Optical amplifier
a technology of optical amplifiers and amplifiers, applied in the field of optical amplifiers, can solve the problems of increasing the loss range, voa loss range, and affecting the performance of the optical amplifier, so as to increase the power of the ld
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0051] the present invention will be described in detail with reference to drawings.
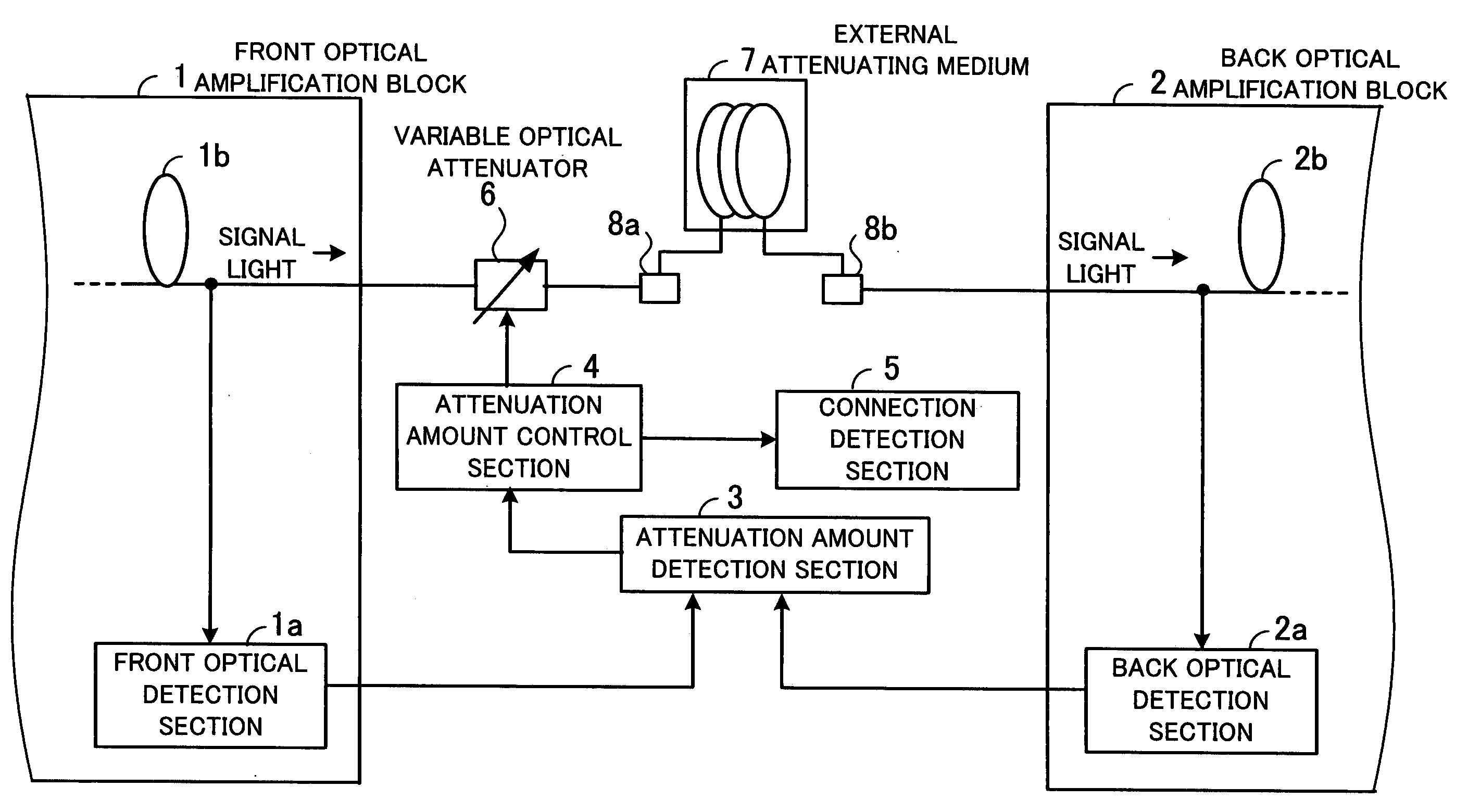
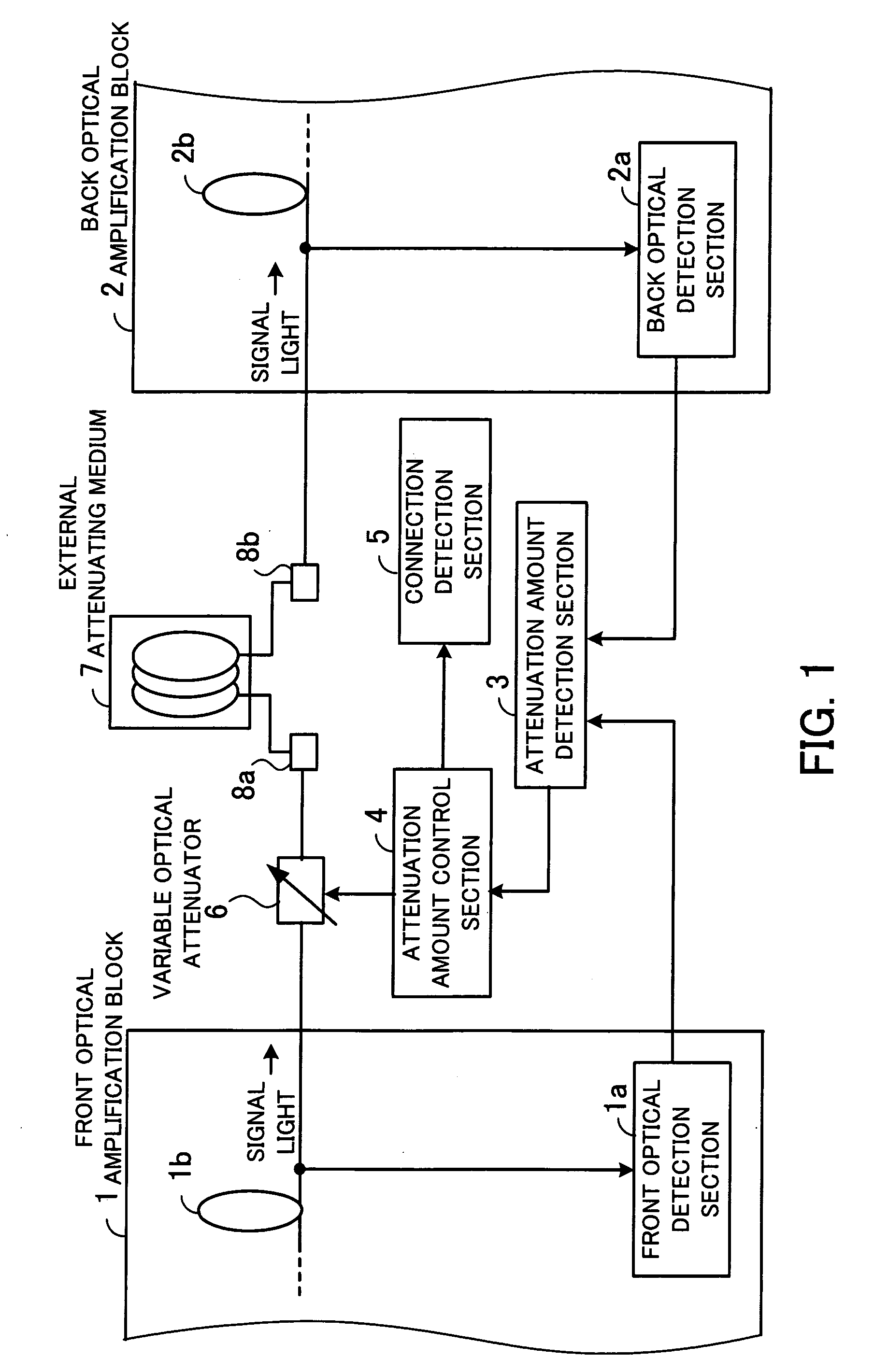
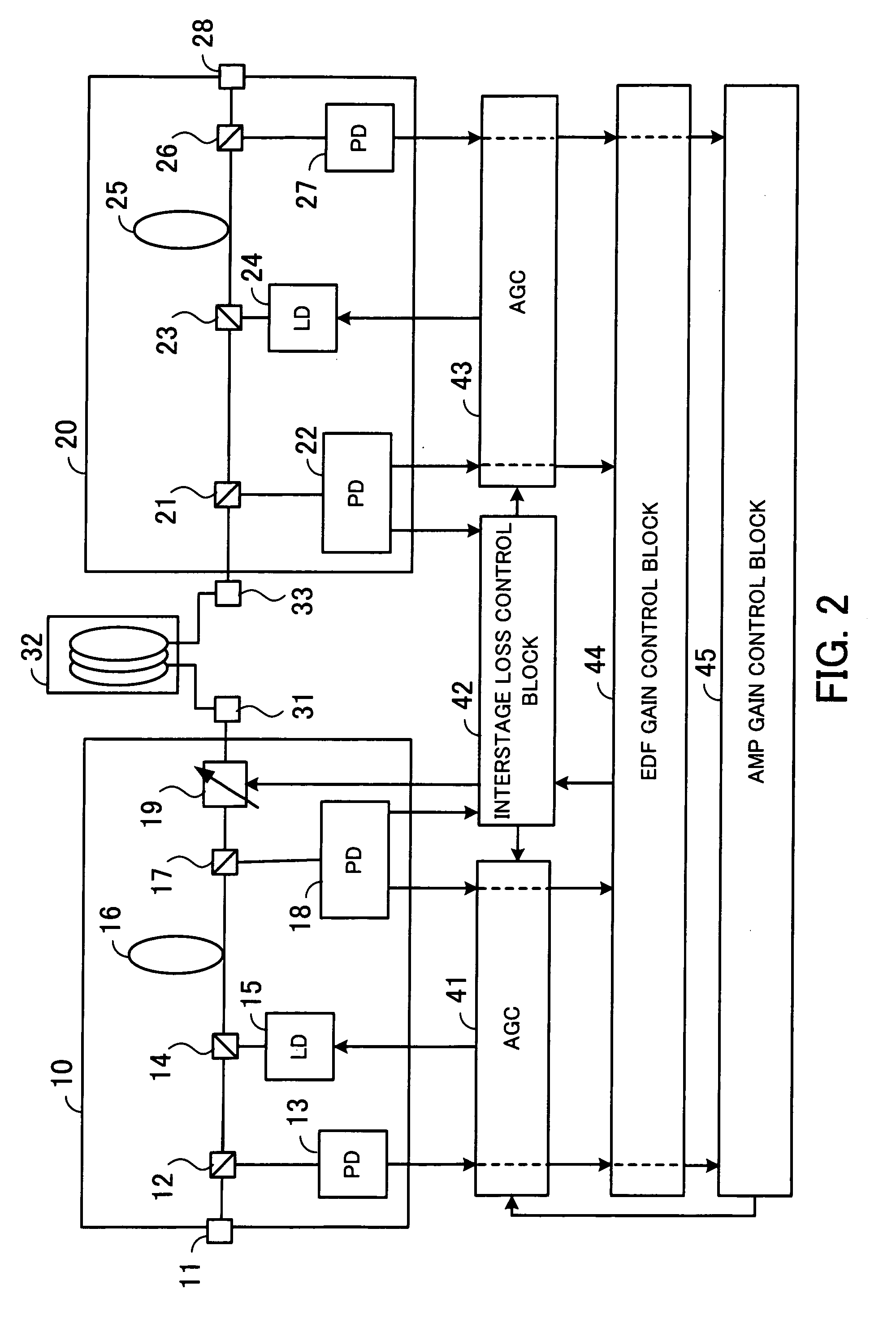
[0052]FIG. 2 is a block diagram of an optical amplifier of the first embodiment. As shown in the figure, the optical amplifier includes a front optical amplification block 10, a back optical amplification block 20, a DCF 32 connected to terminals 31 and 33, automatic gain controllers (AGCs) 41 and 43, an interstage loss control block 42, an EDF gain control block 44, and an AMP gain control block 45. The front optical amplification block 10 includes an input terminal 11, couplers 12, 14, and 17, PDs 13 and 18, an LD 15, an EDF 16, and a VOA 19. The back optical amplification block 20 includes couplers 21, 23, and 26, PDs 22 and 27, an LD 24, an EDF 25, and an output terminal 28.
