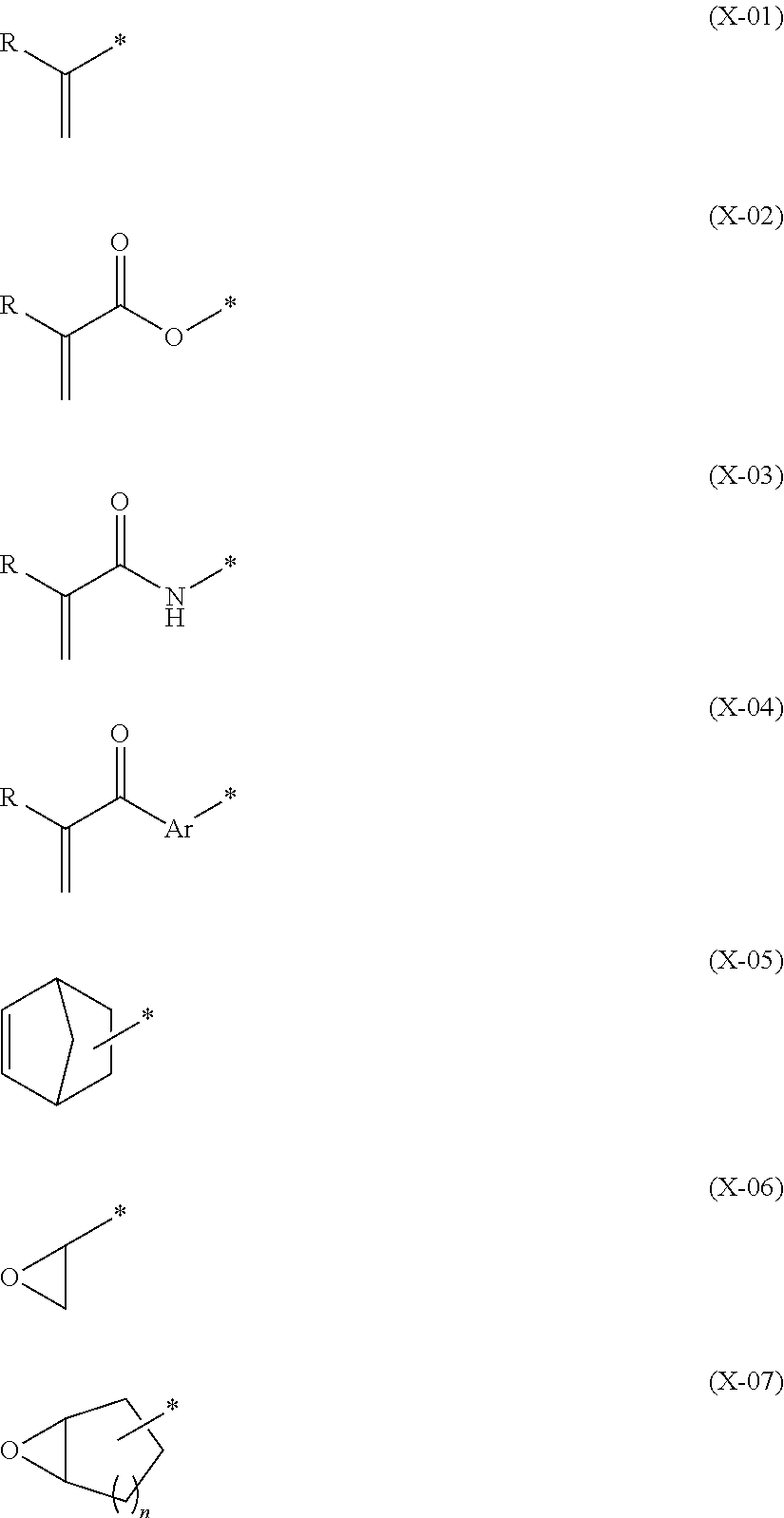
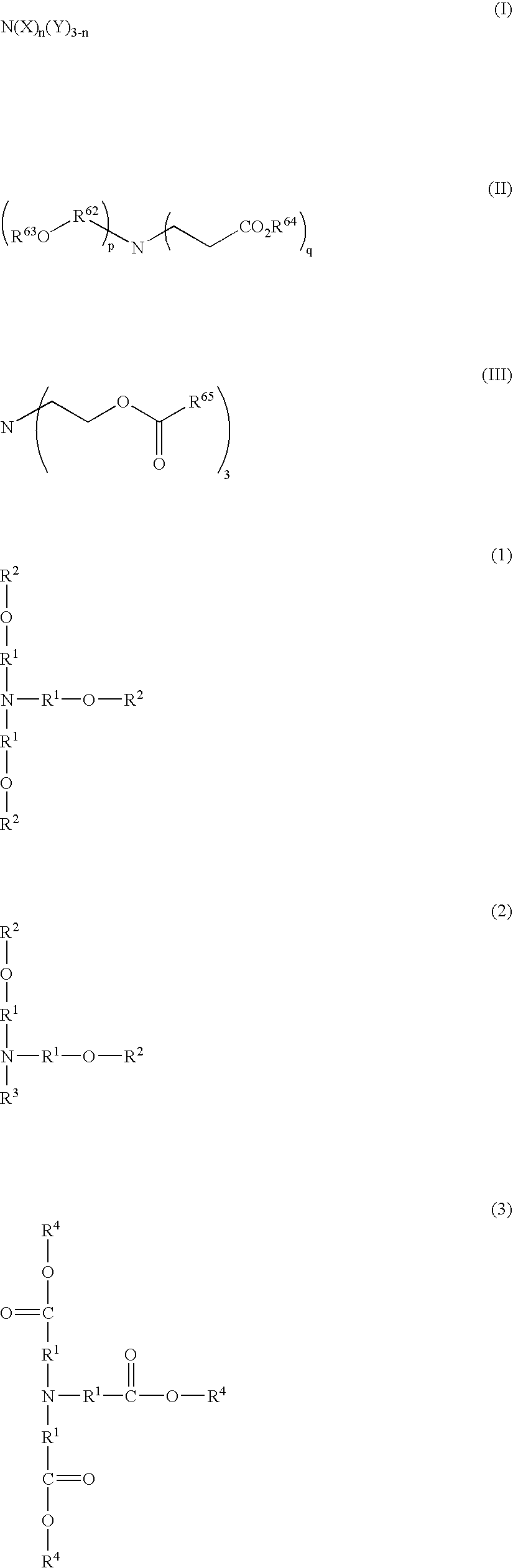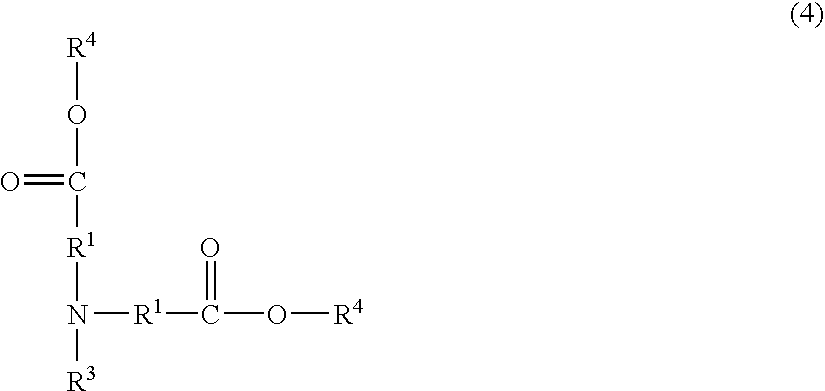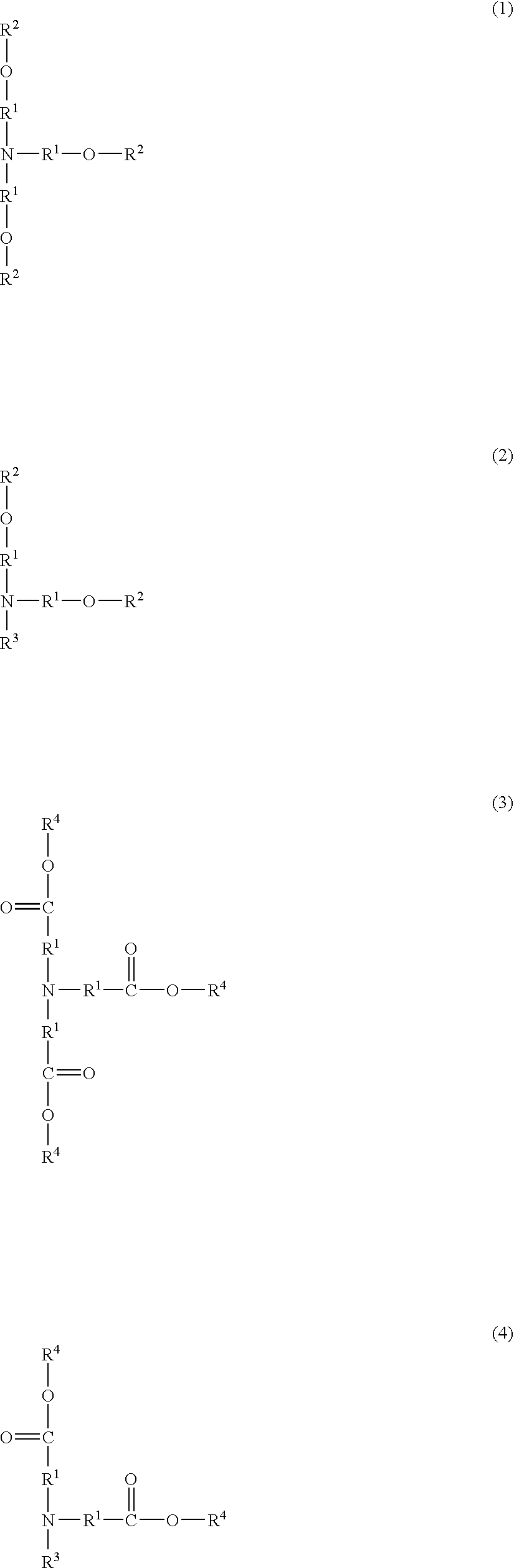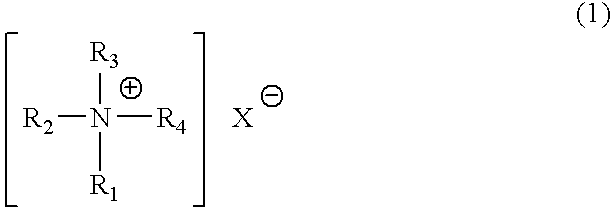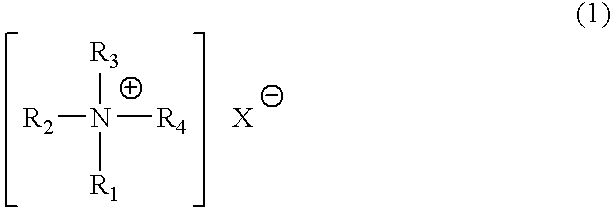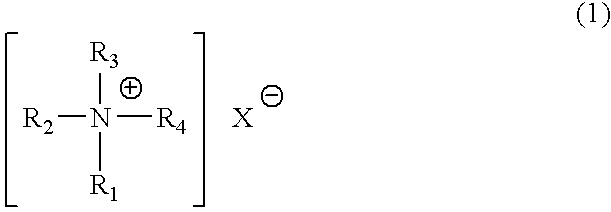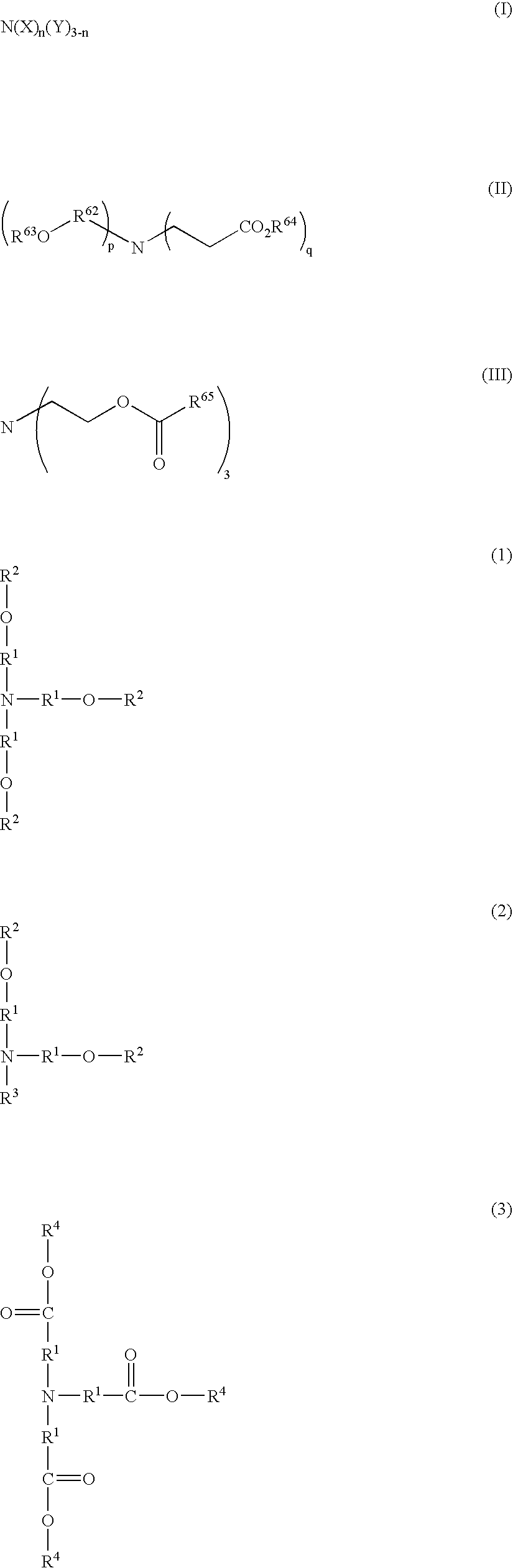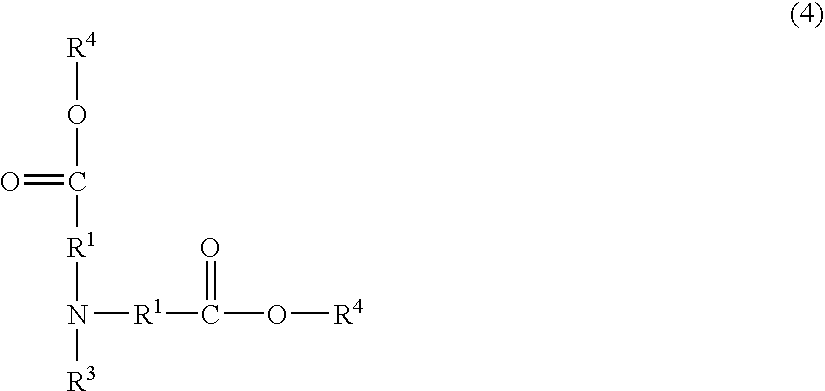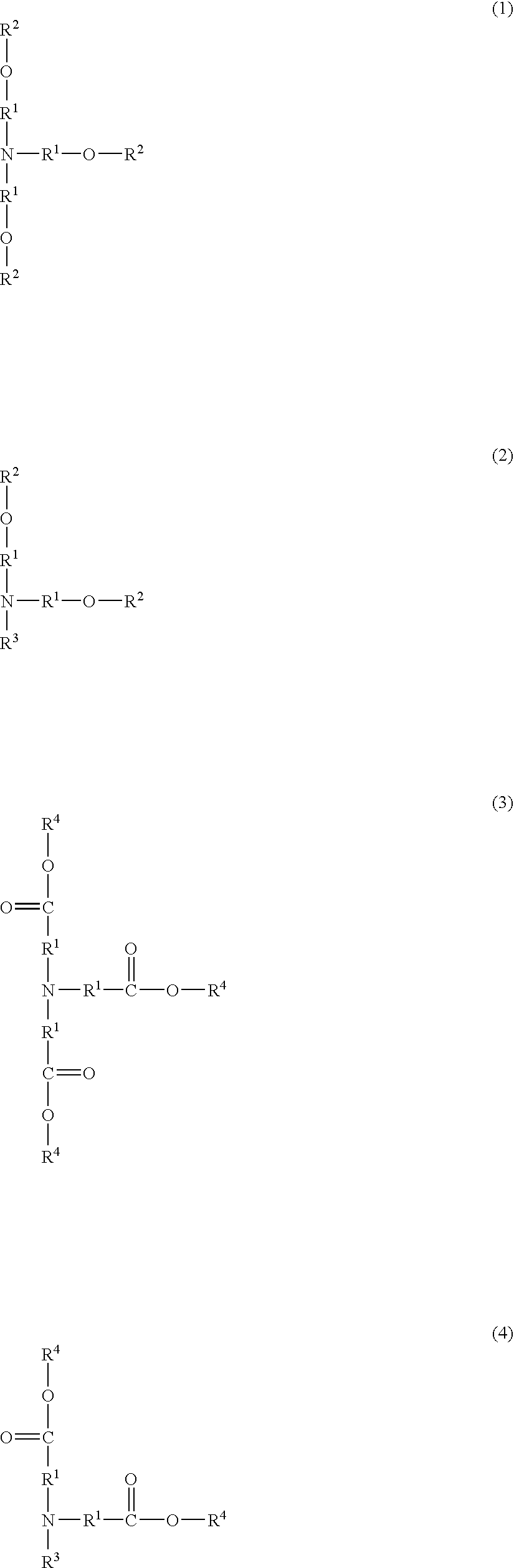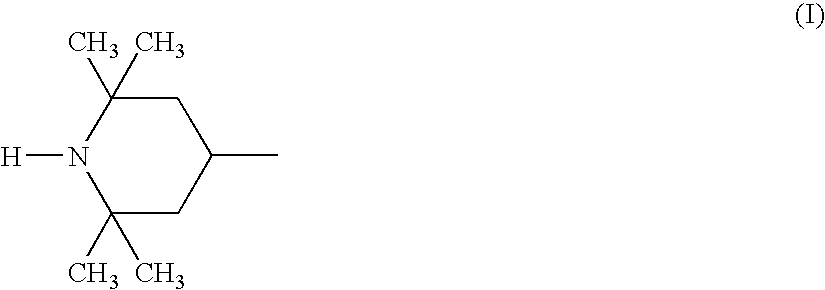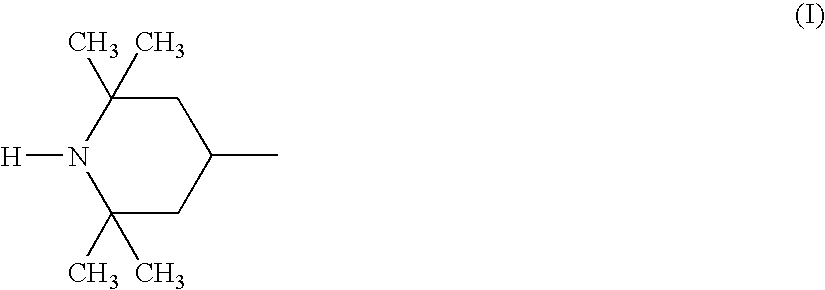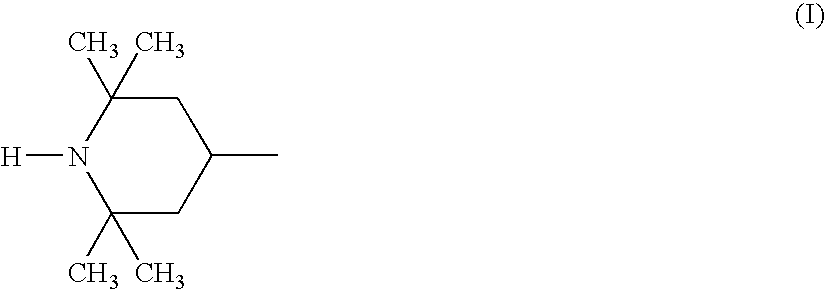Patents
Literature
141 results about "Acid dissociation constant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An acid dissociation constant, Kₐ, (also known as acidity constant, or acid-ionization constant) is a quantitative measure of the strength of an acid in solution. It is the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction HA<=>A⁻+H⁺ known as dissociation in the context of acid–base reactions. The chemical species HA is an acid that dissociates into A⁻, the conjugate base of the acid and a hydrogen ion, H⁺.
