Patents
Literature
73 results about "Solid region" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
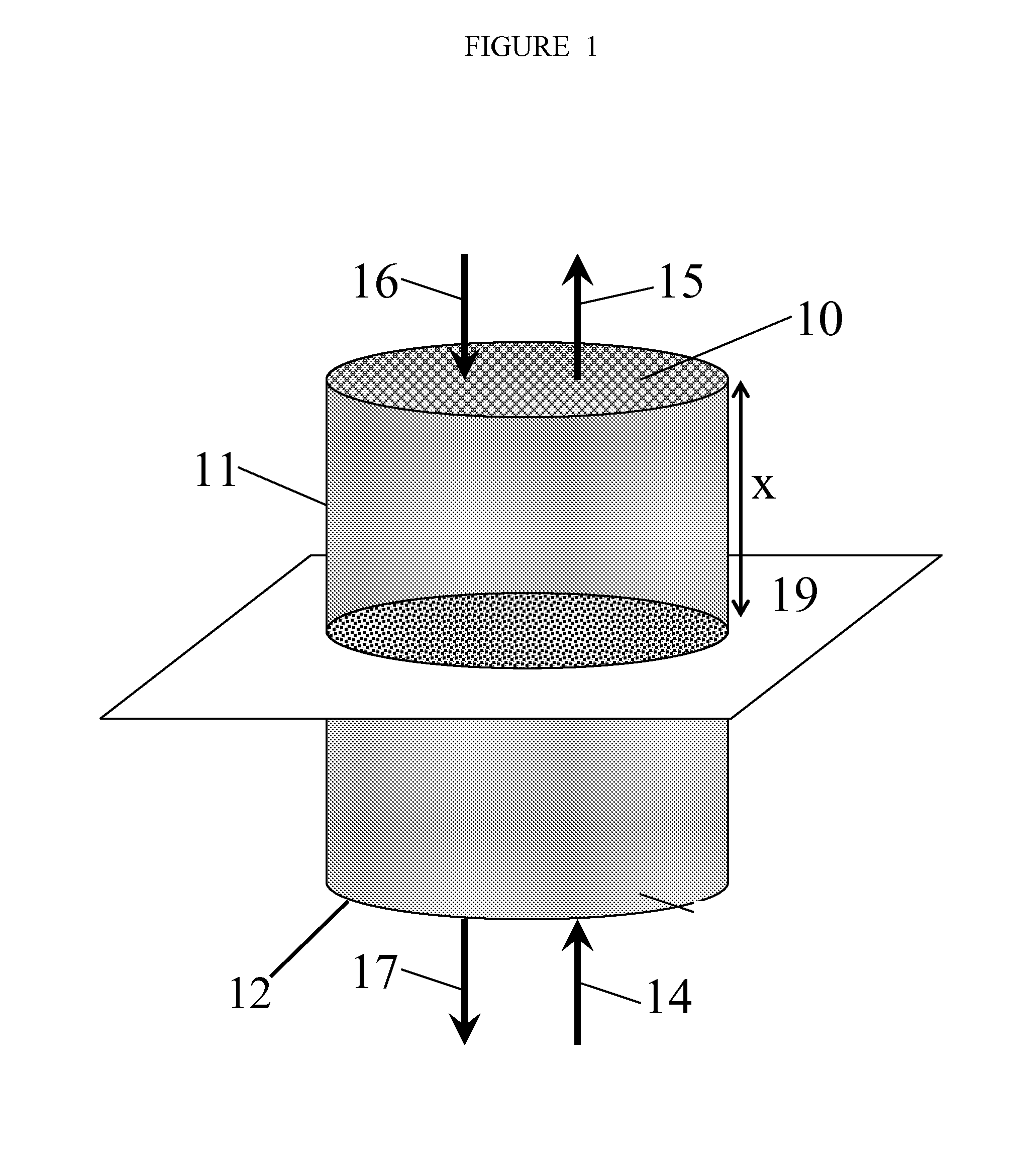
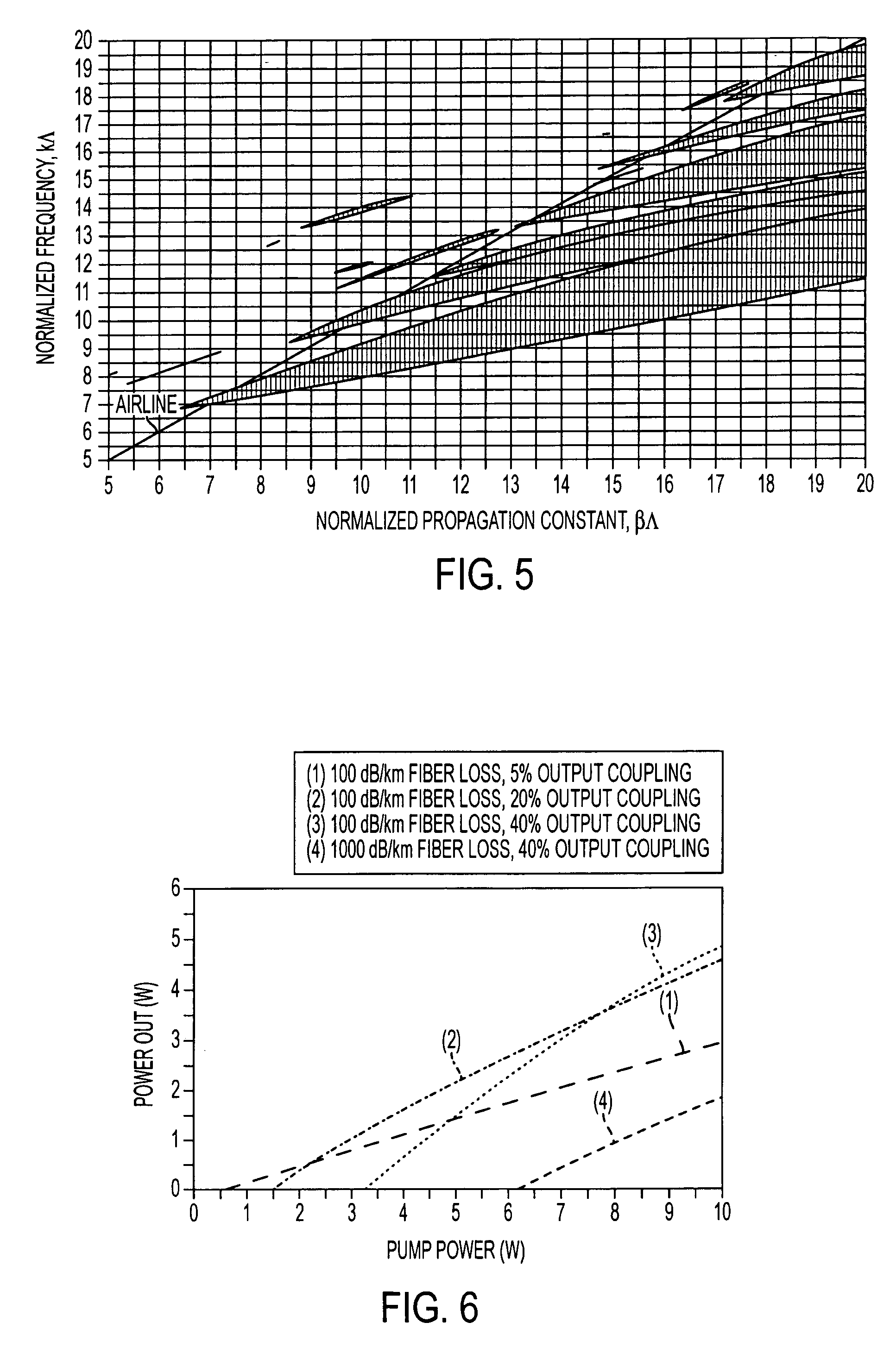
A solid region is any finite three dimensional region. The boundary of this region, a closed surface, is the surface the separates the interior of the solid region from everything else. So long as the region is finite (ie.
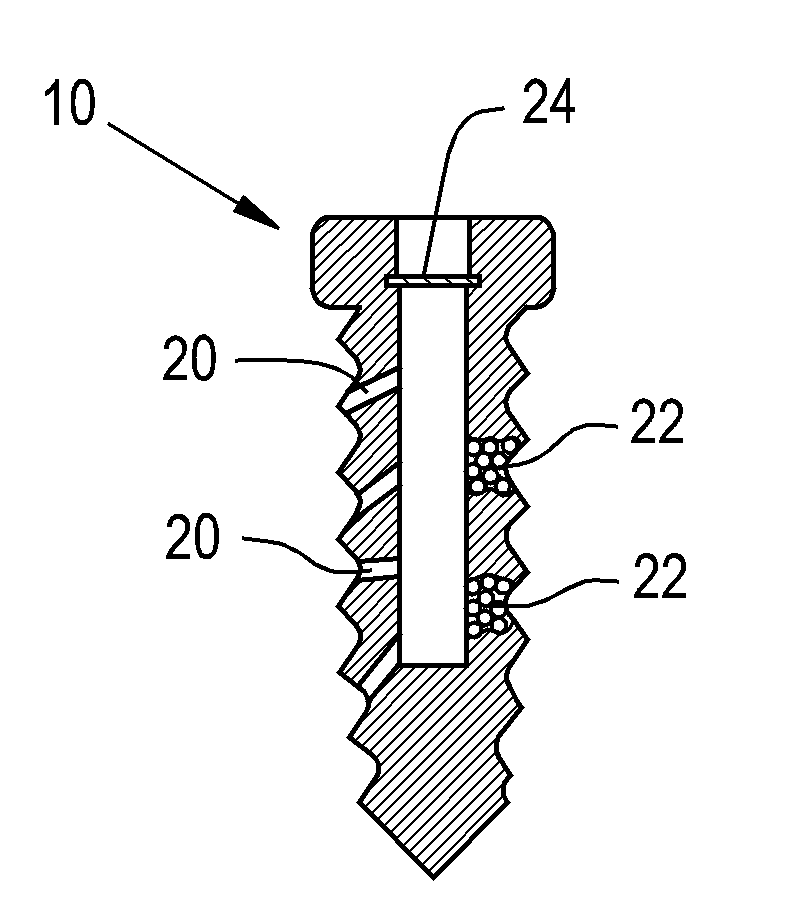
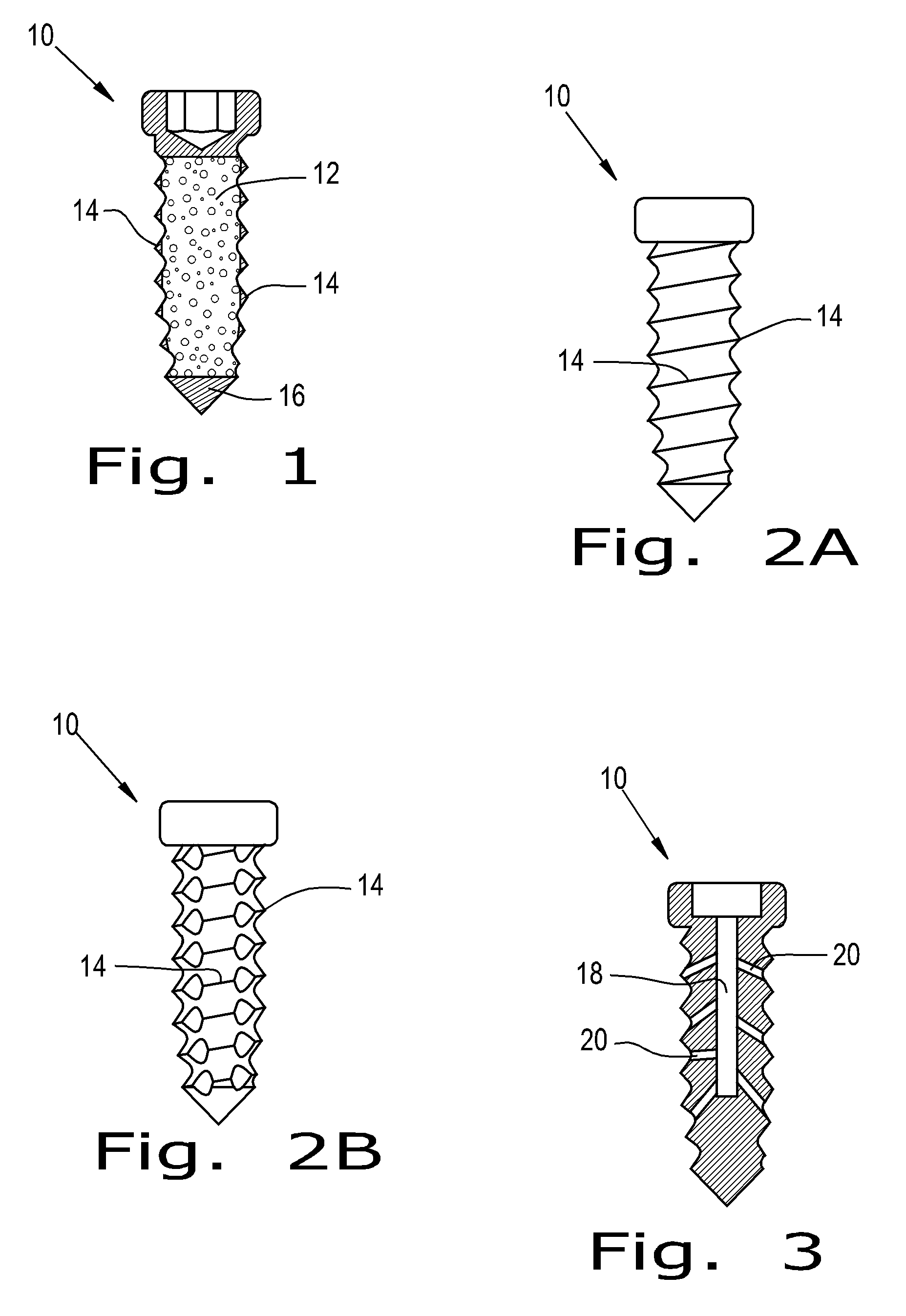
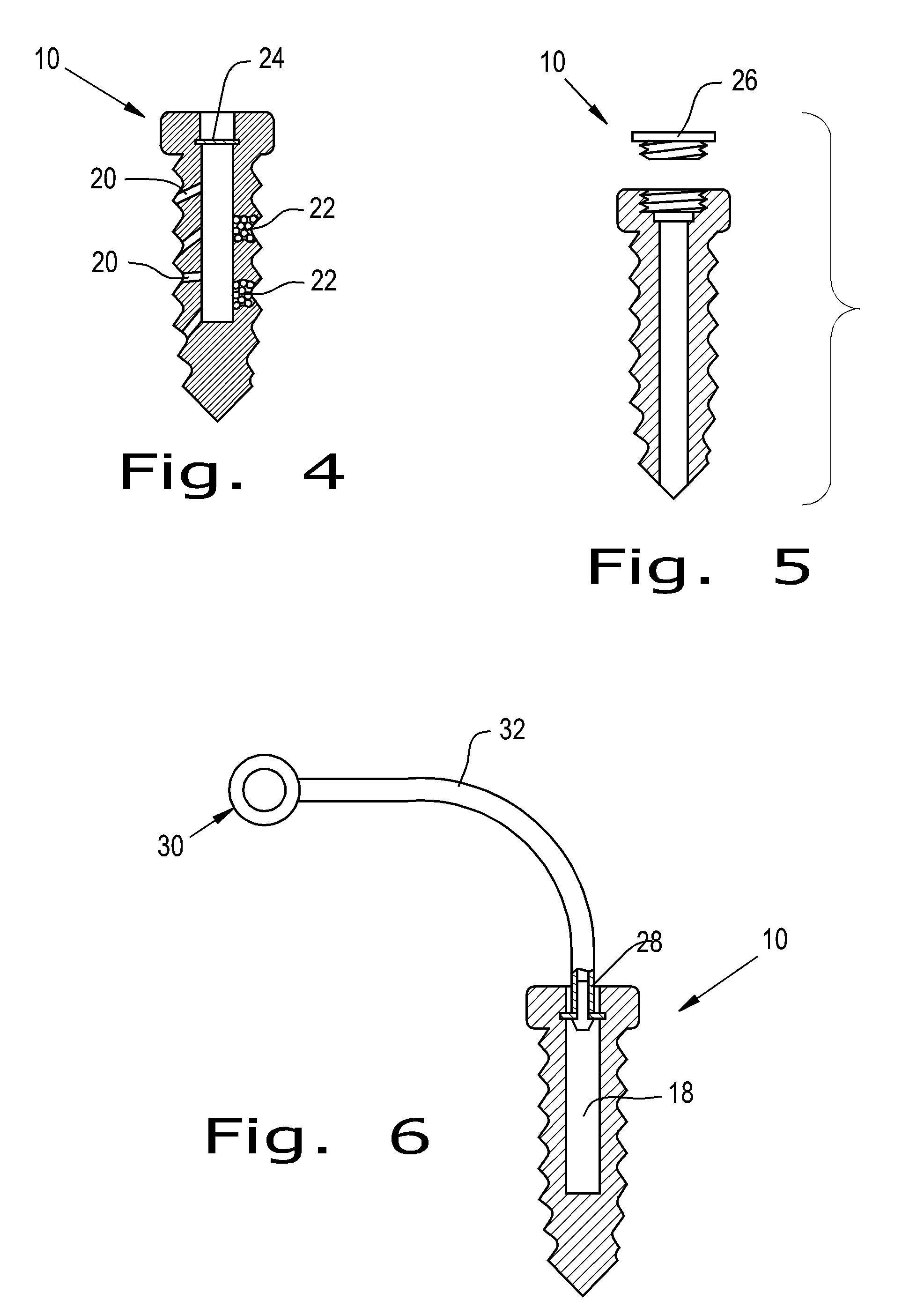
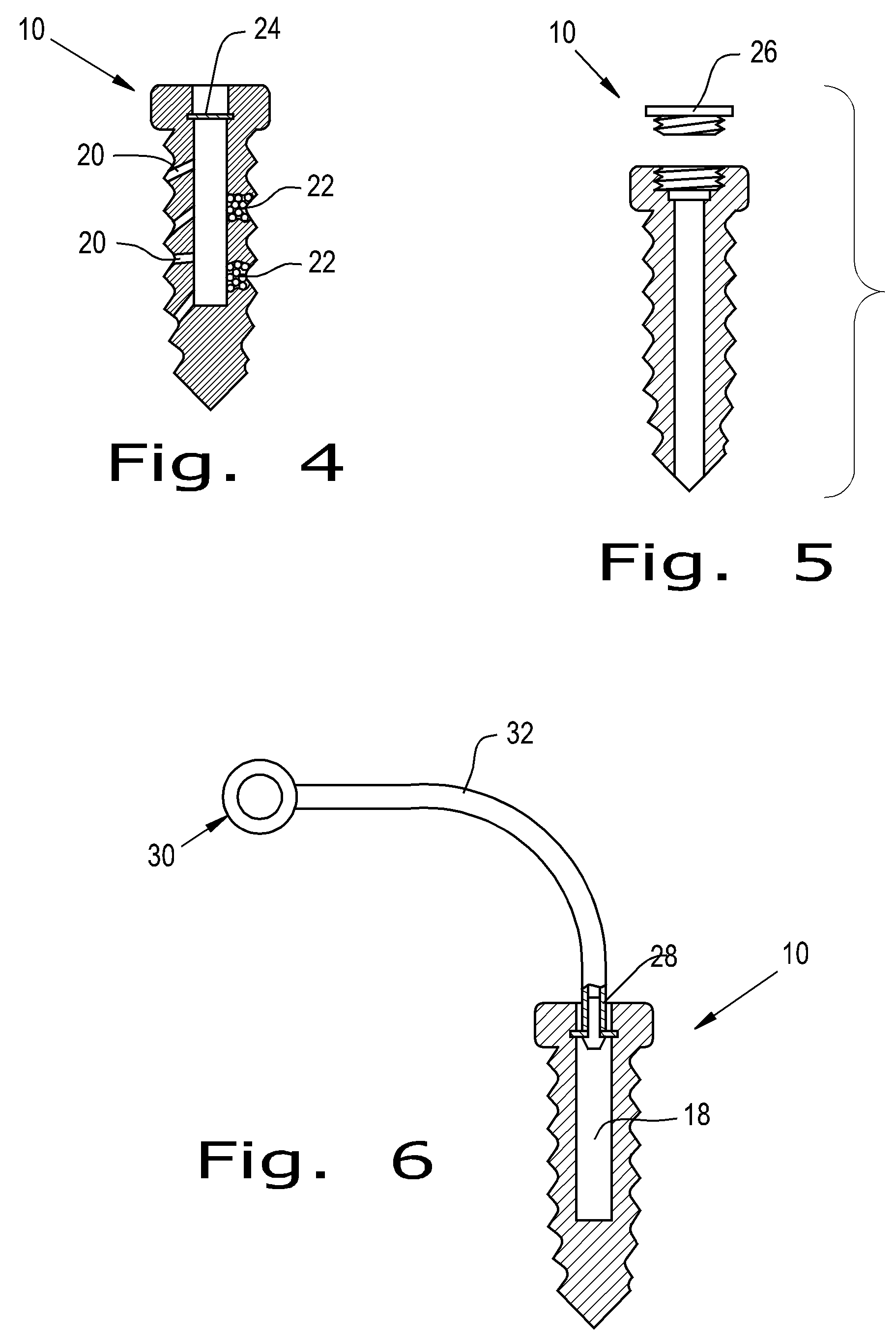
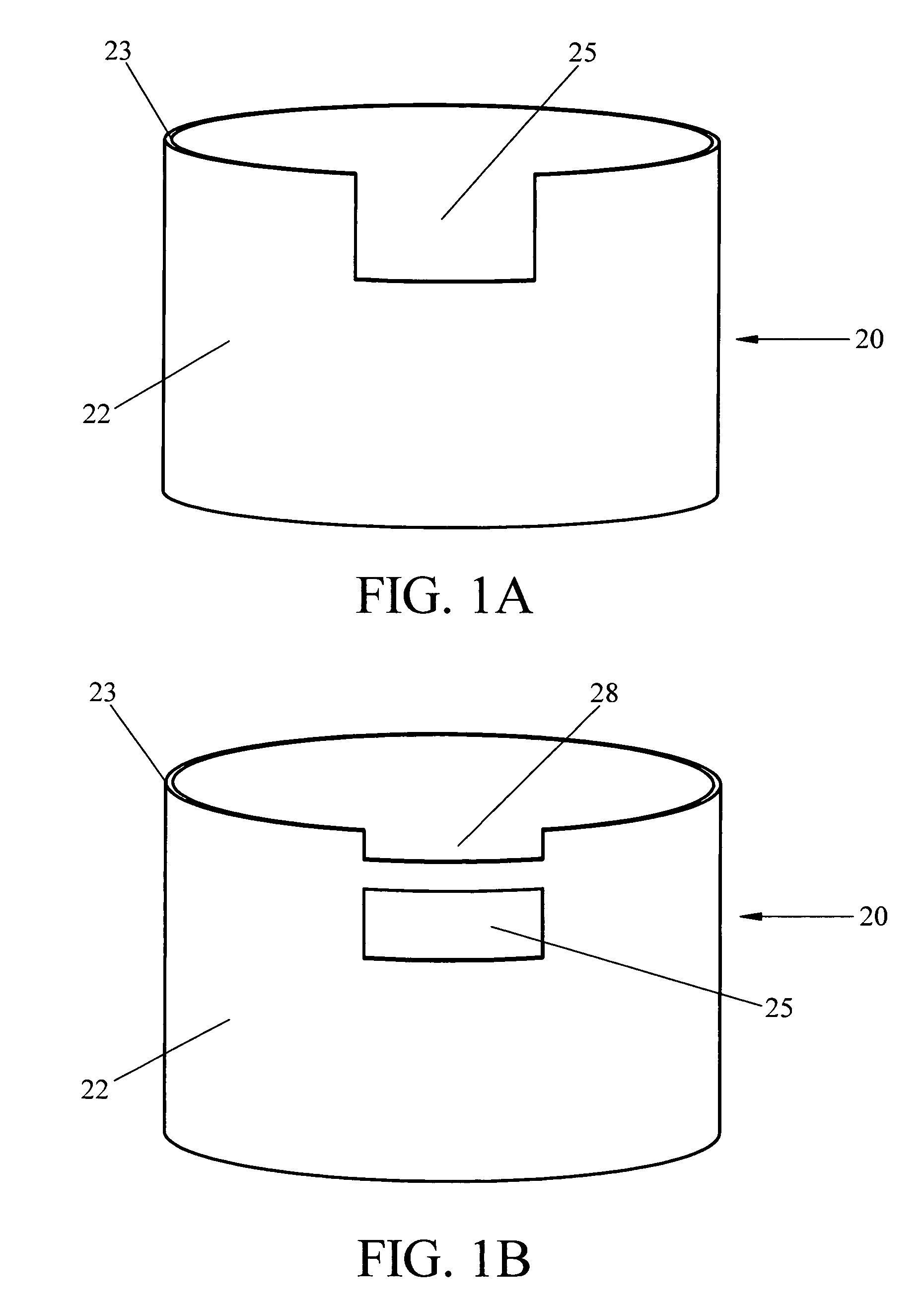
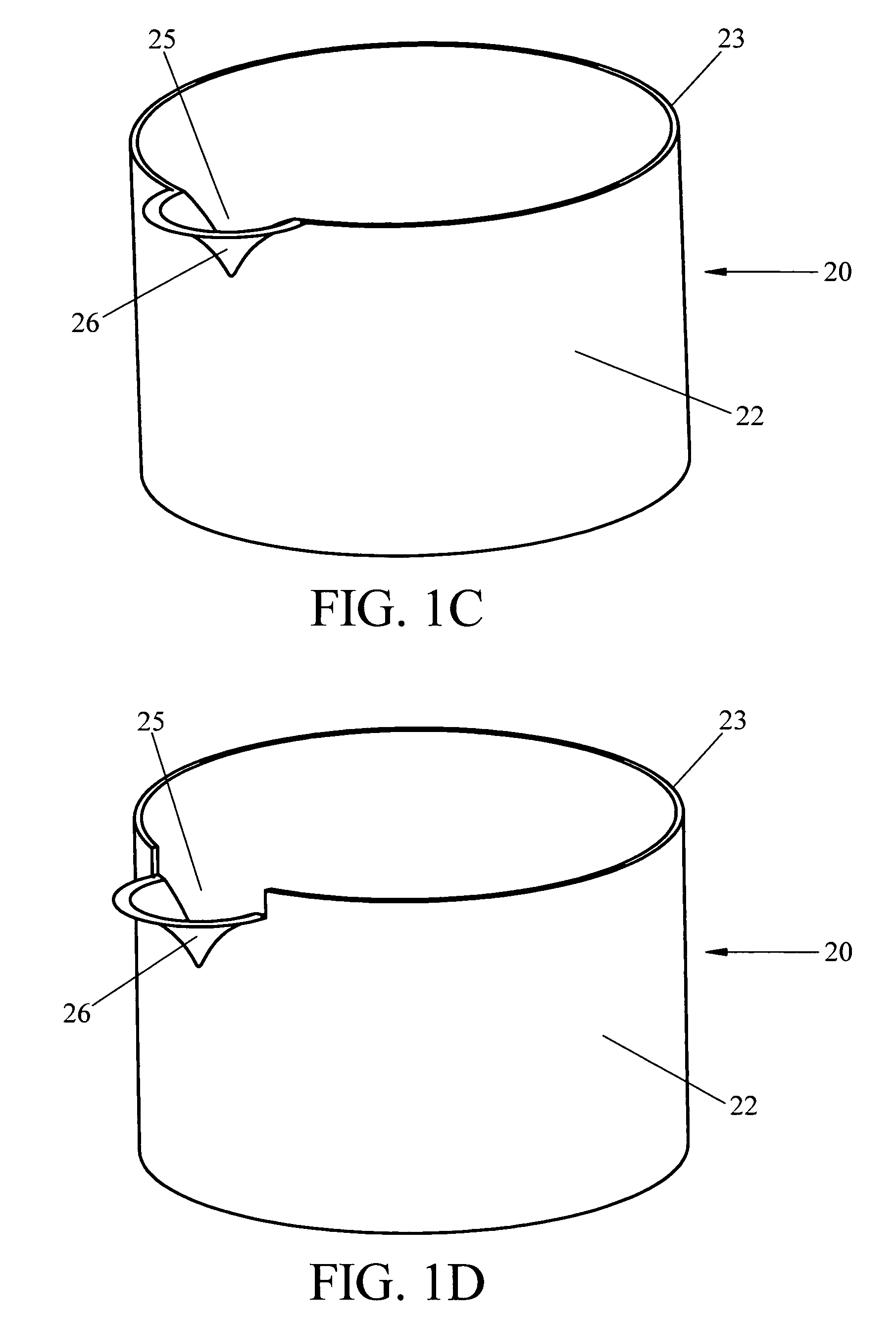
Orthopaedic screws
ActiveUS20100042167A1Successful tissue integrationImprove adhesion strengthSuture equipmentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusPorositySolid region
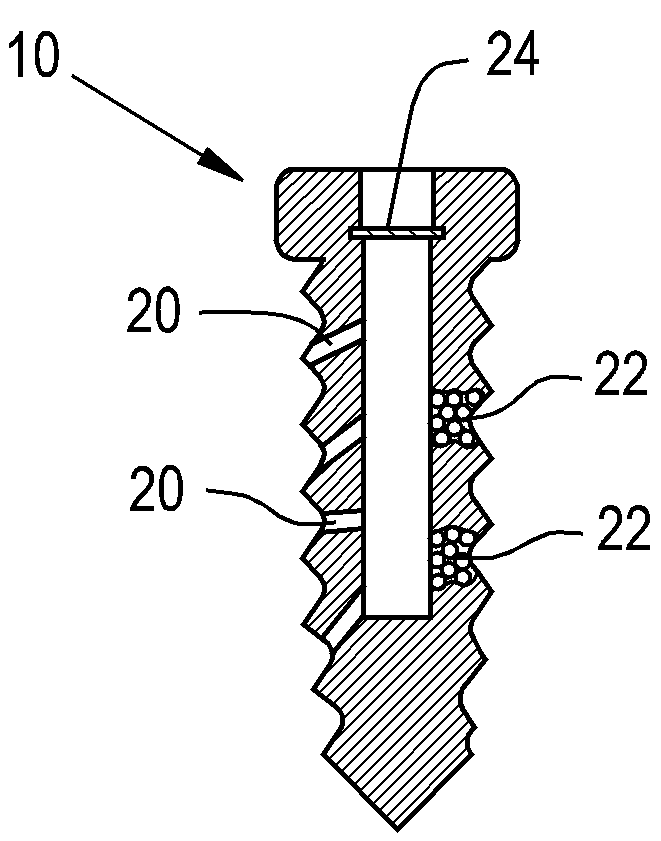
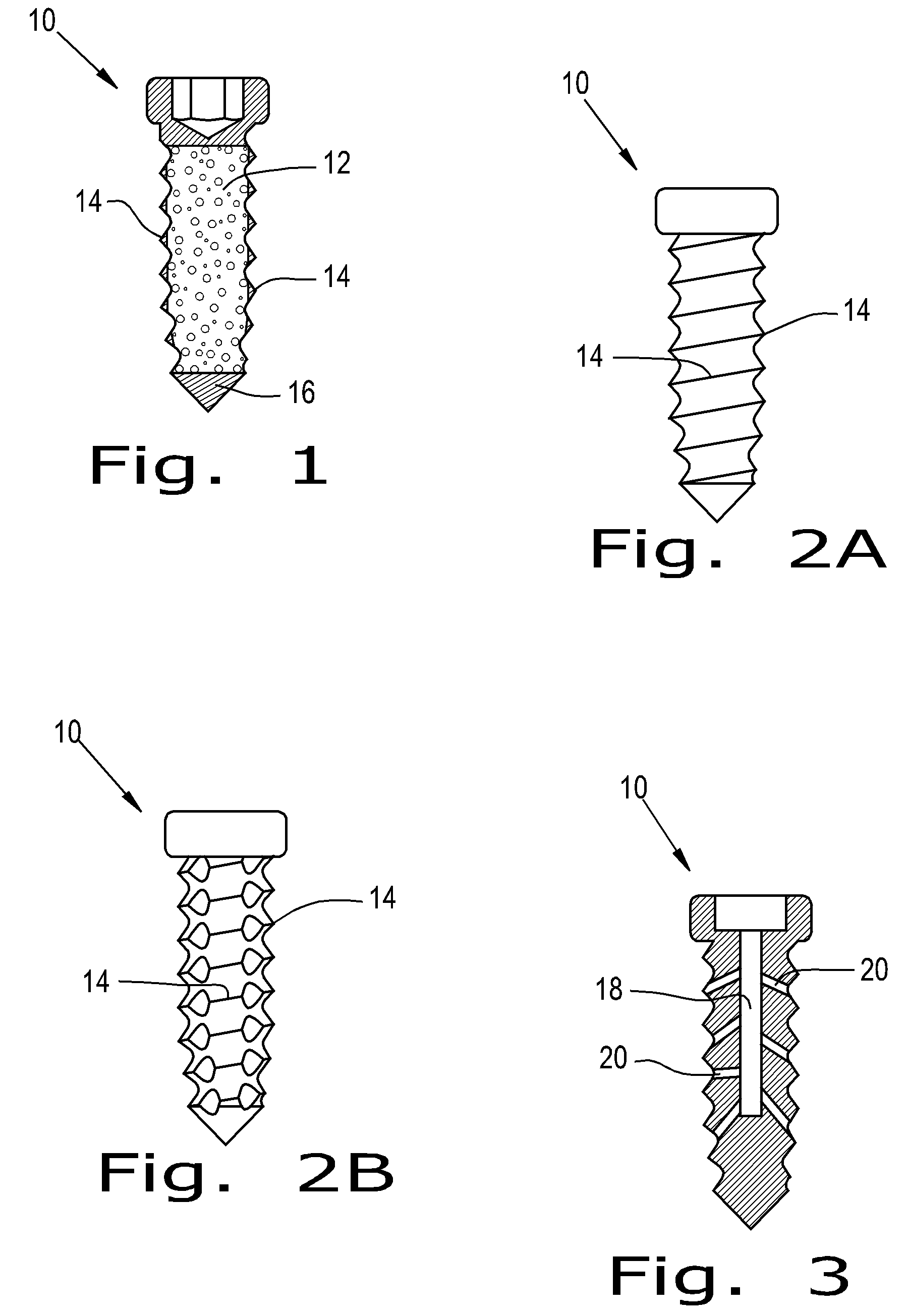
An orthopaedic screw having a plurality of regions, at least one of which may be porous. The orthopaedic screw includes a head, a tip and at least one thread. The porosity of the screw of the present invention can vary within the part or region, including changes in pore shape, size and density. These characteristics can vary along the length of the screw axis and / or radially (from the outer diameter to the axis). The orthopaedic screw may further include at least one solid region formed of any implantable polymer, reinforced polymer or metal.