[0053] The input terminal 11 of the front optical amplification block 10 receives wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) signal light, for instance. The signal light input to the input terminal 11 passes the couplers 12 and 1...
second embodiment
[0106]FIG. 8 is a block diagram of an optical amplifier of the As shown in the figure, the optical amplifier includes a front optical amplification block 50, a back optical amplification block 70, a DCF 82 connected to terminals 81 and 83, AGCs 91 and 93, an interstage loss control block 92, an EDF gain control block 94, a constant loss control block 95, and an AMP gain control block 96. The front optical amplification block 50 includes an input terminal 51, couplers 52, 54, 57, 60, 62, and 65, PDs 53, 58, 61, and 66, LDs 55 and 63, EDFs 56 and 64, and VOAs 59 and 67. The back optical amplification block 70 includes couplers 71, 73, and 76, PDs 72 and 77, an LD 74, an EDF 75, and an output terminal 78.
[0107] The input terminal 51 of the front optical amplification block 50 receives a WDM signal light, for instance. The signal light input to the input terminal 51 is output through the couplers 52 and 54 to the EDF 56. The signal input to the input terminal 51 is also branched off to...
third embodiment
[0162]FIG. 11 shows an optical amplifier of the As shown in the figure, the optical amplifier includes a front optical amplification block 140, a back optical amplification block 150, a DCF 172 connected to terminals 171 and 173, AGCs 181 and 183, an interstage loss control block 182, a constant loss control block 184, an EDF gain control block 185, and an AMP gain control block 186.
[0163] The front optical amplification block 140 includes an input terminal 141, couplers 142, 144, and 147, PDs 143 and 148, an LD 145, and an EDF 146. The back optical amplification block 150 includes couplers 151, 153, 156, 159, 161, and 164, PDs 152, 157, 160, and 165, LDs 154 and 162, EDFs 155 and 163, a VOA 158, and an output terminal 166. The front optical amplification block 140 is analogous to the back optical amplification block 70 shown in FIG. 8, and a detailed description of the front optical amplification block 140 will be omitted. The back optical amplification block 150 is analogous to t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com