Patents
Literature
90 results about "Hierarchical storage management" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
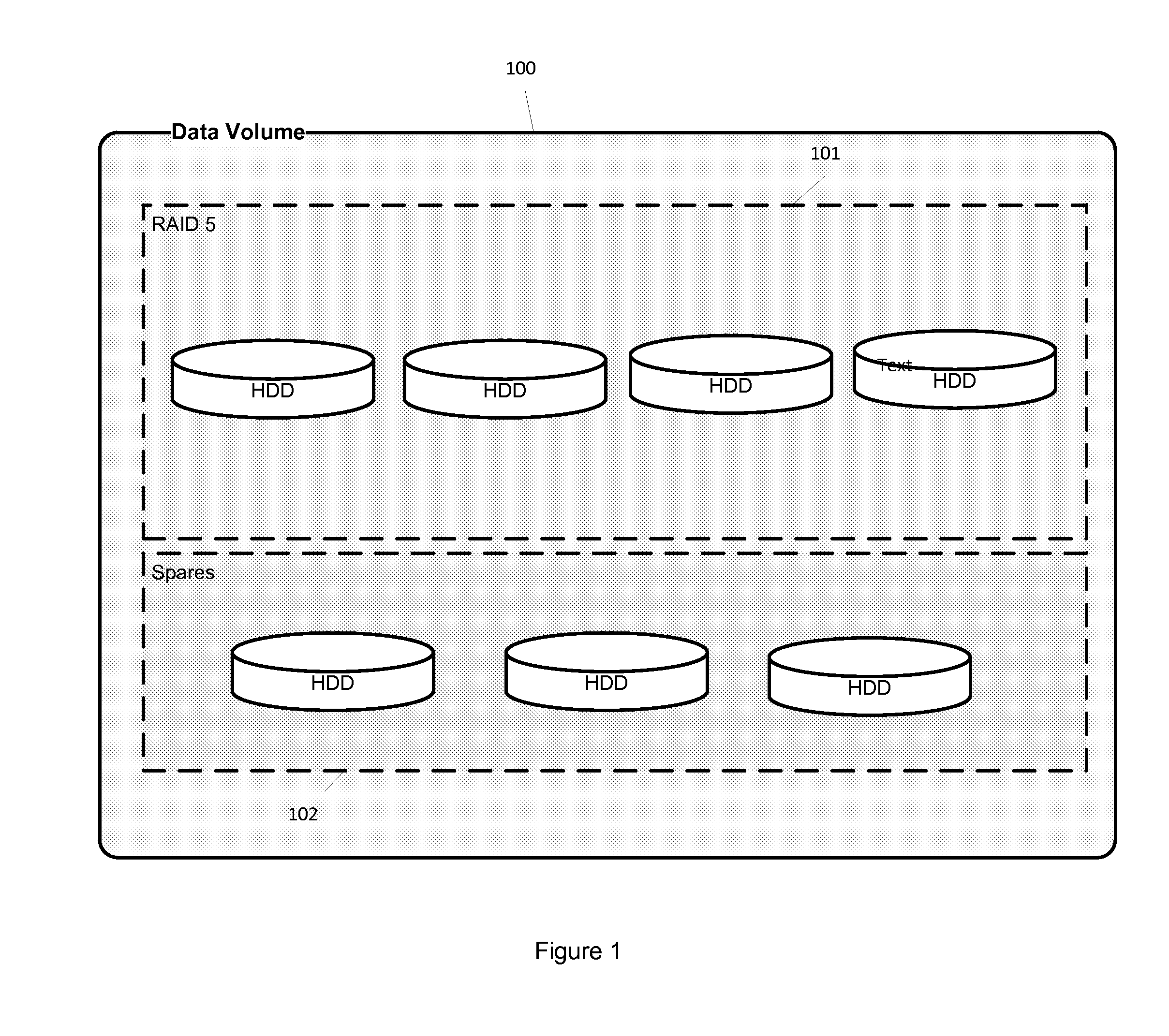
Hierarchical storage management (HSM) is a data storage technique that automatically moves data between high-cost and low-cost storage media. HSM systems exist because high-speed storage devices, such as solid state drive arrays, are more expensive (per byte stored) than slower devices, such as hard disk drives, optical discs and magnetic tape drives. While it would be ideal to have all data available on high-speed devices all the time, this is prohibitively expensive for many organizations. Instead, HSM systems store the bulk of the enterprise's data on slower devices, and then copy data to faster disk drives when needed. In effect, HSM turns the fast disk drives into caches for the slower mass storage devices. The HSM system monitors the way data is used and makes best guesses as to which data can safely be moved to slower devices and which data should stay on the fast devices.
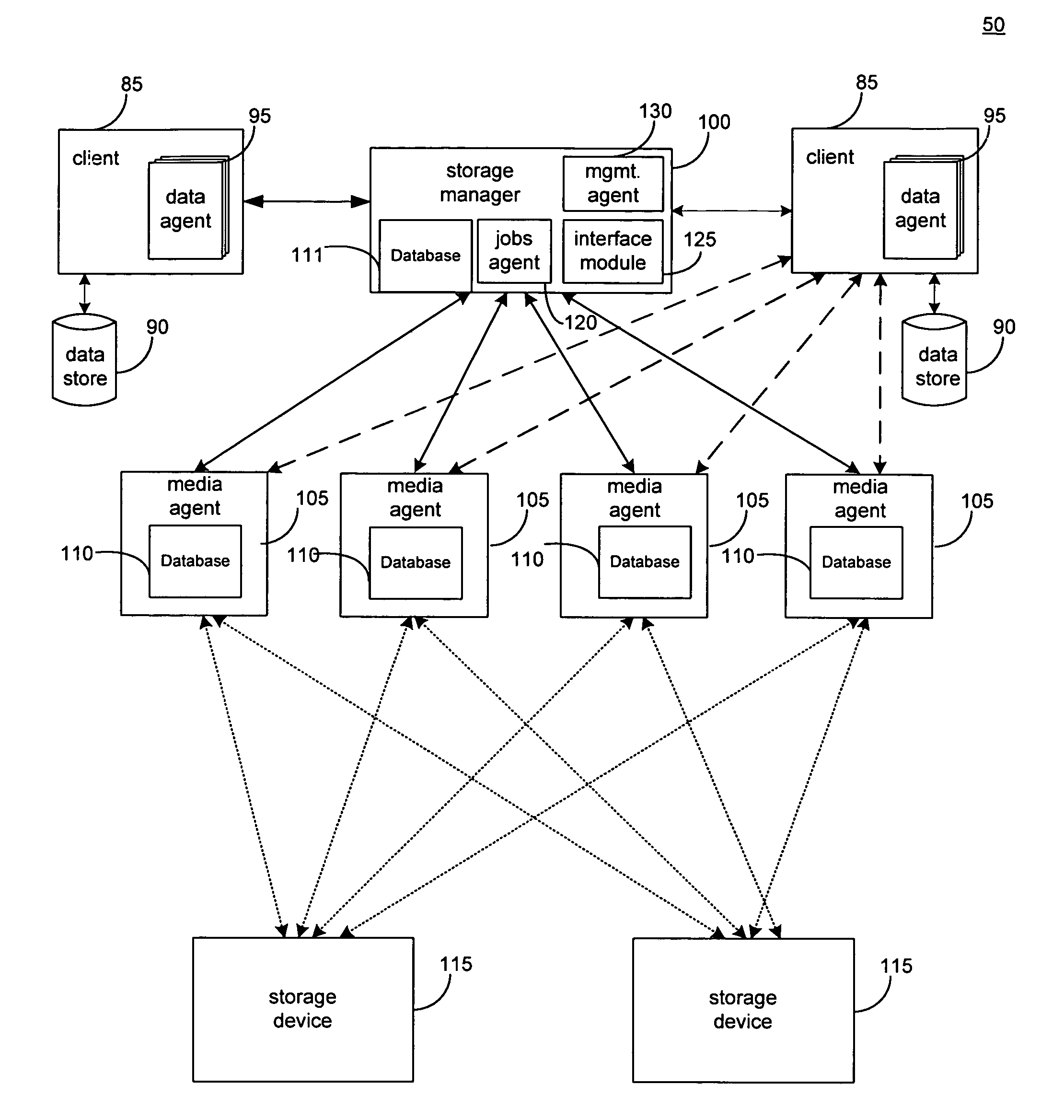
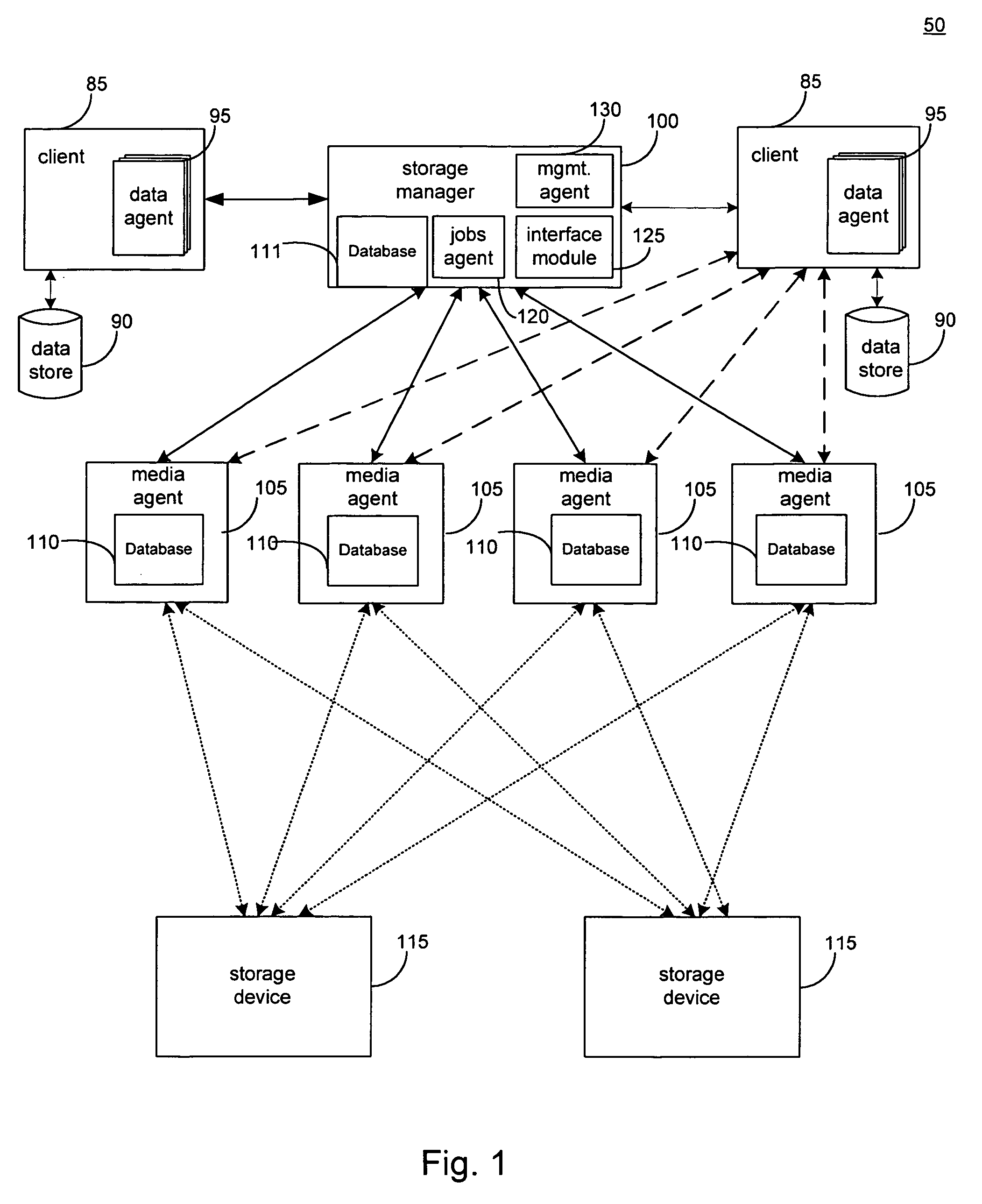
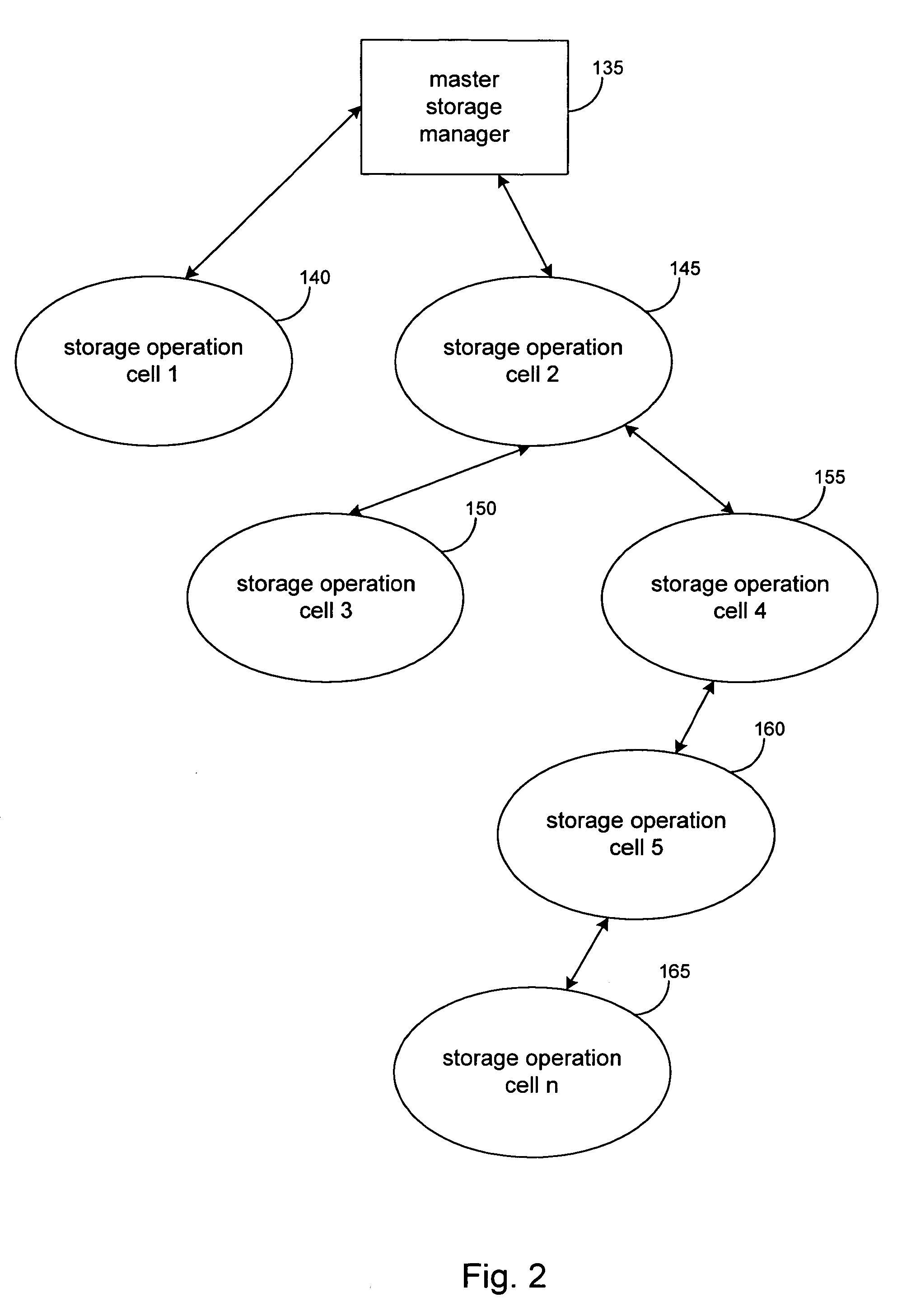
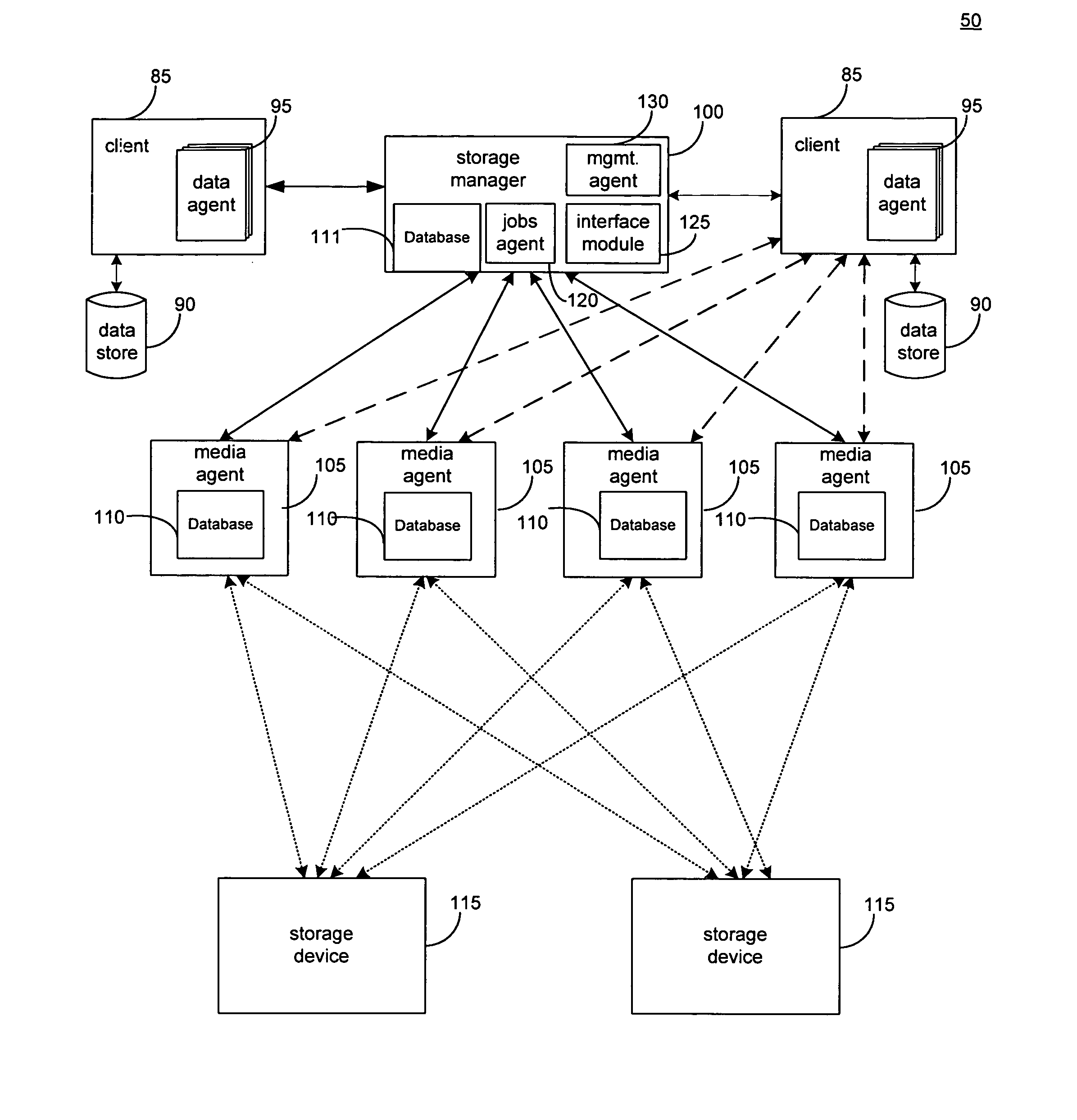
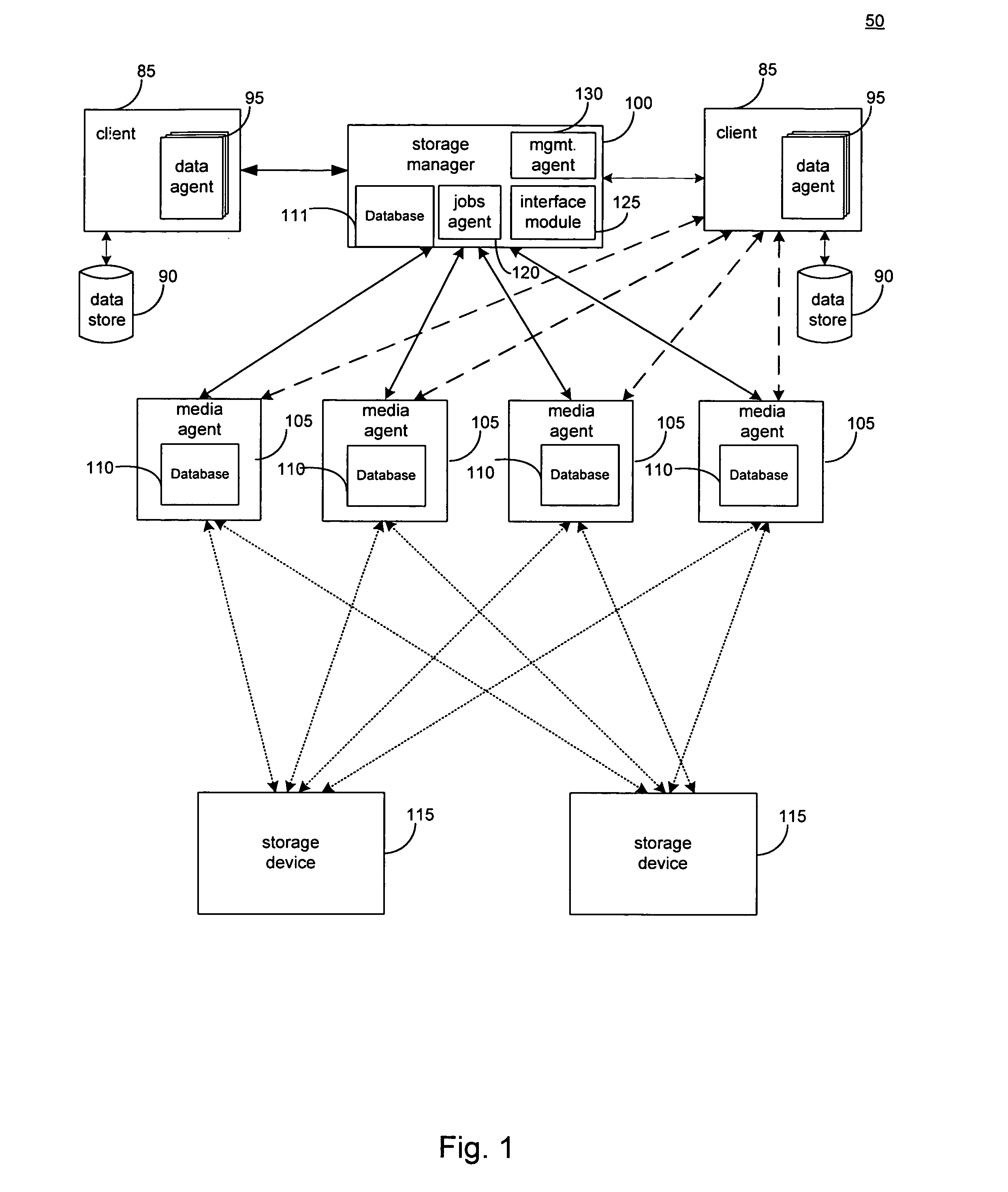
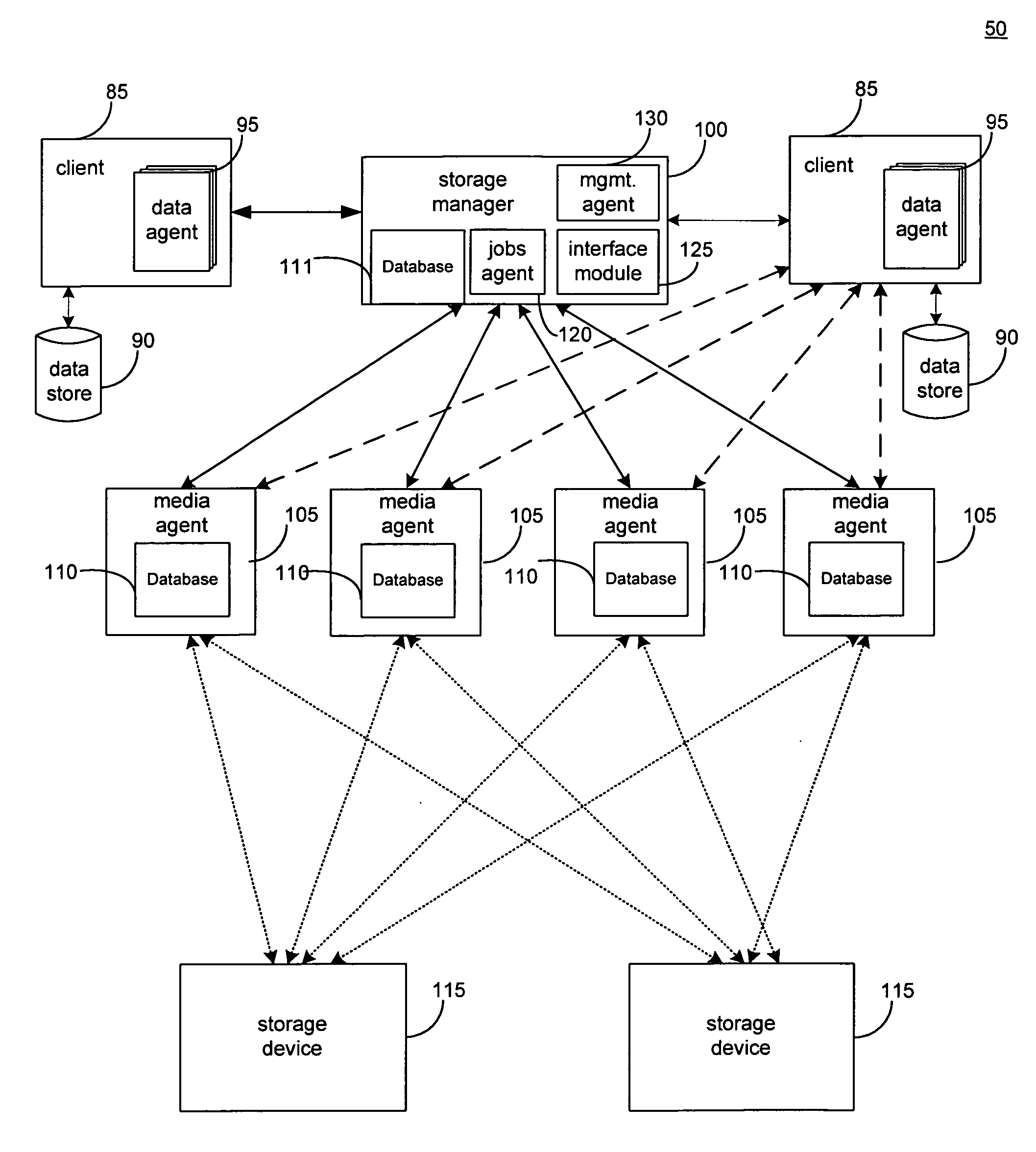
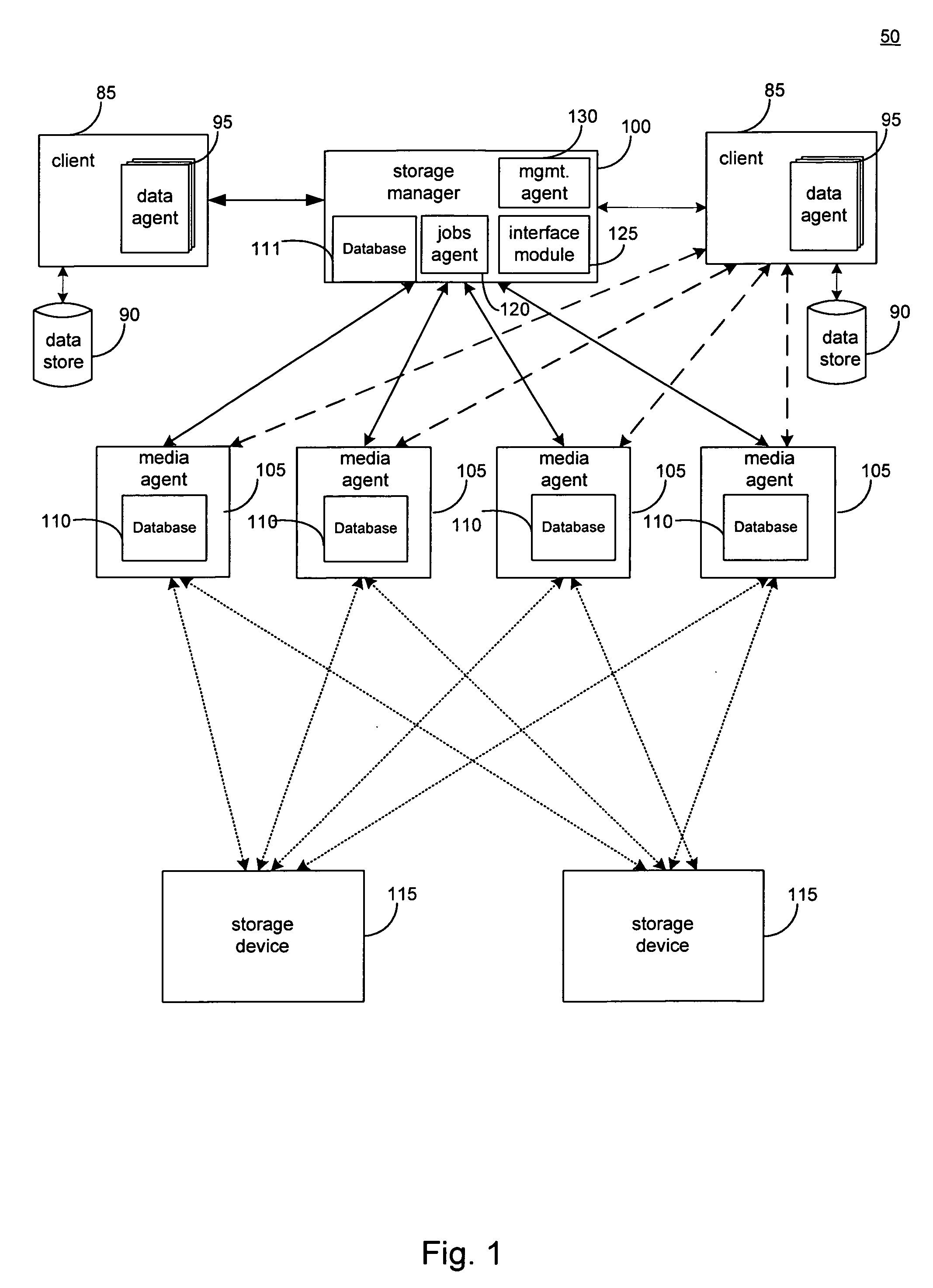
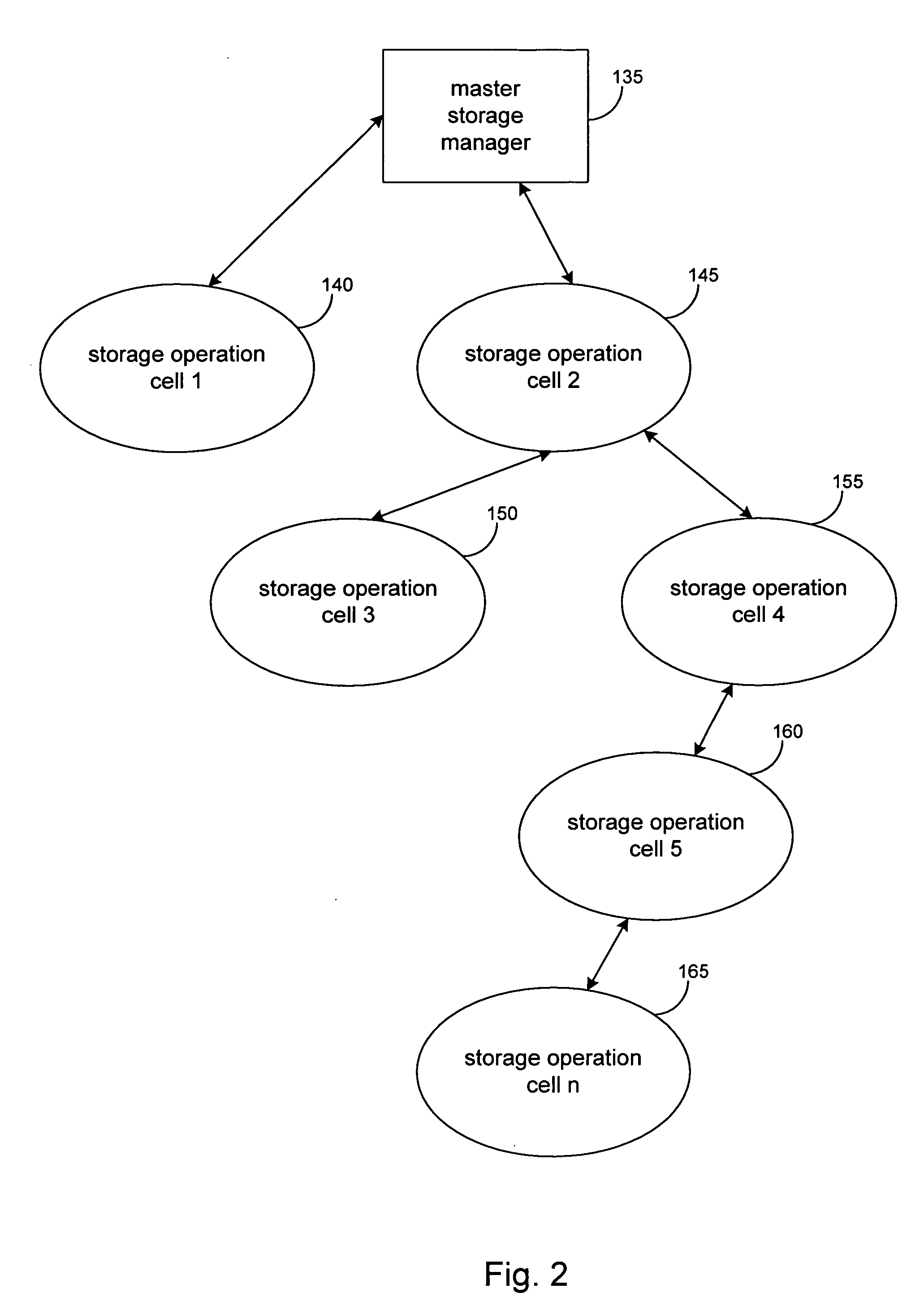
Hierarchical systems and methods for providing a unified view of storage information
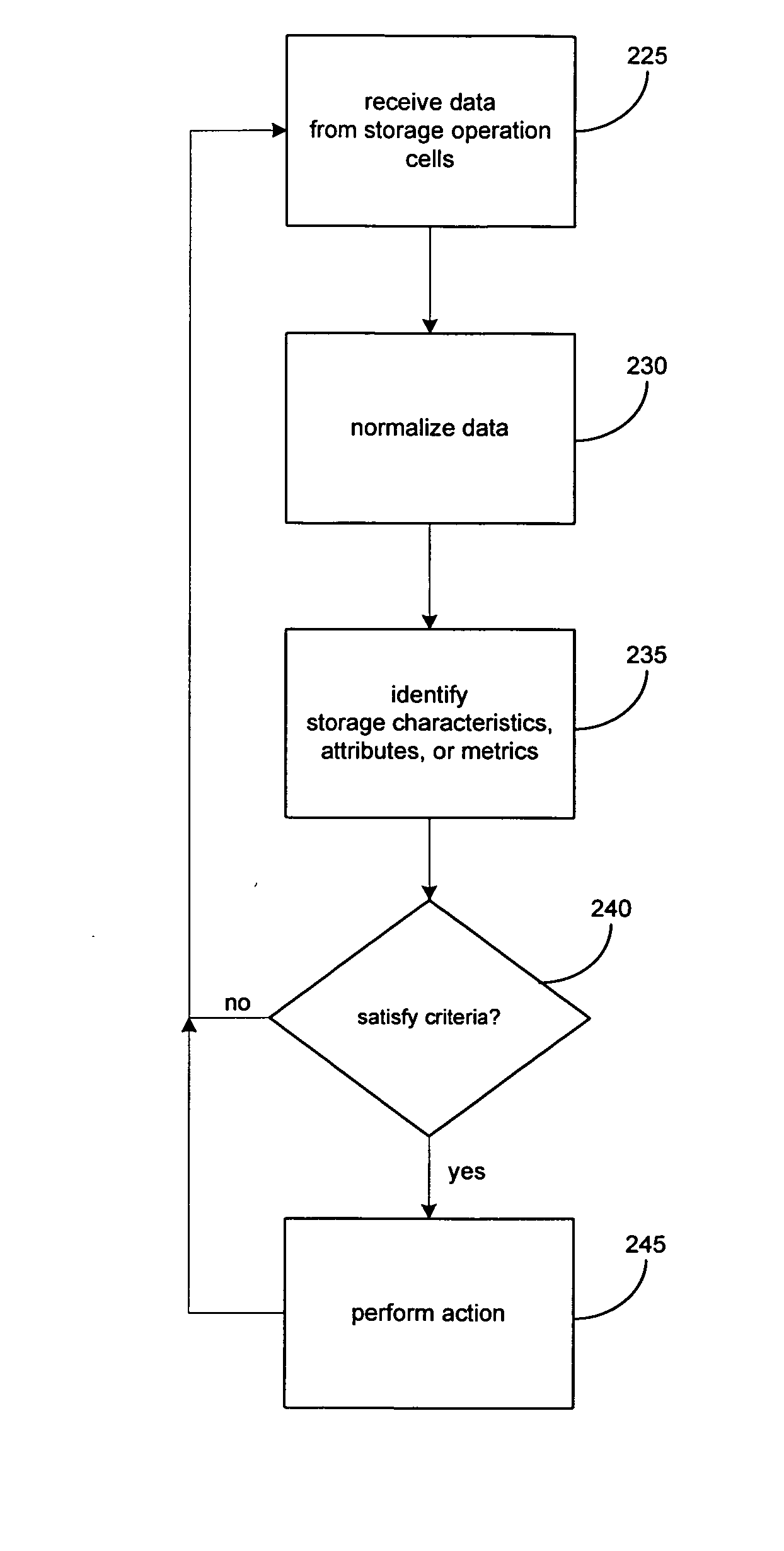
The present invention provides systems and methods for data storage. A hierarchical storage management architecture is presented to facilitate data management. The disclosed system provides methods for evaluating the state of stored data relative to enterprise needs by using weighted parameters that may be user defined. Also disclosed are systems and methods evaluating costing and risk management associated with stored data.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
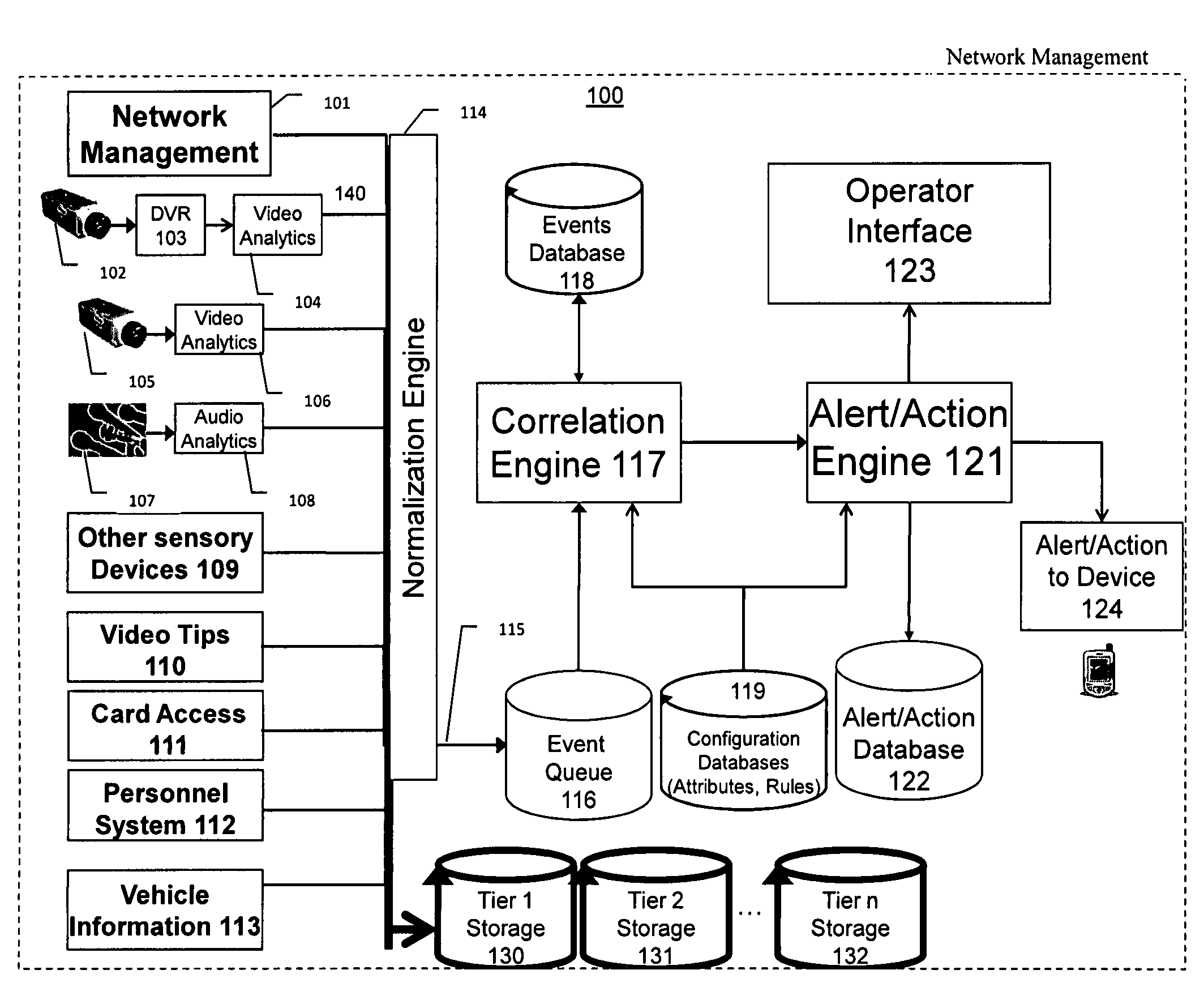
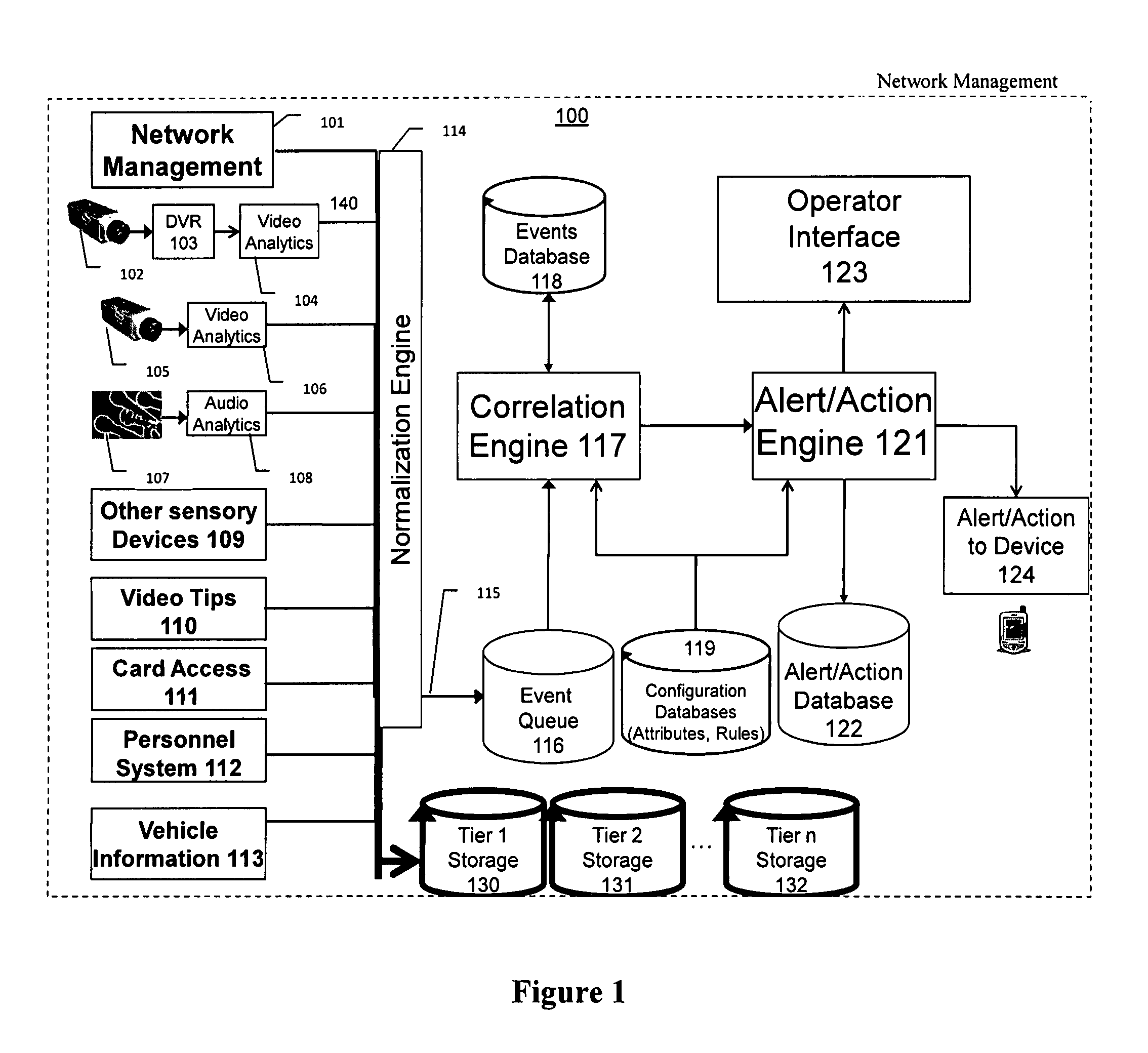
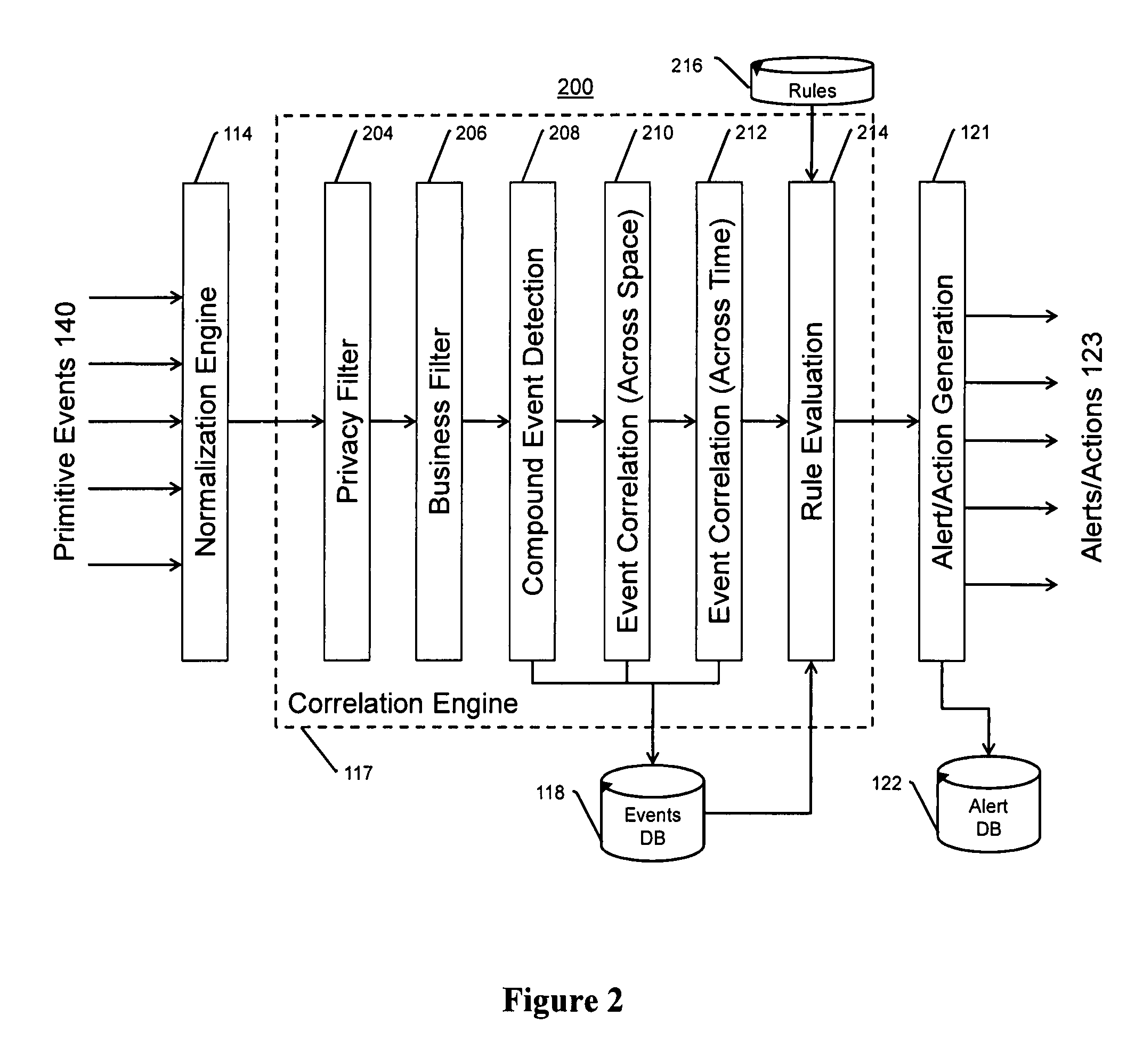