Owner:SMED TATD
Hollow core photonic band gap infrared fibers
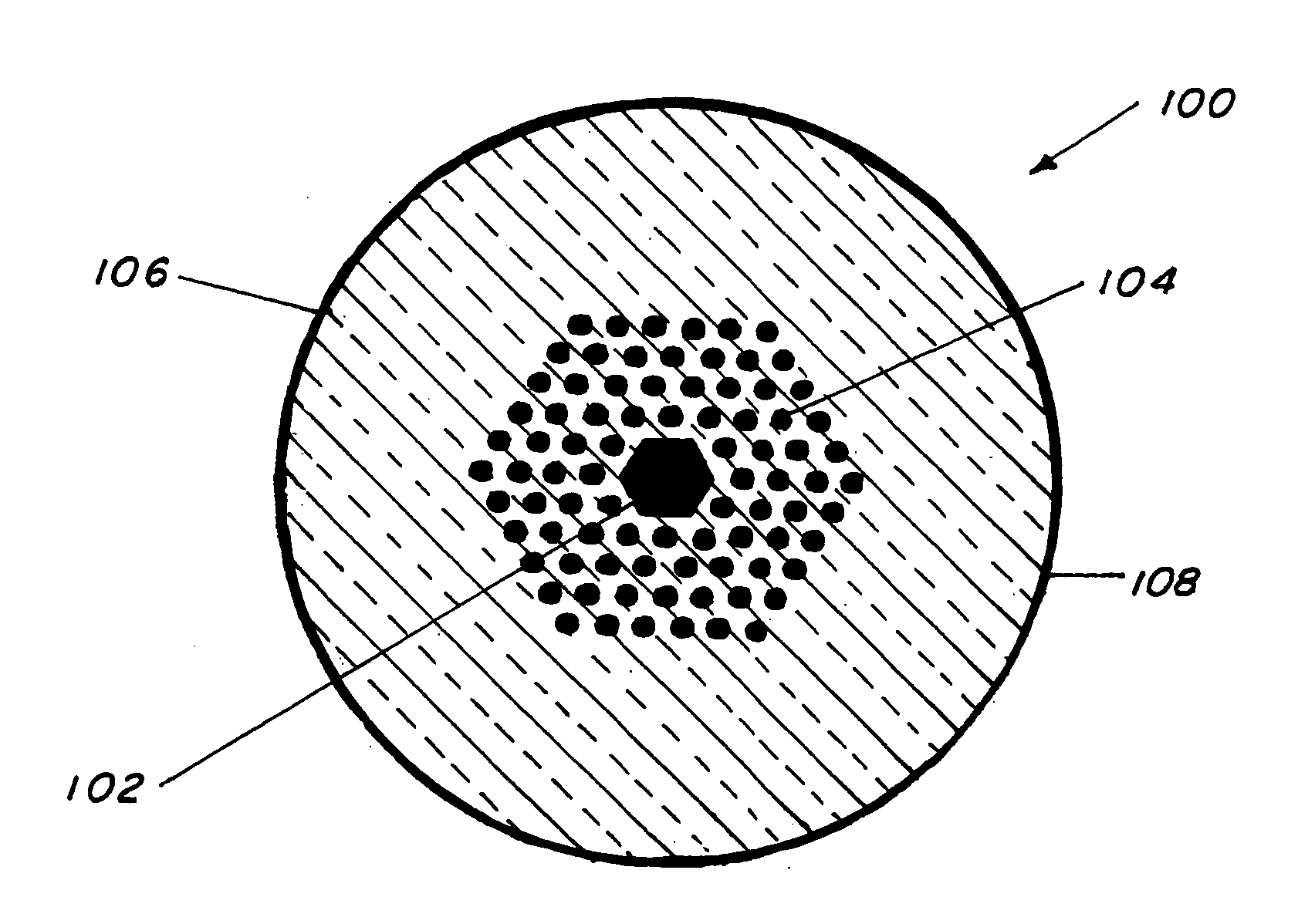
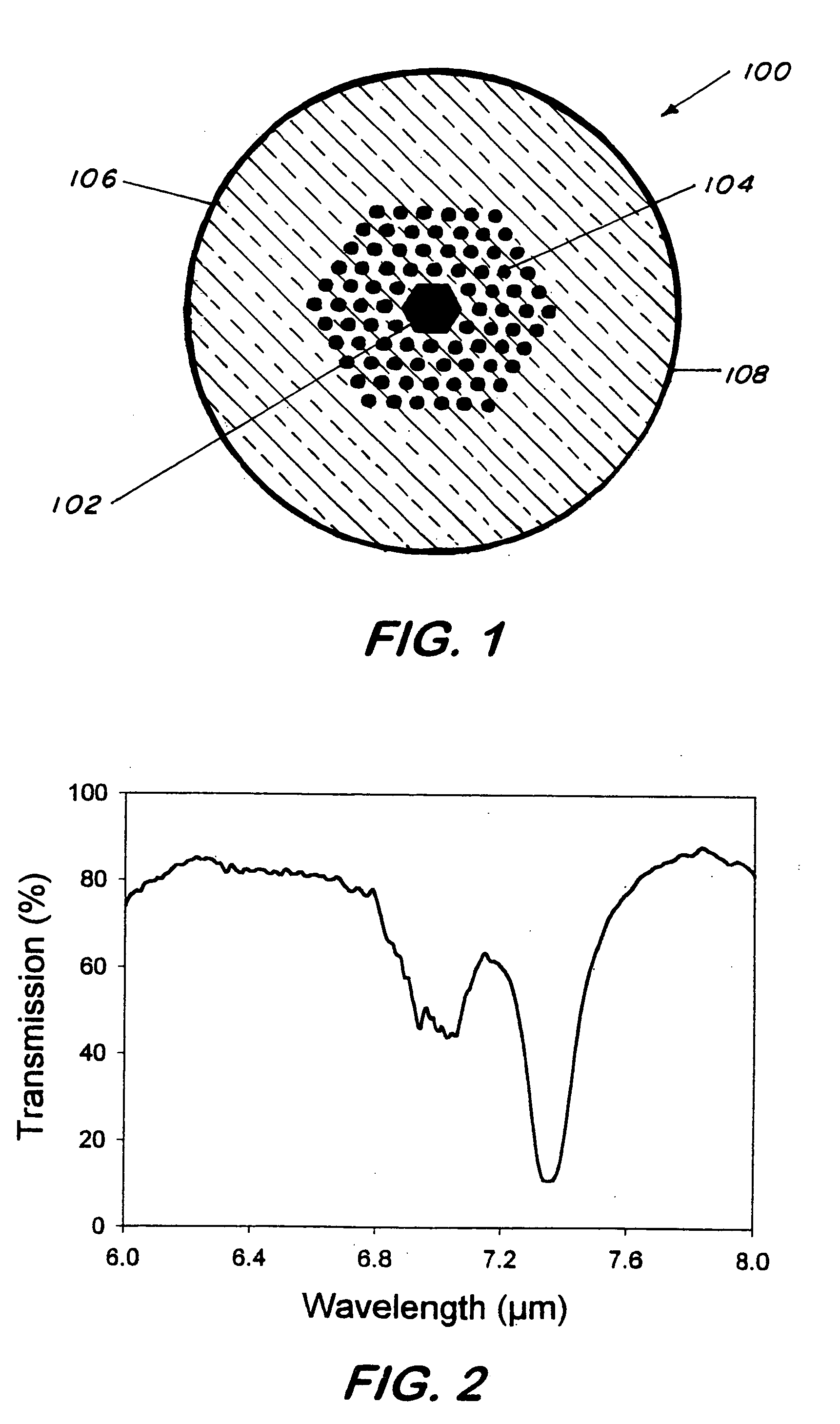
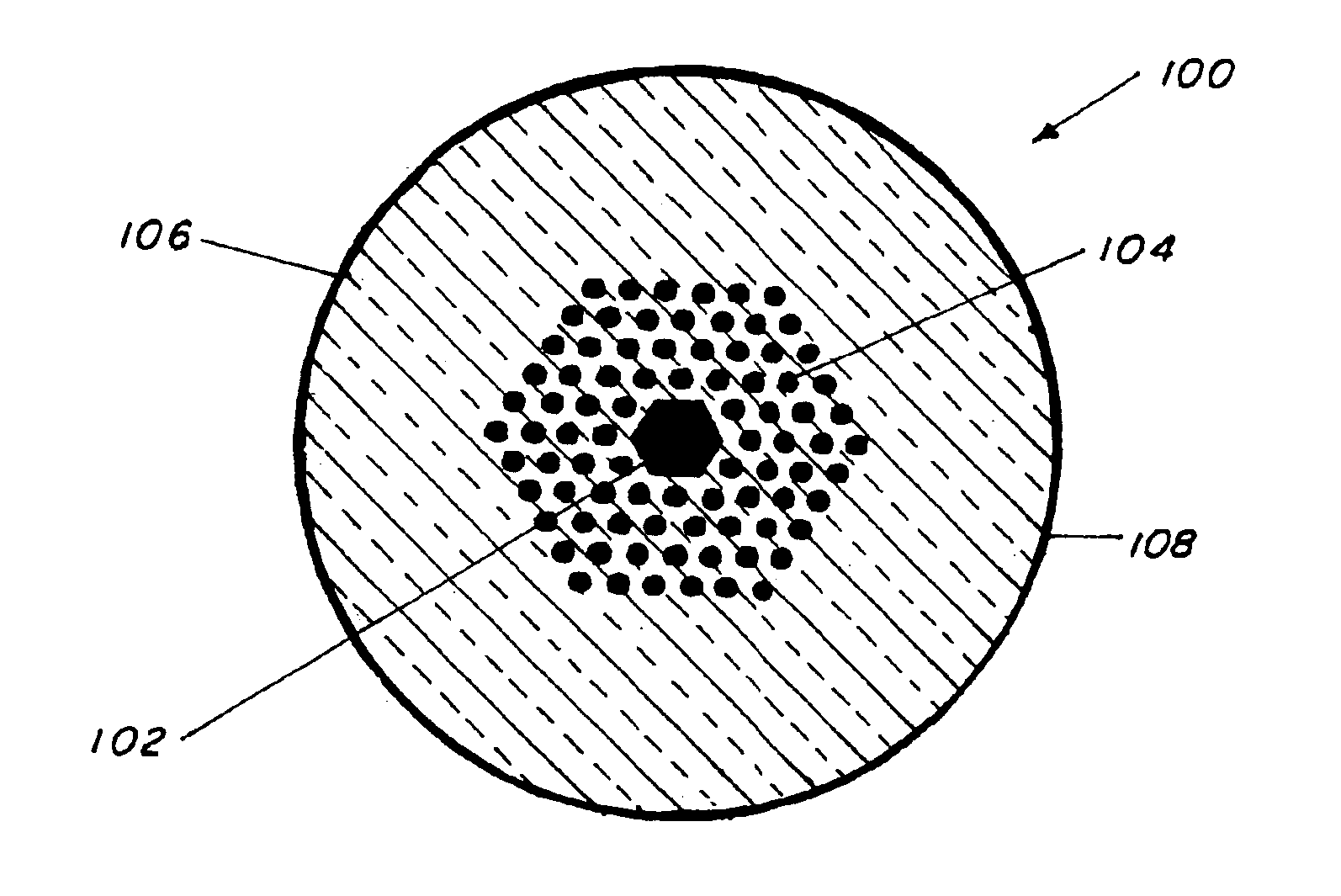
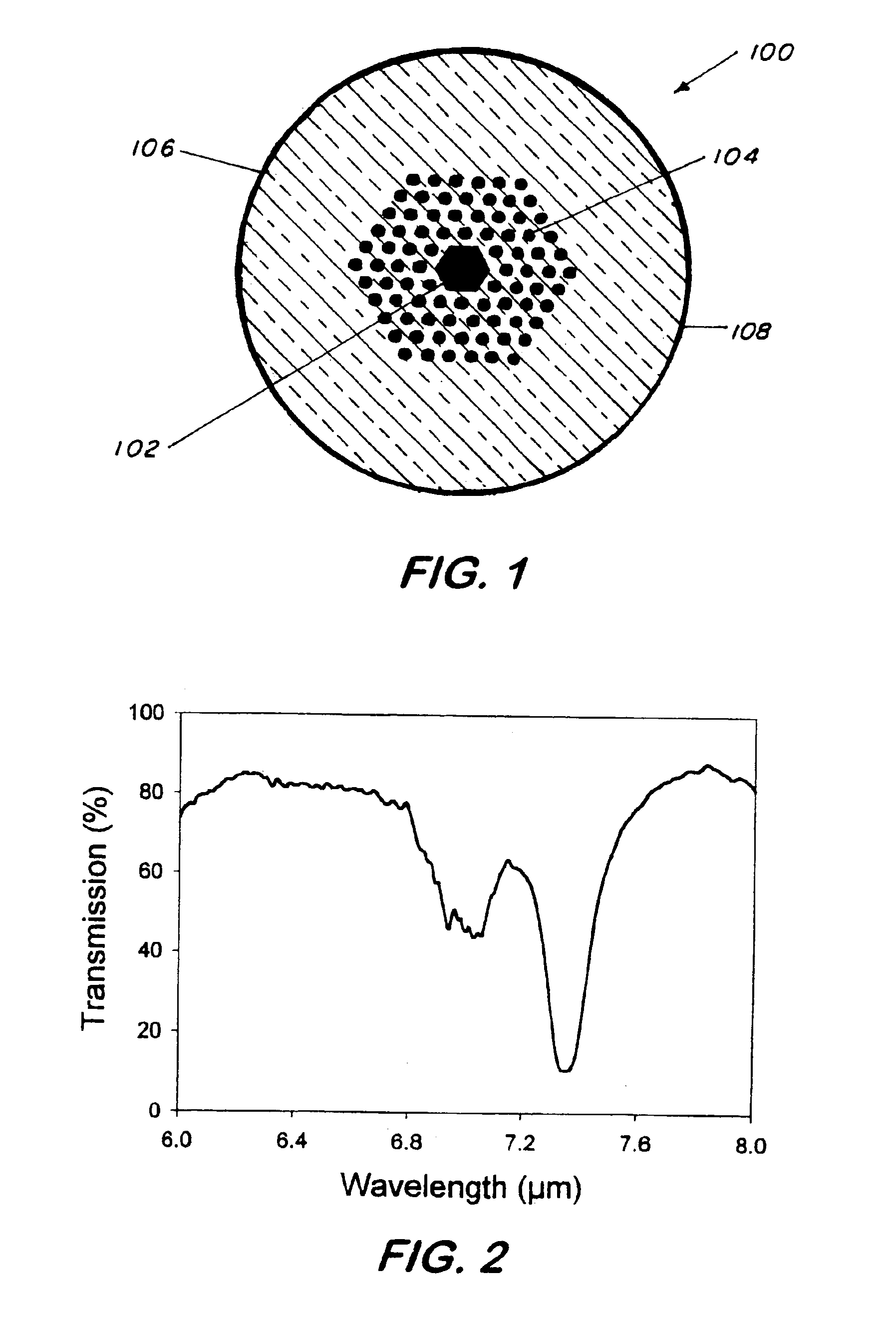
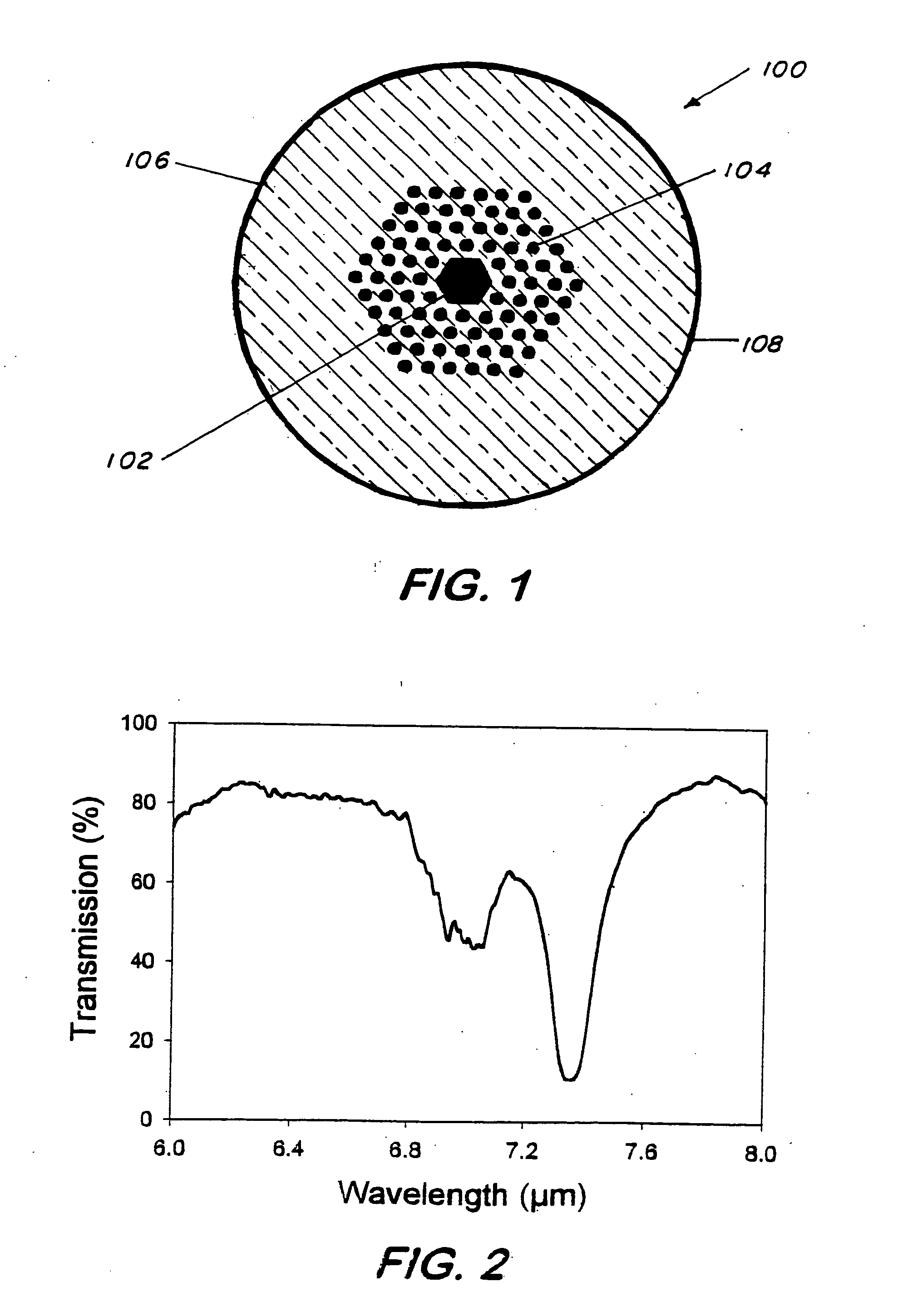
This invention pertains to a hollow core photonic band gap chalcogenide optical glass fiber and to a fabrication method for making the fiber. The fiber, which is 80-1000 microns in outside diameter, is characterized by a solid glass circumferential region and a structured region disposed centrally within the solid region, the structured region includes a hollow core of 1 micron to several hundreds of microns in diameter surrounded by a plurality of parallel hollow capillaries extending parallel to the core, the core being centrally and longitudinally located within the fiber. Ratio of open space to glass in the structured region is 30-99%. The fabrication method includes the steps of providing a mold, placing chalcogenide micro-tubes around the mold, stacking chalcogenide micro-canes around the stacked micro-tubes, fusing the micro-tubes and the micro-canes to form a preform, removing the mold and drawing the preform to obtain the fiber. In an alternative fabrication method, the fiber is made by extruding flowing chalcogenide glass through suitably made plate to form a preform and then drawing the preform to form the fiber.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Orthopaedic screws
ActiveUS8475505B2Improve adhesion strengthStrong bonesSuture equipmentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusPorositySolid region
Owner:SMED TATD
Three-Dimensional Printing of Metallic Materials
InactiveUS20150217367A1Additive manufacturing apparatusMolten metal pouring equipmentsSolid regionMetallic materials
Methods of printing metallic objects include providing parameters of an object for printing, and controlling a deposition of a fluid metallic material to form the object. At least an outer surface region of the fluid metallic material is converted to a solid region after deposition.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
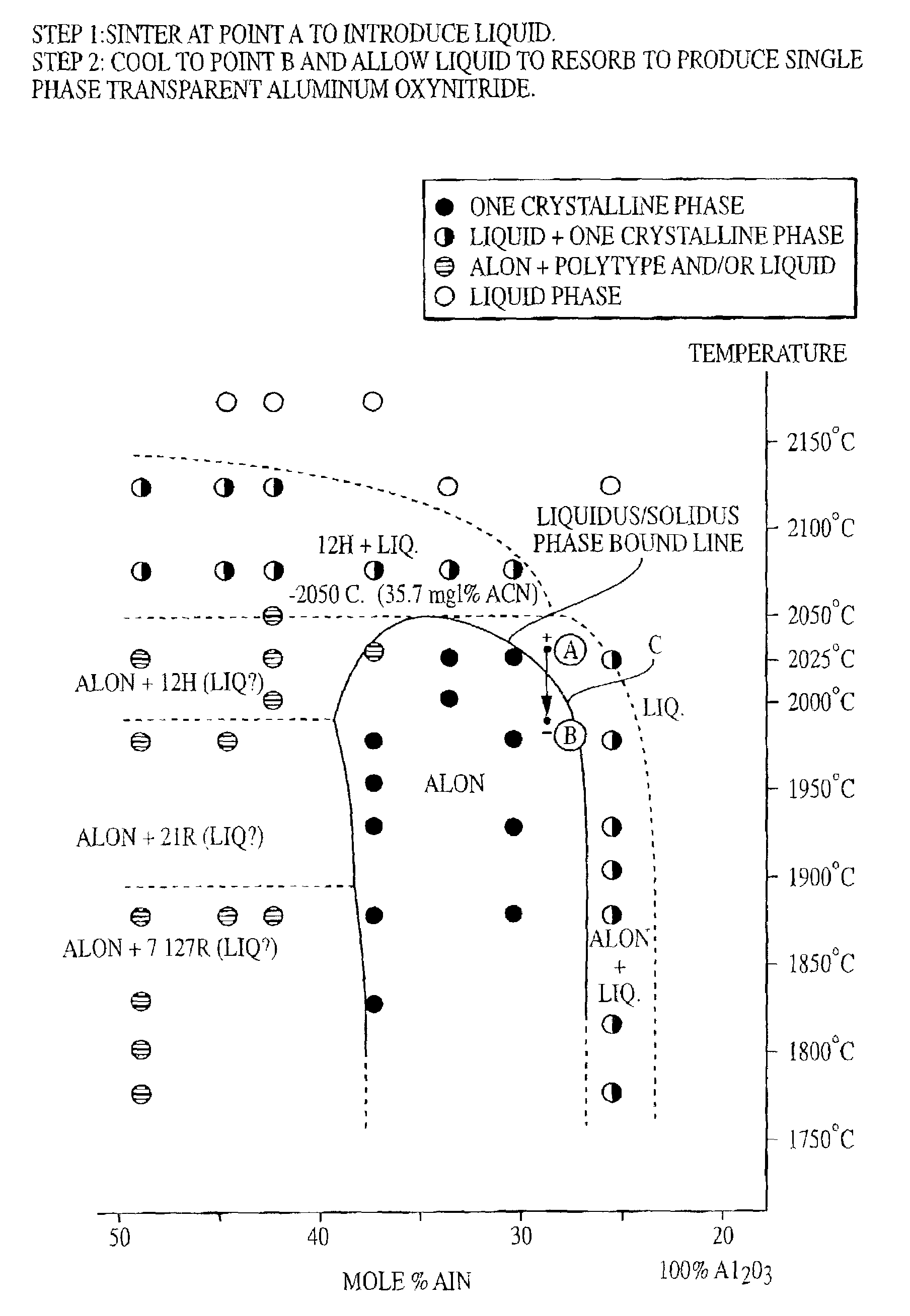
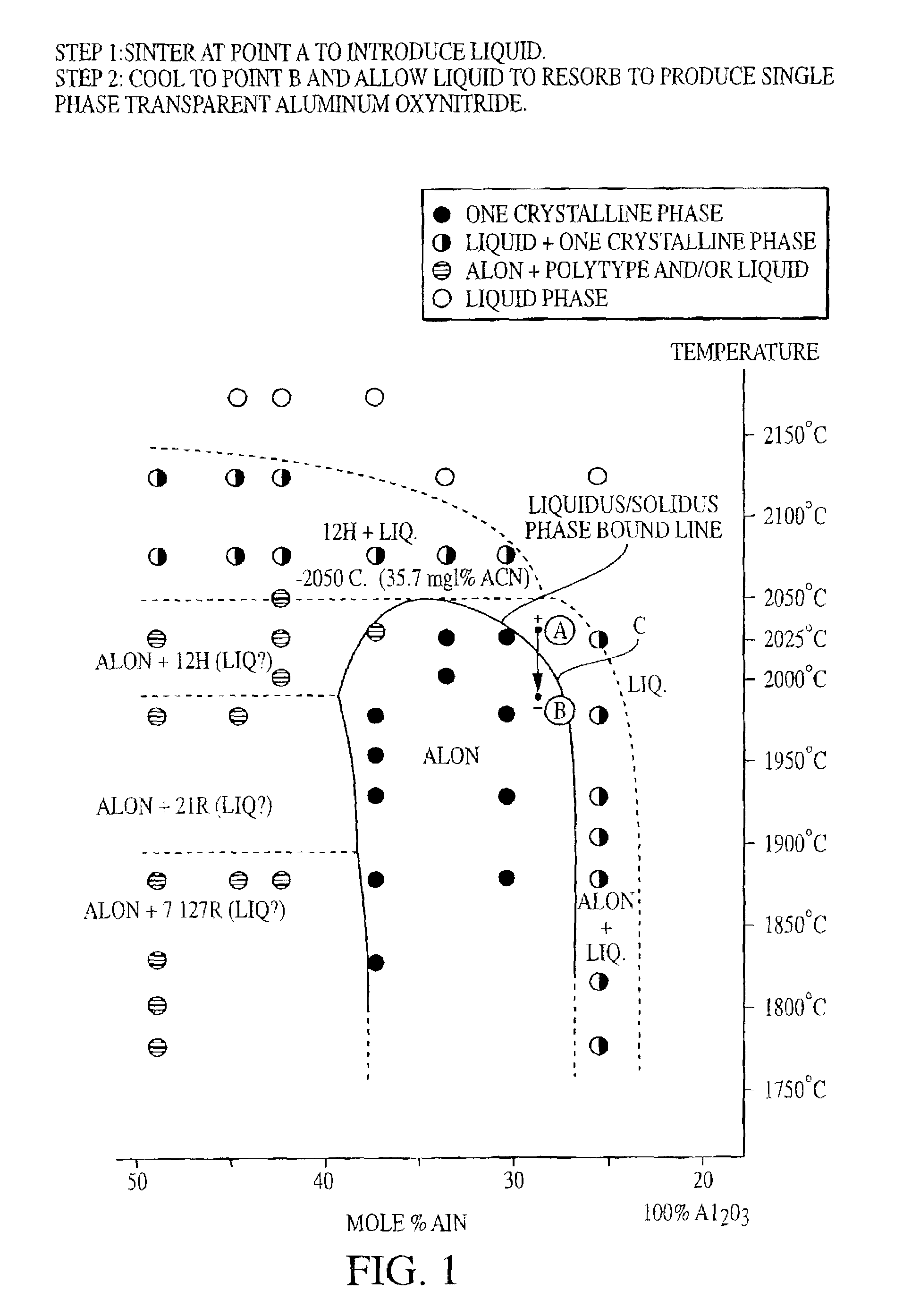
Transient liquid phase reactive sintering of aluminum oxynitride (AlON)
InactiveUS7045091B1Low production costShorten the sintering timeAmmonium nitratesNitrogen compoundsSolid regionAluminum oxynitride
A transparent aluminum oxynitride product is produced by a first heat treating step wherein a combination of Al2O3 and AlN at a temperature within the solid-liquid phase and a second step of sintering the heat treated combination at a temperature at least 50° C. less than the heat treating temperature. The method introduces a small fraction of liquid that aids in pore elimination and densification. In a single step, the material is shifted from the liquid / solid region into a solid AlON solution region, wherein the liquid is fully reacted with the solid AlON phase, with further sintering occurring. The procedure is sufficient to eliminate voids and other imperfections which often result in a reduction in optical clarity.
Owner:ARMY UNITED STATES OF THE AMERICAS AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE
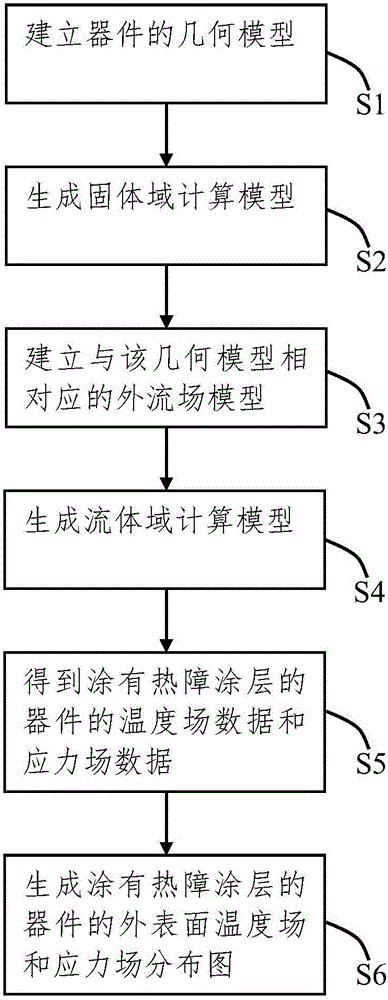
Working condition simulation method for device coated with thermal barrier coating
ActiveCN105046023ASimulation is accurateGuaranteed accuracySpecial data processing applicationsSolid regionEconomic benefits
