Patents
Literature
128 results about "Convergent beam" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
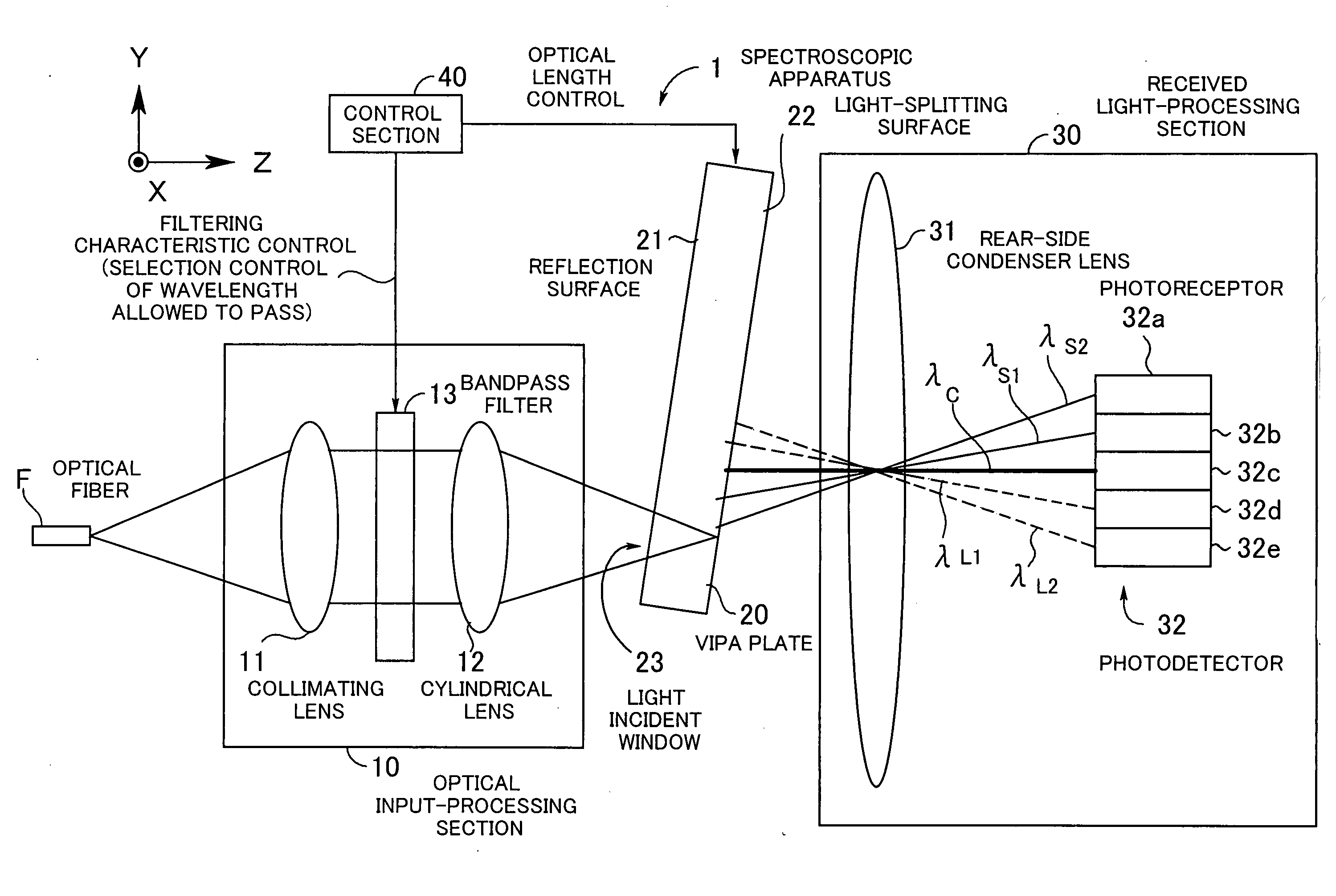
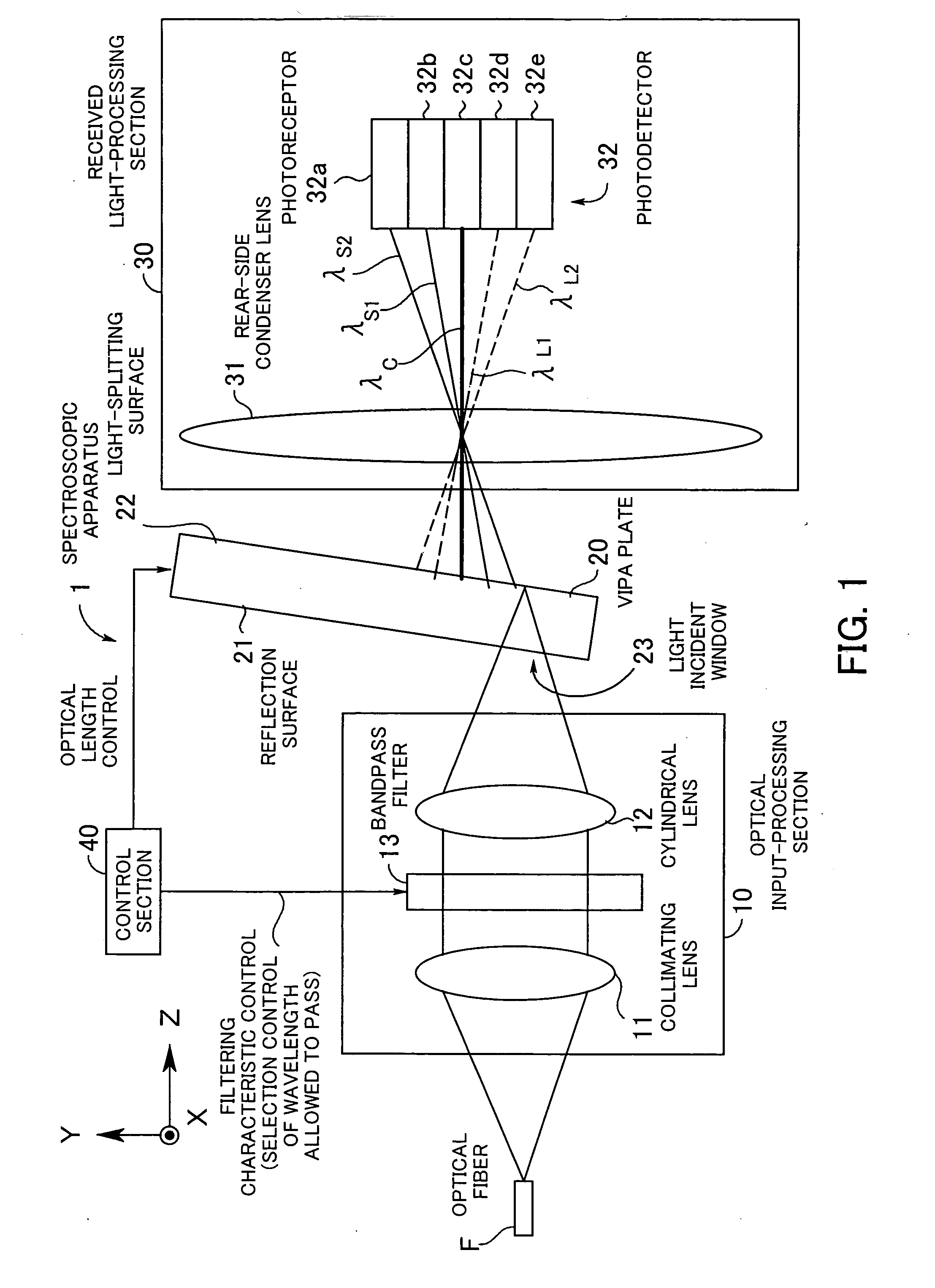
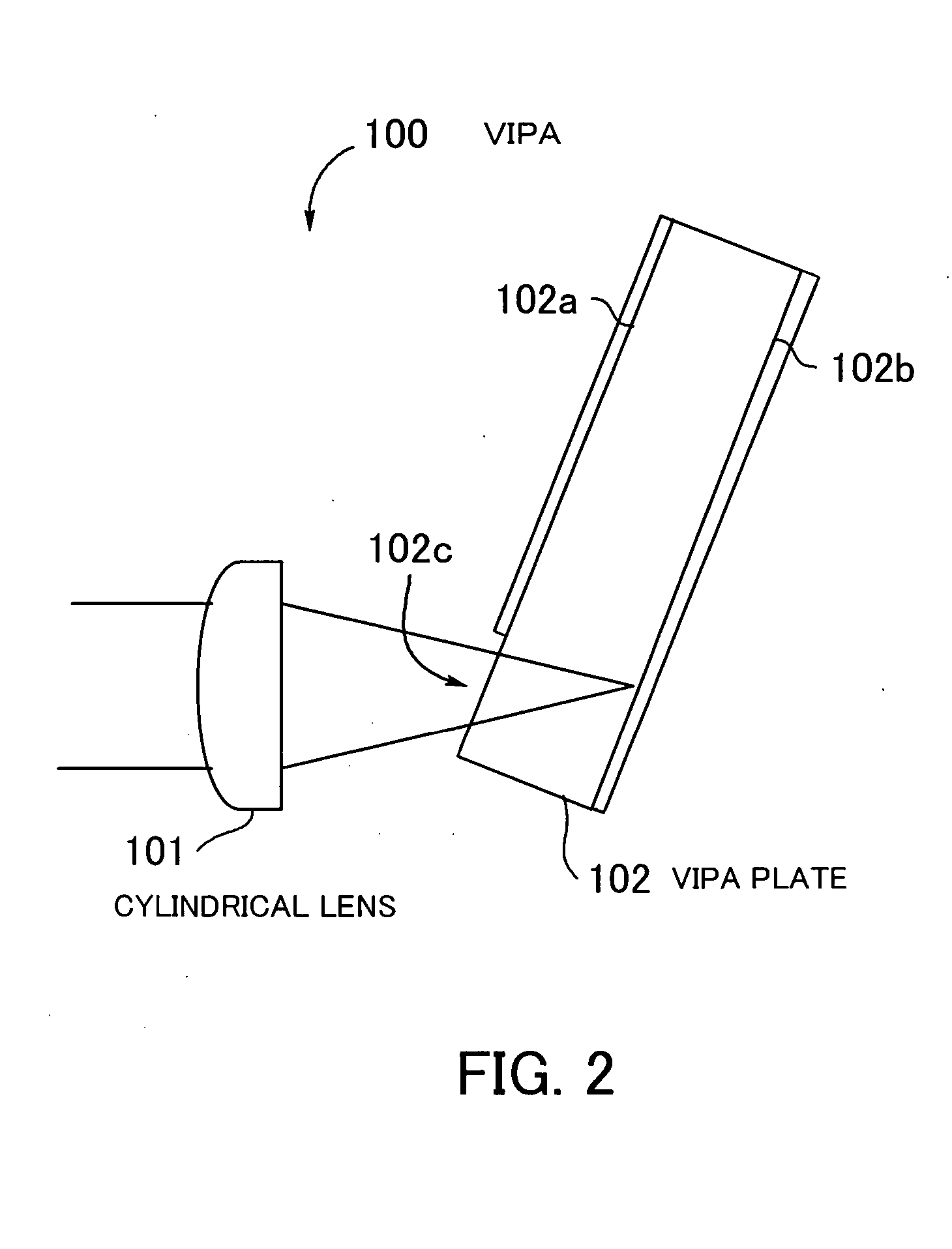
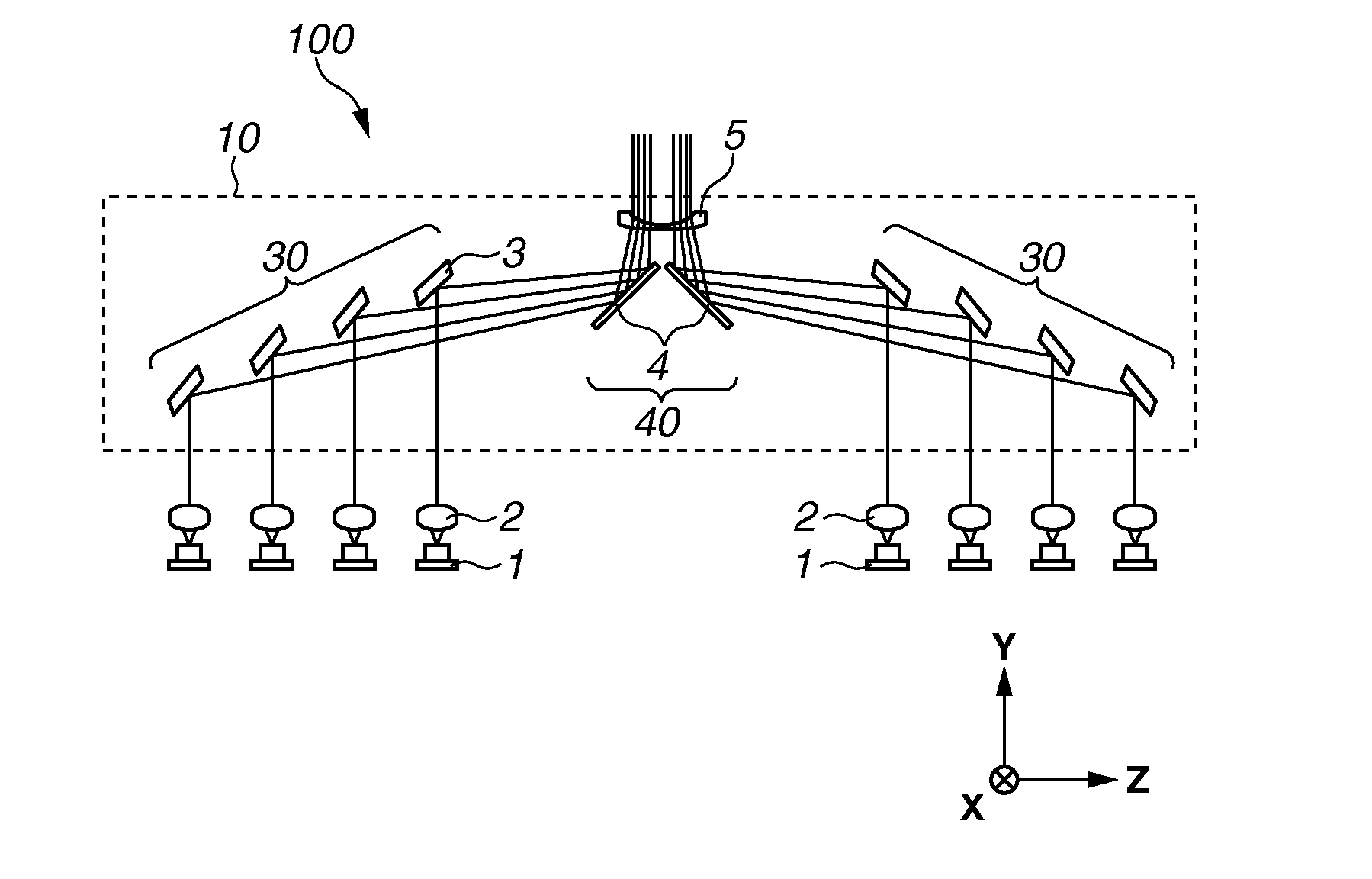
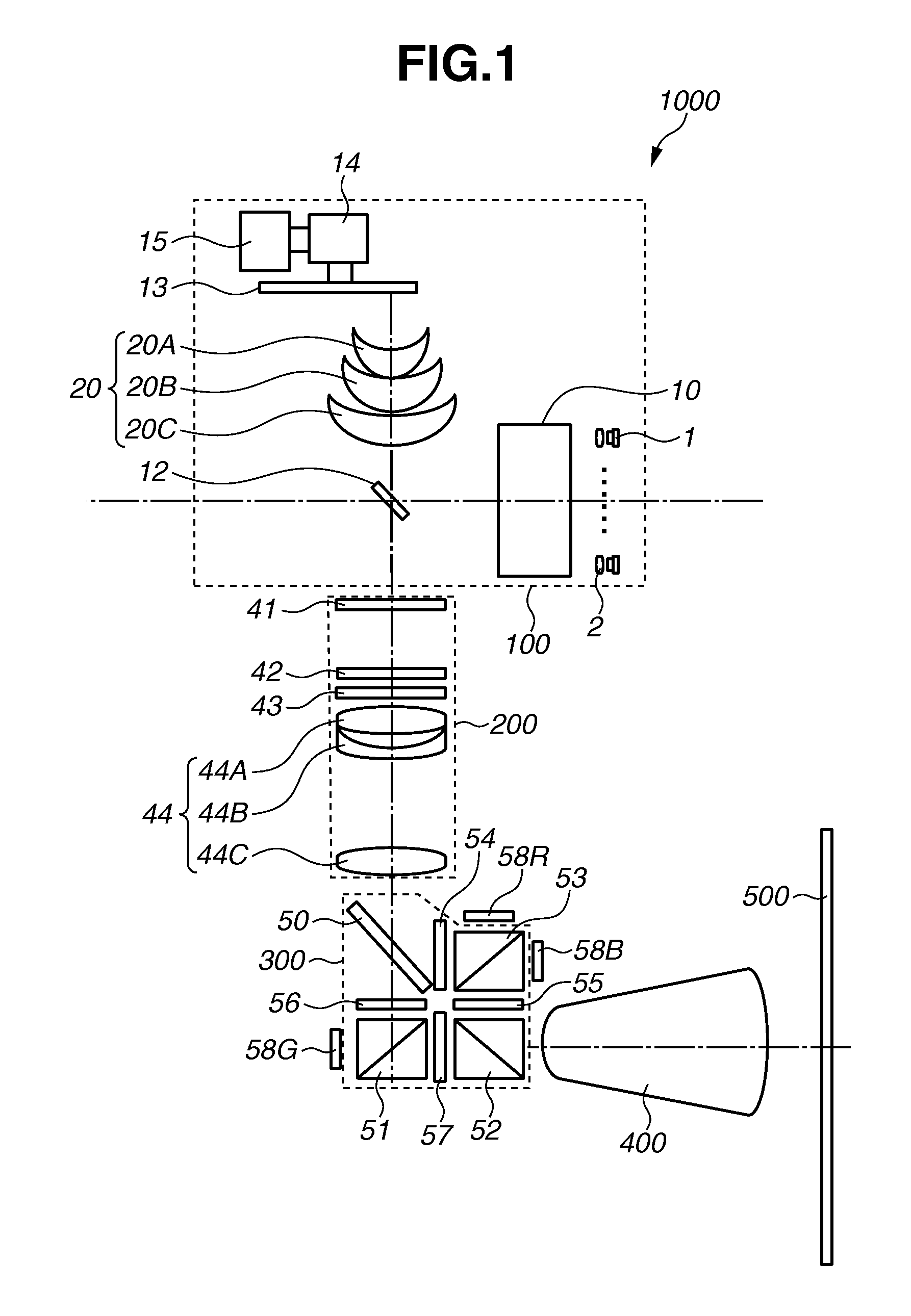
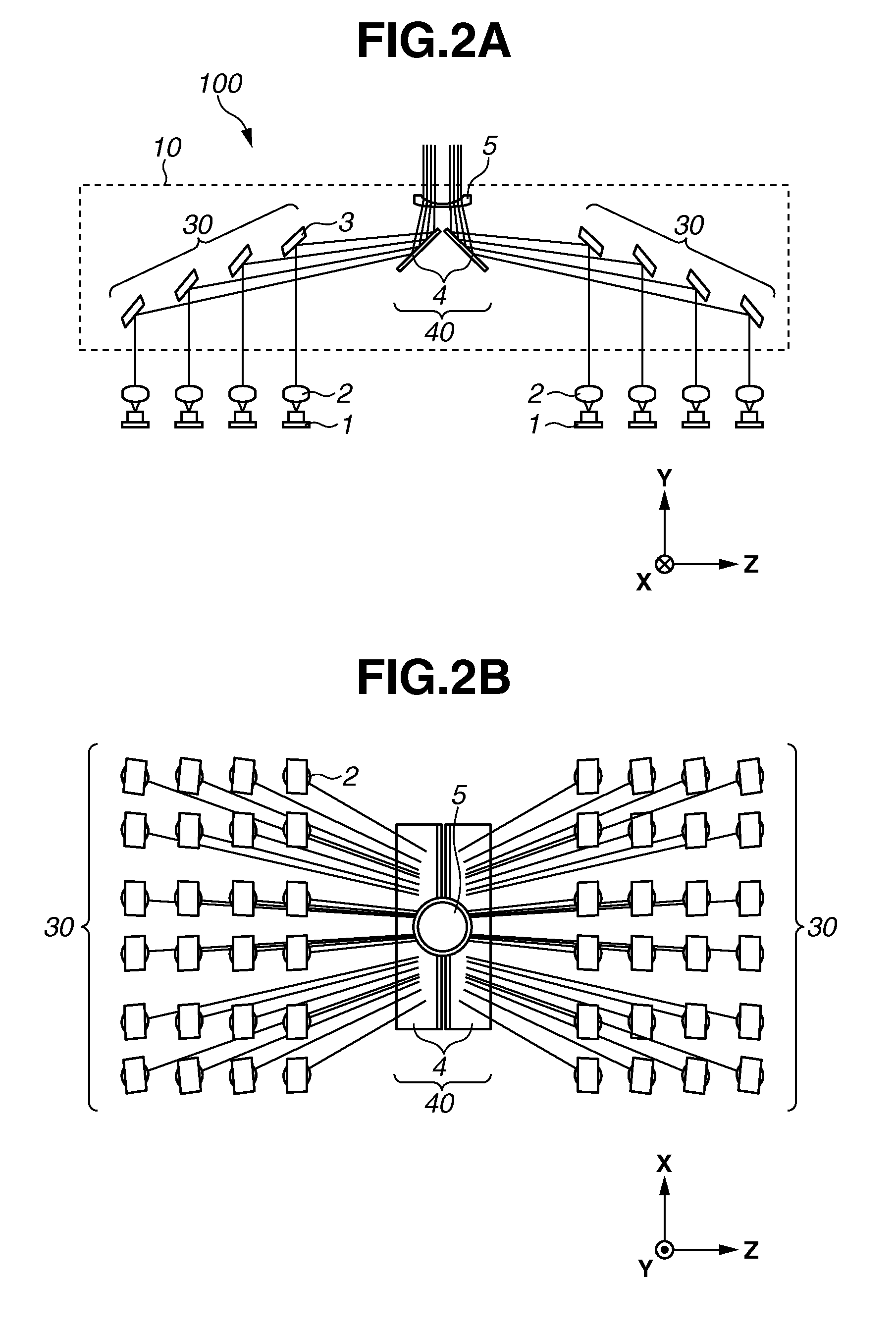
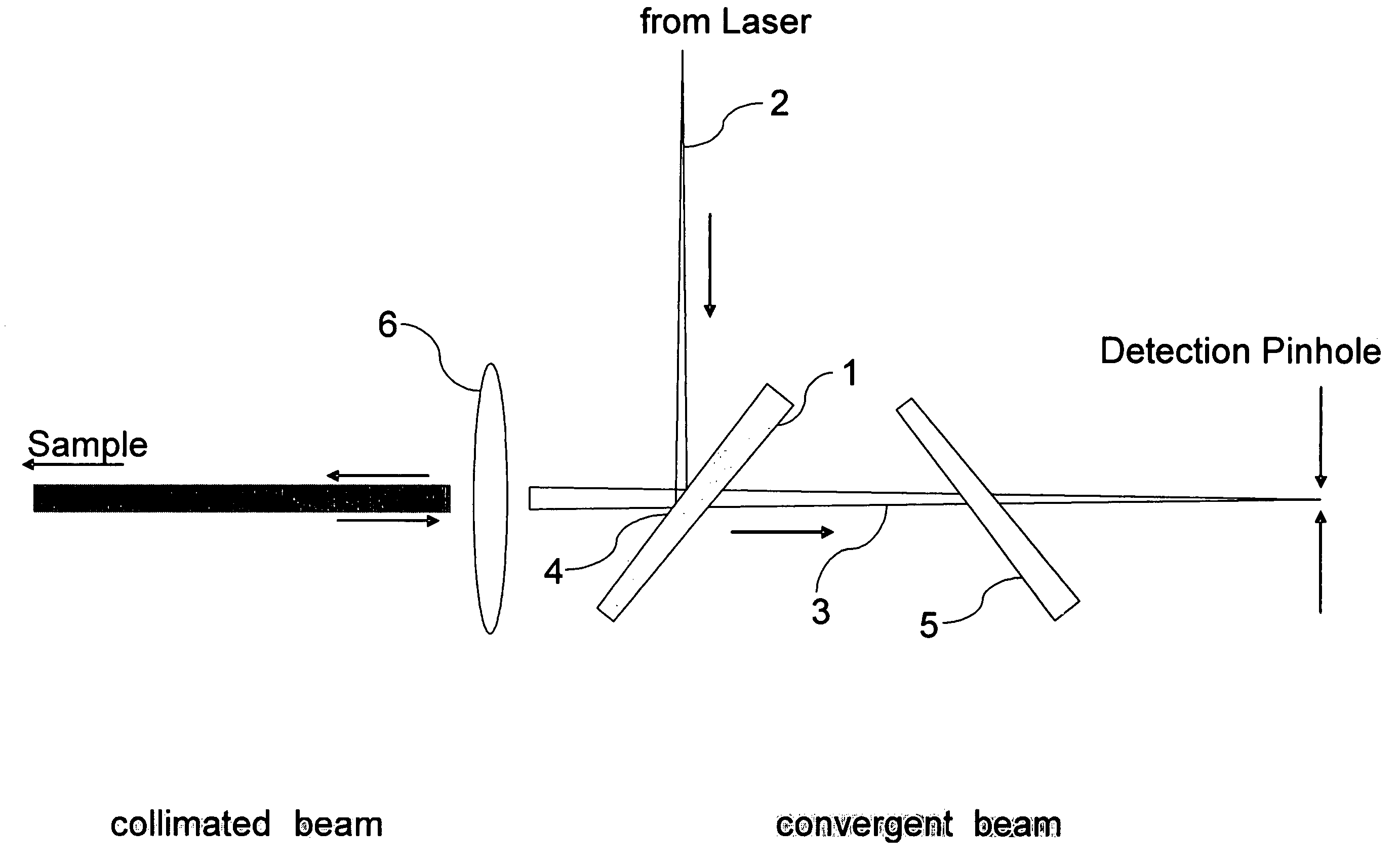
Spectroscopic apparatus
InactiveUS20050046837A1Small sizeLarge angular dispersionRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryBandpass filteringLight beam
A spectroscopic apparatus which is compact in size and performs high-precision light-splitting with a large angular dispersion. An optical input-processing section outputs a filtered transmitted light, using a bandpass filter that transmits only wavelength bands at one period of an input light, and collects the filtered transmitted light to generate a collected beam. An optic includes a first reflection surface and a second reflection surface which are high but asymmetric in reflectivity, and causes the collected beam incident thereon to undergo multiple reflections within an inner region between the first reflection surface and the second reflection surface, to thereby cause split beams to be emitted via the second reflection surface. A received light-processing section performs received light processing of the beams emitted from the optic. A control section variably controls at least one of a filter characteristic of the bandpass filter and an optical length through the optic.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
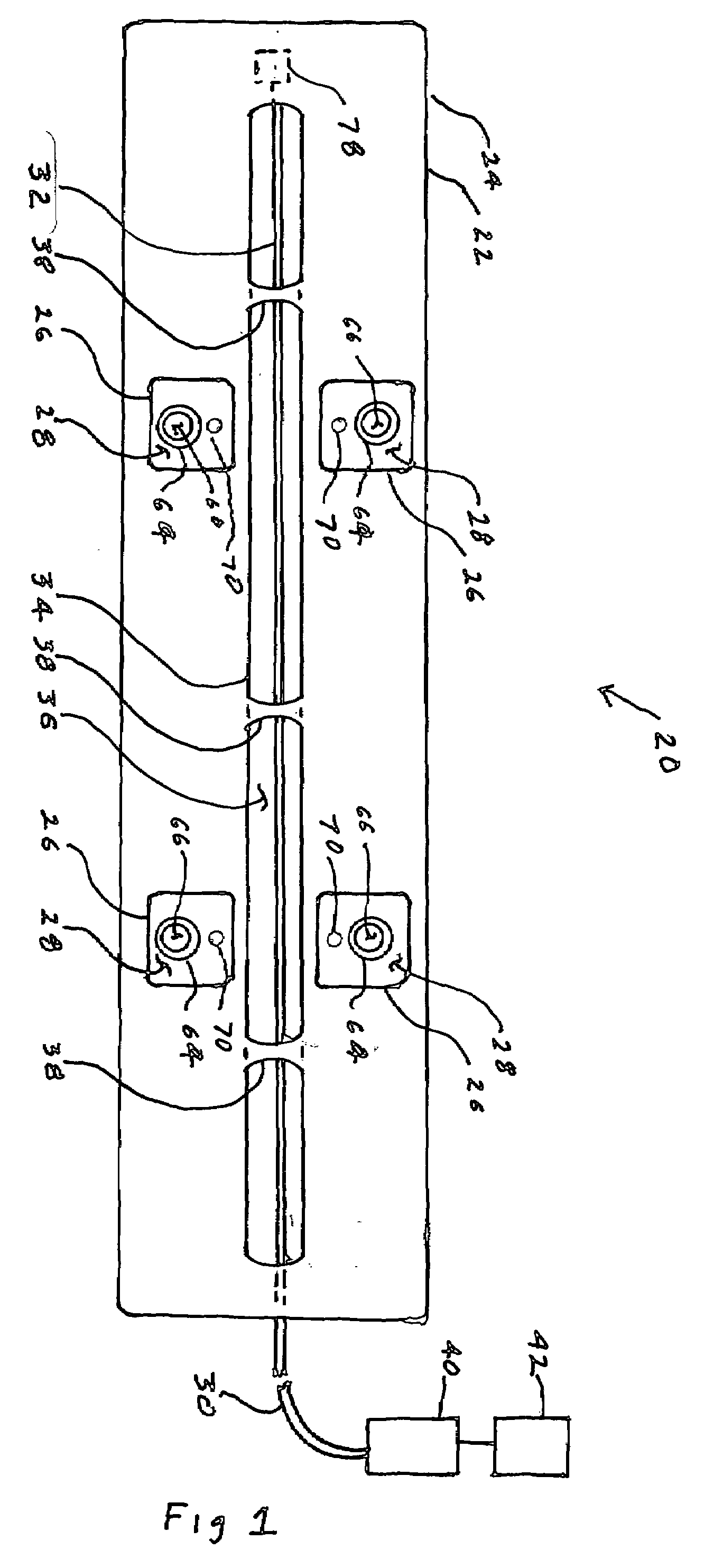
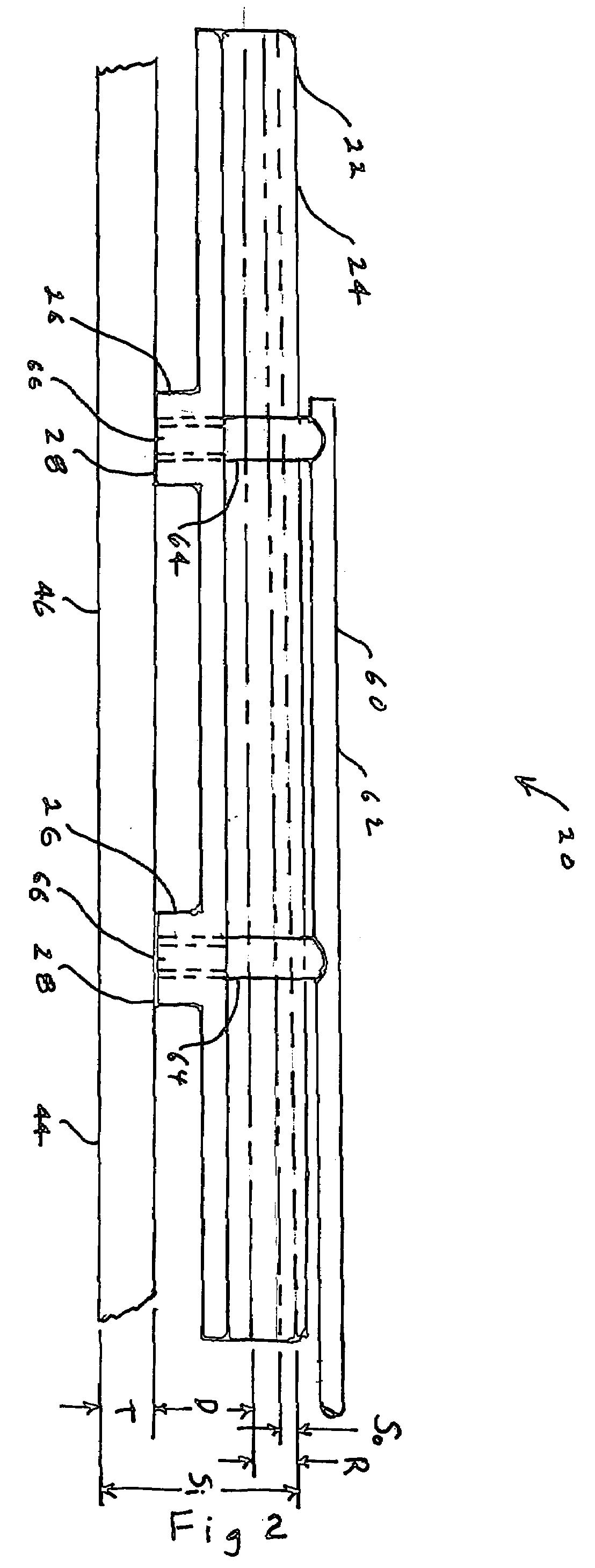
Fiber optic tissue ablation
A catheter tip for delivering laser light energy to create lesions extending to a depth of several millimeters in tissue includes an elongated, flexible housing. A reflector is oriented longitudinally in a channel the housing. A side emitting optical fiber diffuser, extending the length of the reflector, is held at a fixed separation from the reflector. The reflector and the side emitting diffuser are configured and spaced to provide a convergent beam directed through the tissue under treatment. Reflector curvature may be circular or elliptical in cross section, or other selected shape. The diffuser and reflector relative positioning being selected to place the beam focal point (or image) at a predetermined lateral distance from the reflector preferably not closer than the far wall of the tissue under treatment. Temperature probes are provided to monitor the temperature gradient through the tissue thickness. Optionally cooling and / or irrigation fluid are provided. Optionally, the fiber terminates at a retro-reflector.