Video surveillance, storage, and alerting system having network management, hierarchical data storage, video tip processing, and vehicle plate analysis
ActiveUS7382244B1Television system detailsFrequency-division multiplex detailsVideo monitoringDriver/operator
The present invention is a video surveillance, storage, and alerting system having surveillance cameras, video analytics devices, audio sensory devices, other sensory devices, and a plurality of data storage devices. A network management module monitors network status of all subsystems including cameras, servers, storage devices, etc. and shows actively monitored areas on a physical map. A vehicle information module retrieves information from a law enforcement database about vehicles detected in the video data based on the vehicle's license plate, including information about stolen vehicles, as well as warrant, wanted person, and mug shot information for registered drivers of the vehicles. Video tips are received and processed from anonymous and non-anonymous sources. A correlation engine correlates primitive events and compound events from each of the subsystems, weighted by attributes of the events, across both space and time, and an alerting engine generates alerts and performs actions based on the correlation. A hierarchical storage manager manages storage of the vast amounts of data, including video data, based on importance of the data calculated from attributes of the data. A privacy filter ensures no private data is detected, correlated, or stored.
Owner:SECURENET SOLUTIONS GRP
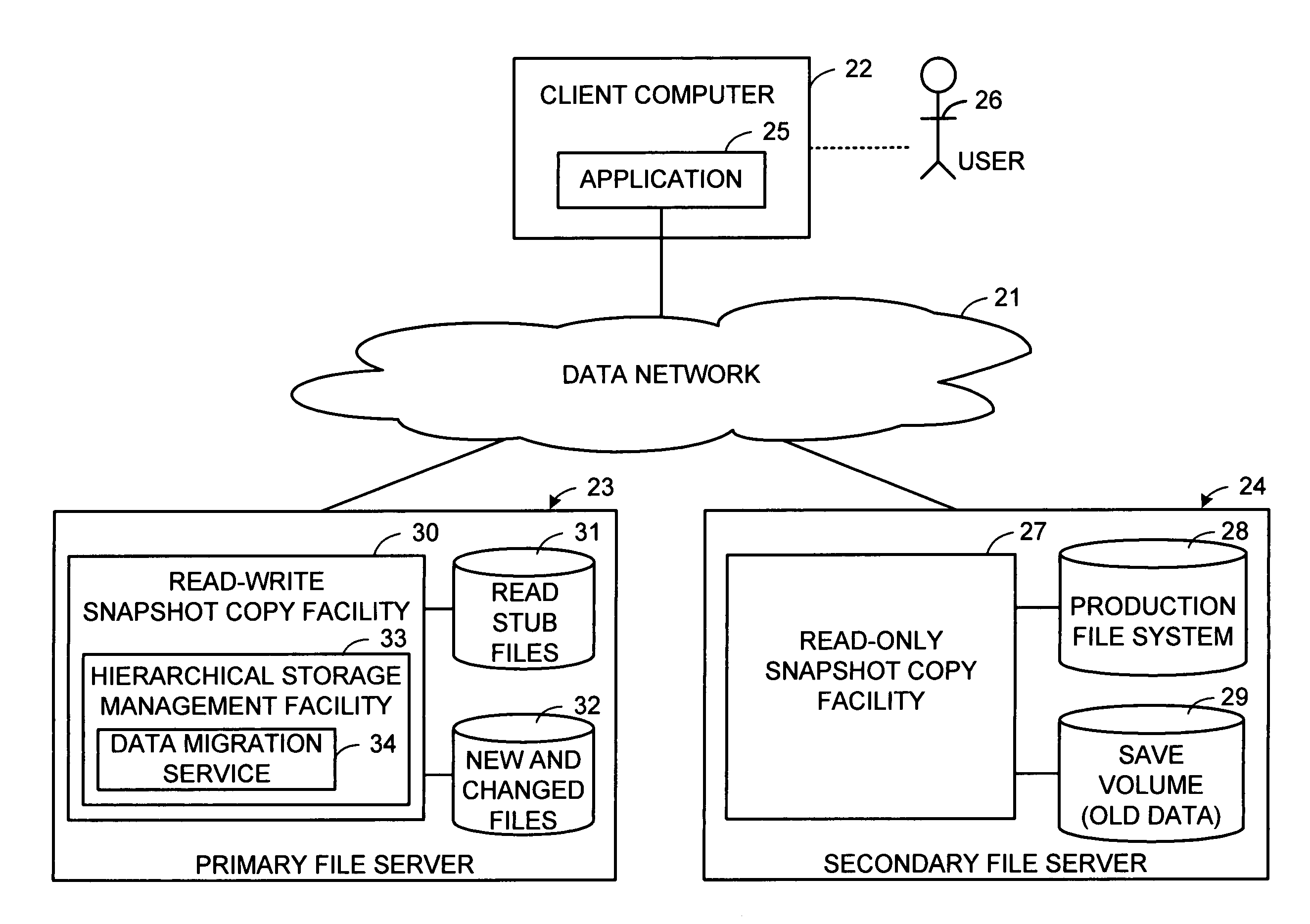
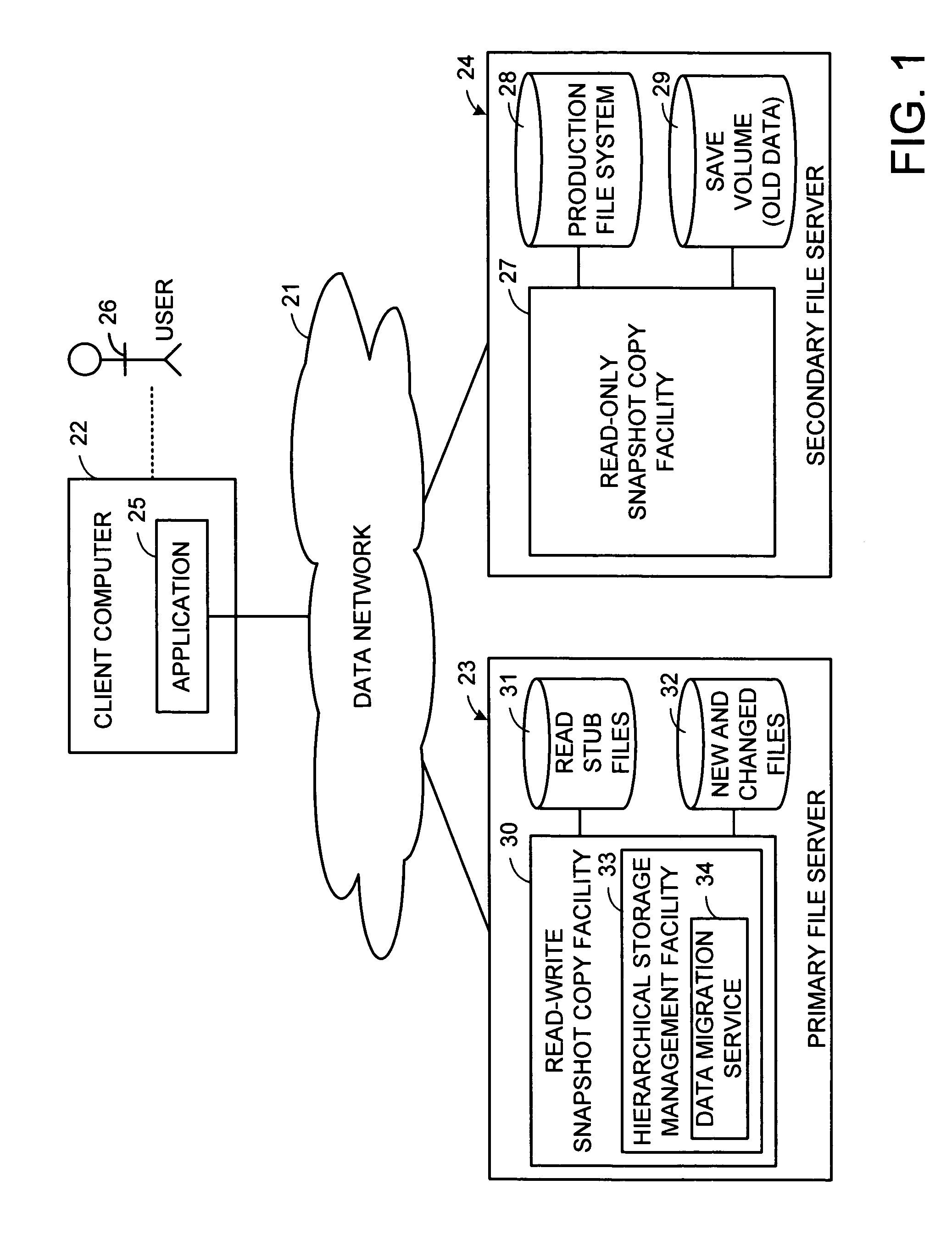
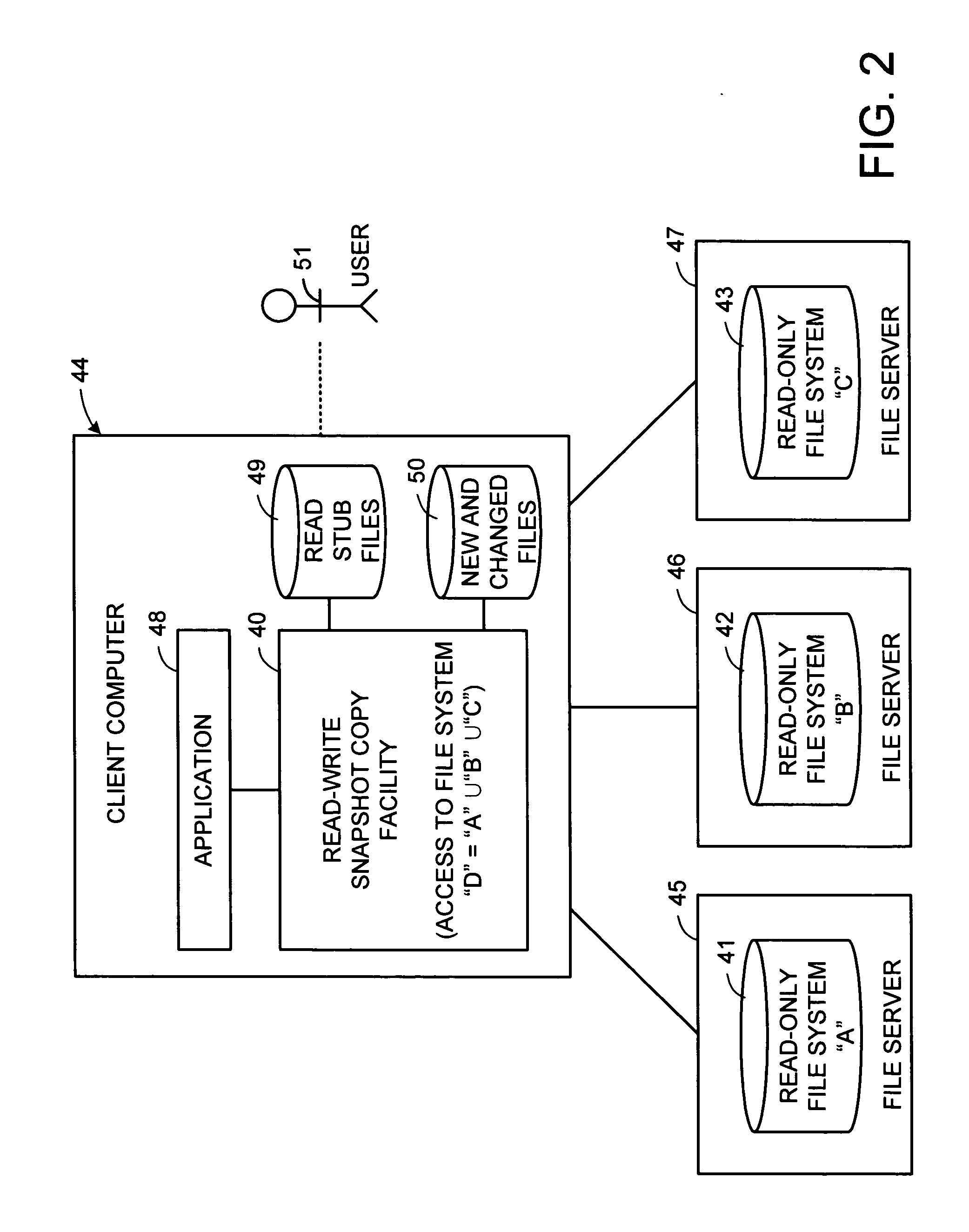
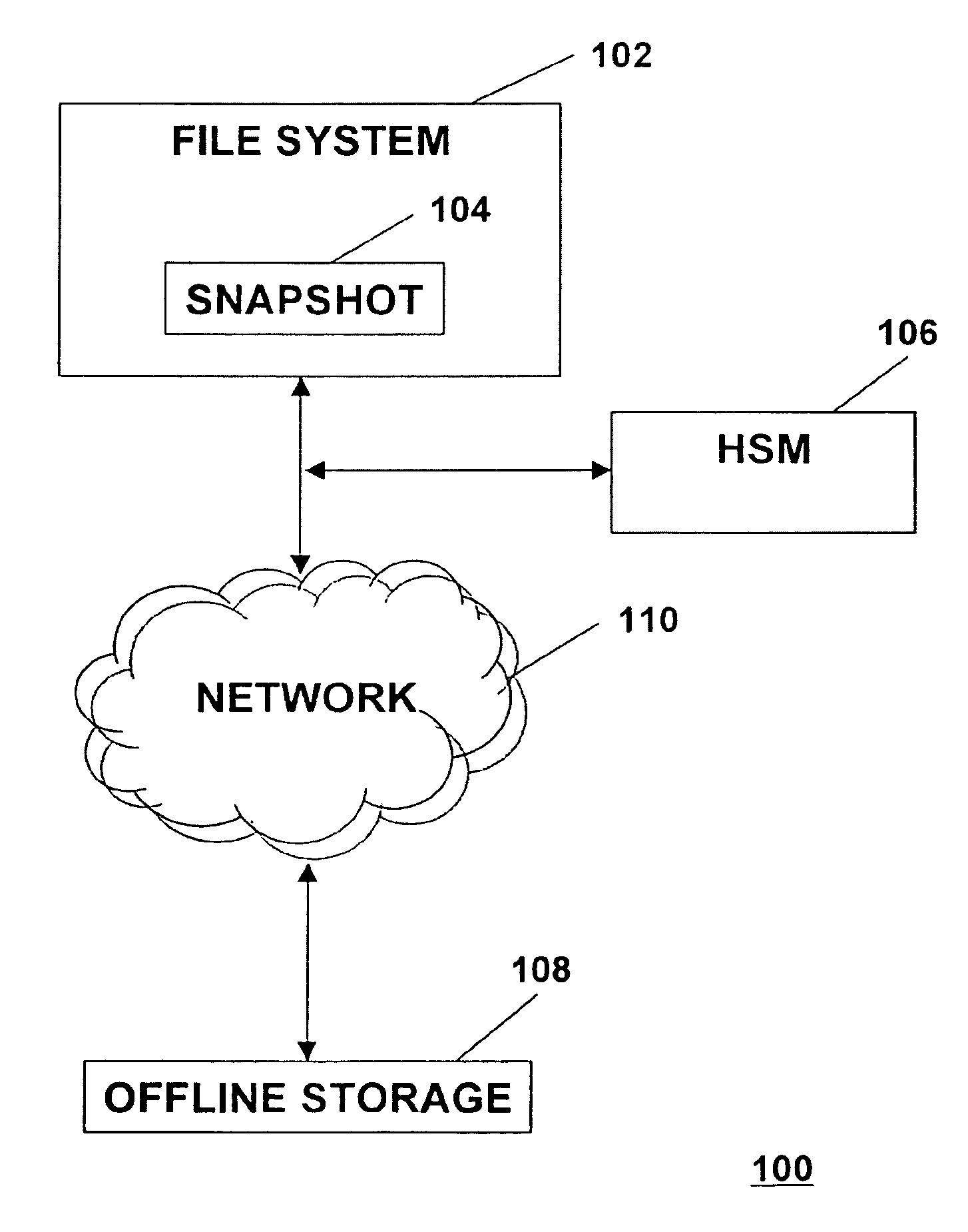
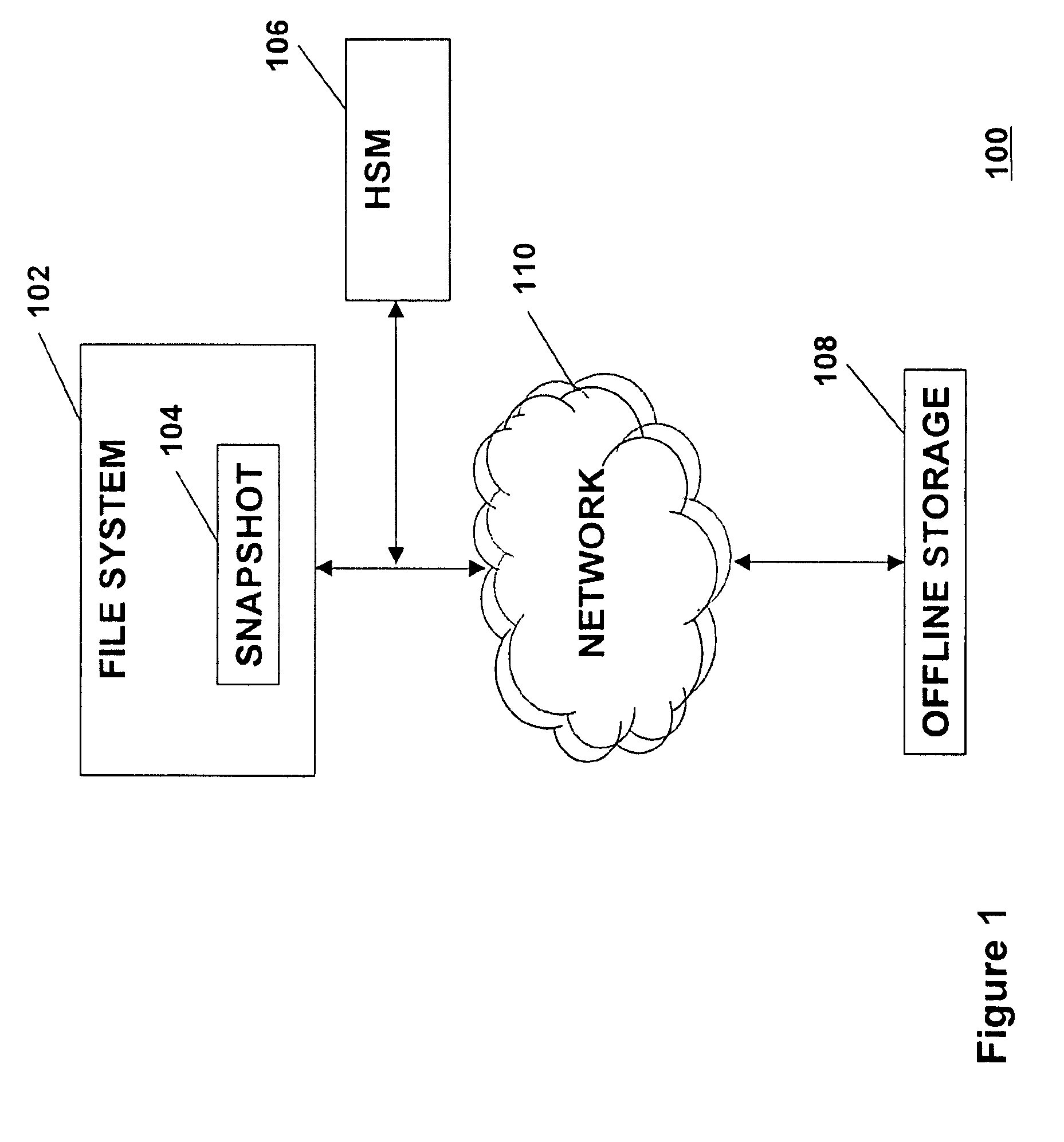
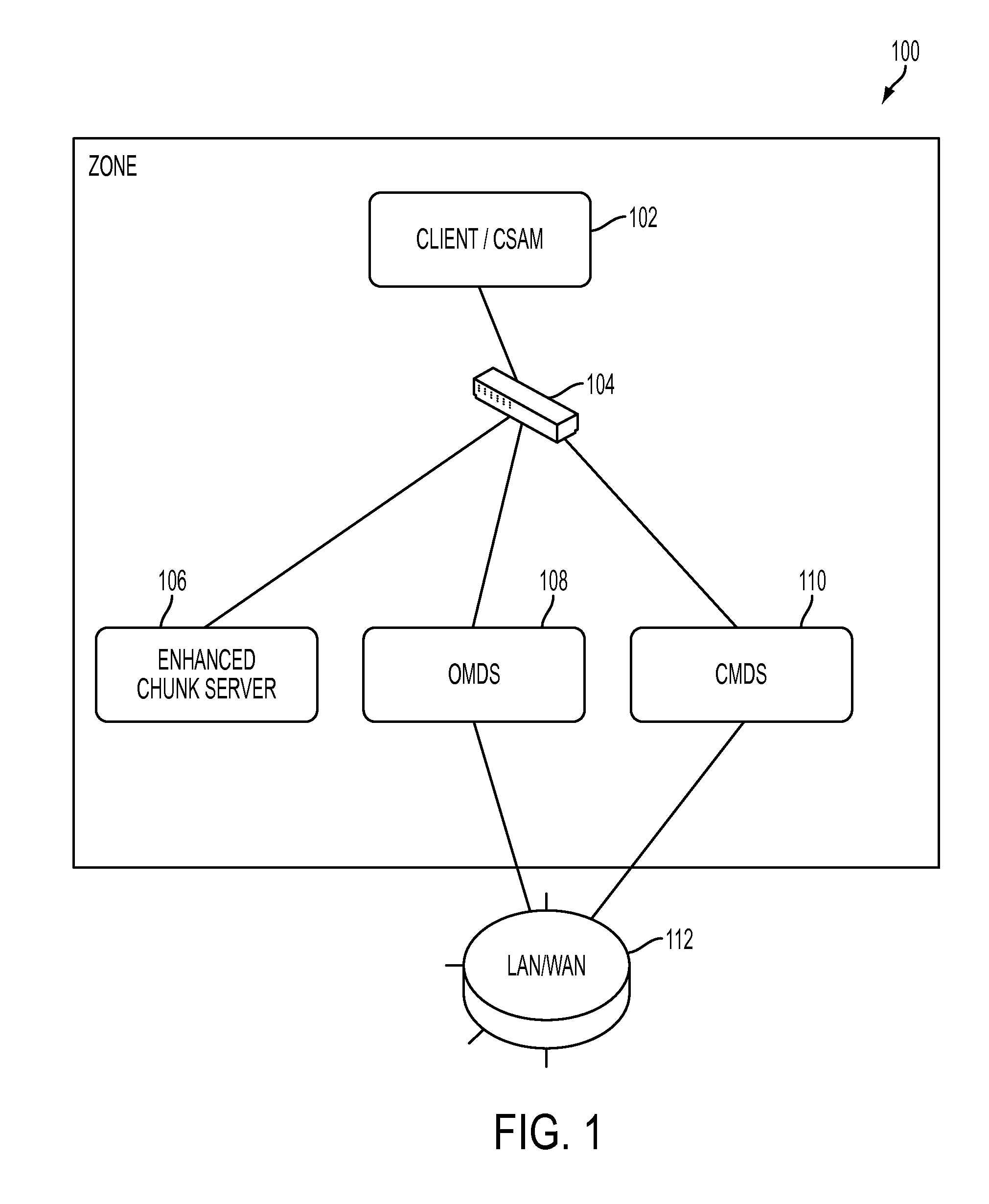
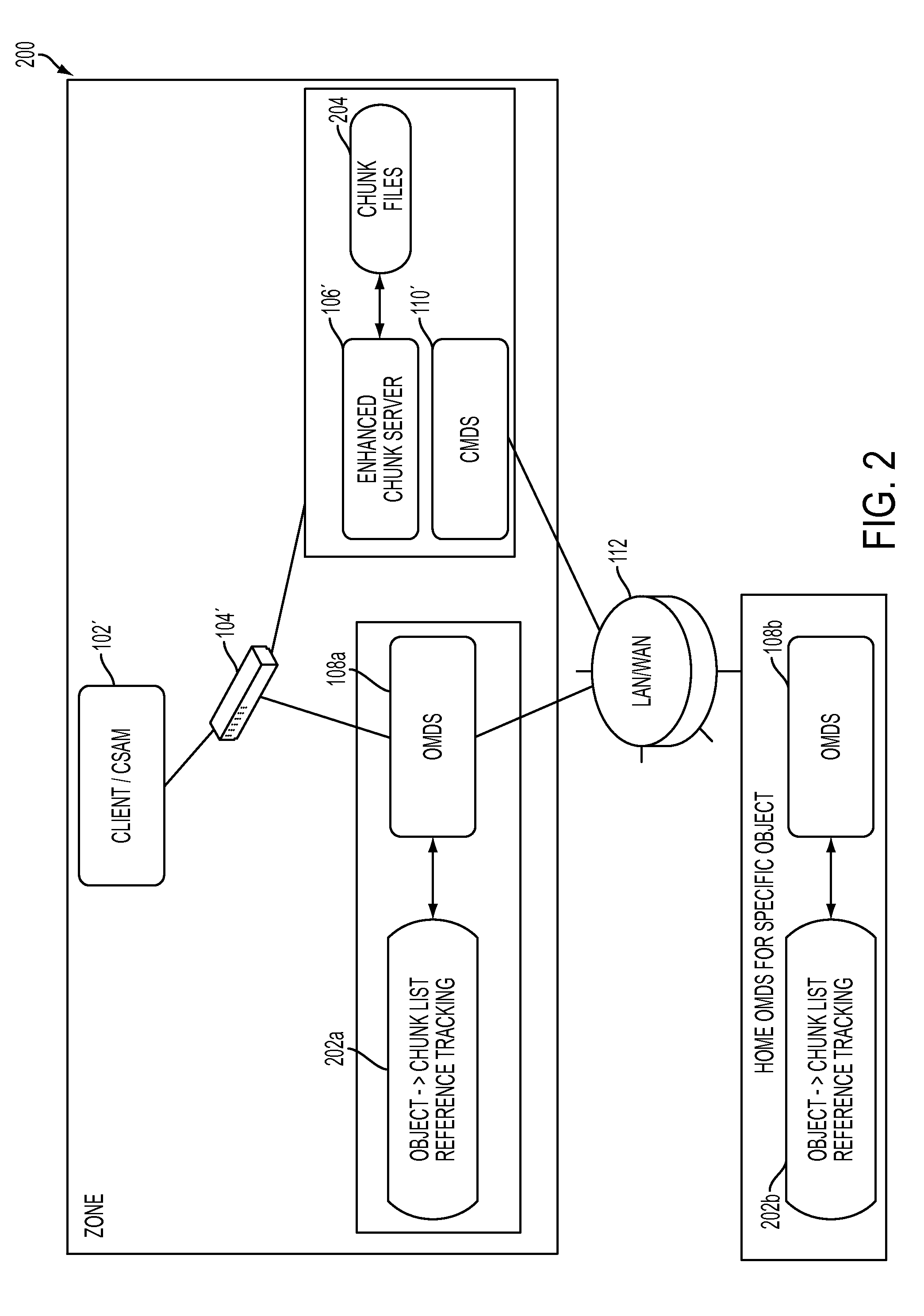
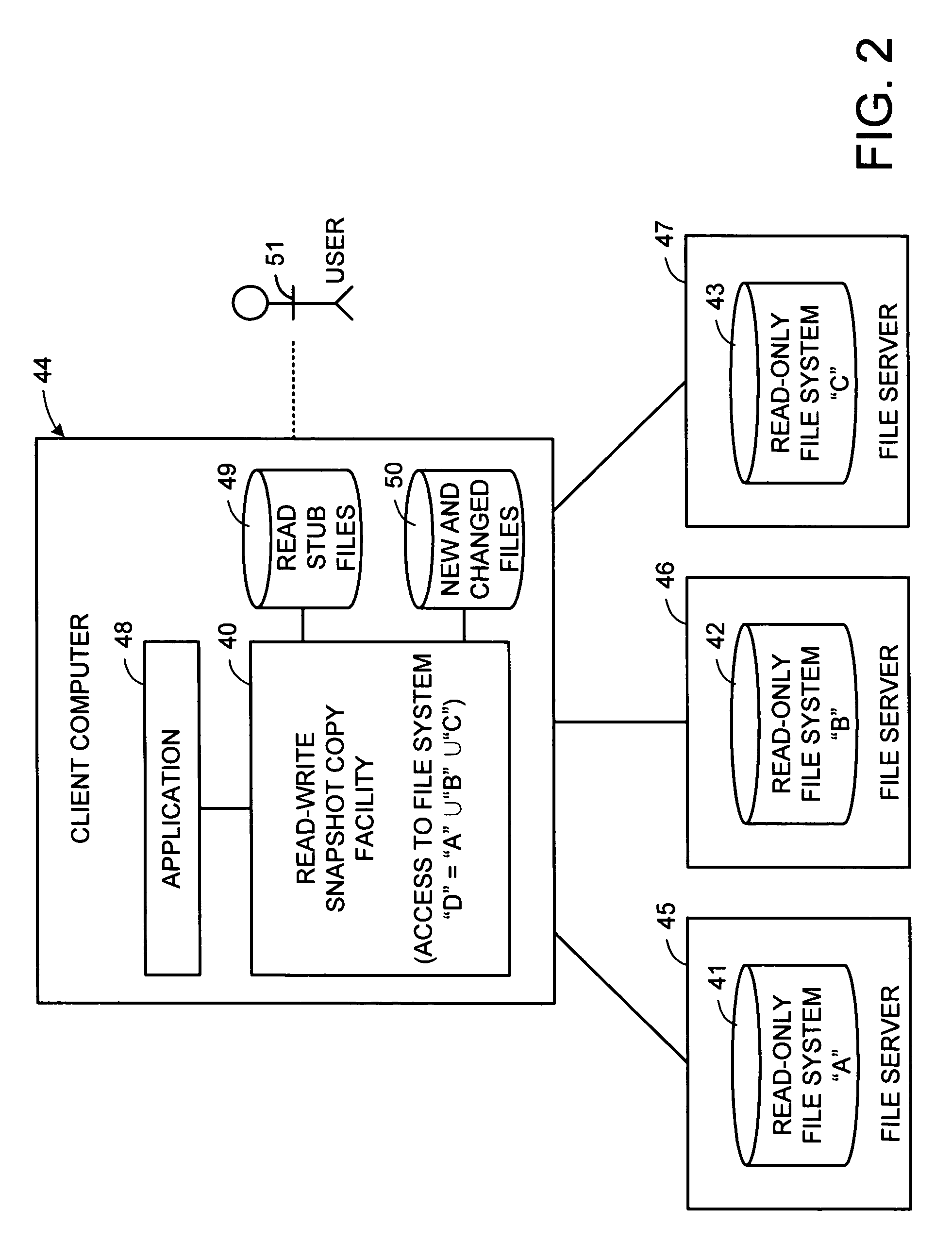
Distributed open writable snapshot copy facility using file migration policies
ActiveUS20060212481A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsFile systemHeterogeneous network
