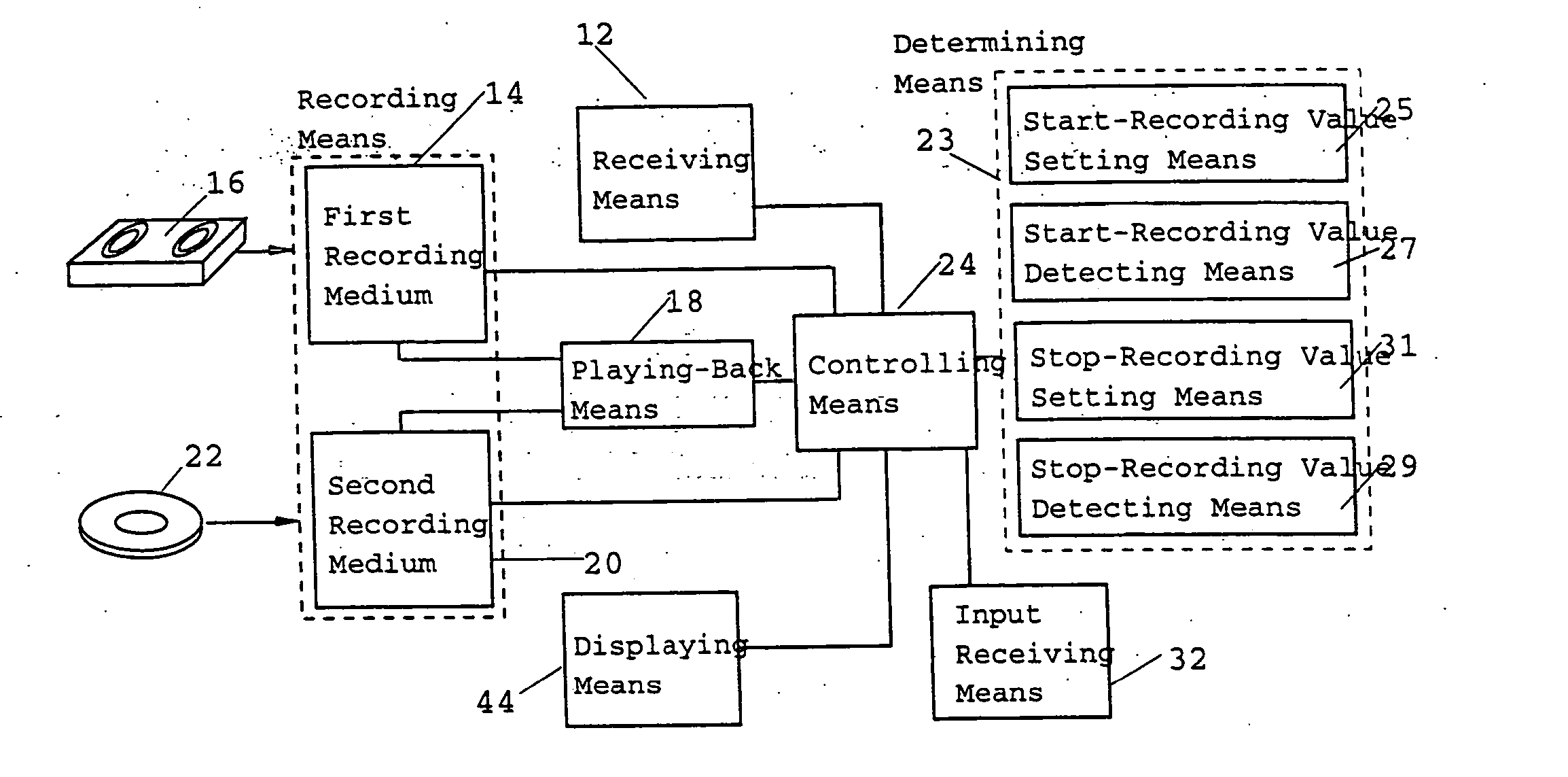
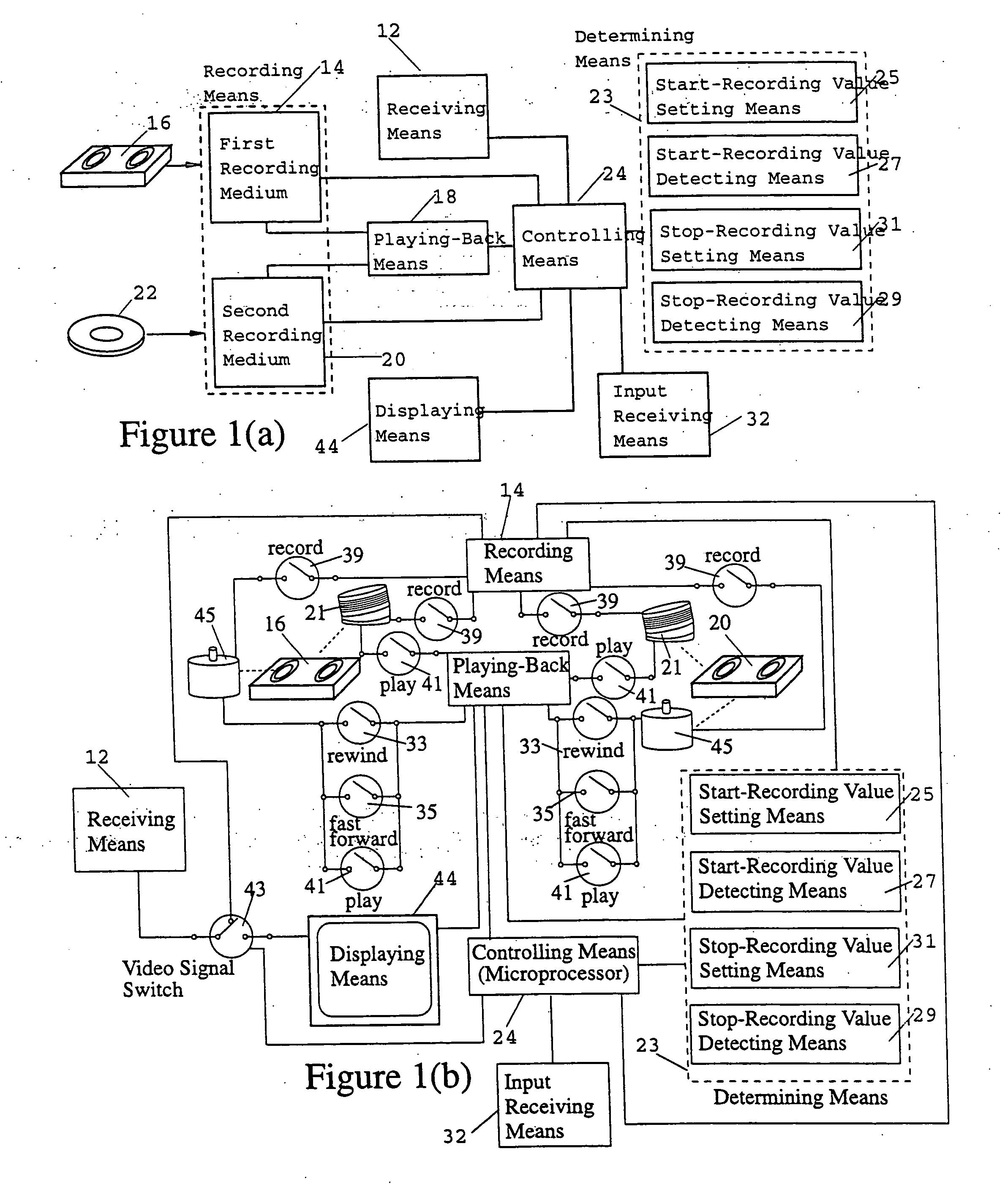
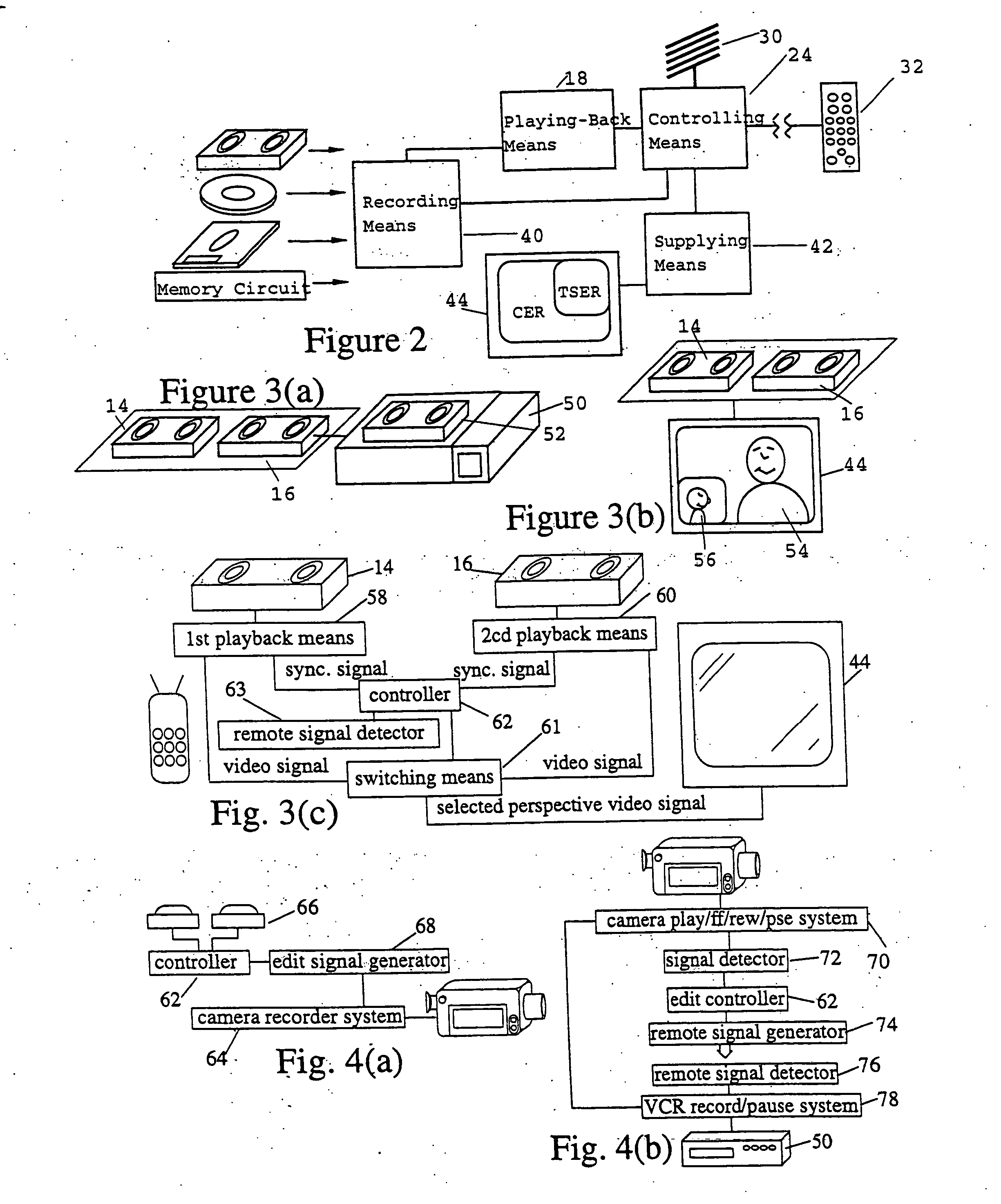
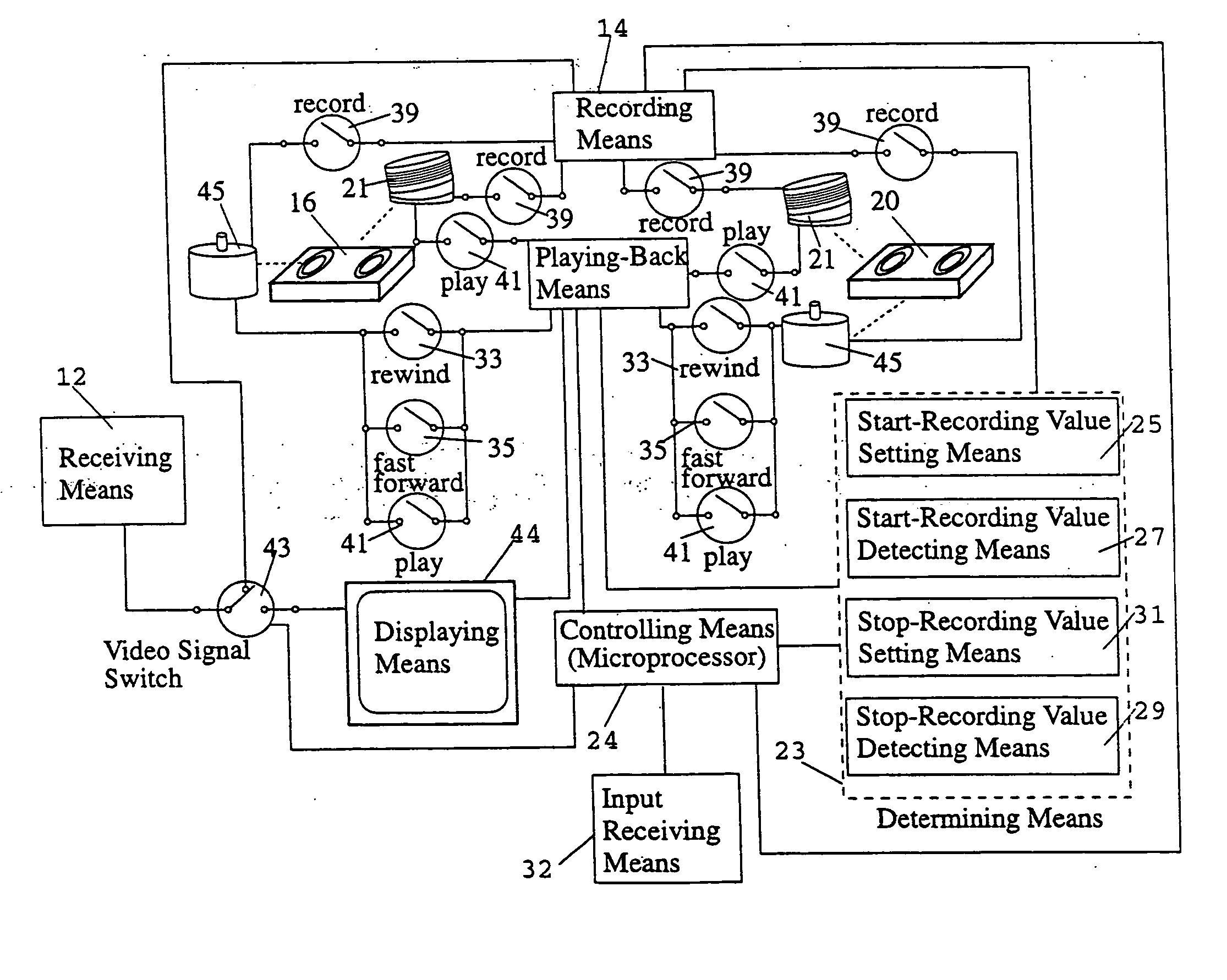
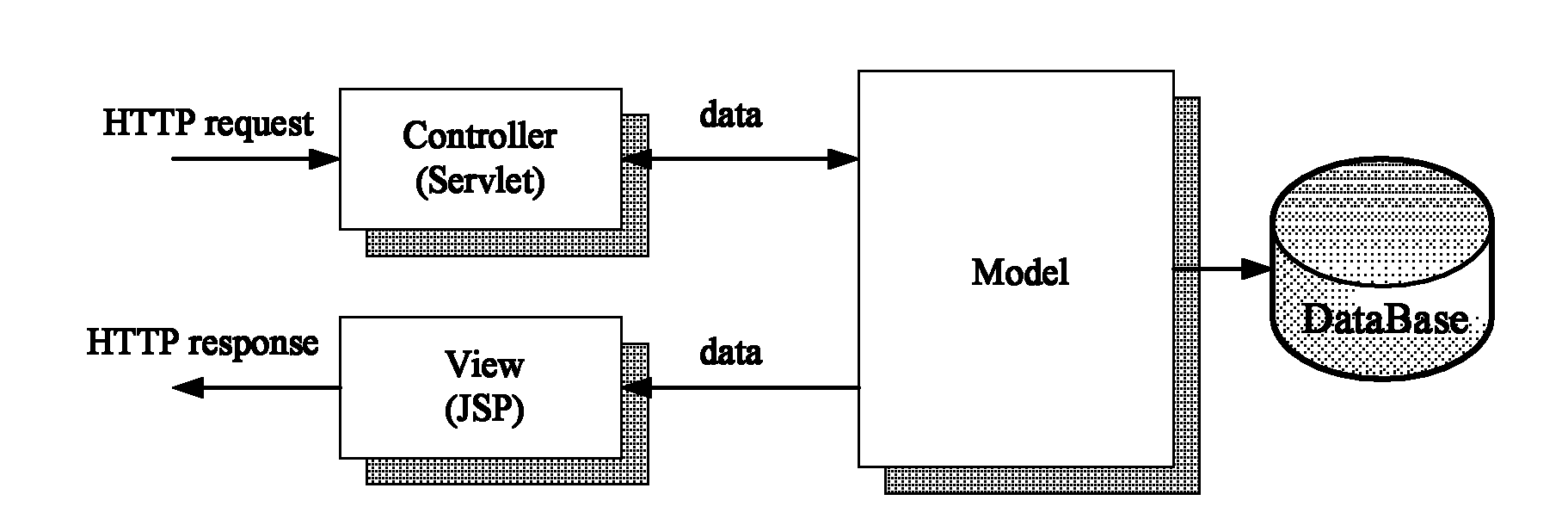
Patents
Literature
40 results about "Near video on demand" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
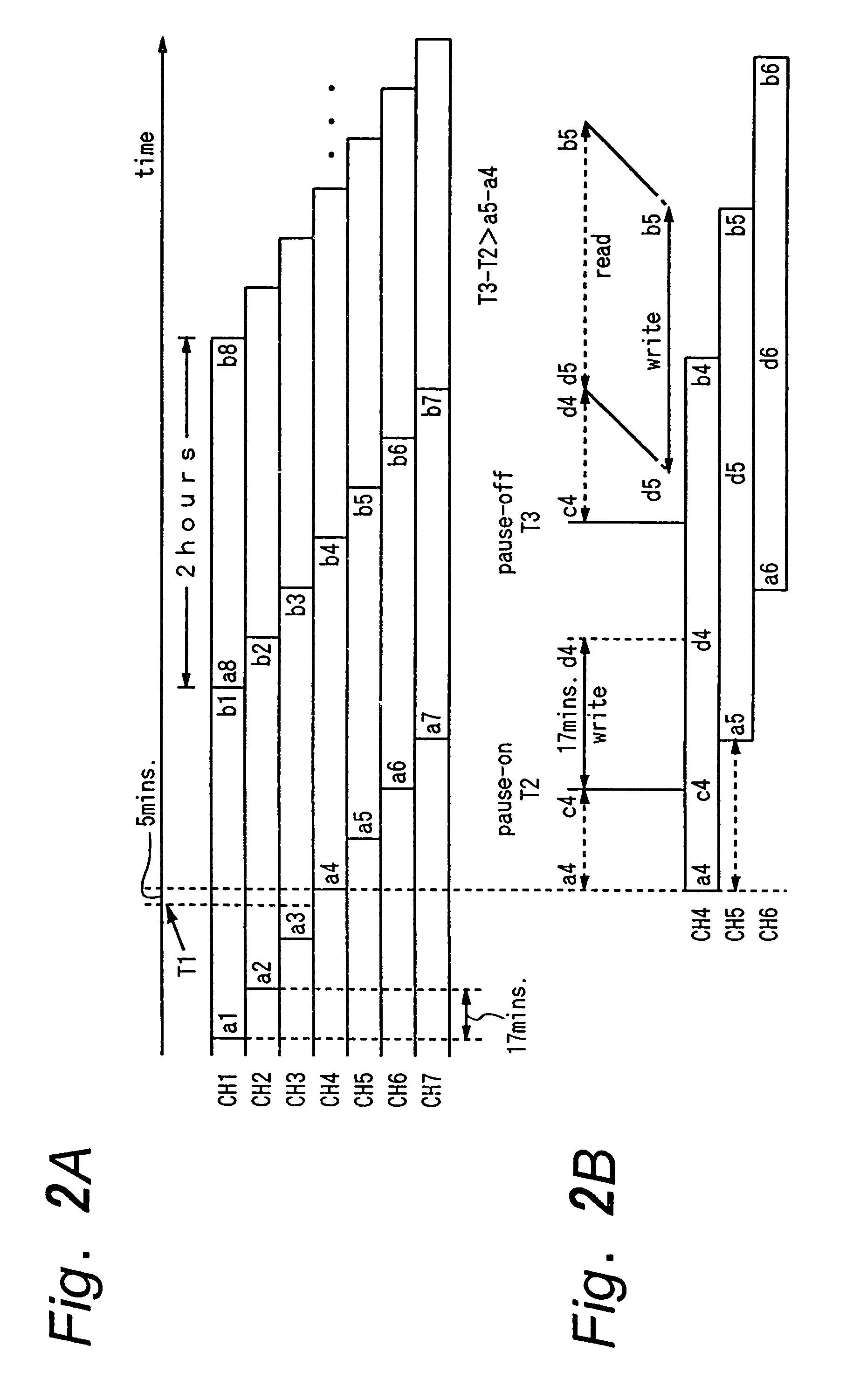
Near video on demand (NVOD) is a pay-per-view consumer video technique used by multi-channel broadcasters using high-bandwidth distribution mechanisms such as satellite and cable television. Multiple copies of a program are broadcast at short time intervals (typically 10–20 minutes) on linear channels providing convenience for viewers, who ...