A working condition simulation method for a device coated with a thermal barrier coating. The working condition simulation method comprises the following steps of: S1, establishing a geometrical model that contains a coating interface and is coated with the thermal barrier coating; S2, establishing a solid region calculation model corresponding to the geometrical model; S3, establishing an external flow field model corresponding to the geometrical model in S1; S4, carrying out fluid pre-analysis processing on the external flow field model to generate a fluid region calculation model; S5, obtaining temperature field data and stress field data of the device coated with the thermal barrier coating; and S6, generating an external surface temperature field and a stress field distribution diagram of the device coated with the thermal barrier coating. With the adoption of the simulation method provided by the invention, the movement of fluid of an external fluid field can be accurately simulated, so that the accuracy of the temperature field is guaranteed and the change of structural thermal stress also can be accurately simulated while sufficiently considering the condition of geometrical complexity of the device; and furthermore, the cost of researching a damage mechanism of the thermal barrier coating under a high-temperature service environment is greatly reduced; and economic benefits are good.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Electrochemical fabrication methods for producing multilayer structures including the use of diamond machining in the planarization of deposits of material
InactiveUS20050202180A1Improve abilitiesFast planarizationCellsLiquid surface applicatorsMulti materialSolid region
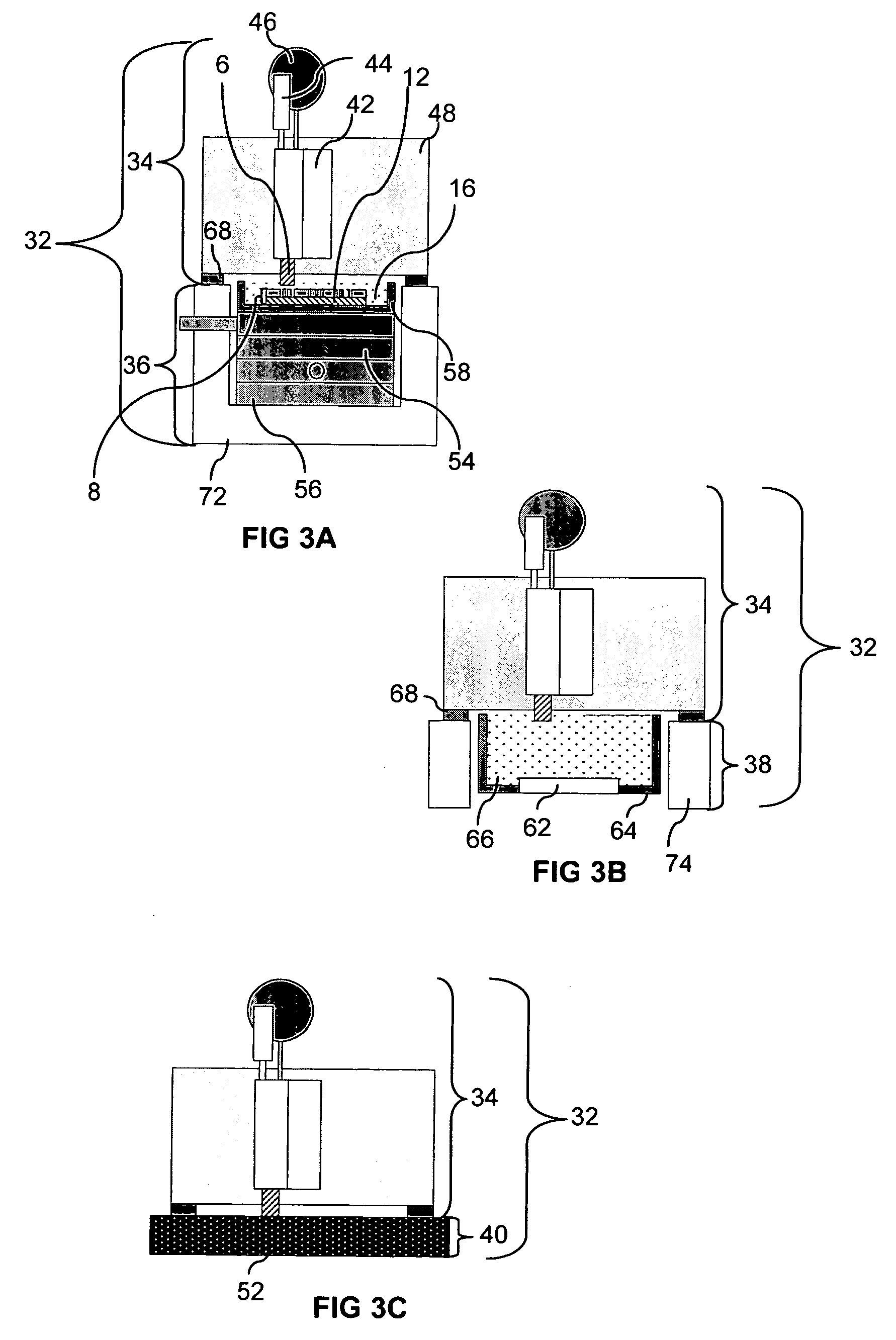
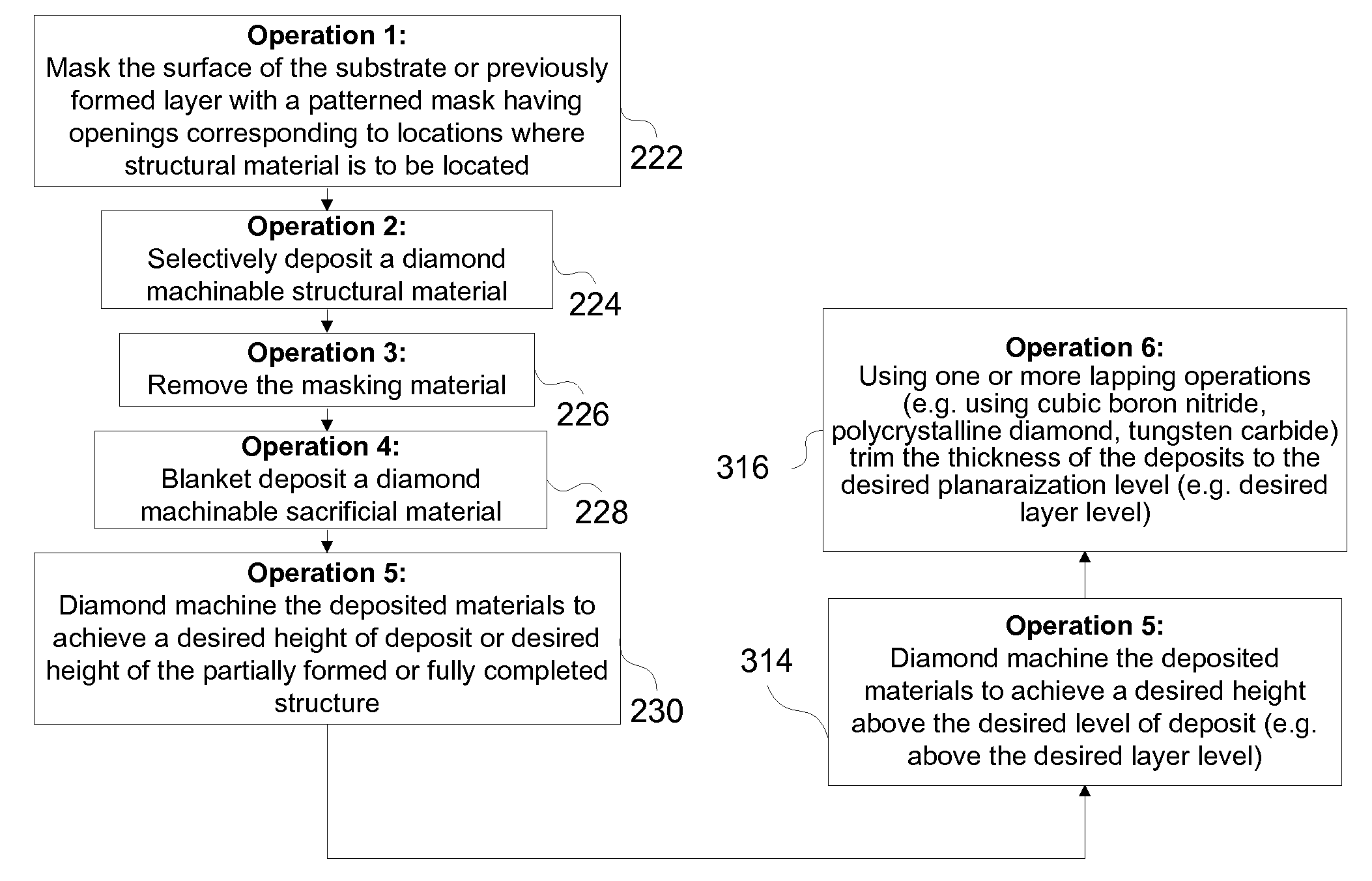
Electrochemical fabrication methods for forming single and multilayer mesoscale and microscale structures are disclosed which include the use of diamond machining (e.g. fly cutting or turning) to planarize layers. Some embodiments focus on systems of sacrificial and structural materials which are useful in Electrochemical fabrication and which can be diamond machined with minimal tool wear (e.g. Ni—P and Cu, Au and Cu, Cu and Sn, Au and Cu, Au and Sn, and Au and Sn—Pb), where the first material or materials are the structural materials and the second is the sacrificial material). Some embodiments focus on methods for reducing tool wear when using diamond machining to planarize structures being electrochemically fabricated using difficult-to-machine materials (e.g. by depositing difficult to machine material selectively and potentially with little excess plating thickness, and / or pre-machining depositions to within a small increment of desired surface level (e.g. using lapping or a rough cutting operation) and then using diamond fly cutting to complete he process, and / or forming structures or portions of structures from thin walled regions of hard-to-machine material as opposed to wide solid regions of structural material.
Owner:MICROFAB
Electrochemical Fabrication Methods for Producing Multilayer Structures Including the use of Diamond Machining in the Planarization of Deposits of Material
InactiveUS20090020433A1Improve abilitiesFast planarizationCellsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMulti materialSolid region
Electrochemical fabrication methods for forming single and multilayer mesoscale and microscale structures are disclosed which include the use of diamond machining (e.g. fly cutting or turning) to planarize layers. Some embodiments focus on systems of sacrificial and structural materials which are useful in Electrochemical fabrication and which can be diamond machined with minimal tool wear (e.g. Ni—P and Cu, Au and Cu, Cu and Sn, Au and Cu, Au and Sn, and Au and Sn—Pb), where the first material or materials are the structural materials and the second is the sacrificial material). Some embodiments focus on methods for reducing tool wear when using diamond machining to planarize structures being electrochemically fabricated using difficult-to-machine materials (e.g. by depositing difficult to machine material selectively and potentially with little excess plating thickness, and / or pre-machining depositions to within a small increment of desired surface level (e.g. using lapping or a rough cutting operation) and then using diamond fly cutting to complete he process, and / or forming structures or portions of structures from thin walled regions of hard-to-machine material as opposed to wide solid regions of structural material.