A read-write snapshot copy facility is constructed from a hierarchical storage management facility. The read-write snapshot copy file system initially comprises stub files pointing to the files in a read-only snapshot copy file system. When an application writes to a file in the read-write snapshot copy, the read-write snapshot copy facility migrates a copy of the file to replace the stub file, and then writes to the migrated file. Because the read-write snapshot copy facility references the files in the read-only snapshot file system in a network namespace using standard protocols such as NFS or CIFS, the read-write snapshot copy facility permits referencing of distributed read-only snapshot file systems in an open (heterogeneous) network environment, and the read-write snapshot copy is scalable by linking the read-write snapshot copy facility to multiple file servers containing read-only snapshot file systems.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
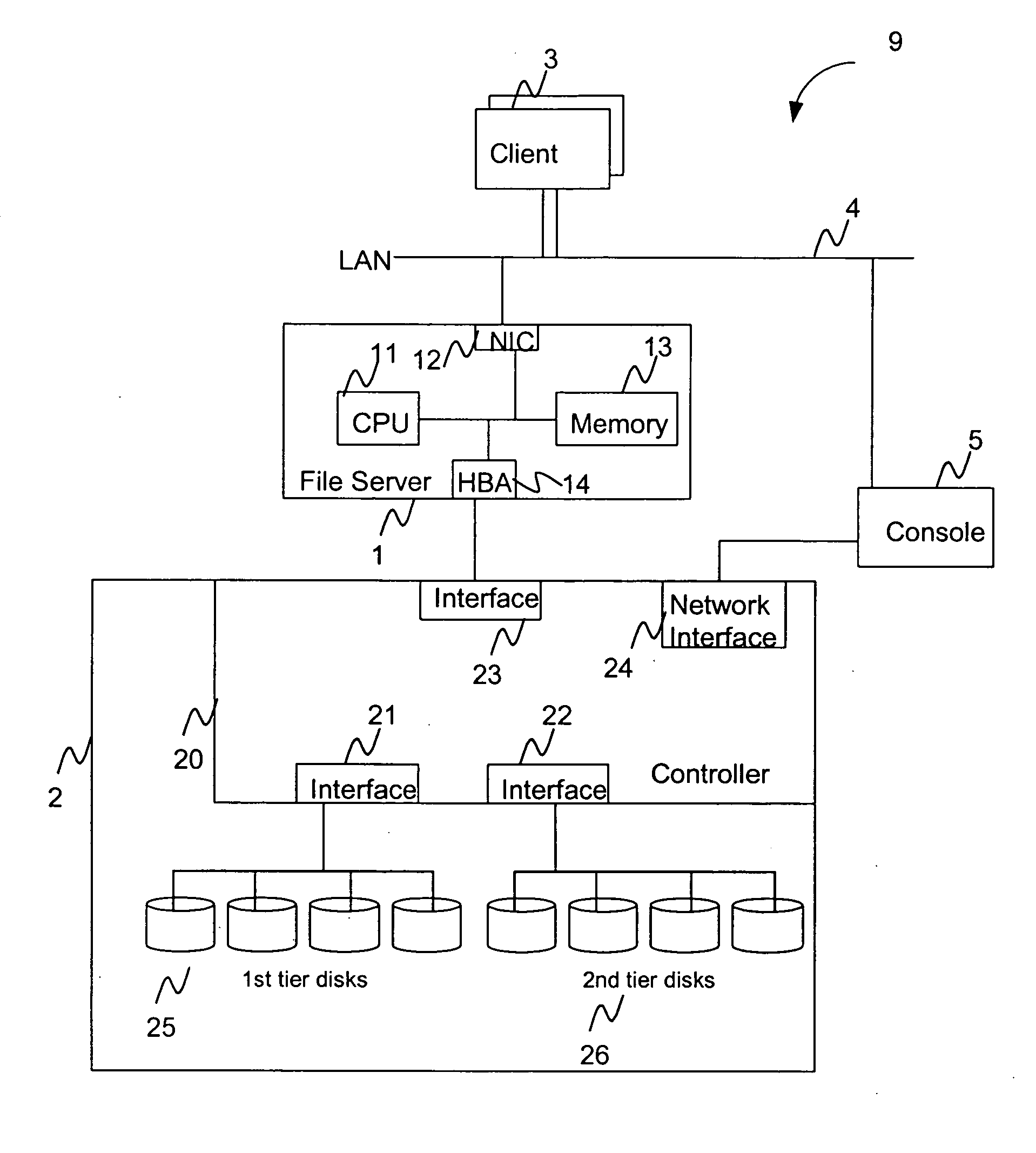
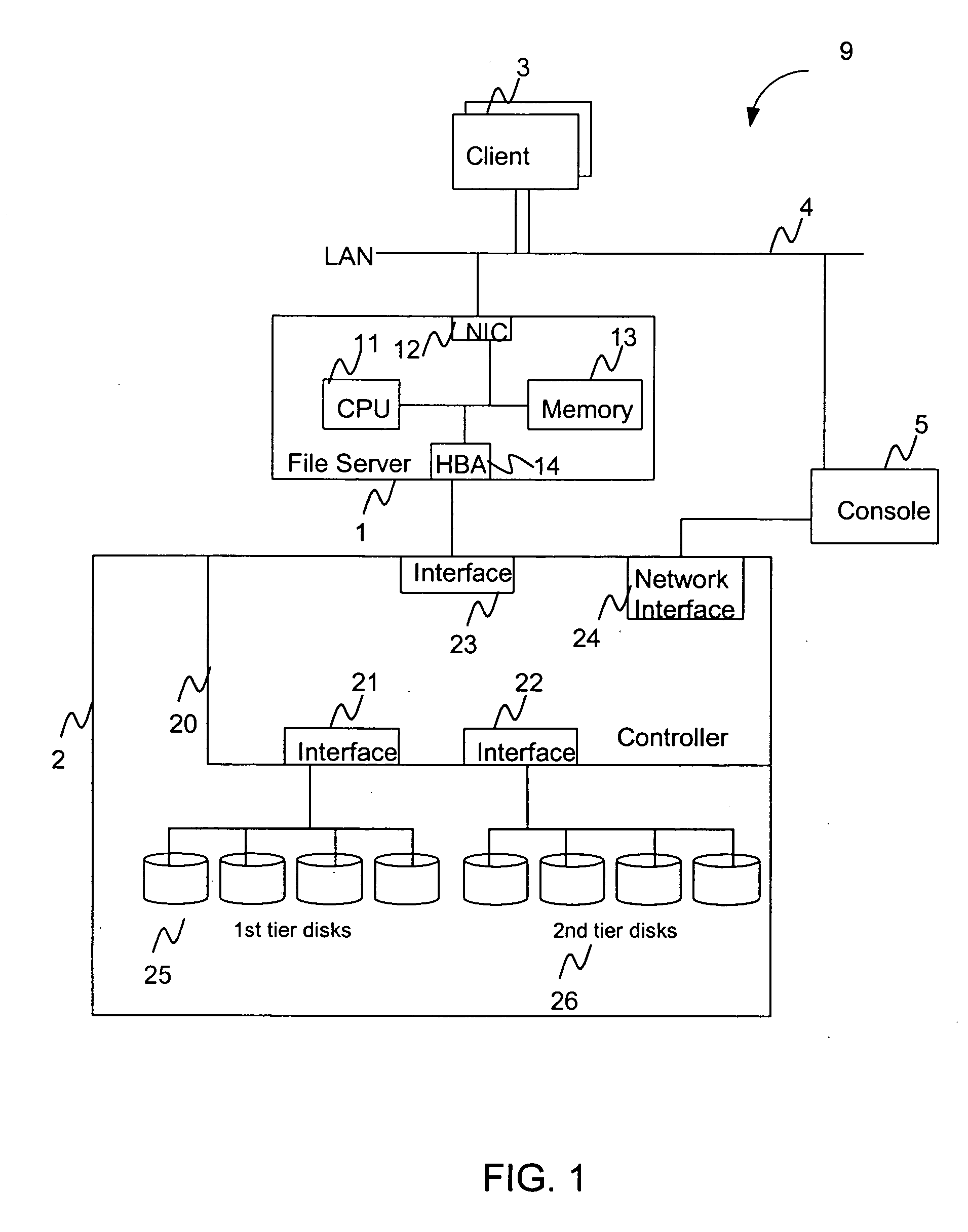
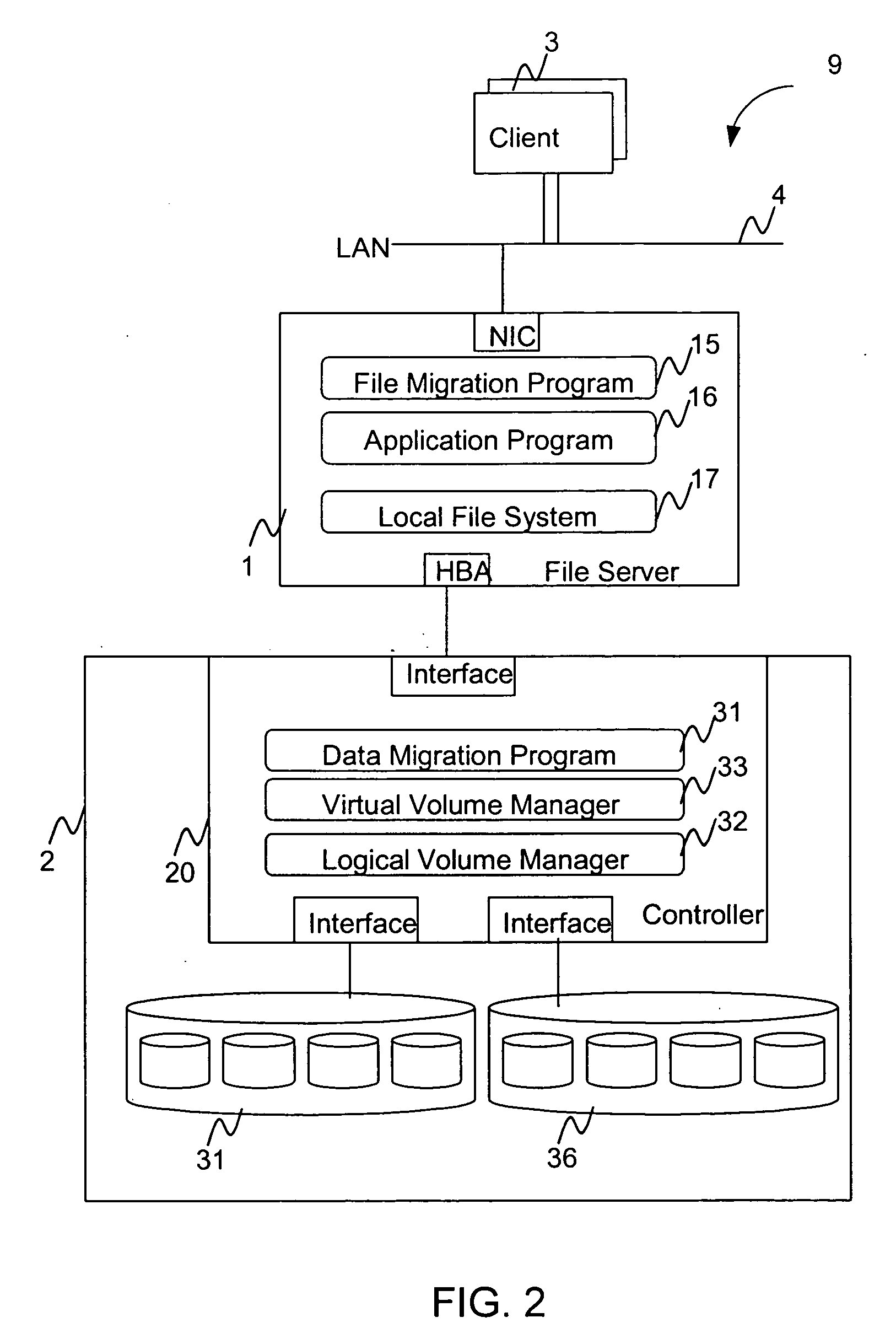
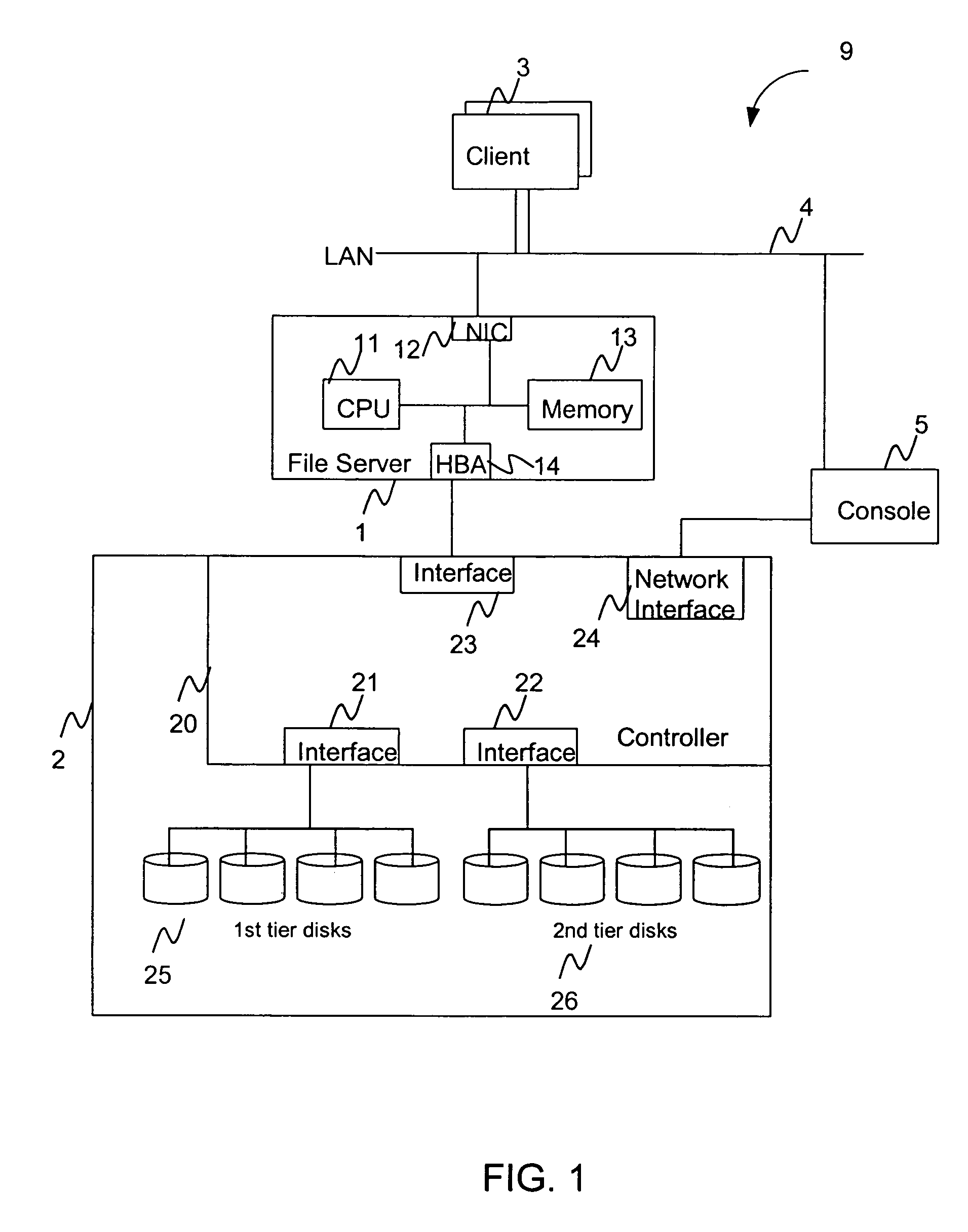
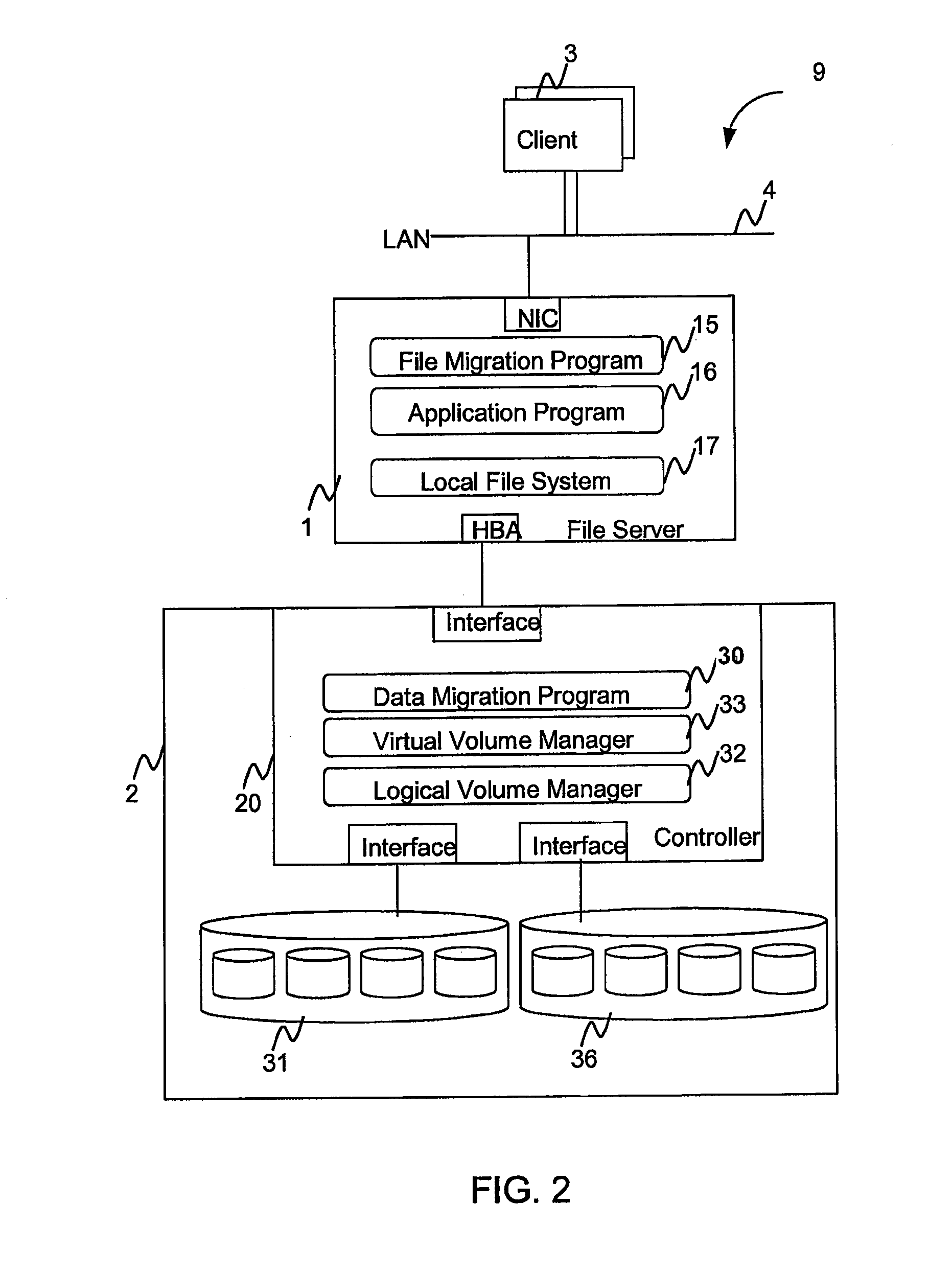
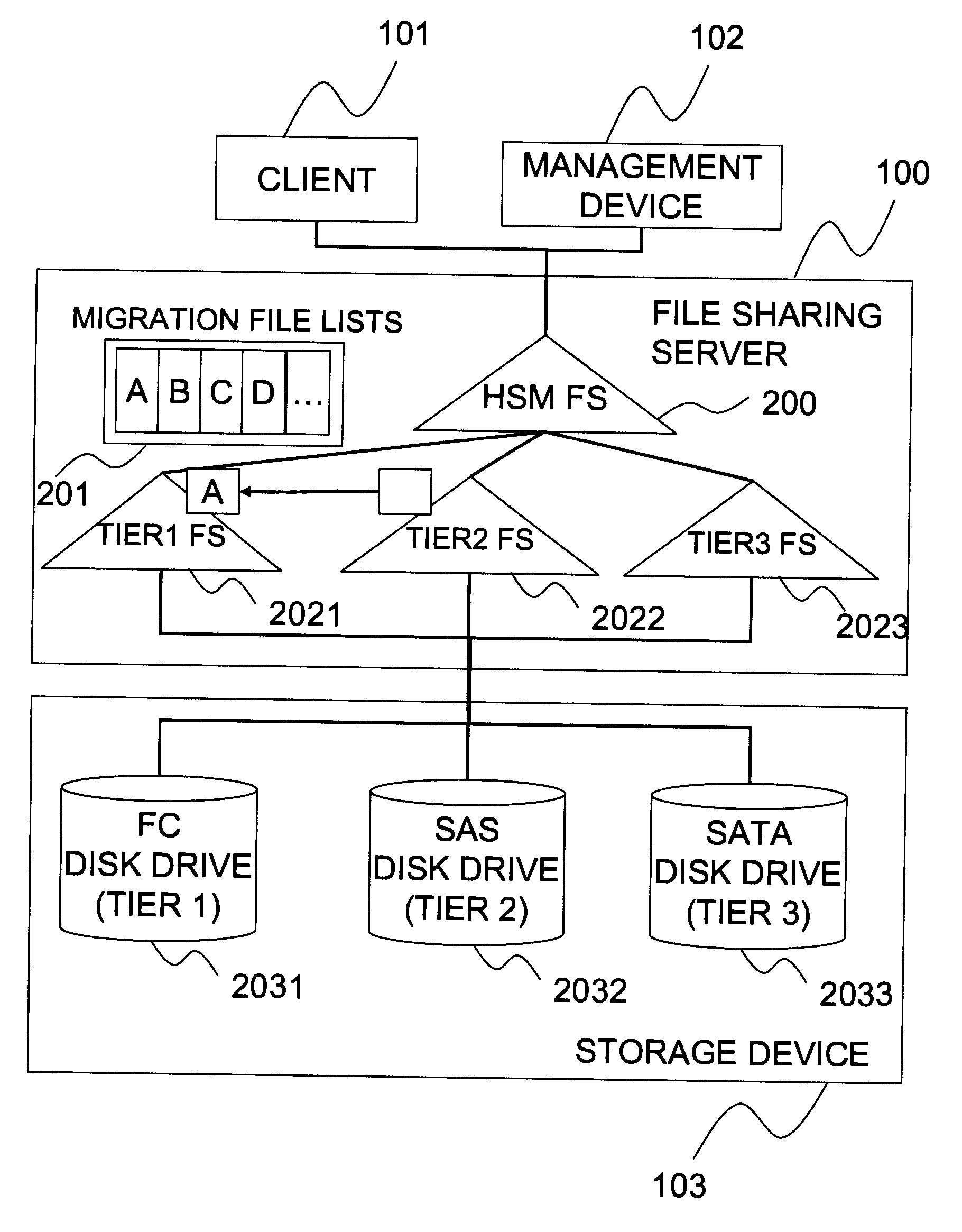
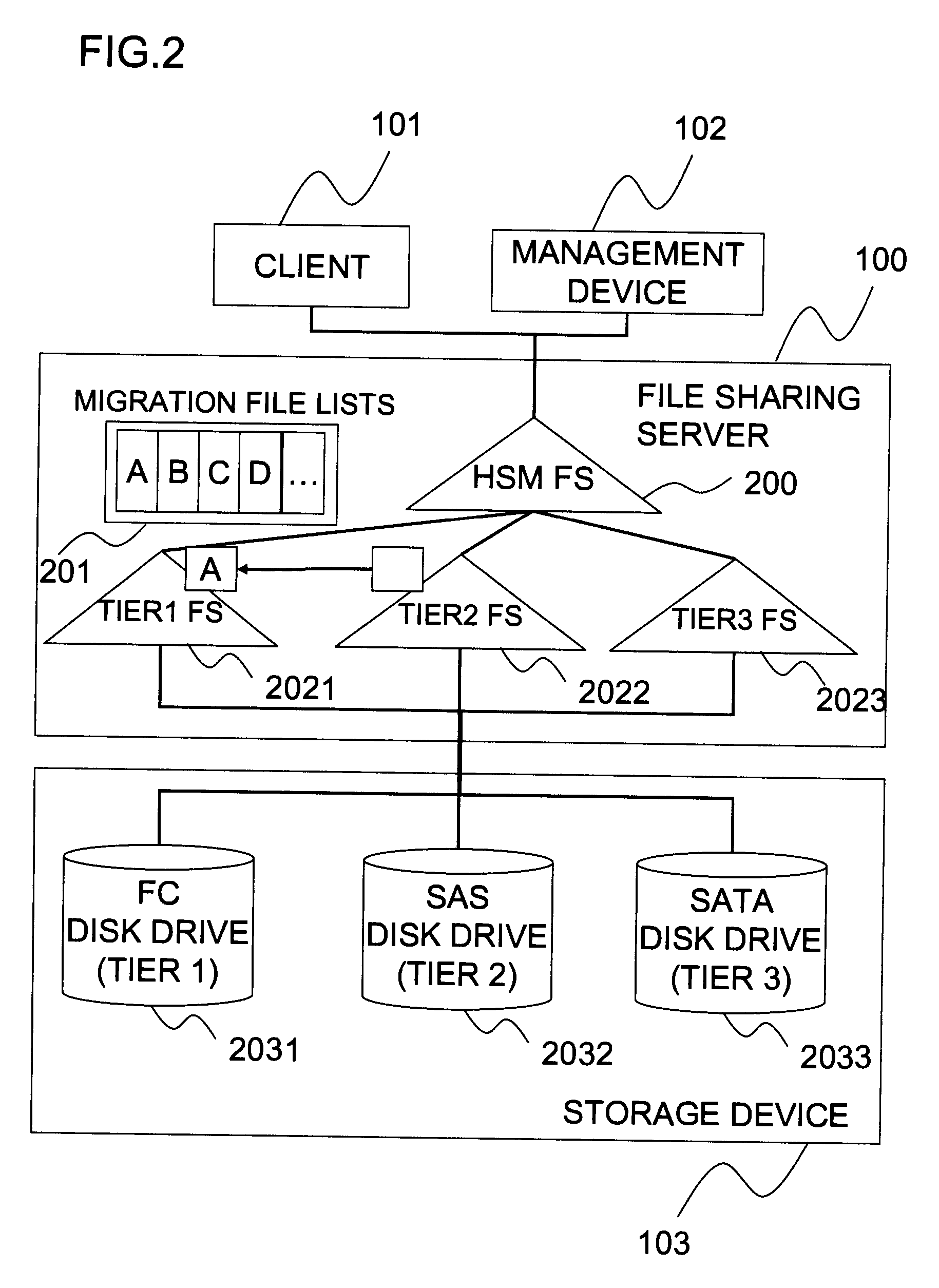
Hierarchical storage management system
InactiveUS20060010169A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsFile systemSecondary layer
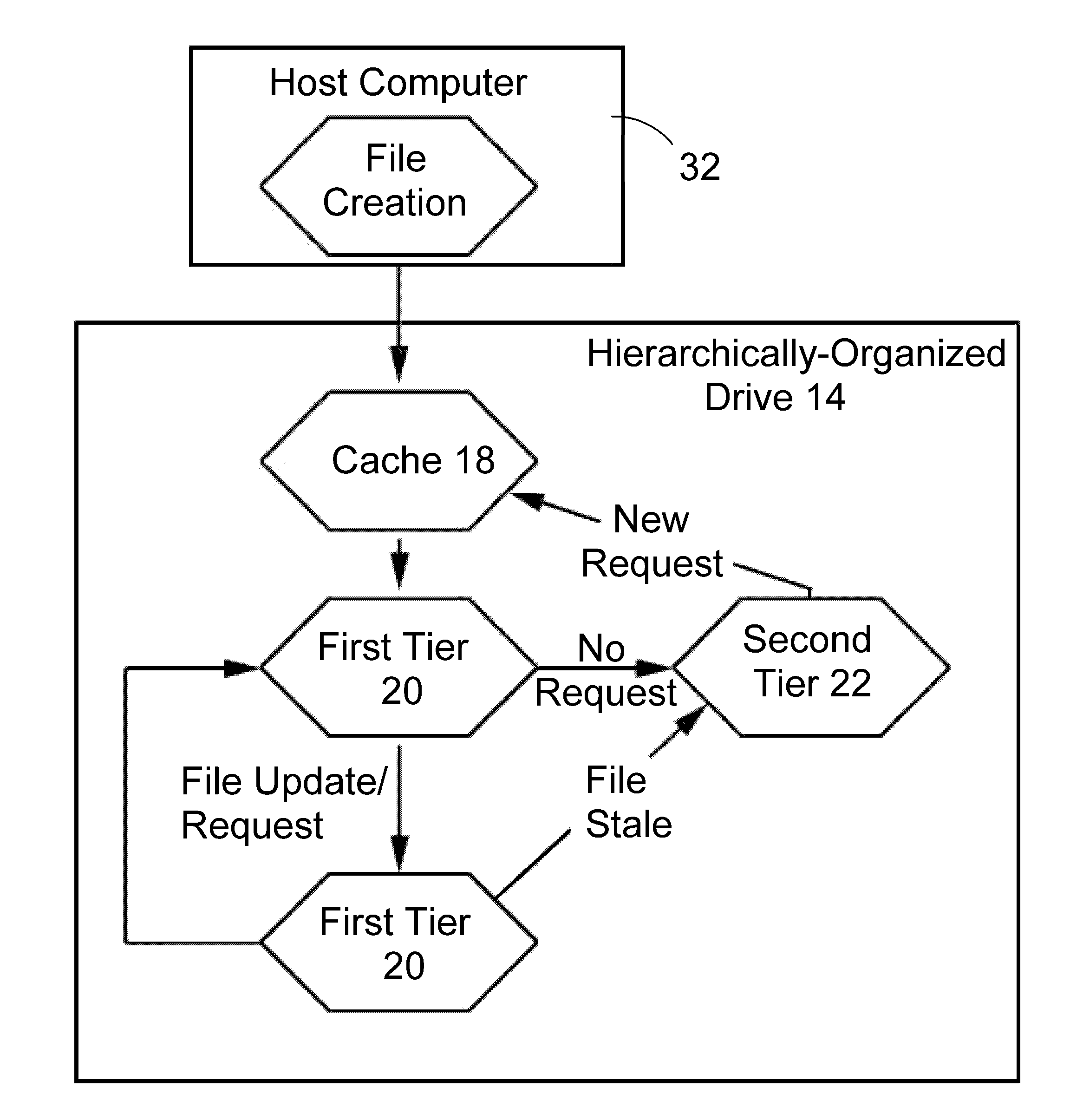
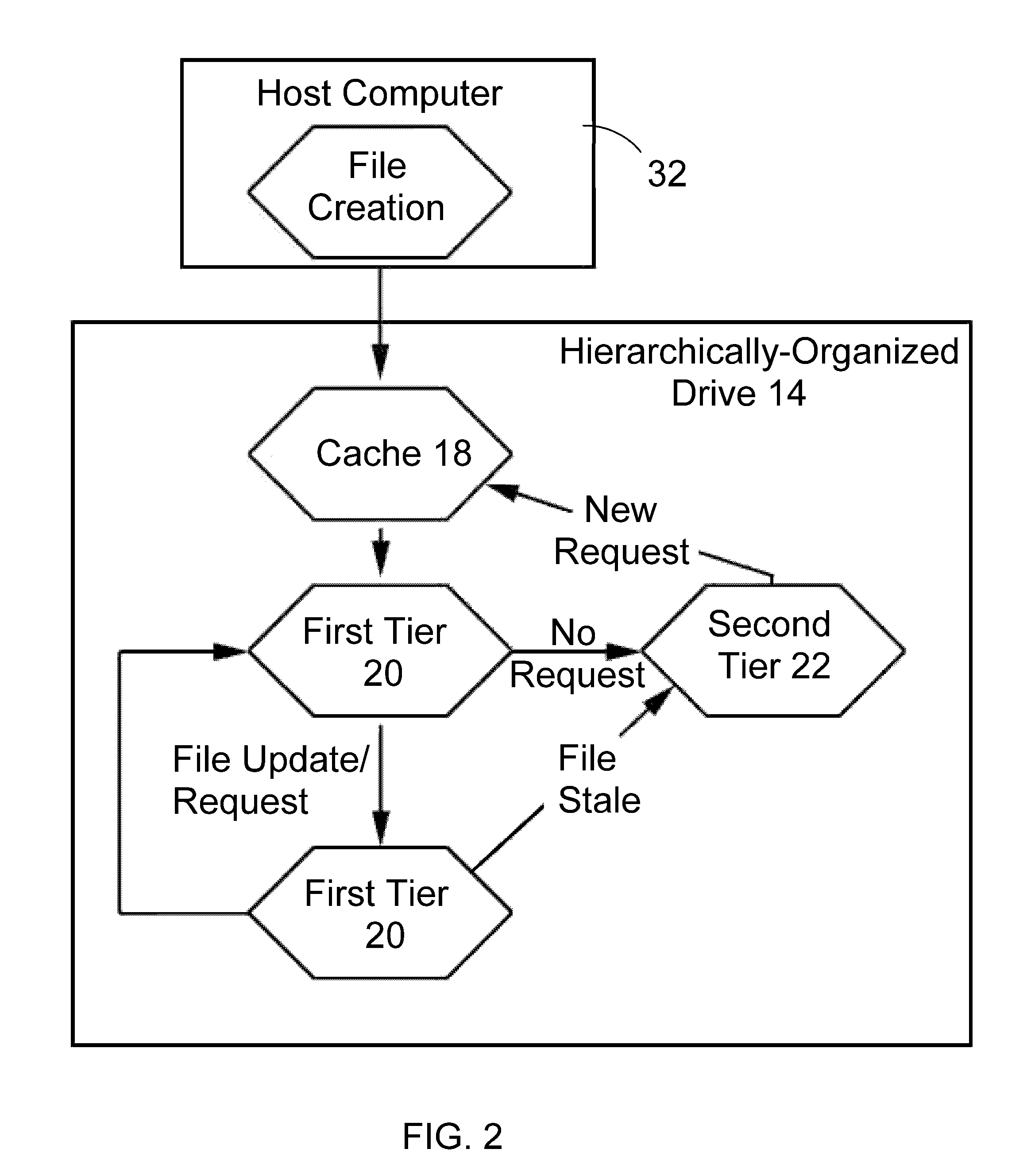
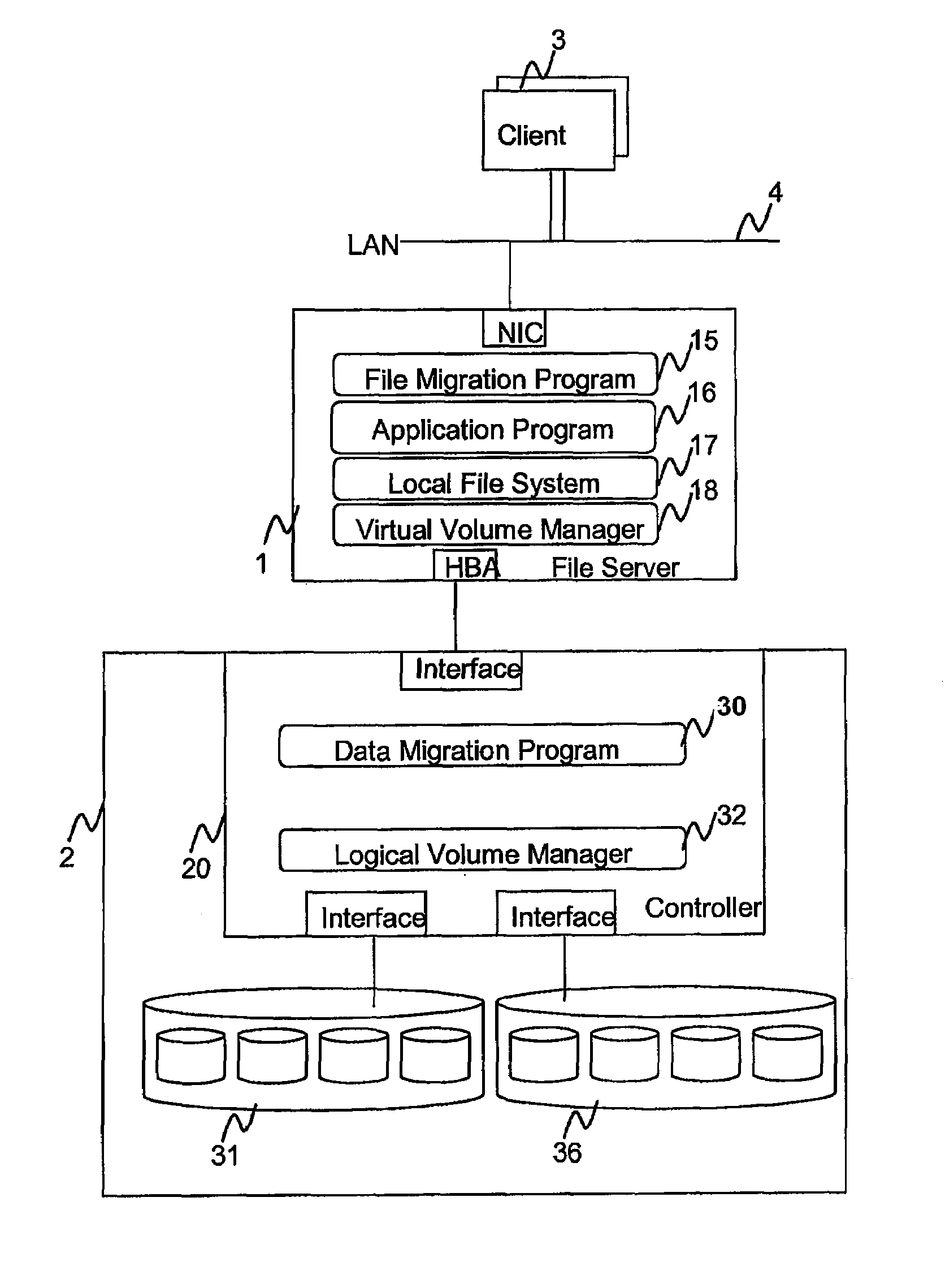
A hierarchical storage system comprises a host computer and a storage system. The storage system comprises at lease two kinds of storage devices, a first tier storage and a second tier storage. The first tier storage is a high performance (or high cost) storage device, and the second tier storage is a lower performance (or lower cost) storage device. The storage system creates a virtual volume based on the first and second tier storages, and enables the host computer to access the virtual volume. A file system in the host computer knows which region of the virtual volume corresponds to the first tier storage and which region of the virtual volume corresponds to the second tier storage. When the file system receives a command to migrate a file from the first tier to the second tier storage, e.g., from a user, the file system examines the address information of the virtual volume where the file resides, and instructs the storage system to migrate the blocks of the designated addresses.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
