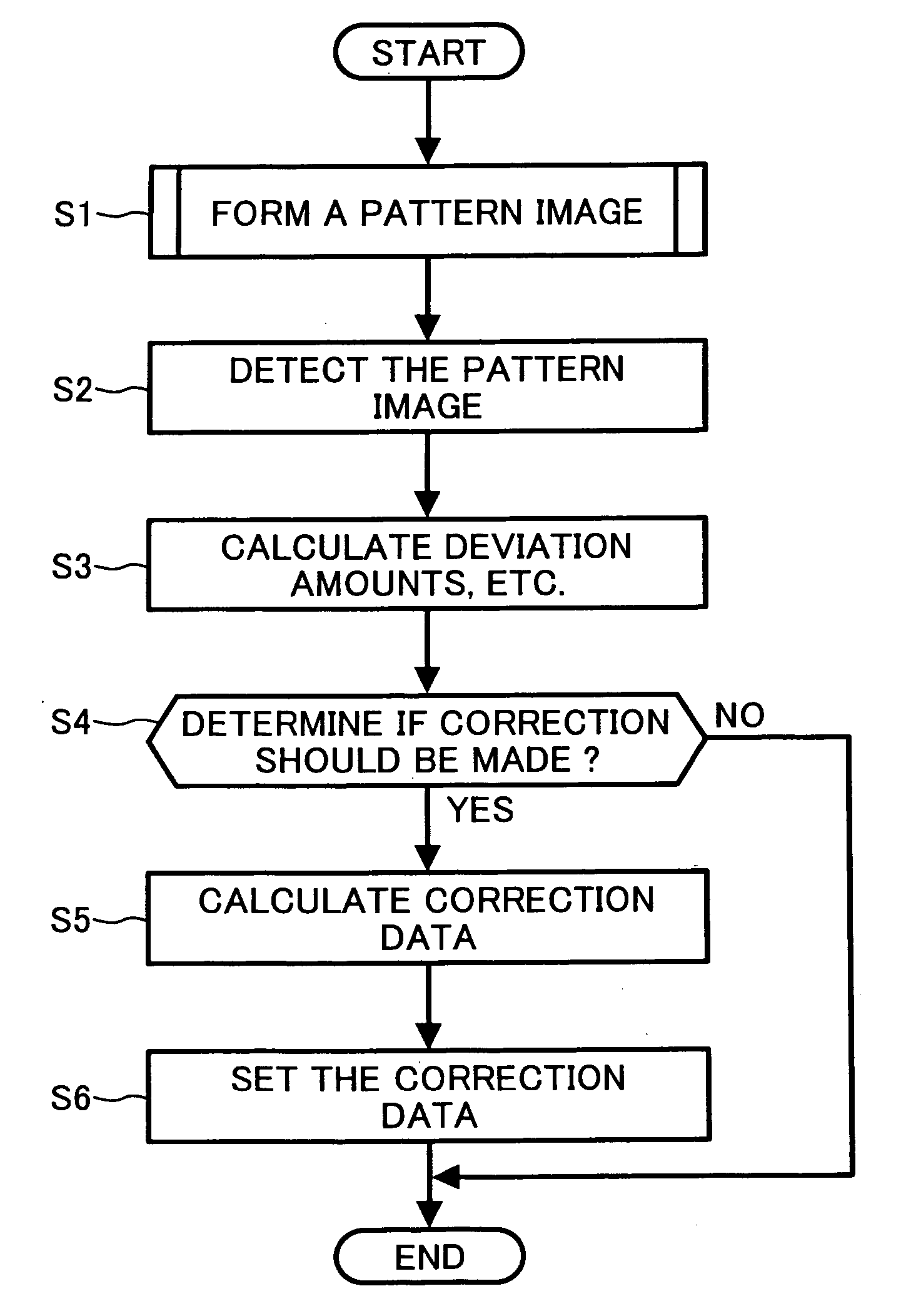
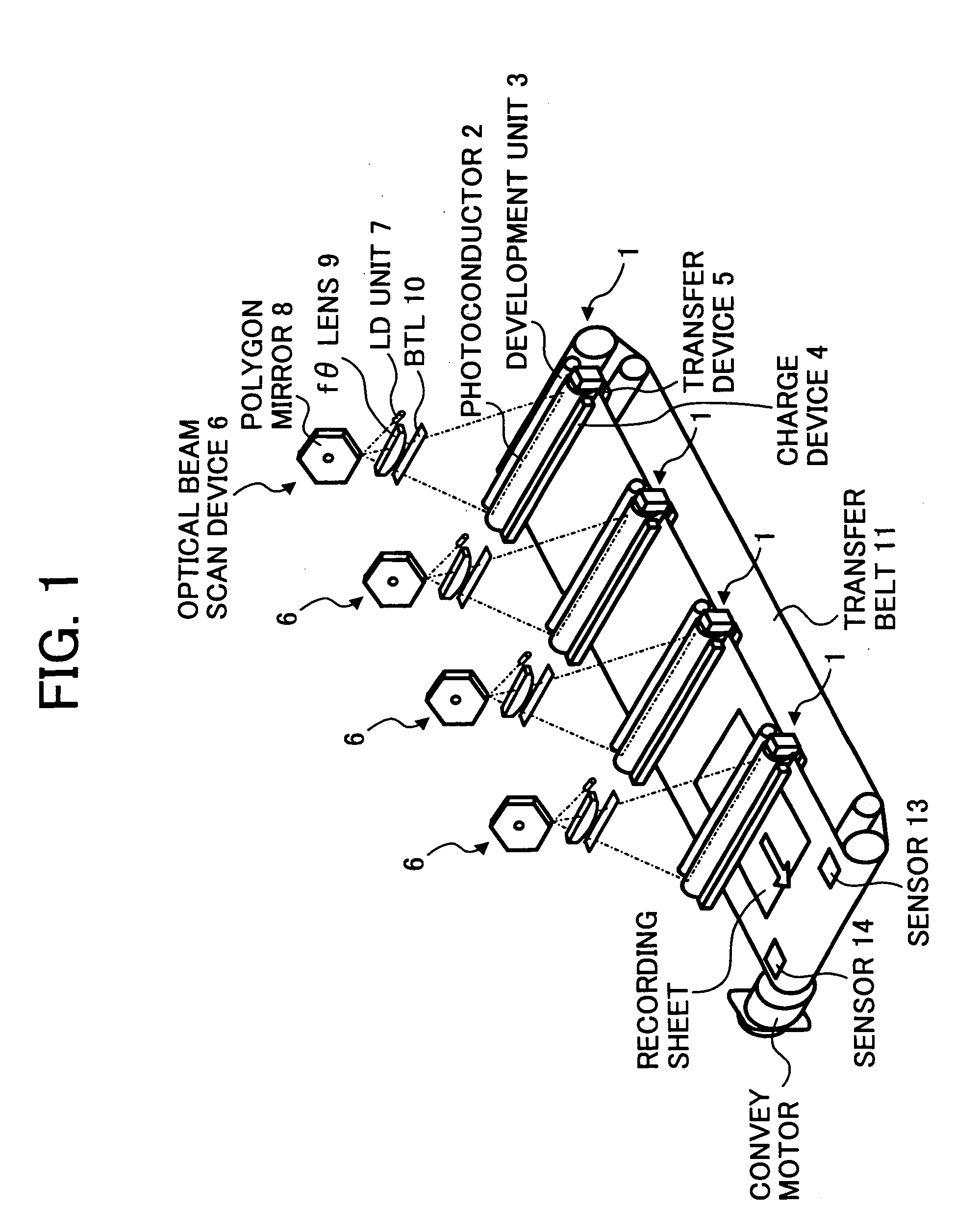
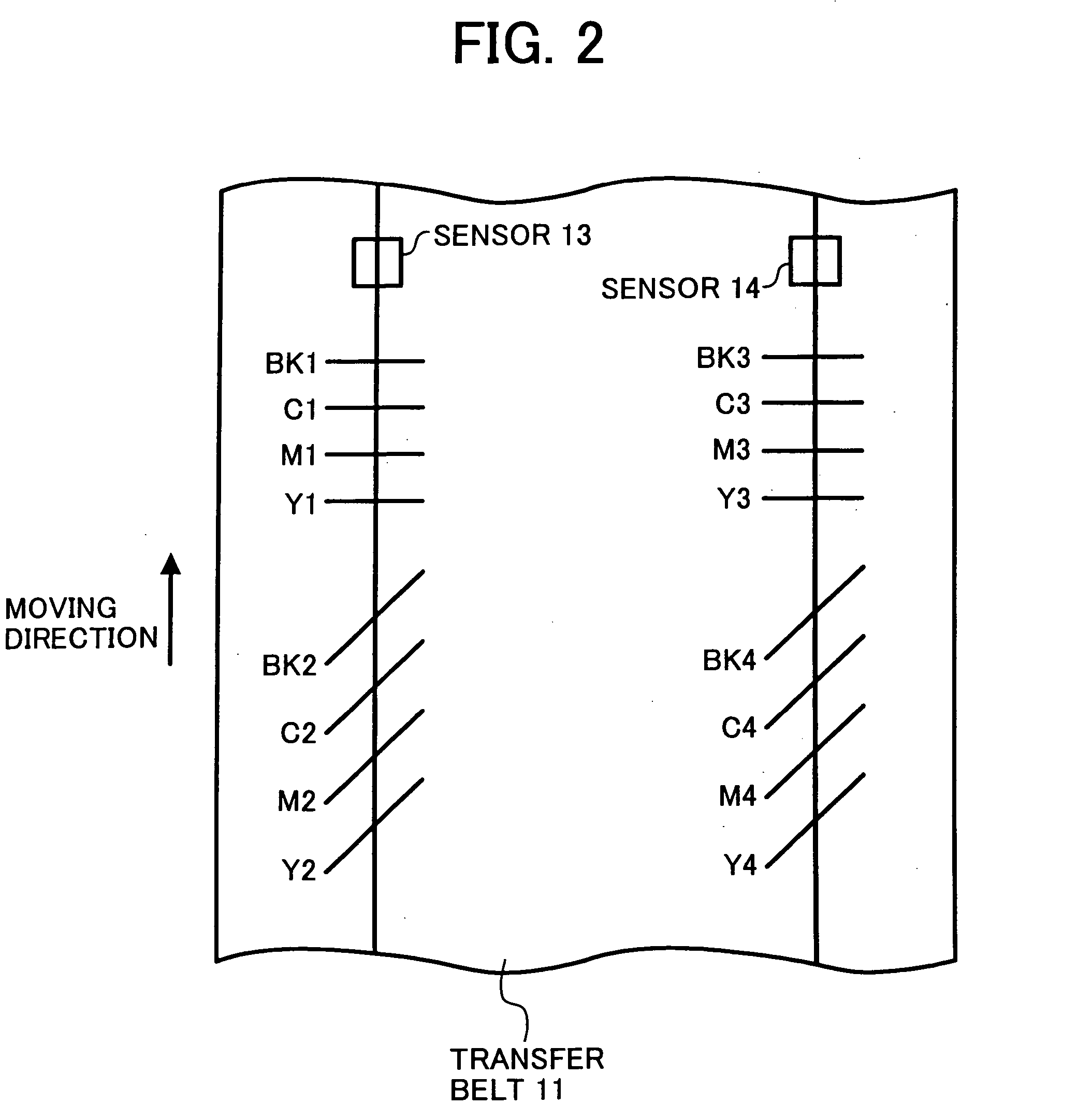
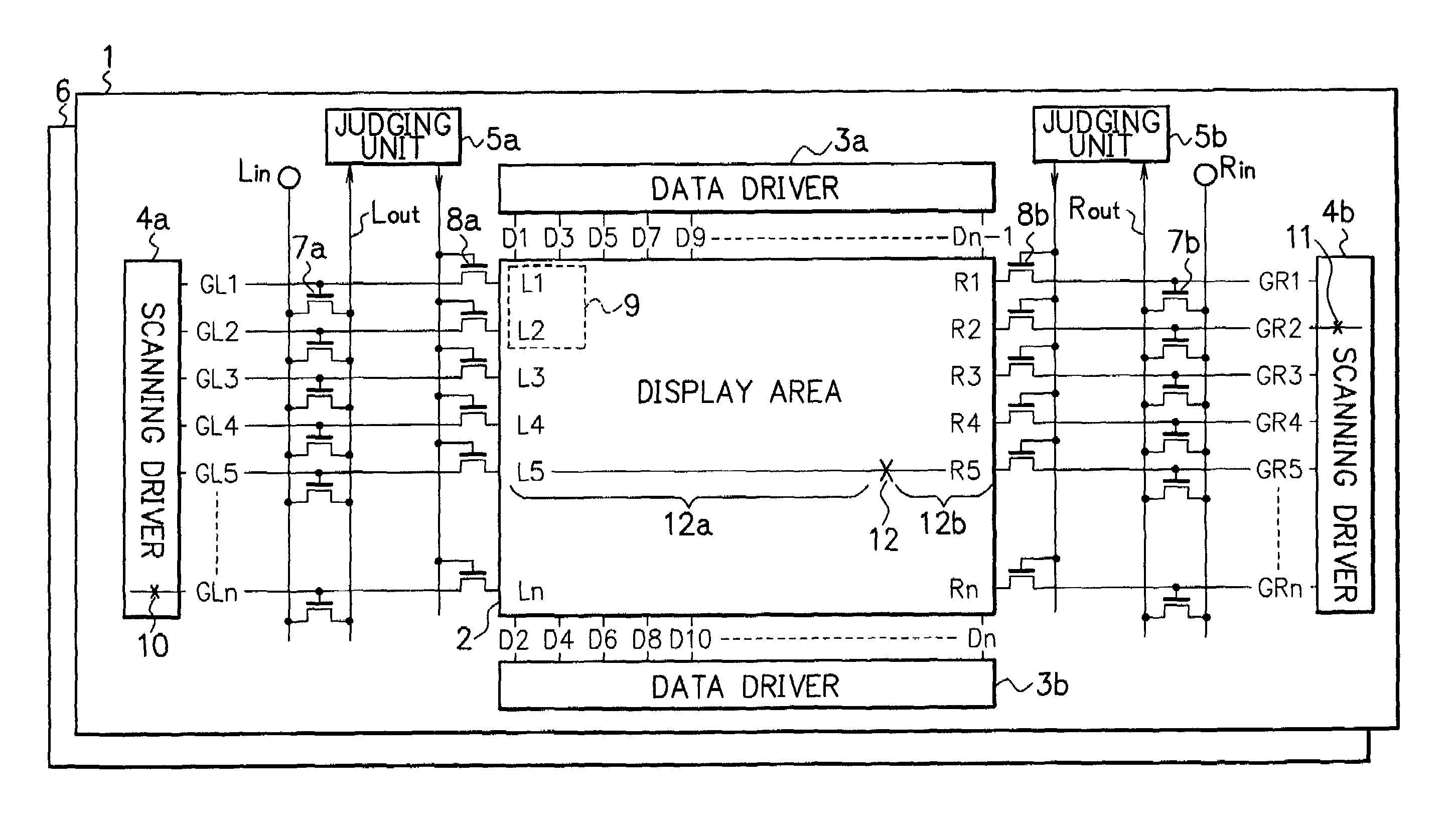
Patents
Literature
163results about How to "Reliable calibration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
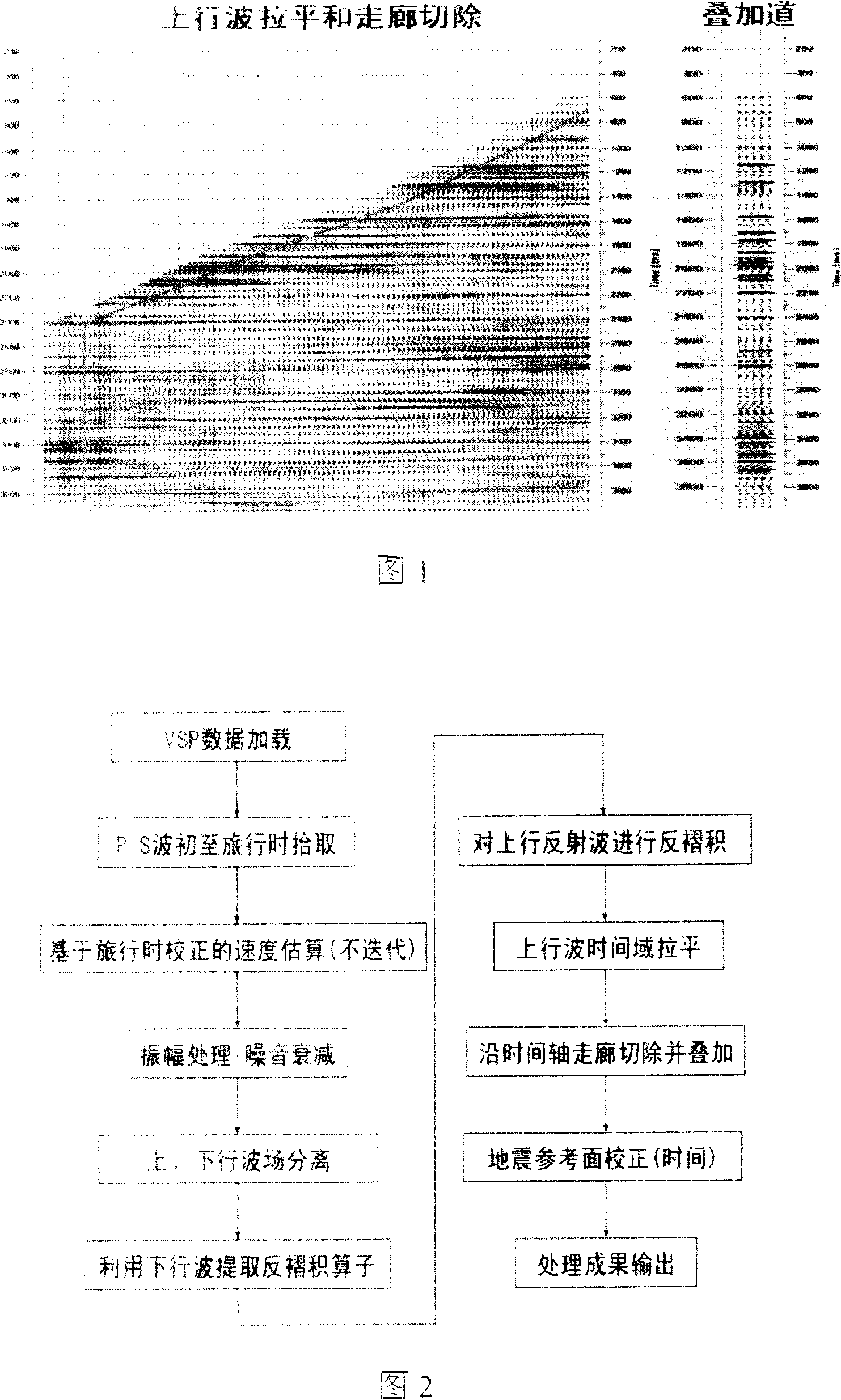
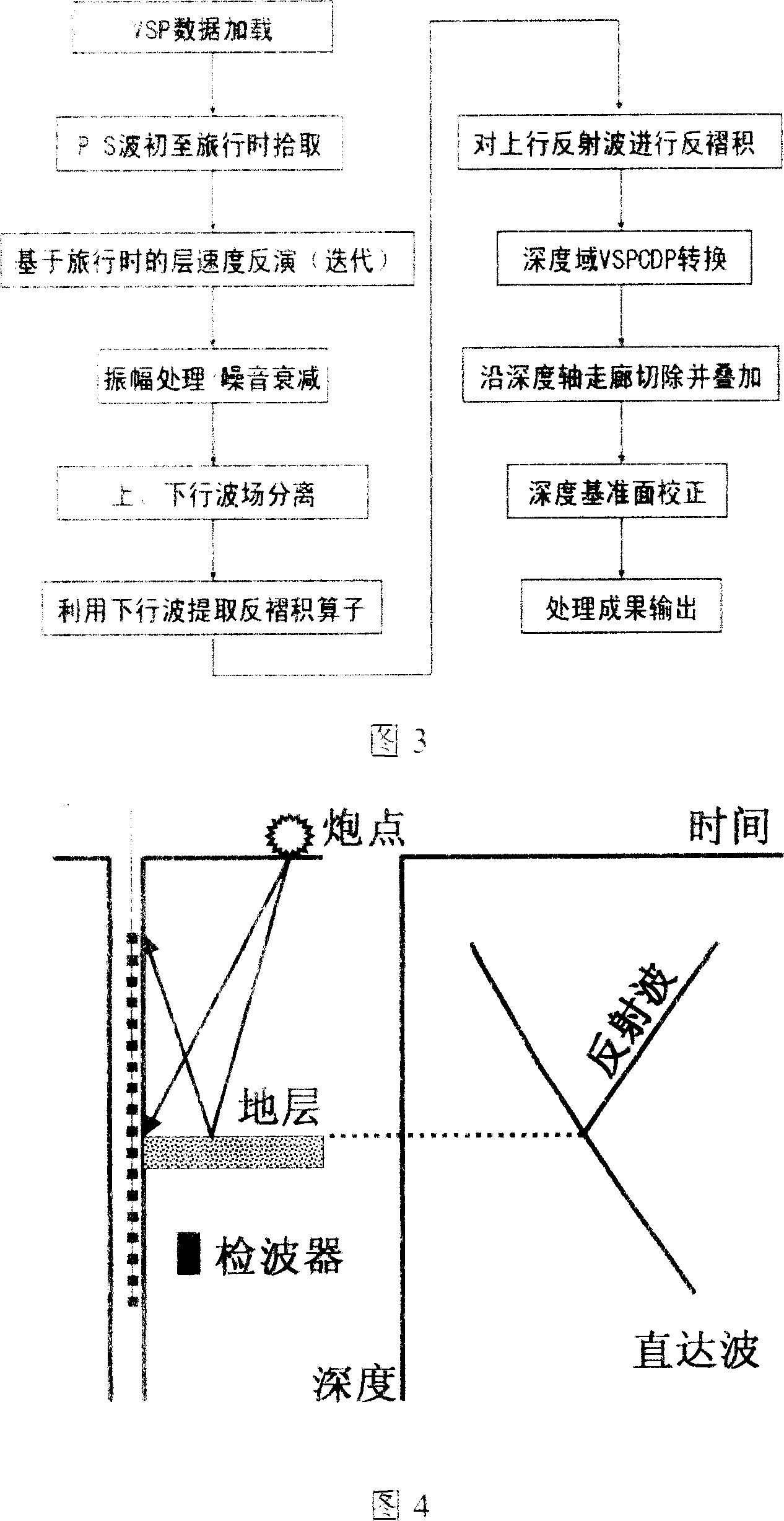
Zero hypocentral distance vertical seismic section compressional-shear wave data depth field corridor stacked section processing method
Geophysical exploration for oil wells, the source from the vertical seismic profile aspect wave data stack depth domain Corridor profile approach is the use of in situ collection of well spacing VSP data, which will all receive points drilling depth of information and hierarchical data with the depth of information, the use of direct wave VSP data travel through and optimization algorithms are highly accurate anti-layer velocity model, the direct wave to the beginning of the reflected wave in the vicinity of the depth and precision homing imaging, further in-depth domain Corridor section and with the superposition of alternative conventional method leveled in the time domain, with corridors and the superposition method, the results can be superimposed for direct comparison with the drilling and seismic data stratified layer identification. More intuitive, but also made full use of VSP data in the depth of information, make geological formation of the earthquake response and drilling, logging data in depth domain direct contrast, a more intuitive geological layer and the relationship between seismic horizon, thereby enabling layer of identification and calibration more reliable.
