Patents
Literature
379results about "Switch condition indication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
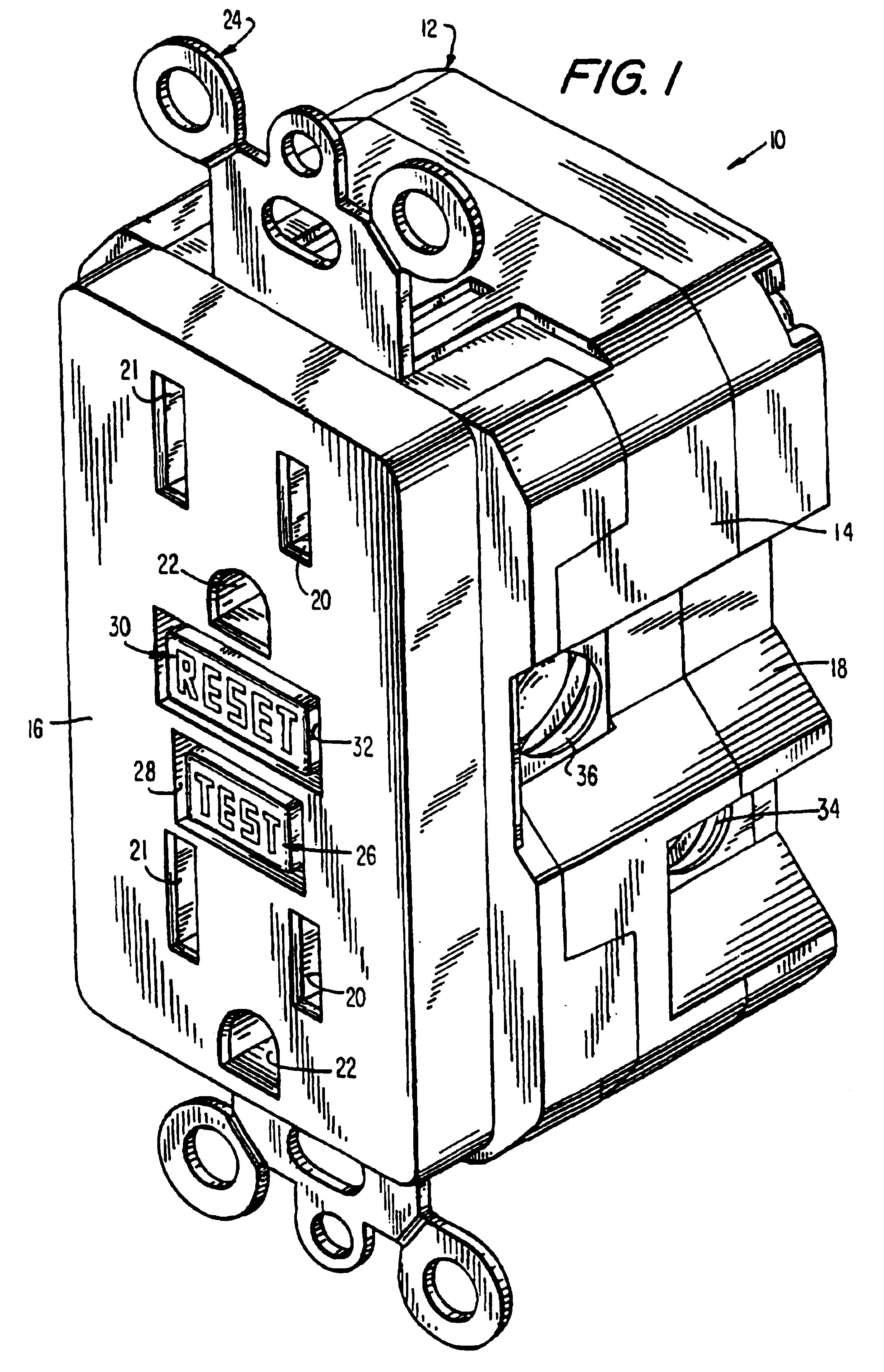
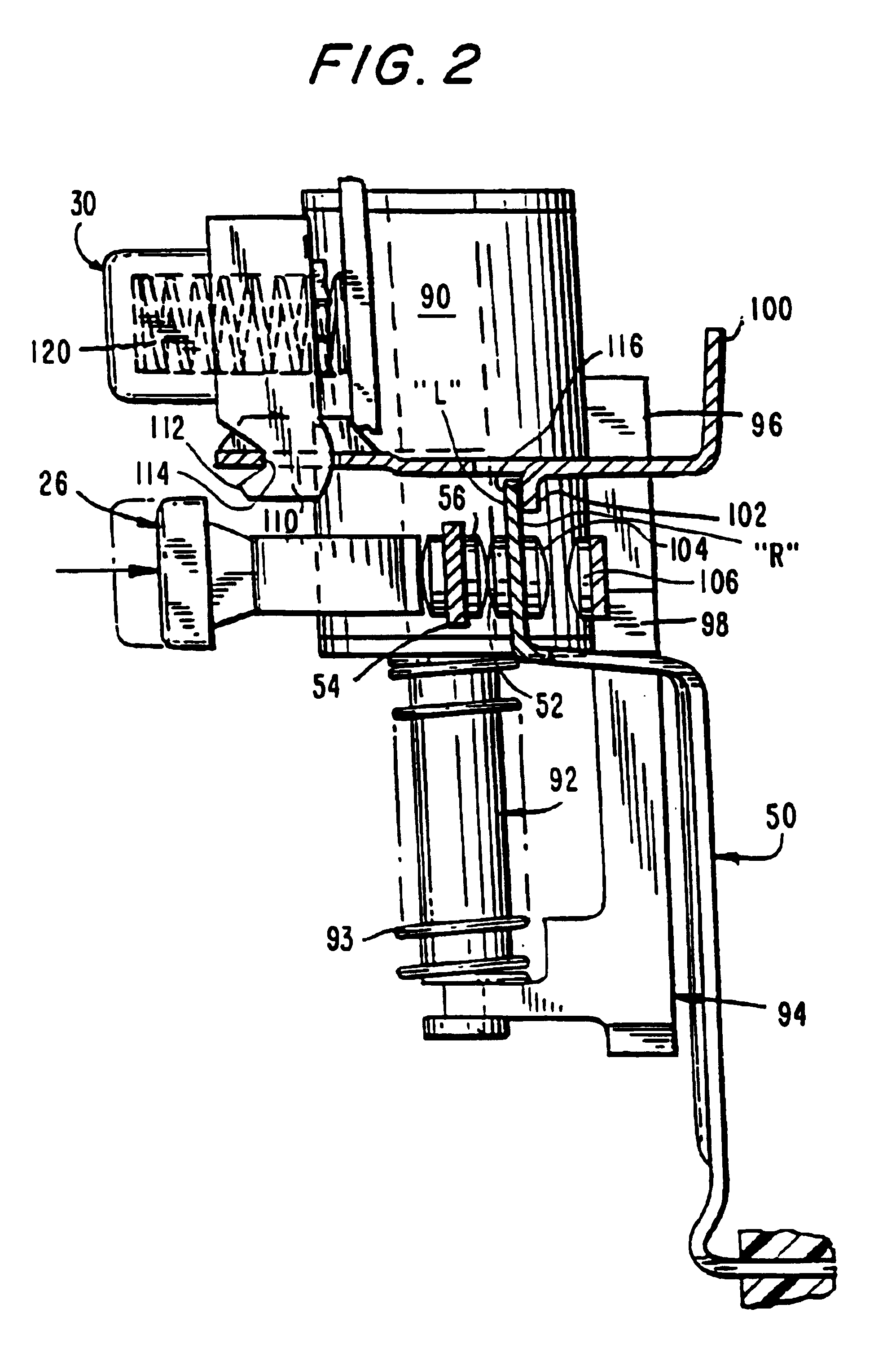
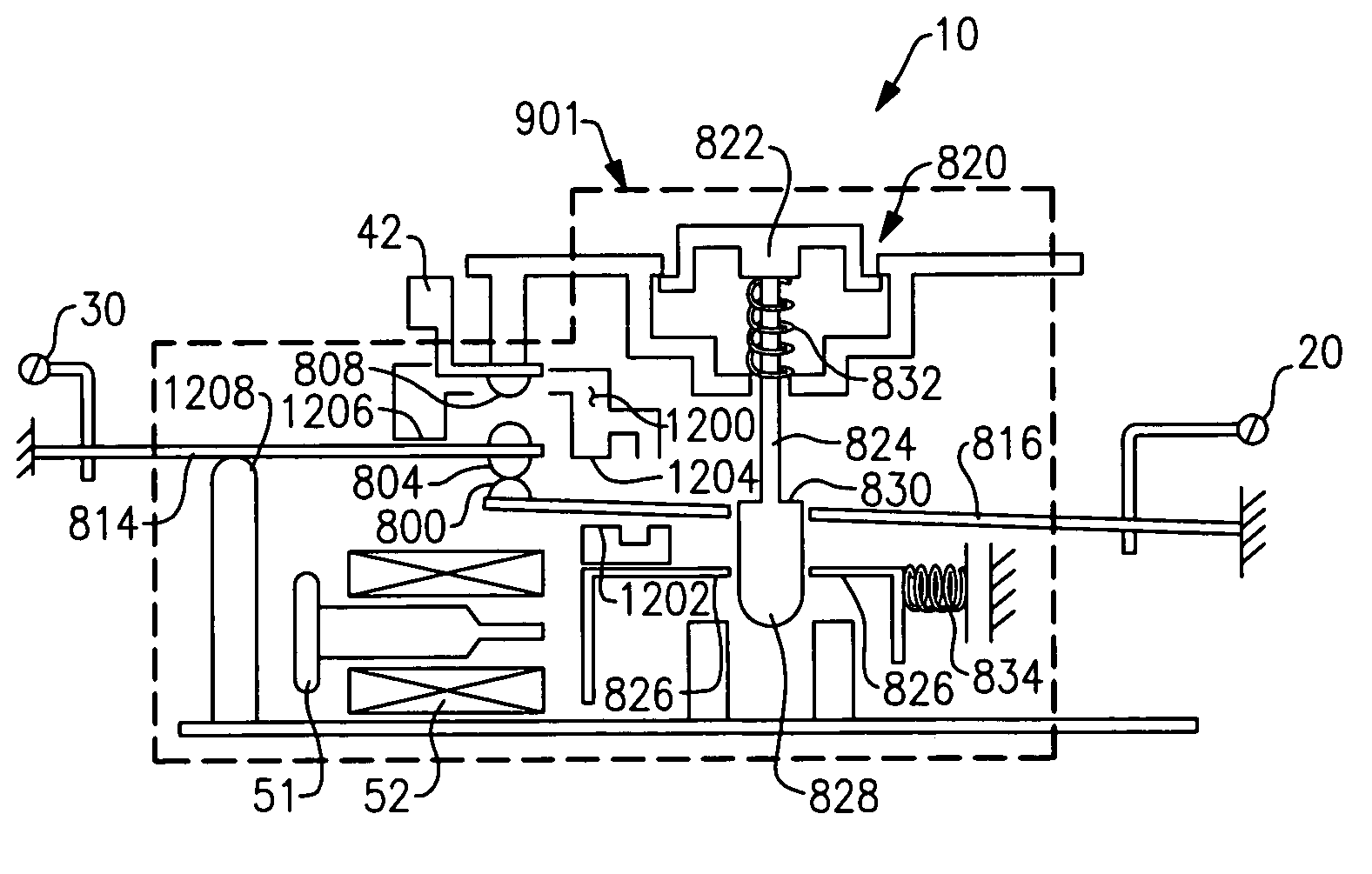
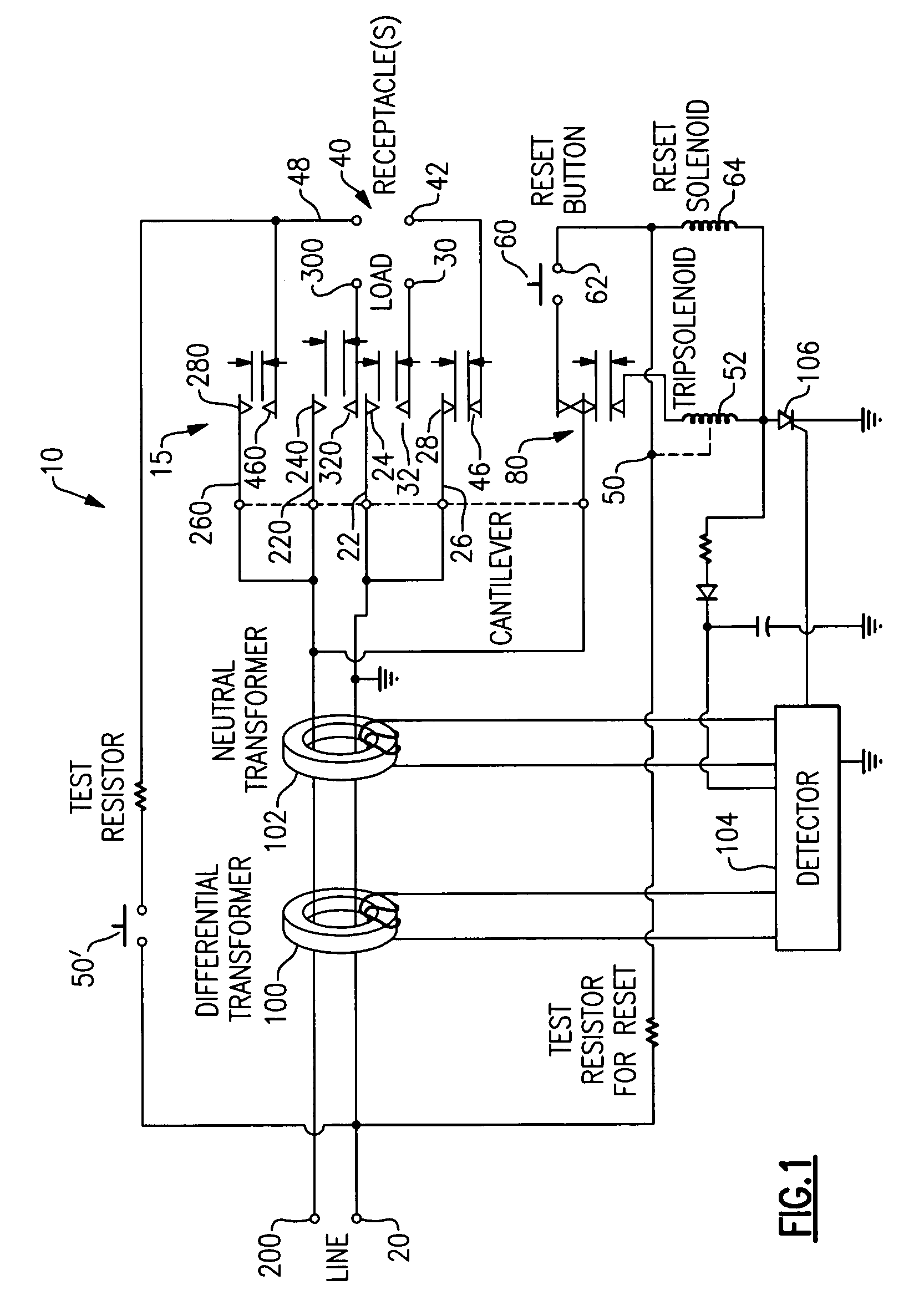
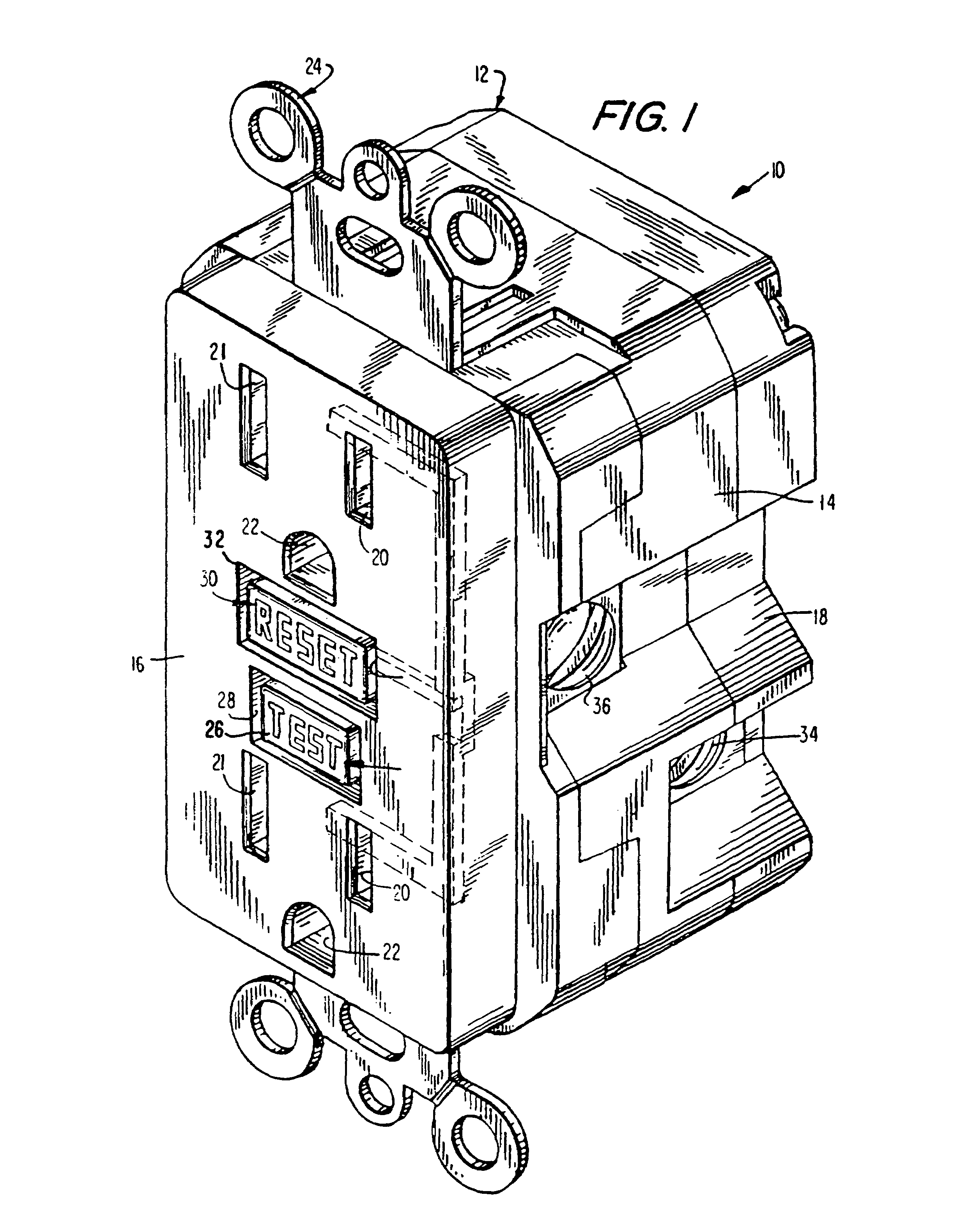
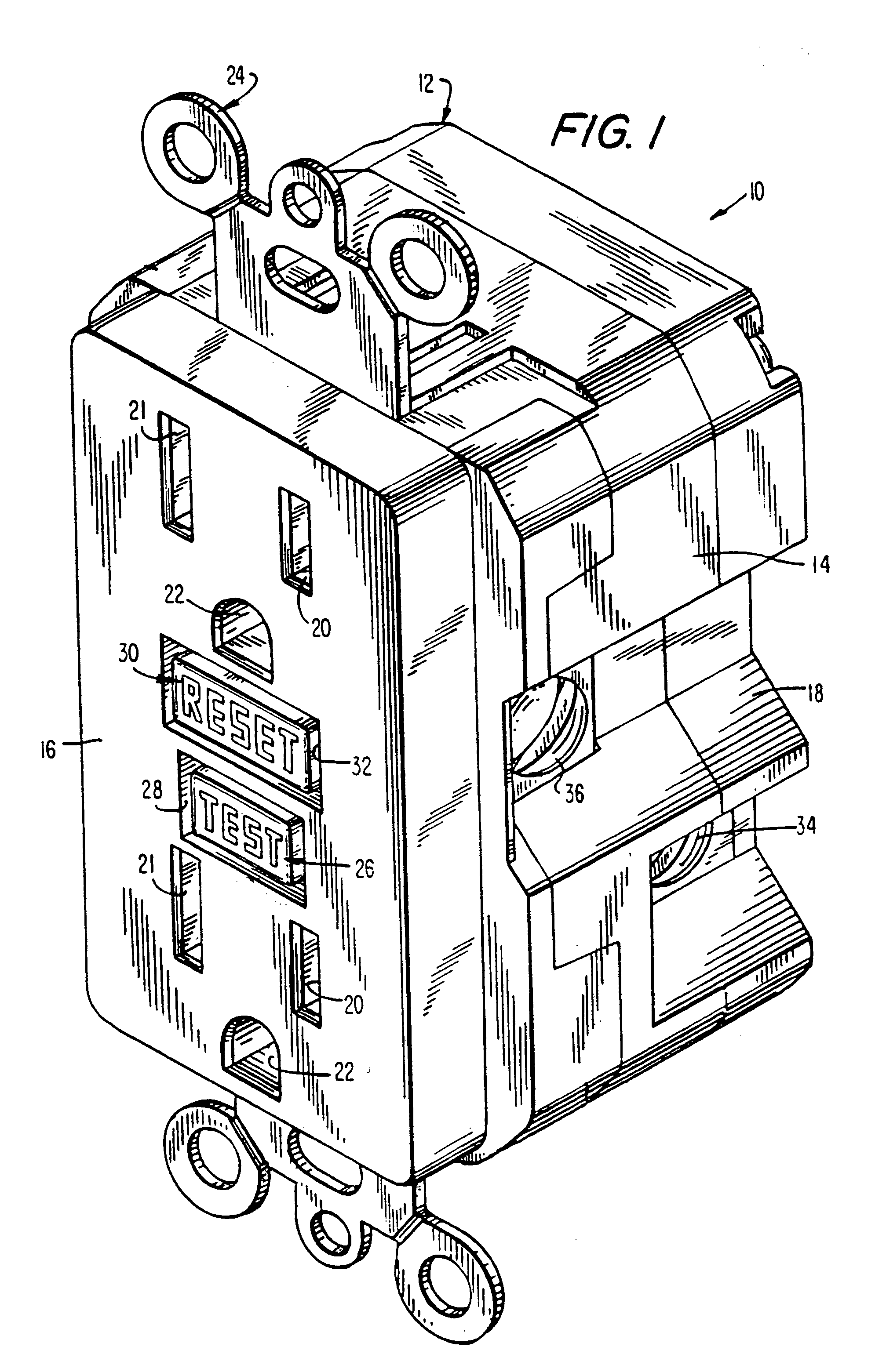
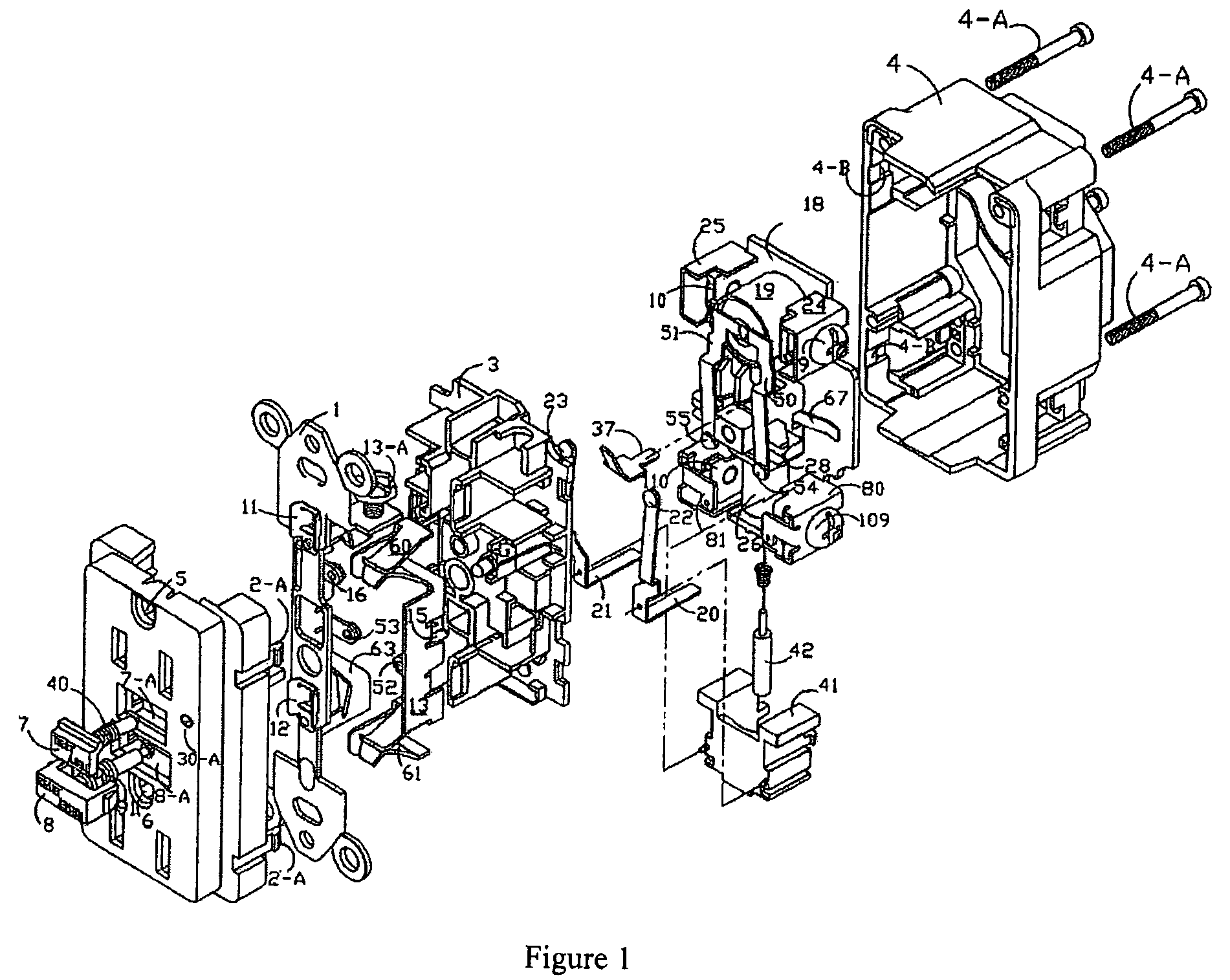
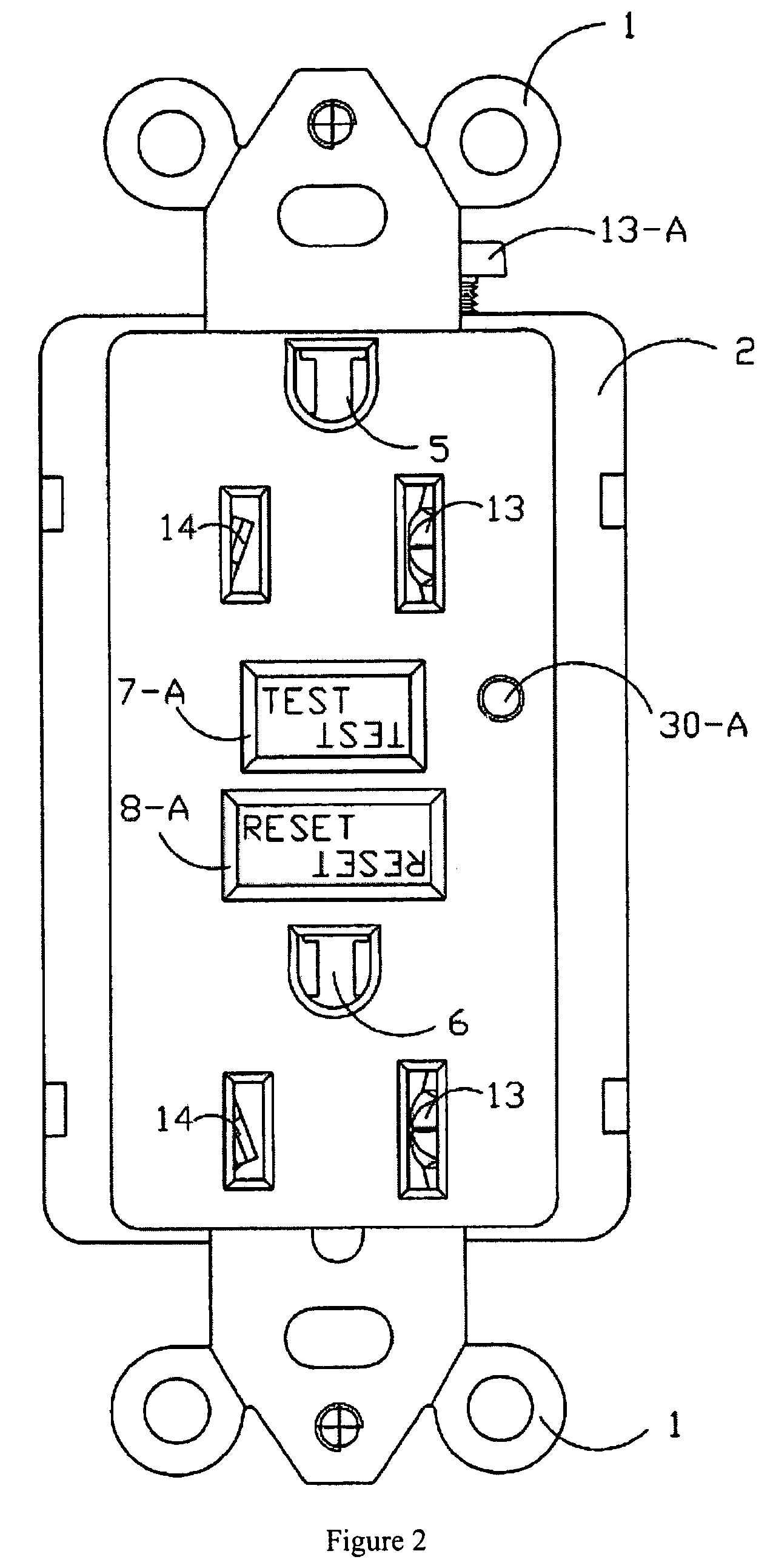
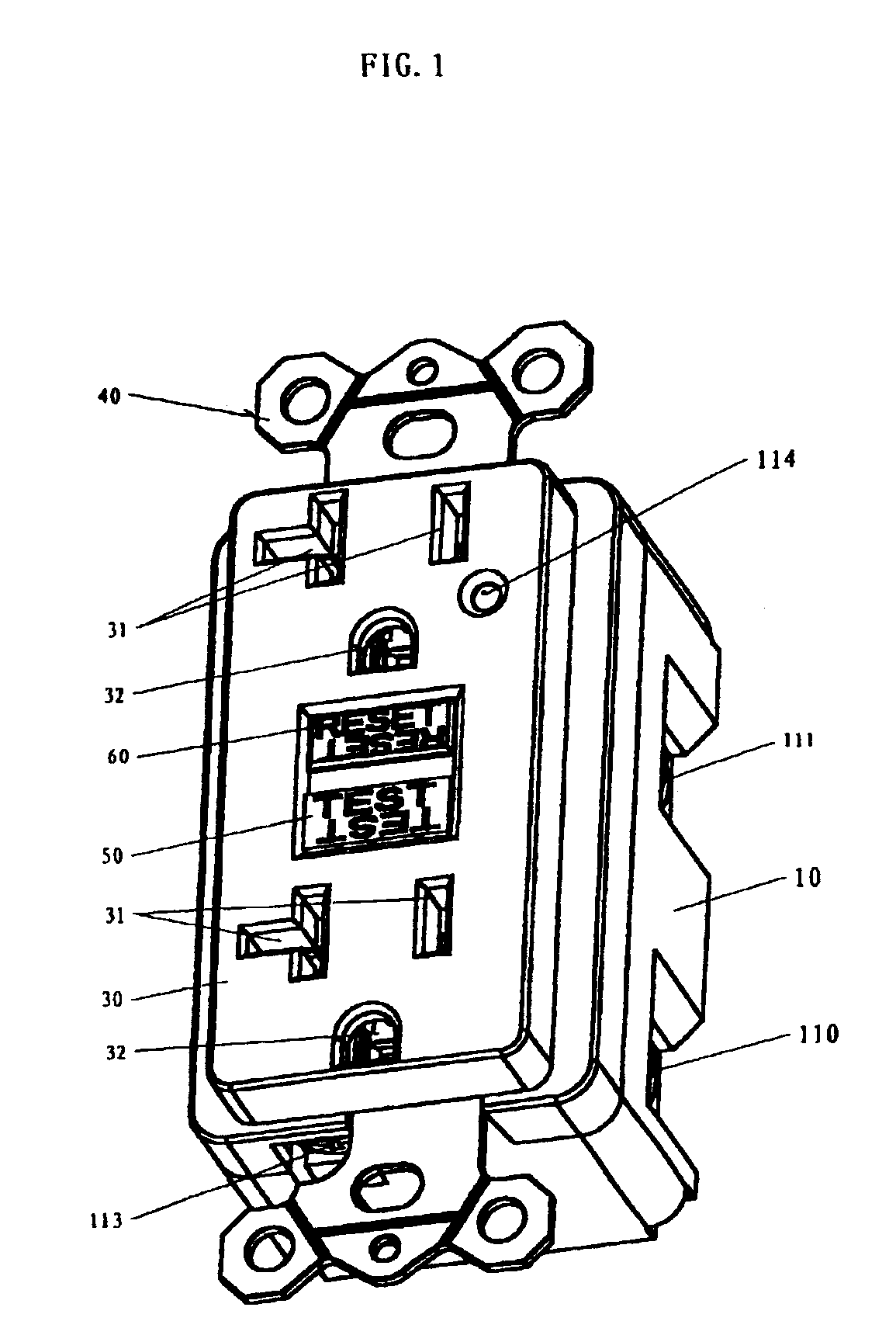
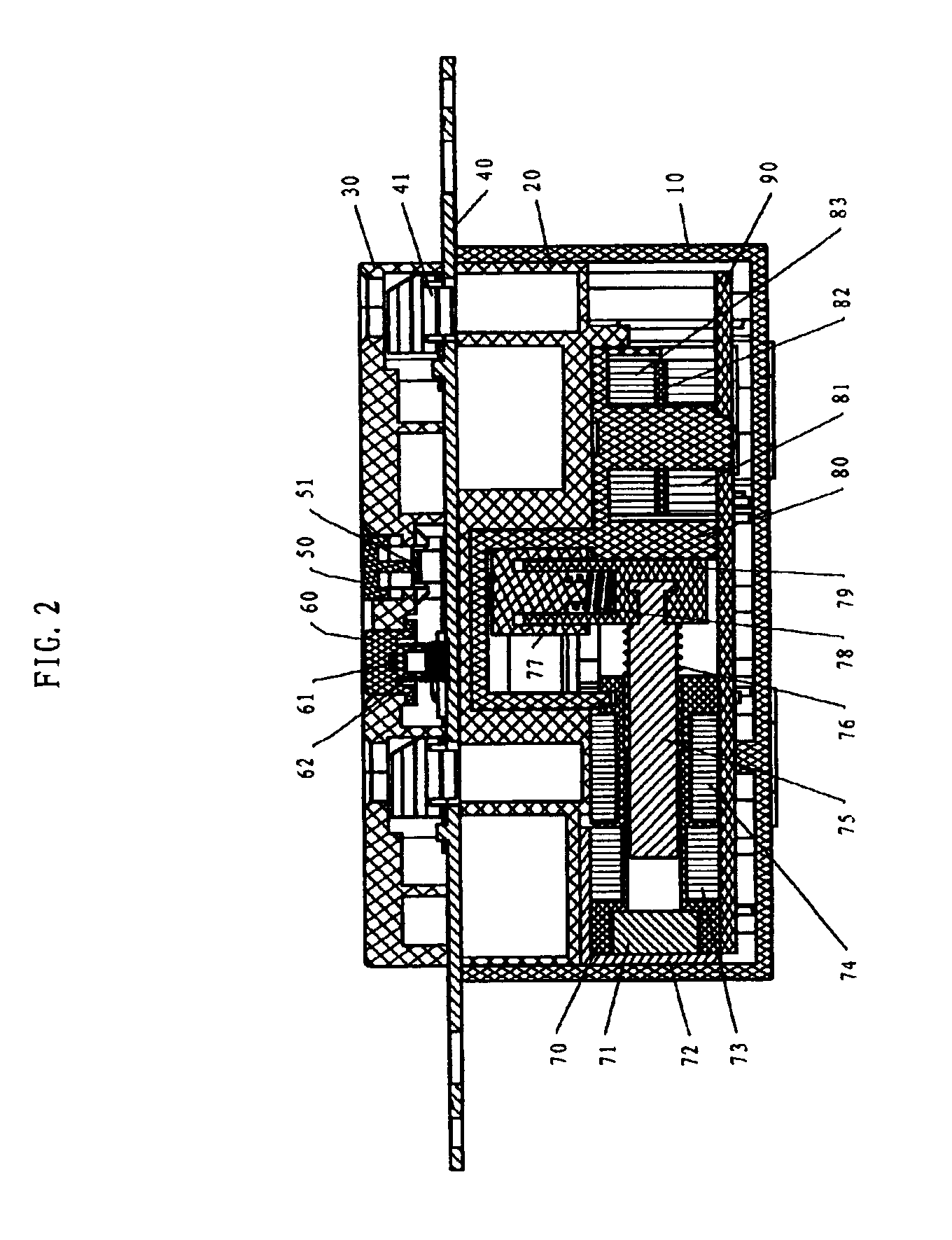
