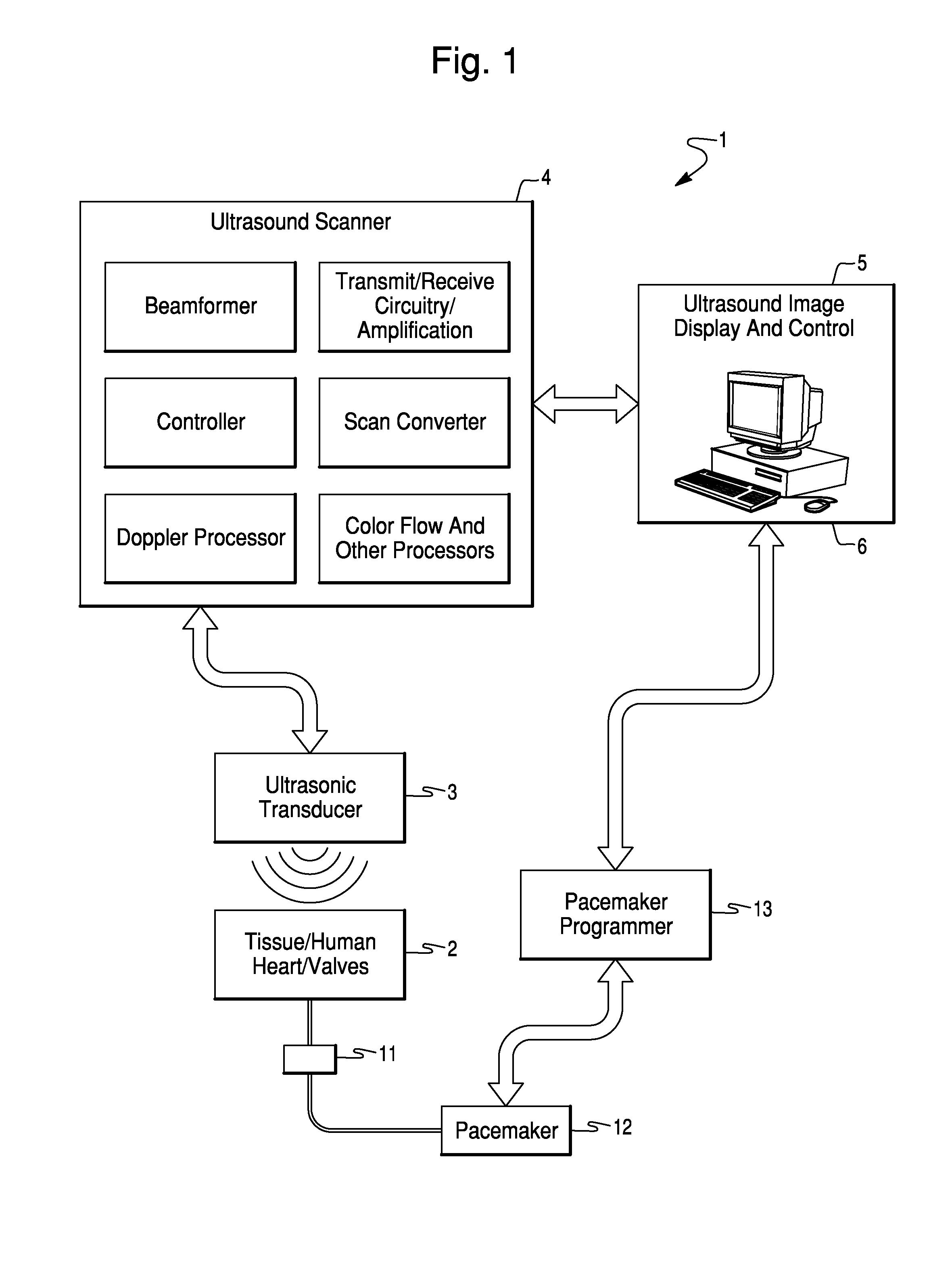
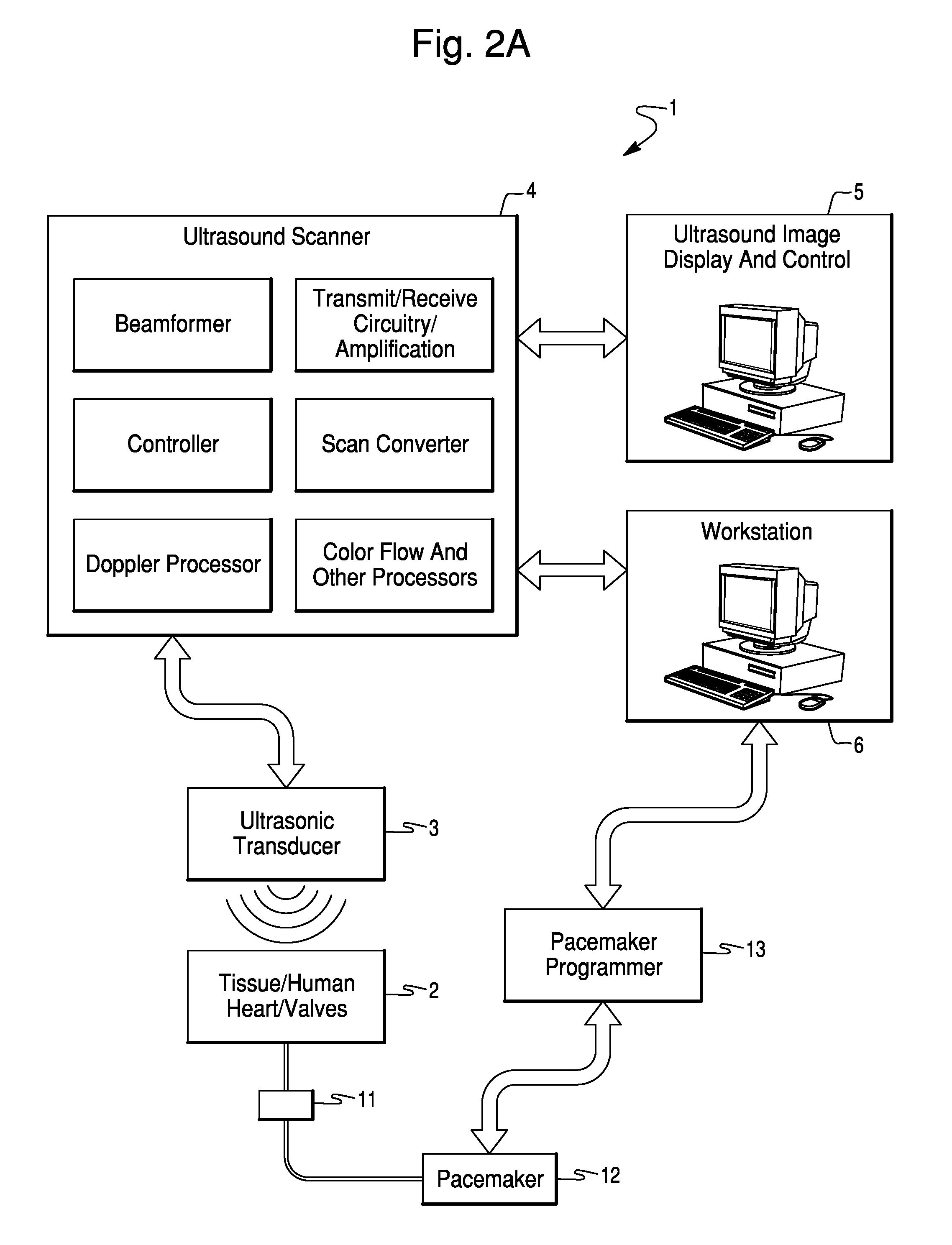
Method and System for Configuration of a Pacemaker and For Placement of Pacemaker Electrodes
InactiveUS20080146928A1Easy to compareEjection volume be maximizedBlood flow measurement devicesCatheterUltrasound imagingUltrasonic sensor
Ultrasound imaging methods and systems for assisting a clinician in configuring the operation of a pacemaker and for determining an optimal site for the pacemaker electrode are presented. The methods and systems provide a toolbox for analyzing and optimizing the effectiveness of the pacemaker and proposed electrode sites. The method includes a function which evaluates one or more electrode sites and pacemaker configurations. The function may be based, for example, on the activation voltage of the pacemaker, on an estimate of the volume of blood ejected from the heart and / or on the cardiac dysynchrony. The ejection volume and the dysynchrony may be estimated using an imaging cardiac catheter ultrasound transducer array and ultrasound unit.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
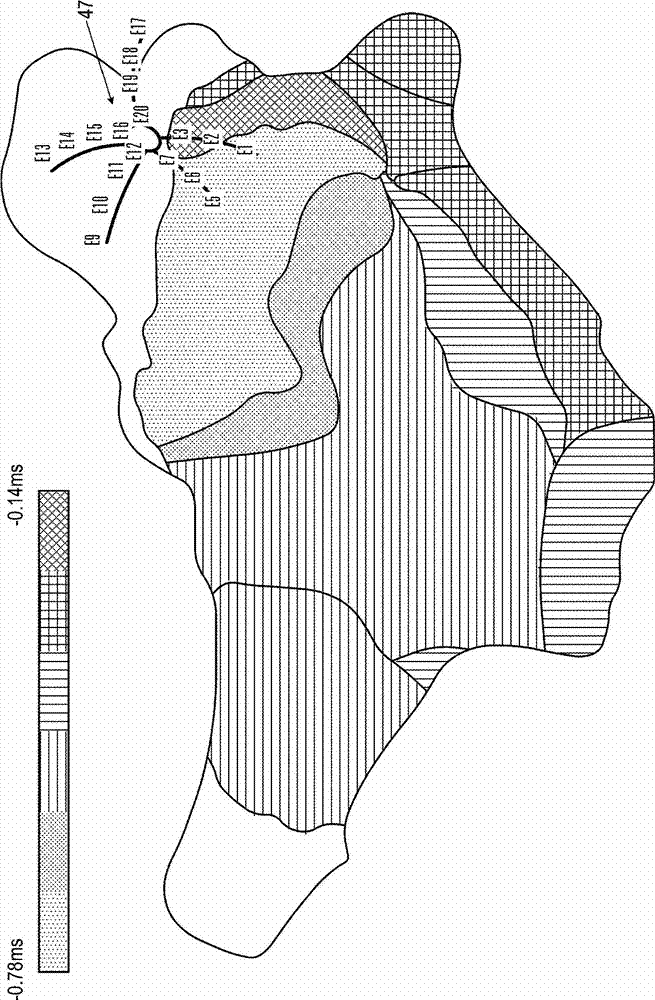
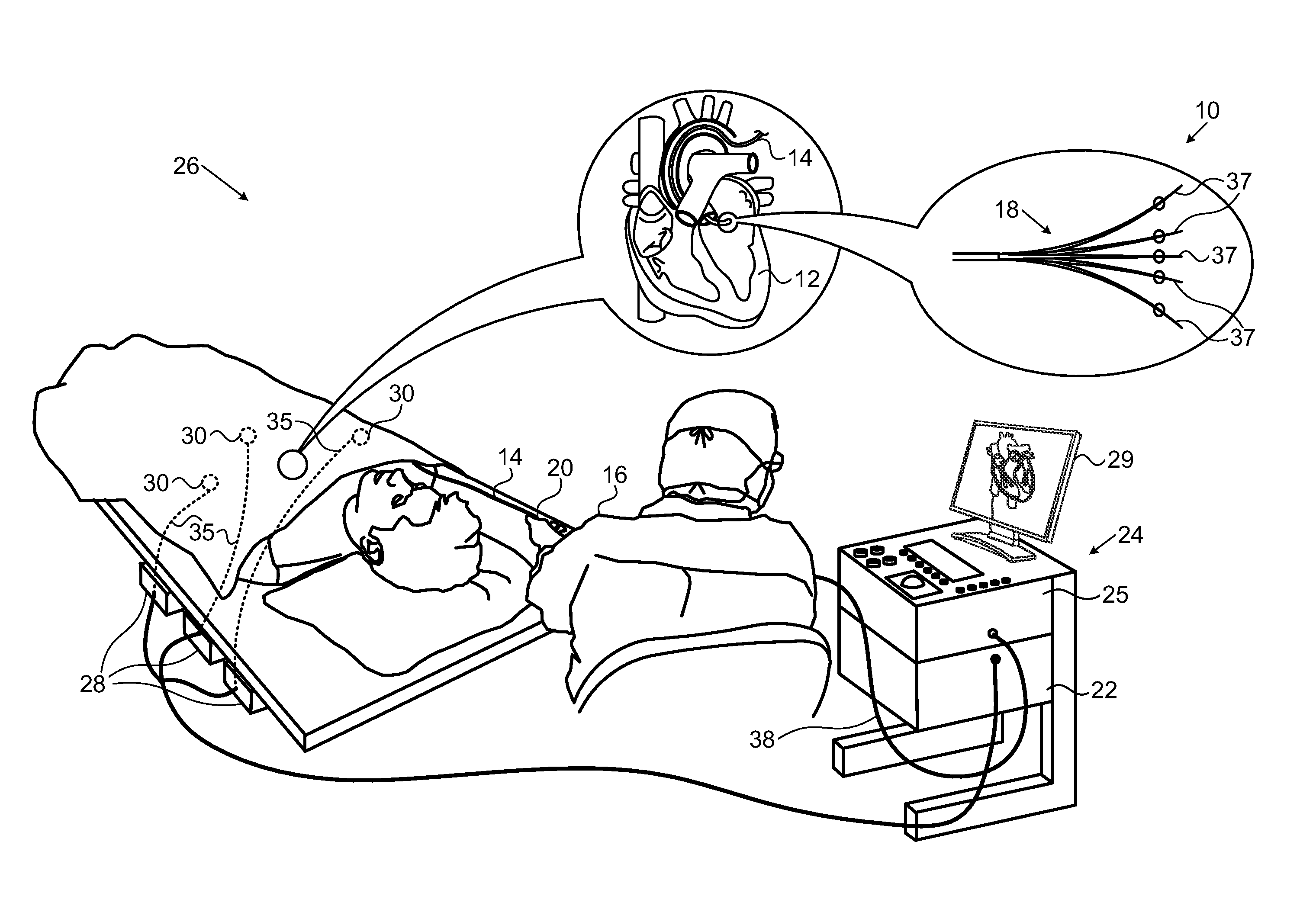
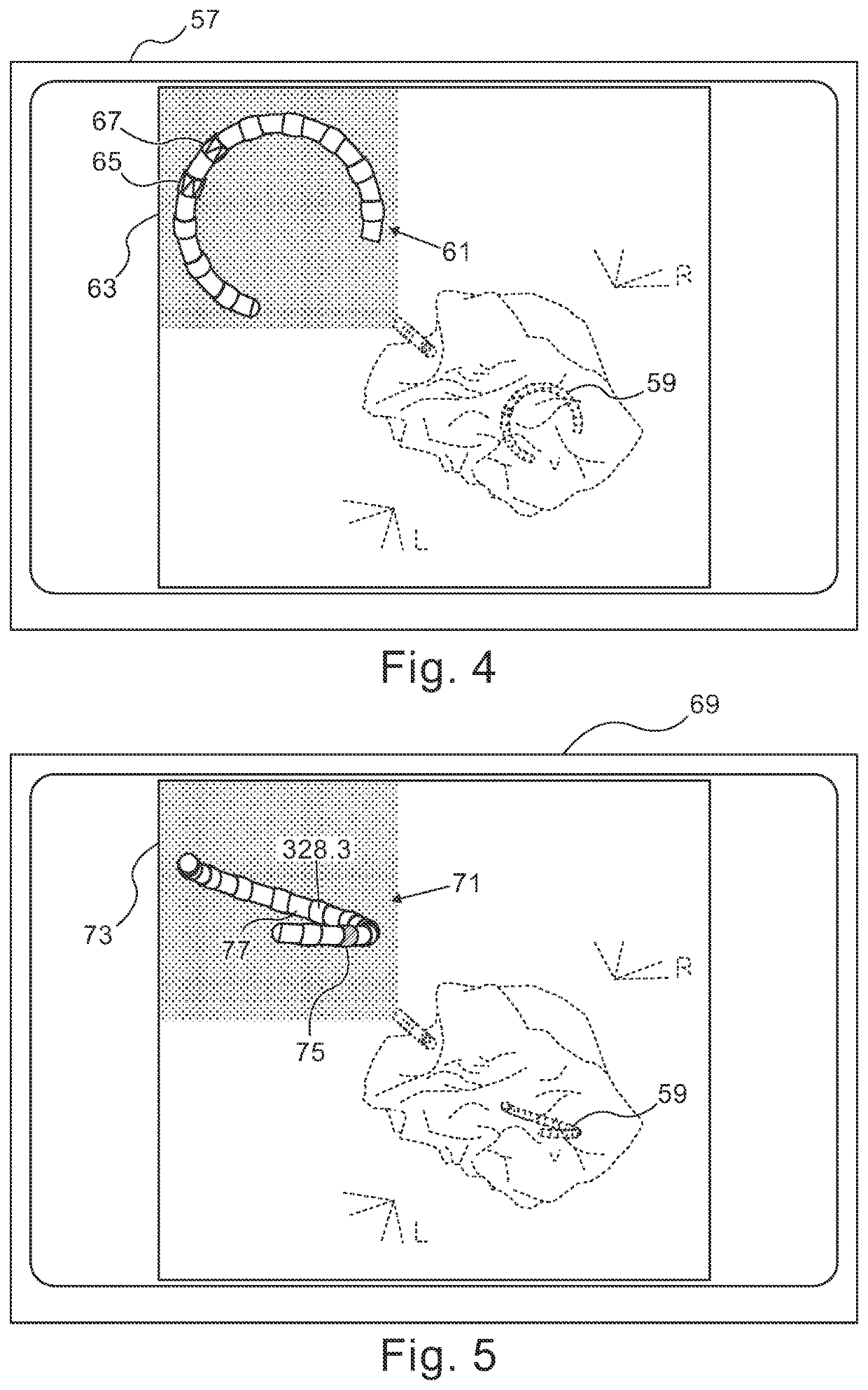
Graphic interface for multi-spine probe
Methods and systems for mapping cardiac electrical activity employ a cardiac catheter having a plurality of spines mounted at the distal end, each spine having a plurality of electrodes. Electrical signal data are obtained from the heart via the electrodes, and respective intracardiac locations and orientations of the spines are sensed. An electroanatomic map of the heart is derived from the signal data, and presented as a graphic representation of the respective intracardiac locations and orientations of the spines, with distinctive graphical indicia of at least portions of the spines. The method is further carried out by displaying the electroanatomic map, and responsively to the displayed electroanatomic map, adjusting at least one of the locations and orientations of at least one of the spines.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Electrophysiology/ablation catheter and remote actuator therefor
