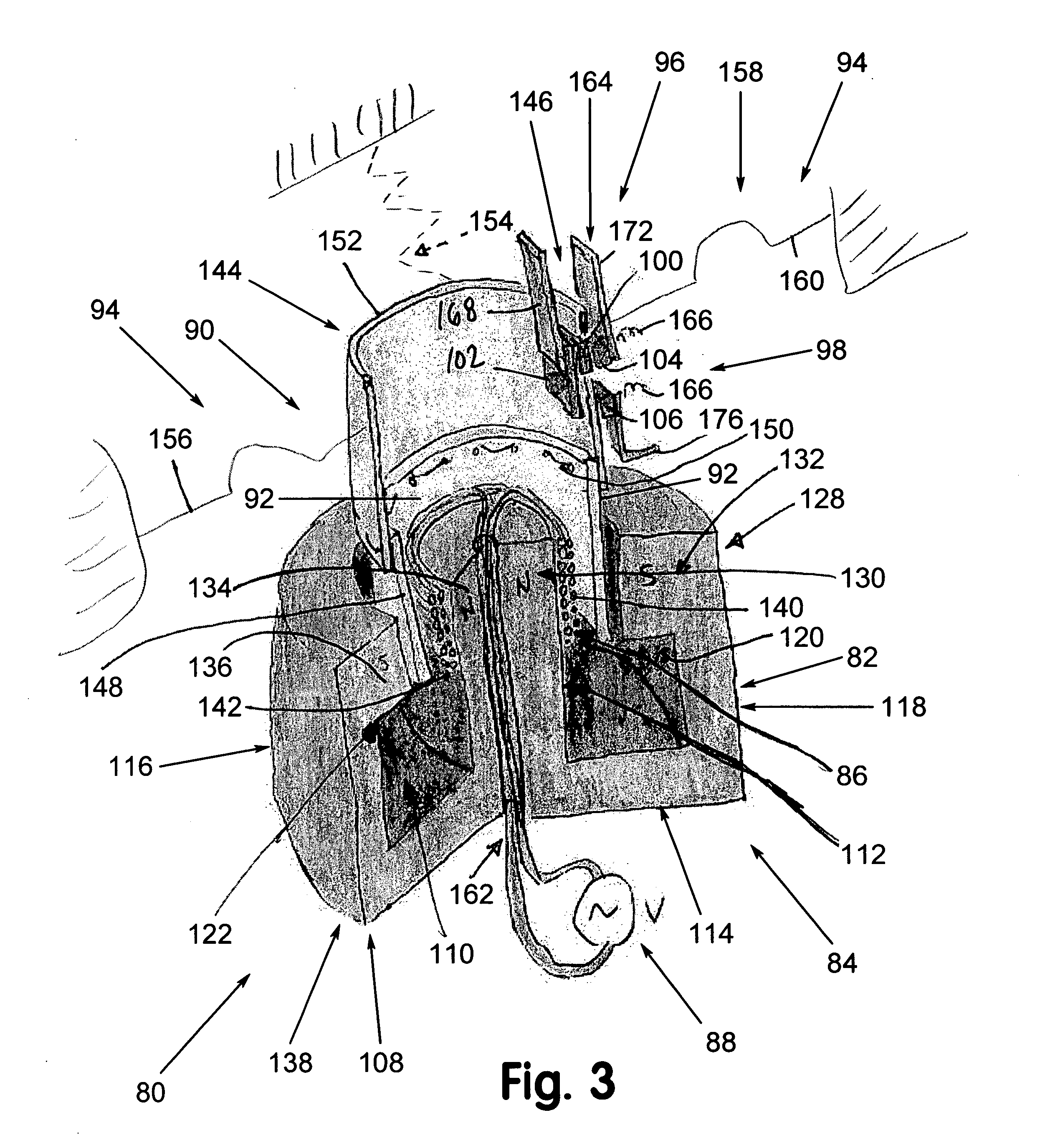
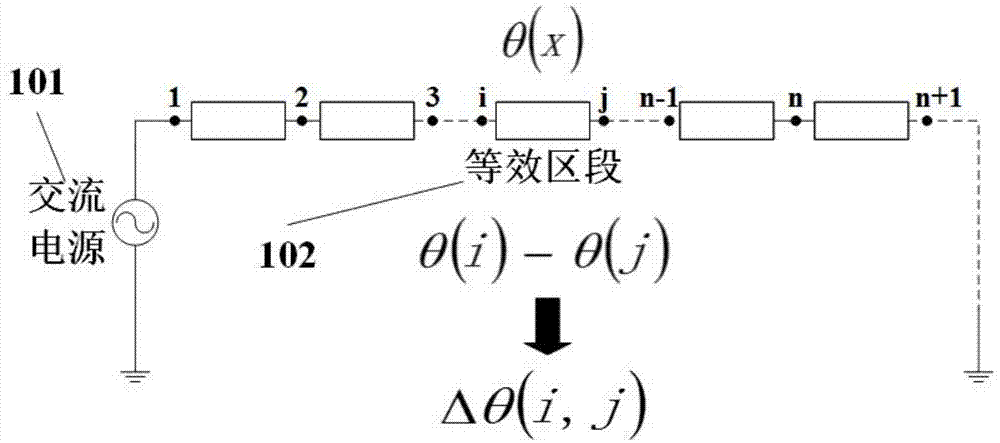
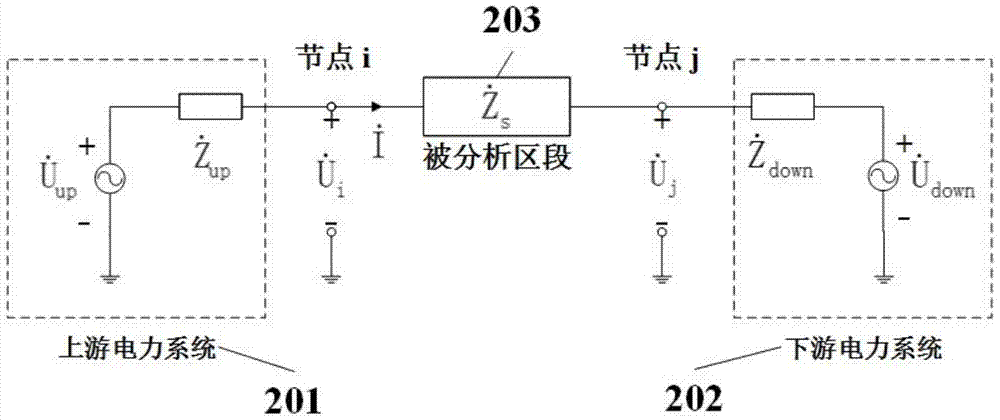
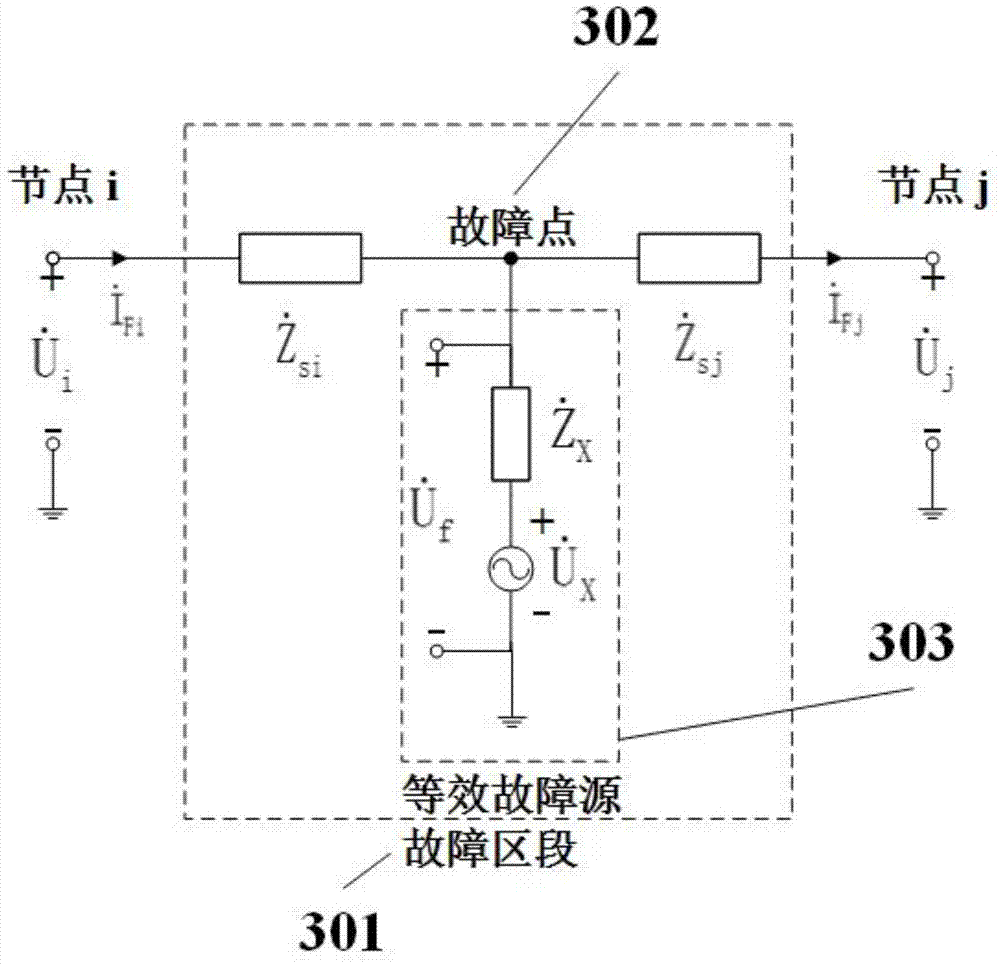
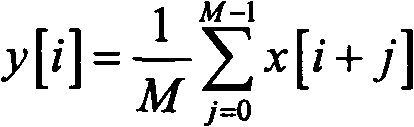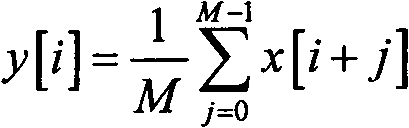Patents
Literature
1231 results about "Grounding Malfunction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
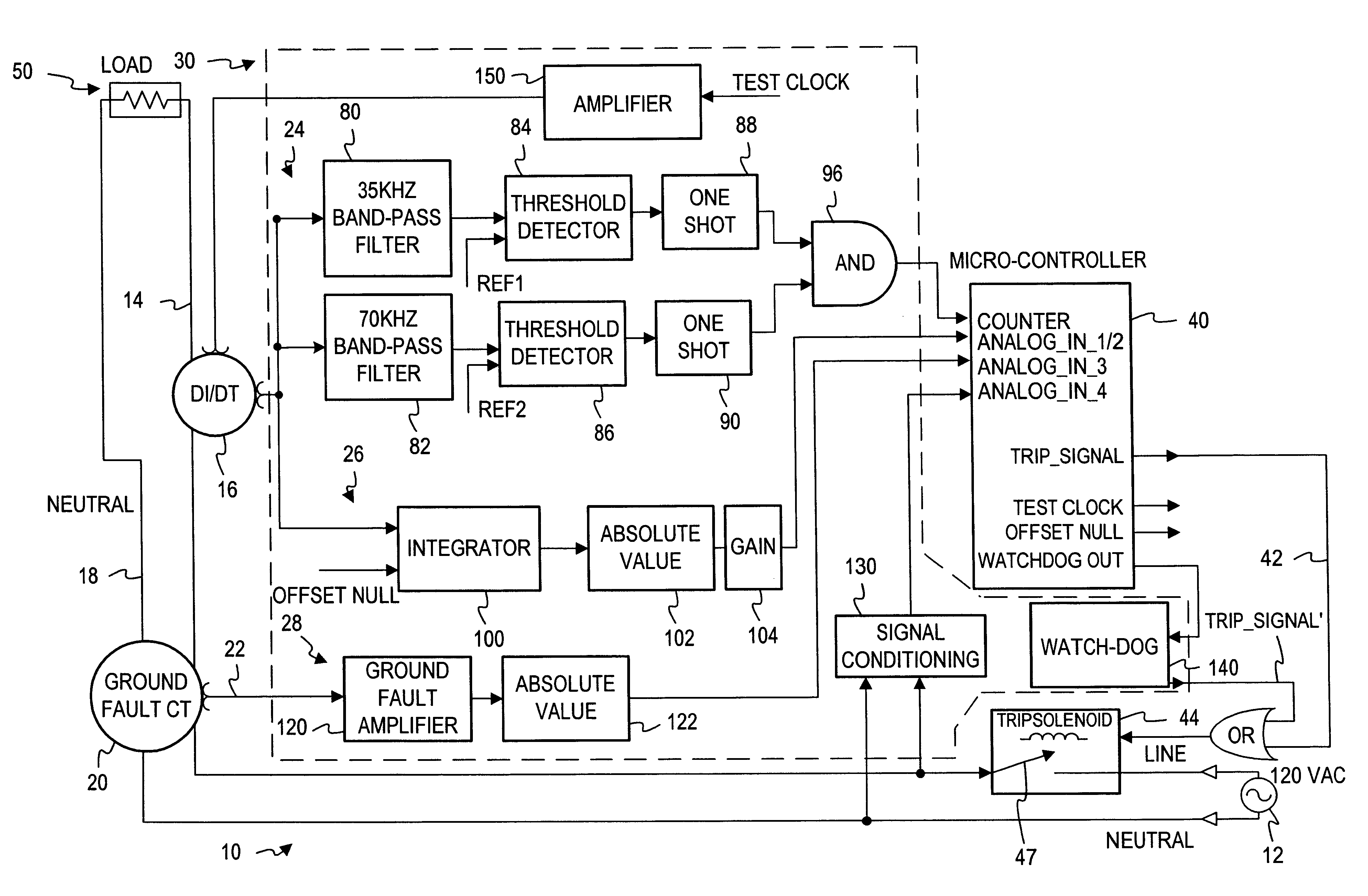
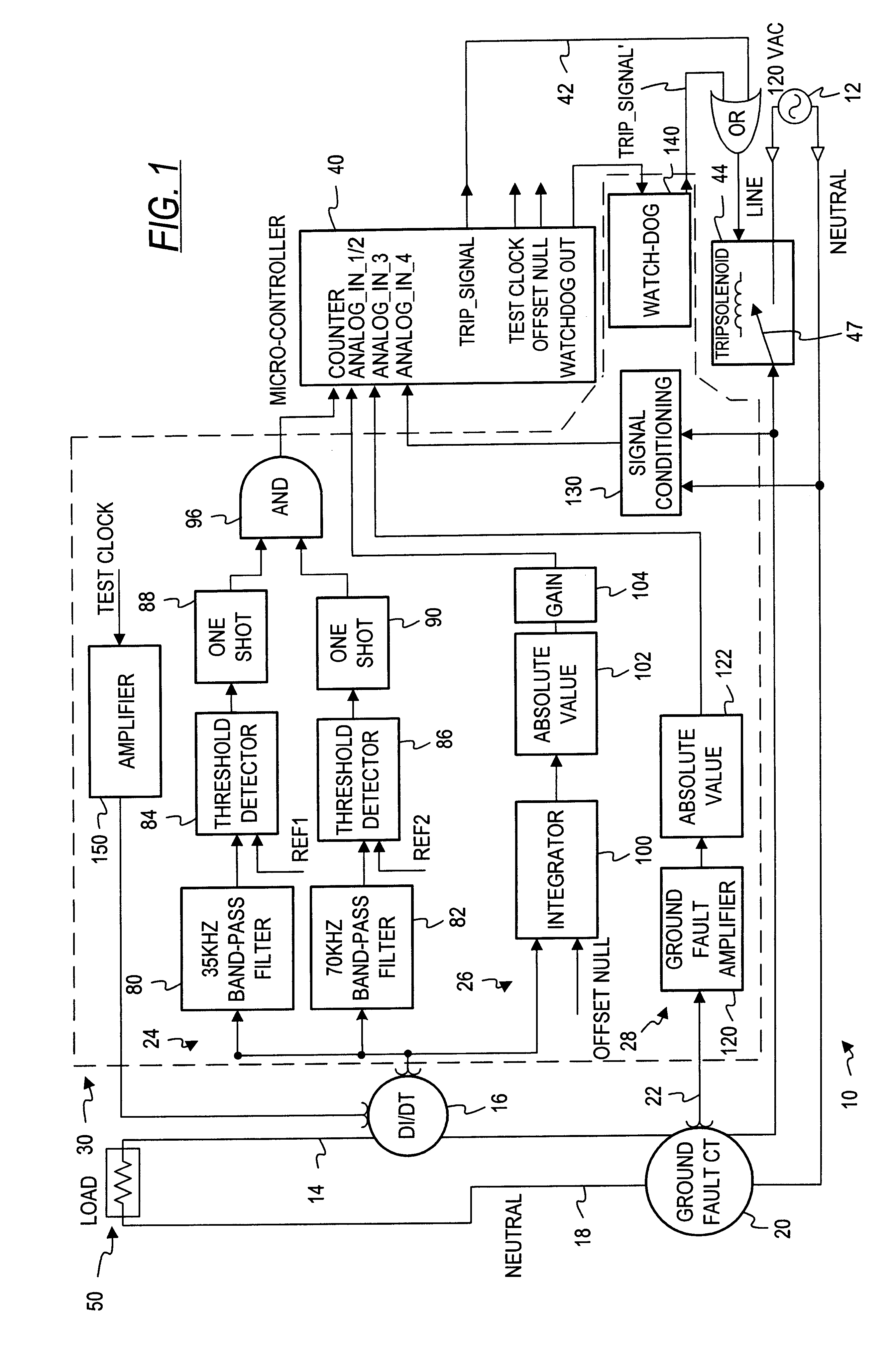
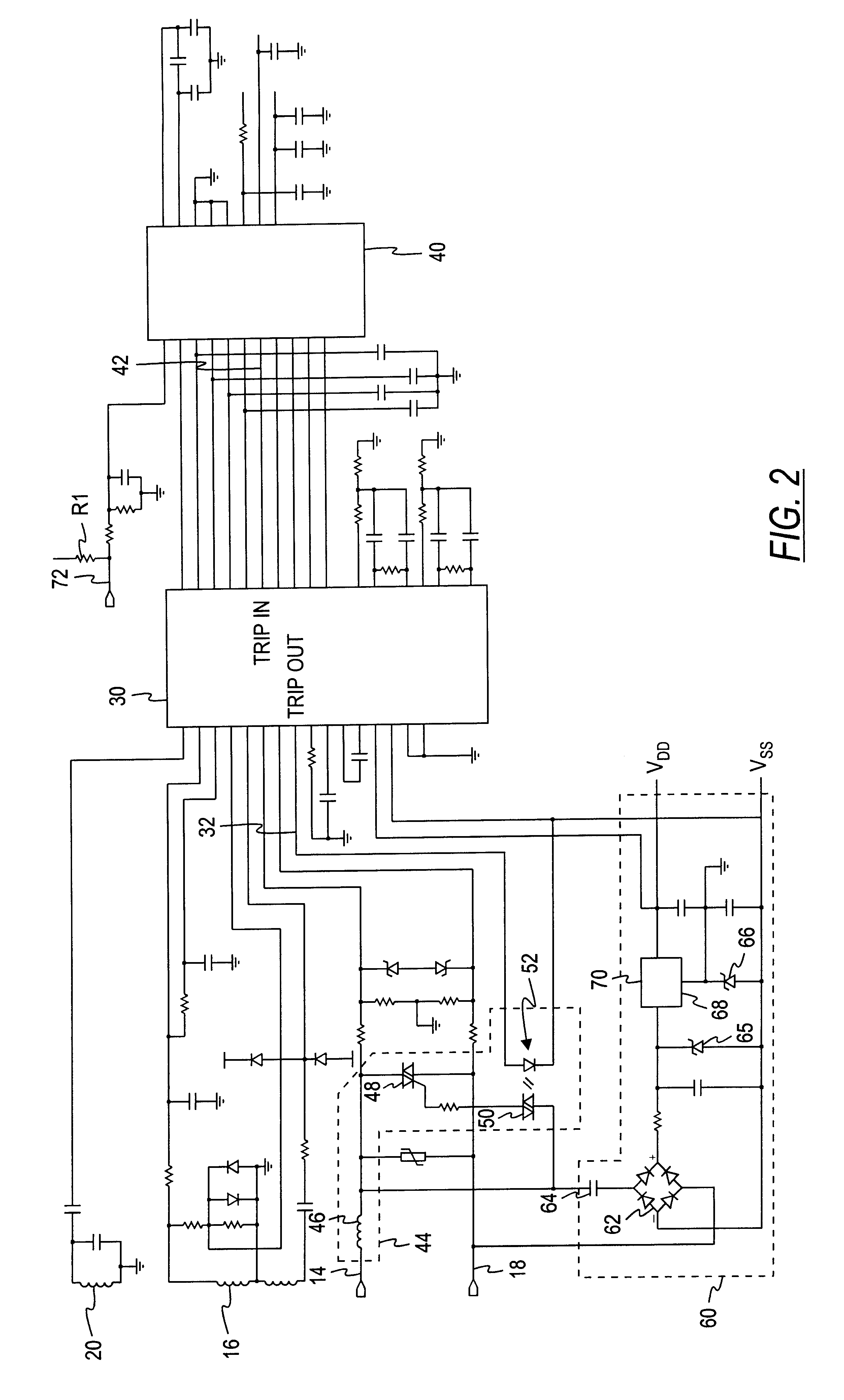
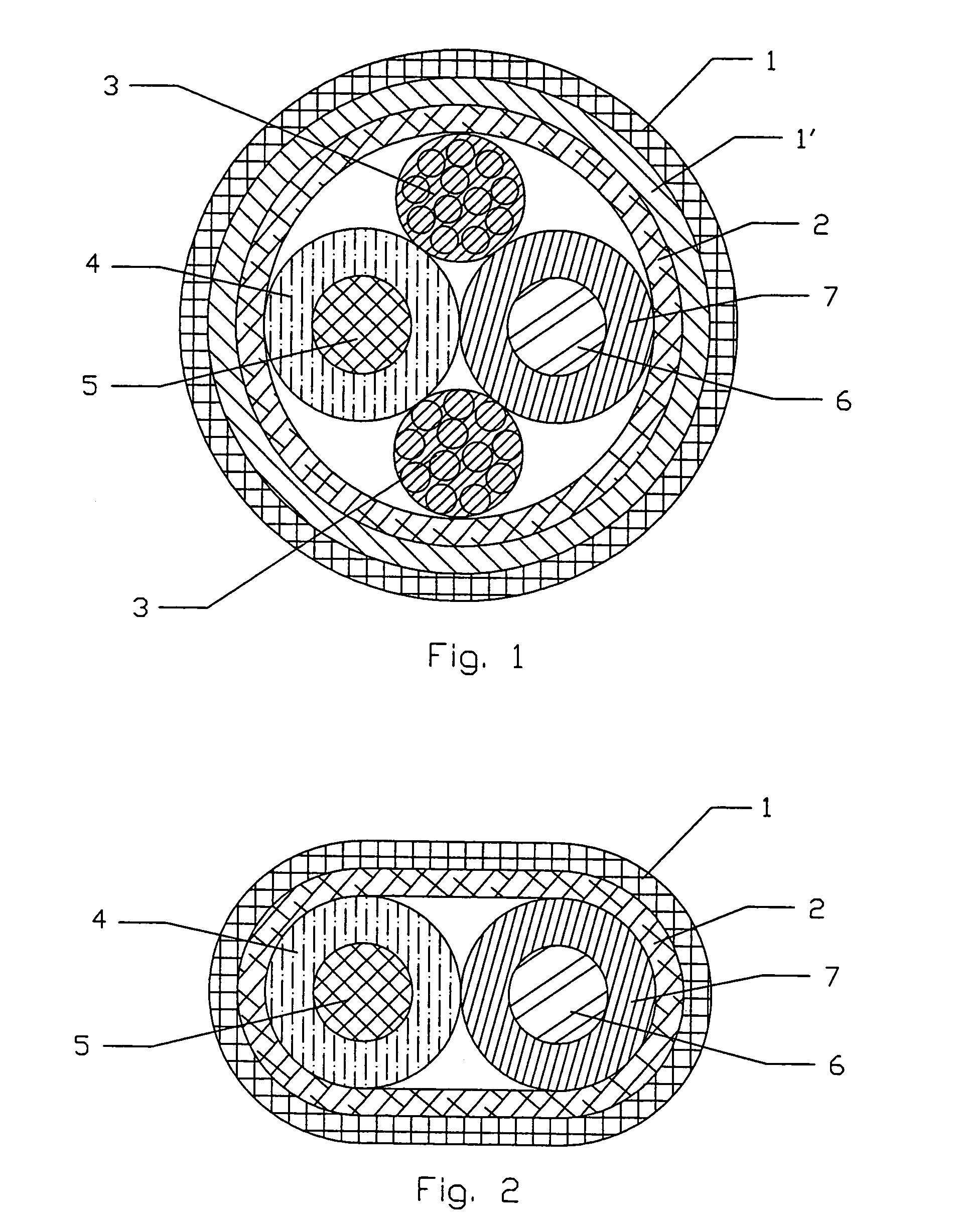
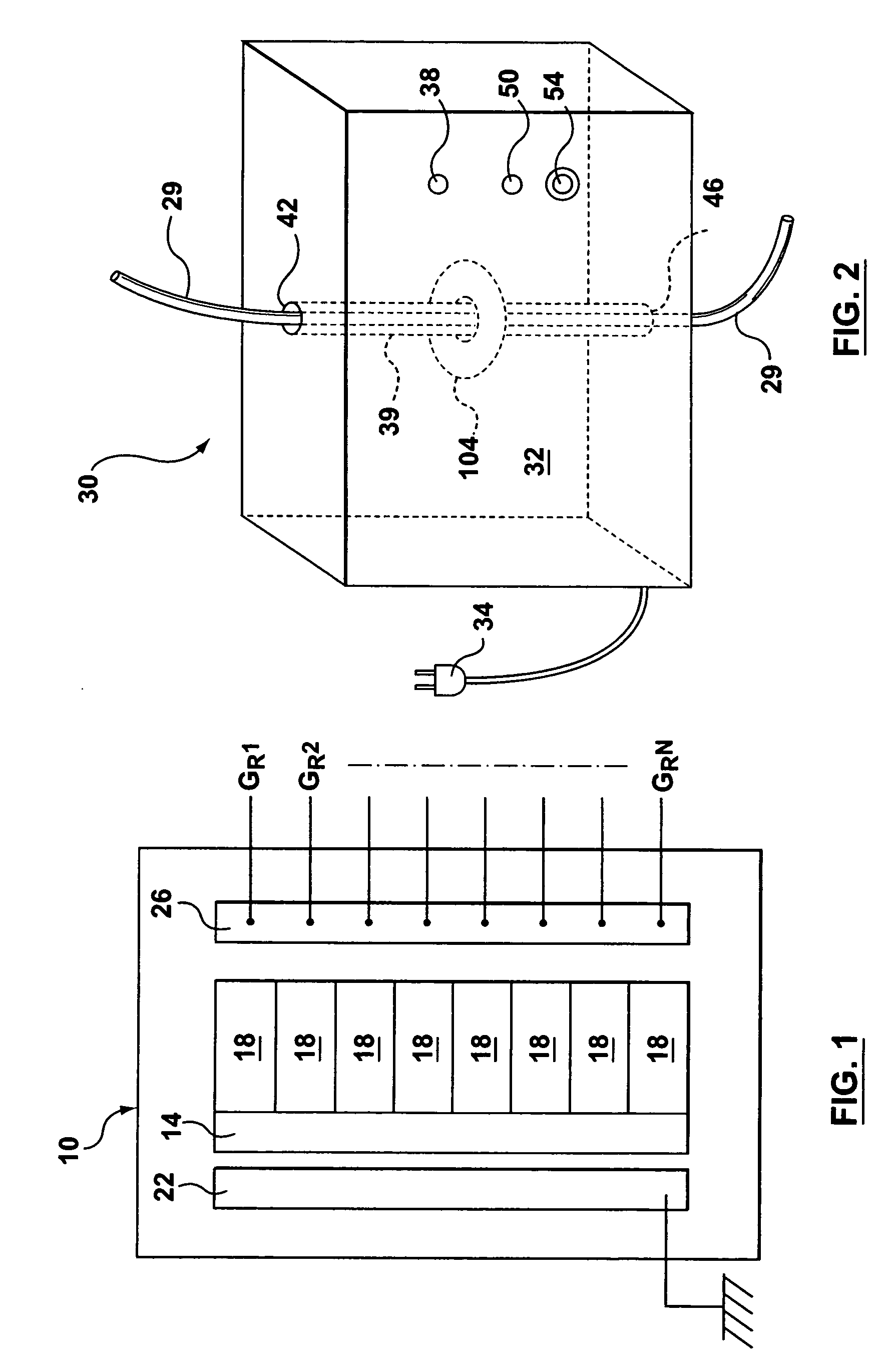
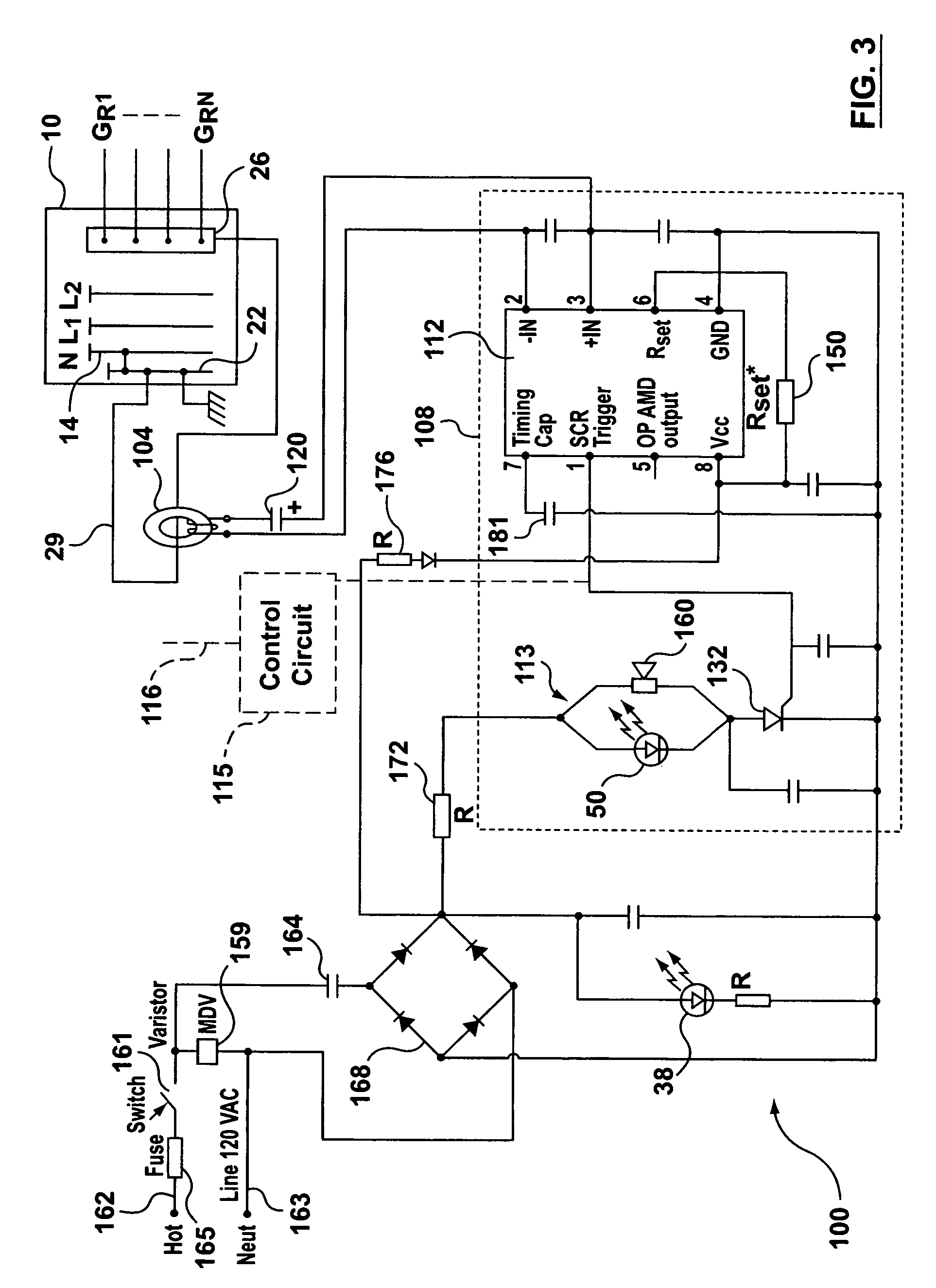
Electrical fault detection system
InactiveUS6246556B1Reliably detectsGuaranteed uptimeEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionEmergency protection for supplying operative powerElectrical FailureElectrical conductor
An electrical fault detector system detects electrical faults in an electrical distribution system by monitoring one or more conductors and producing an input signal representing one or more electrical signal conditions in the circuit to be monitored. This input signal is processed to develop a first signal representing the electrical current flow through the monitored circuit and a second signal representing signal components in a selected frequency range typical of arcing faults, and which exceed a predetermined threshold. The system also detects ground faults in the circuit being monitored.
Owner:SQUARE D CO
Heater with simultaneous hot spot and mechanical intrusion protection
InactiveUS6958463B1Excellent dielectric propertiesPreventing and minimizing current leakageHeating element shapesFiberElectrical conductor
An electrical heater utilizes negative temperature coefficient material (NTC) and current imbalance between live and neutral ends of the heater to simultaneously protect the heater from the hot spot and mechanical intrusion into the heating cable. The NTC layer, separating the heating wire and current leakage conductor, becomes electrically conductive at the temperatures above 60° C., thus “leaking” the current to earth. The hot spot is detected by measuring the current imbalance between line and neutral connections of the heating cable. The mechanical intrusion into the heater, such as cable or insulation damage, water or sharp metal object penetration, is also simultaneously measured by the same current imbalance measuring system such as Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI). The optional return conductor and metal foil / mesh hot spot detection shields cancel electromagnetic field. The heater may contain positive temperature coefficient (PTC) continuous sensor to control the temperature in the heater. Such PTC sensor can be made of electrically conductive fibers and / or metal wires.
Owner:THERMOSOFT INT
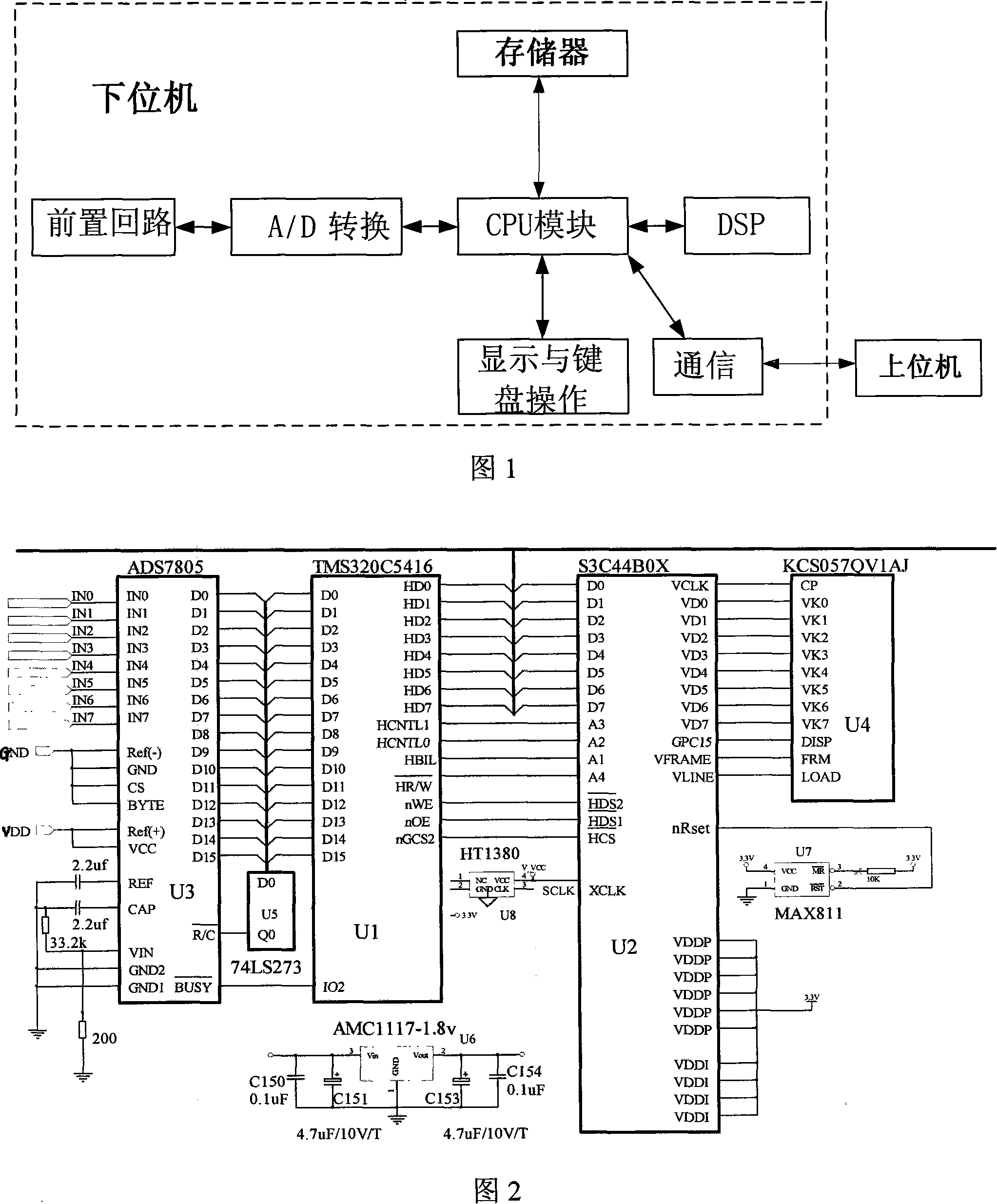
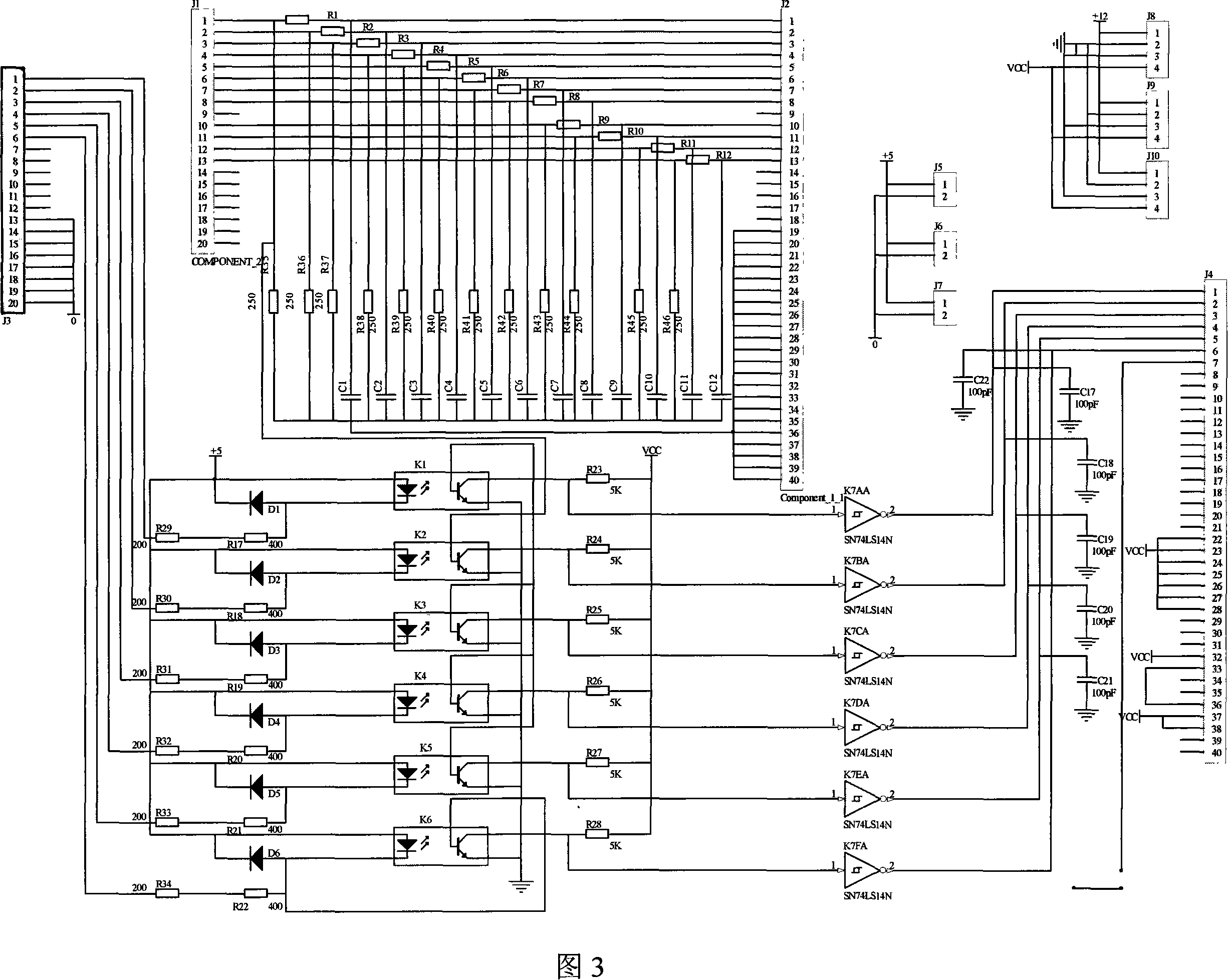
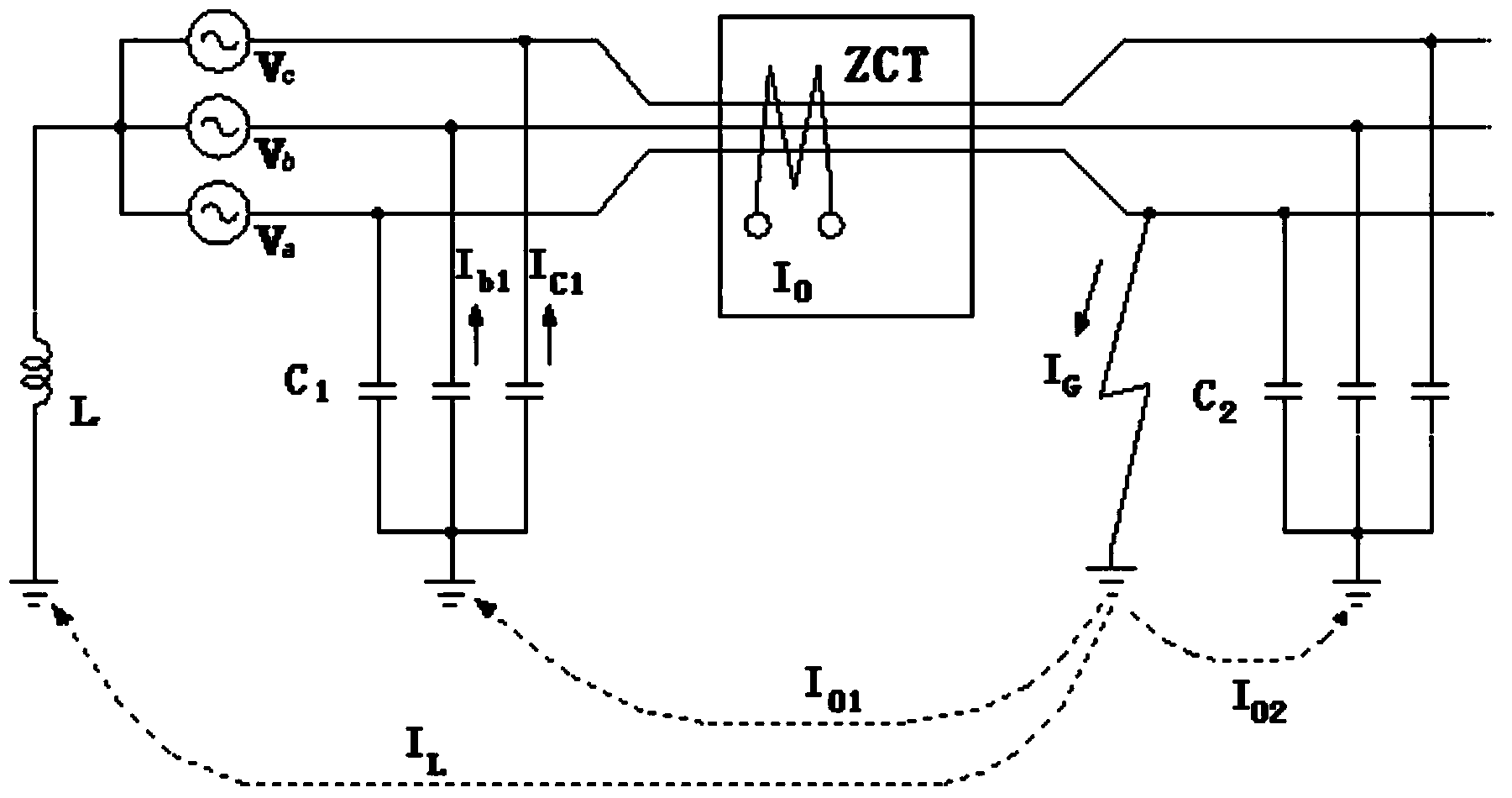
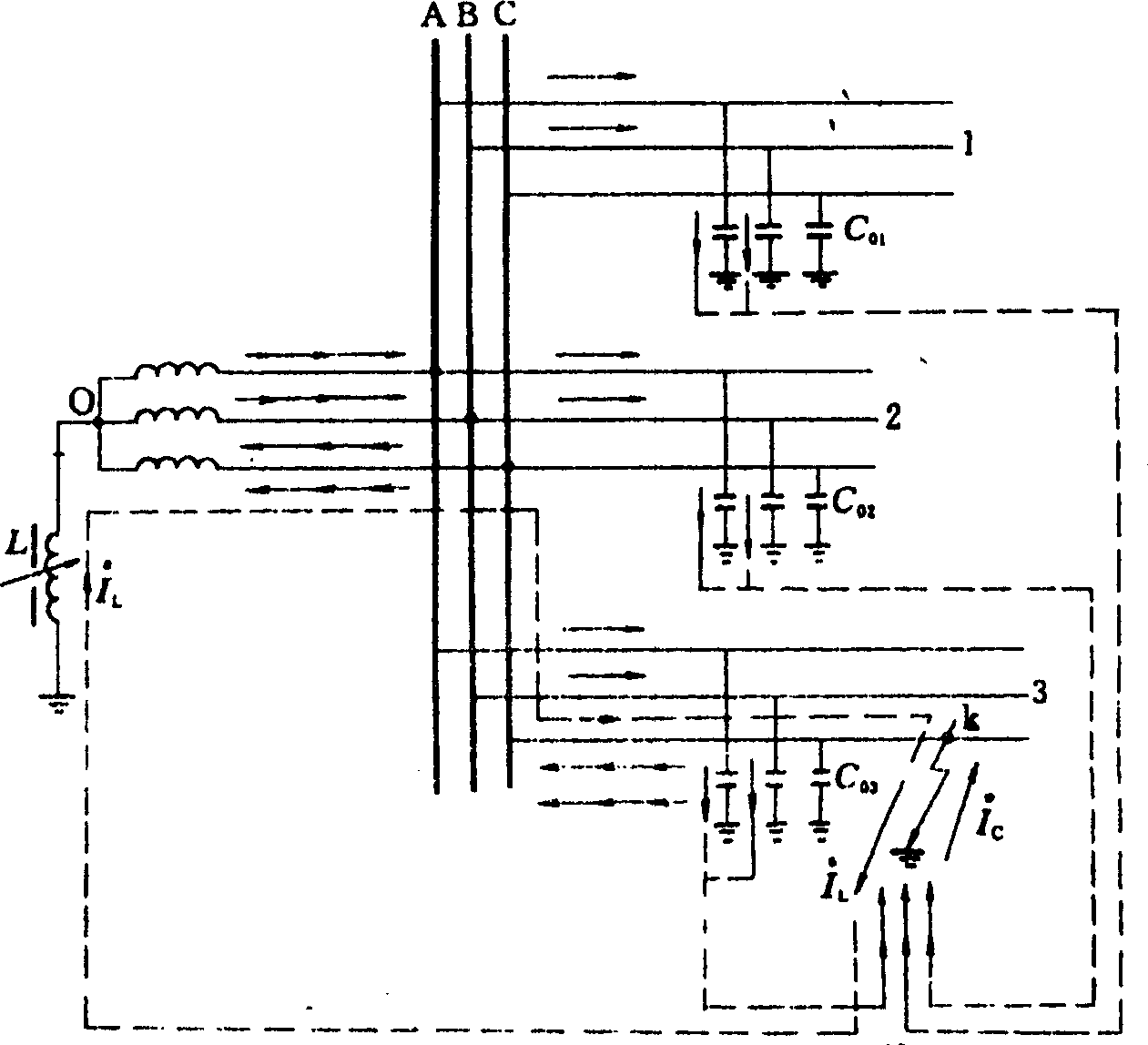
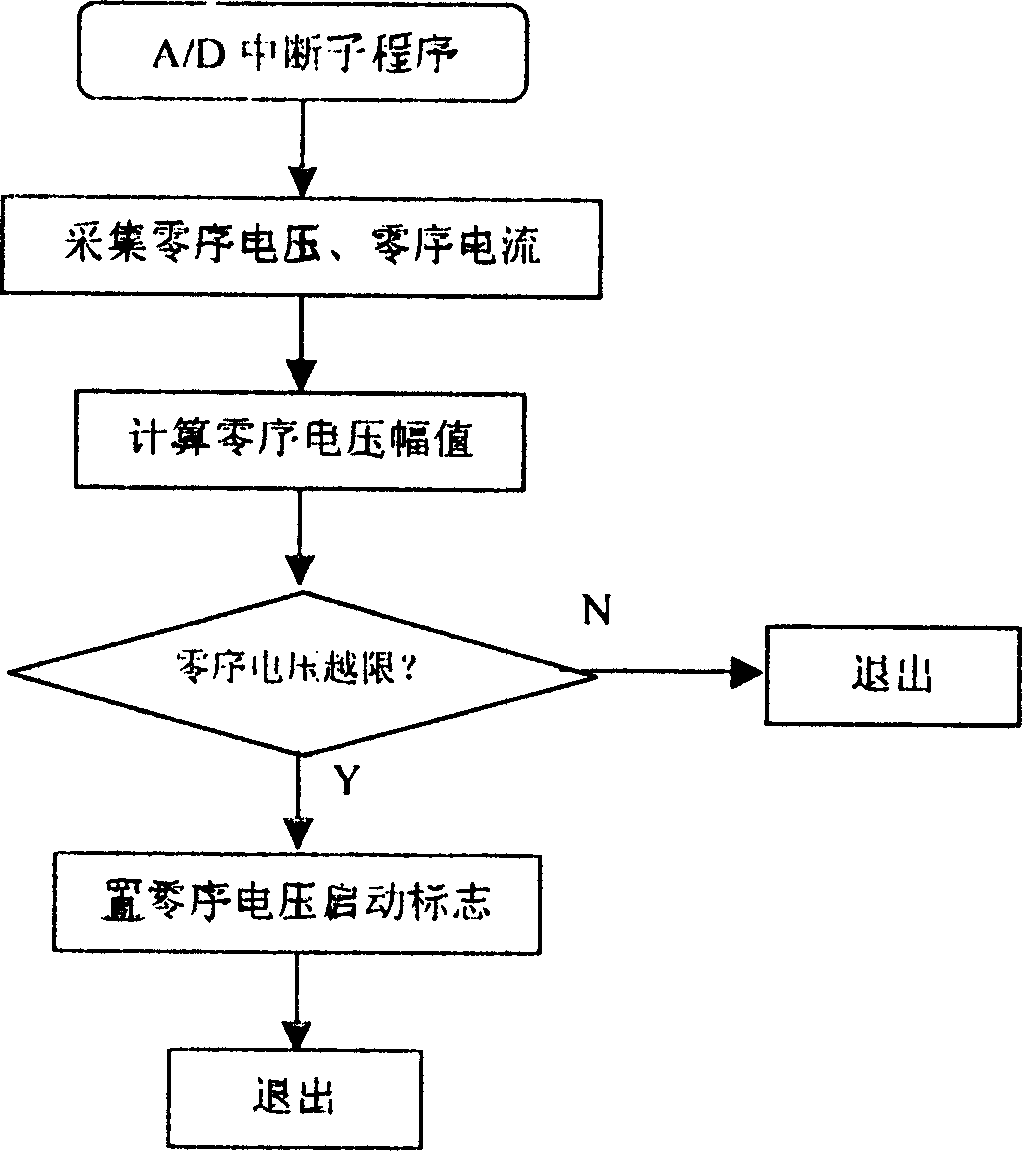
Low current neutral grounding malfunction detection and positioning device and method
