Methods and Systems for Maximum Power Point Transfer in Receivers
a technology of power point transfer and receiver, applied in the direction of electric variable regulation, process and machine control, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of variable power or energy extracted from rf waves
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
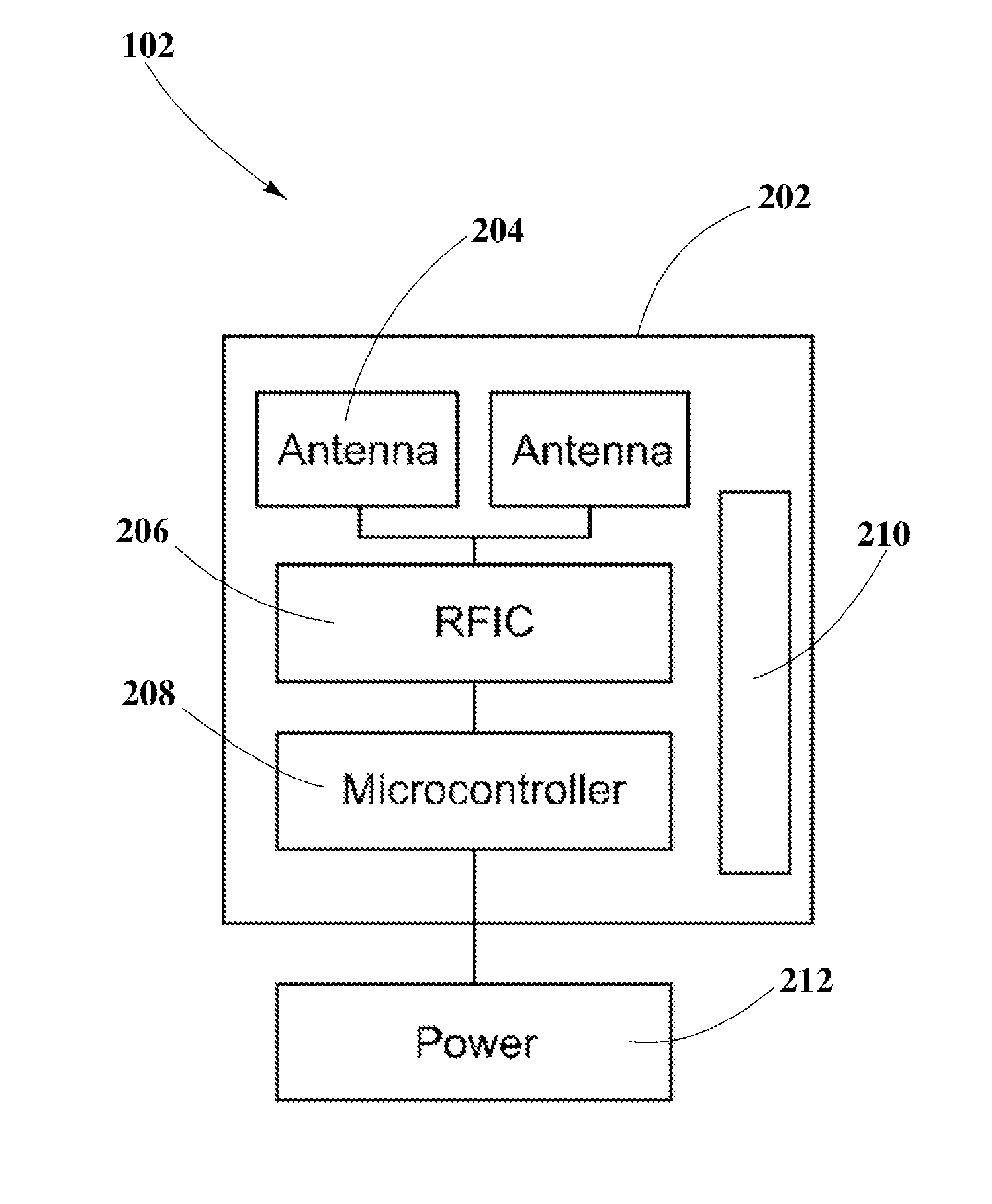
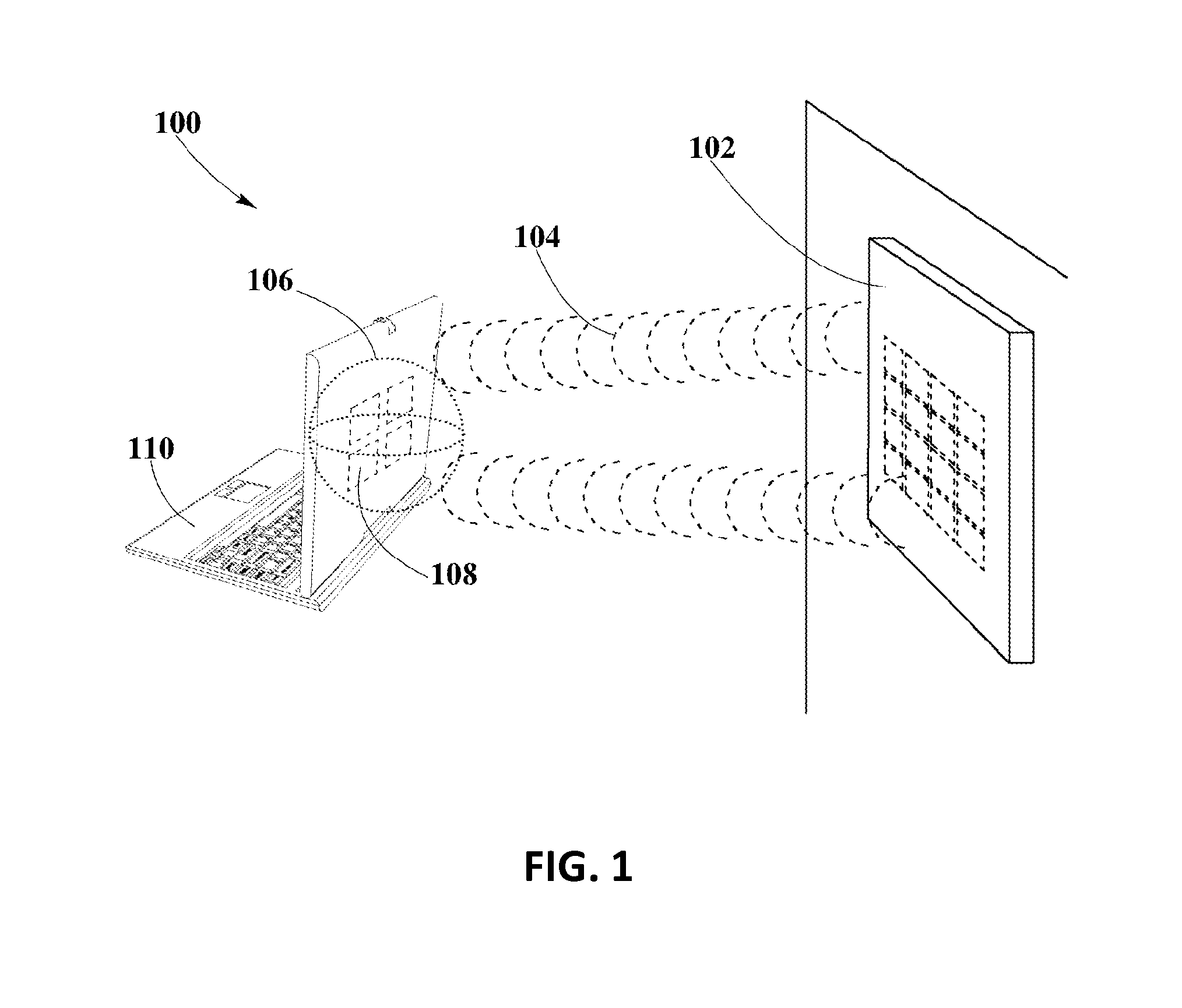
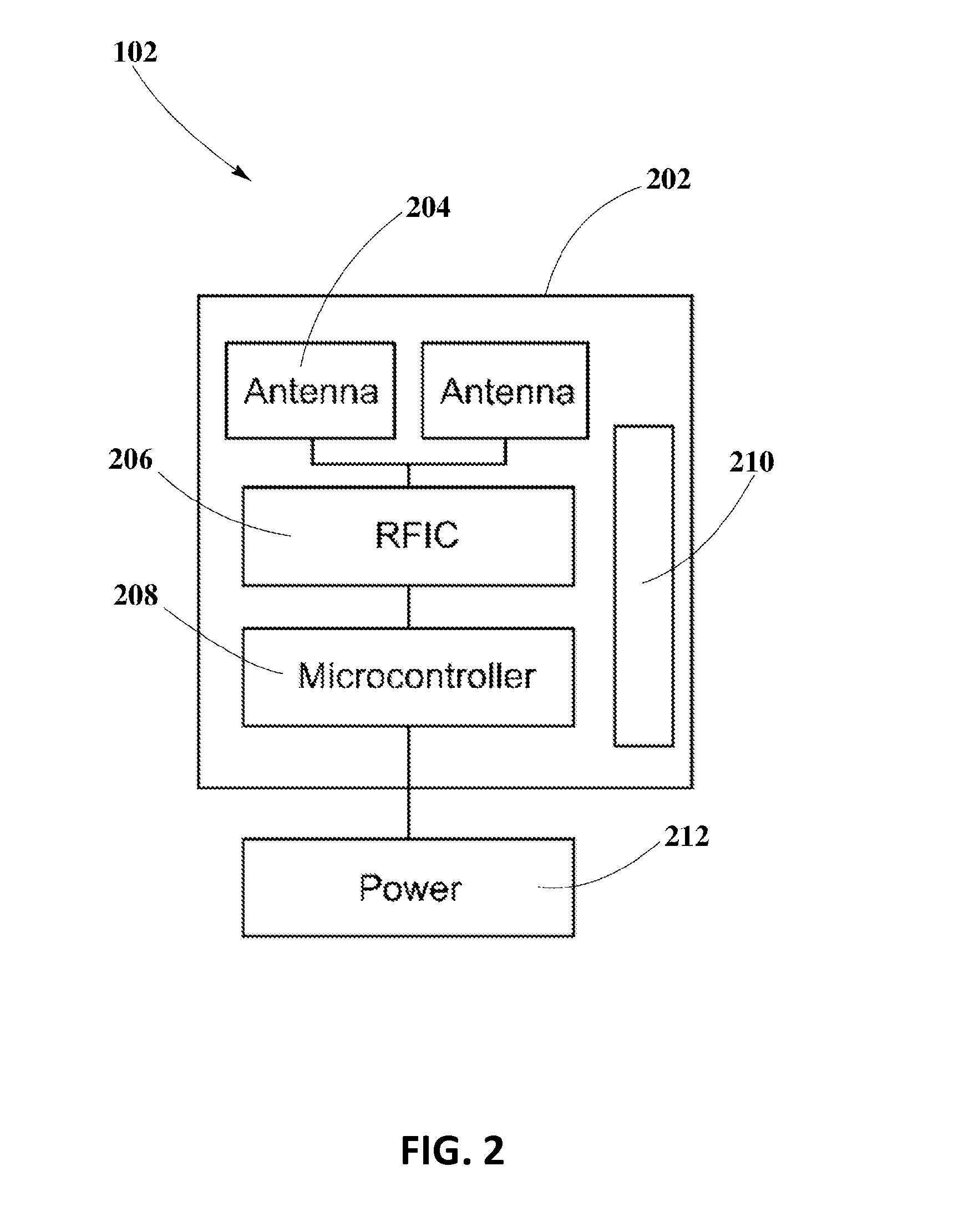
[0018]The present disclosure is here described in detail with reference to embodiments illustrated in the drawings, which form a part here. Other embodiments may be used and / or other changes may be made without departing from the spirit or scope of the present disclosure. The illustrative embodiments described in the detailed description are not meant to be limiting of the subject matter presented here.
Definitions
[0019]As used here, the following terms may have the following definitions:
[0020]“Pocket-forming” refers to generating two or more RF waves that converge in 3-d space, forming controlled constructive and destructive interference patterns.
[0021]“Pockets of energy” refers to areas or regions of space where energy or power may accumulate in the form of constructive interference patterns of RF waves.
[0022]“Transmitter” refers to a device, including a chip which may generate two or more RF signals, at least one RF signal being phase shifted and gain adjusted with respect to othe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com