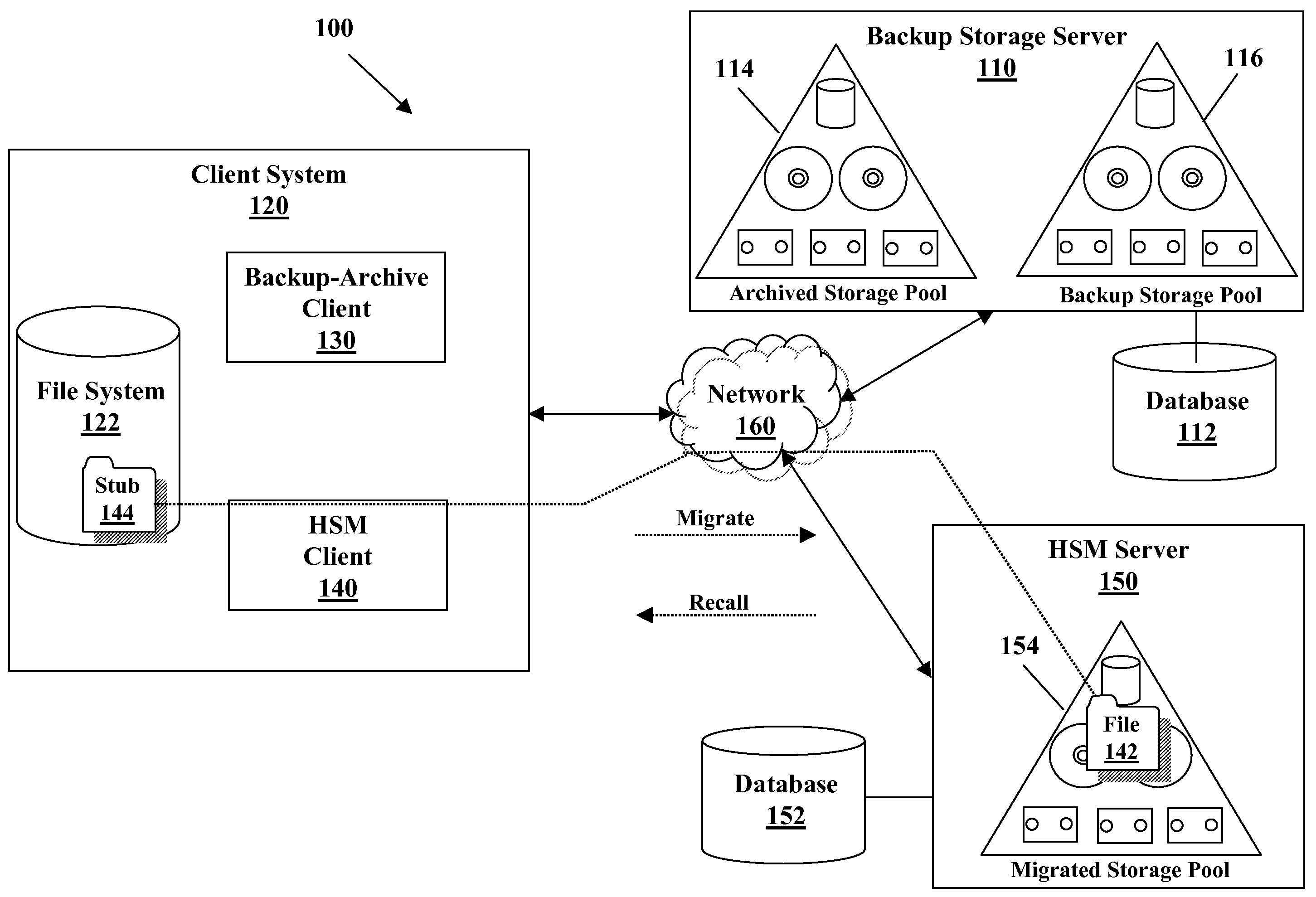
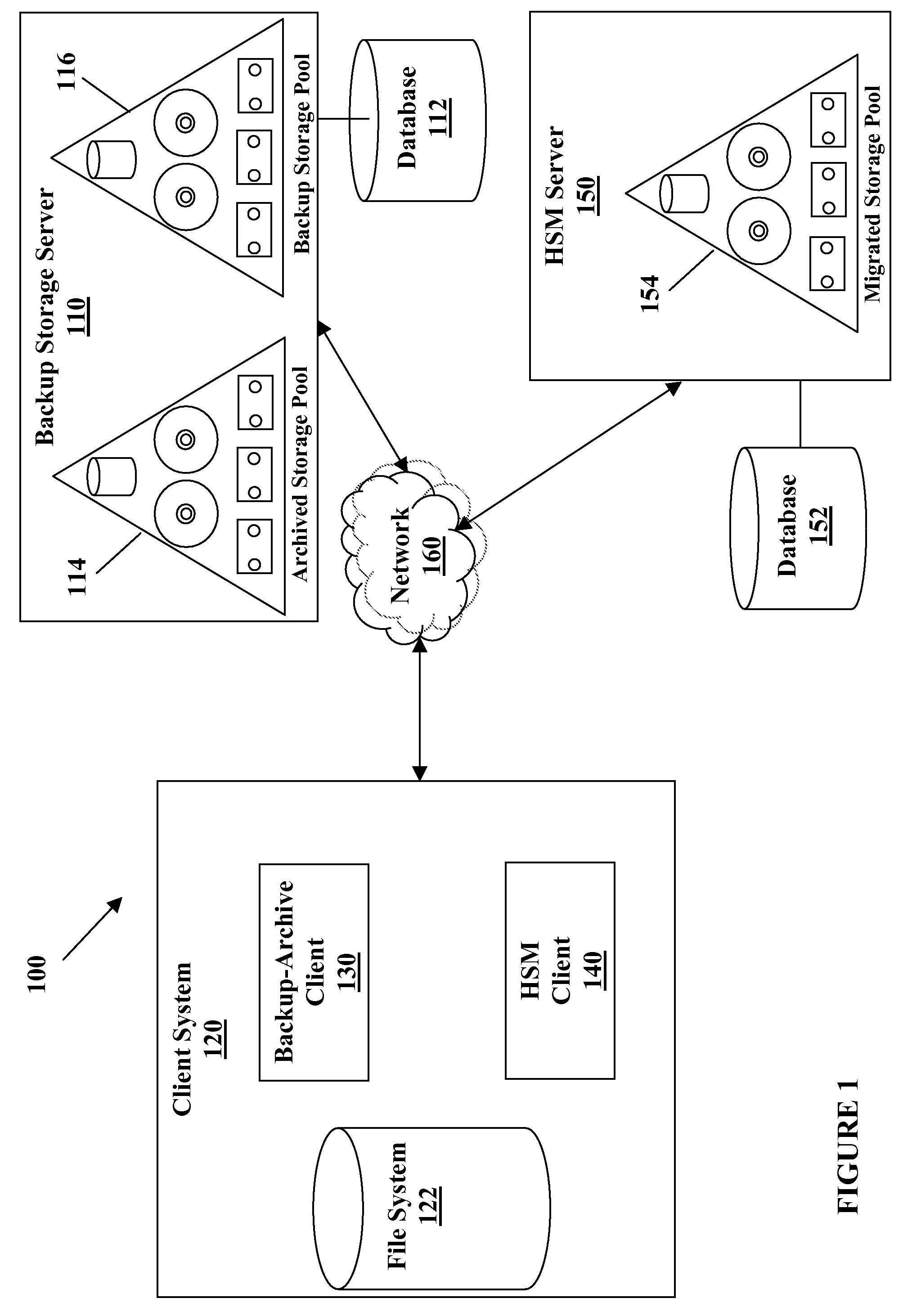
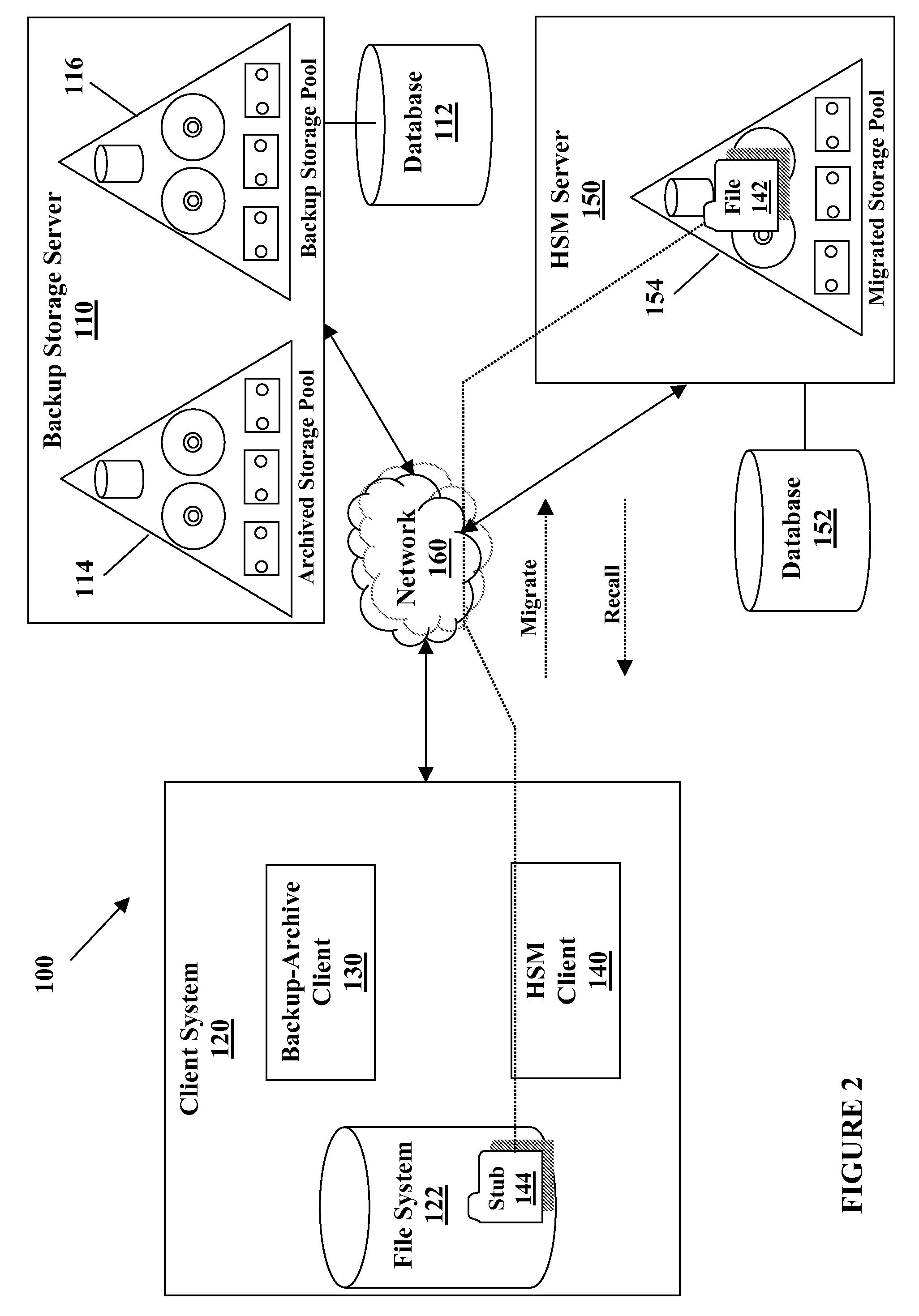
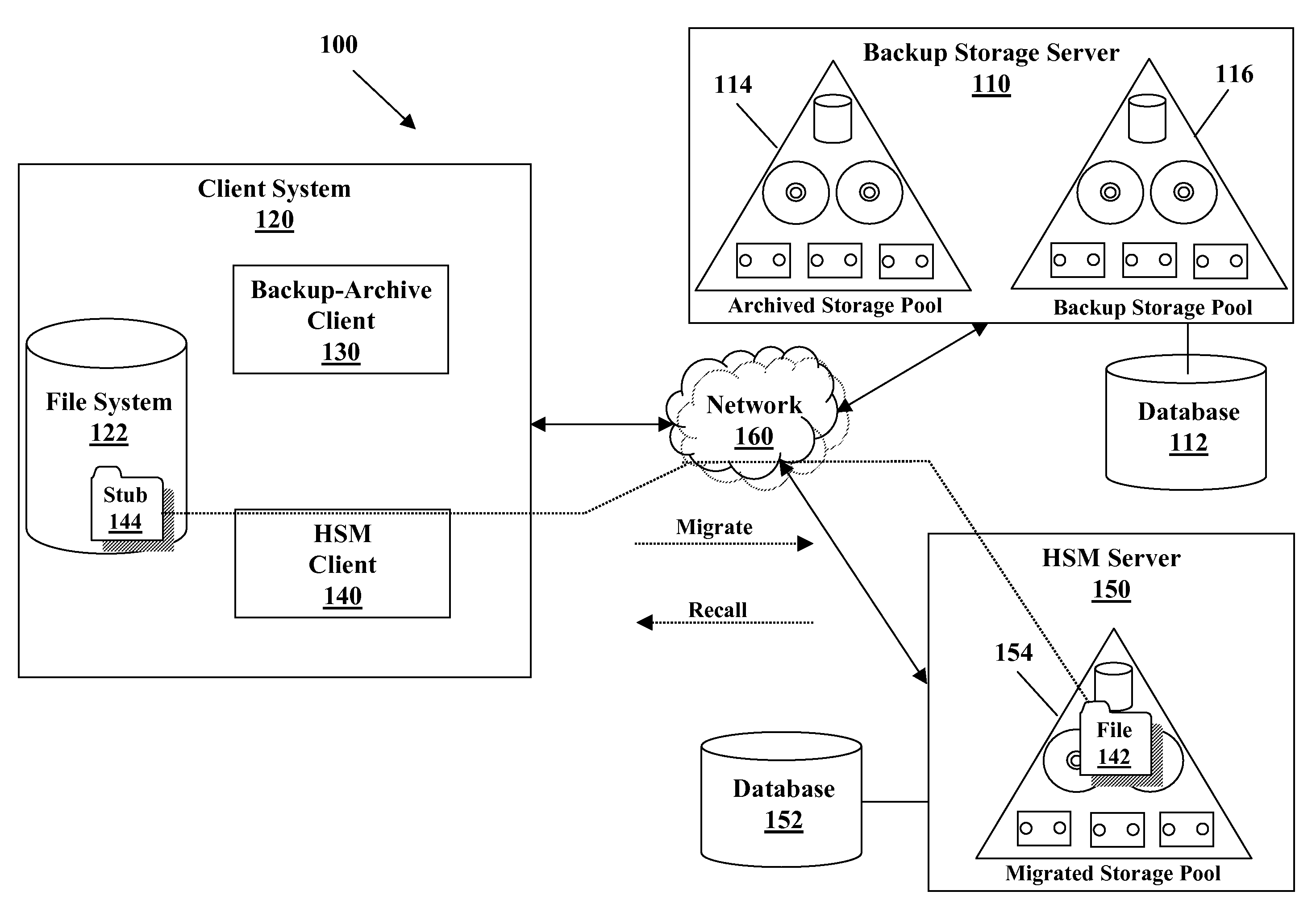
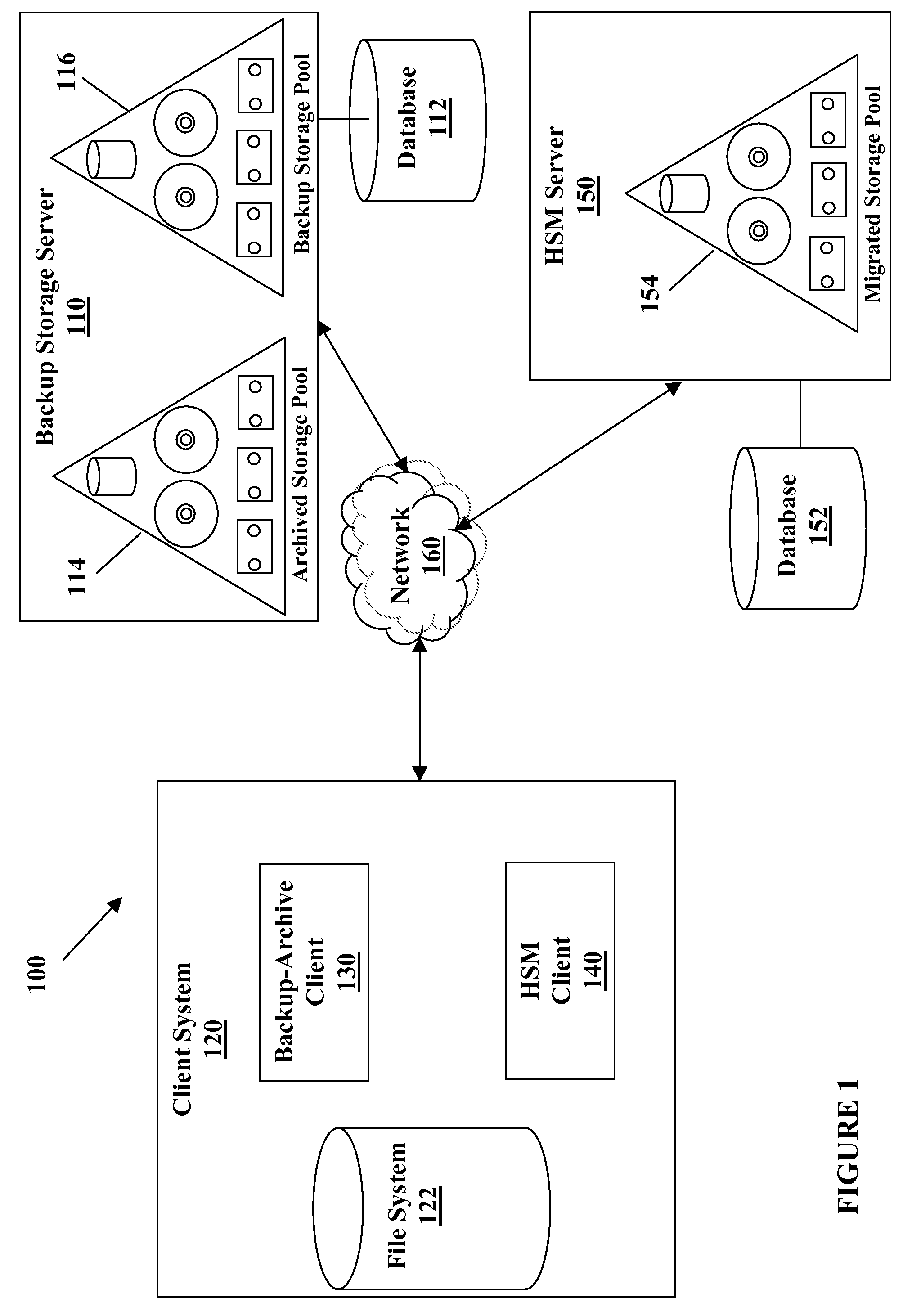
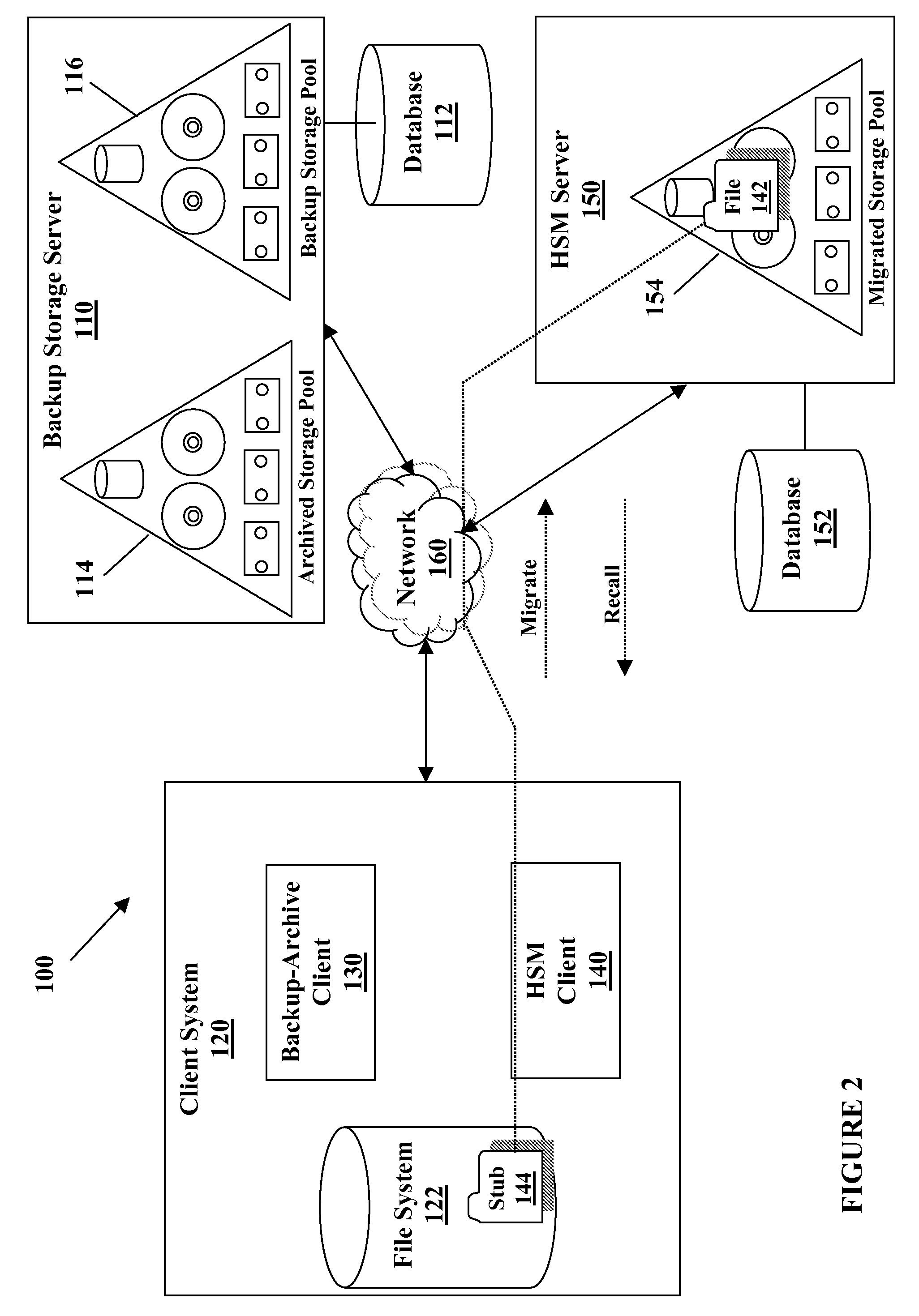
System and method for providing a backup/restore interface for third party hsm clients
InactiveUS20090249005A1Efficient and effective backDigital data information retrievalError detection/correctionThird partyFile system
A method for performing a backup of a stub object located on a file system managed by a hierarchical storage manager configured to migrate data objects from the file system to a migration storage pool is provided. The stub object includes information for recalling a migrated data object. The method comprises determining whether a backup copy of the migrated data object is stored in a backup storage pool if the backup is performed in an incremental backup operation; directing the hierarchical storage manager to recall the migrated data object to the file system if the backup copy of the migrated data object is not stored in the backup storage pool or if the backup is performed in a selective backup operation; creating the backup copy of the migrated data object if the migrated data object is recalled; storing the backup copy of the migrated data object in the backup storage pool if the migrated data object is recalled; creating a backup copy of the stub object if the migrated data object is not recalled; storing the backup copy of the stub object from the file system in the backup storage pool if the migrated data object is not recalled; and logically grouping the backup copy of the migrated data object with the backup copy of the stub object in the backup storage pool such that the backup copy of the migrated data object cannot be deleted from the backup storage pool unless the backup copy of the stub object does not exist in the backup storage pool if the migrated data object is not recalled.