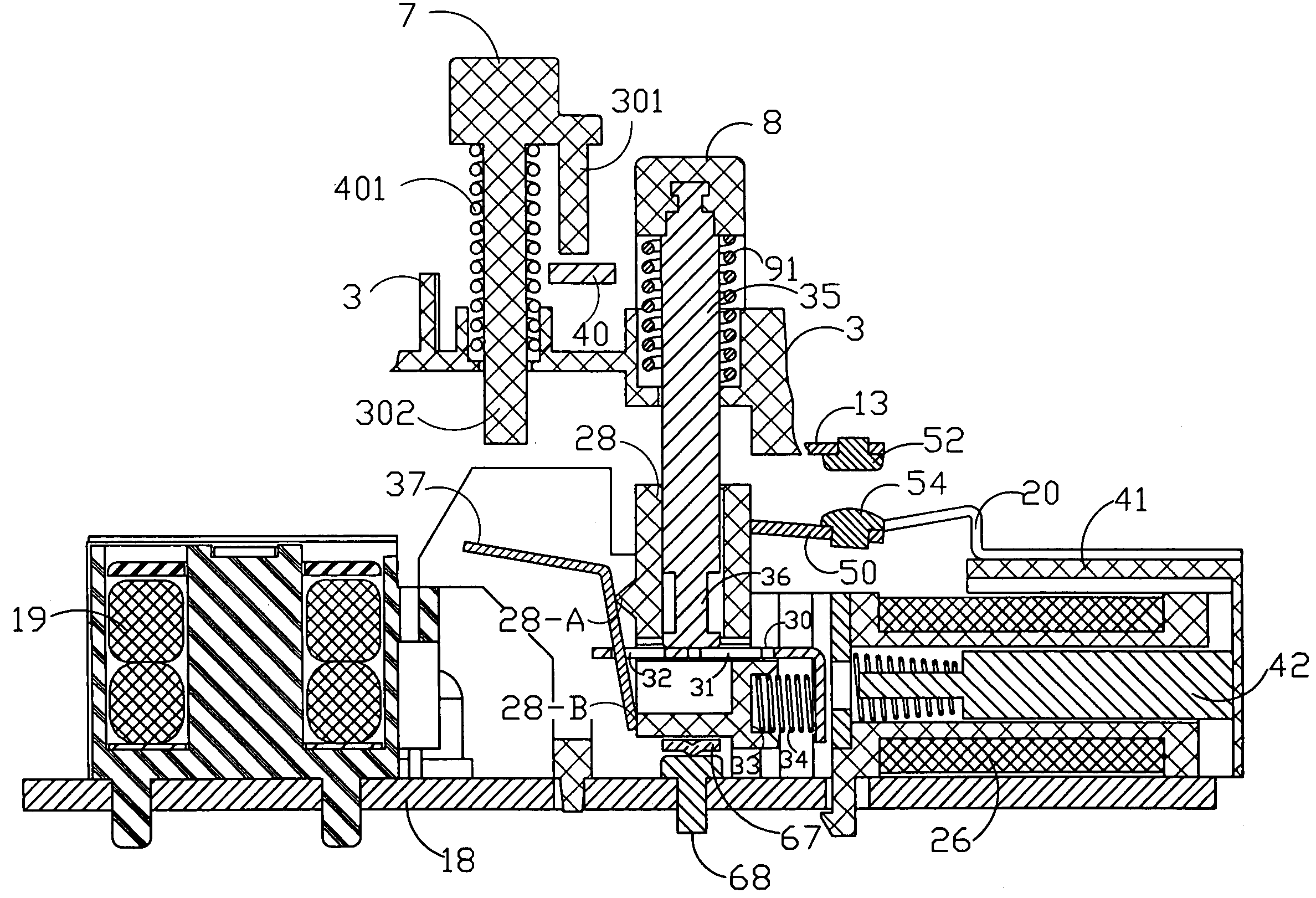
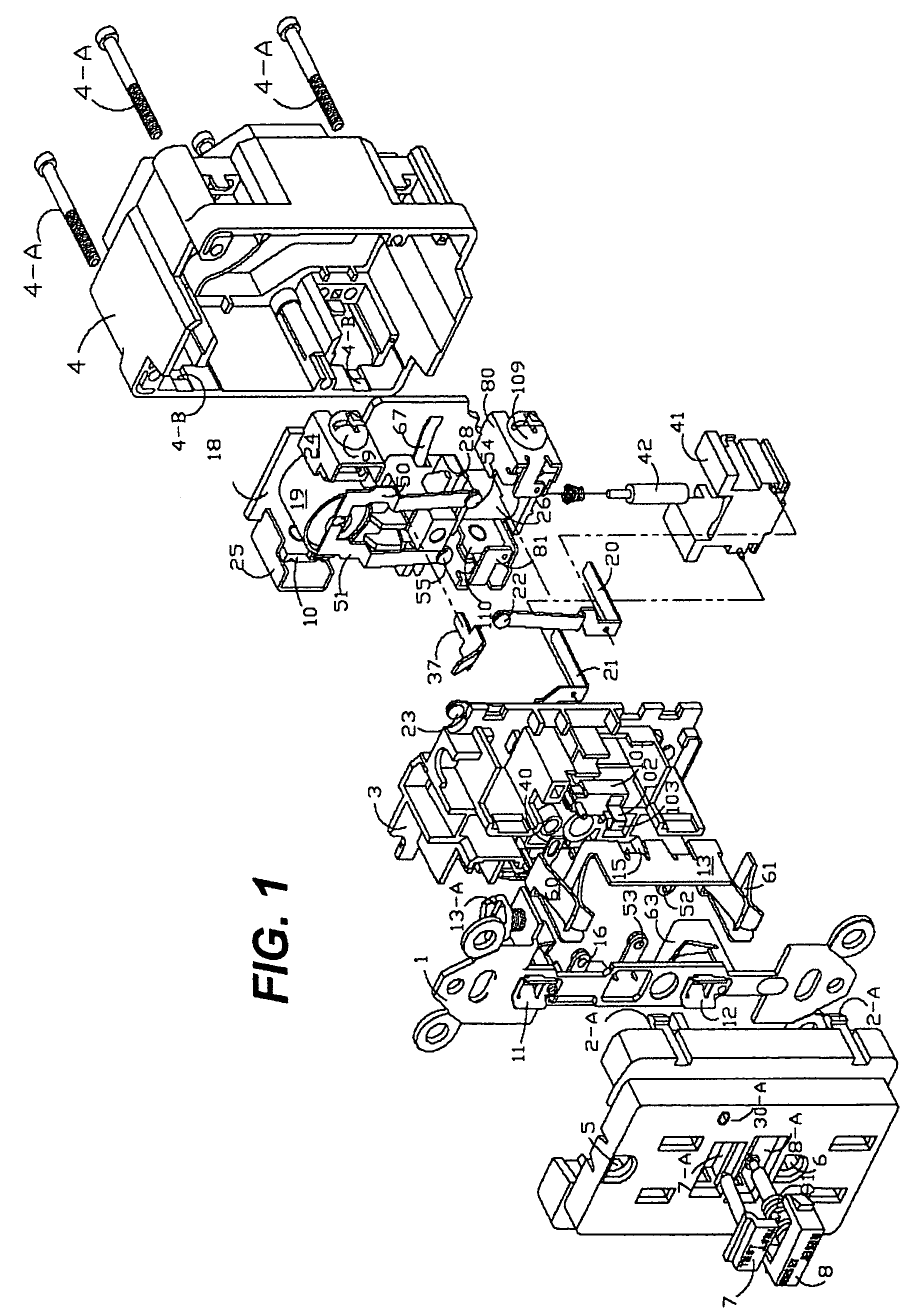
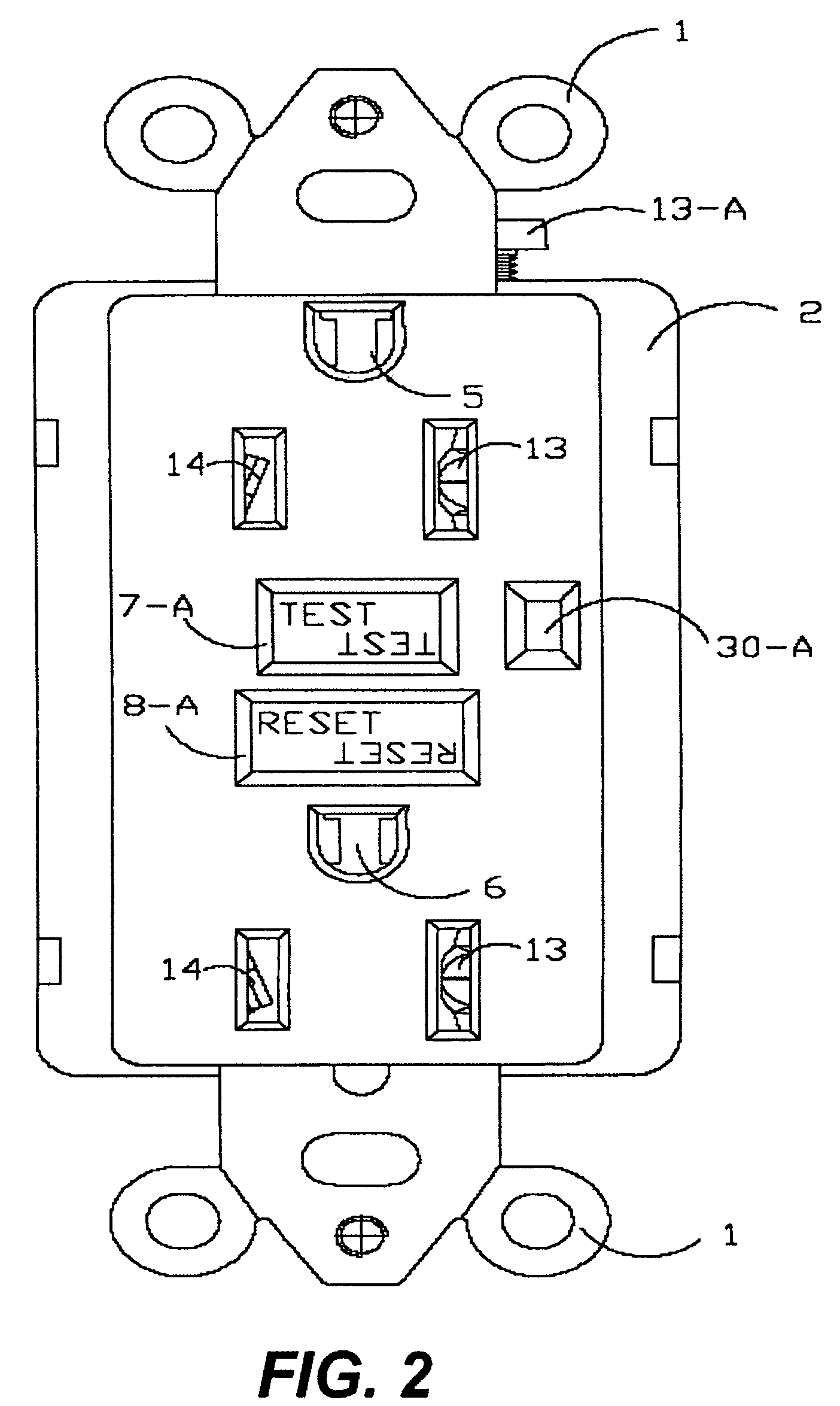
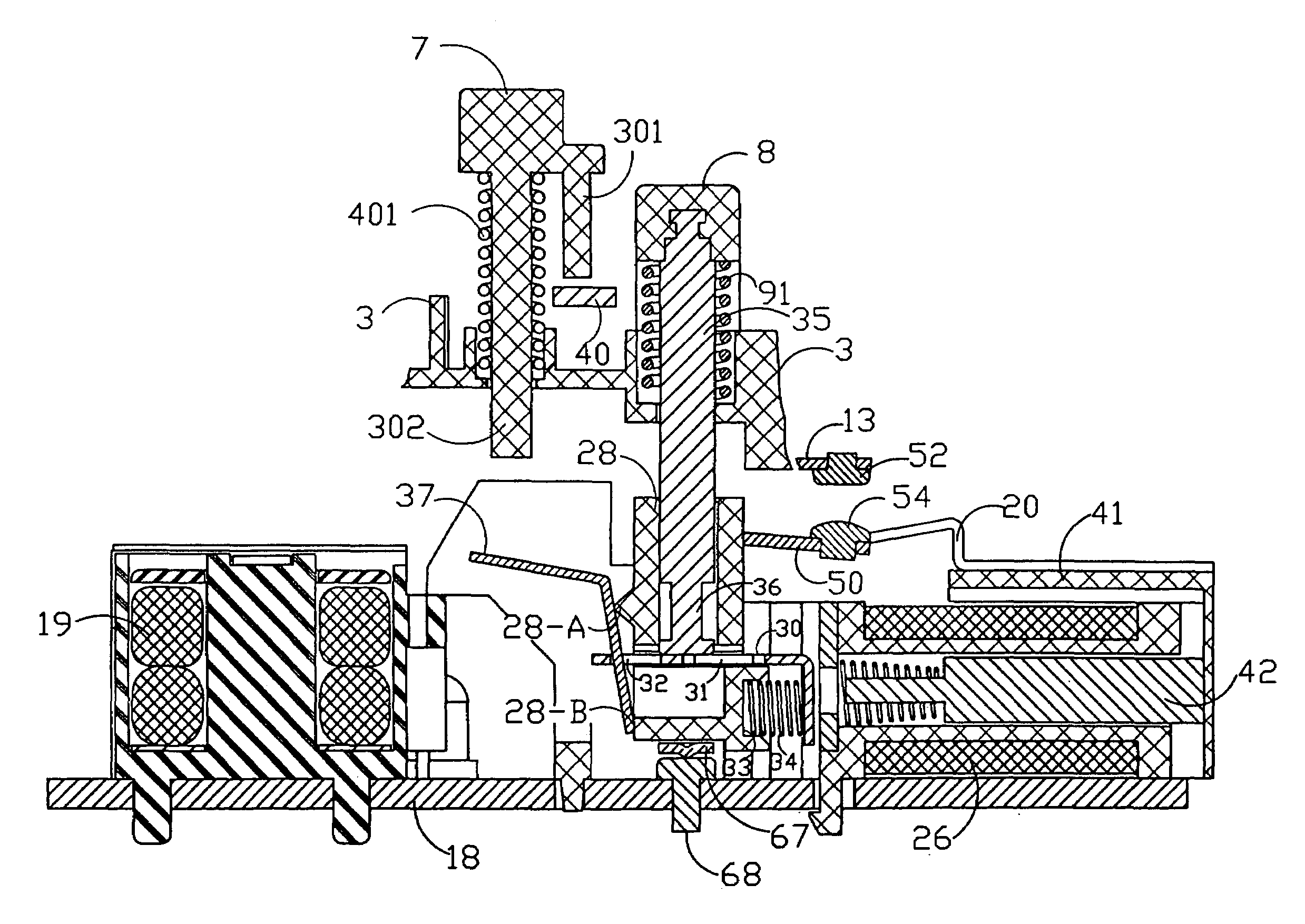
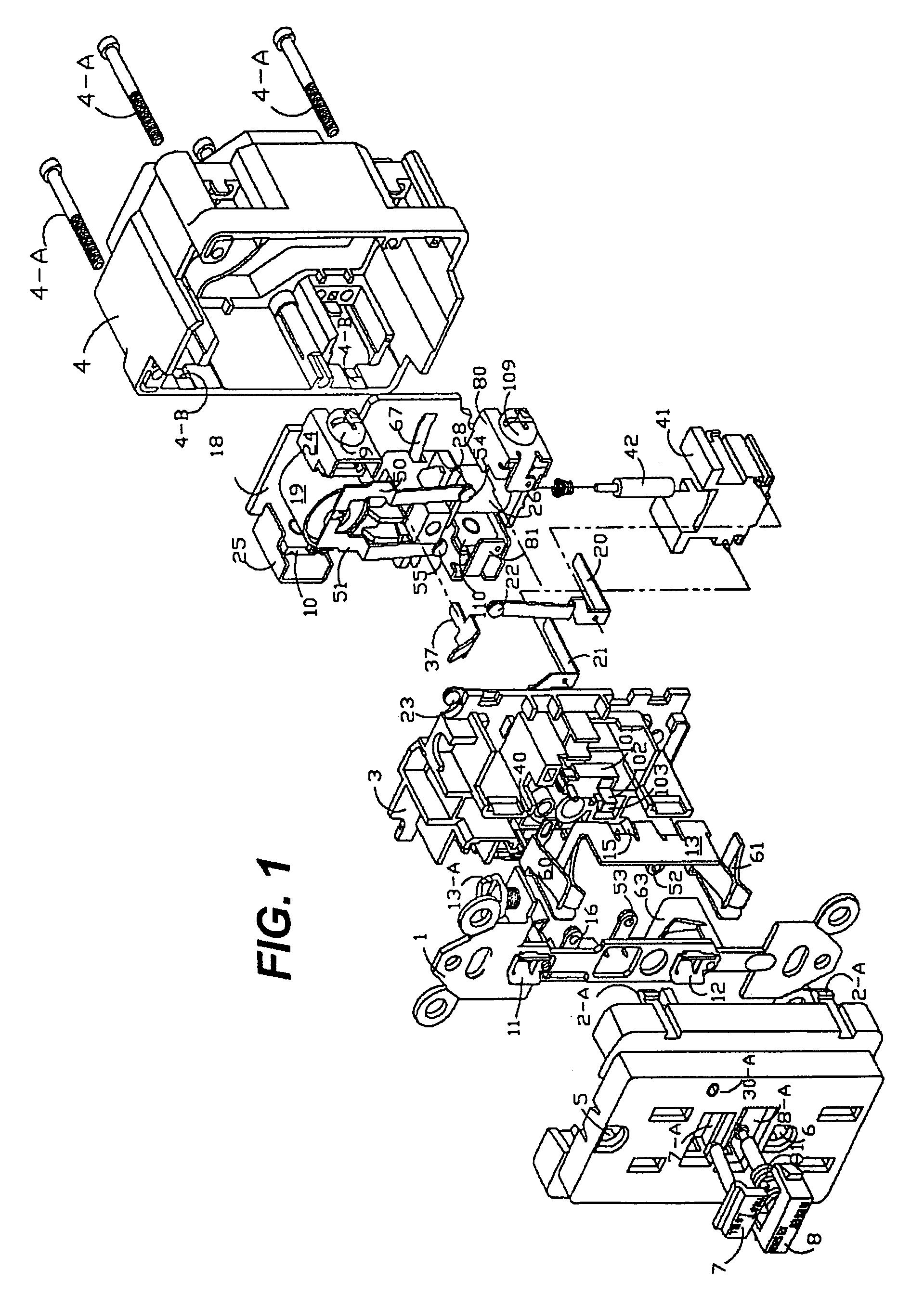
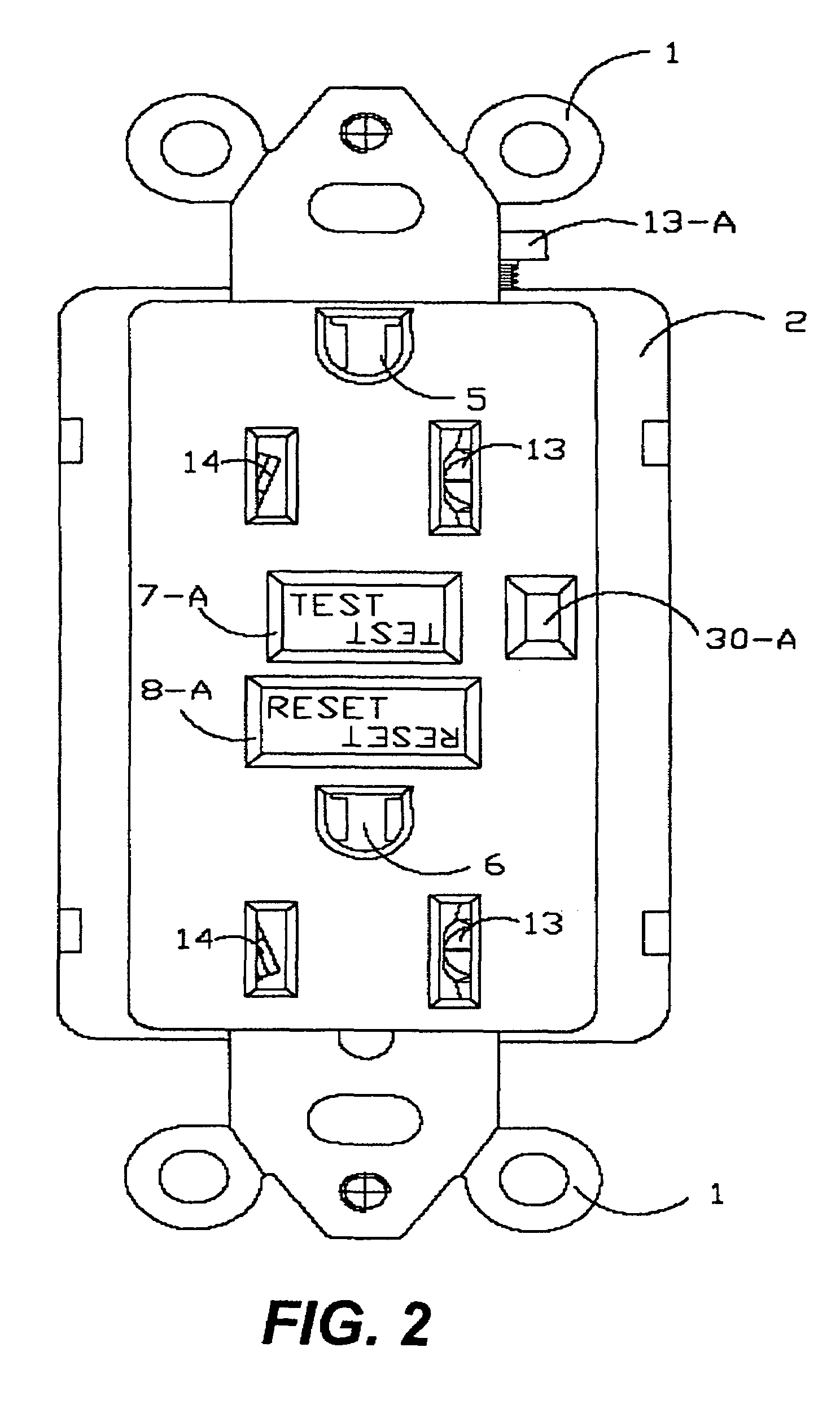
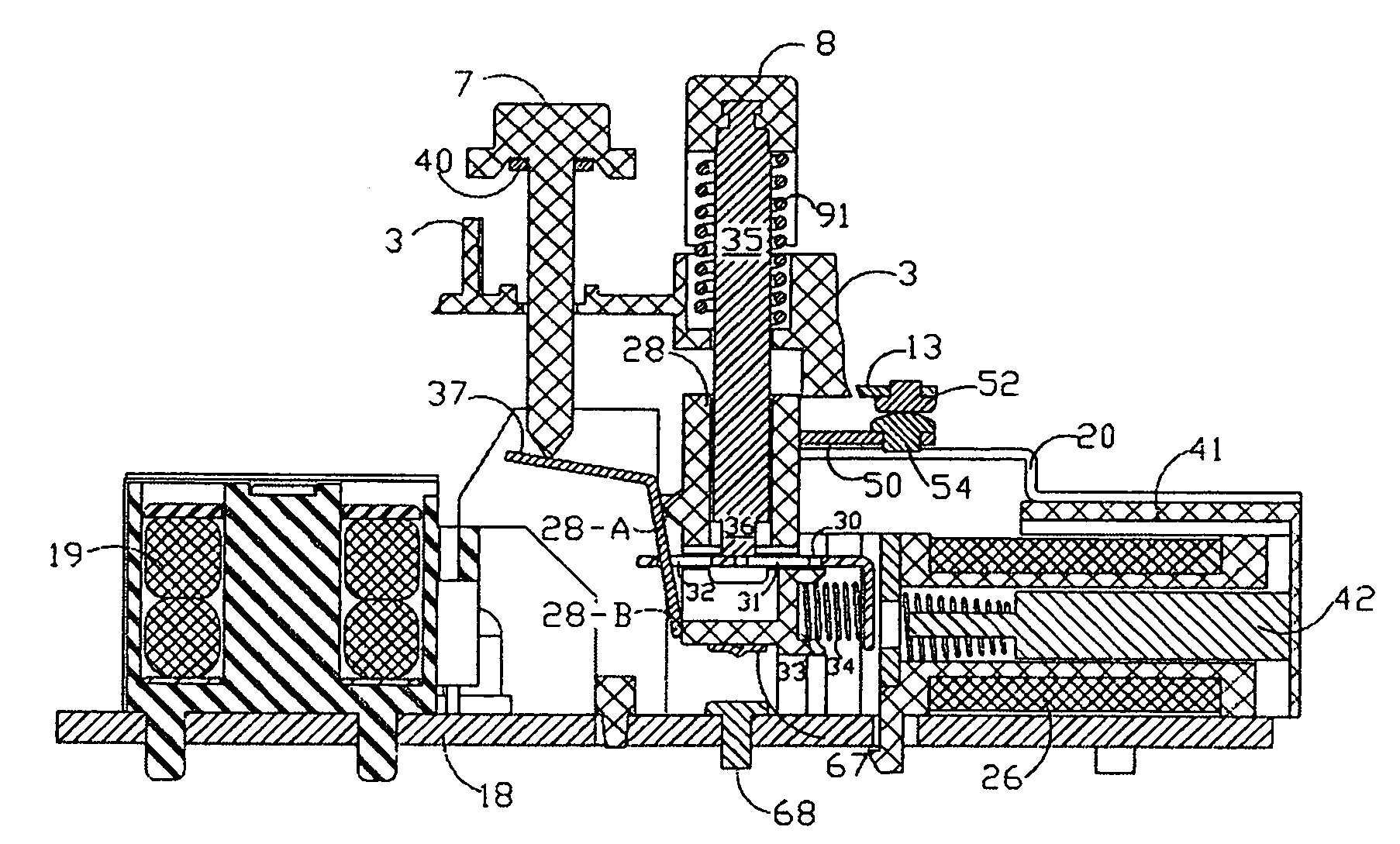
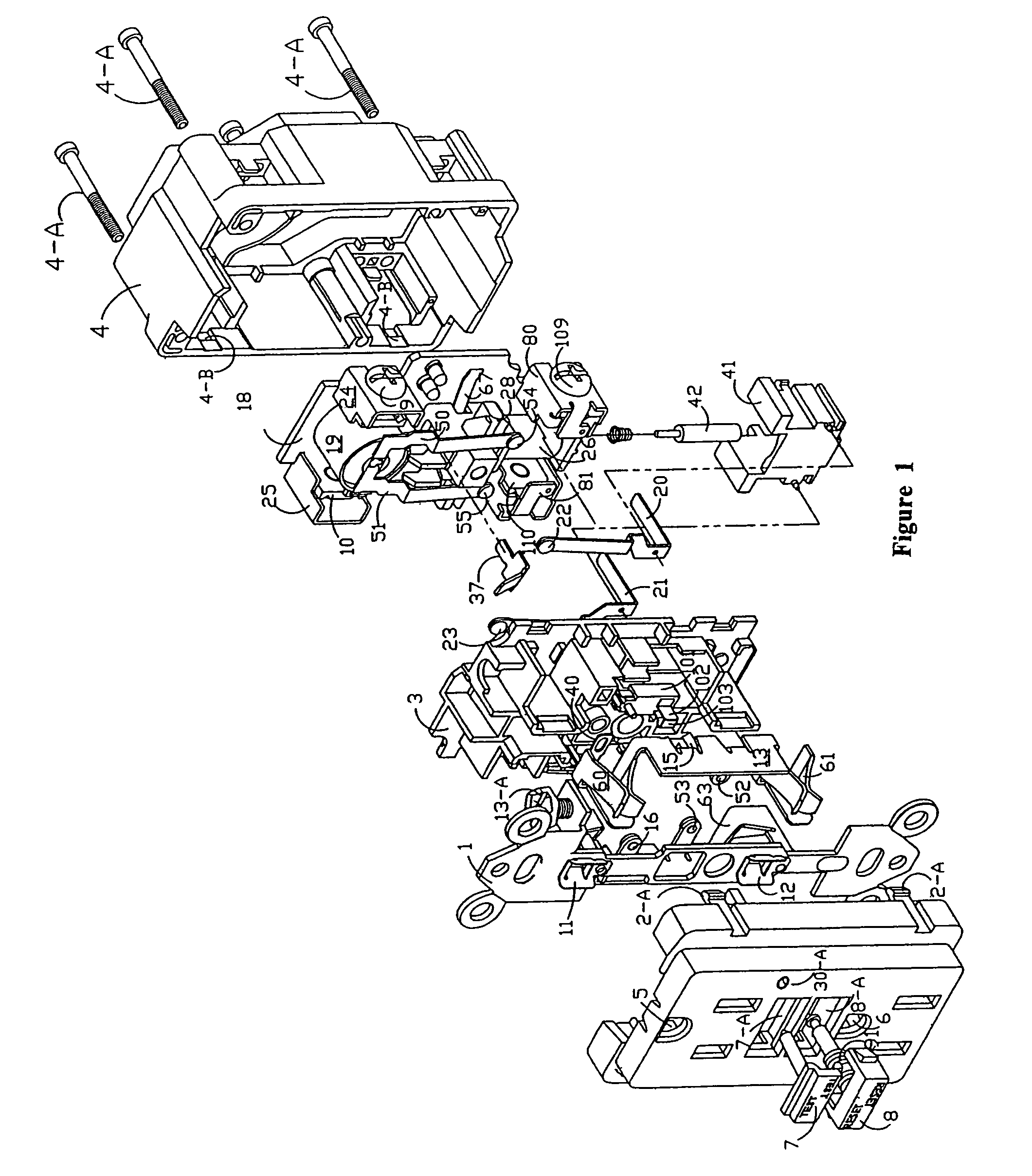
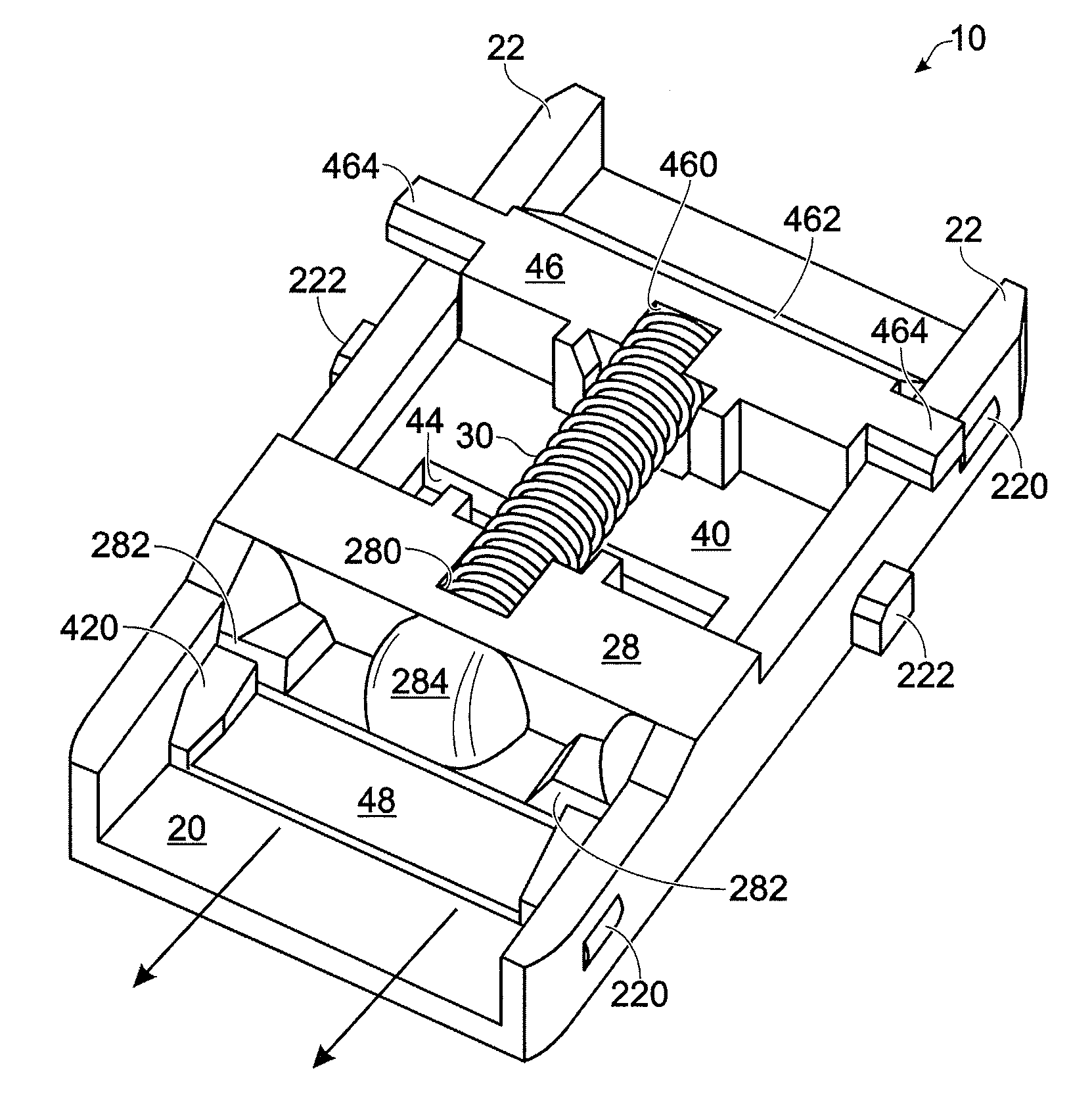
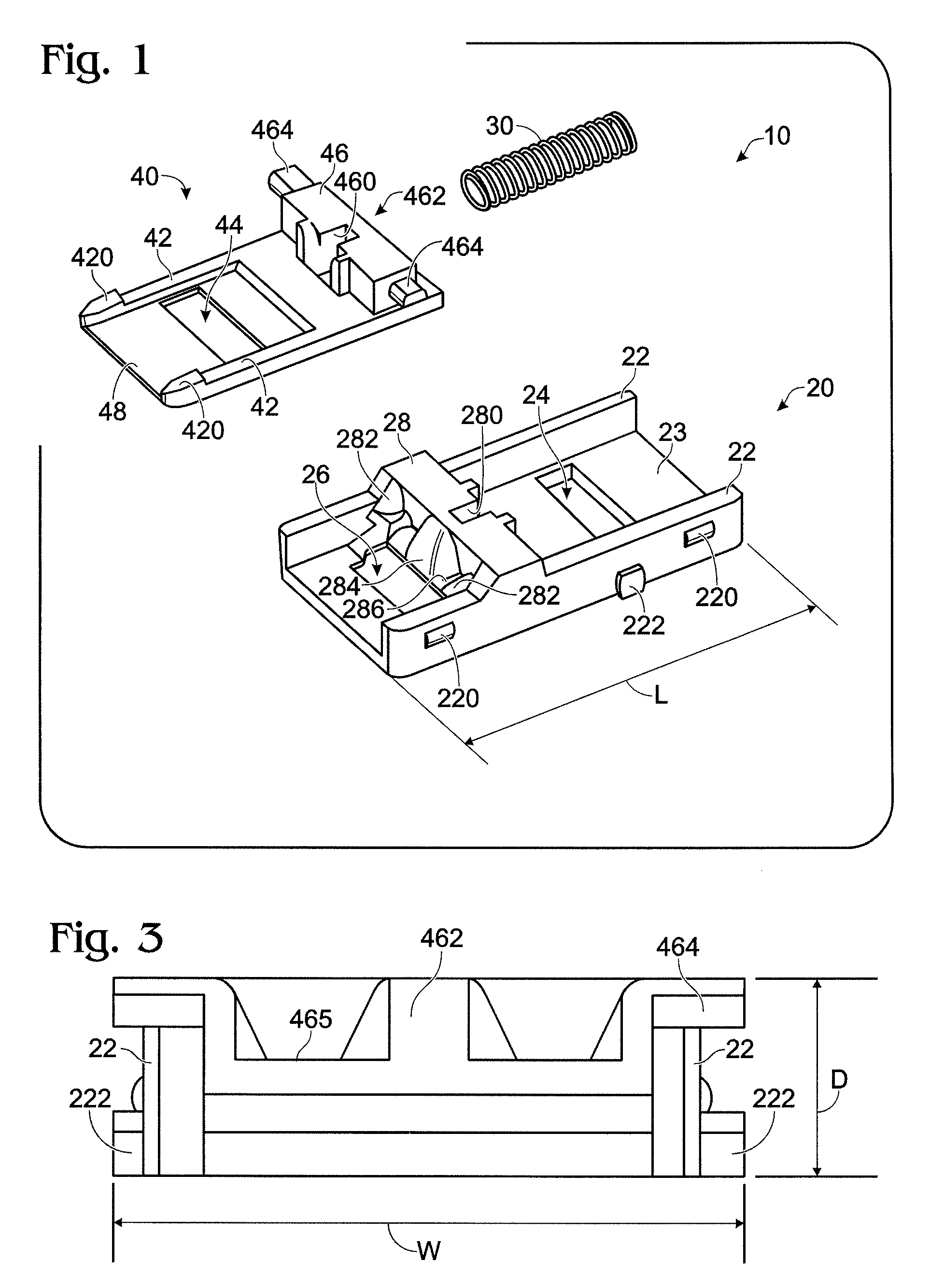
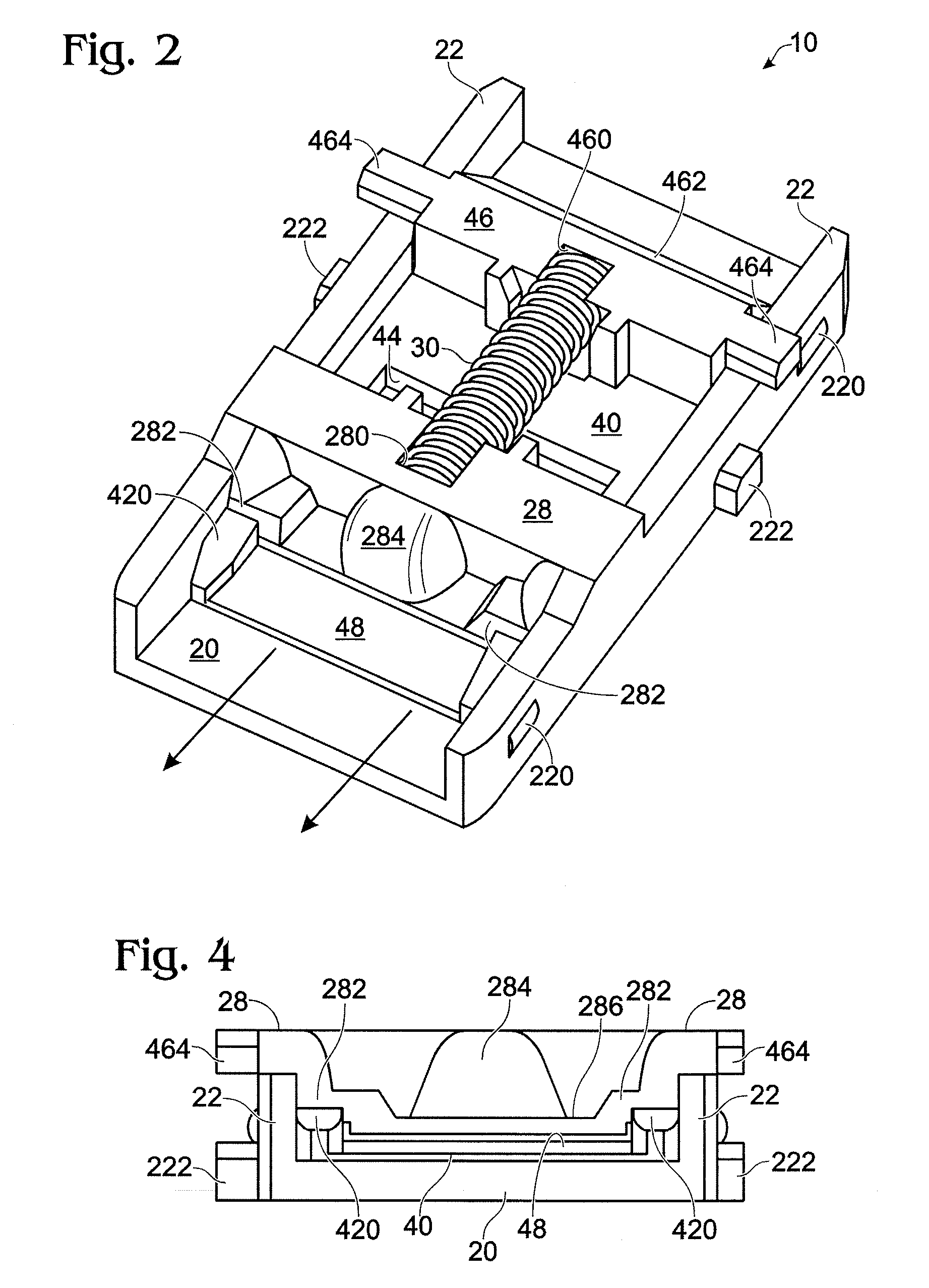
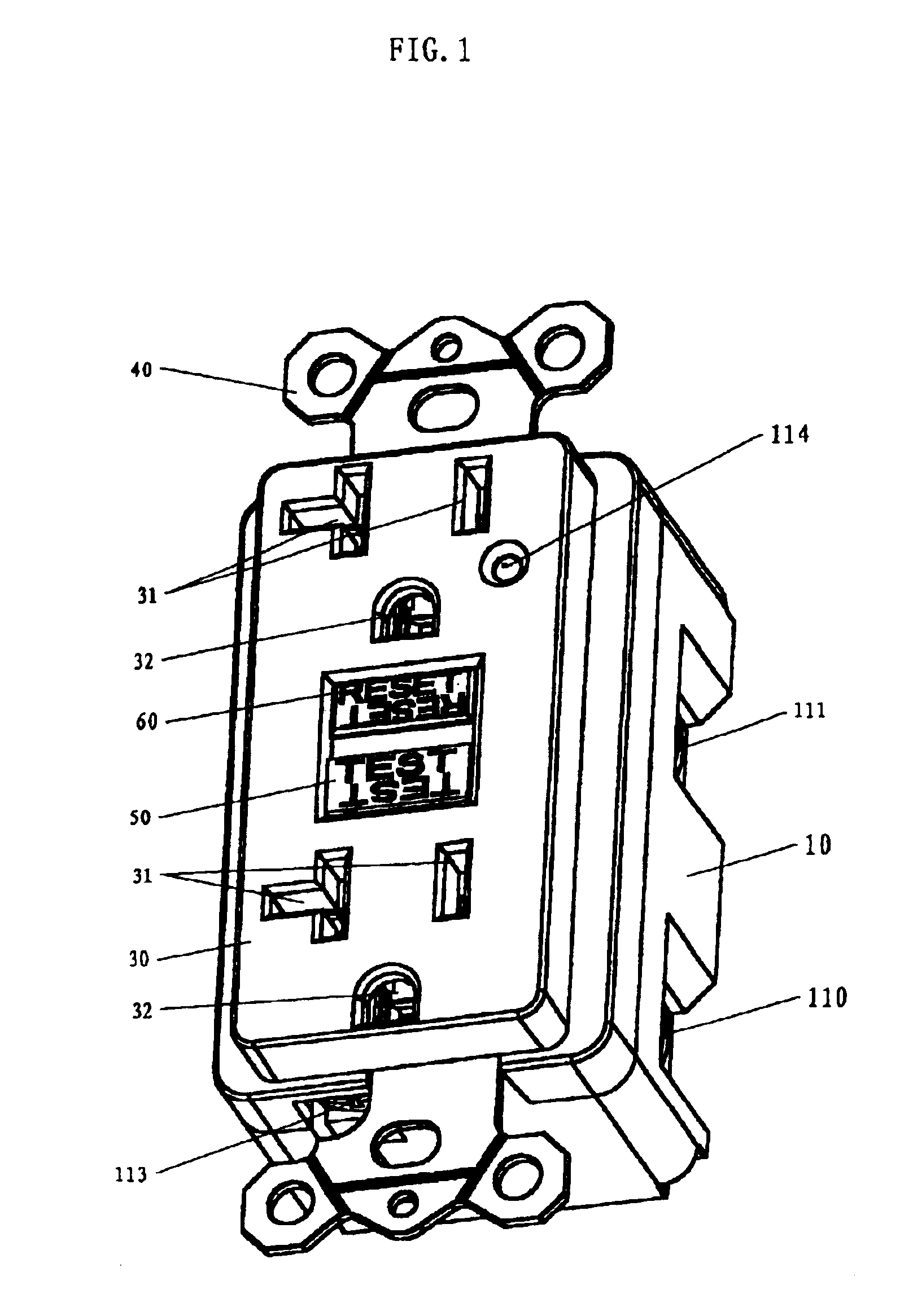
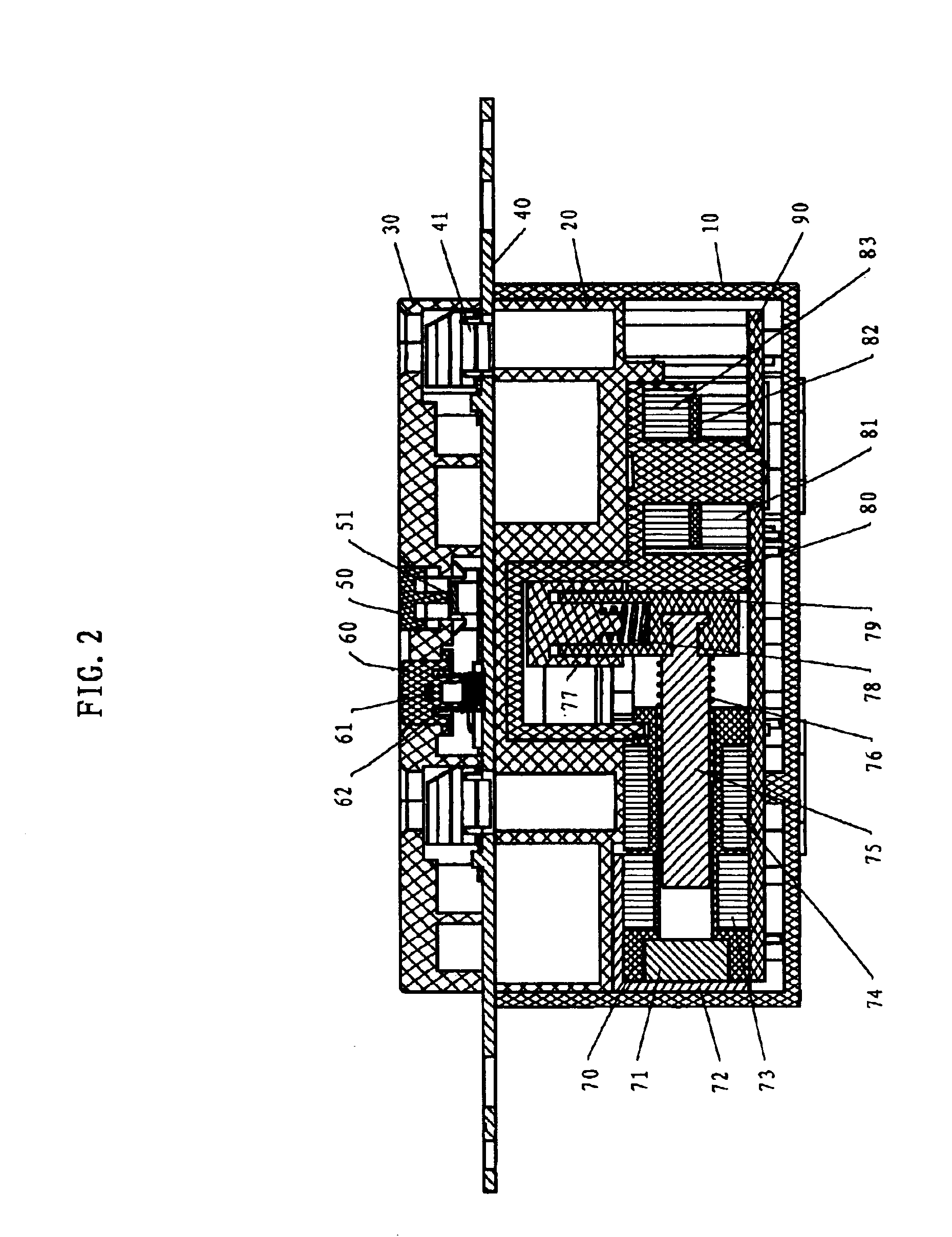
Ground fault interruption receptacle