InactiveUS7881809B2Easily attachable/detachableRemove loadInternal electrodesCatheterHand graspDistal portion
A cardiac catheter for minimally invasive diagnostic and / or ablation procedures includes an elongated cylindrical, electrically non-conductive exterior tube with surface electrodes disposed on its distal portion and a handle on its proximal end. The distal portion can be curved into a curvature retained by a single action on a manual actuator. An electromechanical drive system may be incorporated into the handle. An electrical heating element may be incorporated within the distal electrode for ablation procedures. A removable, disposable blood contacting segment may be provided. The non-blood contacting actuator is thus reusable. The catheter includes two tension / compression members, which are wires with circular cross-sections that are integrally formed into ribbon-like configurations at their distal portions, for curvature formation. The handle includes a pivoted member movable in one direction by the thumb of the user's hand grasping the handle and in the opposite direction by the other fingers of the same hand.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Enhanced ultrasound image display
ActiveUS8075486B2Enhance diagnostic usefulnessEasy to identifyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementSonificationBiological activation
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Graphic interface for multi-spine probe
Methods and systems for mapping cardiac electrical activity employ a cardiac catheter having a plurality of spines mounted at the distal end, each spine having a plurality of electrodes. Electrical signal data are obtained from the heart via the electrodes, and respective intracardiac locations and orientations of the spines are sensed. An electroanatomic map of the heart is derived from the signal data, and presented as a graphic representation of the respective intracardiac locations and orientations of the spines, with distinctive graphical indicia of at least portions of the spines. The method is further carried out by displaying the electroanatomic map, and responsively to the displayed electroanatomic map, adjusting at least one of the locations and orientations of at least one of the spines.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Enhanced ultrasound image display
ActiveUS20070276226A1Enhance diagnostic usefulnessEasy to identifyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementSonificationBiological activation
Using specialized cardiac catheters for image acquisition, features of the heart are readily identifiable on an ultrasound image, based on a previously generated electrical activation map of the heart. The electrical activation map is automatically registered with the ultrasound image using information obtained from position sensors in the catheters. Features identifiable on the electrical activation map, presented as points, tags, design lines, and textual identification, are projected into the plane of the ultrasound fan and overlaid on the ultrasound image, thereby clarifying the features that are visible on the latter.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Method and system for cardiac imaging and catheter guidance for radio frequency (RF) ablation
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
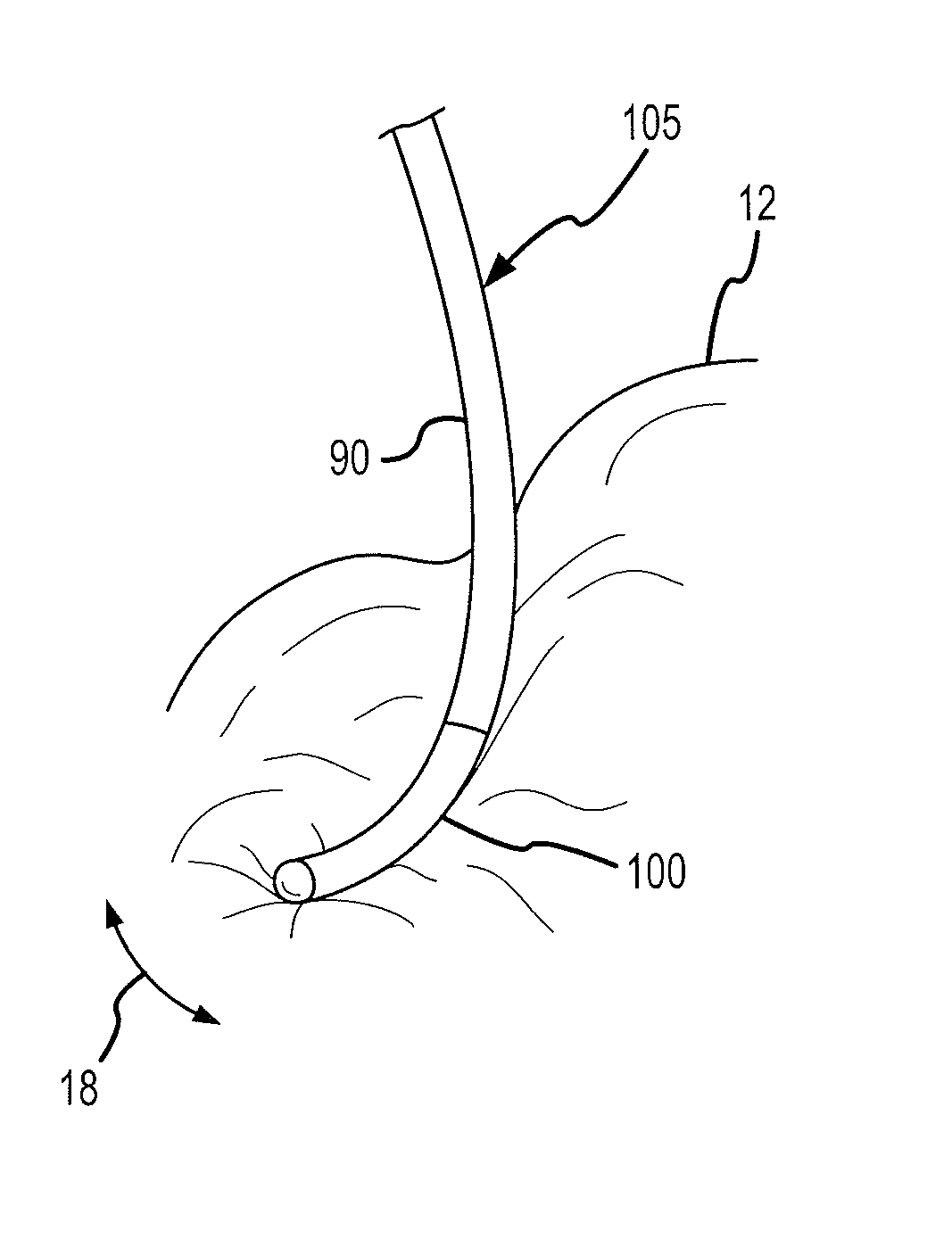
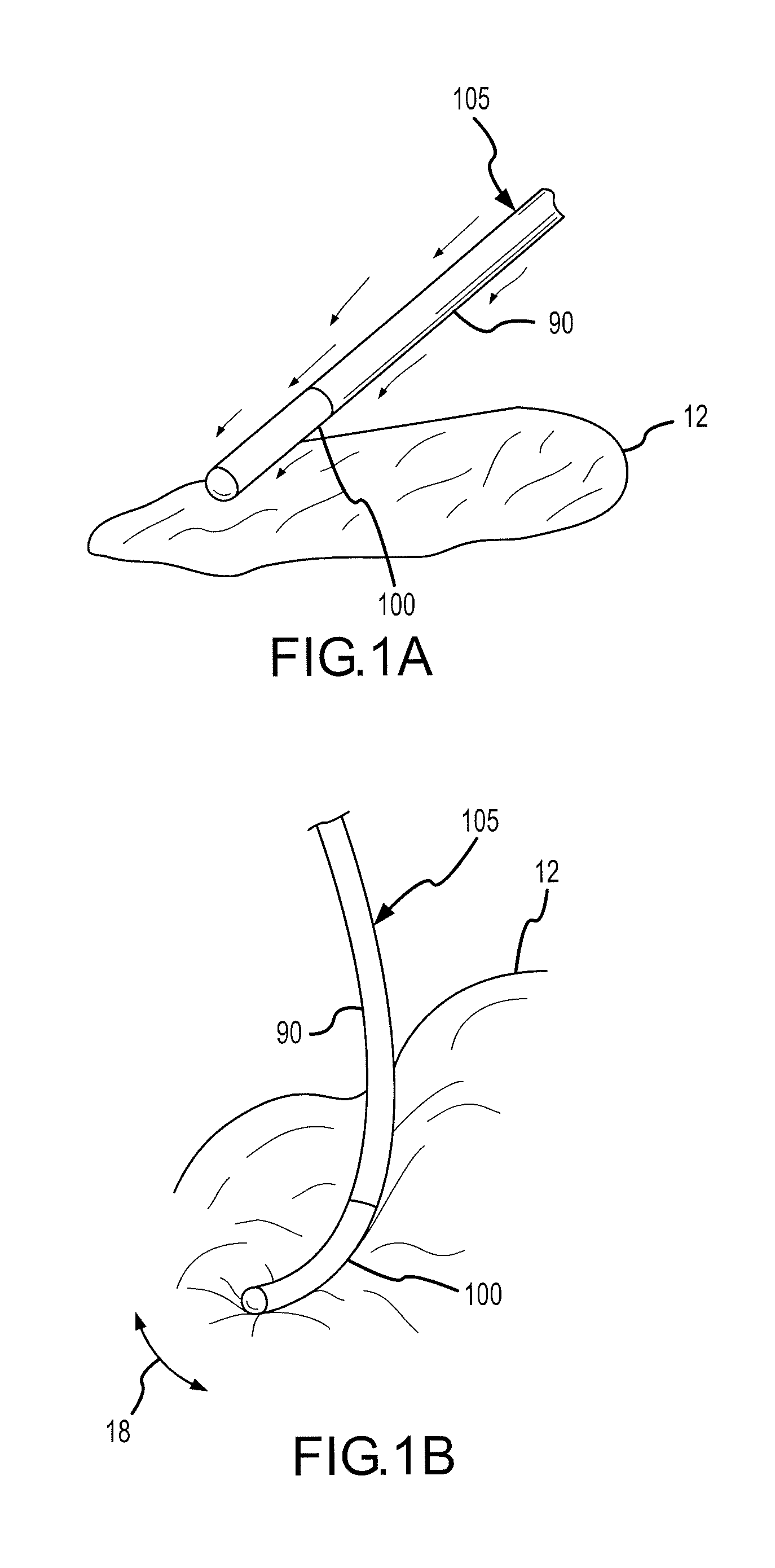
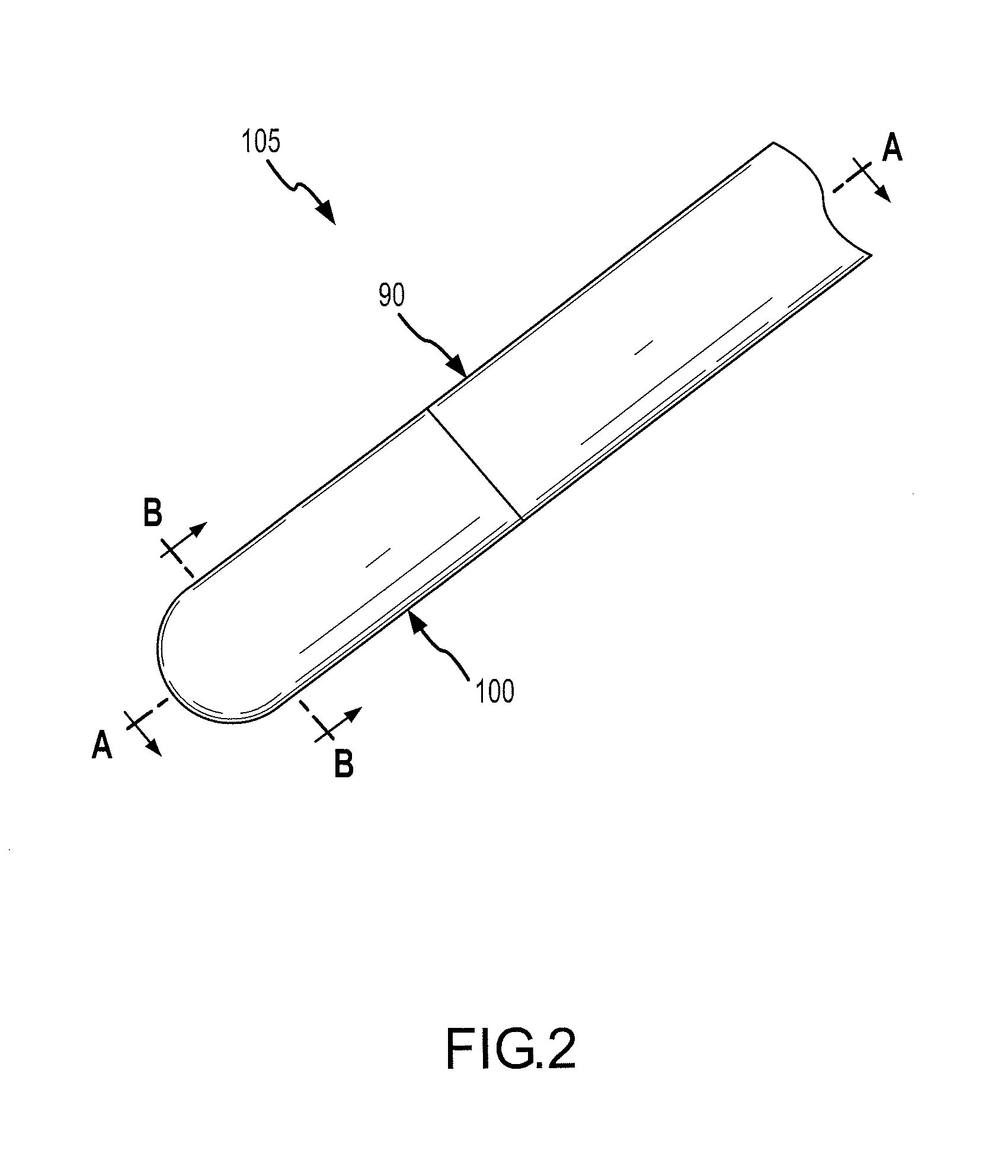
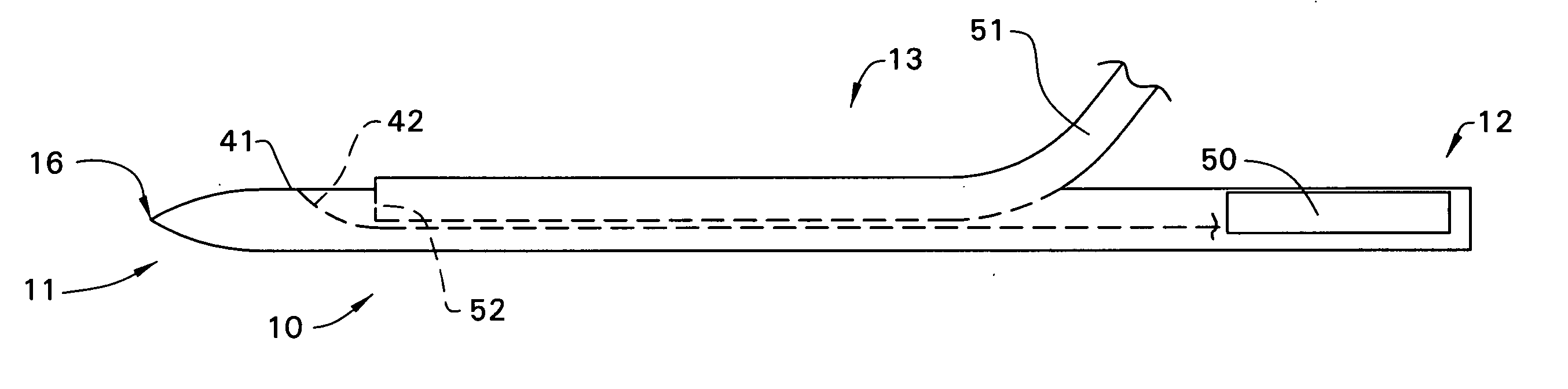
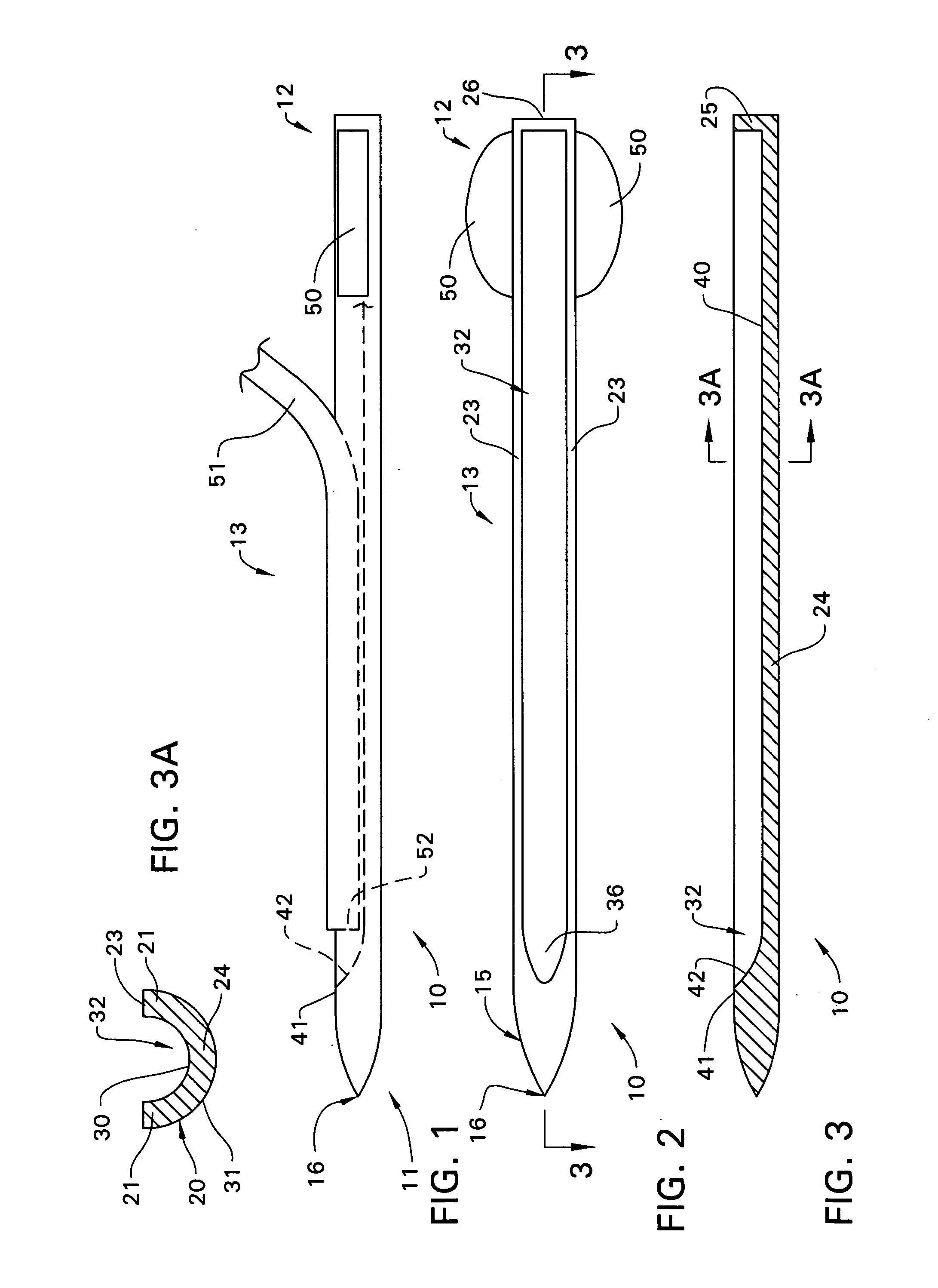
Catheter introducer and method of introducing a catheter into the heart