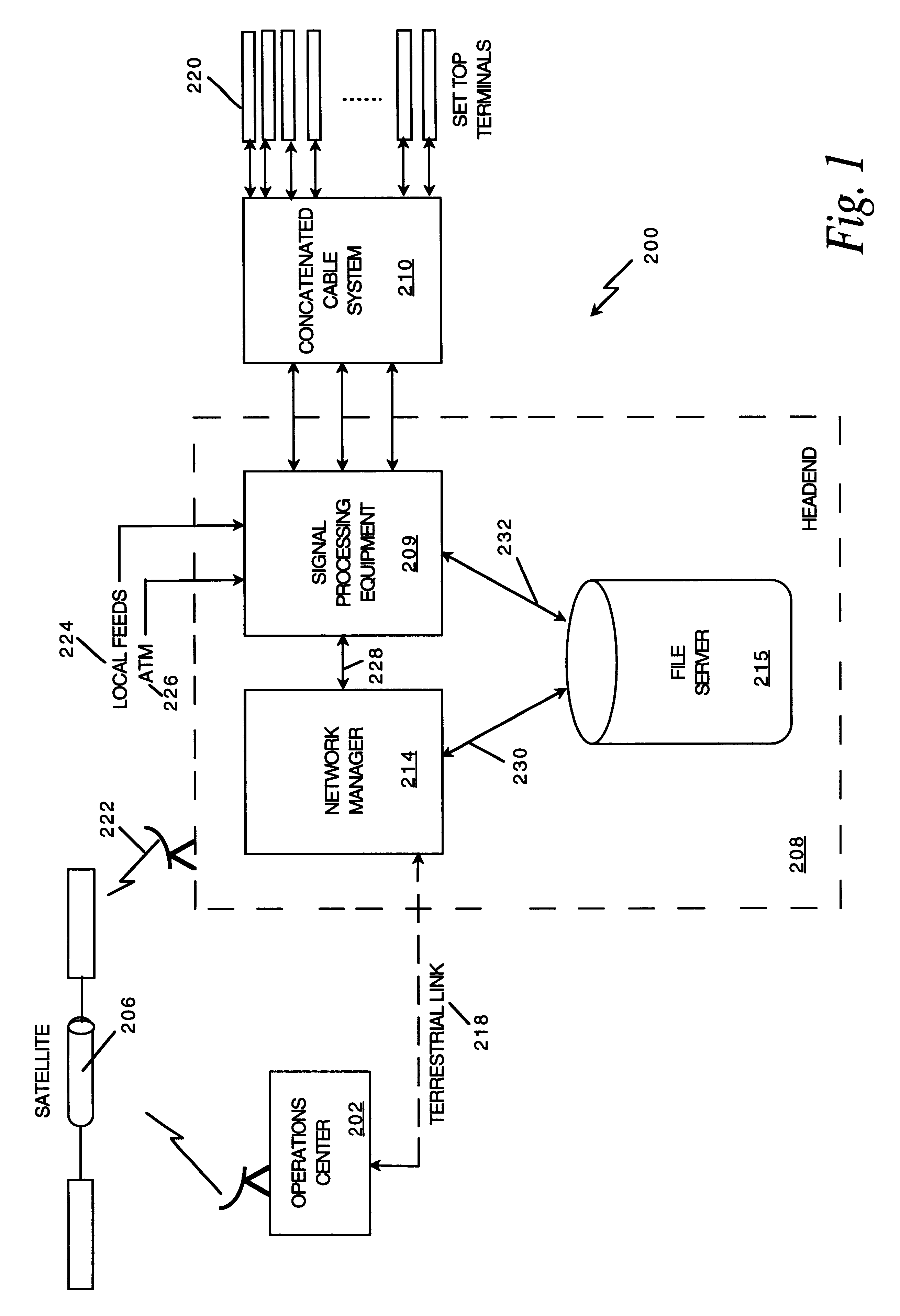
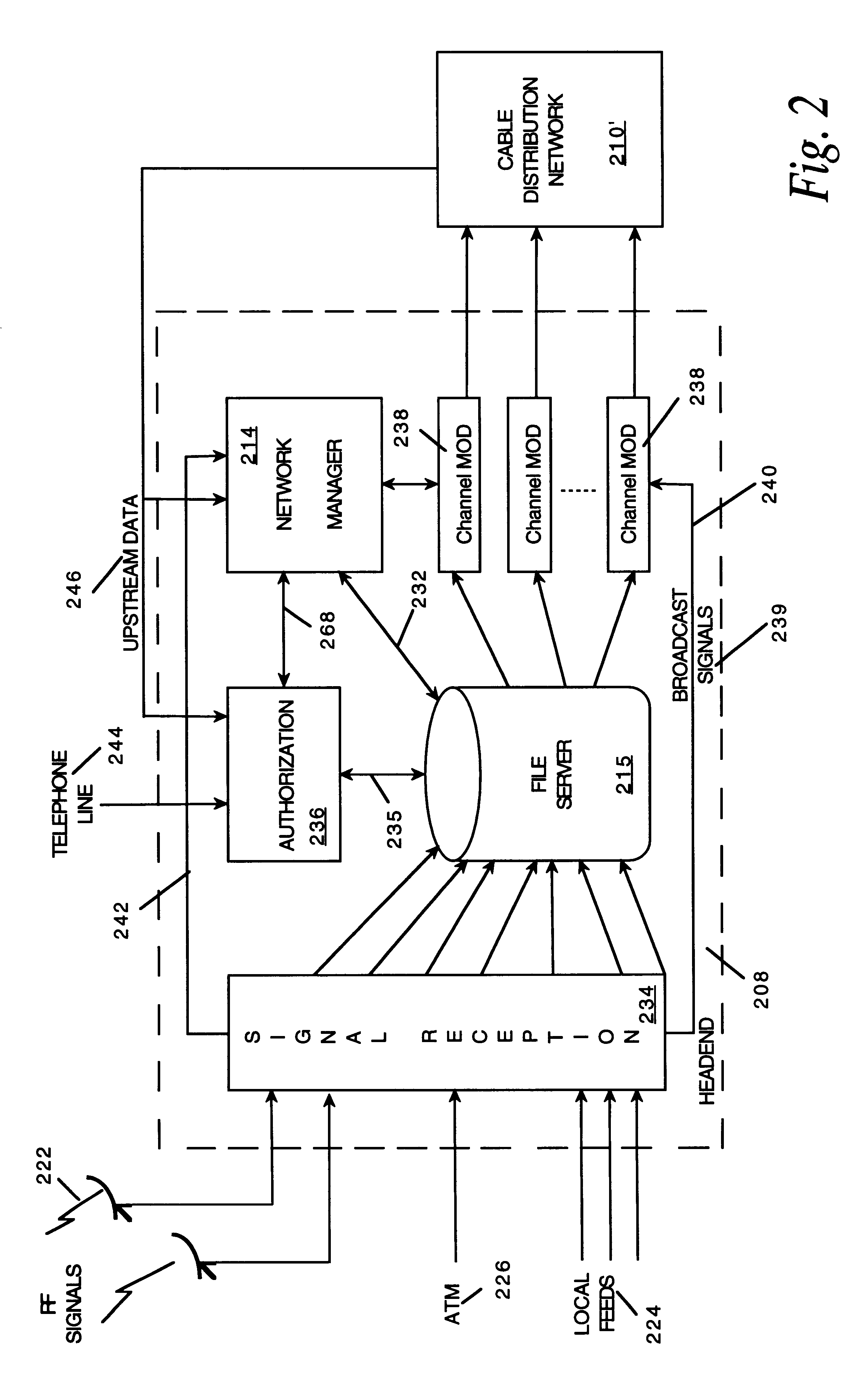
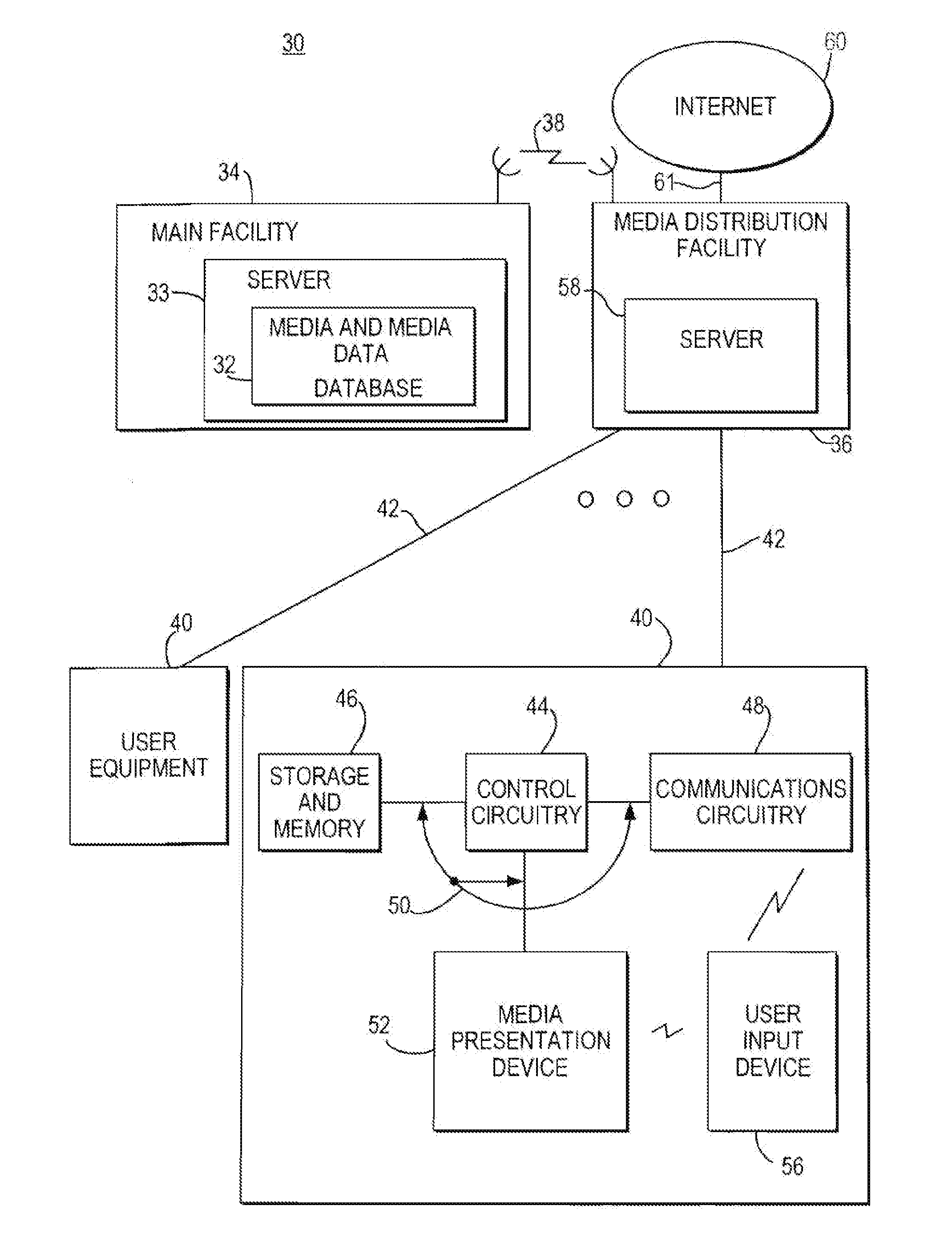
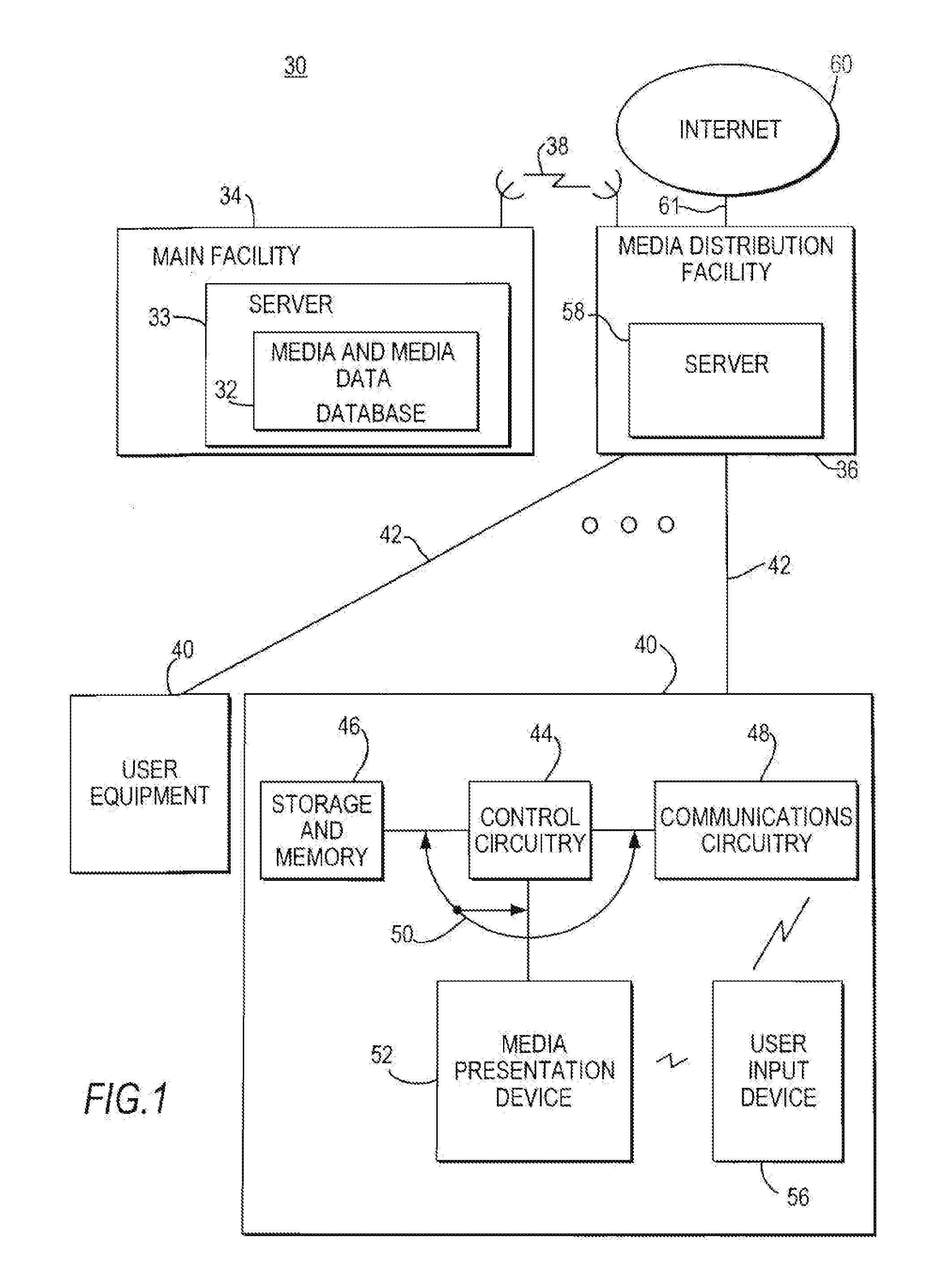
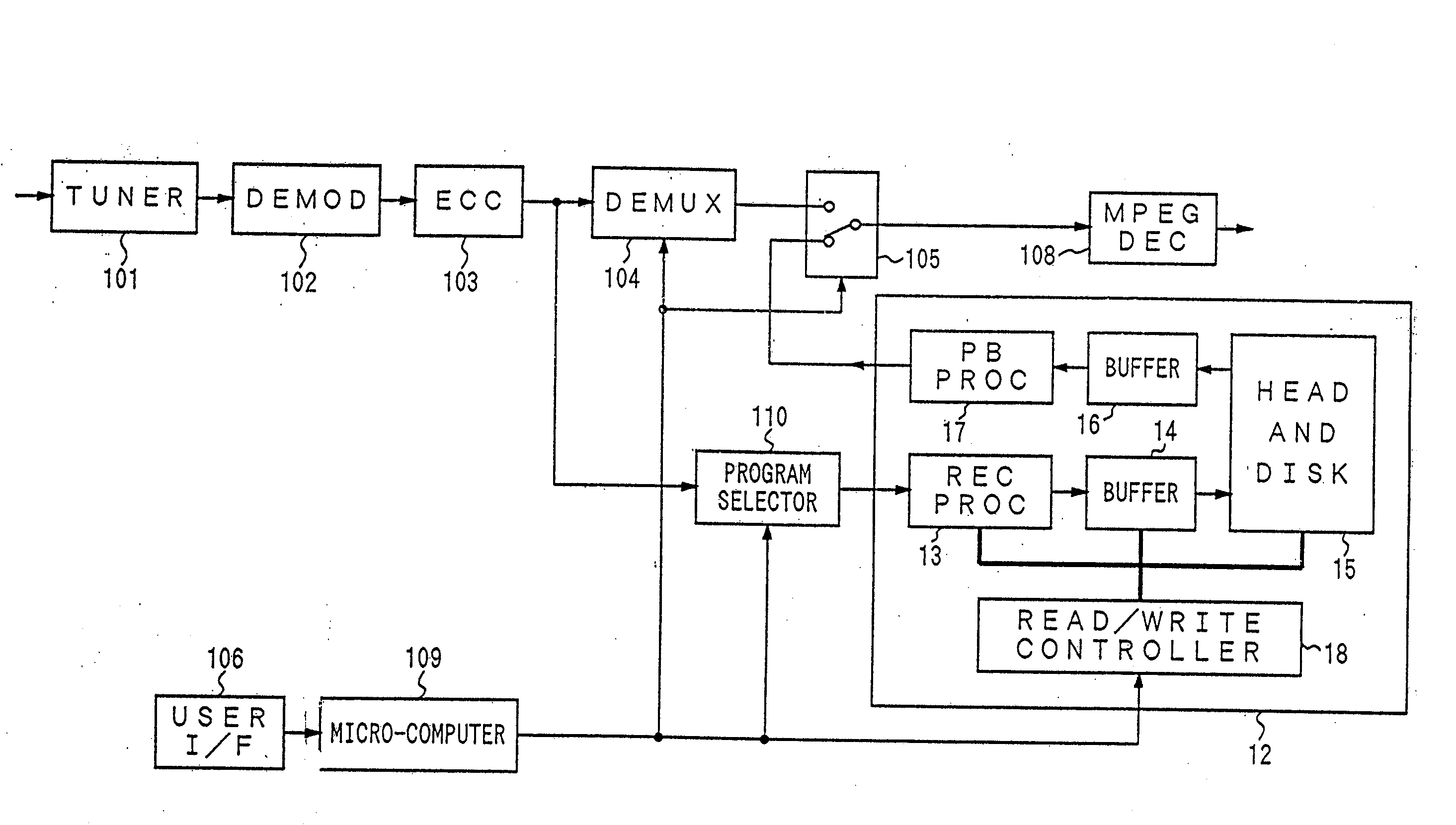
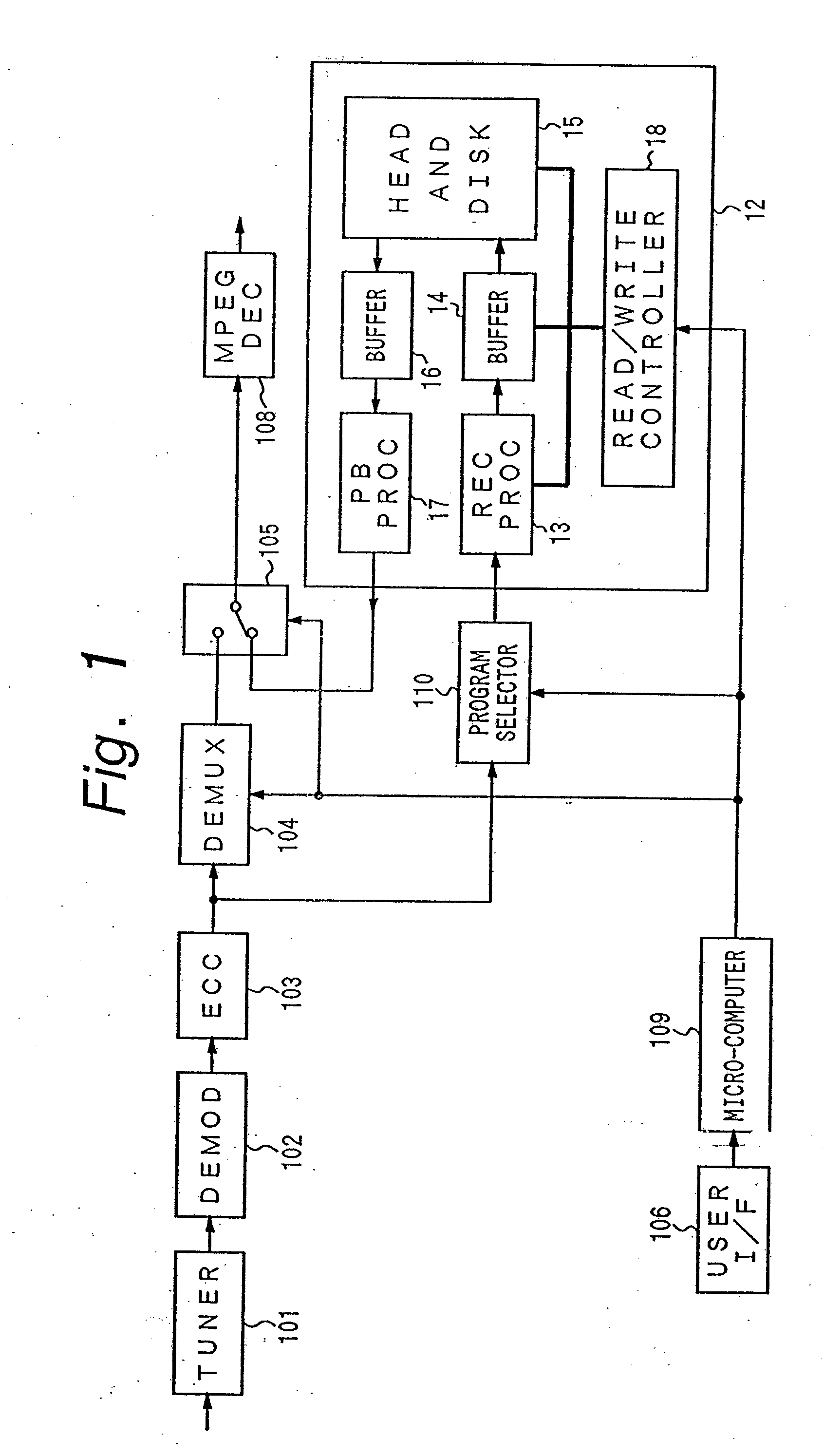
Network manager for cable television system headends
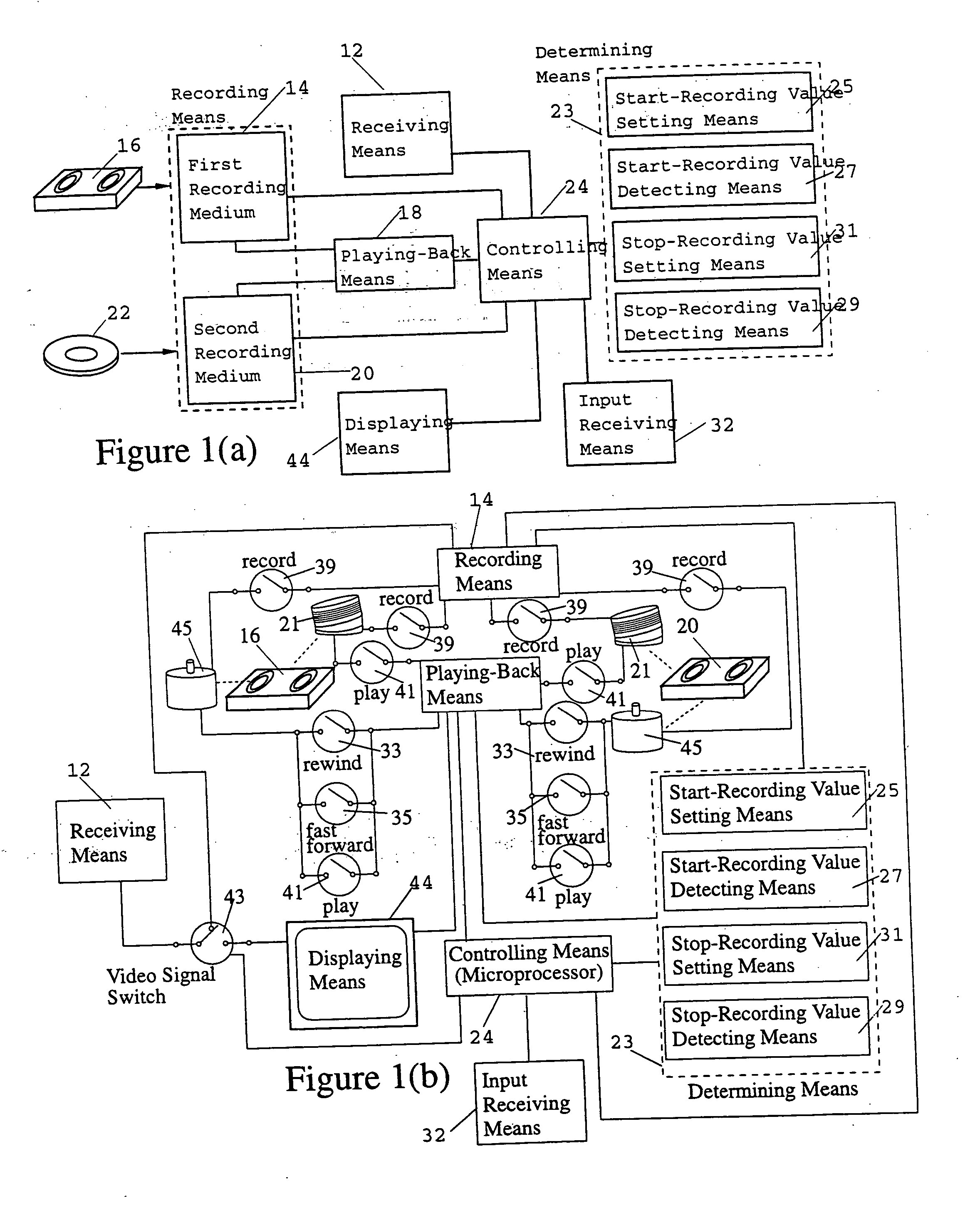
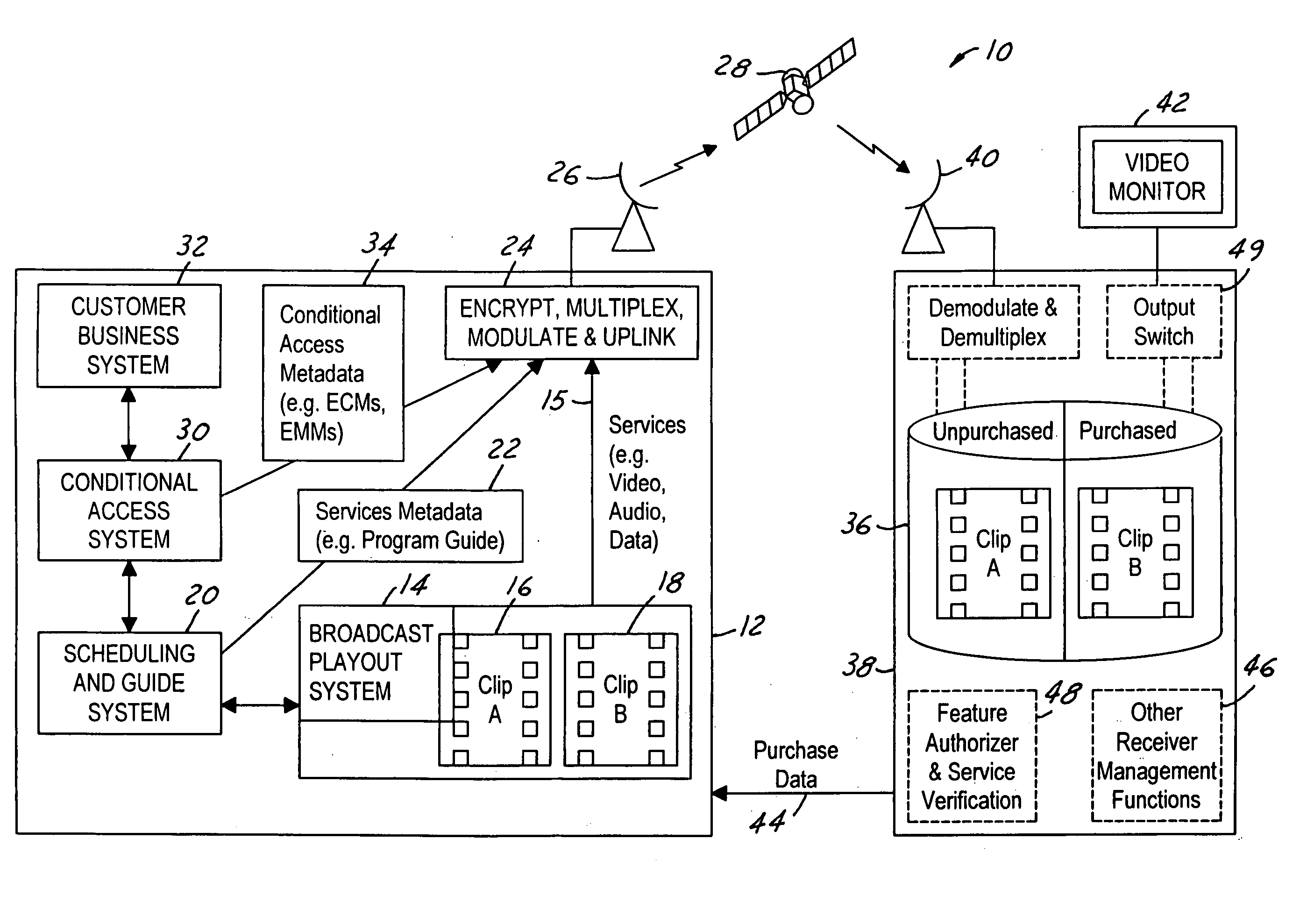
InactiveUS6201536B1Increase flexibilityImprove rendering capabilitiesTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionInformation processingInstruction memory
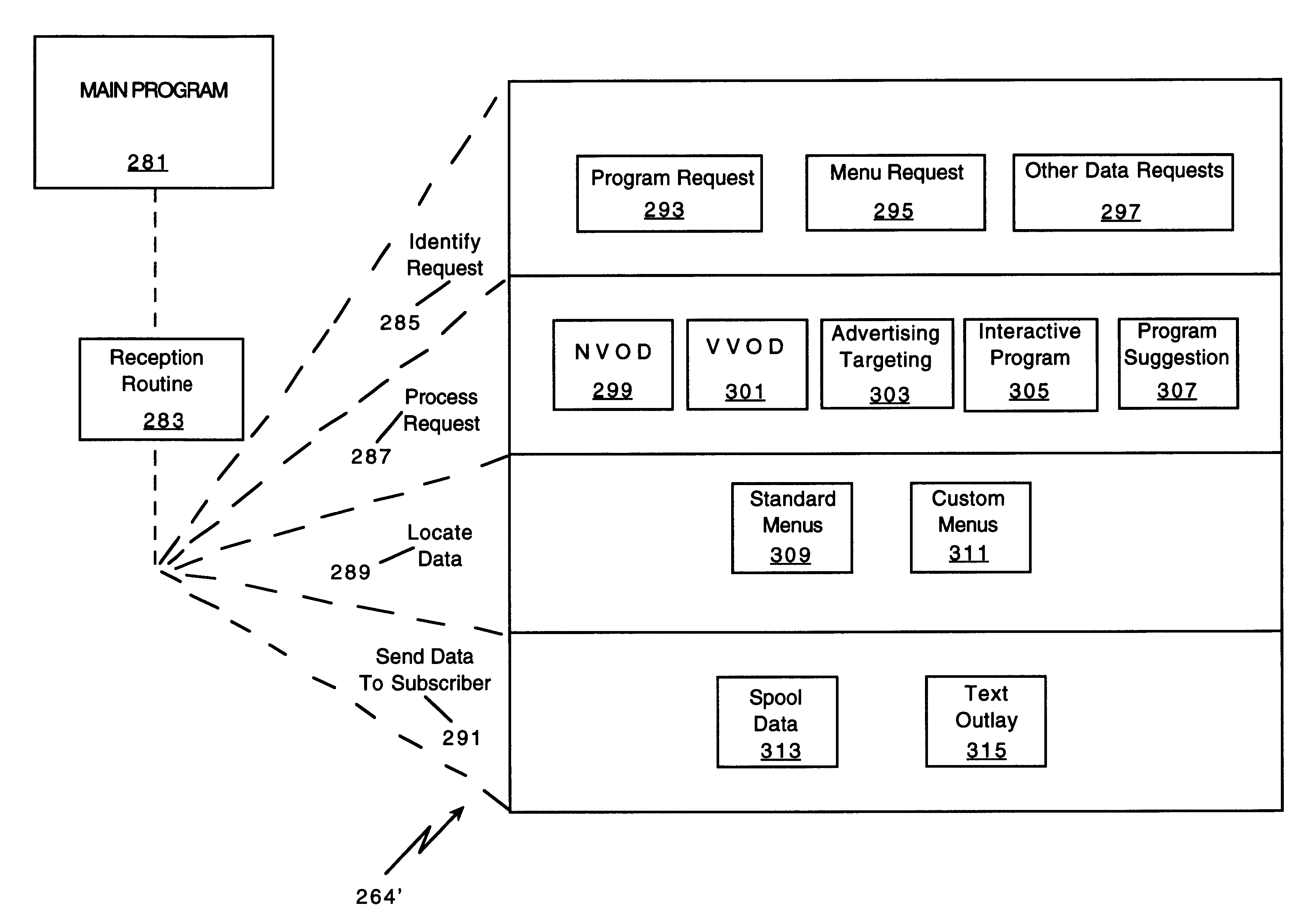
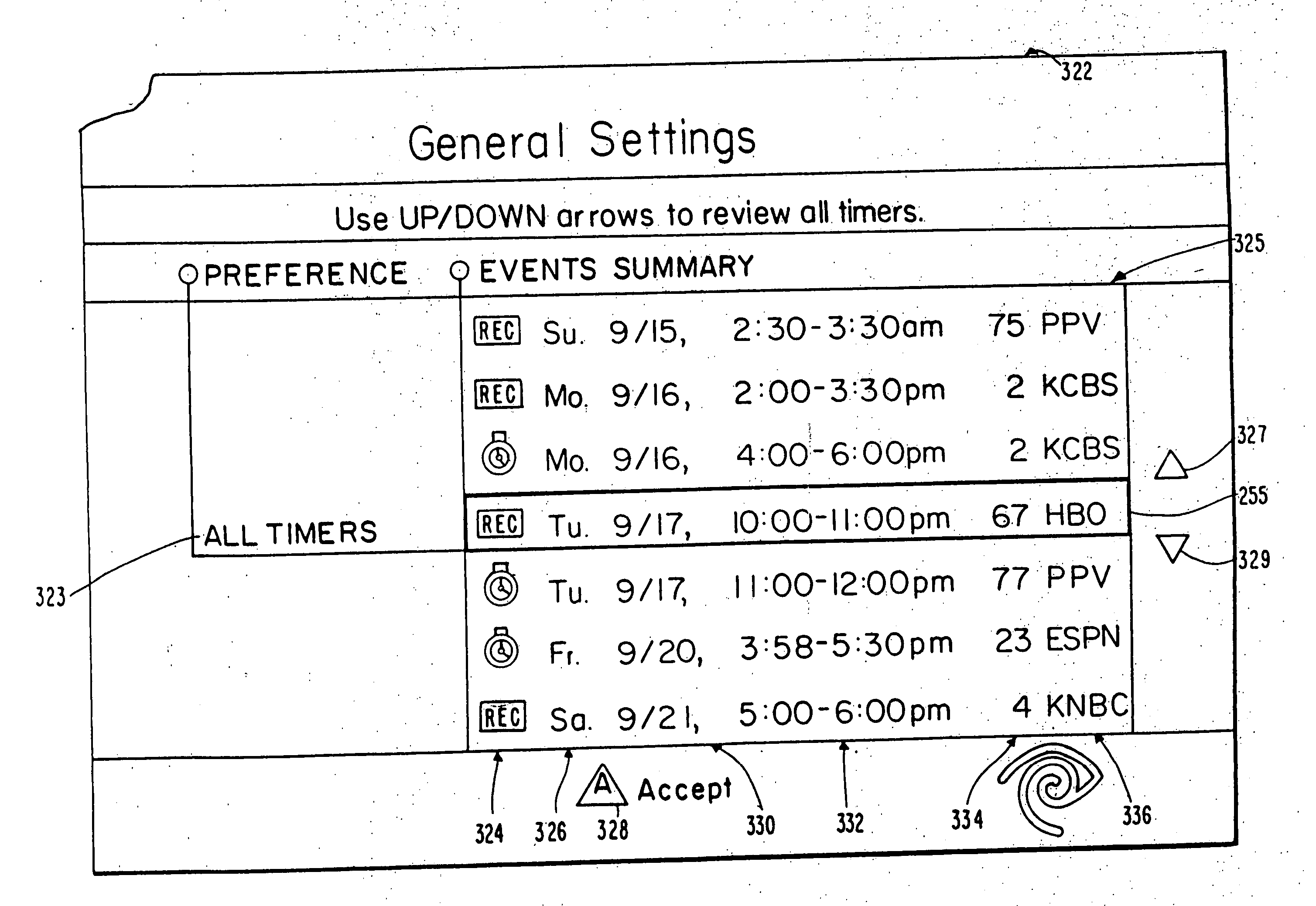
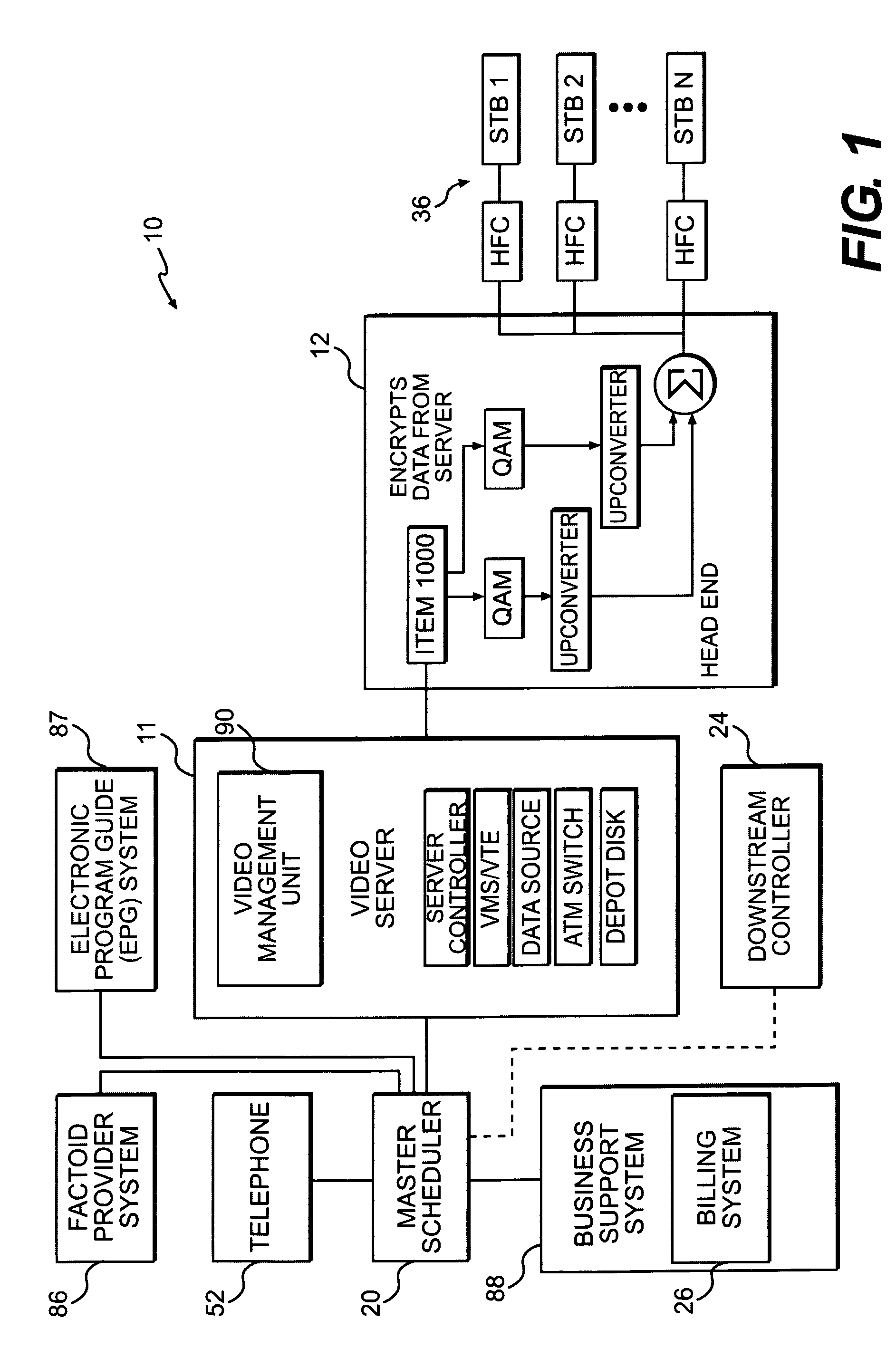
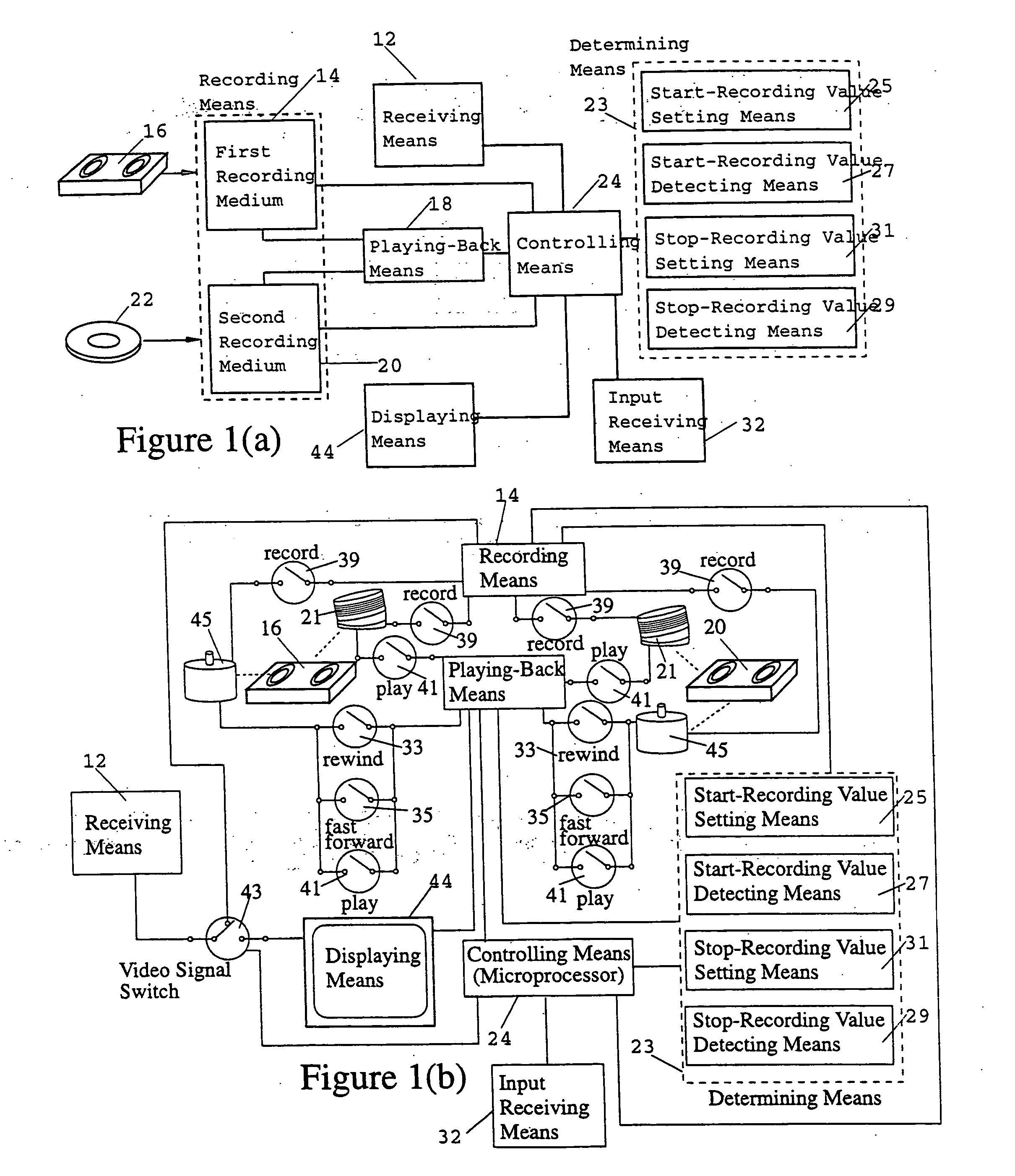
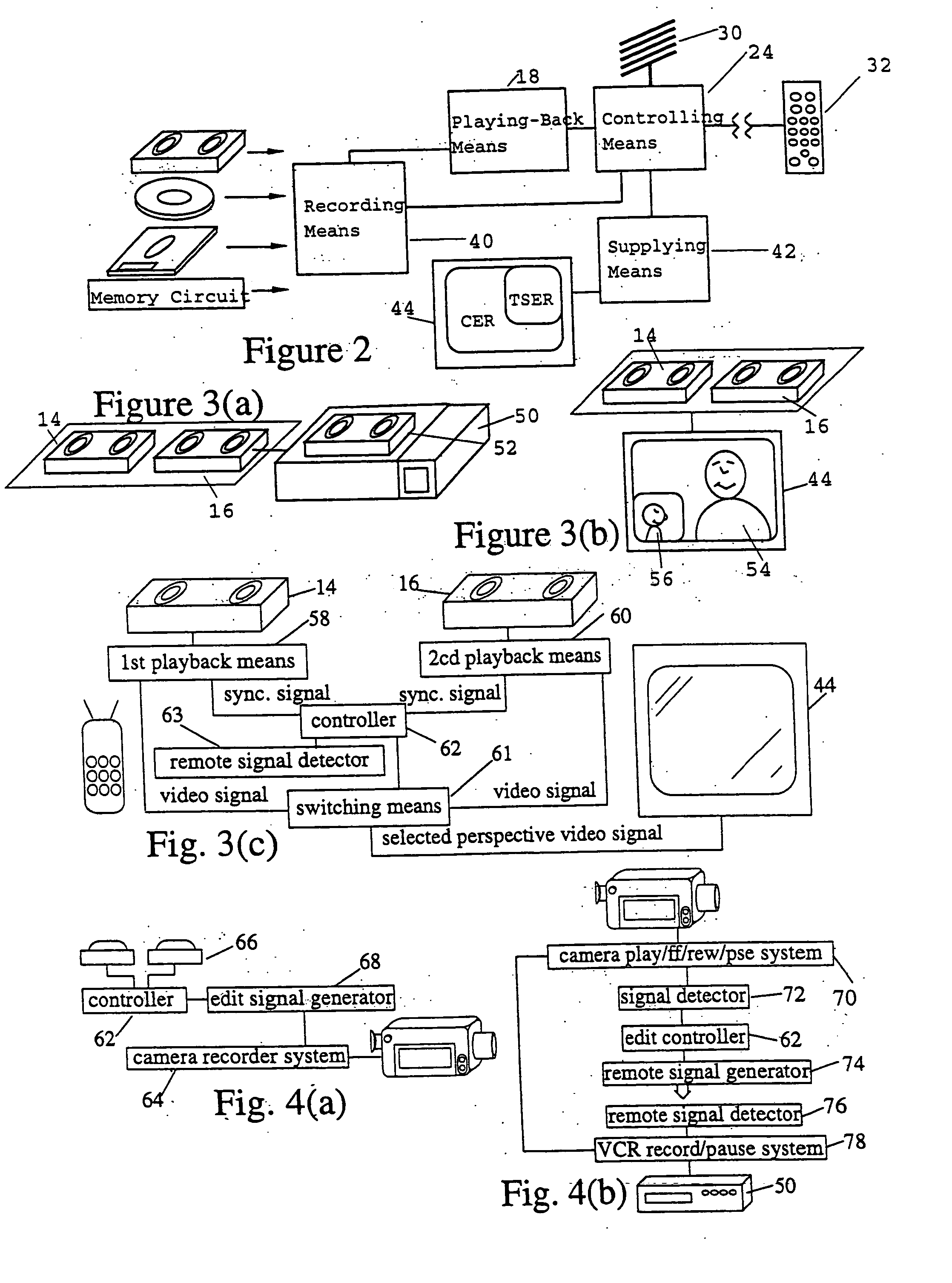
A novel network manager for use with a cable television system headend capable of monitoring and managing headend components and set top terminals in a television delivery system is described. The invention relates to methods and apparatus that manage and coordinate the reception of various programming and control signals at a headend. The invention manages and coordinates the storage of such signals for intelligent selection and distribution to set top terminals. The invention makes use of a receiver or set of receivers, a work station, a program control information processing component, a network management CPU, databases, control software and an instruction memory. The invention uses these components to manage and monitor certain headend components, such as signal reception equipment, an authorization component, a file server, MPEG decoders, a digital buffer with frame repeat and channel modulators. The invention is particularly useful in processing and responding to upstream information and subscriber communications received from set top terminals. In so doing, the invention accommodates various system services, including (1) near video on demand (NVOD), (2) virtual video on demand (VVOD), (3) video on demand (VOD), (4) interactive program services, (5) program suggestion features, (6) advertisement targeting, (7) generation of standard and custom menus, and (8) data spooling and text overlaying.