Owner:BGP OF CHINA NAT GASOLINEEUM CORP
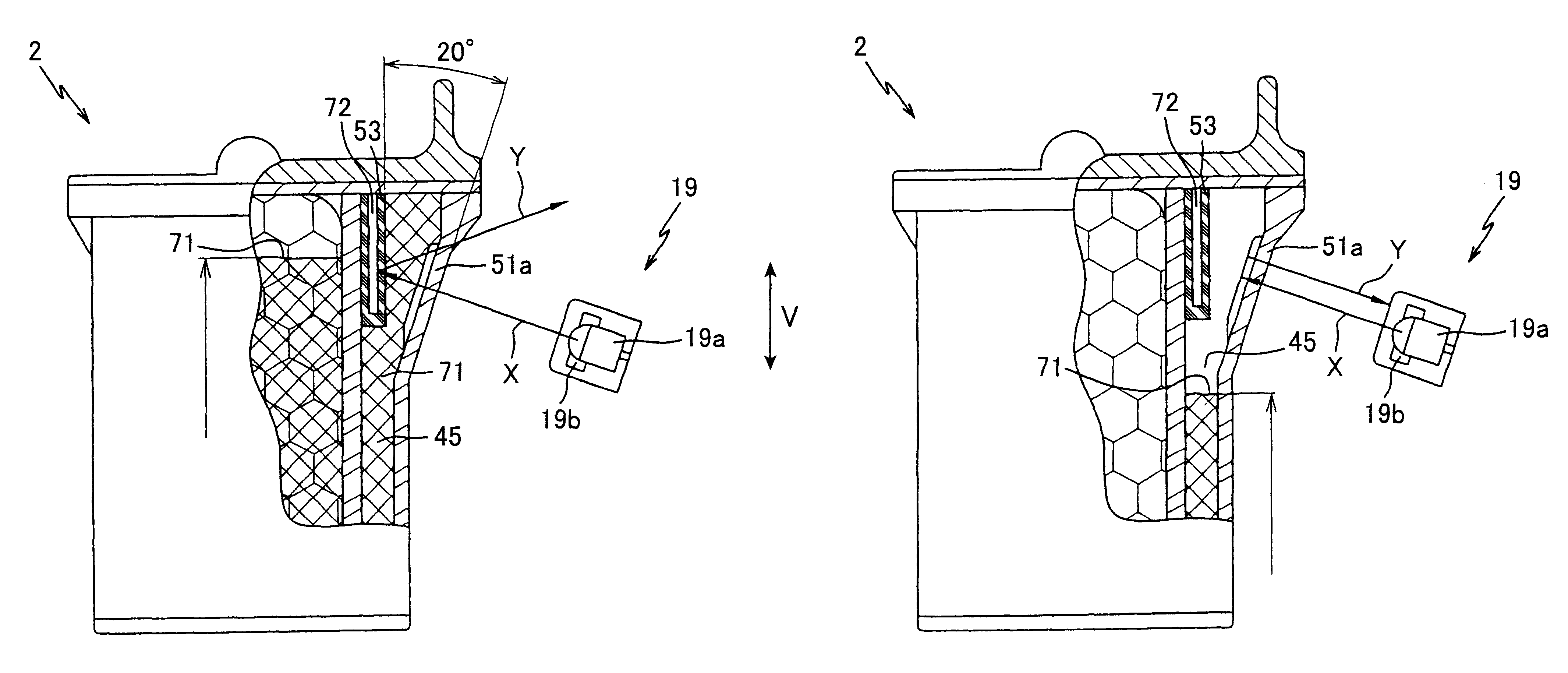
Image forming device capable of detecting existence of ink and ink cartridge with high accuracy
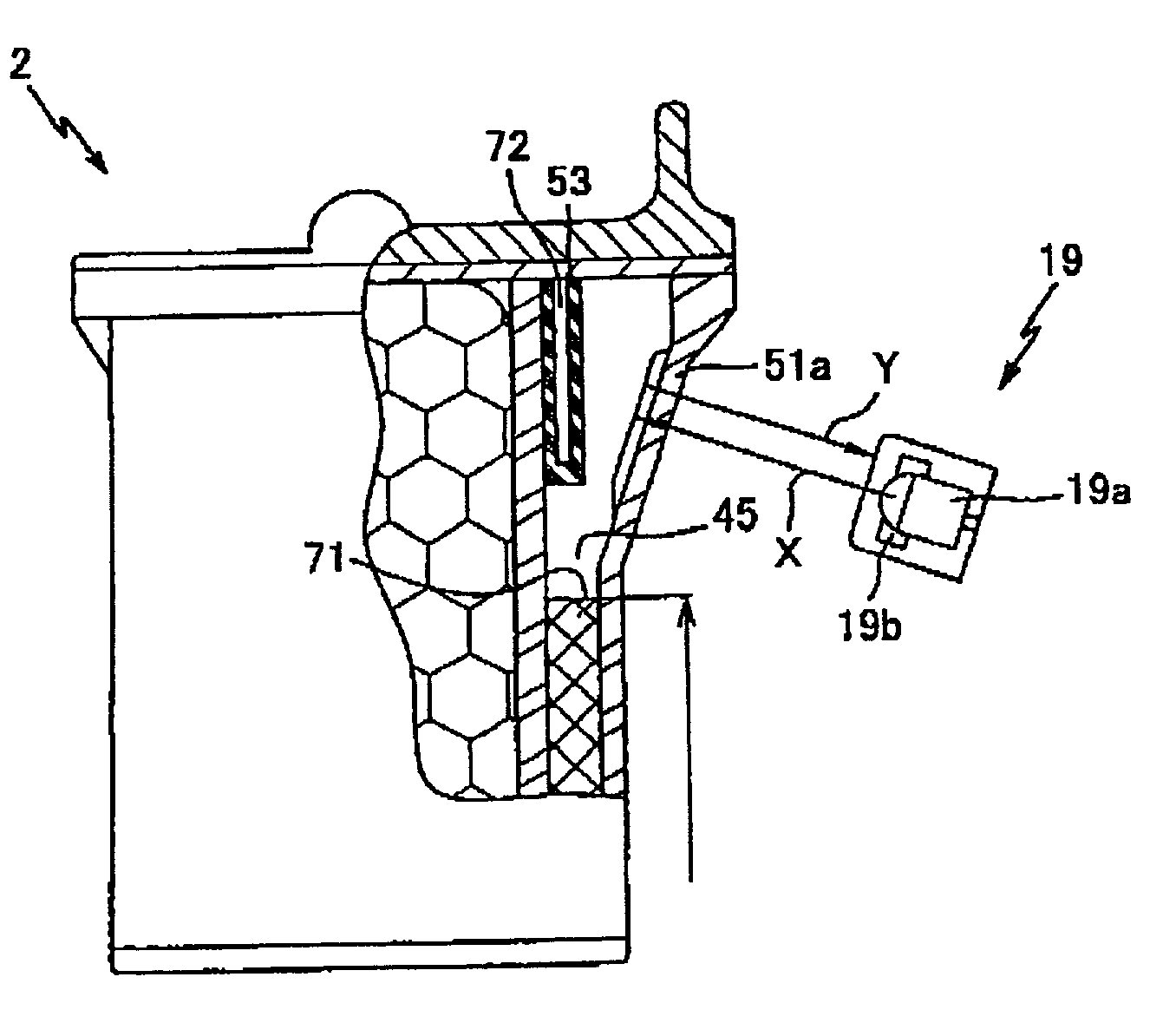
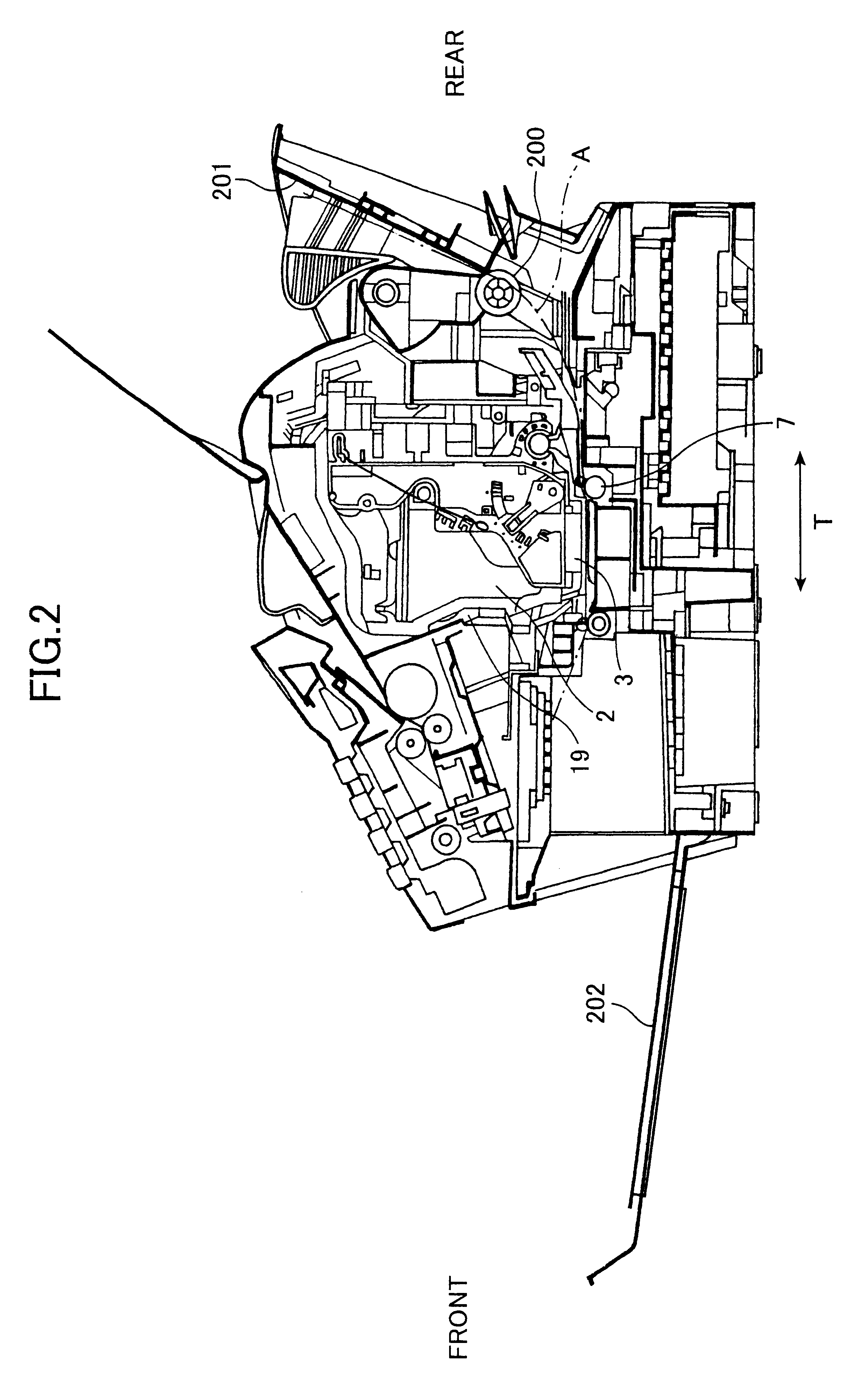
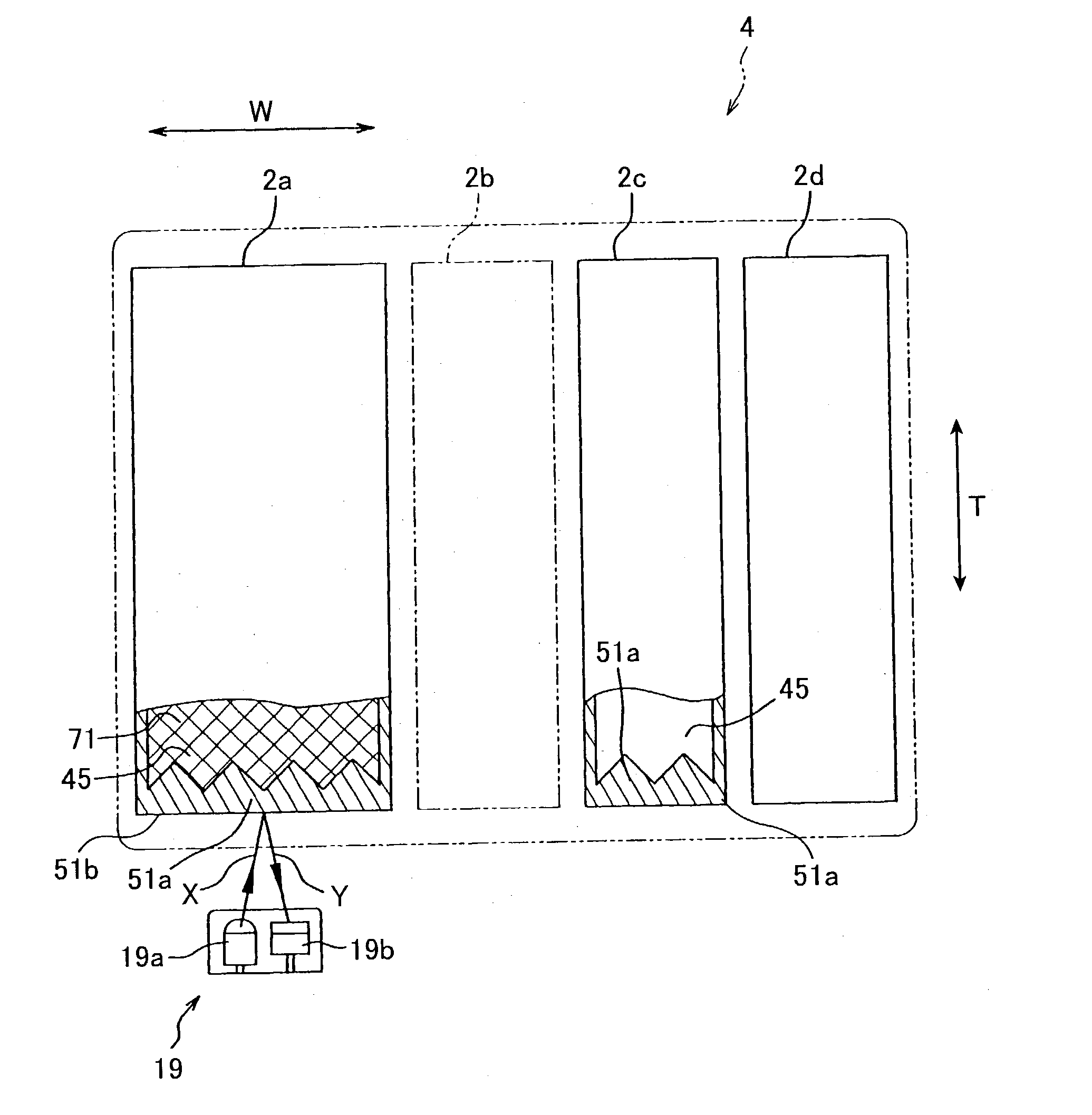
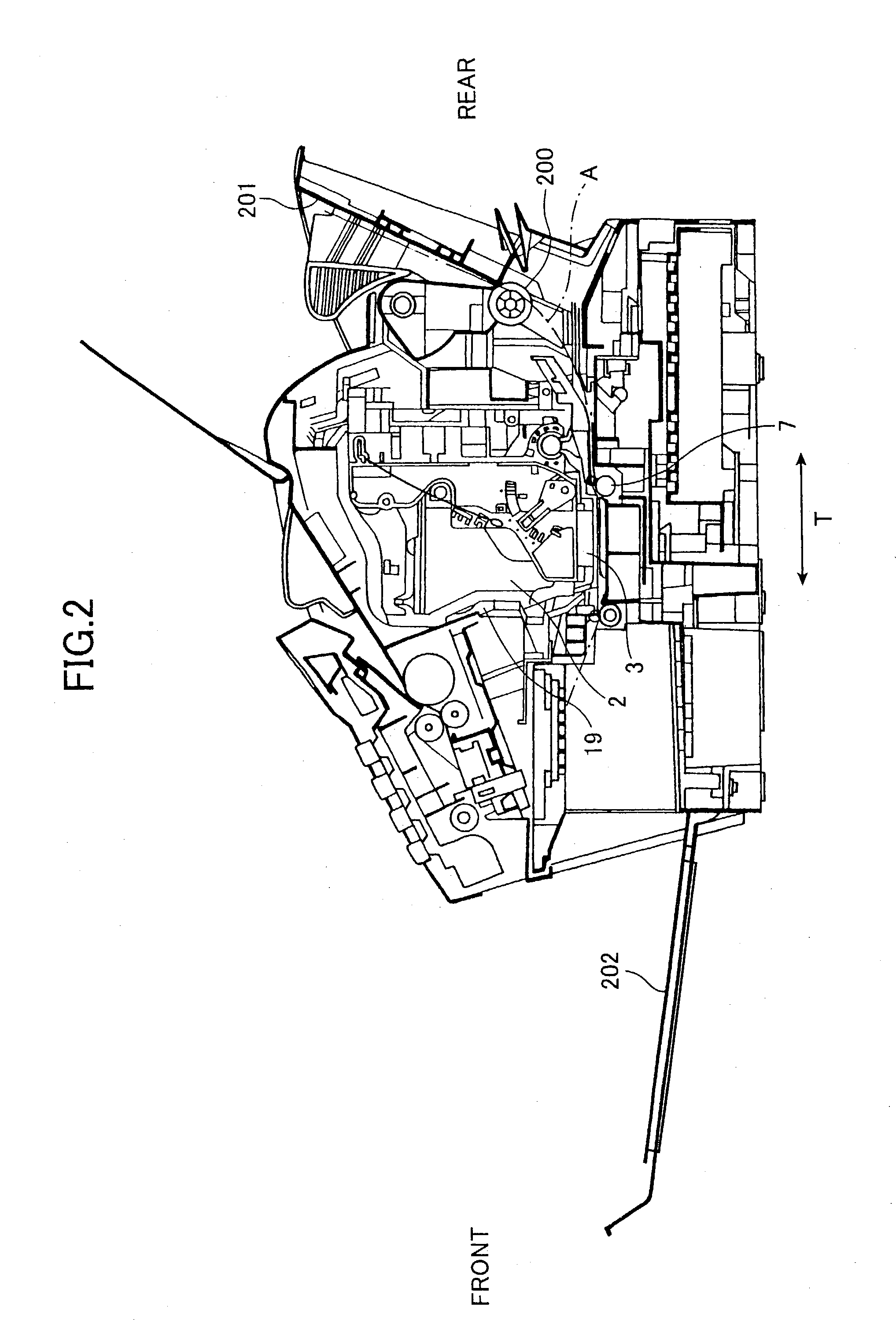
In a calibration data input process, a carriage 5 is moved toward an ink sensor 19 to a prescribed position while the ink sensor 19 detecting levels of reflected light. Then the amount of reflected light is read for over a range wider than the width of the carriage 5 including a theoretical detecting position P2. An actual detecting position P1 is found based on the level of reflected light. The difference between the theoretical detecting position P2 and the actual detecting position P1 is calculated and is stored as the calibration value alpha in a first calibration data memory M1. Accordingly, the actual detecting position P1 is set as P2±alpha. The calibration value alpha is used in a calibration process to calibrate the detecting position, so that the level of reflected light can be detected with accuracy.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
Optical connector
An optical connector for use with a light separator, the optical connector including a first portion and a second portion, the first portion being optically couplable by first optical transmitter to a first input of the light separator and by second optical transmitter to a second input of the light separator. The first and second portions are detachably couplable to couple the first and second optical transmitter to third and fourth optical transmitters, respectively, provided in or coupled to the second portion. The first and second inputs of the light separator can thereby be optically coupled to a first optical instrument coupled to the third optical transmitter and a second optical instrument coupled to the fourth optical transmitter.
Owner:OPTISCAN +1
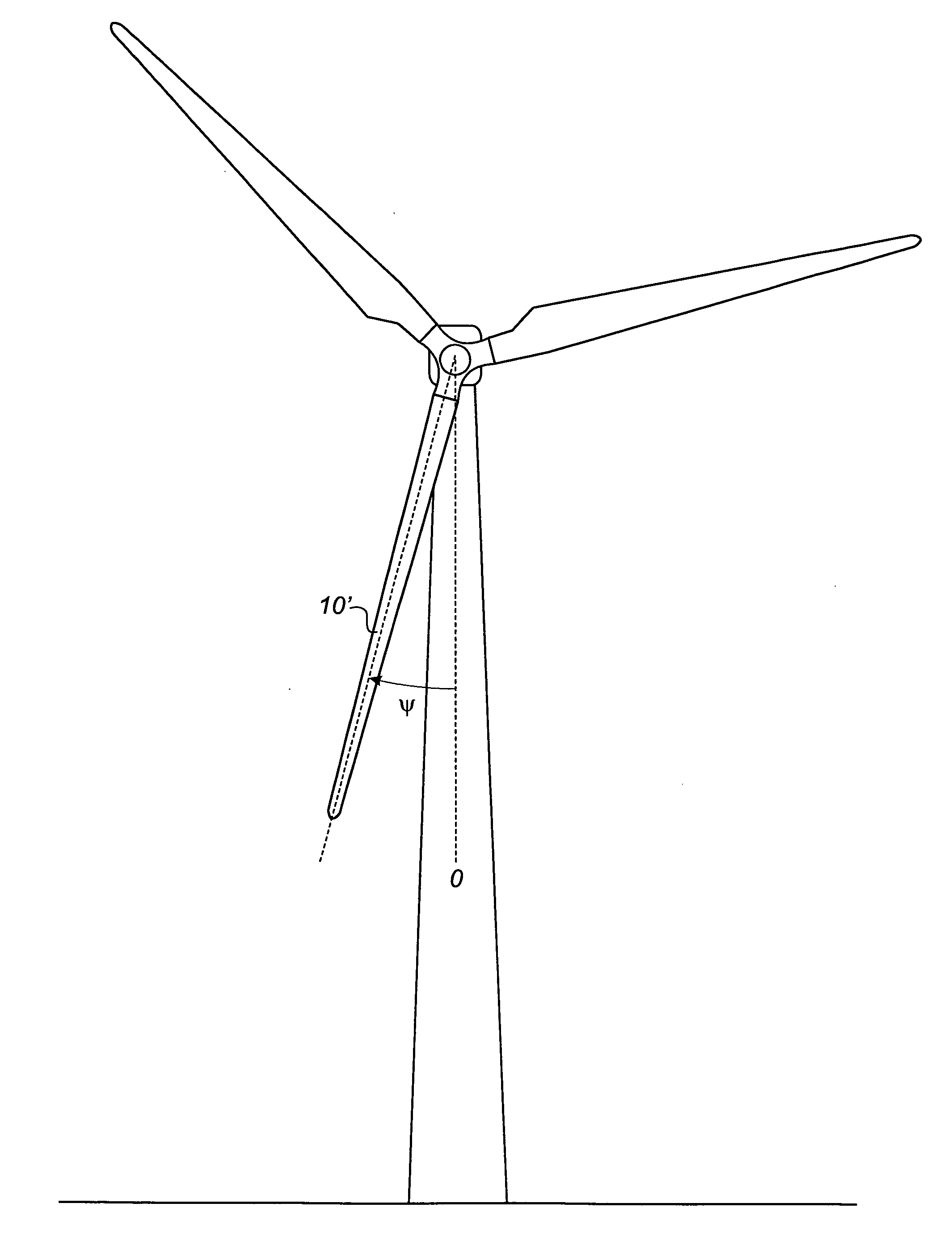
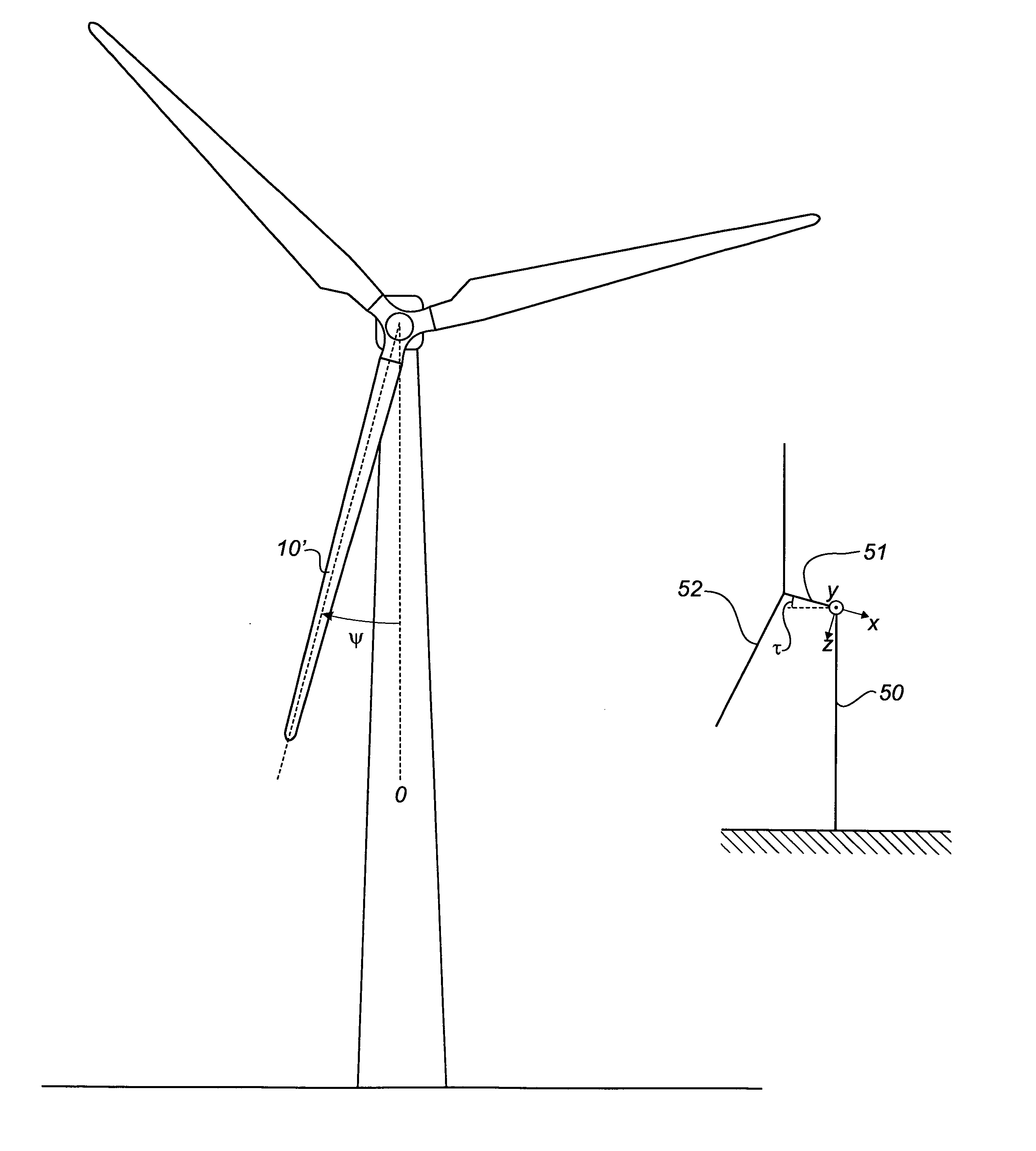
Method of in situ calibrating load sensors of a wind turbine blade
ActiveUS20120292905A1Reliable calibrationReduce needMachines/enginesWind motor combinationsTurbine bladeHorizontal axis
A method of in situ calibrating load sensors of a horizontal axis wind turbine is described. The method comprises the steps of: a) determining a rotor azimuth angle of a first wind turbine blade, b) determining a pitch angle of the first wind turbine blade, c) measuring loads in a first cross-section of the first wind turbine blade using the first load sensors, d) calculating theoretical loads based on at least the rotor azimuth angle and the pitch angle of the blade determined in steps a) and b), e) comparing the loads measured in step c) with the theoretical loads calculated in step d), and f) calibrating the first load sensors based on the comparison of step e), wherein the calibration are based only on measurements carried out, when the generator is cut out.
Owner:LM GLASSFIBER
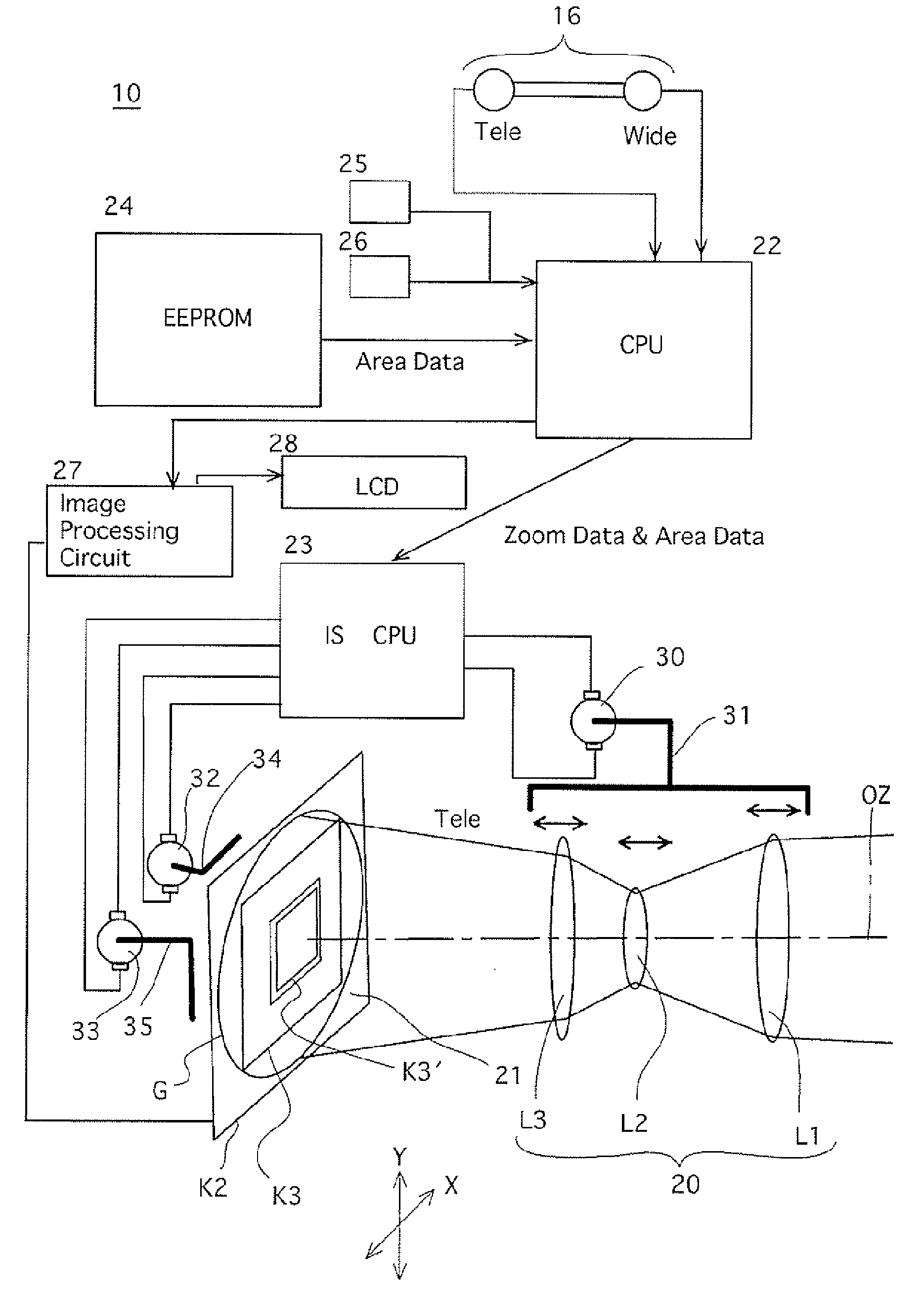
Image stabilizer, and image shake correction method for imaging device
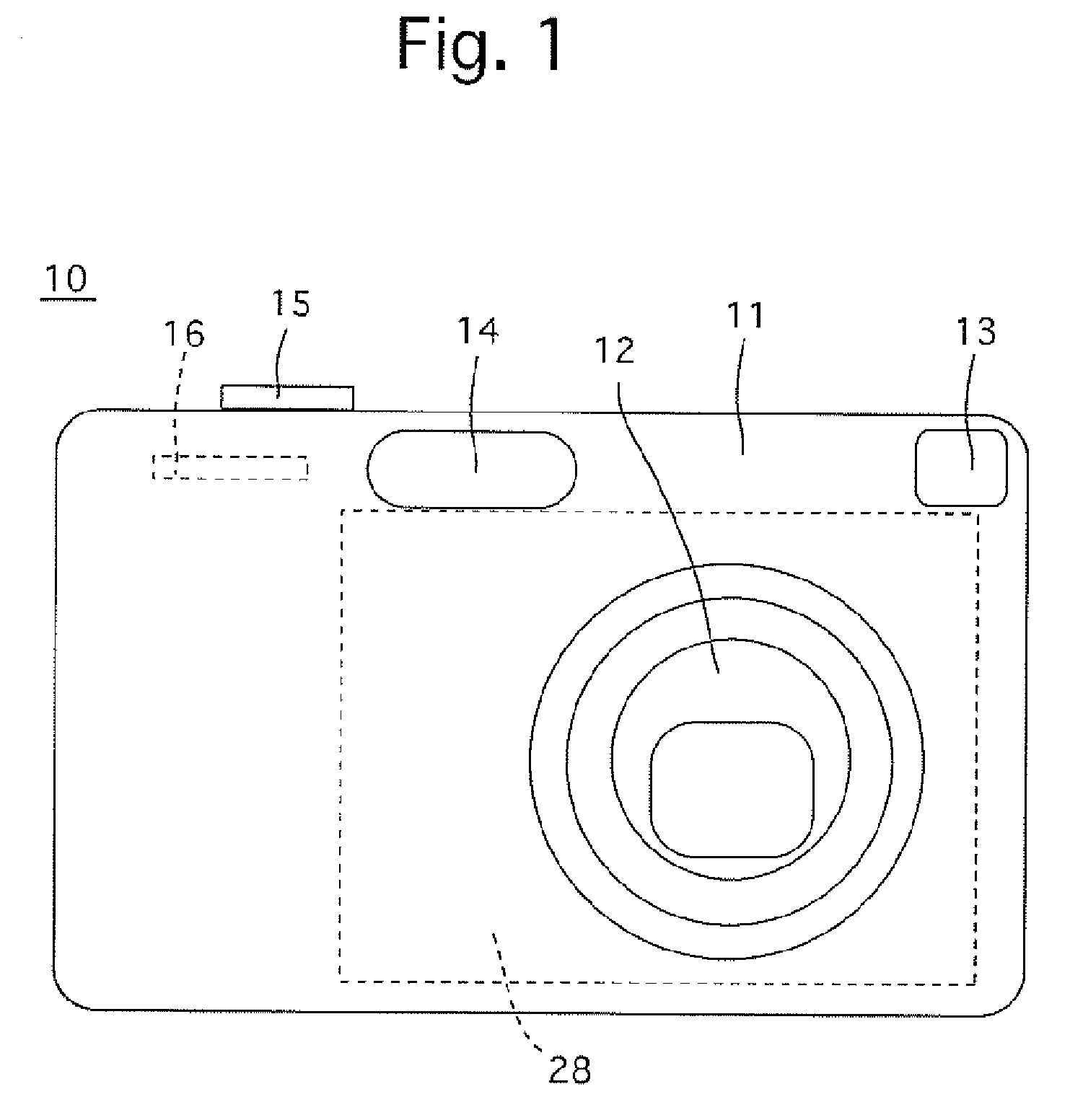
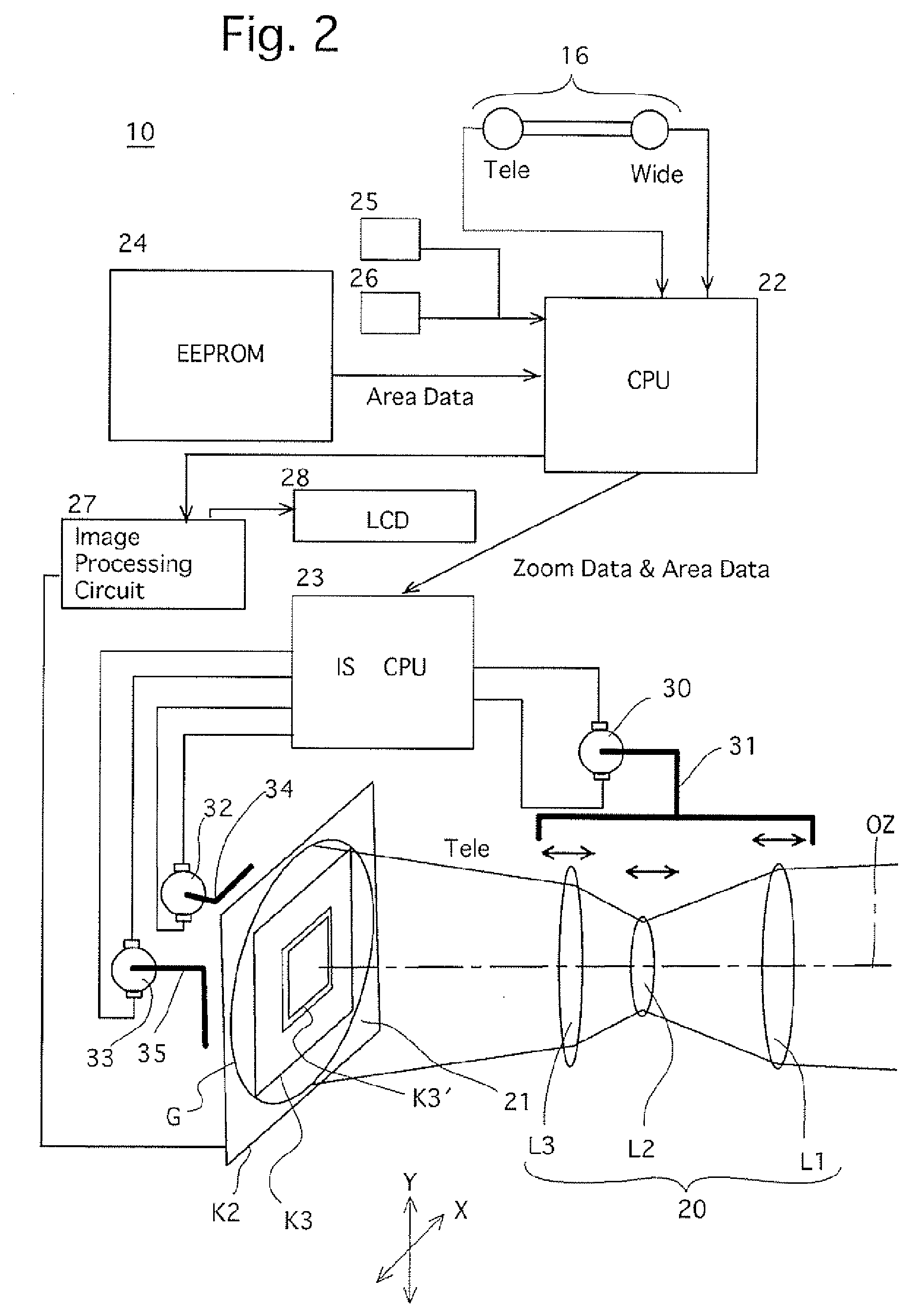
InactiveUS20070097219A1Reliable calibrationExtended range of motionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical axisImage stabilization
An image stabilizer includes an imaging device including an object coverage area changing device for changing an object coverage area, and an image sensor; an image shake correction device which moves a shake correction optical element of the imaging optical system in a plane orthogonal to an optical axis in accordance with a direction and magnitude of vibration applied to the image sensor; a memory, in which area data is prestored, the area data designating changes in relative sizes between an image circle of the imaging optical system and an effective picture area of an imaging surface of the image sensor; and a moving range controller which changes a moving range of the shake correction optical element that corresponds to a change of the object coverage area in accordance with an operating state of the object coverage area changing device based on the area data.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Image forming device capable of detecting existence of ink and ink cartridge with high accuracy
In a calibration data input process, a carriage 5 is moved toward an ink sensor 19 to a prescribed position while the ink sensor 19 detecting levels of reflected light. Then the amount of reflected light is read for over a range wider than the width of the carriage 5 including a theoretical detecting position P2. An actual detecting position P1 is found based on the level of reflected light. The difference between the theoretical detecting position P2 and the actual detecting position P1 is calculated and is stored as the calibration value alpha in a first calibration data memory M1. Accordingly, the actual detecting position P1 is set as P2±alpha. The calibration value alpha is used in a calibration process to calibrate the detecting position, so that the level of reflected light can be detected with accuracy.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