InactiveUS6580344B2Improve protectionSwitch operated by falling currentCoupling device detailsElectric power transmissionElectricity
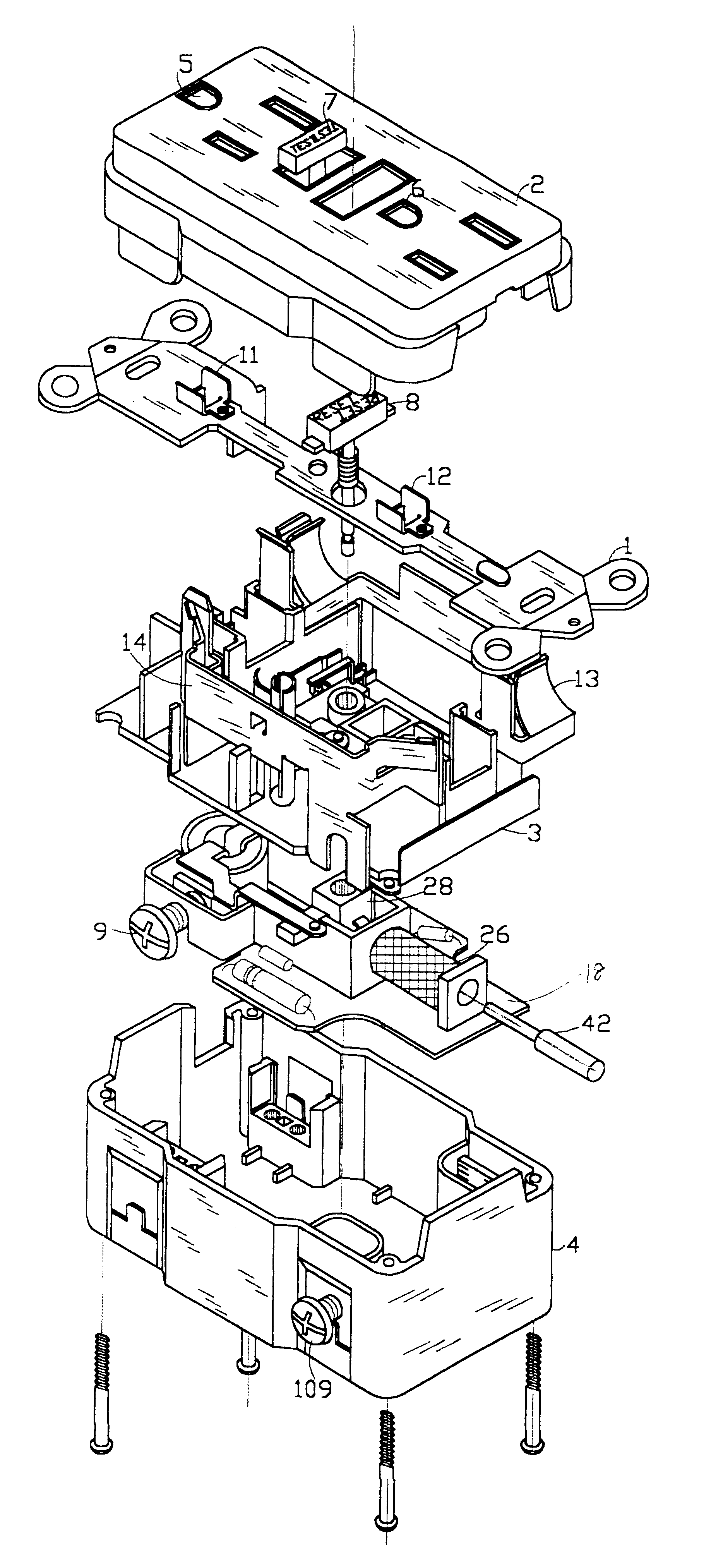
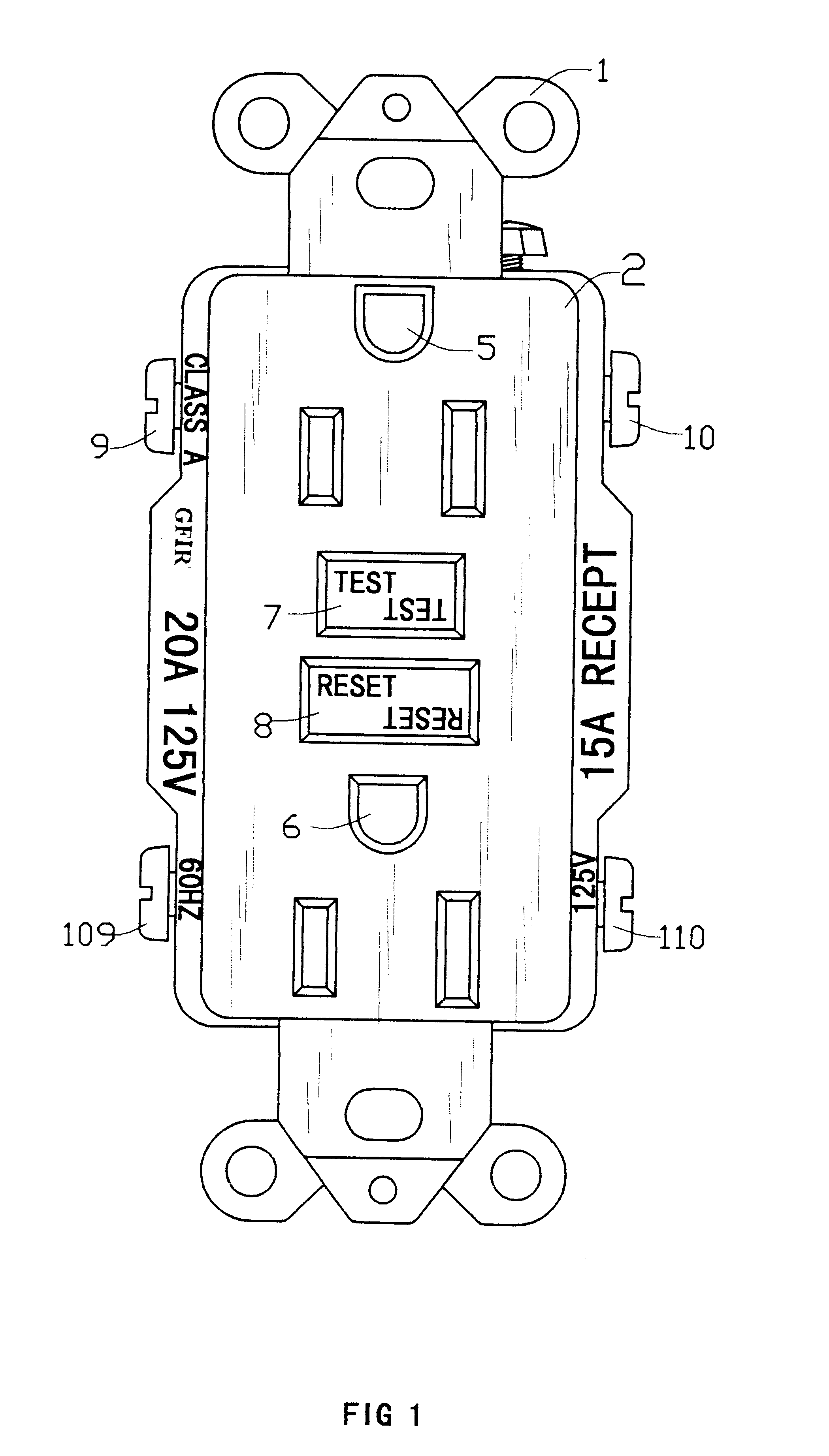
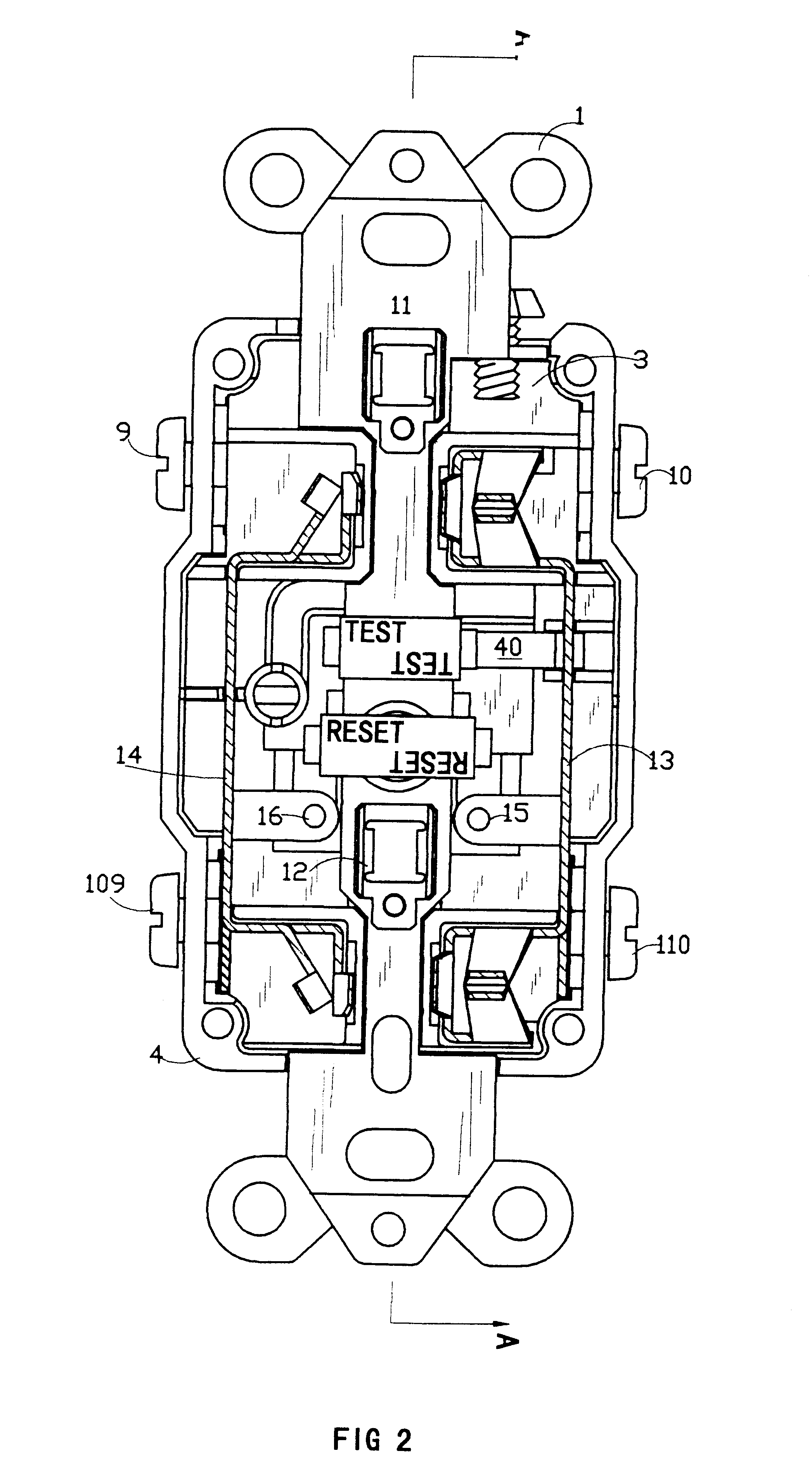
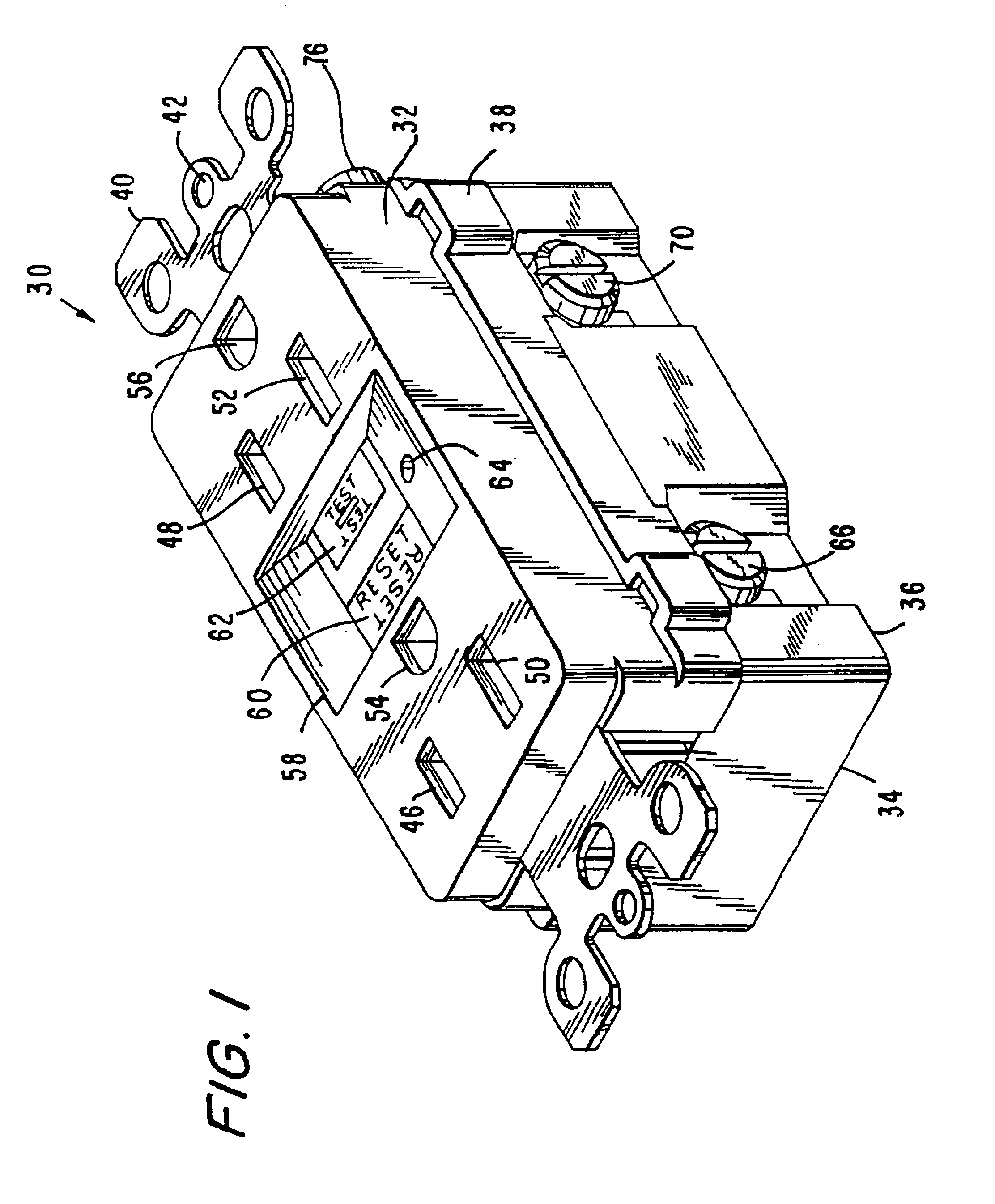
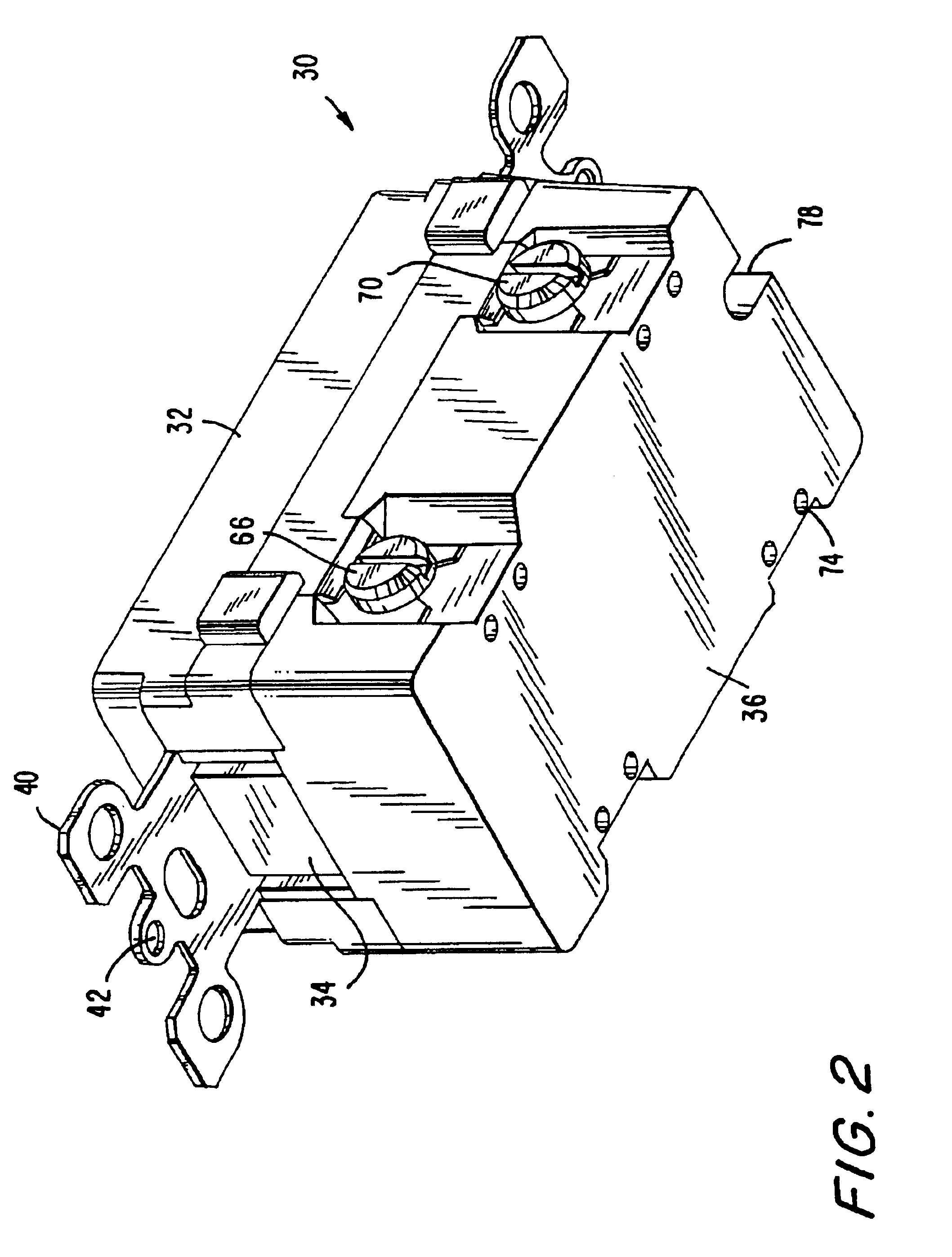
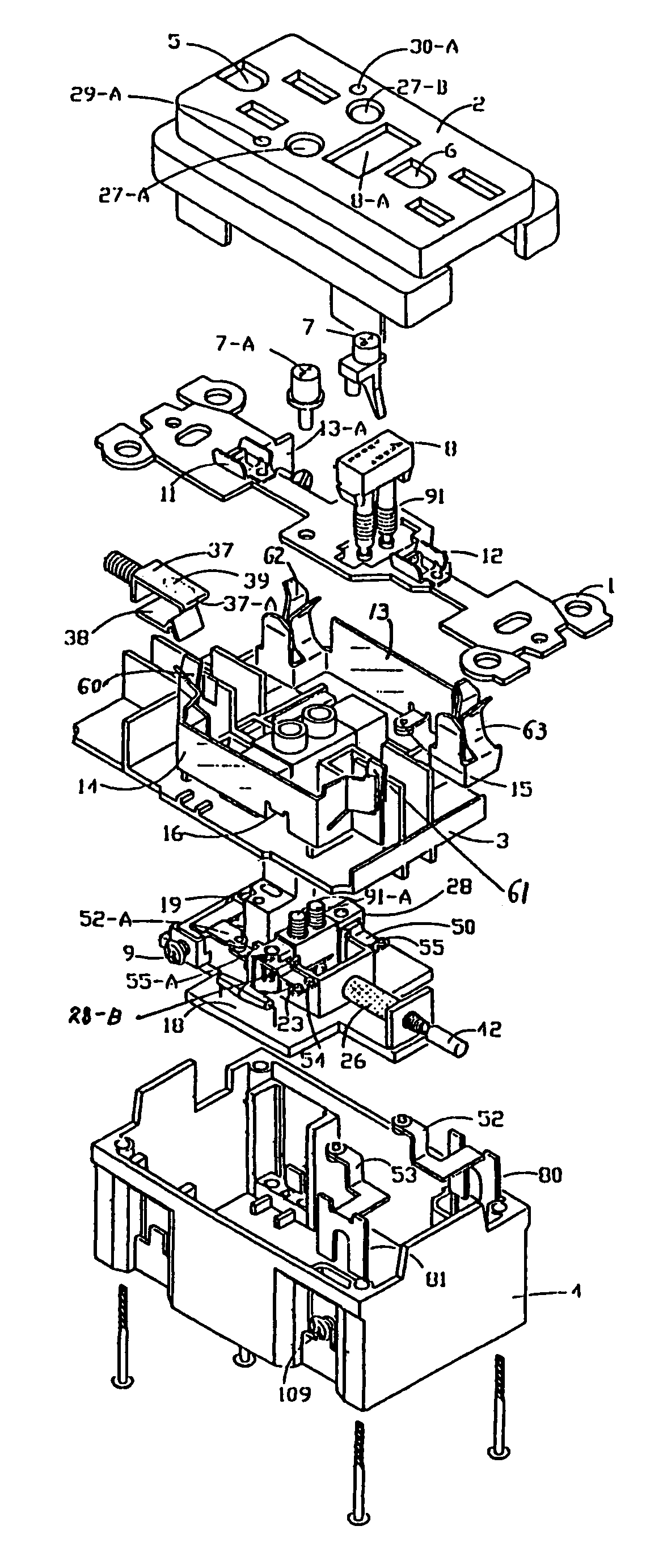
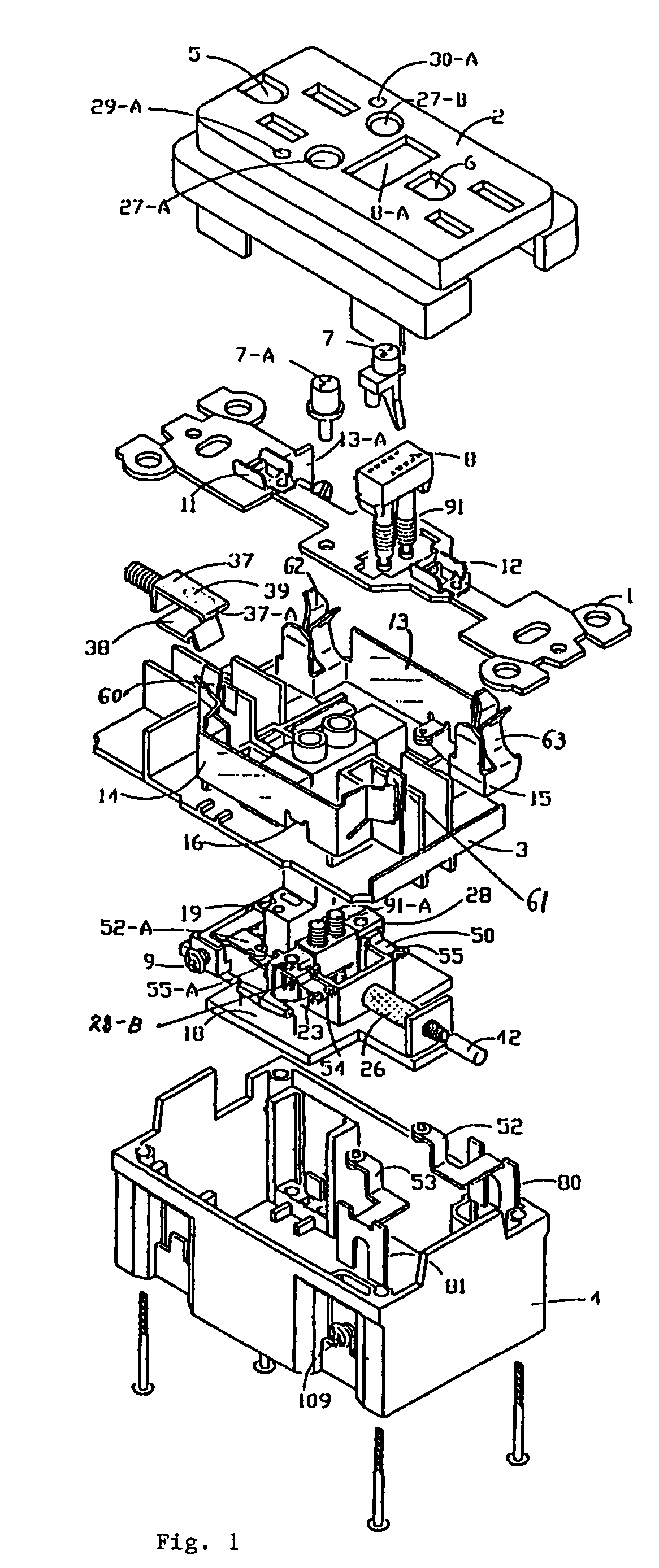
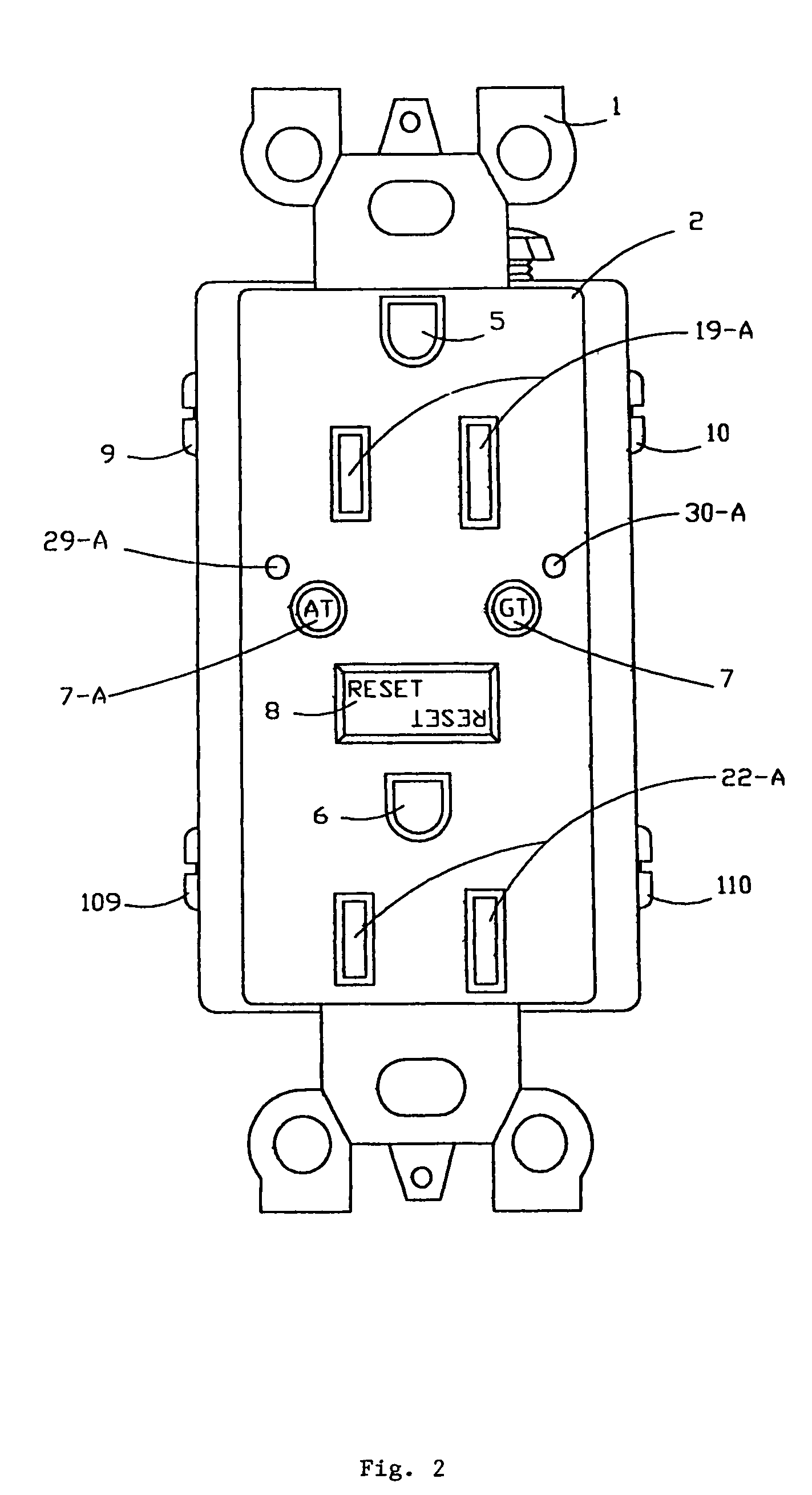
A new and improved type of ground fault interruption receptacle is mainly consists of an upper housing, a middle supporter and a lower holder. Two sets of female power-output socket 5, 6, a simulation test button (i.e. test button for fault detecting) and a reset button are disposed on the upper housing. A metal mounting plate is disposed between the upper housing and the middle supporter. At the two sides of the middle supporter is disposed a pair of metal conductors. Between the middle supporter and the lower holder is disposed a printed circuit board, and thereon a differential transformer within which an iron core is inserted, a reset guide member and a flat spring type of resilient off locking switch are arranged. Using the differential transformer and the resilient off locking switch, the receptacle of the present invention may detect whether the fault current exists and whether the damage of a certain element or member for power transmission occurs. If so, the receptacle of the present invention can electrically disconnect the power-out connectors with the relevant power-input connectors so as to accomplish the ground fault interruption.