Owner:IBM CORP
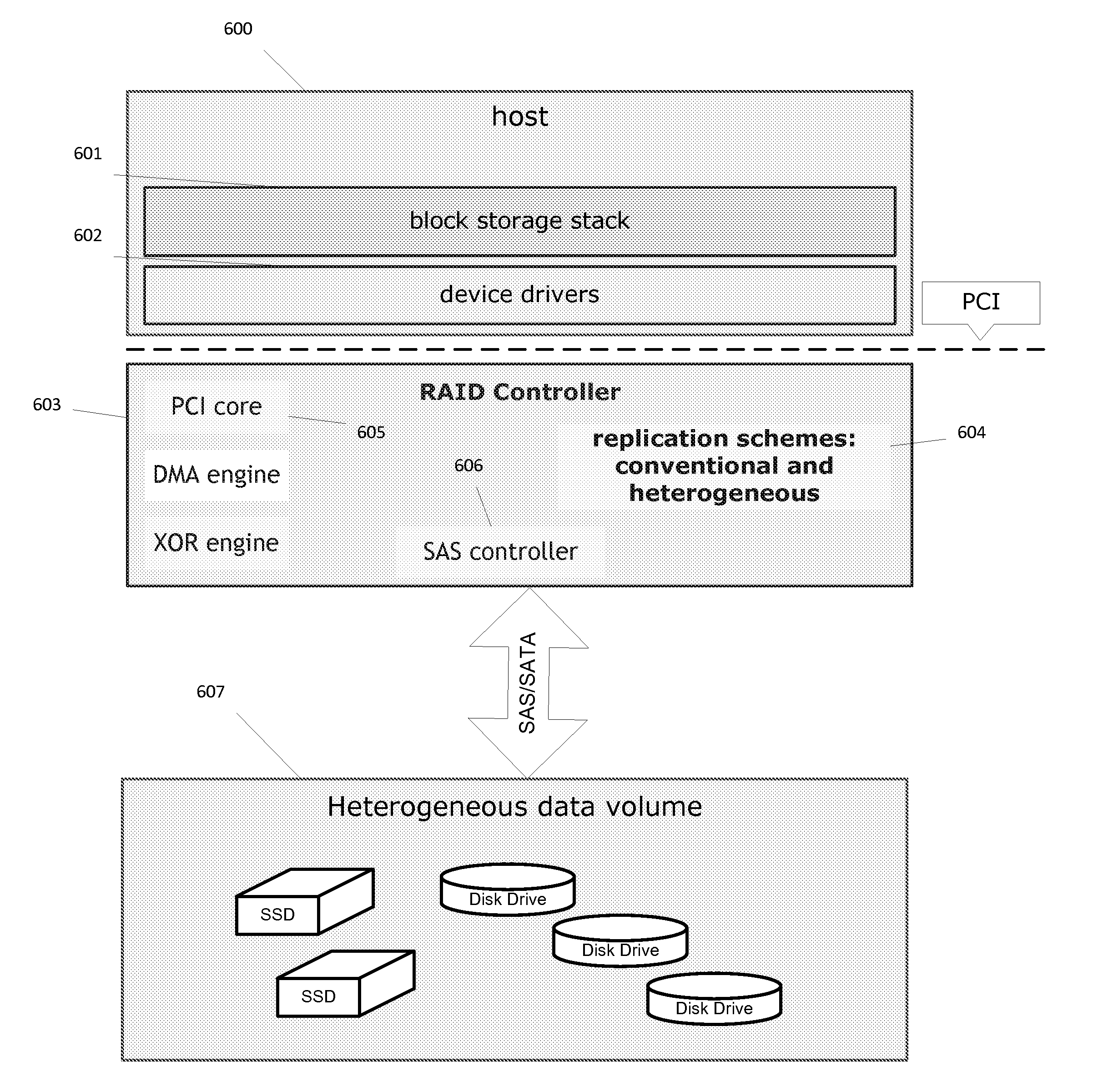
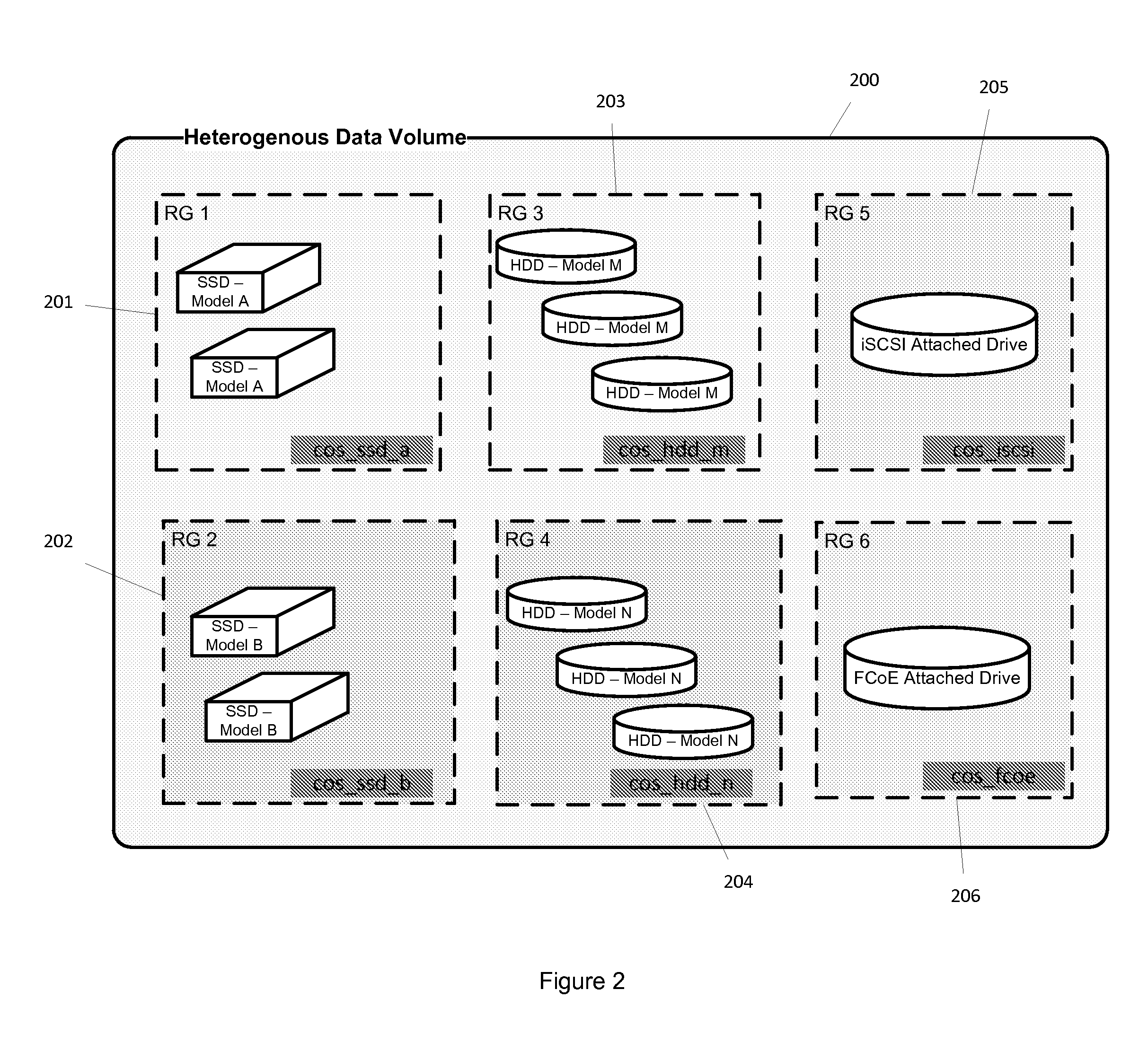
Method and system for heterogeneous data volume
ActiveUS20120017043A1Improve I/O performanceImprove life expectancyDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionData accessModel Number
A method and system is disclosed for providing a heterogeneous data storage comprising a plurality of storage devices of different types with respect to device vendor, model, capacity, performance and / or function. The present invention employs data access mechanisms specific to the type of underlying storage and the type of data to be stored or retrieved, and provides for integrated remote mirroring, disaster recovery and hierarchical storage management (HSM), as well as improved I / O performance and life expectancy of storage disks. A method of writing to and reading from heterogeneous data volume is also disclosed.
Owner:NEXENTA BY DDN INC
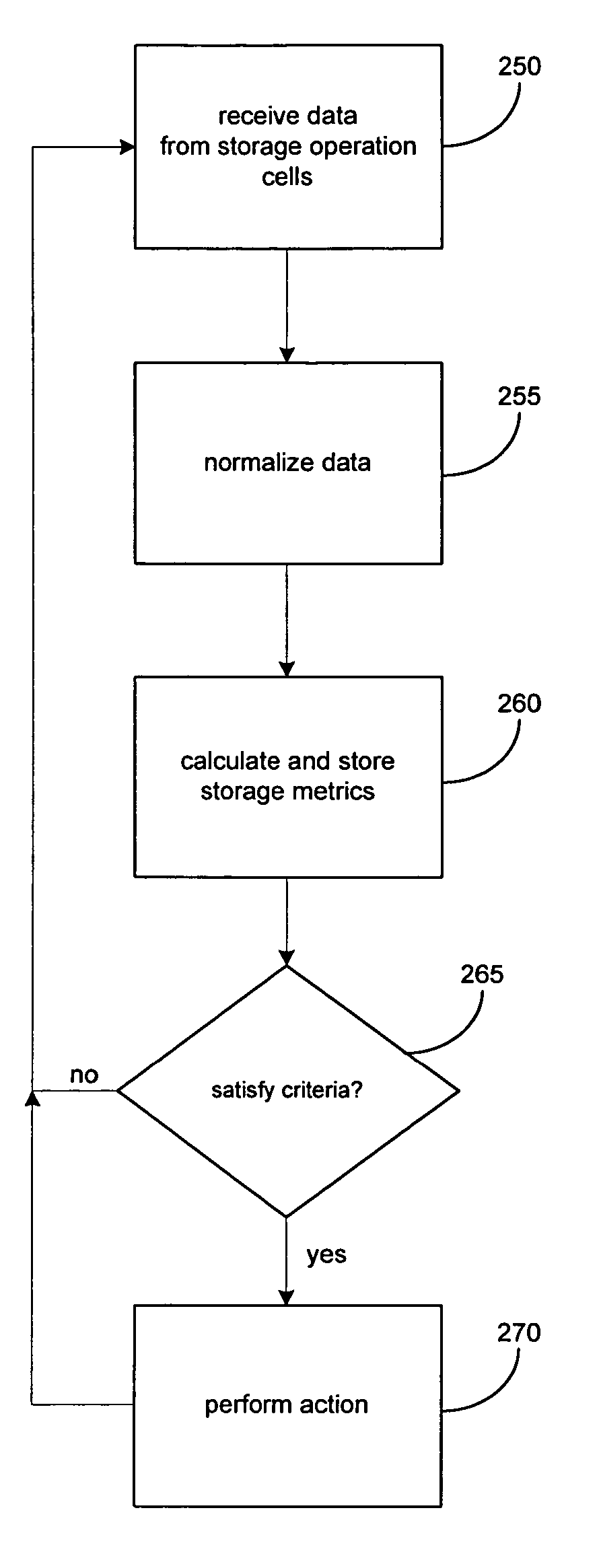
Systems and methods for generating a storage-related metric
ActiveUS20060053263A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionData managementStorage management
The present invention provides systems and methods for data storage. A hierarchical storage management architecture is presented to facilitate data management. The disclosed system provides methods for evaluating the state of stored data relative to enterprise needs by using weighted parameters that may be user defined. Also disclosed are systems and methods evaluating costing and risk management associated with stored data.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
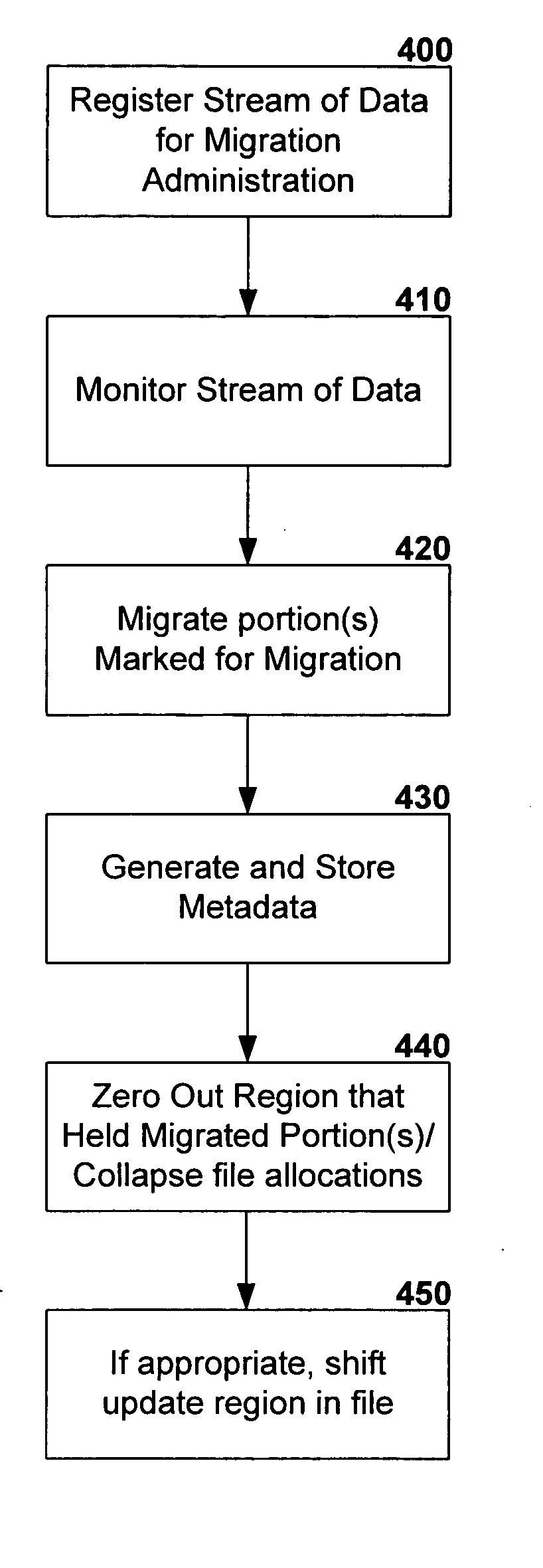
Partial migration of an object to another storage location in a computer system
InactiveUS20050097126A1Maximize system storage efficiencyMaximize efficiencyData processing applicationsRedundant operation error correctionData streamFile system
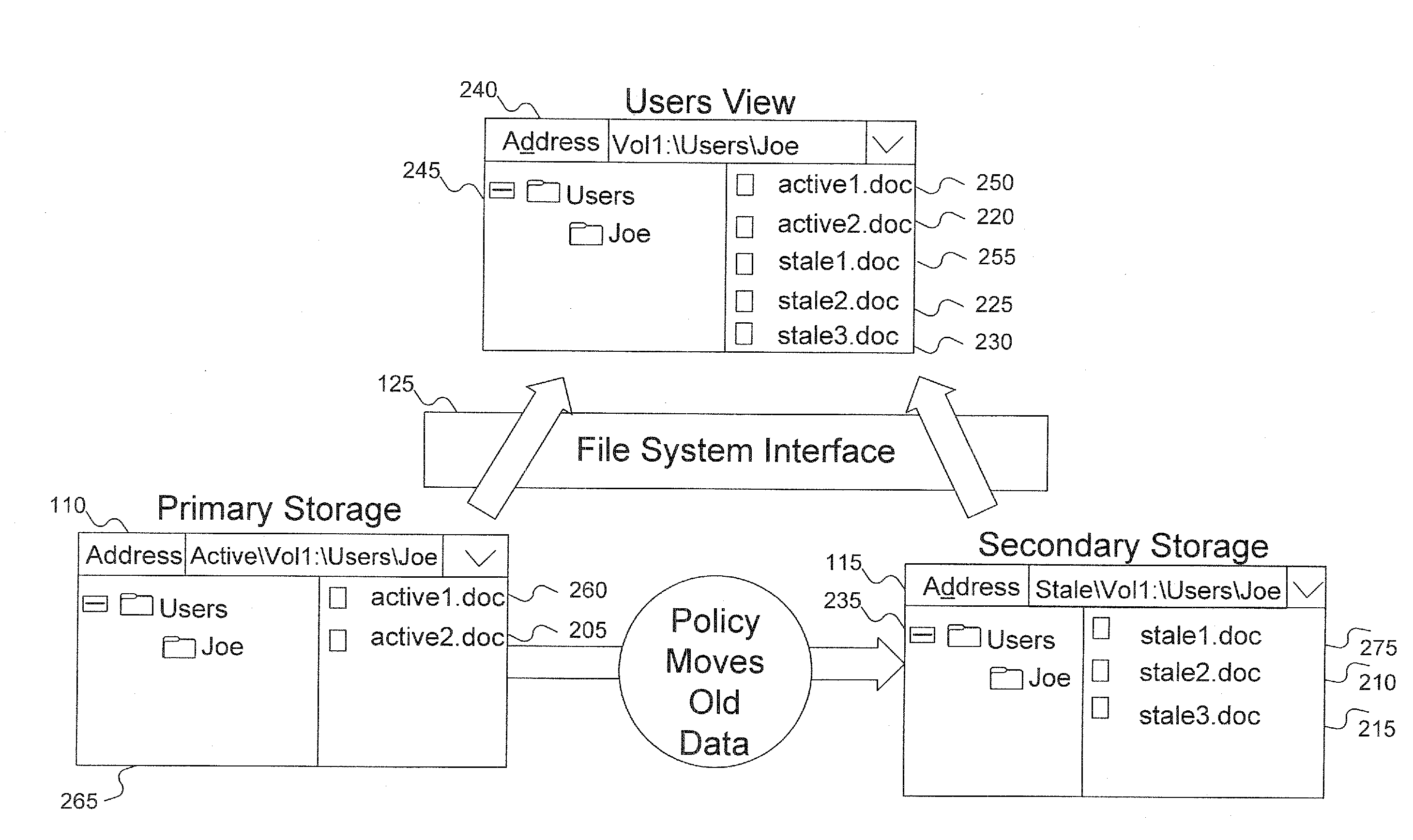
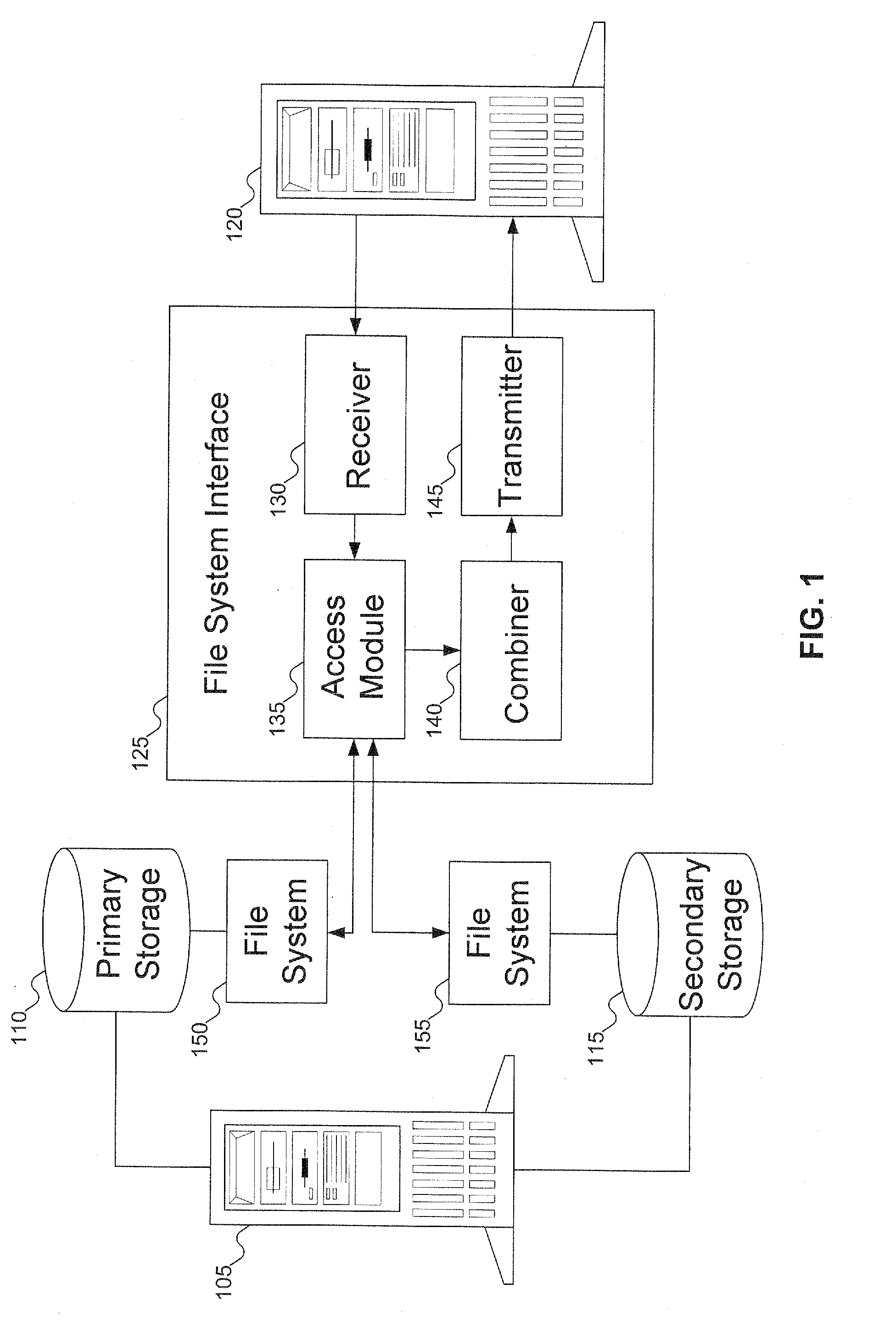
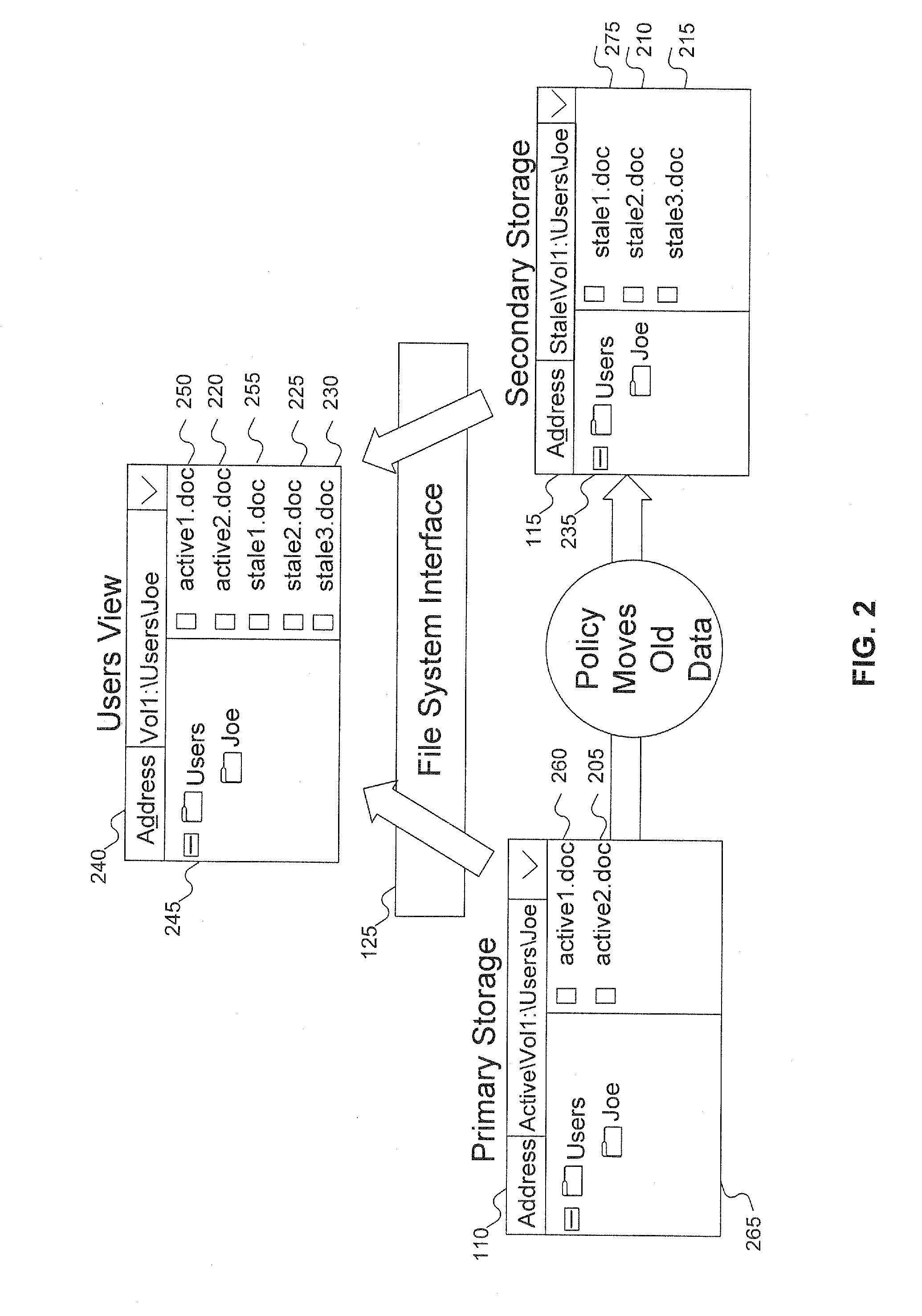
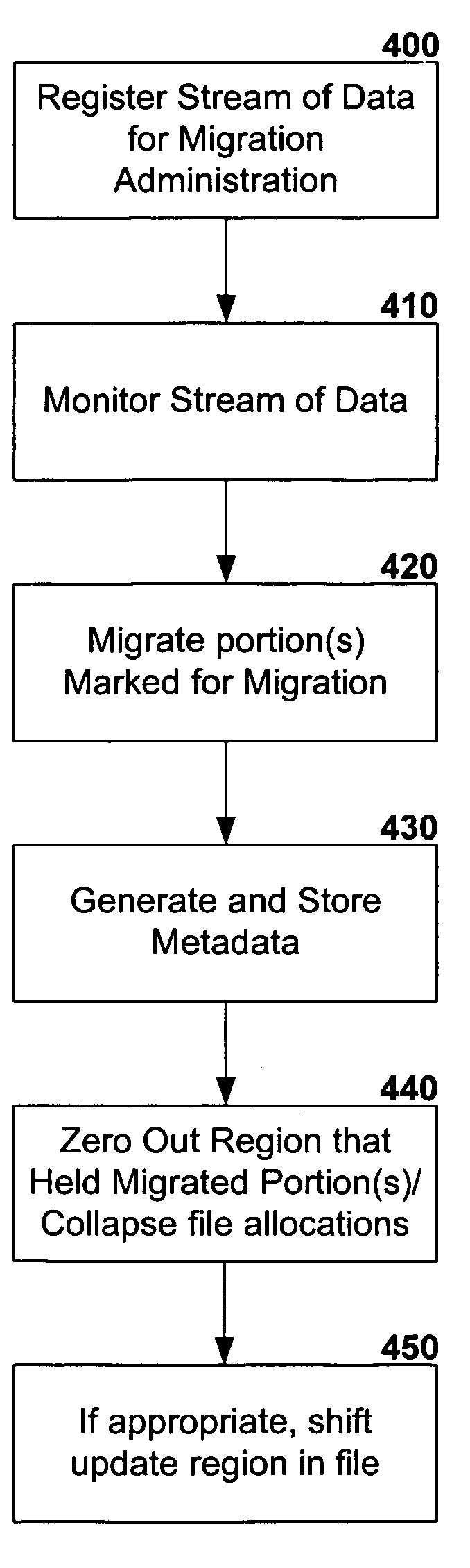
A technique is provided whereby a stream of data located in a first storage location is registered for migration administration and according to preset criteria, portion(s) of the stream of data that are suited to another storage location are migrated to maximize system storage efficiencies. The file system may have use of facilities that enable the monitoring of files / streams that have been registered for migration administration or files / streams may be polled according to preset criteria. If the stream of data has portions to migrate to another storage location, the hierarchical storage management (HSM) system migrates the data to the other storage location, such as to long term or off-line storage, and preserves the data relationships of the stream via metadata. The technique allows for multiple volumes to be spanned by the migration target location, and multiple file systems may service the source and target.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Hierarchically structured mass storage device and method
InactiveUS20100325352A1Faster access timeHigh write enduranceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationAccess timeStorage management
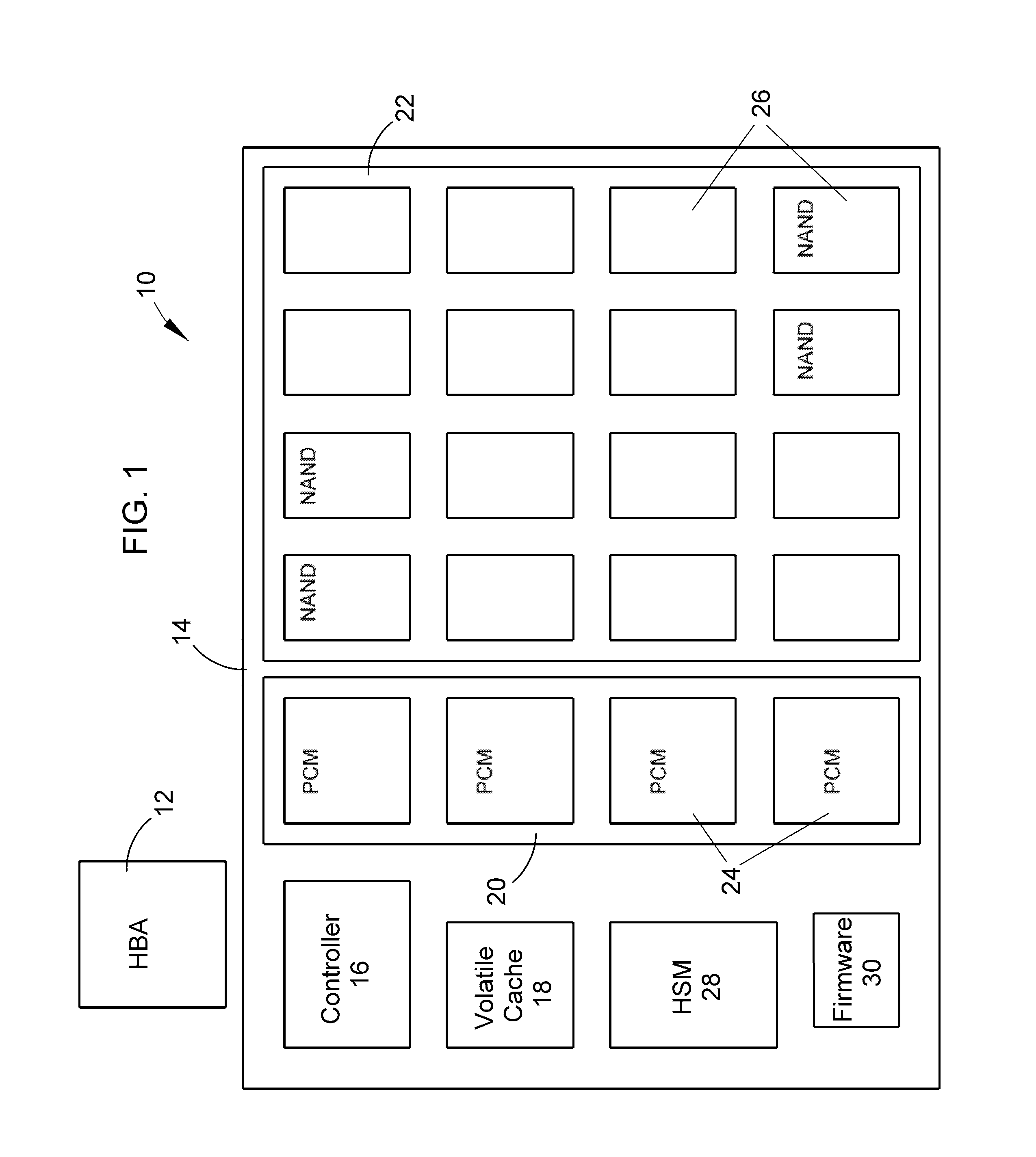
A hierarchically-structured computer mass storage system and method. The mass storage system includes a mass storage memory drive, control logic on the mass storage memory drive that includes a controller and one or more devices for executing a hierarchical storage management technique, a volatile memory cache configured to be accessed by the control logic, and first and second non-volatile storage arrays on the mass storage memory drive and comprising, respectively, first and second non-volatile memory devices. The first and second non-volatile memory devices have properties including access times and write endurance, and at least one of the access time and the write endurance of the first non-volatile memory devices is faster or higher, respectively, than the second non-volatile memory devices. Desired data storage localities on the storage arrays are determined through access patterns and selectively utilizing the properties of the memory devices to match the data storage requirements.