Image forming device capable of detecting existence of ink and ink cartridge with high accuracy
InactiveUS20030210289A1Easy constructionReliable calibrationOther printing apparatusEngineeringData memory
In a calibration data input process, a carriage 5 is moved toward an ink sensor 19 to a prescribed position while the ink sensor 19 detecting levels of reflected light. Then the amount of reflected light is read for over a range wider than the width of the carriage 5 including a theoretical detecting position P2. An actual detecting position P1 is found based on the level of reflected light. The difference between the theoretical detecting position P2 and the actual detecting position P1 is calculated and is stored as the calibration value alpha in a first calibration data memory M1. Accordingly, the actual detecting position P1 is set as P2 ±alpha. The calibration value alpha is used in a calibration process to calibrate the detecting position, so that the level of reflected light can be detected with accuracy.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
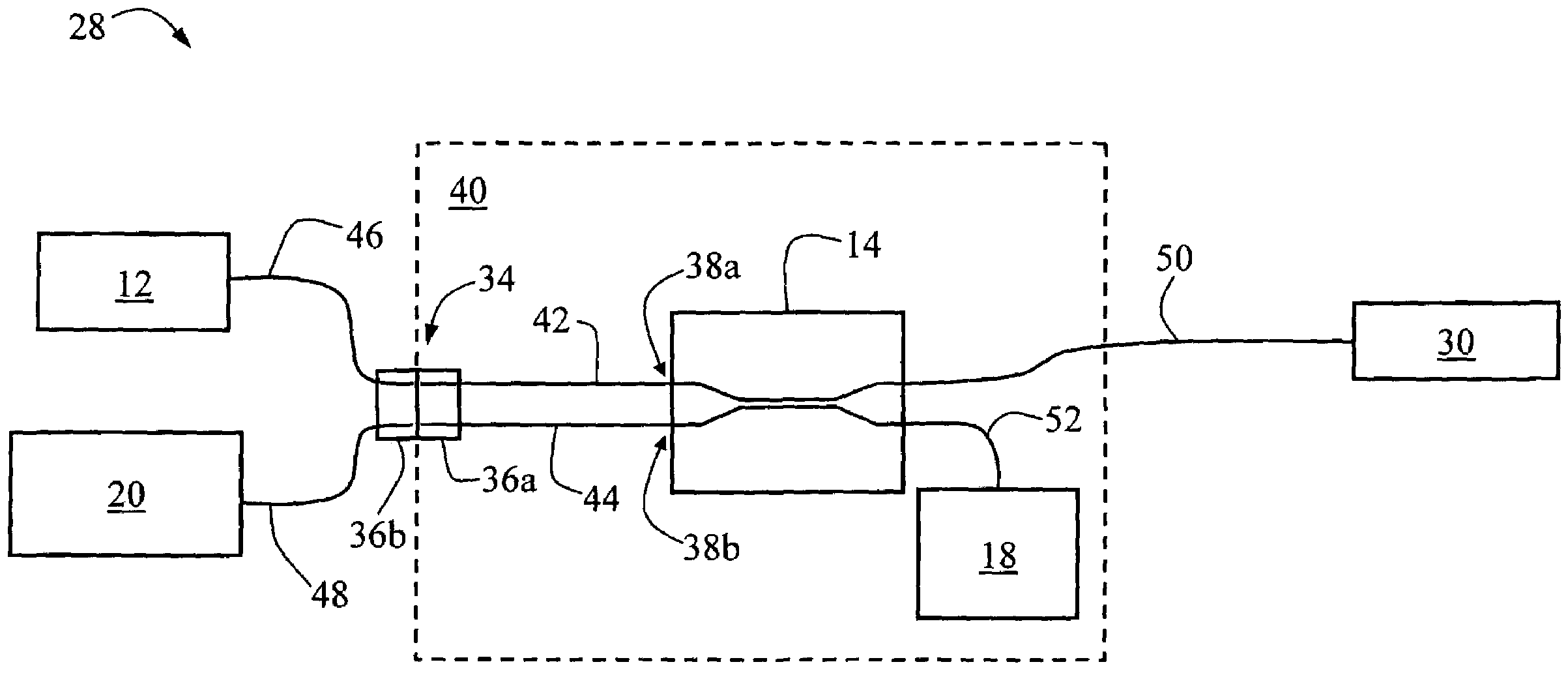
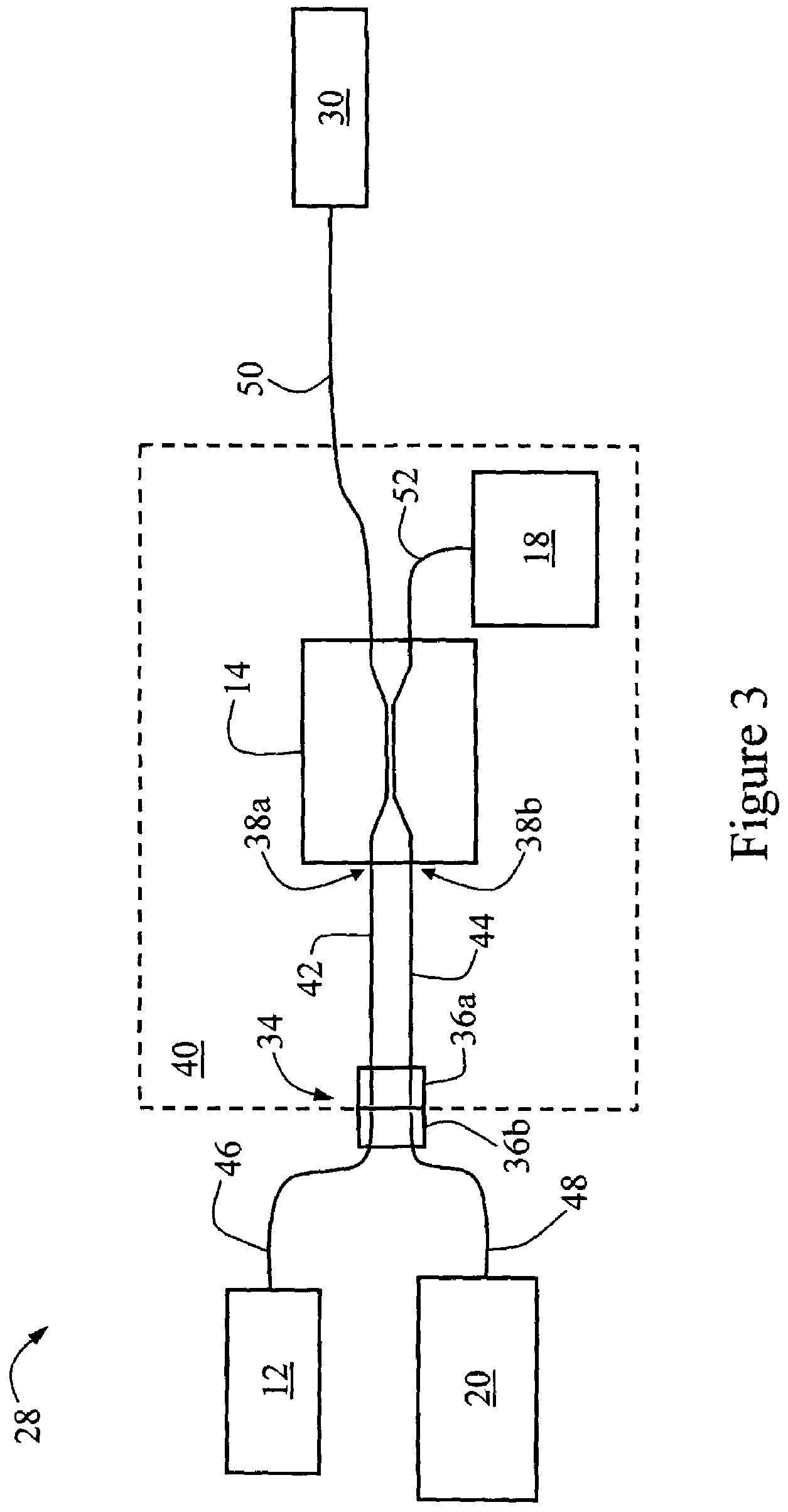
Method for calibrating an image capture device
InactiveUS20140063252A1Reliable calibrationImage enhancementImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Vanishing point
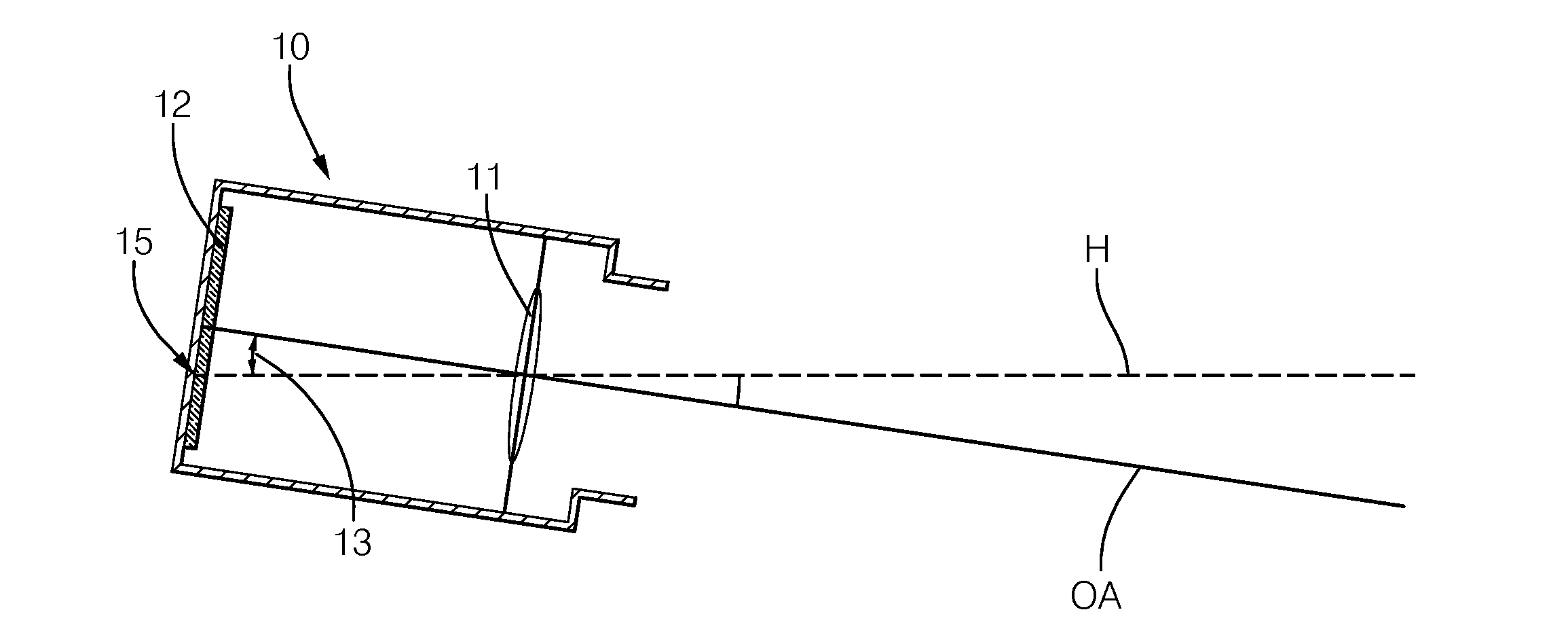
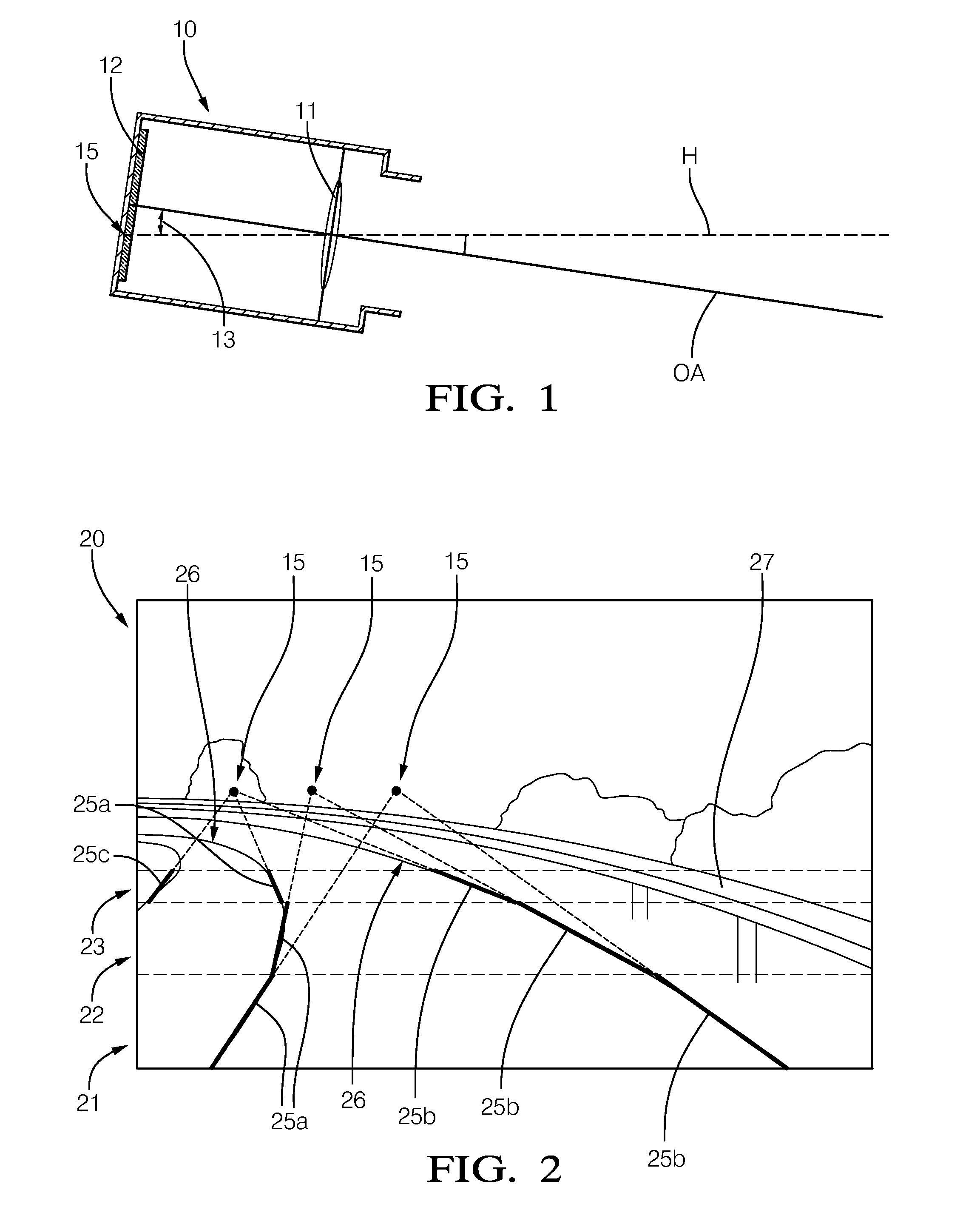
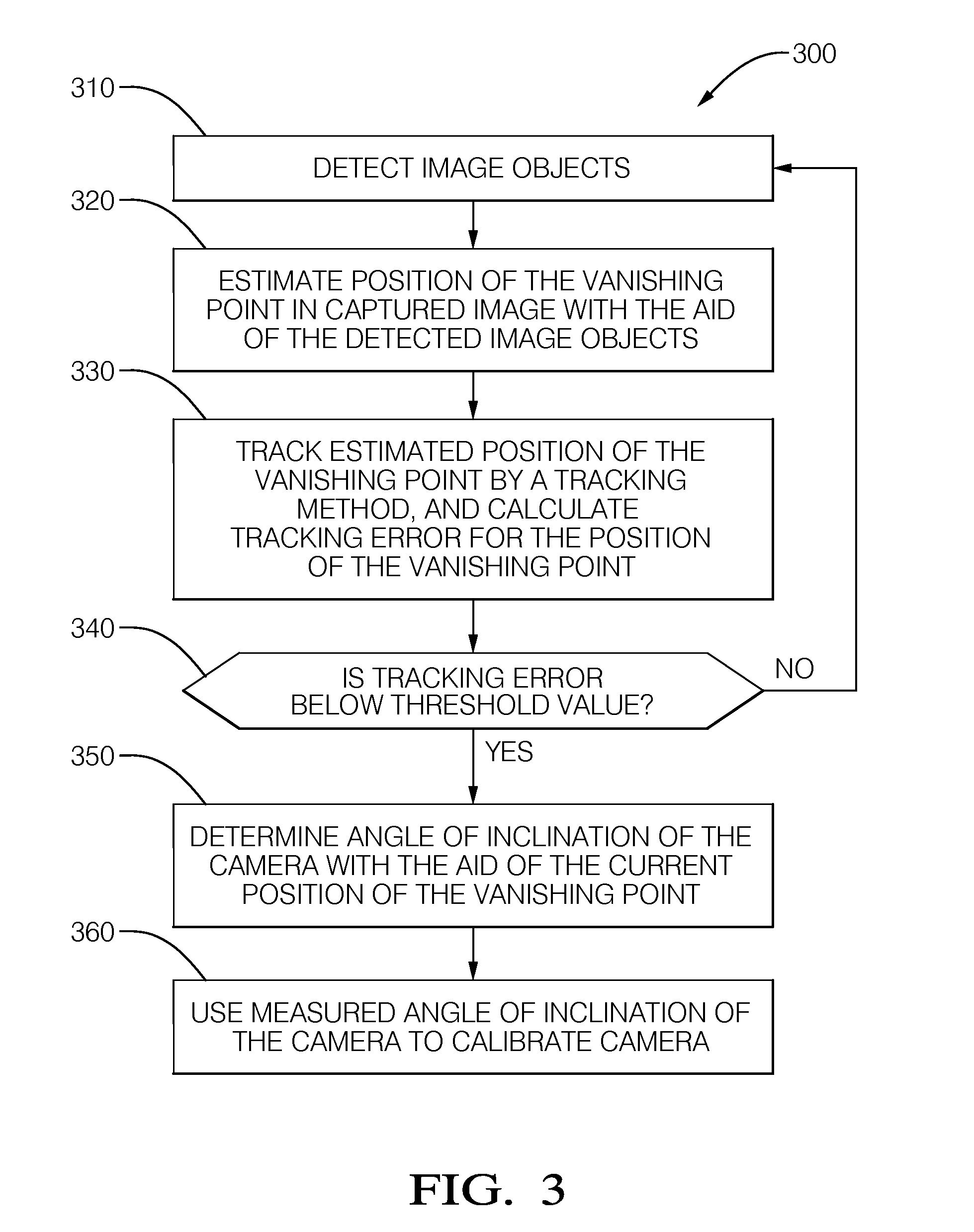
In a method for calibrating an image capture device that is mounted on a motor vehicle and able to successively capture images of a road area located in front of the vehicle, at least two image objects which correspond to line segments which are straight and substantially parallel to each other in world coordinates are detected in a captured image. With the aid of the image objects, the position of a vanishing point in the captured image is estimated and tracked by a tracking method. In the process, an error is calculated for the position of the vanishing point. As soon as the calculated error decreases to less than a predetermined threshold value, the image capture device is calibrated with reference to the position of the vanishing point associated with the error.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
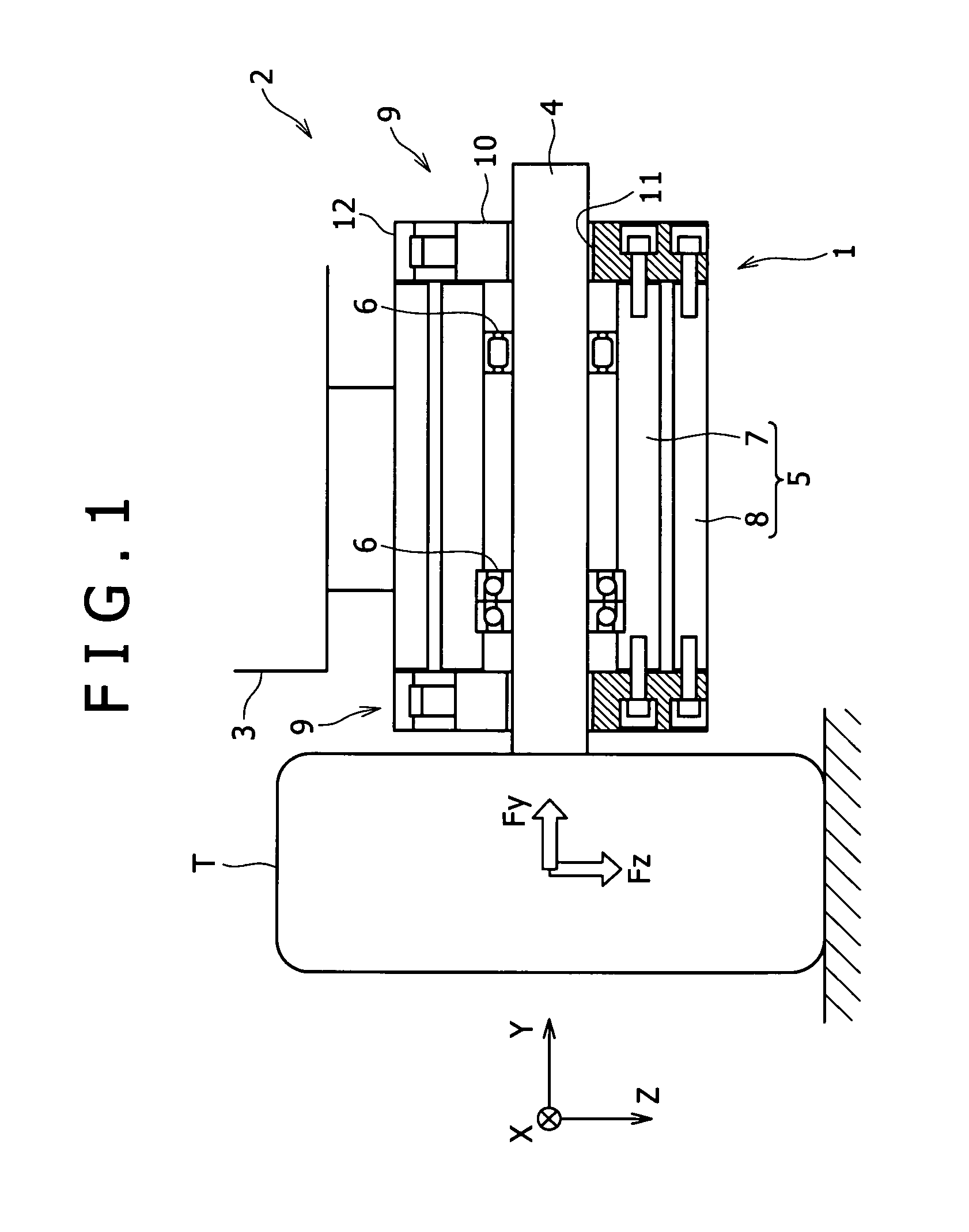
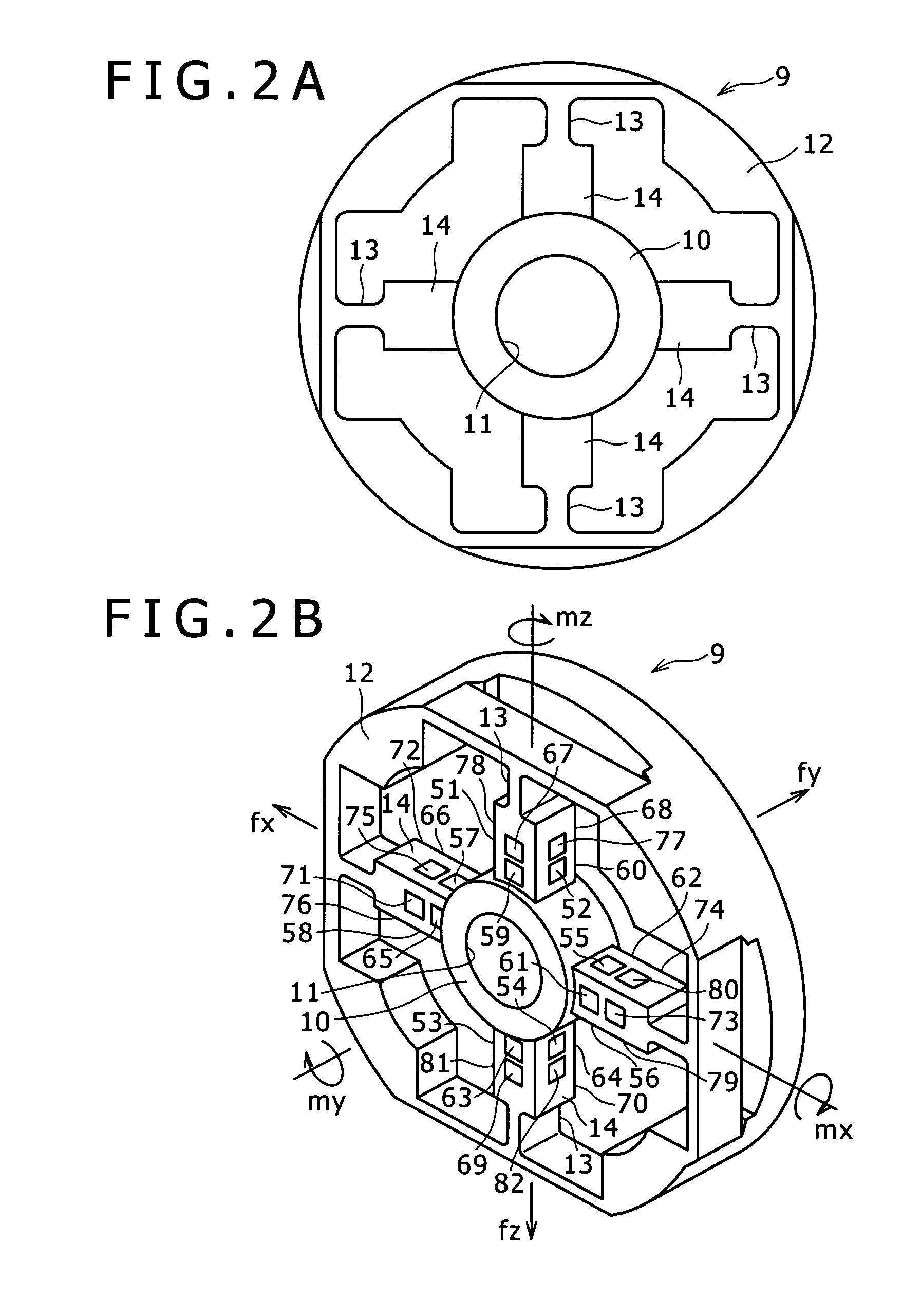
Calibration method for multi-component force measuring spindle unit used in tire testing machine
ActiveUS20120079868A1Accurately calculateHigh precisionVehicle testingWeighing apparatus testing/calibrationArbitrary-precision arithmeticTransformation matrix
A transformation matrix used for finding actual loads acting on a tire can be reliably calibrated. Using the calibrated transformation matrix, the translation and moment loads exerted on the tire can be calculated with a high degree of accuracy in a multi-component force measuring spindle unit including two multi-component force measuring sensors on locations spaced-apart from each other along the axis direction of a spindle shaft. The calibration method includes a step of measuring loads exerted on the spindle shaft, a calculation step using a measured load vector including the loads obtained in the measurement step and the transformation matrix applied to the measured load vector, to find an actual load vector including actual loads on the tire. Before the calculation step, a calibration step determines the measured load vector under a plurality of linearly independent test conditions and calibrates the transformation matrix based on the determined measured load vector.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
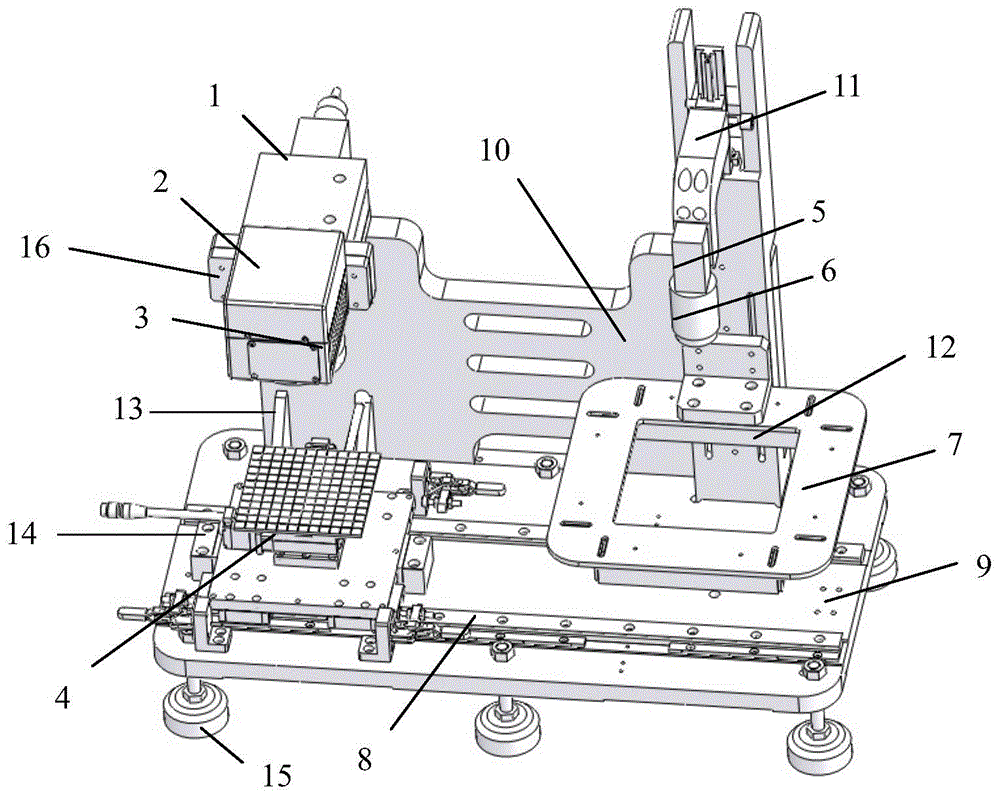
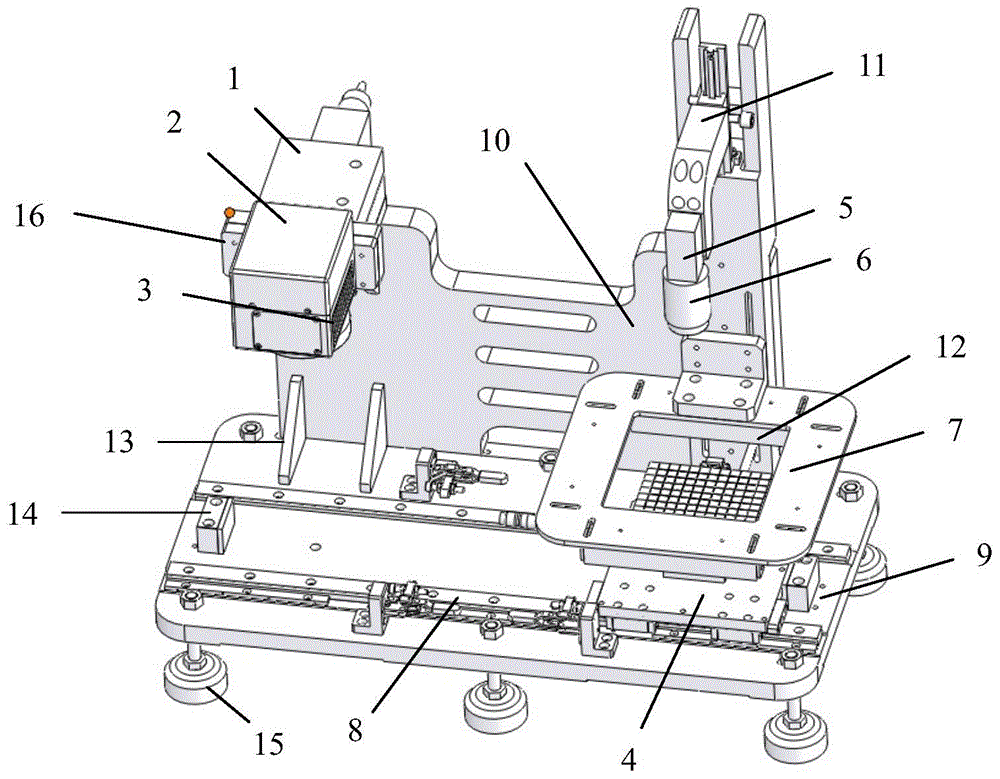
High-precision galvanometer error self-correcting device and high-precision galvanometer error self-correcting method based on machine vision
ActiveCN105620050ARealize self-calibrationSimple structurePrintingNonlinear distortionMachine vision
The invention discloses a high-precision galvanometer error self-correcting device and a high-precision galvanometer error self-correcting method based on machine vision. The self-correcting device comprises a laser, a marking square head, a focusing lens, an XY-axis movement platform, a camera, an X-axis movement guiderail and a mounting base. The mounting base is provided with an X-axis movement guiderail and a vertical plate. The XY-axis movement platform is mounted on the X-axis movement guiderail. The laser and the camera are mounted on the side surface of the mounting base. The camera is connected with an external image processor. The marking square head is mounted on the side surface of the laser. The focusing lens is mounted on the lower end surface of the marking square head. According to the self-correcting method of the invention, a two-dimensional correction table in practical application of laser marking is obtained through a vision method, namely utilizing the camera and the lens; a laser marking device is corrected by means of the vision method; a unique correction table can be generated for each laser marking device, thereby improving precision and reliability in laser marking and preventing linear distortion and nonlinear distortion in the marking process.