Owner:OPTECH VENTURES
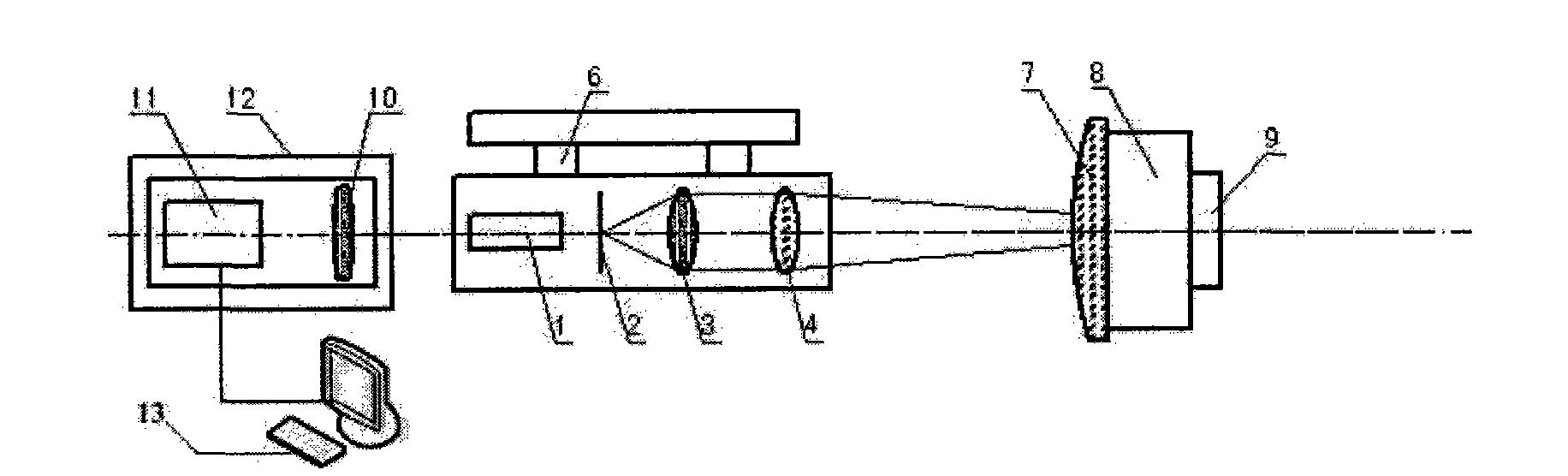
Measurement mechanism of lens focal length, measurement method and thereof and optical quality evaluation method
InactiveCN101140196APrecision Measuring Focal LengthPrecise measurement of depth of focusTesting optical propertiesMeasurement deviceLong-focus lens
The invention relates to a device and a method for measuring lens focal length as well as a method for evaluating optical quality, wherein the device for measuring the lens focal length is composed of a plane mirror, a lens to be measured, a point light source, a vertical incision, a one-dimensional precise flat movable guide rail, a laser distance measuring instrument, a CCD detector and a display, and the method for measuring the lens focal length is as follows: (1) adjusting the autocollimation of the point light source and the lens to be measured; (2) adjusting the plane mirror to make the transflective convergent beam enter the CCD detector; (3) measuring the focal depth of the lens to be measured; (4) measuring the distance L from the point light source to the geometric main plane of the lens to be measured; (5) calculating the focal length f = L + d of the lens to be measured, and the d is the distance between the geometric main plane of the lens and the optical main plane. The optical processing quality of the lens to be measured is qualitatively evaluated through the observation of shape of the far-field focal spot. The device and the method are applied to the measurement and evaluation of the small-bore short-focus and large-bore long-focus lens, and have the advantages of the intuitionism, the high measuring precision and the simple mechanism.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apparatus for synthesizing laser beams
InactiveUS20040233964A1Semiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor laser structural detailsOptical axisLight beam
Laser beams are synthesized by offsetting in different positions in the direction of the fast axis beam bundles radiated from semiconductor lasers, converging the optical axes of the beam bundles in the fast axis view, and introducing the beam bundles into an optical fiber after converging them in the directions of the fast and slow axes. A convergent angle transforming optical system is disposed further upstream of the upstream-most position in the positions where the optical axes of the beam bundles converged in the fast axis view intersect in the fast axis view. The whole beam bundle formed of the beam bundles converged in the fast axis view is passed through the convergent angle transforming optical system so that the angle of convergence of the whole beam bundle or part of the beam bundles is made smaller in the fast axis view, and introduced into the optical fiber.
Owner:ADTEC ENG +1
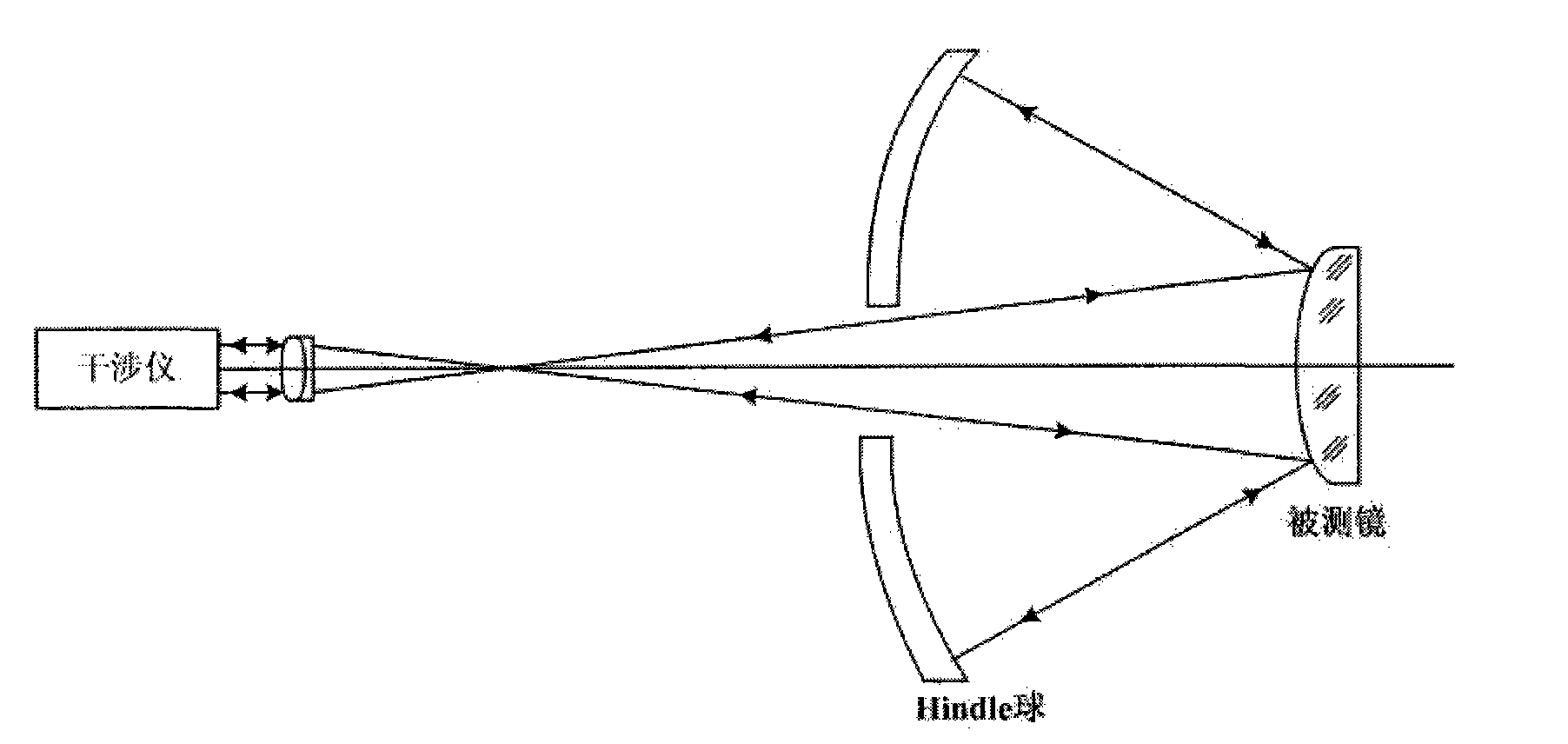
Detecting method and detecting device of surface-shape error of double curved surface convex reflecting mirror
The invention relates to a detecting method and a detecting device of the surface-shape error of a double curved surface convex reflecting mirror, which takes an aberrationless laser convergent beam as an incident beam scanning the convex of the detected reflecting mirror and takes wavefront detector as a measuring tool to coincide the focus of the incident beam with the virtual focus of the detected double curved surface reflector; the incident beam is imaged at the real focus of the detected double curved surface reflecting mirror after being reflected by the detected reflector, an imaging beam enters in the wavefront detector after being collimated by an anaberration collimating lens, and the surface-shape error of a local area is detected by the wavefront detector; the incident beam radically scans around the virtual focus of the detected double curved surface reflector, the detected double curved surface reflecting mirror rotates a circle around an optic axis when the incident beam scans each step, and the surface-shape error of each local area inside a whole mirror surface is detected circularly; and the detected surface-shape error of the local area is subject to matching and Zernike polynomial polynomial fitting to obtain the surface-shape error of the whole double curved surface convex reflecting mirror. The invention provides a low-cost and high-precision detection means of the large-caliber double curved surface convex reflecting mirror.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
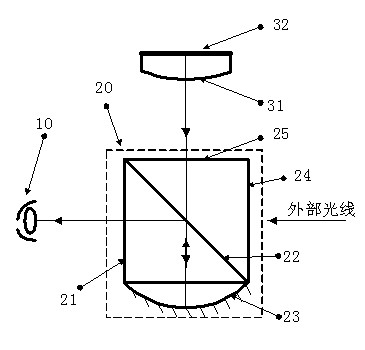
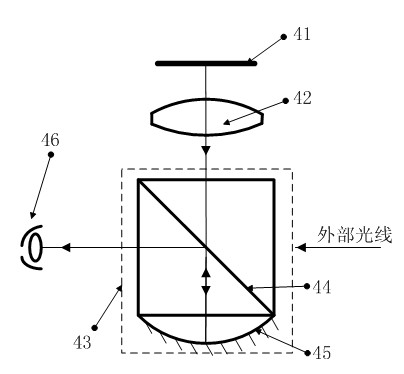
Optical system of helmet displayer