A catheter introducer and a method of introducing a catheter into a heart. The catheter introducer includes a front puncturing end and a main body portion which defines an upwardly-opening trough therein. A catheter is placed in piggy-back fashion within the trough, and the puncturing end of the tool is inserted into the heart, so that the catheter is delivered into the heart essentially simultaneously with the piercing of the heart wall. The catheter introducer results in a faster introduction of the catheter, and minimizes blood loss and trauma to the heart.
Owner:PHARMACIA & UPJOHN CO
Transthoracic minimally invasive heart ventricular septal defect plugging device conveying system and method thereof
InactiveCN101172048AAvoid traumaAvoid reactionSurgeryProsthesisInterventricular septumDelivery system
The invention discloses a transthoracic minimally invasive occlusion interventricular septum defection plugger conveying appliance. The invention is characterized in that the device comprises a locating line, a conveying passage and a cardiac plugger adaptor; one end of the conveying passage is lead to the invasive occlusion part of the interventricular septum guided by the locating line, the cardiac plugger is installed inside the plugger adaptor, after being butted with the conveying passage, the cardiac plugger adaptor enters the position of the interventricular septum defection through the conveying passage and begins to work at the position. The conveying is mainly characterized in that the entire device is short and small, and can be held by hands directly. The defection part can be closed as near as possible, and puncture, direction adjusting, guide rail building, and plugger releasing can be finished by only one person, during the operation, once the septum defection is not suitable for the method or the plugging fails, the incision can be directly extended upward and changed into the traditional thoracotomy, no extra incision is needed, or transferred from the cardiac catheter room to the operating room, and the security of the patient is greatly ensured.