Owner:HANS LASER TECH IND GRP CO LTD +1
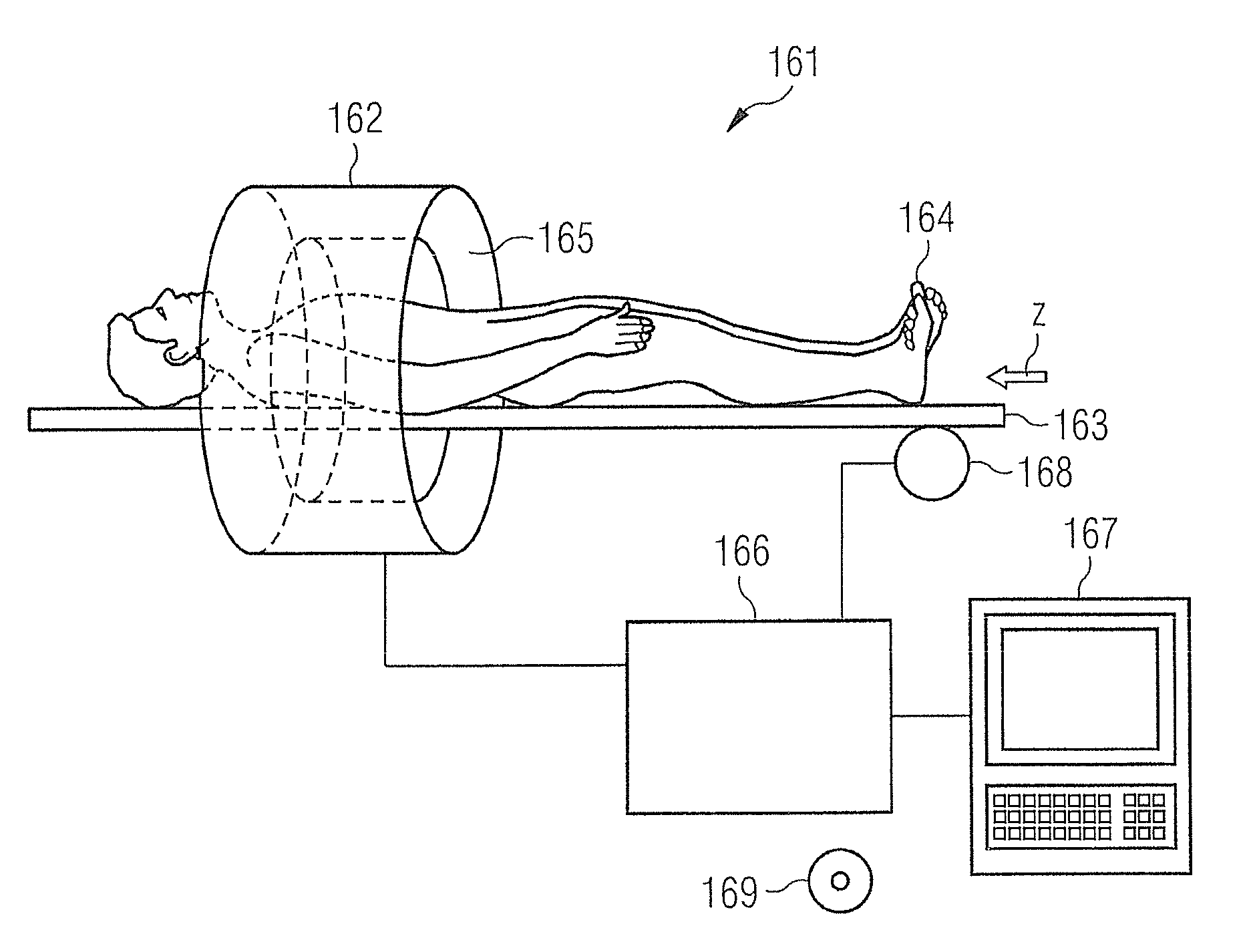
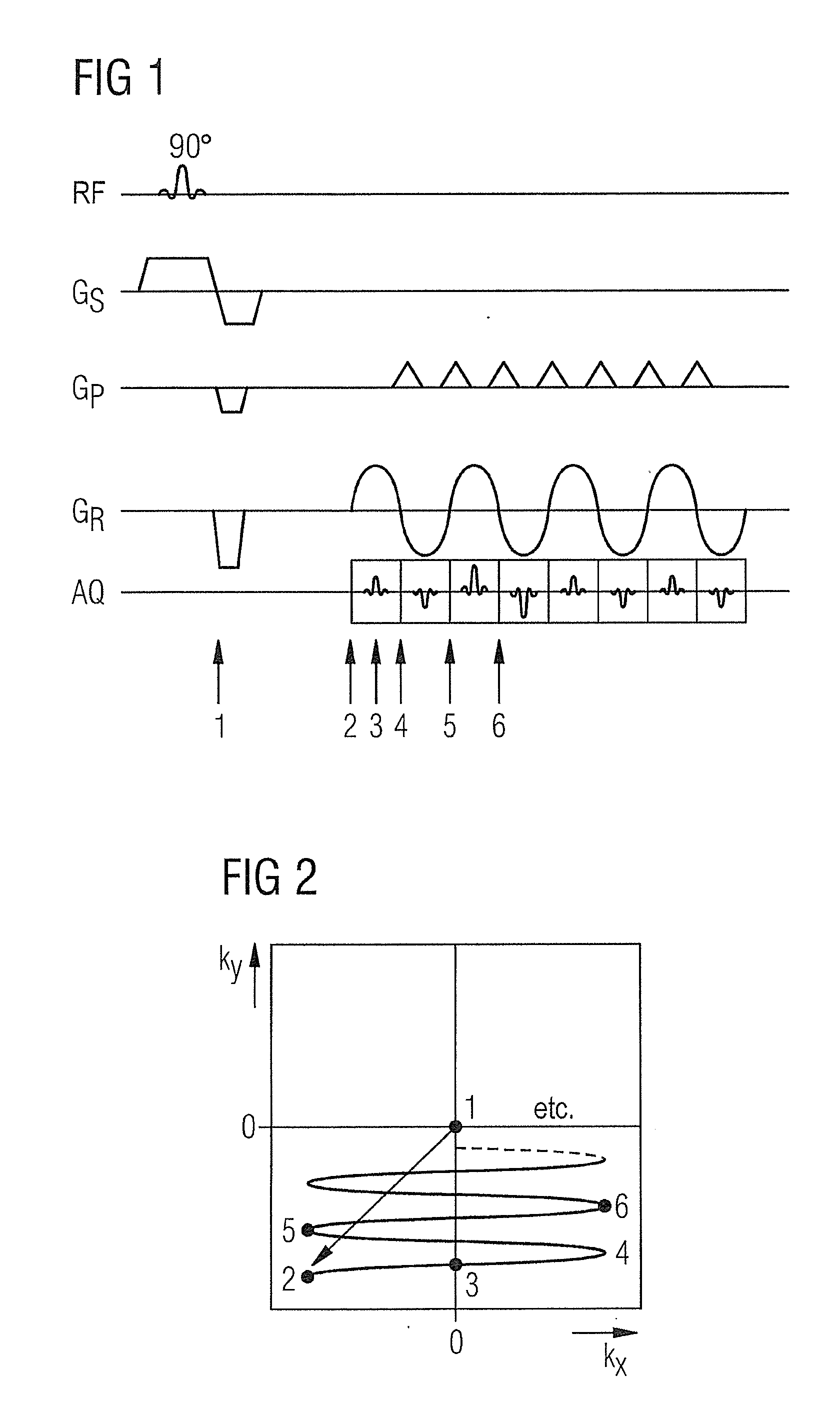
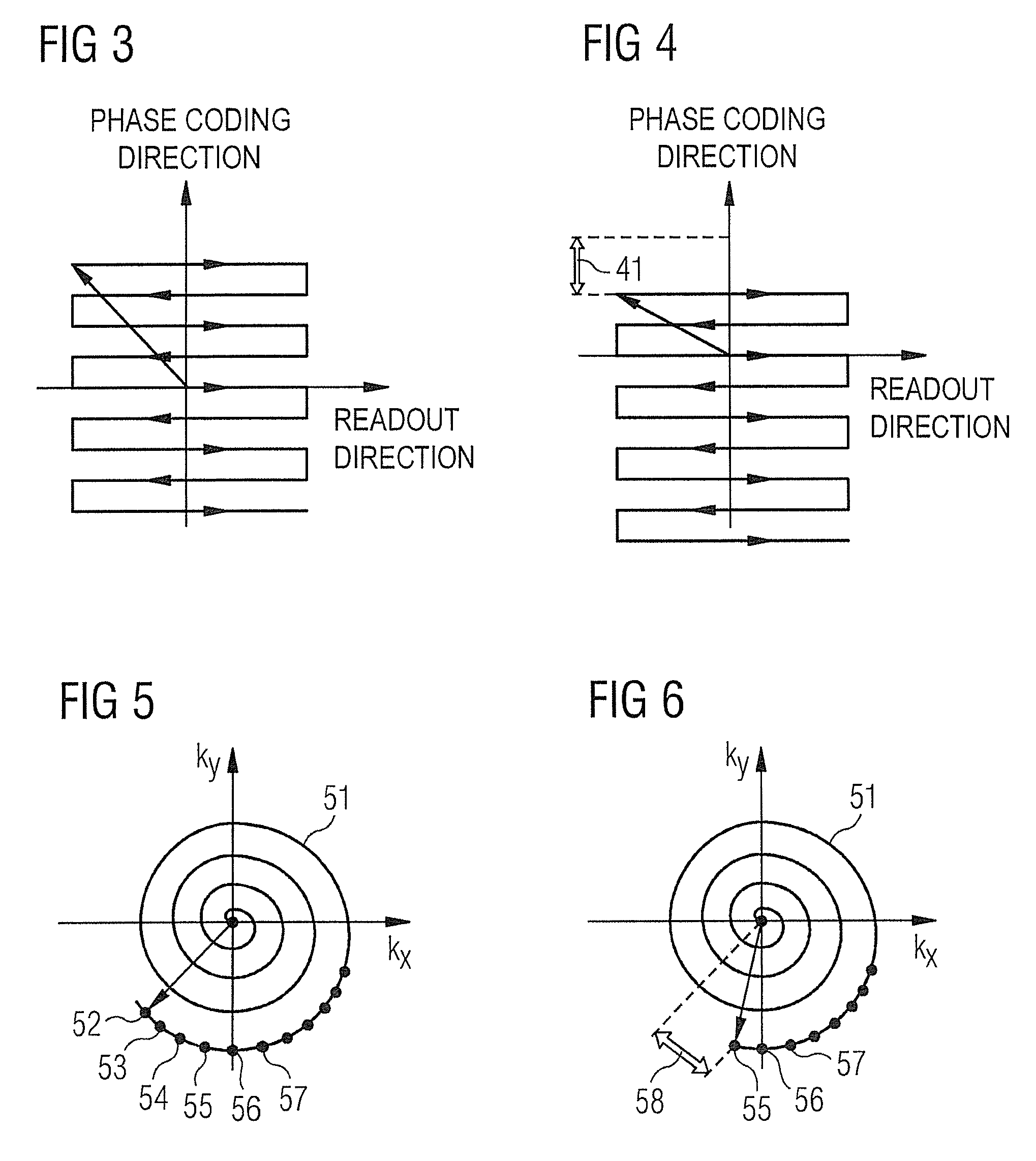
Method and magnetic resonance system for distortion correction in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20120313640A1Correct distortionSmall differenceCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringData setResonance
In a method for distortion correction in spiral magnetic resonance imaging, a first MR data set is acquired by scanning raw data space along a spiral trajectory beginning at a first point. A first complex MR image is determined from the first MR data set, which includes first phase information for image points of the first MR image. A second MR data set is acquired by scanning raw data space along the spiral trajectory beginning at a second point that differs from the first point. A second complex MR image is determined from the second MR data set, which includes second phase information for image points of the second MR image. A geometric distortion for image points of the first or second MR image is determined from the first and second phase information, for example with a PLACE method.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Color image forming apparatus and method
InactiveUS20060045577A1Shorten speedReliable calibrationElectrographic process apparatusColor imageMagnification
Owner:RICOH KK
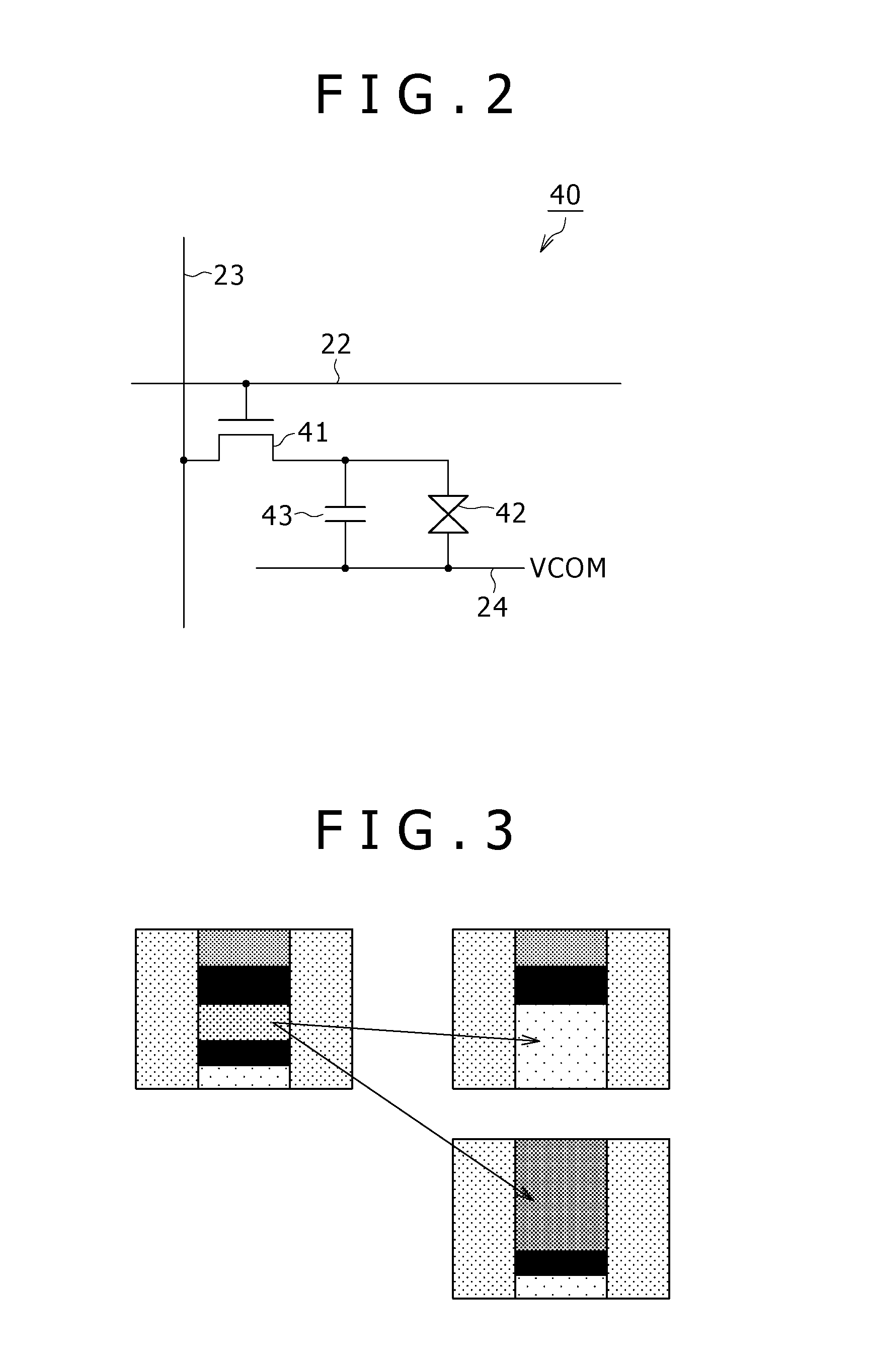
Display device and driving method of the same
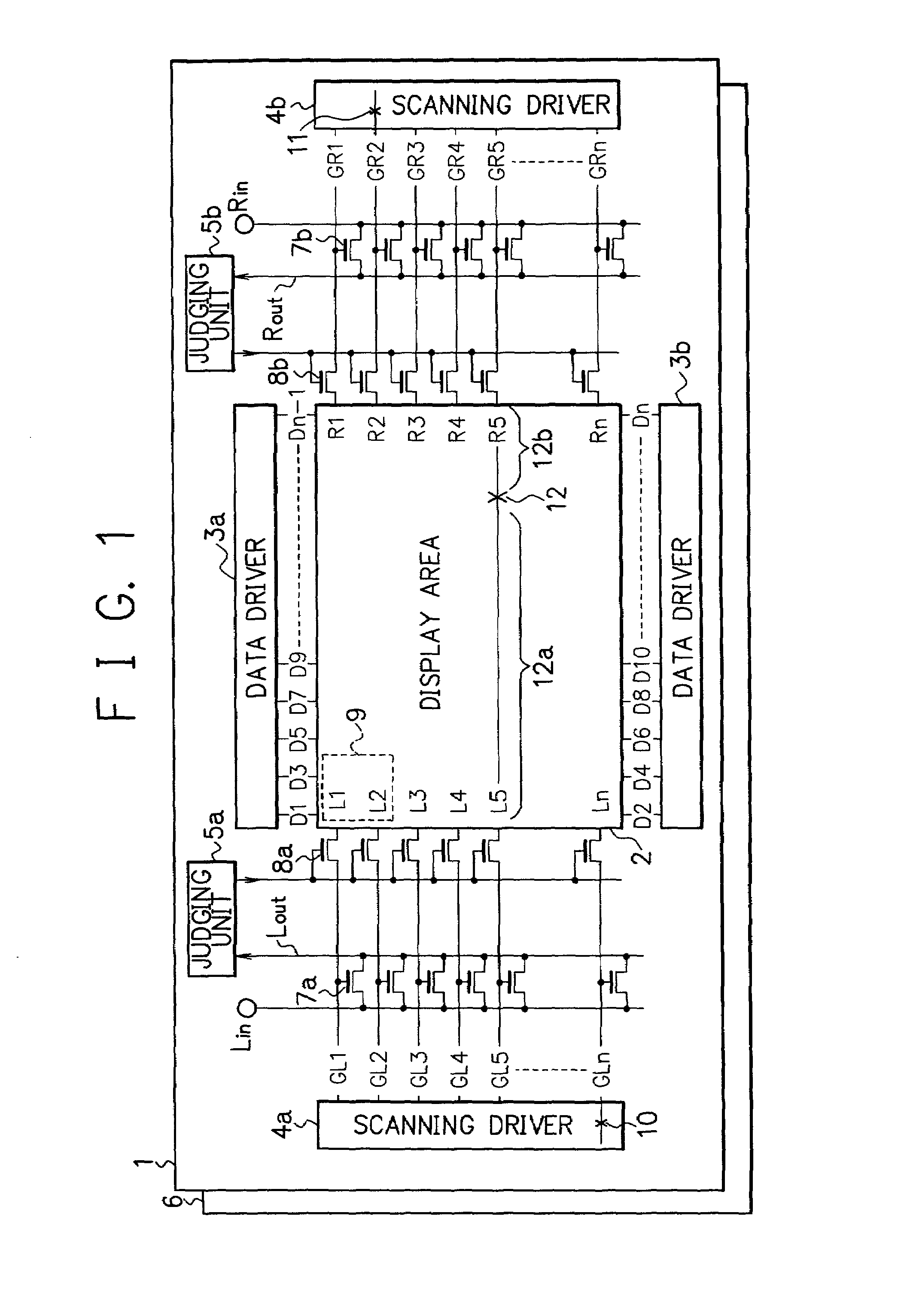
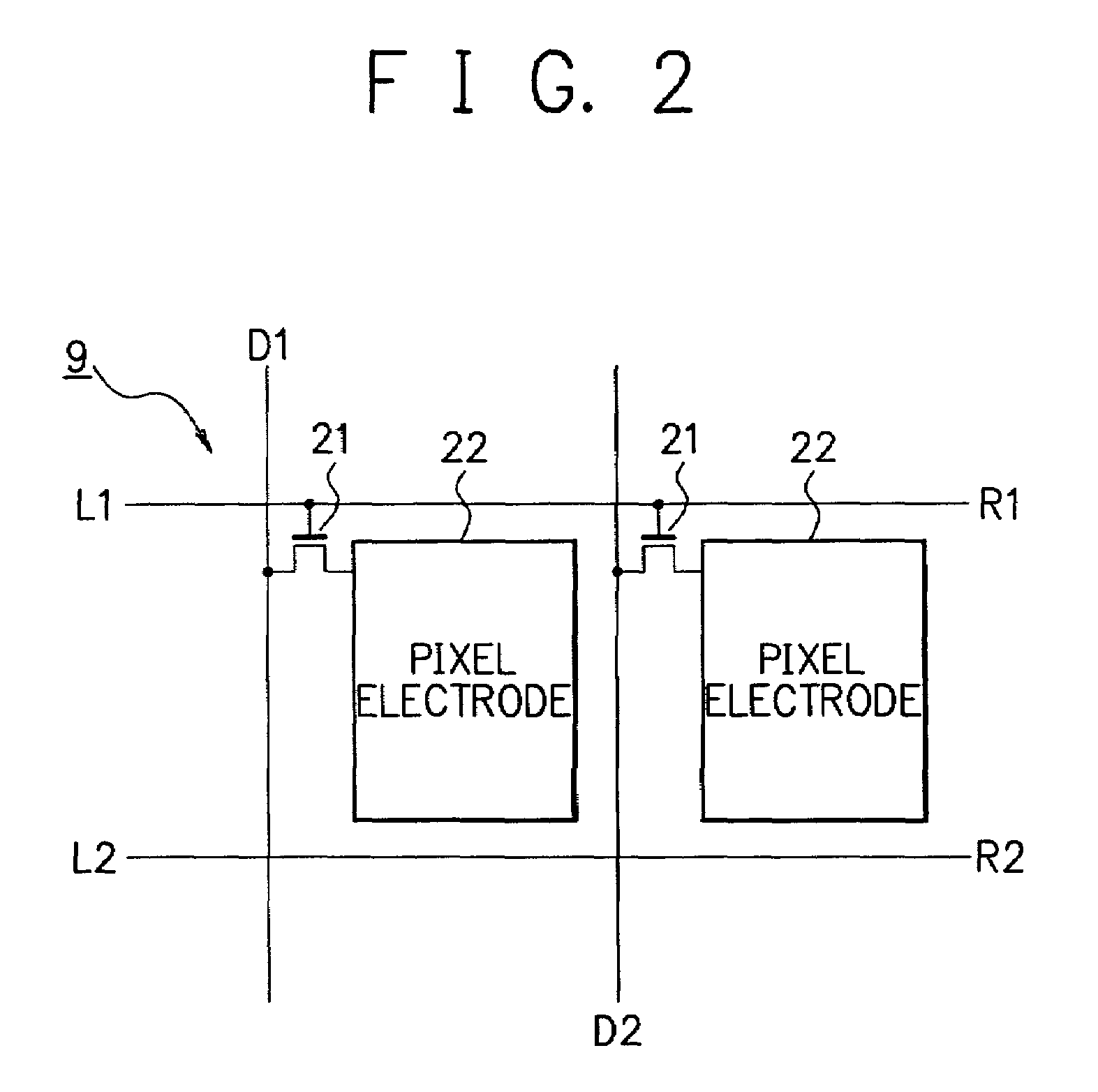
InactiveUS6970274B2Reliably detecting defectReliable calibrationElectrical testingCharacter and pattern recognitionDisplay deviceEngineering
A display device has a display section having scanning lines, and first and second scanning drivers having output lines for supplying scanning signals to the two ends of the scanning lines in the display section. When the potential of at least one of the output lines of the first or second scanning driver is fixed or unfixed due to an error in the first or second scanning driver, the output line at the fixed or unfixed potential is disconnected from the corresponding scanning line in the display section.
Owner:SHARP KK
Display device and driving method of display device
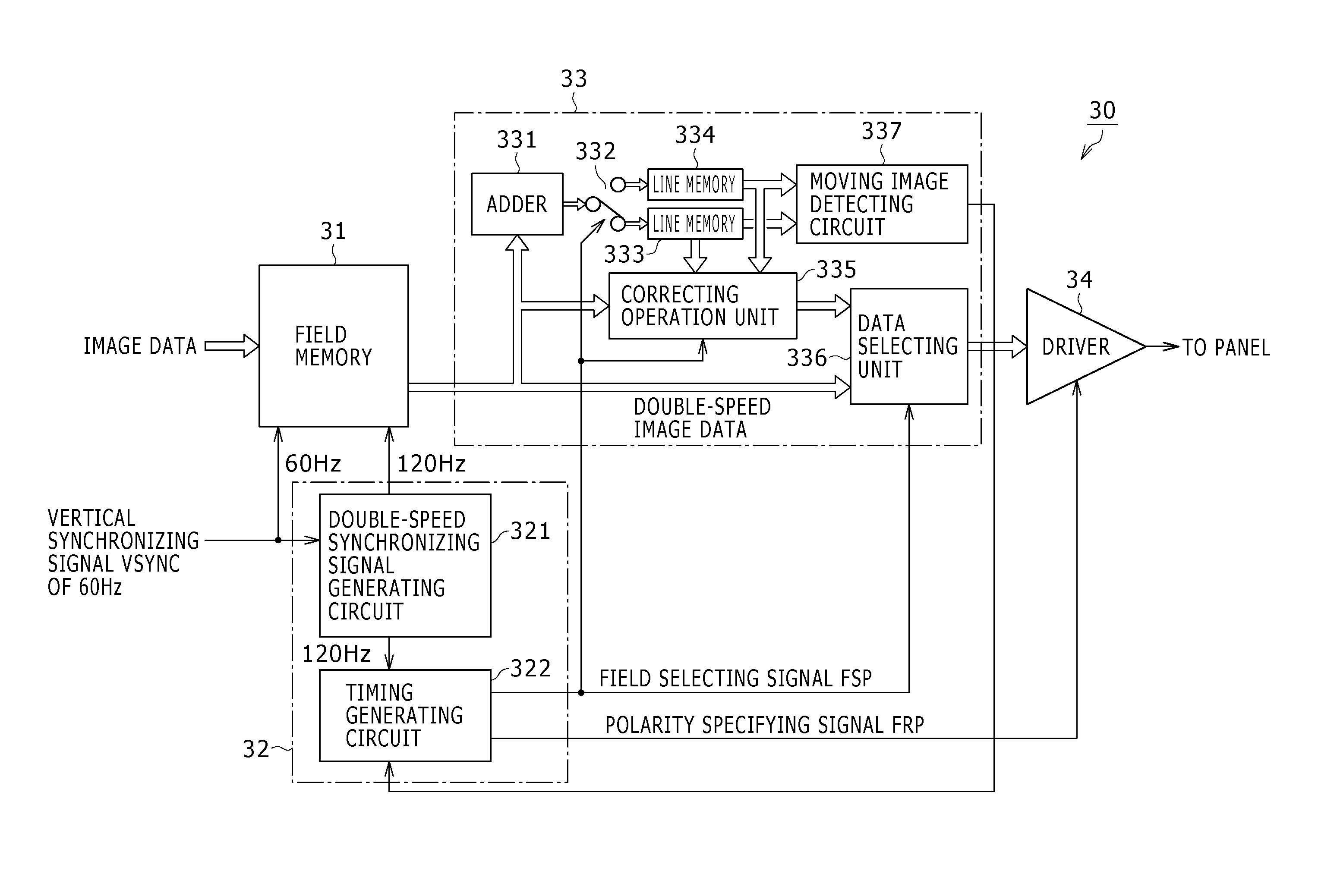
ActiveUS20070146281A1Prevent display quality degradationReliable calibrationCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsDisplay deviceElectrical polarity
Disclosed herein is a display device using a field inversion driving system, the display device being formed by arranging pixels each including an electrooptic element in a form of a matrix and inverting polarity of a display signal to be written to each of the pixels in field periods, the display device including: double-speed converting means for converting an input display signal into a double-speed display signal having a field frequency twice a field frequency of said display signal; and crosstalk correcting means for correcting crosstalk in a second field of two fields as a unit of said double-speed display signal generated by said double-speed converting means, using information of the first field.