An optical system of a helmet displayer comprises a micro displayer, a bonding lens and an optical combiner. The micro displayer and the bonding lens are bonded integrally, the optical combiner comprises two tightly-adhered right-angle prisms forming a 45-degree angle and a concave-surface reflecting mirror, a narrow-band high-reflective optical surface is located at the bonding position of the two right-angle prisms and forms a 45-degree angle respectively with the horizontal optical axis and the vertical optical axis, the concave-surface reflecting mirror and the right-angle prisms are bonded integrally, and the concave surface is the high-reflective optical surface. Light beams are emitted from the micro displayer, are converged through the bonding lens, enter the optical combiner and pass through the narrow-band high-reflective optical surface, then transmitted light beams are converged through the high-reflective optical surface again, and reflected light beams become parallel light beams after the light beams pass through the narrow-band high-reflective optical surface again. An exit pupil is located at the position of a pupil of one human eye, extraneous light enters the optical combiner and passes through the narrow-band high-reflective optical surface, and then the transmitted light beams enter the pupil of one human eye. The optical system of the helmet displayer has the advantages of being compact in system, convenient to correct, good in aberration correction and high in reliability.
Owner:中航华东光电有限公司
Method and apparatus for spectral-beam combining of fanned-in laser beams with chromatic-dispersion compensation using a plurality of diffractive gratings
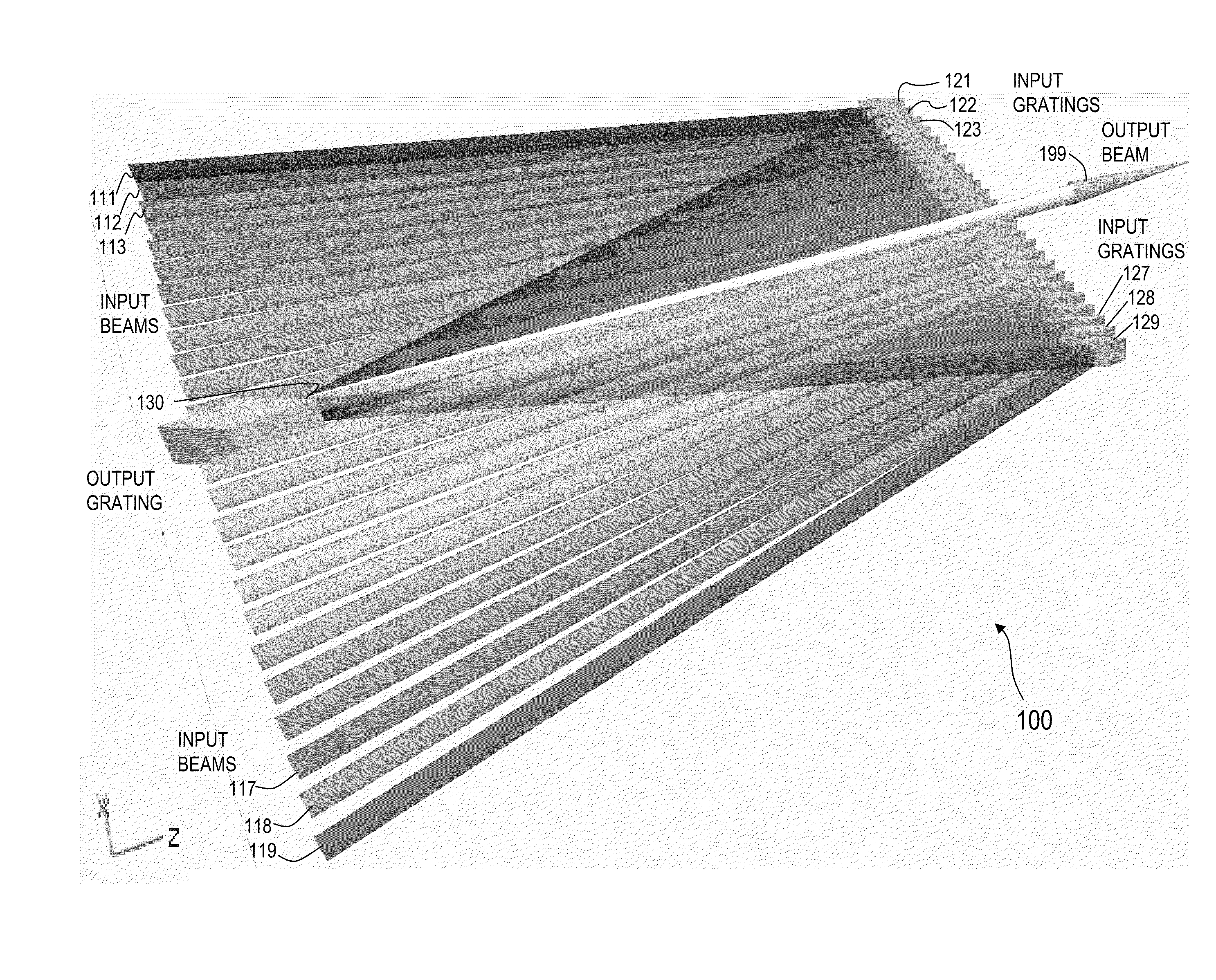
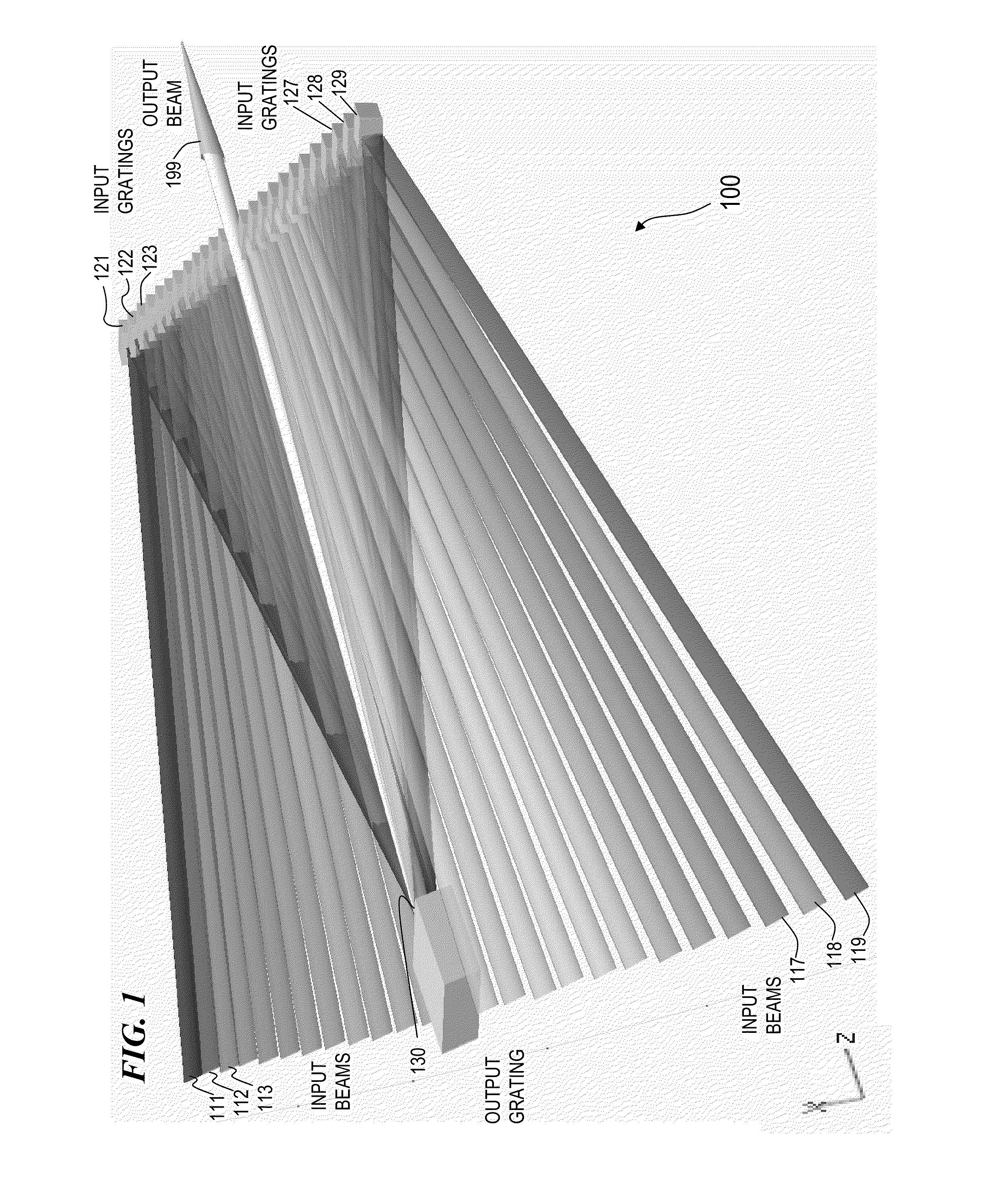
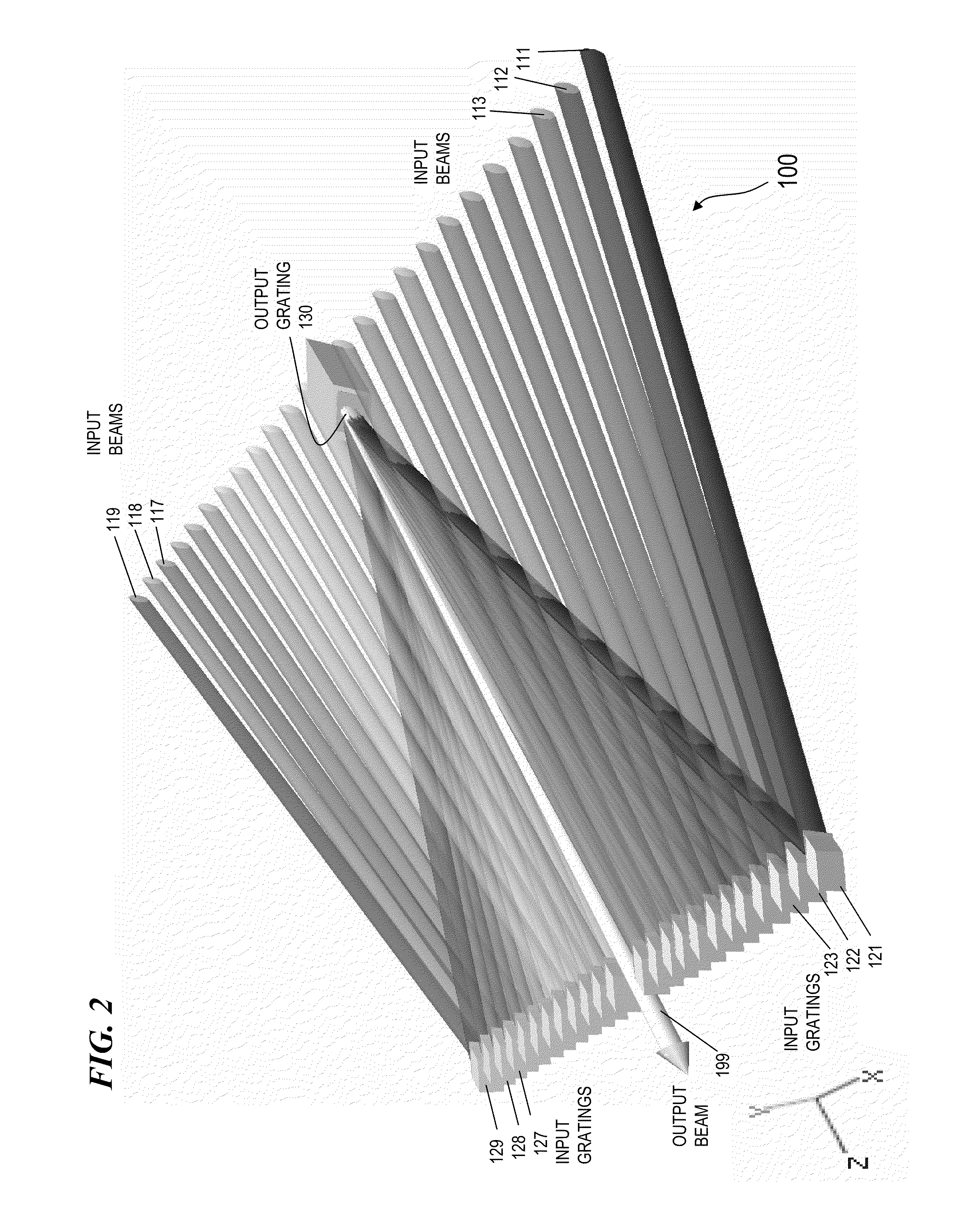
ActiveUS8179594B1Improved and superior output beam qualityDifferent peak wavelengthDistortion/dispersion eliminationOptical devices for laserHigh power lasersLight beam
Apparatus and method for spectral-beam combining of light from a plurality of high-power lasers (e.g., fiber MOPA lasers) that, in some embodiments, use substantially identical diffraction gratings in a 1-D non-parallel, mutually compensating configuration to combine non-parallel converging input beams in one plane each having a slightly different successively higher wavelength into a single output beam of high quality. In other embodiments, an output grating and one or more input gratings in a 1-D parallel, mutually compensating configuration combine non-parallel input beams in one plane into a single output beam of high quality. In other embodiments, a 2-D plurality of input gratings in a non-parallel configuration combine a plurality of non-parallel input beams not in one plane each having a slightly different successively higher wavelength into a set of converging beams in one plane directed towards an output grating that compensates for chromatic dispersions introduced by the input gratings.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
High-na projection objective
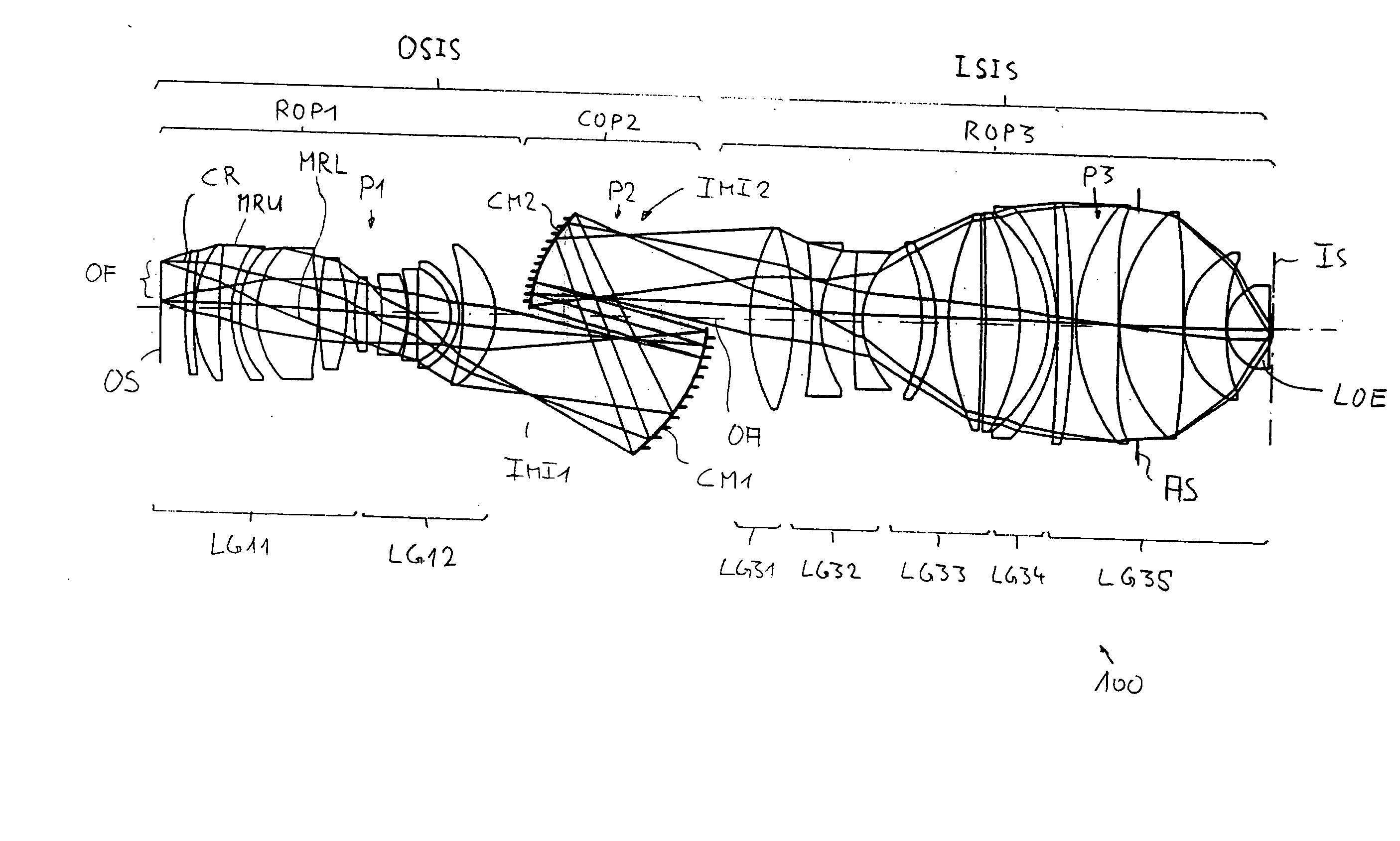
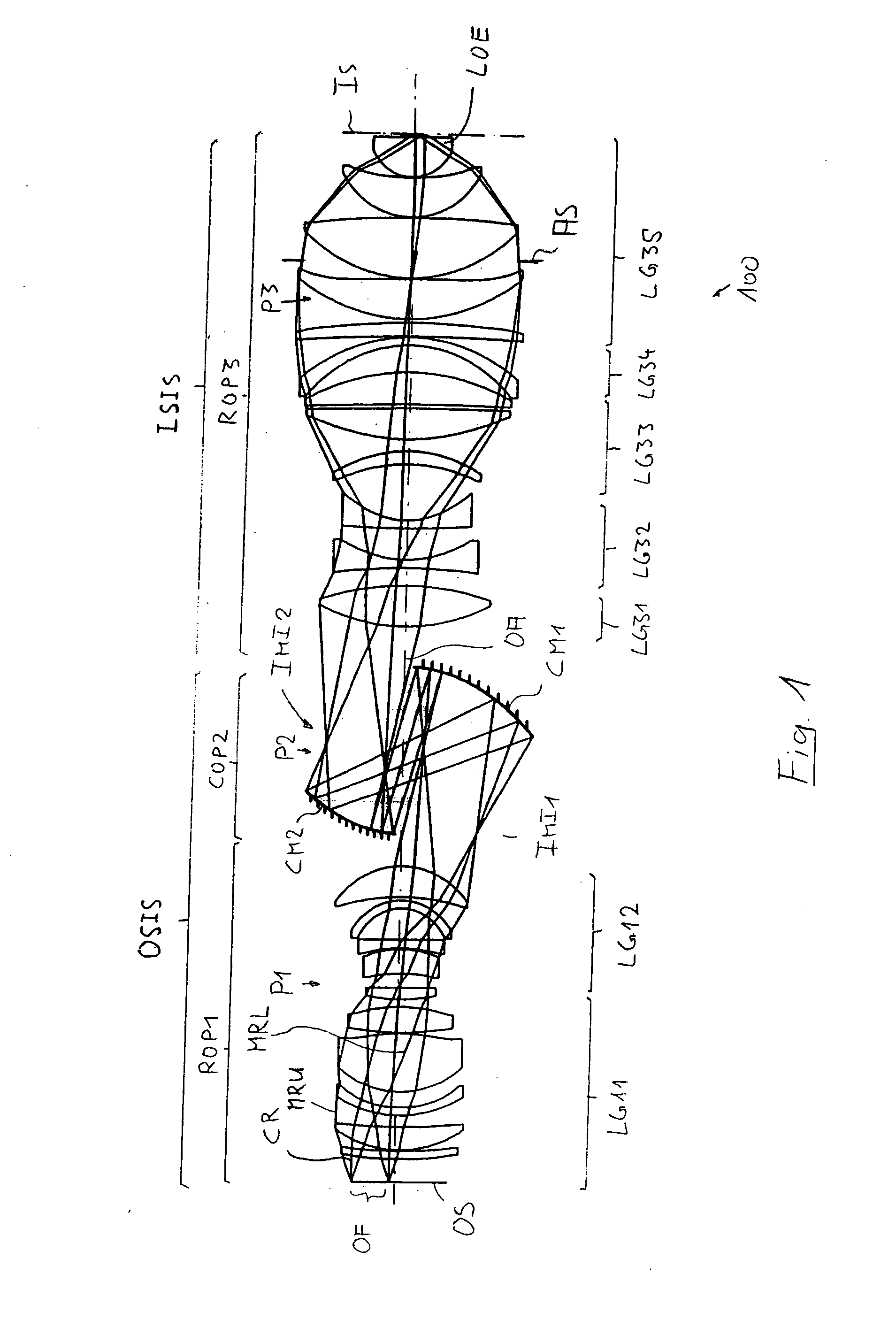
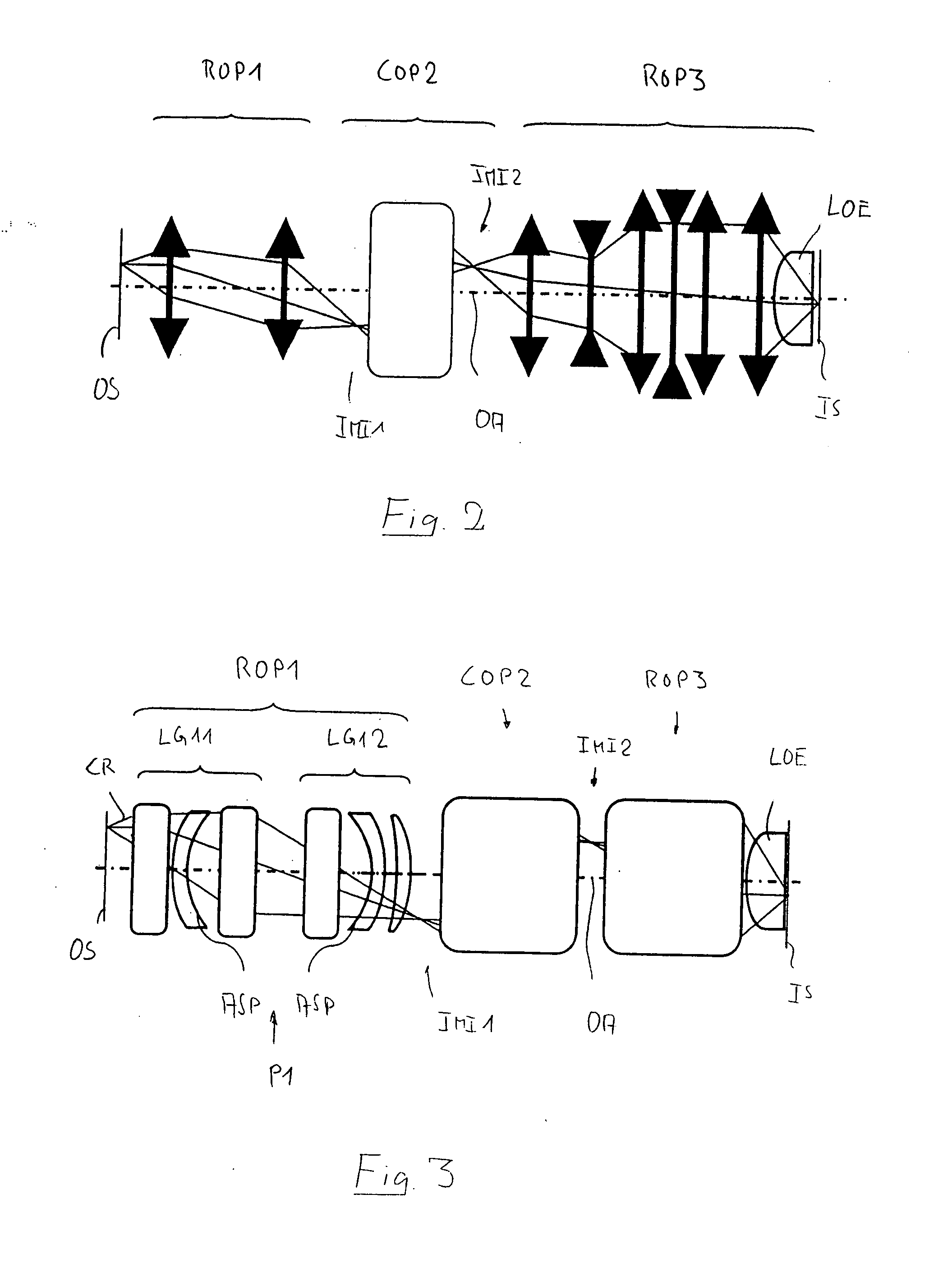
InactiveUS20080007822A1Easy to decoupleMaximum value can be reducedPhotomechanical apparatusMicroscopesIntermediate imageLight beam
A catadioptric projection objective for imaging a pattern provided in an object surface onto an image surface of the projection objective has an object-side imaging subsystem for creating a final intermediate image closest to the image surface from radiation coming from the object surface and an image-side imaging subsystem for directly imaging the final intermediate image onto the image surface. The image-side imaging subsystem includes a last optical element closest to the image surface and is designed for creating a convergent beam having an aperture sin α≧0.8 in the last optical element. The image-side imaging subsystem includes, in this order along a propagation direction of radiation: a primary negative lens group having overall negative refractive power; an intermediate positive lens group having overall positive refractive power; a secondary negative lens group having overall negative refractive power; and a final positive lens group having overall positive refractive power and including the last optical element, where the last optical element has a convex entry surface having a radius RLOE of curvature with RLOE / NA<40 mm.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
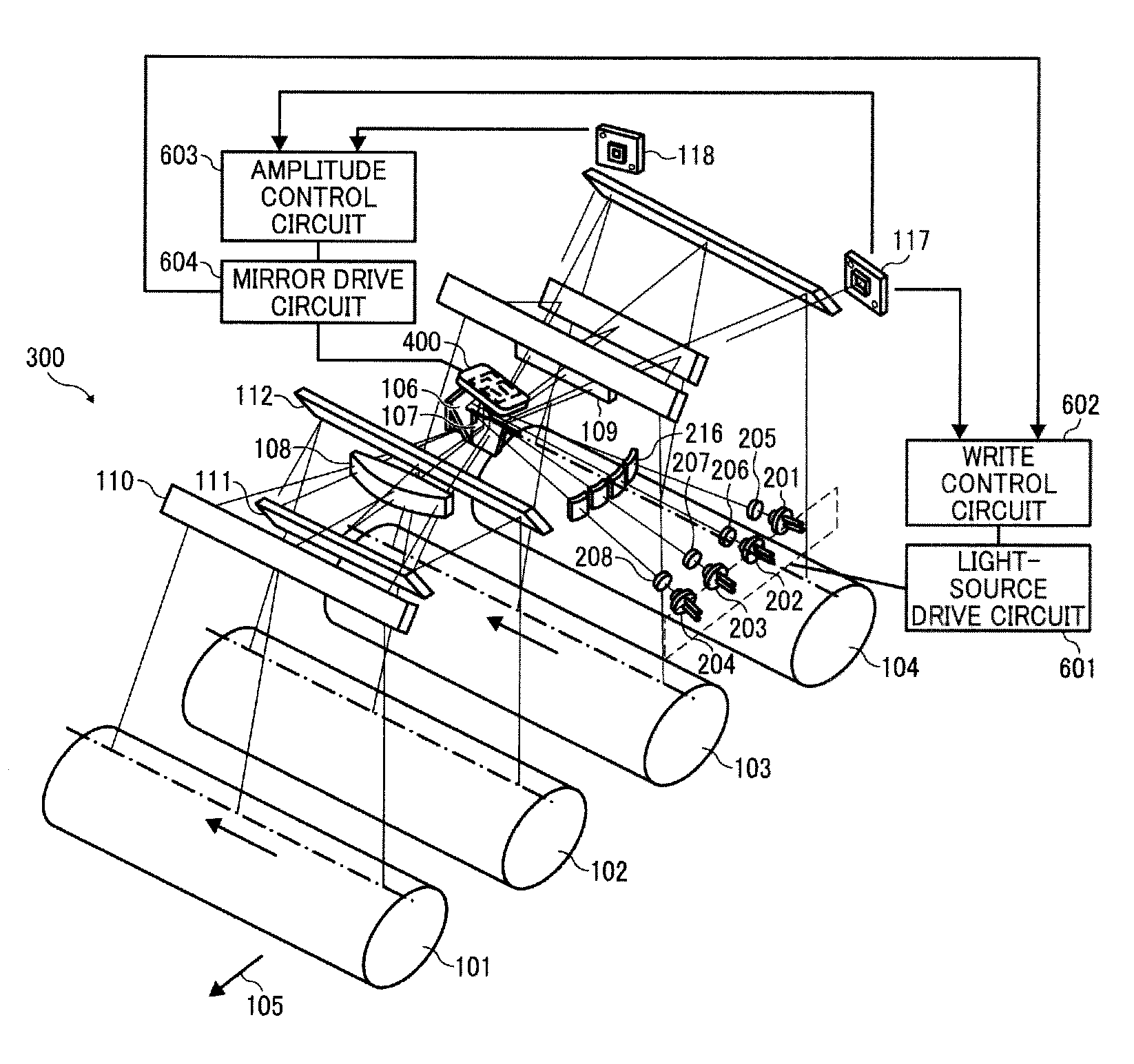
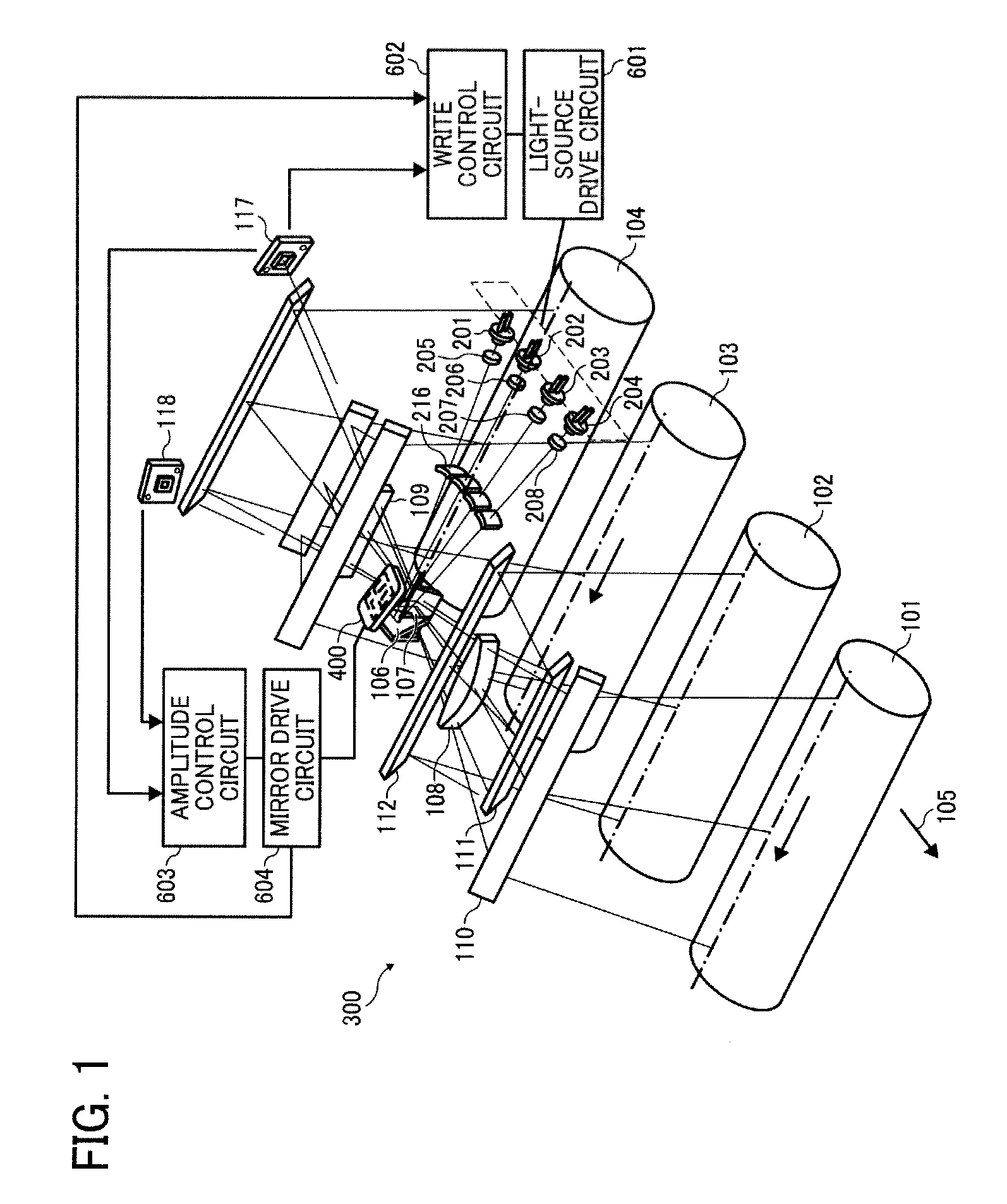
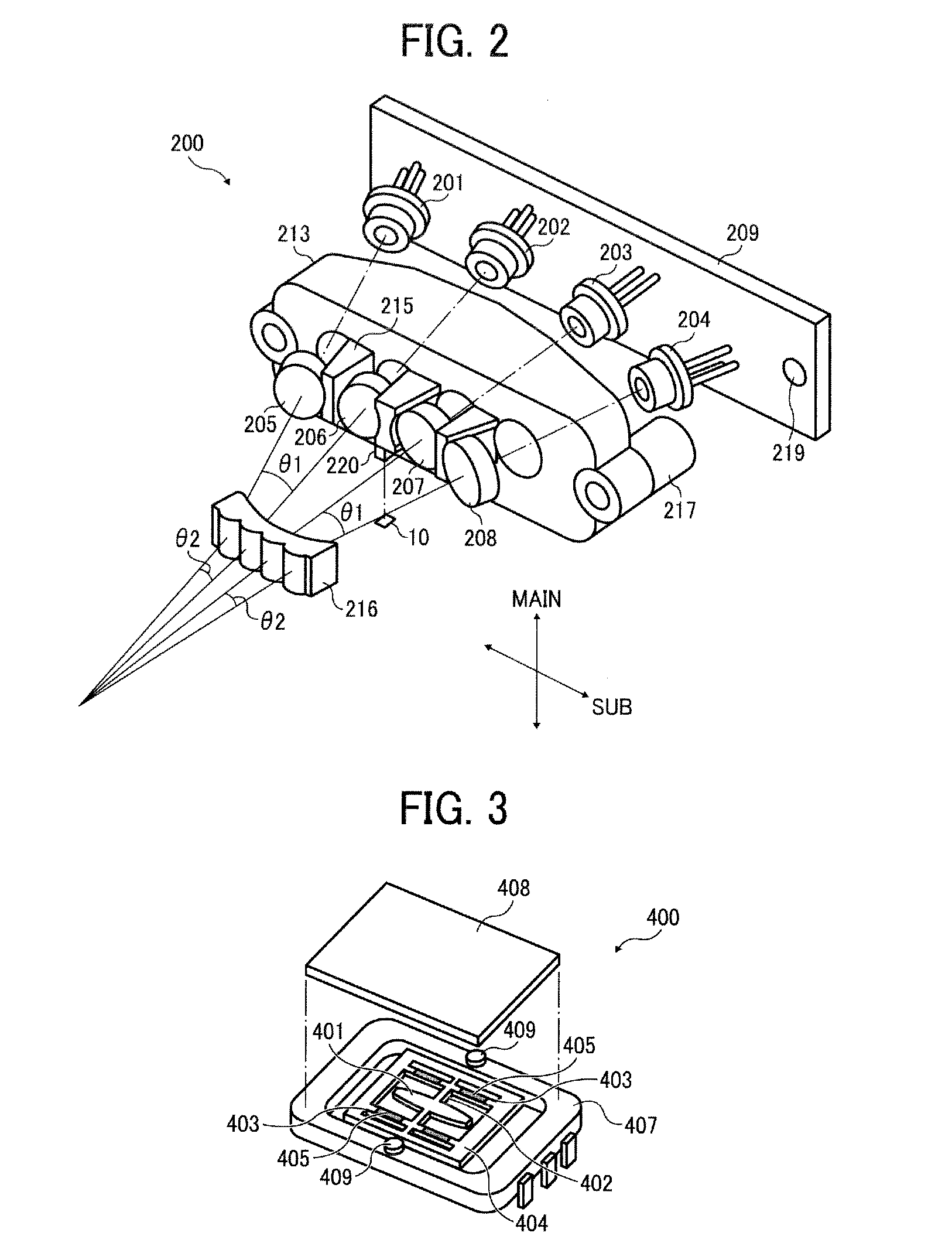