Owner:COMCAST IP HLDG I
Interactive television program guide display
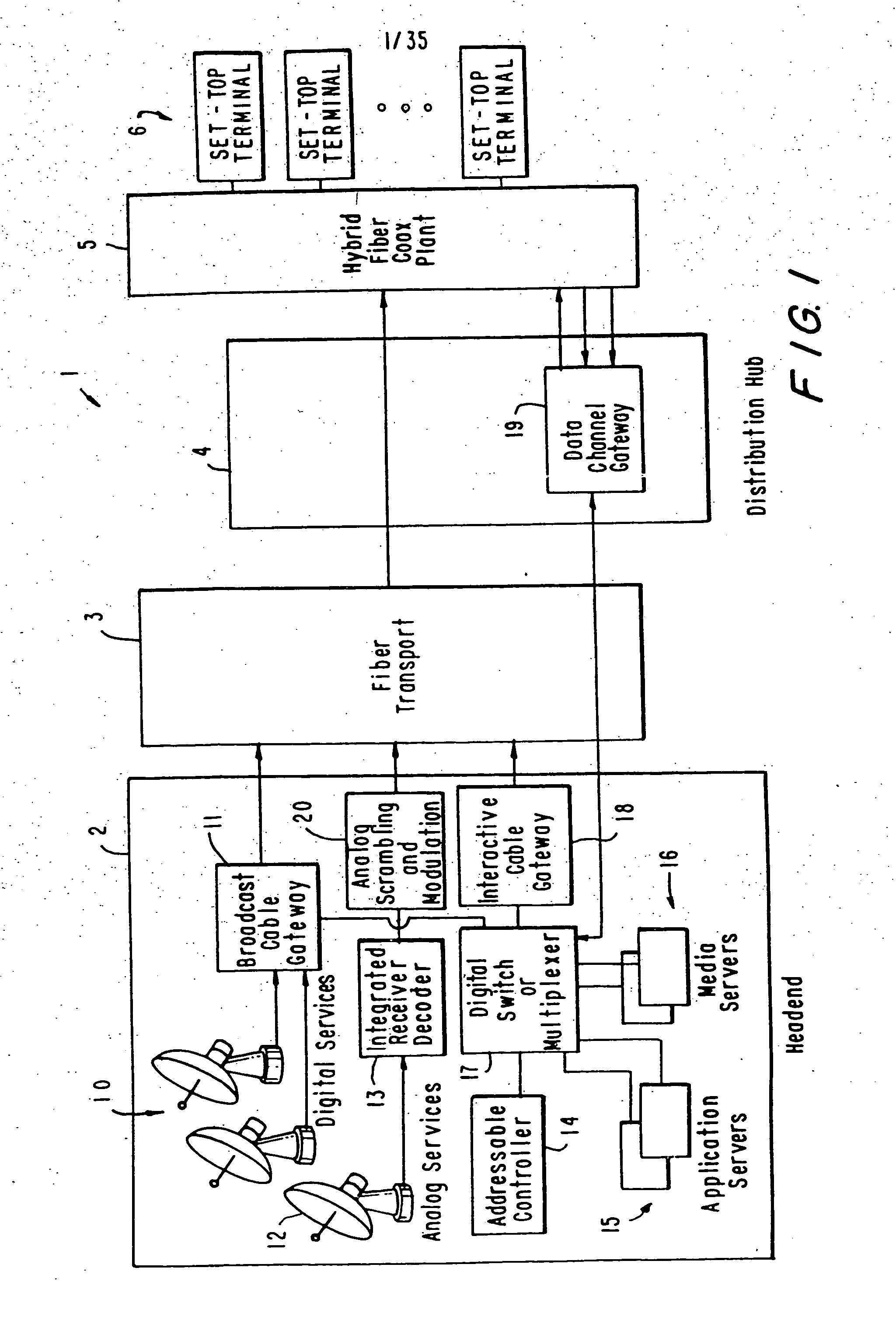
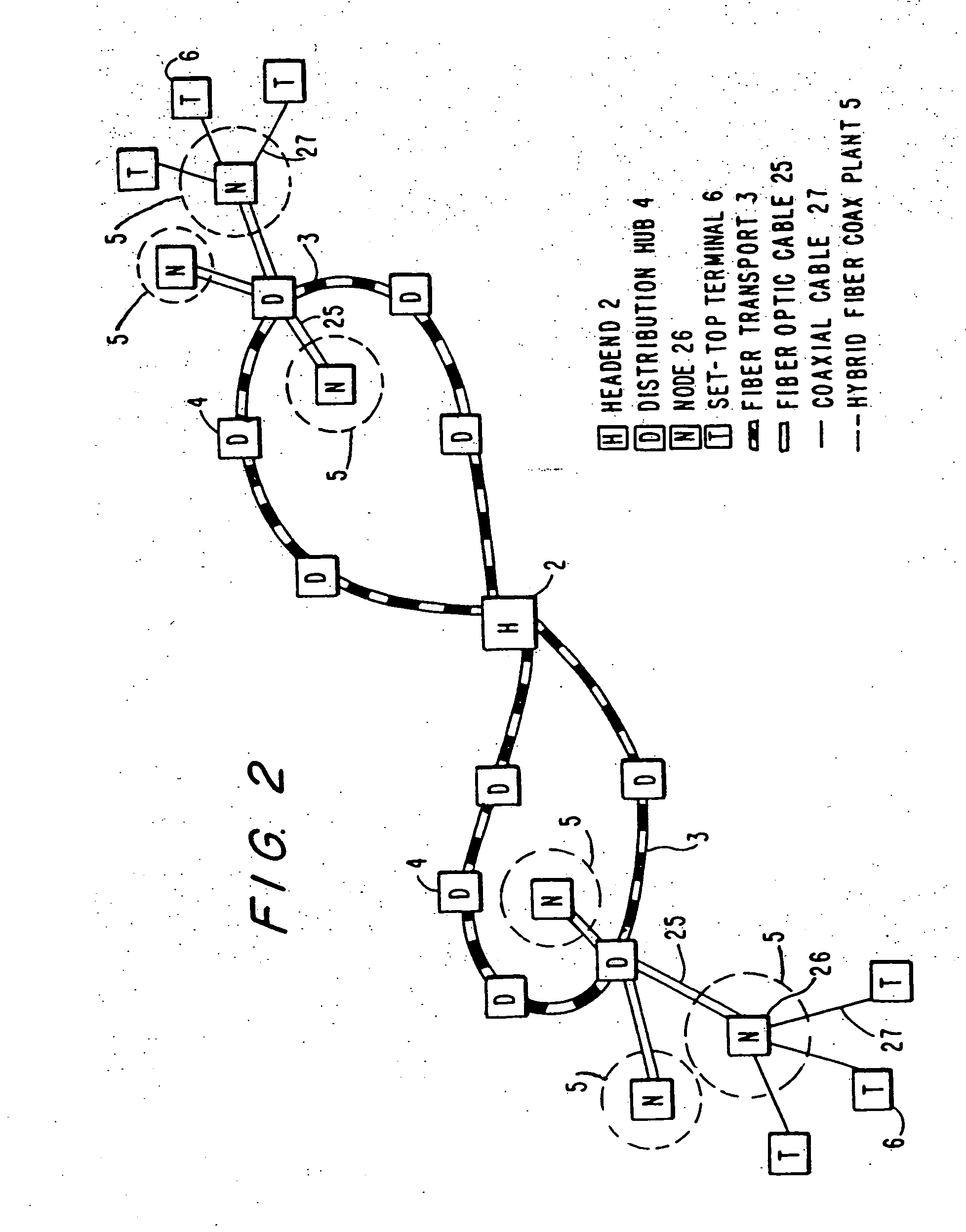
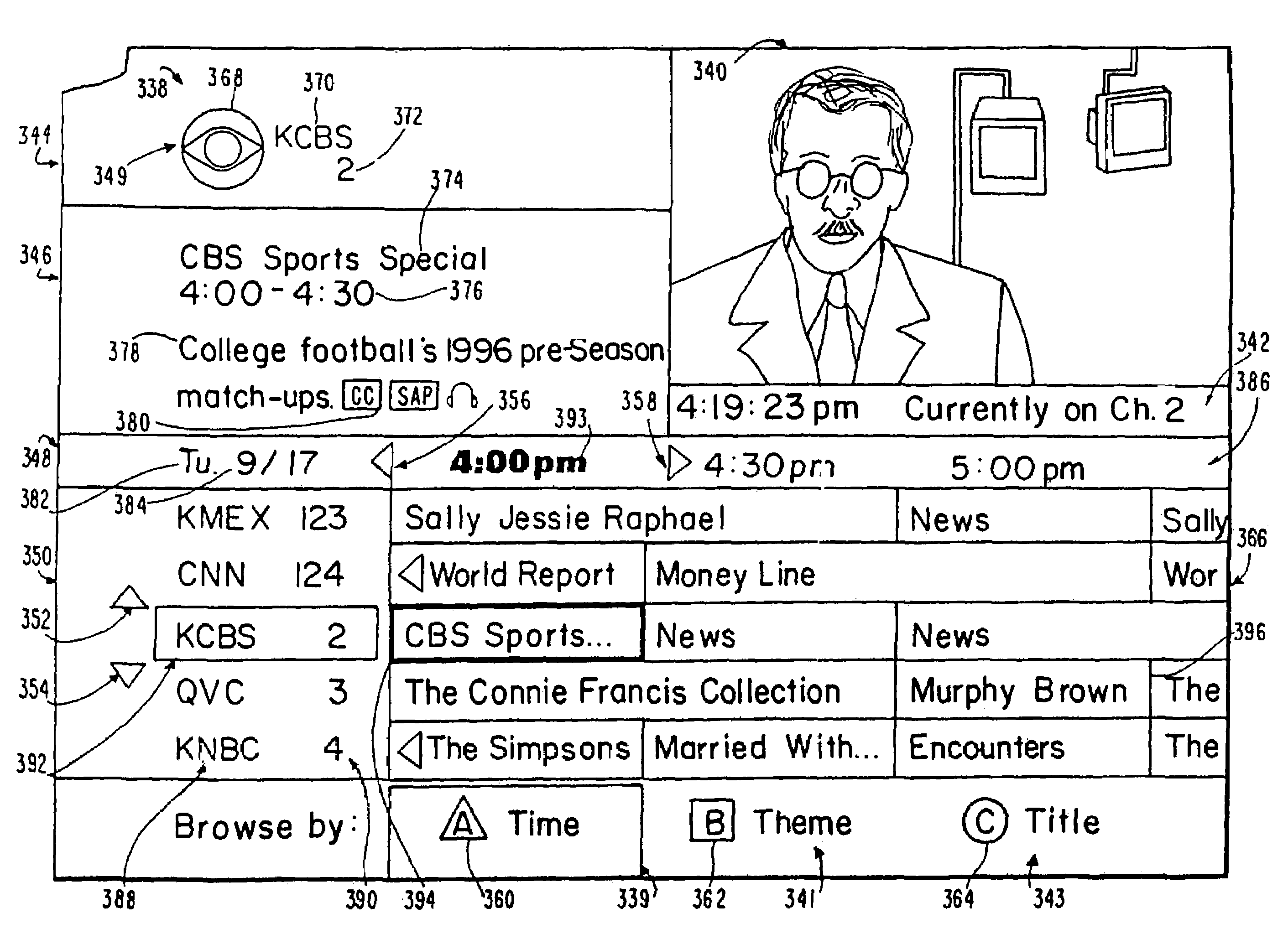
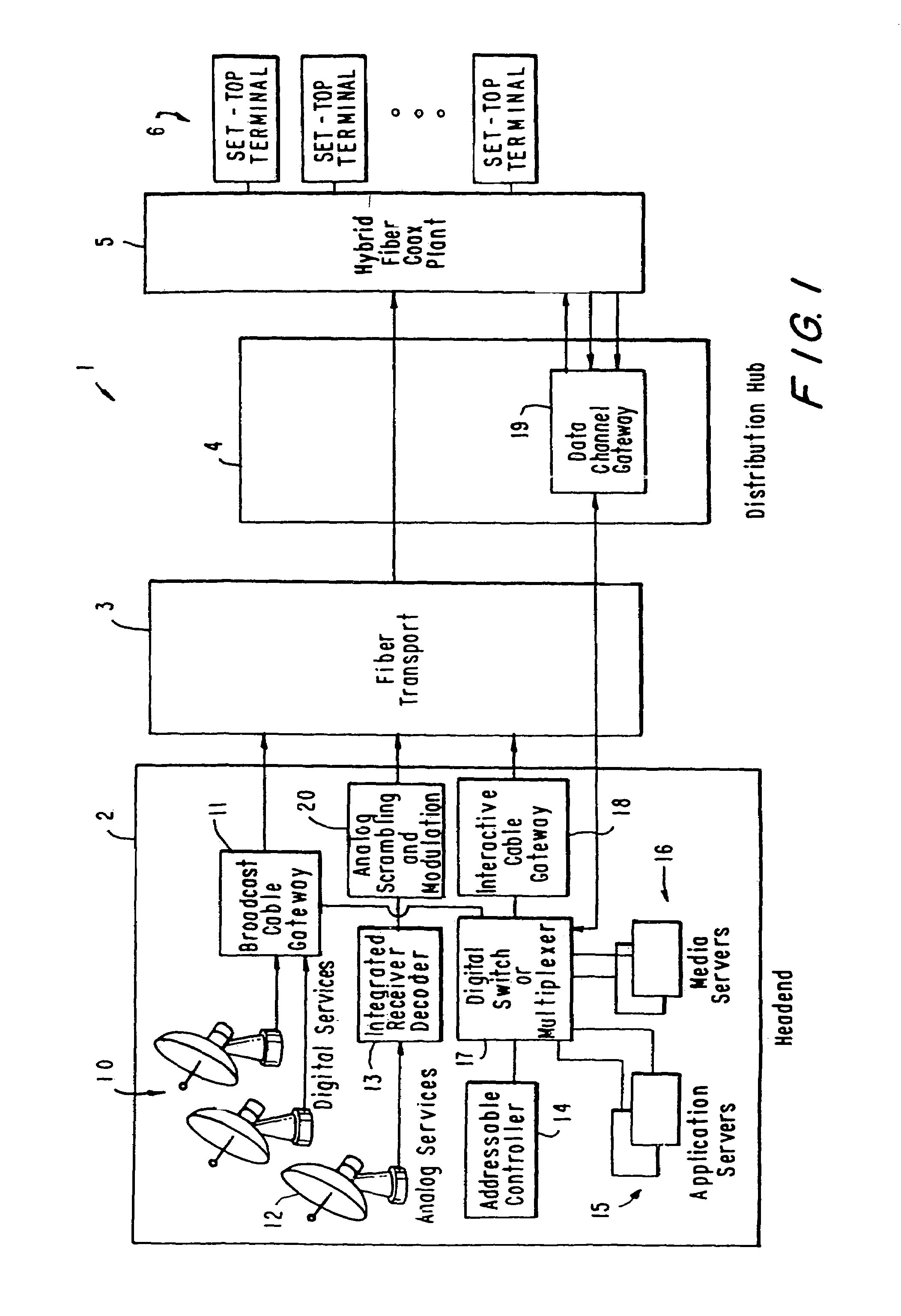
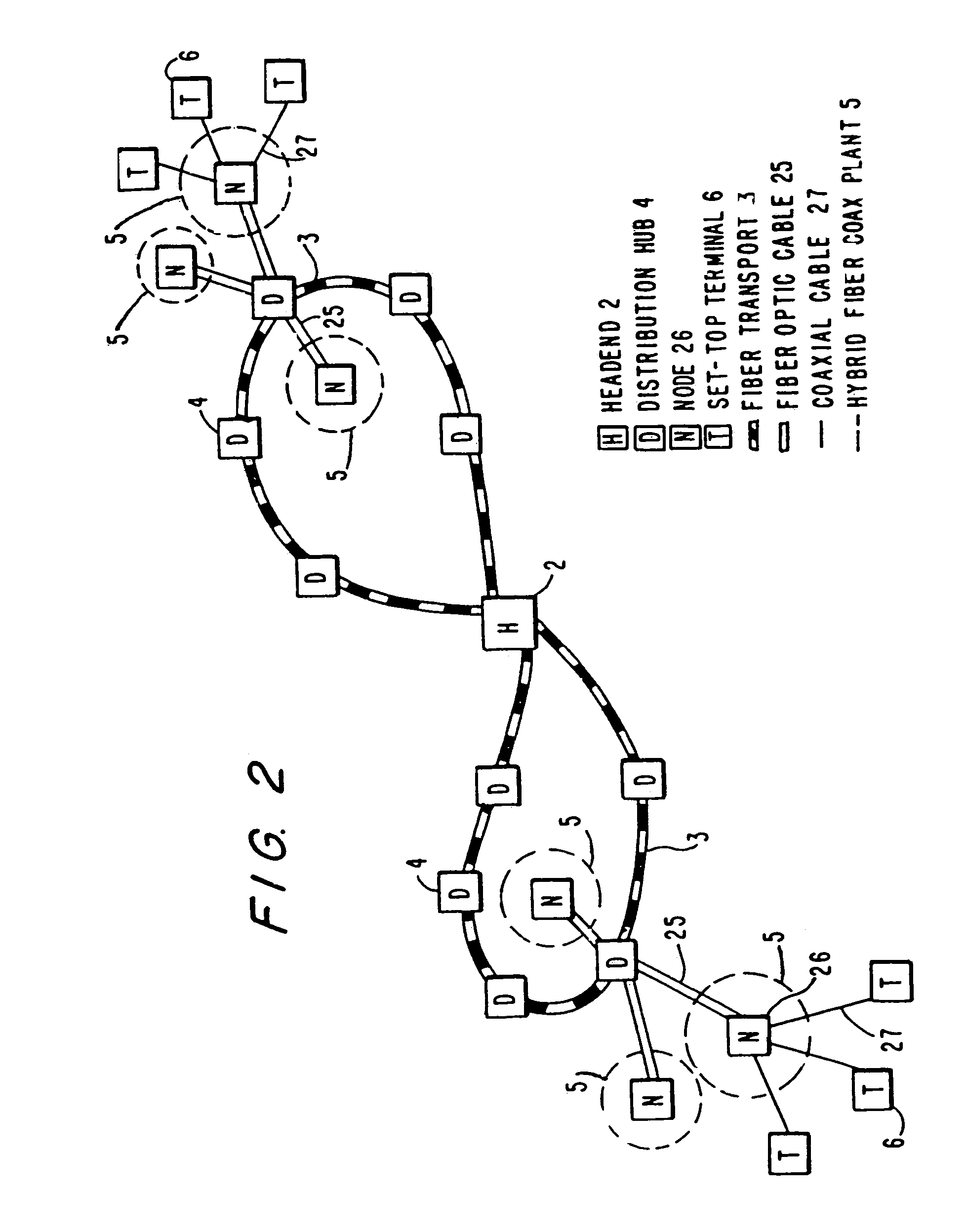
InactiveUS20050015804A1Increase the number ofEnhanced signalTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsThe InternetHybrid fibre-coaxial
A full service cable television system and method are provided. The system comprises a cable headend, at least one fiber transport, at least one distribution hub, at least one hybrid fiber coax plant, and a plurality of set-top terminals. The system delivers television programs, advanced cable services, and online services. Programs and services are transmitted to the set-top terminals in both digital and analog formats to maintain downward compatibility with existing systems. The set-top terminal includes a central processing unit, a unified memory architecture, a memory management unit, communications circuitry, I / O control circuitry, and audio and video output circuitry. Through these components, the set-top terminal provides advanced cable services such as a comprehensive channel navigator, an interactive program guide, impulse Pay-Per-View, Near-Video-On-Demand and Video-On-Demand programming, and advanced configuration controls. The set-top terminal also provides online services such as World Wide Web browsing, Internet e-mail, and home shopping.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
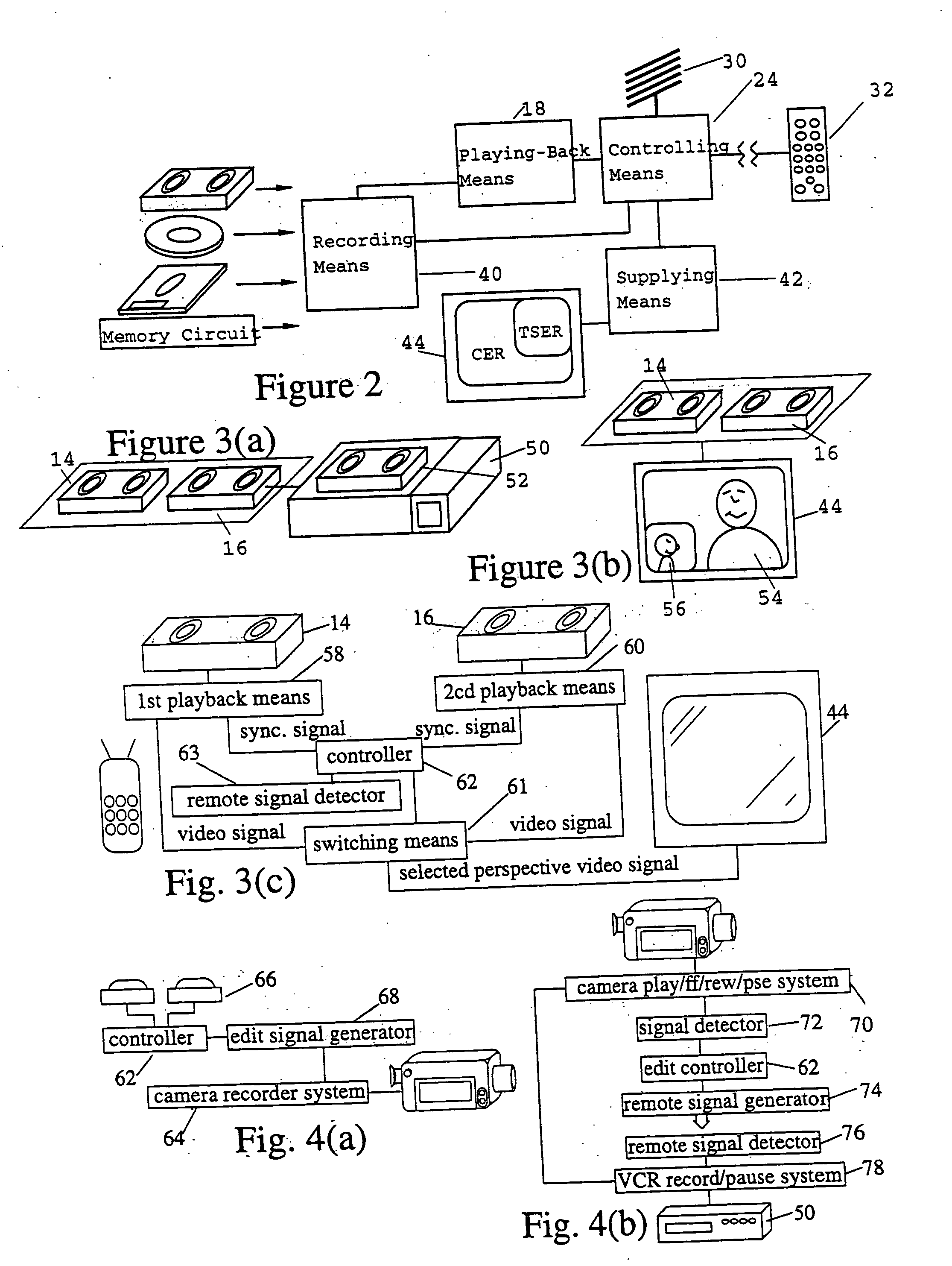
Method and apparatus for near video on demand
InactiveUS7024681B1Easy to implementEnsure consistencyAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsRecord information storageNear video on demandRelevant information
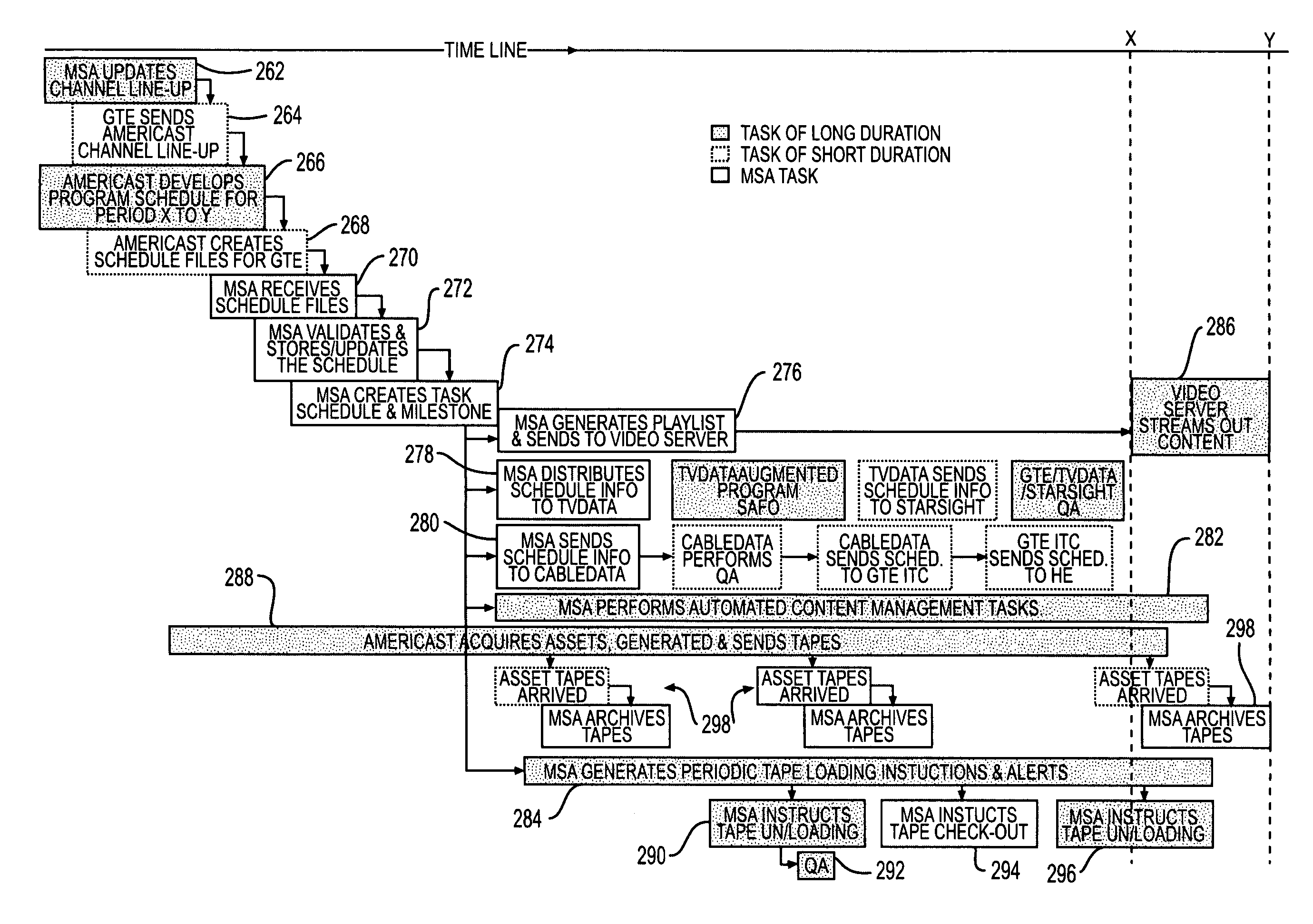
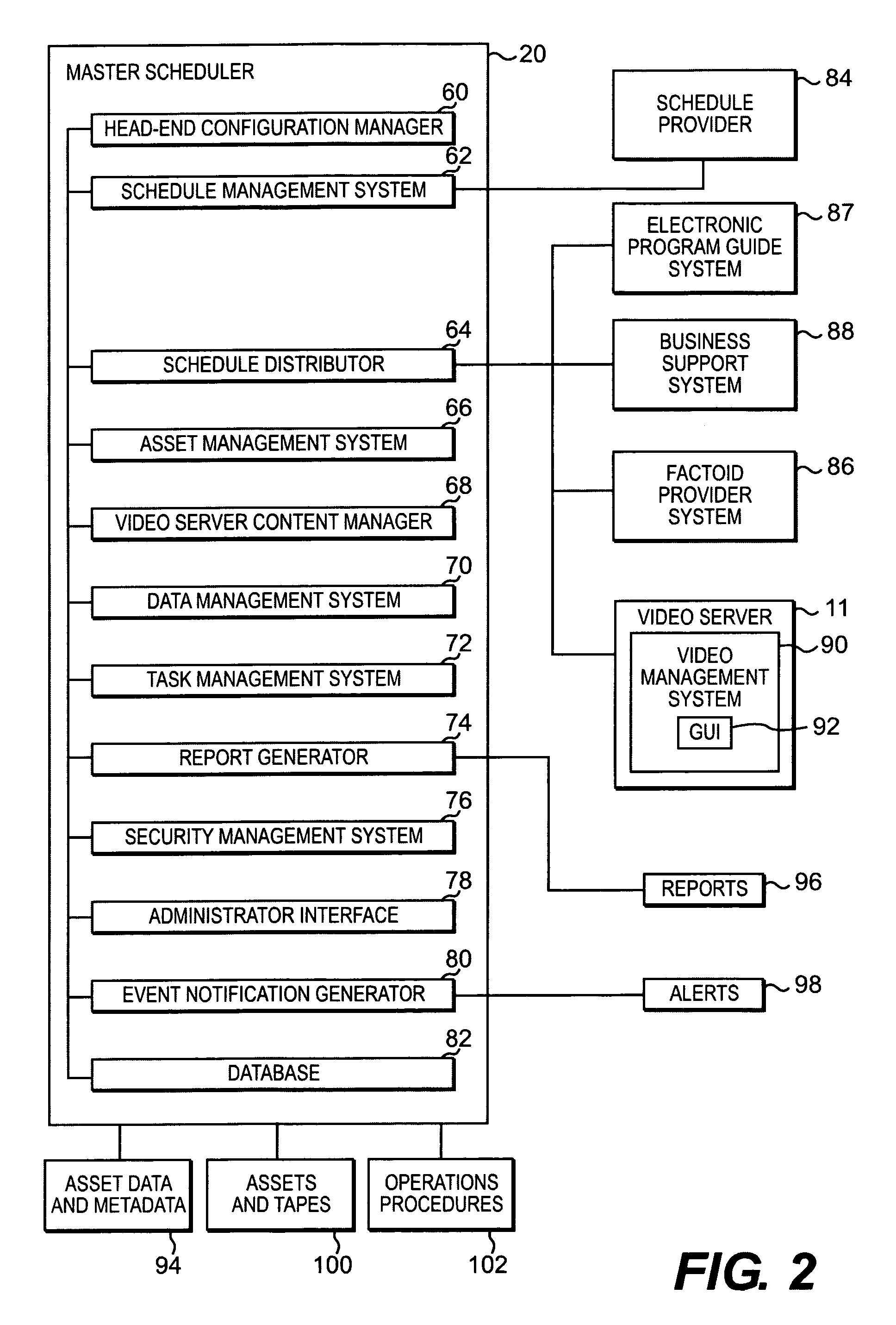
A master scheduler system and method automatically operate and / or coordinate operation of a plurality of relatively independent systems, including manual systems, to function as an NVOD system to provide automating diverse operations for supporting and maintaining an NVOD system. The master scheduler system and method may also be applied to automate manual processes of analog-based and digital broadcast based service. The master scheduler receives, processes, and disseminates NVOD schedule-related information for end-to-end NVOD service; that is, sending video from a back-end which stores video data to a head-end for viewing by a user. The master scheduler also provides operations support for the NVOD system, such as maintaining the head-end configuration, allocating channels, performing asset management, performing content management, etc. The master scheduler provides validation of scheduling information by comparing information such as programmed schedules, asset metadata, and data obtained by measuring asset parameters, for example duration.