InactiveCN101159376AKnowledge reductionImprove control effectEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault locationComputer moduleAnalog signal
The invention relates to a device and a method for detecting and positioning small current earthing fault. The device comprises a slave computer and a host computer composed of a CPU module, a DSP, a pre-loop unit module, a A / D conversion module, a memory module, a display and keyboard operation module as well as a communication module; wherein, the pre-loop unit module, the A / D conversion module, the CPU module and the DSP are connected in sequence; the memory module, the display and keyboard operation unit module and the communication module are respectively connected with the CPU; the host computer is connected with the communication module. The CPU module collects the analog signal of the zero-sequence voltage of the bus and the zero-sequence current of each line, and adjusts the value in proportion to the amplitude range so that the device can deal with. The analog signal is turned into digital signal recognized by the computer module, and analyzed by the DSP to judge whether the fault occurs or not. If the fault occurs, then the DSP gives the line selection result, saves the fault information and transfers the line selection result to the host computer for fault alarm.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
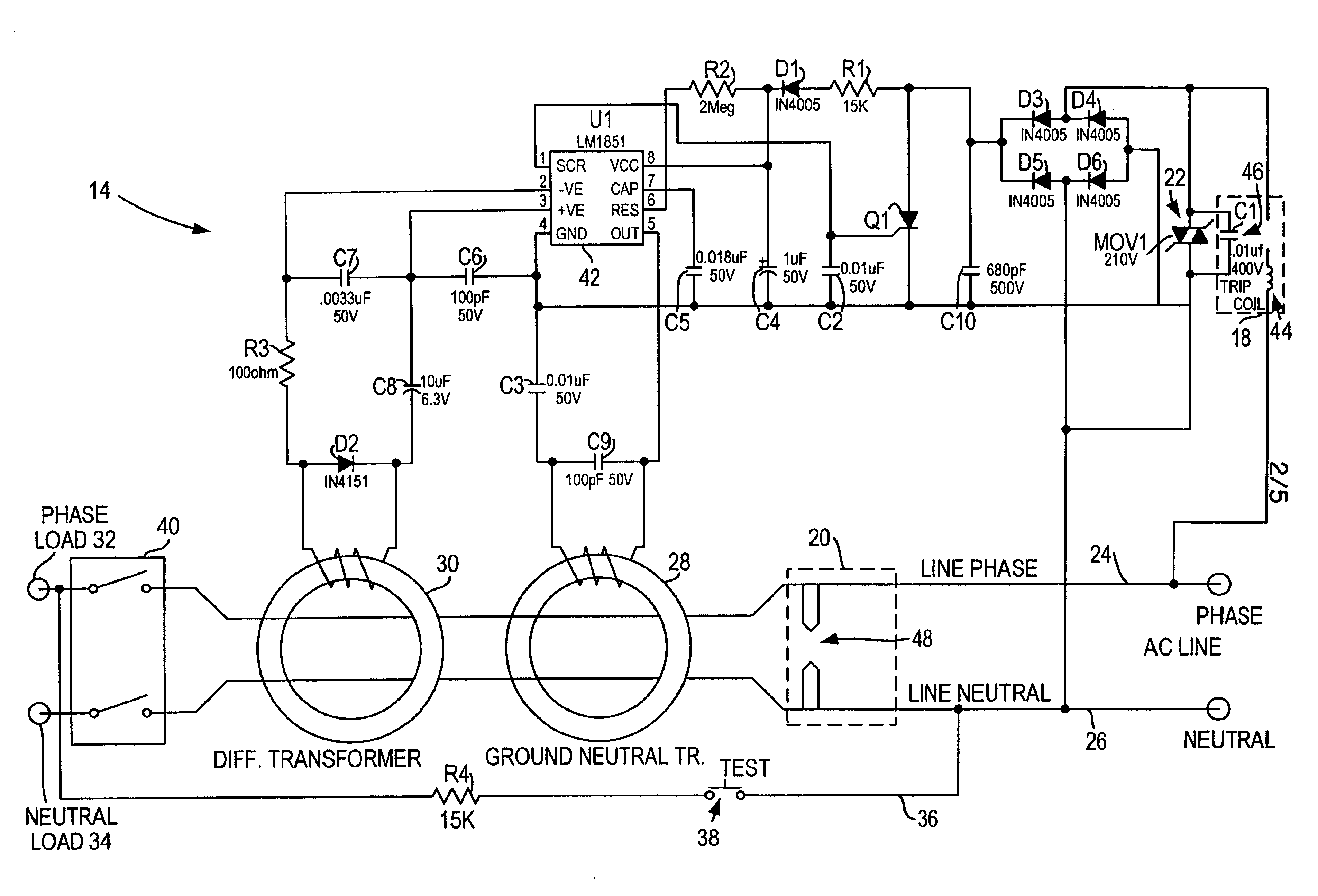
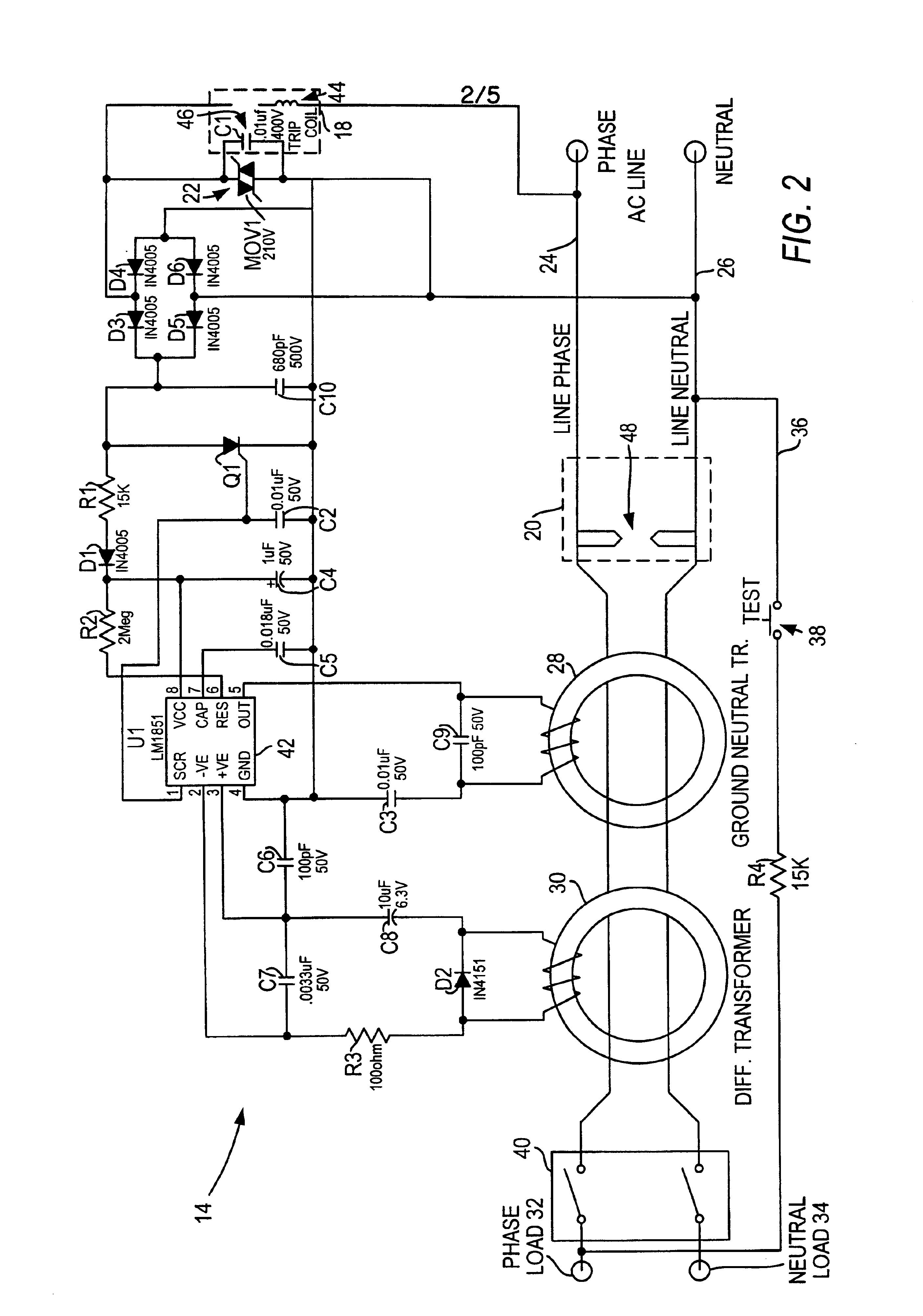
Circuit interrupter with improved surge suppression
InactiveUS6900972B1Switch operated by earth fault currentsArrangements responsive to excess currentOvervoltageLow-pass filter
A suppression and protection circuit is used in conjunction with a circuit interrupter. In one configuration, a voltage clamping device such as a metal oxide varistor is utilized in a ground fault circuit interrupter product for handling transient surges and overvoltage conditions and is placed in series with a solenoid coil. The suppression and protection circuit includes a crowbar device across the line such as a header spark gap to prevent overvoltages, and a low pass filter such as an LC filter for suppressing transient surges.
Owner:LEVITON MFG
Ground fault circuit interrupter with reverse wiring protection
InactiveUS6954125B2Open fastEasy to operateSwitch operated by falling currentSwitch operated by earth fault currentsGrounding MalfunctionEngineering
A new type of switching mechanism for a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) with reverse wiring protection preferably includes two pairs of fixed contact holders, each member of each pair having at least one fixed contact at one end; a pair of movable contact holders, each having an end having one or more of movable contacts, each movable contact being arranged for contacting one of the fixed contacts; and a movable assembly that moves between first and second positions, wherein the first position is a position in which each of the contacts of the fixed contact holders makes contact with one of the contacts of the movable end of one of the movable contact holders, and wherein the second position is a position in which the contacts of the fixed contact holders are separated from the contacts of the movable contact holders.