Owner:OCZ STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Partial file migration mechanism
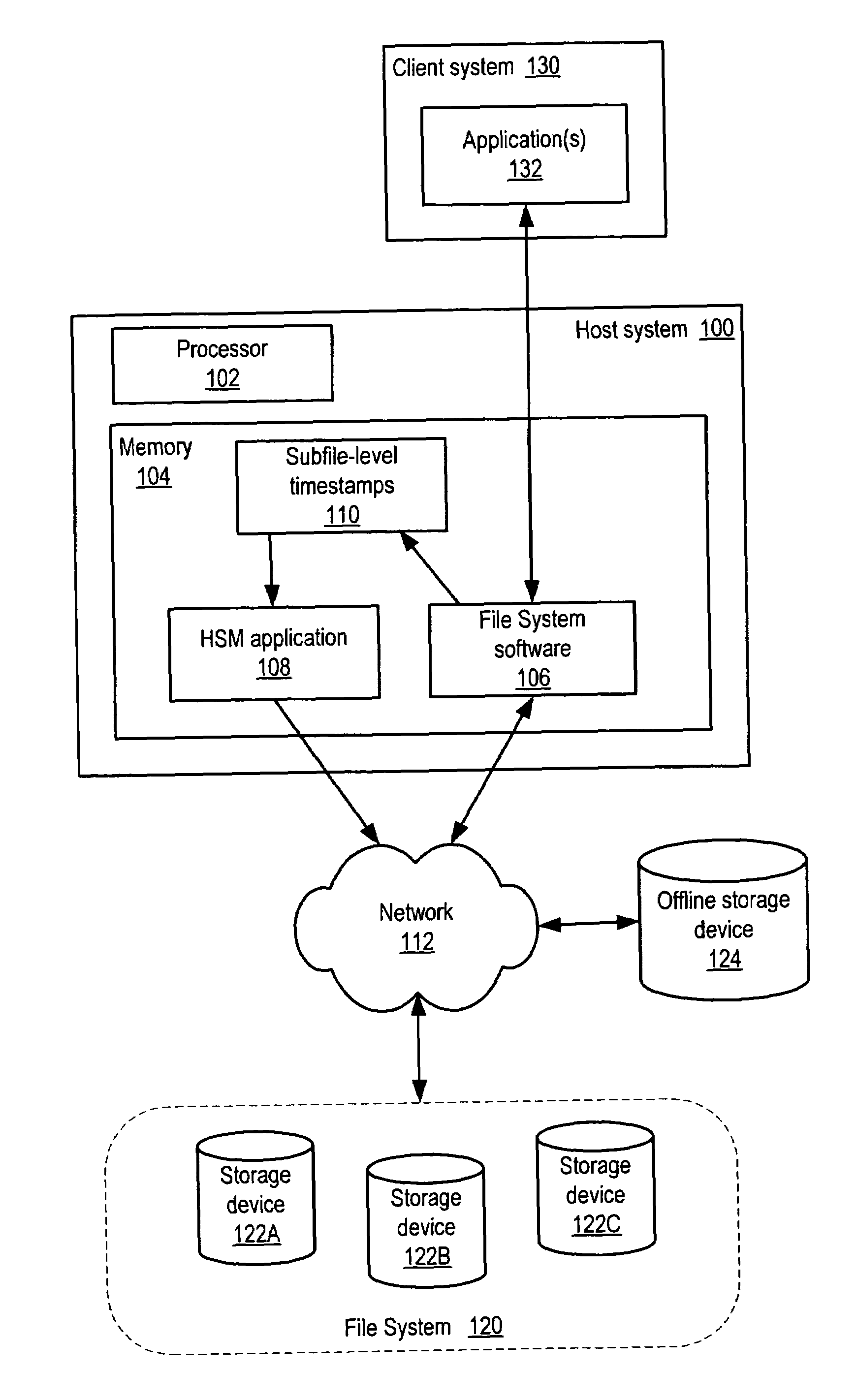
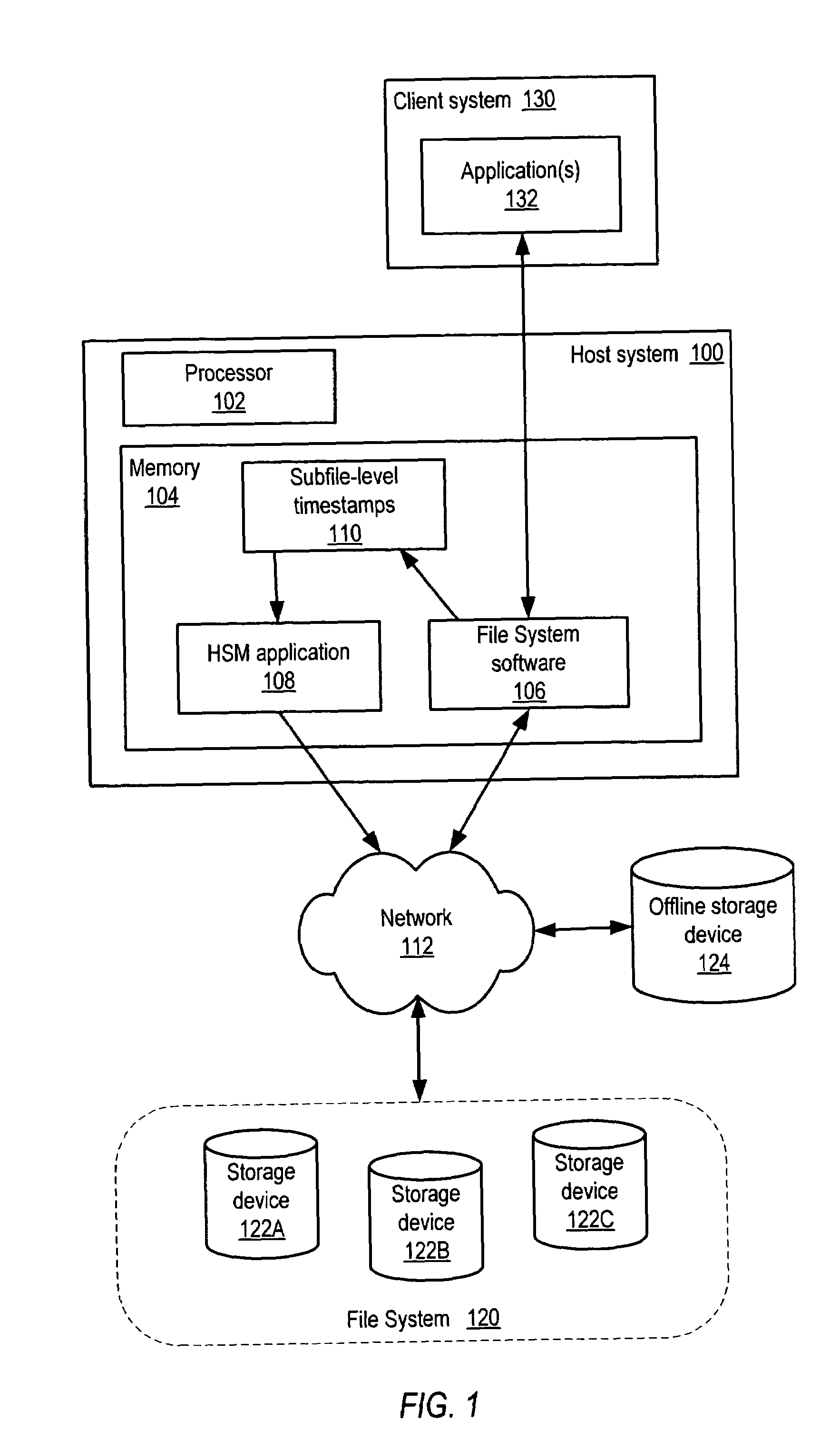
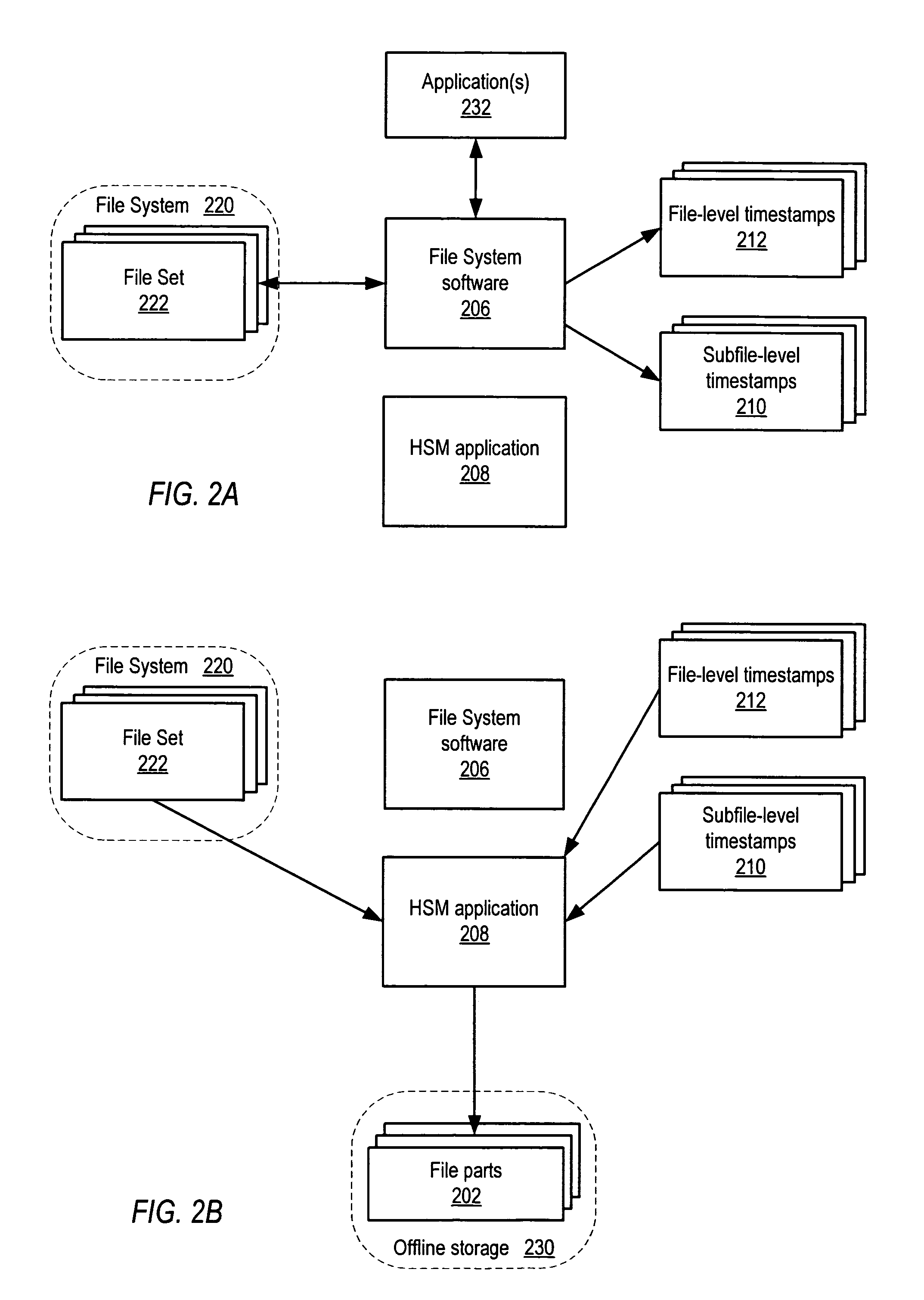
ActiveUS7165059B1Data processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsTimestampFile system
System and method for partial file migration in file systems by Hierarchical Storage Management (HSM) applications. Embodiments may provide an automated mechanism for HSM applications to partially migrate files by migrating the inactive parts of the files to offline storage while leaving the active parts of the files on disk and active in the file system. In embodiments, access information including timestamps may be recorded and maintained at the subfile level to enable detection of inactivity at the subfile level and hence partial file migration by migrating only the inactive parts of files. The parts of files may be extents, blocks, or ranges. The access information may be recorded and maintained in-memory only, in a separate file on disk, or in extent descriptors for the files.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
Hierarchical storage system
InactiveUS20050097132A1Efficiently and cost-effectively usEfficiently and usInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer architectureStorage management
A storage system comprises a storage array containing an hierarchy of storage devices of at least three types and having a respective class hierarchy, and a controller. The controller is coupled to the storage device hierarchy and can execute an hierarchical storage management capability that selectively controls access to the hierarchy of storage devices.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
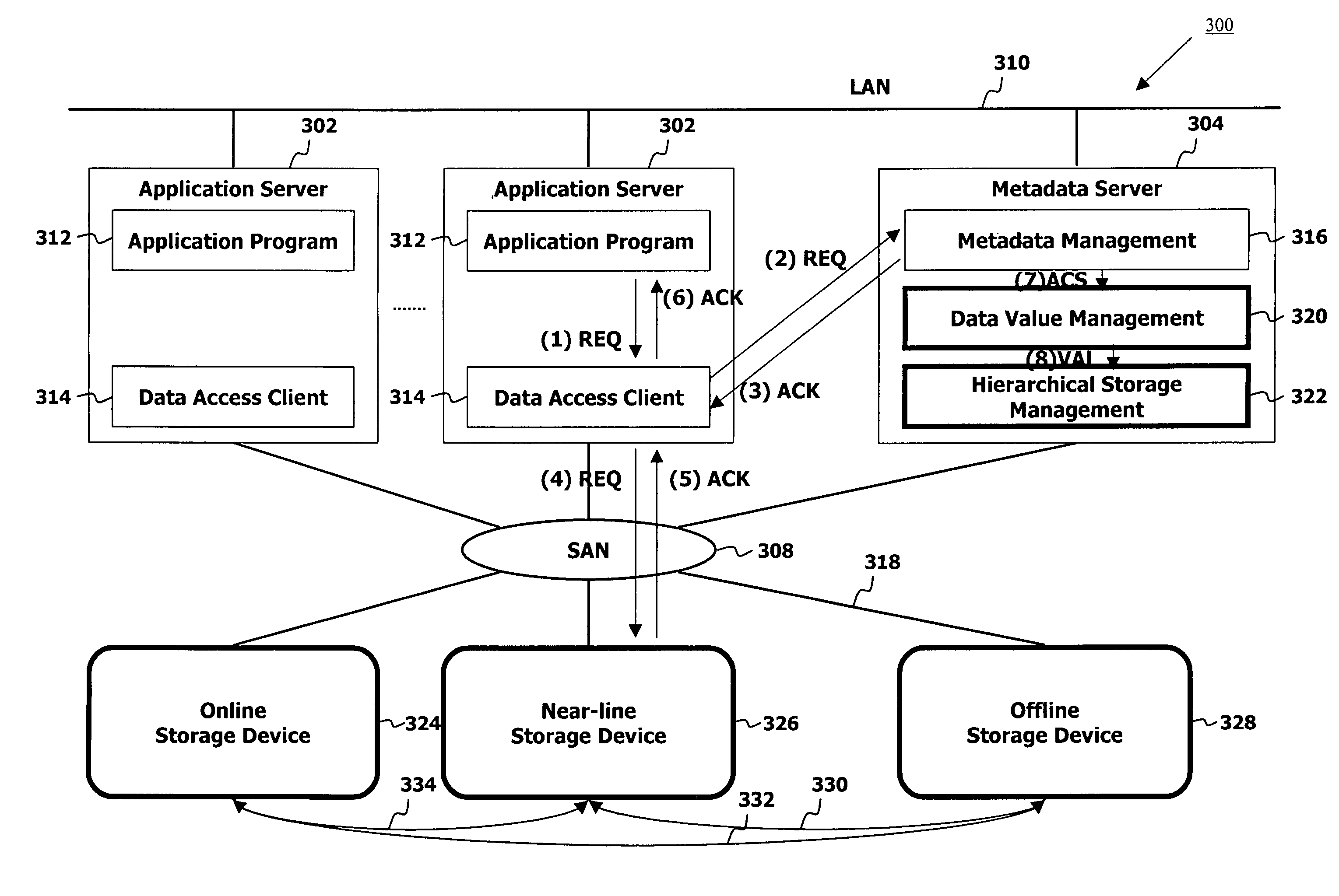
Method and apparatus of hierarchical storage management based on data value
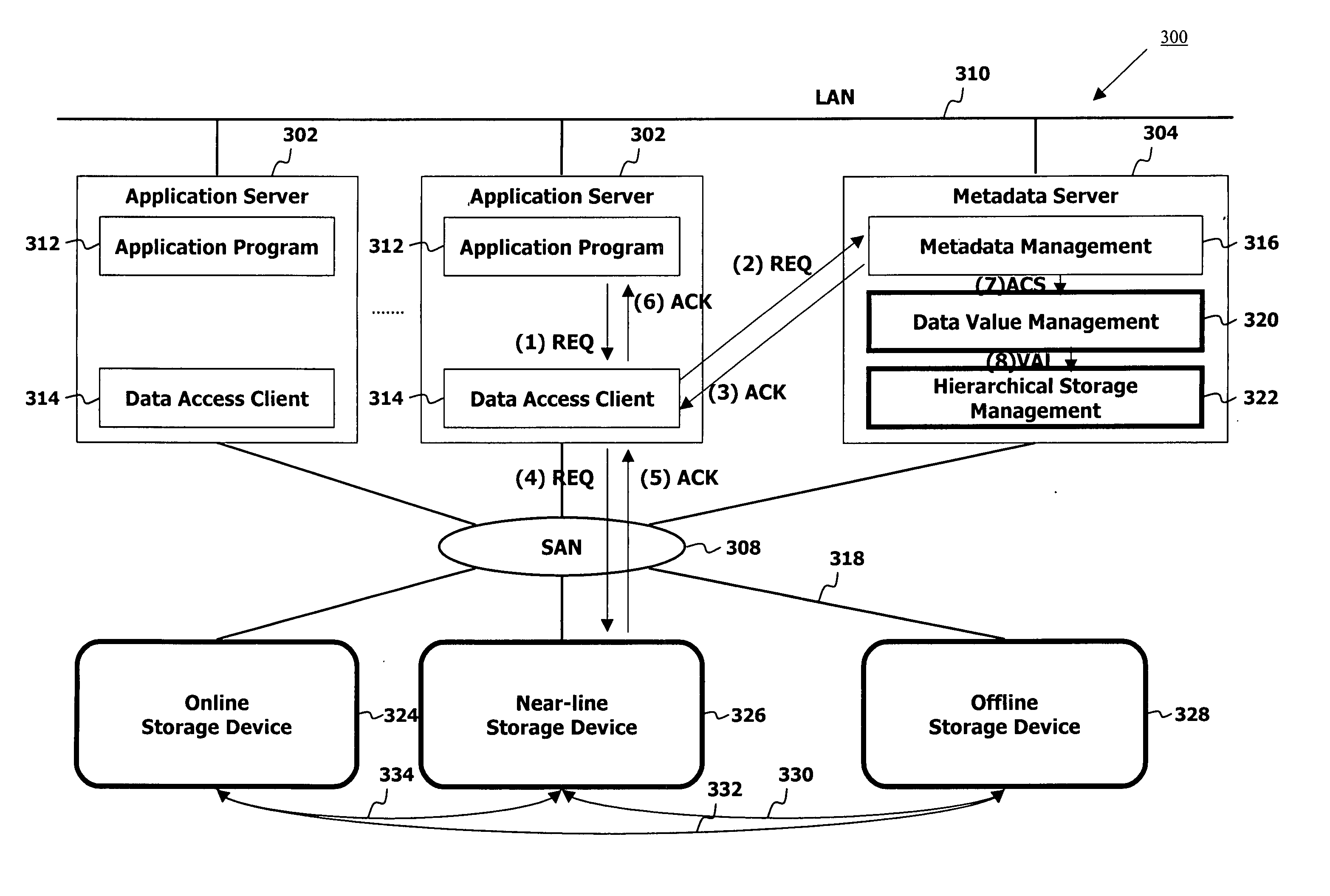
InactiveUS20060015529A1Manage data volumesMinimal costData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsData streamMetadata management
A hierarchical storage data management system includes application servers, a metadata server interconnected with the application servers through a local area network, storage devices interconnected through data flow paths, and a storage network connecting the storage devices to the application servers and to the metadata server. The metadata server including a metadata management element, a data value management unit, and a hierarchical storage management element calculates a data value for each of stores data objects in the system, assigns a storage cost value for each of storage areas in the system, normalizes calculated data values and assigned storage costs to an identical value range, compares normalized data values with normalized storage costs thereby determining whether to relocate the data objects to different storage areas, and relocates data objects to storage areas with storage cost values identical with data values of the data objects.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Systems and methods for storage modeling & costing
The present invention provides systems and methods for data storage. A hierarchical storage management architecture is presented to facilitate data management. The disclosed system provides methods for evaluating the state of stored data relative to enterprise needs by using weighted parameters that may be user defined. Also disclosed are systems and methods evaluating costing and risk management associated with stored data.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
Hierarchical storage management system
InactiveUS7441096B2Digital data information retrievalMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFile systemSystem migration
A hierarchical storage system comprises a host computer and a storage system. The storage system comprises at lease two kinds of storage devices, a first tier storage and a second tier storage. The first tier storage is a high performance (or high cost) storage device, and the second tier storage is a lower performance (or lower cost) storage device. The storage system creates a virtual volume based on the first and second tier storages, and enables the host computer to access the virtual volume. A file system in the host computer knows which region of the virtual volume corresponds to the first tier storage and which region of the virtual volume corresponds to the second tier storage. When the file system receives a command to migrate a file from the first tier to the second tier storage, e.g., from a user, the file system examines the address information of the virtual volume where the file resides, and instructs the storage system to migrate the blocks of the designated addresses.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
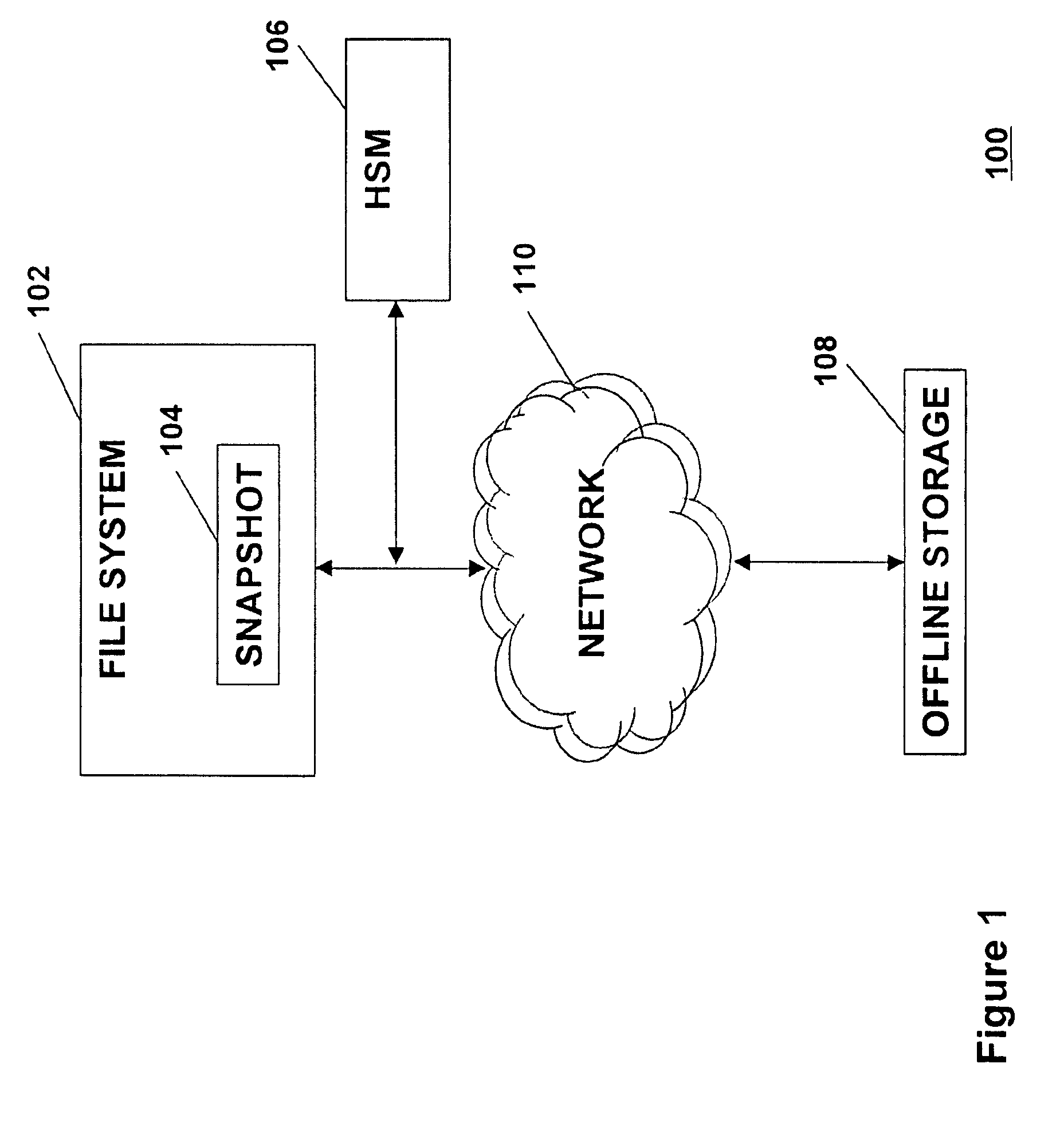
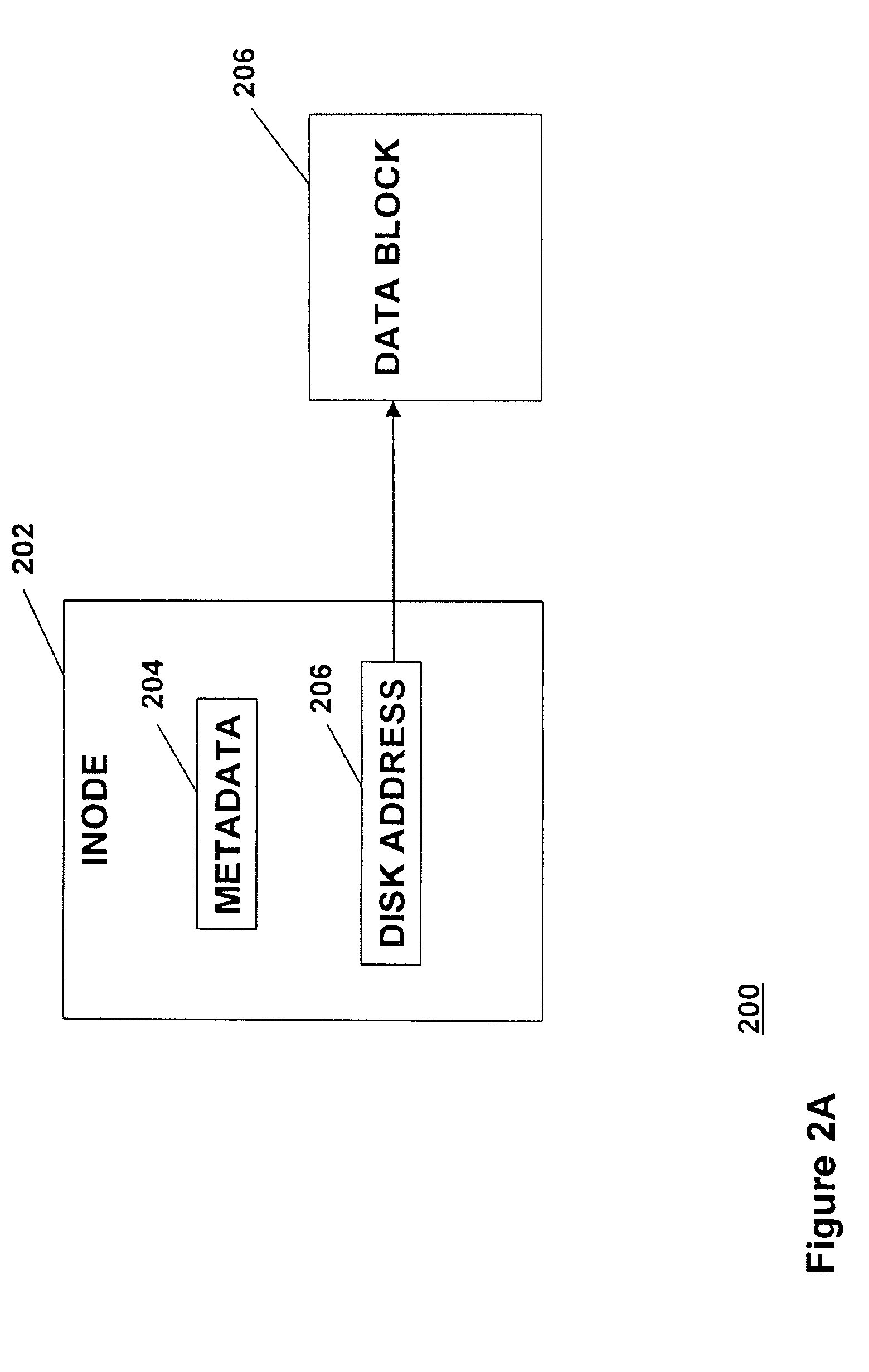
Efficient hierarchical storage management of a file system with snapshots
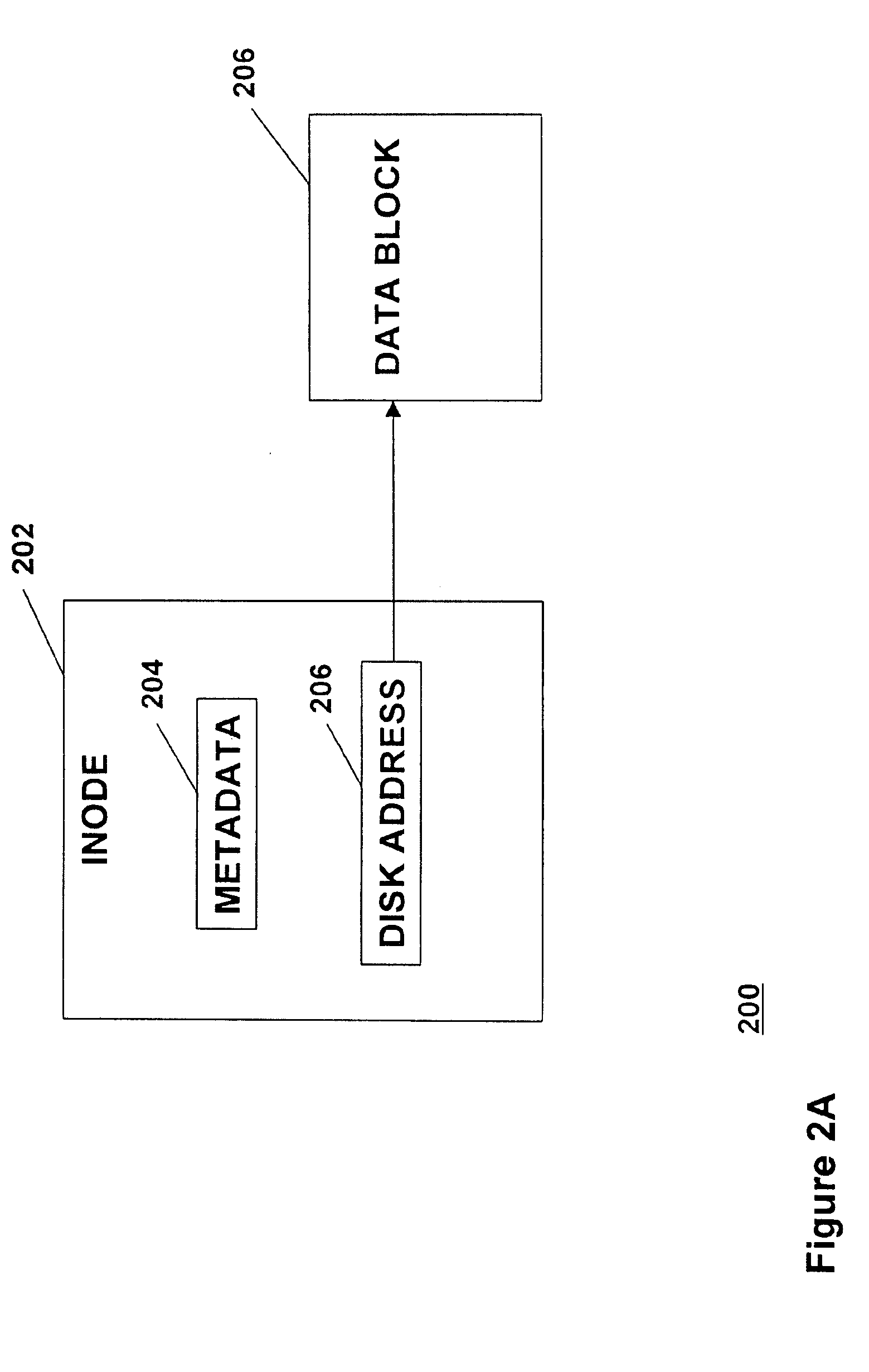
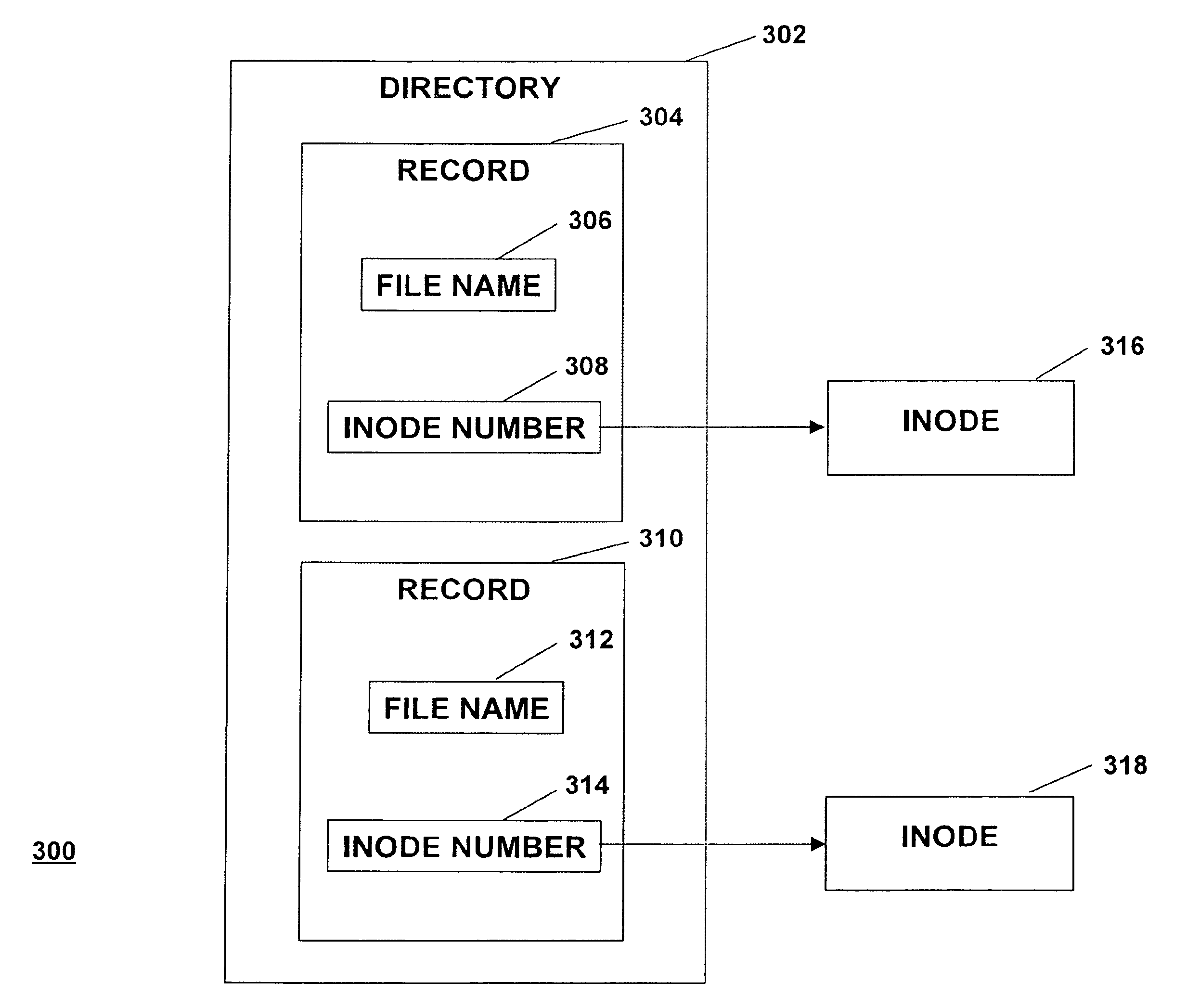
InactiveUS20090043978A1Minimal costEffective Storage ManagementDigital data information retrievalMemory loss protectionInodeMagnetic disks
A method is provided for managing the storage of a file that has been selected for migration from a first storage level within a file system to a second storage level. The method comprises copying each of one or more data blocks of the selected file that are stored in the first storage level at a physical disk address maintained in a corresponding reference of an inode for the selected file from the first storage level to the second storage level; maintaining a logical ditto address in each reference of an inode for each snapshot file in the file system that refers to one of the one or more data blocks of the selected file that were copied to the second storage level; and updating the file system to include a managed region for controlling access to the one or more data blocks through the inode for the selected file.