Process for converting a hydroxycarboxylic acid, or salts thereof, to an unsaturated carboxylic acid and/or its esters
ActiveUS20090076297A1Preparation from carboxylic acid saltsOrganic compound preparationAmmonium CationIon-exchange resin
A process for converting a salt of a hydroxycarboxylic acid to an unsaturated carboxylic acid, or esters thereof. The process involves converting an ammonium salt of a hydroxycarboxylic acid in aqueous solution to a corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acid and ammonium cation in aqueous solution; and separating the ammonium cation from the aqueous solution, leaving the hydroxycarboxylic acid in aqueous solution. The converting and separating steps may be accomplished by employing a hydrophobic acid or an acid ion exchange resin, each of which must have an acid dissociation constant, i.e., pKa, at least 0.5 less that that of the salt of the hydroxycarboxylic acid. Where a hydrophobic acid is used, it must be immiscible in water, and its salt must also be immiscible in water, and the resulting multi-phase solution comprises an aqueous phase comprising the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acid, as well as a non-aqueous phase comprising a neutralized acid. Alternatively, where the ion exchange resin is used, the aqueous solution of the ammonium salt of a hydroxycarboxylic acid is contacted with the resin, thereby converting the salt to a hydroxycarboxylic acid and capturing the ammonium cations on the resin. In either case, the aqueous solution is treated, such as by heating, to separate and recover the hydroxycarboxylic acid. The non-aqueous phase or resin is treated to separate and recover ammonia useful for preparing additional ammonium salt of a hydroxycarboxylic acid.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
Liquid composition for ink jet, ink set for ink jet, ink jet recording method and ink jet recording apparatus
It is an object to provide a liquid composition for ink jet which contains at least an organic acid having an acid dissociation constant pKa of 4.5 or less, a water-soluble solvent, and water, further comprising at least one of compounds selected from the following group, and this is utilized for an ink set for ink jet, an ink jet recording method and an ink jet recording apparatus, (a): a polyvalent metallic salt having an amount of addition to the organic acid which is equal to or more than 0.01 and is less than 1 in a mole ratio (the polyvalent metallic salt / organic acid); and (b): an organic amine compound having an amount of addition to the organic acid which is equal to or more than 0.1 and is equal to or less than 0.9 in a mole ratio (an organic amine compound / organic acid).
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
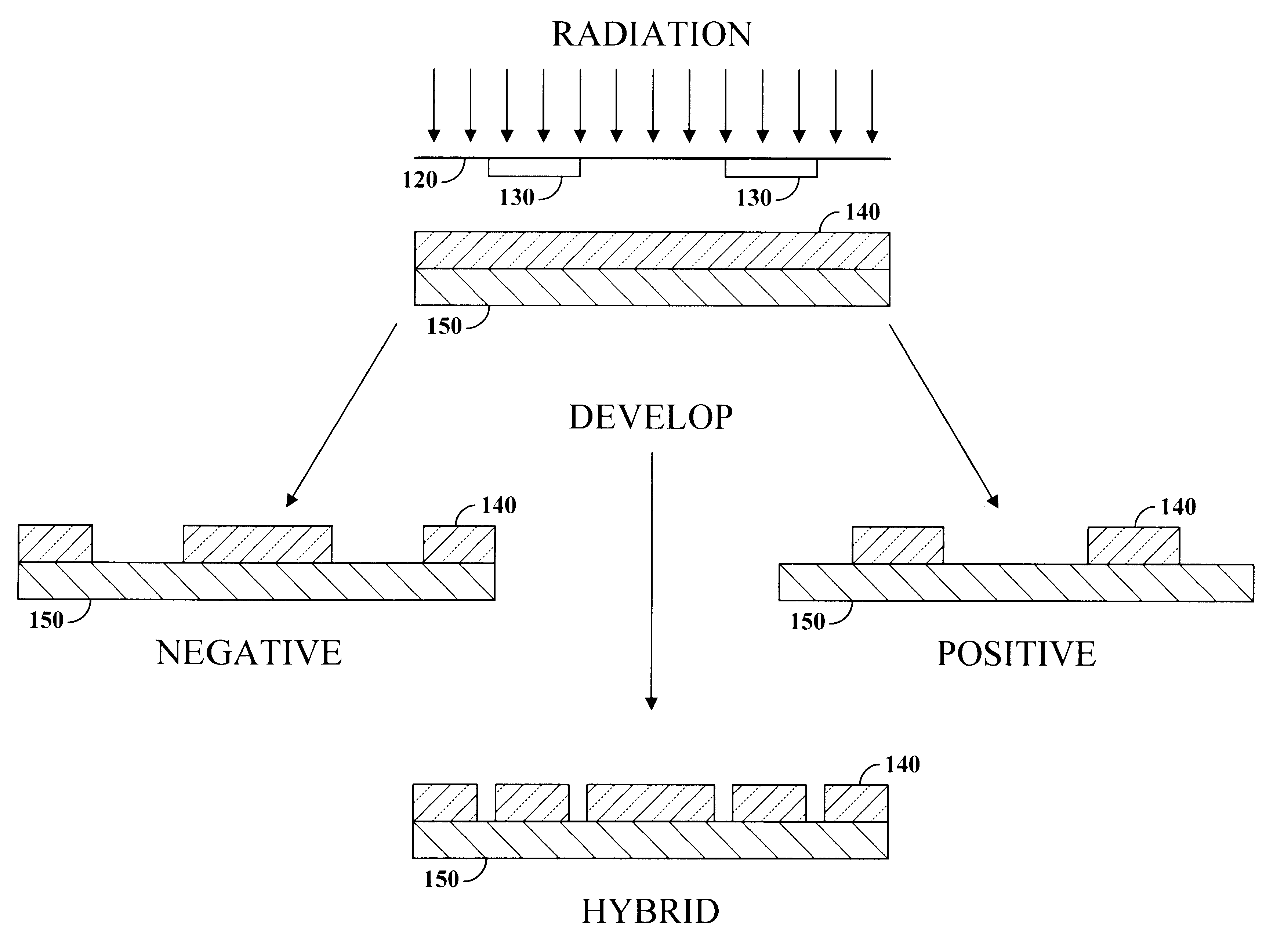
Optimization of space width for hybrid photoresist
InactiveUS6200726B1Optimizing space widthHigh densityPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsResistStrong acids
A photo resist composition contains at least one photoacid generator (PAG), wherein at least two photoacids are produced upon exposure of the photo resist to actinic energy and wherein the photo resist is capable of producing a hybrid response. The function of providing generation of two photoacids in a hybrid resist is to optimize the use of hybrid resist by varying the hybrid space width. The at least two photoacids may differ in their effectiveness at catalyzing at least one mechanism of the hybrid response. In particular, one photoacid may be a weaker acid and another may be a stronger acid, wherein there exists a difference of at least four orders of magnitude between the acid dissociation constant (Ka) of the weaker acid and the stronger acid. A method for optimizing space width in a hybrid photo resist includes the steps of: 1) selecting a desired space width; 2) selecting at least one photoacid generator (PAG), wherein at least two photoacids will be produced upon exposure to actinic energy in relative proportions sufficient to produce the desired space width in the hybrid photo resist; and 3) forming a hybrid photo resist composition comprising the at least one PAG. The step of selecting at least one PAG may include first determining the space width produced alone by each photoacid in a group of candidate photoacids and then selecting the photoacids and corresponding at least one PAG that will produce the desired space width.
Owner:IBM CORP
Toner and process for producing toner
A toner having a toner particle which contains a binder resin, a fatty acid metal salt, and a resin having an ionic functional group, in which the fatty acid metal salt is a fatty acid metal salt of a polyvalent metal with valency of 2 or higher and a fatty acid with carbon atom number of at least 8 and not more than 28, and the acid dissociation constant pKa of the resin having an ionic functional group is at least 6.0 and not more than 9.0.