Owner:CHEN HENG
Ground fault circuit interrupter with reverse wiring protection
ActiveUS6946935B2Improve operational sensitivityMore energySwitch operated by falling currentSwitch operated by earth fault currentsControl circuitCircuit breaker
A new type of ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) with reverse wiring protection preferably includes a pair of fixed contact holders, each having a contact at one end; a pair of movable contact holders, each having a fixed end and a movable end, each of the movable ends having a contact; a movable assembly that moves between first and second positions, wherein the first position is a position in which each of the contacts of the fixed contact holders makes contact with one of the contacts of the movable end of one of the movable contact holders, and wherein the second position is a position in which the contacts of the fixed contact holders are separated from the contacts of the movable contact holders; an electromagnetic resetting component, which, when energized, causes the movable assembly to be in the first position; an electromagnetic tripping component, different from the electromagnetic resetting component, which, when energized, causes the movable assembly to be in the second position; and a control circuit, which, upon detection of a fault condition, energizes the electromagnetic tripping component, and which, upon detection of a reset condition, energizes the electromagnetic resetting component.
Owner:CHEN HENG
Electrical power distribution network single-phase earth fault type and phase distinguishing method
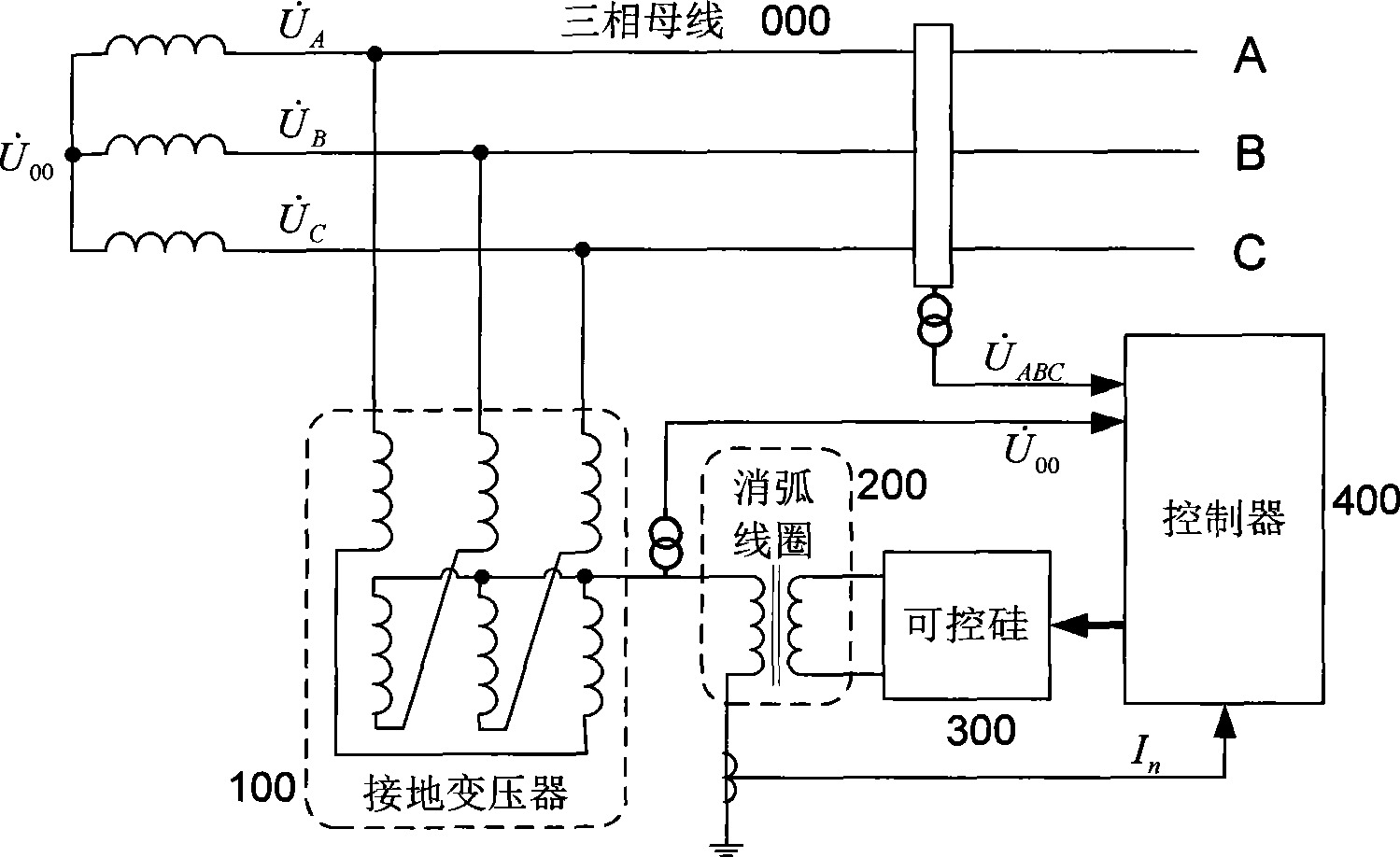
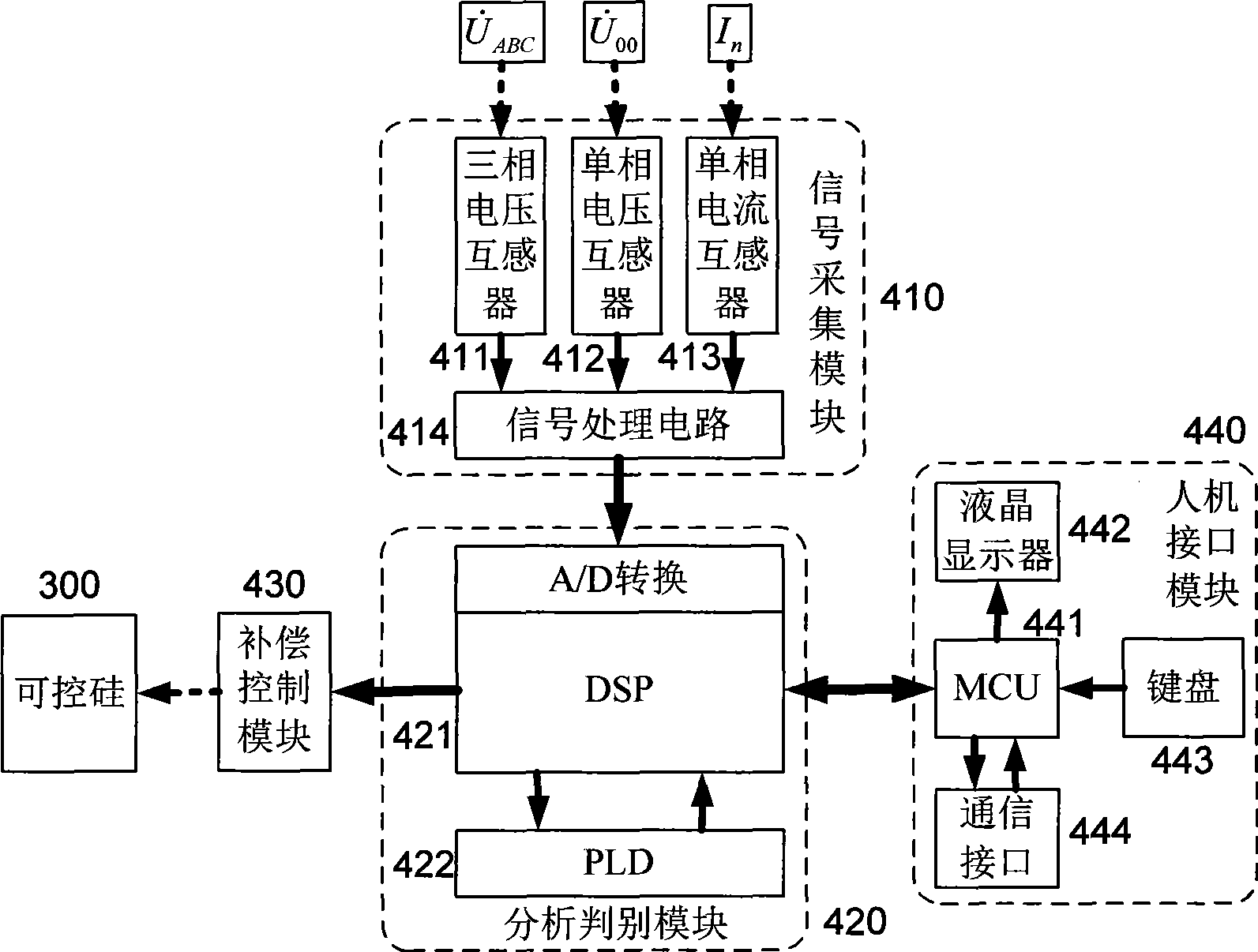
ActiveCN101452041ALess analogSimple calculationFault locationEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentElectric cablesElectric power
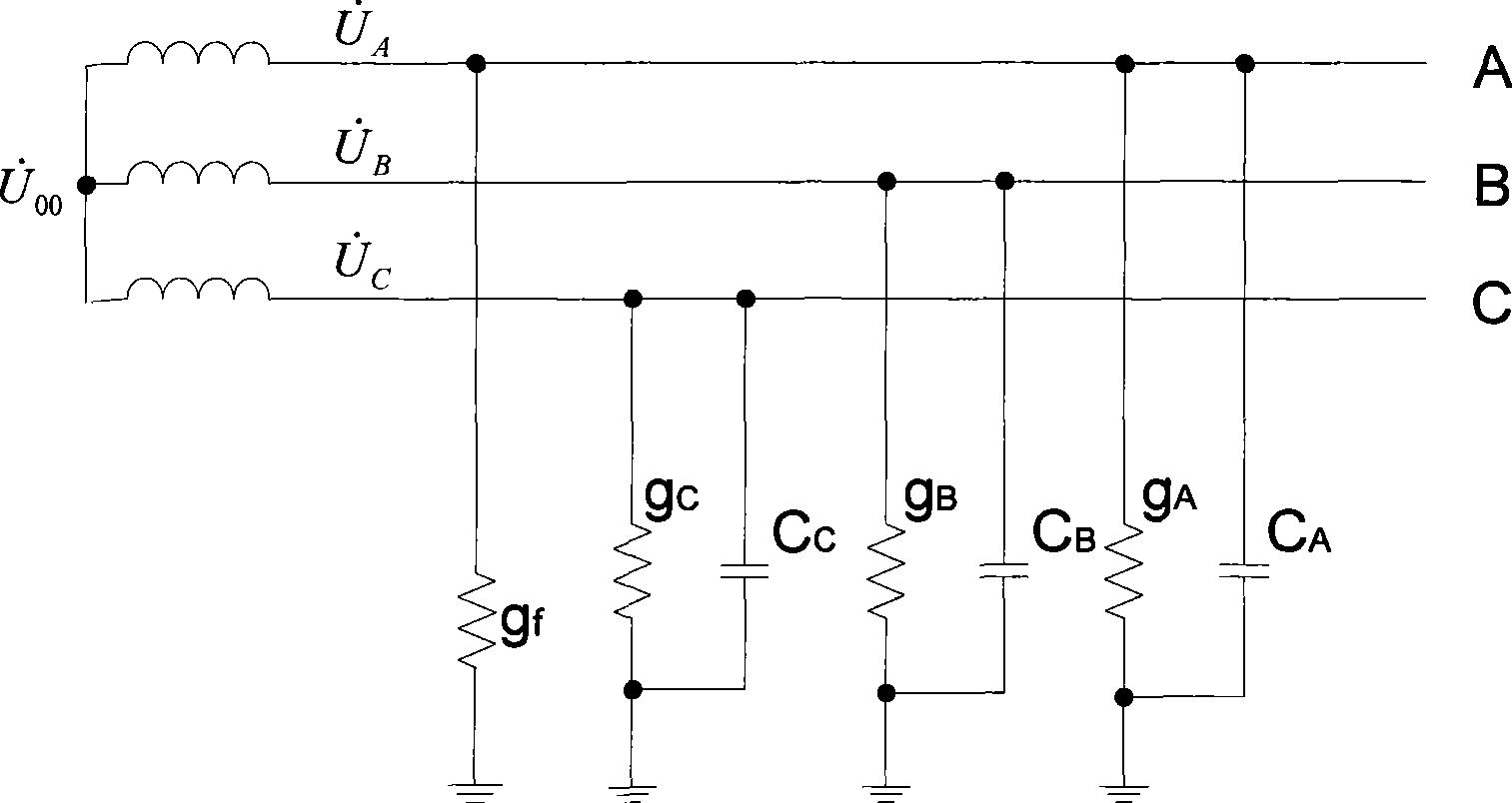
The invention discloses a distributing net single phase earth fault type and a distinguishing method of phase identification, relating to a distributing net single phase earth fault distinguishing method in the field of AC distributing net testing and relaying protection technology. According to the invention, through collecting three-phase voltage of the distributing net system and neutral point voltage of the distributing net system, phase angle of each eigenvector is computed through a special relation, the type of the fault and the phase identification can be fast distinguished through the phase angle distinguishing logic. The inventive working system is that a three-phase bus (000), a grounding transformer (100), a linear side of an arc suppression coil (200) are connected in turn with the earth; a controller (400), a thyristor (300) and a secondary side of an arc suppression coil (200) are connected in turn. The invention is simple in criterion, small in collection quantity, fast in distinguishing speed, high in accuracy, reliable in security, which is suitable for 3-66 KV distributing net based on an aerial line or a power cable.
