Raman distributed feedback fiber laser and high power laser system using the same
A Raman laser, pump laser technology, applied in lasers, laser parts, laser monitoring devices, etc., can solve the problems of high power, loss, and difficulty of long grating for narrowband signals.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0060] Tunable lasers with a single frequency and narrow linewidth have the potential to be used in a wide variety of applications, such as remote sensing, LIDAR, spectroscopy, optical coherence tomography, and others.
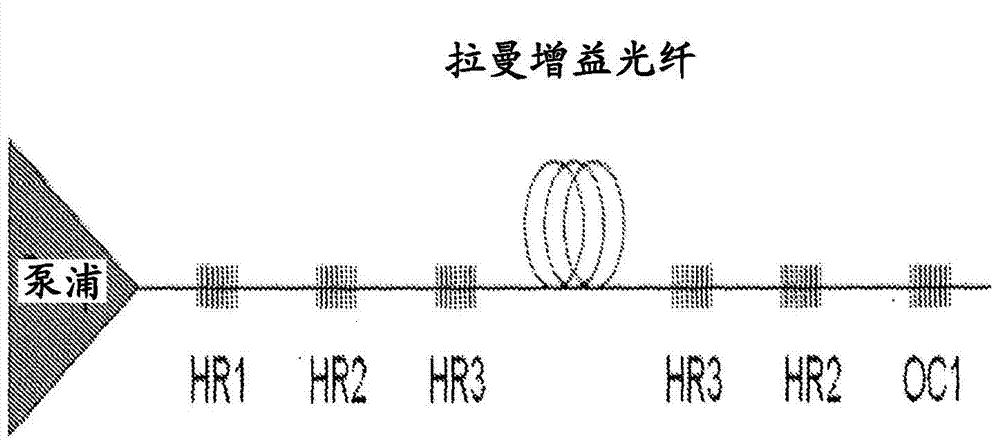
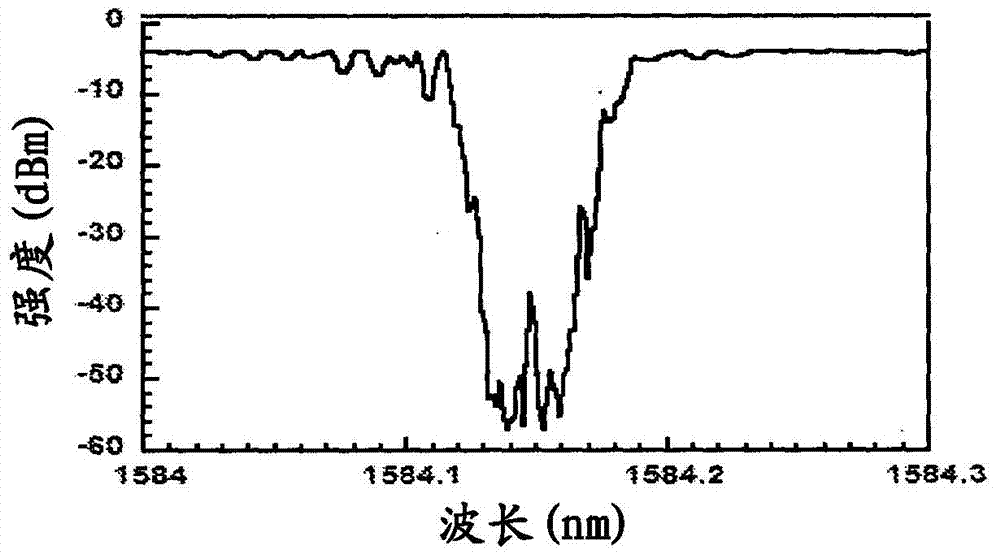
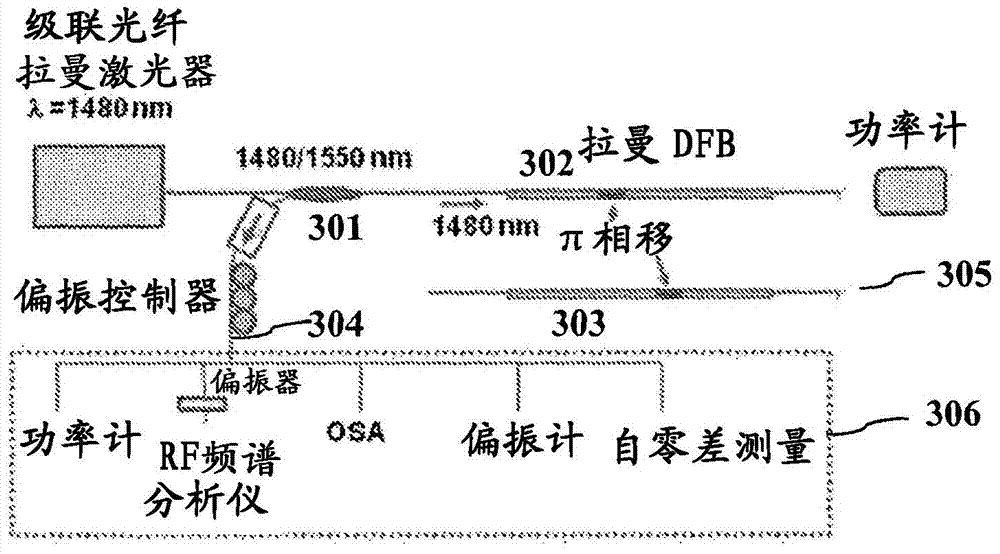
[0061] There are many ways in which laser radiation can be obtained, including external cavity lasers, semiconductors, fiber distributed feedback (DFB) lasers. DFB lasers can be created with fiber Bragg gratings written in the core of an active fiber waveguide and are capable of producing narrowband laser radiation when pumped at the appropriate wavelength. Compared with semiconductor DFB lasers, fiber DFB lasers are attractive because of their superior optical properties, including low noise and narrower linewidth. Furthermore, the in-fiber design of this fiber DFB laser enables efficient coupling to fiber amplifiers and other fiber components. "Pumping" as mentioned here means supplying an energy source that is usually converted into laser signal (output) e...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com