Owner:SONY CORP
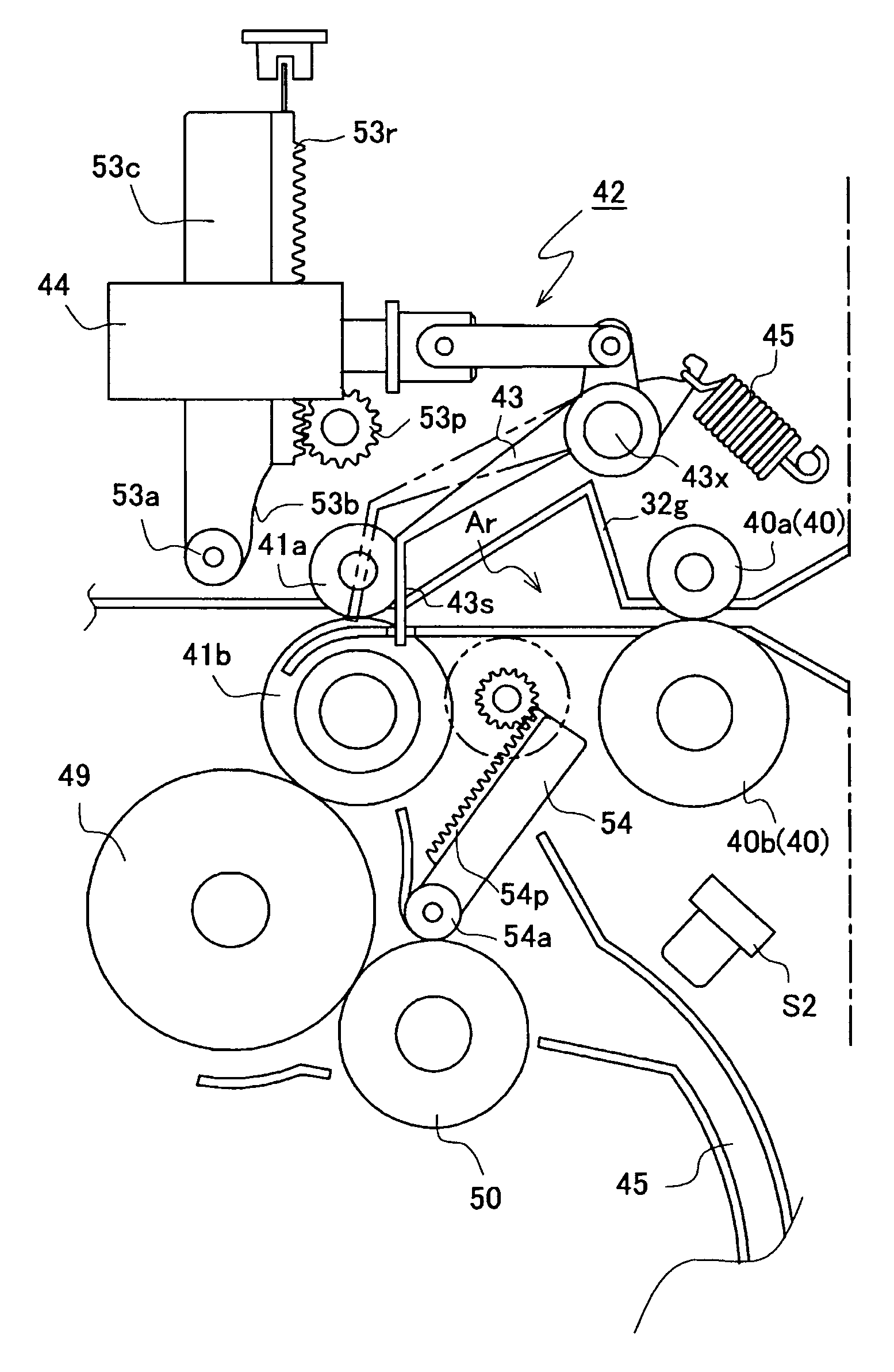
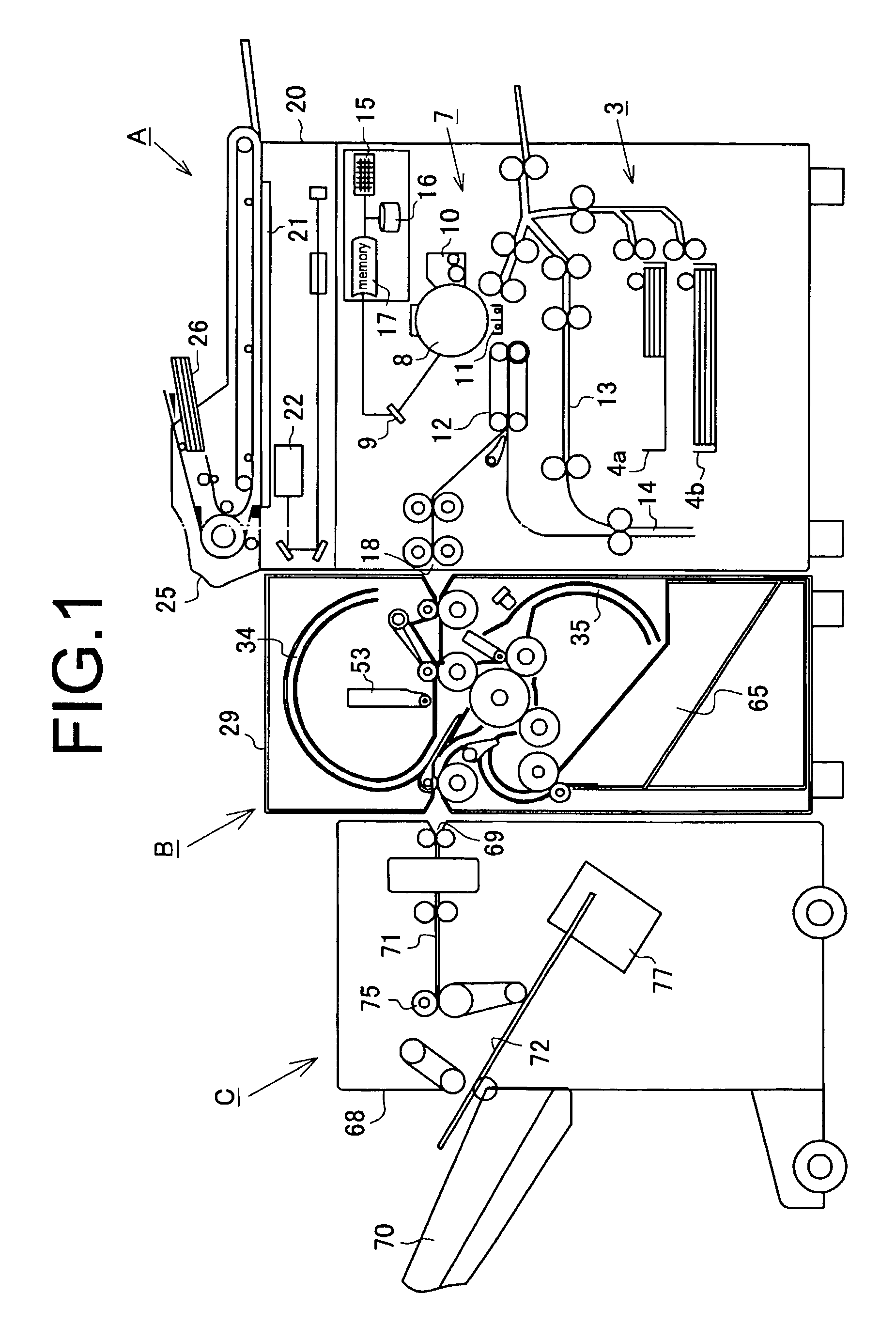
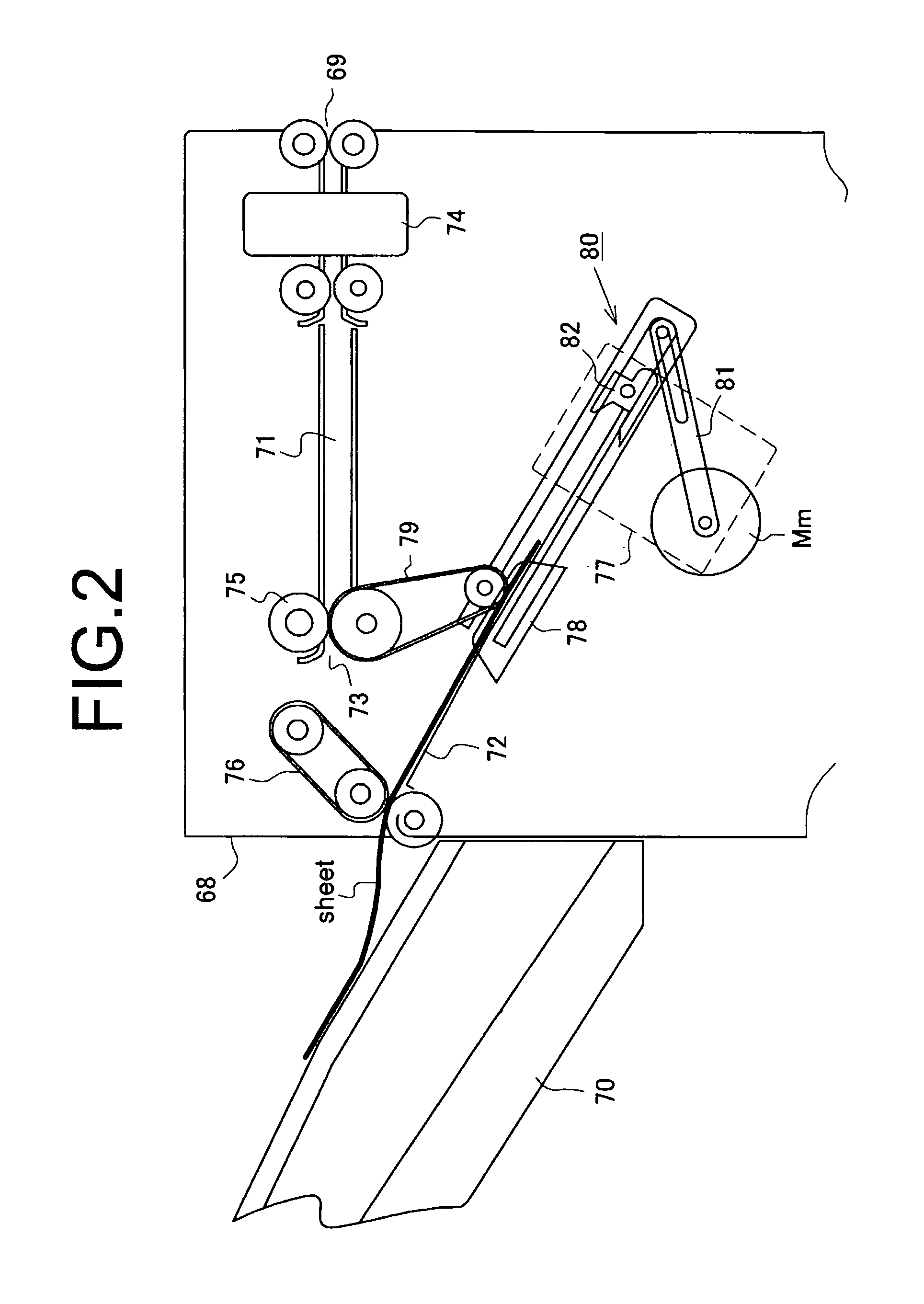
Sheet folding apparatus with skew correction mechanism and image formation system provided with the sheet folding apparatus
InactiveUS8256757B2Simple structureEfficient processingMechanical working/deformationFolding thin materialsImage formationEngineering
A sheet folding apparatus for performing folding processing on a sheet from a carry-in entrance to carry out to a carrying-out exit has a sheet feeding apparatus, a first transport path, a second transport path, and a folding processing device. The sheet feeding apparatus includes a transport roller pair in press-contact with each other, a gate stopper device having a stopper member, a register area to curve and deform the sheet with the front end regulated, and a stopper driving device for shifting the gate stopper device. The stopper member is formed so that a shift trajectory of the regulation surface is to guide the front end of the sheet to the press-contact portion of the transport roller pair. The first transport path is provided with the sheet feeding apparatus for aligning a front end of the sheet fed from the carry-in entrance to feed to a predetermined processing position.
Owner:NISCA KK
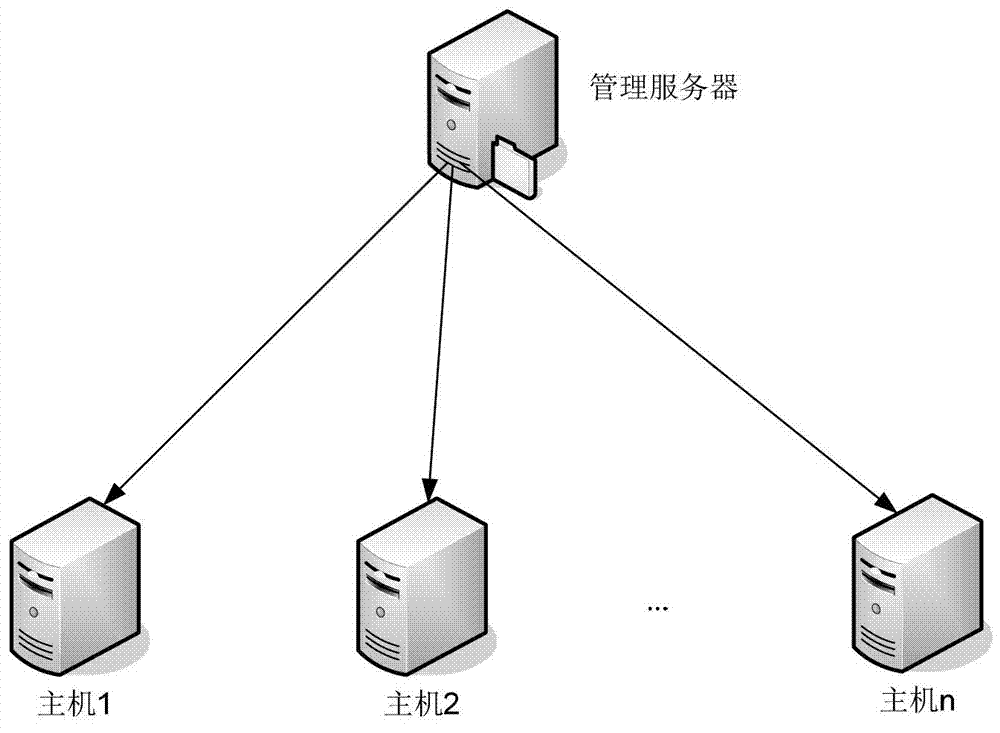
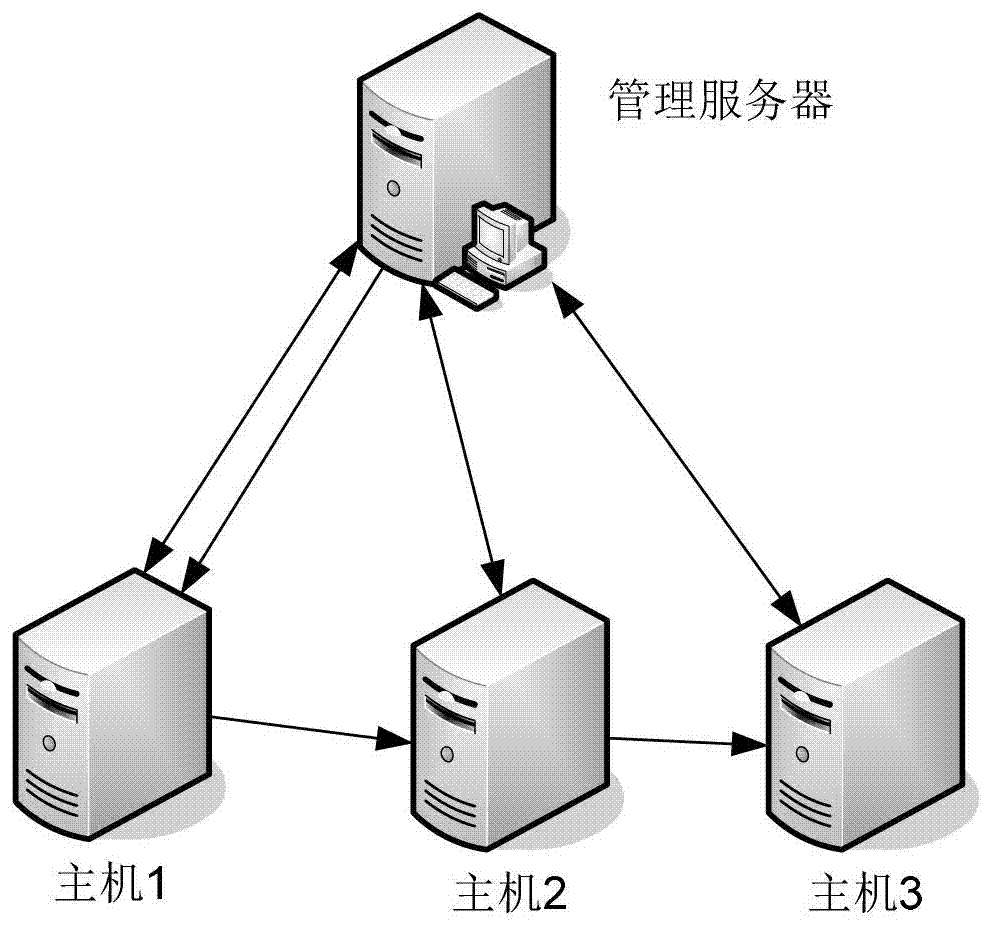
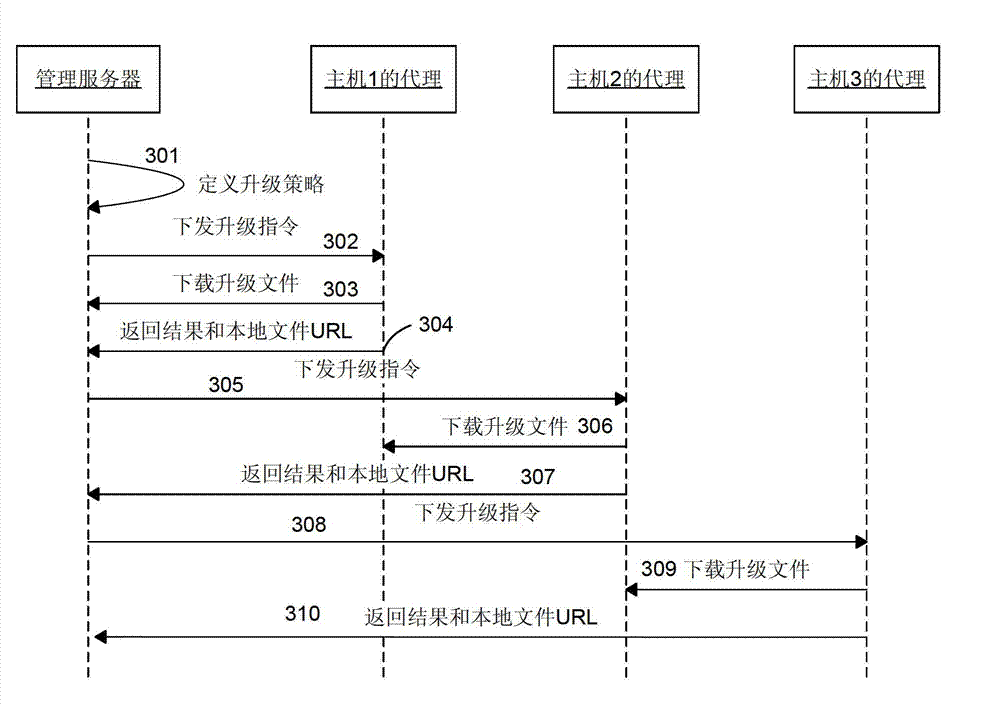
Scalable file distribution method used in distributed system
InactiveCN102761599AImplement automatic upgrade installationAvoid congestionTransmissionDistribution methodApplication software
The invention discloses a scalable file distribution method used in a distributed system which comprises a management server and at least one host computer and adopts the scalable file distribution method for file distribution. The management server is in charge of scalability management of all host computers of the whole network, can control each host computer to select one address, from an address pool, for downloading a specified scalable file according to the predefined distribution strategy and scalability dispatching algorithm, and conducts installation upgrading for application programs on the host computers. The host computers inform the management server of the access addresses of locally downloaded scalable files, and the management server allows other host computers to access the addresses to download the scalable files. Each host computer can not only download the scalable files from other host computers but also serve as a download server to provide download service for other host computers. The scalable file distribution method can be used by any distributed systems including a cloud system, effectively prevent the management server from bottlenecks, makes the best of resource capabilities of all servers in the whole network, and can quickly achieve file distribution in a controllable manner.
Owner:UTSTARCOM TELECOM CO LTD
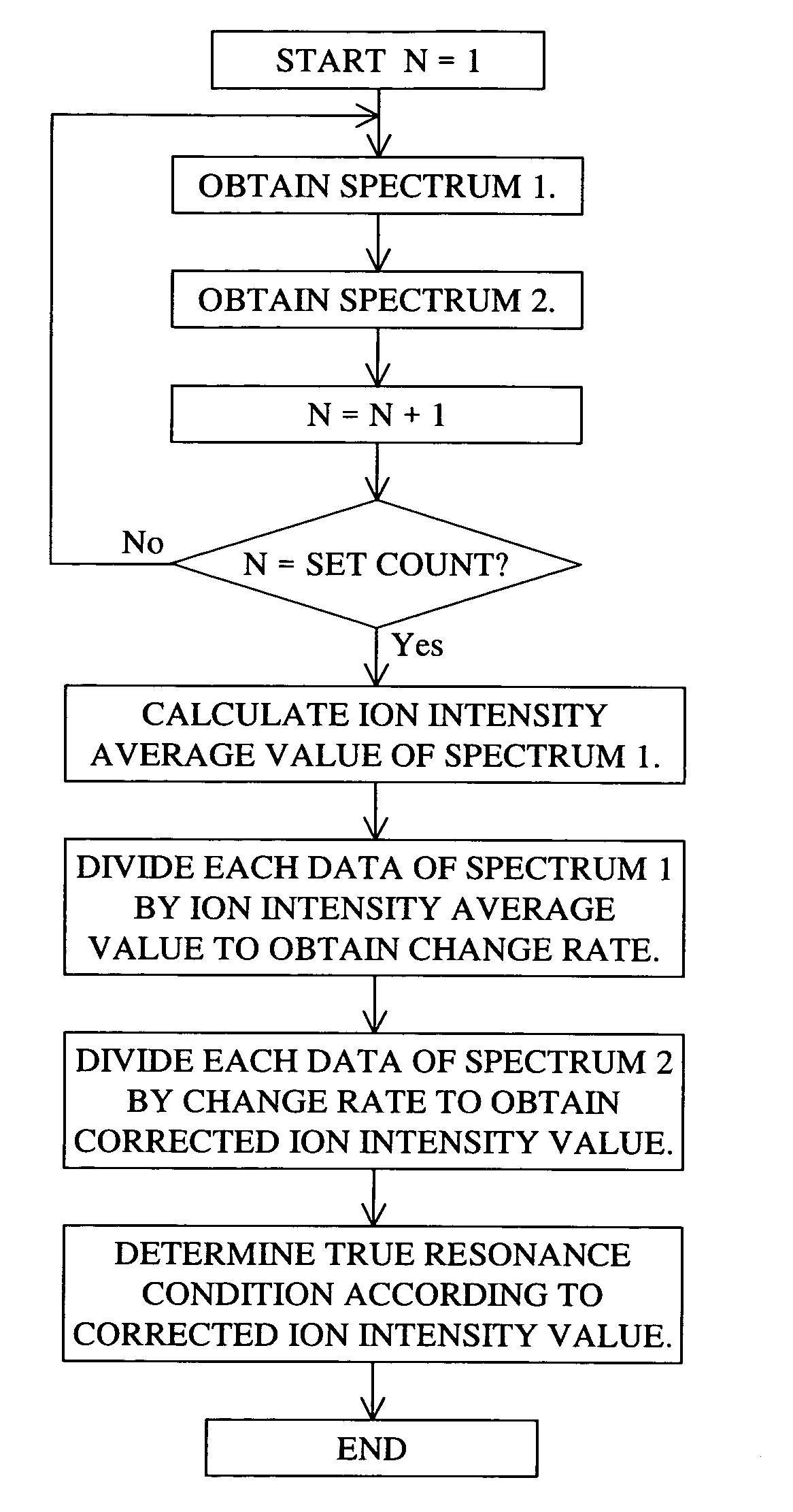
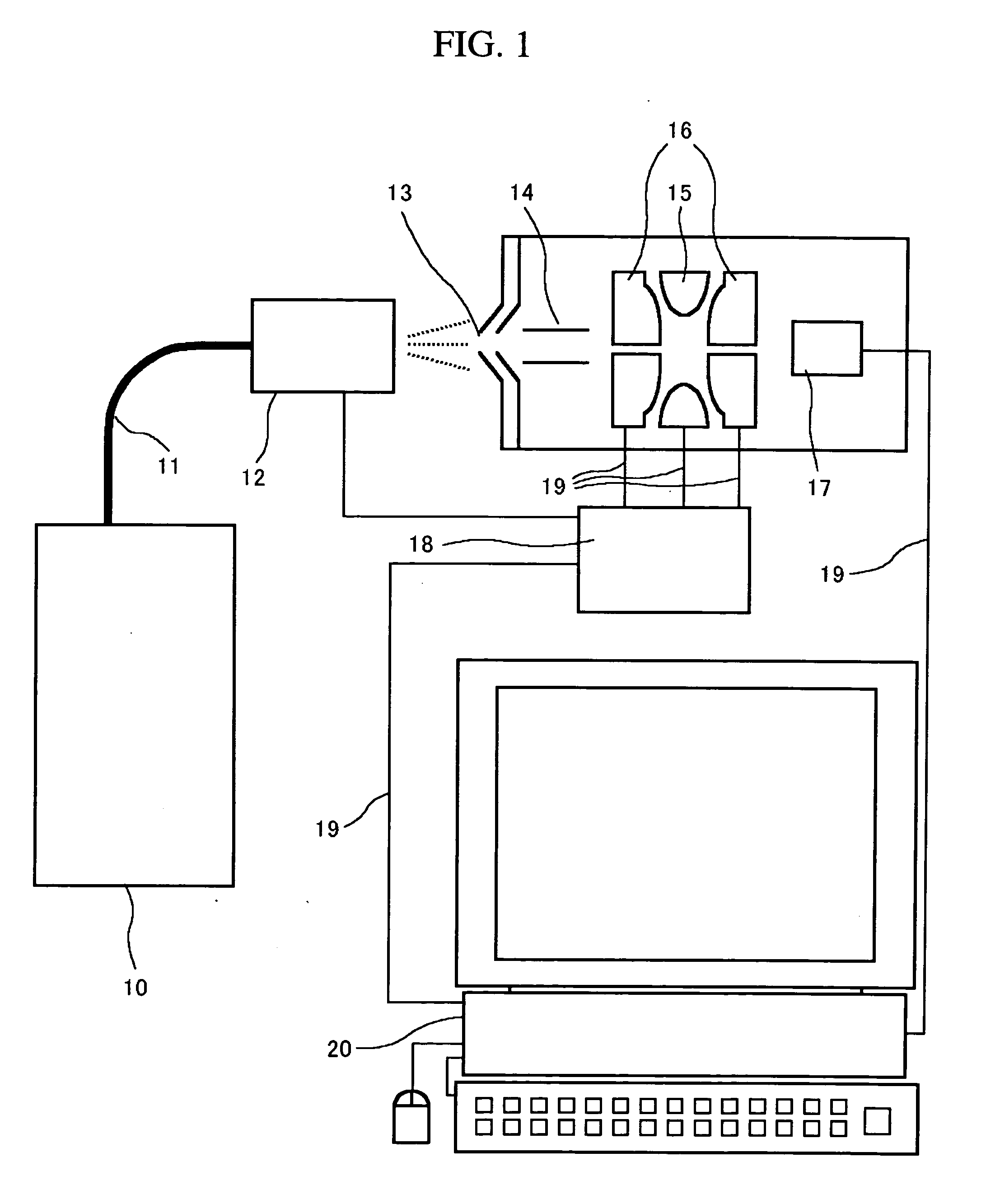
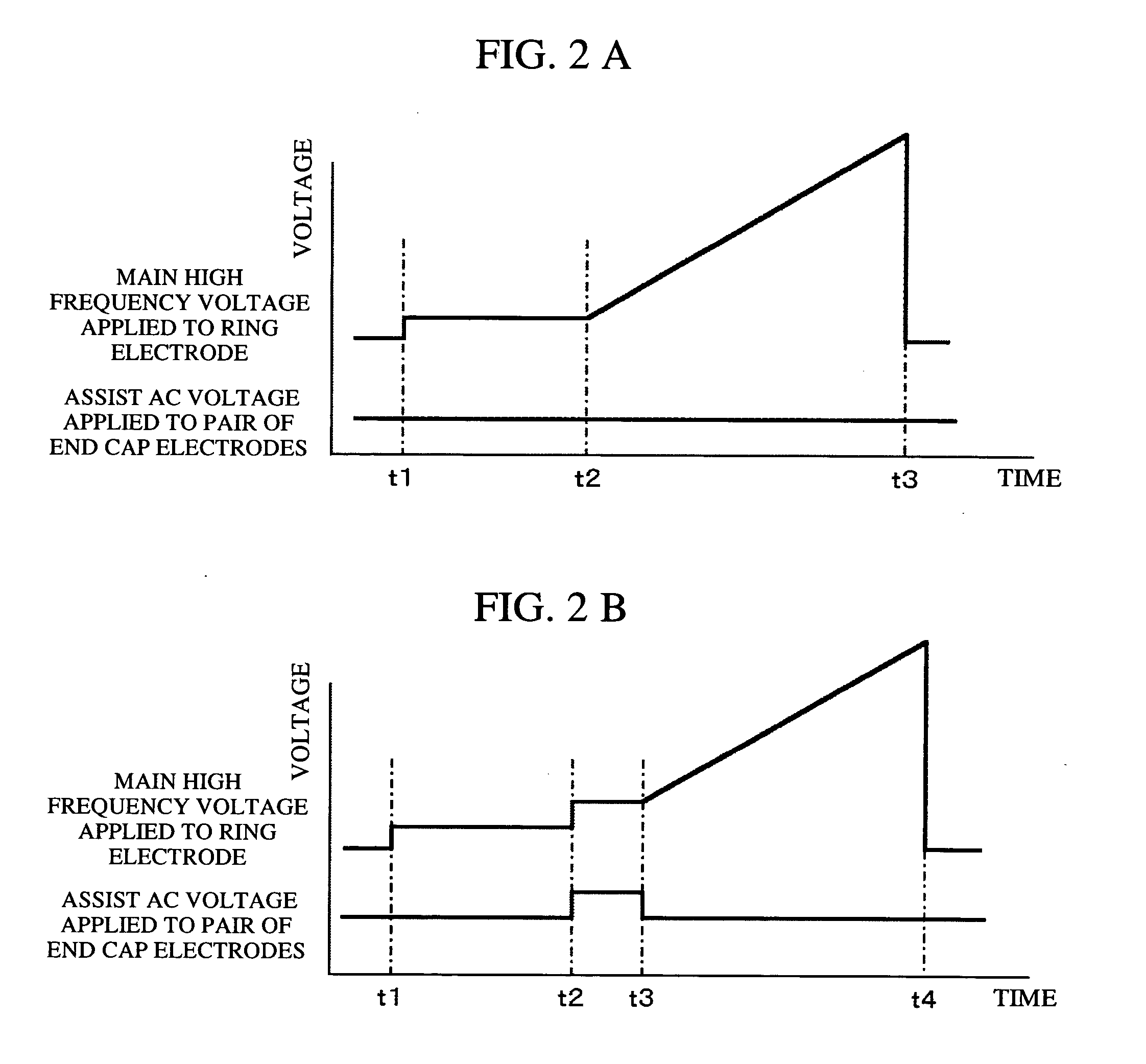
Mass spectroscope and method of calibrating the same
ActiveUS20050139763A1Improve efficiencyHighly reliable calibrationStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersIon trap mass spectrometryResonance
An ion resonance condition is corrected accurately in an ion trapping device. Measurements are repeated by alternately applying and not applying a resonance frequency voltage while spectral data is obtained continuously. Data obtained in the absence of the resonance frequency voltage is used as reference data to correct the set data of a resonance condition. As a result, calibration can be made while taking into consideration the variations in the amount of ions that are introduced into the ion trap.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
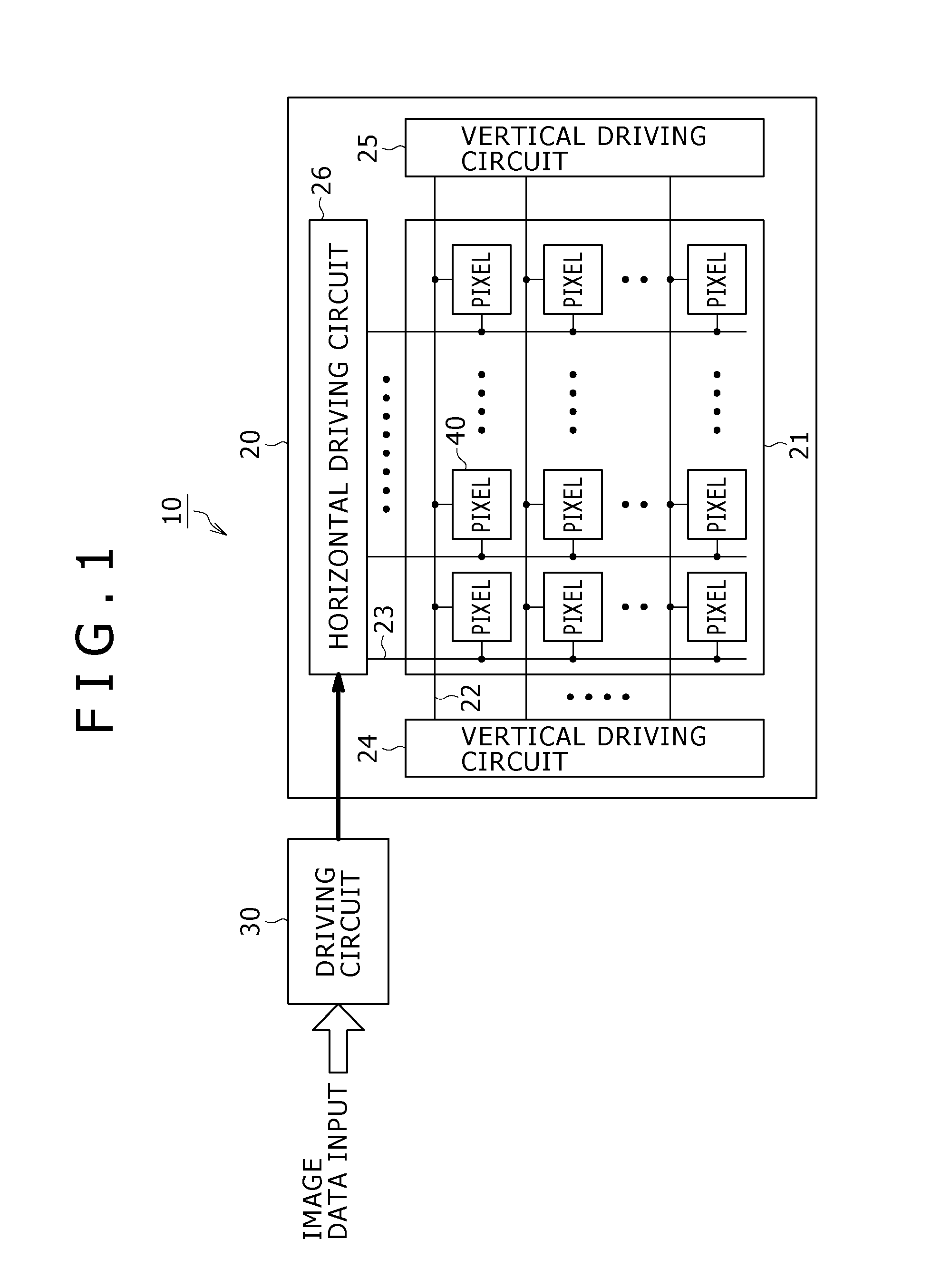
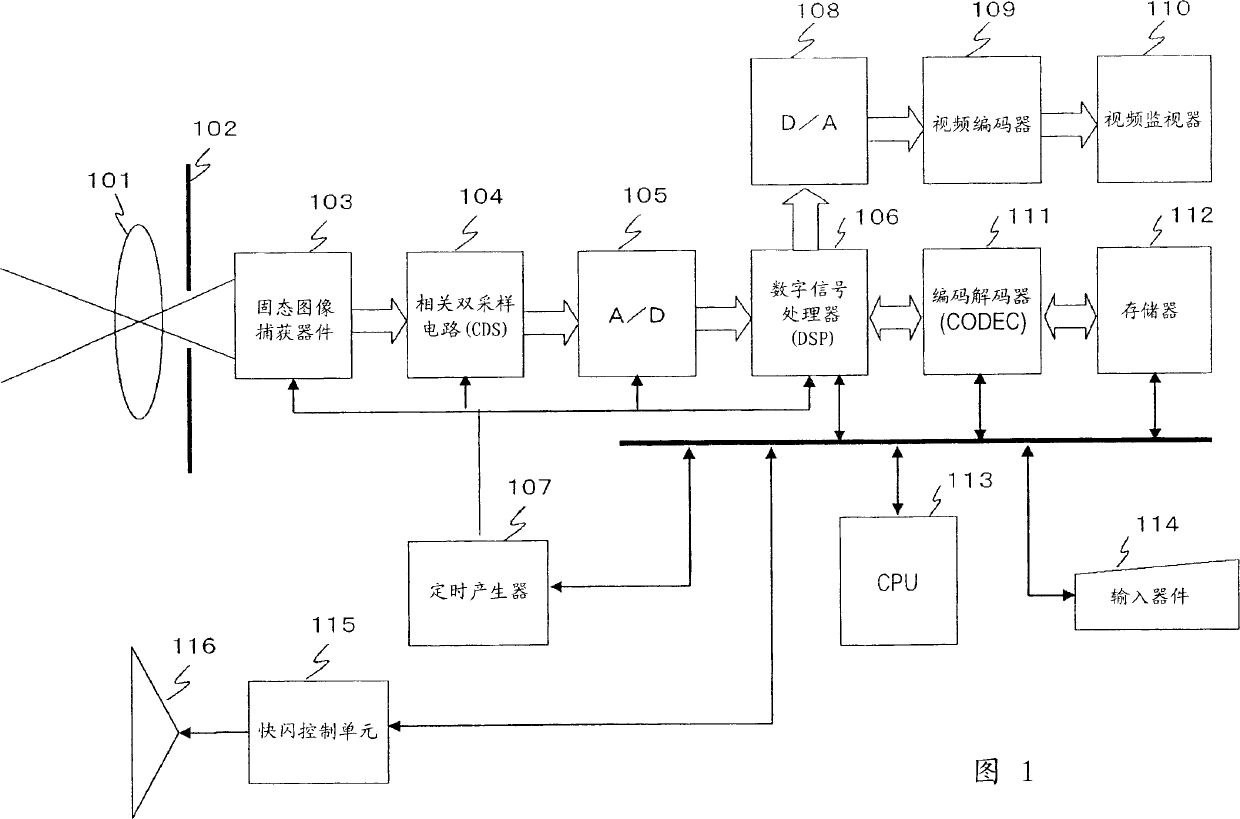
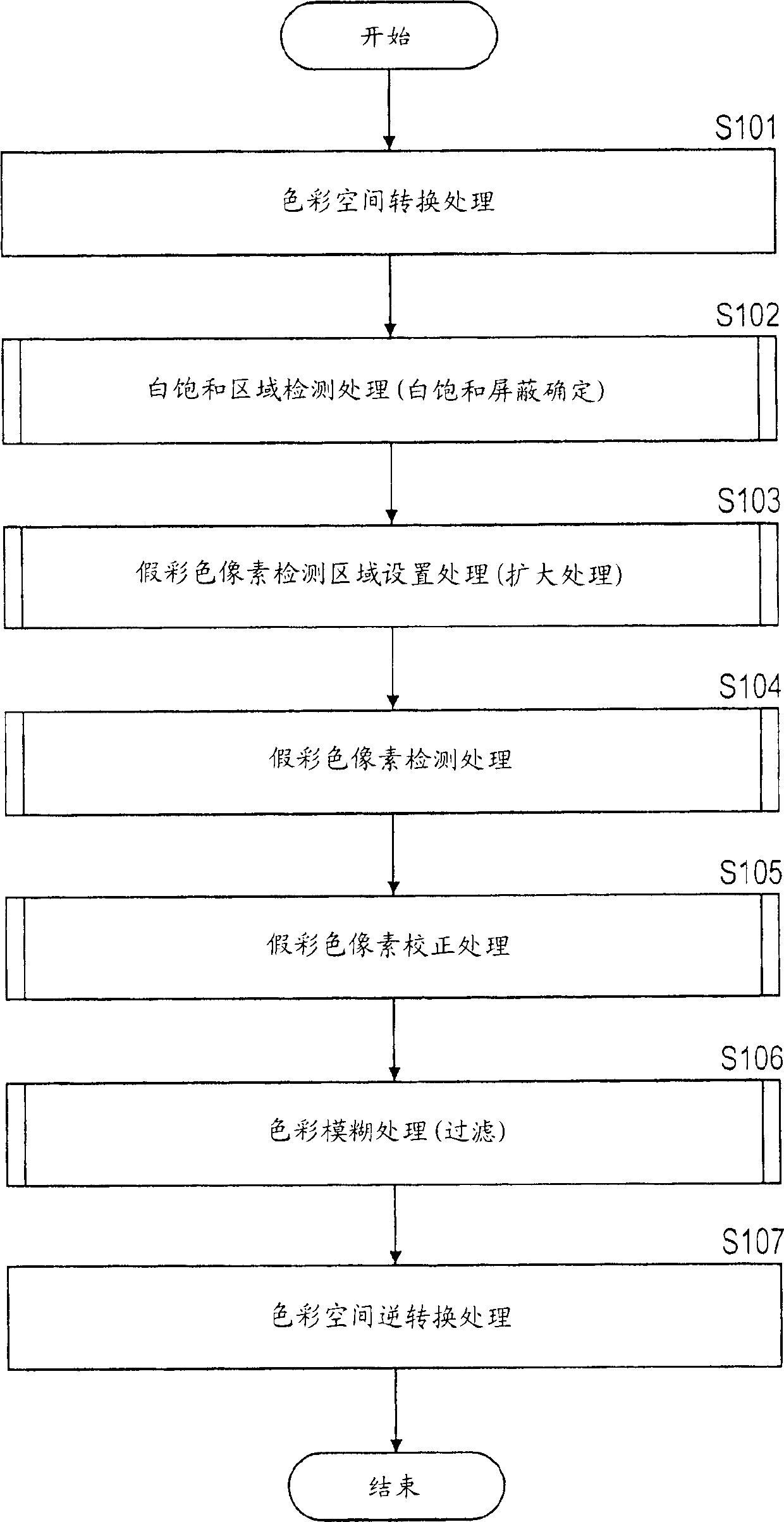
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and computer program
InactiveCN1806449AEfficient detectionIncrease freedomSignal generator with single pick-up deviceImaging processingFalse color
An apparatus and method for efficiently executing a correction of false colors, such as purple fringe or the like, caused by chromatic aberration to produce and output high quality image data. White non-gradation pixels are detected from image data, and a false color pixel detected area is established around the detected white non-gradation pixels. In the established area, pixels having a color corresponding to the false color such as purple fringe or the like are detected, and the detected pixels are specified as false color pixels. The specified false color pixels are corrected based on a periphery pixel value. This arrangement allows an efficient detection of false color area of the purple fringe or the like occurring in the vicinity of the white non-gradation pixels, and also allows a partial pixel value correction, thereby allowing the production and output of high quality image data without affecting the whole image.