Owner:STATE GRID HUBEI ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
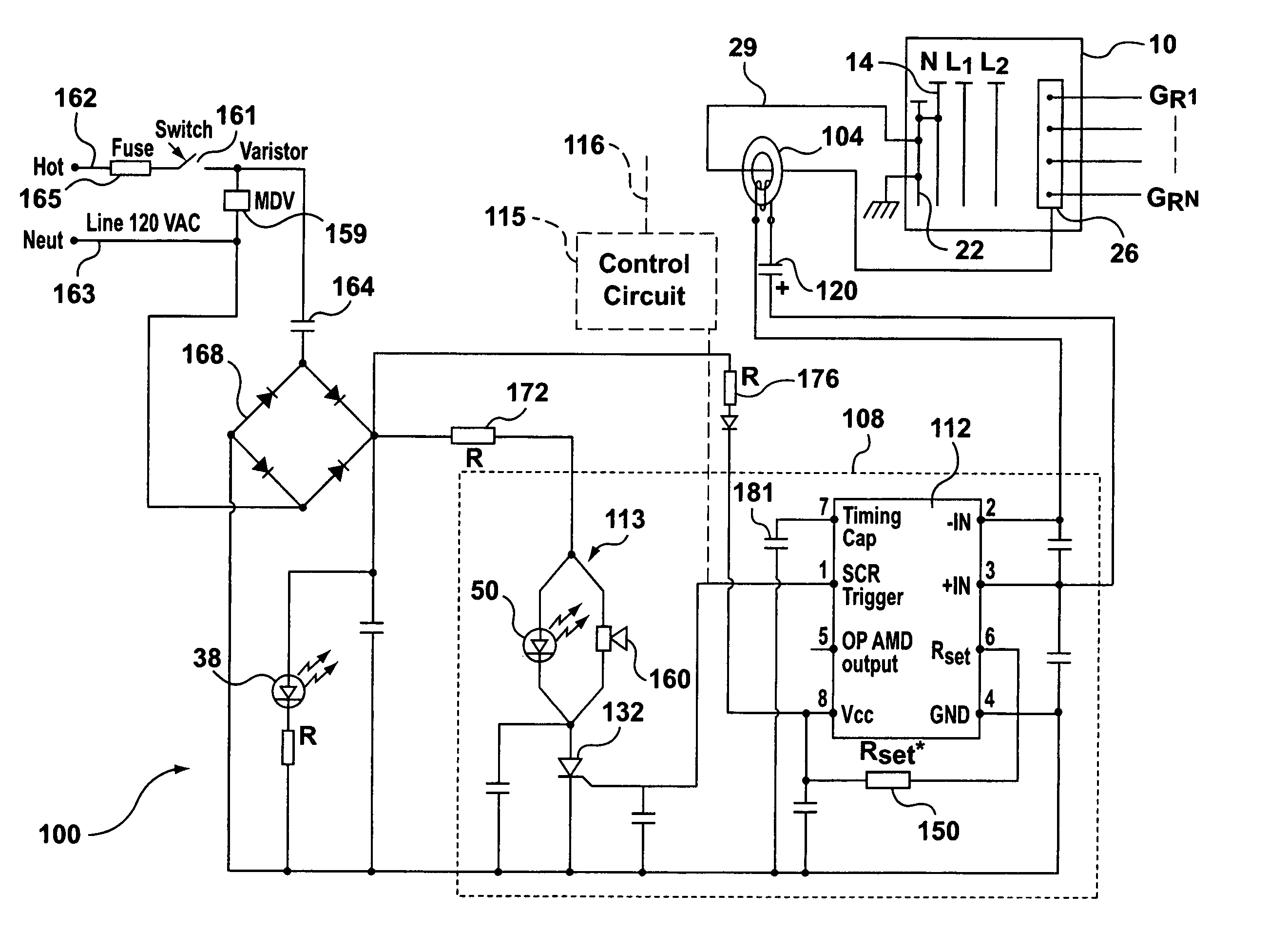
Self testing ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) with end of life (EOL) indicator, secondary power supply for EOL and self test circuitry, and device for opening line hot when EOL occurs
ActiveUS20070279814A1Increase surface temperatureProtective switch detailsSwitch operated by earth fault currentsDiode bridgePrinted circuit board
A self test (ST) ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) provides a half wave rectifier for powering circuitry for determining and annunciating end of life (EOL) of the GFCI regardless of a shorted diode bridge or opening of a printed circuit board (PCB) trace. A fuse resistor is provided to open before an open PCB trace can occur. A microprocessor-controlled heat-conducting circuit is provided adjacent to a thermal fuse to controllably open the thermal fuse and remove power from face receptacle contacts and load terminals when EOL occurs.
Owner:HUBBELL INC
Power strip with self-contained ground fault circuit interrupter module
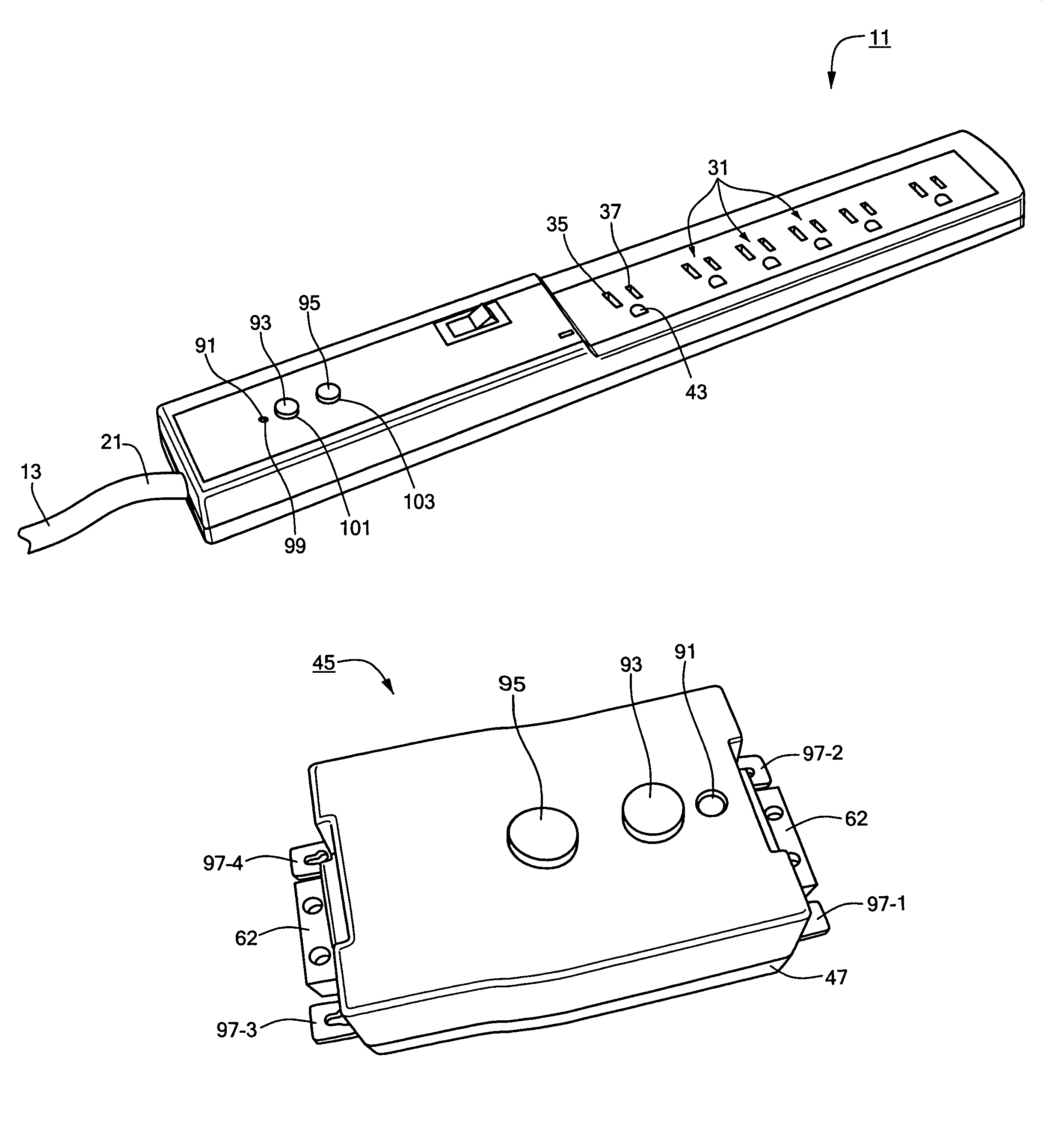
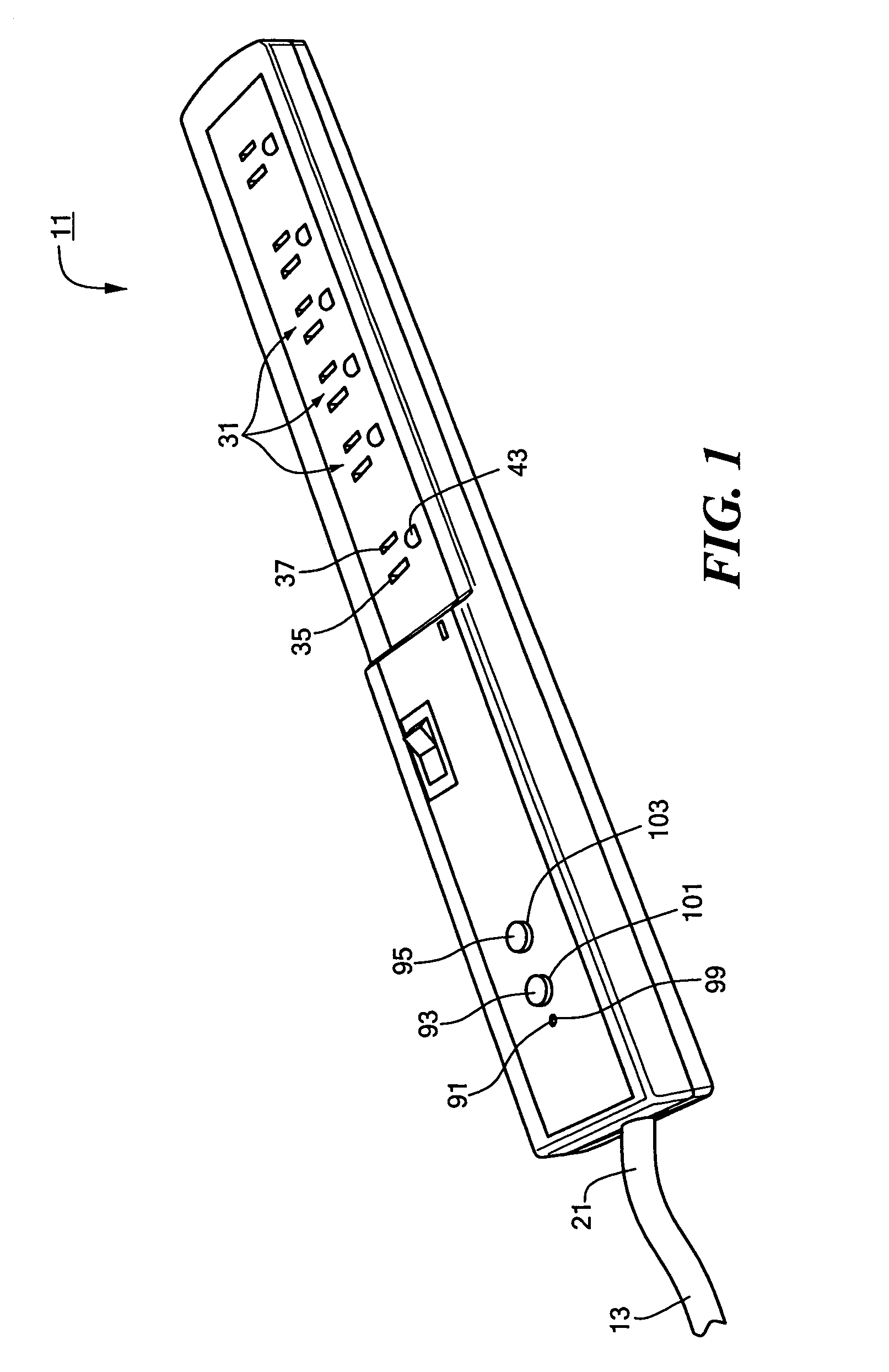
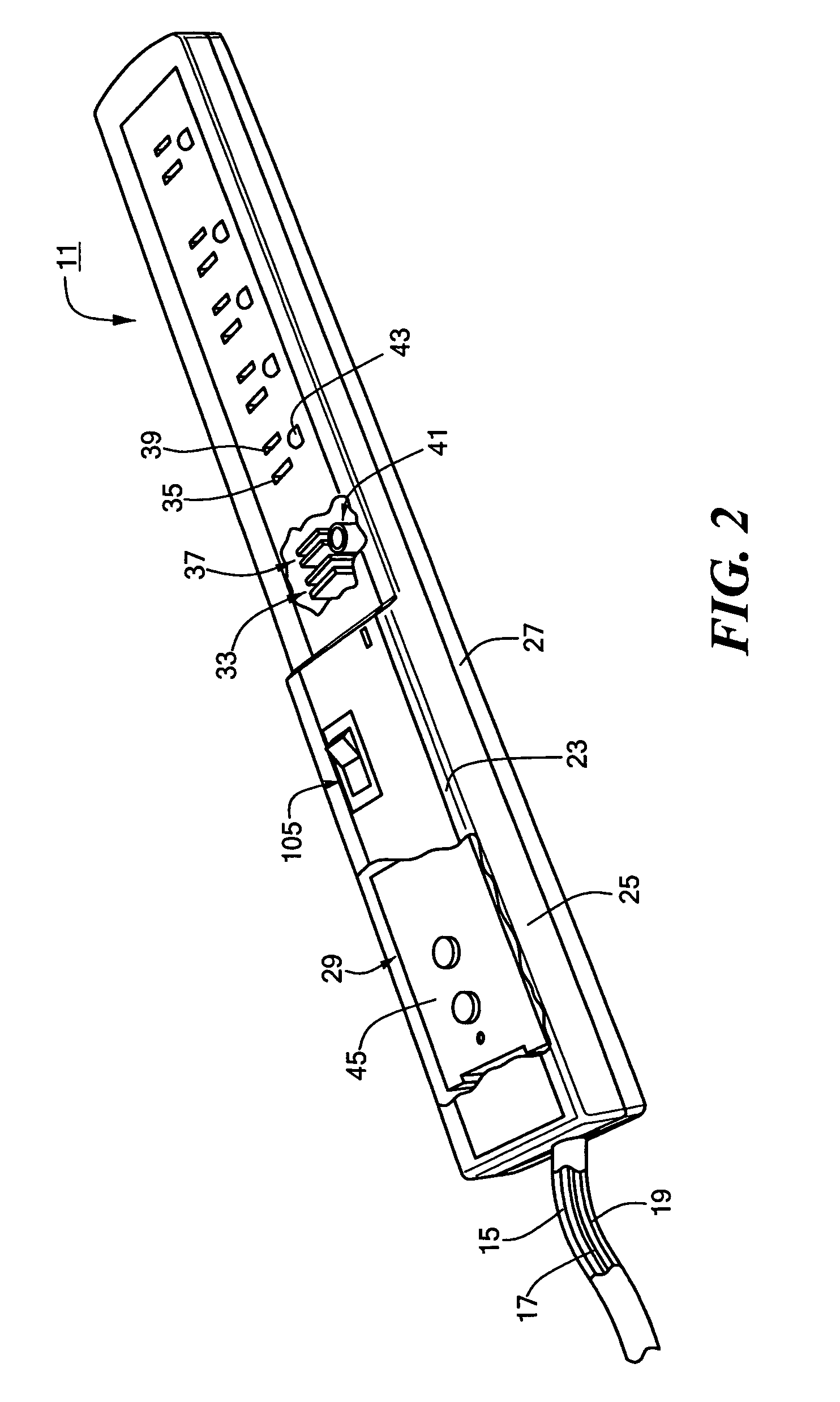
InactiveUS6991495B1Easy to detectMinimal numberSwitch operated by current/voltage unbalanceContact mechanismsElectricityEngineering
A power strip includes a power cord and a plastic casing mounted onto one end of the power cord. A plurality of outlets are disposed in the casing in a side-by-side relationship. A ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) is disposed in the casing and electrically connects the power cord to each of the plurality of outlets. The GFCI is self-contained and modular in form and comprises an outlet-free housing and GFCI circuitry disposed within the outlet-free housing. The GFCI circuitry includes an indicator light, a test button and a reset button which fittingly protrude through corresponding openings formed in both the outlet-free housing and the insulated casing. In use, power cord delivers current to each of the plurality of outlets. However, GFCI serves to interrupt the flow of current from the power cord to each of the plurality of outlets upon detecting a ground fault condition in the power cord.
Owner:TOWER MFG
Transformer interface for preventing EMI-based current imbalances from falsely triggering ground fault interrupt
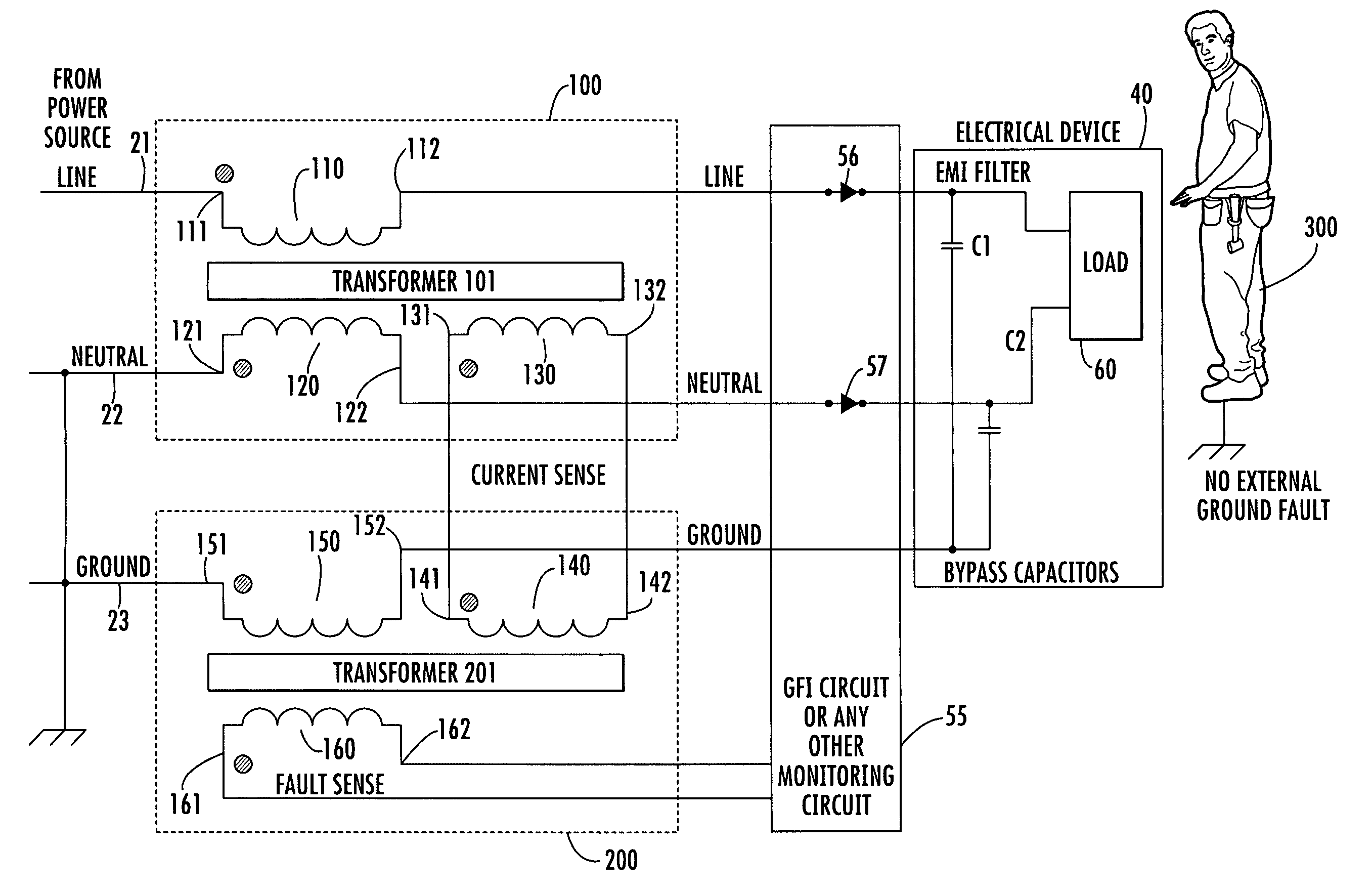
ActiveUS7375940B1Non-zero differential magnetic fieldTotal current dropArrangements resposive to fault currentCurrent sensorElectrical and Electronics engineering
A transformer interface prevents a false ground fault interrupt in a power supply arrangement. The power supply arrangement has a line wire and a neutral wire connected by way of a ground fault interrupt circuit to an electrically powered device, to which a ground wire is also coupled. The interface has current imbalance sensor transformer windings coupled to the line and neutral wires. A ground wire current sensor transformer winding is coupled to the ground wire. A detector transformer winding produces a signal that triggers operation of the ground fault interrupt circuit, in response to the difference between currents produced by the current imbalance sensor transformer windings exceeding detected ground wire current by a prescribed value.