Optical scanning device and image forming apparatus
An oscillating mirror module as a deflecting unit is disposed so that a movable mirror faces a plane where image carriers are arranged. A plurality of light source units are disposed within a plane parallel to the plane where the image carriers are arranged so that main light fluxes of light beams emitted from the light sources form predetermined angles with each other. The oscillating mirror module includes an incidence mirror that bends a plurality of light beams emitted from the light source units to direct the light beams to the movable mirror, and a separation mirror that separates the light beams scanned by the movable mirror into two opposite directions with respect to a cross-section including a surface normal of the movable mirror and perpendicular to the rotation axis of the movable mirror. A light collecting unit collects light beams so that output optical axes of the light beams corresponding to the light source units intersect on a surface of the movable mirror of the deflecting unit.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method for on-line detection of film growth rate and stress
InactiveCN101515558ARealize real-time detectionRealize industrial scale productionSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor materialsLight spot
The invention discloses a method for on-line detection of film growth rate and stress, which comprises the following steps: (1) putting a film sample in a light path of an optical sensor, and detecting light spot position distribution information and light intensity change information of each light spot of a reflected light beam array of the detected sample so as to obtain a reflectivity curve of the film growth; (2) performing parameter fitting on the reflectivity curve through MATLAB software so as to obtain the film growth rate and refractive index information; (3) irradiating the surface of the film sample by a two-dimensional convergent beam array, detecting reflected light beam array information in a reflection direction of the surface of the film sample by a CCD device, and measuring the space length d of an incident laser beam, the incident angle alpha, the relative distance L between the sample and an array sensor, the deflection displacement delta of a light beam at the L position, and the parameter of the film thickness hf; and (4) calculating the film stress sigma by a Stoney relation equation according to the measured film substrate curvature parameters. The method can be applied to film on-line measurements in the field of manufacturing semiconductor materials and devices.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
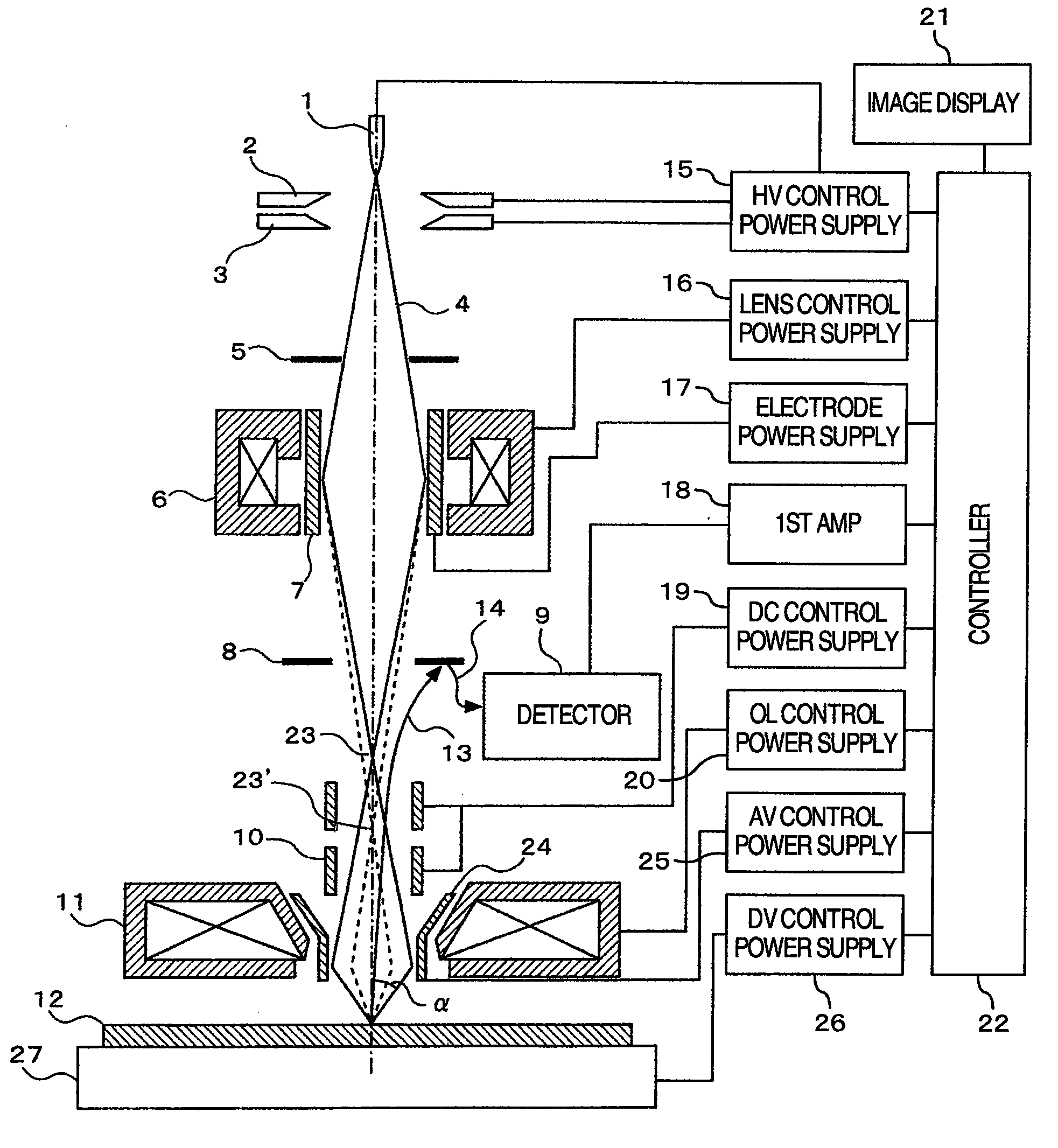
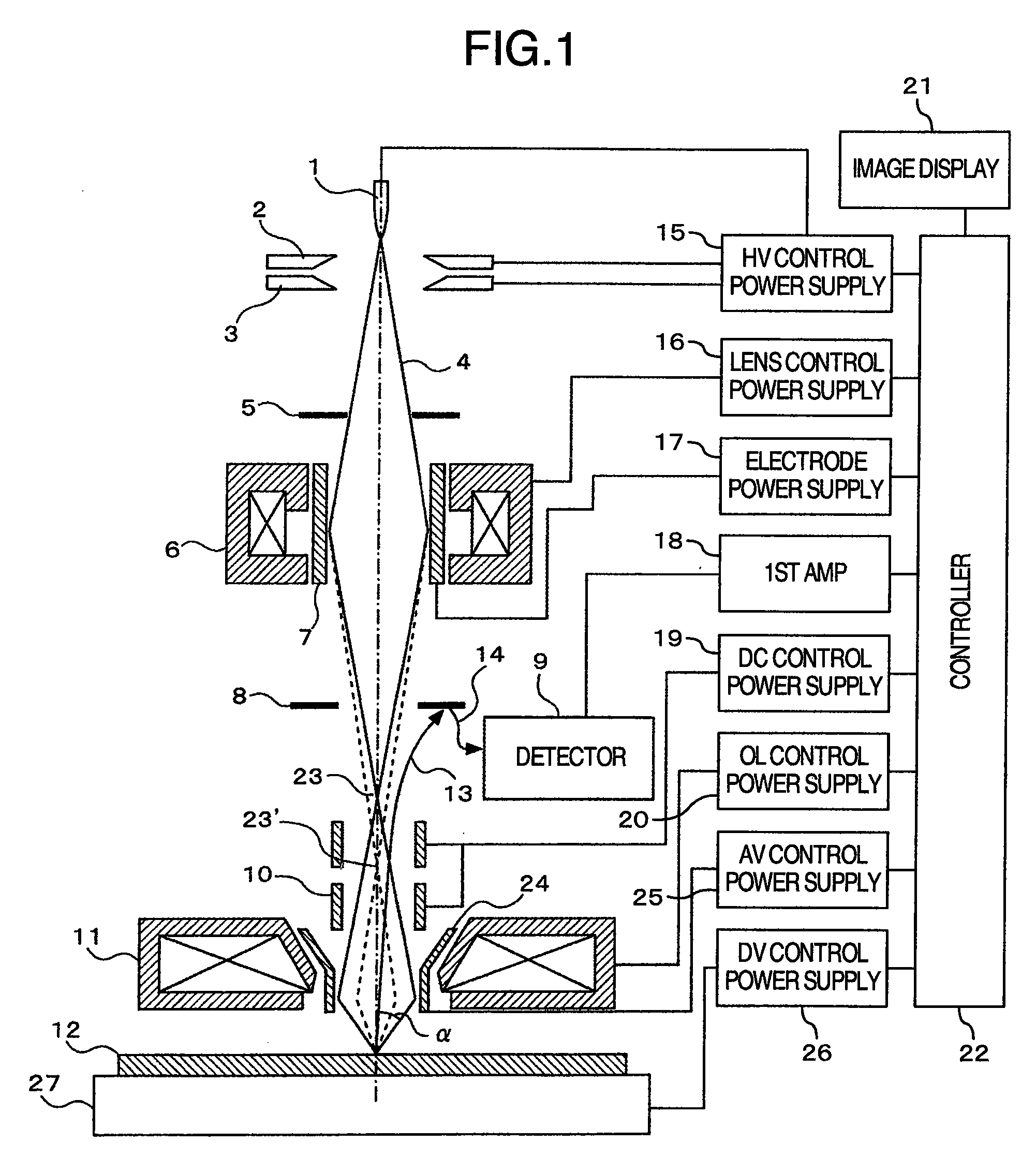
Scanning electron microscope and method of imaging an object by using the scanning electron microscope
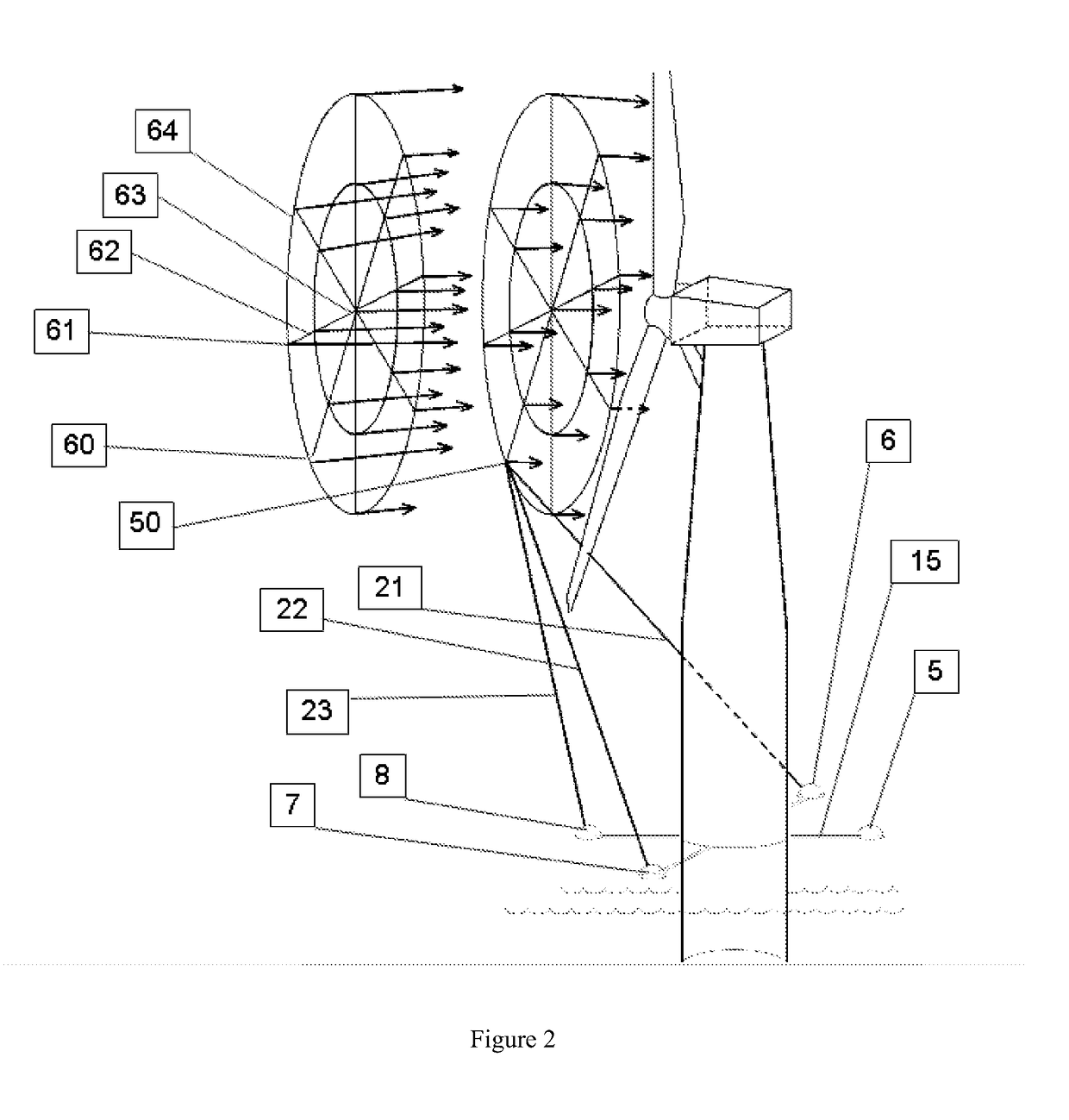
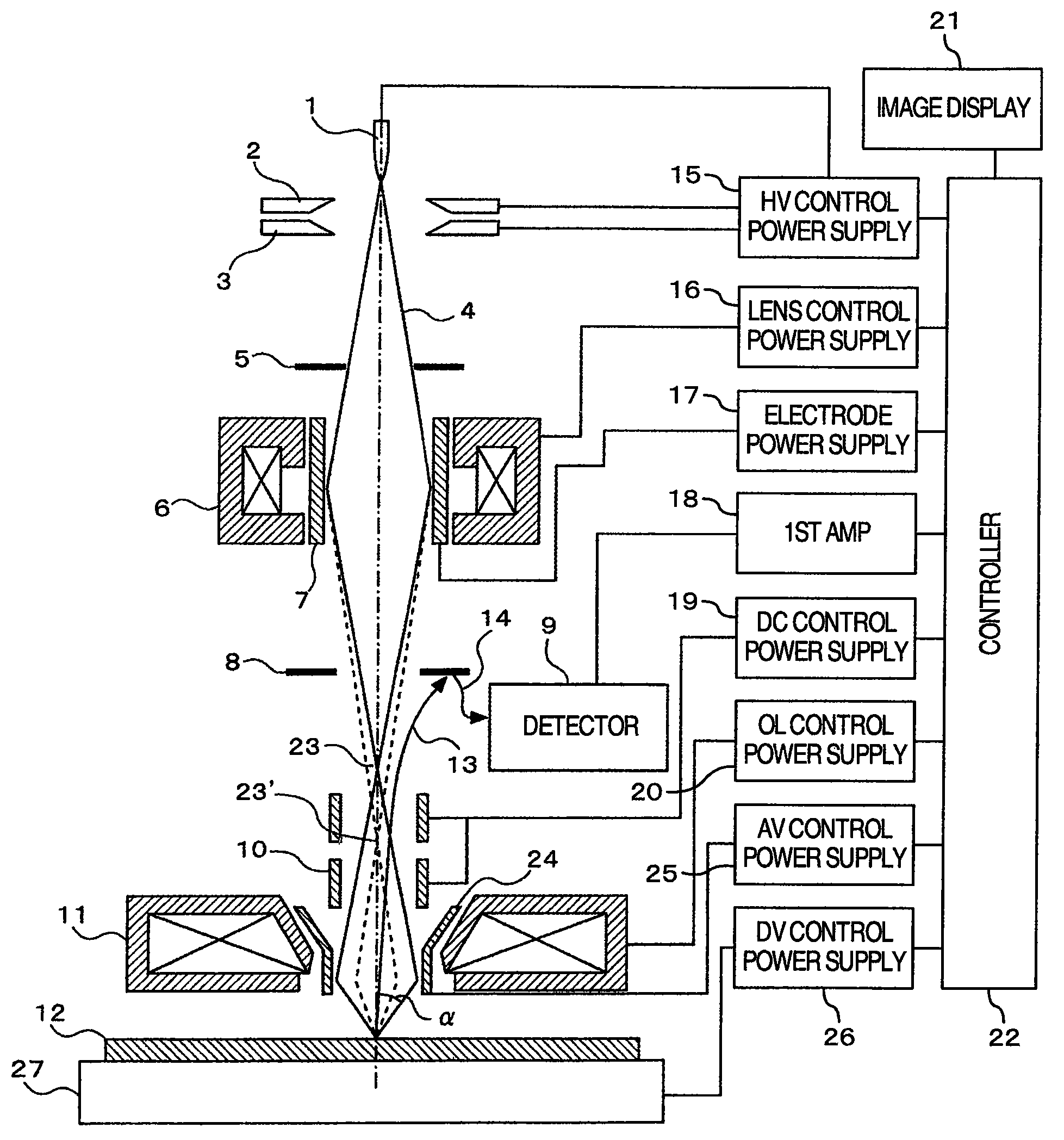
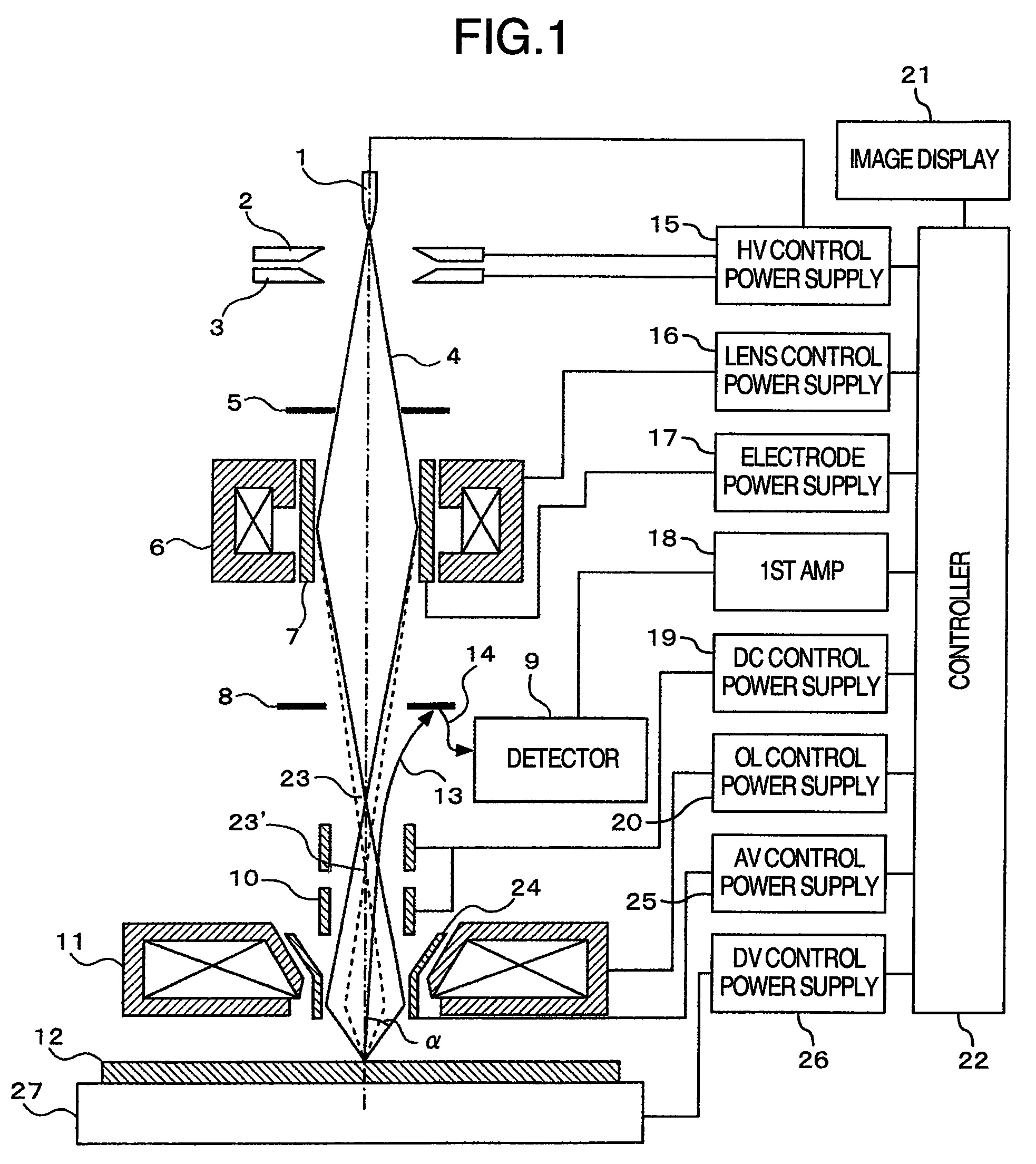
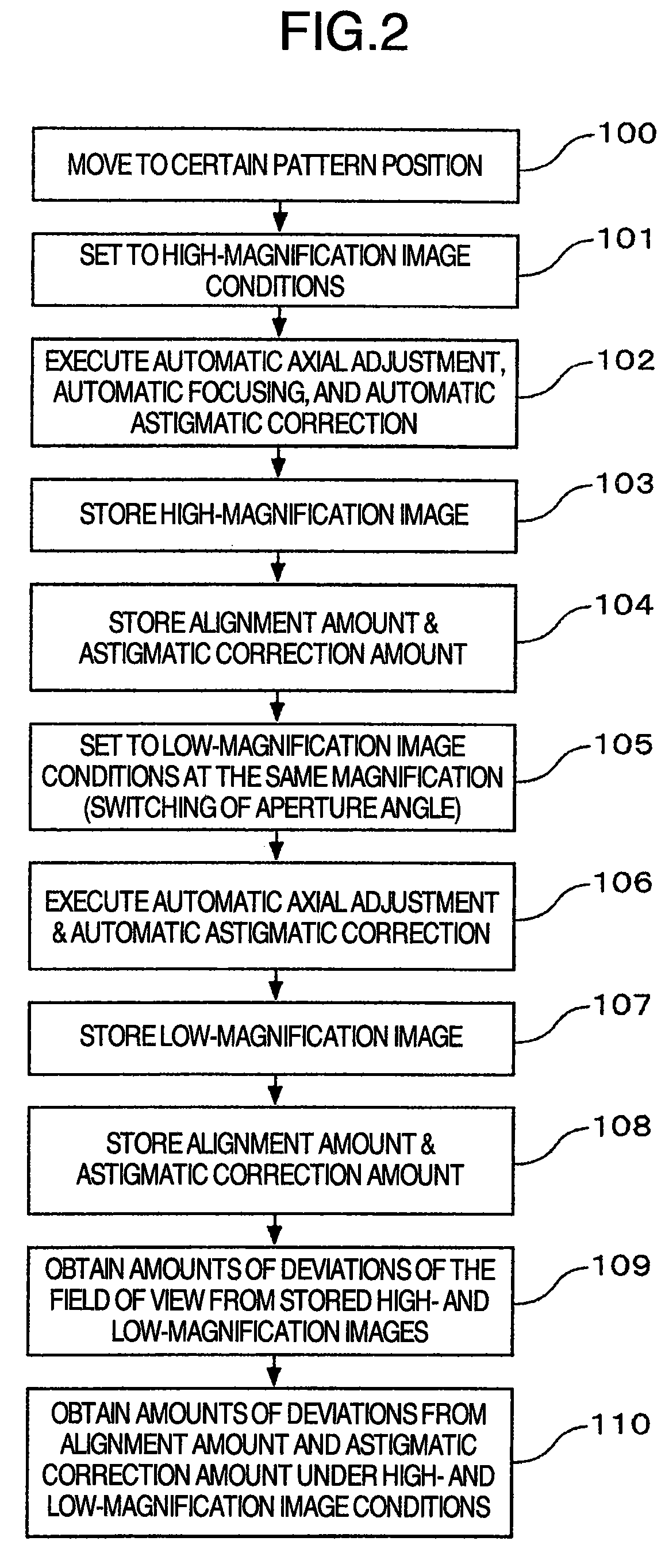
InactiveUS20080310704A1Increase speedGood reproducibilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesBeam sourceFocal position
A scanning electron microscope capable of modifying the focal position of a condenser lens with high speed and high reproducibility in order that low-magnification images are obtained at large depths of focus and that high-magnification images are obtained at high resolution. The microscope has a specimen-holding portion, an electron beam source, a condenser lens for converging the electron beam, an objective lens for focusing the converged beam into a very small spot onto a specimen, scan coils, a detector for detecting a specimen signal emanating from the specimen, and a display portion for displaying the detected specimen signal as an image. An axisymmetric electrode is disposed within the magnetic field produced by the condenser lens. A voltage is applied to the electrode.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Front Lamp for vehicle
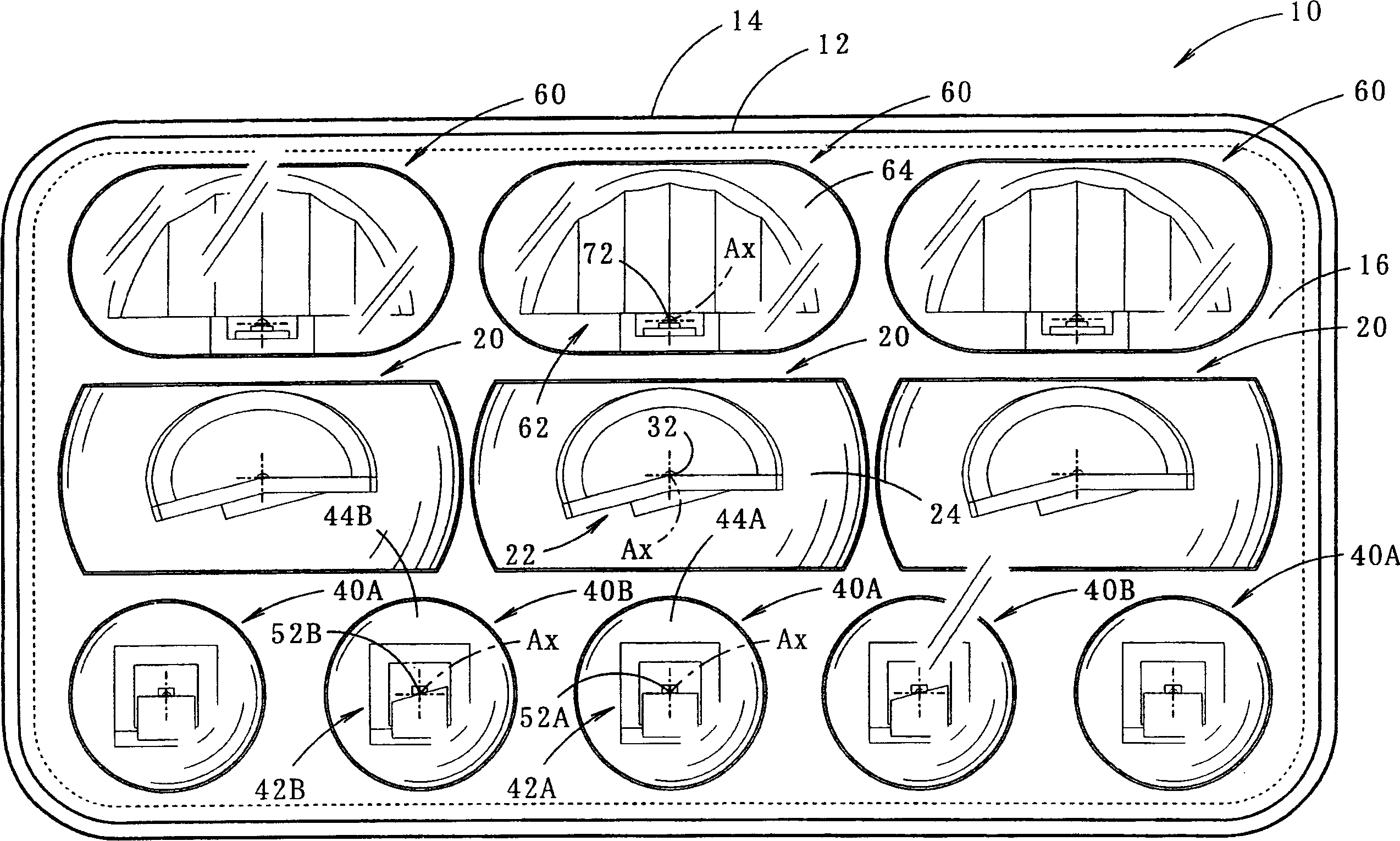
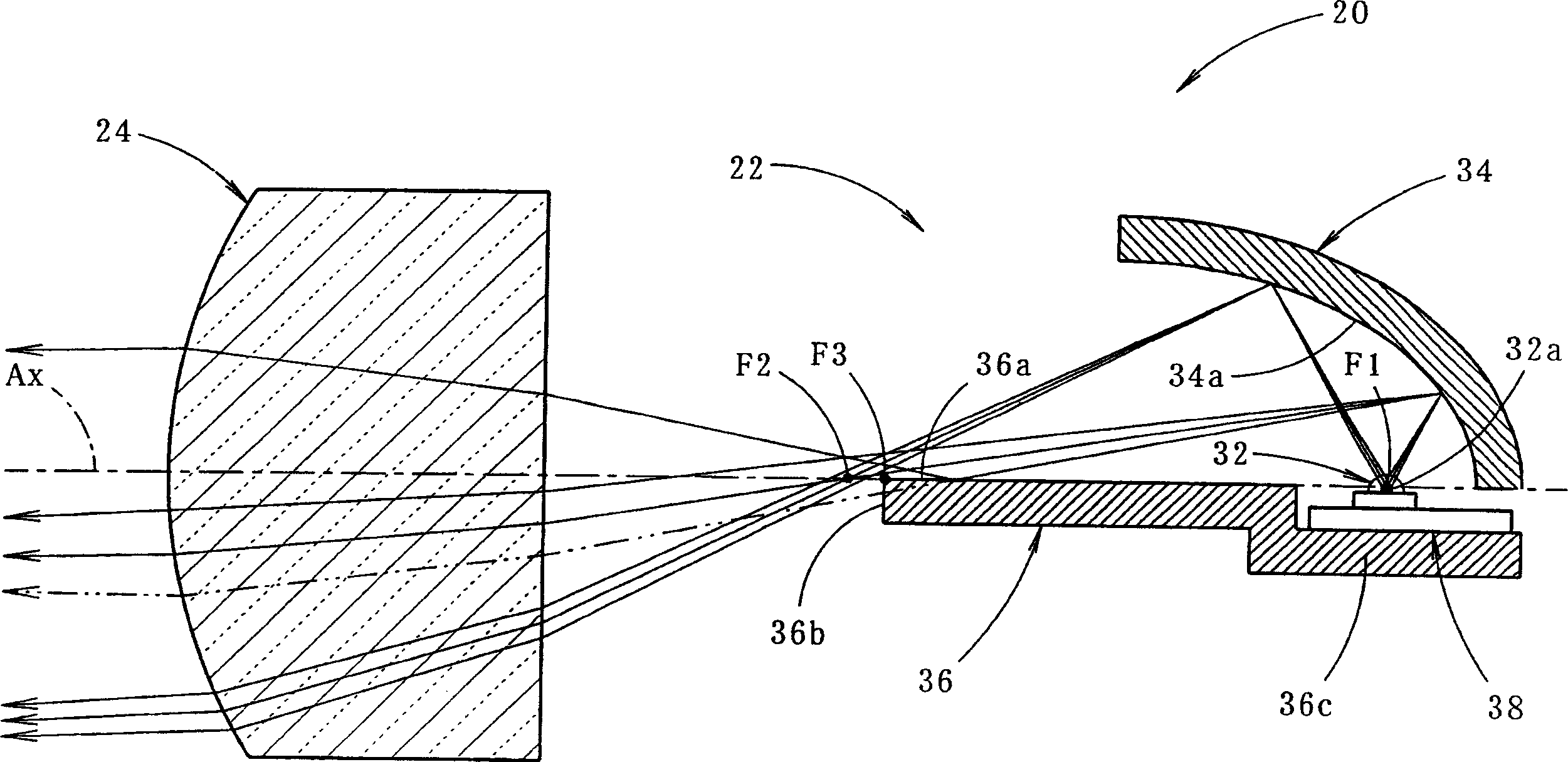
InactiveCN1487232AHigh degree of freedom of shapeAchieve compactnessVehicle headlampsPoint-like light sourceDirect illuminationLight-emitting diode
The headlamp has multiple lamp units (20,40A,40B,60) each using light-emitting diodes (LED) as light sources. One type of lamp unit (20) uses a reflector and a lens to produce a convergent beam combining direct and reflected light, another type (40A,40B) uses a convergent lens to produce direct illumination, and the third type (60) delivers only reflected light.