Owner:VERIZON LAB
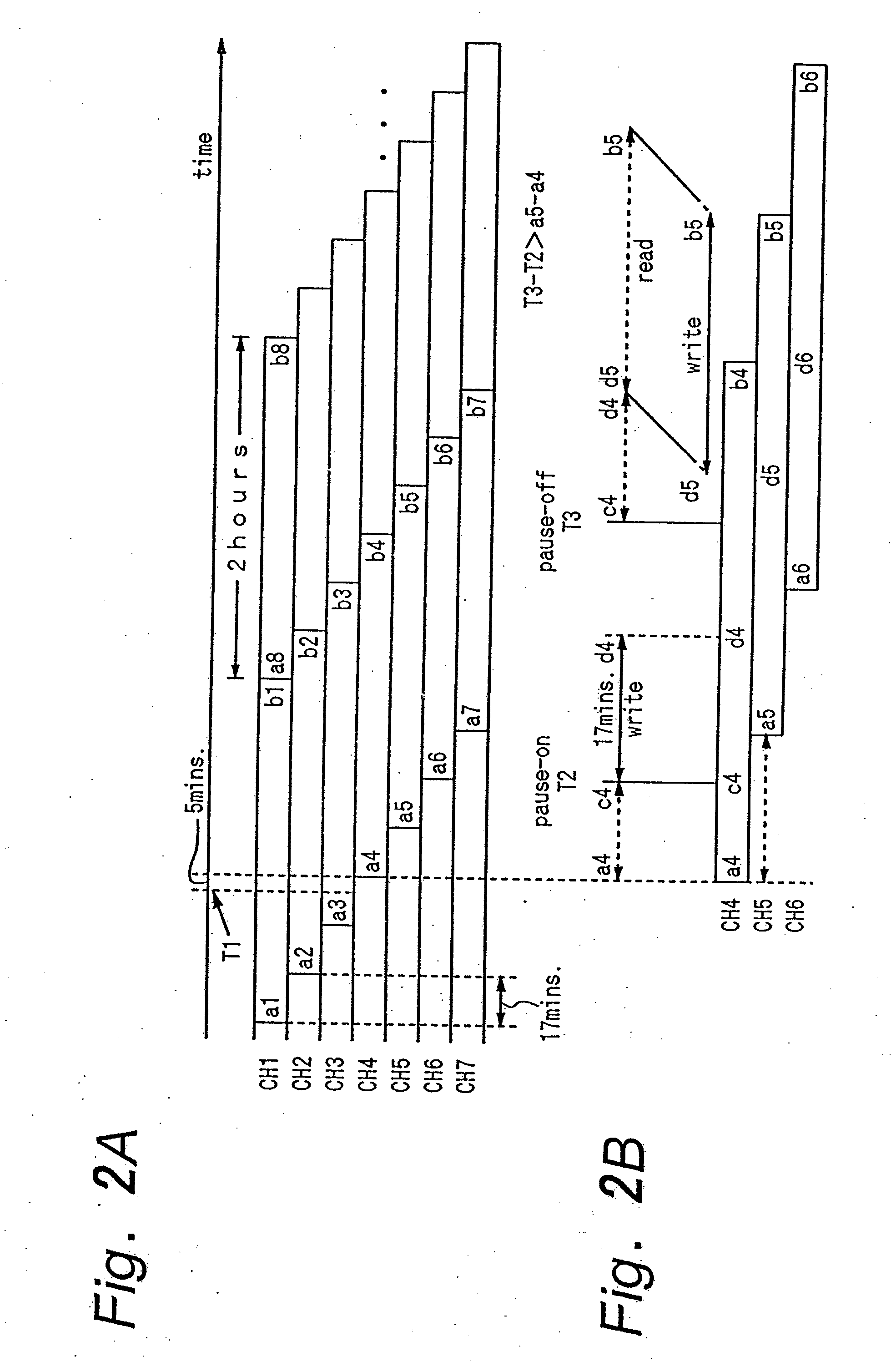
Local near video on demand storage
InactiveUS7024679B1Two-way working systemsSelective content distributionNear video on demandStart time
The invention relates to delivering a program to an individual business or residence. In one embodiment, a process for pre-storing a portion of a program distributed on a plurality of distribution conduits and in a linear schedule with staggered start times is described. A first start time of the program is determined for a first distribution conduit, and a second start time of the program is determined for a second distribution conduit. A stagger time between the first start time and the second start time is also determined. A segment of the program equal in length to the stagger time is stored.
Owner:STARZ ENTERTAINMENT GROUP
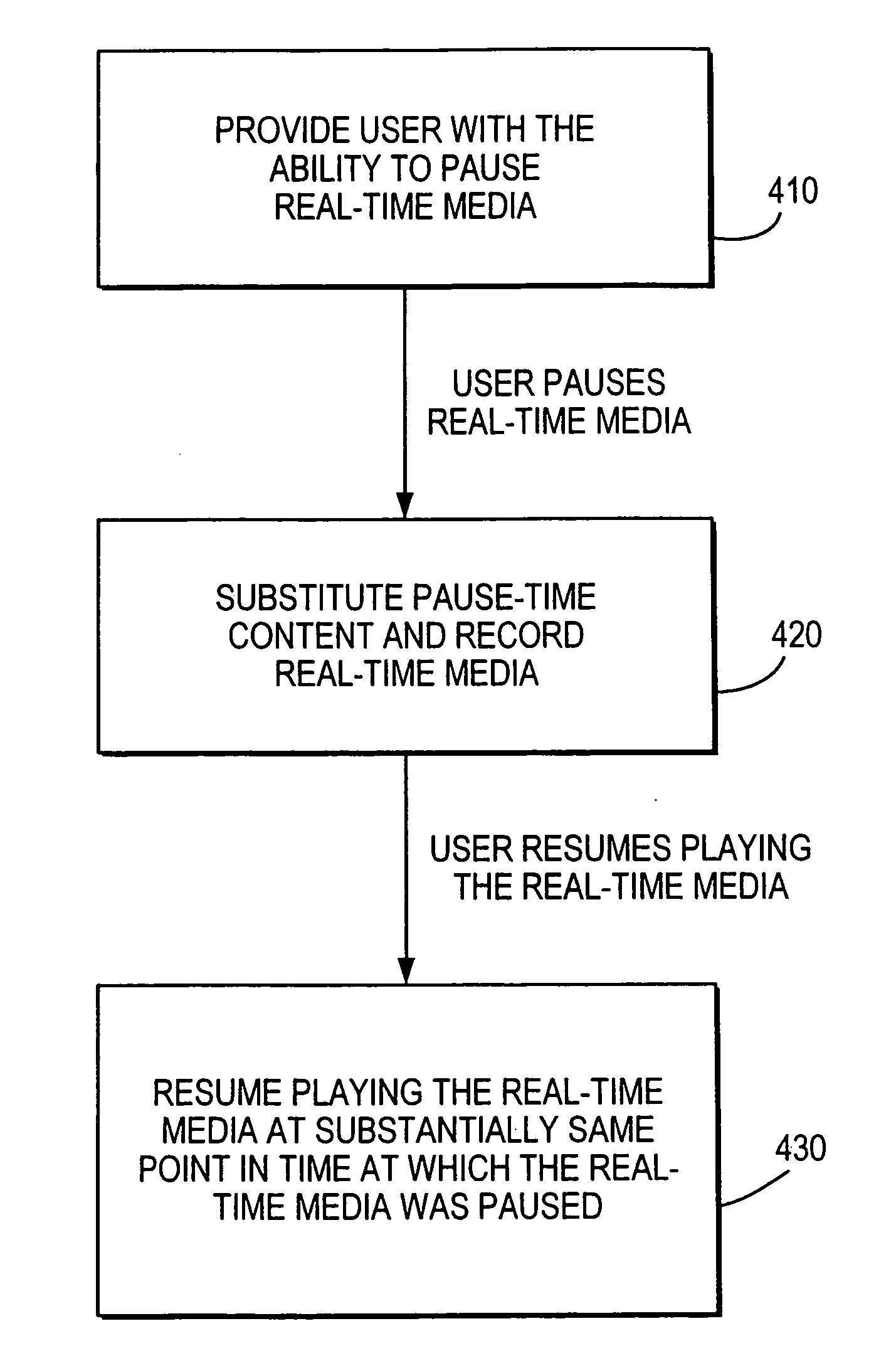
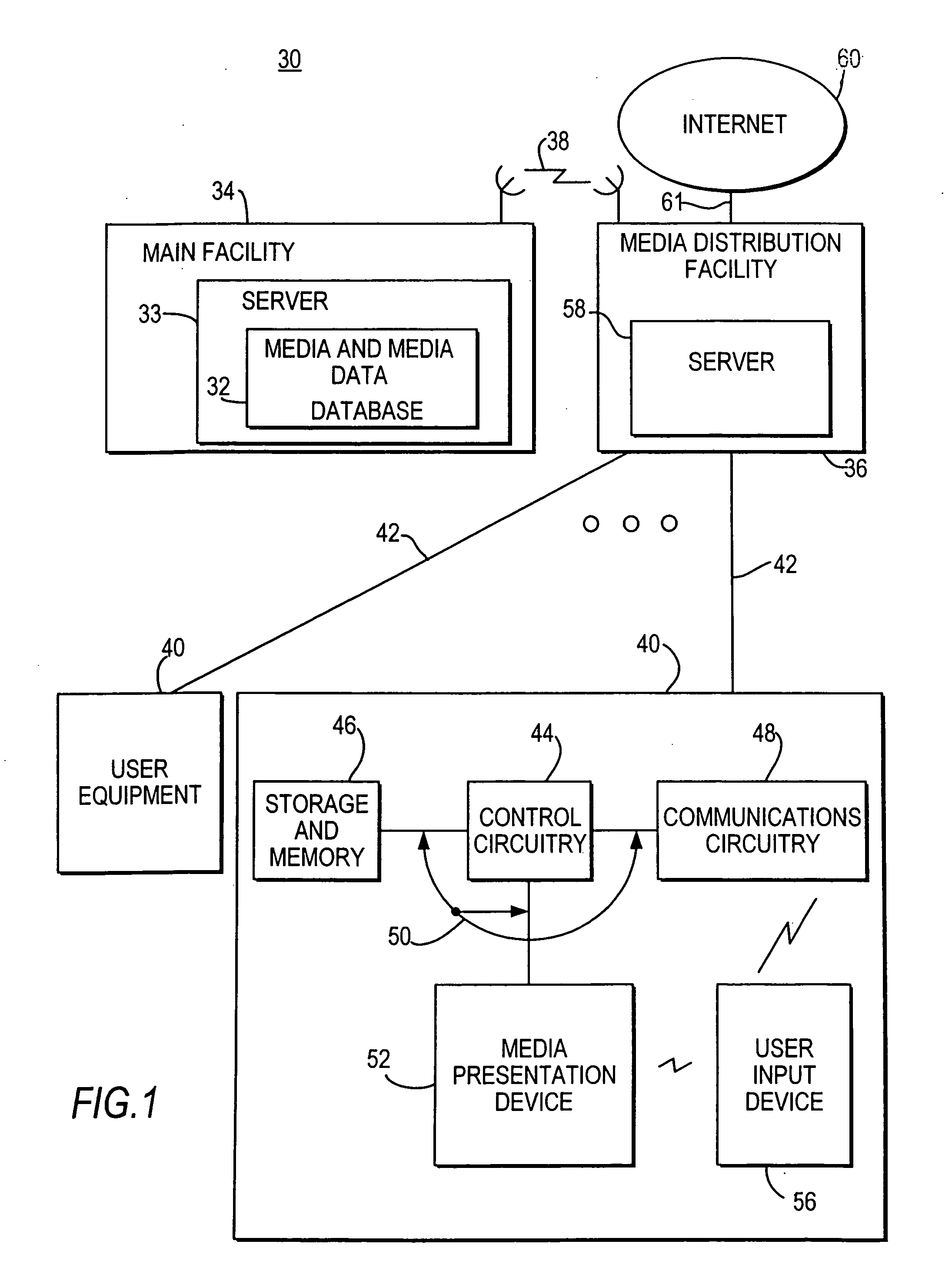
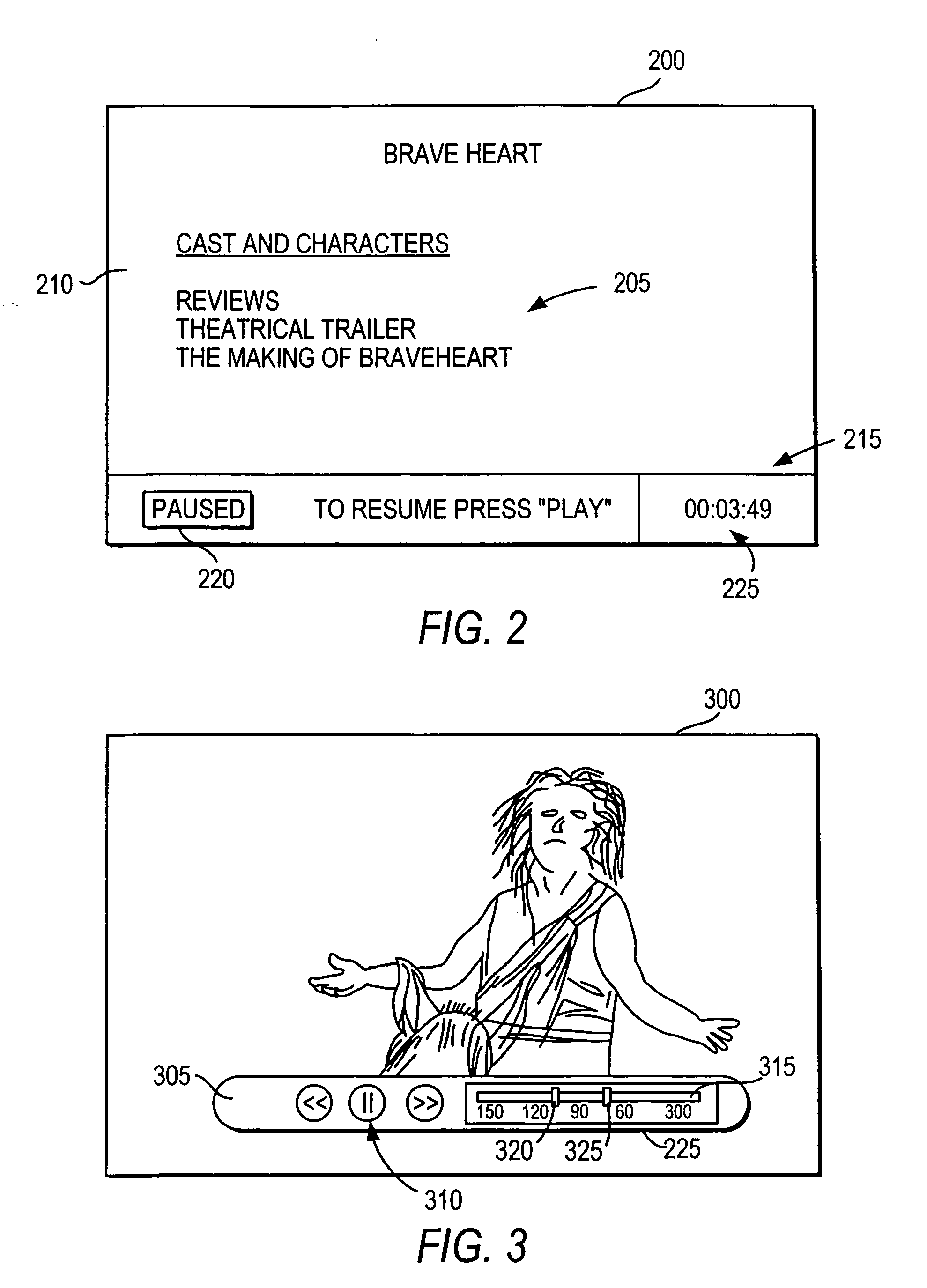
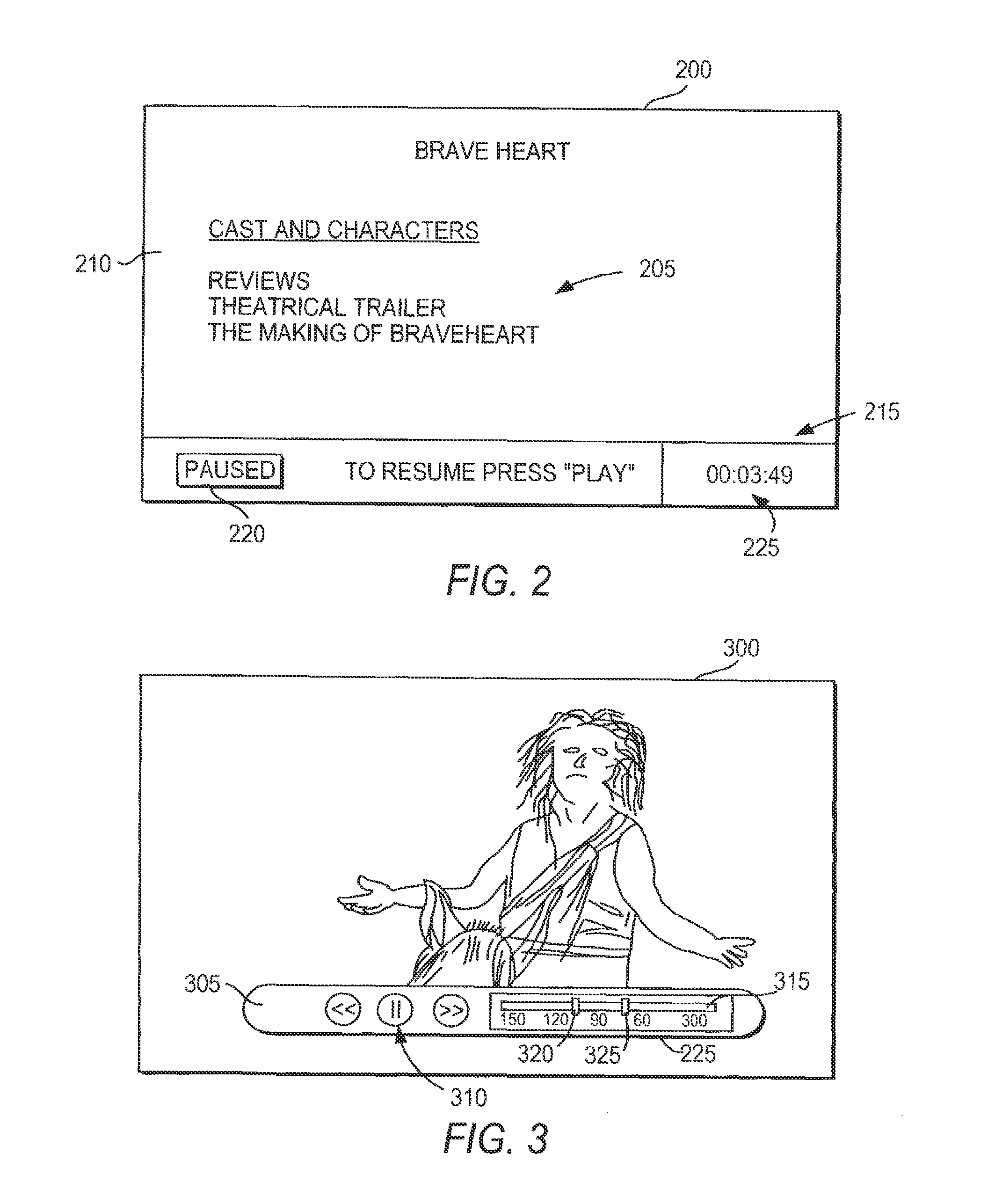
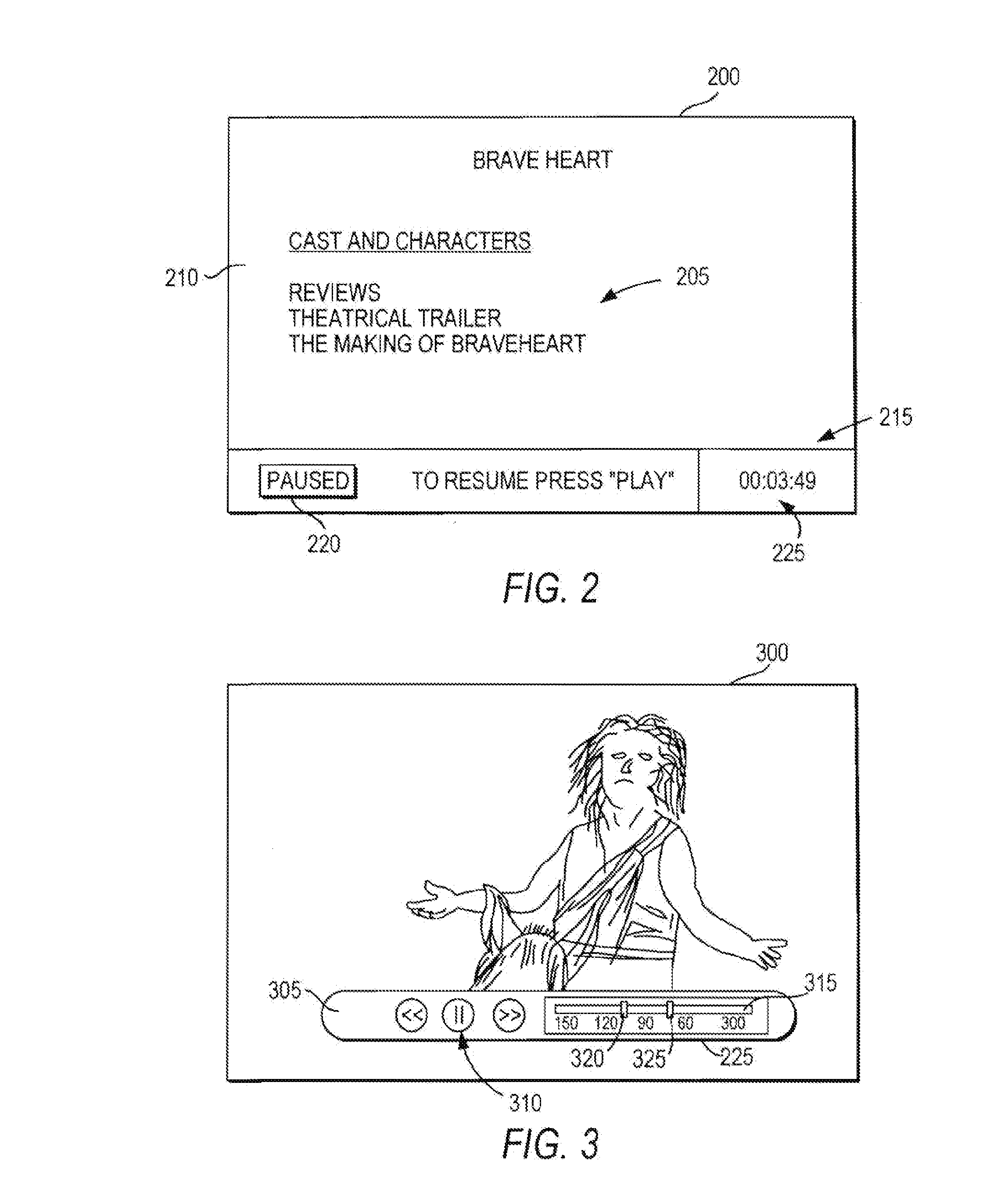
Interactive media system and method for presenting pause-time content
InactiveUS20080282285A1Inhibition featureTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsNear video on demandVideo Media
Interactive media systems and methods are provided for substituting pause-time content in place of media that has been paused. The user may pause media such as real-time media, video-on-demand media, near video-on-demand, or recorded media. If the user pauses real-time media or near video-on-demand media, the interactive media application may store the media. The interactive media application may also provide the user with the ability to rewind, resume play of, and fast-forward the media. The pause-time content may be audio or video media and may be an advertisement, trivia, program summaries or any other suitable pause-time content. The interactive media application may provide customized pause-time content specific to the user or specific to the media paused by using media data associated with the media. The interactive media application may also prevent the user from accessing features (e.g., fast-forward) of the system.