Owner:ADTRAN
Reverse wiring protection device for ground fault circuit interrupter
InactiveUS6867954B2Safe and reliableSwitch operated by earth fault currentsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionEngineeringControl circuit
The present invention relates to a reverse wiring protection device for ground fault circuit interrupter that includes a tripper and control circuit. The tripper comprises: a pull rod with flat, a L-shaped latch, a balance frame coupled with the latch moving up and down with the pull rod, a trip coil, a plunger and a contact switch (K) which is capable of energizing and de-energizing the trip coil. The reset can't be depressed when an installer or user miswires the line and the load. GFCI can only be operating normally when it is installed properly
Owner:CHEN HENG
Method for locating single-phase disconnection non-ground fault of power distribution network
ActiveCN103308823AImprove economyImprove practicalityFault locationInformation technology support systemDistribution transformerLow voltage
The invention relates to a method for locating a single-phase disconnection non-ground fault of a power distribution network. After the single-phase disconnection non-ground fault occurs, the positive sequence voltage of the high-voltage side of each distribution transformer after a fault point is far lower than the positive sequence voltage of the high-voltage side of each distribution transformer before the fault point and the positive sequence voltage of the high-voltage side of each distribution transformer of a non-faulty line, and the positive sequence voltage of the low-voltage side of each distribution transformer after the fault point also correspondingly becomes about 50 percent of the positive sequence voltage before the fault point. For three-phase voltage information acquired by different types of measuring devices installed at load points, the positive-sequence component of the voltage of each load point is calculated in real time; and if the positive sequence voltage of a certain load point and the positive sequence voltages of all downstream load points of the load point are obviously reduced at one point, and the positive sequence voltages of upstream load points of the load point are constant, the single-phase disconnection non-ground fault can be determined in an upstream adjacent line connected with the load point. According to the method for locating the single-phase disconnection non-ground fault of the power distribution network disclosed by the invention, new equipment does not need to be equipped; the calculation is simple; and the fault can be located between two load points to realize the diagnosis and the location of the single-phase disconnection non-ground fault.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Apparatus and method for ground fault detection and location in electrical systems
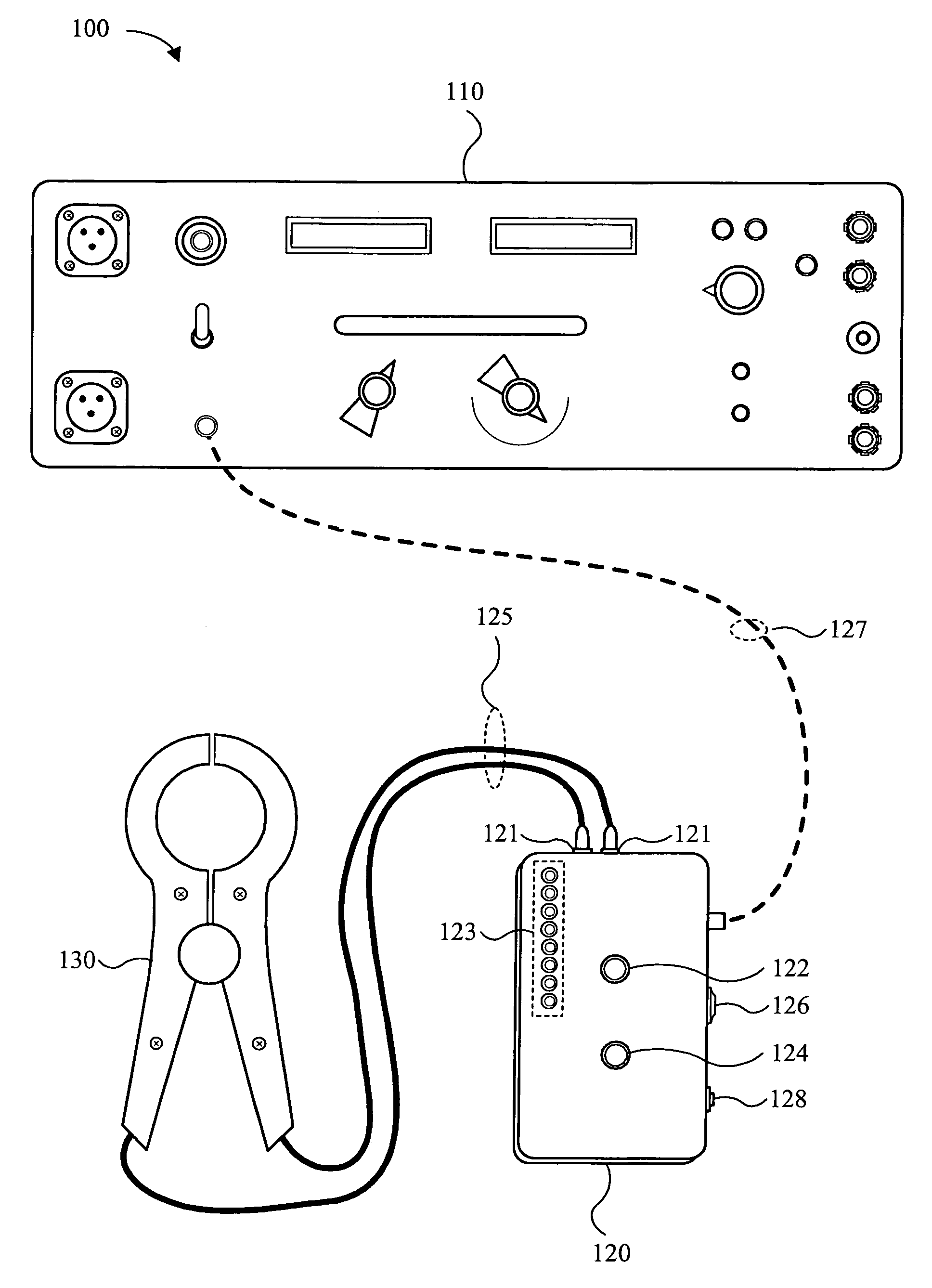
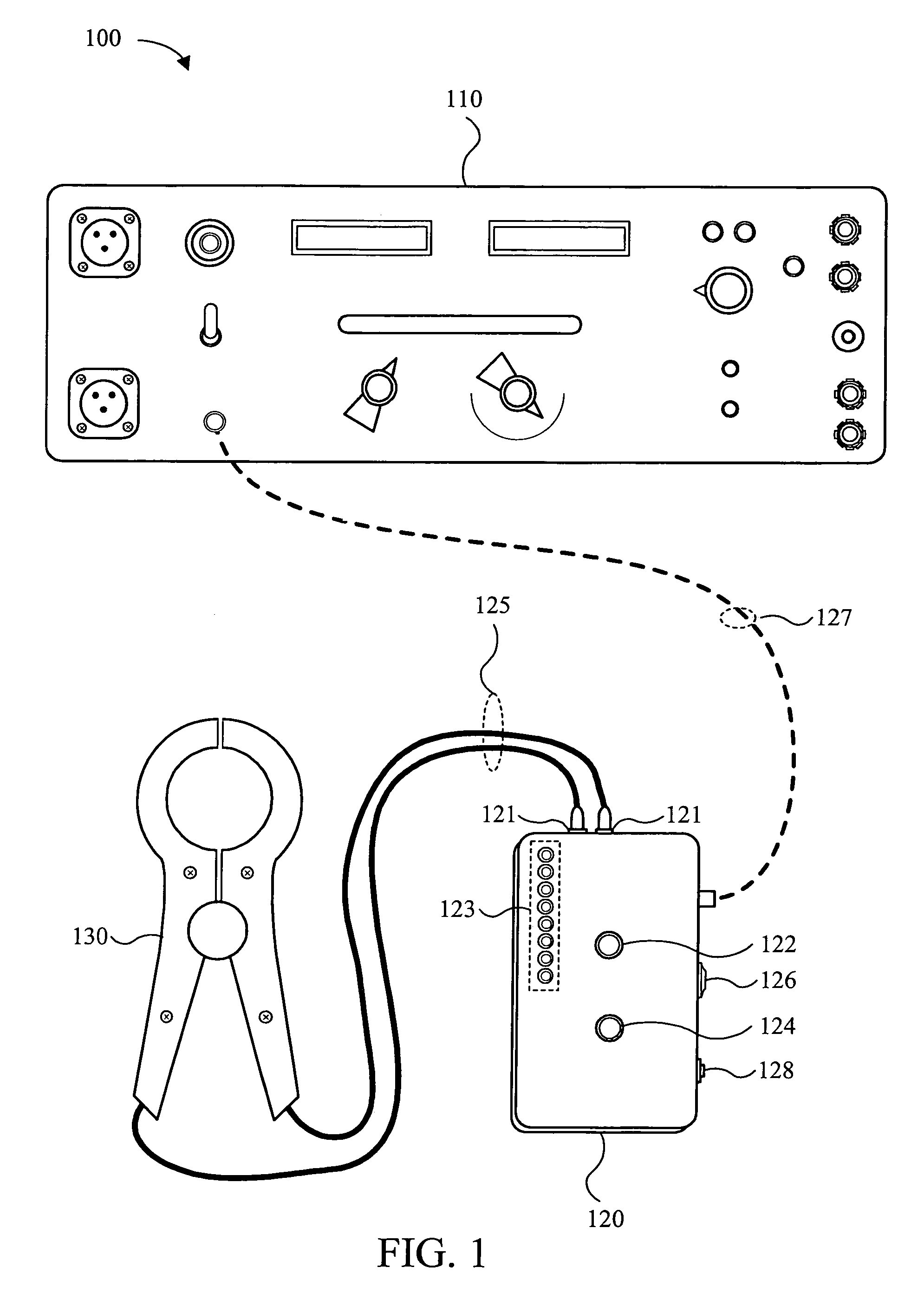
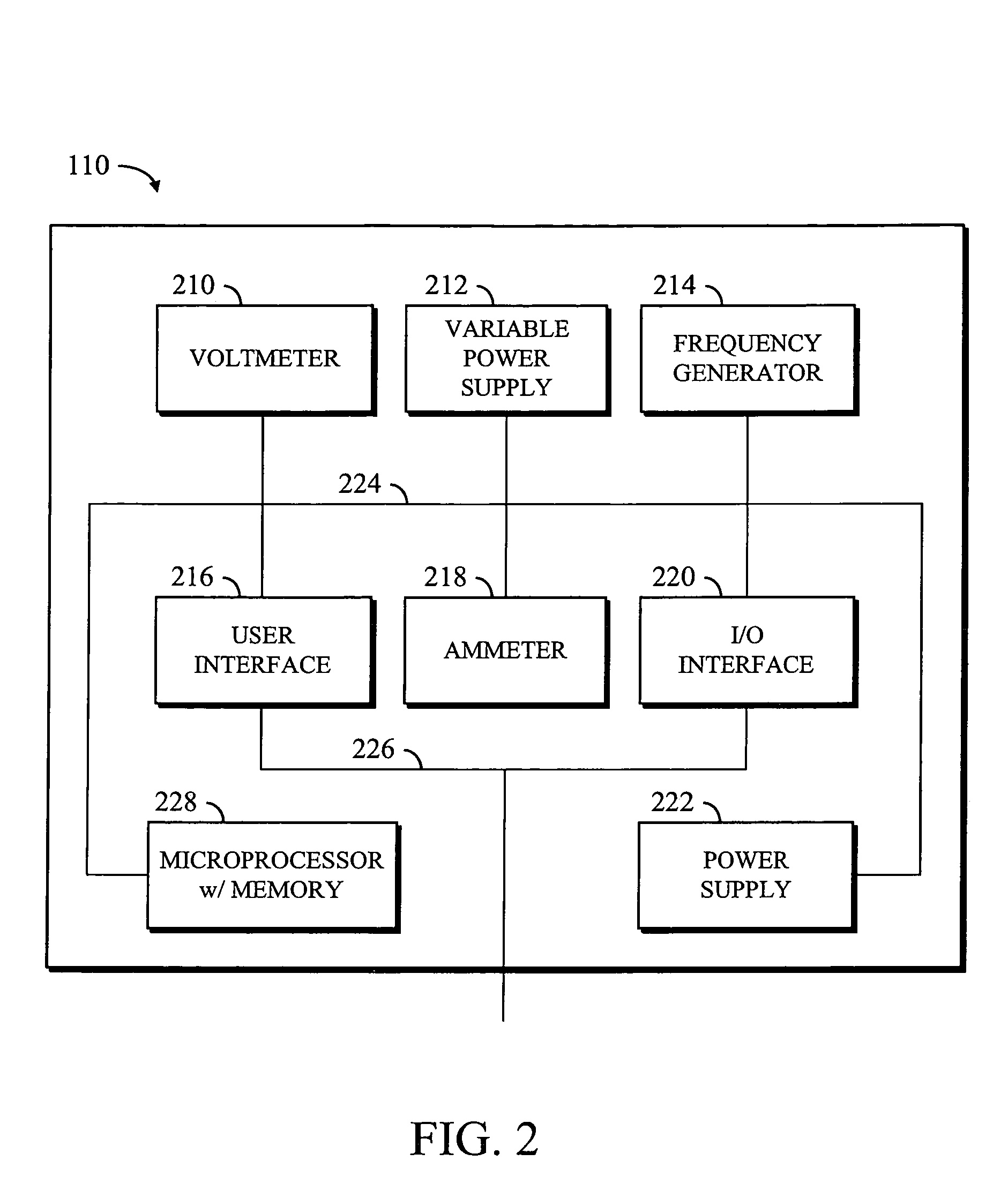
InactiveUS7529069B1Precise positioningRapid and efficient repairShort-circuit testingEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionVoltmeterHemt circuits
The present invention is implemented by deploying an enhanced ground fault detection and location apparatus and by using the apparatus in conjunction with specific circuit analysis methods, using the information generated by the ground fault detection and location apparatus. The ground fault detection and location apparatus comprises the functionality of a voltmeter, an ammeter, a frequency generator, and a variable power supply, thereby providing for a variety of signals and analyses to be performed on a unintentionally grounded circuit in an ungrounded AC or DC power distribution system. The apparatus includes a main unit and a remote unit, which may be a portable hand-held unit. In a first mode, the apparatus of the present invention can be used to detect ground faults. By switching to a second mode, the apparatus of the present invention can be used to locate ground faults. The methods of the present invention involve the generation of various signals by the main ground fault detection and location unit. The generated signals are introduced into the electrical distribution system and monitored by various means, including one or more remote units. By analyzing the system-level response to the generated signals, the specific location of the ground fault or faults can be more readily ascertained, thereby promoting rapid and efficient repair and recovery practices. The apparatus of the present invention may be implemented as a dedicated, permanent installation or as a temporary portable system. Additionally, the system may be implemented as an automatic computer-controlled ground fault location and detection system.
Owner:WEEMS II WARREN A +2
Power distribution network fault circuit selection method based on transient zero-sequence current time-frequency characteristic vectors
ActiveCN103245883AThe principle is simpleImprove timelinessFault locationElectric power systemTransient current
The invention relates to a power distribution network fault circuit selection method based on transient zero-sequence current time-frequency characteristic vectors, and belongs to the technical field of power system relay protection. When a power distribution network runs into a single-phase earth fault via an arc suppression coil grounding system, a transient zero-sequence current component detected by a measuring end is a nonlinear non-stationary signal formed by different frequency components. By taking the fault component as a study object, time-frequency characteristics of a fault transient current of the fault component are analyzed by utilizing the wavelet packet theory, time-frequency distribution regularities among all feeder lines under different fault conditions are described according to similarity of the time-frequency characteristics, and consequently line selection criteria based on transient zero-sequence current time-frequency characteristics can be obtained. The method is simple in principle, only utilizes short-time window zero-sequence current data of 5ms after the fault, can identify faulty feeders under the conditions of small fault angle and high resistance ground fault, has excellent timeliness and robustness, is free from influence of an arc fault or a resistance ground fault, requires a low sampling rate for hardware, and is highly practical.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Eddy current inductive drive electromechanical linear actuator and switching arrangement
ActiveUS20060061442A1Reliable and reliableSimple designContact mechanismsElectromagnetic relaysTransfer switchEngineering
The present invention is directed to an inductively driven electromagnetic linear actuator arrangement employing eddy currents induced by a fixed drive coil to drive its armature. Eddy current focusing fields are employed to direct the eddy currents using Lorentz forces to maximize armature speed. The armature includes a shorted driven coil in a DC magnetic field. This can be supplied by a permanent magnet. When current is applied, a force is felt by the coil in a direction perpendicular to the magnetic field. Such an actuator is well suited for electrical switching applications including transfer switching applications, circuit breaker applications, and ground fault interrupter applications.
Owner:POWERPATH TECH INC
Method for detecting and positioning section faults of a power distribution network containing distributed generators
ActiveCN104297629AReliable detectionAccurate detectionFault locationPhase angle differenceDistribution grid
The invention relates to a method for detecting and positioning section faults of a power distribution network containing distributed generators, which comprises a fault judging and positioning part and a fault type recognition part. A fault judging and positioning method comprises the steps of detecting a fault and recognizing a fault phase through comparing the relation between an absolute value of the phase angle difference of each phase current of each power system section and a threshold value, finding out a section where a fault point is located, and timely removing the fault section so as to complete a protection action. A fault type recognizing method comprises the steps of comparing zero-sequence current amplitude values at two end nodes of the fault section at the fault determination moment with a set threshold value on the basis of recognizing the fault phase, and judging whether the zero-sequence current amplitudes at the two end nodes of the fault section at the fault determination moment are less than or equal to the threshold value or not, thereby determining whether the fault is a phase-to-phase fault or a grounding fault. The method provided by the invention can be applied to detecting and positioning the section faults of the power distribution network containing the distributed generators under high permeability.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Solid-state line disturbance circuit interrupter
ActiveUS20190207375A1Reduce power consumptionLow costAc-dc conversion without reversalEmergency protection detectionLow voltageHigh pressure
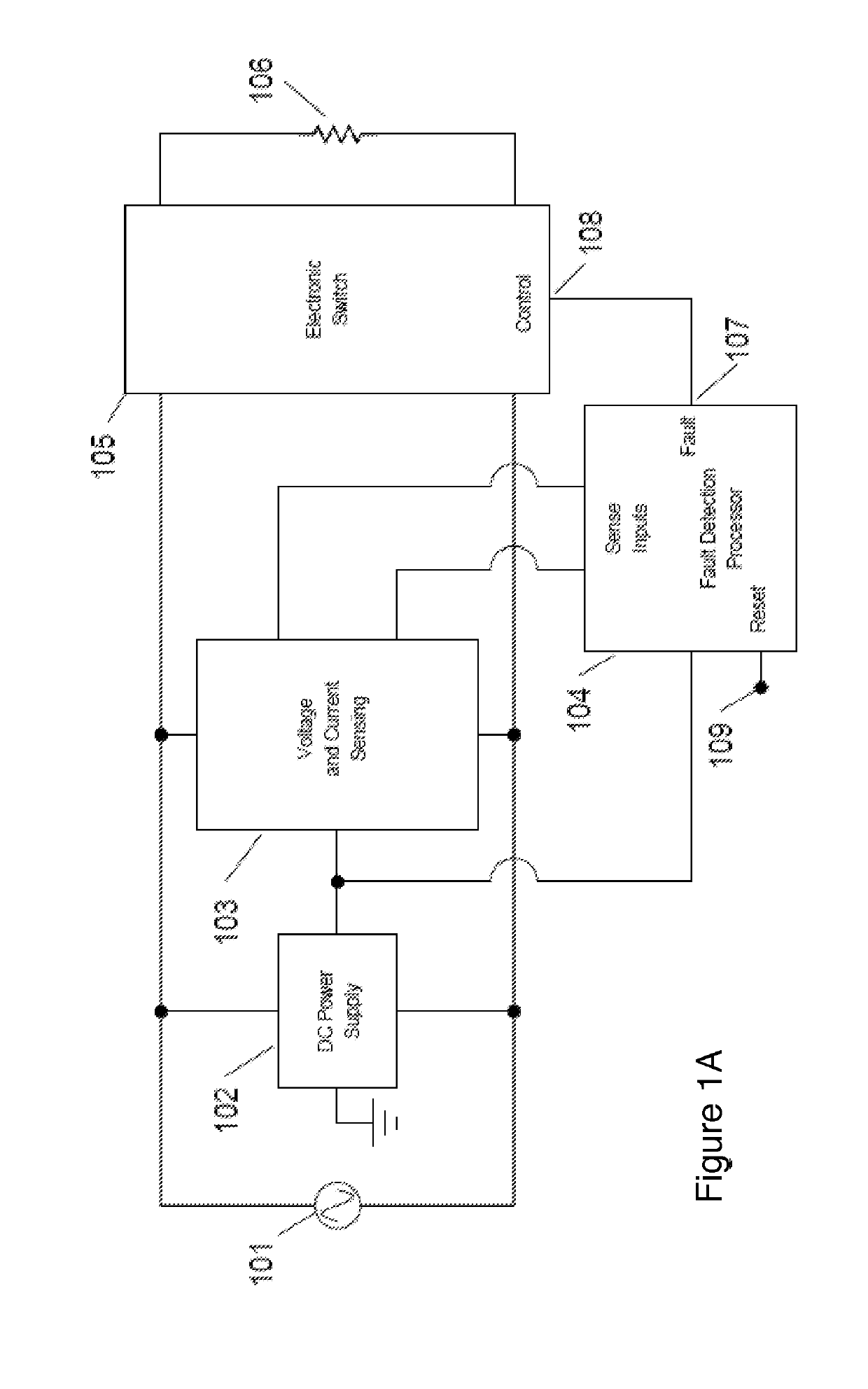
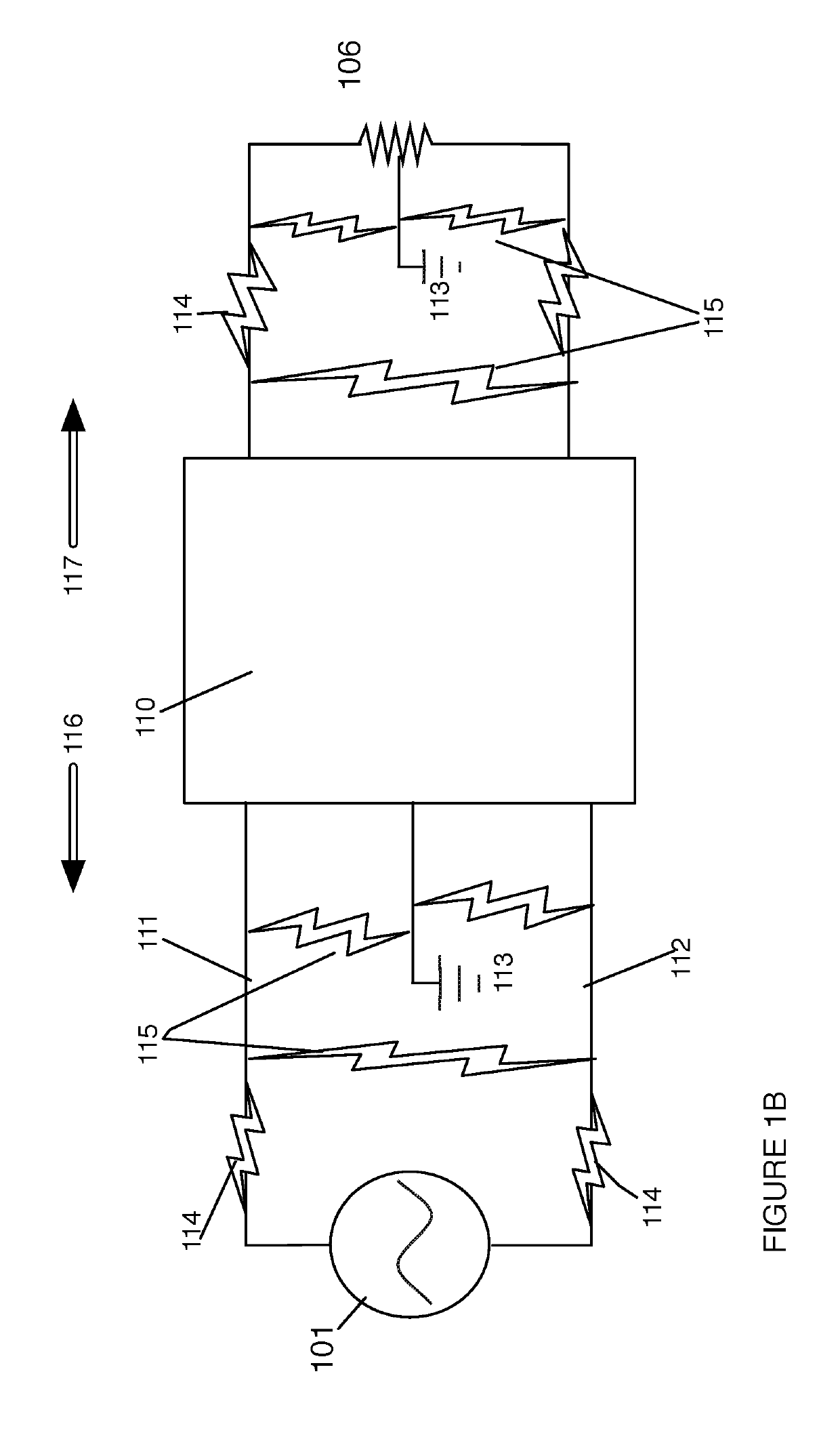
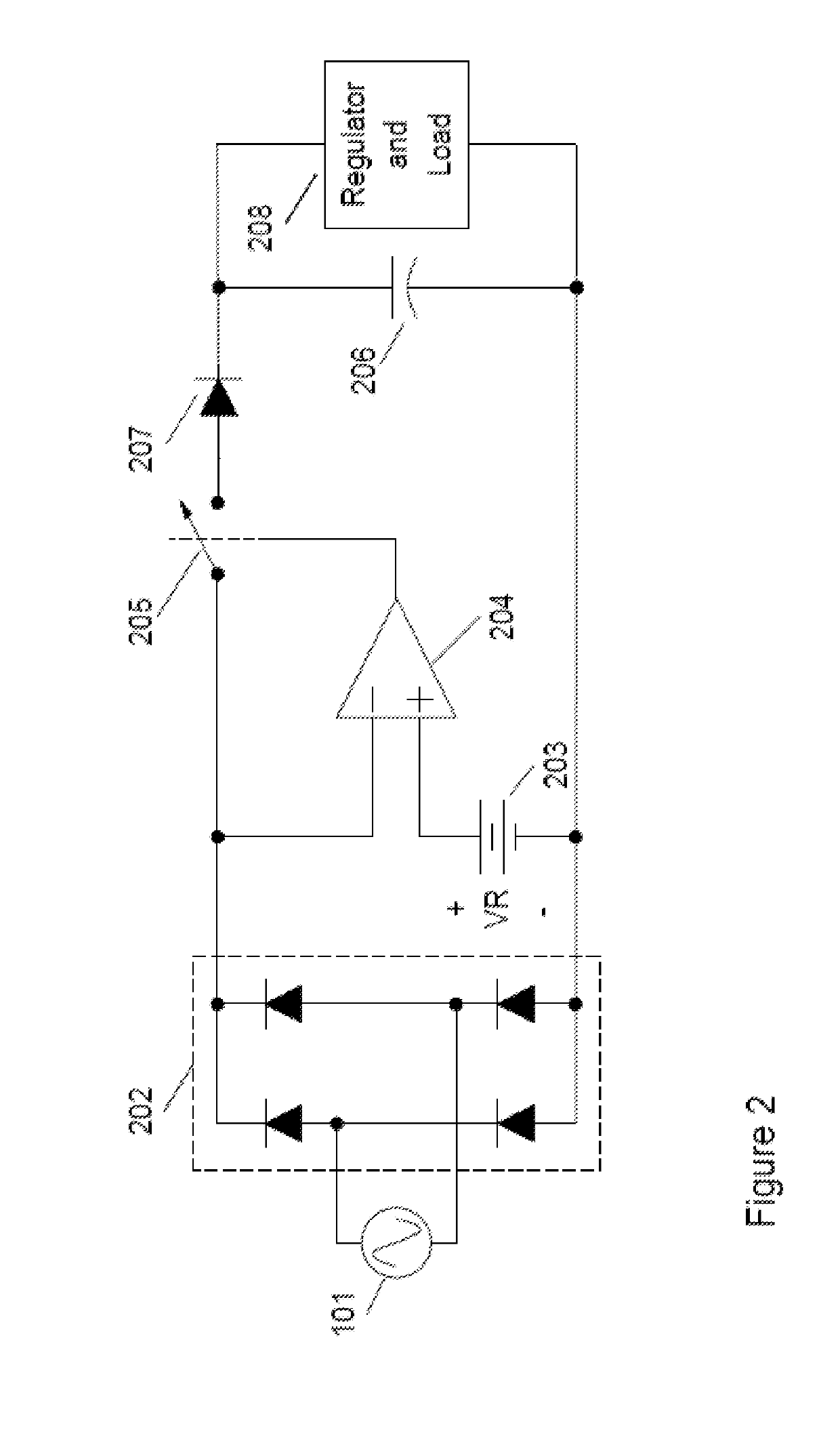
The invention relates to a novel approach for the protection of electrical circuits from ground faults and parallel and series arc faults in a fully solid-state circuit configuration. Solid-state circuits and methods of use are described that provide the key functions of low-voltage DC power supply, mains voltage and current sensing, fault detection processing and high voltage electronic switching.