Owner:KOITO MFG CO LTD
Floodlight with tiltable beam
InactiveUS20100039819A1Easy to provideMechanical apparatusOutdoor lightingClassical mechanicsLight beam
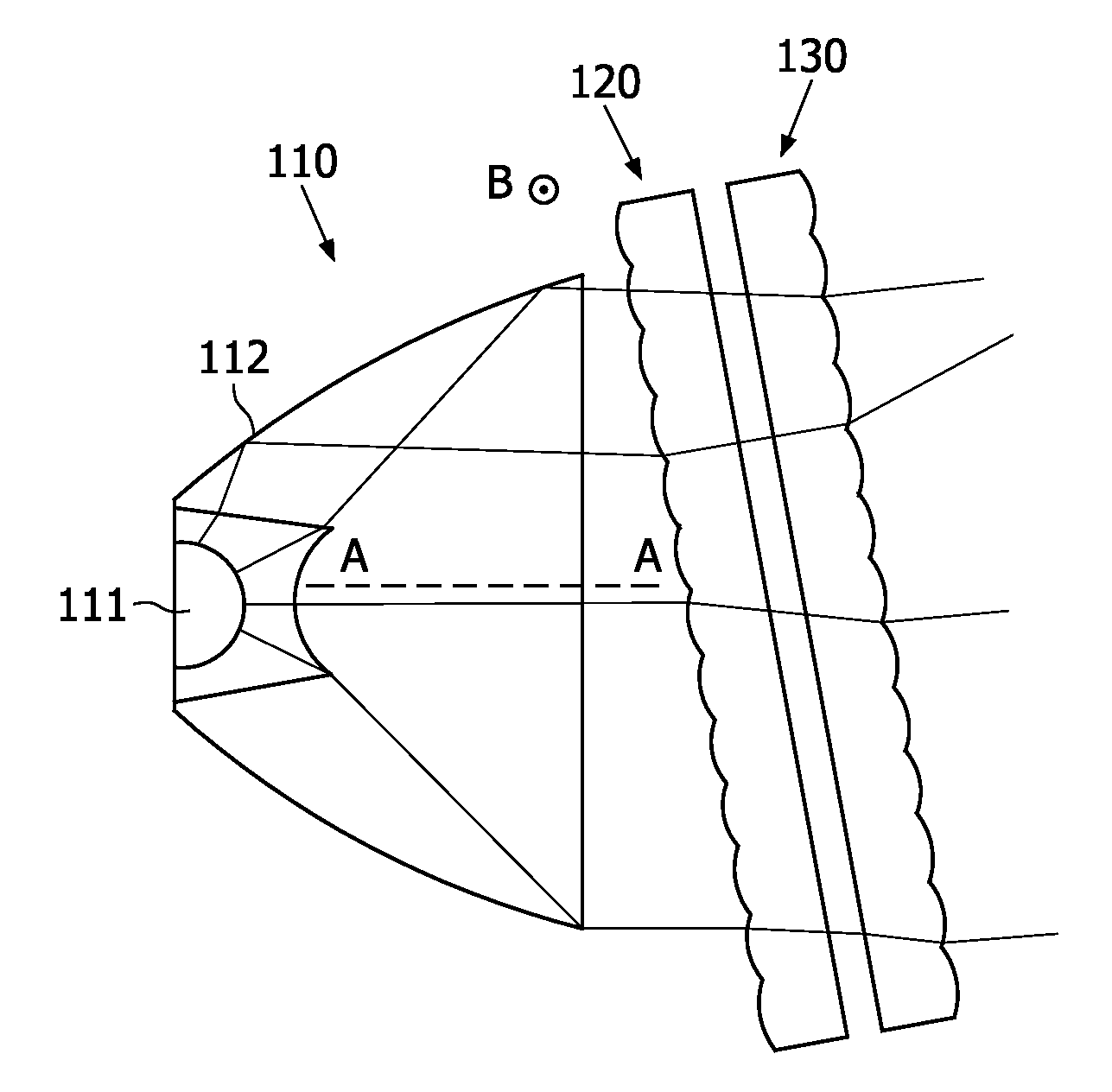
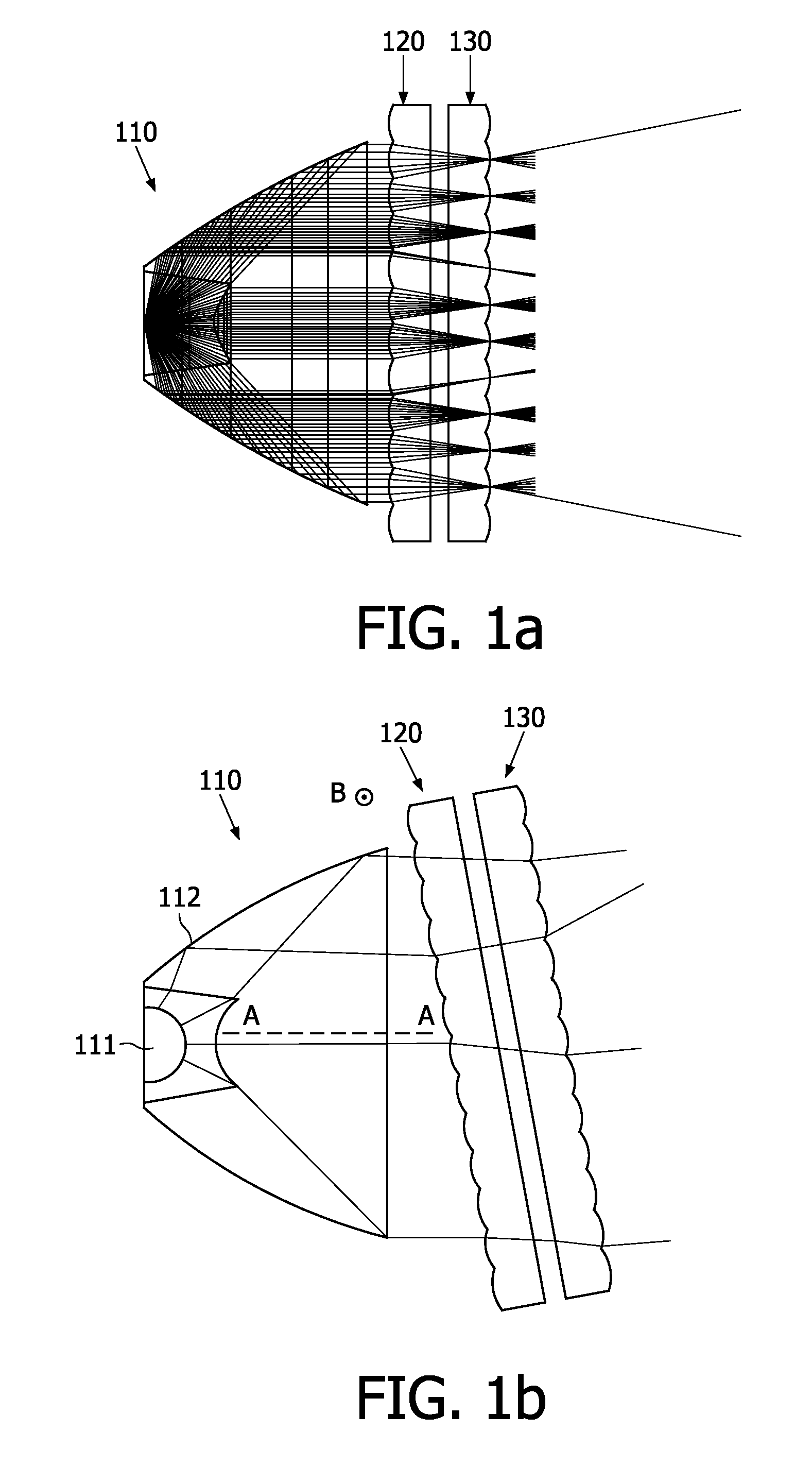
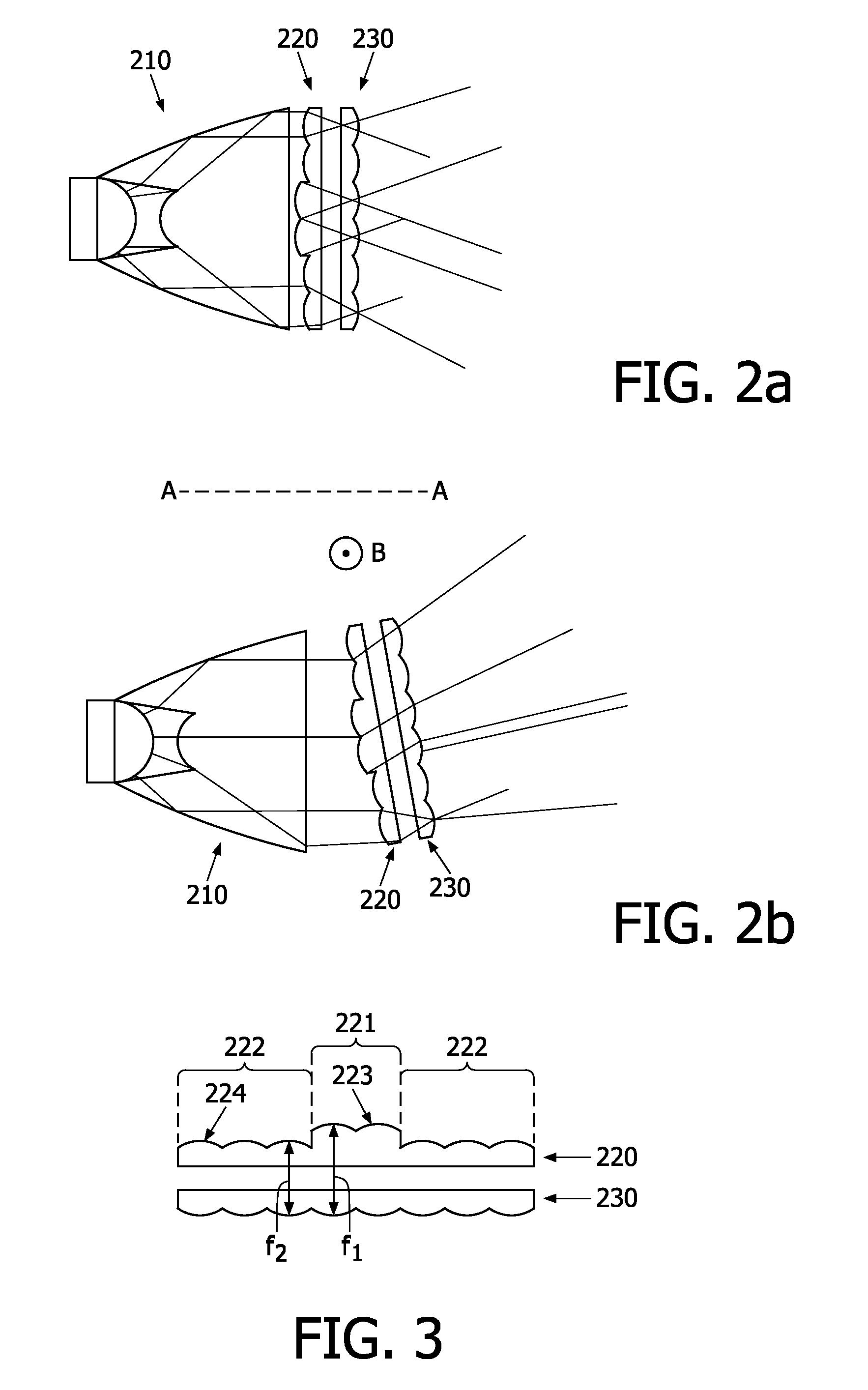
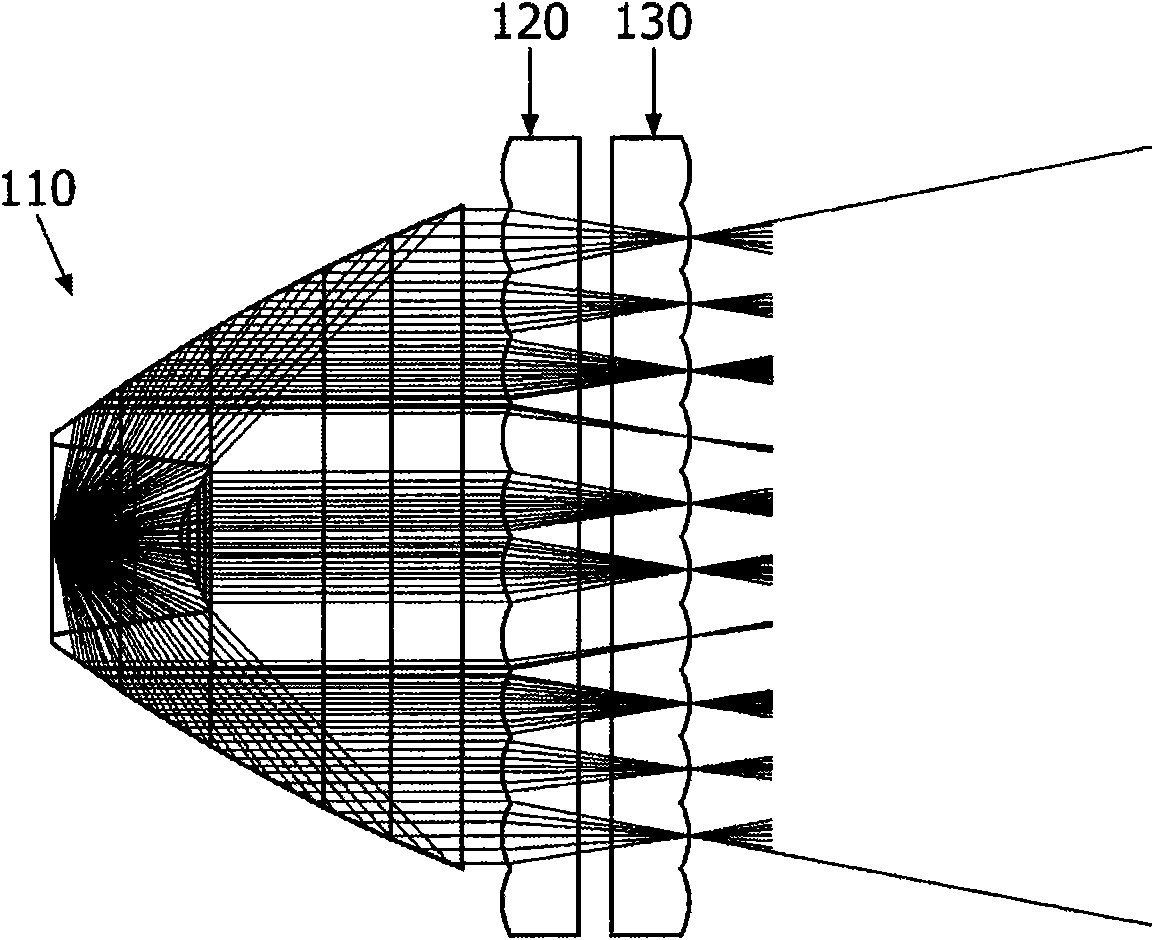
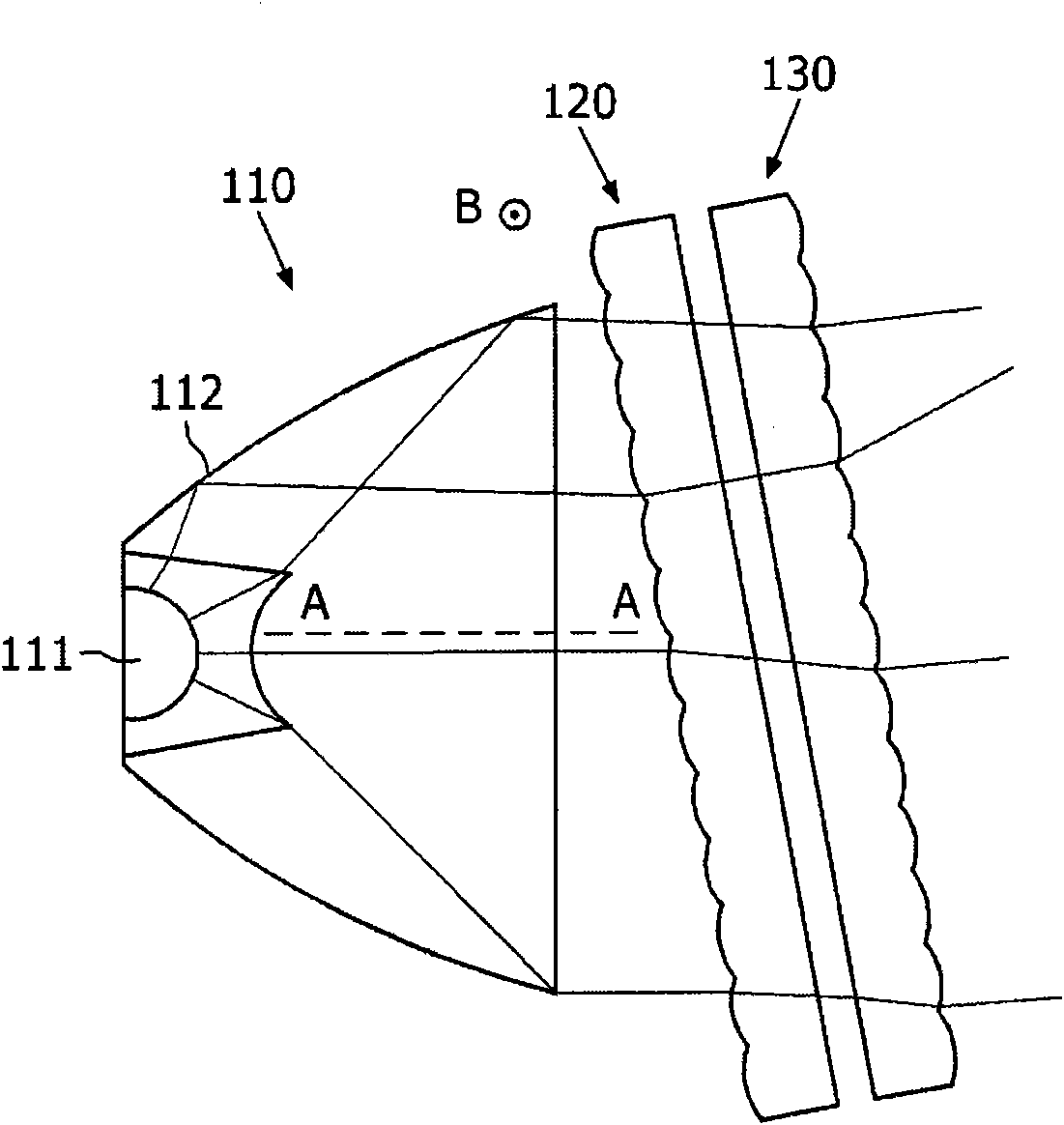
A floodlight comprises means (110) for generating a parallel beam having a general direction (AA), a first convergent lenses array (120) for generating a plurality of convergent beams from said parallel beam, and a second lenses array (130) parallel to and integral with said first lenses array. The floodlight further comprises means for rotating simultaneously said first and second lenses arrays about an axis perpendicular to the general direction of the parallel beam.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Curved-top total reflection type twice concentration and illumination balancing integration device
ActiveCN101694541AIncrease the concentration ratioImprove uniformity of spot intensityPhotovoltaicsCondensersLight spotLight beam
The invention discloses a curved-top total reflection type twice concentration and illumination balancing integration device, which is in a V-shaped prism trapezoid structure made of solid glass. In the invention, a curved-top surface is plated with an anti-reflection film, a curved-top bottom surface is the incidence surface of a light beam, a lower bottom surface is the emitting surface of the light beam, and the area of the curved-top bottom surface is larger than the area of the lower bottom surface. The curved-top total reflection type twice concentration and illumination balancing integration device works in the following steps: the light beam is changed into a convergent light beam by passing through the once condenser of a spotlight photovoltaic module group, the convergent light beam with a large caliber enters the incidence surface of the curved-top total reflection type twice concentration and illumination balancing integration device, after the refraction of the incidence surface and multiple total reflections of sidewalls, the convergent light beam is then refracted from the emitting surface to the solar cell with a small caliber, thereby achieving the purpose of twice concentration, and the multiple total reflections from the sidewalls can promote the light spots with uneven intensity distribution to be more even, thereby realizing the homogenization of the solar cell photic surface light spot.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
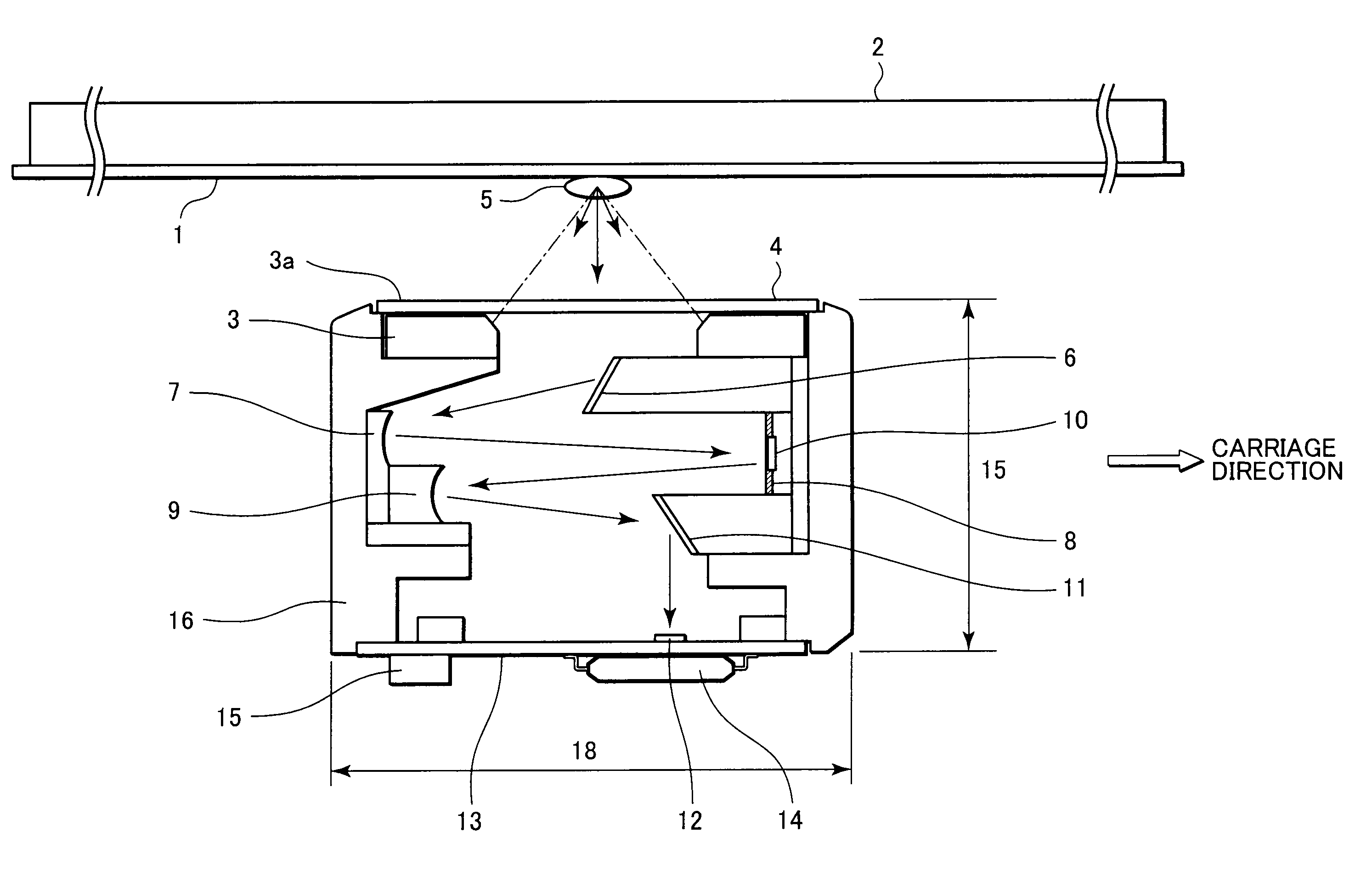
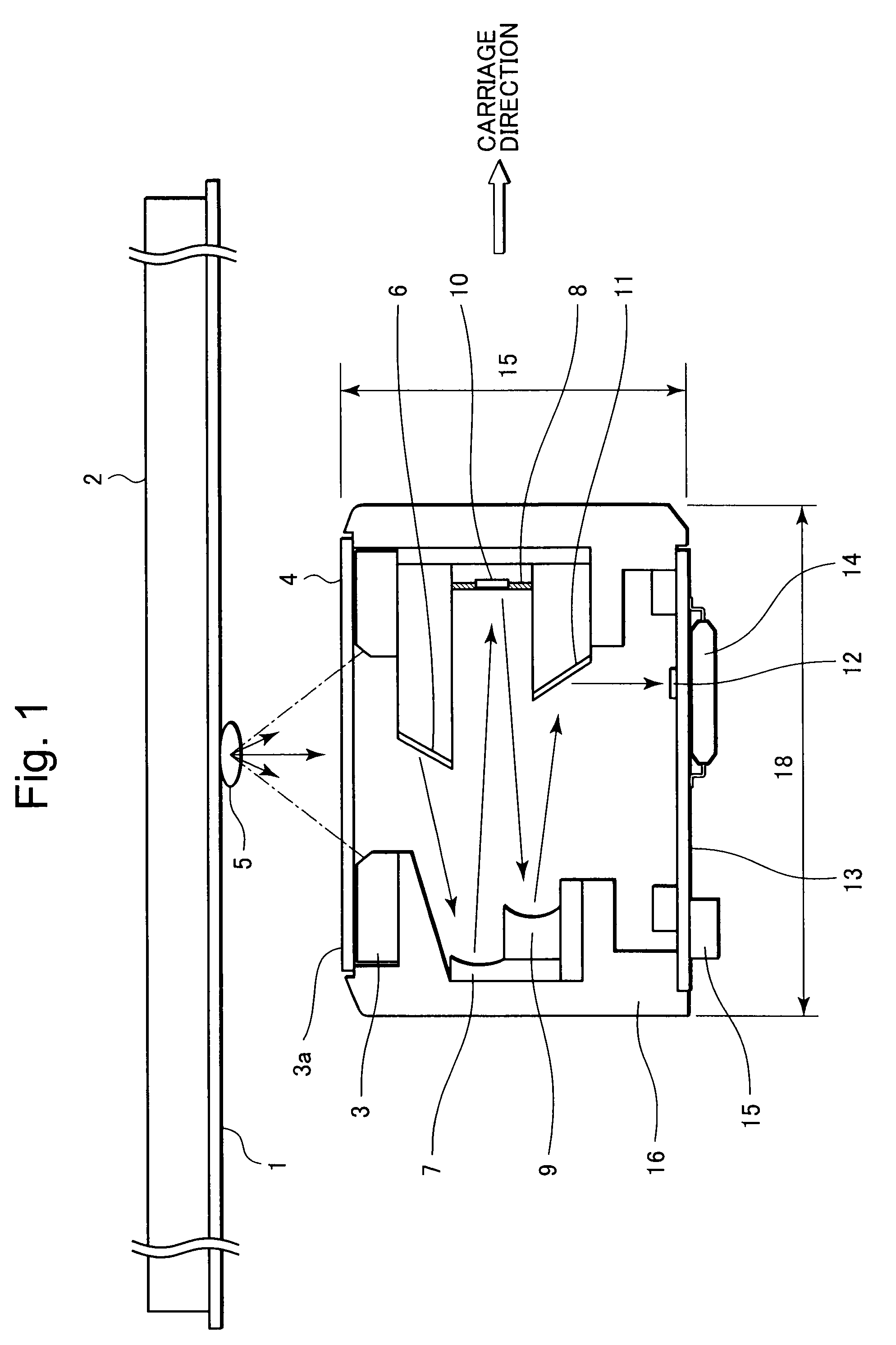
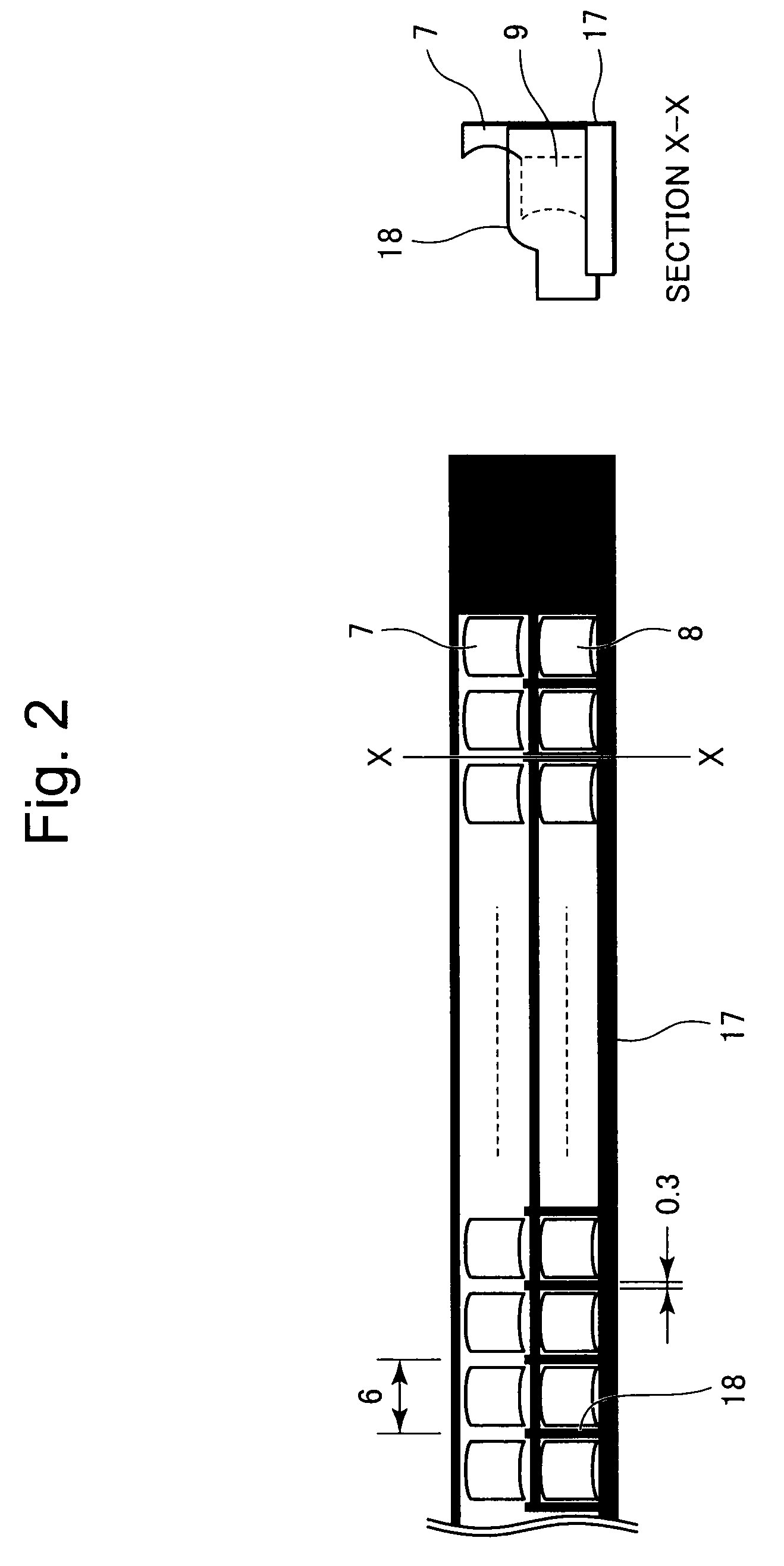
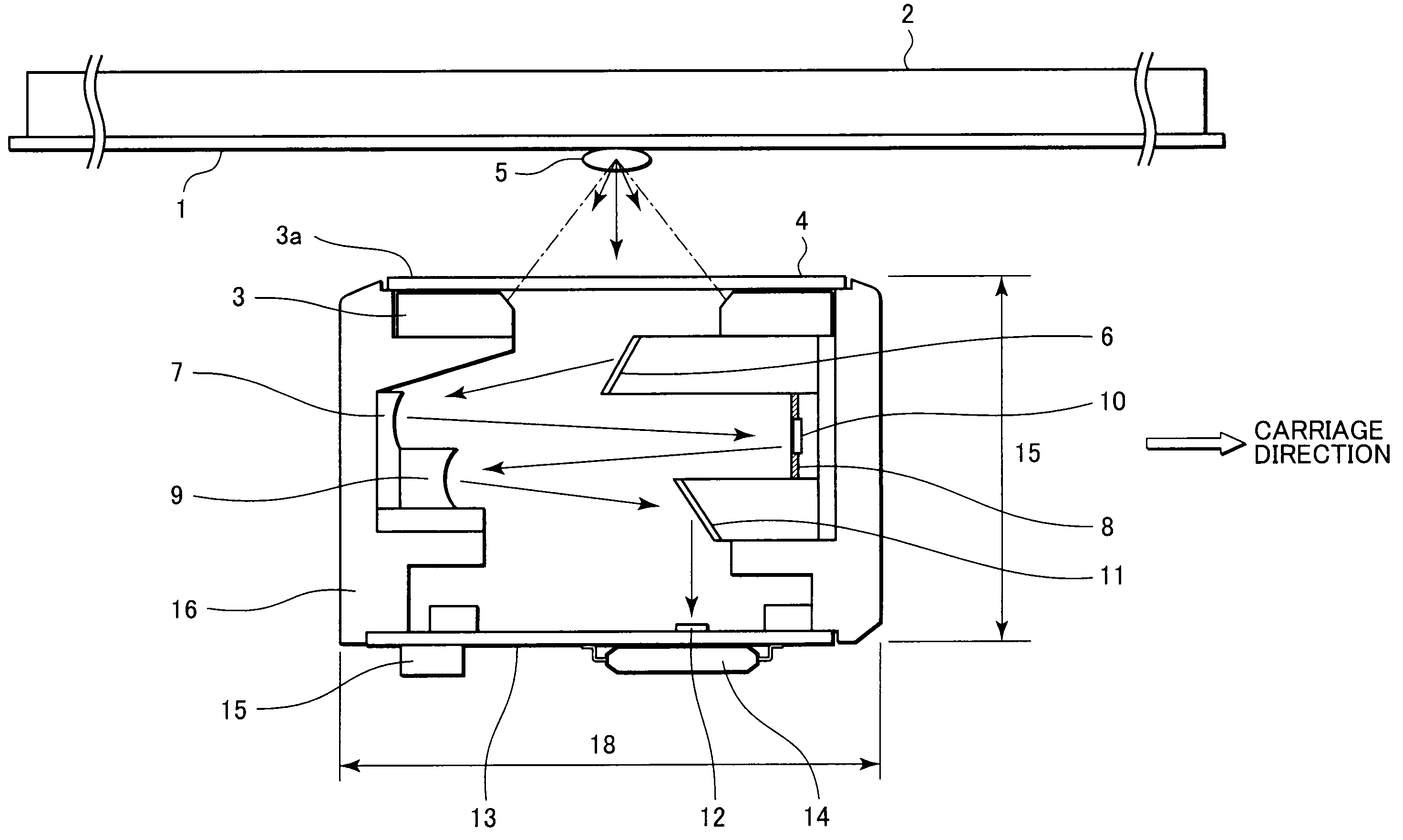
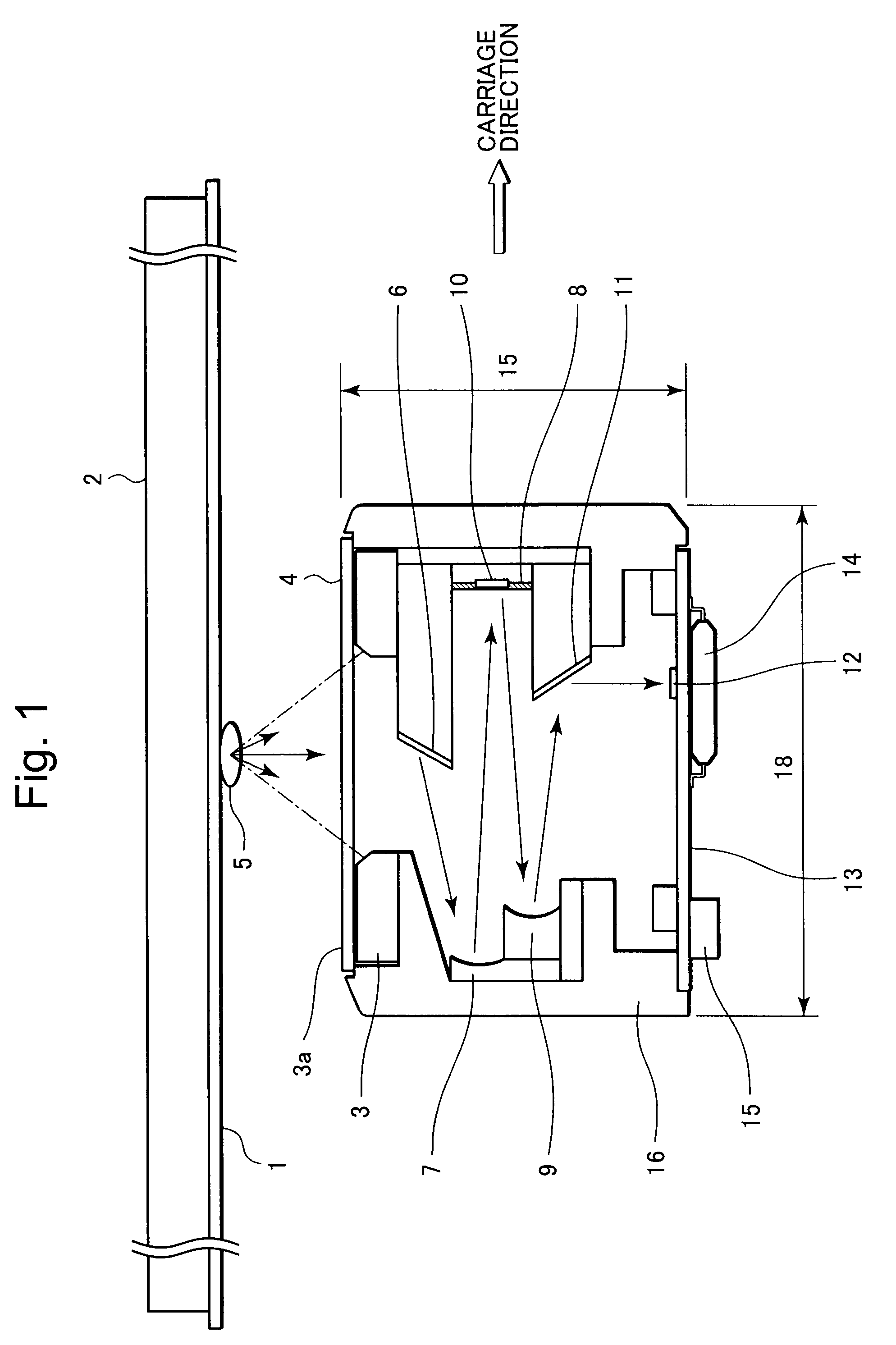
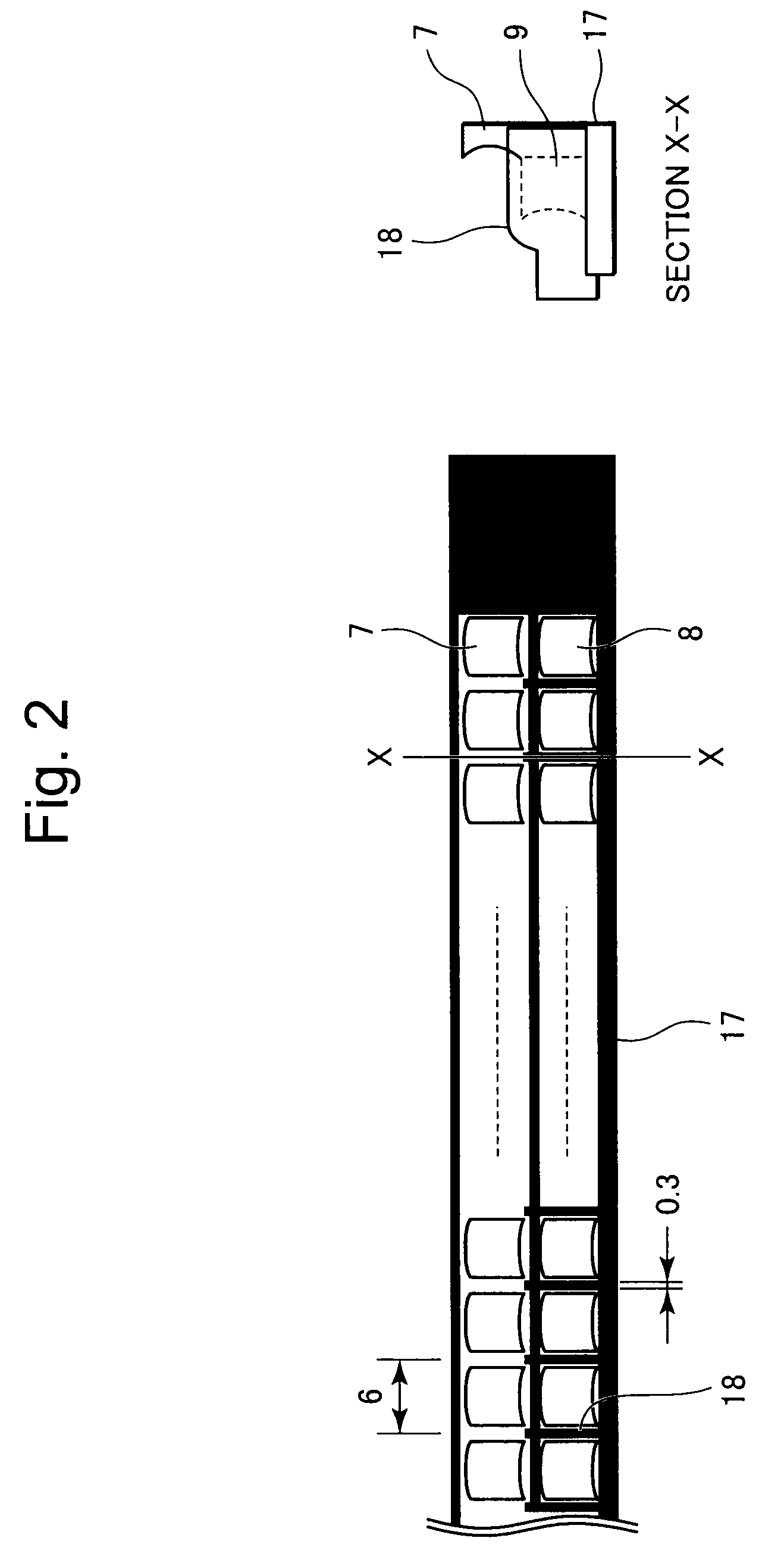
Image sensing apparatus