Owner:邢泉生
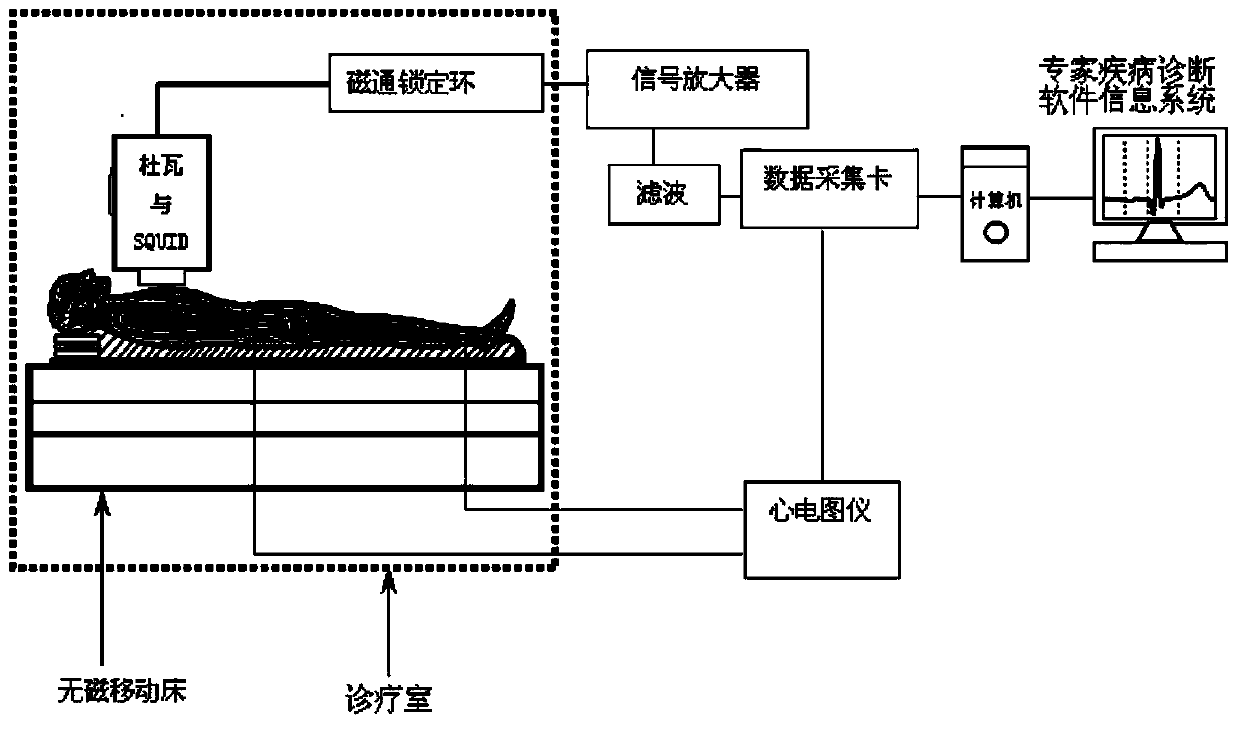
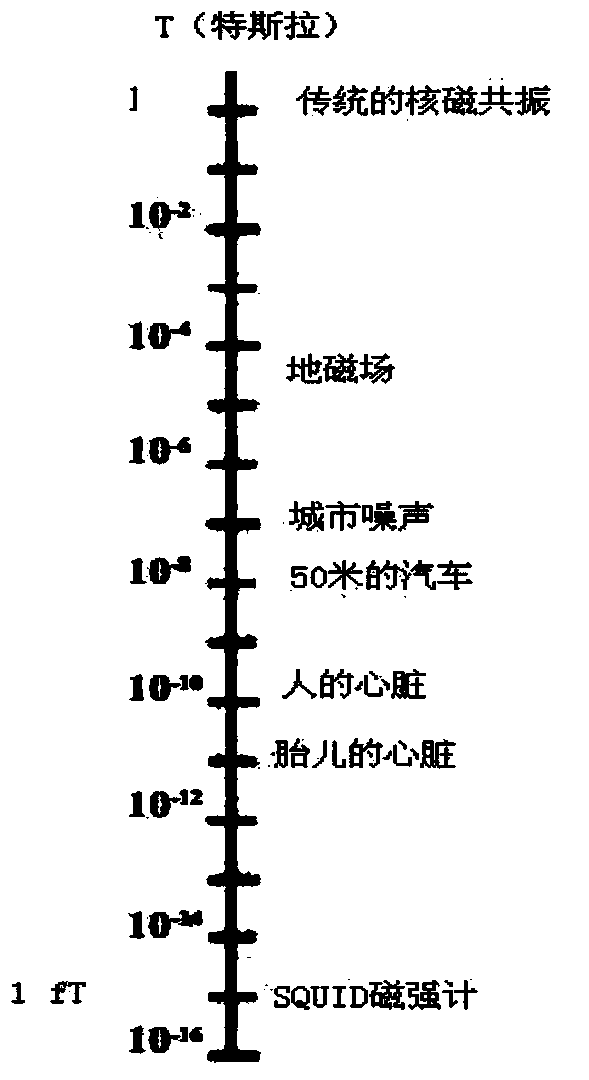
Unshielded magnetocardiogram instrument
ActiveCN104188650ASuppression of magnetic field interferenceRealize unshielded inspection methodDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiseaseData acquisition
The invention discloses an unshielded magnetocardiogram instrument. The unshielded magnetocardiogram instrument comprises a superconducting quantum interfere device, a non-magnetic Duvel, a magnetic flux locking ring, a signal amplifier, a wave filter, a data acquisition card, an electrocardiograph, a non-magnetic moving bed, an expert disease diagnostic software information system and a master computer. Conventional electric measuring transducers are replaced by the superconducting quantum interfere device as a cardiac weak magnetic signal measuring probe; cardiac weak magnetic signal detection sensitivity and precision are improved; the unshielded magnetocardiogram instrument is the