Owner:INTELESOL LLC
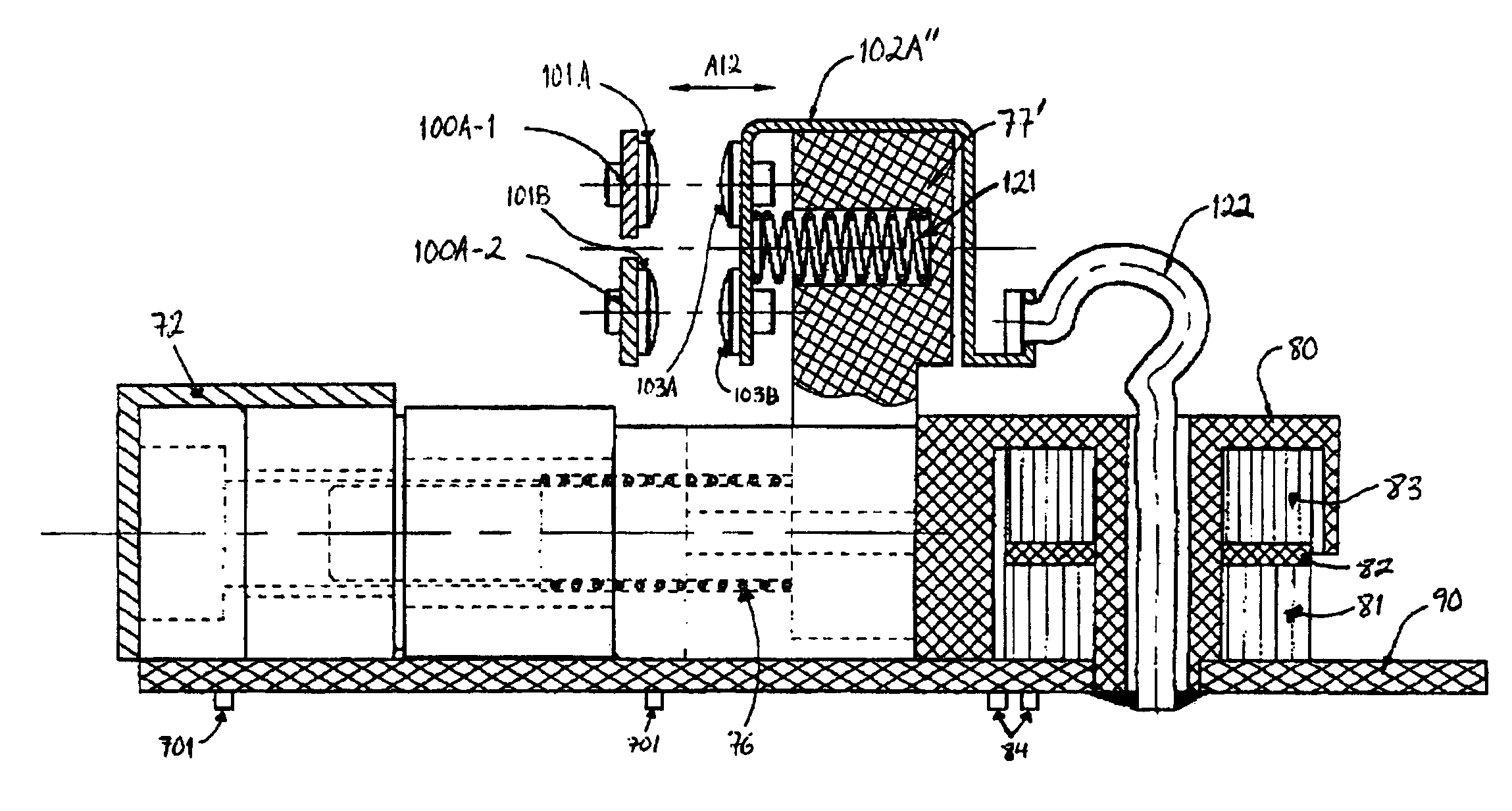
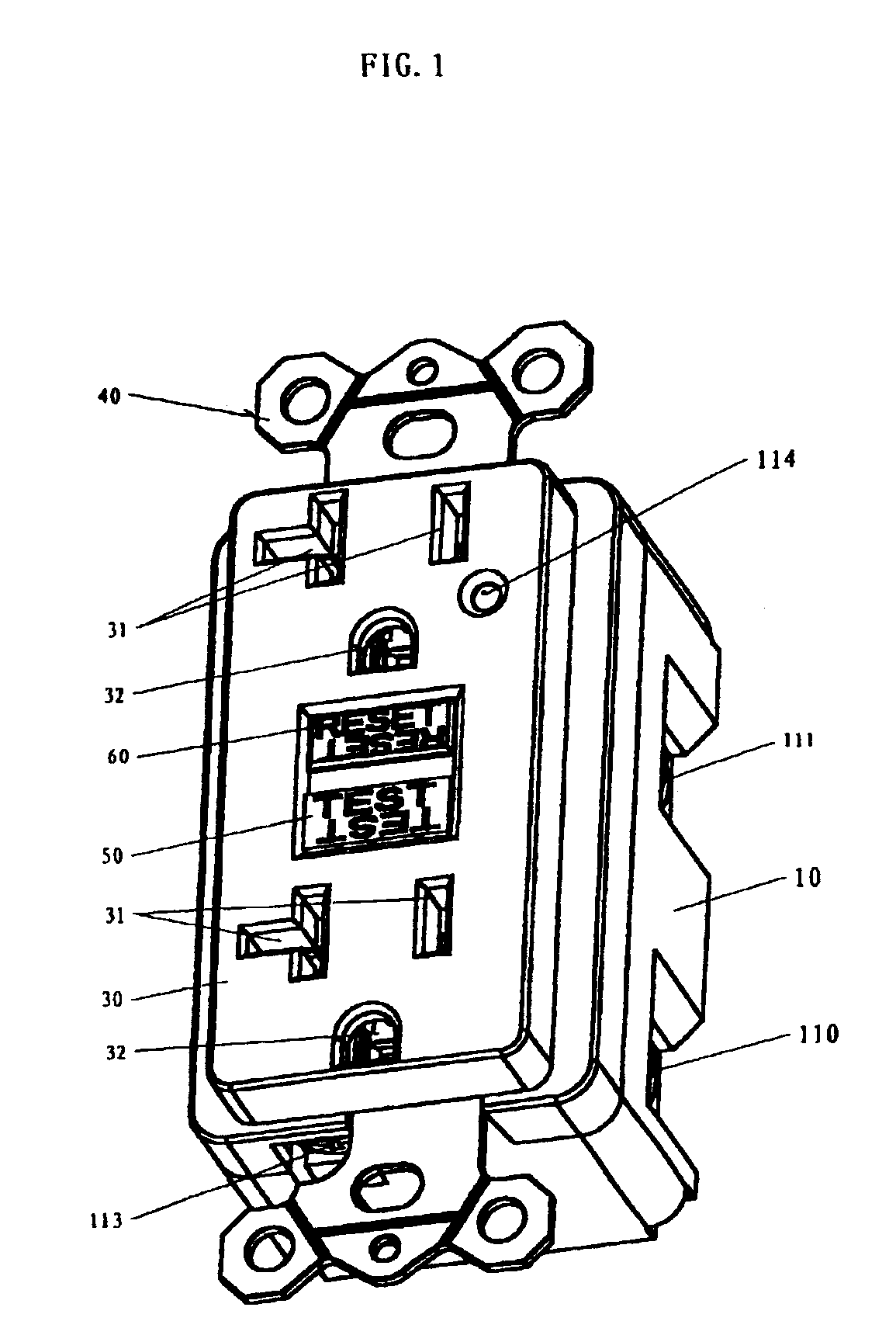
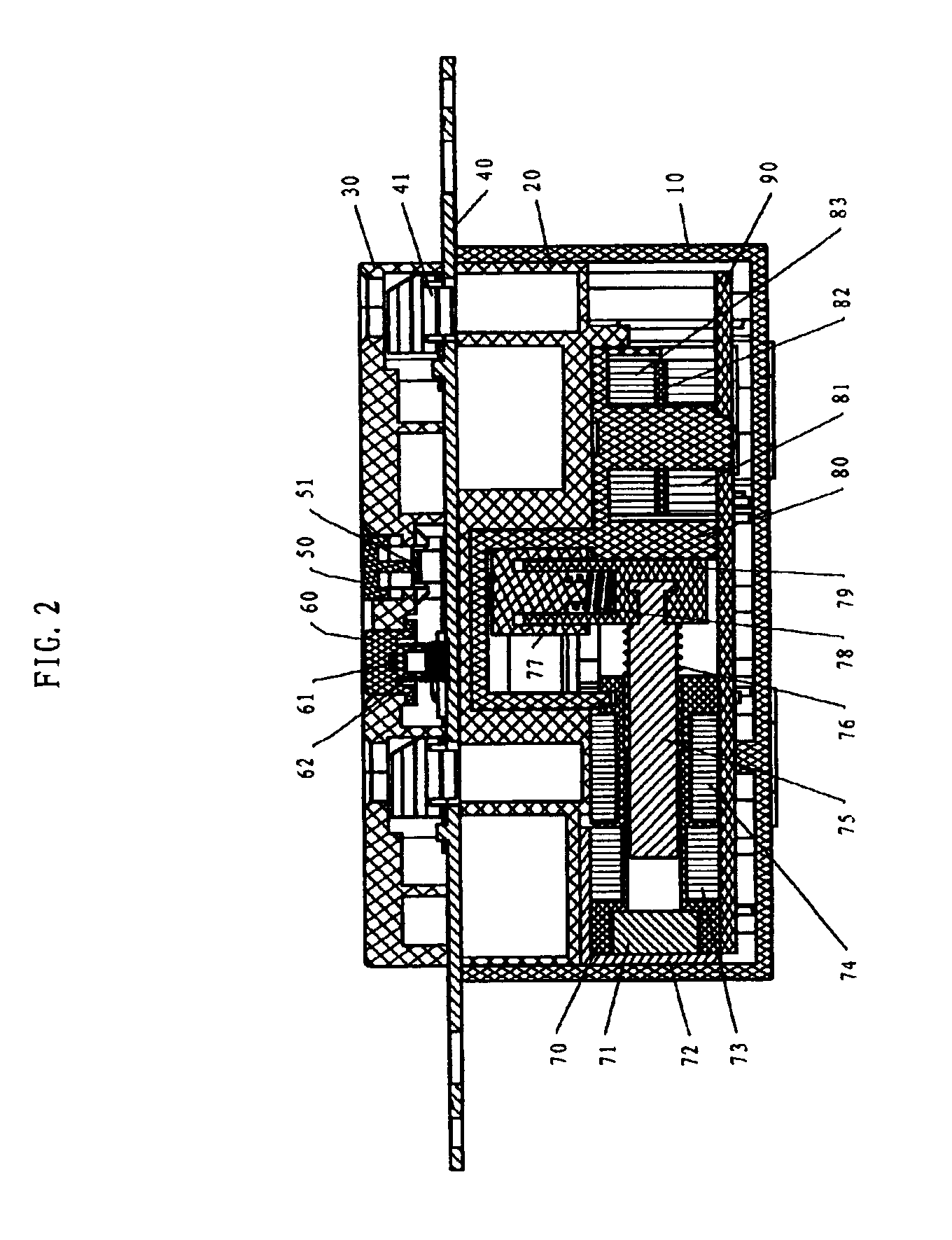
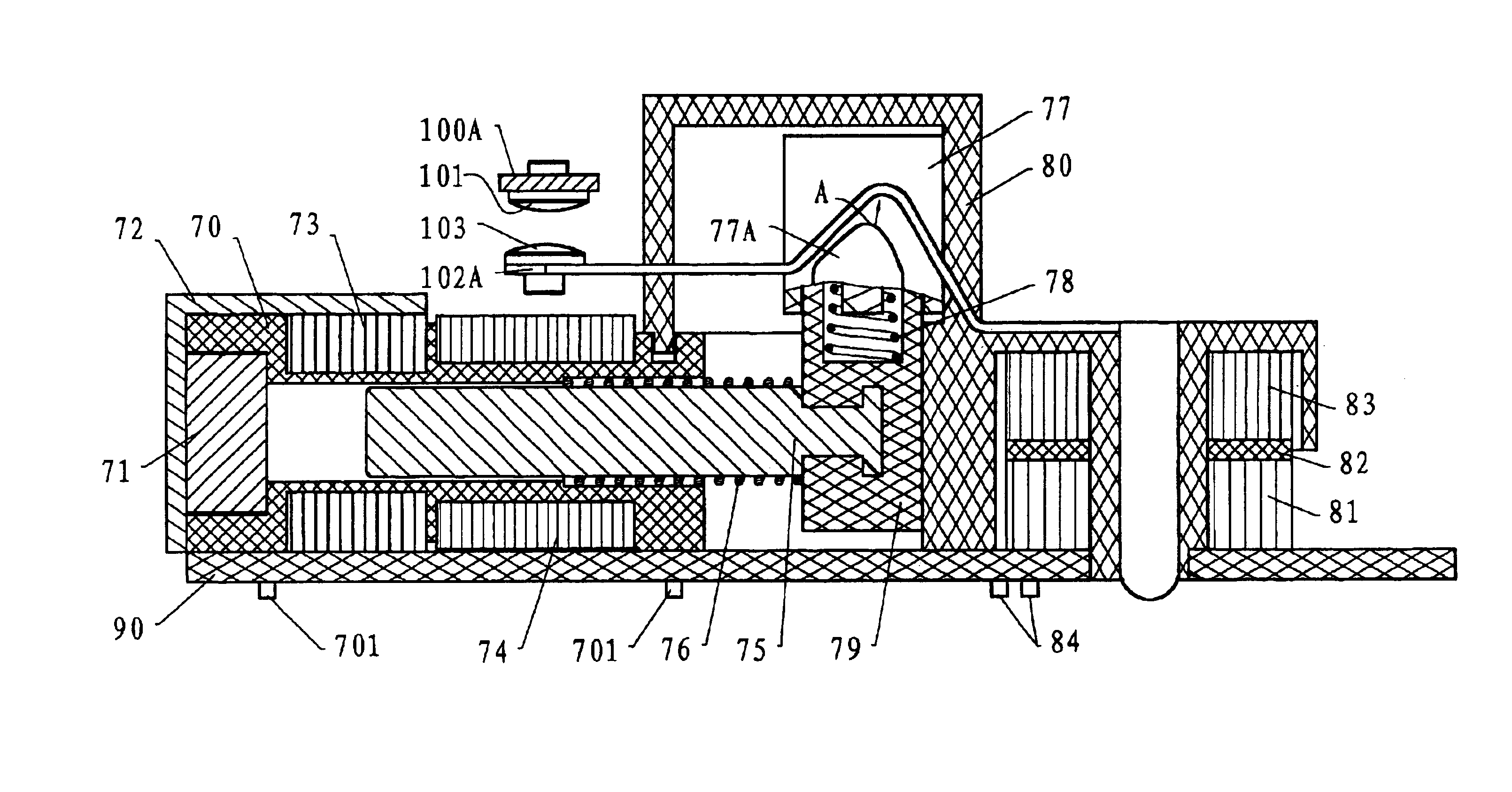
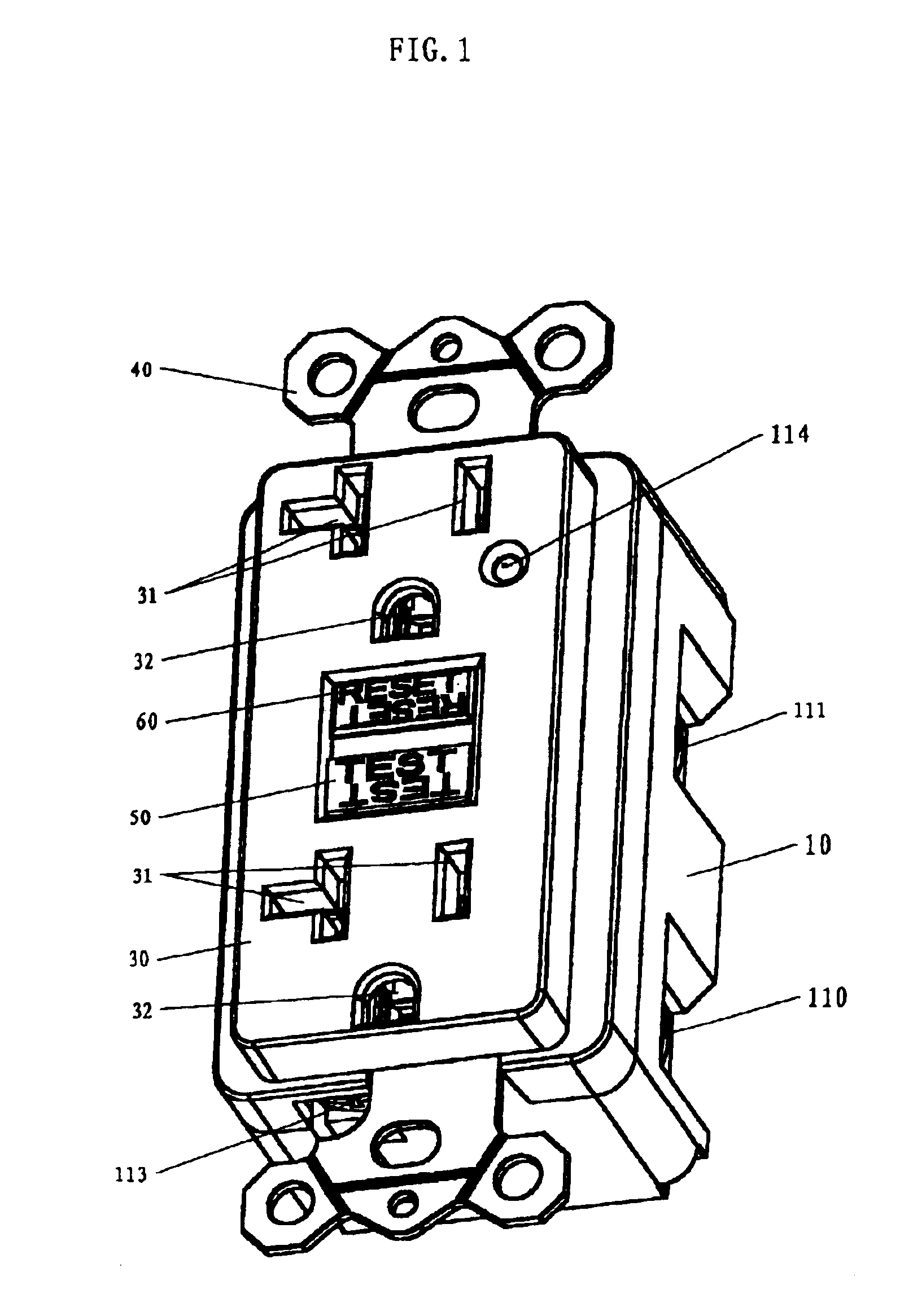
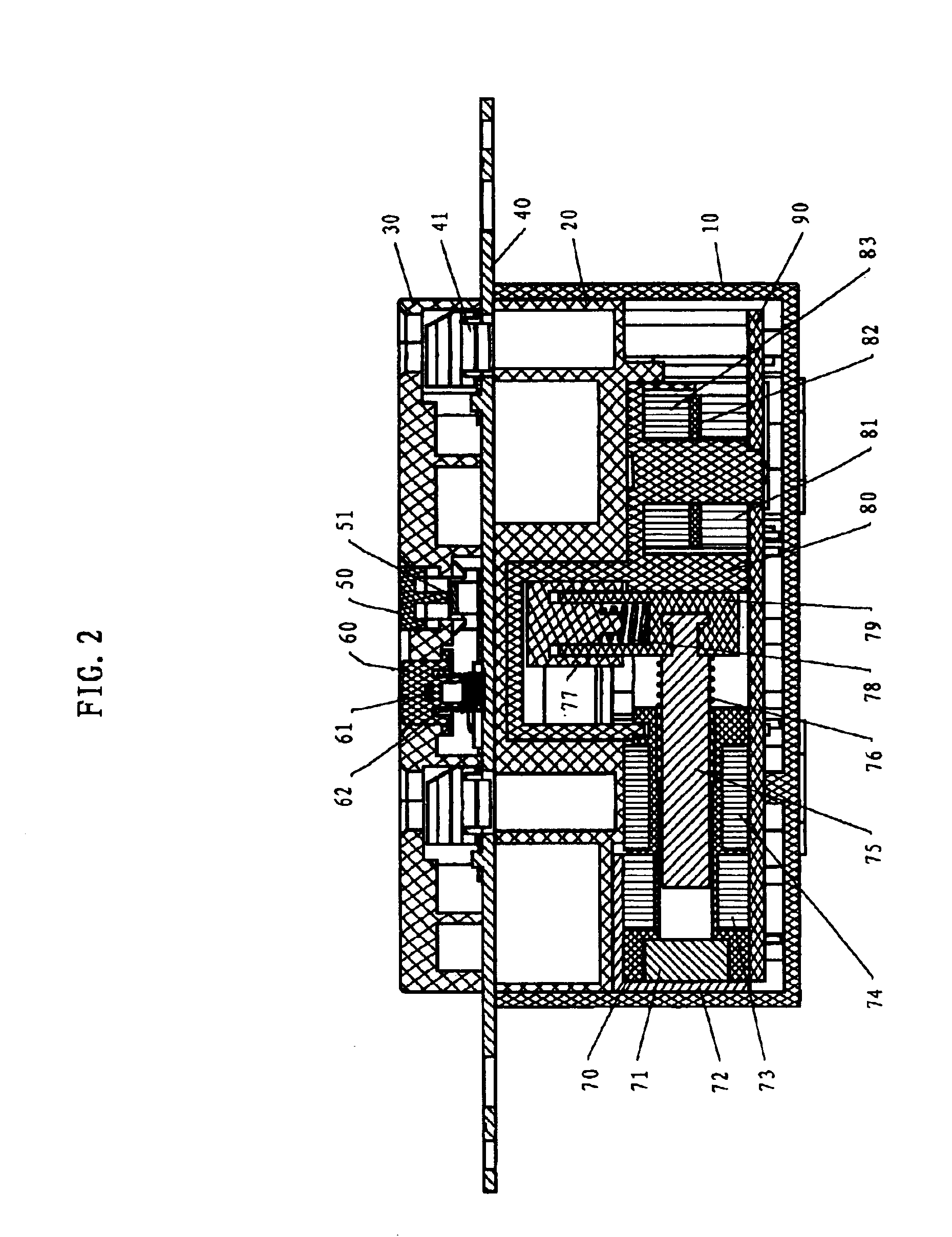
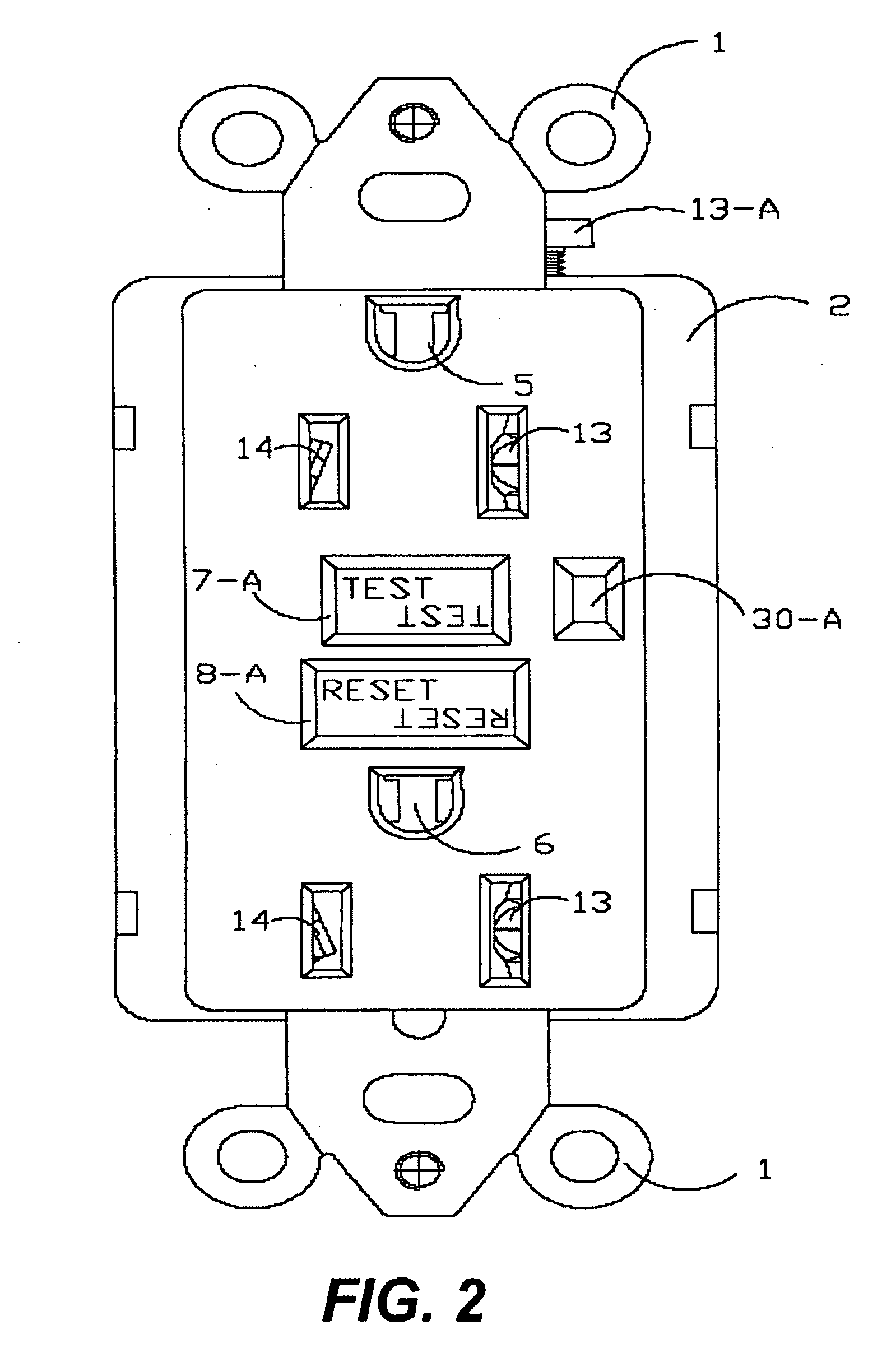
Ground fault circuit interrupter containing a dual-function test button
The present invention provides a circuit interrupting device, preferably a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI), which contains a dual-function test button having a short pole and a long pole positioned underneath the dual-function test button. When the GFCI is properly wired and powered, a depression of the dual-function test button allows the short pole to operatively connect to a conductive pin and generate a leakage current to test the components of the GFCI. If all of the components are functioned properly, the GFCI can be reset. If not, the GFCI cannot be reset. When the GFCI is miswired or reverse wired and not powered, a depression of the dual-function test button does not test the components of the GFCI. However, a further depression of the dual-function test button allows the long pole presses against a tripping lever on a locking member in a tripping device which mechanically trip the GFCI. The present invention further provides an end-of-life detection circuit which can automatically generates a simulated leakage current to test the components in the GFCI. If one or more components are not functioned properly, the end-of-life circuit prevents the GFCI from resetting.