Owner:UNITED VIDEO PROPERTIES
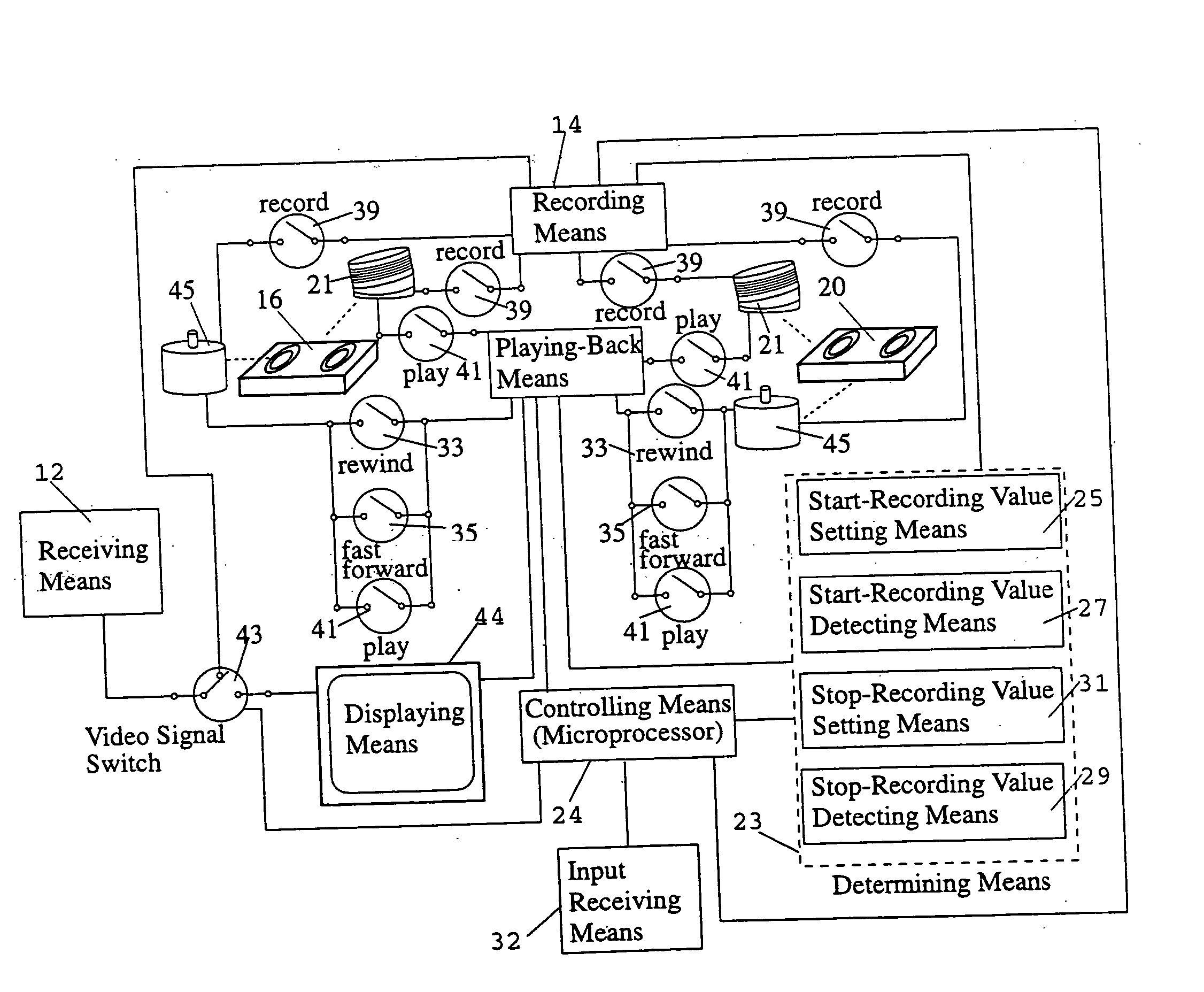
Methods for enabling near video-on-demand and video-on-request services using digital video recorders
InactiveUS20050055730A1Overcomes drawbackTelevision system detailsElectronic editing analogue information signalsDigital videoVideocassette recorder
A near video-on-demand (VOD) service enabled using a digital video recorder (DVR) for the simultaneous storage and playback of multimedia data. A DVR is connected over a network to a multimedia network source. A VOD selection is requested by the DVR from the network source. A multimedia data signal is received by the DVR from the network source. The data signal contains the requested VOD selection. A first received portion of the received data signal is stored on the DVR. The first received segment is played by the DVR for display on a display device. Simultaneously during the playing of the first received segment, a second received segment of the received data signal is received from the network source and stored on the DVR while the first received segment is played the display device. Thus, the requested VOD selection begins playing on the display device prior to the reception of the entire compressed multimedia data signal so that a requested VOD selection can begin being displayed nearly instantaneously after the request for it is made. A video-on-request (VOR) service is also enabled using a DVR. VOR selection data is received by a centralized database device, such as a network server, from a plurality of users. Each VOR selection data includes at least one requested video selection and video recorder identifying information for identifying each particular video recorder. A transmission priority of requested video selections is determined dependent on the frequency of requests ‘received from the plurality of users. A transmission channel and time is determined based on the transmission priority. DVR control signals are transmitted to automatically tune in the determined transmission channel at the determined transmission time and record the particular video selection.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Video on demand in a broadcast network
ActiveUS7801303B2Storage requirements is greatly reducedLowering the risk that the program content may be accessedDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsDigital videoNear video on demand
Owner:DIRECTV LLC
Methods for enabling near video-on-demand and video-on-request services using digital video recorders
InactiveUS20050060756A1Television system detailsHelical scan formatVideocassette recorderDigital video
A near video-on-demand (VOD) service enabled using a digital video recorder (DVR) for the simultaneous storage and playback of multimedia data. A DVR is connected over a network to a multimedia network source. A VOD selection is requested by the DVR from the network source. A multimedia data signal is received by the DVR from the network source. The data signal contains the requested VOD selection. A first received portion of the received data signal is stored on the DVR. The first received segment is played by the DVR for display on a display device. Simultaneously during the playing of the first received segment, a second received segment of the received data signal is received from the network source and stored on the DVR while the first received segment is played the display device. Thus, the requested VOD selection begins playing on the display device prior to the reception of the entire compressed multimedia data signal so that a requested VOD selection can begin being displayed nearly instantaneously after the request for it is made. A video-on-request (VOR) service is also enabled using a DVR. VOR selection data is received by a centralized database device, such as a network server, from a plurality of users. Each VOR selection data includes at least one requested video selection and video recorder identifying information for identifying each particular video recorder. A transmission priority of requested video selections is determined dependent on the frequency of requests received from the plurality of users. A transmission channel and time is determined based on the transmission priority. DVR control signals are transmitted to automatically tune in the determined transmission channel at the determined transmission time and record the particular video selection.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Methods for enabling near video-on-demand and video-on-request services using digital video recorders
InactiveUS20050060755A1Television system detailsHelical scan formatDigital videoVideocassette recorder