Owner:HUANG HUADAO
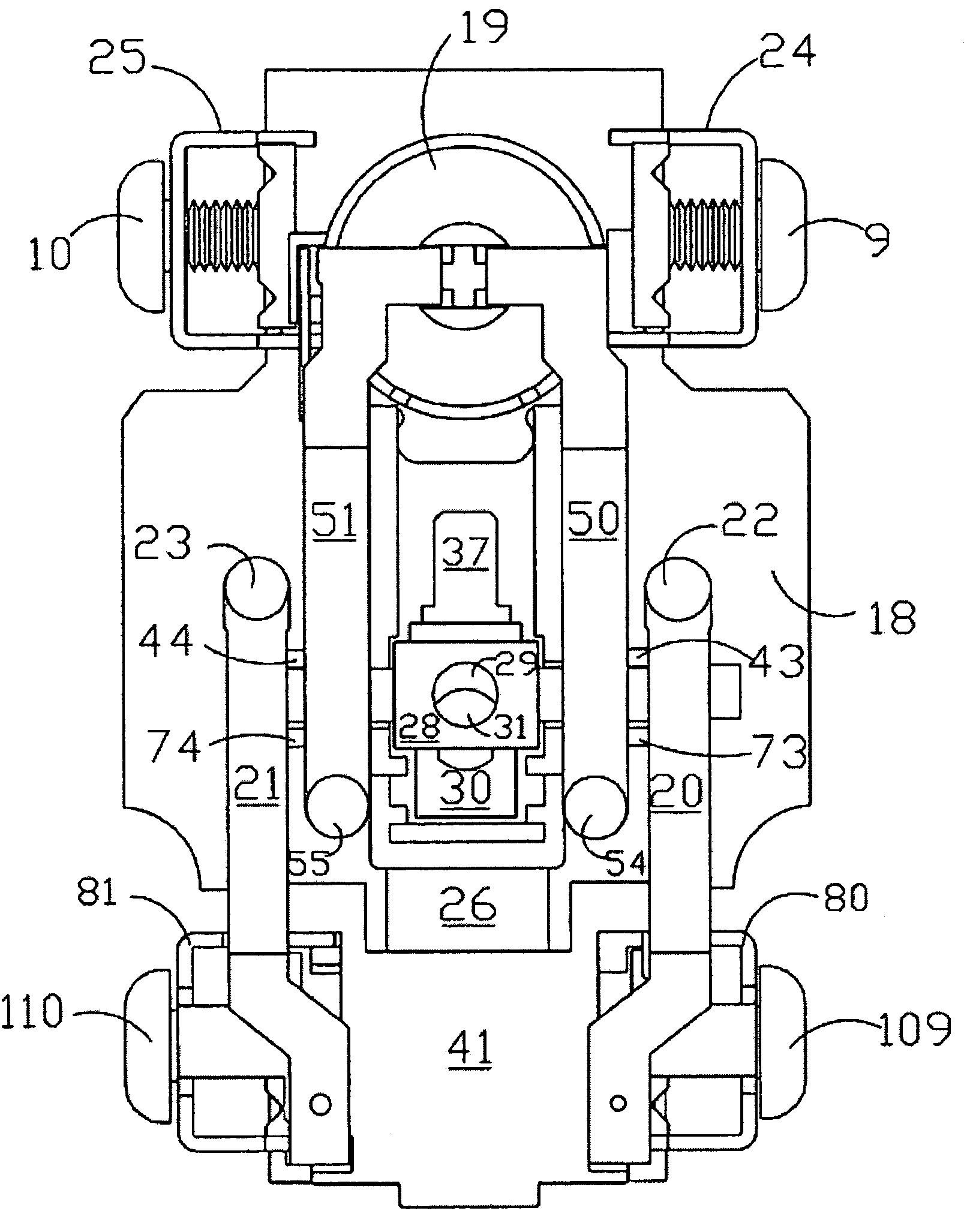
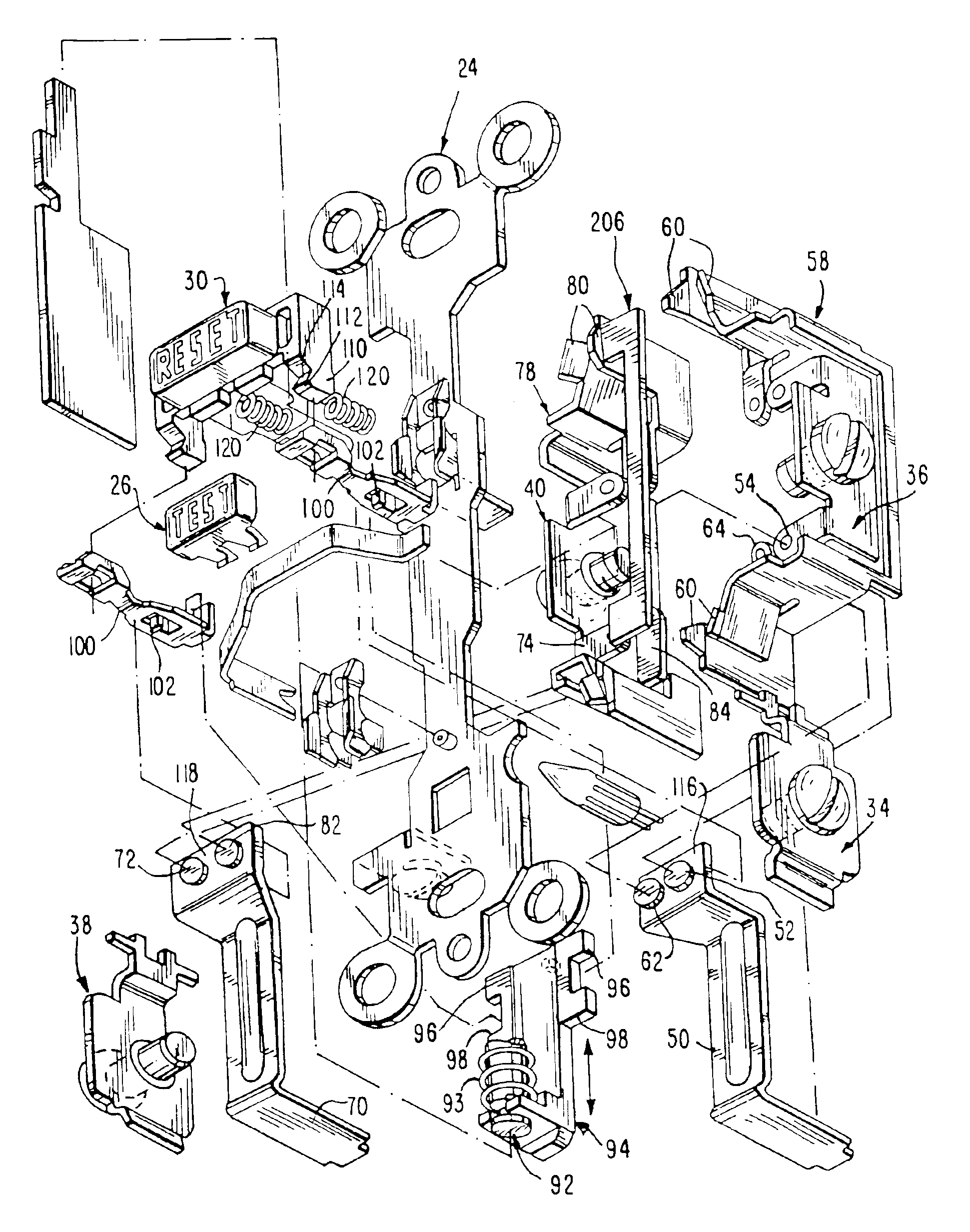
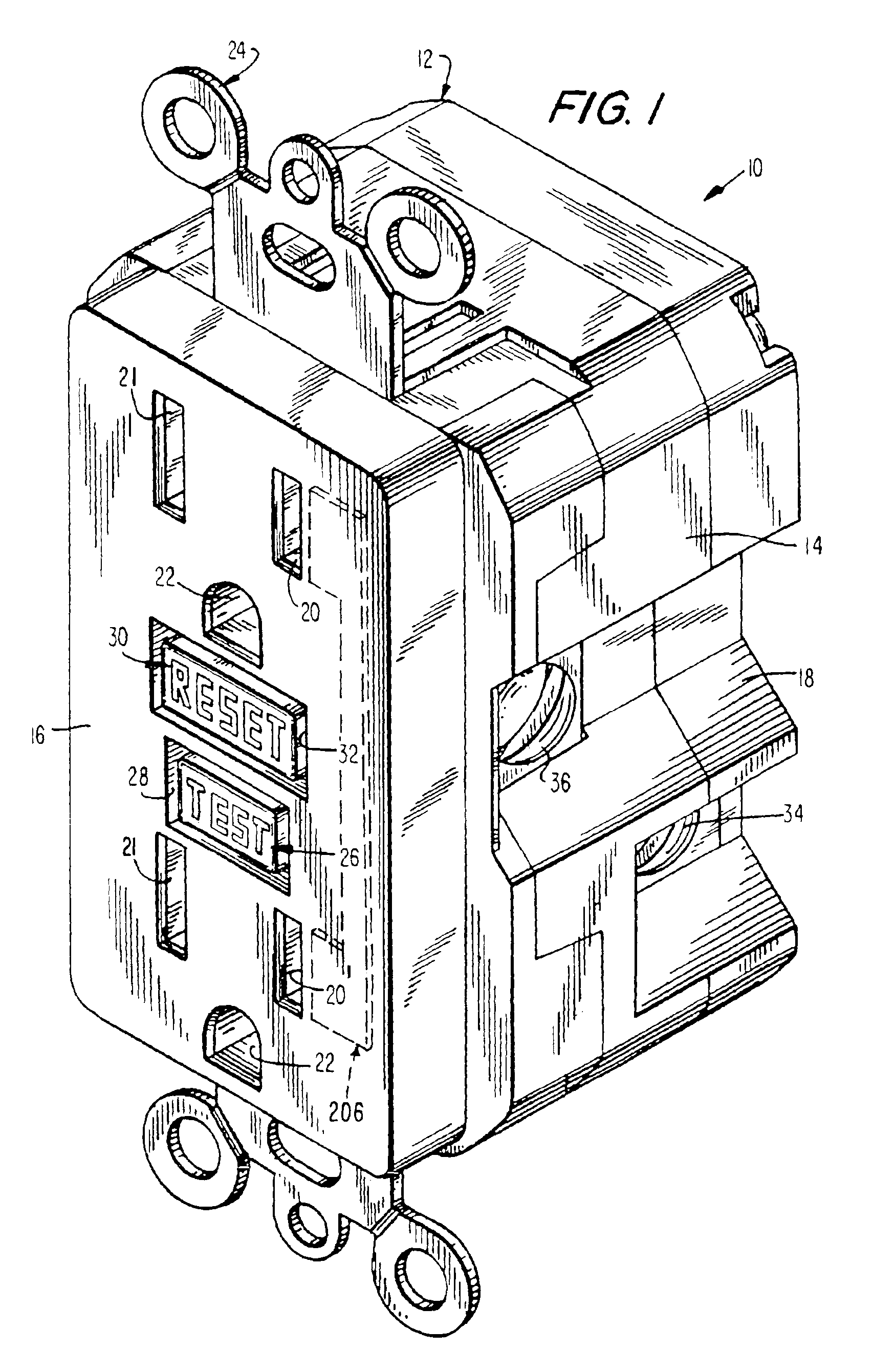
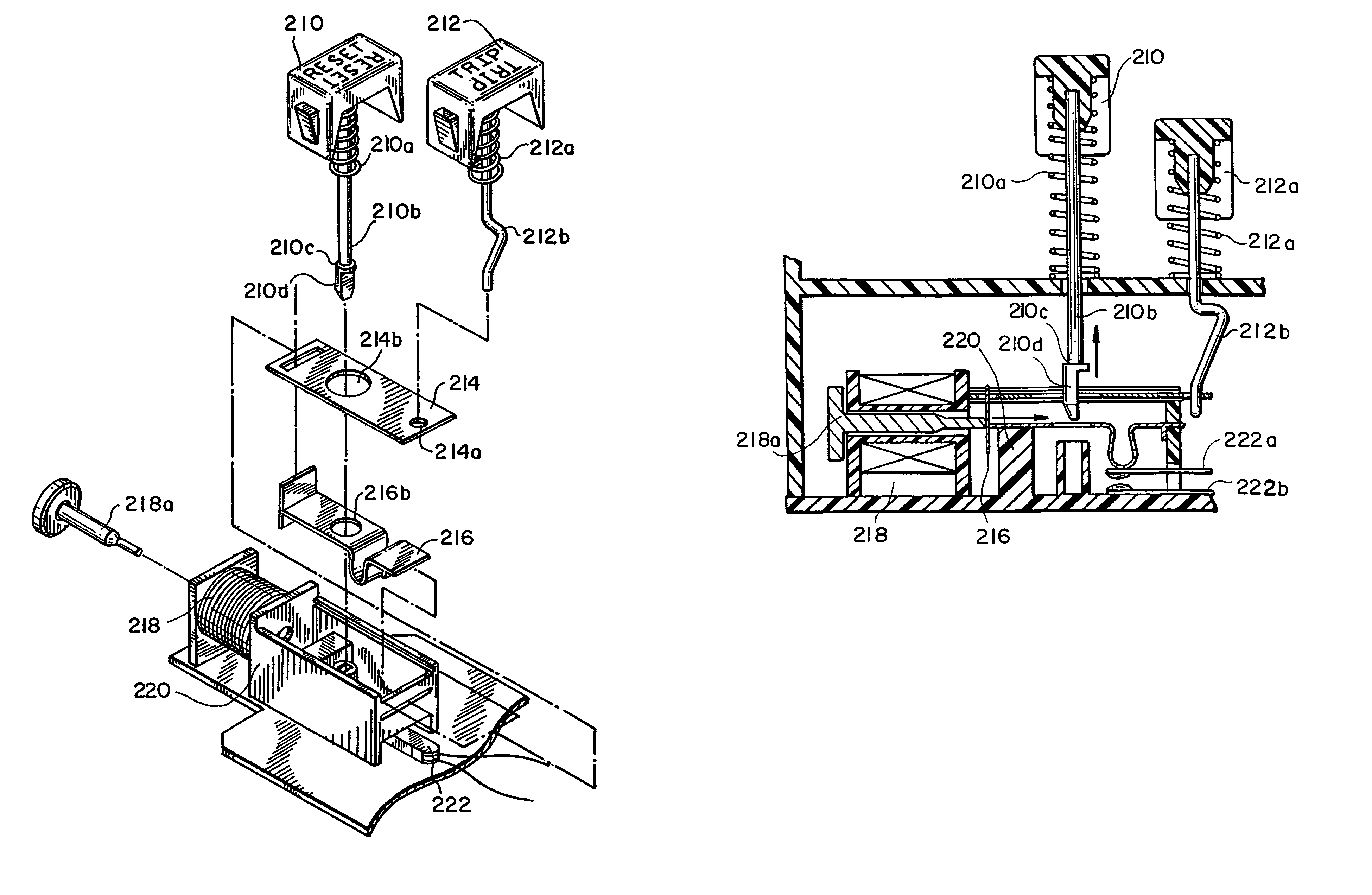
Pivot point reset lockout mechanism for a ground fault circuit interrupter
InactiveUS6771152B2Switch operated by falling currentEmergency protective arrangement detailsElectrical conductorElectrical connection
Resettable circuit interrupting devices, such as GFCI devices that include a reset lockout mechanism, are provided. The reset lockout comprises a member coupled to swing from a pivot which moves with a reset button to permit the resetting of electrical connections between input and output conductors if the circuit interrupting mechanism used to break the connection is non-operational or if an open condition exists.
Owner:LEVITON MFG
Protection device with a contact breaker mechanism
The present invention is directed to an electrical wiring protection device including a housing assembly including at least one receptacle, the at least one receptacle being configured to receive plug contact blades inserted therein. The housing assembly includes a hot line terminal, a neutral line terminal, a hot load terminal, a neutral load terminal, a hot user-accessible receptacle contact, and a neutral user accessible receptacle contact. A fault detection circuit is coupled to the hot line terminal and the neutral line terminal. The fault detection circuit is configured to detect at least one fault condition and provide a fault detect signal in response thereto. An interrupting contact assembly is coupled to the fault detection circuit. A weld breaker mechanism is coupled to the interrupting contact assembly. The weld breaker mechanism is configured to strike the first pair of contacts and / or the second pair of contacts in response to the tripping stimulus.
Owner:PASS SEYMOUR
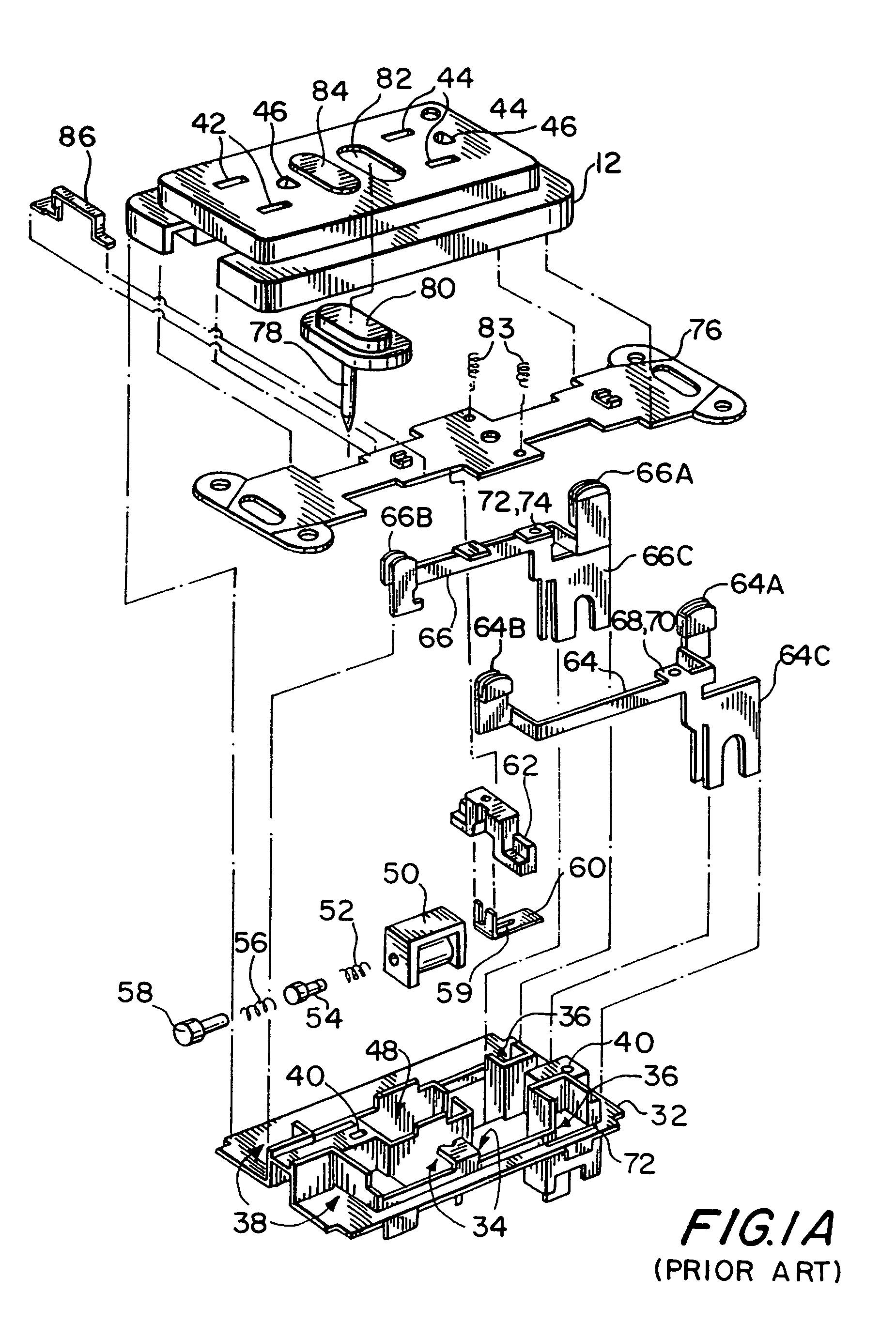
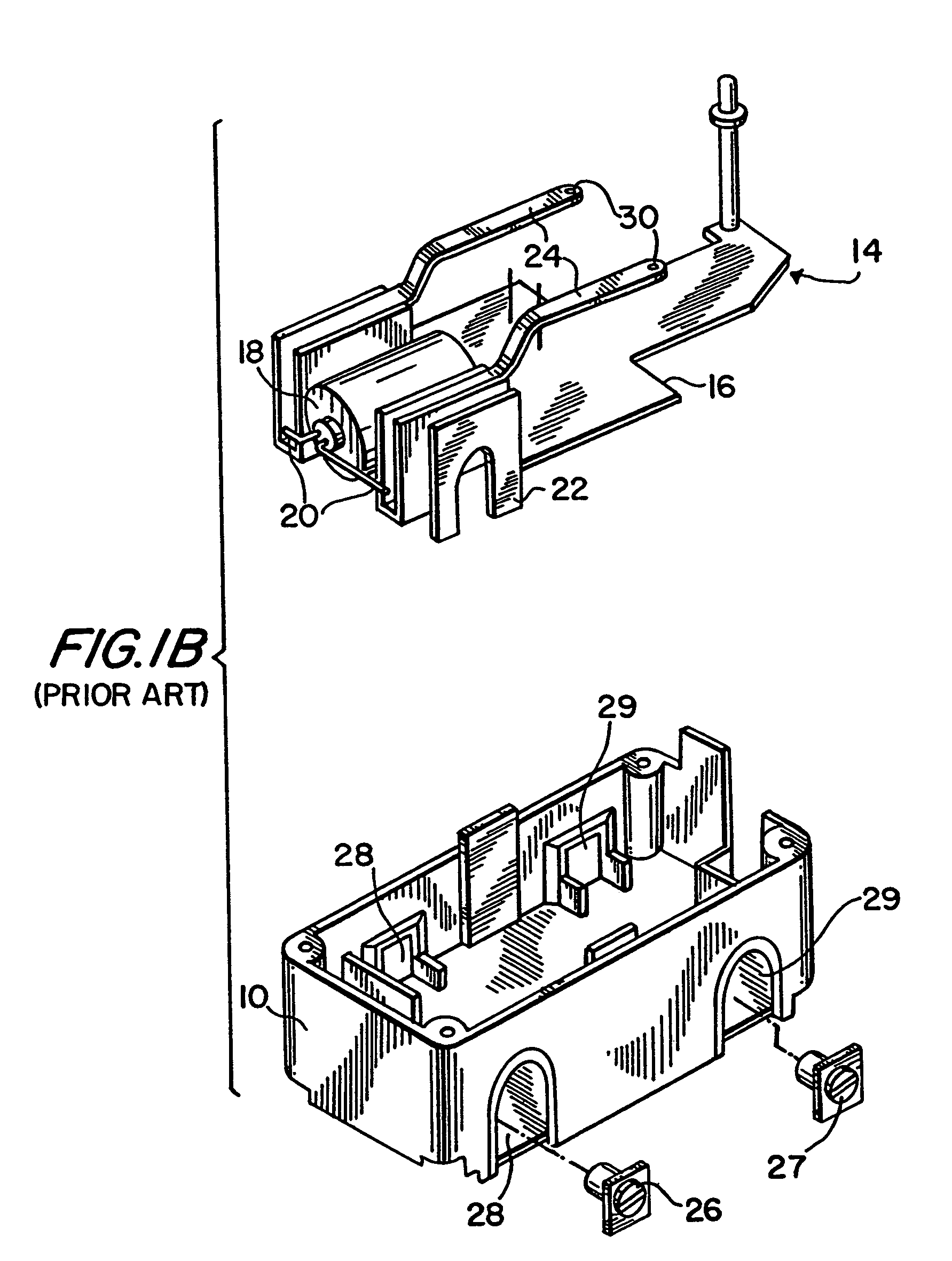
Reset lockout mechanism and independent trip mechanism for center latch circuit interrupting device
InactiveUS6828886B2Switch operated by falling currentEmergency protective arrangement detailsLockout MechanismEmbedded system
Owner:LEVITON MFG
Circuit interrupting device and system utilizing electromechanical reset
ActiveUS7049911B2Switch operated by falling currentSwitch operated by earth fault currentsElectric powerEngineering
Owner:LEVITON MFG
GFCI receptacle having blocking means
InactiveUS6963260B2Switch operated by falling currentSwitch operated by earth fault currentsEngineeringReset button
Located within a GFCI device having receptacle openings in its face is a movable contact bearing arm held in either a closed or open position by a latching member connected to a spring loaded reset button. The reset button assumes a first depressed position when the GFCI is in a conducting state, and a second extended position when the GFCI is in a non conducting state. A blocking member located within the body of the GFCI is adapted to be moved to a first position to blocks at least one opening of each receptacle, or to a second position to allow the prongs of a plug to enter the receptacle openings. When the GFCI is in the conducting state, the reset button is in its first position and holds the blocking member in its first position to permit the prongs of a plug to be inserted into the receptacle openings. When the GFCI is in a non-conducting state or is defective, the reset button and the blocking member are in their second positions and the prongs of a plug are prevented from entering the receptacle.
