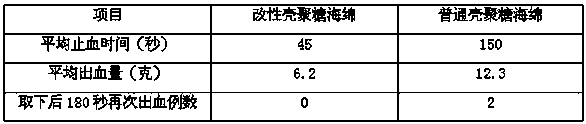
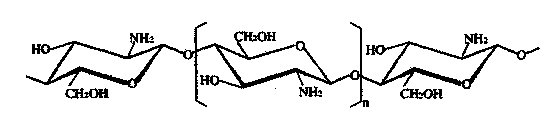
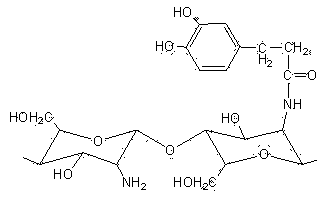
Modified chitosan having catechol group and biomedical material prepared from modified chitosan
A biomedical, catechol-based technology, applied in the field of chitosan, can solve the problems of high brittleness, poor water absorption, poor solubility, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0037] 1. Select dry chitosan powder with particle size less than 400 mesh, molecular weight greater than 200,000, and degree of deacetylation greater than 85%, 50g.
[0038] 2. Dissolve the above-mentioned dry powder in a 4% acetic acid solution at 60°C, keep stirring at this temperature, stop stirring after 36 hours, and filter the insoluble matter.
[0039] 3. Dissolve 5g of dopa or 3-(3,4-dihydroxy) phenylpropionic acid in water, add helium gas, add 2 times the amount of EDC condensing agent under the protection of helium gas, adjust the pH to 6-12, React overnight to prepare EDC ester.
[0040] 4. Disperse the EDC ester prepared in step 3 into the chitosan solution prepared in step 2, adjust the pH to 4-10, stir overnight, and let stand for 24 hours.
[0041] 5. Under vigorous stirring, add glutaraldehyde dropwise to the product obtained in the previous step to control the amount of glutaraldehyde to control the degree of cross-linking at 0.1-10%.
[0042] 6. Drop the product obta...
example 2
[0044] 1. Select dry chitosan powder with particle size less than 400 mesh, molecular weight greater than 200,000, and degree of deacetylation greater than 85%, 50g.
[0045] 2. Dissolve the above dry powder in a 4% acetic acid solution at 60°C, keep the temperature and stir, stop stirring after 36 hours, and filter the insoluble matter.
[0046] 3. Dissolve 5 g of dopamine in water, pass in helium gas, add 2 times the amount of epichlorohydrin under the protection of helium gas, adjust the pH to 5-12, and react overnight to prepare a grafted activator.
[0047] 4. Disperse the product prepared in step 3 into the chitosan solution prepared in step 2, adjust pH to 4-10, stir overnight, and let stand for 24 hours.
[0048] 5. Under vigorous stirring, add genipin dropwise to the product obtained in the upper step to control the amount of genipin and control the degree of crosslinking to 0.1-10%.
[0049] 6. The product obtained in the previous step is freeze-dried, and a hemostatic sponge ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com