A near video-on-demand (VOD) service enabled using a digital video recorder (DVR) for the simultaneous storage and playback of multimedia data. A DVR is connected over a network to a multimedia network source. A VOD selection is requested by the DVR from the network source. A multimedia data signal is received by the DVR from the network source. The data signal contains the requested VOD selection. A first received portion of the received data signal is stored on the DVR. The first received segment is played by the DVR for display on a display device. Simultaneously during the playing of the first received segment, a second received segment of the received data signal is received from the network source and stored on the DVR while the first received segment is played the display device. Thus, the requested VOD selection begins playing on the display device prior to the reception of the entire compressed multimedia data signal so that a requested VOD selection can begin being displayed nearly instantaneously after the request for it is made. A video-on-request (VOR) service is also enabled using a DVR. VOR selection data is received by a centralized database device, such as a network server, from a plurality of users. Each VOR selection data includes at least one requested video selection and video recorder identifying information for identifying each particular video recorder. A transmission priority of requested video selections is determined dependent on the frequency of requests 1received from the plurality of users. A transmission channel and time is determined based on the transmission priority. DVR control signals are transmitted to automatically tune in the determined transmission channel at the determined transmission time and record the particular video selection.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Methods for enabling near video-on-demand and video-on-request services using digital video recorders
InactiveUS20050055717A1Overcomes drawbackTelevision system detailsHelical scan formatDigital videoVideocassette recorder
A near video-on-demand (VOD) service enabled using a digital video recorder (DVR) for the simultaneous storage and playback of multimedia data. A DVR is connected over a network to a multimedia network source. A VOD selection is requested by the DVR from the network source. A multimedia data signal is received by the DVR from the network source. The data signal contains the requested VOD selection. A first received portion of the received data signal is stored on the DVR. The first received segment is played by the DVR for display on a display device. Simultaneously during the playing of the first received segment, a second received segment of the received data signal is received from the network source and stored on the DVR while the first received segment is played the display device. Thus, the requested VOD selection begins playing on the display device prior to the reception of the entire compressed multimedia data signal so that a requested VOD selection can begin being displayed nearly instantaneously after the request for it is made. A video-on-request (VOR) service is also enabled using a DVR. VOR selection data is received by a centralized database device, such as a network server, from a plurality of users. Each VOR selection data includes at least one requested video selection and video recorder identifying information for identifying each particular video recorder. A transmission priority of requested video selections is determined dependent on the frequency of requests 1received from the plurality of users. A transmission channel and time is determined based on the transmission priority. DVR control signals are transmitted to automatically tune in the determined transmission channel at the determined transmission time and record the particular video selection.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Interactive television program guide display
InactiveUS7546621B2Increase the number ofEnhanced signalTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsThe InternetEngineering
A full service cable television system and method are provided. The system comprises a cable headend, at least one fiber transport, at least one distribution hub, at least one hybrid fiber coax plant, and a plurality of set-top terminals. The system delivers television programs, advanced cable services, and online services. Programs and services are transmitted to the set-top terminals in both digital and analog formats to maintain downward compatibility with existing systems. The set-top terminal includes a central processing unit, a unified memory architecture, a memory management unit, communications circuitry, I / O control circuitry, and audio and video output circuitry. Through these components, the set-top terminal provides advanced cable services such as a comprehensive channel navigator, an interactive program guide, impulse Pay-Per-View, Near-Video-On-Demand and Video-On-Demand programming, and advanced configuration controls. The set-top terminal also provides online services such as World Wide Web browsing, Internet e-mail, and home shopping.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