latest international noninvasive cardiac function inspection equipment, and is a novel noninvasive and hypersensitive inspection instrument provided for undiagnosed coronary heart disease patients; the unshielded magnetocardiogram instrument is popular among medical staff and patients, in particular to the patients who are not suitable for exercise tests and catheter inserting and fear of cardiac catheter inspection.
Owner:BEIJING MILESTONE SCI & TECH DEV
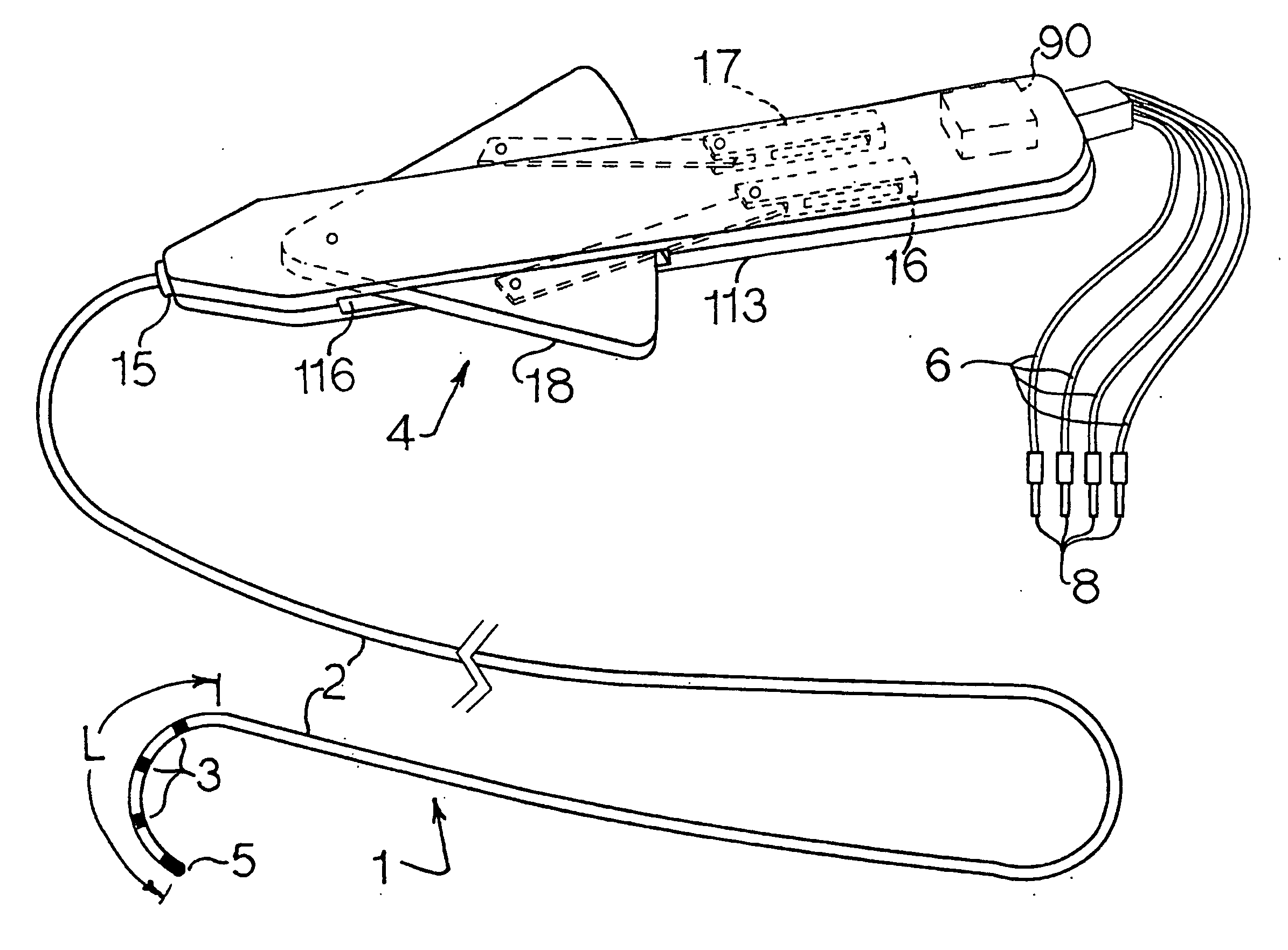
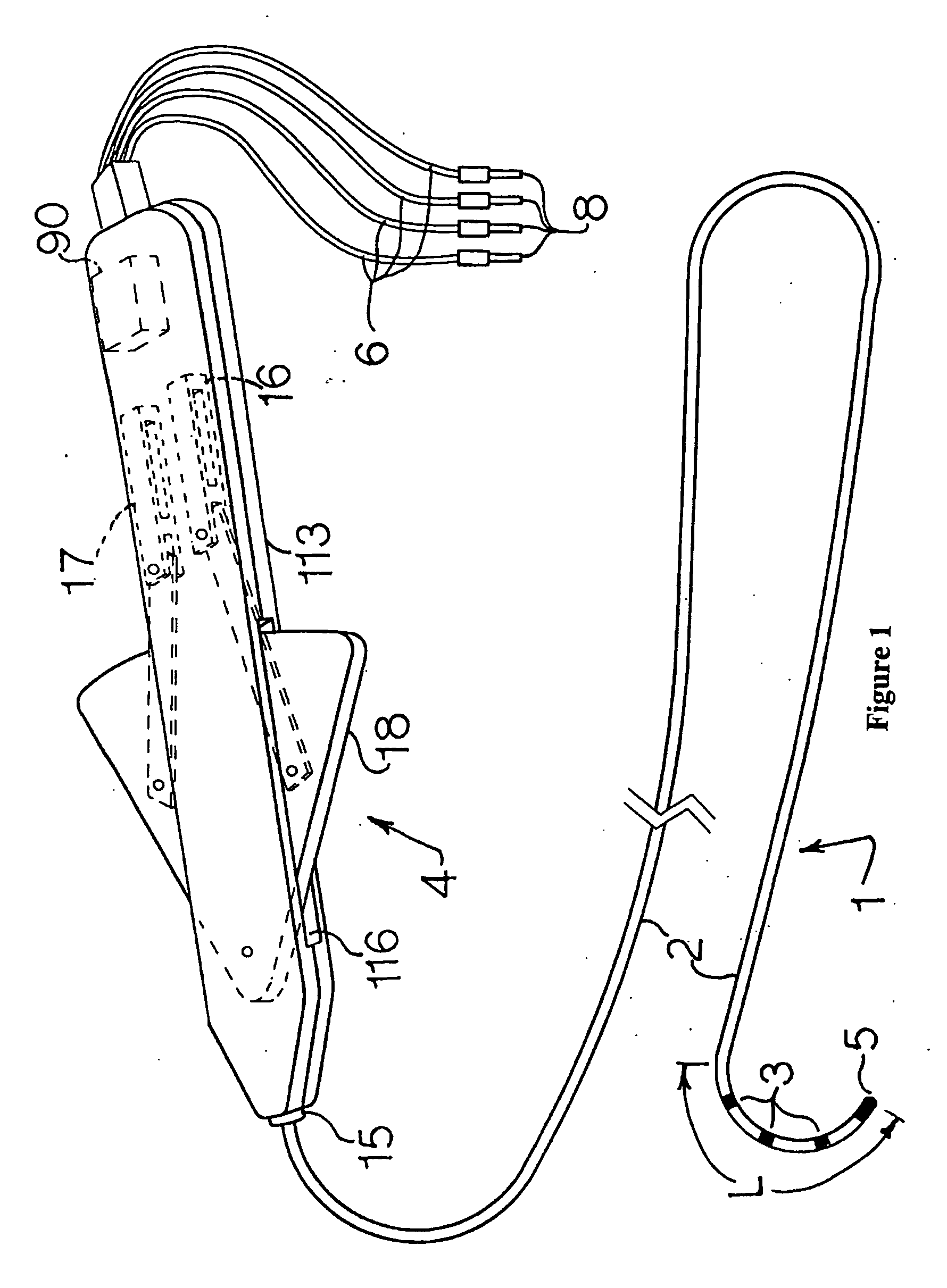
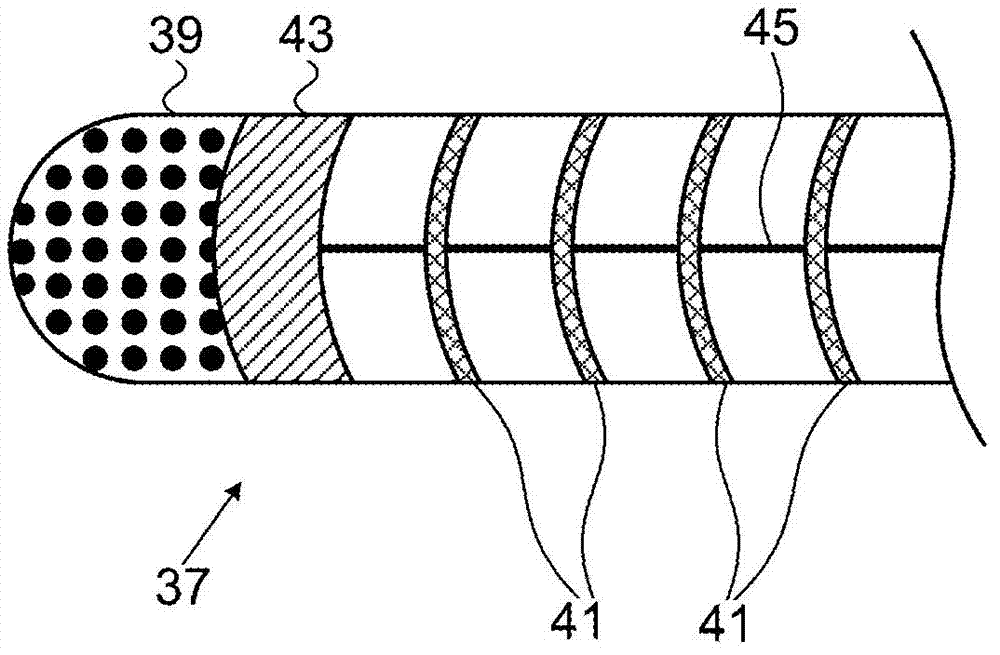
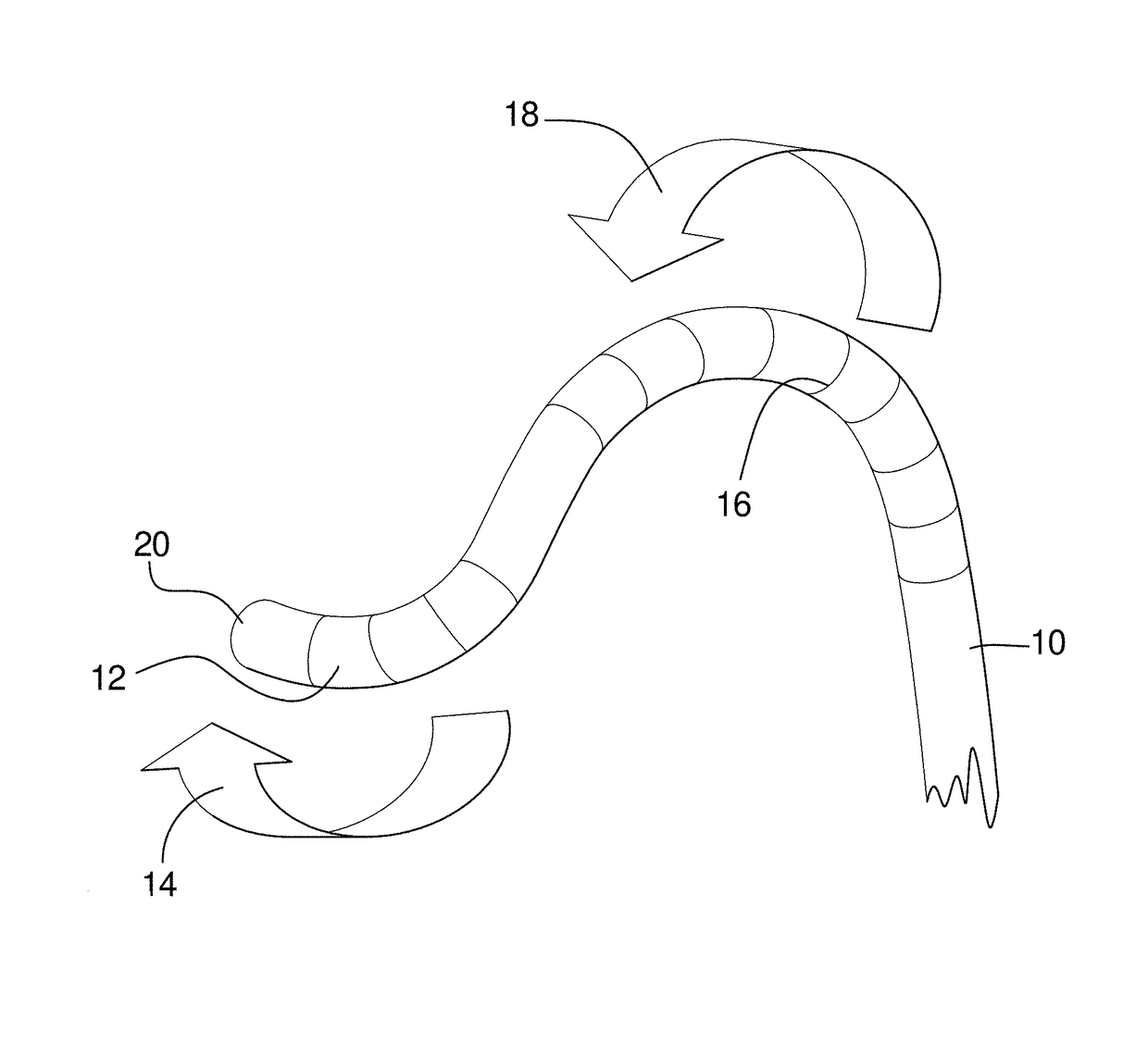
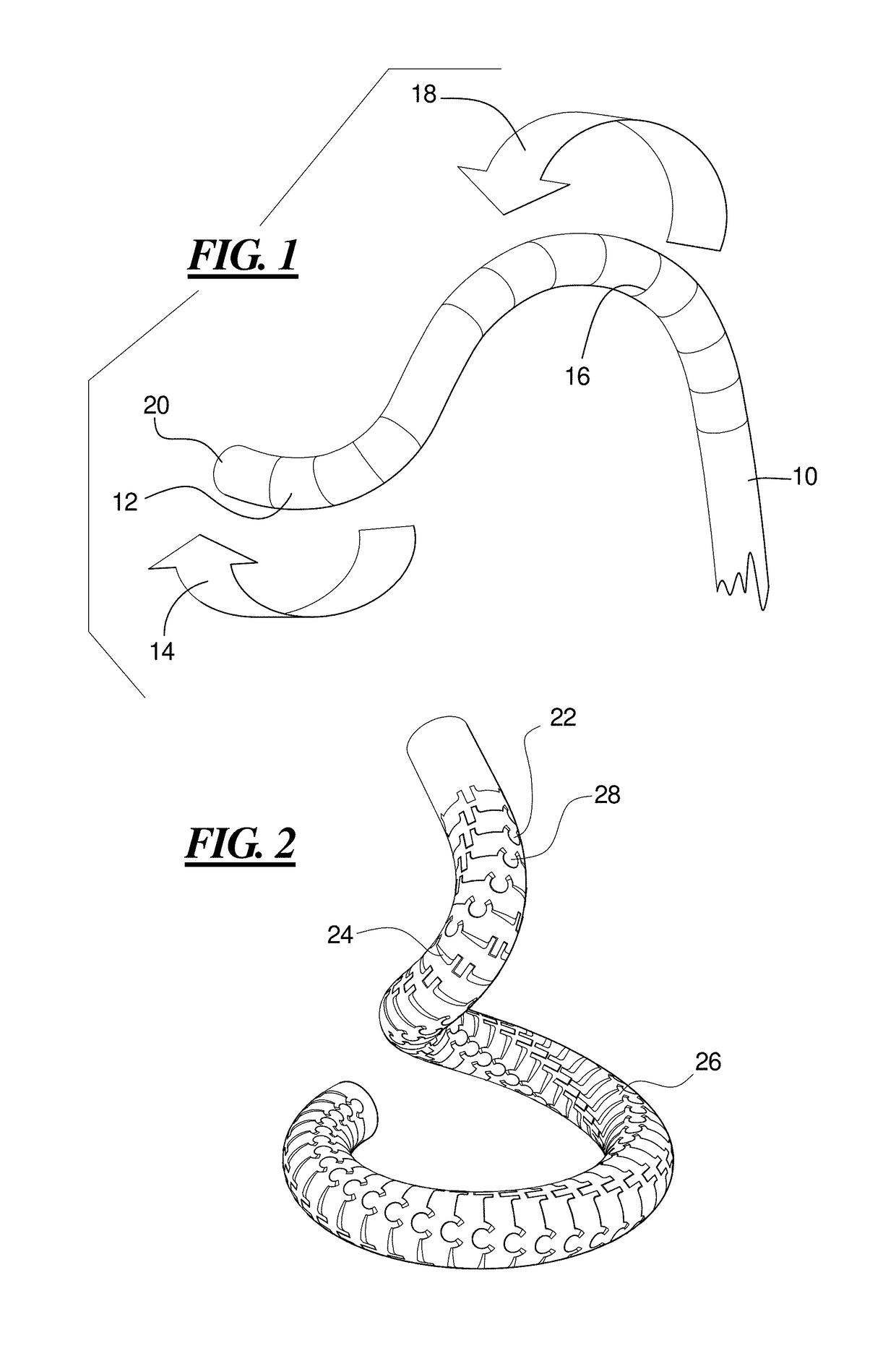
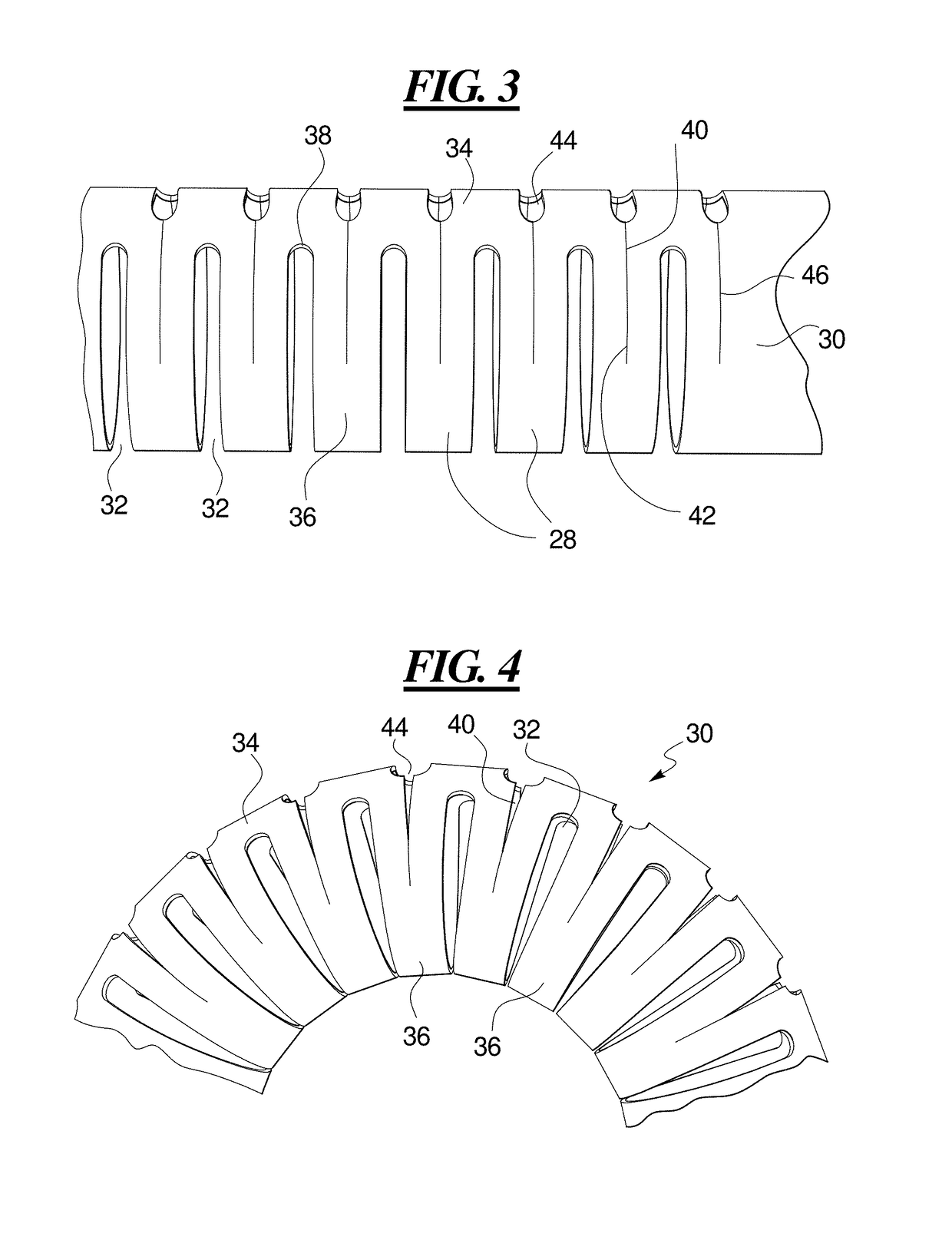
High load steerable shaft and method for cardiac catheter
A tube or skeleton for a steerable catheter includes a cylindrical body structured to permit bending in at least one bending direction and to resist bending in directions transverse to the bending direction. The cylindrical body may