Owner:HUANG HUADAO
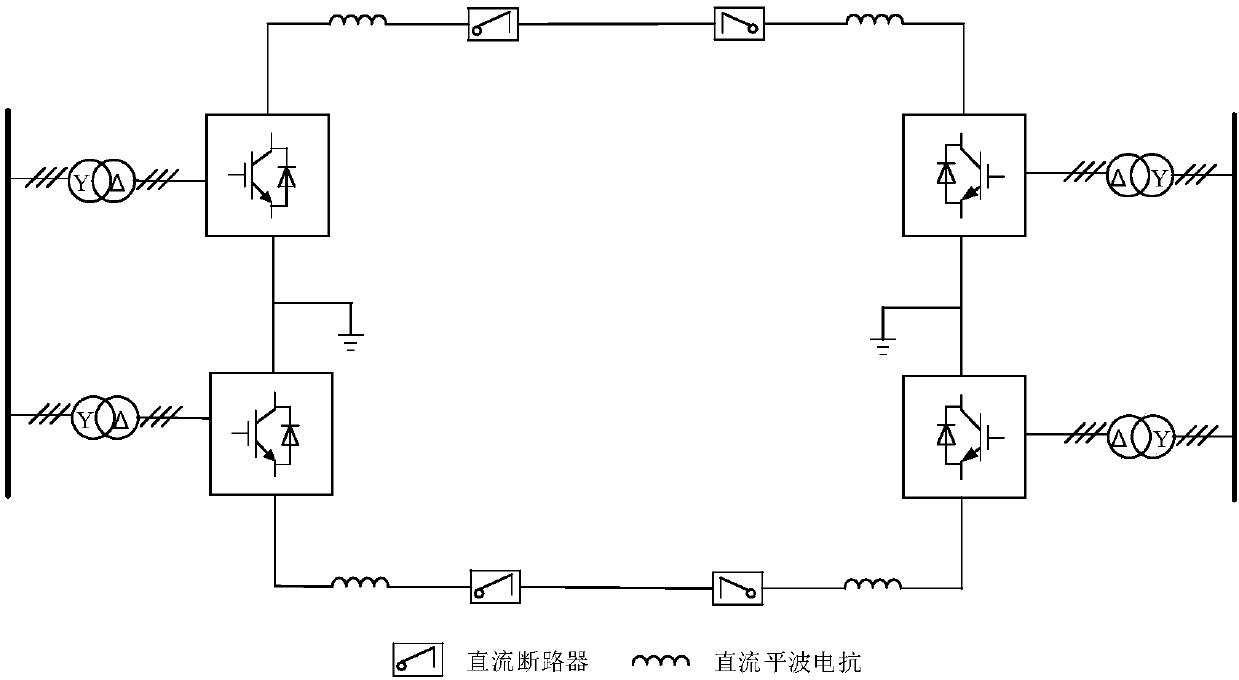
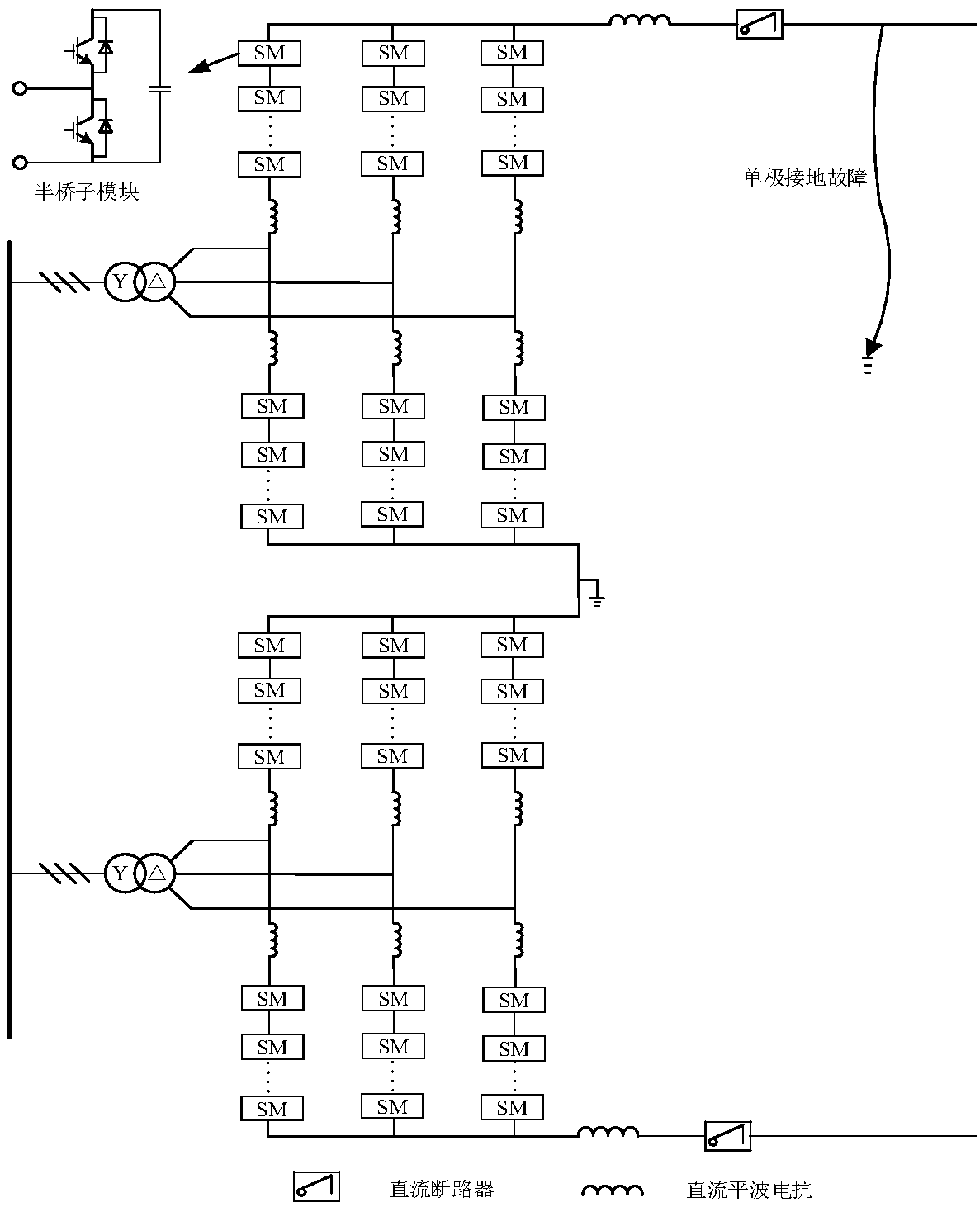
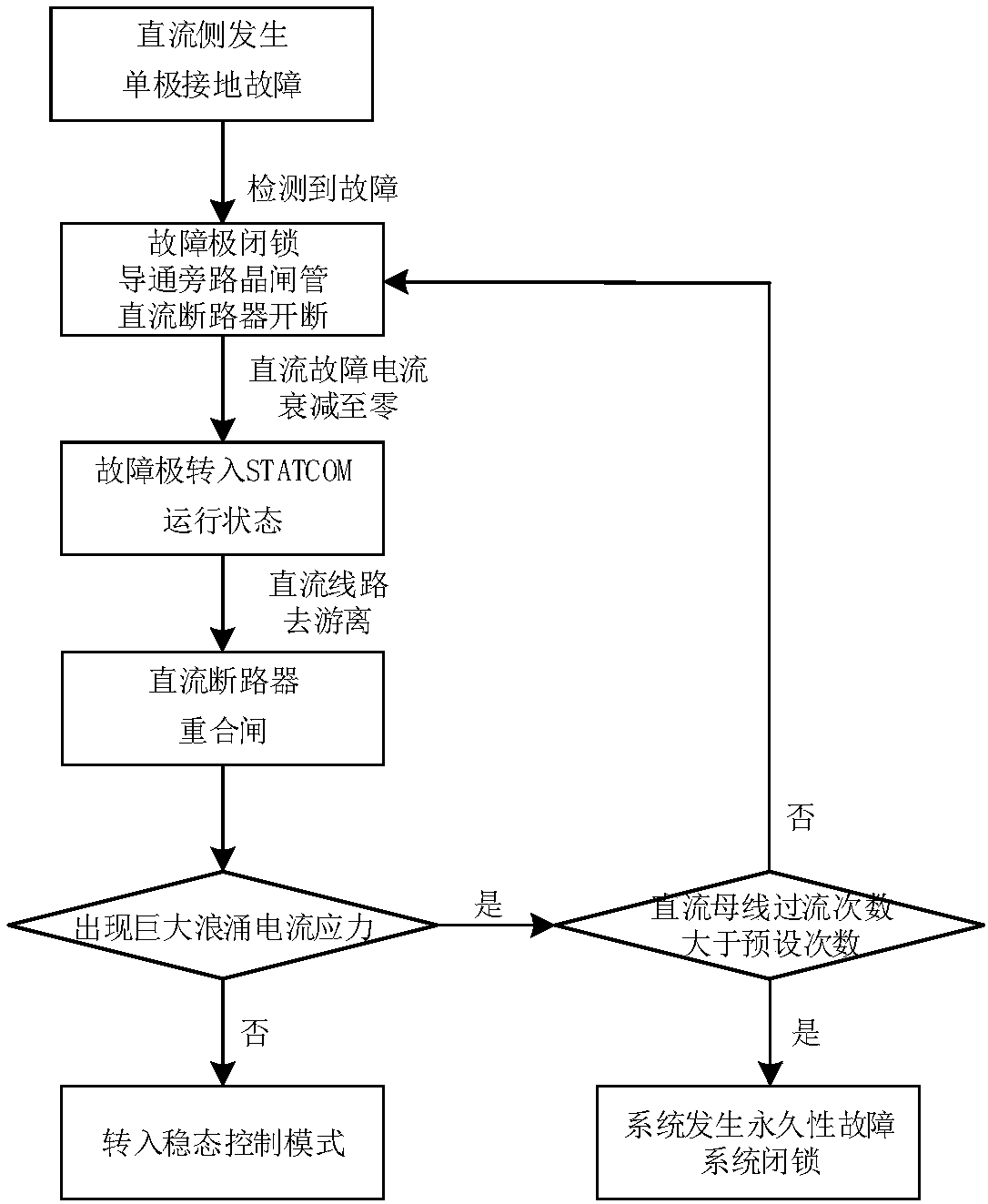
Symmetrical bipolar MMC DC-side single-pole ground fault ride-through and recovery method
ActiveCN107069679AReduce shockReduce power deficitEmergency protective circuit arrangementsRecovery methodDc circuit breaker
The invention provides a symmetrical bipolar MMC DC-side single-pole ground fault ride-through and recovery method. Through cooperation of a DC circuit breaker and a converter, DC fault current cut-off and power recovery are realized, and safe operation of the converter is protected. Through cooperation of active power and reactive power of the sound pole and the faulty pole, the active power deficiency of a converter station in the failure period is reduced. Rated reactive power is supplied to the grid, and therefore, the impact of a fault to an AC system is reduced. By actively controlling the common-mode components of the reference voltages of the upper and lower bridge arms of the converter, the risk brought to the safe operation of the system by excessive current surge stress of the converter due to reclosing failure is avoided. Based on the fact that a dual-pole short-circuit fault at the DC side of a symmetrical bipolar MMC can be regarded as a special case of single-pole ground faults of both positive and negative DC buses, the method of the invention can be used to handle a dual-pole short-circuit fault at the DC side of a symmetrical bipolar MMC.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
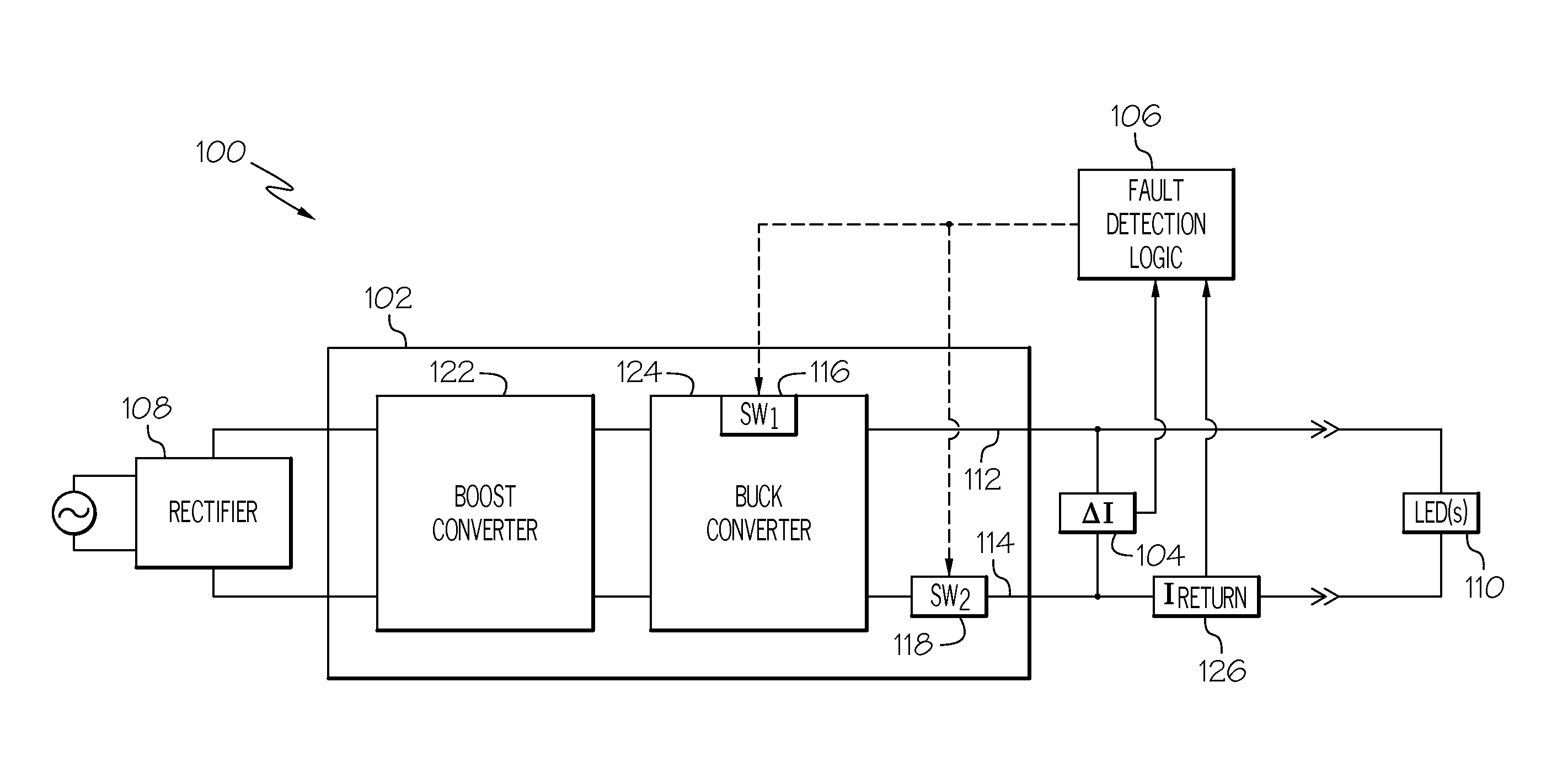
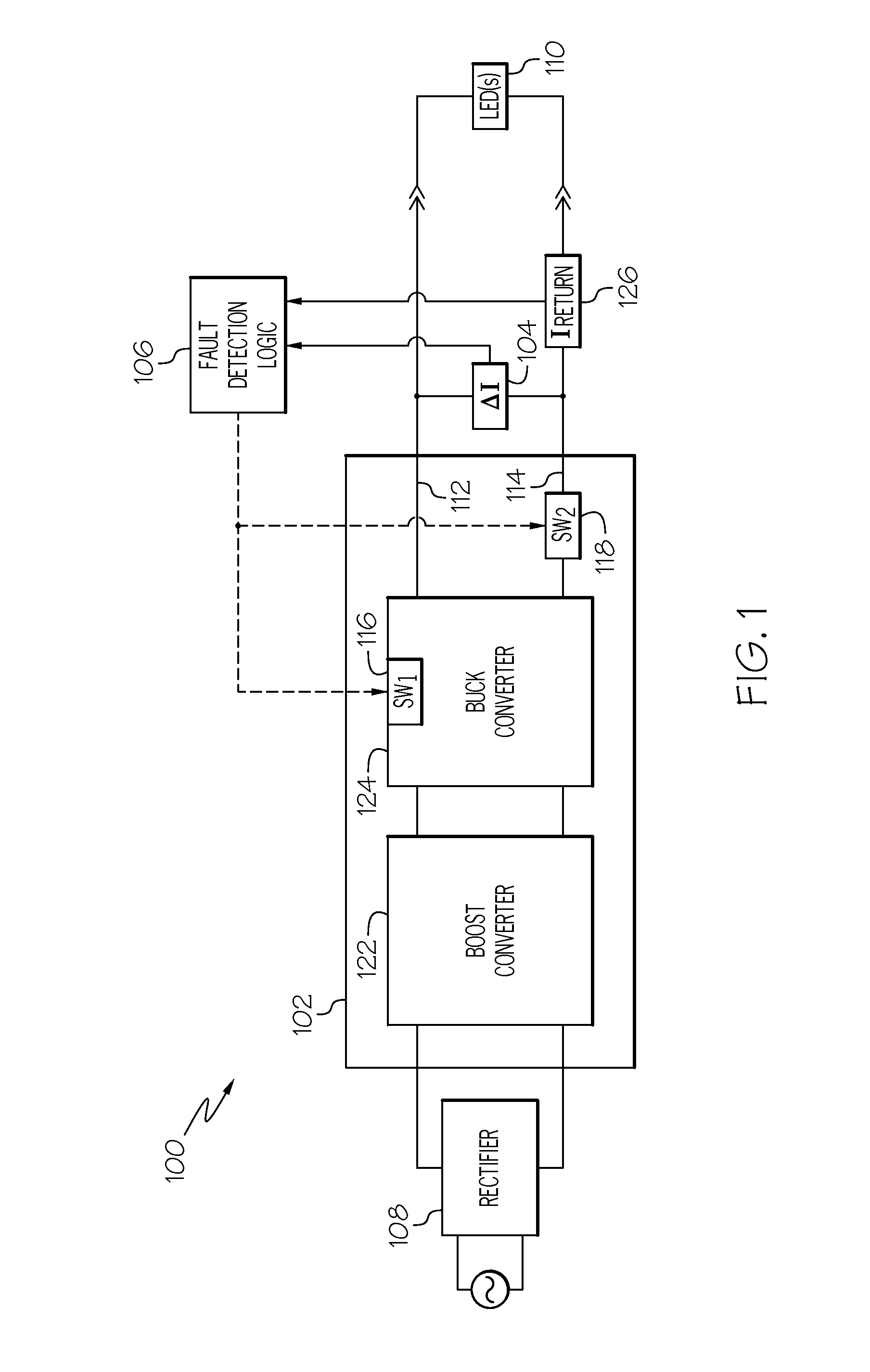
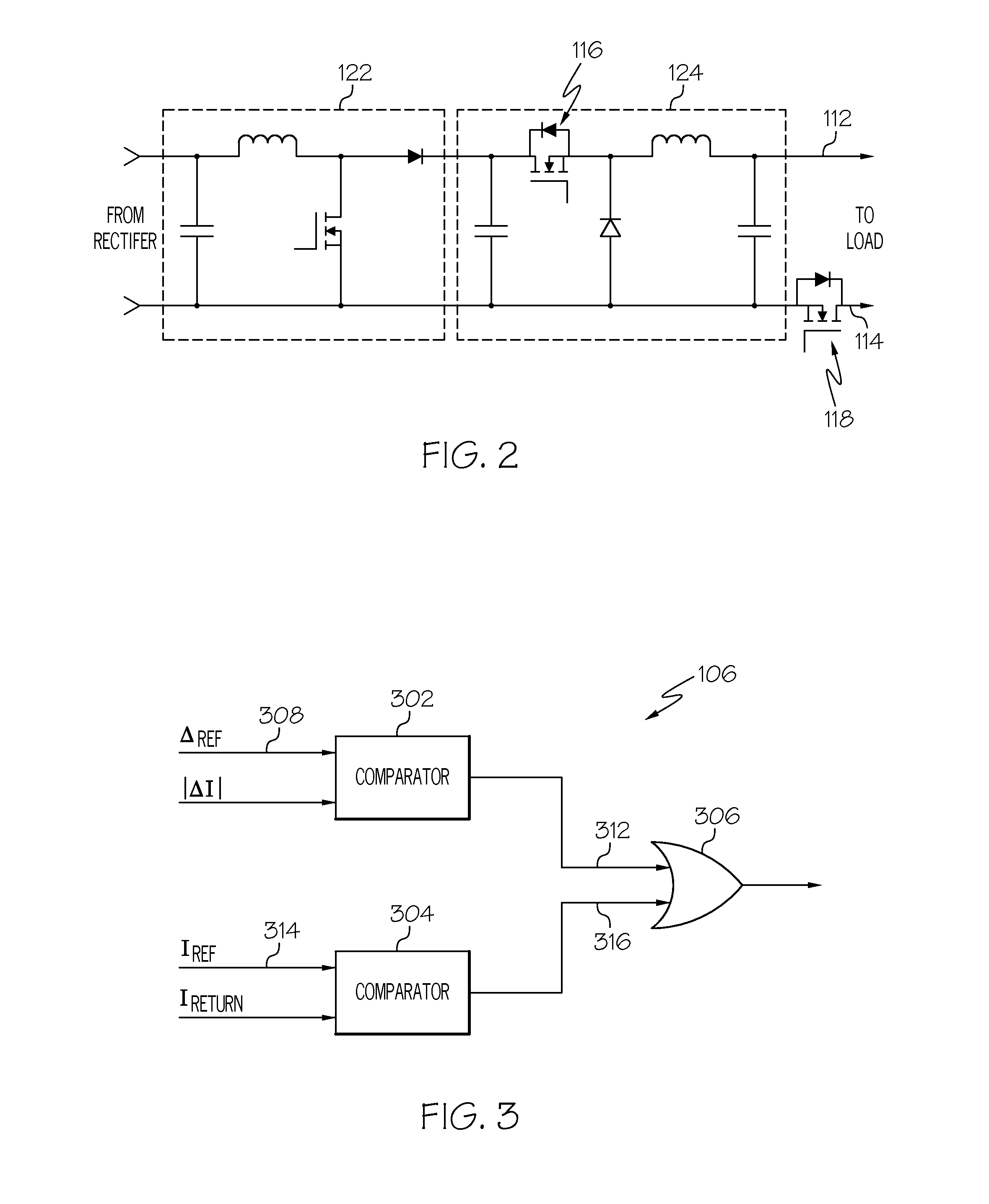
Non-isolated power supply output chassis ground fault detection and protection system
ActiveUS20160118784A1Apparatus without intermediate ac conversionArrangements responsive to excess currentPower flowCurrent sensor
A non-isolated power supply is configured to receive an input voltage and supply an output voltage, and includes a supply line, a return line, a first semiconductor switch coupled in series in the supply line, and a second semiconductor switch coupled in series in the return line. The first and second semiconductor switches are each configured to operate in an ON state and an OFF state. The differential current sensor is configured to sense differential current between the supply line and the return line. The fault detection logic is coupled to the differential current sensor, the first semiconductor switch, and the second semiconductor switch, and is configured to detect when the differential current exceeds a predetermined current magnitude, and command the first and second semiconductor switches to operate in the OFF state upon detecting that the differential current exceeds the predetermined current magnitude.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Single-phase earth fault location system for distribution network of power system and method thereof
ActiveCN101846718AFunction increaseLow costFault locationInformation technology support systemElectric power systemTransformer
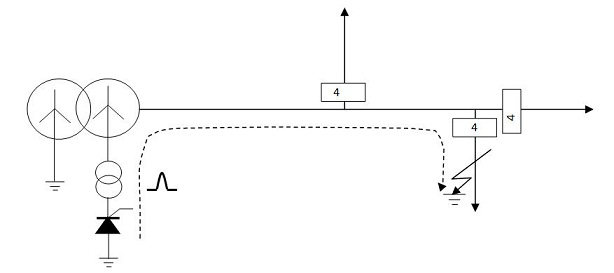
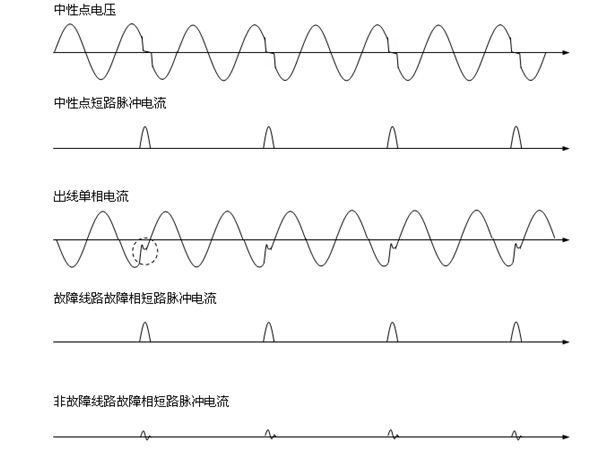
The invention relates to a single-phase earth fault location system for a distribution network of a power system and a method thereof. The single-phase earth fault location system comprises a pulse signal generator, which is arranged between the neutral point of a main substation transformer and the ground, and the initial end of each outlet branch is provided with a current sensor; and a main station is also mounted in a substation, and is communicated with the current sensors. The method installs the thyristor-based short-circuit current generator at a corresponding position in the substation, thyristors are controlled to instantaneously conduct in order to generate and inject short-circuit current into a faulty line, the sensors mounted on the initial ends of the outlet branches detectthe short-circuit current, each sensor detecting the short-circuit current informs a host positioned in the substation of own state information via communication, and according to calculated fault impedance coupled with the locations of the sensors detecting the short-circuit current, the host determines the location where a single-phase earth fault occurs.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +1
Ground-fault monitor for multiple circuits
ActiveUS7312964B2Emergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentArrangements resposive to fault currentElectricityElectrical conductor
A ground fault monitor for an electrical system having a plurality of branch circuits each having a respective ground conductor extending to a service panel that includes a ground connection to which the ground conductors are electrically connected. The ground fault monitor includes a current transformer for sensing current flow through the plurality of ground conductors to the ground connection and generating a current flow signal representative of any sensed current flow, and a monitoring circuit responsive to the current transformer for monitoring the current flow signal and generating an alarm when the current flow signal indicates the presence of a ground fault.