Owner:SONY CORP
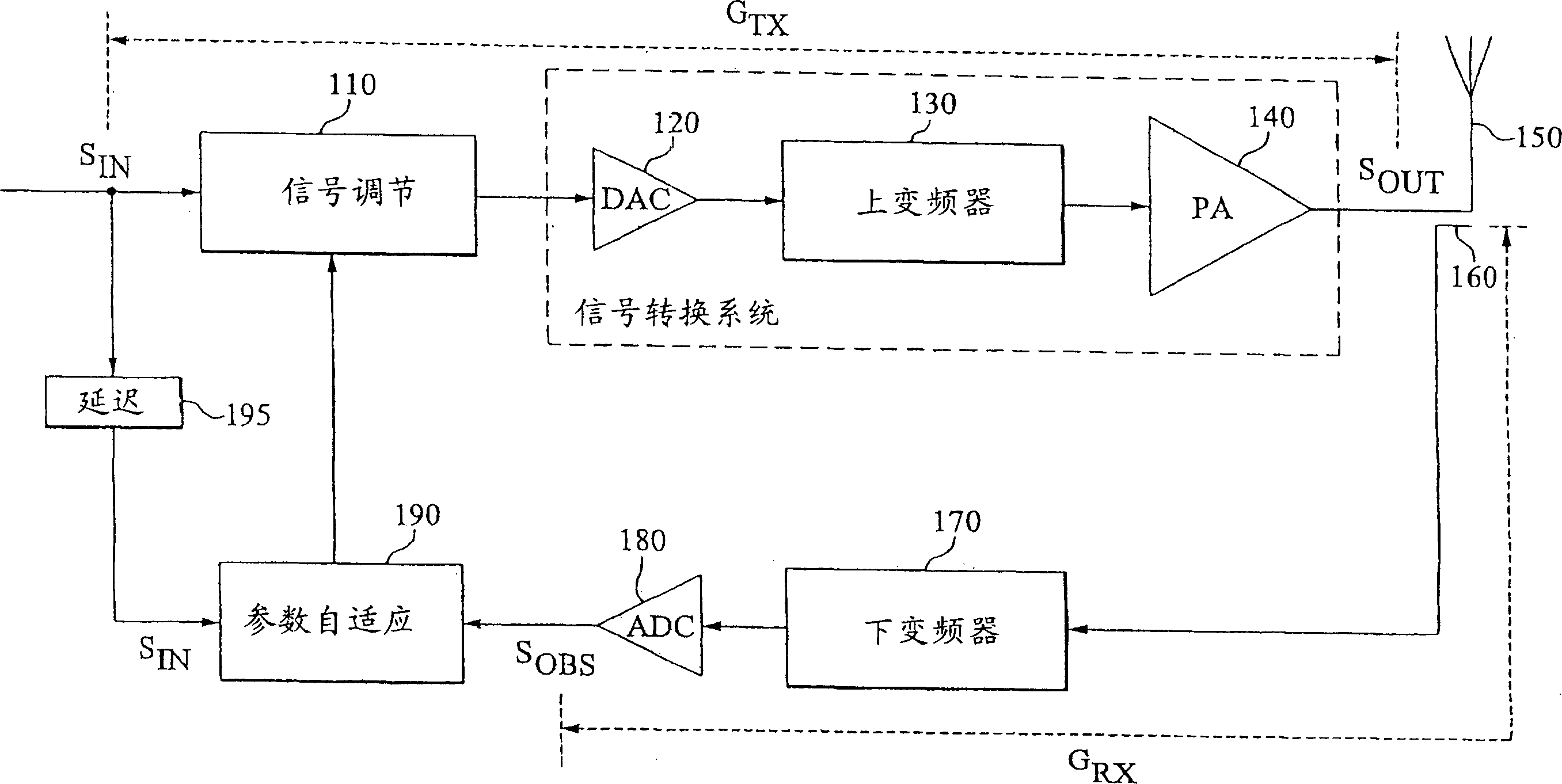
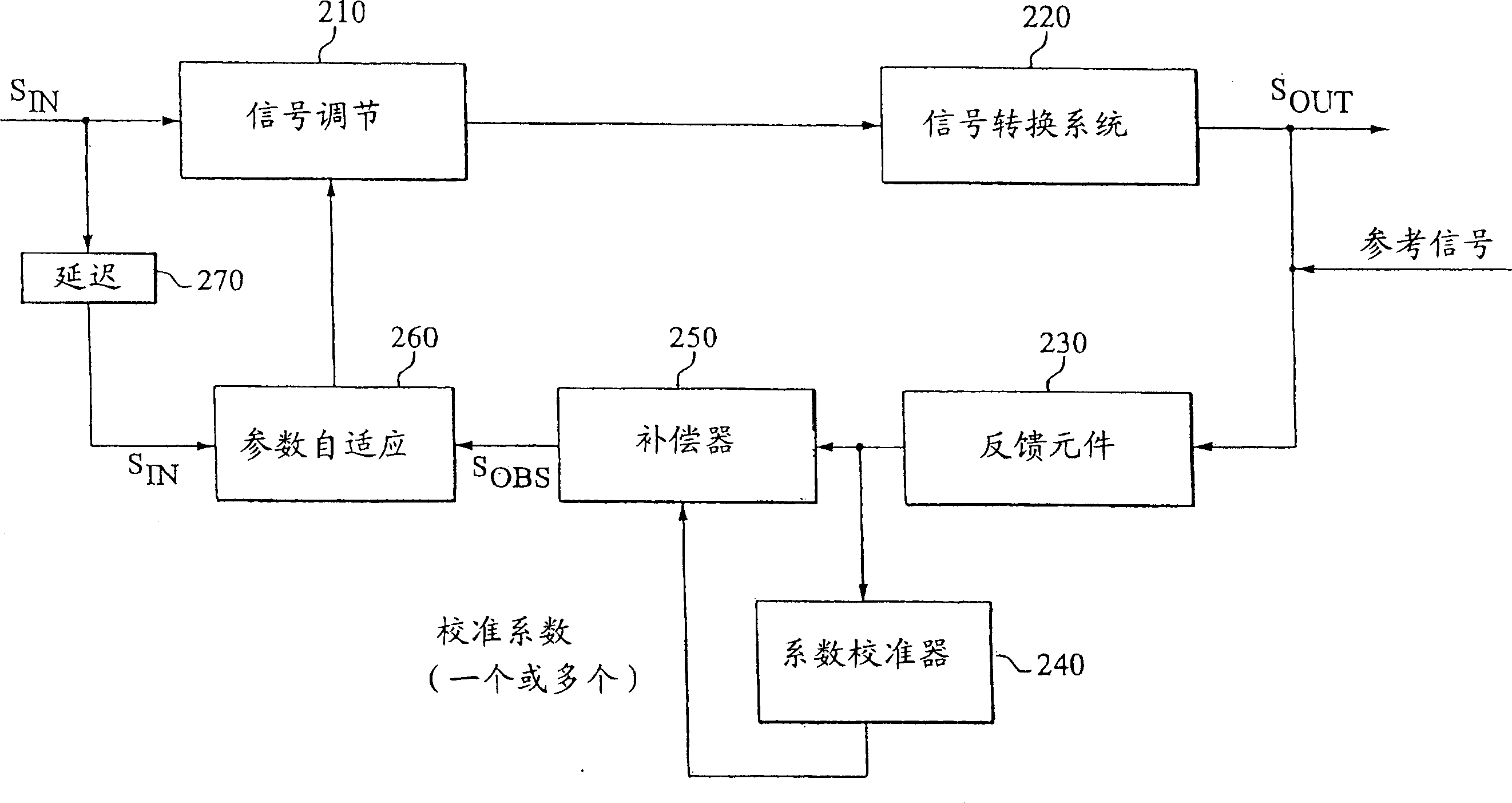
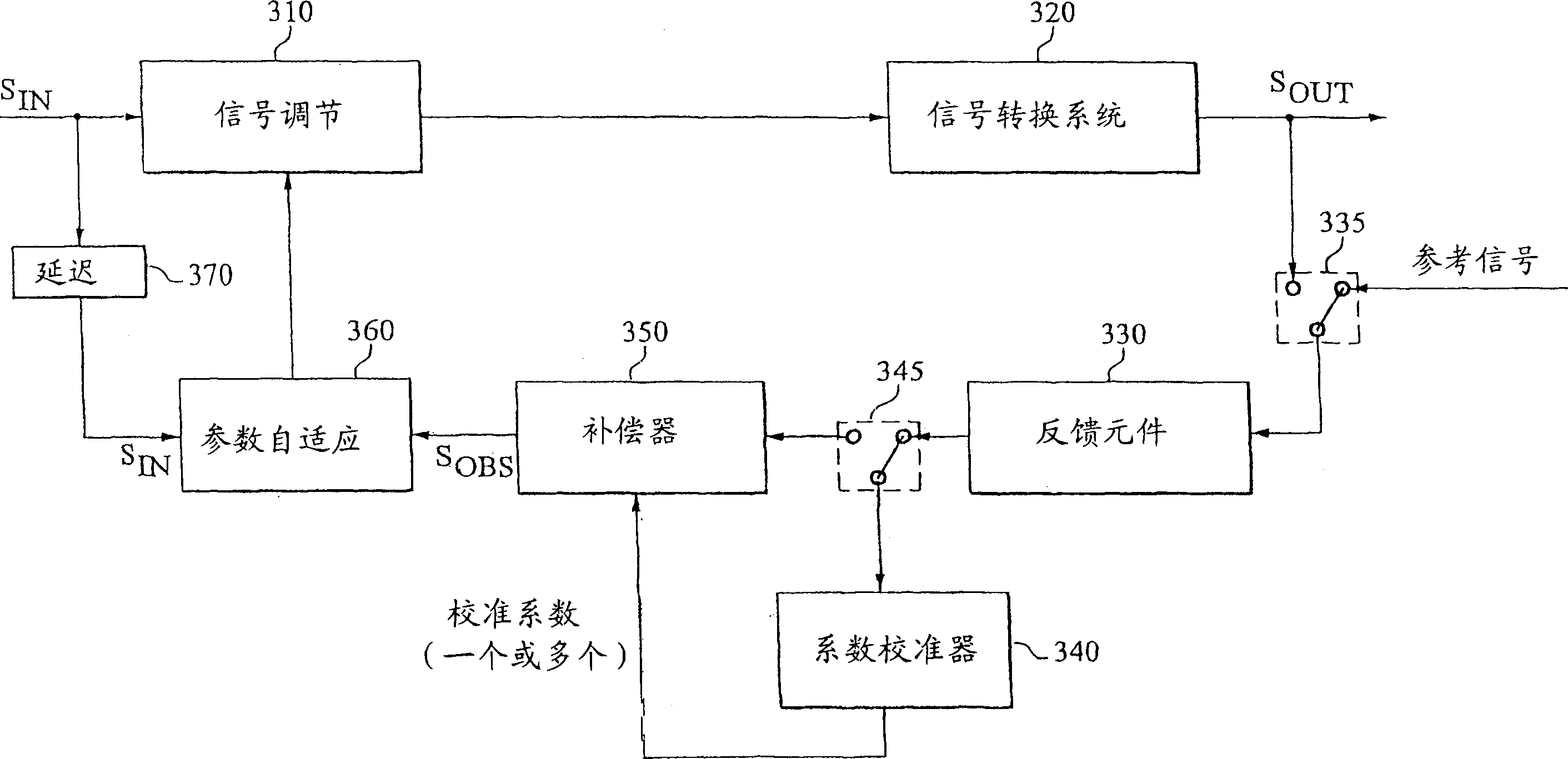
Calibration of an adaptive signal conditioning system
InactiveCN1550064AReliable calibrationWithout disrupting normal operationAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionSignal conditioningEngineering
The invention provides robust and non-invasive calibration of an adaptive signal conditioning system having a signal conditioning block in the signal path to a signal conversion system, and a feedback path with a number of feedback components for enabling adaptation, by means of a parameter adaptation block, of the parameters used in the signal conditioning. In order to calibrate the feedback path, a well-defined reference signal is inserted into the feedback path, and an appropriate calibration coefficient is then determined by a coefficient calibrator in response to the received reference signal. The calibration coefficient is provided to a compensator, which effectively compensates for changes in the transfer characteristics of the feedback path due to factors such as variations in ambient temperature and component aging. Accordingly, the feedback signal transferred over the calibrated feedback path will be an accurate representation of the output signal of the signal conversion system, thus allowing accurate adaptive signal conditioning.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Printer calibration method, printer and recording material
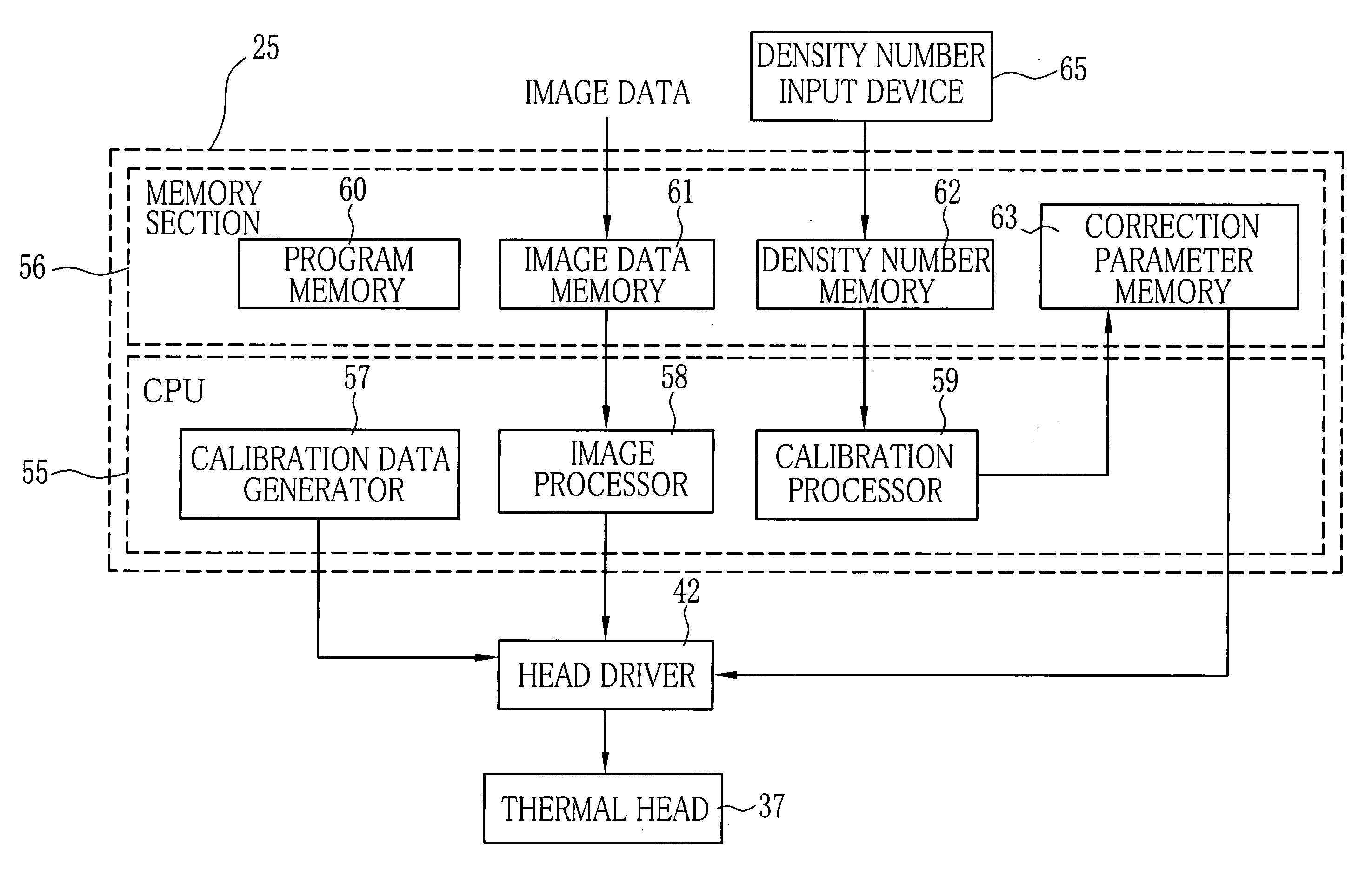
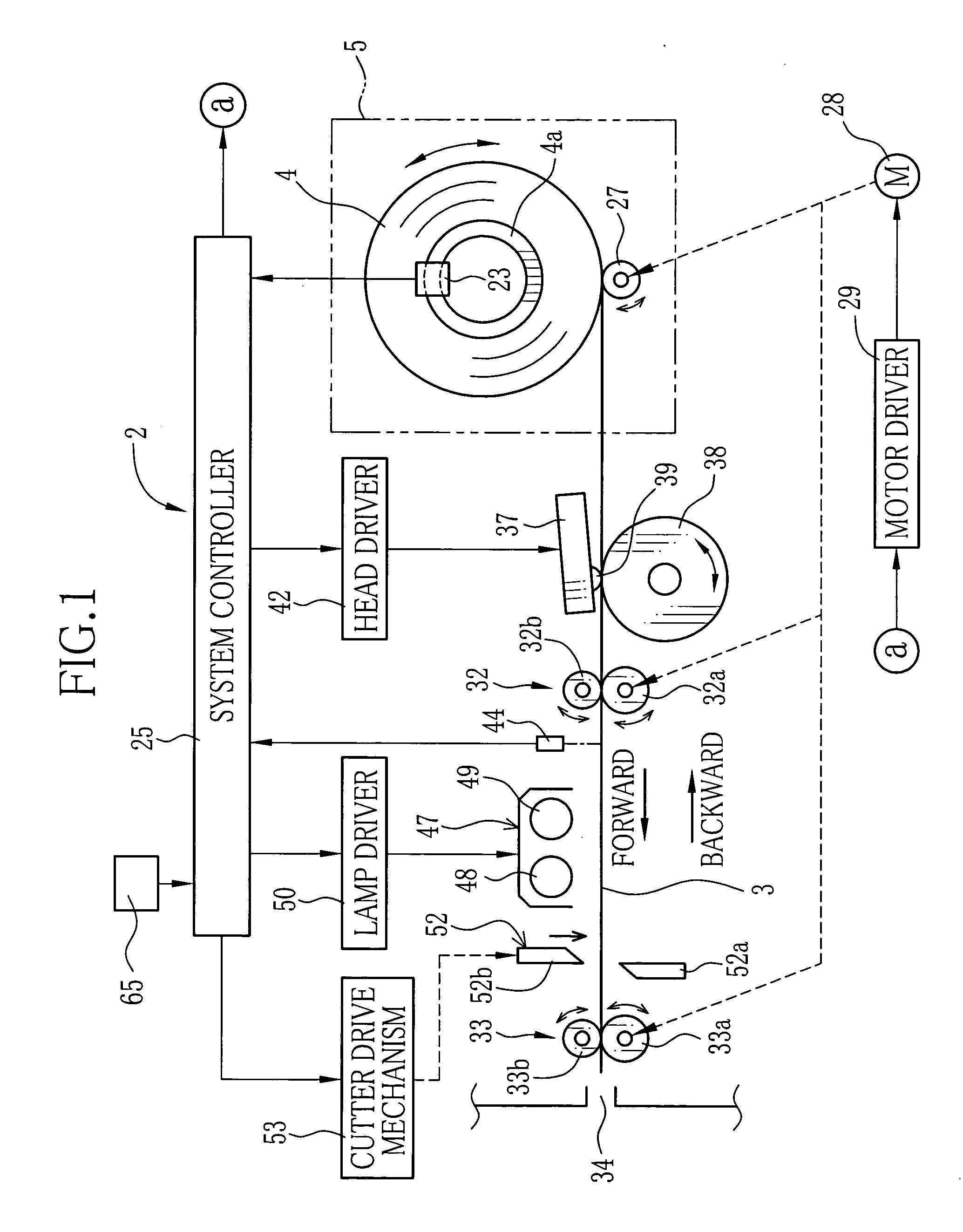
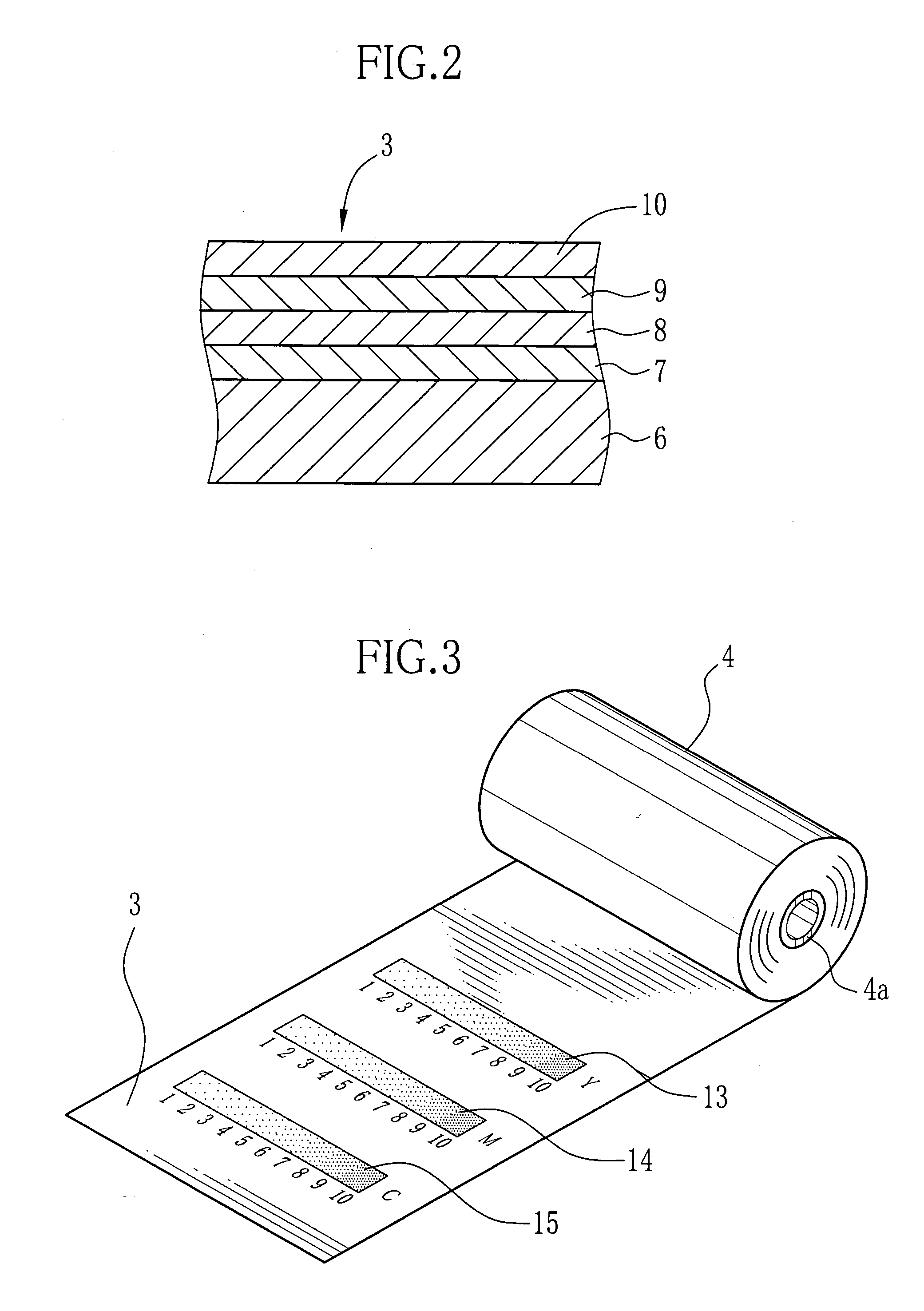
InactiveUS20050105112A1Easy to manufactureCalibration can be slowDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionComputer printing
Yellow reference patterns, magenta reference patterns and cyan reference patterns are printed as a gradation scale of each color on a leading end of a long web of color heat sensitive recording paper in the factory. Respective density grades of each color are indicated by density numbers. Yellow, magenta and cyan calibration patterns are printed by a color thermal printer to calibrate, at a constant density on the recording paper adjacently to the reference patterns of the corresponding colors. The user compares the calibration pattern of each color to the reference patterns of the corresponding color, to determine the density grade of the actual density of the calibration pattern. By entering the density number of the determined density grade for each color, the color thermal printer automatically corrects three color densities on the basis of the entered density numbers.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
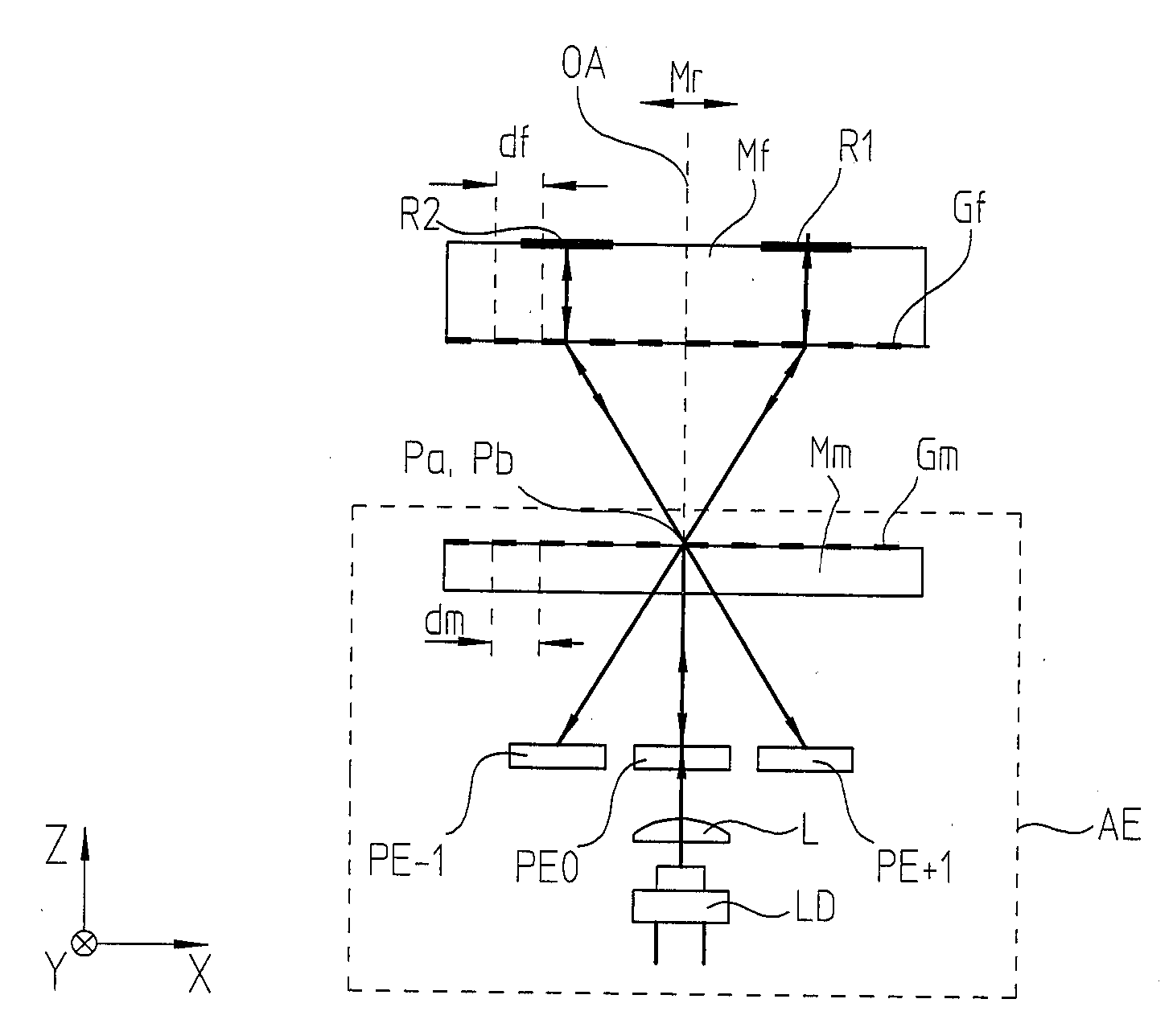
Optical position-measuring device
ActiveUS20080285058A1Reliable calibrationMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansLight beamOptoelectronics
An optical position-measuring device is arranged for recording the relative position of a scanning unit and a scale movable to it in at least one measuring direction. The scale is configured as a combined unit which includes at least one reflector element as well as a measuring graduation. A light source and one or more detector elements are assigned to the scanning unit. The scanning unit includes splitting device(s) which split the beam of rays, emitted by the light source, into at least two partial beams of rays in the measuring direction, which after being split, propagate in the direction of the scale.