Owner:CANON KK
Protective film of polarizer, polarizer and liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS20110134374A1Increased durabilityIncrease pointsOrganic non-macromolecular adhesiveCoatingsOrganic acidSolubility
A protective film of polarizer comprising an organic acid that has a solubility in water at 25° C. of at most 0.1% by mass and has an acid dissociation constant in a mixed solvent of tetrahydrofuran / water=6 / 4 by volume at 25° C. of from 2 to 7 can improve polarizer durability.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Resist composition
InactiveUS6916593B2Small sizeReduce film thicknessRadiation applicationsDiazo compound compositionsResistChemical compound
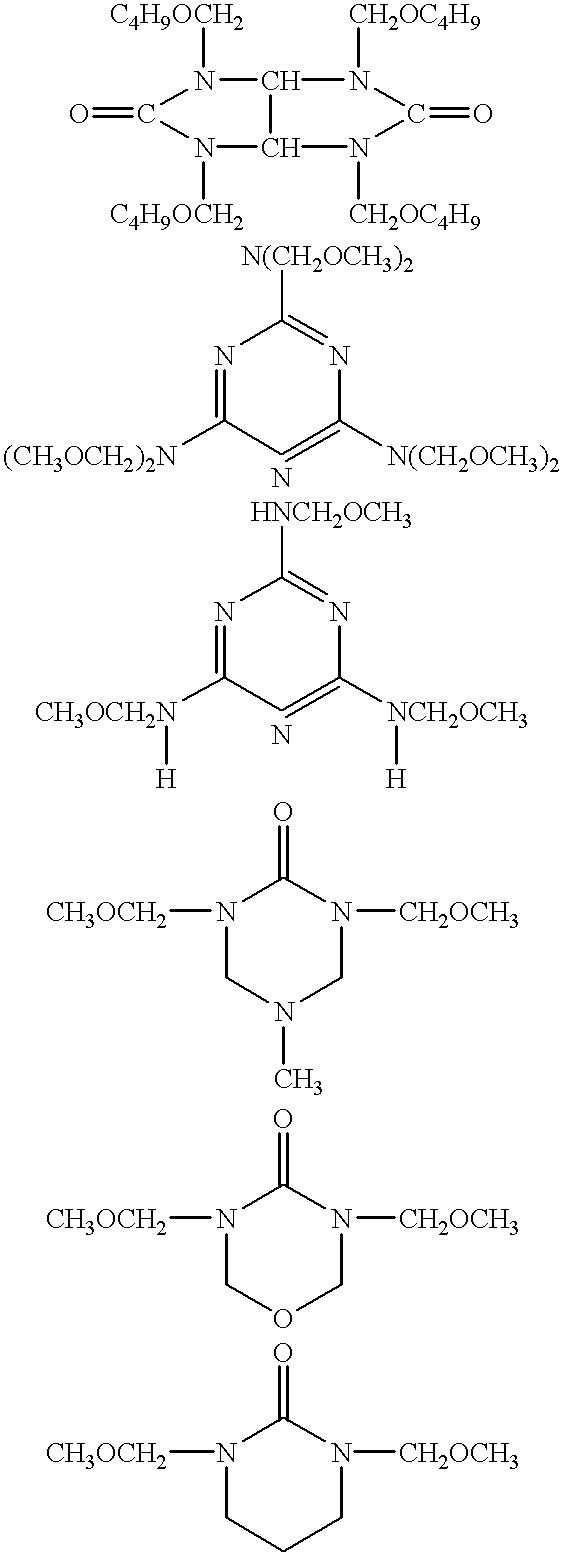
Although use of a nitrogen-containing compound as a basic compound component of a resist composition makes it possible to ease the T-top problem at an acid dissociation constant pKa falling within a range of 2 to 6, it is accompanied with the problem that the reaction, that is, acid diffusion upon use of a highly-reactive acid-labile group cannot be controlled. In order to overcome this problem, one or more basic compounds selected from those represented by the following formulas (I) to (III) and (1) to (4) are employed.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Method for producing toner particle
ActiveUS9423708B2High charging stability and durabilityDevelopersHigh humidityHydrogen-Ion Concentrations
A method for producing a toner particle having high charging stability and durability under environments at high temperature and high humidity is provided.A method for producing a toner particle including an step of adhering a resin particle to surface of a toner base particle containing a binder resin and a colorant in an aqueous medium, wherein the resin particle contain a resin having an ionic functional group and having an acid dissociation constant pKa of 6.0 or more and 9.0 or less, and the pH (hydrogen ion concentration) of the aqueous medium is equal to or greater than pKa of the resin particle−2.0.
Owner:CANON KK
Catalyst composition for production of rigid polyurethane foam and isocyanurate-modified rigid polysurethane foam and raw-material composition containing the same
An object of the present invention is to provide a catalyst for producing a rigid polyurethane foam and an isocyanurate-modified rigid polyurethane foam excellent in storage stability in the case that water is contained as a blowing agent, and a raw material-blended composition using the same. In the present invention, a catalyst composition comprising the following amine compounds of (A) and (B) and / or (C) is used and further, a raw material-blended composition further containing a polyol component and water is used. (A) A quaternary ammonium salt represented by the following general formula (1): wherein each of R1 to R3 represents a hydrocarbon group having 1 to 12 carbon atoms, R4 represents an alkyl group or an aromatic hydrocarbon group having 1 to 18 carbon atoms, and X represents an organic acid group having an acid dissociation constant (pKa) of 4.8 or less; (B) A hydrophobic amine compound; (C) A heterocyclic tertiary amine compound.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
Resist composition
InactiveUS20040106063A1High rectangularityImprove reducibilityRadiation applicationsDiazo compound compositionsResistChemical compound
Although use of a nitrogen-containing compound as a basic compound component of a resist composition makes it possible to ease the T-top problem at an acid dissociation constant pKa falling within a range of 2 to 6, it is accompanied with the problem that the reaction, that is, acid diffusion upon use of a highly-reactive acid-labile group cannot be controlled. In order to overcome this problem, one or more basic compounds selected from those represented by the following formulas (I) to (III) and (1) to (4) are employed.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
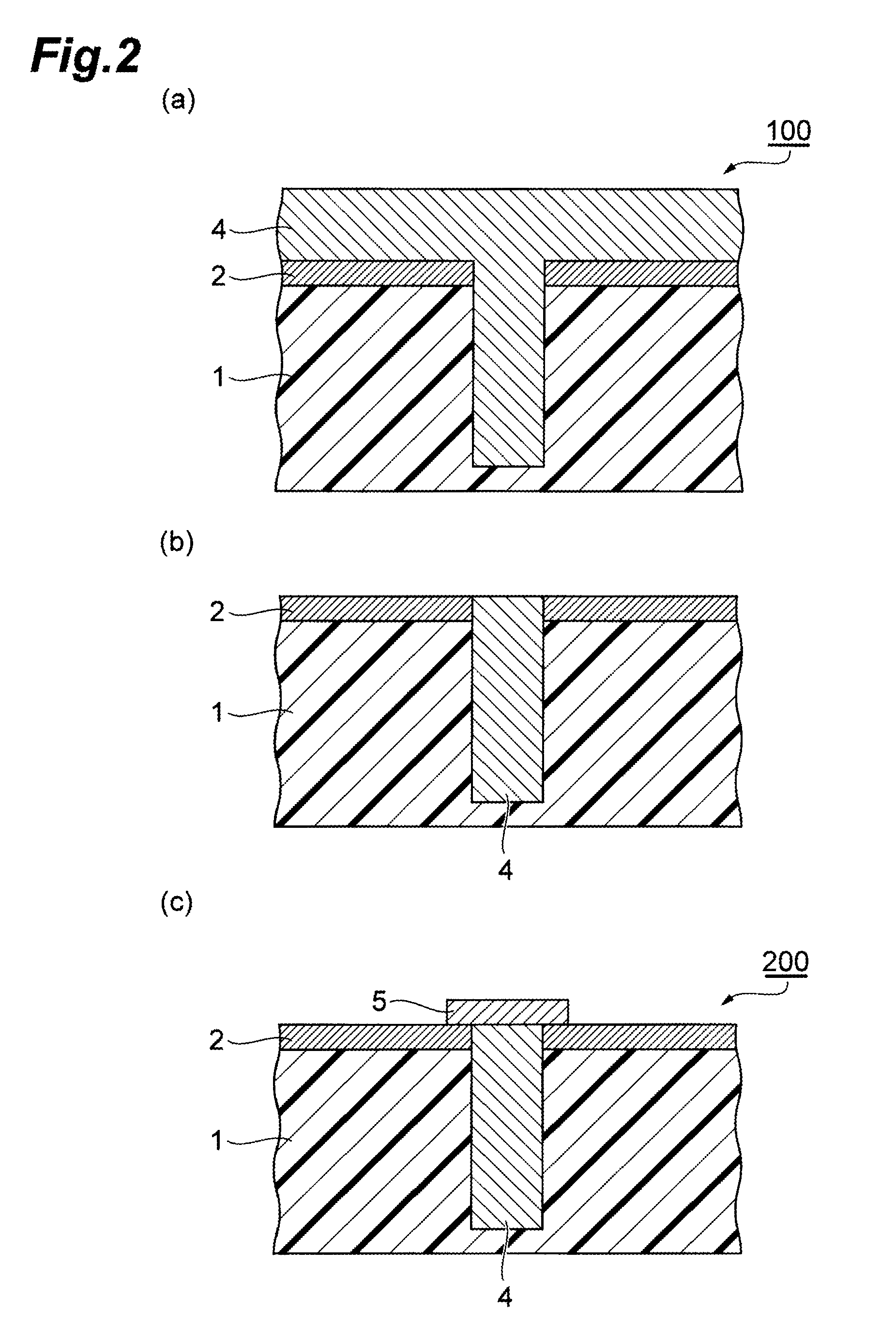
Semiconductor device manufacturing method and substrate processing apparatus
ActiveUS20100210118A1Reduce the temperatureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingElectronegativityPyridine
A thin film can be formed on a substrate at a low temperature with a practicable film-forming rate. There is provided a semiconductor device manufacturing method for forming an oxide or nitride film on a substrate. The method comprises: exposing the substrate to a source gas; exposing the substrate to a modification gas comprising an oxidizing gas or a nitriding gas, wherein an atom has electronegativity different from that of another atom in molecules of the oxidizing gas or the nitriding gas; and exposing the substrate to a catalyst. The catalyst has acid dissociation constant pKa in a range from 5 to 7, but a pyridine is not used as the catalyst.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Negative resist composition, method of forming resist pattern, and complex
ActiveUS20150192851A1Good time stabilityHigh light absorptionPhotosensitive materialsElectric discharge tubesResistHafnium
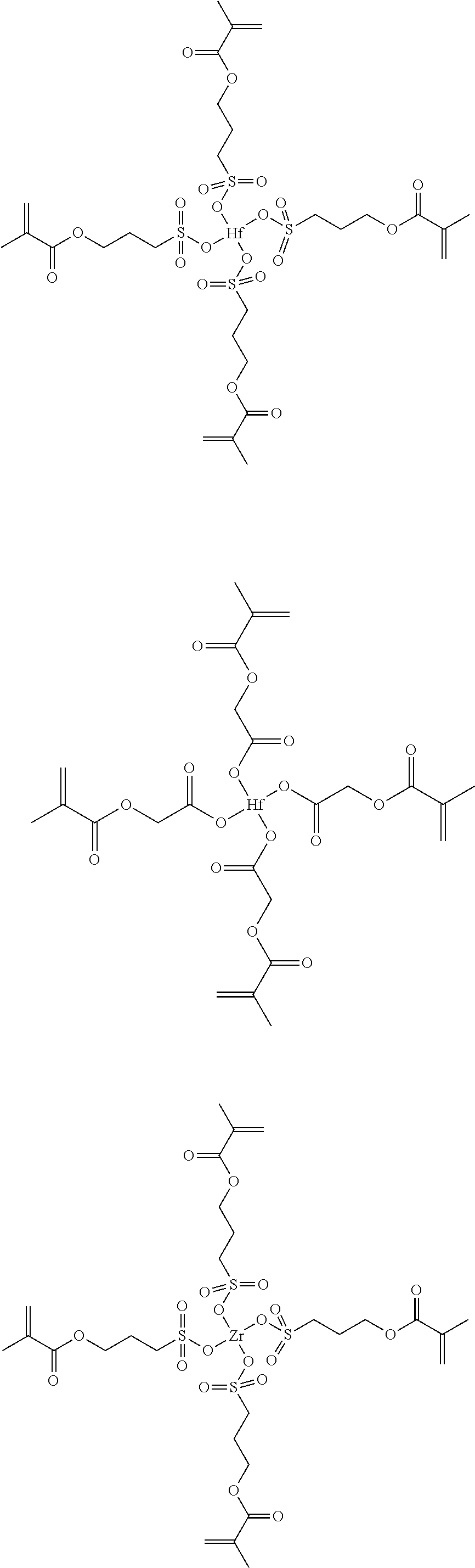
A negative resist composition including a complex represented by the general formula (1); and a polymerization initiator. in which M represents hafnium (Hf) or zirconium (Zr), X represents a ligand including a conjugate base of an acid which has an acid dissociation constant (pKa) of 3.8 or less and has a polymerizable group, Y represents a ligand having no polymerizable group, and n represents an integer of 1 to 4.[MXnY4-n] (1)
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Coated preparation
ActiveUS20100166853A1Increase maximum blood concentration and AUCReduce deviationBiocideMetabolism disorderSolubilityBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention provides a preparation containing pioglitazone or a salt thereof as an active ingredient, which shows high bioavailability of pioglitazone and less interindividual variation in blood drug concentration, as well as a preparation with suppressed color change during preservation. The preparation contains a core containing a pharmaceutically acceptable organic acid with water solubility at 20° C. of not less than 10 mg / mL and pKa1 (a negative common logarithm of the first acid dissociation constant Ka1) at 25° C. of not more than 5, and a coating layer containing pioglitazone or a salt thereof. The coating layer may further contain mannitol or trehalose.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Technological method for producing inorganic fibers from red mud
The invention discloses a technological method for producing inorganic fibers from red mud and belongs to the field of comprehensive utilization of the red mud. According to the technological method, a curing agent and an acidity coefficient modifier are added to the red mud, a mixture and coke are molten at the high temperature, element resources including Si, Ca, Fe, Al, Na and Mg in the red mud, the curing agent and the acidity coefficient modifier are sufficiently utilized, the red mud is taken as a main material for production of the inorganic fibers, the ratio of the dosage of the red mud can be higher than 70%, red mud pollution is effectively treated, the produced inorganic fibers reach the level of rock wool, and economic, social and environmental benefits are remarkable. The technology is simple, the production cost is low, and large-scale production of the red mud for comprehensive utilization can be realized.