Owner:TCHERNOBRIVETAB SERGUEI
Radiation net fault location method by means of zero mode and aerial mode time difference independent of double-end synchronization and with matching of magnitude of voltages and magnitude of currents
ActiveCN103941151ANot subject to fault transition resistanceUnaffected by fault initial phase angleFault locationElectric power systemCable fault location
The invention provides a radiation net fault location method by means of a zero mode and aerial mode time difference independent of double-end synchronization and with matching of the magnitude of voltages and the magnitude of currents, and belongs to the technical field of power system relay protection. The two sides of a feeder are respectively provided with a traveling wave fault location device, and fault location is carried out according to information on the two sides. After a ground fault of the feeder of a power distribution net occurs, due to sudden changes of the voltage at a fault point, an aerial mode traveling wave component spreading between wires and a zero mode traveling wave component spreading between the wires and the ground are generated. Due to the fact that the spreading speeds of an aerial mode and a zero mode are different, the arrival moment of an aerial mode traveling wave detected by the measurement end and the arrival moment of a zero mode traveling wave detected by the measurement end are different. According to original aerial mode voltage and current traveling wave data and original zero mode voltage and current traveling wave data detected by the measurement end, wave arrival moment calibration is carried out by means of a wavelet modulus maximum value under a fifth dimension, and then the fault position is calculated according to a calculation formula of a ground fault single-end traveling wave fault location method of modulus transmission time differences. Fault location is carried out according to measurement information of the single-end modulus transmission time differences at two sides.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fault location method based on travelling wave
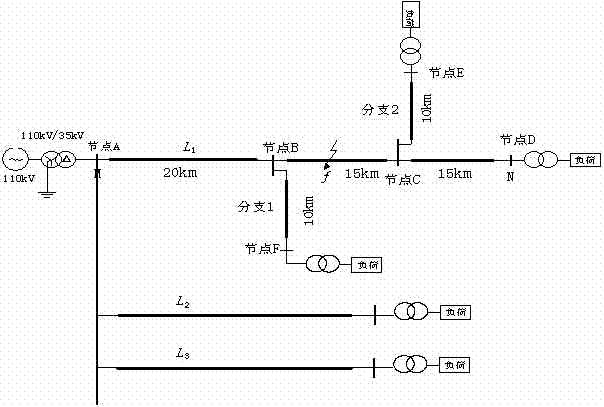
ActiveCN101666848AOvercome the effects of high-resistance faults, etc.Realize fault locationFault locationCapacitive effectCapacitance
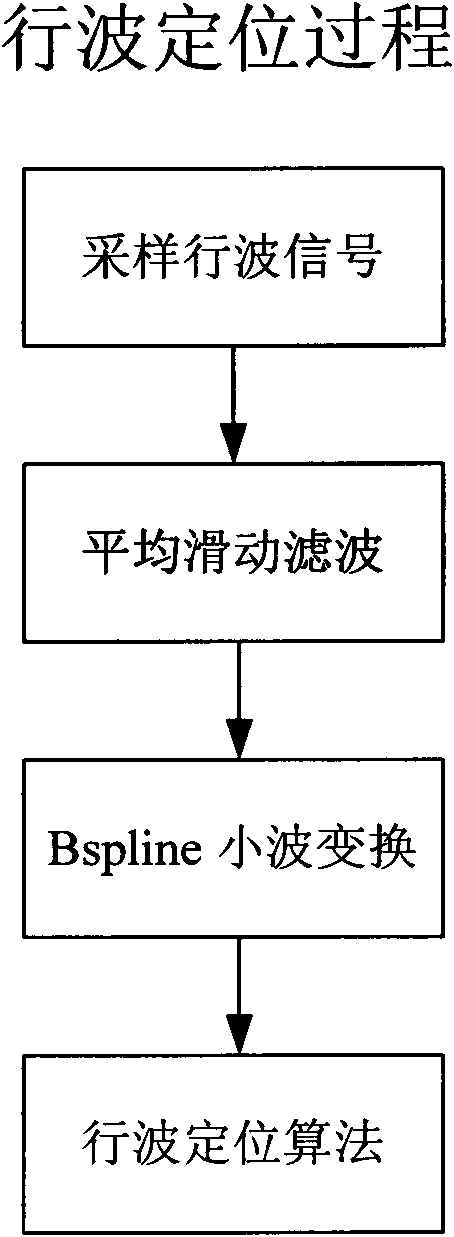
The invention discloses a fault location method based on a travelling wave when the signal / noise ratio is at a lower level. Because of the strengthening of capacitance effects of a high-voltage powertransmission line, the travelling wave decays comparatively large when is transmitted along the line, in particular when high resistance fault or low voltage inception angle ground fault occurs, the initial energy of the travelling wave is very low, and the energy is comparatively low after line capacitance decaying, and is mainly overwhelmed by noise. Therefore, as far as the present used travelling wave method is concerned, if a sampled signal is not preprocessed, wavelets transformation is directly used for carrying out fault location, but correct result can't be obtained. In the fault location method, a moving average filter is firstly used to preprocess the sampled signal, and then Bspline wavelet transformation is used to realize fault location. Because the moving average filter can effectively restrain the noise without decaying an abrupt signal, based on this, fault location at a low signal / noise ratio can be realized by utilizing the Bspline wavelet transformation.
Owner:BEIJING SIFANG JIBAO AUTOMATION +2
Single-phase earth fault direction judgment and processing method of small current grounding system
ActiveCN103760465AGuaranteed power supplyImprove power supply reliabilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault locationSingle phaseFeed line
The invention relates to a single-phase earth fault direction judgment and processing method of a small current grounding system. In terms of a fault direction judgment method, the session which a single-phase fault point belongs to on a main line is judged according to zero-sequence currents, zero-sequence voltage and the included angle relation between the zero-sequence currents and the zero-sequence voltage tested through a section switch on the main line where a single-phase earth fault occurs, the fault session is isolated according to the judgment result, and normal power supply of a non-fault session line is guaranteed to the largest extent. According to the judgment and processing method, the single-phase earth fault session of the main line can be automatically isolated, and power supply reliability of a power distribution network is improved; additionally, according to the single-phase grounding direction judgment method, a main line boundary function is embedded in the section switch of a 10kV feeder line, the range in power failure caused by the single-phase earth fault can be shortened to the largest extent, and accordingly reliability and safety of power supply are improved.
Owner:泉州维盾电气有限公司
Fault diagnosis comprehensive positioning method for intelligent distribution network
InactiveCN111596170ARealize no blind spot monitoringPrecise Fault Location ServiceTransmission systemsFault location by conductor typesFault indicatorTransformer
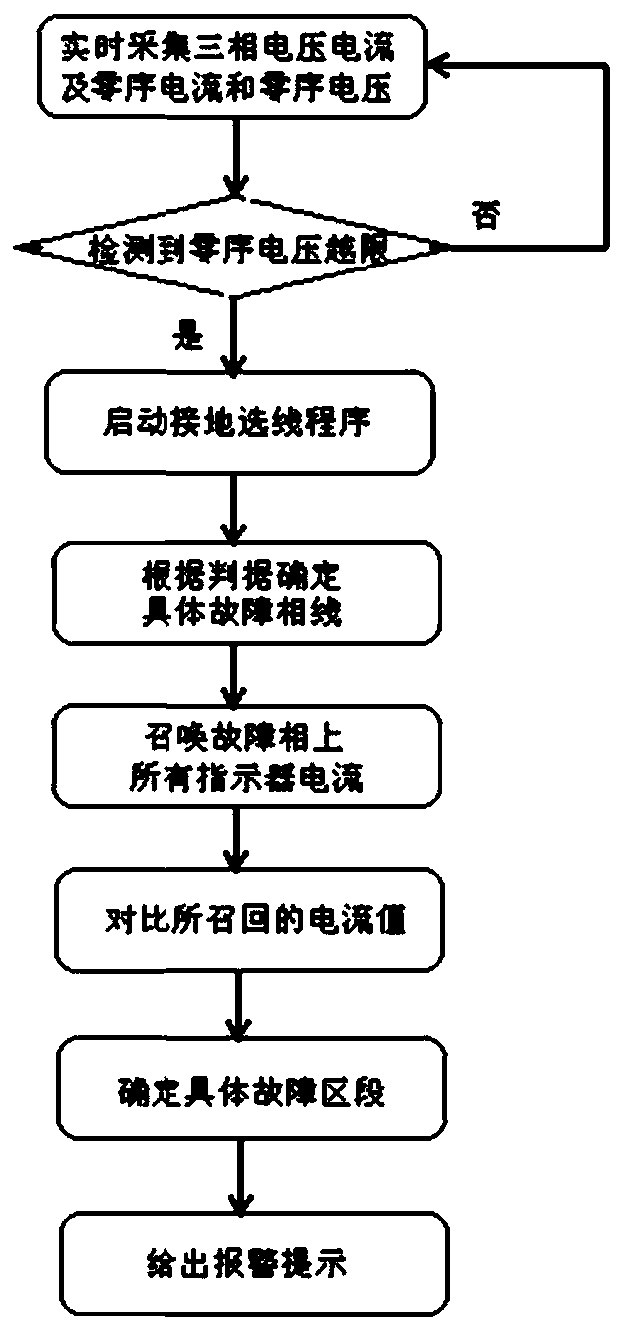
The invention discloses a fault diagnosis comprehensive positioning method for an intelligent distribution network, and belongs to the field of fault monitoring. Based on a fault indicator, a wirelesscommunication technology and a ground fault line selection technology, the method comprises the following steps: monitoring zero-sequence voltage of a transformer neutral point in real time, startingzero-sequence fault diagnosis when detecting that a zero-sequence voltage change value exceeds a preset value, and identifying whether the zero-sequence voltage change value is a single-phase grounding fault; if the zero-sequence voltage change value is single-phase grounding fault, performing grounding line selection through a fault diagnosis device in a station, and positioning the grounding fault on a certain phase of a certain line; when the single-phase earth fault is judged to be a stable fault, recalling the real-time current data of the fault indicators on the fault phase line, comparing the signals collected by the fault indicators, comparing the difference of the real-time current data before and after a fault point, judging the two fault indicators with abrupt changes, and thendetermining the specific section of the fault. The method can be widely applied to the field of power distribution network operation fault monitoring and positioning.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Grounding detection device for power distribution system and fault detection method thereof
InactiveCN101813735AAvoid out-of-production testingRealize online detectionFault locationInformation technology support systemDistribution power systemSystem usage
The invention provides a grounding detection device for a power distribution system and a fault detection method thereof, and aims to solve the problem that the detection operation is not easy and convenient, and the problem that the conventional detection device is not suitable to be used for various power systems existing in the conventional detection device. The device consists of a signal acquisition treatment display device used for acquiring and treating zero sequence current of a feeder line to be detected and a power circuit, wherein the signal acquisition treatment display device comprises n groups of acquisition treatment display devices with the same structure for detecting the signals of the detected zero sequence current in n different measuring ranges respectively; and the power circuit may adopt a mains supply or a battery supply. The method comprises the following steps of: estimating the zero sequence current of the system; measuring the zero sequence current of the feeder line by using the grounding detection device for the power distribution system; and determining and troubleshooting the fault line. By using the device, an operator can quickly, safely and accurately detect the feeder line having the grounding fault in a short time, and the device is suitable to be used for various power systems.
Owner:BAOWU CHARCOAL MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Ground fault circuit interrupter
InactiveUS7692904B2Electric shock preventionSimple configurationEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentPhase currentsControl signal
A method of preventing an overload current from a power supply to a load through a ground fault circuit interrupter includes the steps of: obtaining an interrupted fault current from a hot wire to a ground wire via a first zero-phase current inductor and a fault current from a neutral wire to the ground wire via a second zero-phase current inductor; amplifying a signal of the fault current by an Op-Amp; and determining the fault current by a programmable control module, wherein when the fault current is larger than a preset threshold, the programmable control module sends a control signal to a control switch such that the control switch electrifies a second coil of a trip breaker to drive an armature at an unlocked position, so as to separate a movable terminal with a fixed terminal for electrically disconnecting the load with the power supply.
Owner:HISETEC ELECTRONICS
Coal mine grid system insulation state monitoring method
ActiveCN103135031AAccurate measurementEliminate measurement errorsImpedence measurementsShort-circuit testingCapacitanceElectric power system
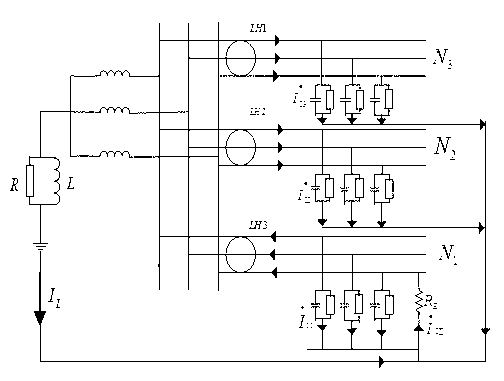
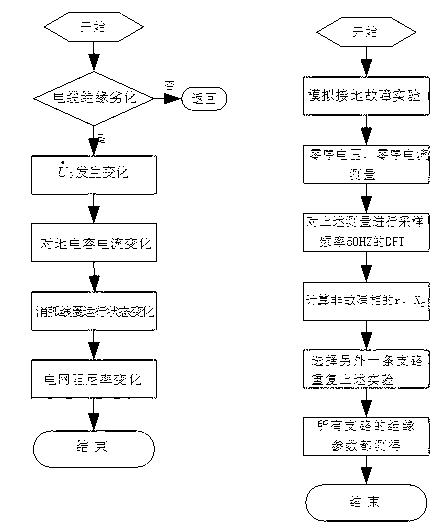
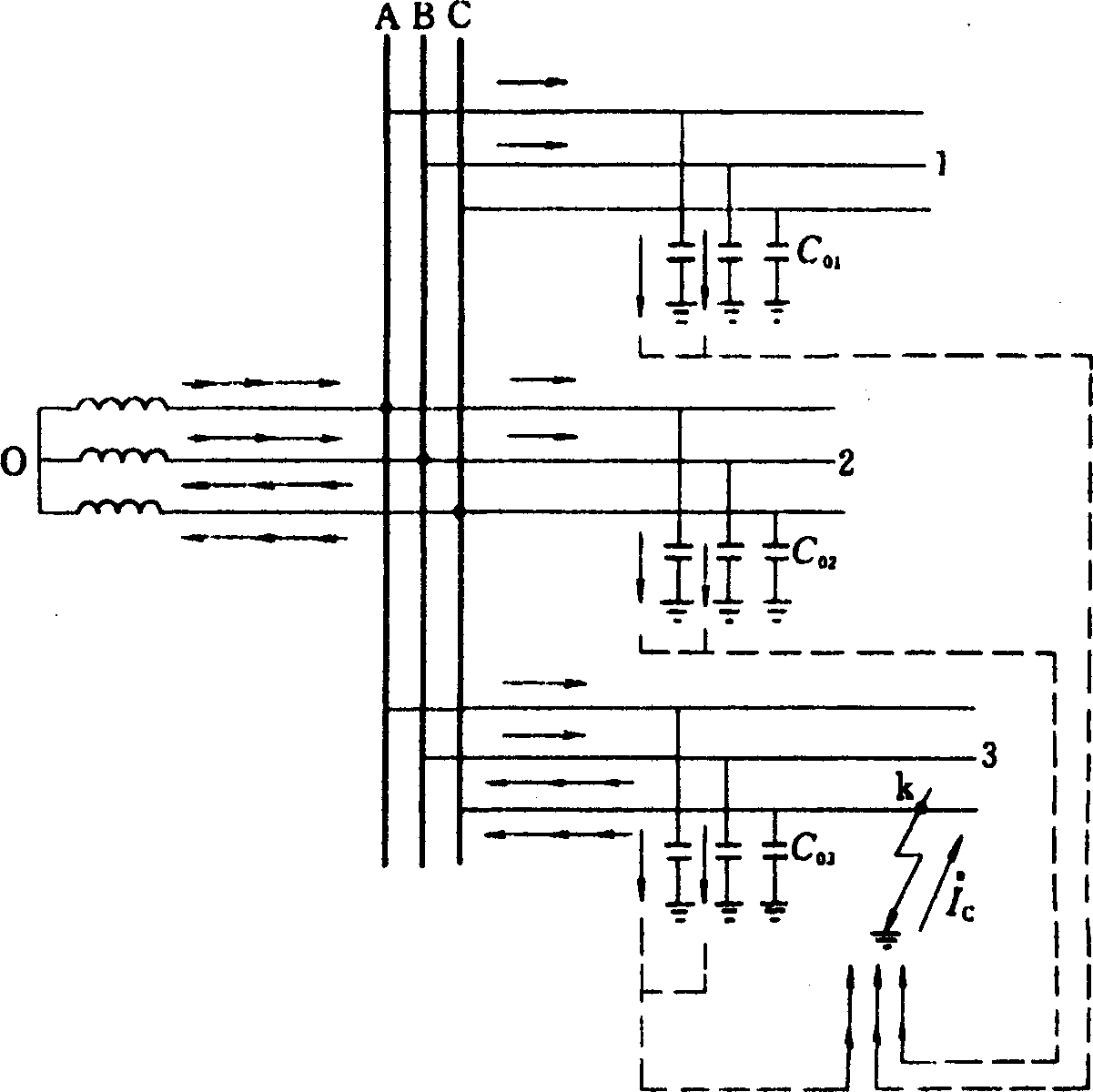
The invention provides a coal mine grid system insulation state monitoring method and belongs to an electrical power system feed line insulation state monitoring method. A feed line branch circuit is selected for doing single-phase longitude metal grounding experiment, zero sequence voltage of a bus and zero sequence current of a non-malfunction branch circuit are tested, zero sequence impedance of the non-malfunction branch circuit is obtained, namely, insulation resistance and ground capacitance, for obtaining insulation parameters of all circuits, another branch circuit is reselected to do a single-phase connection low resistance ground experiment or the next circuit with the non-branch-circuit number 1 is waited for generating single-phase ground malfunction, the experiment is repeated, insulation parameters of a first experiment malfunction circuit are obtained, and the insulation parameters of all feed line branch circuits are obtained by synthesizing results of the two experiments. The coal mine grid system insulation state monitoring method has the advantages that insulation degradation degree of the circuits is analyzed from state change of the bus zero sequence voltage and an arc suppression coil, the zero sequence voltage changes to a certain extent, switching-in situations of damping resistance change, and the degradation degree of circuit insulation is forecasted by monitoring change of transient states of a plurality of feature quantities.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Fault line selection method for single-phase-to-ground fault in small ground current distribution network
InactiveCN1804649ASimple operation and maintenanceEasy to measureFault locationVoltage amplitudeSignal on
The invention relates to a small earth current grid single-phase grounding fault wire-choosing method, which comprises: 1) Collecting the zero order voltage and the zero order current signal on the voltage sensor and the current sensor of each wire and computing the zero order voltage amplitude, if the amplitude is over the limit, it quotes that it occurs the fault and collects the zero order current after four period of the fault; 2) computing the second, third and forth period effect value I1, I2 and I3 when each line zero order current fault starts and computing the gradient factor K1, K2 of each line zero order current; 3) quoting weather it satisfies K1ú¥KSET and K2ú¥KSET, wherein KSET is the gradient factor setting value with the range 1.2-2.0; 4) if it satisfies K1ú¥KSET and K2ú¥KSET, the wire is earth fault wire. The wire-choosing system comprises a microcomputer including a fault detecting open unit, a zero order current gradient computing unit and a transient gradient wire-choosing unit.
Owner:杭州佳和电气股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com