Owner:LEVITON MFG
Circuit interrupting device with reset lockout and reverse wiring protection and method of manufacture
InactiveUS7049910B2Switch operated by falling currentElectric connection testingElectricityEngineering
Owner:LEVITON MFG
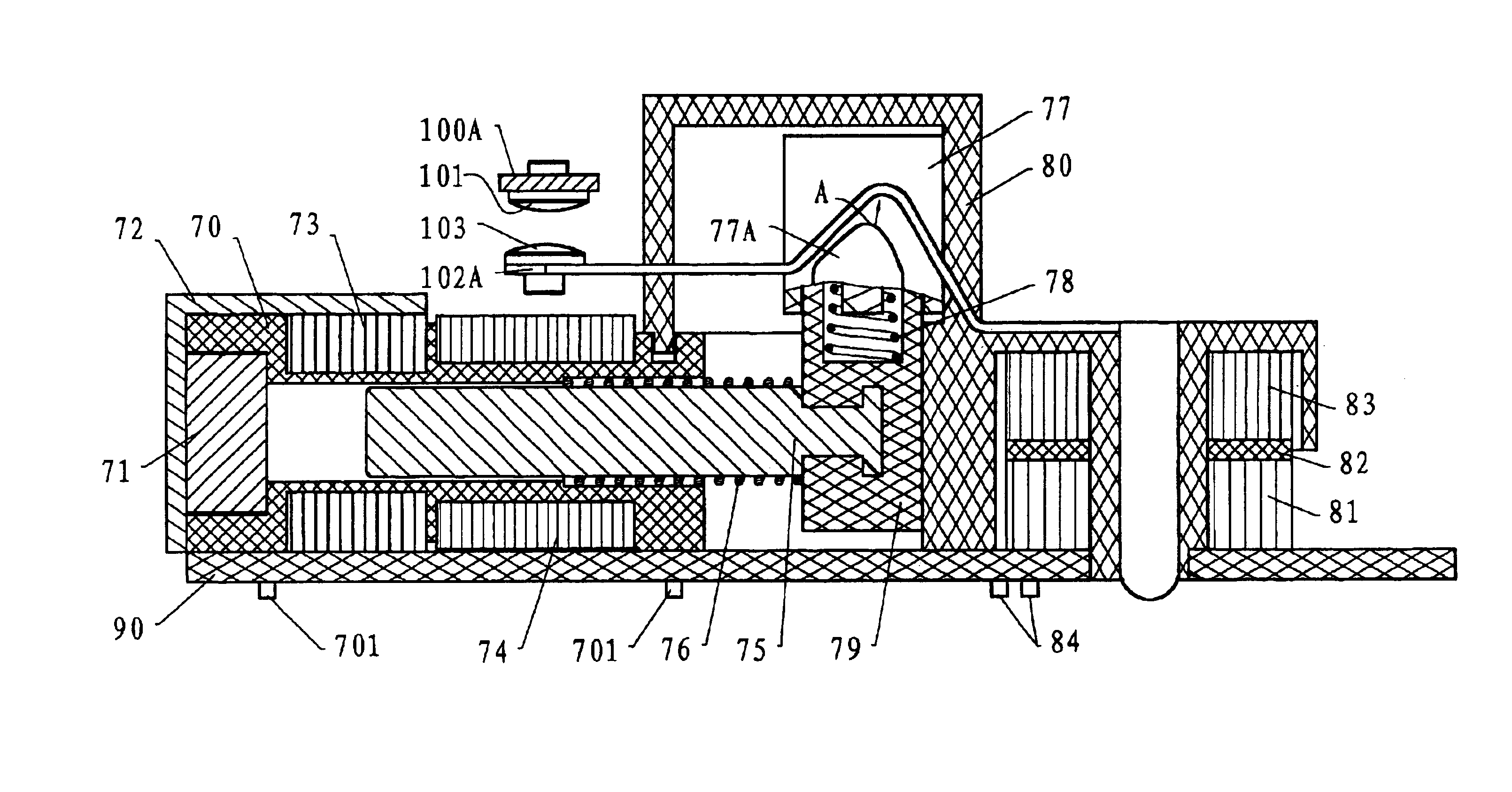
Arc fault circuit breaker
InactiveUS6232857B1Switch operated by current/voltage unbalanceSwitch operated by falling currentElectromagnetic interferenceEngineering
An arc fault circuit breaker (10) conducting an electric current to a protected load is presented. The circuit breaker (10) has a first (mechanical) compartment (24) and a second (electrical) compartment (62). A bimetal resistor (50) is disposed within the first compartment (24) and conducts the current therethrough. The bimetal resistor (50) has a stud (56) extending into the second compartment (62). A single sense line (60) is electrically connected to the bimetal resistor (50) and routed into the second compartment (62). The sense line (60) and said stud (56) conduct a voltage signal indicative of arcing of the current. A circuit board (84) is disposed within the second compartment (62) and is connected to the sense line (60) and stud (56) within the second compartment (62) to process the voltage signal. The circuit board (84) has a first conductive path (104) electrically connected to the stud (56), and a second conductive path (106) electrically connected to the sense line (60). The first and second conductive paths (104,106) run substantially parallel and proximate to each other such that electromagnetic interference of the voltage signal is substantially reduced.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Ground fault circuit interrupter with end of life indicators
InactiveUS7195500B2Freedom of movementProtective switch detailsSwitch operated by falling currentLife detectionLife time
The present invention provides a GFCI that not only has ground fault protection, but also is capable of providing reverse wiring protection as well as detection of end of the service life of the GFCI by way of utilizing an end of life detection control circuit in connection with the reset button. In addition, the GFCI of the present invention provides a forcible mechanical tripping assembly by way of utilizing the test button. Finally, the present invention provides method for detecting whether the service life of the GFCI has ended.
Owner:HUANG HUADAO
Reset lockout for sliding latch GFCI
InactiveUS7031125B2Switch operated by earth fault currentsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:LEVITON MFG
Low voltage device used as an electrical outlet base plate
ActiveUS6943297B2Avoid possibilitySwitch operated by falling currentCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsLow voltageInterrupter
A low voltage device to be used as an electrical outlet base plate has a frame, an external plate fittable under pressure on the frame and fastenable by elastic plugs having protrusions for easy removal of the external plate, the frame having a rectangular central opening allowing to place one or several mechanisms to be installed and fastened, while the external plates being provided with one or several related openings depending on the mechanisms to be installed, the mechanisms having a body for application of a first base plate for electrical outlet with a base having two poles, and earth connection, a second base plate for electrical outlet with a base having two pairs of poles with its related earth connection in a duplex arrangement, and a third base plate for electrical outlet of the duplex arrangement provided with a differential ground fault circuit interrupter, each of the base plates being provided with a safety plate device for preventing access within an area of contacts.
Owner:SIMON SA
GFCI receptacle having blocking means
InactiveUS6873231B2Eliminate needFacilitate mechanical breaking of electrical continuitySwitch operated by falling currentSwitch operated by earth fault currentsFree accessElectrical conductor
Located within a GFCI device having a receptacle is a movable contact bearing arm which is held in either a closed or open position with a fixed contact by a latching member that is connected to the spring loaded reset button. The reset button assumes a first or a second position which is determined by the conductive state of the GFCI. When the GFC is in a conducting state, the reset button is substantially fully depressed within the housing of the GFCI. When the GFCI is in a non-conductive state, the reset button projects outward beyond the top surface of the housing of the GCFI. Thus, the movable contact bearing arm, acting through a latching member, determines the position of the reset button. A blocking member located within the body of the GFCI is positioned by the reset button to allow free access of the prongs of a plug into the openings of the receptacle when the reset button is depressed or to block at least one opening of the receptacle to prevent a plug from entering the openings of the receptacle when the reset button projects out beyond the surface of the housing. Thus, when the GFCI is in a conducting state, the reset button is recessed within the GFCI housing and positions the blocking member to the first position to allow the prongs of a plug to be inserted into the receptacle openings. When the GFCI is in a non-conducting state, the reset button protrudes outward from the housing of the GFCI to position the blocking member to the second position to block at least one opening of the receptacle to prevent the prongs of a plug from entering the receptacle. GFCI's normally have two separate sets of internally located contacts known as bridge contacts where one set is used to connect a load to the source of electricity and the second set is used to connect a user accessible load to the source of electricity. The bridge contacts provide isolation between the conductors to the load and the conductors to the contacts of the GFCI receptacle when the GFCI is in a fault state. In the GFCI here disclosed, the blocking member prevents the prongs of a plug from entering the receptacle when the GFCI is in a fault state and, therefore, can eliminate the need for the bridge contacts.
Owner:LEVITON MFG
Receptacle device having protection against arc faults and leakage currents
InactiveUS6998945B2Avoid disadvantagesEasy to useSwitch operated by falling currentEmergency protective arrangement detailsElectrical conductorTransformer
A receptacle device for protection against arc faults and leakage currents, including an arc fault test button, a leakage test button, and a reset button. Test resistors are arranged below the arc fault test button and the leakage test button wherein the test resistors are coupled to an electrical circuit board. The electrical circuit board includes an arc sampling resistor to detect arc faults and a leakage detection differential transformer to detect leakage currents. In order to provide good contacts between mobile and stationary electrical contacts of the receptacle device, a reset button bias member having mobile contact bridges at its two arms is provided. Each of the mobile contact bridges has three triangularly spaced electrical contacts, corresponding to stationary electrical contacts of flexible input fingers, output conductors and electrical output leads of the receptacle device. In order to balance the mobile contact bridges and provide better contacts, the receptacle device of the present invention can utilize a unique system of dual directional locks, i.e., below the reset button, there are two axially symmetrical directional locks provided within a reset button bias member of the receptacle device.
Owner:HUANG HUADAO
Ground fault circuit interrupter with reverse wiring protection
InactiveUS6954125B2Open fastEasy to operateSwitch operated by falling currentSwitch operated by earth fault currentsGrounding MalfunctionEngineering
A new type of switching mechanism for a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) with reverse wiring protection preferably includes two pairs of fixed contact holders, each member of each pair having at least one fixed contact at one end; a pair of movable contact holders, each having an end having one or more of movable contacts, each movable contact being arranged for contacting one of the fixed contacts; and a movable assembly that moves between first and second positions, wherein the first position is a position in which each of the contacts of the fixed contact holders makes contact with one of the contacts of the movable end of one of the movable contact holders, and wherein the second position is a position in which the contacts of the fixed contact holders are separated from the contacts of the movable contact holders.
Owner:CHEN HENG
GFCI without bridge contacts and having means for automatically blocking a face opening of a protected receptacle when tripped
ActiveUS6949994B2Eliminate needSwitch operated by falling currentElectric switchesElectricityElectrical conductor
Located within a GFCI is a movable contact bearing arm which cooperates with at least one fixed contact. When the movable arm is moved up to allow the at least one contact on the arm to close with at least one fixed contact, the GFCI is in a conducting state and current flows from a source of electricity through the closed contacts to a load and to the contacts of a receptacle. When the movable arm is moved down to open the contacts, the GFCI is in a non-conducting state and current cannot flow from the source of electricity to either the load or the receptacle contacts. In this invention, the up and down movement of the movable contact bearing arm is harnessed to move a blocking member located within the housing of the GFCI to a first position to block at least one opening of the receptacle as the movable arm is moved down or to a second position to allow the prongs of a plug to enter the openings of the receptacle as the movable arm is moved up. The downward movement of the movable contact bearing arm occurs when the GFCI goes into a non-conducting state. Resetting the GFCI by pressing in and then releasing a reset button causes the movable contact bearing arm to move up to make contact with the at least one fixed contact. As the movable arm moves up, the blocking member moves to the first or non-blocking position to allow the prongs of a plug to freely enter the openings in the face of the receptacle. GFCI's normally have two separate sets of internally located contacts known as bridge contacts where one set is used to connect a load to the source of electricity and the second set is used to connect a user accessible load to the source of electricity. The bridge contacts provide isolation between the conductors to the load and the conductors to the contacts of the GFCI receptacle when the GFCI is in a non-conducting state. In the GFCI here disclosed, the blocking member prevents the prongs of a plug from entering the receptacle when the GFCI is in a non-conducting state and, therefore, the need for the bridge contacts is diminished.
Owner:LEVITON MFG
Protective device with end of life indicator
InactiveUS6952150B2Switch operated by falling currentSwitch operated by earth fault currentsTime segmentDistribution system
The present invention is directed to a protective device that includes a plurality of line terminals configured to be connected to an electrical distribution system, and a plurality of load terminals configured to be connected to a load. The device includes a fault detection circuit coupled to the plurality of line terminals and the plurality of load terminals. The fault detection circuit is configured to detect at least one fault in the electrical distribution system. A power interruption circuit couples the plurality of line terminals to the plurality of load terminals to thereby provide power to the load under normal operating conditions. The power interruption circuit also is coupled to the fault detection circuit, and configured to decouple the plurality of line terminals from the plurality of load terminals in response to the fault detection circuit detecting the at least one fault. A test circuit is coupled to the fault detection circuit and the power interruption circuit. The test circuit is configured to provide a simulated fault signal to the fault detection circuit in response to a user stimulus. An end-of-life indication circuit is coupled to the test circuit and the power interruption circuit. The end-of-life indication circuit provides the user with an end-of-life alarm indicator if the fault detection circuit fails to respond to the simulated fault signal within a predetermined period of time.
Owner:PASS SEYMOUR
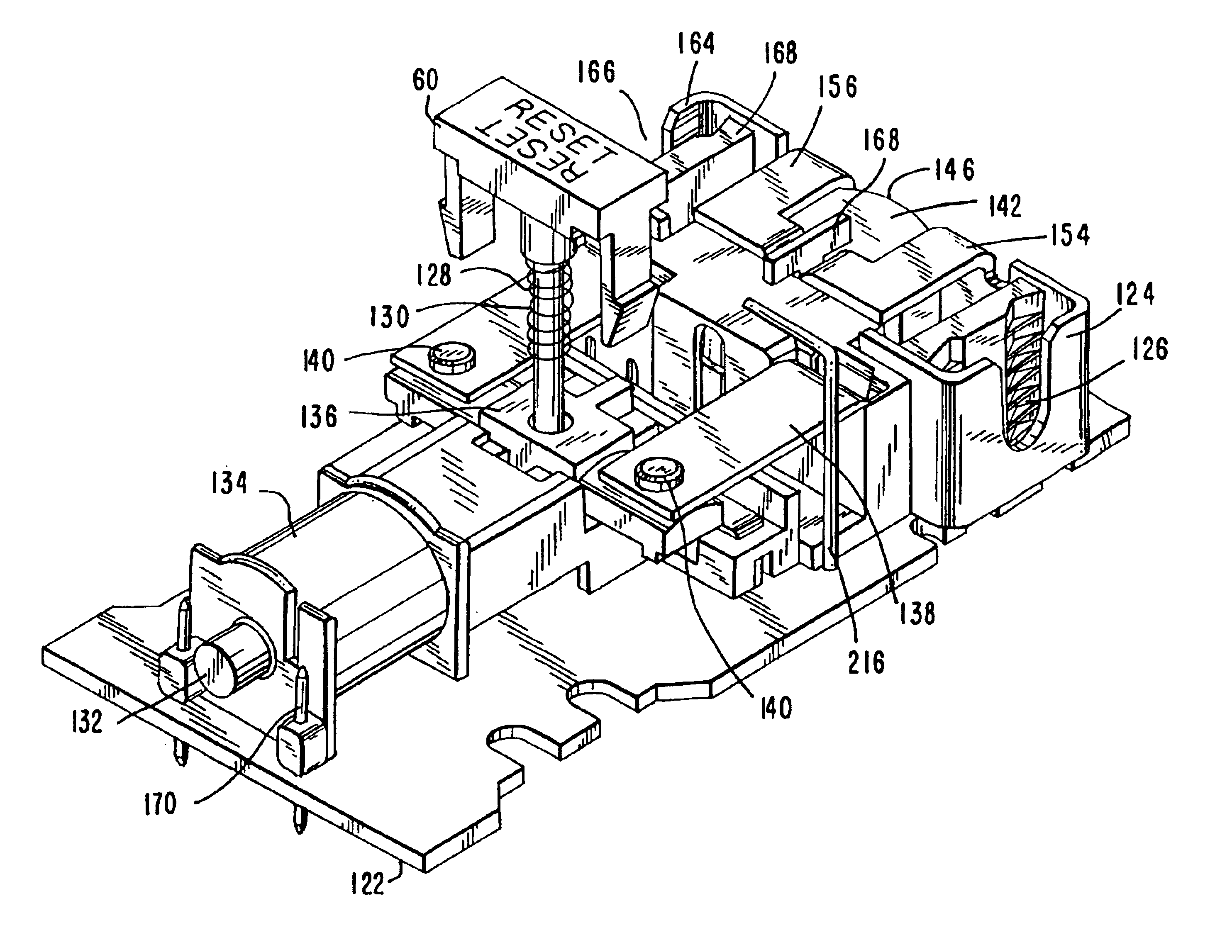
Ground fault circuit interrupter containing a dual-function test button
Owner:HUANG HUADAO
Ground fault circuit interrupter containing a dual-function test button
InactiveUS7289306B2Protective switch detailsSwitch operated by earth fault currentsElectricityLife detection
Owner:HUANG HUADAO
Circuit interrupting device with automatic end of life test
The present invention provides to a circuit interrupting device, particularly a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI), with a test circuit which is capable of automatically generating a simulated leakage current to detect whether the service life of the circuit interrupting device has ended, i.e., whether the main components of the device are working properly, when the device is properly connected to power input terminals and in a tripped state. The test circuit contains an end-of-service-life integrated circuit chip, which is connected to a switch that interacts with the reset button, thereby, by observing whether the device is capable of resetting, a user can determine whether the service life of the device has ended, i.e., if the device can be reset, the device is working properly; if the device cannot be reset, the service life of the device has ended. Optionally, the circuit interrupting device contains an indicating light on the face of the device, thereby, by observing whether a normal status indicating light or a problem status indicating light is turned on and displayed on the face of the device, the user can determine whether the service life of the device has ended. The circuit interrupting device also possesses a forcible tripping mechanism through the operation of the test button to interrupt the power output to the device. The present invention also provides methods for detecting the end of service life of the circuit interrupting device.
Owner:HUANG HUADAO
GFCI receptacle having plug blocking means
ActiveUS7026895B2Achieve electrical continuitySwitch operated by falling currentSwitch operated by earth fault currentsManufacturing cost reductionElectrical conductor
A shaped member having at least one window is located within a GFCI protected receptacle and is operated by movement of the contact arm of the GFCI to assume a first position to block at least one plug receiving opening in the receptacle and a second position which locates the window to allow the prong of a plug to freely enter the face of the receptacle. In operation, when the circuit interrupting device goes into a tripped state, the contact arm moves down to open the circuit. The downward movement of the contact arm, acting through a connecting linkage causes the shaped member to move to the first position, that of blocking at least one opening in the face of the receptacle. Resetting the circuit interrupting device by pressing in and then releasing the reset button of the GFCI causes the main contacts in the circuit interrupting device to close by the upward movement of the contact arm. As the contact arm moves up, it moves the connecting linkage to position the window of the shaped member to allow the prongs of a plug to freely enter the openings in the face of the receptacle. GFCI's normally have two separate sets of internally located contacts known as bridge contacts, one set for connecting a load to the source of electricity and a second set for connecting a user accessible load to the source of electricity. In the GFCI here disclosed the bridge contacts have been eliminated, thus reducing the cost of manufacture by coupling the conductors for both the load and the user accessible load to a single set of contacts.
Owner:LEVITON MFG
Protective device with tamper resistant shutters
InactiveUS7312394B1Switch operated by falling currentCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsWindow shutterEngineering
The present invention is directed to a protective shutter assembly for use within a cover assembly of an electrical wiring device. The assembly includes a frameless shutter sub-assembly movable between a closed position and an open position. The frameless shutter sub-assembly is configured to move from the closed position to the open position in response to engaging at least one plug blade having a predetermined plug blade geometry. A spring member is disposed within the frameless shutter sub-assembly. The spring member is configured to bias the frameless shutter sub-assembly in the closed position. At least one retainer element is disposed in the frameless shutter sub-assembly. The at least one retainer element being configured to retain the spring member within the frameless shutter sub-assembly. At least one registration member is disposed on the frameless shutter sub-assembly, the at least one registration member being configured to position and align the protective shutter assembly within the cover assembly.
Owner:PASS SEYMOUR
Ground fault circuit interrupter with reverse wiring protection
ActiveUS6946935B2Improve operational sensitivityMore energySwitch operated by falling currentSwitch operated by earth fault currentsControl circuitCircuit breaker
A new type of ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) with reverse wiring protection preferably includes a pair of fixed contact holders, each having a contact at one end; a pair of movable contact holders, each having a fixed end and a movable end, each of the movable ends having a contact; a movable assembly that moves between first and second positions, wherein the first position is a position in which each of the contacts of the fixed contact holders makes contact with one of the contacts of the movable end of one of the movable contact holders, and wherein the second position is a position in which the contacts of the fixed contact holders are separated from the contacts of the movable contact holders; an electromagnetic resetting component, which, when energized, causes the movable assembly to be in the first position; an electromagnetic tripping component, different from the electromagnetic resetting component, which, when energized, causes the movable assembly to be in the second position; and a control circuit, which, upon detection of a fault condition, energizes the electromagnetic tripping component, and which, upon detection of a reset condition, energizes the electromagnetic resetting component.
Owner:CHEN HENG
GFCI receptacle having blocking means
InactiveUS7088205B2Eliminate needSwitch operated by falling currentLive contact access preventionFree accessElectrical conductor
Located within a GFCI device having a receptacle is a movable contact bearing arm which is held in either a closed or open position with a fixed contact by a latching member that is connected to the spring loaded reset button. The reset button assumes a first or a second position which is determined by the conductive state of the GFCI. When the GFC is in a conducting state, the reset button is substantially fully depressed within the housing of the GFCI. When the GFCI is in a non-conductive state, the reset button projects outward beyond the top surface of the housing of the GCFI. Thus, the movable contact bearing arm, acting through a latching member, determines the position of the reset button. A blocking member located within the body of the GFCI is positioned by the reset button to allow free access of the prongs of a plug into the openings of the receptacle when the reset button is depressed or to block at least one opening of the receptacle to prevent a plug from entering the openings of the receptacle when the reset button projects out beyond the surface of the housing. Thus, when the GFCI is in a conducting state, the reset button is recessed within the GFCI housing and positions the blocking member to the first position to allow the prongs of a plug to be inserted into the receptacle openings. When the GFCI is in a non-conducting state, the reset button protrudes outward from the housing of the GFCI to position the blocking member to the second position to block at least one opening of the receptacle to prevent the prongs of a plug from entering the receptacle. GFCI's normally have two separate sets of internally located contacts known as bridge contacts where one set is used to connect a load to the source of electricity and the second set is used to connect a user accessible load to the source of electricity. The bridge contacts provide isolation between the conductors to the load and the conductors to the contacts of the GFCI receptacle when the GFCI is in a fault state. In the GFCI here disclosed, the blocking member prevents the prongs of a plug from entering the receptacle when the GFCI is in a fault state and, therefore, can eliminate the need for the bridge contacts.
Owner:LEVITON MFG
Ground fault circuit interrupter against reverse connection error
ActiveUS6930574B2Safety can be assuredAvoid damageCoupling device detailsSwitch operated by falling currentElectricityState of art
A ground fault circuit interrupter against RCE suitable for various electrical instruments, equipments and systems fed by electrical power supply is characterized in that an erroneous reverse connection mechanism is included in its load end and the reset button comprises a reverse trip mechanism. When electric power is mistakenly connected to the load ends, the reset button will be always in trip situation and the socket on its upper lid will be kept free of electricity even the reset is attempted unless the error connection is corrected. As compared to prior art, the circuit interrupter of this invention has a simple mechanical trip structure which can effectively prevent equipment damage and personal hazard caused by reverse connection. Of course, it had successfully passed the 6 KV / 3 KA electric surge test and is highly anti-moist and anticorrosive.
Owner:LISHUI TRIMONE ELECTRICAL TECH CO LTD
Protective device with tamper resistant shutters
InactiveUS20090311892A1Switch operated by falling currentCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsWindow shutterElectrical wiring
The present invention is directed to a modular shutter assembly for use within various types of electrical wiring devices having differing amperage ratings. Each of the electrical wiring devices includes a housing assembly. The housing assembly further includes a cover assembly and a rear body member. The cover assembly includes at least one set of receptacle openings configured to receive a corded plug blade set having a hot plug blade and a neutral plug blade. The modular shutter assembly includes a first shutter member having a first blade engagement structure. The first shutter member is configured to be disposed within an interior portion of the cover assembly and disposed between the at least one set of receptacle openings and the at least one set of receptacle contacts. A second shutter member includes a second blade engagement structure. The second shutter member is slidably disposed within the first shutter member. An interface is formed in either the first shutter member or the second shutter member or both. The interface is configured to connect a third shutter member to the modular shutter assembly. The interface is configured to drive the third shutter into an open position only when the first shutter member and the second shutter member move relative to each other in response to the first blade engagement structure and the second blade engagement structure being substantially simultaneously engaged by a set of plug blades. The interface does not interfere with the operation of the first shutter member and the second shutter member when the modular shutter assembly is used without the third shutter member.