Owner:MICROFAB
Apparatus and method for resonant chemical and biological sensing
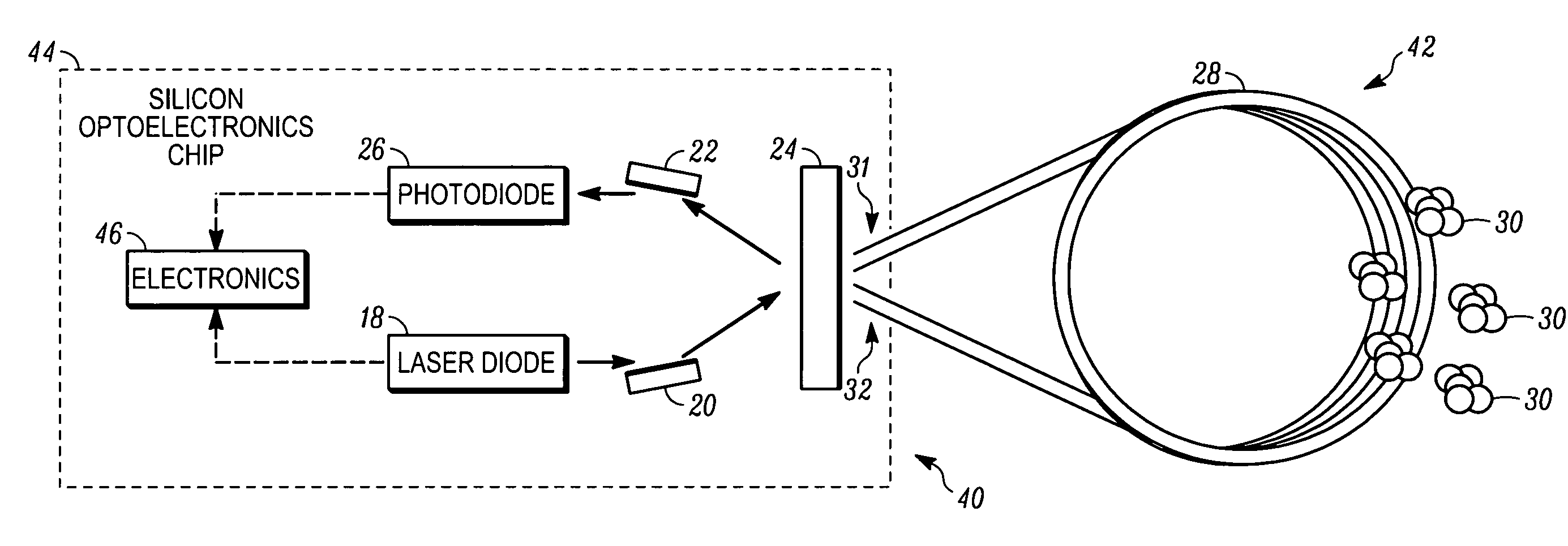
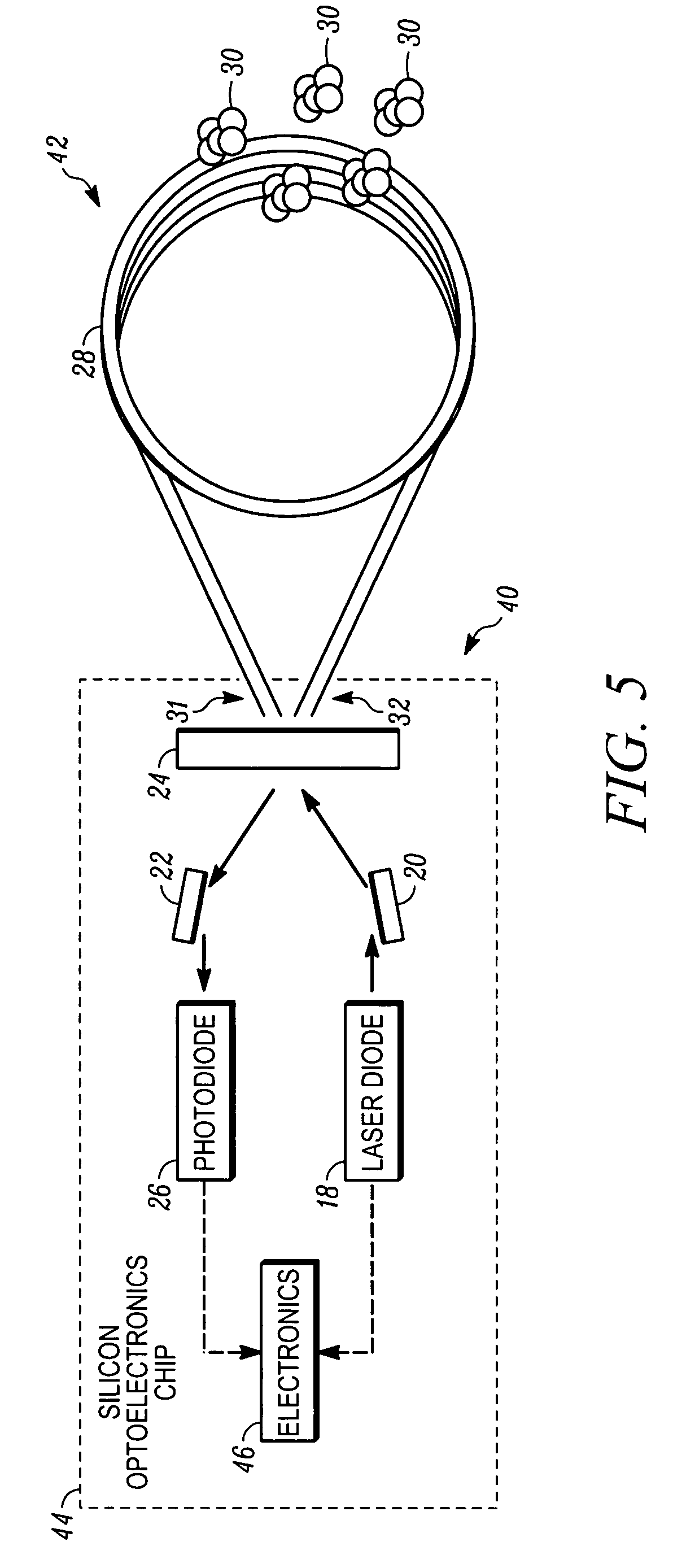
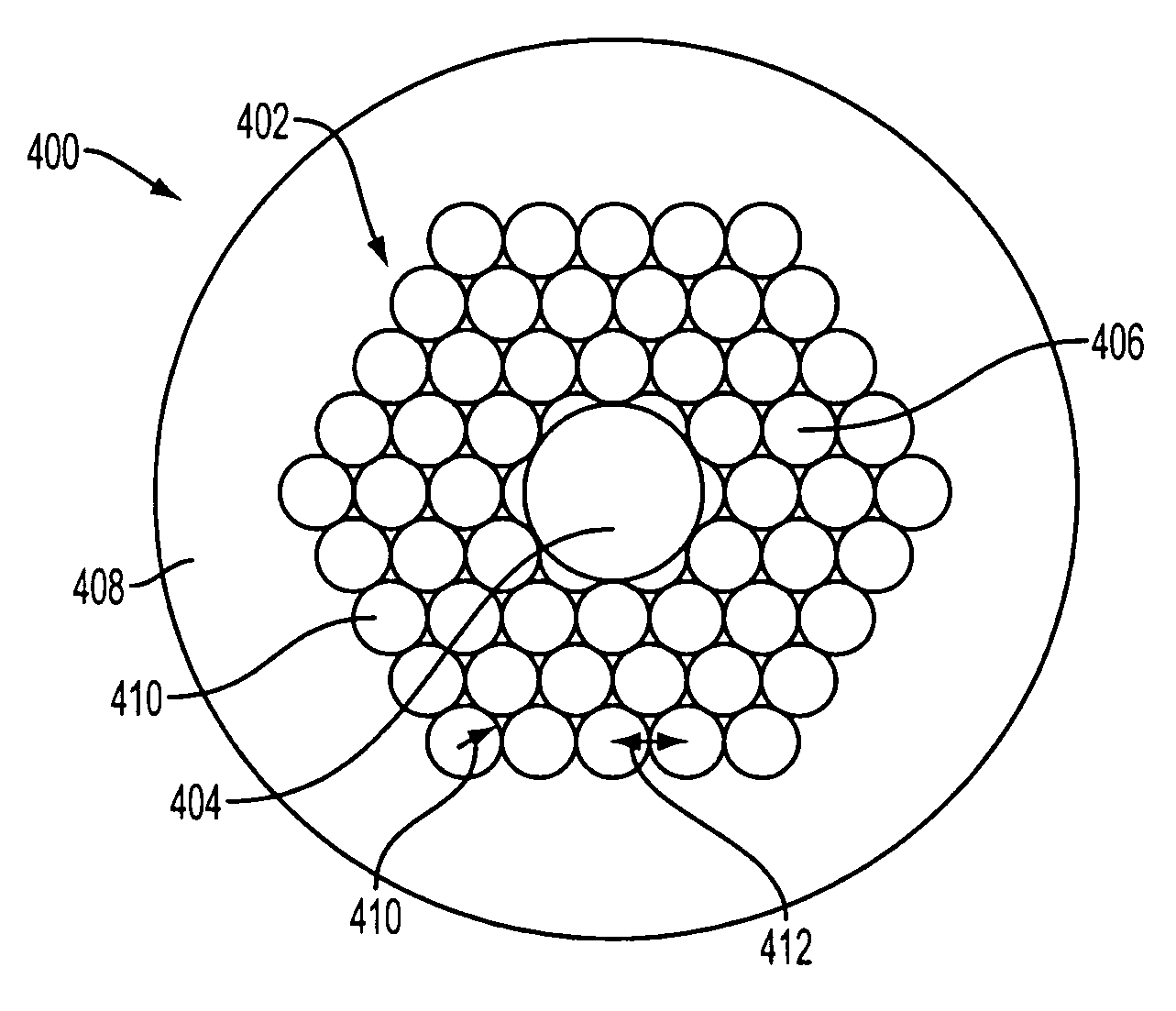
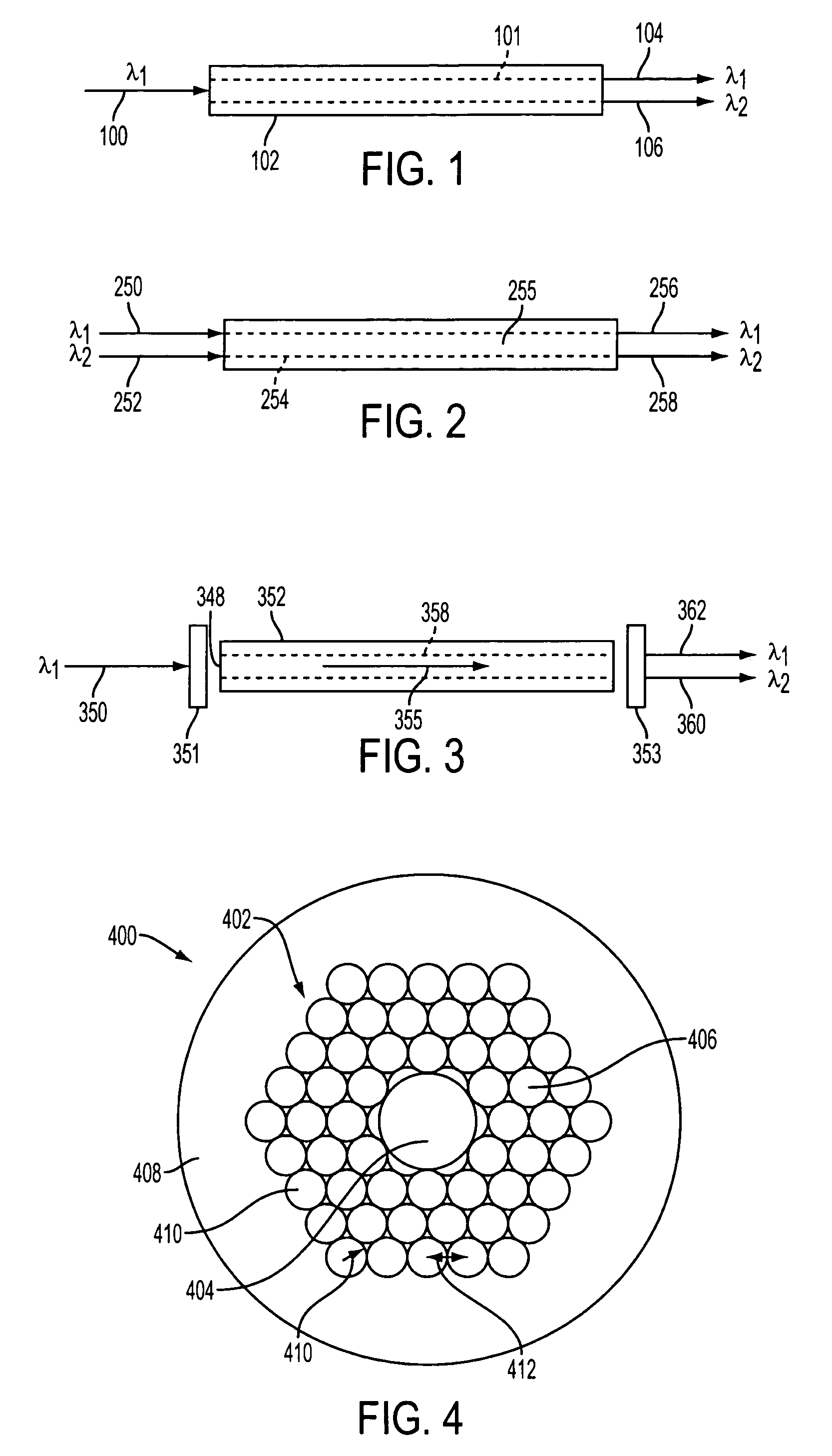
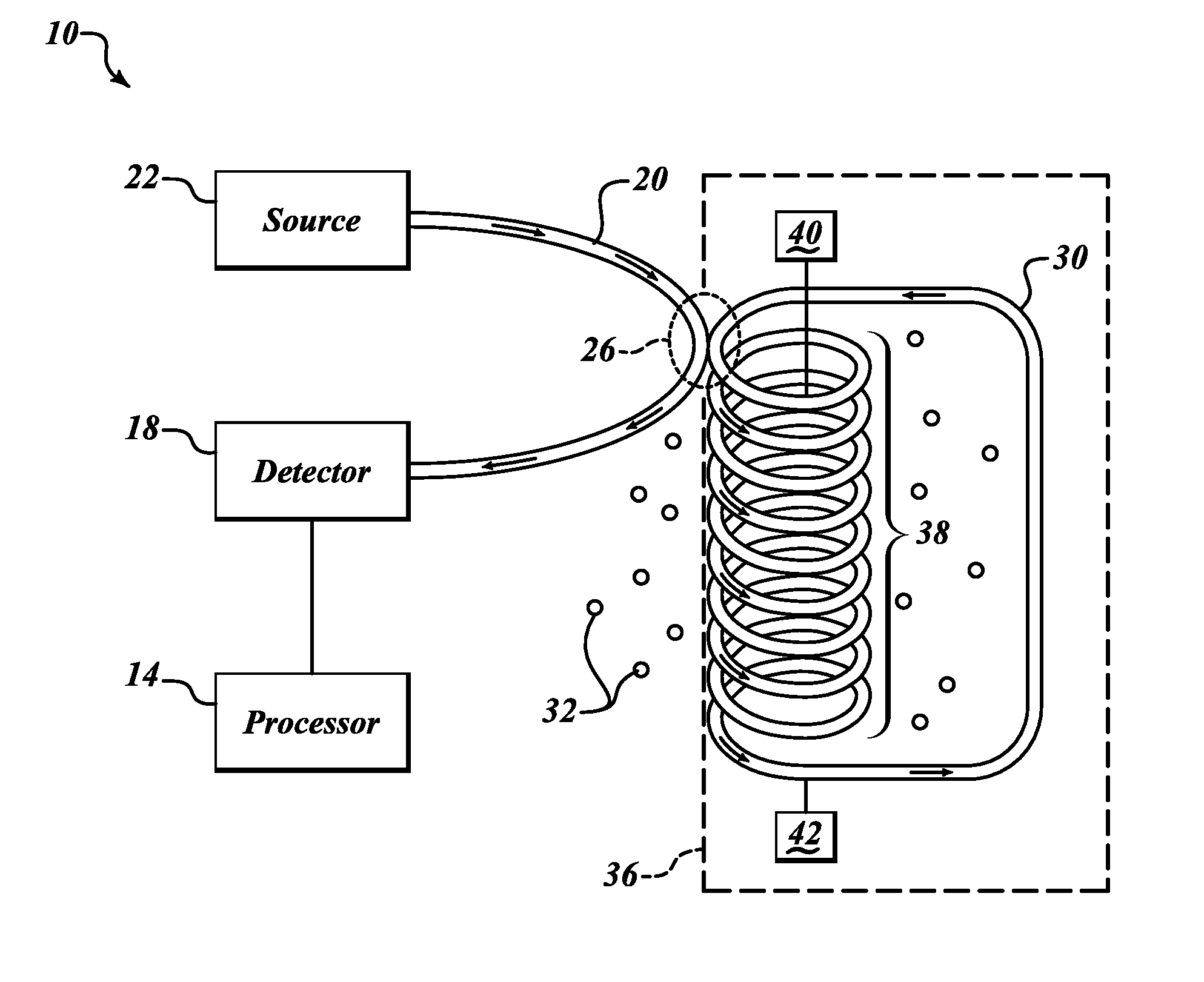
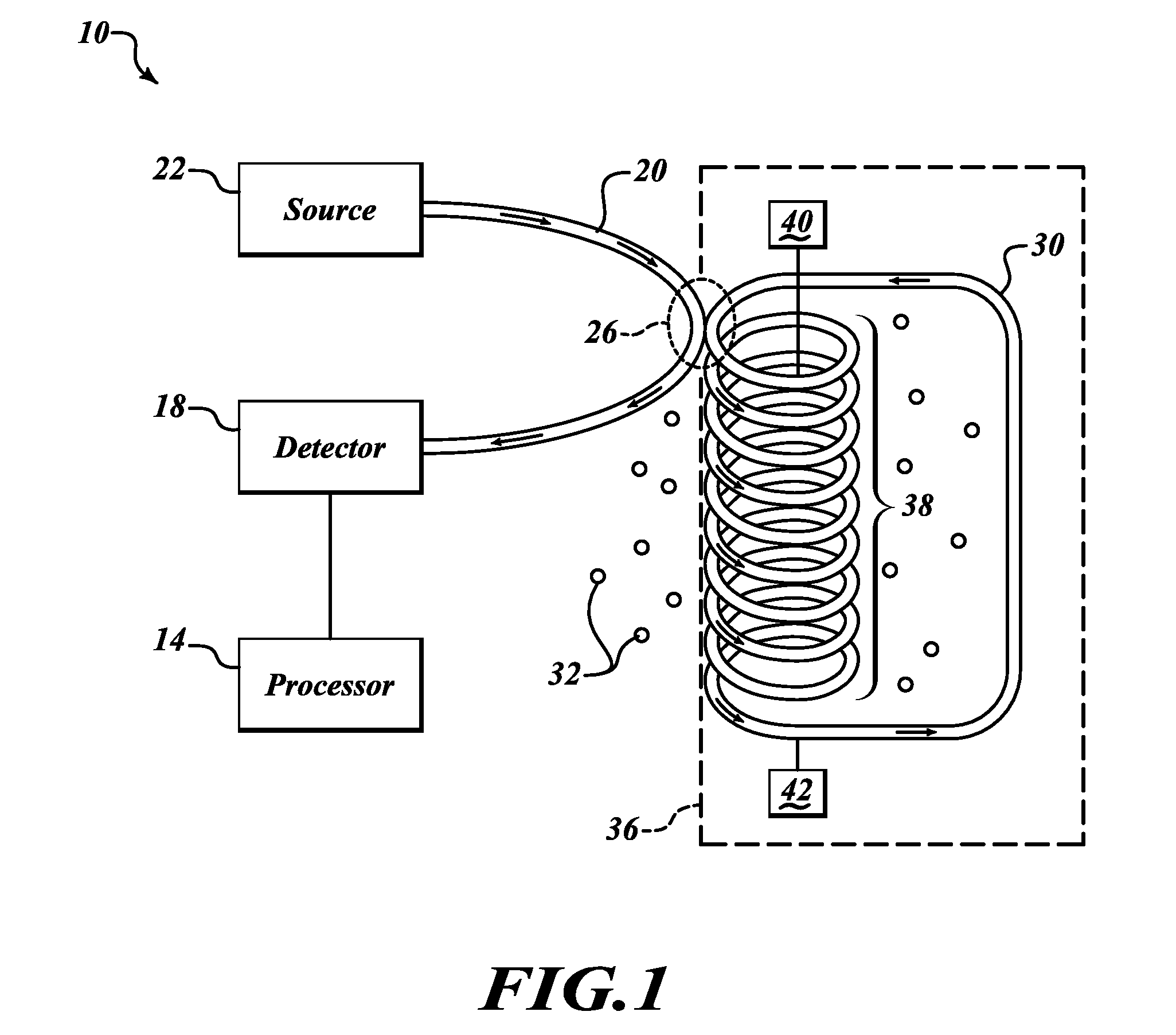
Apparatus and method are provided for chemical and biological agent sensing. The sensing apparatus includes a resonator having a resonance frequency. The resonator includes a coil of a photonic crystal fiber. The photonic crystal fiber has a solid region configured to guide a substantially single optical mode of light having an evanescent tail, a first cladding surrounding an exterior of the solid region, and a polymer coating the first cladding. The polymer has an embedded indicator. The first cladding and polymer are together configured to extend a portion of the evanescent tail into the polymer. The resonator is configured to produce a resonance shape centered at the resonance frequency. A predetermined change in the resonance shape or the free spectral range indicates a reaction of the indicator to the agent.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
In-situ vaporizer and recuperator for alternating flow device
InactiveUS20120111315A1Minimized size and weightImprove efficiencyLiquid fuel feeder/distributionHydrogenSolid regionRecuperator
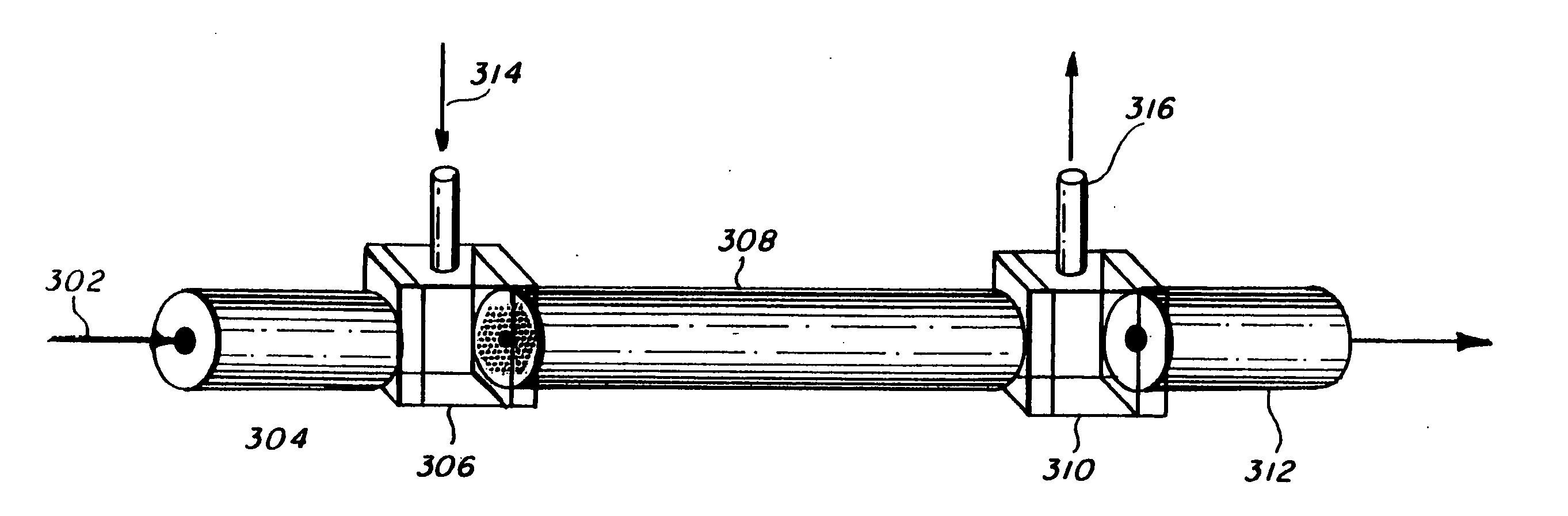
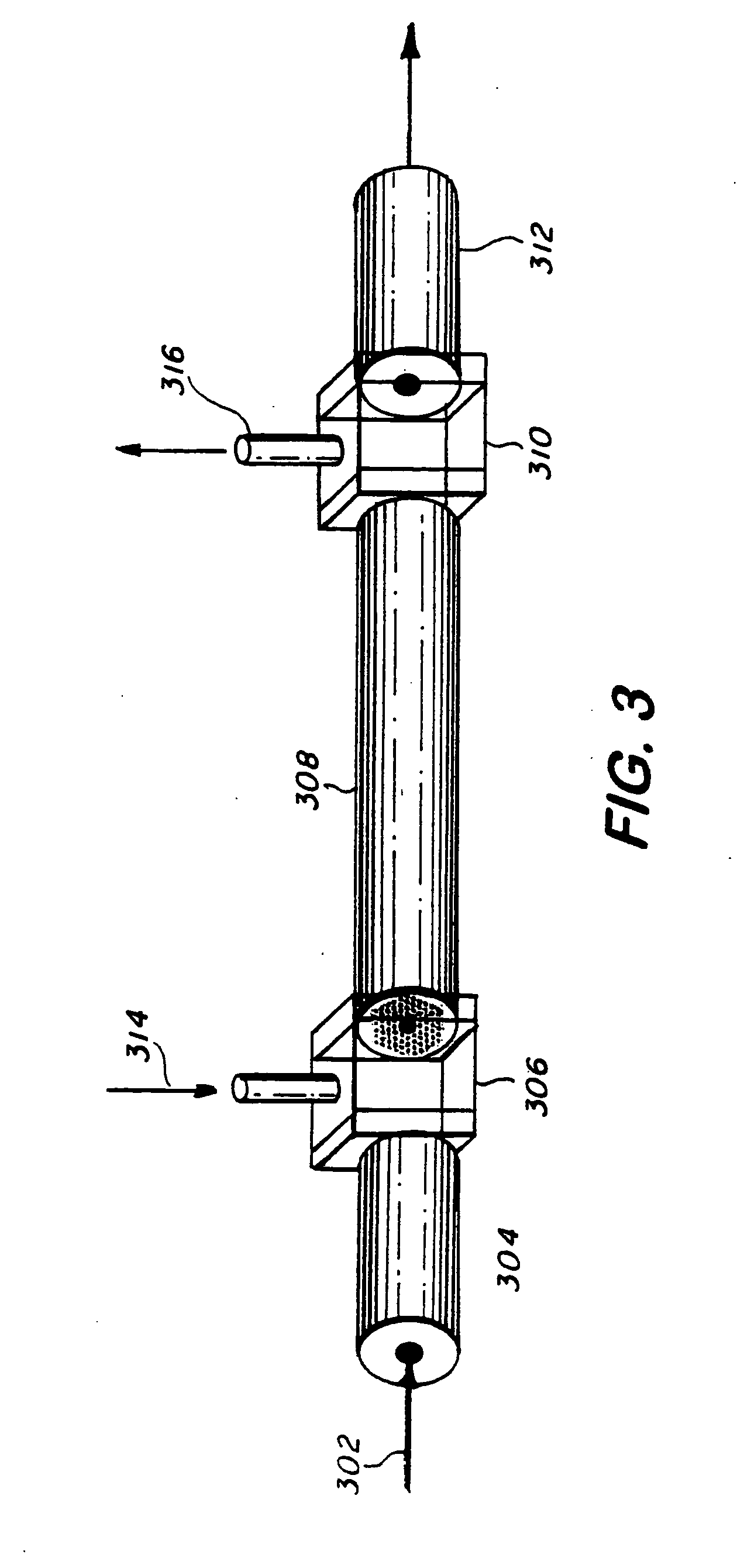
The present invention relates to a device for converting a liquid feed stream to a gaseous vapor stream comprising: (a) channel means having a first and second end, said channel means having a plurality of channels connecting said first and second end, said channel means having a substantially solid region and a void region, (b) inlet means for directing the liquid feed stream to the first end of the plurality of channels, and (c) outlet means for directing the gaseous vapor stream from said plurality of channels, where said channels have, at any distance d between the inlet and outlet, a geometric configuration, perpendicular to the feed flow direction, wherein the average void fraction ranges from about 0.3 to about 0.95.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
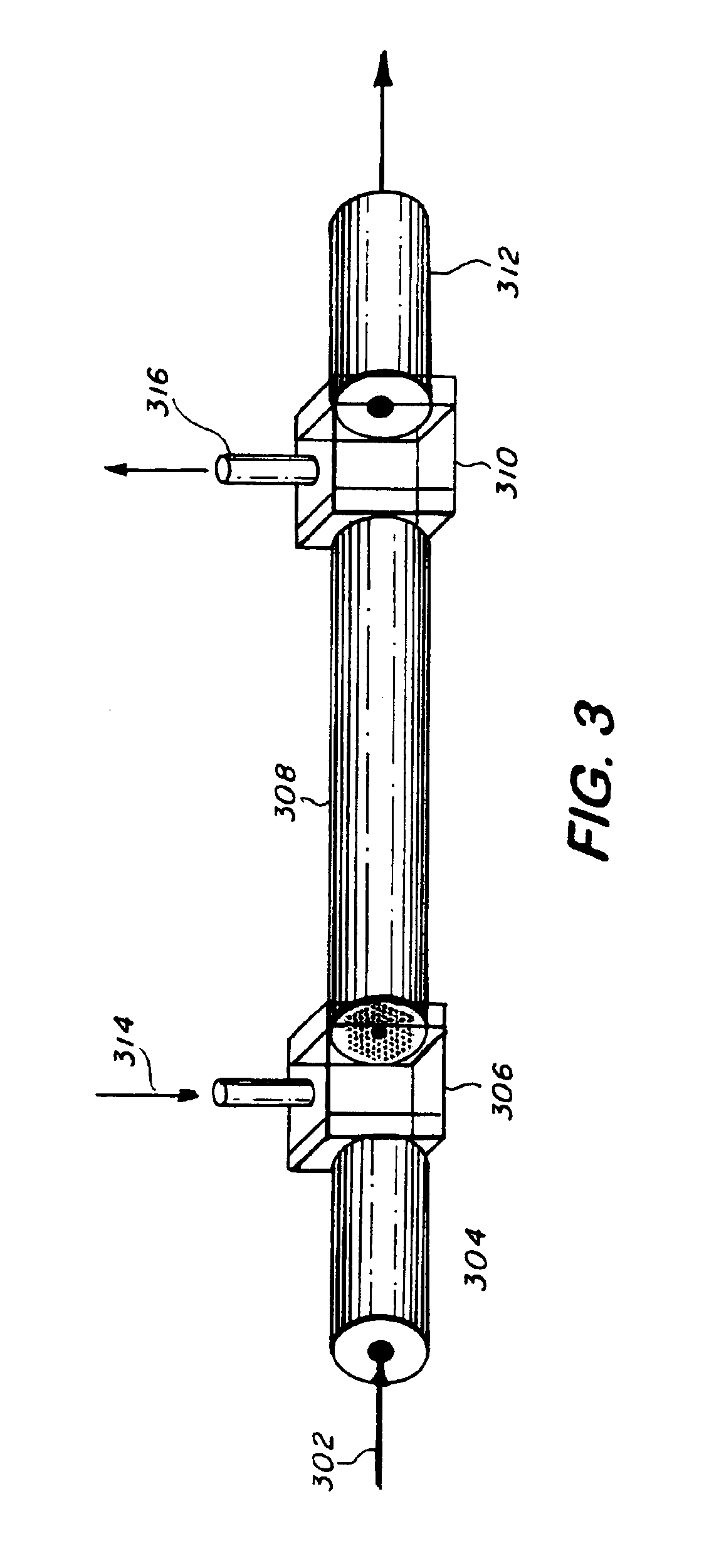
Gas filled hollow core chalcogenide photonic bandgap fiber raman device and method
ActiveUS20060251369A1Improve efficiencyHigh average power sourceLaser detailsCladded optical fibreSolid regionPhotonic bandgap
This invention pertains to a glass fiber, a Raman device and a method. The fiber is a hollow core photonic bandgap chalcogenide glass fiber that includes a hollow core for passing light therethrough, a Raman active gas disposed in said core, a microstructured region disposed around said core, and a solid region disposed around said microstructured region for providing structural integrity to said microstructured region. The device includes a coupler for introducing at least one light signal into a hollow core of a chalcogenide photonic bandgap fiber; a hollow core chalcogenide photonic bandgap glass fiber; a microstructured fiber region disposed around said core; a solid fiber region disposed around said microstructured region for providing structural integrity to said microstructured region; and a Raman active gas disposed in the hollow core. The method includes the steps of introducing a light beam into a hollow core chalcogenide photonic bandgap glass fiber filled with a Raman active gas disposed in the core, conveying the beam through the core while it interacts with the gas to form a Stokes beam of a typically higher wavelength, and removing the Stokes beam from the core of the fiber.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Multi-field coupling transient numerical method for hypersonic flow-heat transfer and structural response
ActiveCN105095603AImprove calculation accuracySustainable transportationSpecial data processing applicationsSolid regionHeat flux
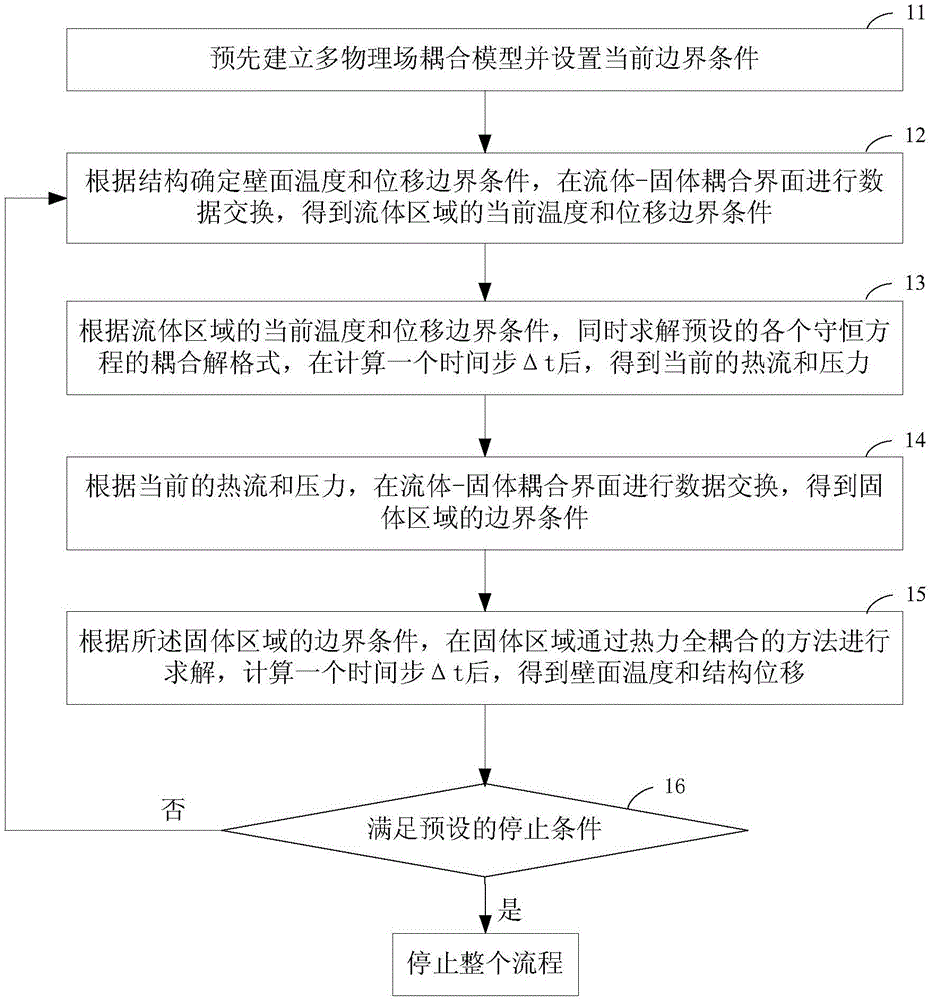
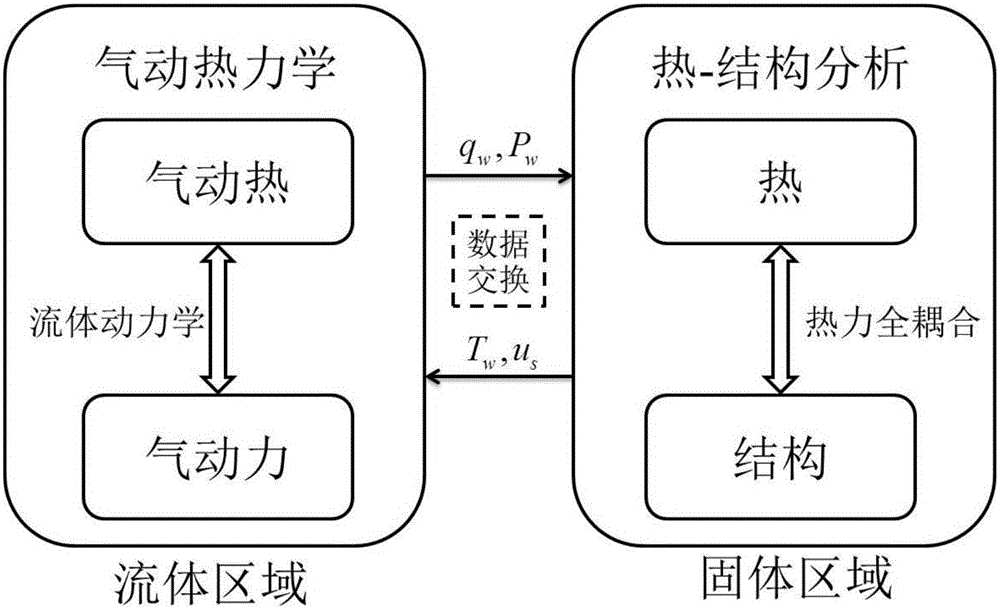
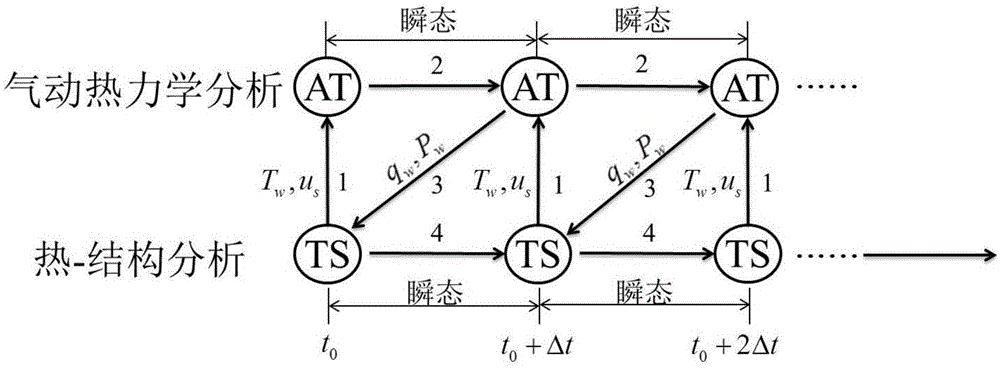
The invention discloses a multi-field coupling transient numerical method for hypersonic flow-heat transfer and structural response. The method comprises the following steps of: determining wall temperature and displacement boundary condition according to structure, performing data exchange at a fluid-solid coupling interface, and obtaining the current temperature and displacement boundary condition; simultaneously solving coupled solution format of each preset conservation equation to obtain the current heat flux and pressure; performing data exchange at the fluid-solid coupling interface to obtain the boundary condition of a solid region; according to the boundary condition of the solid region, solving out the wall temperature and structure displacement through a thermal mechanical unity coupling method; and executing the steps above repeatedly until meeting a preset stop condition. Using the method provided by the invention, multi-field coupling calculation where a hypersonic non-equilibrium flow solver and a structural thermal / mechanical unity coupling solver are coupled is realized, prediction on pneumatic thermodynamic environment and structural thermodynamic response of a hypersonic aircraft meets physical reality better, and calculation precision can be guaranteed.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