An image sensing apparatus having a large depth of focus (DOF) and being compact in size is provided. The image sensing apparatus includes a plurality of light sources that shines light beams on an illumination portion of a document; a first mirror that receives incident light scattered by reflection from the document, to reflect the scattered light in the secondary scan direction; a plurality of first concaved aspheric mirrors that collimates light beams from the first mirror, to reflect therefrom the collimated light beams as substantially collimated light fluxes; an aperture mirror that reflects therefrom the light beams from the respective first aspheric mirrors, through apertures each having a light-shielded portion formed therearound and selectively passing the light beams therethrough; a plurality of second concaved aspheric mirrors that receives the light beams incident from the respective aperture mirror, to reflect the incident light beams as converging light beams; a second mirror that reflects the light beams in a direction perpendicular to the surface of the document, disposed on a path of the light beams to be converged by means of the second aspheric mirrors; a plurality of light receivers each having a light-receiving area that receives the light beams from the second mirrors, to form images according to the light beams from the respective apertures; and a casing where the first and second aspheric mirrors are disposed on a first side of the casing in the secondary scan direction, and the aperture mirror is disposed on a second side thereof in the secondary scan direction.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Illumination system with reduced heat load
InactiveUS6611574B2Reduce heat loadHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGratingLight beam
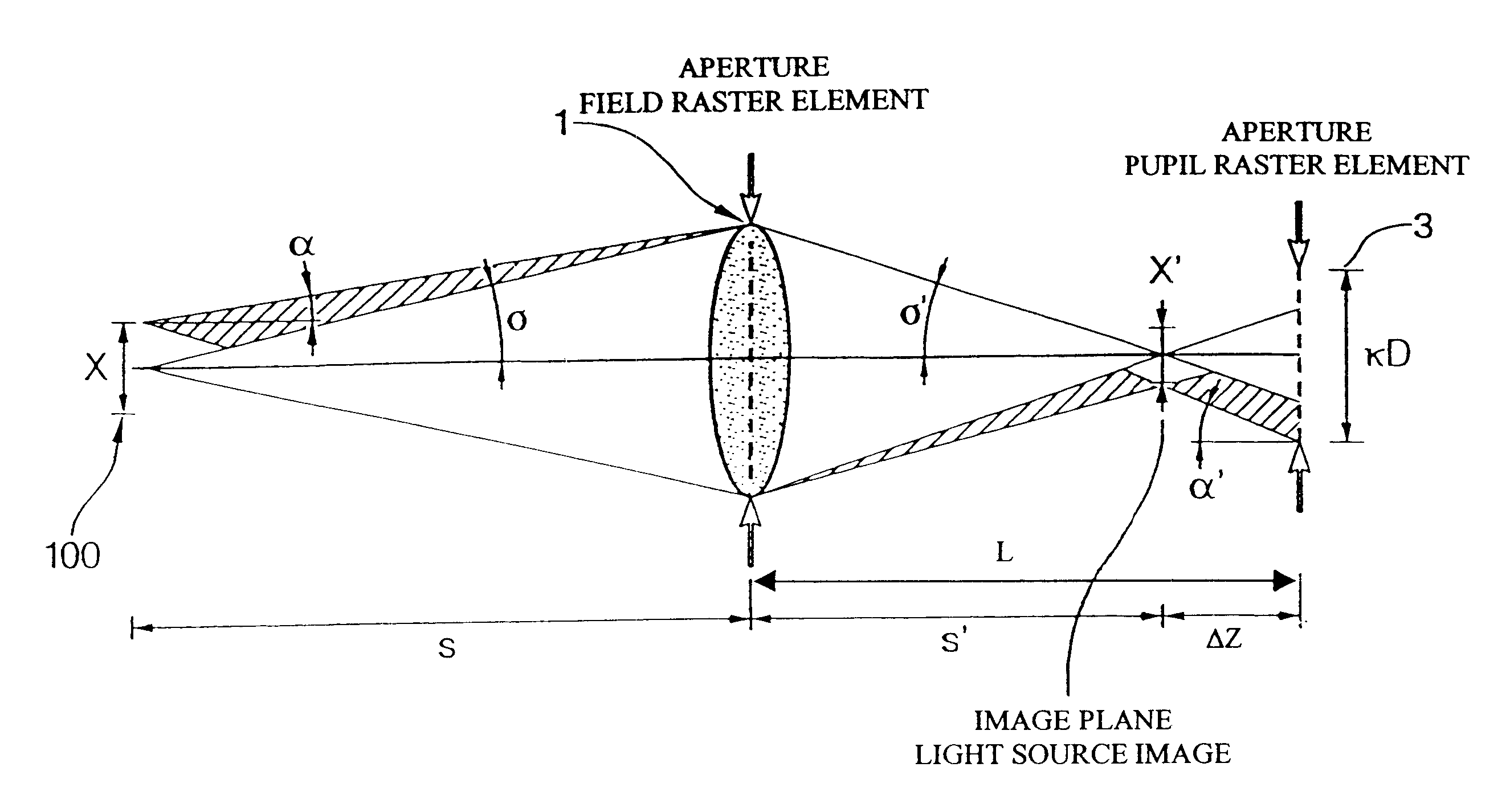
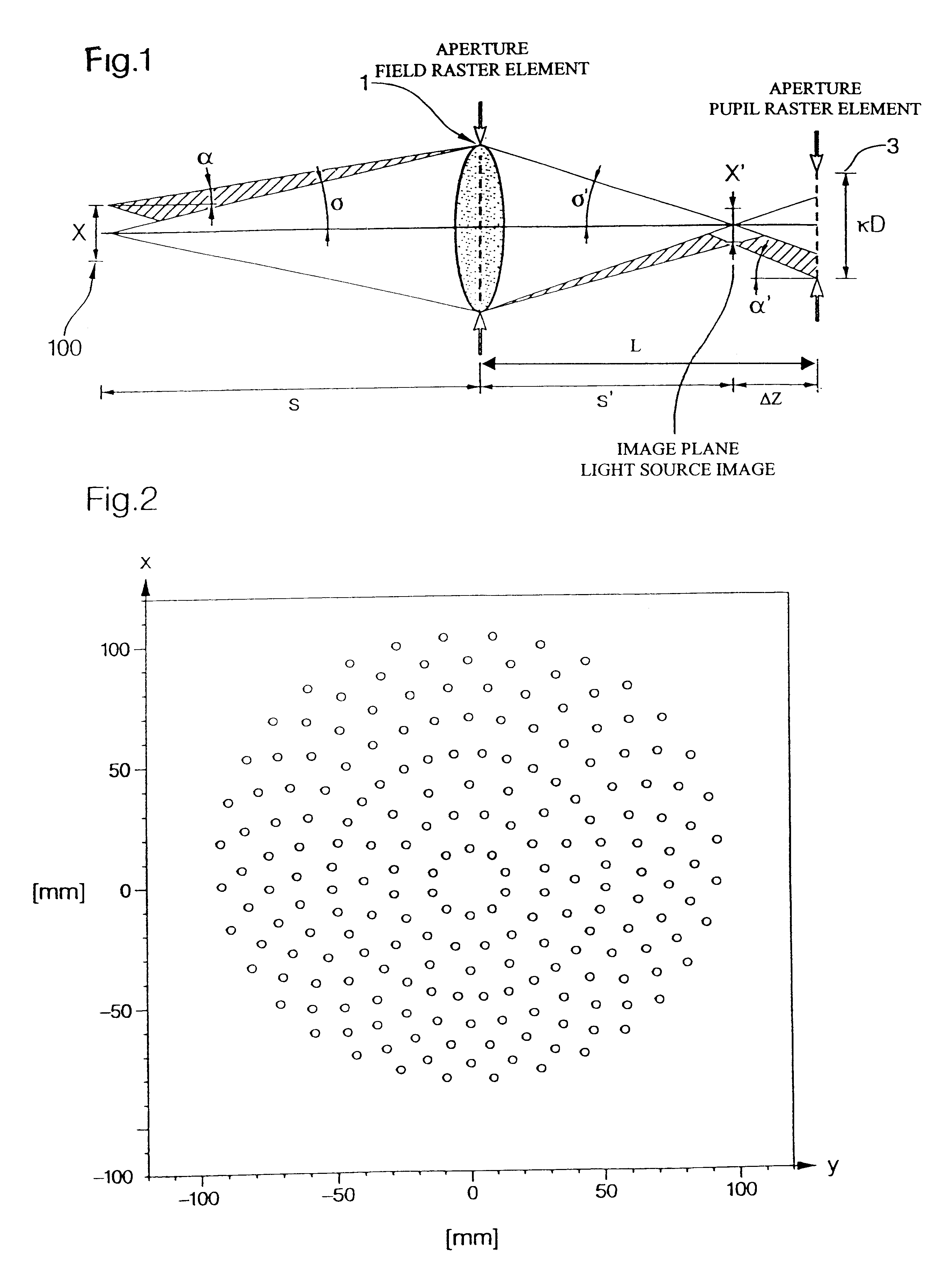
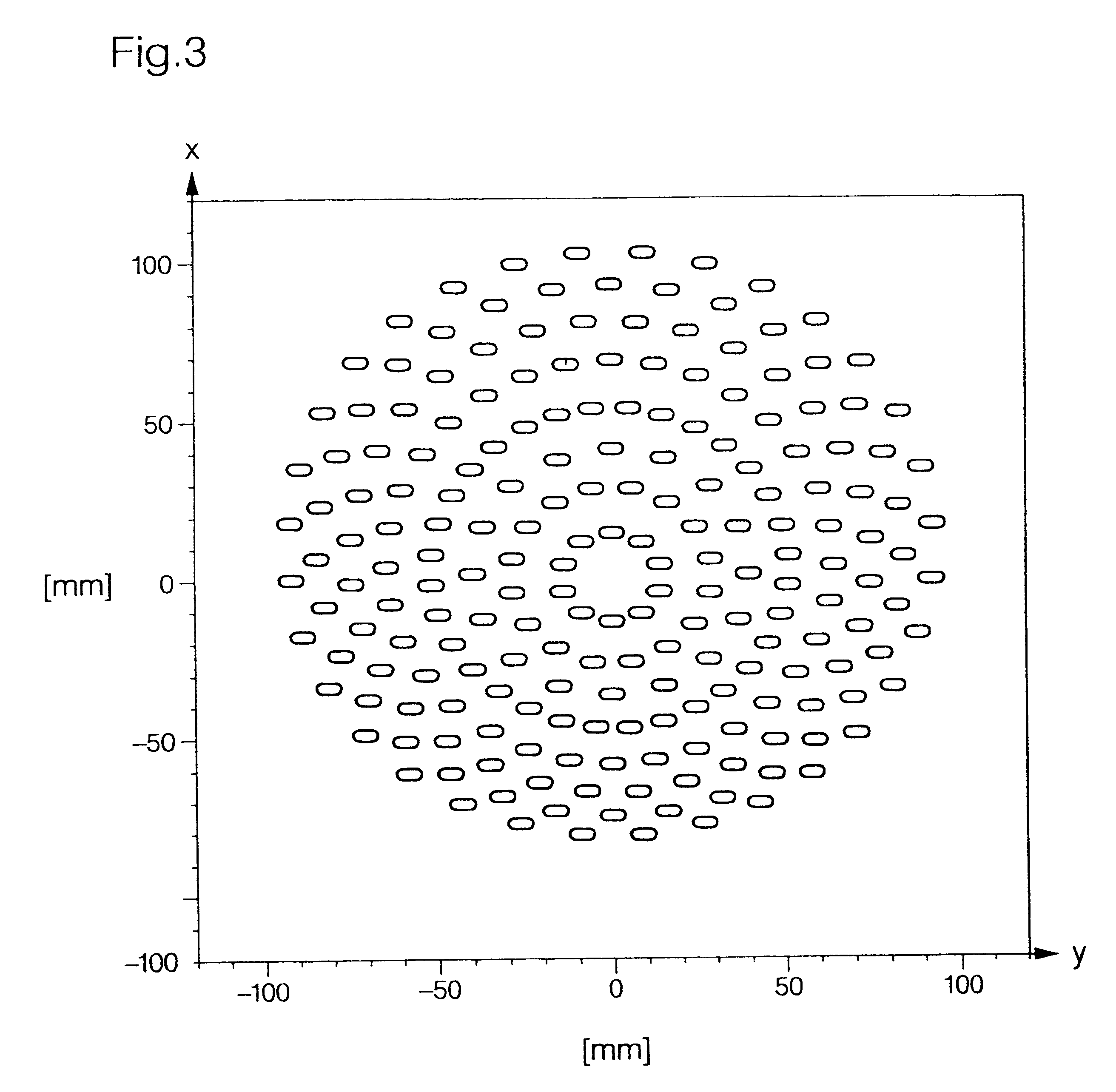
An illumination system for wavelengths <=193 run comprises (a) a first raster element upon which a light bundle emitted from a light source impinges, for producing a convergent light bundle having a focal point, and (b) a second raster element. The convergent light bundle impinges on the second raster element outside the focal point. There is also provided an illumination system for wavelengths <=193 nm, comprising (a) a first plurality of raster elements upon which a light bundle emitted from a light source impinges, for producing a plurality of convergent light bundles, where a member of the first plurality of raster elements produces a member of the plurality of convergent light bundles having a focal point, and (b) a second plurality of raster elements. The member of the plurality of convergent light bundles impinges on a member of the second plurality of raster elements outside the focal point.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SEMICON MFG
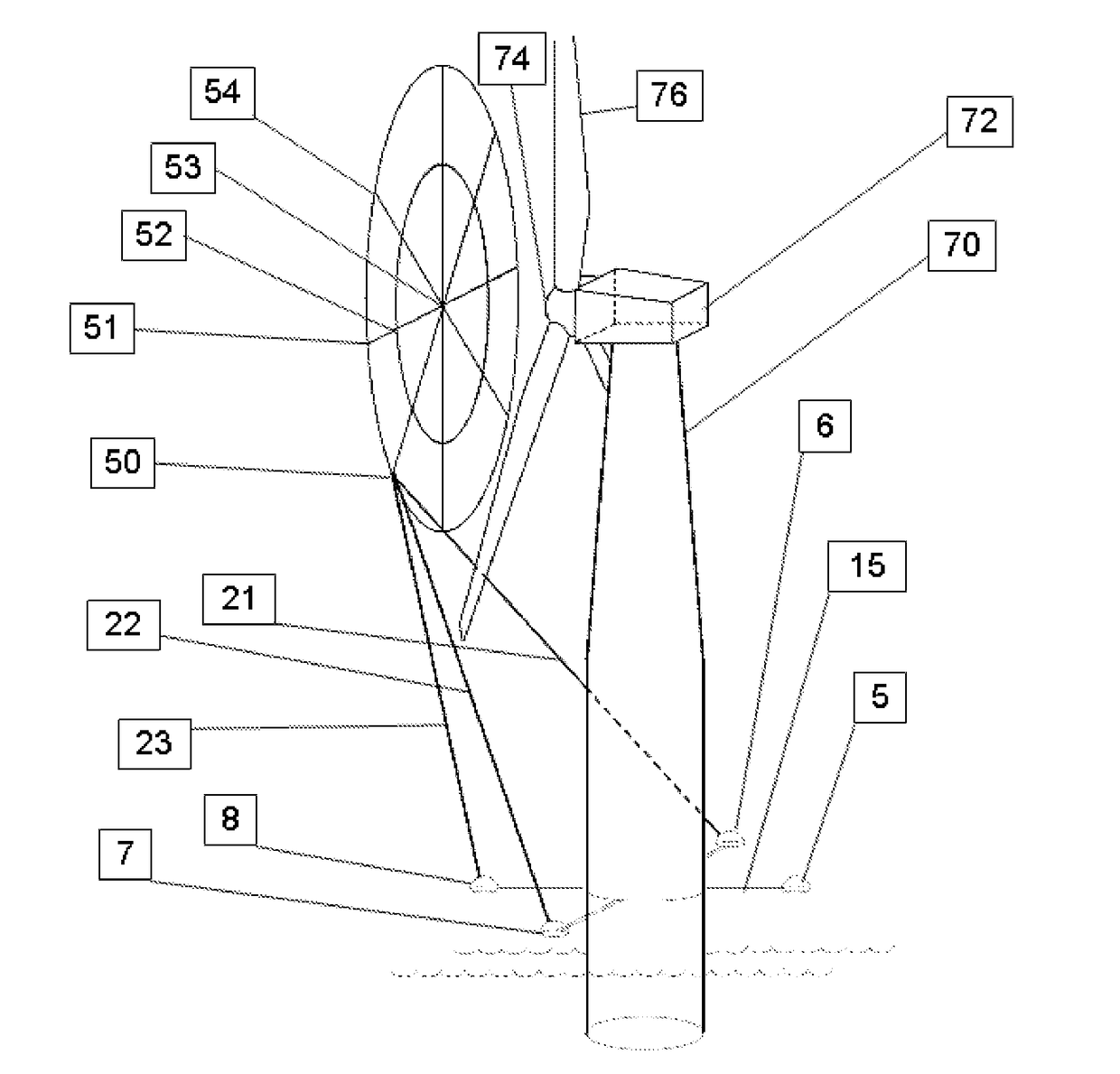
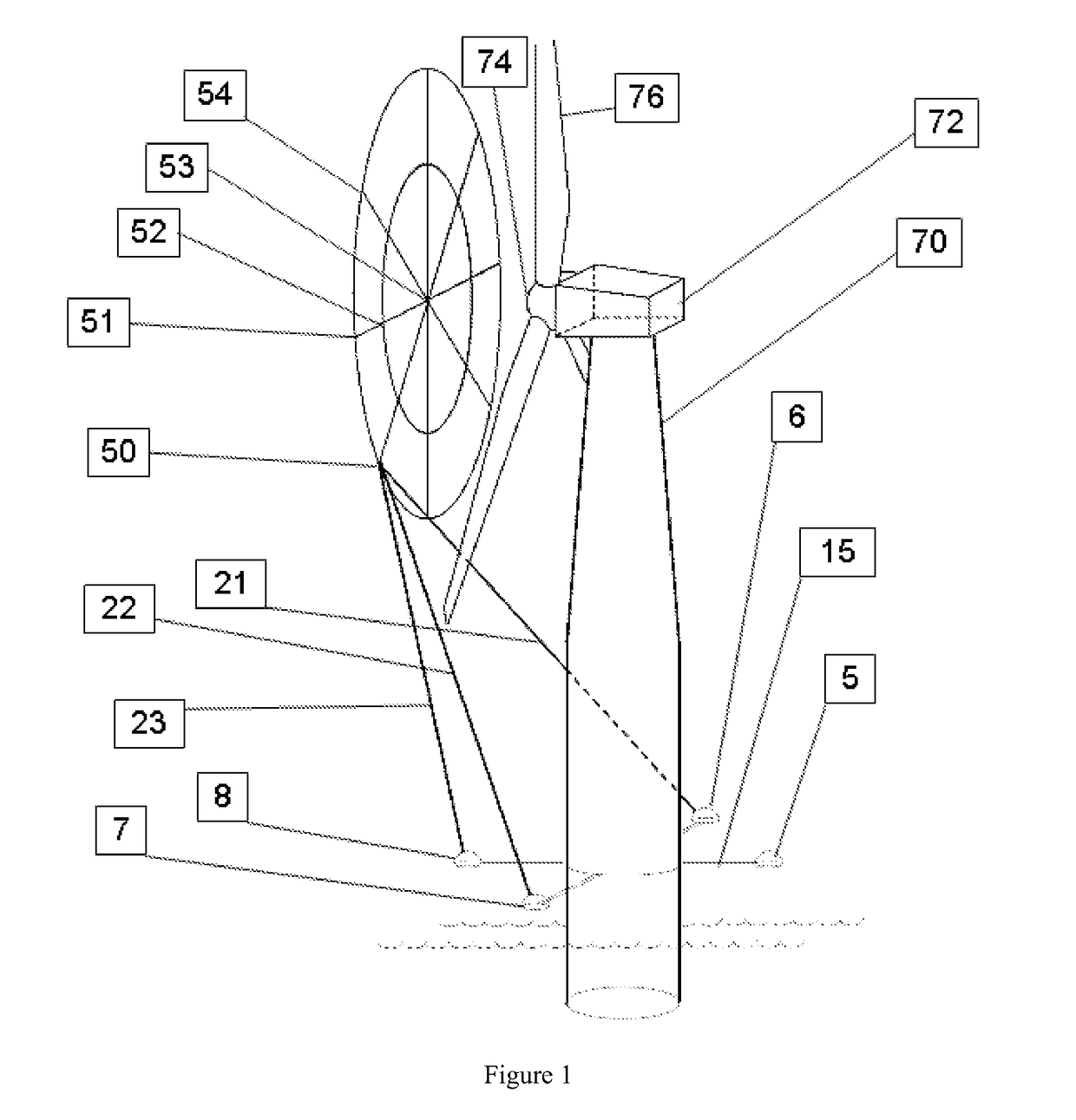
Turbine Fluid Velocity Field Measurement
A method of three-dimensional Doppler velocimetry applicable to turbines such as wind turbines achieves improved velocimetry by use of various possible convergent beam geometries and employing beam sources mounted on the turbine such as on a wind turbine nacelle, rotor hub or rotor blades.