Owner:DR JOHANNES HEIDENHAIN GMBH
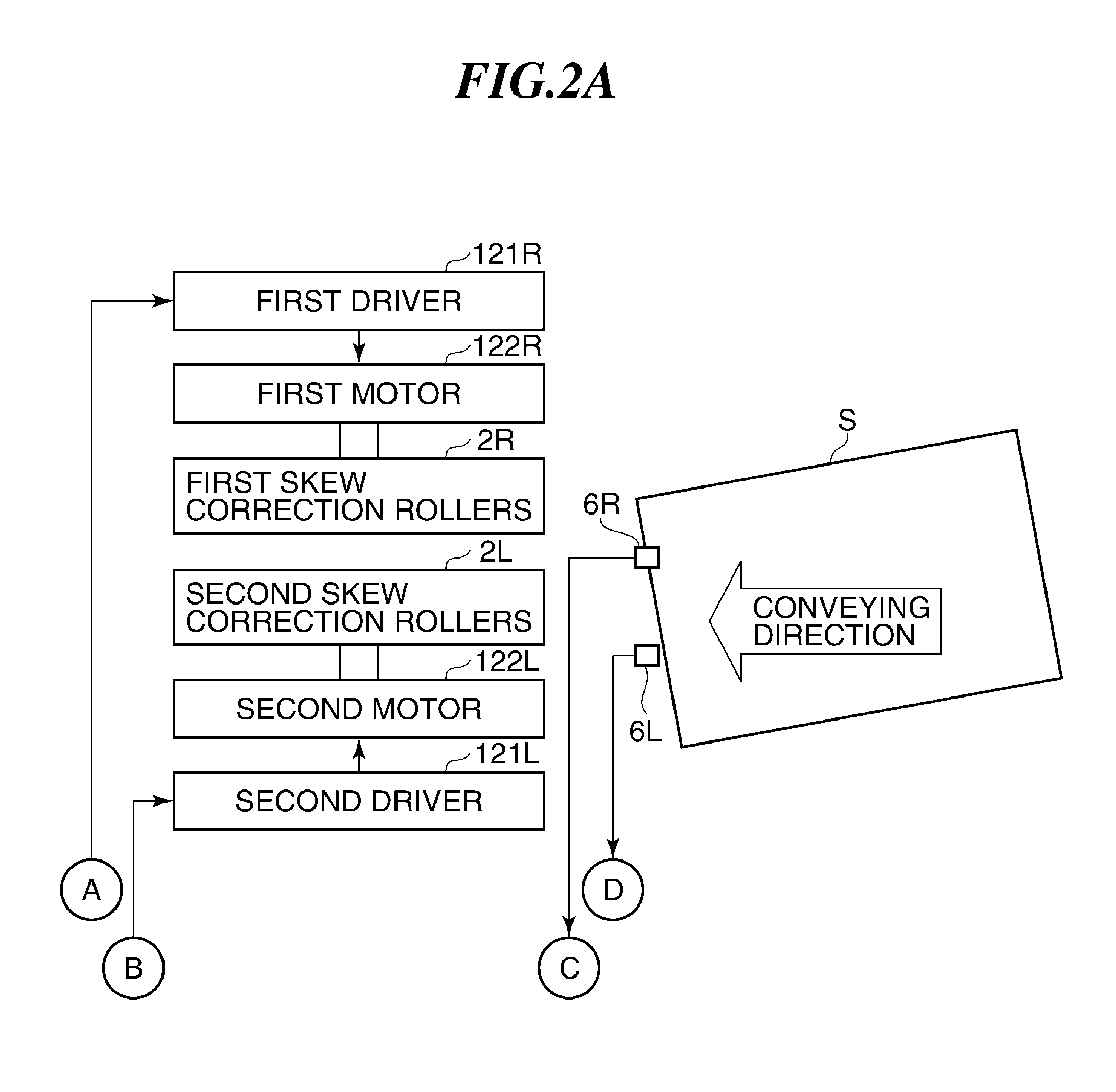
Image forming apparatus and sheet conveying method that correct for skew of sheet conveyed to image forming unit
InactiveUS20110081181A1Reliably correct for skew of a sheet being conveyedReliable calibrationRegistering devicesFunction indicatorsEngineeringMechanical engineering
An image forming apparatus that can reliably correct for skew of a sheet being conveyed. The amount of skew of the sheet is detected, and the amount of toner used for an image formed on a first surface of the sheet is determined. When the sheet with the image formed on the first surface thereof is conveyed so as to form an image on a second surface of the sheet, a skew correction roller unit is controlled so as to correct for the skew of the sheet based on the detected amount of skew and the determined amount of toner used.
Owner:CANON KK
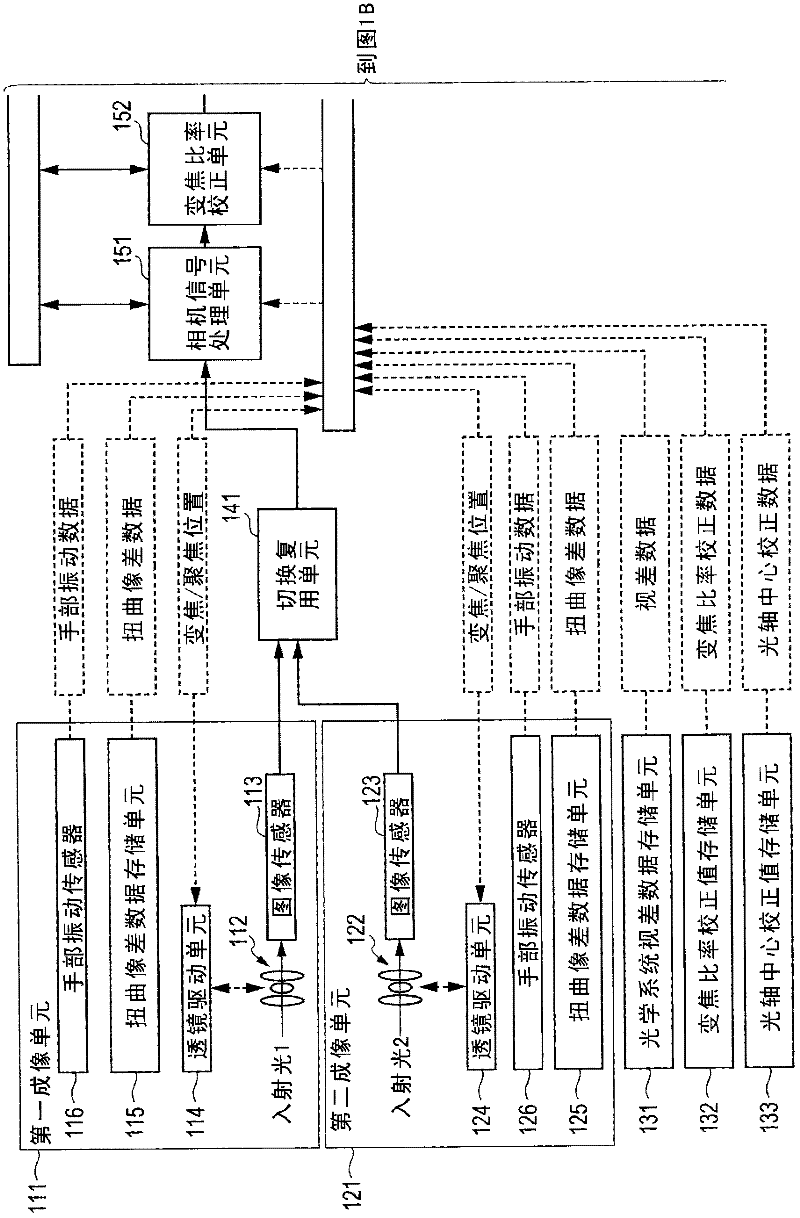
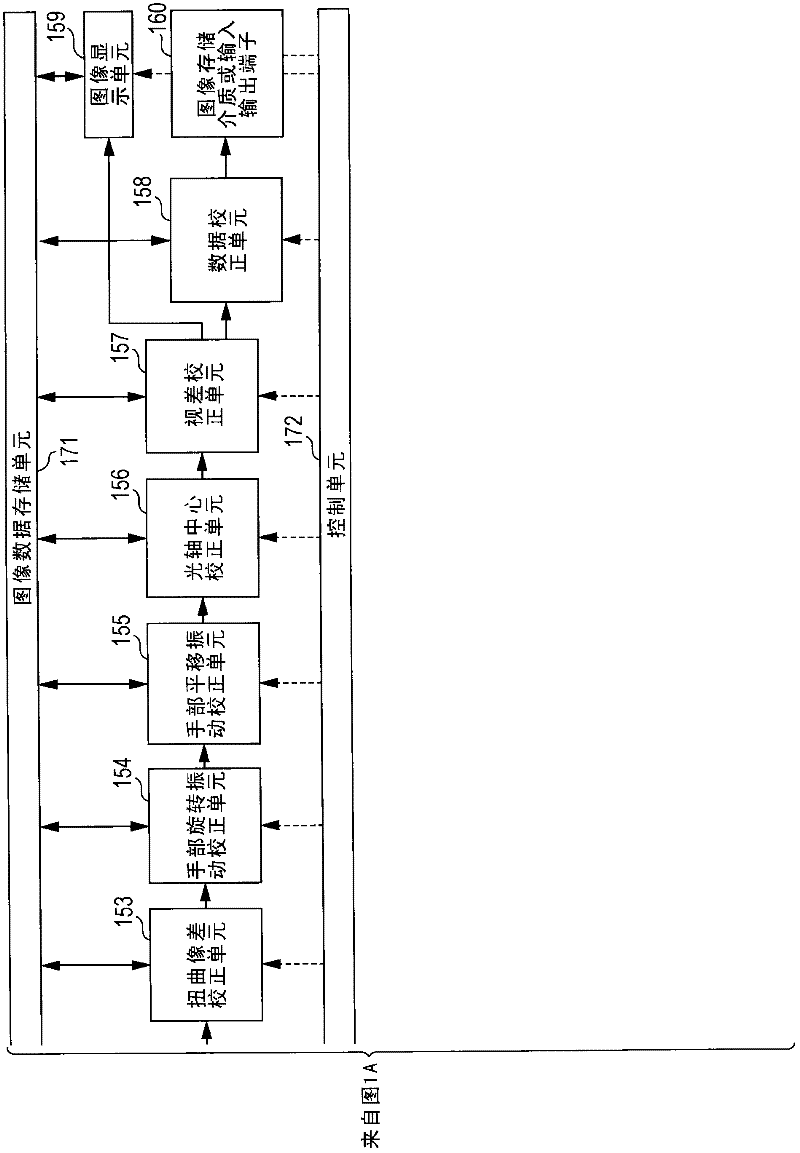
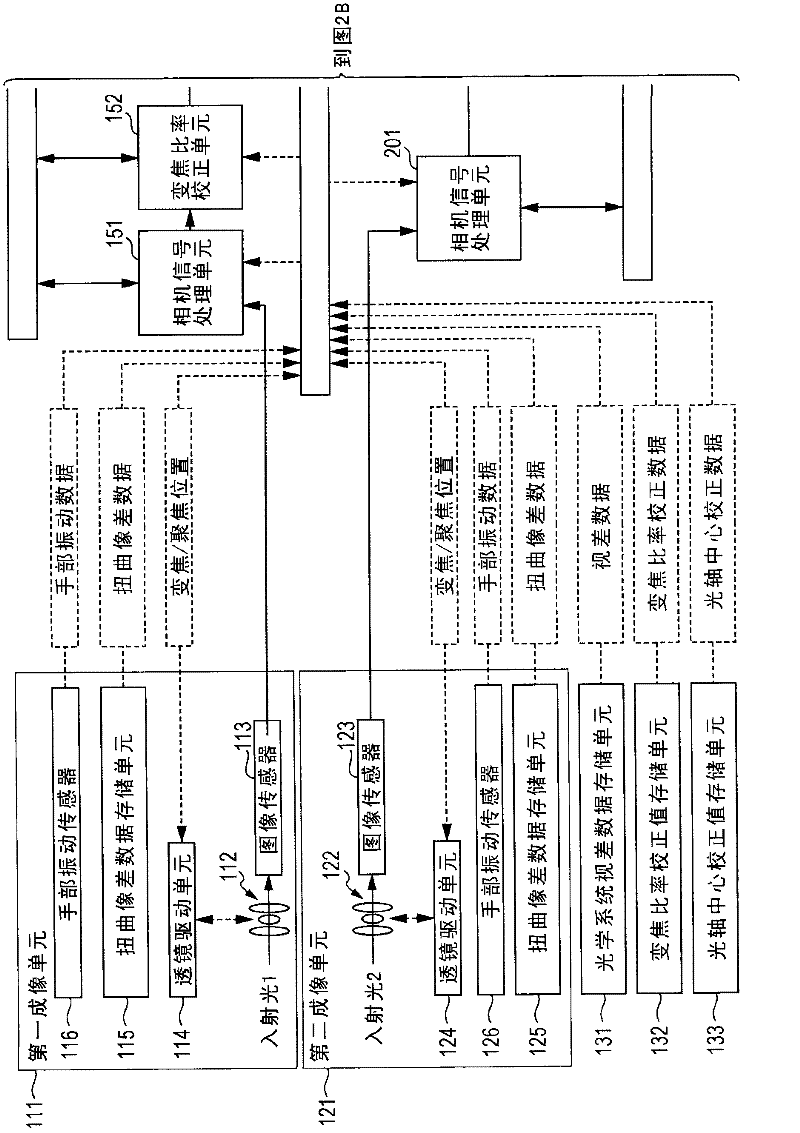
Imaging apparatus, image processing apparatus, and image processing method, and program
ActiveCN102457752AReliable calibrationQuality improvementTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging processingImaging equipment
Disclosed is an imaging apparatus including a plurality of imaging units; a correction unit that executes a correction process for images captured by a plurality of the imaging units; and a control unit that computes a correction parameter applied to a correction process in the correction unit, wherein the correction unit executes distortion aberration correction and hand-vibration correction for each of the captured images and an image characteristic matching correction process for matching characteristics between a plurality of images captured by a plurality of the imaging units.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method of in situ calibrating load sensors of a wind turbine blade
ActiveUS9353727B2Reliable calibrationReduce needMachines/enginesWind motor combinationsTurbine bladeHorizontal axis
A method of in situ calibrating load sensors of a horizontal axis wind turbine is described. The method comprises the steps of: a) determining a rotor azimuth angle of a first wind turbine blade, b) determining a pitch angle of the first wind turbine blade, c) measuring loads in a first cross-section of the first wind turbine blade using the first load sensors, d) calculating theoretical loads based on at least the rotor azimuth angle and the pitch angle of the blade determined in steps a) and b), e) comparing the loads measured in step c) with the theoretical loads calculated in step d), and f) calibrating the first load sensors based on the comparison of step e), wherein the calibration are based only on measurements carried out, when the generator is cut out.
Owner:LM GLASSFIBER
Error identification method of machine tool and error identification system of the same
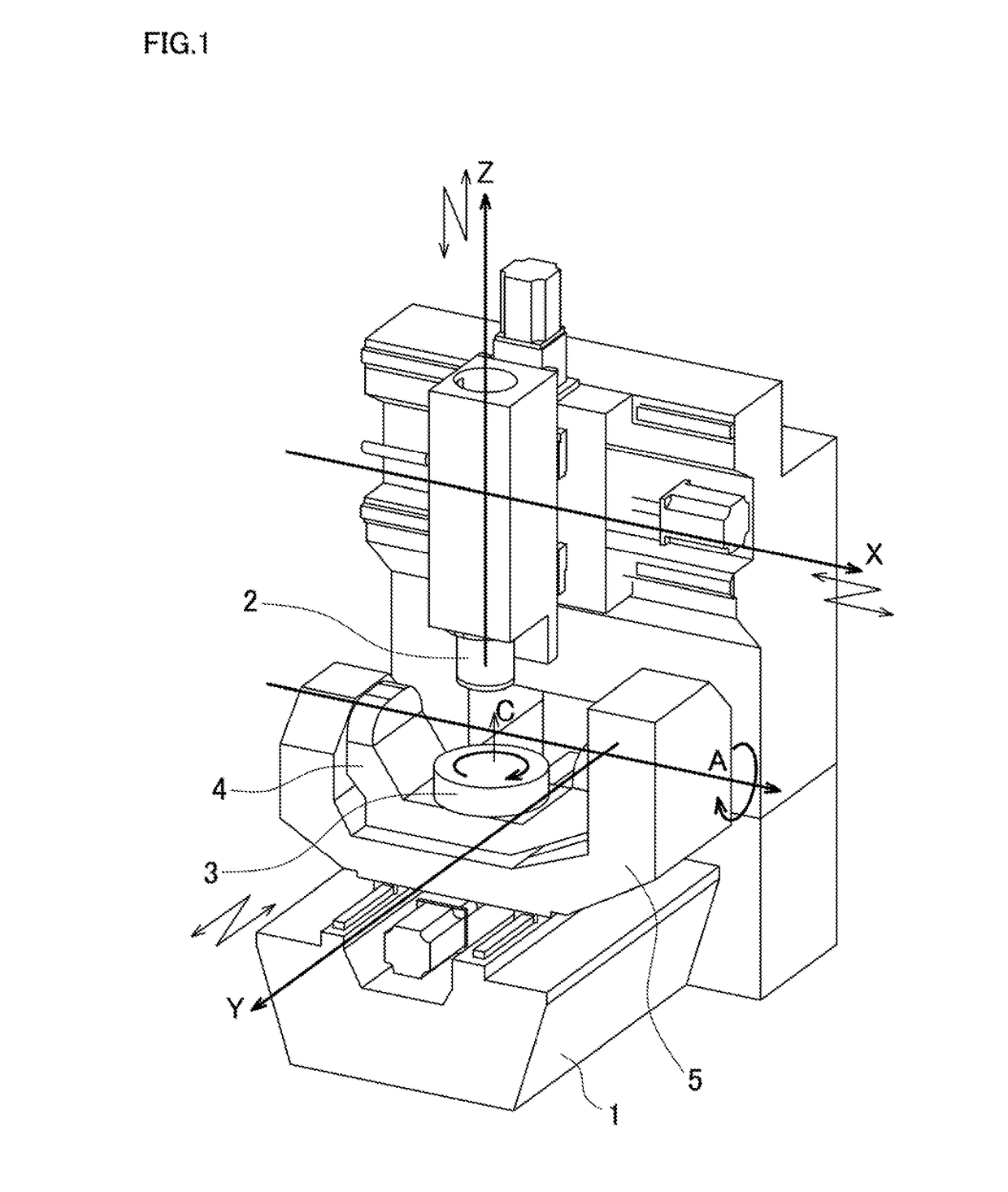
ActiveUS20170297160A1Reduce loadReliably performing calibrationMeasurement/indication equipmentsLarge fixed membersGeometric errorEngineering
An error identification method includes a tool sensor position acquisition stage, a reference block position acquisition stage, a relative position calculation stage, a reference tool position acquisition stage, a position measurement sensor measurement stage, a length compensation value calculation stage, a diameter compensation value acquisition stage, a position measurement stage, a position compensation stage, and a geometric error identification stage. The diameter compensation value acquisition stage acquires a radial direction compensation value of the position measurement sensor with the measured jig. The position measurement stage indexes the rotation axis to a plurality of any given angles and measures respective positions of the measured jig. The position compensation stage compensates the position measurement value at the position measurement stage using the length direction compensation value and the radial direction compensation value. The geometric error identification stage identifies the geometric error from the plurality of position measurement values.
Owner:OKUMA CORP
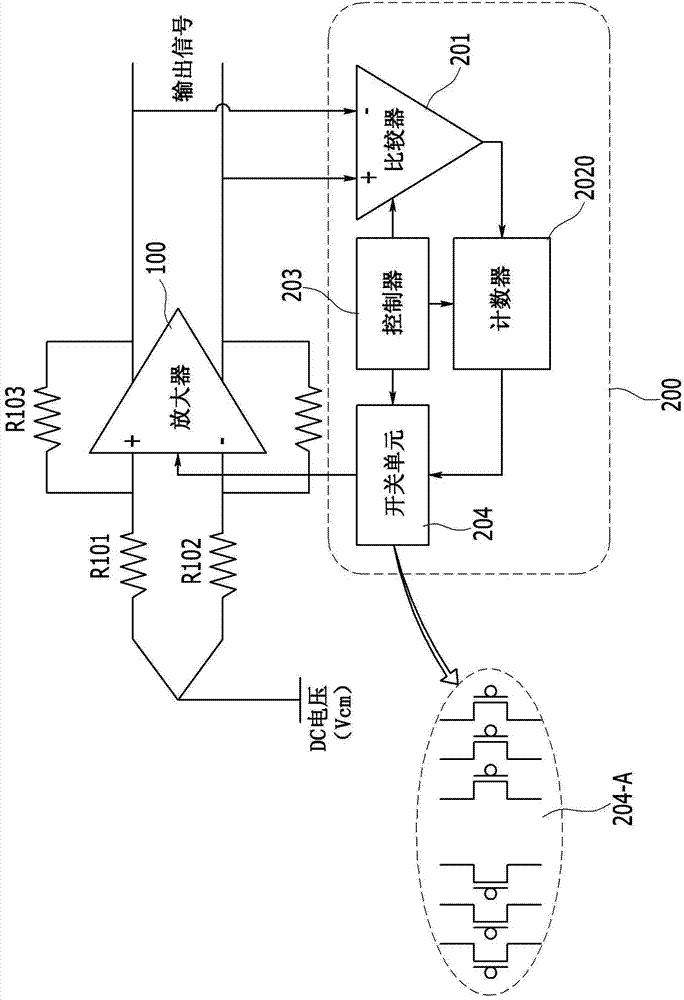
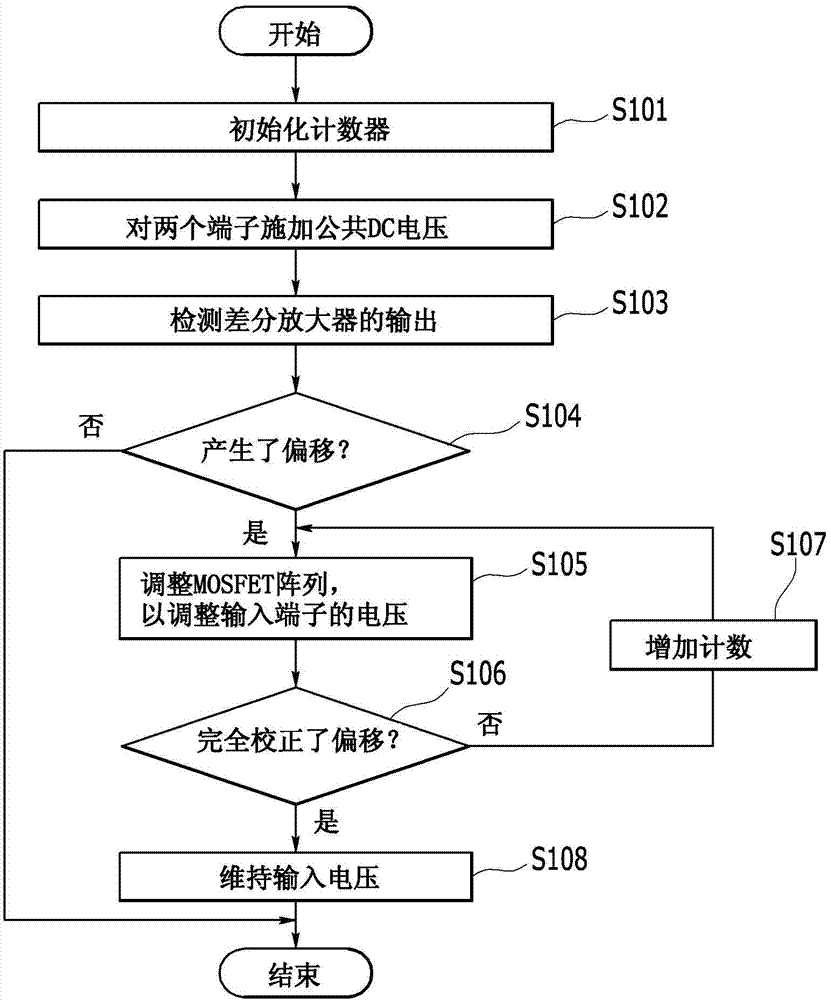
Offset correction apparatus for differential amplifier and method thereof
ActiveCN104716914AReliable calibrationSimple structureAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationDifferential amplifiersAmplification factorDifferential amplifier