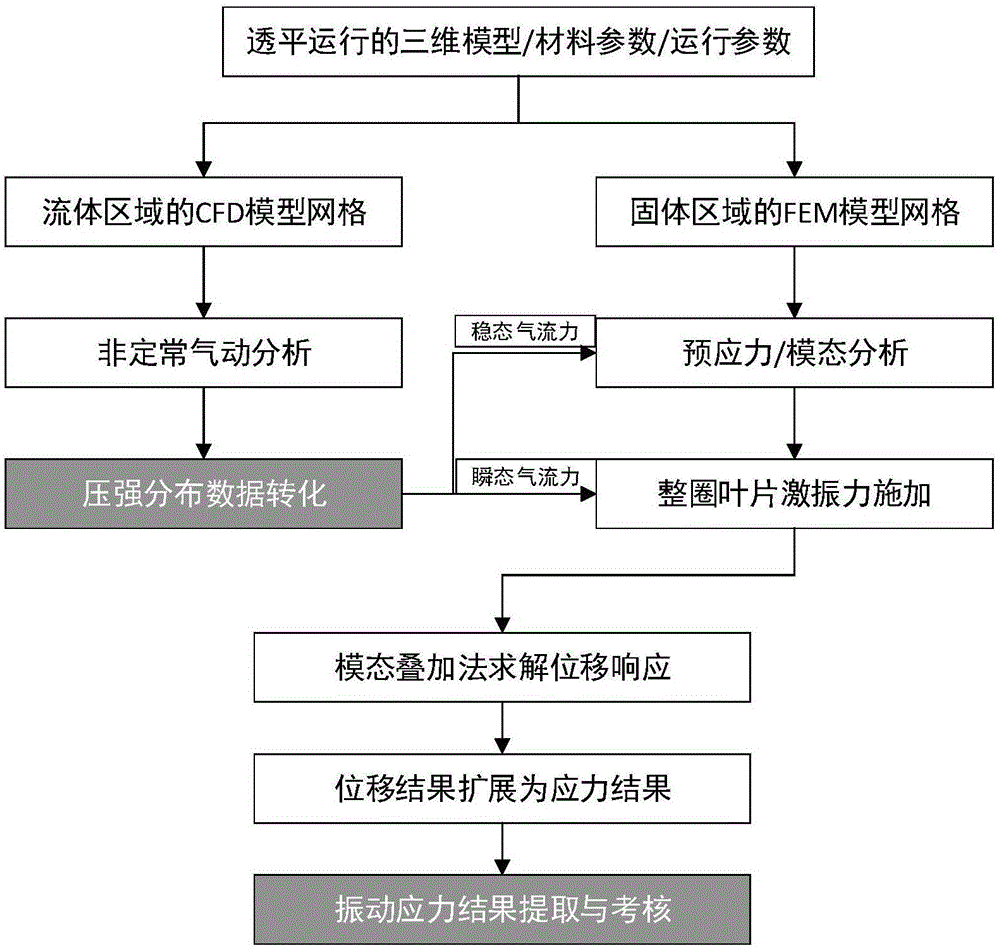
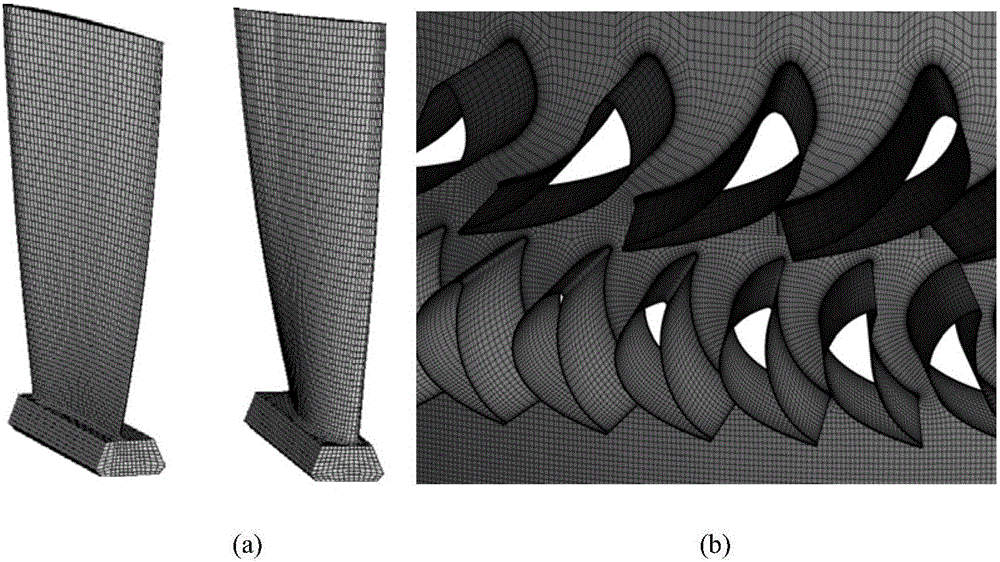
Vibration stress numerical analysis method for turbomachinery blades
ActiveCN106528932AImprove calculation accuracyCalculation speedDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSolid regionEngineering
The invention discloses a vibration stress numerical analysis method for turbomachinery blades. The method comprises the steps of 1, building an FEM model of a solid region of an entire circle of the blades and CFD models of periodically symmetric fluid regions; 2, obtaining steady-state pressure intensity field distribution of meshes of the fluid regions of the blades and instant pressure intensity field distribution of each time step in a pneumatic period; 3, converting pressure intensity field distribution data; 4, performing finite element mode analysis of the entire circle of the blades; 5, obtaining node force load vectors of blade surfaces of all time steps; 6, solving a vibration displacement response by a mode superposition method; 7, expanding a displacement response result into a stress result; and 8, performing vibration stress result extraction and check. According to the method, the pressure intensity distribution of the blade surfaces is obtained by adopting a non-steady computing method, and an accurate air exciting-vibration force load is obtained by interpolation from the meshes of the fluid regions of the blades to the pressure intensity of the meshes of the solid region, so that the computing precision is improved; and each sector adopts a CPU+GPU heterogeneous parallel computing mode, so that the computing speed is greatly increased.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
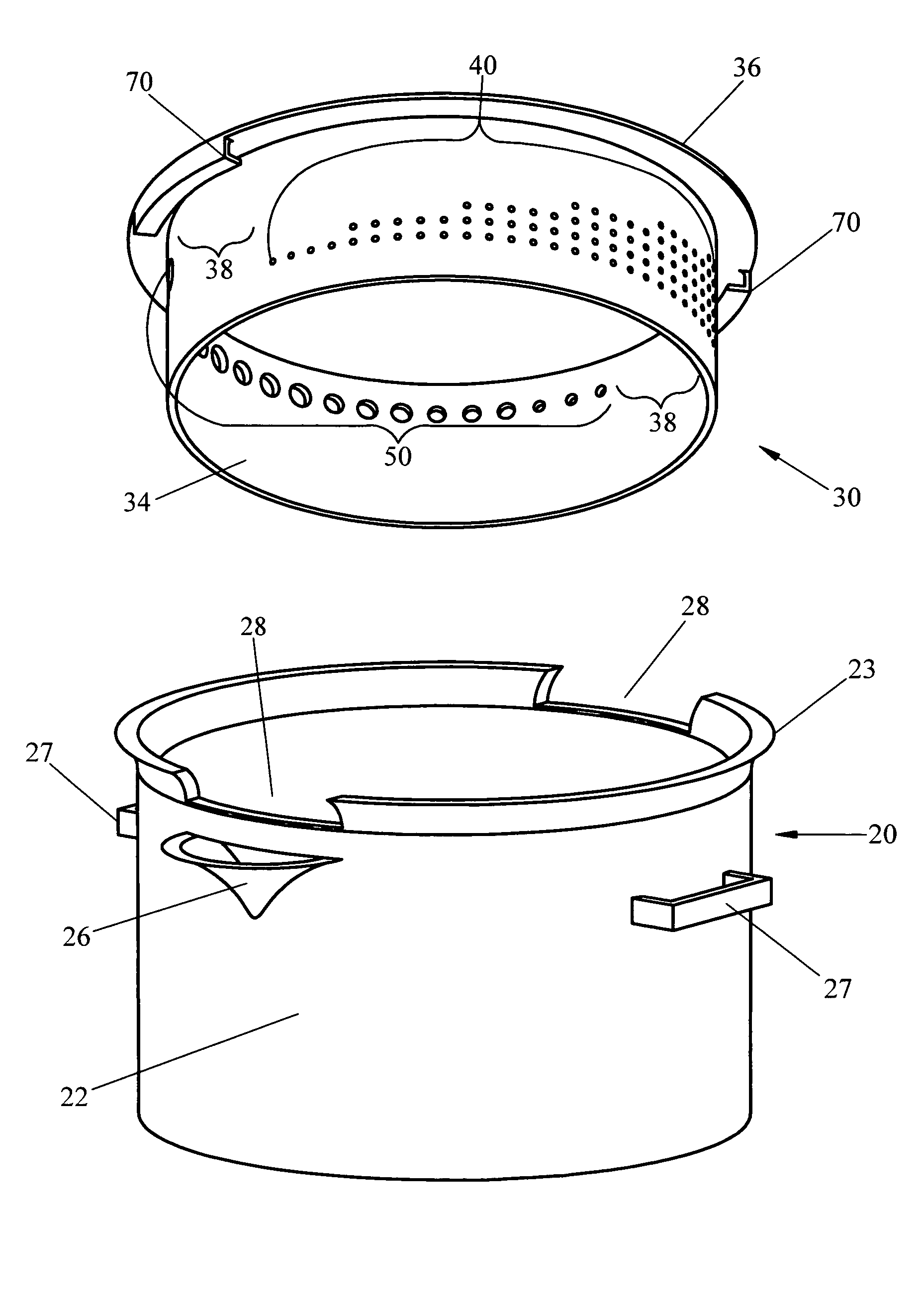
Adjustable lock and drain apparatus
ActiveUS7878110B1Safely drainGradually adjust amountPouring-spoutsCooking-vessel lids/coversSolid regionEngineering
An apparatus which serves as a single utensil allowing to gradually adjust vapor escape, liquid drainage speed, and particle drainage and filtering. A few of the apparatus applications are cooking utensils, pitchers, drinking cups, gardening watering and fertilizing cans, etc. The apparatus comprises a vessel having pouring regions and a lid having draining and solid regions. In use, the solid regions of the lid must be aligned with the vessel pouring regions, which is the non-straining or opened position with no vapor release. If the lid is rotated in either direction, it slides into a locking engagement with the vessel until the desired draining regions of the lid are aligned with the vessel pouring regions. This is the straining or locked position where a desirable degree of steam or liquid and particles can be released.
Owner:MICHNIK ALISA +1
Hollow core photonic band gap infrared fibers
This invention pertains to a hollow core photonic band gap chalcogenide optical glass fiber and to a fabrication method for making the fiber. The fiber, which is 80-1000 microns in outside diameter, is characterized by a solid glass circumferential region and a structured region disposed centrally within the solid region, the structured region includes a hollow core of 1 micron to several hundreds of microns in diameter surrounded by a plurality of parallel hollow capillaries extending parallel to the core, the core being centrally and longitudinally located within the fiber. Ratio of open space to glass in the structured region is 30-99%. The fabrication method includes the steps of providing a mold, placing chalcogenide micro-tubes around the mold, stacking chalcogenide micro-canes around the stacked micro-tubes, fusing the micro-tubes and the micro-canes to form a preform, removing the mold and drawing the preform to obtain the fiber. In an alternative fabrication method, the fiber is made by extruding flowing chalcogenide glass through suitably made plate to form a preform and then drawing the preform to form the fiber.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Gas filled hollow core chalcogenide photonic bandgap fiber Raman device and method
ActiveUS7283712B2Higher Stokes shift of a gasImprove efficiencyLaser detailsCladded optical fibreGlass fiberSolid region
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
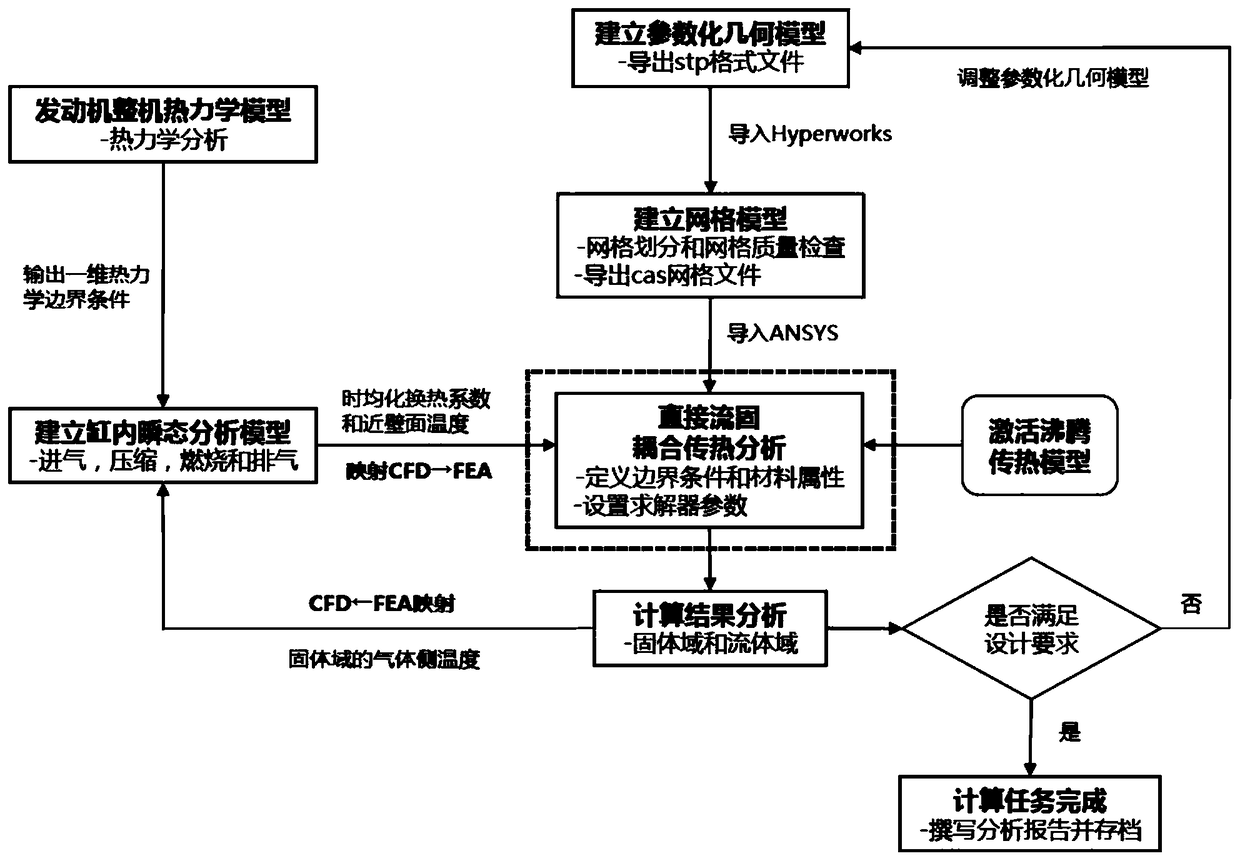
A direct fluid-solid coupling heat transfer analysis method for engine cooling water jacket
ActiveCN108984920ASolve crackingExtended service lifeGeometric CADSustainable transportationSolid regionCoolant flow
The invention discloses a direct fluid-solid coupling heat transfer analysis method for an engine cooling water jacket. The method comprises the following steps: 1, establishing a solid domain and a fluid domain parametric geometric model; 2, carrying out grid partition and grid quality inspection; 3, defining material attributes; 4, defining boundary conditions; 5, defining a coupling heat transfer interface; 6, setting solver parameters; 7, carrying out direct fluid-solid coupling heat transfer analysis considering boiling heat transfer and obtaining calculation results. The method can compensate for the inability to effectively evaluate the heat transfer process and the coolant flow condition between the solid region and the fluid region in a conventional engine cooling water jacket design process, and the method avoids the risk of cracking failure caused by the high temperature of the bridge area of the cylinder head fire surface.