Owner:PASS SEYMOUR
Circuit interrupting device with reverse wiring protection
InactiveUS20050063110A1Switch operated by falling currentEmergency protective arrangement detailsElectricityElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:LEVITON MFG
Electronic switching device, in particular circuit-breaker and associated operating method
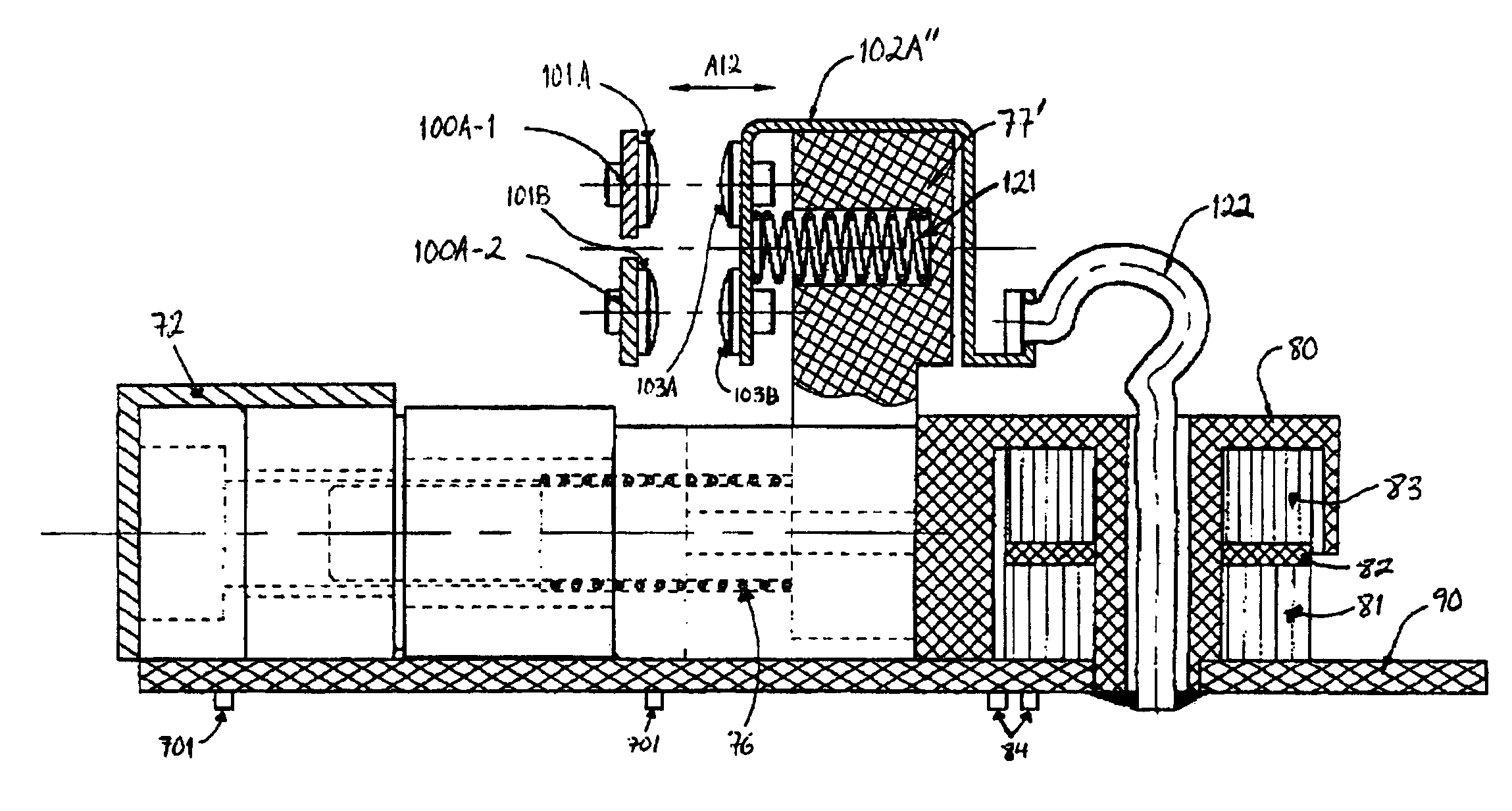
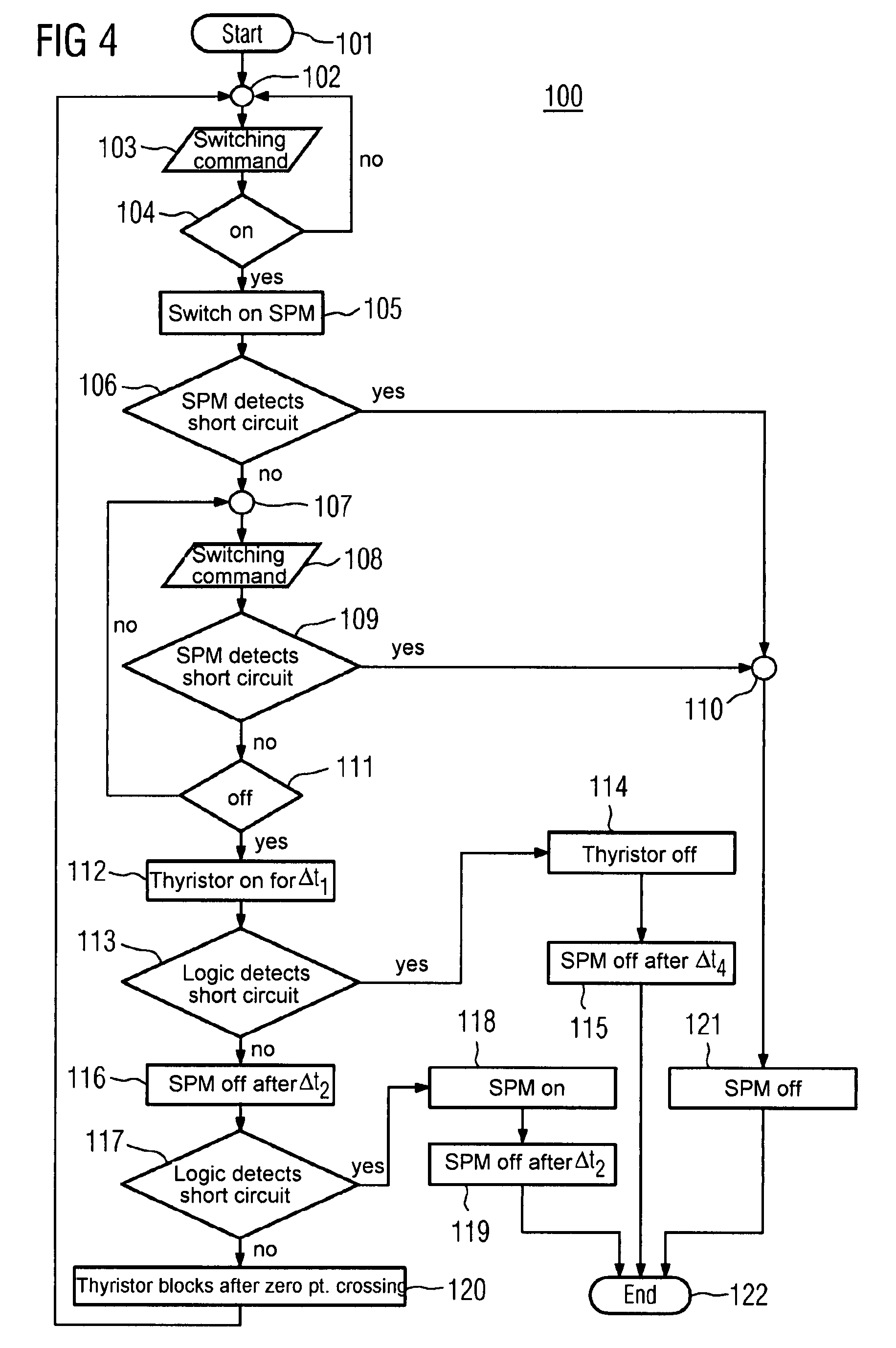
An anti-serial cascade circuit including two silicon carbide JFETs and two silicon MOSFETs is known. Disclosed is a combination of a JFET, a smart power MOSFET SPM and a thyristor with an associated trigger circuit, which is connected in parallel to the SPM. According to an embodiment of the invention, a logic circuit co-ordinates the functional sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Reinstallable Circuit Interrupting Device with Vibration Resistant Miswire Protection
ActiveUS20130241678A1Switches with electromagnetic openingSwitch operated by falling currentEngineeringActuator
A GFCI device includes a latch assembly provided with a rigid electrically conducting bar connected thereto such that when a user presses a reset button the latch assembly is moved toward a pair of contacts provided as part of a reset circuit to initiate a reset operation. When the electrically conducting bar on the latch assembly connects the pair of contacts, the reset circuit is closed and an actuator is activated to place the GFCI device in the latched, reset, condition. If the GFCI device is correctly wired, the latch assembly enters the latched state. If the device is not properly wired no power is provided to the actuator and the device remains in the tripped, or open, state.
Owner:HUBBELL INC
Reset lockout mechanism and independent trip mechanism for center latch circuit interrupting device
InactiveUS7098761B2Switches with electromagnetic openingTwo pole connectionsLockout MechanismEmbedded system
Resettable circuit interrupting devices, such as GFCI devices, that include a reset lockout mechanism, an independent trip mechanism and reverse wiring protection. A conical reset plunger is notched to force a successful test before reset.
Owner:LEVITON MFG
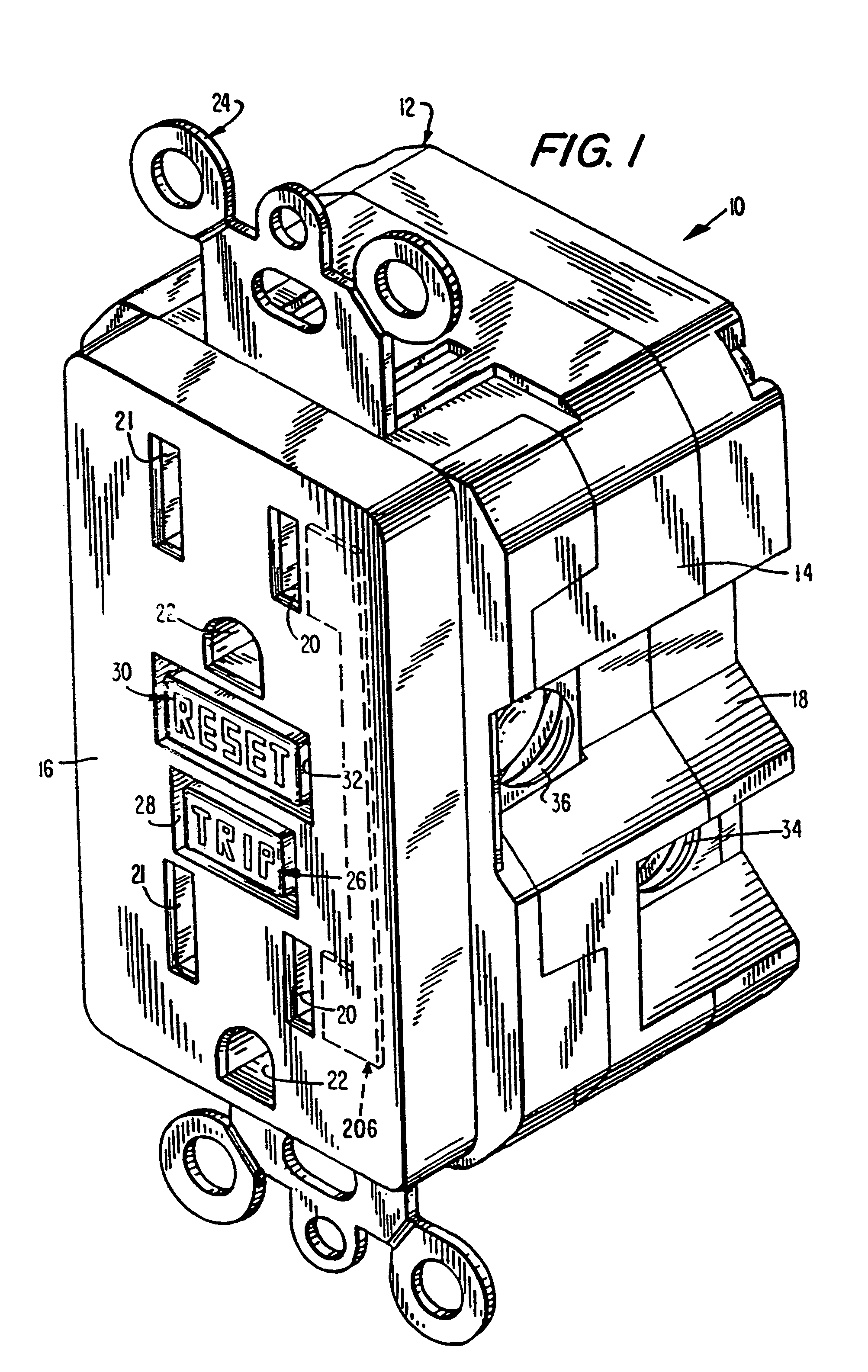
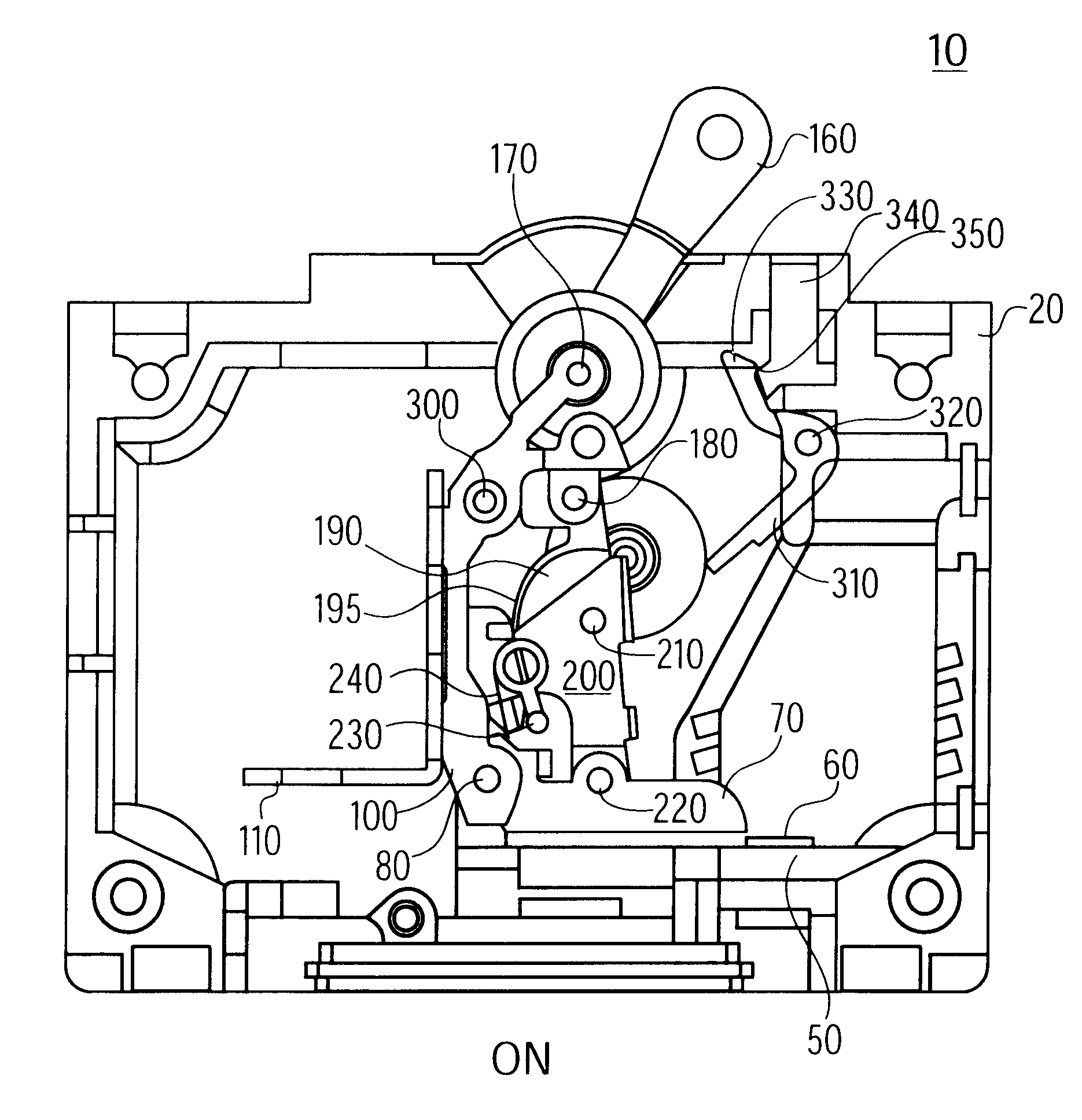
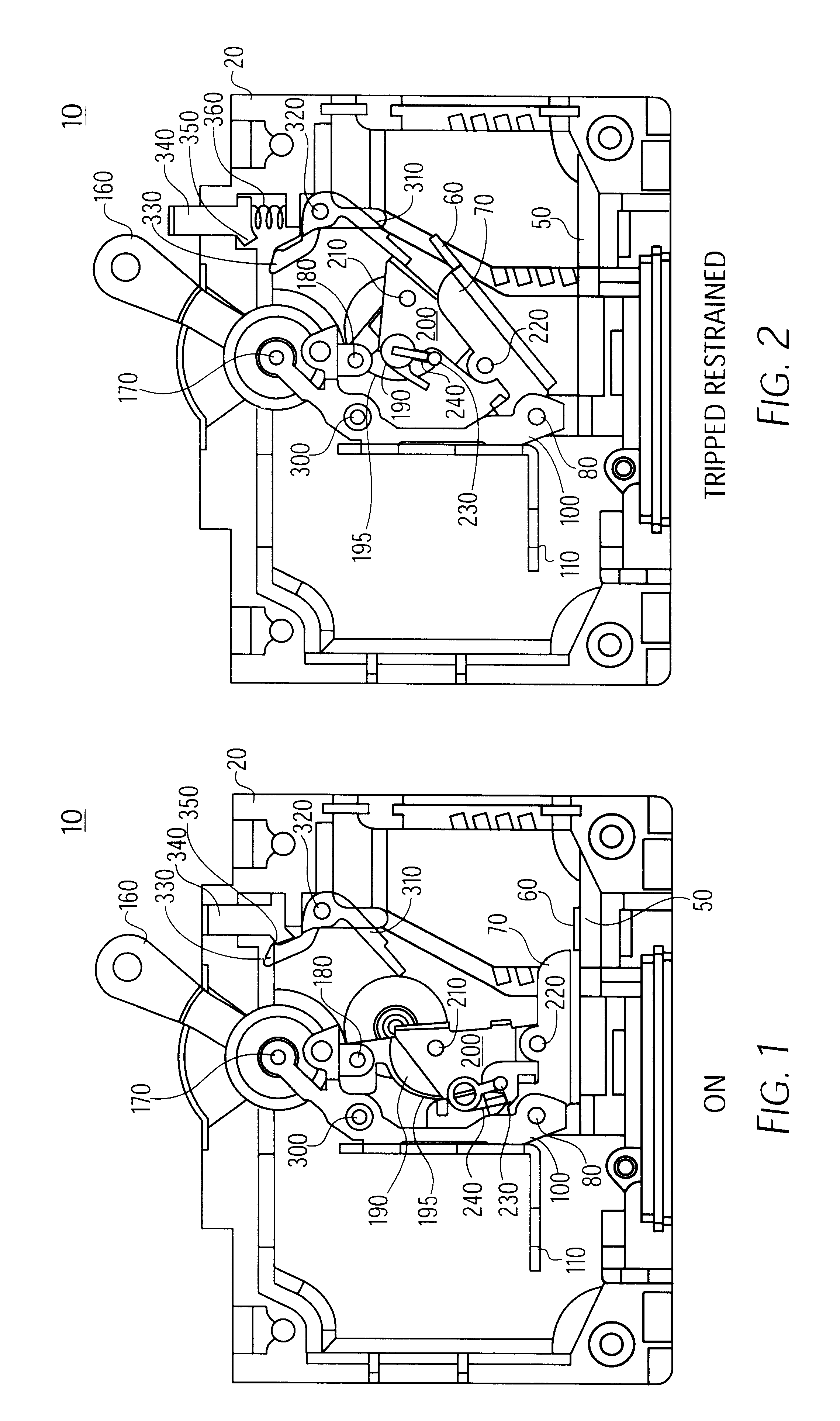
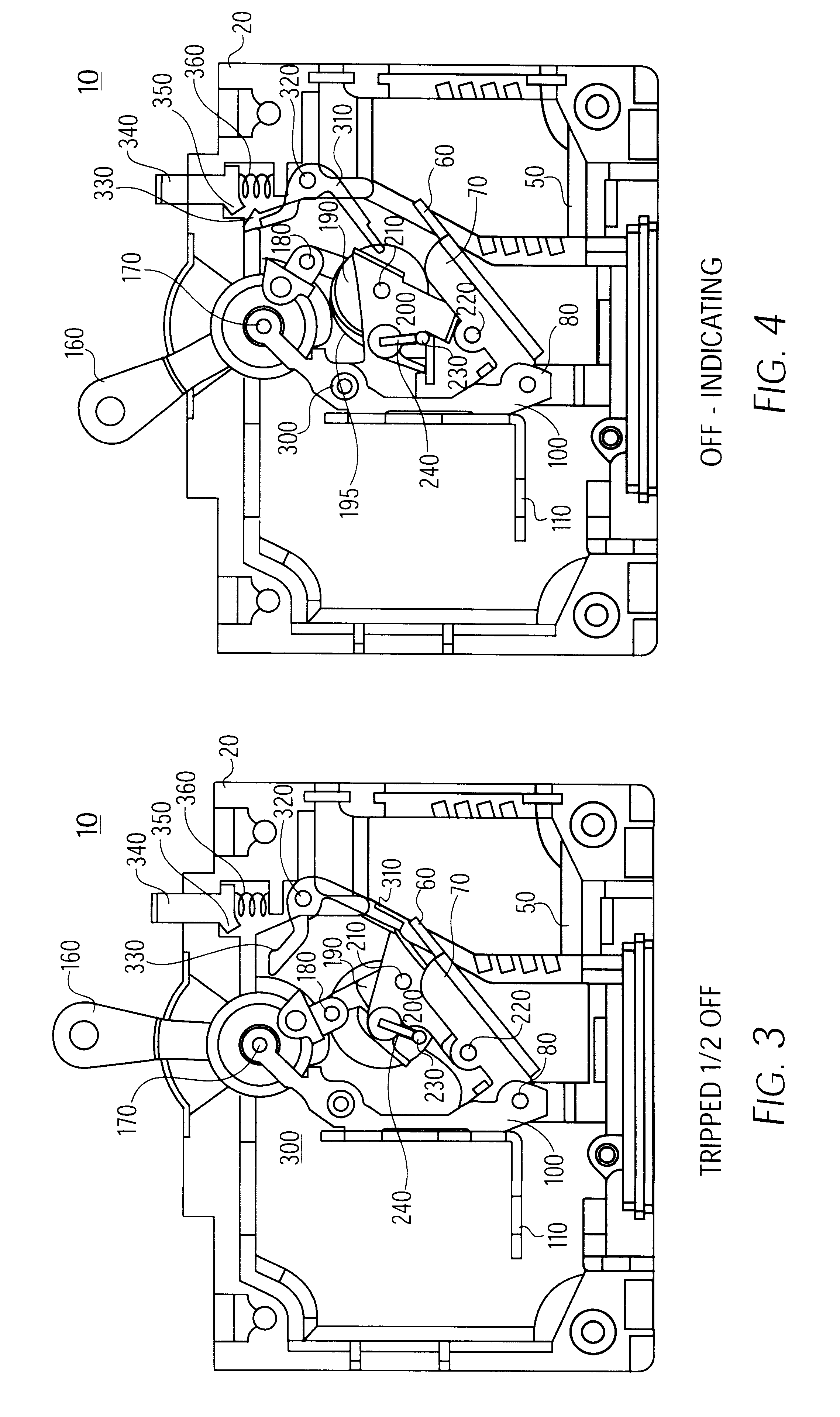
Trip indicating circuit breaker
A circuit breaker having an external trip indicator, having a circuit breaker housing, a trip mechanism within the housing, sensing a trip condition and being responsive thereto to mechanically break an electrical circuit, an indicator, having a selectively operable retaining mechanism and being biased outward from the circuit breaker housing, and a linkage, sensing a trip condition of the trip mechanism and selectively releasing the selectively operable retaining mechanism to allow the indicator to move outwardly from the housing. The external trip indicator is operated by sensing an overcurrent condition with the trip mechanism, breaking the electric circuit in response to the overcurrent, sensing a mechanical movement of the trip mechanism, and thereby releasing a positional restraint on the mechanical indicator; and allowing the mechanical indicator to protrude from the housing. The external trip indicator is reset by first resetting the trip mechanism and then displacing the mechanical indicator into the housing.
Owner:AIRPAX
Popular searches
Arrangements responsive to excess current Emergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/current Switch operated by excess current and arc fault Protective switch operating/release mechanisms Contact-welding prevention/breaking Short-circuit testing Switches with electrothermal and electromagnetic release Coupling protective earth/shielding arrangements Connection contact member material Two-part coupling devices
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com