An apparatus of correcting an offset for a differential amplifier which compensates a direct current (DC) offset voltage in a differential analog signal amplifier using a resistive feedback structure to minimize a deviation and a method thereof are provided. The apparatus includes a differential amplifier that is configured to amplify a common DC voltage input via a first resistor and a second resistor with a predetermined amplification factor to output the amplified voltage. A controller is configured to compare voltages output from both output terminals of the differential amplifier to determine whether to generate an offset. In addition, the offset is corrected using a switching unit coupled in parallel to an input terminal of the differential amplifier in response to detecting a generated offset. The controller is also configured to adjust an asymmetric property of the input terminal of the differential amplifier to correct the generated offset.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Optical arrangement for microscope and microscope
An optical arrangement for a microscope, in particular for a scanning microscope, with a beam splitter 1 arranged in a divergent and / or convergent beam path for separating an illumination light 2 that is produced by an illumination source from a detection light 3 that is emitted by a sample being tested, which with regard to reliable correction of imaging errors can be implemented and developed even when using thick beam splitters 1 such that the beam splitter 1 is wedge-shaped and implemented as a beam splitter plate for reflection primarily at a glass-air interface 4. Furthermore, a microscope with such an optical arrangement is disclosed.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
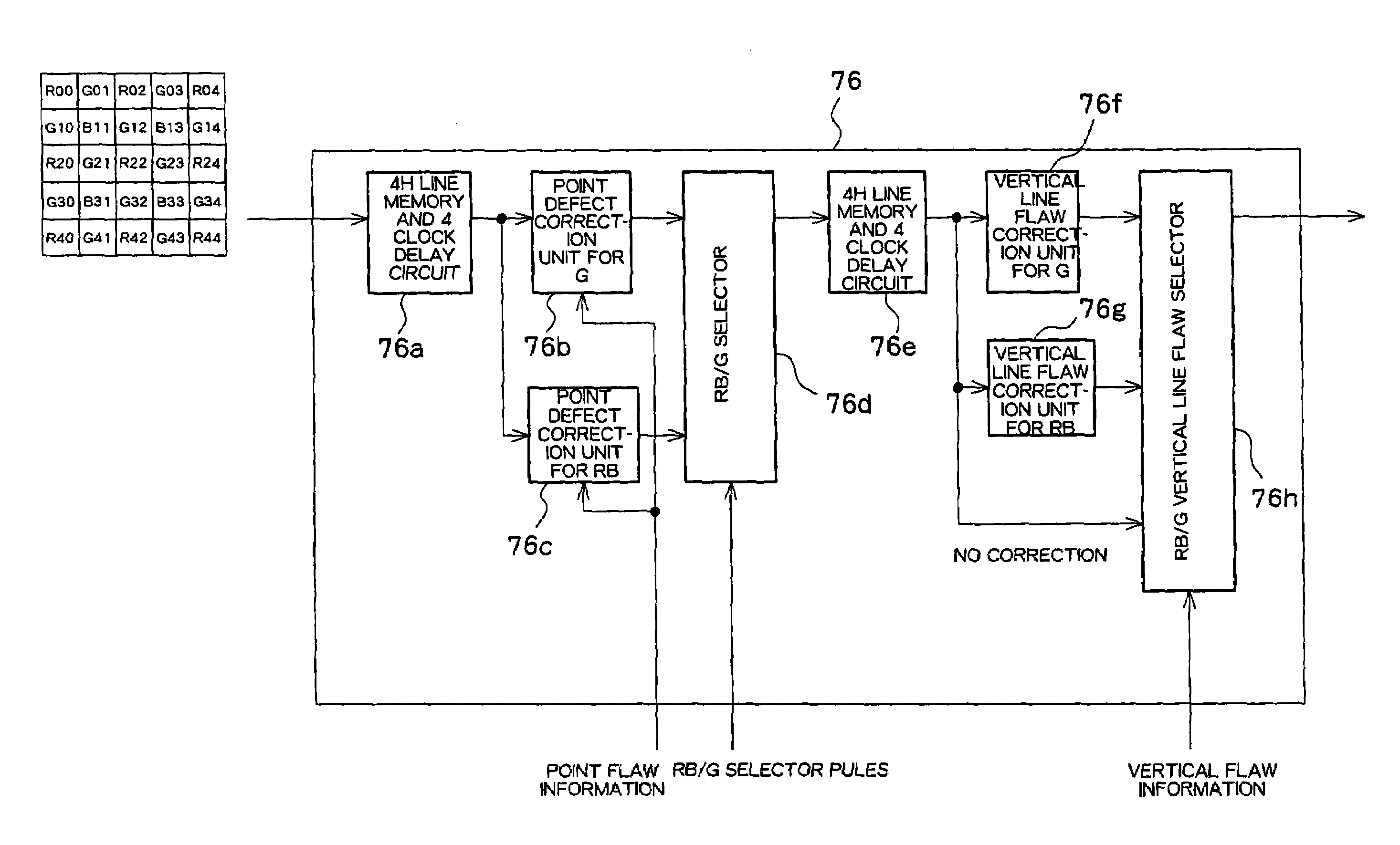
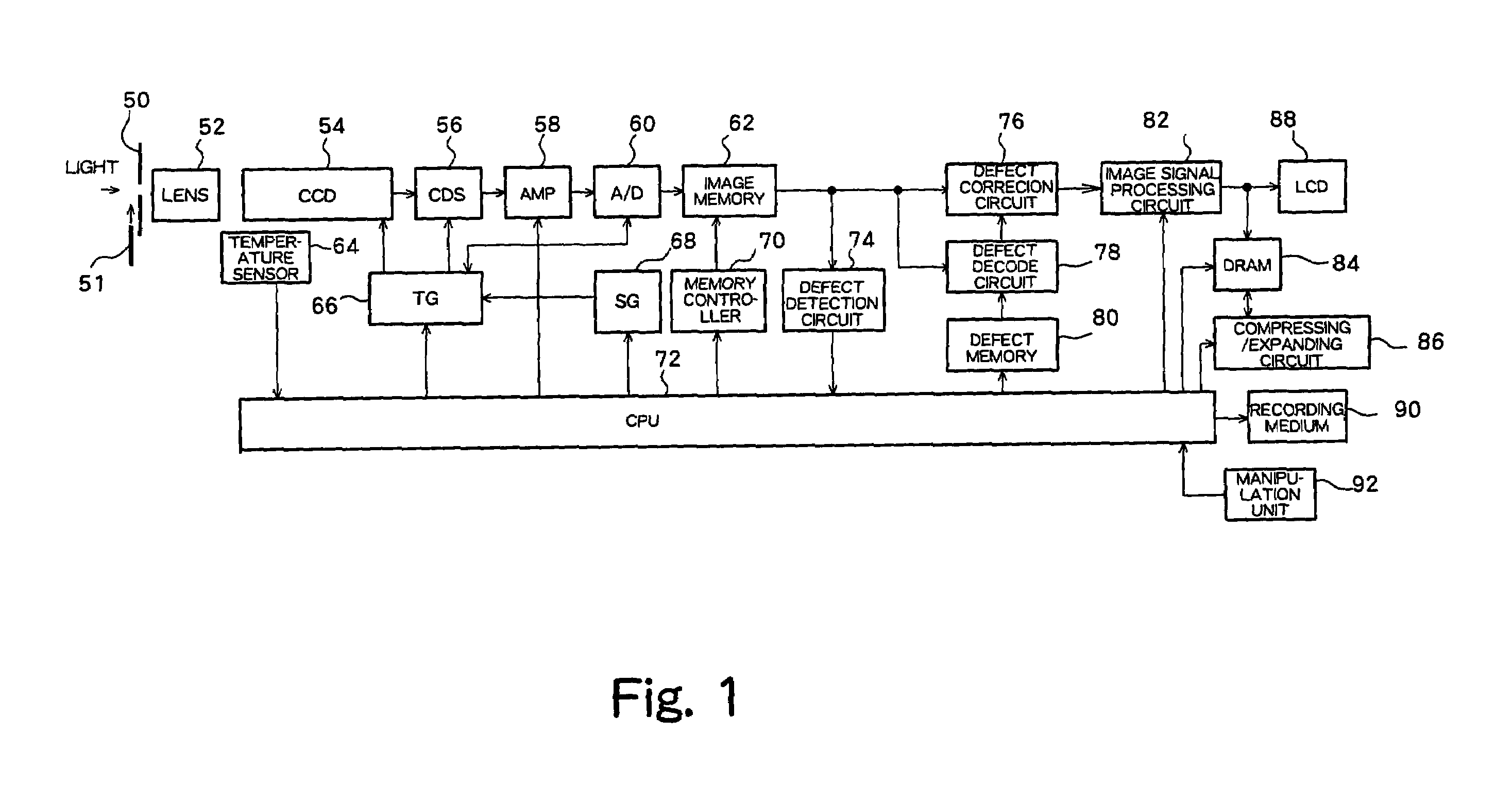
Pixel defect correction device
InactiveUS7593569B2Reliable calibrationTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsLine defectsComputer science
A point defect and a line defect in a captured image resulting due to an imaging element defect in a digital camera are interpolated. A defect correction circuit of a digital camera simultaneously corrects a point flaw, a vertical line flaw, and a horizontal line flaw in a captured image. In consideration of cases in which a point flaw and a vertical line flaw are present adjacent to each other, the defect correction circuit executes predetermined difference calculations using pixels surrounding a target pixel to be corrected and determines an interpolation pattern based on a comparison of magnitude among the difference calculation values. The defect correction circuit also selects, for interpolation, an interpolation pattern from among interpolation patterns prepared in advance based on an adjacent pattern of the point flaw and line flaw. The adjacent pattern is detected by a defect decode circuit 78.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
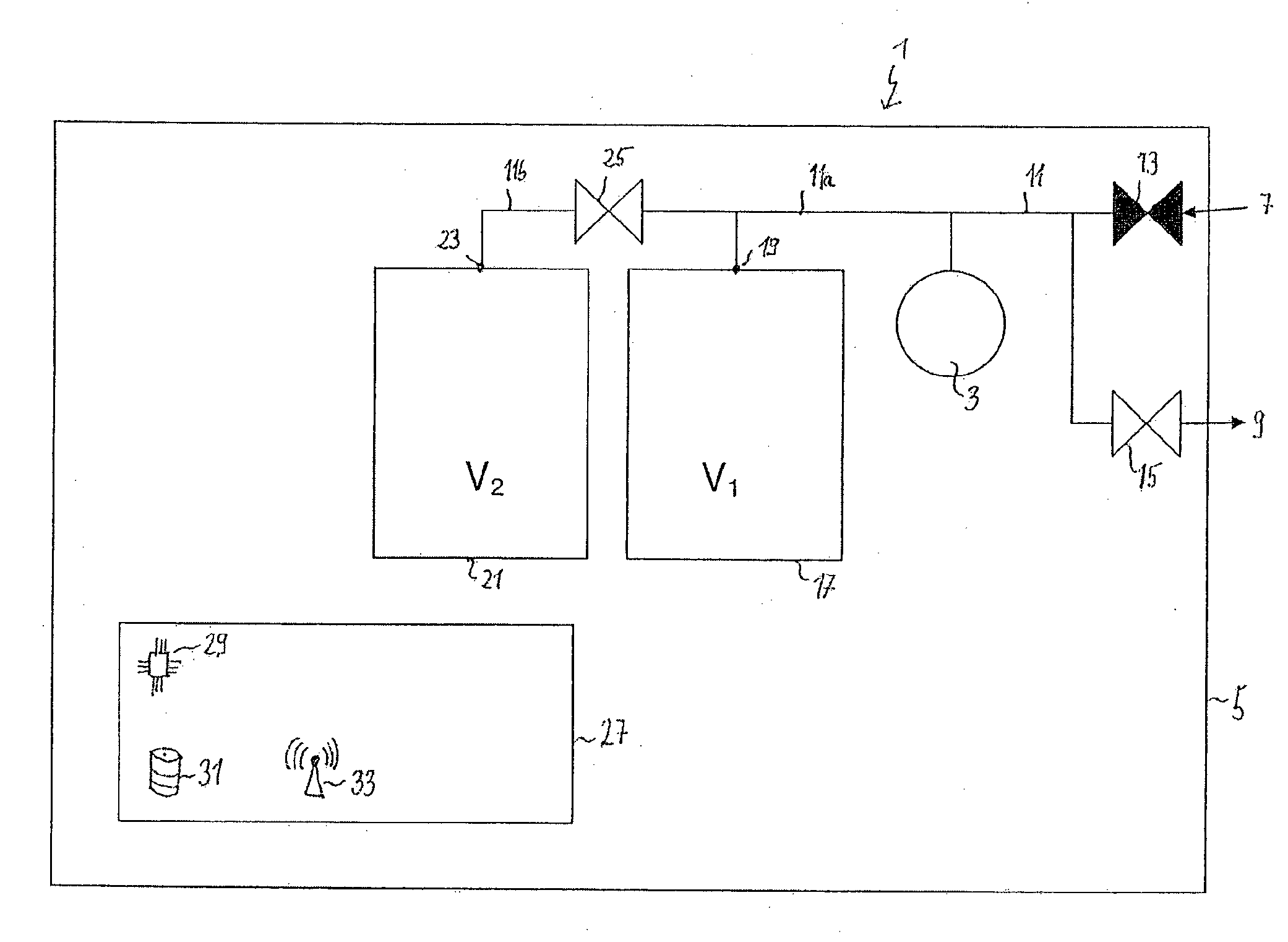
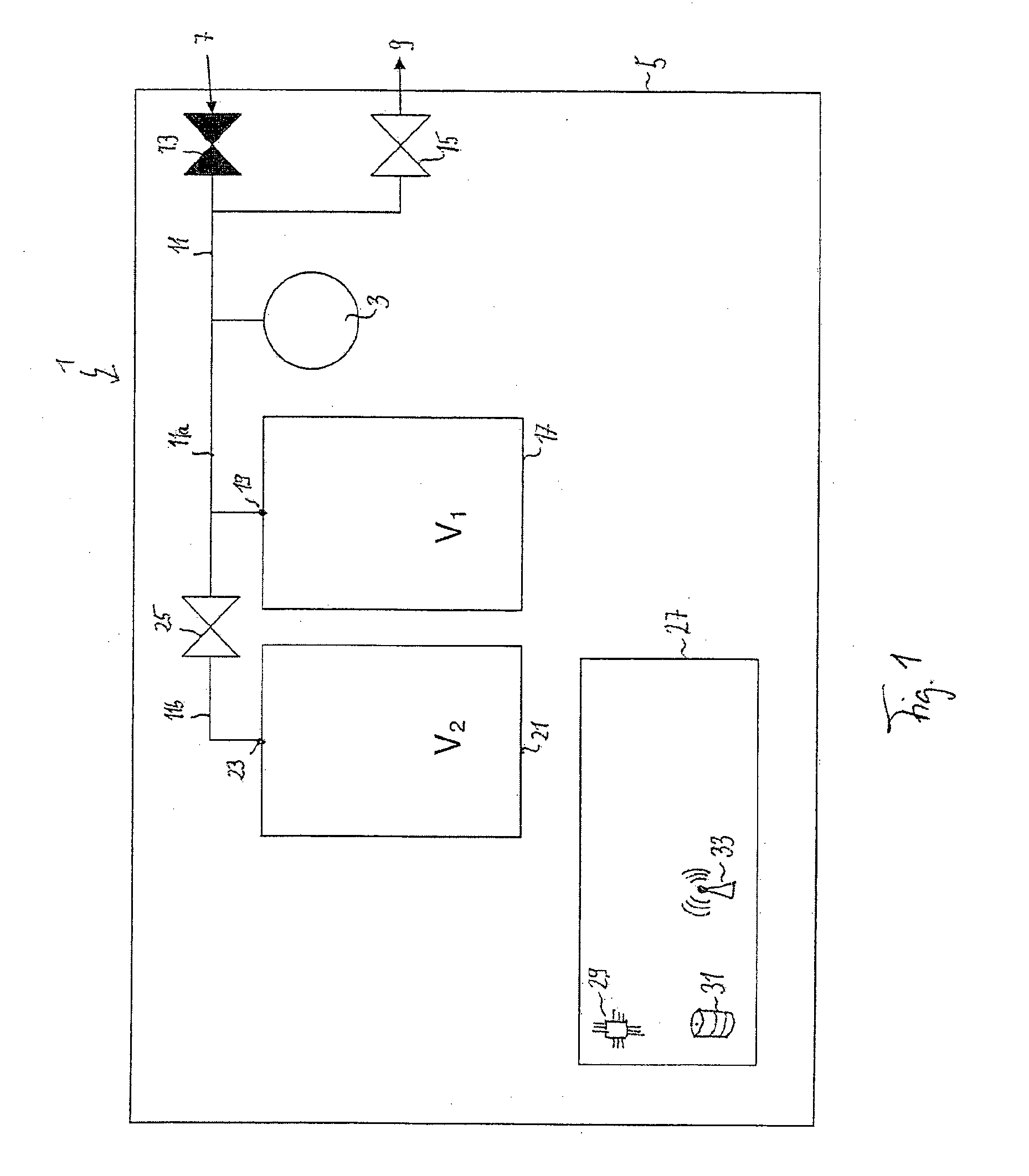
Method and device for verification and/or calibration of a pressure sensor
ActiveUS20150226628A1Improve accuracyReliable calibrationFluid pressure measurementEngineeringForce sensor
A method for calibrating a pressure sensor includes connecting the pressure sensor to first and second fluid storage vessels; providing an initial fluid pressure at the pressure sensor and at the fluid storage vessels; and carrying out a pressure measurement of the initial fluid pressure at a time t0. The method then disconnects the second fluid storage vessel from the pressure sensor and the first fluid storage vessel; provides a first fluid pressure at the second fluid storage vessel; and carries out a pressure measurement of the first fluid pressure at a time t1. The method then connects the second fluid storage vessel with the pressure sensor and the first fluid storage vessel, so that a second fluid pressure between the initial and first fluid pressures is provided at the pressure sensor; and carries out a pressure measurement of the second fluid pressure at a time t2.
Owner:SARTORIUS STEDIM BIOTECH GMBH
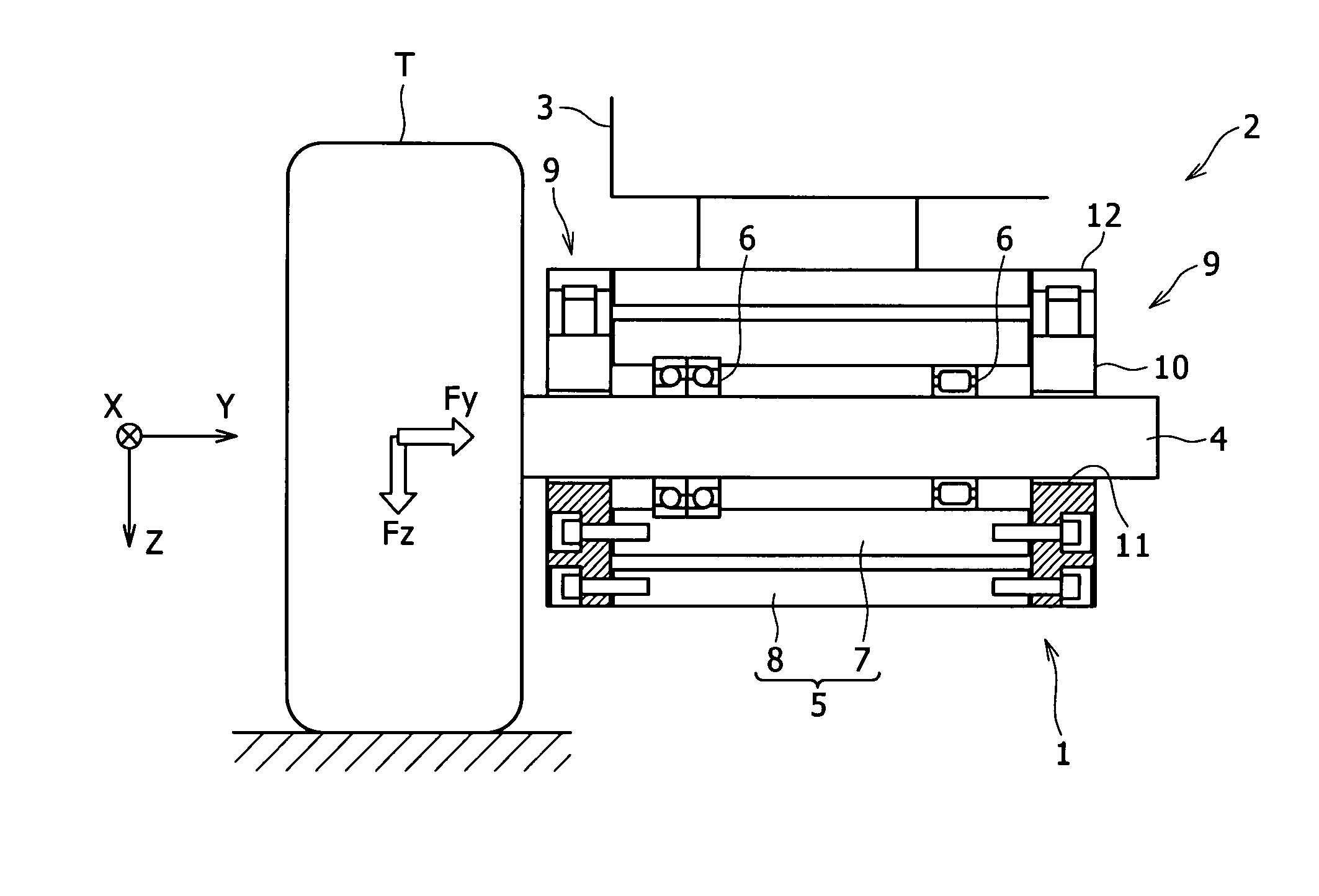
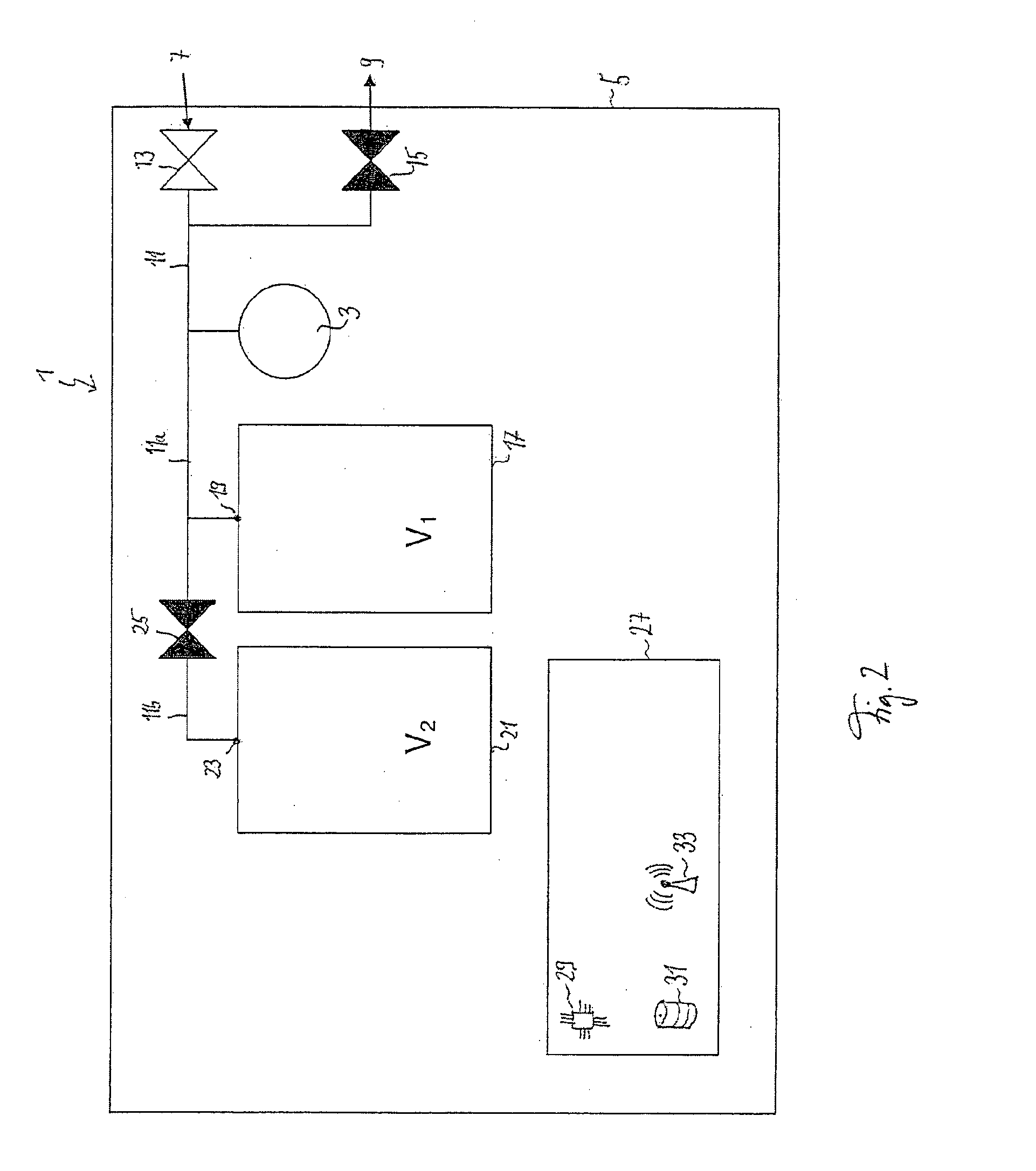
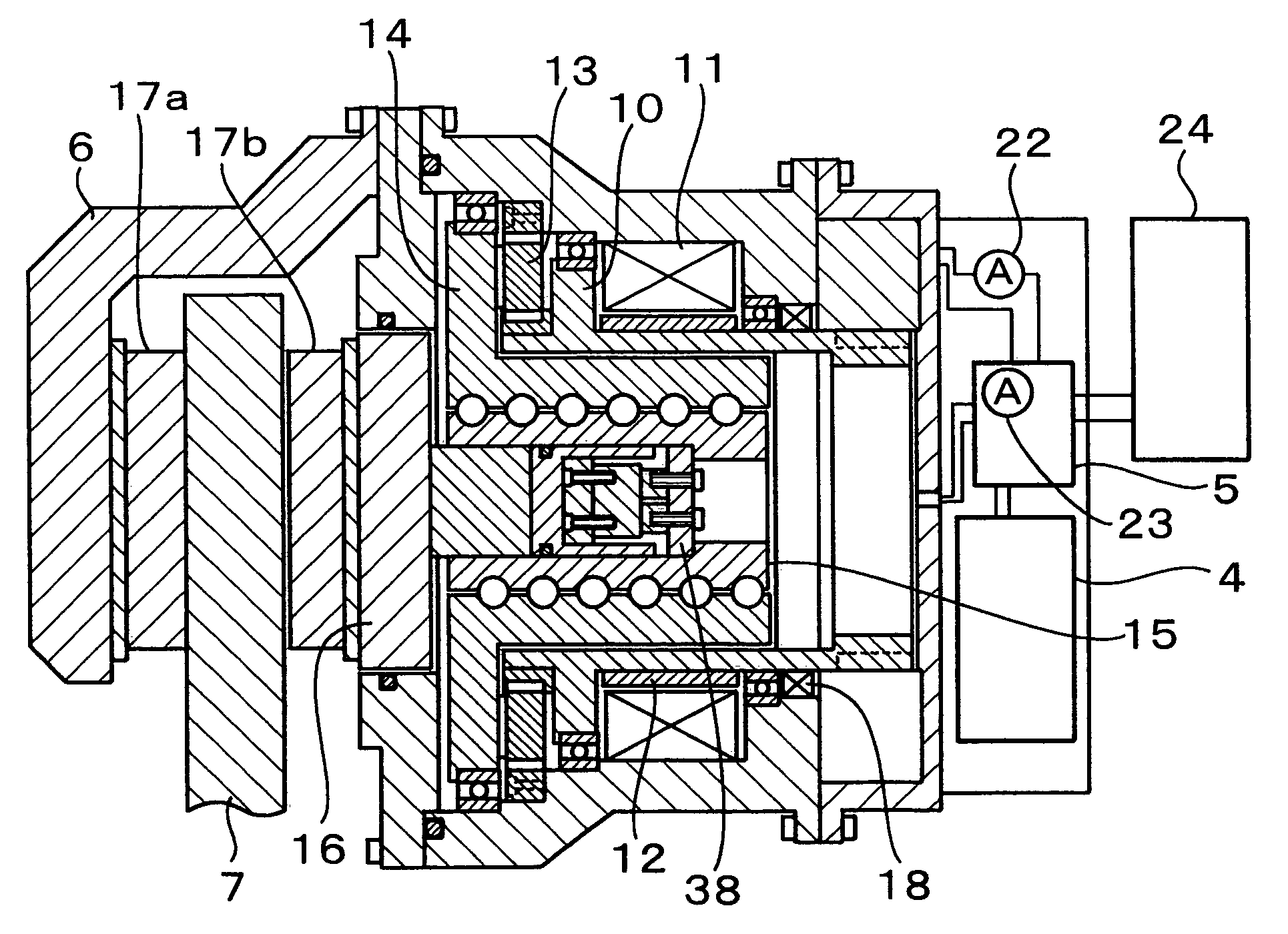
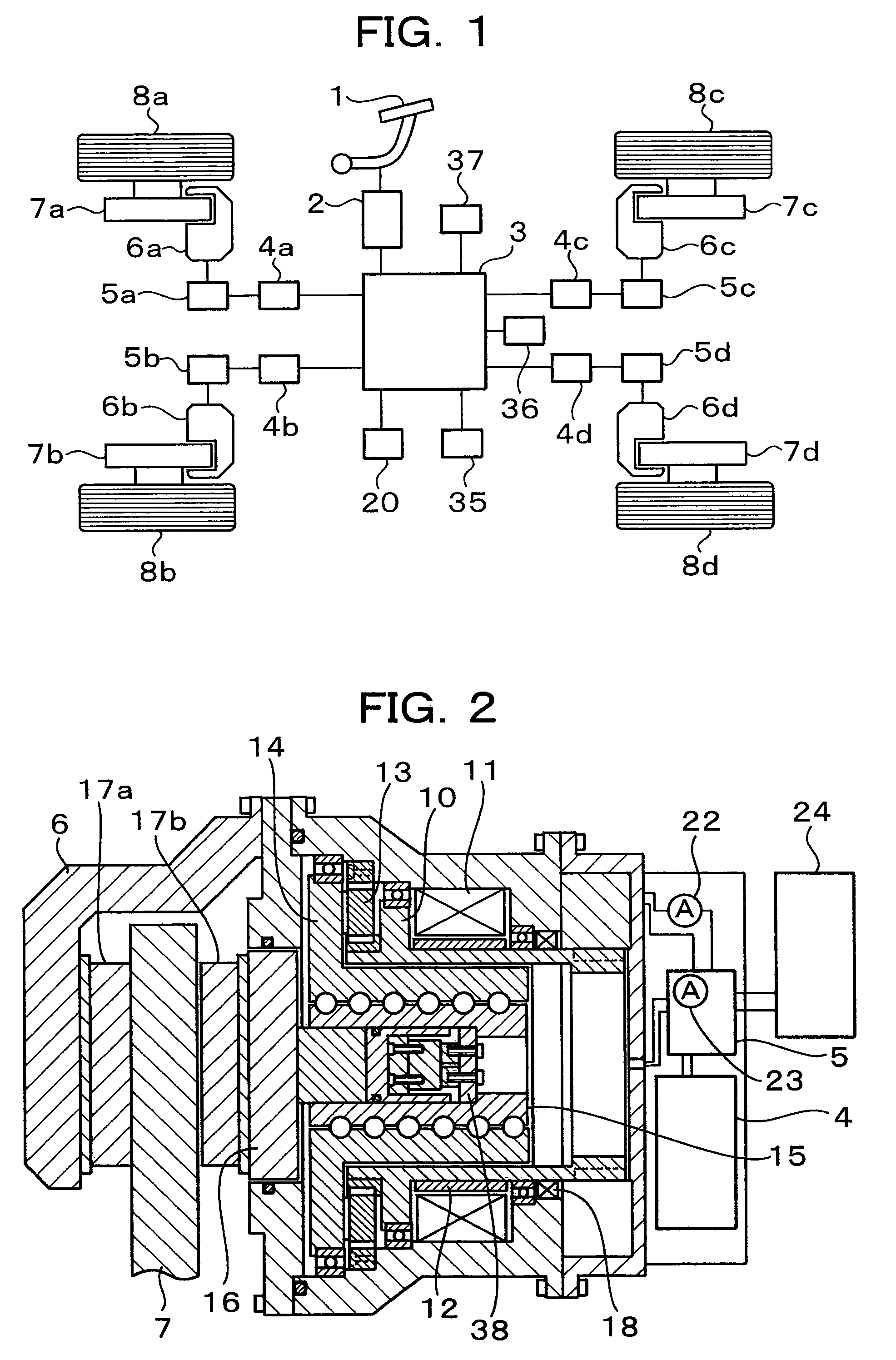
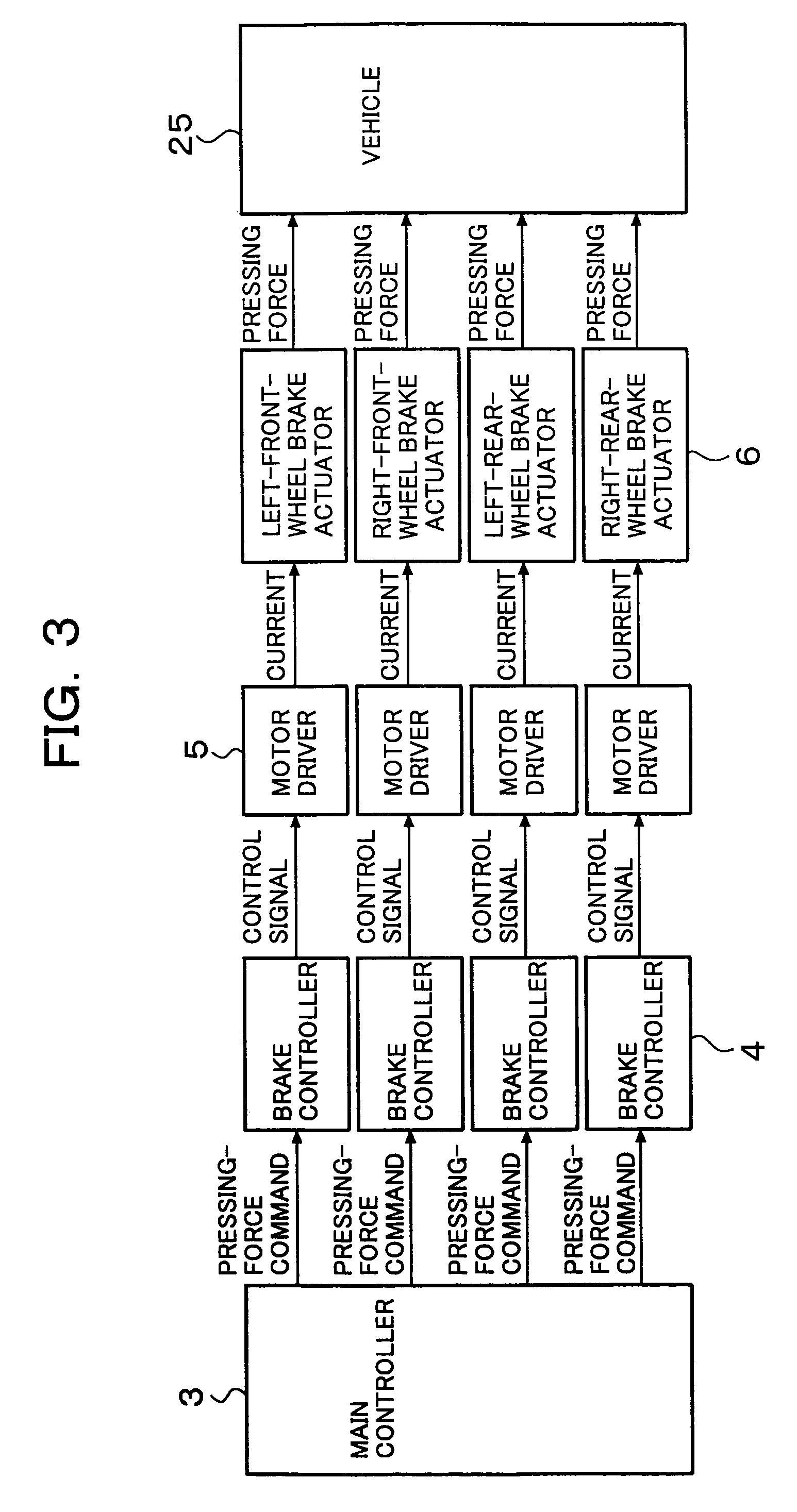
Brake control apparatus for vehicle
ActiveUS7565954B2Improve driving stabilityImprove securityBraking action transmissionMechanically actuated brakesEngineeringActuator
A brake control apparatus for a vehicle having brake devices for generating pad-pressing forces at respective wheels includes brake control units for individually controlling the pad-pressing forces at the respective wheels; a storing unit for storing drive data required for controlling the pad-pressing force at each wheel; a vehicle-driving-state detector for detecting a driving state of the vehicle; and a vehicle controller for controlling a vehicle driving state using the brake control unit for each wheel. Memory data representing the relationship between a motor position and the pad-pressing force is updated using the state of brake actuators obtained when the driving state of the vehicle is stabilized by operating the brake devices during braking.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com