Owner:ANHUI JIANGHUAI NAVISTAR DIESEL ENGINE CO LTD
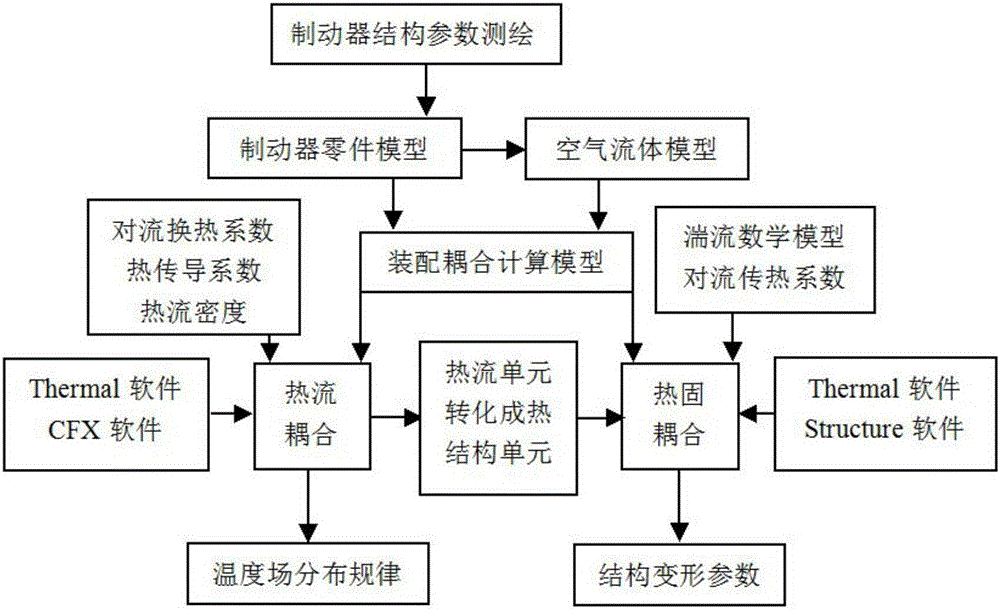
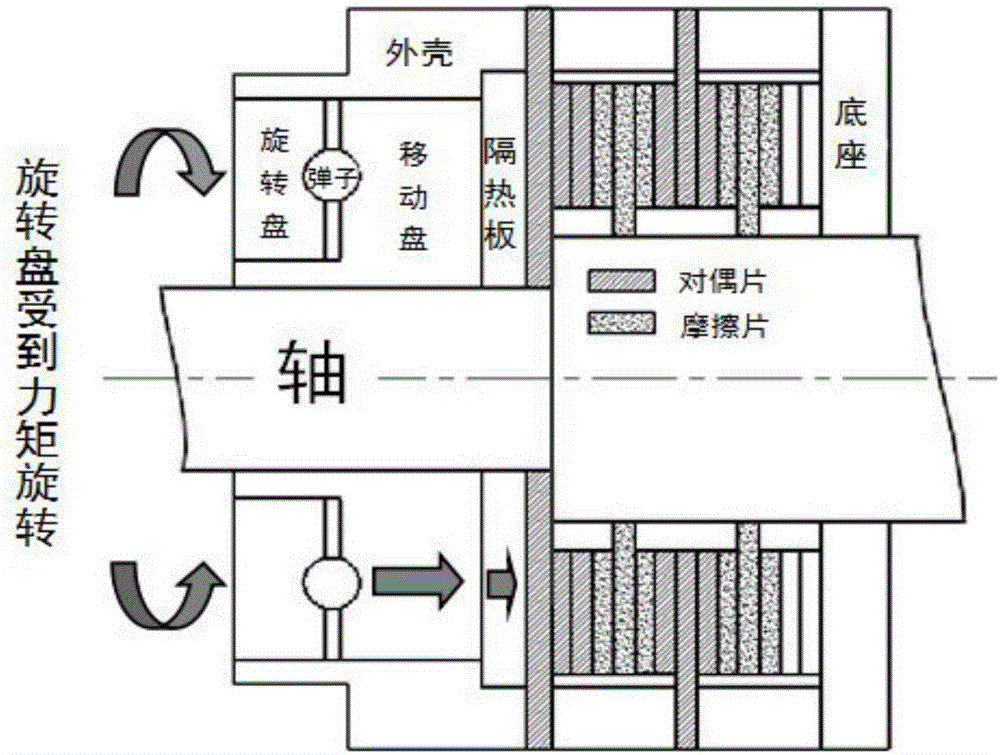
Temperature field simulated analysis method applied to multi-disk dry brake under comprehensive action of multiple physical fields
InactiveCN105956264ASimplify the difficulty of operationReduced simulation timeGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsSolid regionHeat flux
The invention discloses a temperature field simulated analysis method applied to a multi-disk dry brake under the comprehensive action of multiple physical fields. Firstly, a three-dimensional model of the brake is established by starting from the mechanism and movement principle of the multi-disk dry brake. Then according to the complementarity between a fluid field and the brake structure, a rough fluid model is established and then modified and cut, and thus a final fluid model is acquired. Then fluid region and solid region boundary conditions are computed, a heat-flux coupling analysis is performed, and a temperature distribution rule of the whole brake is acquired. At last, a thermo-solid coupling analysis is performed, and a temperature field-to-brake structure deformation parameter is acquired. The temperature field simulated analysis method can achieve the temperature field simulated analysis of the multi-disk dry brake under the comprehensive action of multiple physical fields, is more accurate and reliable than the traditional single temperature field analysis, adopts zonal solving and boundary coupling methods, thus optimizing the information flow among the physical fields, and thus, the simulation is simpler, the operation is convenient and the consumed time is greatly shortened.
Owner:LIAONING INST OF SCI & TECH +1
Hollow core photonic band gap infrared fibers
InactiveUS20060230792A1High sensitivityGlass making apparatusCladded optical fibreGlass fiberSolid region
This invention pertains to a hollow core photonic band gap chalcogenide optical glass fiber and to a fabrication method for making the fiber. The fiber, which is 80-1000 microns in outside diameter, is characterized by a solid glass circumferential region and a structured region disposed centrally within the solid region, the structured region includes a hollow core of 1 micron to several hundreds of microns in diameter surrounded by a plurality of parallel hollow capillaries extending parallel to the core, the core being centrally and longitudinally located within the fiber. Ratio of open space to glass in the structured region is 30-99%. The fabrication method includes the steps of providing a mold, placing chalcogenide micro-tubes around the mold, stacking chalcogenide micro-canes around the stacked micro-tubes, fusing the micro-tubes and the micro-canes to form a preform, removing the mold and drawing the preform to obtain the fiber. In an alternative fabrication method, the fiber is made by extruding flowing chalcogenide glass through suitably made plate to form a preform and then drawing the preform to form the fiber.
Owner:NAVY SEC OF THE THE U S A AS REPRESENTED BY THE
Multi-phase hygienic cleansing system and skin care device
InactiveUS20090019656A1Easy to eliminateReduce the amount requiredBoard cleaning devicesPersonal careParticulatesSolid region
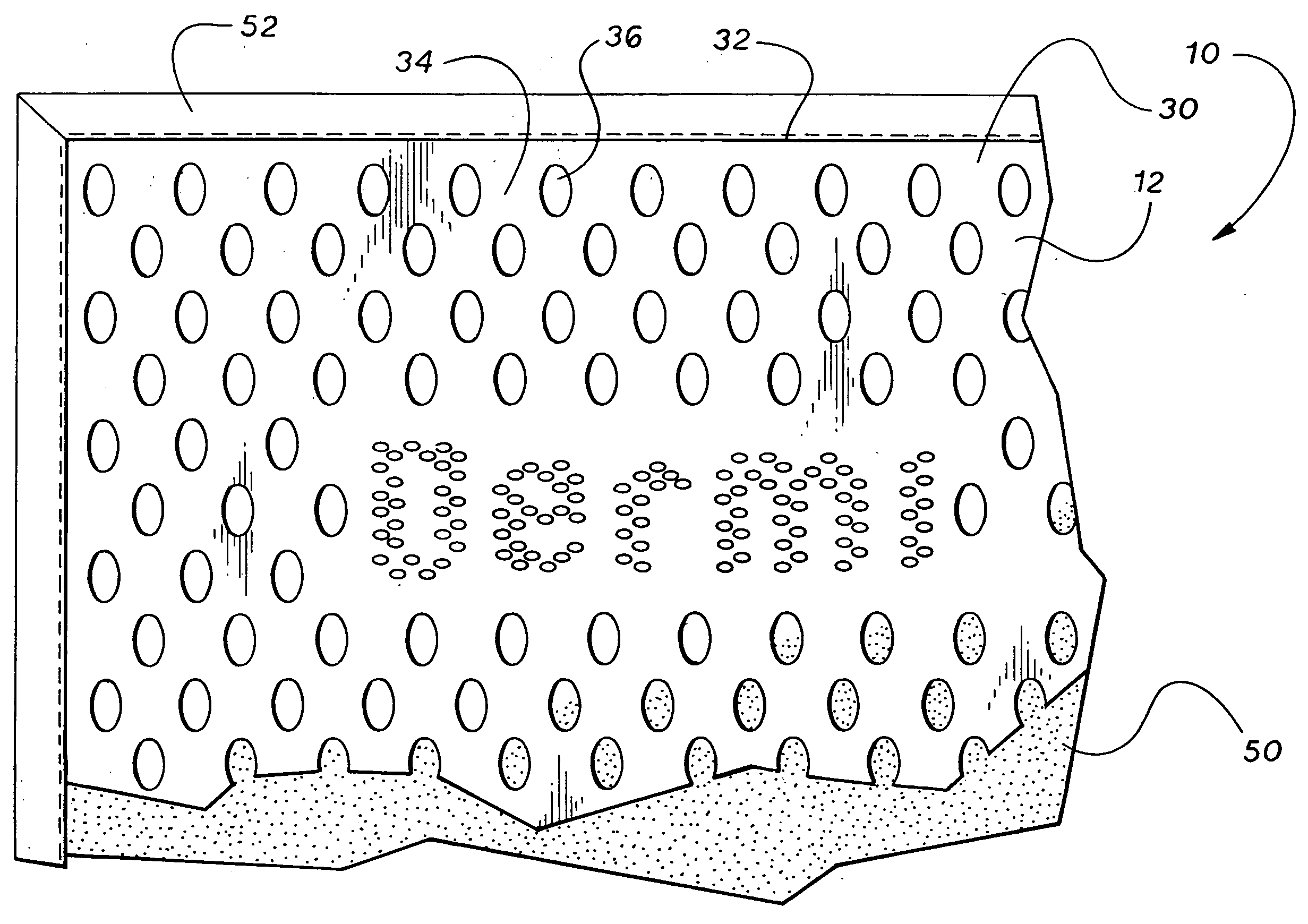
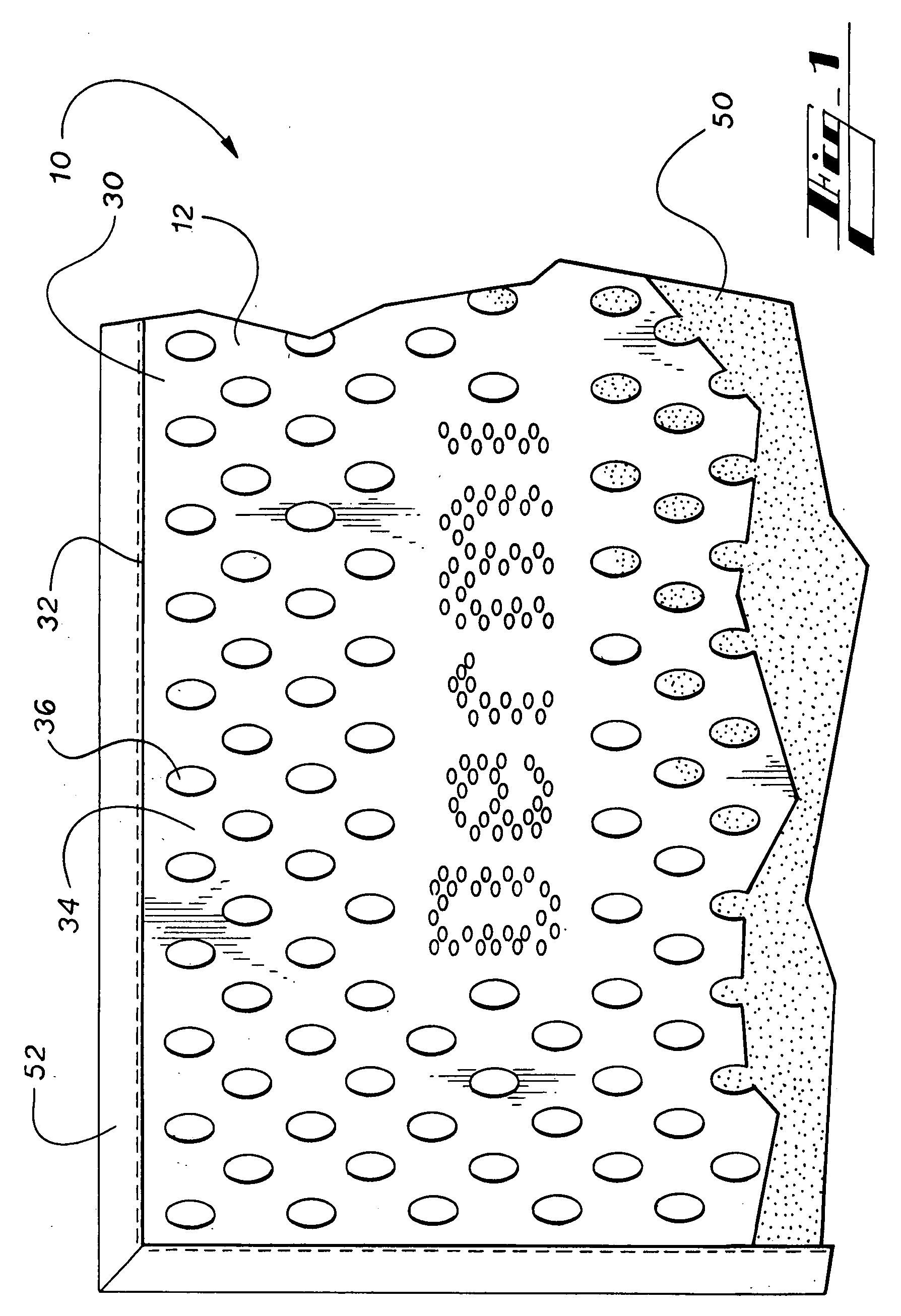
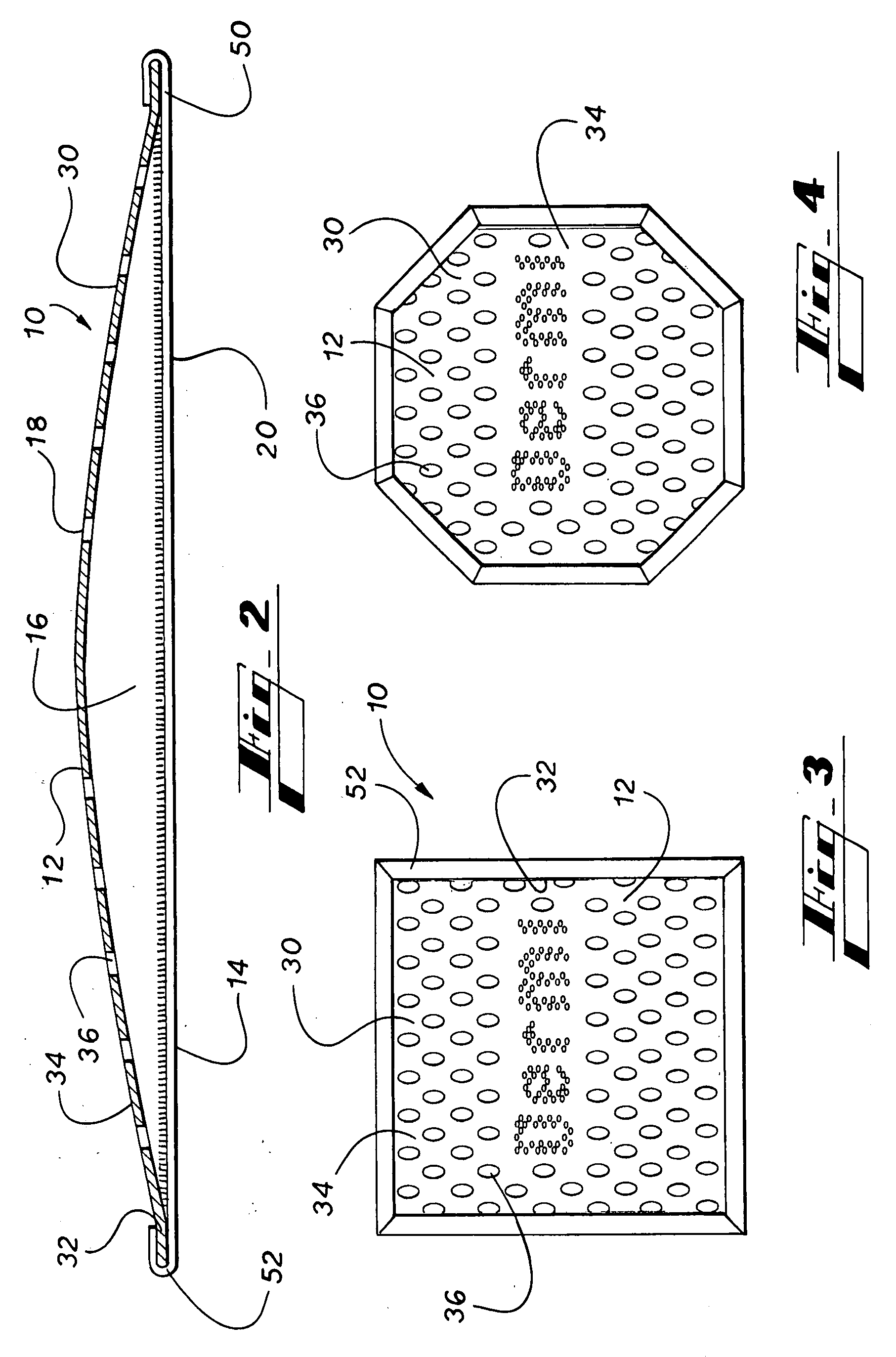
A multi-phase hygienic cleansing system and skin care device, comprising an inter-related network of cleansing features defined by an openweave fabric attached to a cloth, wherein the openweave fabric is further structurally defined by a plurality of essentially tightly-woven or solid fabric regions interspersed in a grid-like arrangement about a plurality of openings, such that the tightly-woven or solid fabric regions function to absorb moisture and dirt, and to visually identify successful cleansing, such that the grid-like arrangement of the openings proximate the solid regions function to exfoliate and scrub, and such that the plurality of openings function to receive particulate matter and dead skin debris from the cleansing surface, removing same from risk of reapplication to the body.
Owner:MITCHELL DERRICK
Generation method for three-dimensional metal advertisement word model
ActiveCN107767439AEnter exactlyGood reproducibilityGeometric image transformation3D modellingTwo-dimensional graphGraphics
The invention discloses a generation method for a three-dimensional metal advertisement word model. The method comprises the following steps that: identifying a connected region and a sealed outline from the two-dimensional graph of the advertisement word; obtaining an entity region corresponding to each connected region; establishing the coordinate system of the advertisement word; enabling the yshaft of the coordinate system of the advertisement word to be in parallel or coincident with the y shaft of a world coordinate system to obtain the height of a two-dimensional graph on the y shaft;inputting the inclination angle, the front end height and the initial rear end height of the top surface of the advertisement word; taking the x shaft of the coordinate system of the advertisement word as a rotation shaft, and rotating the two-dimensional graph to a first datum plane; upwards translating the two-dimensional graph along the normal direction of the first datum plane to obtain S1 anda second datum plane; translating the S1 to obtain a second outline group; projecting S1 to obtain S3; and taking the first outline group as the top surface shape of the advertisement word, and obtaining the bottom surface shape and the side surface shape of the advertisement word through S2 and S3. The generation method has the advantages that the two-dimensional graph of the advertisement wordcan be automatically identified to generate the top surface, the bottom surface and the side surface of the three-dimensional advertisement word, and production efficiency is high.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
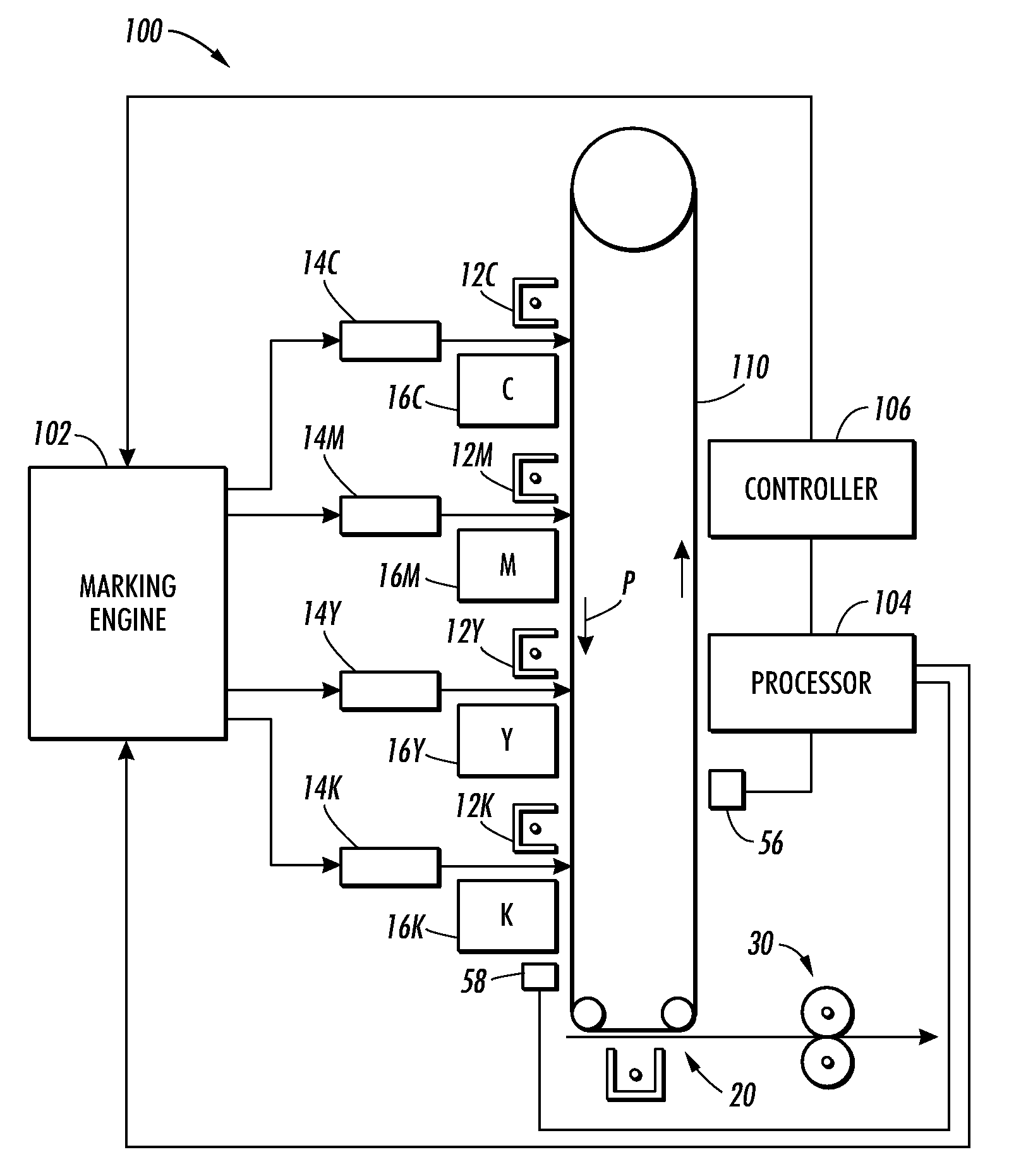
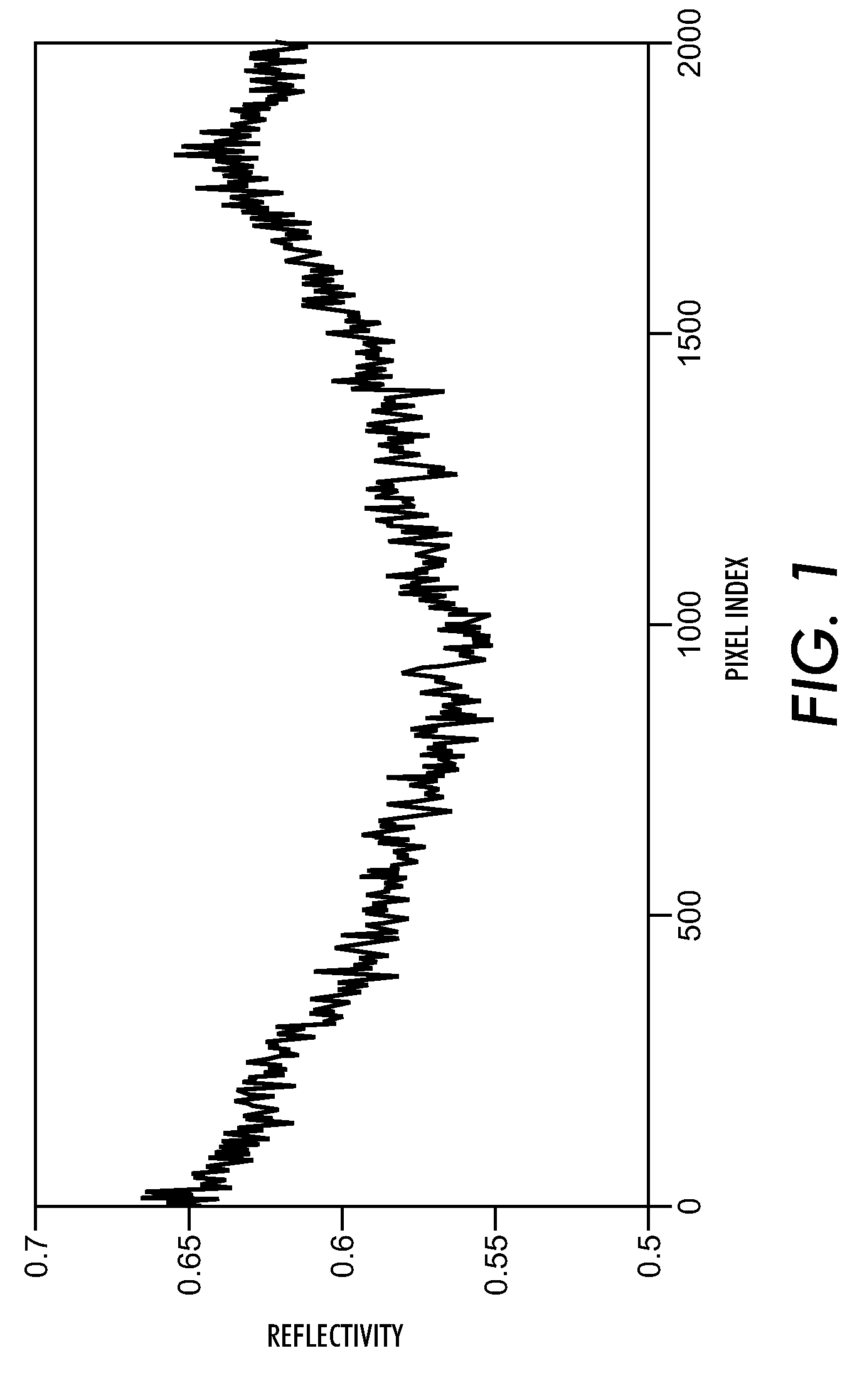
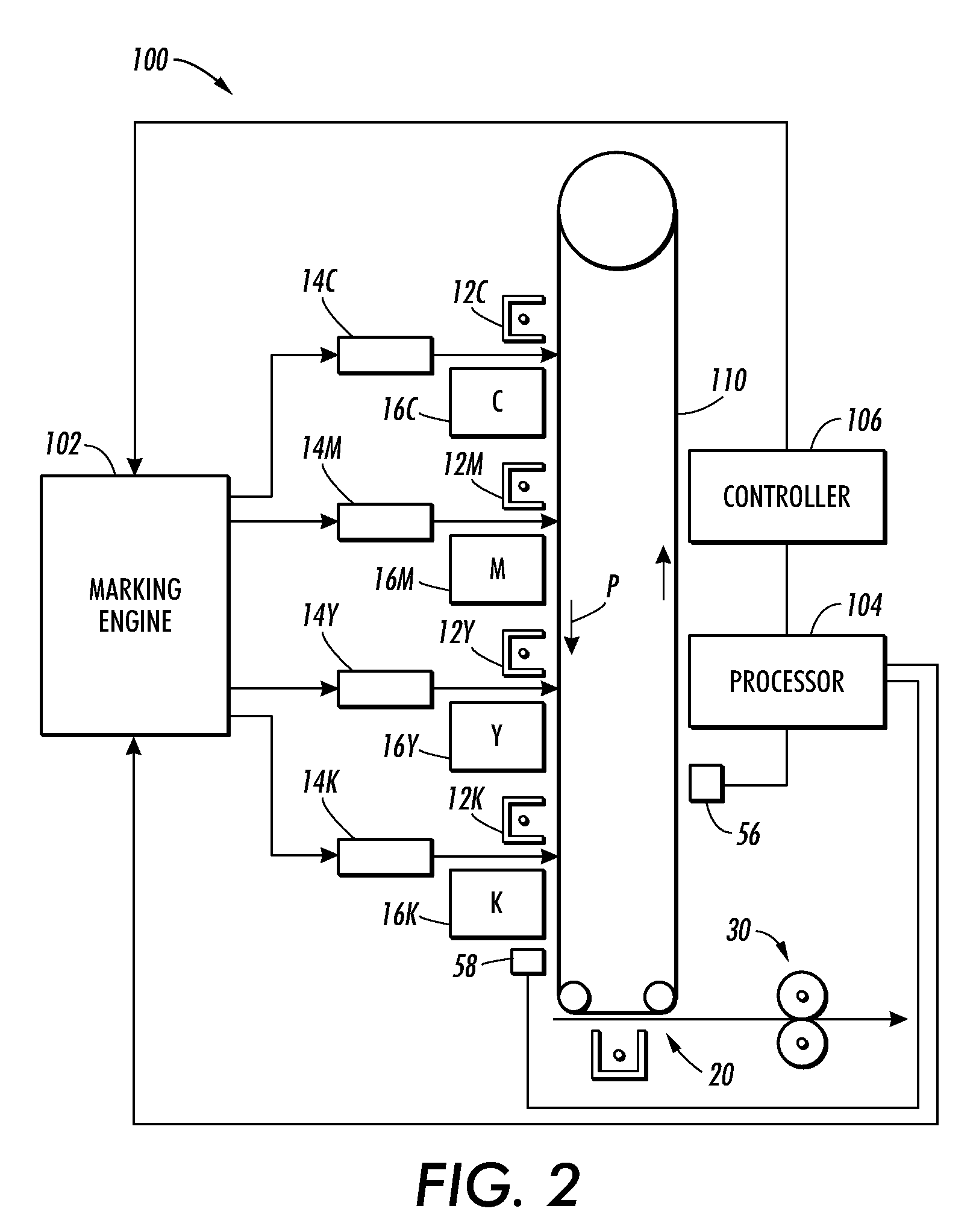
Method and system for improved solid area and heavy shadow uniformity in printed documents