include a laser cut metal tube, wires bent and connected to one another, or one or more coiled wires with axial support wires attached to the coil to define one or more bending directions to form bending segments. The skeleton includes axially stiff portions that resist compression when a pull wire is pulled to cause bending movement. The axially stiff portions may include a backbone, an alignment of pivot structures, connected axially extending portions of wire elements, or axially extending support wires or rods. Two or more bending portions may be provided, each with different bending directions. Complex bending shapes may be provided by arranging the segments in rotated positions along the skeleton.
Owner:CREGANNA UNLTD
Method and devices for cardiac radiofrequency catheter ablation
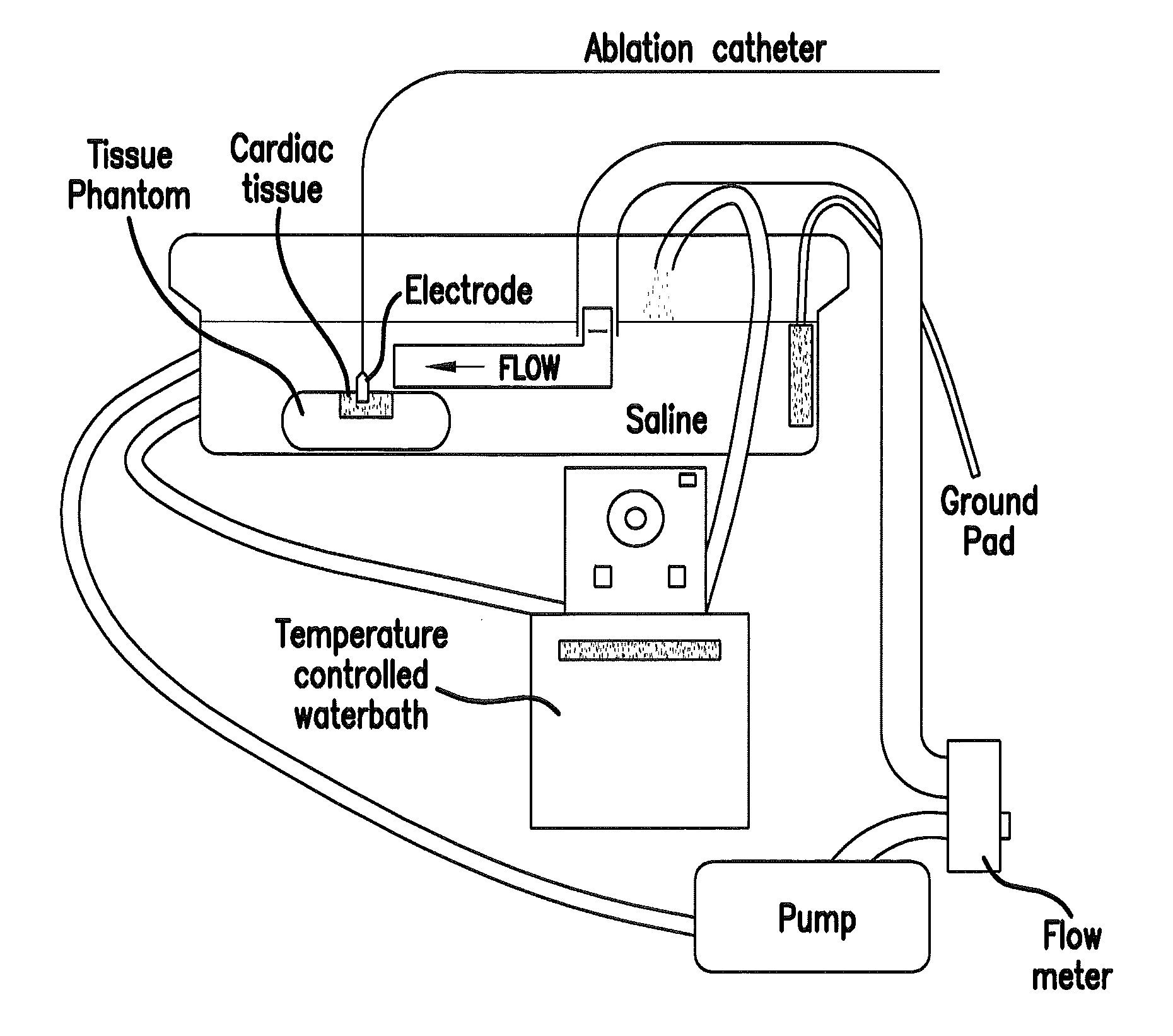
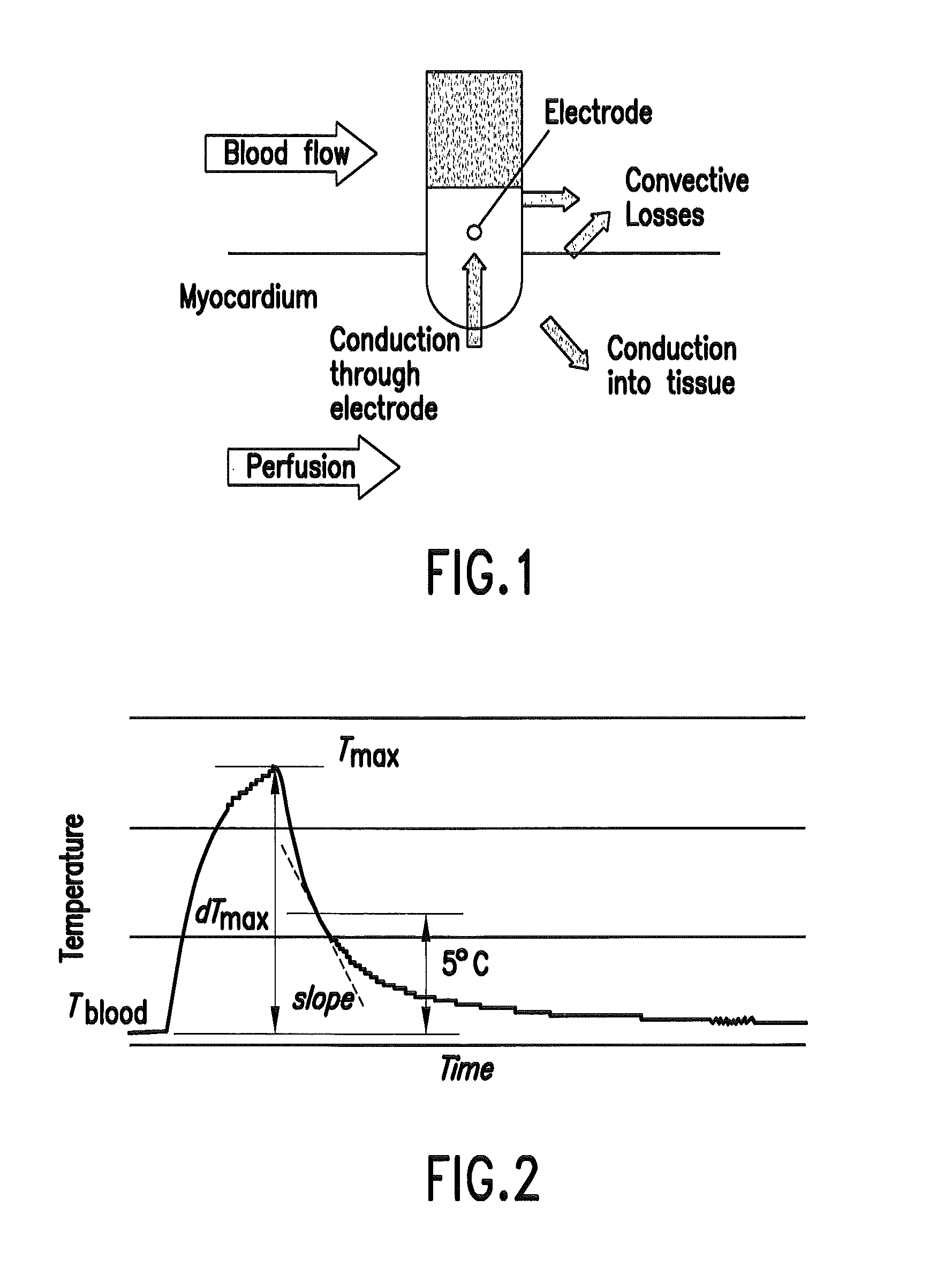
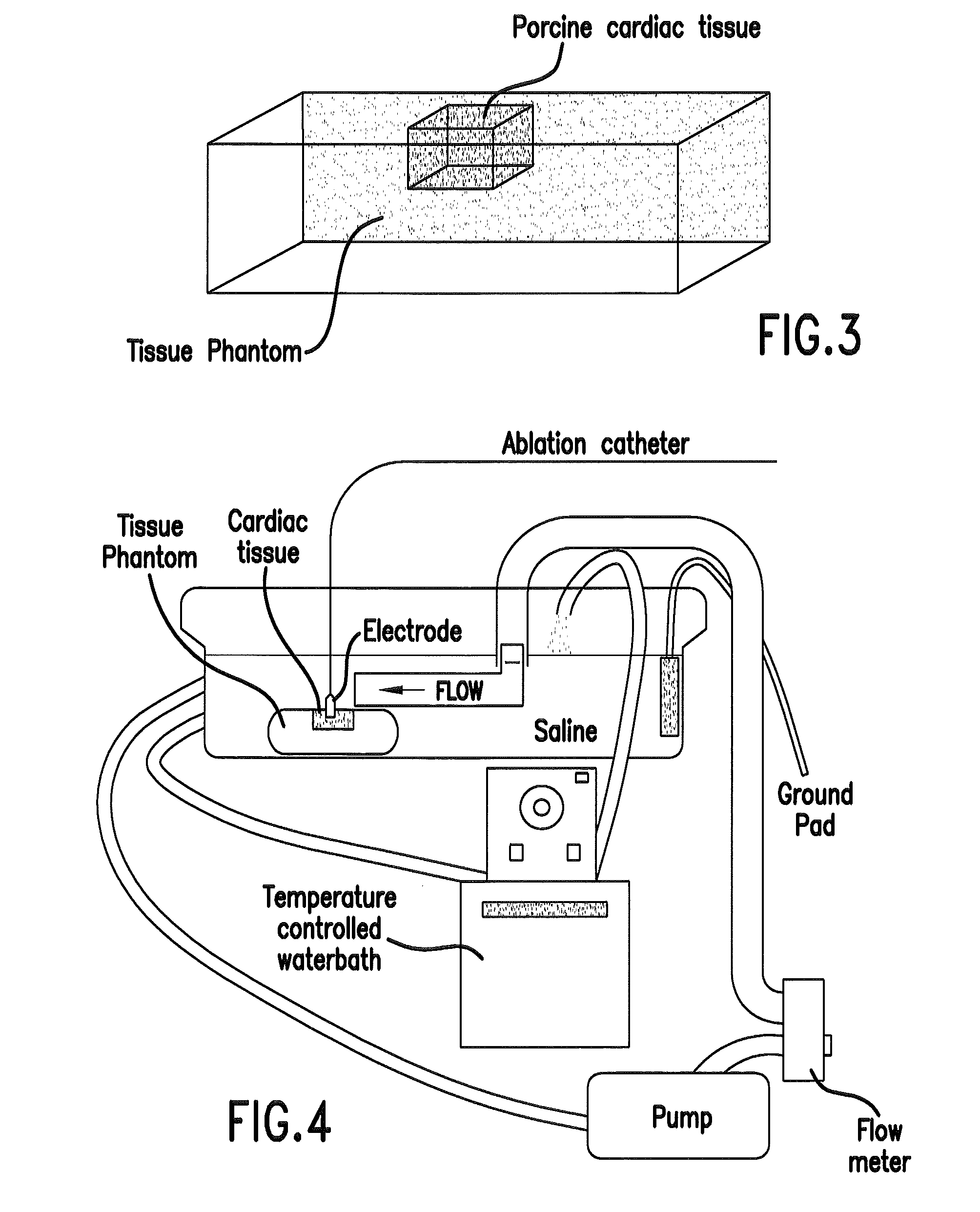