Owner:张勇
Polishing composition for semiconductor wafer, production method thereof, and polishing method
InactiveUS20080038996A1Conductivity adjustablePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesColloidal silicaSilicic acid
A polishing composition for semiconductor wafers containing colloidal silica is disclosed, wherein the colloidal silica is prepared from an active silicic acid aqueous solution obtained by removing alkali from an alkali silicate aqueous solution and a quaternary ammonium base, and is stabilized with a quaternary ammonium base. The polishing composition contains no alkali metals. The polishing composition contains a buffer solution that is a combination of a weak acid having a pKa from 8.0 to 12.5 at 25° C. (pKa is a logarithm of the reciprocal of acid dissociation constant) and a quaternary ammonium base, and exhibits a buffer action in the range from pH8 to pH11.
Owner:NIPPON CHECMICAL IND CO LTD +1
Metal oxide etching solution and an etching method
InactiveUS20150075850A1Suppress reprecipitationIncrease solution lifeZinc oxides/hydroxidesGallium/indium/thallium compoundsDisplay deviceFlat panel display
The object of the present invention is to provide an etching solution composition for etching a metal oxide containing In and a metal oxide containing Zn and In used as a transparent electrode or an oxide semiconductor of an electronic device such as a semiconductor element or a flat panel display (FPD), the etching solution composition being controllable to give a practical etching rate, having high dissolving power toward Zn, and enabling a long solution life due to suppressed variation of the formulation during use. The object is solved by an etching solution composition that enables microfabrication to be carried out for a metal oxide containing In and a metal oxide containing Zn and In used as a transparent electrode or an oxide semiconductor of an electronic device such as a semiconductor element or an FPD, the composition containing water and at least one type of acid, excluding hydrohalic acids, perhalic acids, etc., having an acid dissociation constant pKan at 25° C. in any dissociation stage of no greater than 2.15, and the composition having a pH at 25° C. of no greater than 4, and an etching method using the etching solution composition.
Owner:KANTO CHEM CO INC
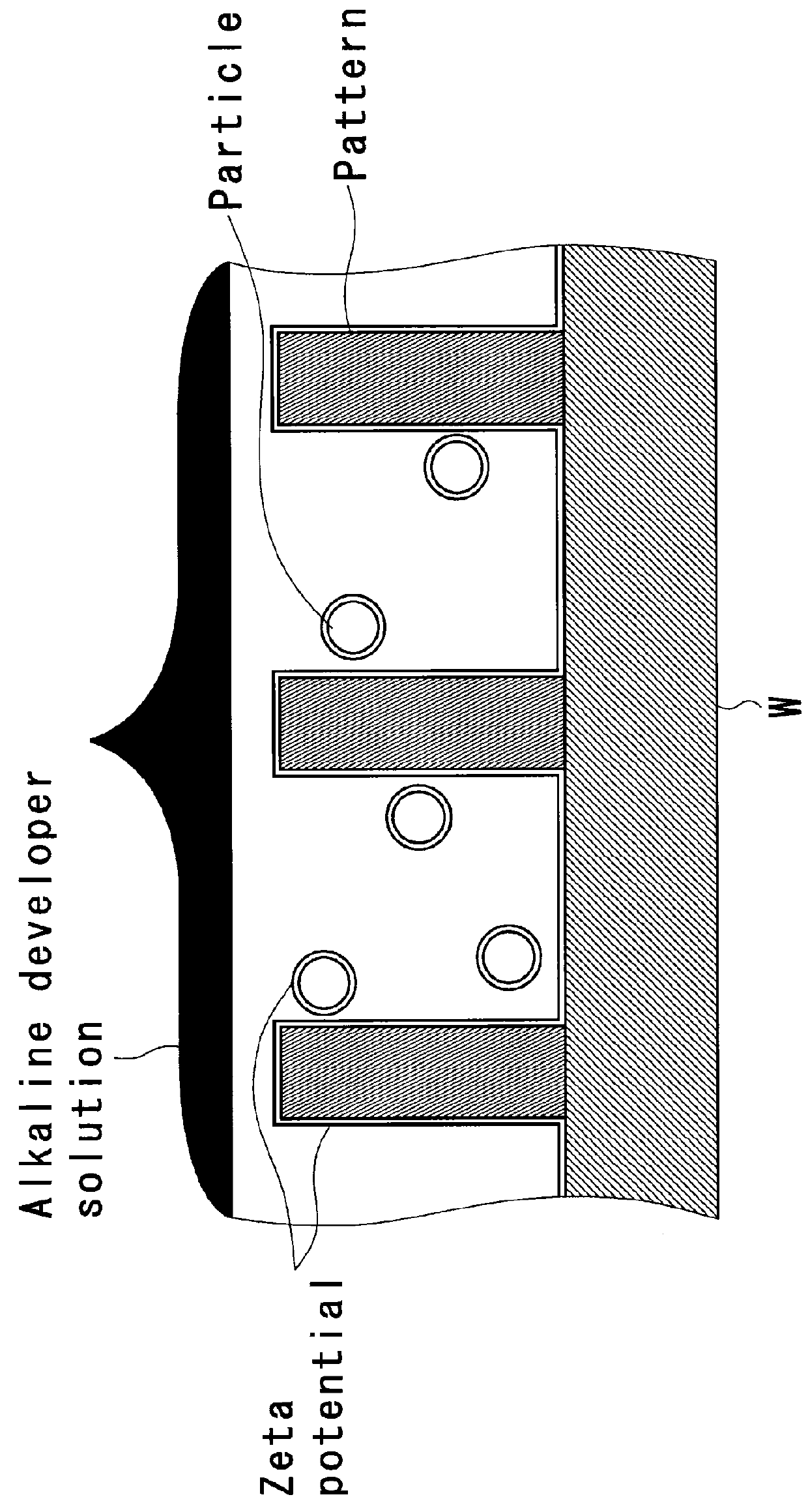
Polishing composition, polishing method using same, and method for producing substrate
ActiveCN104285284AOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingColloidal silicaZeta potential
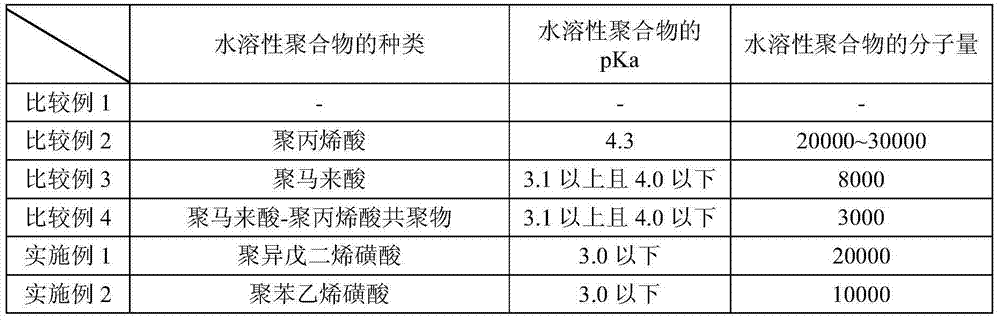
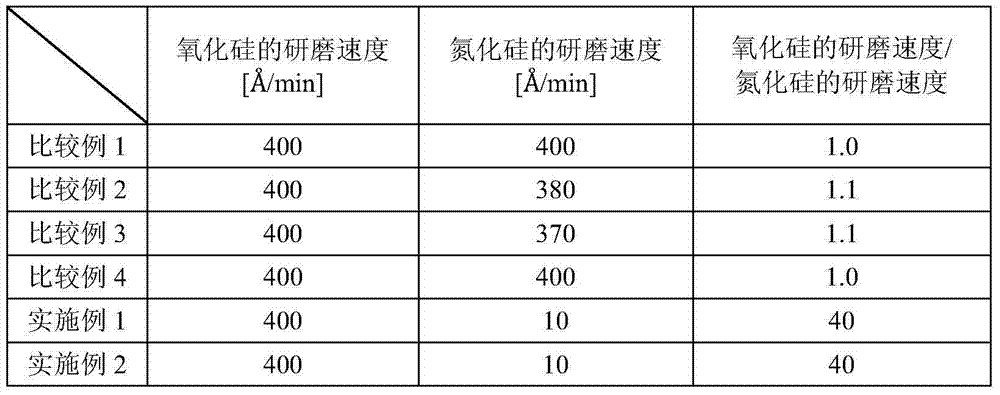
This polishing composition contains an abrasive grit and a water-soluble polymer. The water-soluble polymer is an anionic compound having an acid dissociation constant (pKa) of no greater than 3. Cited as specific examples of such a compound are polyvinyl sulfonic acid, polystyrene sulfonic acid, polyallyl sulfonic acid, polyacrylic acid ethyl sulfonic acid, polyacrylic acid butyl sulfonic acid, poly(2-acrylamide-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid), and polyisoprene sulfonic acid. The abrasive grit exhibits a negative zeta potential at a pH of 3.5 and lower. Colloidal silica can be cited as a specific example of such an abrasive grit.