Owner:IBM CORP
Hierarchical systems and methods for providing a unified view of storage information
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
System and method for hierarchical storage management using shadow volumes
InactiveUS20070220029A1Guaranteed accuracyDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsShadow volumeData file
Data partitioned onto two or more storage devices is presented to a user as if the data resided on a single storage area. Data is divided between the storage areas based on policies. Data on the primary storage can utilize frequent back up or other storage management to ensure the accuracy of the data. The data on the secondary storage can employ other data management than the data management for the primary storage. The subdirectory structure is replicated in each area so a data file can be located in either physical area. This allows data files to migrate between the storage areas based on policy.
Owner:NOVELL INTPROP HLDG
Partial migration of an object to another storage location in a computer system
InactiveUS6981005B1Maximize efficiencyData processing applicationsRedundant operation error correctionData streamFile system
A technique is provided whereby a stream of data located in a first storage location is registered for migration administration and according to preset criteria, portion(s) of the stream of data that are suited to another storage location are migrated to maximize system storage efficiencies. The file system may have use of facilities that enable the monitoring of files / streams that have been registered for migration administration or files / streams may be polled according to preset criteria. If the stream of data has portions to migrate to another storage location, the hierarchical storage management (HSM) system migrates the data to the other storage location, such as to long term or off-line storage, and preserves the data relationships of the stream via metadata. The technique allows for multiple volumes to be spanned by the migration target location, and multiple file systems may service the source and target.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method for clipping migration candidate file in hierarchical storage management system
InactiveUS20100274826A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsFile migrationHierarchical storage management
The system of the present invention curbs an unnecessary inter-tier file migration and provides an inter-tier file migration that conforms to the utilization state. The hierarchical storage management system respectively migrates a frequently accessed file to the upper Tier, and an infrequently accessed file to the lower Tier. This system carries out inter-tier file migration in conformance with the utilization state. This system provides functions for anchoring a Tier for storage for a specified file, and for not permitting an inter-tier file migration.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Systems and methods for detecting & mitigating storage risks
The present invention provides systems and methods for data storage. A hierarchical storage management architecture is presented to facilitate data management. The disclosed system provides methods for evaluating the state of stored data relative to enterprise needs by using weighted parameters that may be user defined. Also disclosed are systems and methods evaluating costing and risk management associated with stored data.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
Hierarchical storage management using dynamic tables of contents and sets of tables of contents
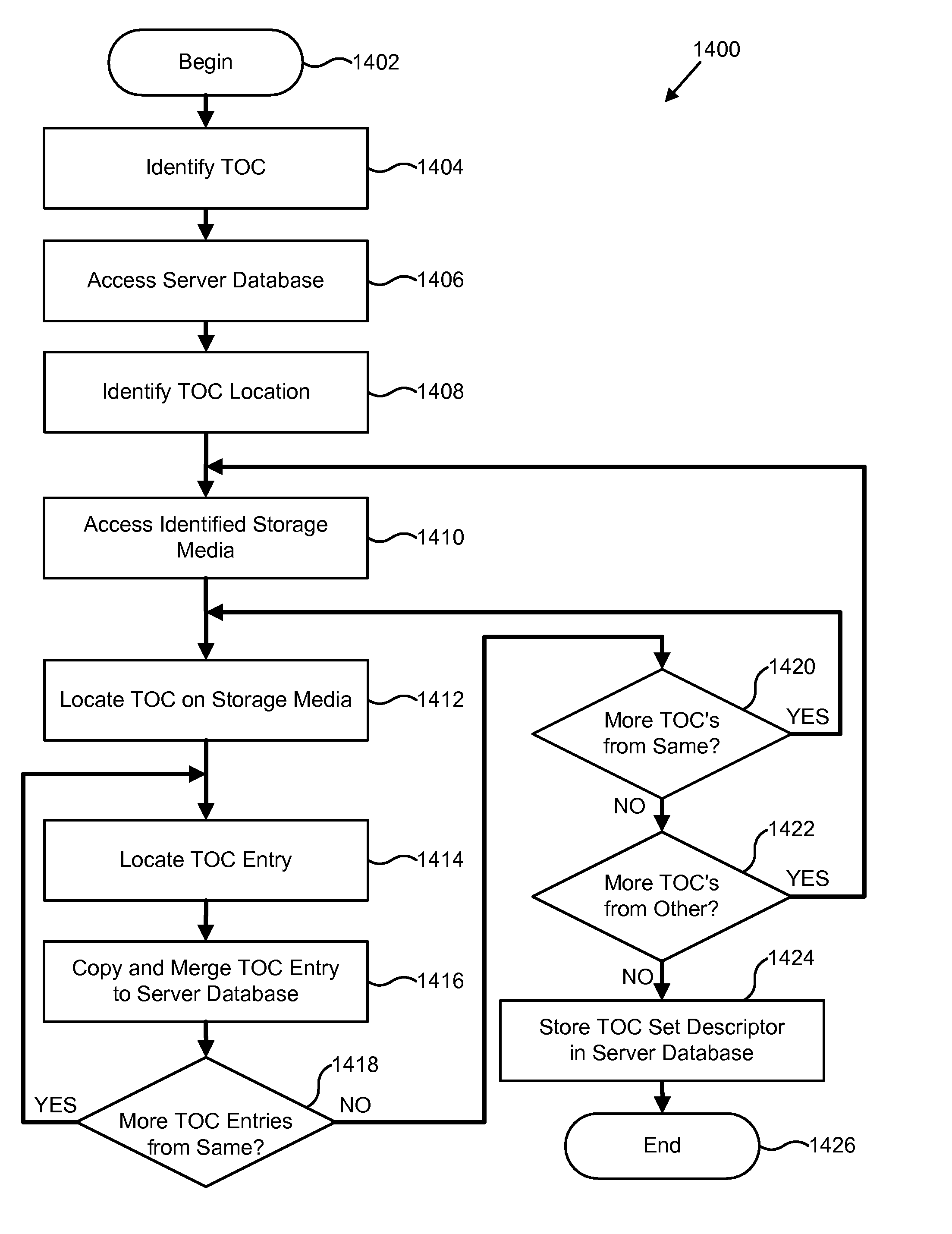
InactiveUS20080294611A1Overcomes shortcomingData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsMemory hierarchyStorage management
A system, apparatus, and process creates a table of contents (TOC), including one or more table of contents (TOC) entries, to manage data in a hierarchical storage management system. Each TOC entry contains metadata describing the contents and attributes of a data object within an image, which is an aggregation of multiple data objects into a single object for storage management purposes. The TOC is stored in a storage hierarchy, such as magnetic disk, for fast access of and efficient operation on the aggregated TOC entries. The system, apparatus, and process also provide for aggregating the TOC entries from one or more TOCs into a TOC set in the storage management server database. The TOC set may be manipulated and queried in order to find a particular data object or image referenced by a TOC entry. The TOC entries, TOCs, and TOC sets may be dynamically managed by the hierarchical data storage management system through implementation of a set of policy management constructs that define appropriate creation, retention, and movement of the objects within the database and storage hierarchy.
Owner:IBM CORP
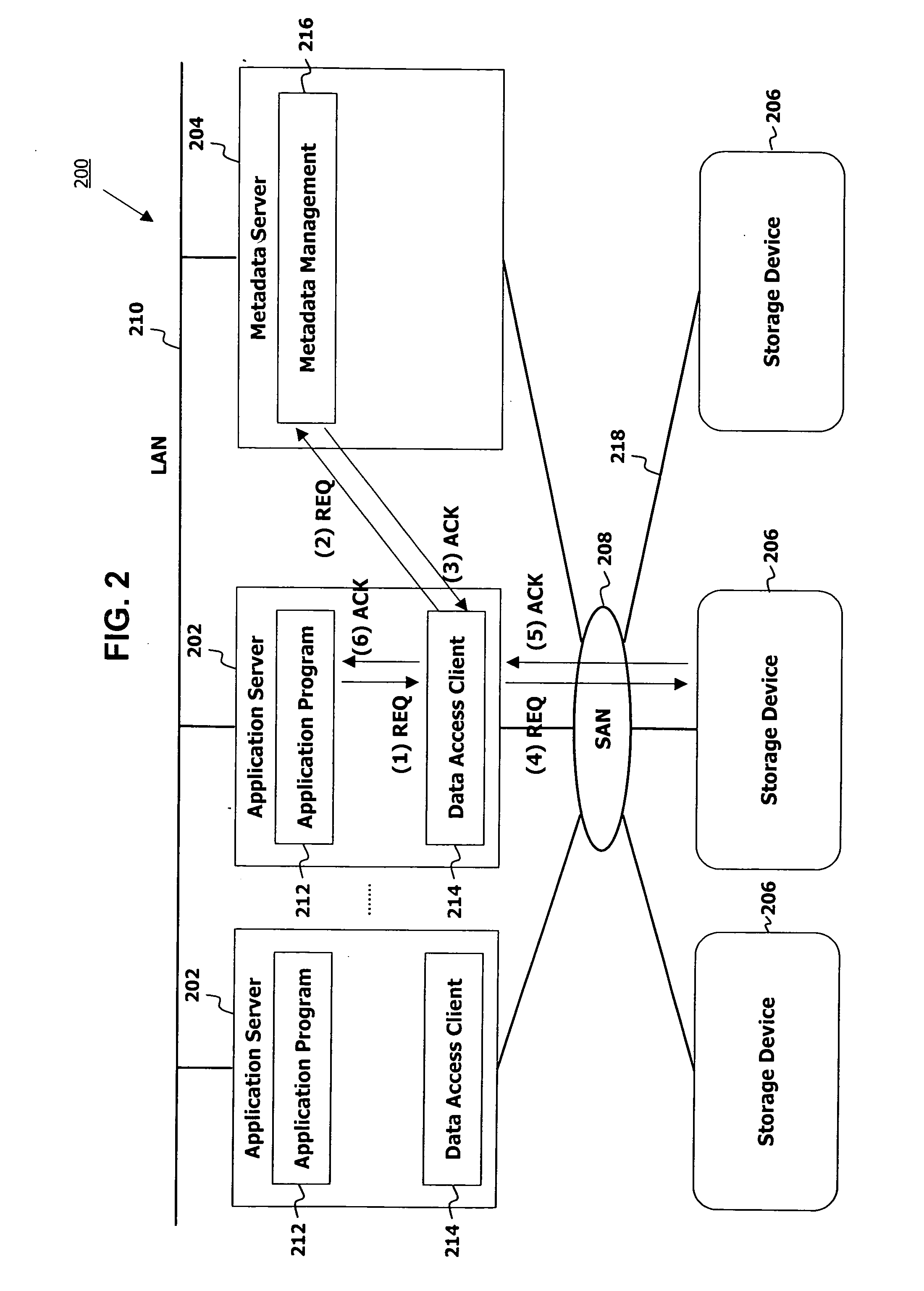
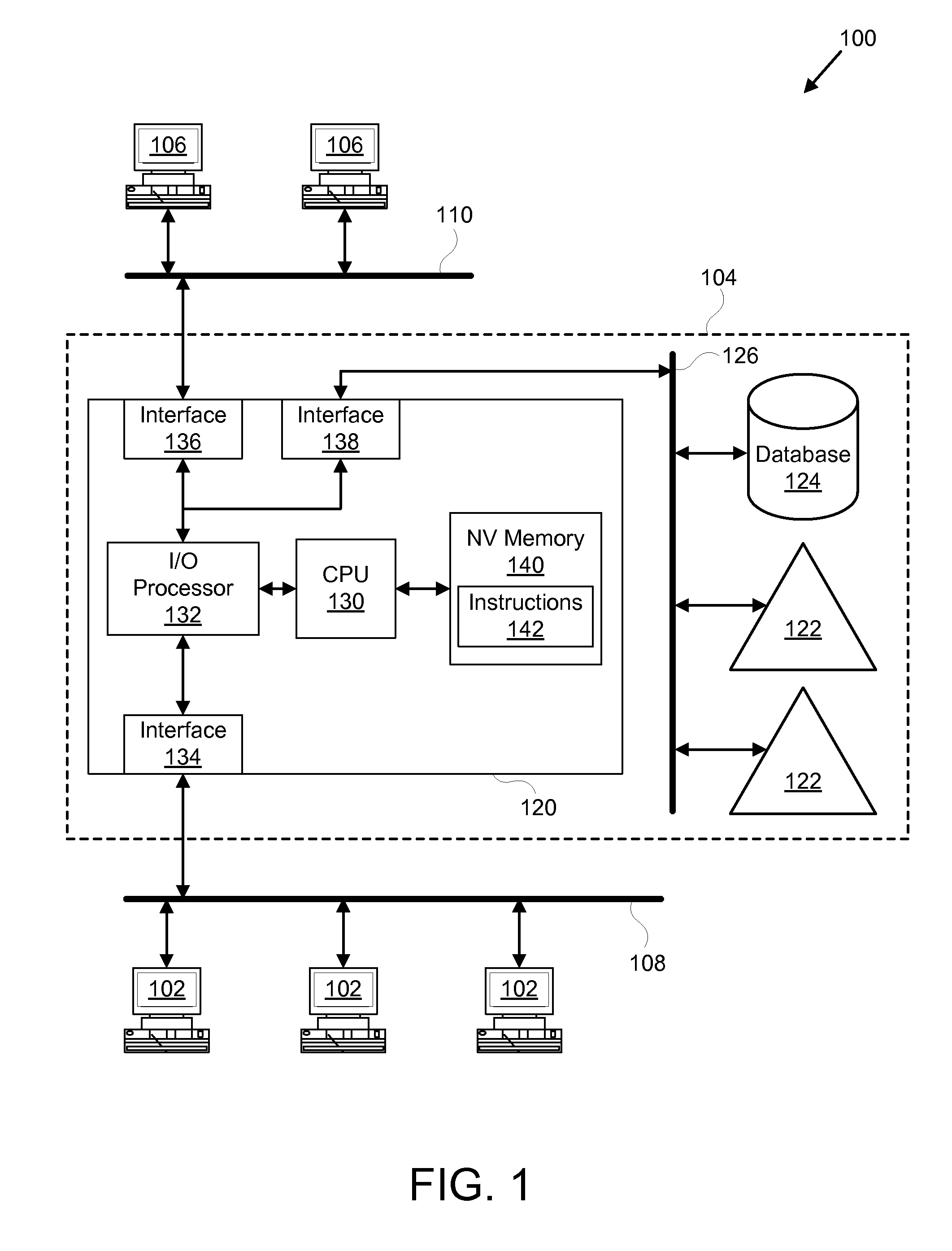
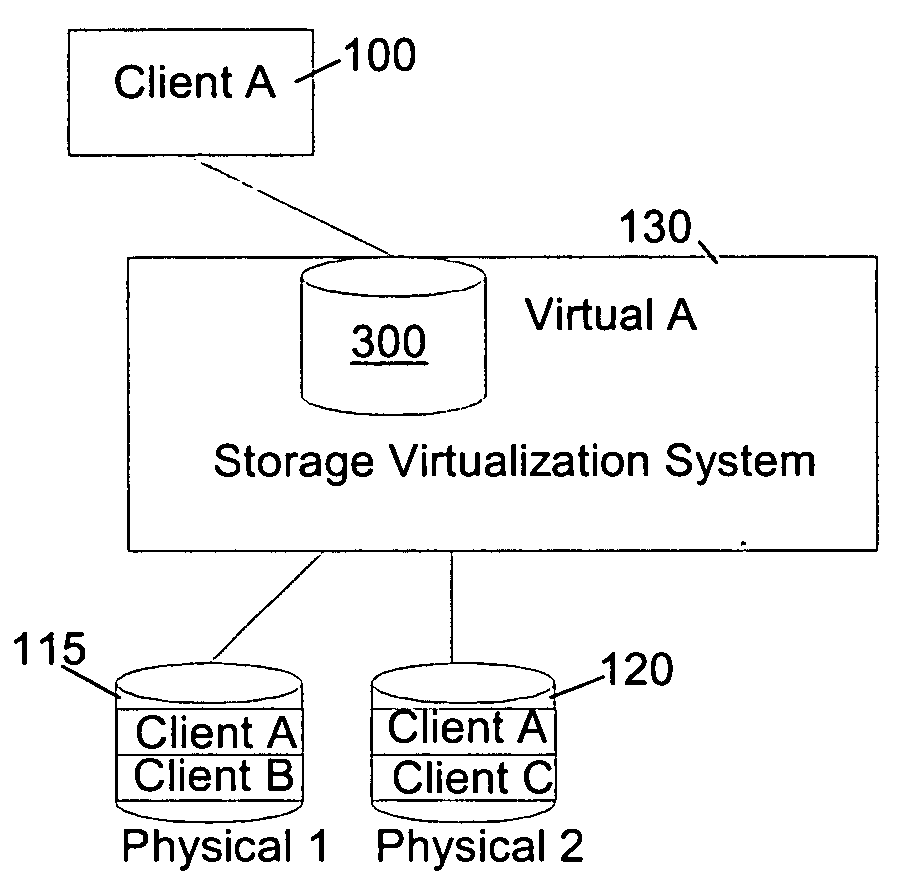
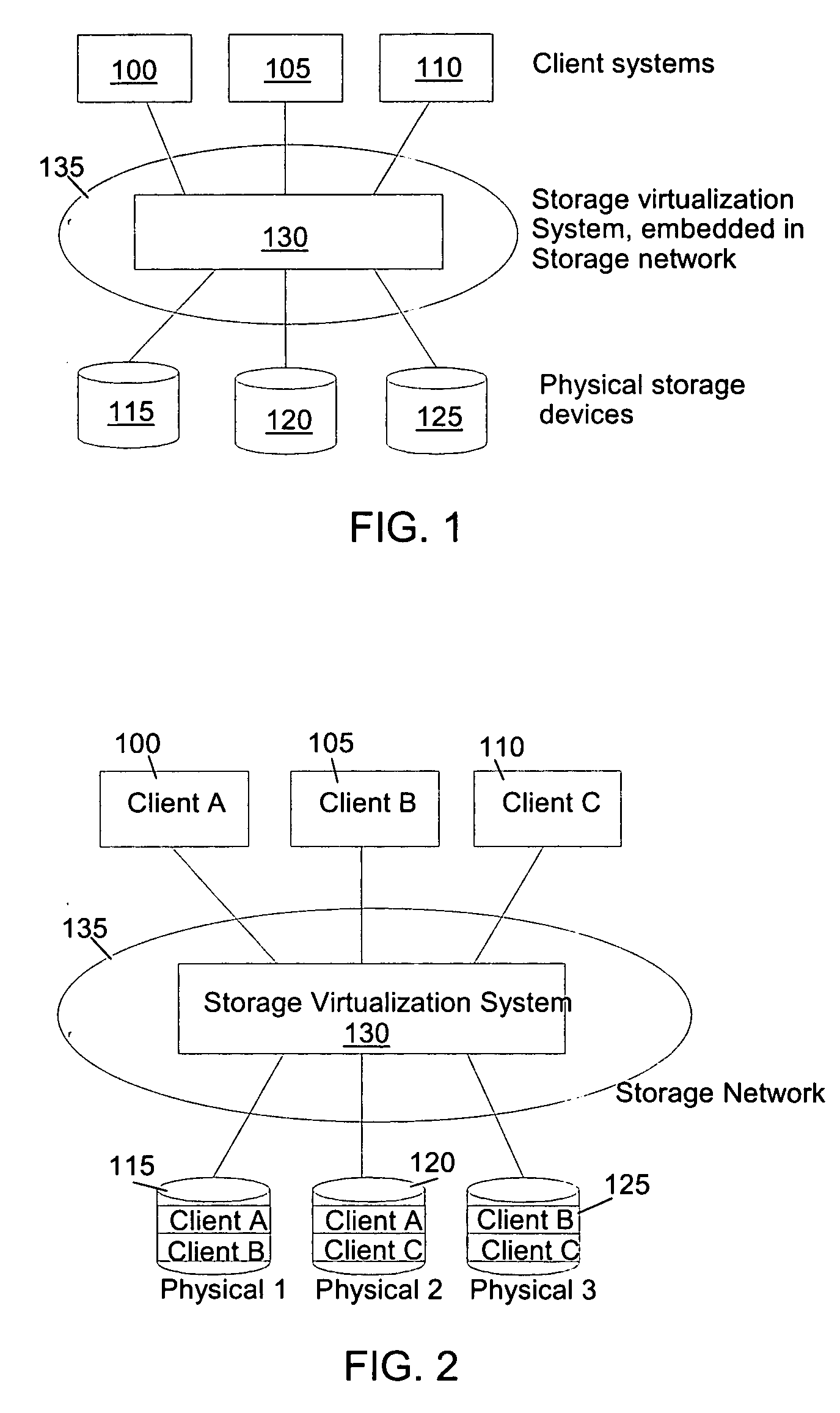
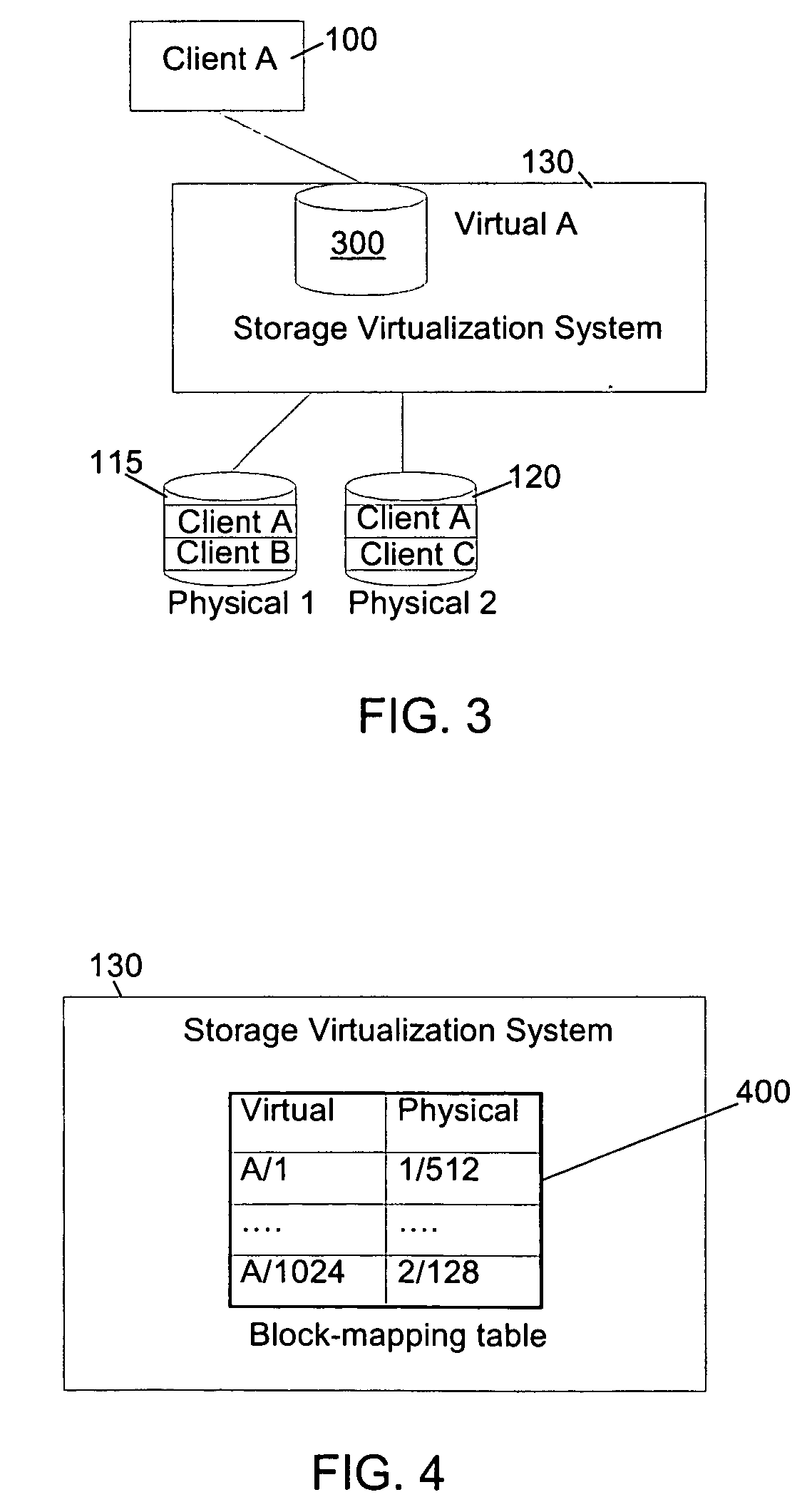
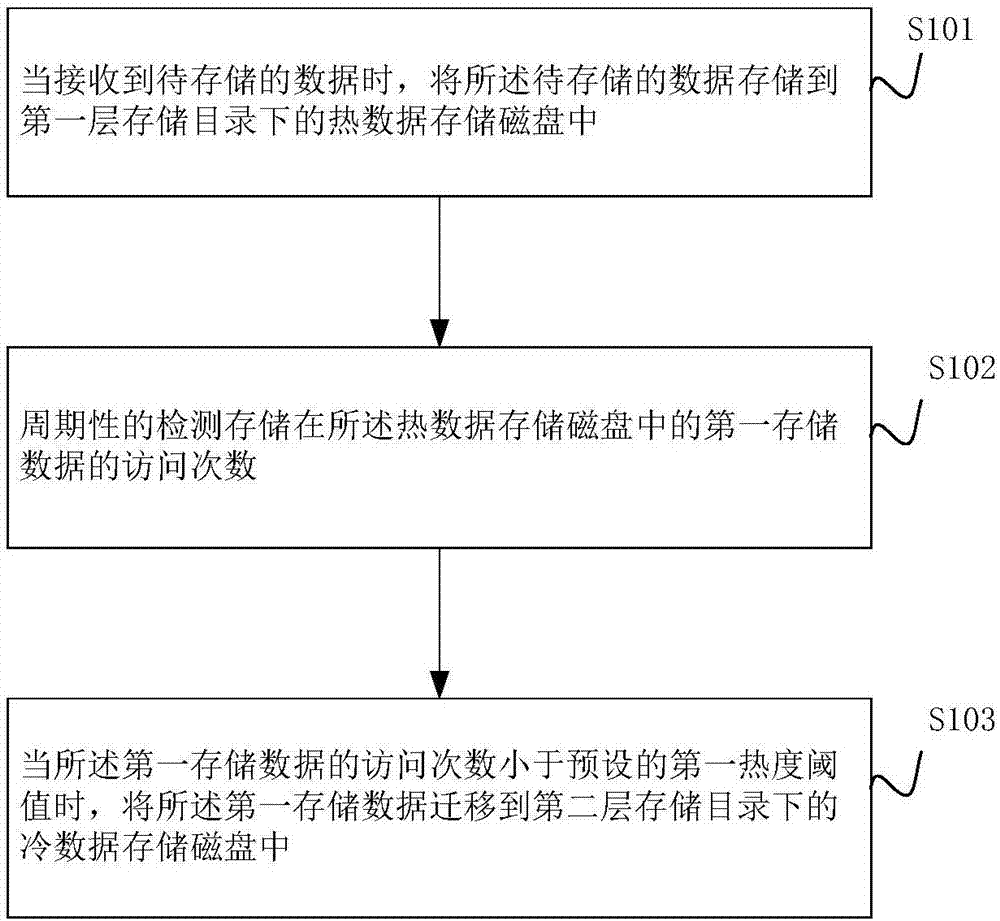
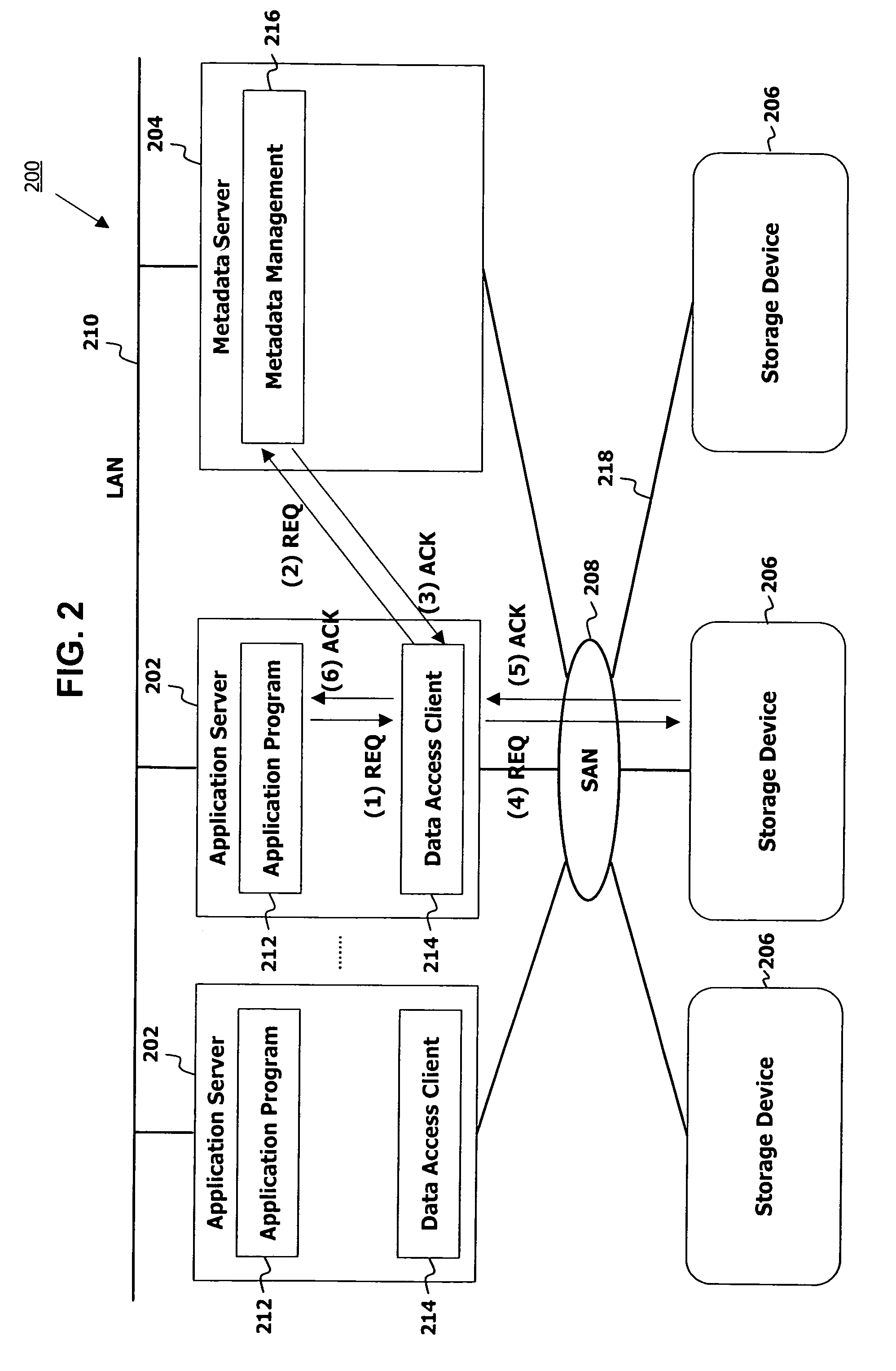
Autonomic block-level hierarchical storage management for storage networks
InactiveUS20050071560A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationSecuring communicationClient-sideComputer science
A Hierarchical Storage Management (HSM) system connects client systems to physical storage devices via a storage virtualization system (SVS) which is embedded in a storage network. The SVS provides virtual disk volumes to the client systems as an abstraction of the physical storage devices. The client systems have no direct connection to the physical storage devices and the SVS provides an abstract view of these devices, which allows it to utilize the available physical storage space by spreading storage assigned to the individual client systems across the physical storage devices. Within the SVS, a block-mapping table (BMT) translates each virtual block address being issued by the client systems to a corresponding physical block address.