Owner:WIND FARM ANALYTICS
Deep UV optical system confocal alignment device and method
ActiveCN106646867AFast confocal alignmentHigh precisionTesting optical propertiesOptical elementsVena contracta diameterBeam splitter
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
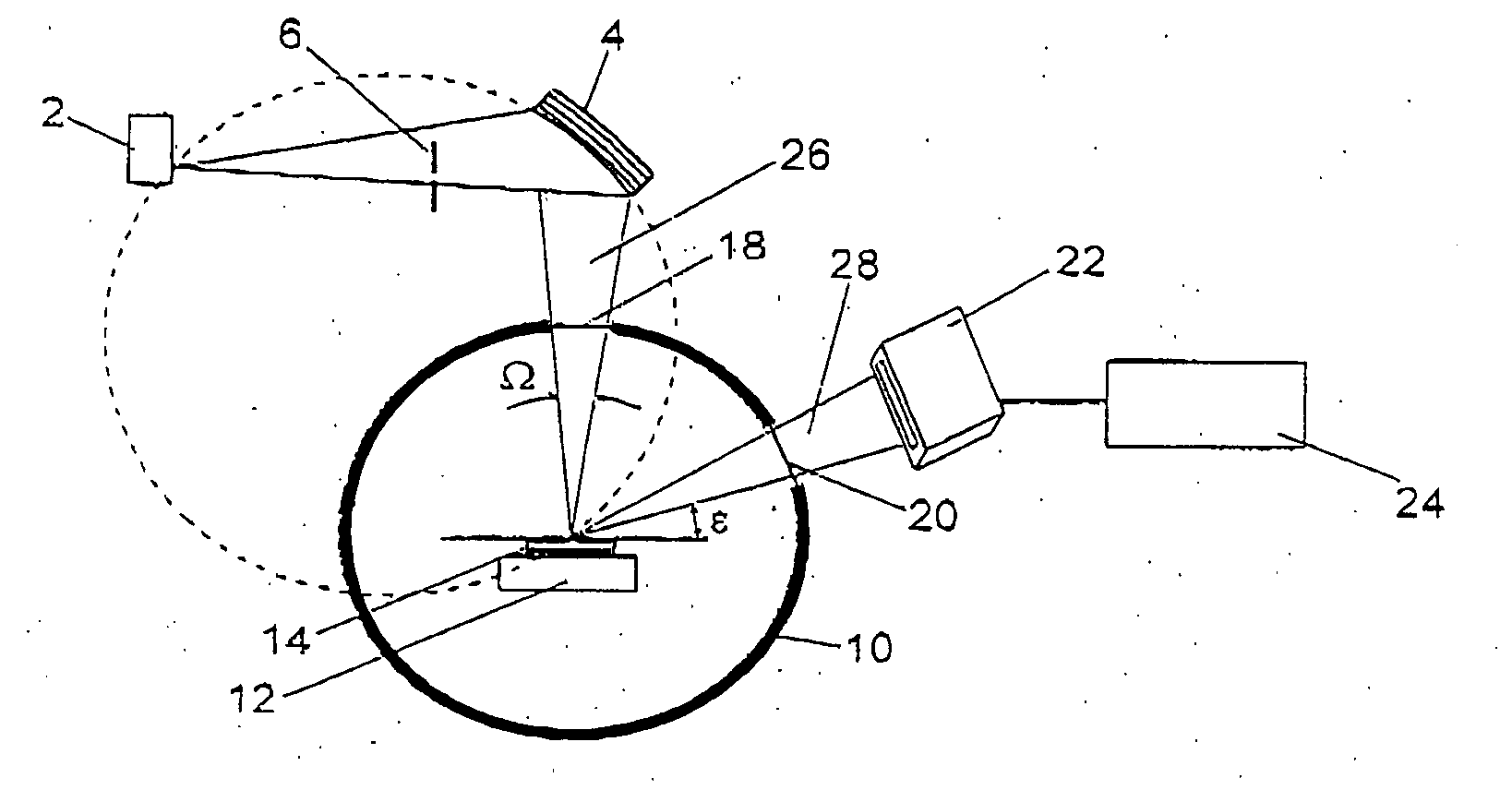
Diffractometer
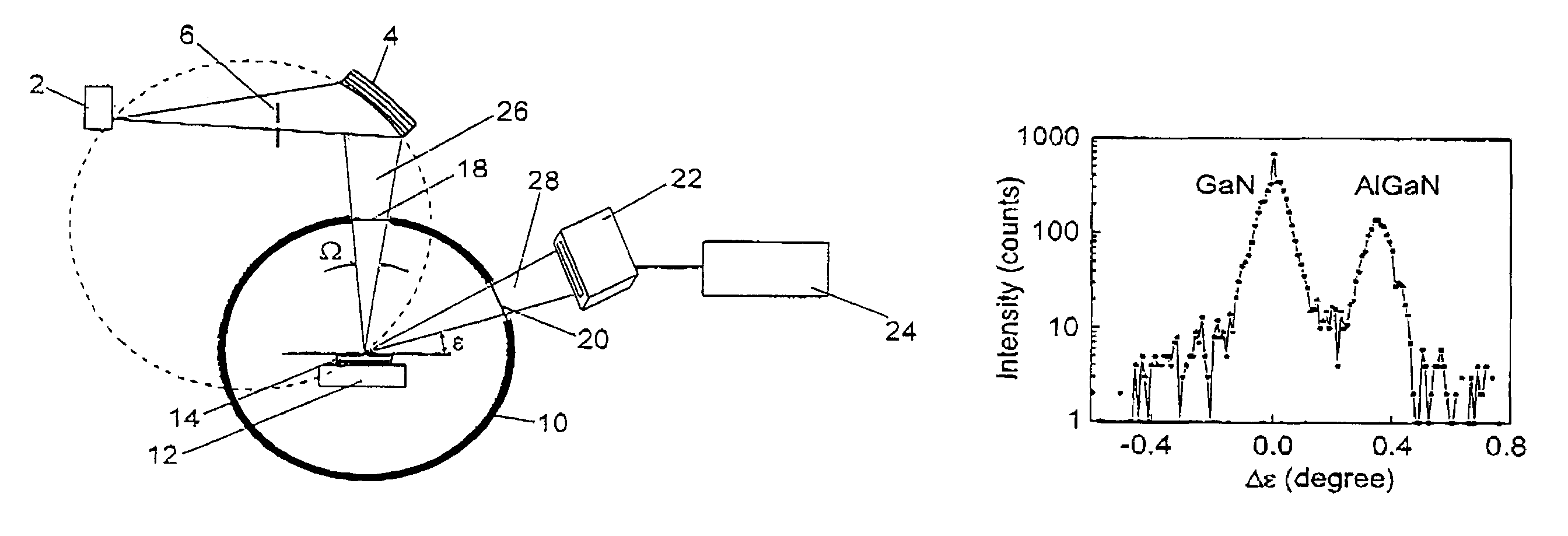
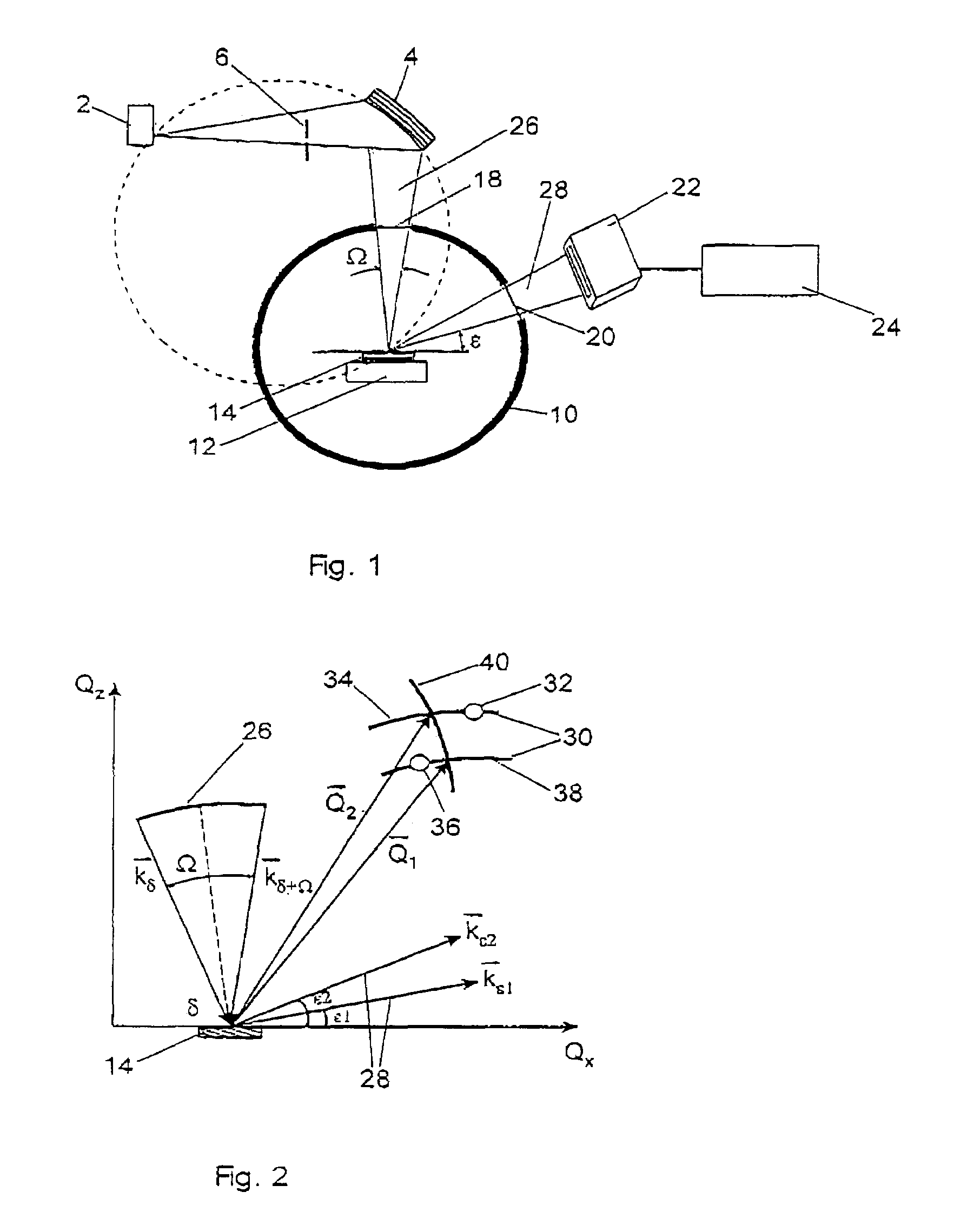
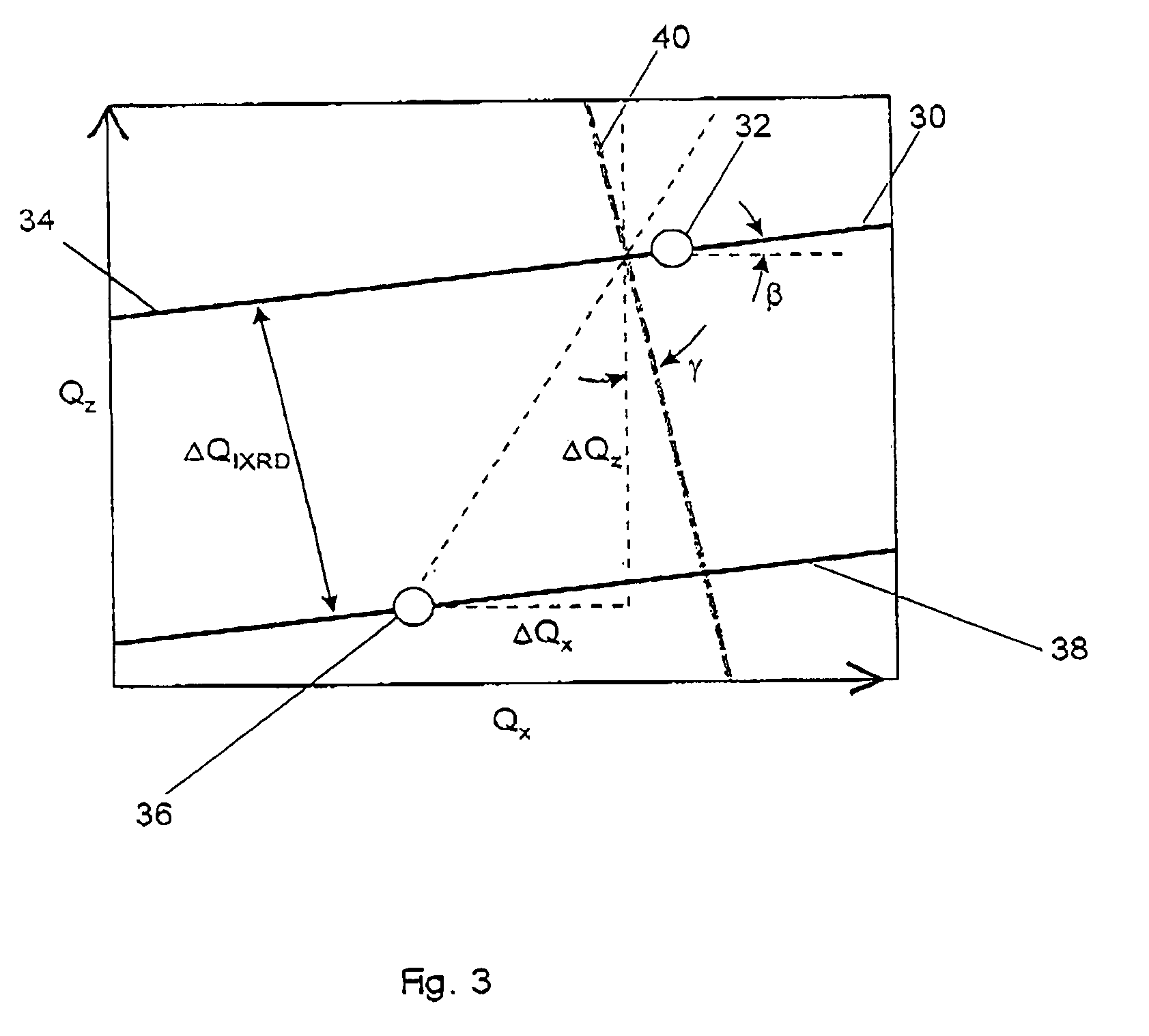
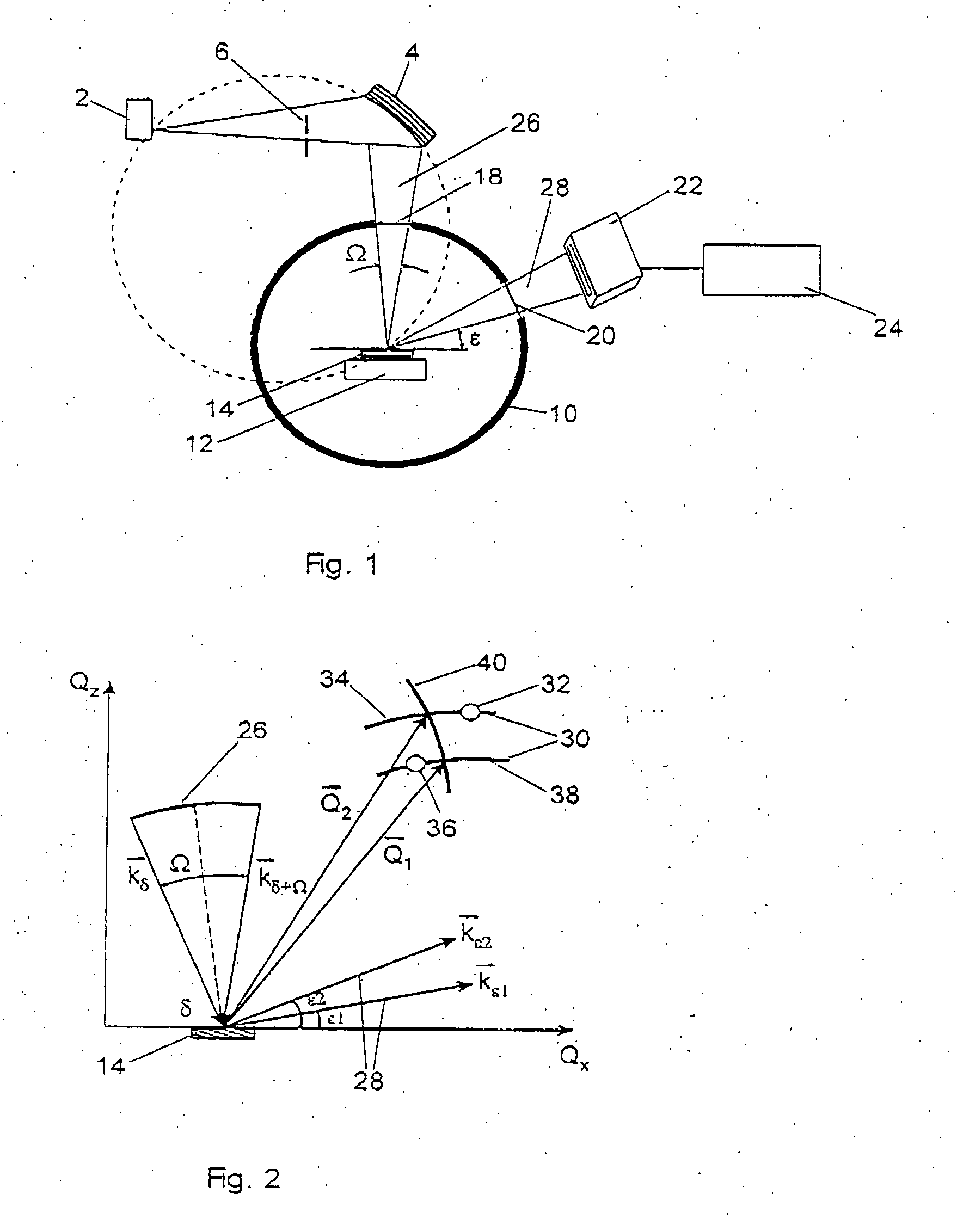
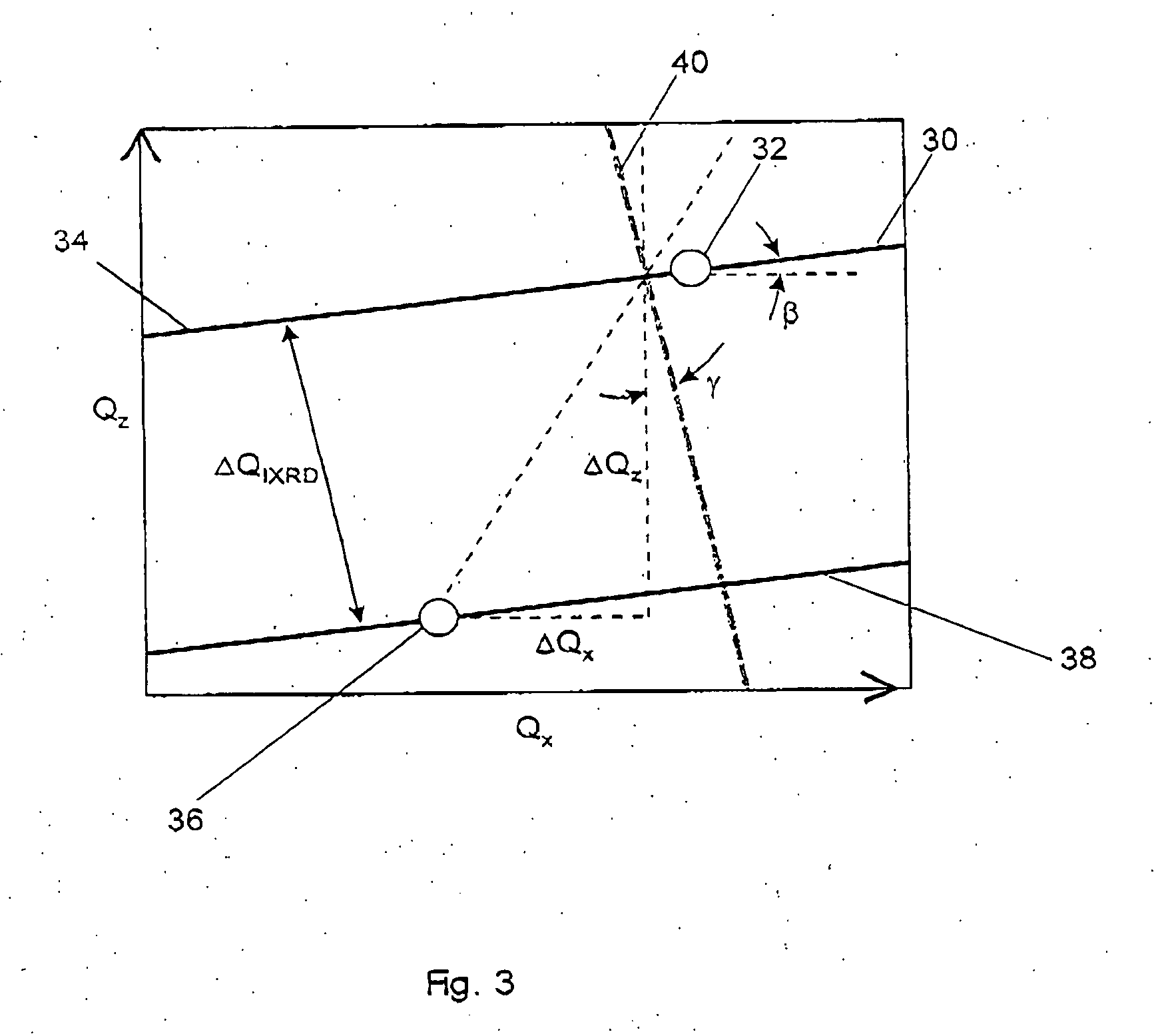
ActiveUS7116754B2Quick fixAfter-treatment apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiffractometerX-ray
A monochromator 4 is used to direct X-rays from X-ray source 2 onto a sample 14 as a convergent beam. The sample 14 is in a growth chamber. The sample is rotated, and diffraction measurements are made in parallel with multichannel detector 22. A specific reflection is used so that the intensity against angle graph measured in the multichannel detector gives information about the vertical lattice parameter. To compensate for wobble inevitably introduced by the rotation of the sample, short time measurements are made and summed.
Owner:PANALYTICAL BV
Optical unit, optical apparatus using the same, light source apparatus, and projection display apparatus
An optical unit includes a plurality of paraboloid mirrors configured to reflect light fluxes from a plurality of LDs and to guide them to a concave lens. The light fluxes from the paraboloid mirrors are a plurality of convergent light fluxes, and the paraboloid mirrors reflect the light fluxes from the LDs such that as the convergent light fluxes travel farther away from the paraboloid mirrors, distances therebetween become shorter.