Owner:FUJIMI INCORPORATED
Negative-type photosensitive resin composition, cured film, display device provided with cured film, and production method therefor
ActiveUS20190072851A1High sensitivityExcellent halftone characteristicSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNegative typeDisplay device
The present invention provides a negative type photosensitive resin composition having high sensitivity, excellent halftone characteristics, capability to form a small tapered pattern shape, and alkali-developability.The negative type photosensitive resin composition includes, as an alkali-soluble resin (A), at least a weakly acidic group-containing resin (A1) and an unsaturated group-containing resin (A2), the weakly acidic group-containing resin (A1) containing an acidic group having an acid dissociation constant in the range of 13.0 to 23.0 in dimethyl sulfoxide, and the unsaturated group-containing resin (A2) containing an ethylenically unsaturated double bond group.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Abrading agent and abrading method
ActiveUS20110300778A1Reduce surface roughnessIncrease polishing speedOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic acidPotassium hydroxide
A polishing agent which comprises a composition containing an inorganic acid, an amino acid, a protective film-forming agent, an abrasive, an oxidizing agent, an organic acid and water, adjusted to a pH of 1.5-4, wherein the amount of potassium hydroxide required to raise the pH of the composition without the organic acid to 4 is at least 0.10 mol with respect to 1 kg of the composition without the organic acid, and the organic acid contains at least two carboxyl groups, wherein the logarithm of the inverse of the first acid dissociation constant (pKa1) is no greater than 3.
Owner:RESONAC CORP
Resist composition and method of forming resist pattern
ActiveUS20160363860A1Easy to controlGood lithography performancePhotomechanical exposure apparatusPhotosensitive material processingSolubilityCombinatorial chemistry
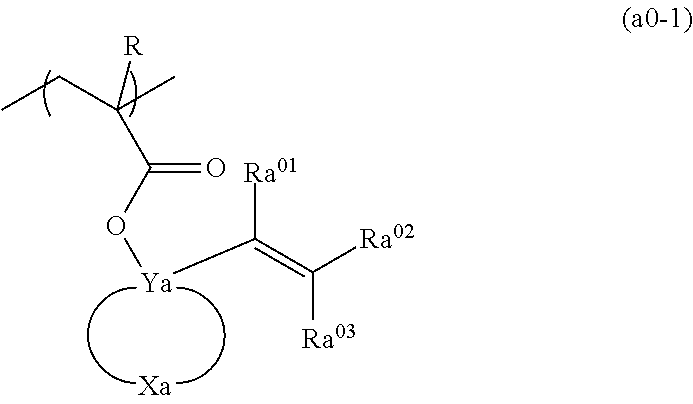
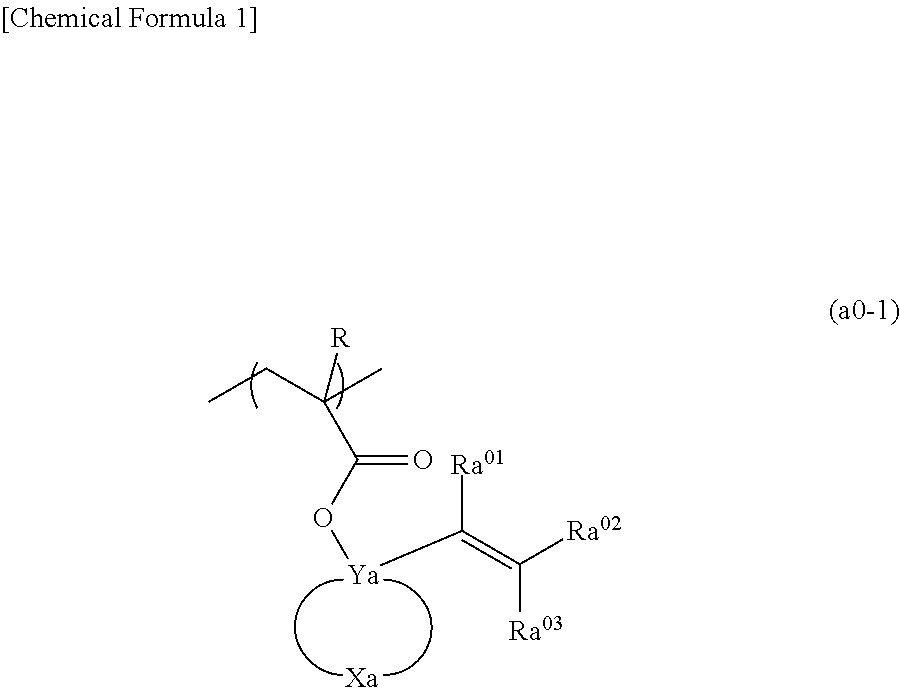
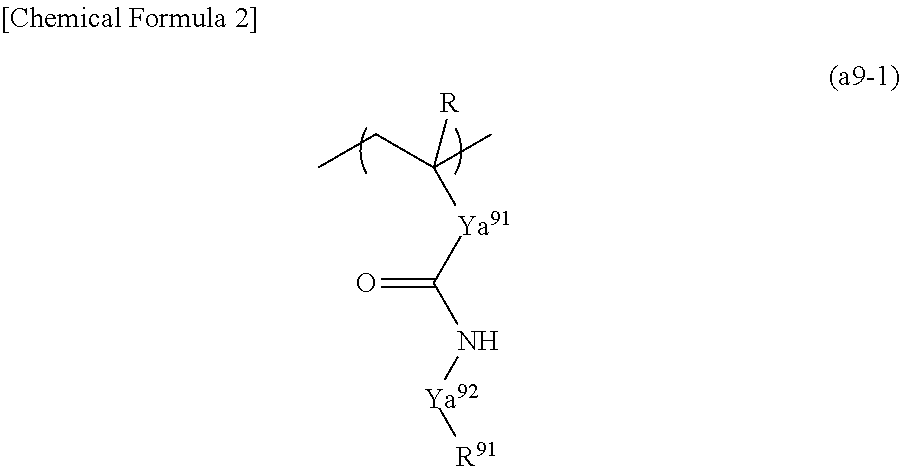
A resist composition which generates acid upon exposure and exhibits changed solubility in a developing solution under action of acid, including a base component which exhibits changed solubility in a developing solution under action of acid and an acid diffusion control agent, the base component including a structural unit represented by general formula (a0-1) shown below in which R represents H, C1-C5 alkyl group or C1-C5 halogenated alkyl group; Ya represents C; Xa represents a group which forms a divalent cyclic hydrocarbon group with Ya; Ra01 to Ra03 represents H, C1-C10 monovalent saturated chain hydrocarbon group or C3-C20 monovalent saturated cyclic hydrocarbon group; the acid diffusion control agent containing an acid which exhibits an acid dissociation constant of 1.5 or more.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Metal-compound-removing solvent and method in lithography
ActiveUS20180039182A1Detergent mixture composition preparationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolubilityLithography process
A photoresist layer is coated over a wafer. The photoresist layer includes a metal-containing material. An extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography process is performed to the photoresist layer to form a patterned photoresist. The wafer is cleaned with a cleaning fluid to remove the metal-containing material. The cleaning fluid includes a solvent having Hansen solubility parameters of delta D in a range between 13 and 25, delta P in a range between 3 and 25, and delta H in a range between 4 and 30. The solvent contains an acid with an acid dissociation constant less than 4 or a base with an acid dissociation constant greater than 9.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Solid electrolyte composition, electrode sheet for battery and all-solid-state secondary battery in which solid electrolyte composition is used, and method for manufacturing solid electrolyte composition
ActiveUS20160359195A1Preventing decrease of ion conductanceImprove bindingSolid electrolytesFinal product manufactureAll solid stateElectrolyte composition
Provided is a solid electrolyte composition including nonspherical polymer particles; a dispersion medium; and an inorganic solid electrolyte, in which the nonspherical polymer particles is formed of a polymer having at least one of a specific functional group, an acidic group having an acid dissociation constant pKa of 14 or less, or a basic group having a conjugate acid pKa of 14 or less.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Toner and toner manufacturing method
ActiveUS10295922B2Excellent tinting strength and transferabilityDevelopersHydroxide potassiumPigment dispersion
A toner containing a toner particle including a binder resin, a resin A having a pKa of 6.0-9.0, and a pigment having a pKb of 4.0-7.0, wherein the pKa is an acid dissociation constant measured by preparing a resin solution in which 1.0 part by mass of the resin A, 70.0 parts by mass of toluene and 30.0 parts by mass of ethanol are mixed, and carrying out neutralization titration with a potassium hydroxide ethanol solution of 0.1 mol / L, and the pKb is a basic dissociation constant measured by preparing a pigment dispersion in which 10.0 parts by mass of the pigment, 140.0 parts by mass of toluene and 60.0 parts by mass of ethanol are mixed, and carrying out neutralization titration with a hydrochloric acid ethanol solution of 0.1 mol / L.