InactiveUS20100214580A1Minimizing cross-process non-uniformitiesImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersOptical propertyTone reproduction
A method for minimizing cross-process non-uniformities in solid and heavy shadow regions of printed documents is provided. The method includes marking with a marking engine an image on an image bearing surface moving in a process direction; generating profile data of the image by sensing an optical characteristic of the image in a cross-process direction; adjusting at least one control actuator of the marking engine so as to shift the characteristic of a subsequent marked image in the cross-process direction to at least a target value; and generating a spatially varying tone reproduction curve to smooth the characteristic of the subsequent marked image towards the target value.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Self-aligning stencil device and method of producing a multi-color composite image
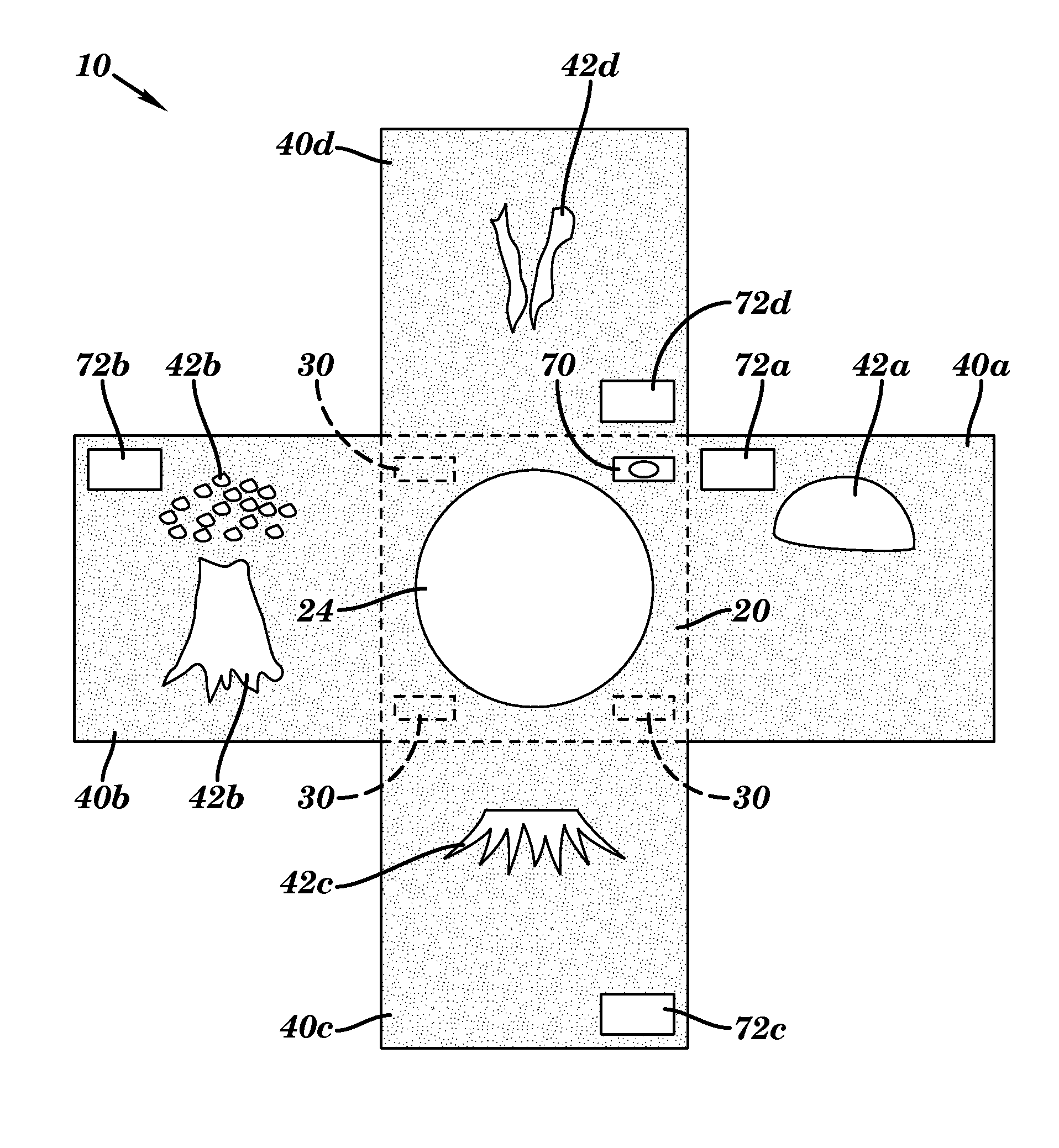
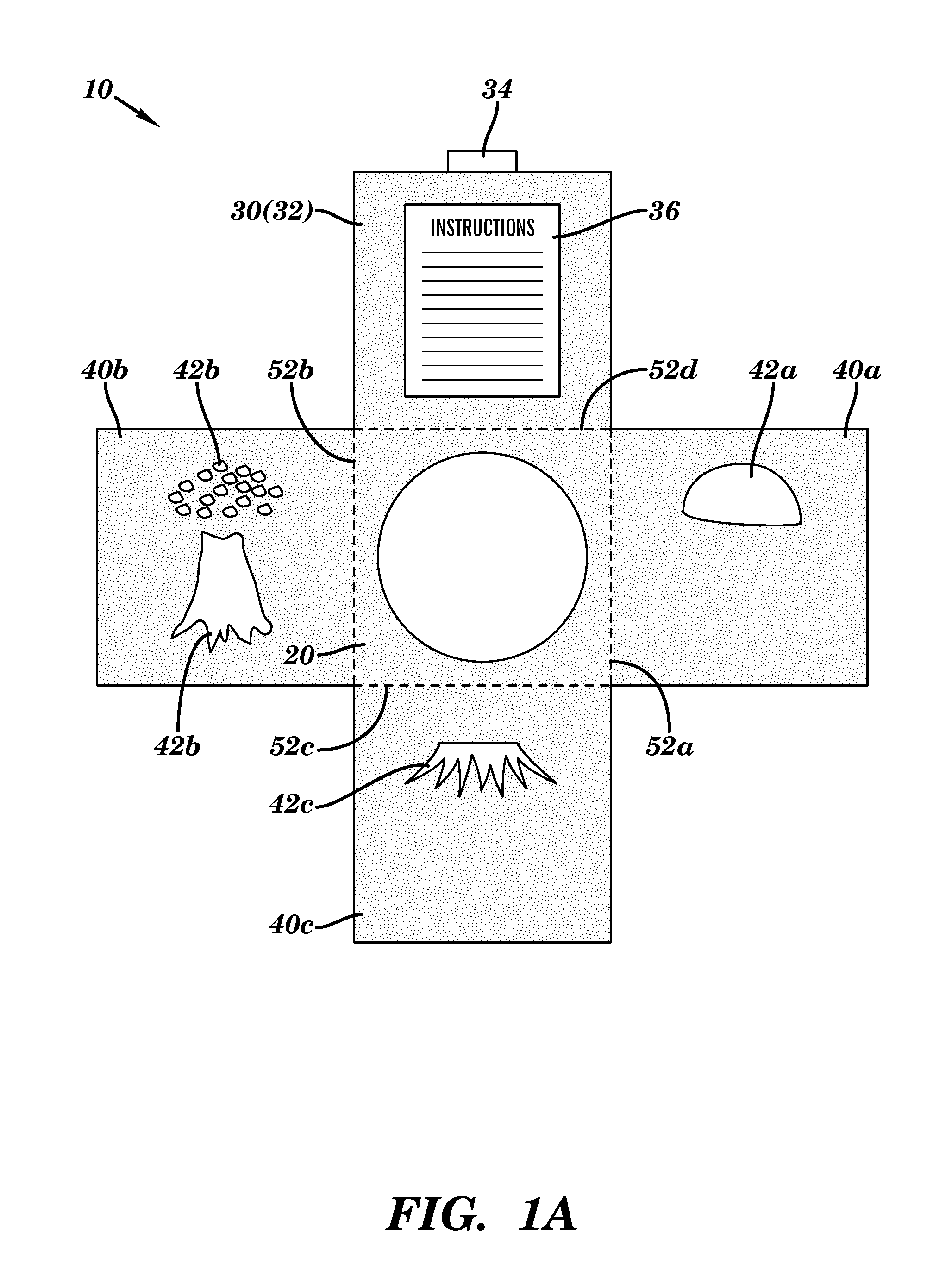
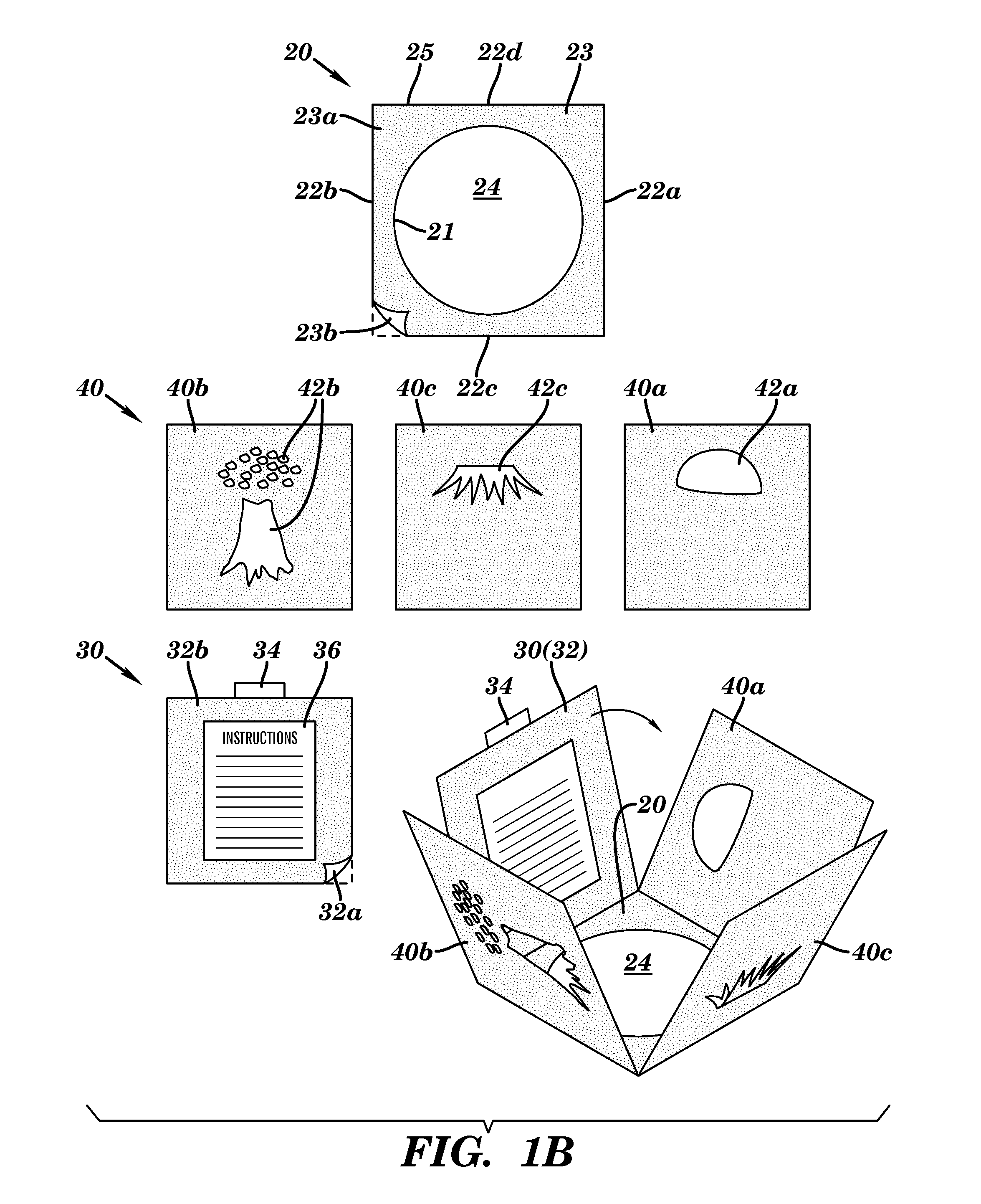
ActiveUS8590448B2Facilitating multi-colorLiquid surface applicatorsScreen printersTarget surfaceSolid region
The present invention relates to a self-aligning stencil device for producing a multi-color composite image on a target surface. The self-aligning stencil device includes a central panel and a plurality of stencil panels foldably connected to the central panel. The central panel includes a solid region and a cut-out region. The solid region of the central panel includes a front surface and a back surface, and is defined by an outer border of the central panel and an inner border of the central panel. The cut-out region is vacant space that is defined by the inner border of the central panel. Each stencil panel has its own distinct stencil pattern and is foldably connected to a different corresponding portion of the outer border of the central panel, thereby forming a connection fold between each stencil panel and its corresponding portion of the outer border of the central panel. The plurality of stencil panels, when folded at their connection folds upon the central panel, self-align to collectively form a composite image, so that painting each distinct stencil pattern with a different color is effective to yield a multi-color composite image on a region of the surface imposed behind the cut-out region of the central panel. Also disclosed are kits and methods for producing multi-color composite images using the device of the present invention.
Owner:INNOVATIVE ART CONCEPTS
Improved level set topology optimization method for stable hole formation
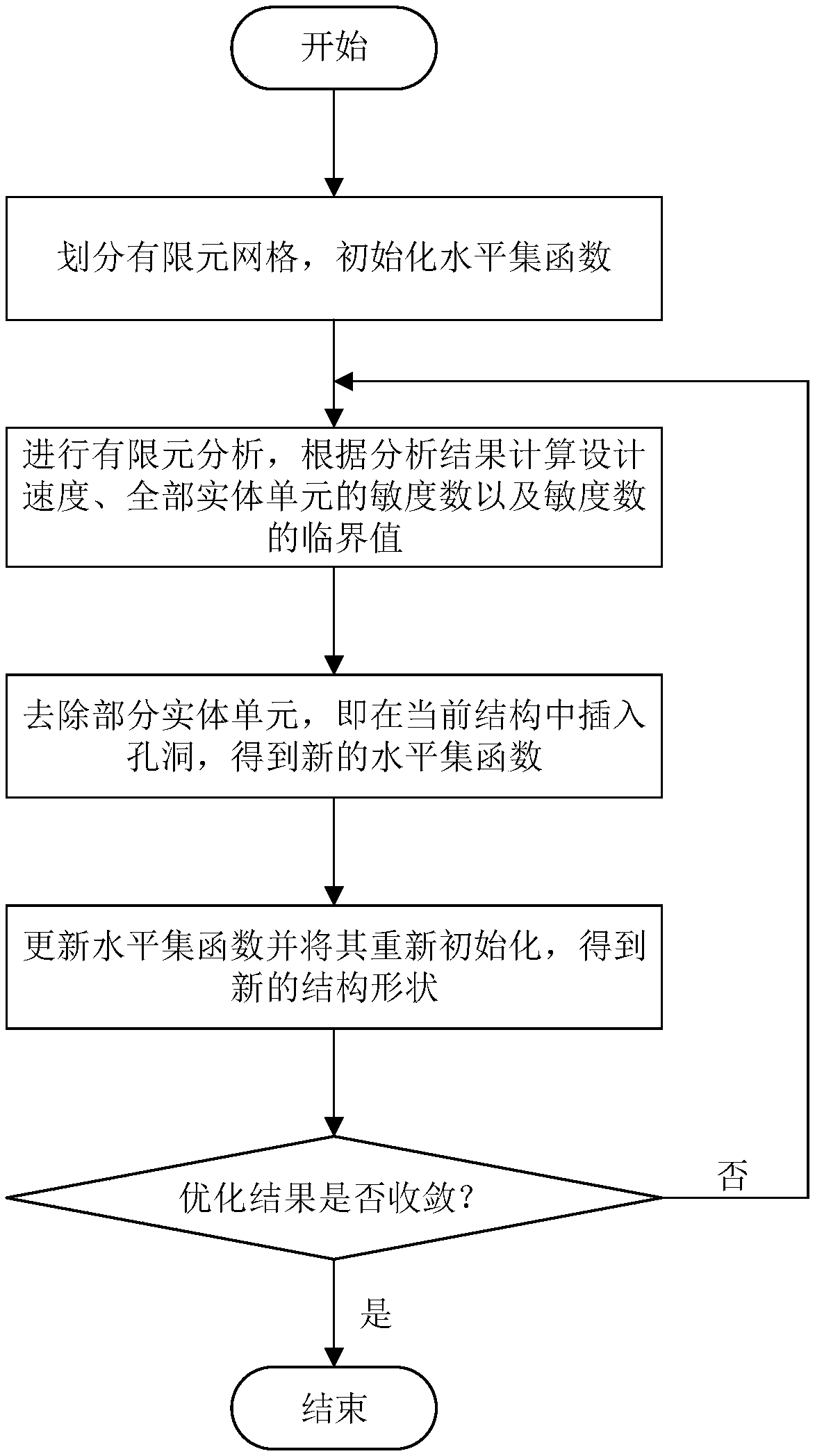
ActiveCN109002614AAvoid dependencyImprove reliabilityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSolid regionGrid cell
The invention belongs to the technical field of structural topology optimization, and discloses an improved level set topology optimization method for stable hole formation. The method includes: (a) dividing the finite element mesh into design domains, initially dividing the mesh into solid and cavity domains, and initially assigning values to the level set functions; (b) calculating a displacement vector in the design domain; (c) calculating the sensitivity of each grid cell in the velocity field and the physical region; (d) optimizing the initialized solid region, the cavity region and the level set function for the first time by using the sensitivity number; (e) using the velocity field to update the level set function of each grid cell in the entity and the cavity region respectively so as to redivide the entity region and the cavity region, thereby realizing the second optimization; (f) judging whether the result of the second optimization converges or not according to the flexibility and volume error. The invention overcomes the defect that the traditional level set topology optimization method cannot form holes in the structure, and solves the dependence of the optimizationproblem on the initial design, which is stable and effective.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
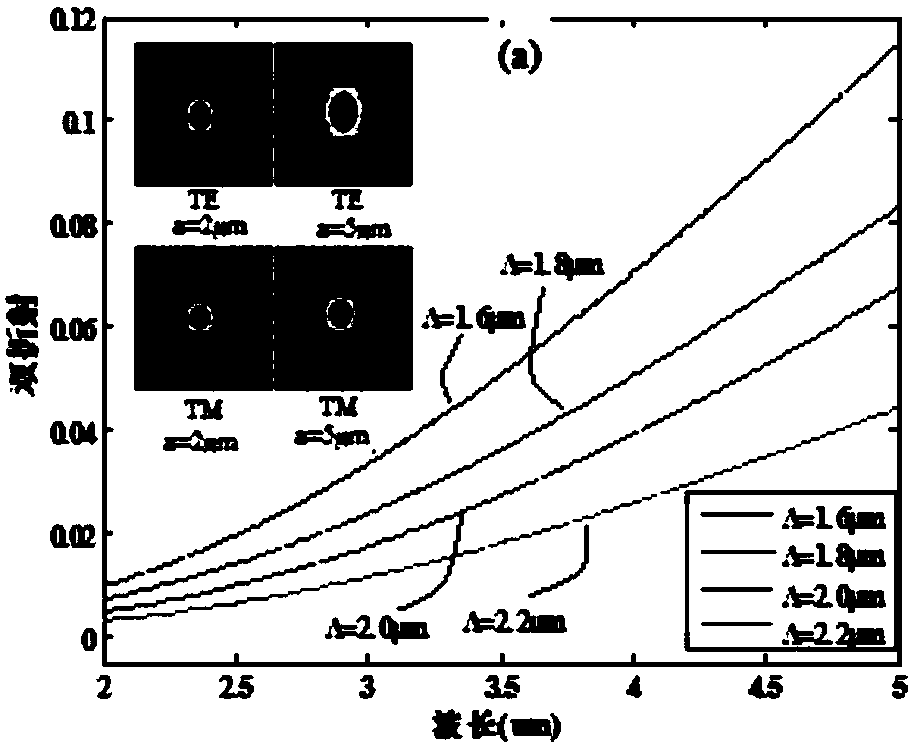
Sulfur high-birefringence photonic crystal fiber in waveband range from 2 micrometers to 5 micrometers
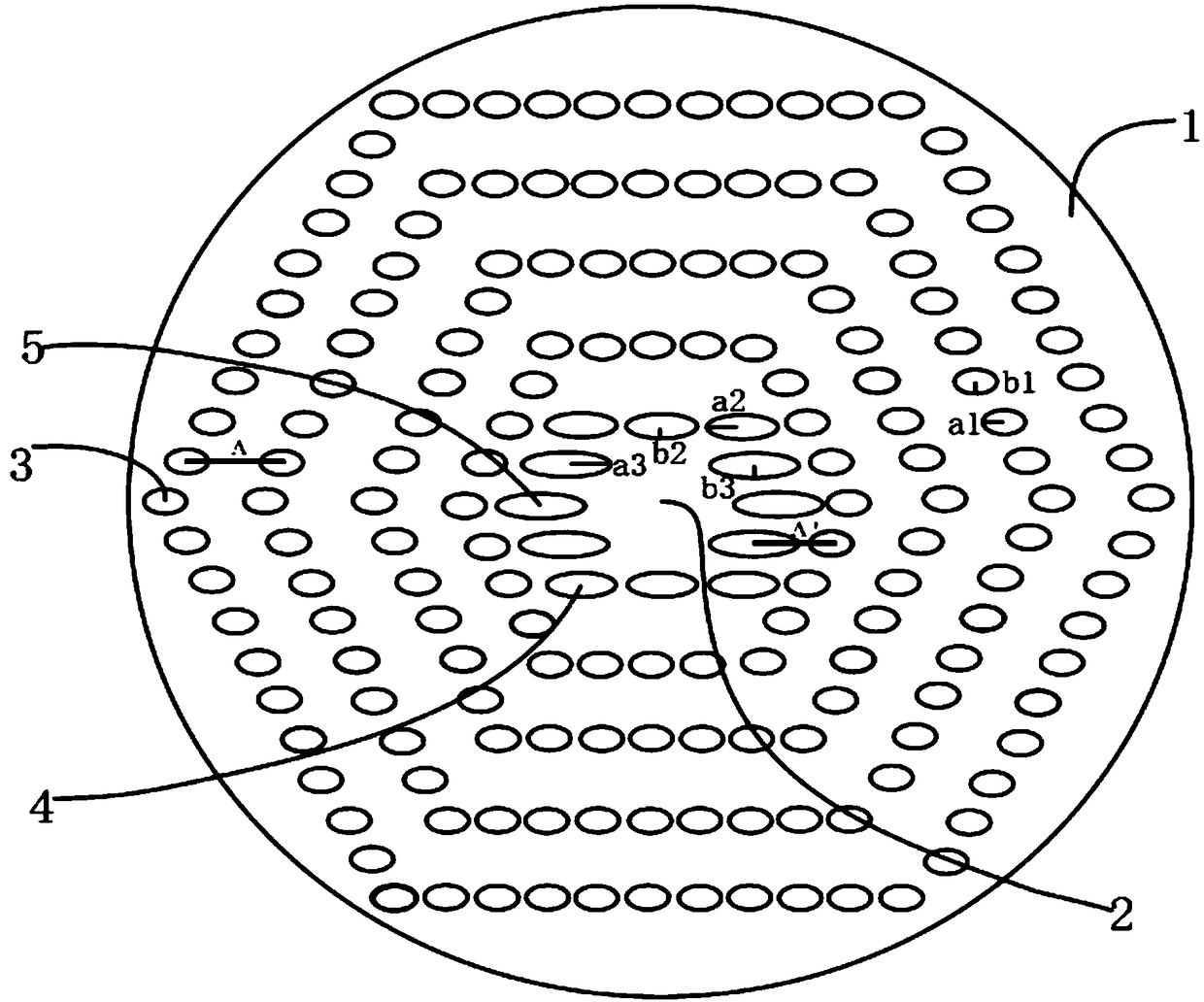
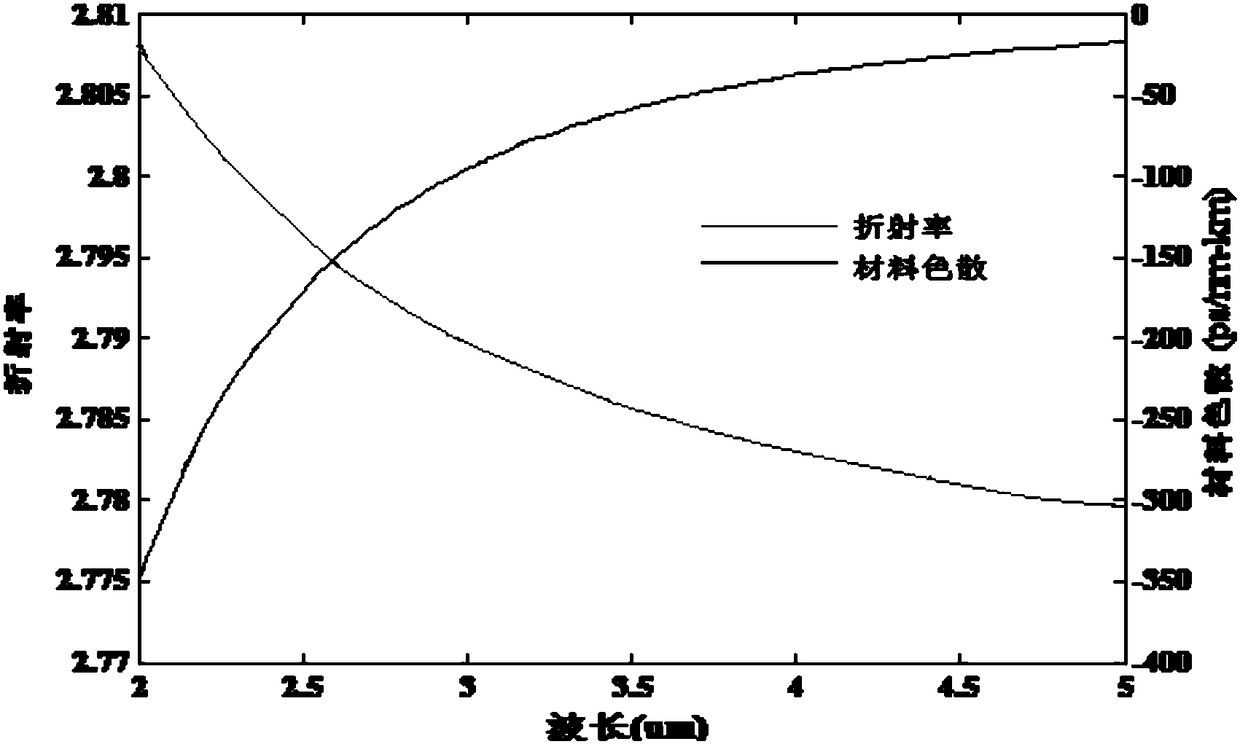
ActiveCN108152881AOvercome the shortcoming of only working in the near-infrared bandCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideSolid regionPolarization-maintaining optical fiber
The invention provides a sulfur high-birefringence photonic crystal fiber in the waveband range from 2 micrometers to 5 micrometers. An elliptical air hole is absent in a hexagonal lattice photonic crystal structure to form the sulfur high-birefringence photonic crystal fiber. The sulfur high-birefringence photonic crystal fiber comprises a fiber core and cladding. The fiber core and the claddingare positioned on a fiber background material, the cladding is of a hexagonal lattice elliptical air hole array structure, the hexagonal lattice elliptical air hole array structure comprises four outer first elliptical hole systems and inner second elliptical hole systems, the first elliptical hole systems comprise concentric hexagons, and the fiber core is a solid region in the center of the fiber background material. The sulfur high-birefringence photonic crystal fiber has the advantages that light fields in the sulfur high-birefringence photonic crystal fiber are restrained by the claddingwith multiple types of elliptical air hole structures, accordingly, the problem of required long lengths of common polarization maintaining fibers can be solved, the shortcoming that silicon-dioxide-based high-birefringence fibers only can work in near infrared wavebands can be overcome, and complicated fiber core doping technologies can be omitted.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
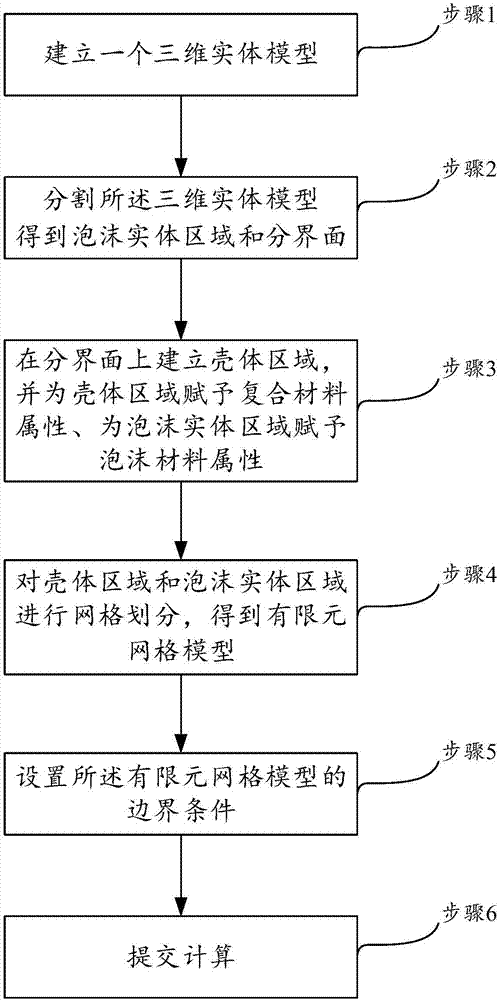
Simple finite element modeling method for composite stiffened skin-foam sandwich structure
InactiveCN107292010AEasy to masterEasy to useDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSolid regionElement model