Embodiments of the invention comprise methods and devices that allow quantification of blood convective cooling at the cardiac RF catheter ablation site and allow for prediction of lesion size and / or computation of RF energy parameters and characteristics.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
Graphical user interface for medical imaging system
ActiveUS11324419B2Easy to handleSurgical systems user interfaceDiagnostic recording/measuringGraphical user interfaceDisplay device
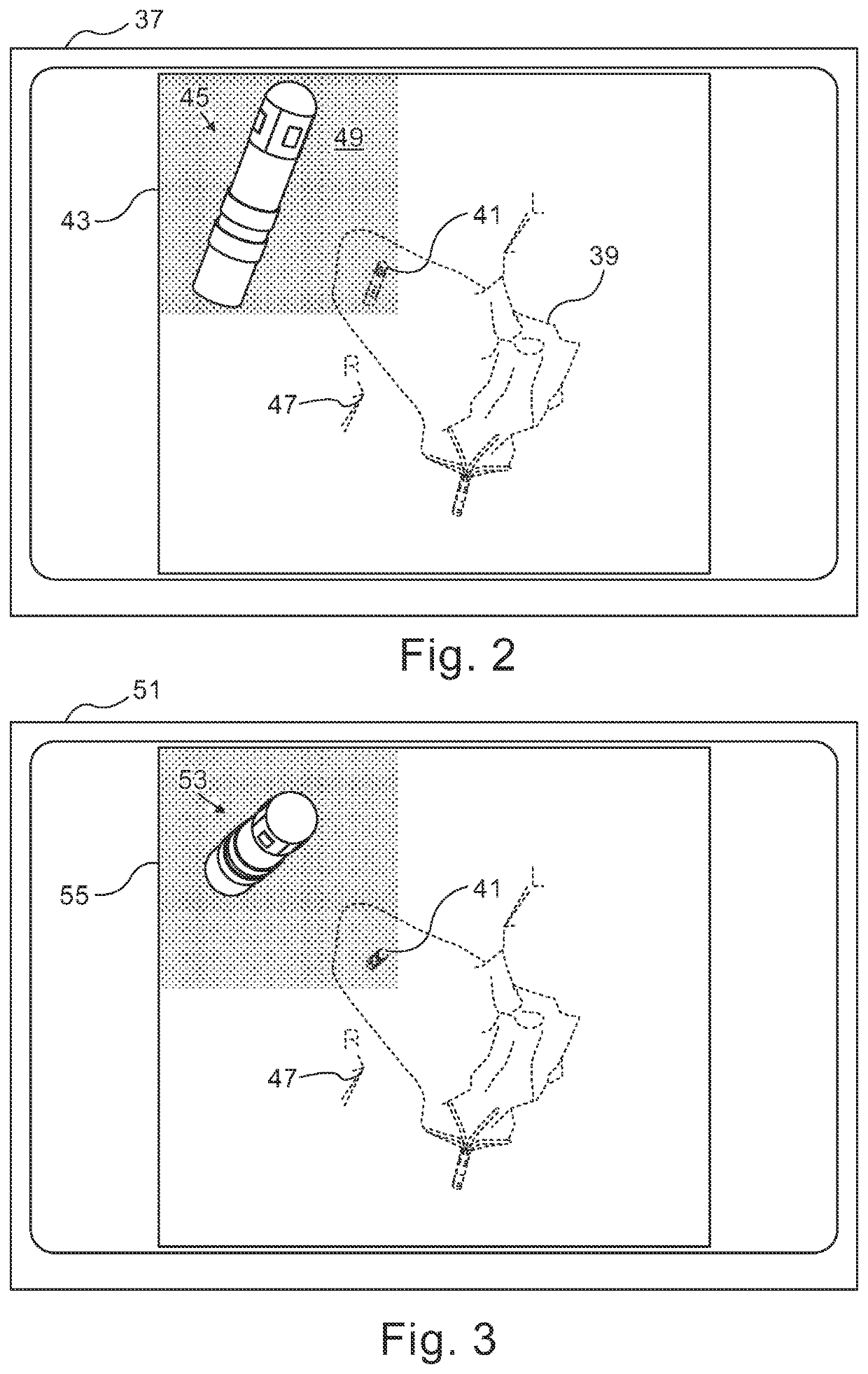
While obtaining electrophysiologic data from a cardiac catheter a series of visual displays are presented. The displays include a respective current image of the heart and the distal portion of the cardiac catheter therein and further include a catheter icon that represents the distal portion of the cardiac catheter, The catheter icon is separated from the image of the heart in the displays. The catheter icon has indicia that represent functional elements of the cardiac catheter.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com