Owner:CANON KK
Polyolefin resin composition and foam molded article
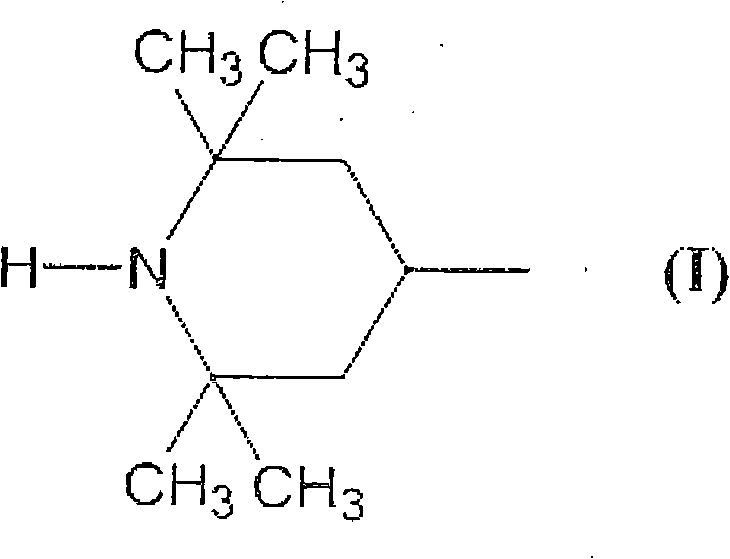
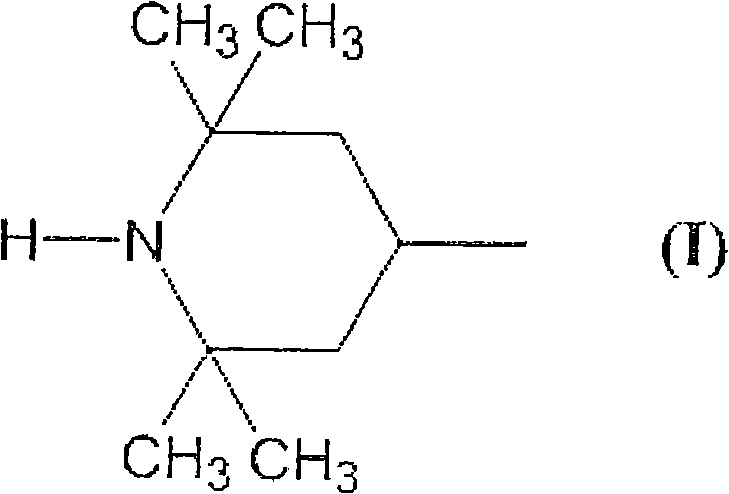
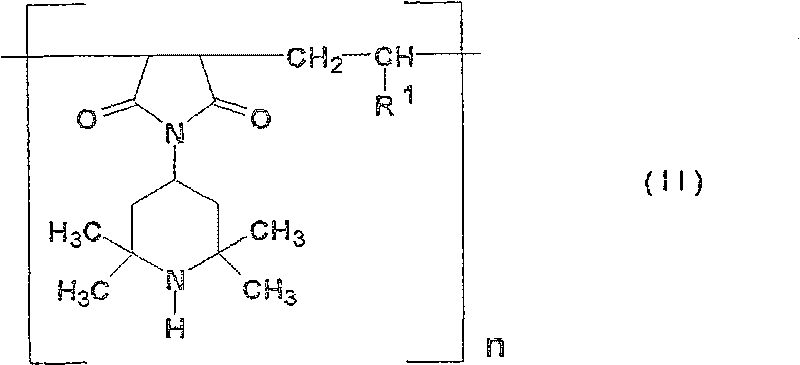
A resin composition, comprising (A) a polyolefin resin, (B) a foaming agent, (C) a black pigment, and 0.05 to 5 parts by mass of (D) a hindered amine light stabilizer which satisfies the following requirements (a) and (b), provided that the content of the polyolefin resin (A) is let be 100 parts by mass:requirement (a): having a 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidyl group represented by formula (I) that is attached to any of a carbon atom, an oxygen atom and a nitrogen atom:requirement (b): having an acid dissociation constant (pKa) of less than 8.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Liquid composition for ink jet, ink set for ink jet, ink jet recording method and ink jet recording apparatus
It is an object to provide a liquid composition for ink jet which contains at least an organic acid having an acid dissociation constant pKa of 4.5 or less, a water-soluble solvent, and water, further including at least one of compounds selected from the following group, and this is utilized for an ink set for ink jet, an ink jet recording method and an ink jet recording apparatus,(a): a polyvalent metallic salt having an amount of addition to the organic acid which is equal to or more than 0.01 and is less than 1 in a mole ratio (the polyvalent metallic salt / organic acid); and(b): an organic amine compound having an amount of addition to the organic acid which is equal to or more than 0.1 and is equal to or less than 0.9 in a mole ratio (an organic amine compound / organic acid).
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Absorber and absorbent article using the same
ActiveCN104125839AEasy to deodorizePharmaceutical delivery mechanismAbsorbent padsCrosslinked polymersSURFACTANT BLEND
To provide an absorbent body and an absorbent article having excellent deodorization effect. The present invention provides an absorber comprising, a crosslinked polymer mainly composed of acrylic acid and having carboxyl groups thereof being at least partially neutralized as a water-absorbent resin powder, and an antibacterial cationic surfactant, wherein the antibacterial cationic surfactant is a compound neutralized with an acid having an acid dissociation constant pKa in water at 25 degrees centigrade in a range from 3.0 to 5.5.
Owner:LIVEDO CORP
Membrane-electrode-assembly and fuel cell
InactiveUS20130052560A1Lower internal resistanceImprove the immunityCell electrodesFinal product manufacturePolymer electrolytesPolymer science
A membrane-electrode-assembly contains two or more types of solid polymer electrolytes having different acid dissociation constants in an electrode catalyst layer, a solid polymer electrolyte of small acid strength covers the surface of a catalyst, and a solid polymer electrolyte of large acid strength is disposed to the periphery thereof, which makes the resistance to dissolving of the catalyst metal and the ion conductivity in the catalyst electrode layer compatible.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