The invention discloses a simple finite element modeling method for a composite stiffened skin-foam sandwich structure. The method comprises the steps that 1, a three-dimensional entity model is established; 2, the three-dimensional entity model is partitioned to obtain a foam entity area and an interface; 3, a layer of shell area is established on the interface, composite properties are given to the shell area, and foam material properties are given to the foam entity area; 4, meshing is performed on the shell area and the foam entity area; 5, boundary conditions are set; and 6, submission is performed for calculation. The improved simple finite element modeling method for the composite stiffened skin-foam sandwich structure is proposed creatively, the modeling workload is greatly reduced, coupling calculation precision is effectively improved, and therefore the stress transmission effect and the strain transmission effect between finite element model nodes are improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACE LAUNCH TECH +1
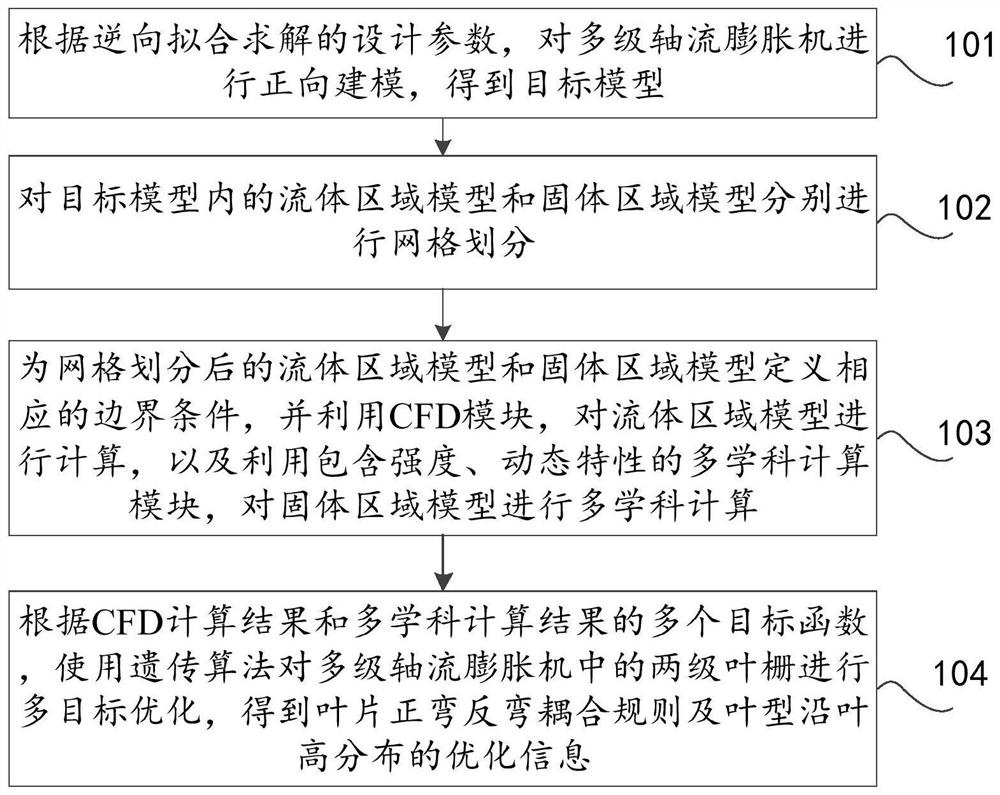
Multi-disciplinary optimization design method, device and equipment for multistage axial flow expander
PendingCN112417773AImprove unit efficiencyImprove stabilityDesign optimisation/simulationGenetic algorithmsSolid regionGenetics algorithms
The invention discloses a multi-disciplinary optimization design method, device and equipment for a multistage axial flow expander, and relates to the technical field of expander designs. The method comprises the steps: firstly carrying out the forward modeling of the multistage axial flow expander according to design parameters solved through reverse fitting, and obtaining a target model; defining corresponding boundary conditions for the fluid region model and the solid region model after grid division, calculating the fluid region model by using a CFD module, and performing multidisciplinary calculation on the solid region model by using a multidisciplinary calculation module containing strength, dynamic characteristics and the like; and finally, according to a plurality of target functions of the CFD calculation result and the multidisciplinary calculation result, performing multi-target optimization on two stages of blade grids in the multistage axial flow expander by using a genetic algorithm to obtain a forward bending and backward bending coupling rule of the blade and optimization information of distribution of the blade profile along the blade height. The multi-disciplinary optimization design of the multi-stage axial flow expander can be effectively carried out.
Owner:SHENYANG BLOWER WORKS GROUP CORP
Photonic crystal fiber sensor
Apparatus and method for chemical and biological agent sensing. An example sensing apparatus includes a resonator having a resonance frequency. The resonator includes a coil of a photonic crystal fiber. The photonic crystal fiber has a solid region configured to guide a substantially single optical mode of light having, a cladding surrounding an exterior of the solid region, and at least one hollow core within the cladding. The cladding contains at least one hollow core. The photonic crystal fiber is configured to introduce a fluid that may contain an analyte to the hollow core. The photonic crystal fiber is configured so that the light interacts with the fluid. The resonator is configured to produce a resonance signal centered at the resonance frequency. A predetermined change in the resonance signal indicates a presence of a quantity of the analyte in the fluid.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Research method for fuel oil liquid drop evaporation process in porous medium model structure
ActiveCN106354963AImprove combustion efficiencyEmission reductionGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsSolid regionPorous medium
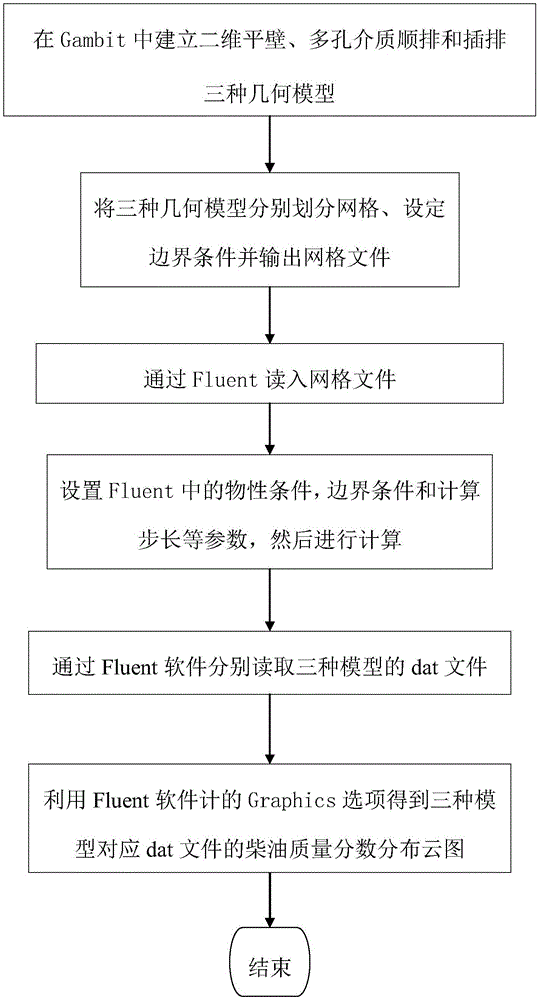
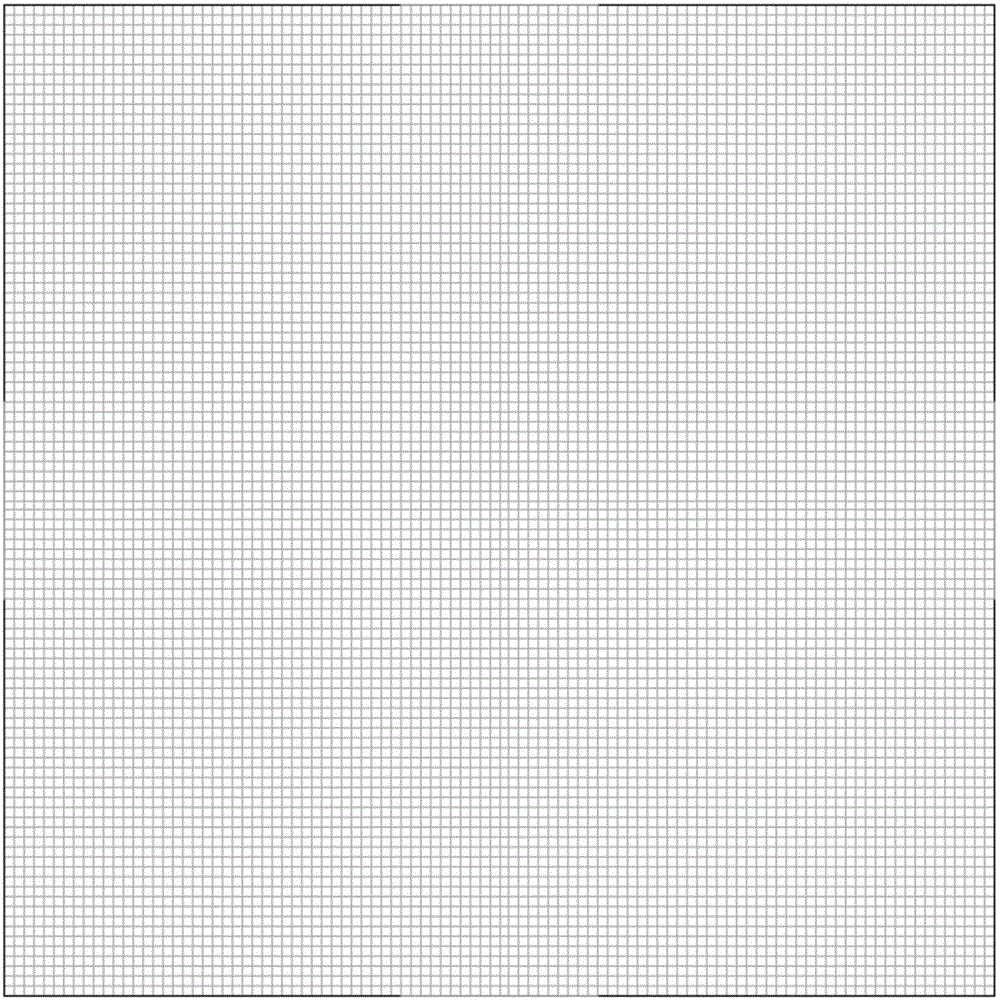
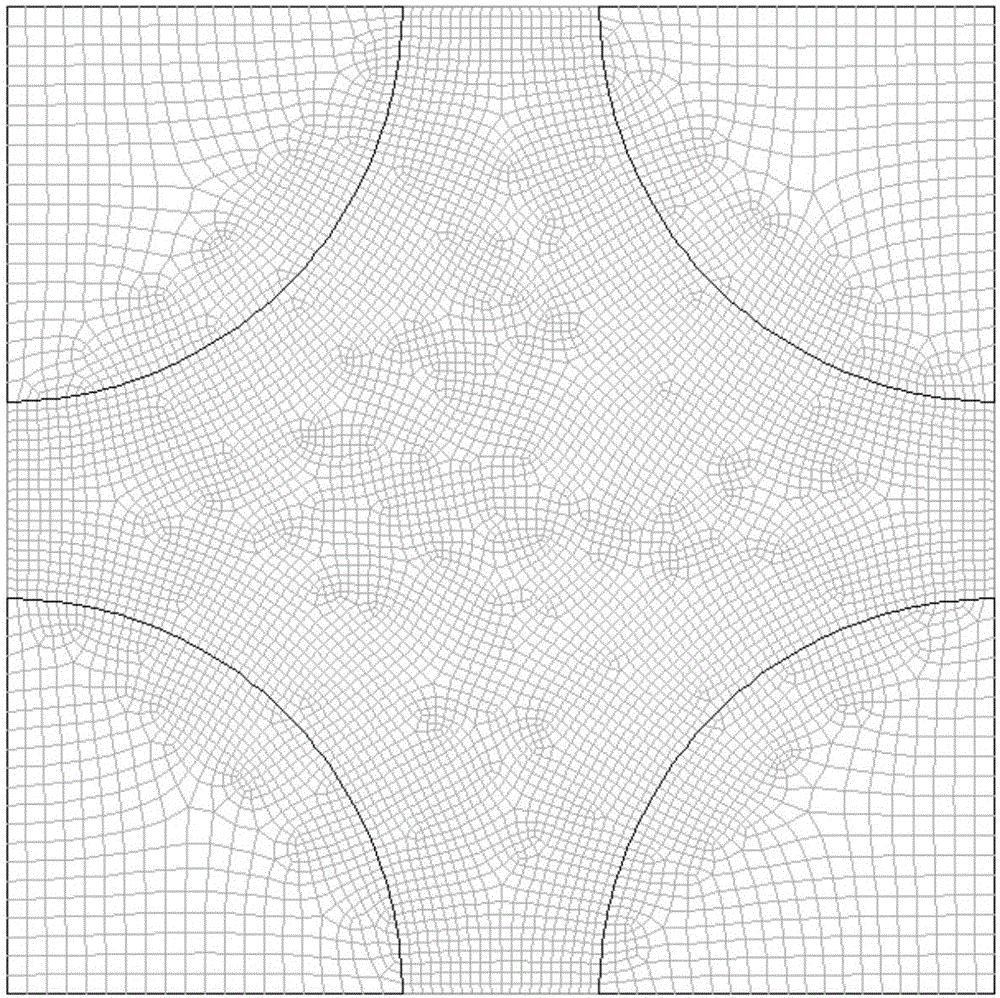
The invention provides a research method for the fuel oil liquid drop evaporation process in a porous medium model structure. The method includes the steps that Gambit software is used for constructing three model structures (including aligned arrangement and interleaved arrangement structure porous medium models instead of a porous medium model), corresponding grids are drawn, and wall surface attribute in the models as well as a fluid region and a solid region are set; grid files of the three kinds of models manufactured by Gambit are guided into Fluent software, and calculation method in the three models and the physical property parameters of fuel oil liquid drops are set by the Fluent software and calculated respectively, and then the fuel oil liquid drop evaporation processes in the three kinds of models are compared to obtain a mass fraction distribution cloud picture of the fuel oil liquid drops. The distribution rule of the mass fraction of the fuel oil liquid drops can be researched and analyzed, which is of great significance in further improving fuel combustion efficiency, reducing pollutant emission and researching and developing a new porous medium model.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
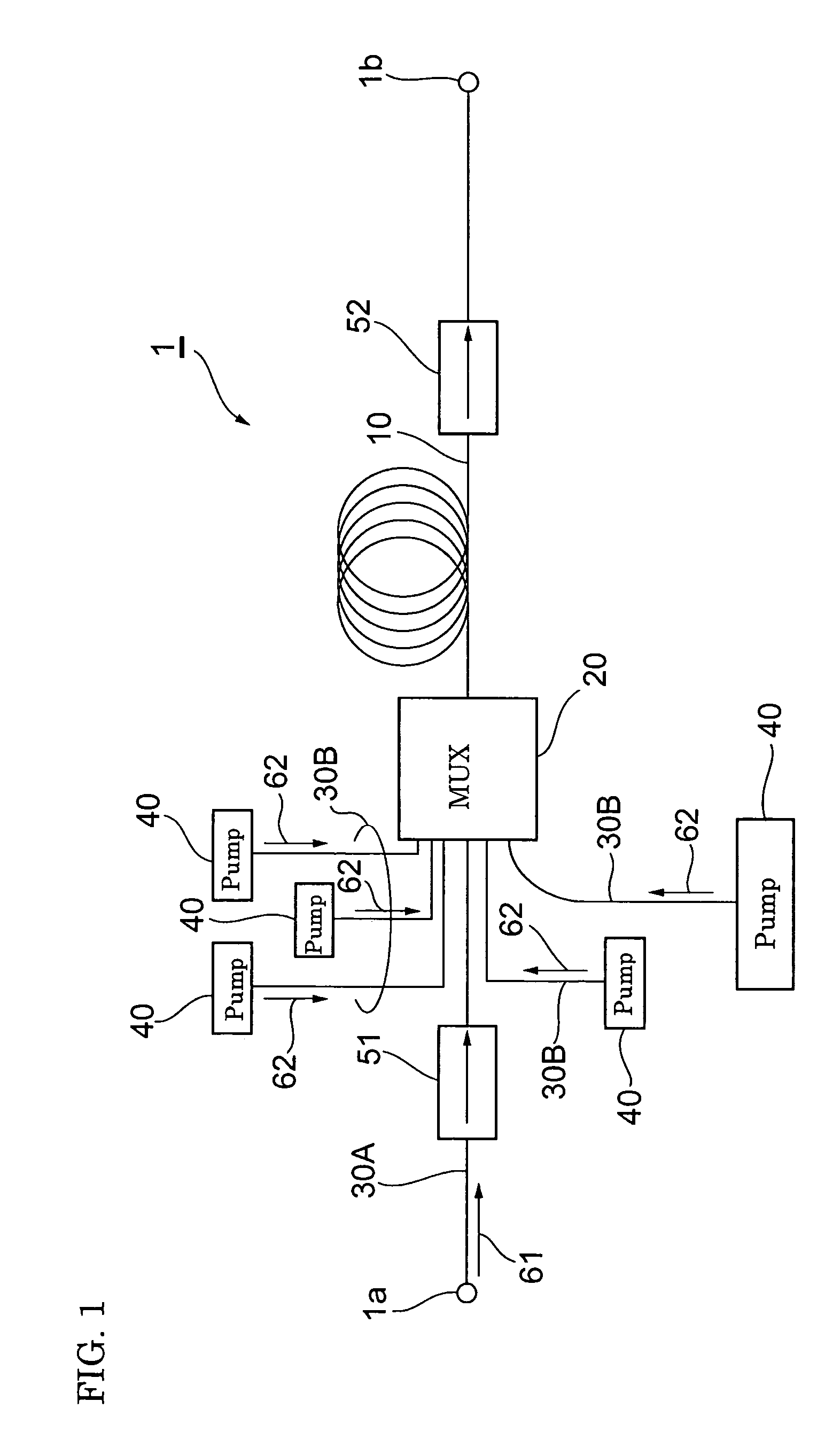
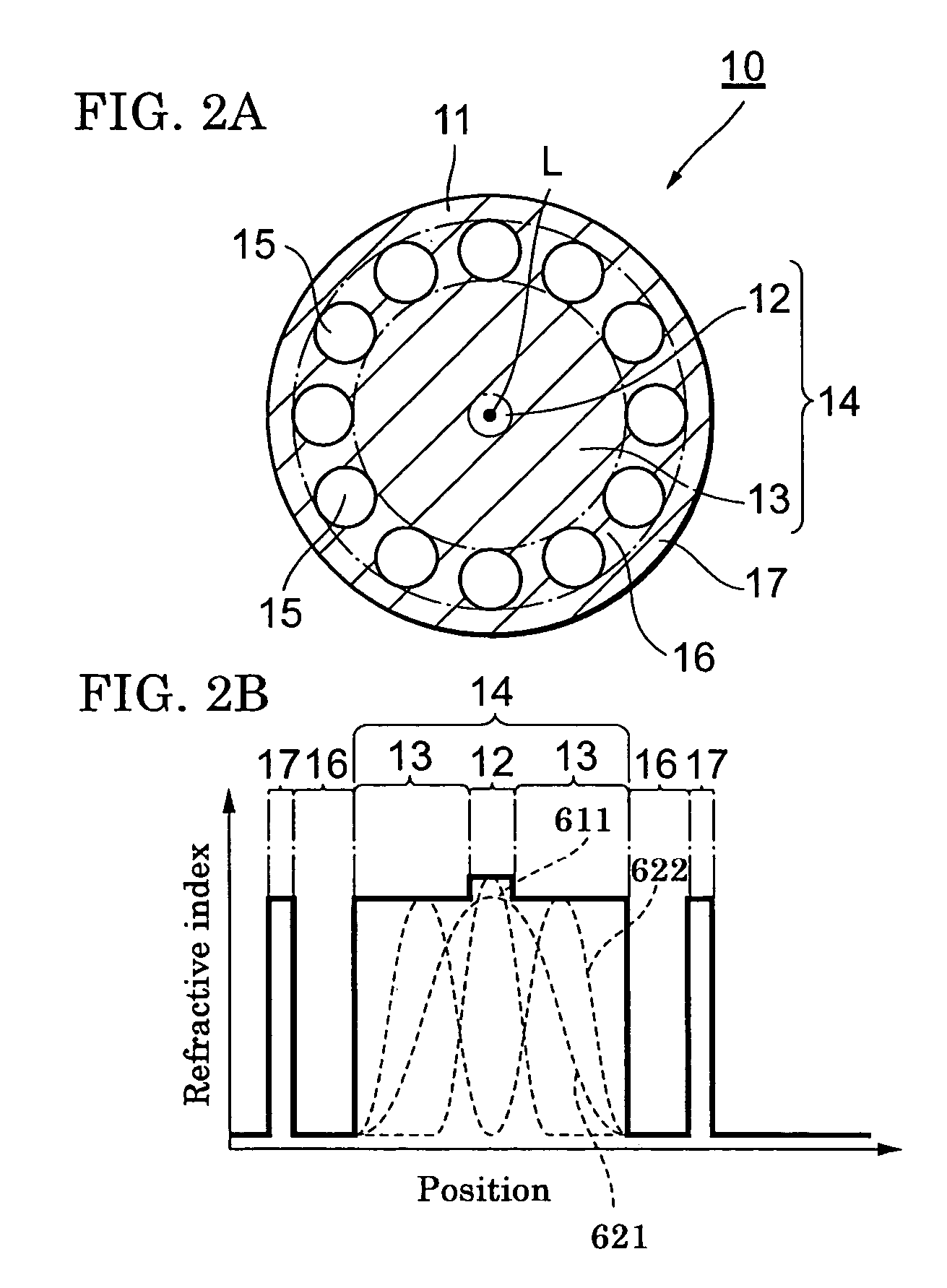
Optical fiber, optical fiber amplifier, and optical fiber laser light source
InactiveUS7362937B2Efficiently excitedLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingSolid regionOptical fiber amplifiers
An optical fiber can efficiently excite metallic ions by a pump lightwave, and an optical fiber amplifier and an optical fiber laser light source both incorporate the optical fiber. The optical fiber comprises (a) a solid region that has a first region doped with metallic ions and a second region surrounding the first region and that allows a lightwave for exciting the metallic ions to travel in a multiple mode and (b) a third region surrounding the second region and having a plurality of holes stretching along the length of the optical fiber. The optical fiber has a structure in which the first region is supplied with the power of a lightwave that is included in the pump lightwave and that is in a mode having no intensity peak at the center axis of the solid region.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com