Owner:IBM CORP
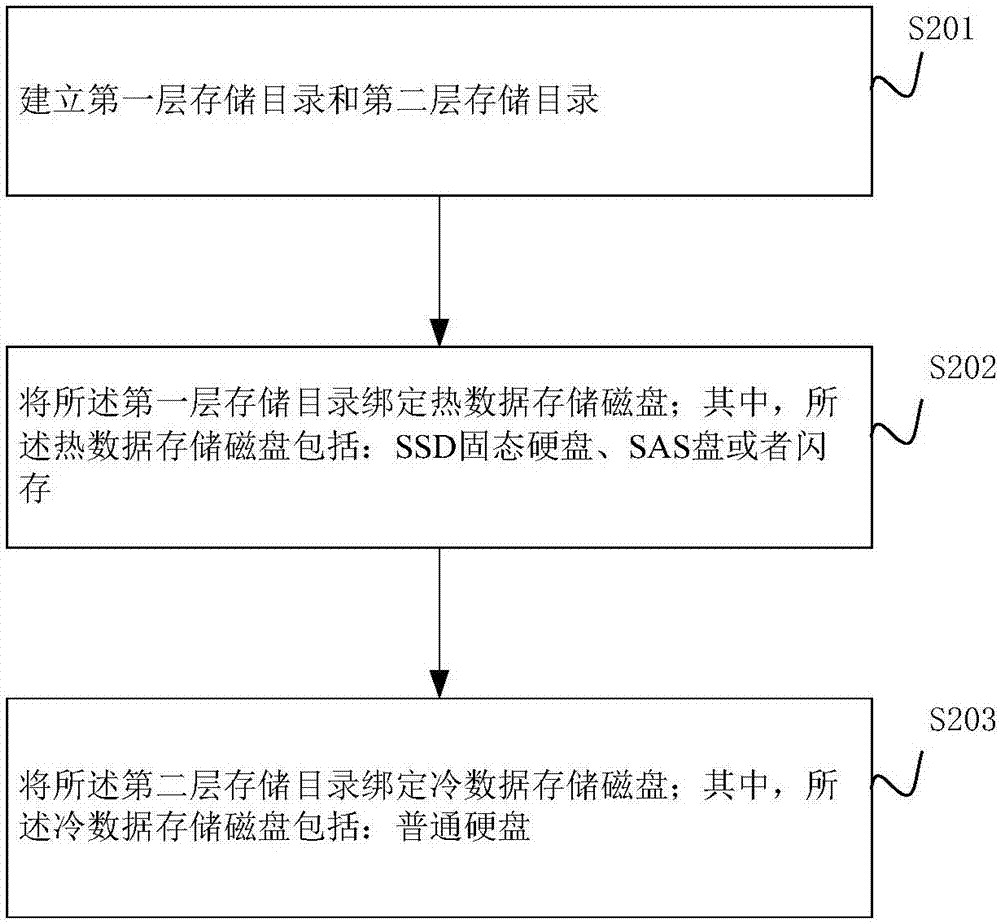
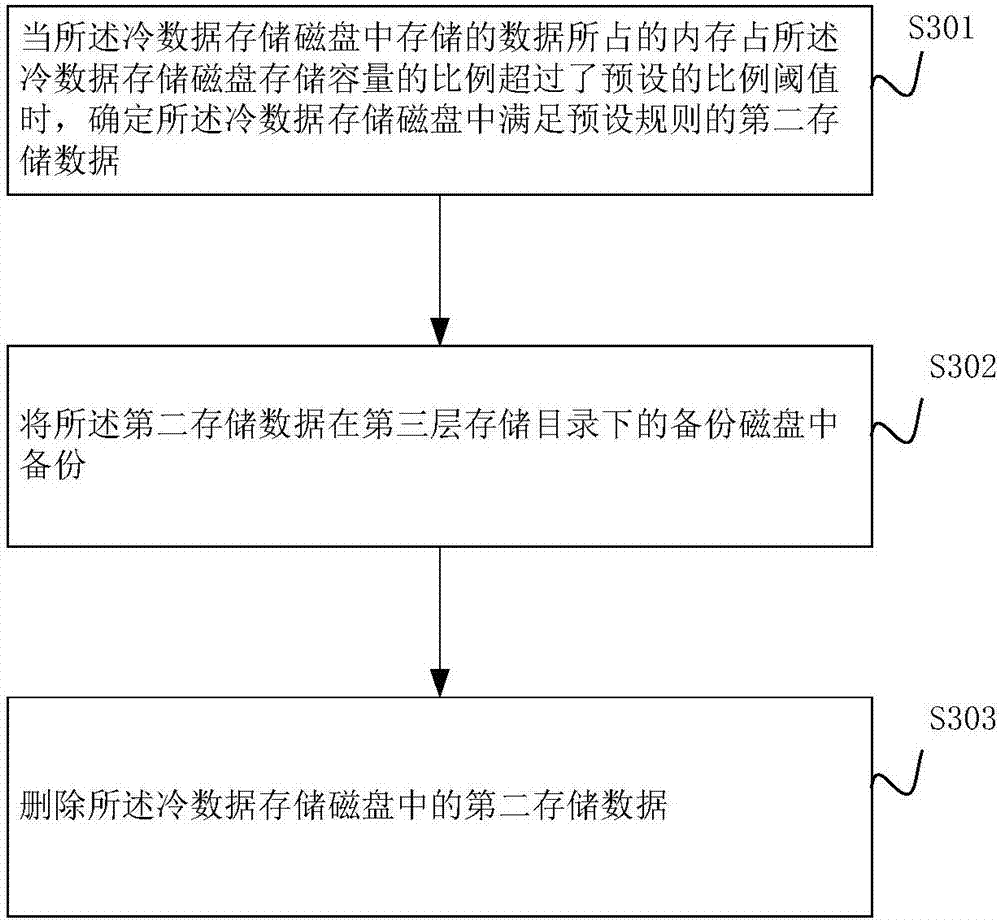
Distributive file system hierarchical storage method and system
InactiveCN107193500AInput/output to record carriersRedundant operation error correctionFile systemAccess time
The invention provides a distributive file system hierarchical storage method and system. The method comprises the following steps of when data to be stored is received, storing the data to be stored into a hot data storage disk under the first layer storage directory; periodically detecting the number of access times of the first storage data in the hot data storage disk; when the number of the access times of the first storage data is smaller than a preset first heat threshold value, migrating the first storage data into a cold data storage disk in the second layer storage directory; and when the proportion of the data stored in the cold data storage disk in the storage volume of the cold data storage disk exceeds the preset proportion threshold value, backing up the second storage data meeting the preset rule in a backup disk in the third layer storage directory. By using the method provided by the embodiment, data of different access quantities is stored in different layers; the use cost of the disks is controlled; and the data storage flow process of a distributive file system is simplified.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
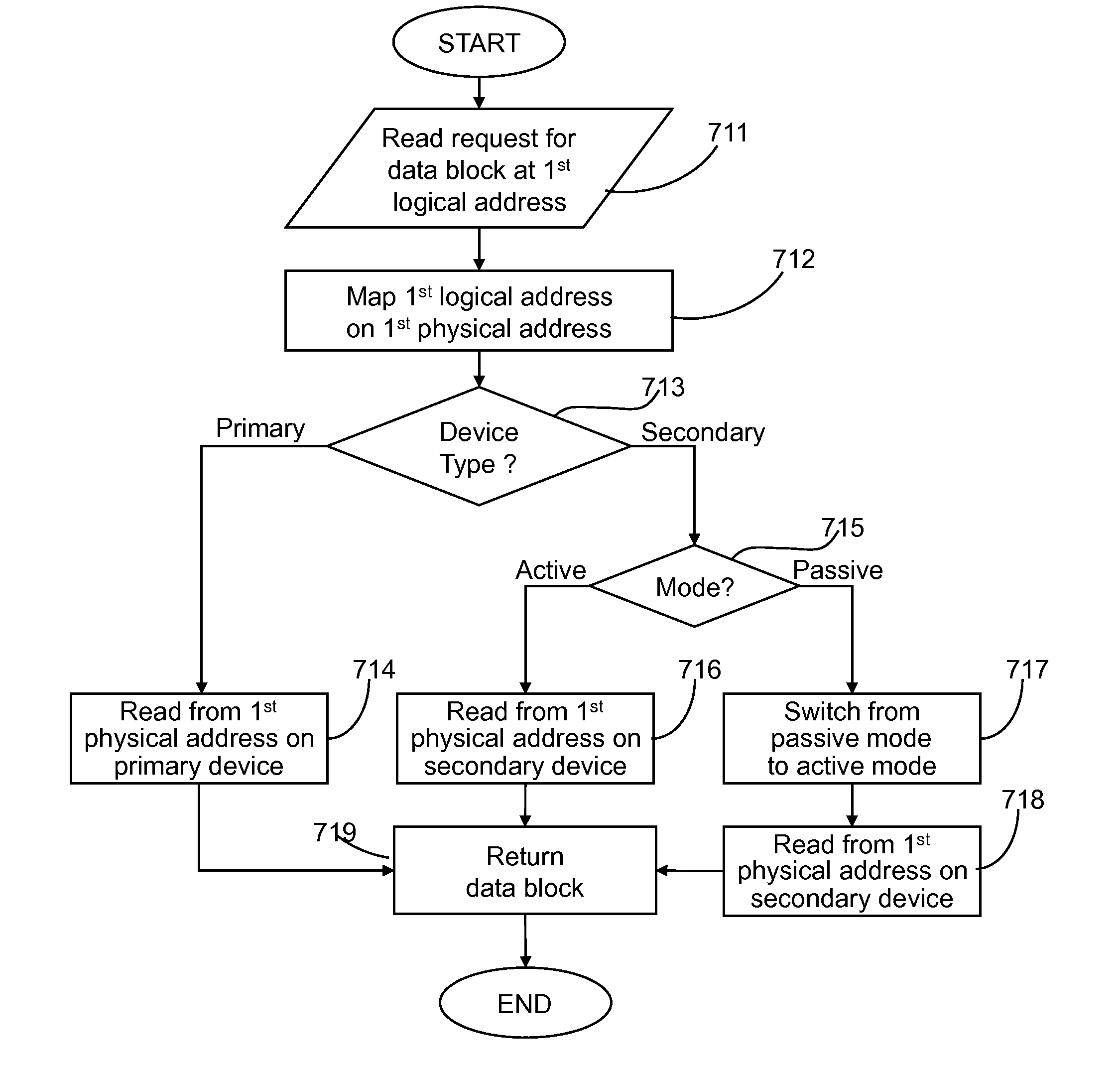
Hierarchical storage management for database systems
ActiveUS20110040937A1Conserve costEasy accessEnergy efficient ICTDigital data information retrievalComputer hardwareBiological activation
Embodiments for managing data in a hierarchical storage server storing data blocks of a database system comprising primary storage devices being in an active mode and secondary storage devices being in one of an active and passive mode are provided. In response to read and write requests for data blocks at logical storage locations, a block mapping device determines physical storage locations on the storage devices. Read requests switch over secondary storage devices to the active mode when they are in the passive mode. Write requests write data blocks only to the primary storage devices. Secondary storage devices that have not been accessed for a minimum activation time may be switched over from the active to the passive mode to save power consumption and cooling. Data migration and data recall policies control moving of data blocks between the primary and secondary storage devices and are primarily based on threshold values.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
System and method for providing a backup/restore interface for third party HSM clients
InactiveUS7953945B2Digital data information retrievalError detection/correctionThird partyFile system
A method for performing backup of a stub object located on a file system managed by a hierarchical storage manager configured to migrate data objects from the file system 10 a migration storage pool includes determining whether a backup copy of the migrated data object is stored in a backup storage pool if the backup is performed in an incremental backup operation. The storage manager recalls the migrated data object to the file system if the backup copy of the migrated data object is not stored in the backup storage pool or if the backup is performed in a selective backup operation. If the migrated data object is recalled, the backup copy of the migrated data object is created and stored in the backup storage pool. If the migrated data object is not recalled, a backup copy of the stub object is created and stored in the backup storage pool.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Cloud storage system with distributed metadata
ActiveUS8533231B2Efficient storageEasy to scaleDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData integrityCloud storage system
Owner:NEXENTA BY DDN INC
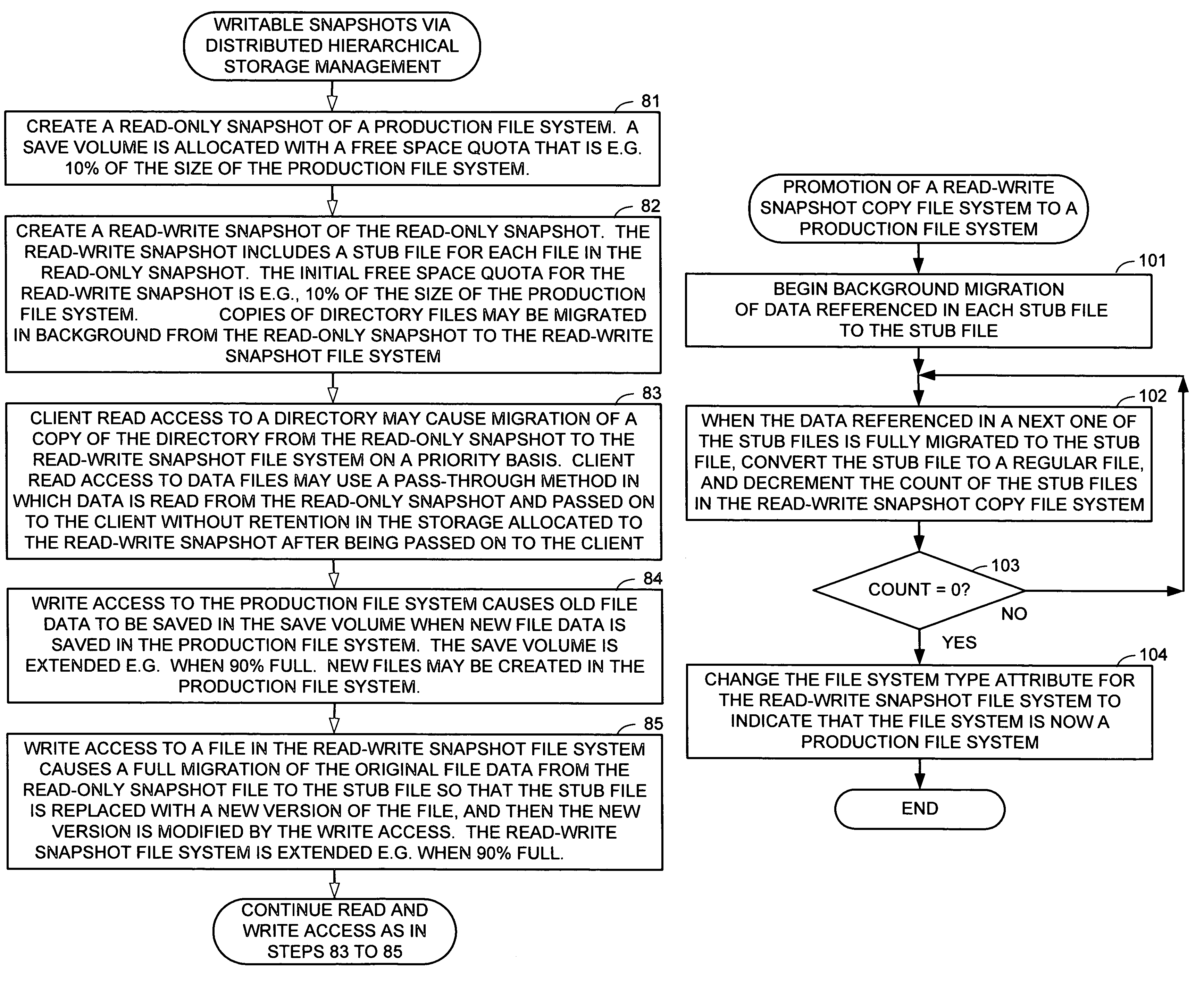
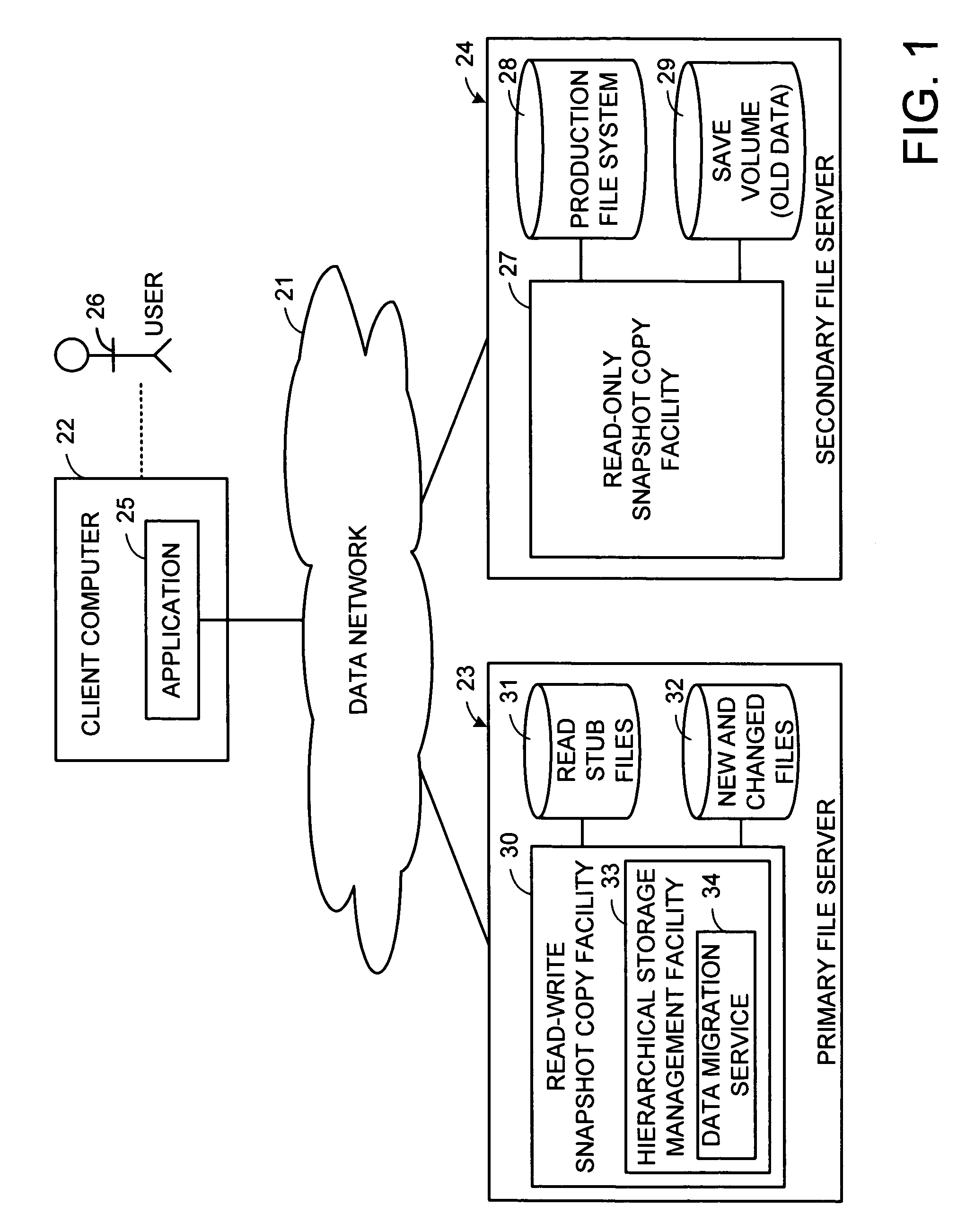
Distributed open writable snapshot copy facility using file migration policies
A read-write snapshot copy facility is constructed from a hierarchical storage management facility. The read-write snapshot copy file system initially comprises stub files pointing to the files in a read-only snapshot copy file system. When an application writes to a file in the read-write snapshot copy, the read-write snapshot copy facility migrates a copy of the file to replace the stub file, and then writes to the migrated file. Because the read-write snapshot copy facility references the files in the read-only snapshot file system in a network namespace using standard protocols such as NFS or CIFS, the read-write snapshot copy facility permits referencing of distributed read-only snapshot file systems in an open (heterogeneous) network environment, and the read-write snapshot copy is scalable by linking the read-write snapshot copy facility to multiple file servers containing read-only snapshot file systems.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Method and apparatus for hierarchical storage management based on data value and user interest
InactiveUS7177883B2Manage data volumesMinimal costData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsData streamMetadata management
A hierarchical storage data management system includes application servers, a metadata server interconnected with the application servers through a local area network, storage devices interconnected through data flow paths, and a storage network connecting the storage devices to the application servers and to the metadata server. The metadata server including a metadata management element, a data value management unit, and a hierarchical storage management element calculates a data value for each of stores data objects in the system, assigns a storage cost value for each of storage areas in the system, normalizes calculated data values and assigned storage costs to an identical value range, compares normalized data values with normalized storage costs thereby determining whether to relocate the data objects to different storage areas, and relocates data objects to storage areas with storage cost values identical with data values of the data objects.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
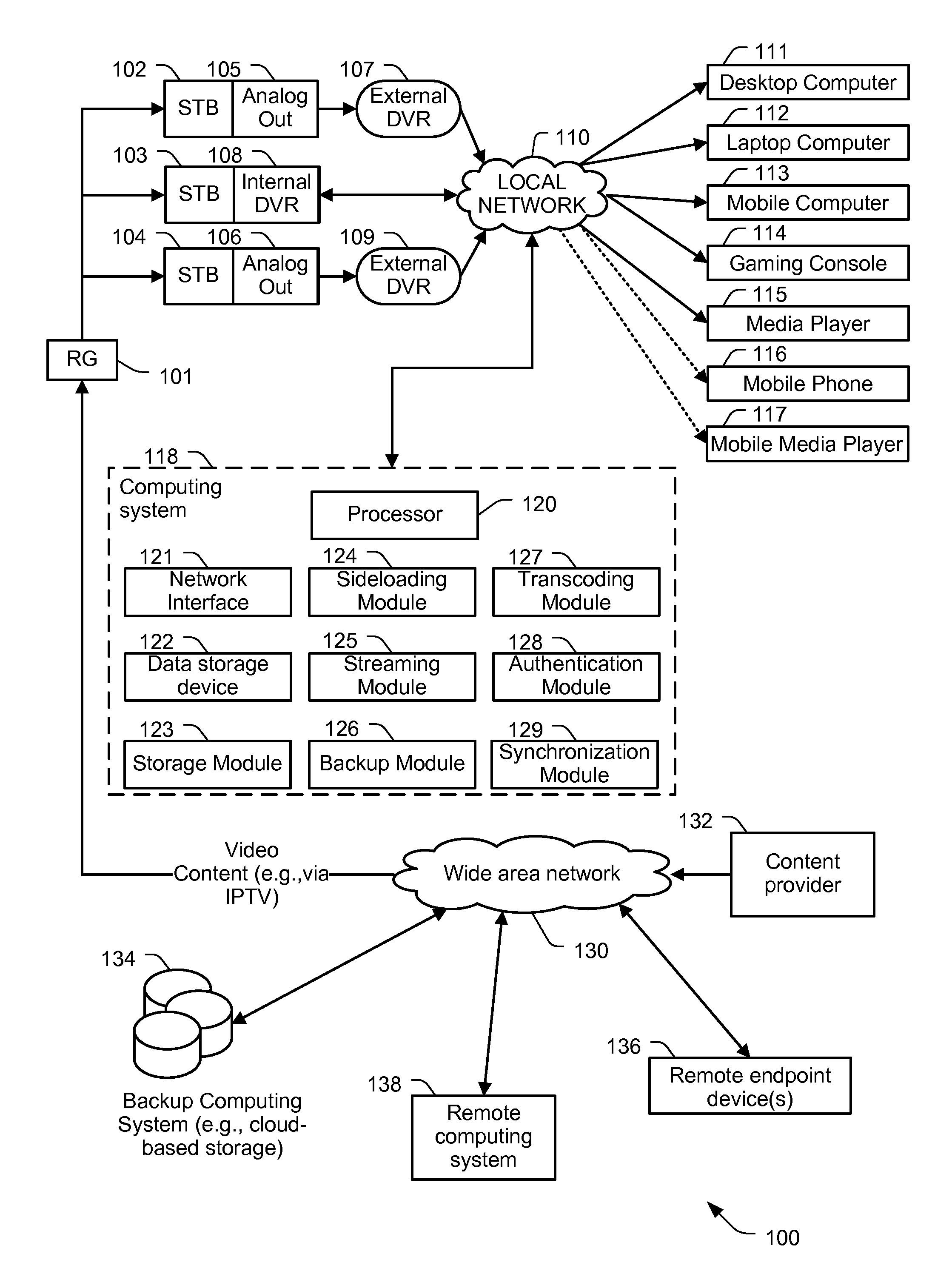
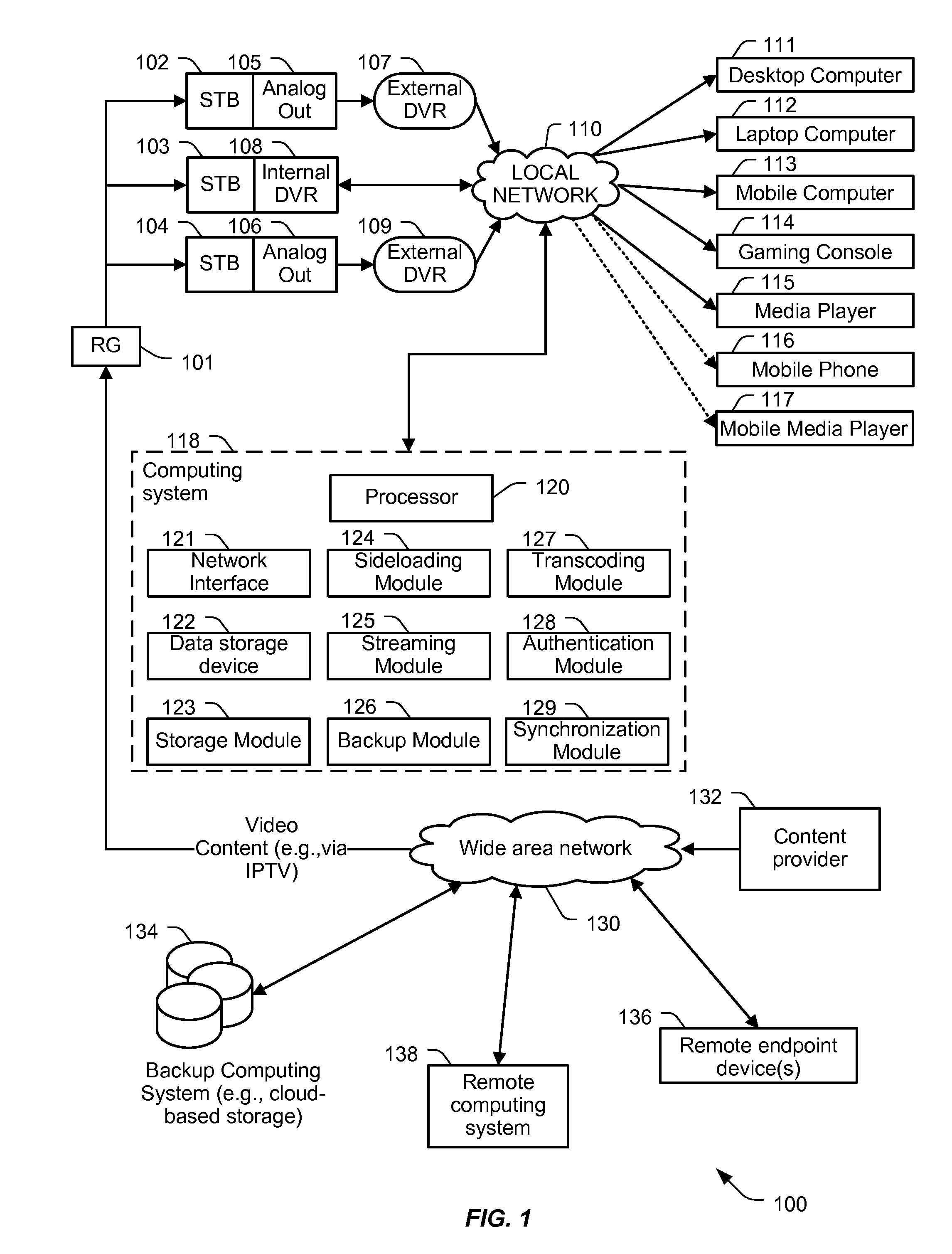
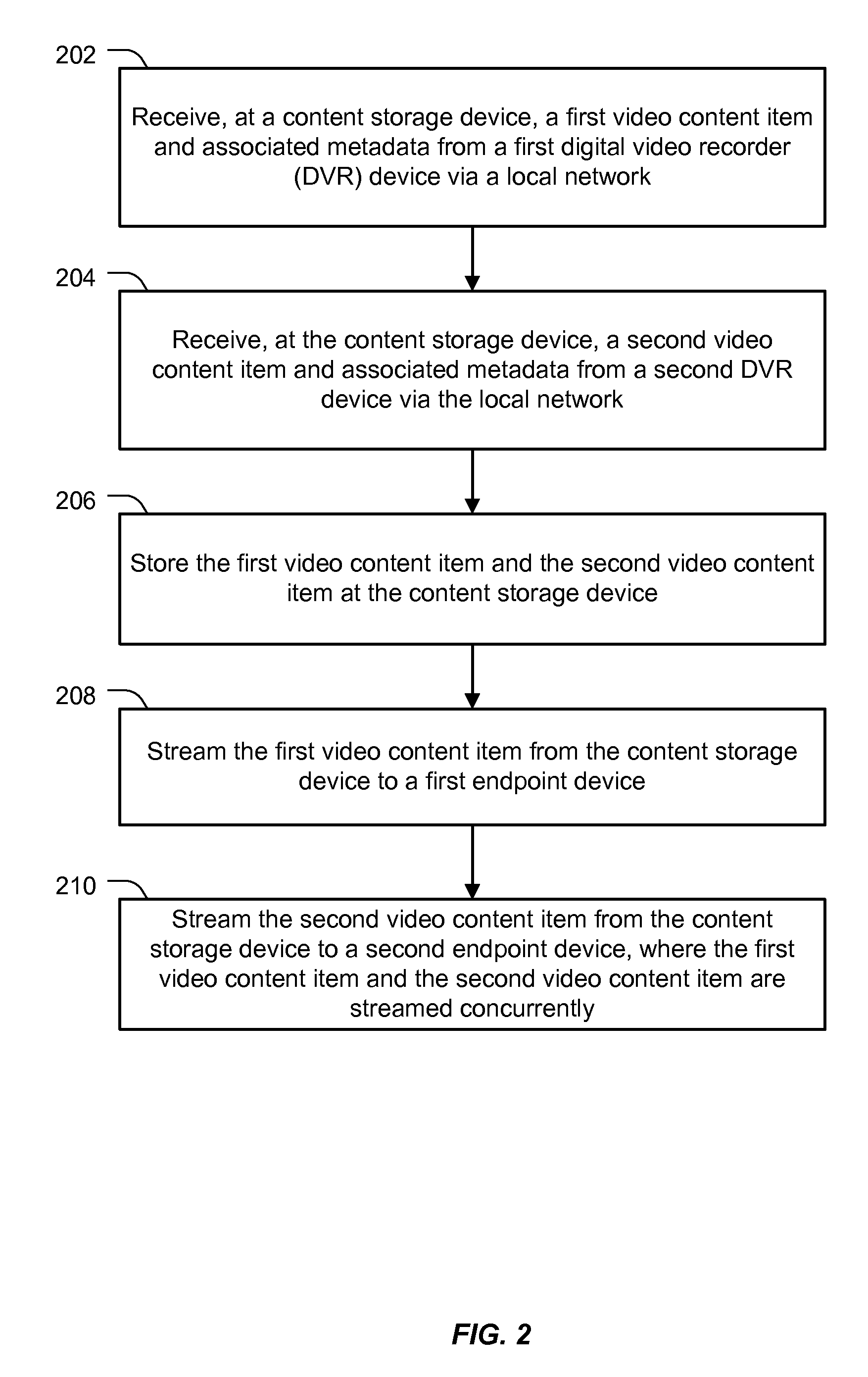
Hierarchical Storage Management for Data
ActiveUS20120141092A1Television system detailsColor television signals processingComputing systemsNetwork interface
A particular computing system includes a processor and a network interface to receive media content from one or more media recorder devices. The media content is transcoded into a portable media format. The computing system also includes a storage module executable by the processor to store the received media content to a data storage device. The computing system further includes a sideloading module executable by the processor to sideload stored media content from the data storage device to one or more first endpoint devices. The computing system also includes a streaming module executable by the processor to stream the stored media content from the data storage device to one or more second endpoint devices. The computing system further includes a backup module executable by the processor to transmit the stored media content from the data storage device to a second data storage device.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Efficient hierarchical storage management of a file system with snapshots
InactiveUS8055864B2Overcomes shortcomingDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsInodeComputer science
A method is provided for managing the storage of a file that has been selected for migration from a first storage level within a file system to a second storage level. The method comprises copying each of one or more data blocks of the selected file that are stored in the first storage level at a physical disk address maintained in a corresponding reference of an inode for the selected file from the first storage level to the second storage level; maintaining a logical ditto address in each reference of an inode for each snapshot file in the file system that refers to one of the one or more data blocks of the selected file that were copied to the second storage level; and updating the file system to include a managed region for controlling access to the one or more data blocks through the inode for the selected file.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com