Owner:CANON KK
Optical arrangement for microscope and microscope
An optical arrangement for a microscope, in particular for a scanning microscope, with a beam splitter 1 arranged in a divergent and / or convergent beam path for separating an illumination light 2 that is produced by an illumination source from a detection light 3 that is emitted by a sample being tested, which with regard to reliable correction of imaging errors can be implemented and developed even when using thick beam splitters 1 such that the beam splitter 1 is wedge-shaped and implemented as a beam splitter plate for reflection primarily at a glass-air interface 4. Furthermore, a microscope with such an optical arrangement is disclosed.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
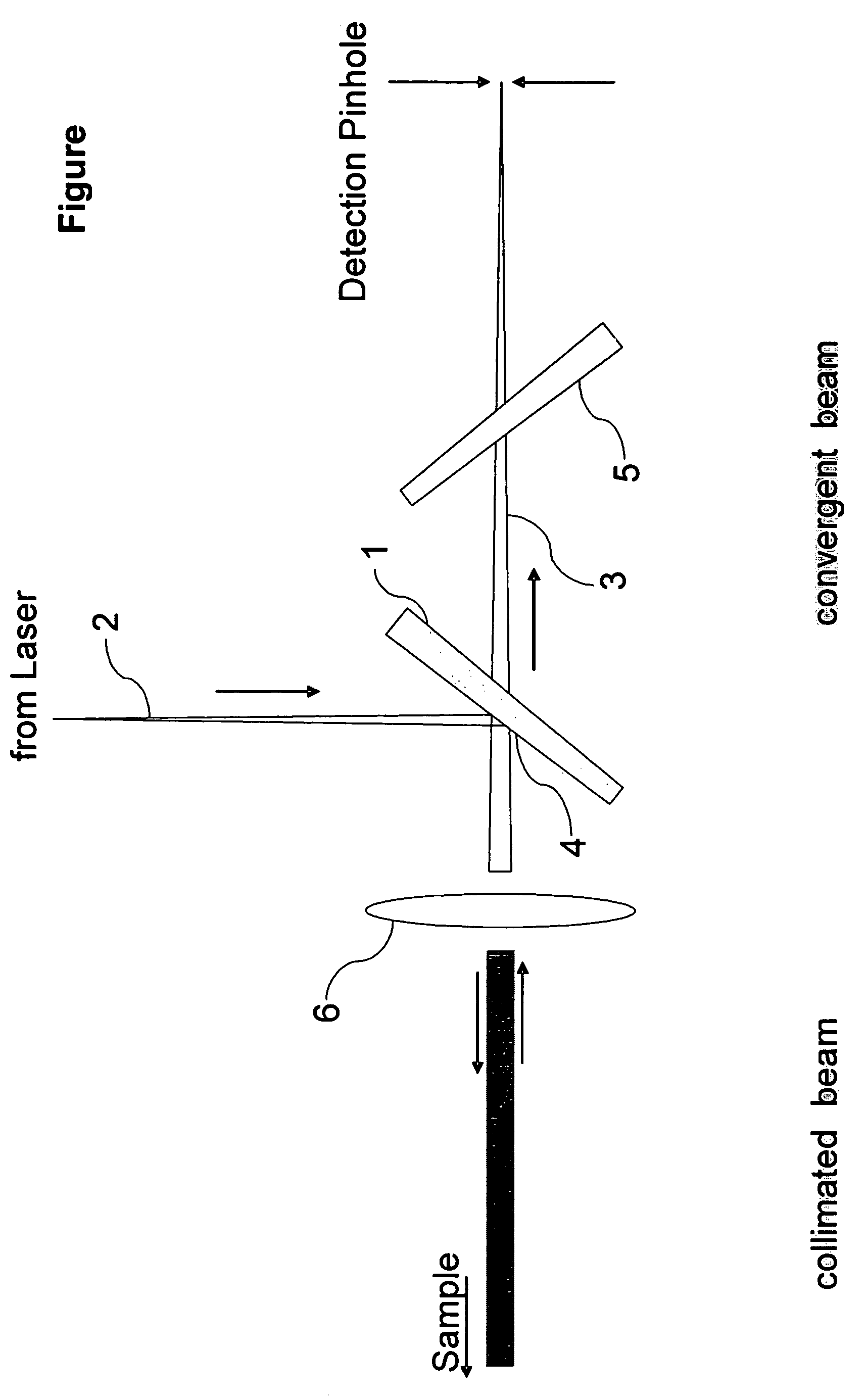
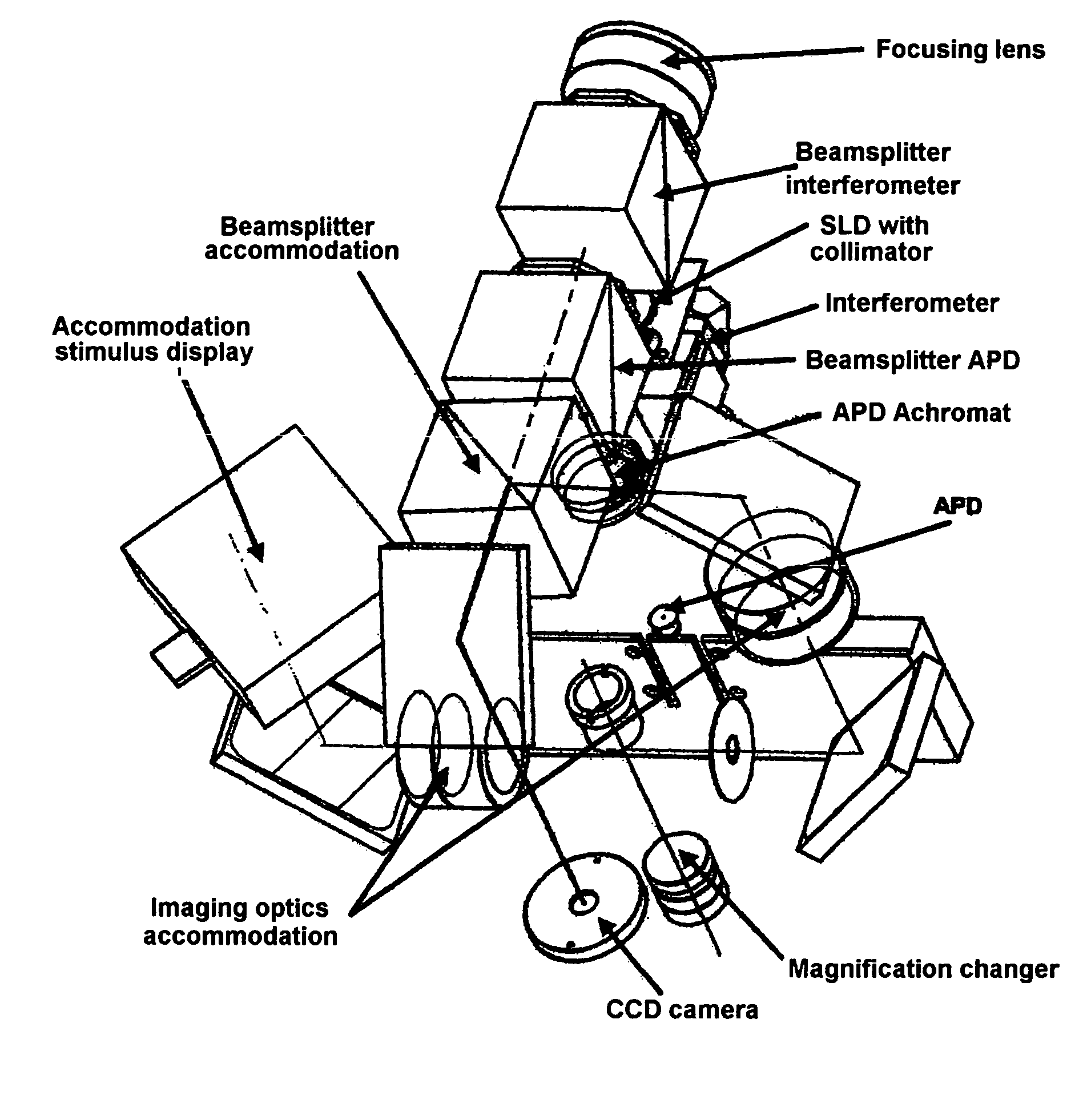
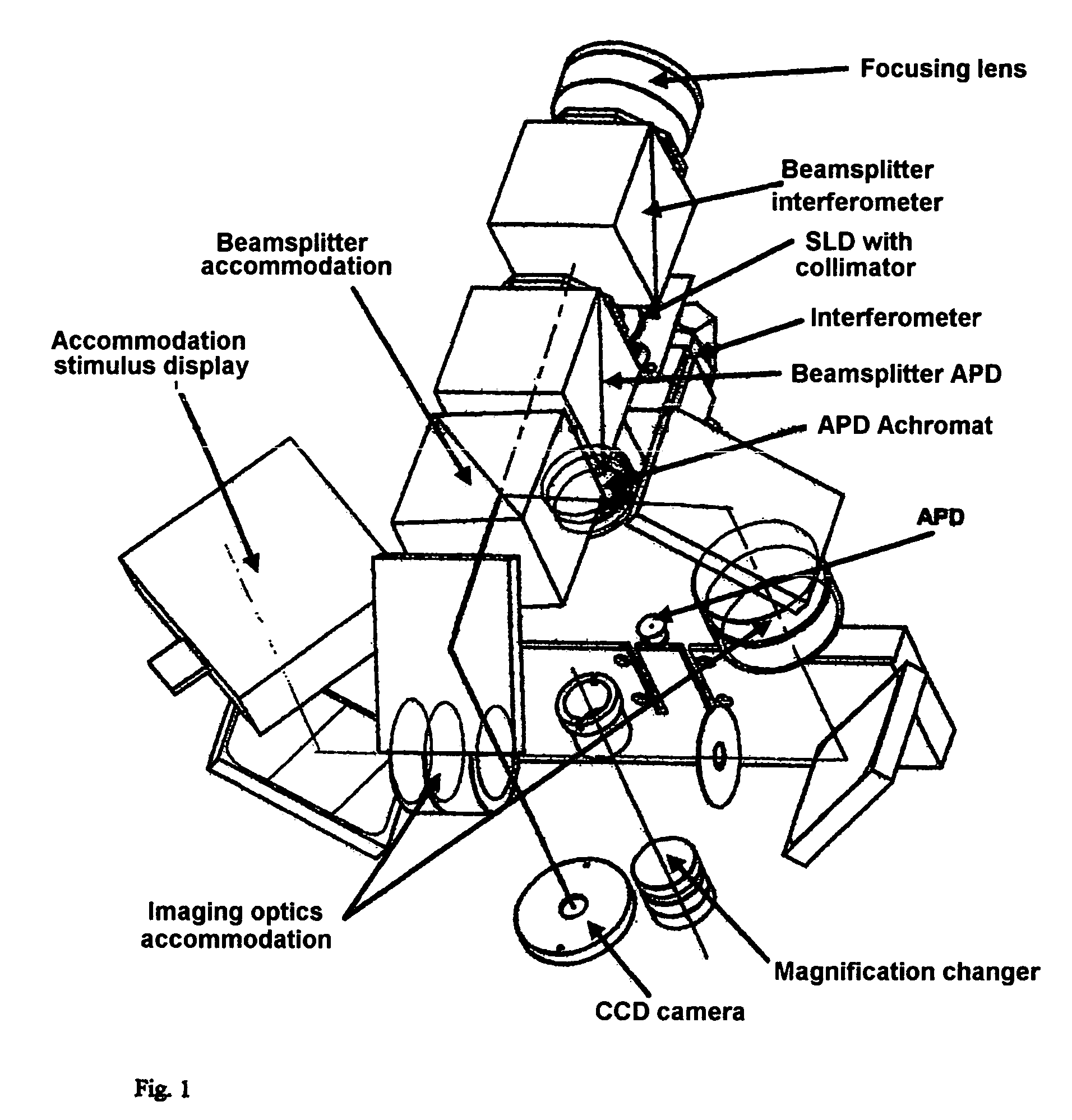
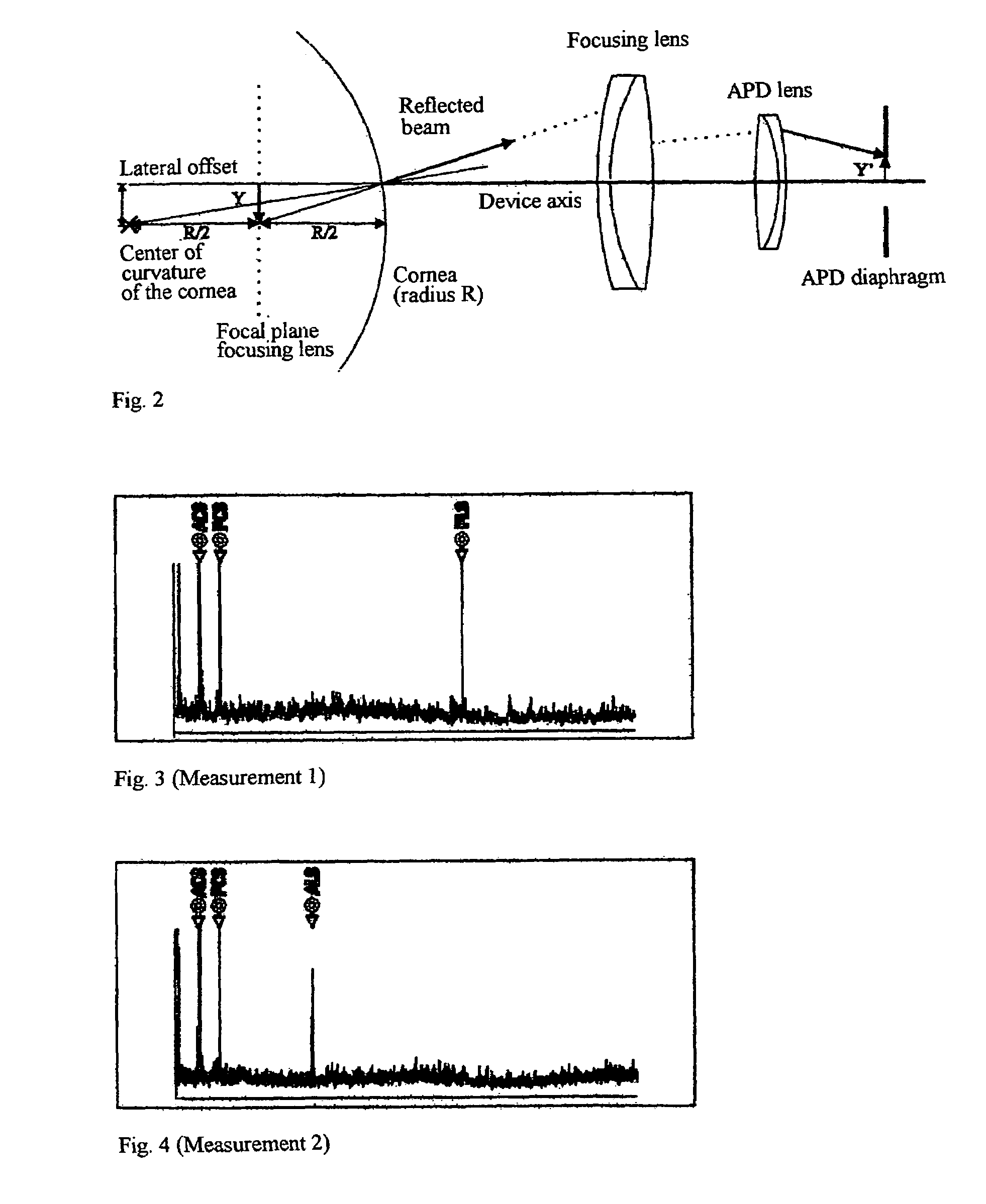
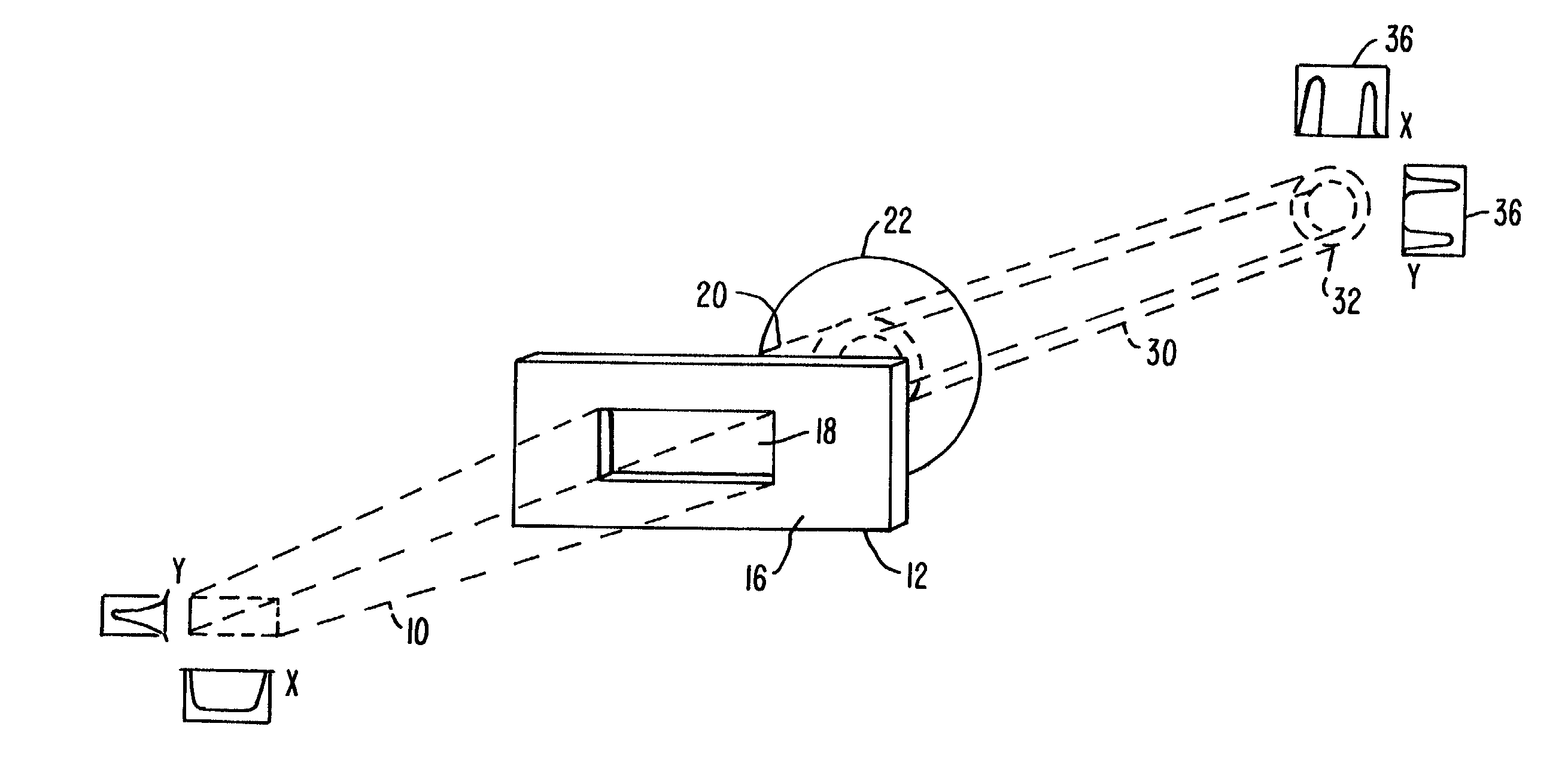
Method and arrangement for the measurement of the anterior segment of the eye
InactiveUS7380939B2Quick measurementNew-spun product collectionUsing optical meansMeasurement deviceOptical axis
The invention is directed to an arrangement and a method for measuring the anterior segment of the eye using interferometric means. The eye is illuminated by a convergent beam bundle and aligned with the optical axis of the measuring device by generating directional stimuli and accommodation stimuli by means of a display which is mirrored into the beam path.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Floodlight with tiltable beam
The present invention discloses a floodlight comprises means (110) for generating a parallel beam having a general direction (AA), a first convergent lenses array (120) for generating a plurality of convergent beams from said parallel beam, and a second lenses array (130) parallel to and integral with said first lenses array. The floodlight further comprises means for rotating simultaneously said first and second lenses arrays about an axis perpendicular to the general direction of the parallel beam.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
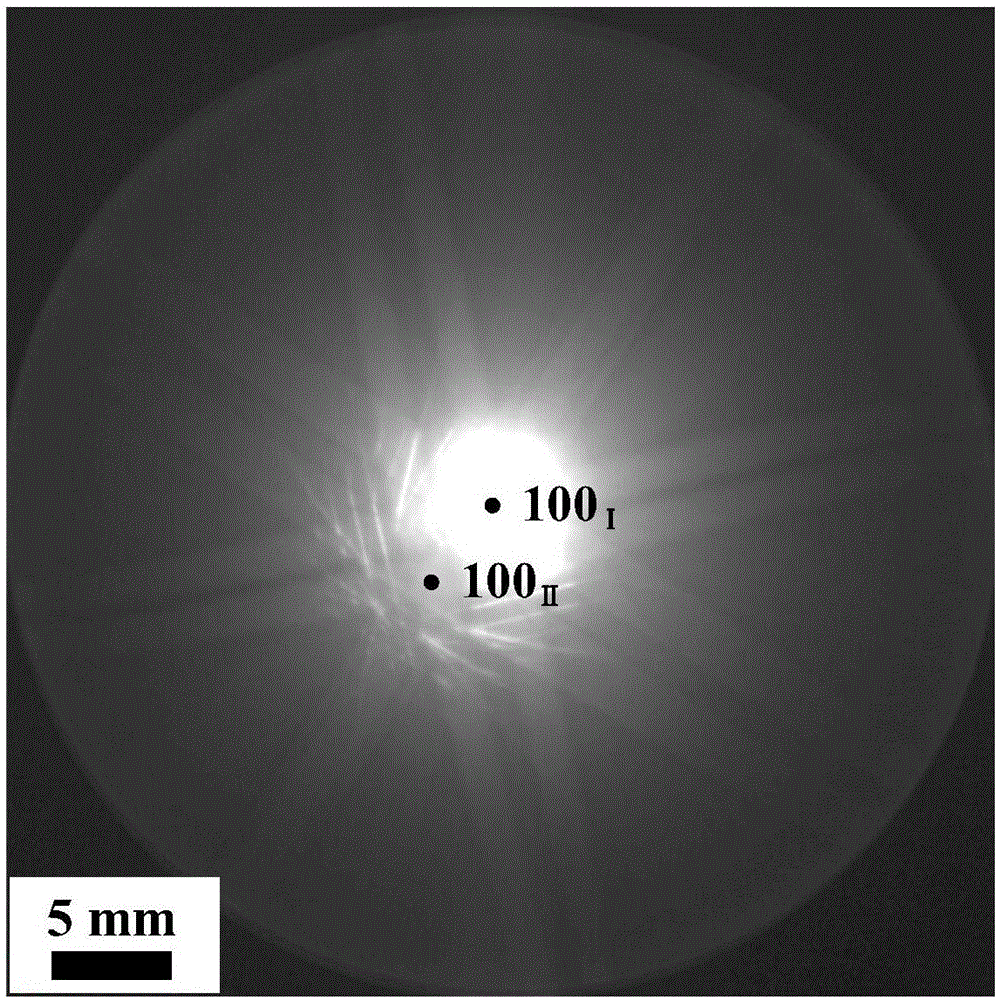
Method for rapidly and accurately measuring low angle grain boundary orientation under transmission electron microscope
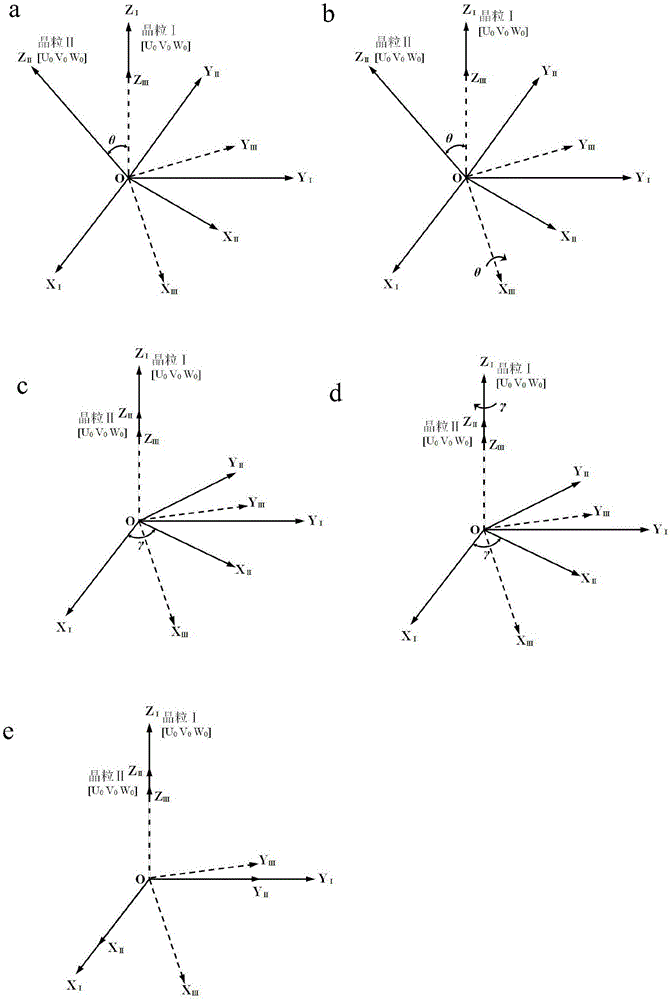
ActiveCN106802306AQuick measurementAccurate measurementMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionConventional transmission electron microscopeKikuchi line
The invention discloses a method for rapidly and accurately measuring low angle grain boundary orientation under a transmission electron microscope. The method comprises the following steps: using a transmission electron microscope double bar-tilting rotation tilting sample, enabling a zone axis of a crystalline grain I in a coordinate system I to be at the position of a positive zone axis, and collecting a convergent beam electron diffraction pattern of the crystalline grain I at the moment; keeping a camera constant L of the transmission electron microscope and the parameter of the convergent beam diffraction condition unchanged, and collecting a convergent beam electron diffraction pattern of a crystalline grain II in a coordinate system II; superposing a kikuchi pattern of the collected crystalline grain I and a kikuchi pattern of the collected crystalline grain II by using software; measuring the distance S between a kikuchi pole of the crystalline grain I and a kikuchi pole of the crystalline grain II as well as the rotation angle gama of the kikuchi pole of the crystalline grain II vertical to the pattern surface relatively to the kikuchi pole of the crystalline grain I; calculating the angle theta according to the geometric characteristic of the kikuchi line, theta=arctan(s / L)=s / L; using a formula (6) cos theta=(cosgama+cosgamacostheta+costheta-1) / 2 to calculate the orientation of the crystalline grain I and the crystalline grain II. The method does not need the additional installation of hardware and software, and the common transmission electron microscope is used to measure the orientation.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Method and system for scanning non-overlapping patterns of laser energy with diffractive optics
InactiveUS20020111606A1Improve uniformityFacilitates dosage controlLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsBeam expanderLight beam
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Image sensing apparatus
InactiveUS20090147321A1Solid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansLight beamOptoelectronics
An image sensing apparatus having a large depth of focus (DOF) and being compact in size is provided. The image sensing apparatus includes a plurality of light sources that shines light beams on an illumination portion of a document; a first mirror that receives incident light scattered by reflection from the document, to reflect the scattered light in the secondary scan direction; a plurality of first concaved aspheric mirrors that collimates light beams from the first mirror, to reflect therefrom the collimated light beams as substantially collimated light fluxes; an aperture mirror that reflects therefrom the light beams from the respective first aspheric mirrors, through apertures each having a light-shielded portion formed therearound and selectively passing the light beams therethrough; a plurality of second concaved aspheric mirrors that receives the light beams incident from the respective aperture mirror, to reflect the incident light beams as converging light beams; a second mirror that reflects the light beams in a direction perpendicular to the surface of the document, disposed on a path of the light beams to be converged by means of the second aspheric mirrors; a plurality of light receivers each having a light-receiving area that receives the light beams from the second mirrors, to form images according to the light beams from the respective apertures; and a casing where the first and second aspheric mirrors are disposed on a first side of the casing in the secondary scan direction, and the aperture mirror is disposed on a second side thereof in the secondary scan direction.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Diffractometer
ActiveUS20050195941A1Quick fixAfter-treatment apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiffractometerMonochromator
A monochromator 4 is used to direct X-rays from X-ray source 2 onto a sample 14 as a convergent beam. The sample 14 is in a growth chamber. The sample is rotated, and diffraction measurements are made in parallel with multichannel detector 22. A specific reflection is used so that the intensity against angle graph measured in the multichannel detector gives information about the vertical lattice parameter. To compensate for wobble inevitably introduced by the rotation of the sample, short time measurements are made and summed.
Owner:PANALYTICAL BV
Wind Vector Field Measurement System
ActiveUS20180246138A1Improved Energy HarvestingGood prospectsWind motor controlMachines/enginesBuoyWind field
A three-dimensional wind vector field measurement system employs convergent beams for localised velocity measurement enabling mapping of the wind field across an extended spatial region. This enables characterisation of complex field signatures. This enables advanced control and protective systems for wind turbines. This also enables improved wind harvesting. This also enables improved prospecting. This also enables improved equipment selection. Buoy mounted systems enable measurement in an offshore environment.
Owner:WIND FARM ANALYTICS
Scanning electron microscope and method of imaging an object by using the scanning electron microscope
InactiveUS7888640B2High resolutionGood reproducibilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesBeam sourceRadiology
A scanning electron microscope capable of modifying the focal position of a condenser lens with high speed and high reproducibility in order that low-magnification images are obtained at large depths of focus and that high-magnification images are obtained at high resolution. The microscope has a specimen-holding portion, an electron beam source, a condenser lens for converging the electron beam, an objective lens for focusing the converged beam into a very small spot onto a specimen, scan coils, a detector for detecting a specimen signal emanating from the specimen, and a display portion for displaying the detected specimen signal as an image. An axisymmetric electrode is disposed within the magnetic field produced by the condenser lens. A voltage is applied to the electrode.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Off-axis three-mirror prepositive optic system
ActiveCN105467569AReduce manufacturing difficultyReduce development costsOptical elementsLight beamOptoelectronics
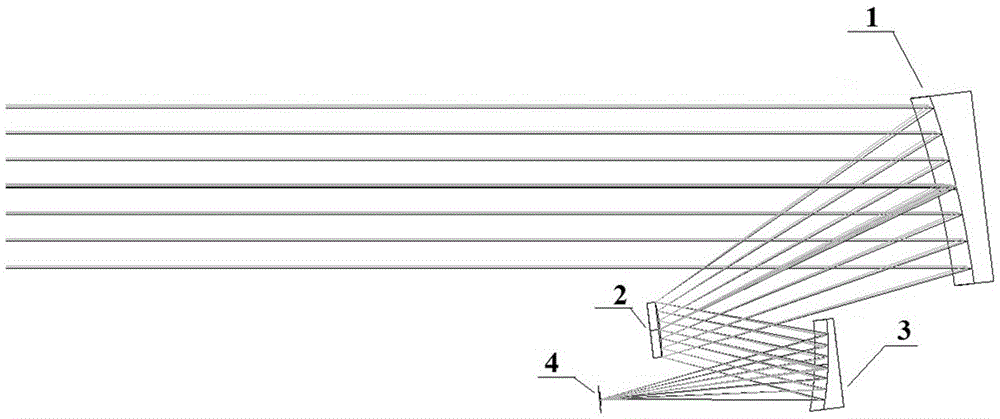
The invention discloses an off-axis three-mirror prepositive optic system, which is a reflective prepositive optic system applied to a spectral imager. The structure of the system is as follows: in an incident light direction, light is reflected via a main mirror and then forms a convergent beam, the convergent beam is incident to a secondary mirror, the convergent beam is then reflected via the secondary mirror and is then incident to a three-mirror, and the three-mirror converges the beam for imaging; the main mirror is an aspheric concave mirror with a curvature radius of 147.59 to 149.59 mm and a secondary curve coefficient of -1.52 to -1.53; the secondary mirror is a convex spherical mirror with a curvature radius of 41.6 to 42.6 mm; and the three-mirror is a concave spherical mirror with a curvature radius of 56.4 to 56.7 mm. The system of the invention has the advantages that the structure is simple, the making difficulty and the making cost are low, assembling and adjustment are easy and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com