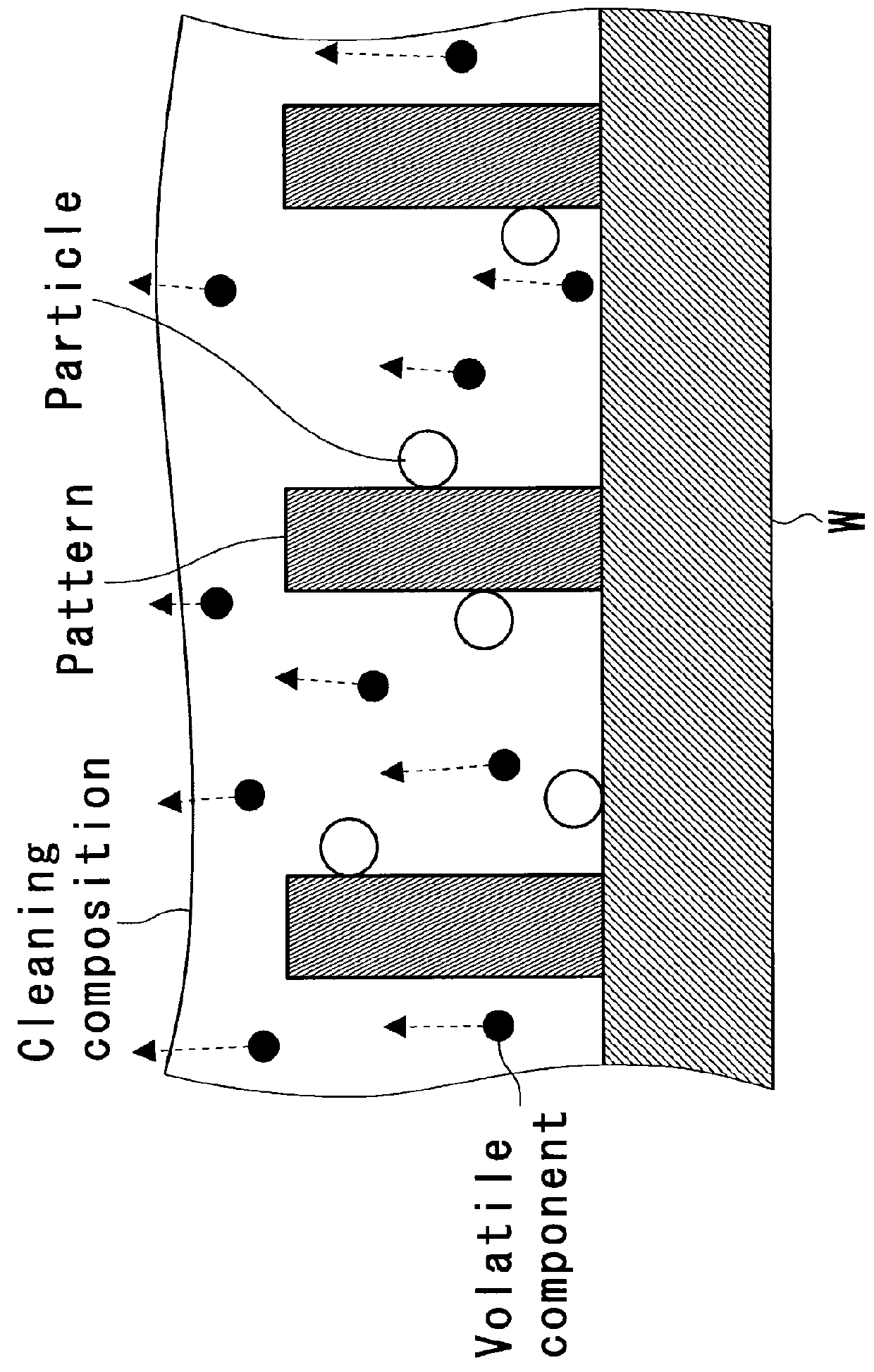
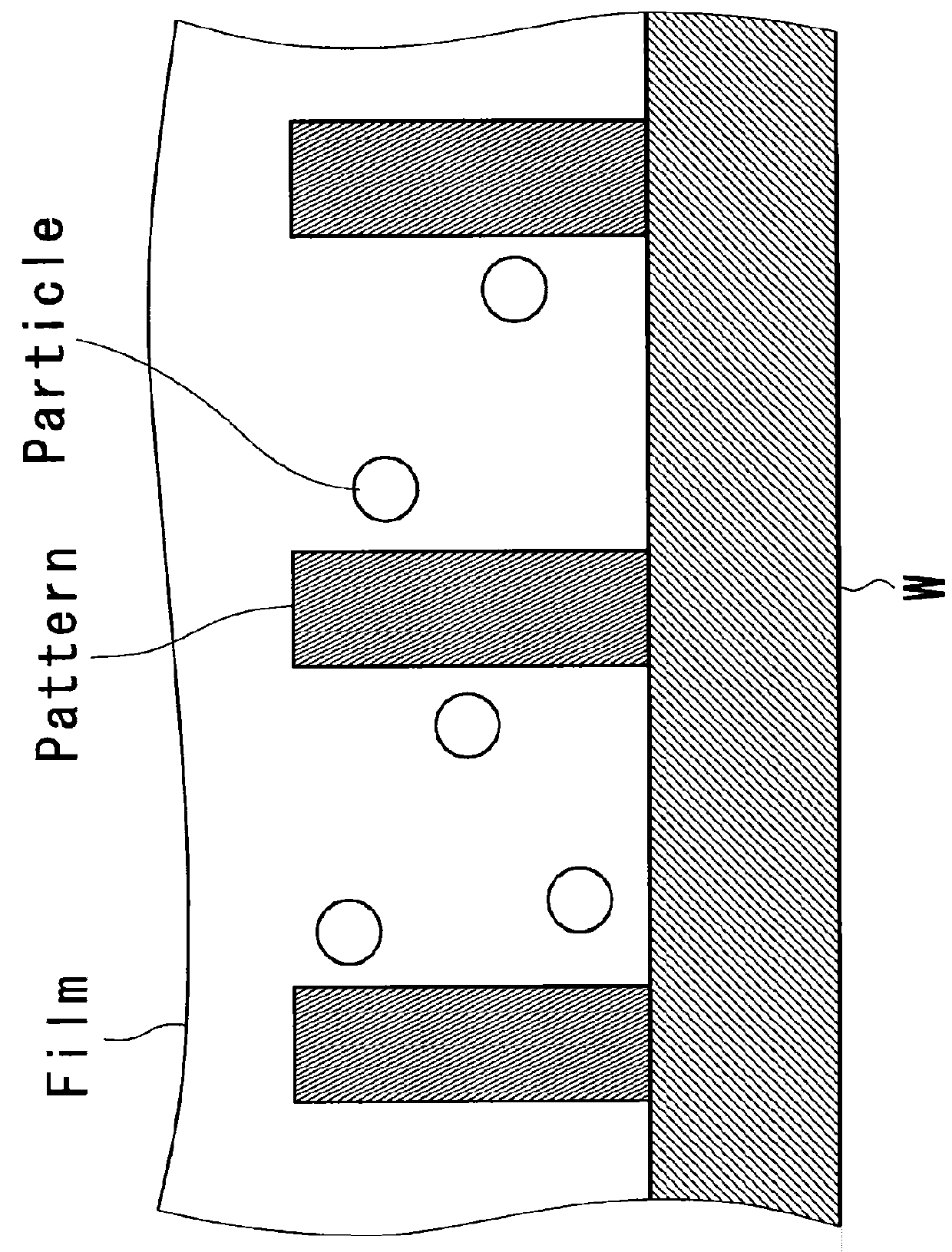
Cleaning composition for semiconductor substrate and cleaning method
InactiveUS20160032227A1Efficient removalEasy to disassembleDetergent mixture composition preparationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic acidSolubility
A cleaning composition for a semiconductor substrate contains a solvent, and a polymer that includes a fluorine atom, a silicon atom or a combination thereof. The content of water in the solvent is preferably no greater than 20% by mass. The cleaning composition preferably further contains an organic acid which is a non-polymeric acid. The organic acid is preferably a polyhydric carboxylic acid. The acid dissociation constant of the polymer is preferably less than that of the organic acid. The solubility of the organic acid in water at 25° C. is preferably no less than 5% by mass. The organic acid is preferably a solid at 25° C.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Polishing composition for semiconductor wafer, production method thereof, and polishing method
PendingCN101126012AOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingColloidal silicaSilicic acid
Owner:NIPPON CHECMICAL IND CO LTD +1
Polyolefin resin composition and foam molded article
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Multilayer porous film, separator for nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery, and nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery
ActiveUS20150111109A1Improve heat resistanceImprove breathabilityNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsSynthetic resin layered productsPolyolefinHeat resistance
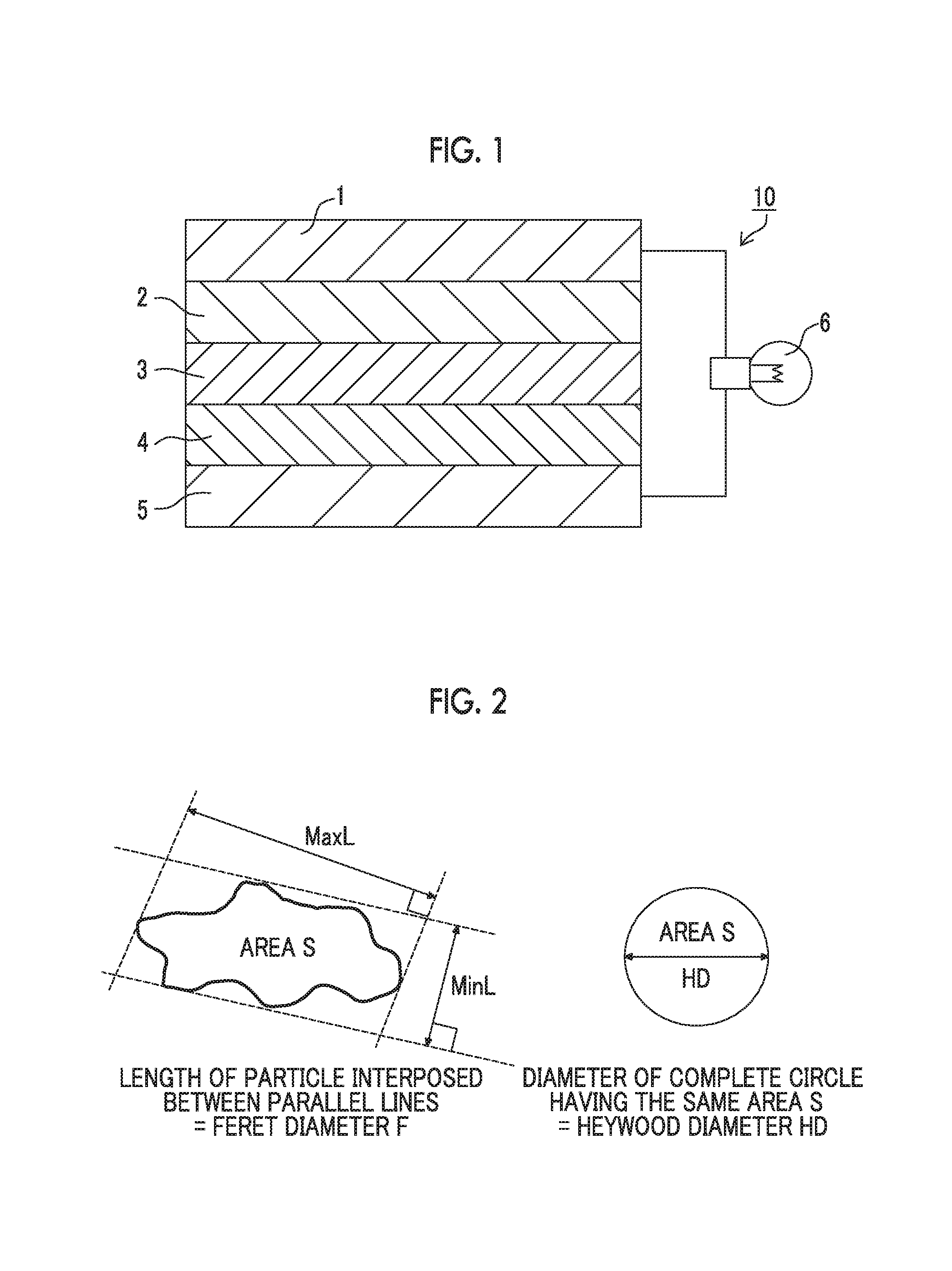
There is provided a multilayer porous film that includes a covering layer formed from a coating liquid on at least one surface of a porous film. The coating liquid has high stability and coatability. The covering layer does not decrease the intrinsic high air permeability of the porous film and has high heat resistance and adhesiveness. The multilayer porous film has excellent handleability as a battery separator without causing curling. The multilayer porous film includes the covering layer on at least one surface of a porous polyolefin resin film. The covering layer is formed from a coating liquid and contains a filler and a resin binder. The multilayer porous film satisfies the following conditions 1) and 2): 1) the filler has an average circularity of 0.3 or more and less than 0.7; and 2) an acid component in the coating liquid has a first acid dissociation constant of 5 or less and has no second acid dissociation constant or a second acid dissociation constant of 7 or more in a dilute aqueous solution at 25° C.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com