IPTV APPLICATION SYSTEM AND METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PLAYING NEAR VoD PROGRAMS
InactiveUS20090106803A1Improve user experiencePulse modulation television signal transmissionTwo-way working systemsTime scheduleNear video on demand
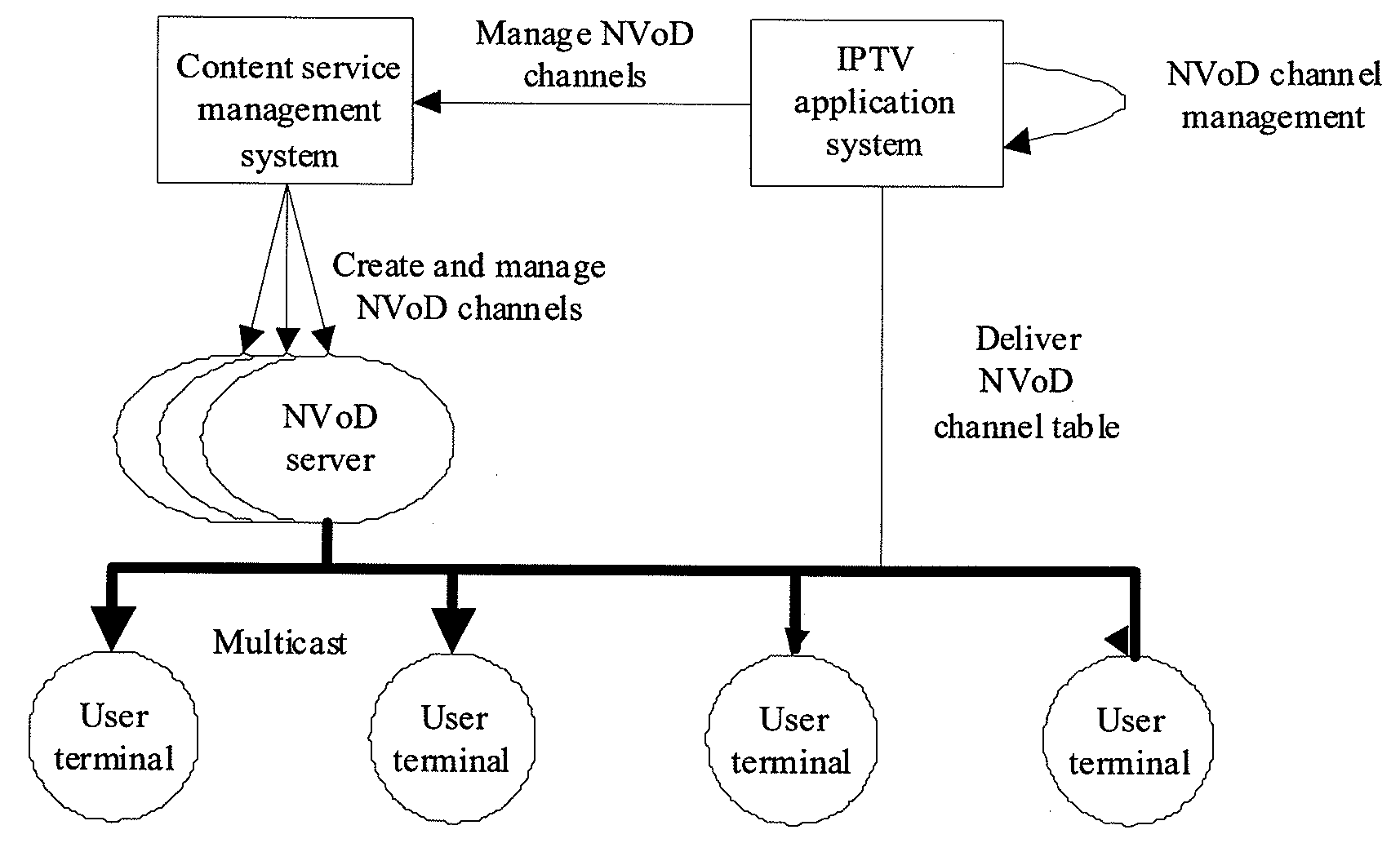
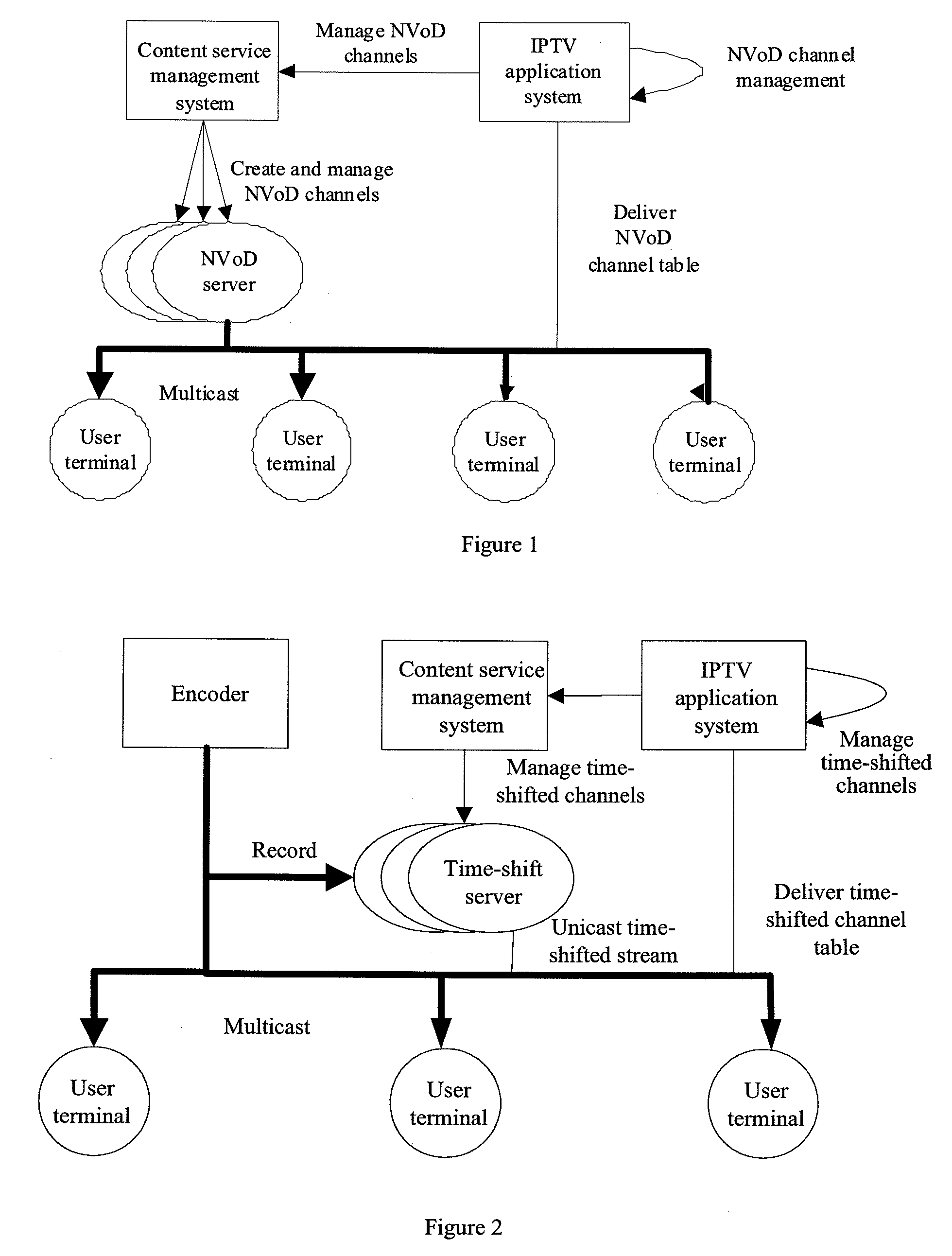
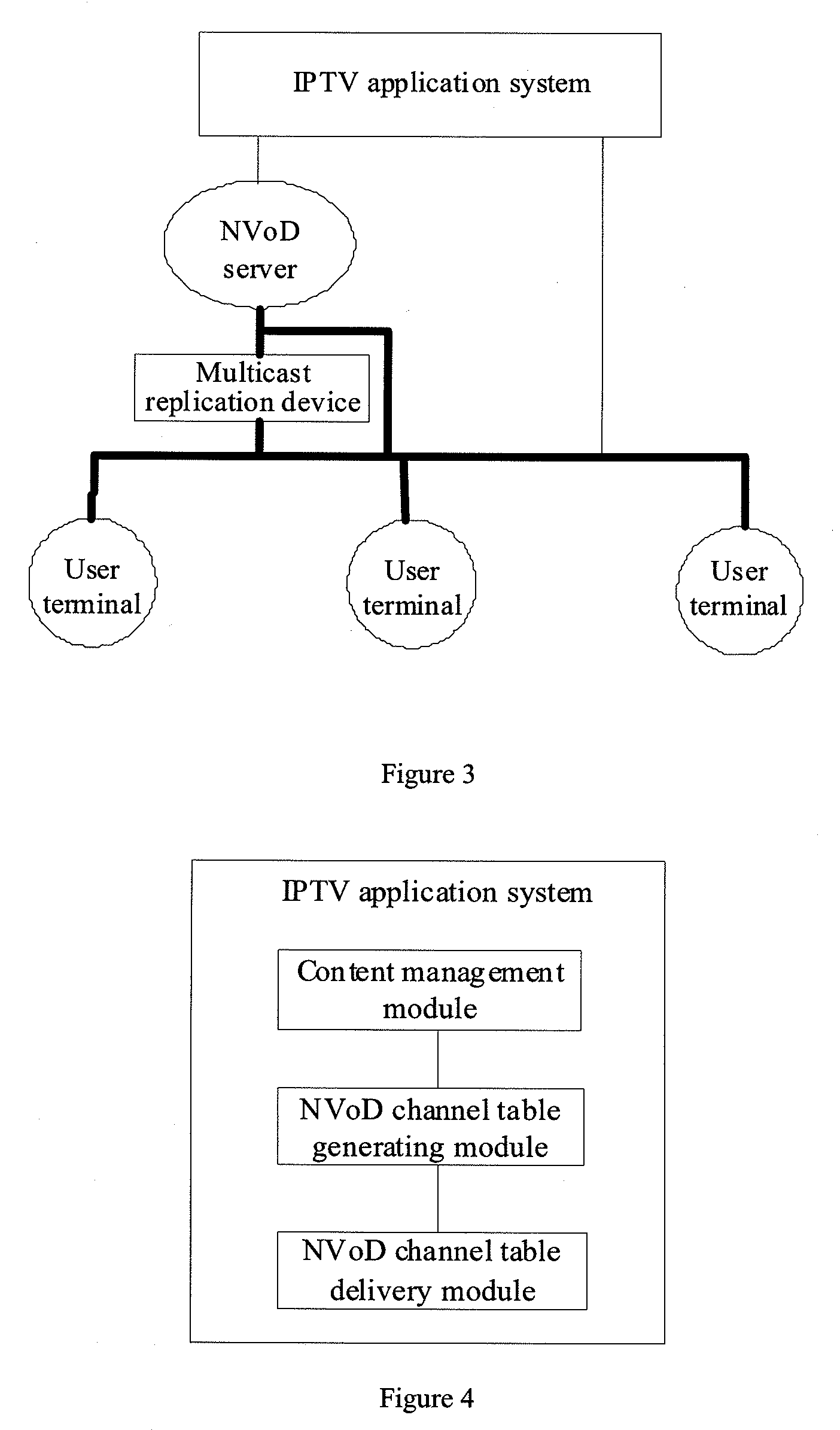
An IPTV application system and a method and system for playing near video on demand (NVoD) programs. The system for playing NVoD programs includes: an IPTV application system, adapted to create NVoD channels and generate an NVoD channel table that contains attribute information indicating whether NVoD channels support time-shifting operations; an NVoD server that intercommunicates with the IPTV application system, adapted to play a program specified by an operator in a multicast and / or unicast mode following a scheduled timetable according to control of the IPTV application system. The present invention implements time-shifting under the NVoD state and adds to user experience under the NVoD state, and in addition, provides a new channel for operators to sell on-demand programs.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method, apparatus, and system for redundancy backup of video services
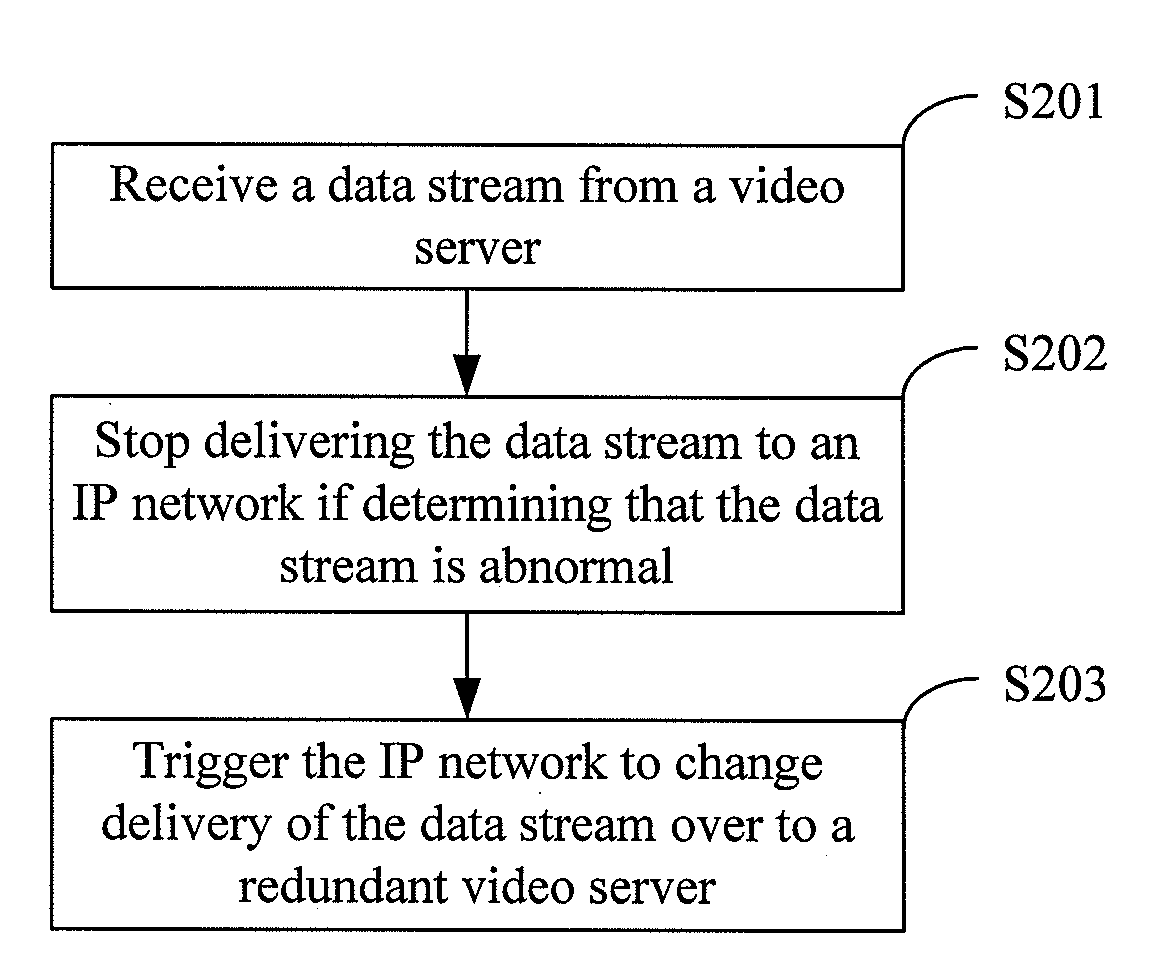
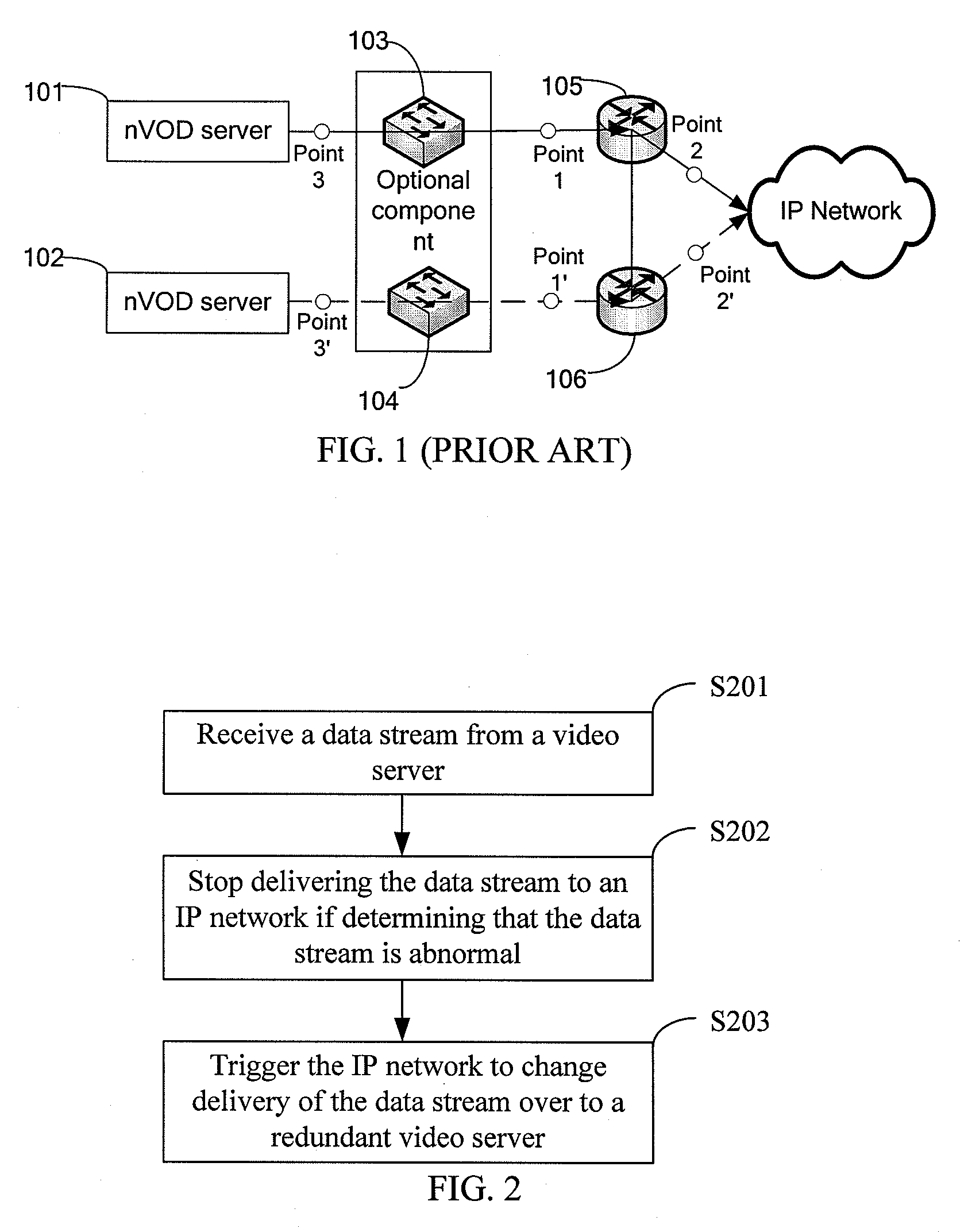
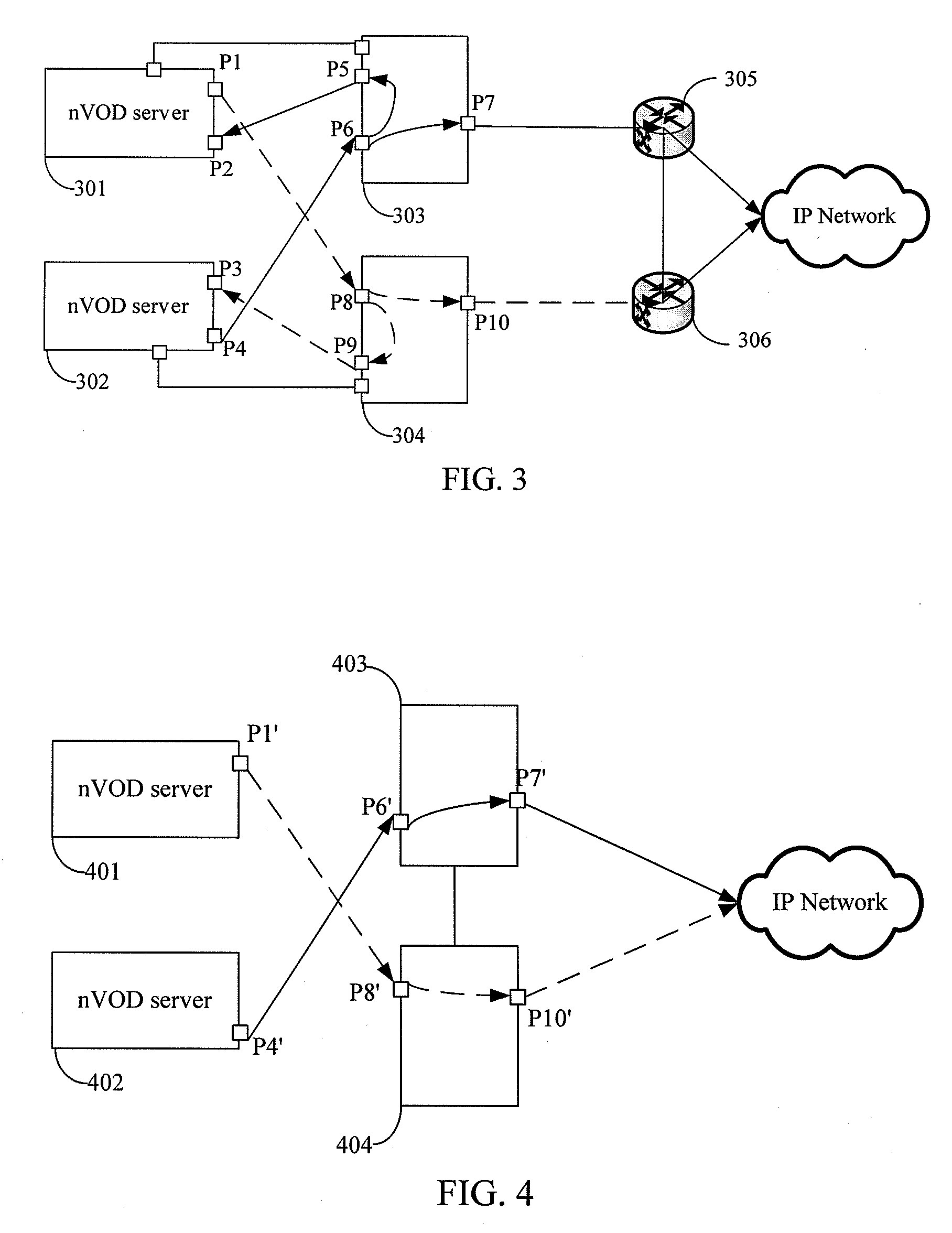
InactiveUS20090260046A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionNear video on demandData stream
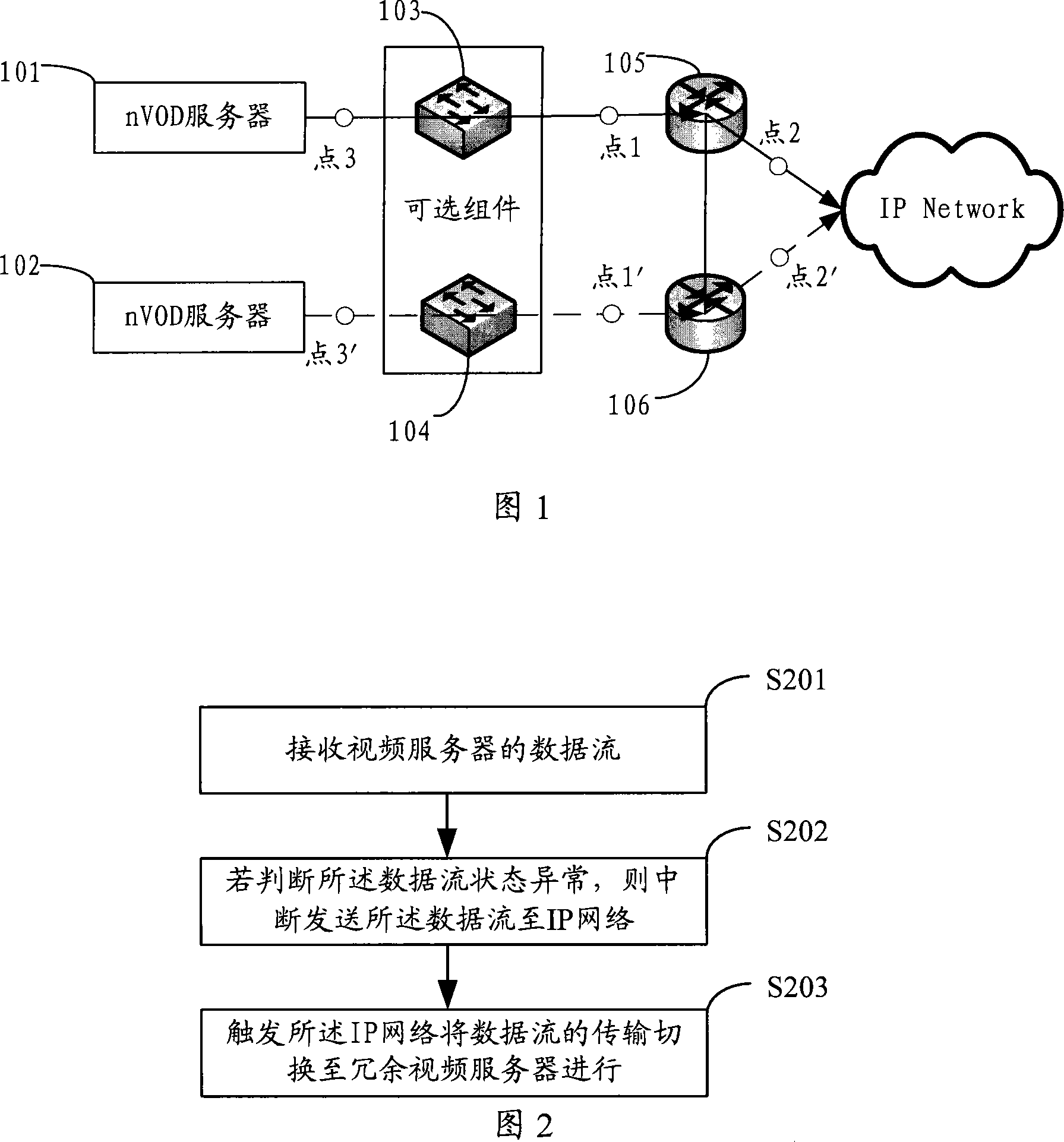
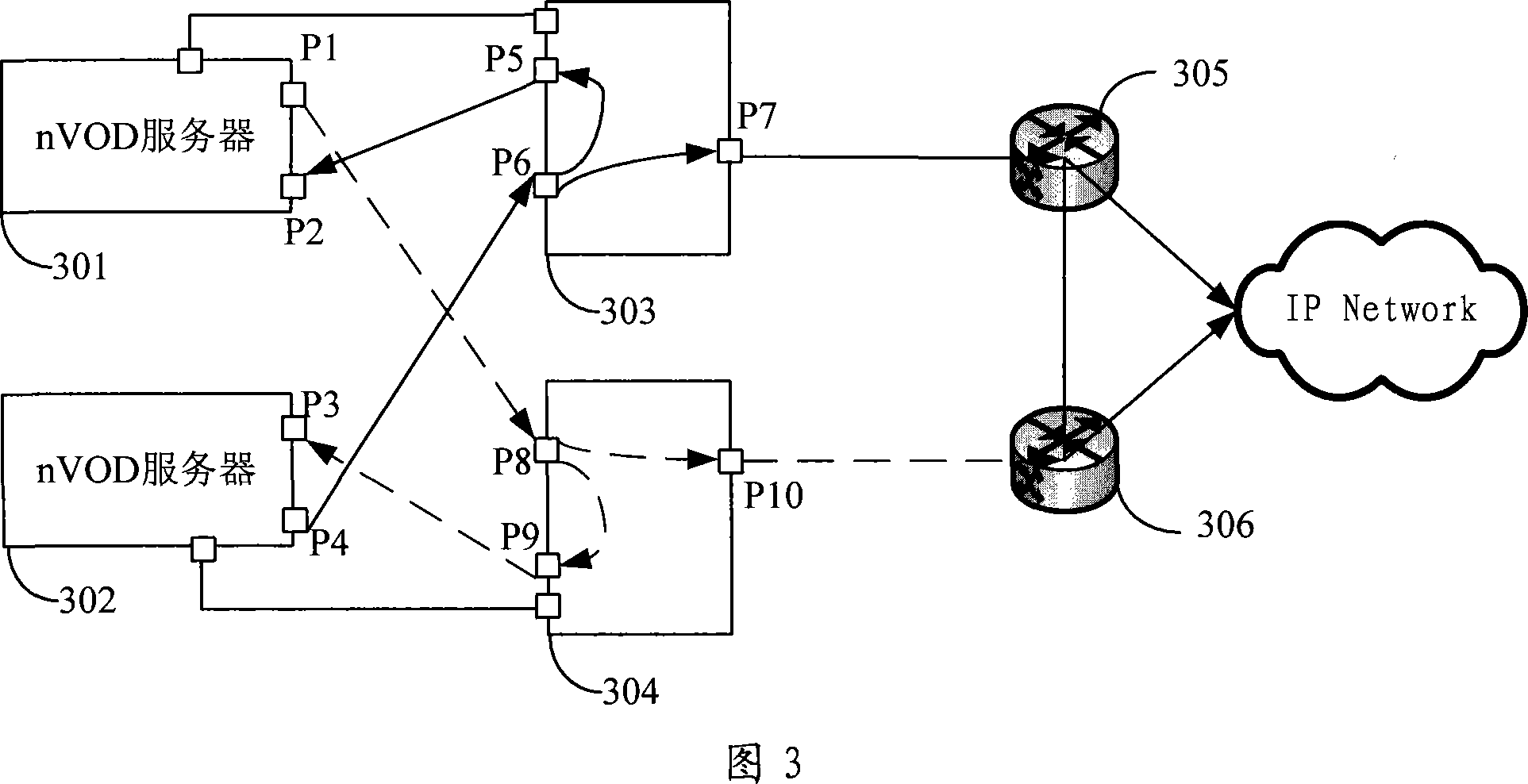
A method, apparatus and system for redundancy backup of video services are provided. The method includes: receiving a data stream from a video server; stopping delivering the data stream to an Internet Protocol (IP) network if determining that the data stream is abnormal; and triggering the IP network to change delivery of the data stream over to a redundant video server. With the method provided by the present disclosure, when the data stream played by the Near Video on Demand (nVOD) system is detected as abnormal, a route changeover can be completed so that the program stream of a redundant nVOD server is delivered to the IP network.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
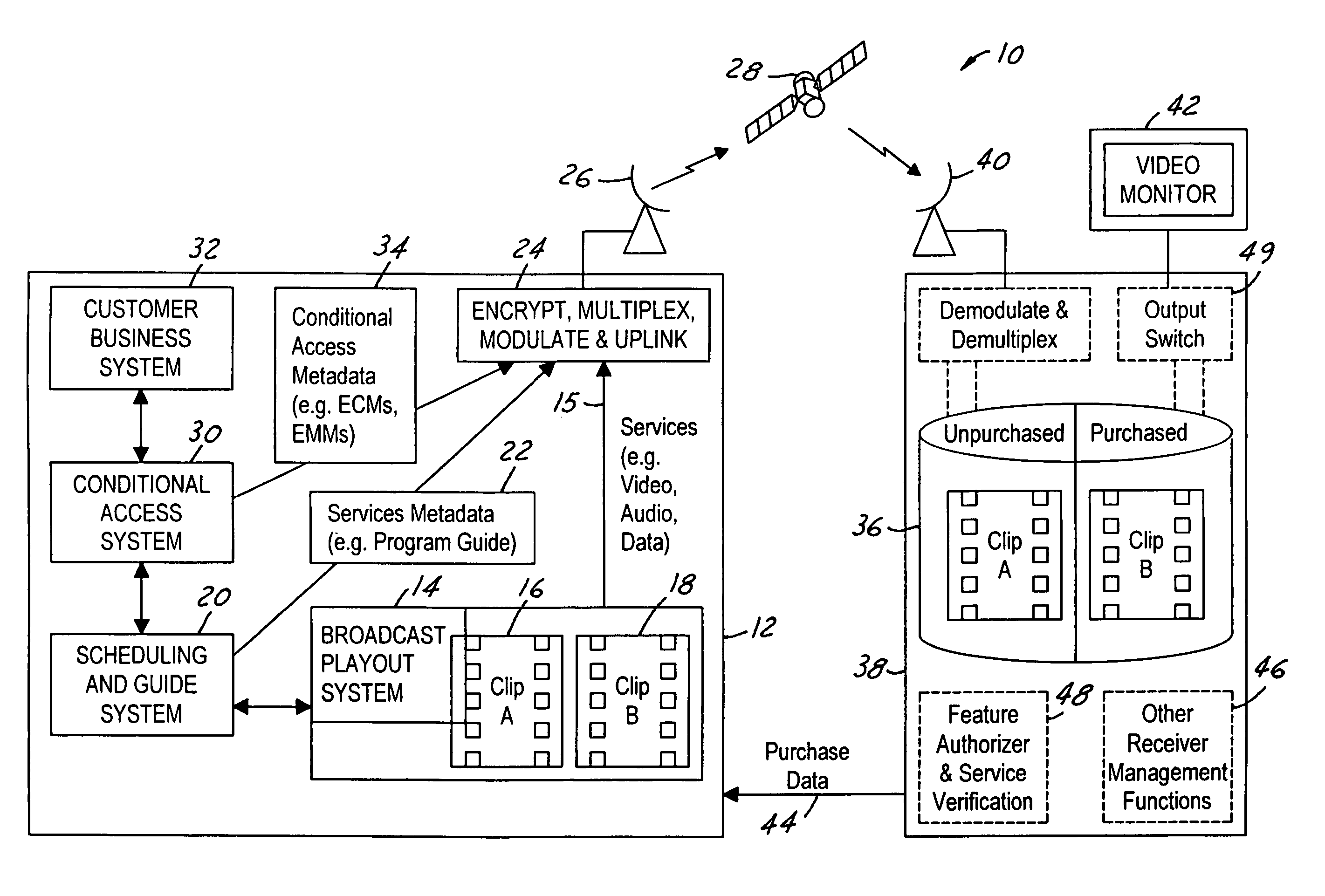
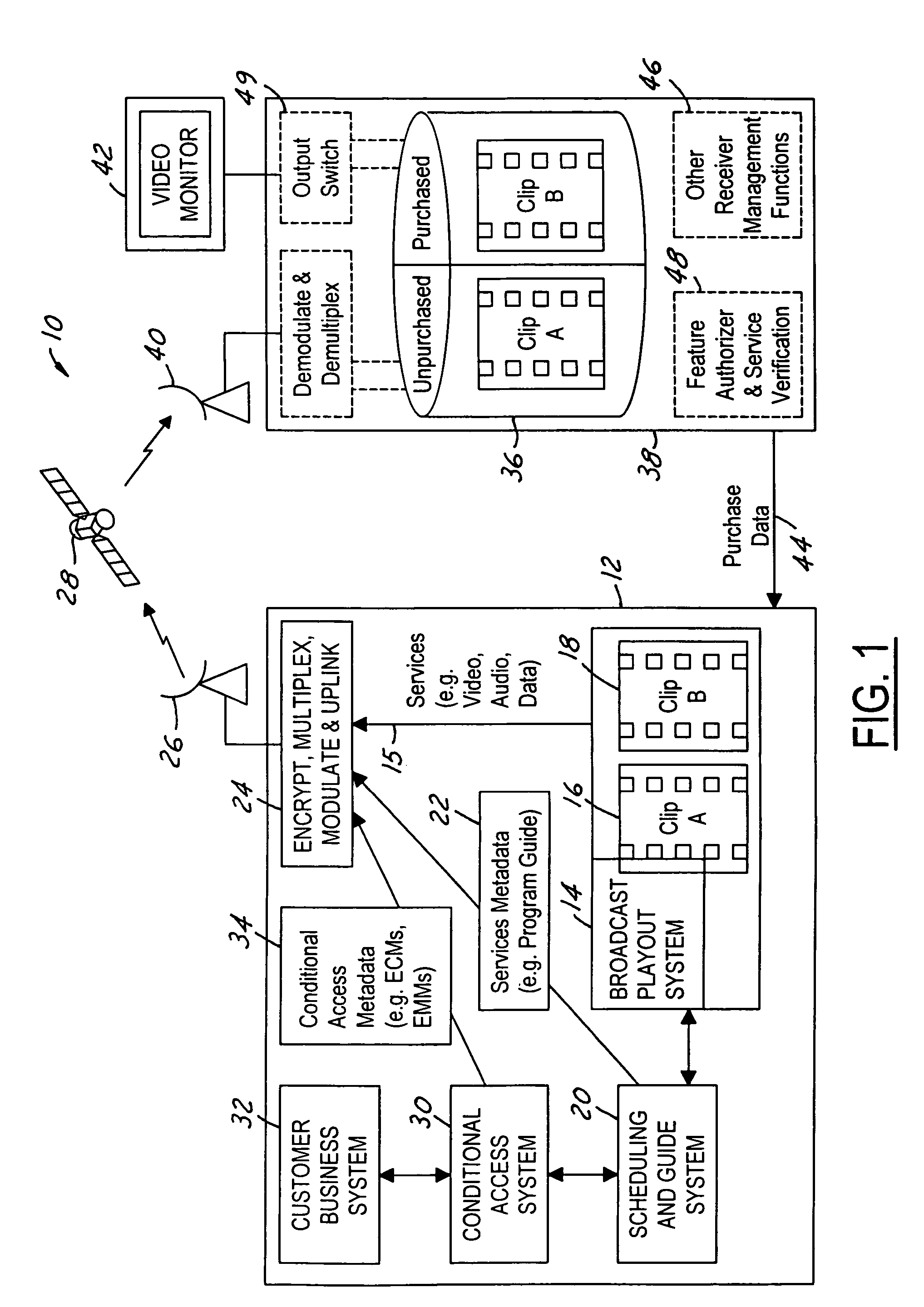
Video on demand in a broadcast network
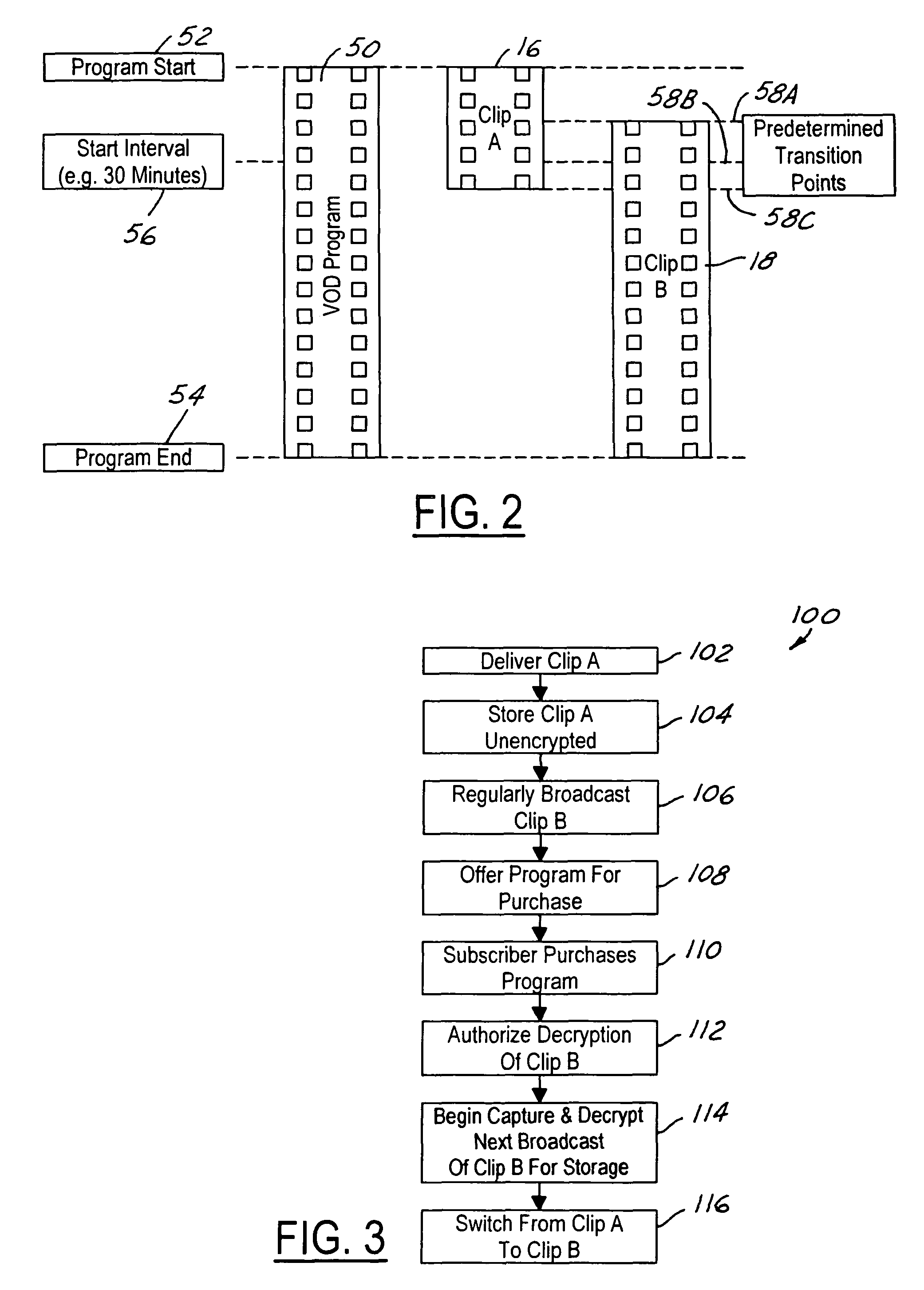
ActiveUS20050190947A1Lower requirementStorage requirements is greatly reducedDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsNear video on demandStart time
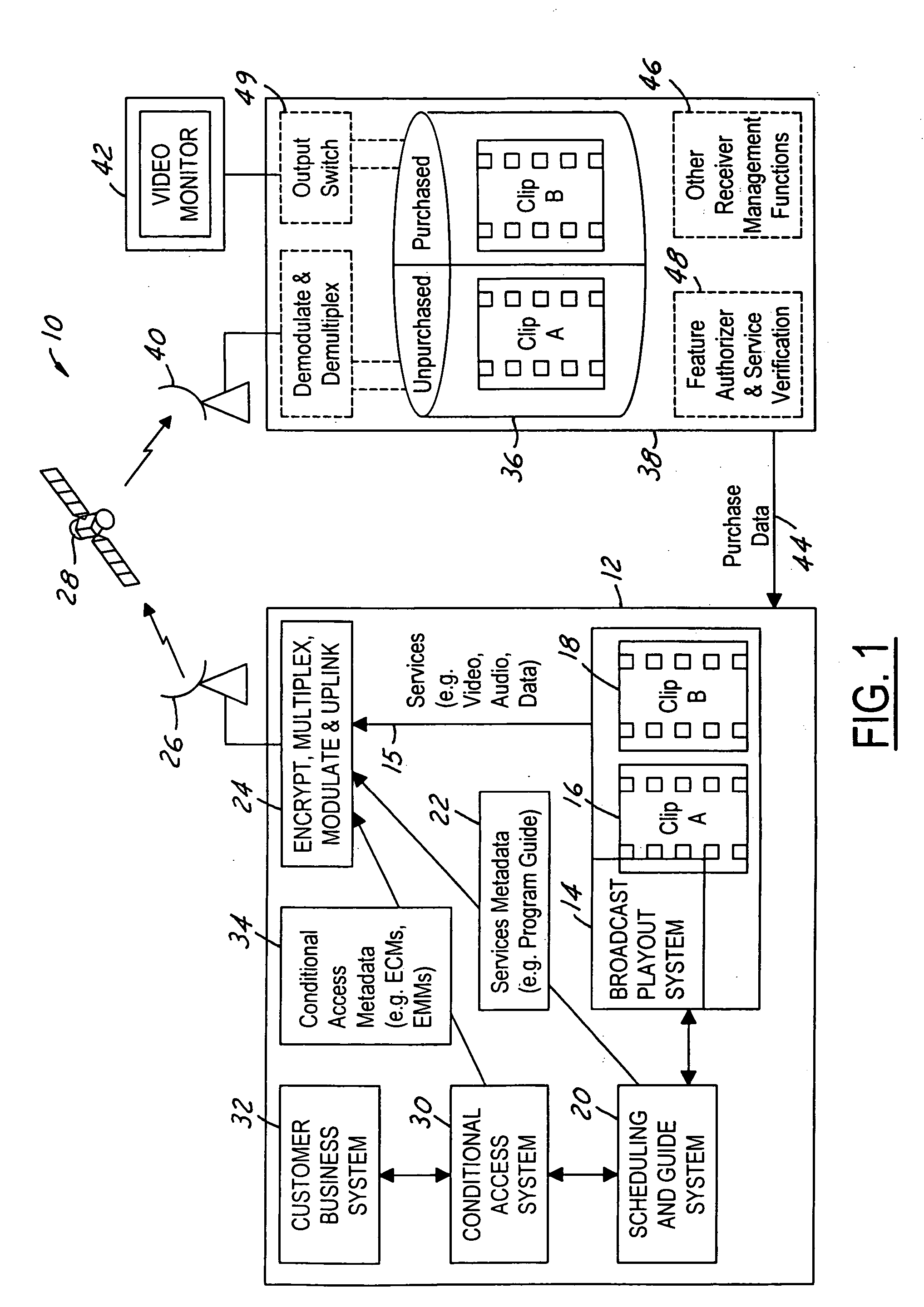
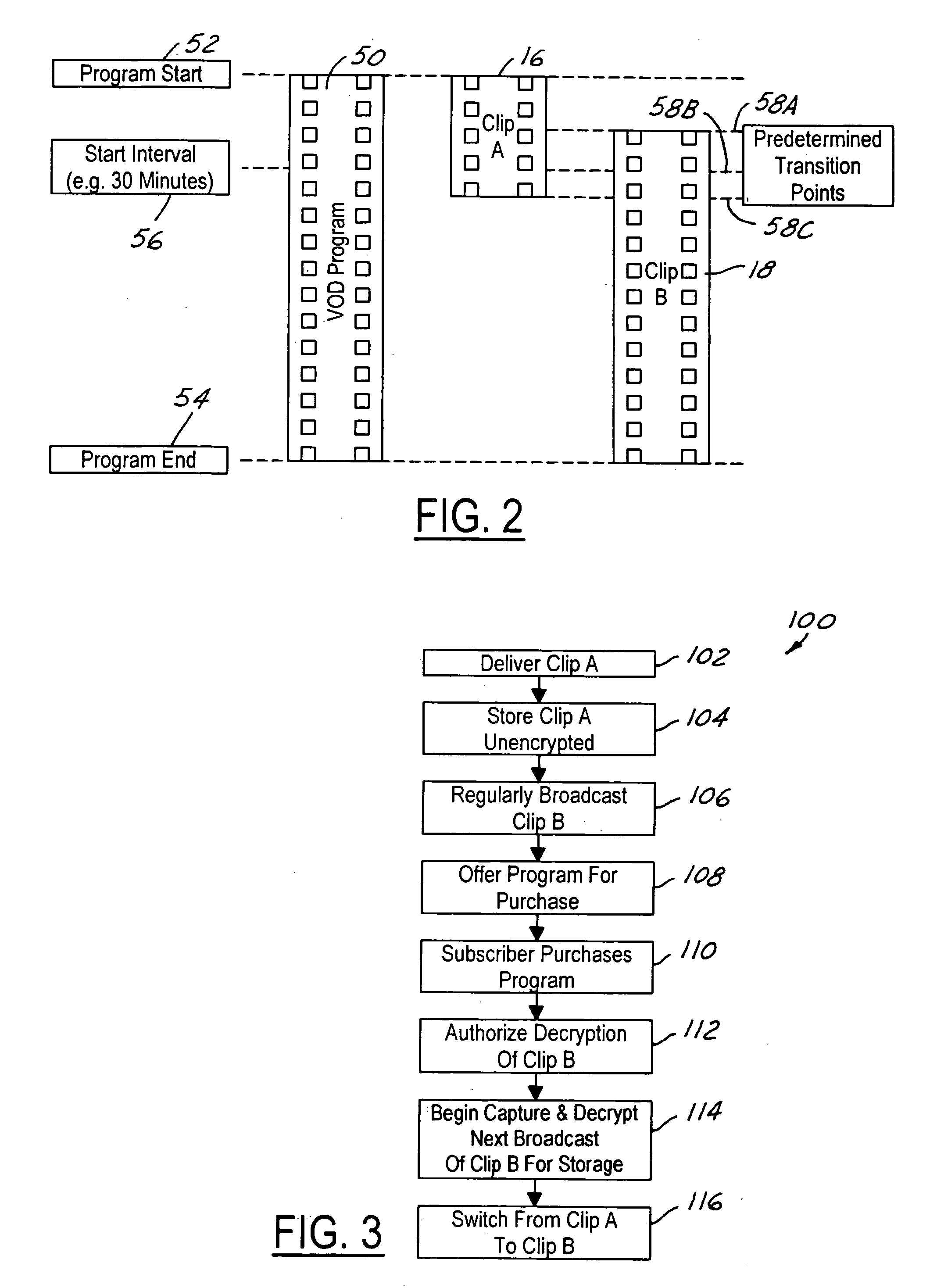
The present invention is a video on demand service enabled from a near video on demand service. A desired program is split into portions, or clips. The first clip is delivered a priori to the customer's DVR using a hidden channel and it is made available for purchase on demand. The remaining portion is broadcast regularly using the start time of the NVOD service, for as long as the program is available for VOD purchase. Upon purchase, the remaining portion is authorized for capture by the DVR. The clips are spliced together upon playback to form a complete program.
Owner:DIRECTV LLC
Near video-on-demand signal receiver
InactiveUS7607157B1Television system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsNear video on demandDisplay device
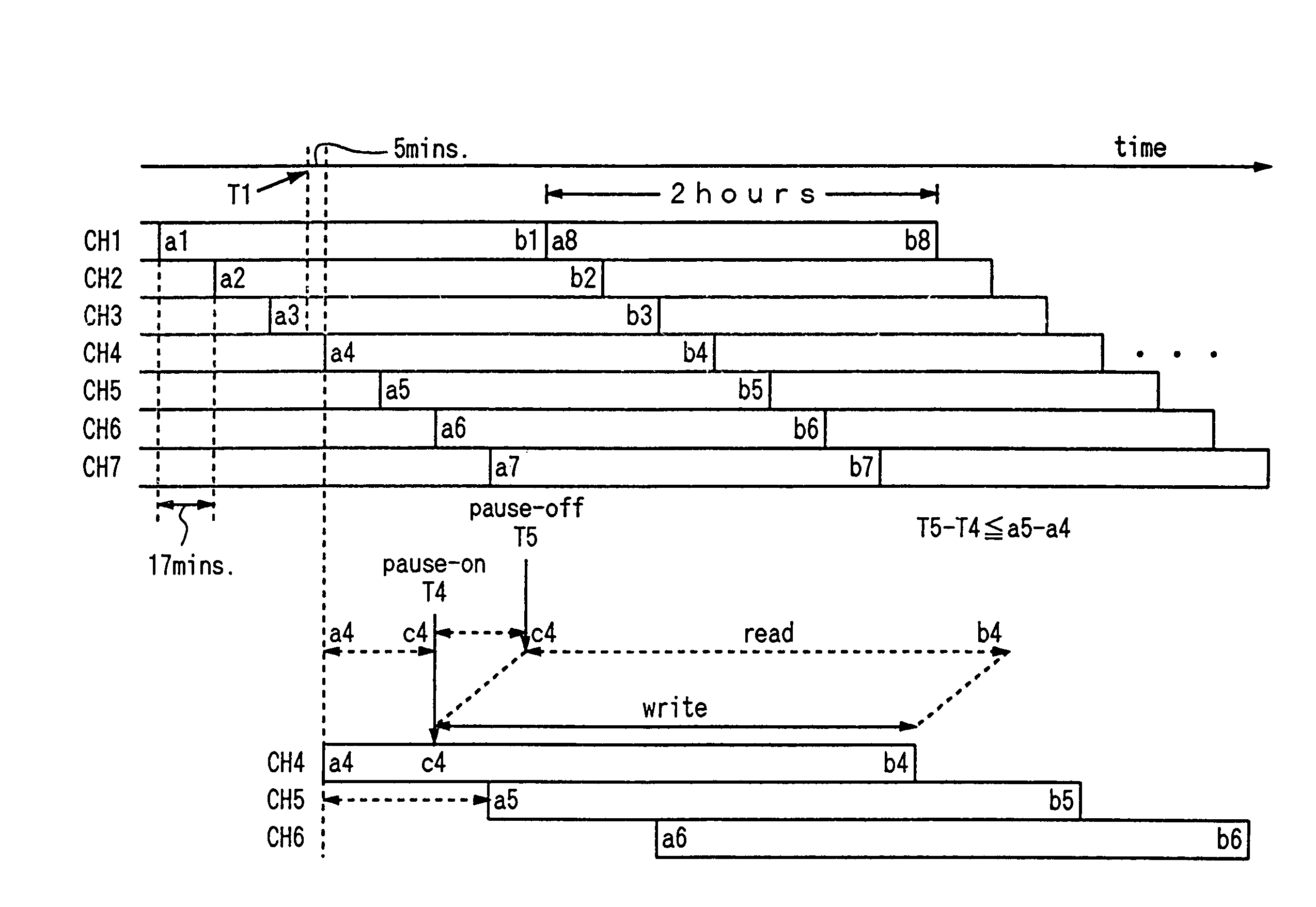
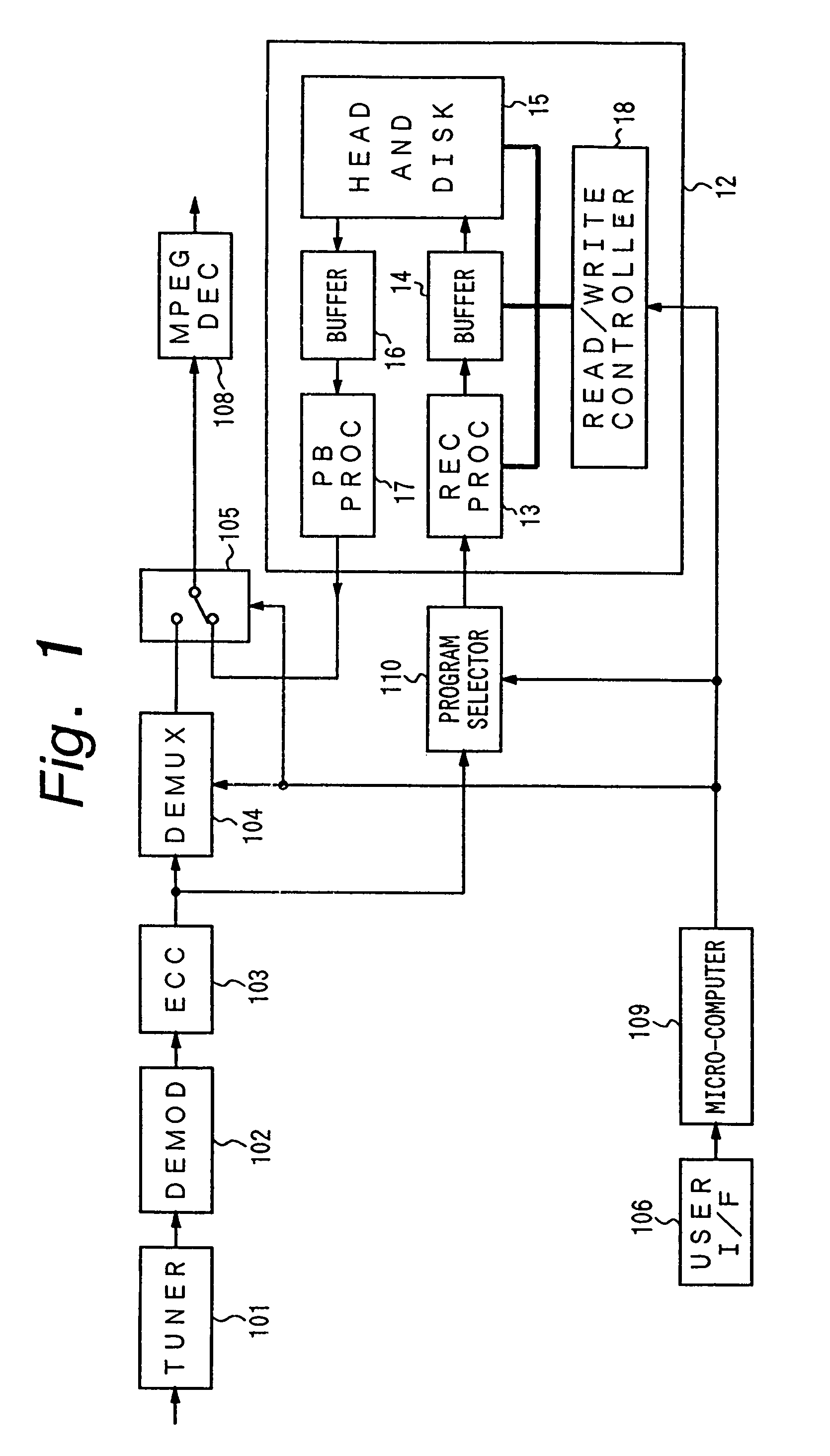
A video signal receiver receives a plurality of video channels simultaneously carrying, offset by a transmission interval, a single video program, selects one channel from which to obtain the program for display to a user, and achieves a pause function in the display of the transmitted video program by temporarily storing a segment of the video program equal to the length of the transmission interval and obtaining the remainder of the program at a later time from the same or another channel.
Owner:SONY CORP
Video service redundant backup method, device and system based on multicast
InactiveCN101146215AImplement redundant backupTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionNear video on demandData stream
A method, apparatus and system for redundancy backup of video services are provided. The method includes: receiving a data stream from a video server; stopping delivering the data stream to an Internet Protocol (IP) network if determining that the data stream is abnormal; and triggering the IP network to change delivery of the data stream over to a redundant video server. With the method provided by the present invention, when the data stream played by the Near Video on Demand (nVOD) system is detected as abnormal, a route changeover can be completed so that the program stream of a redundant nVOD server is delivered to the IP network.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
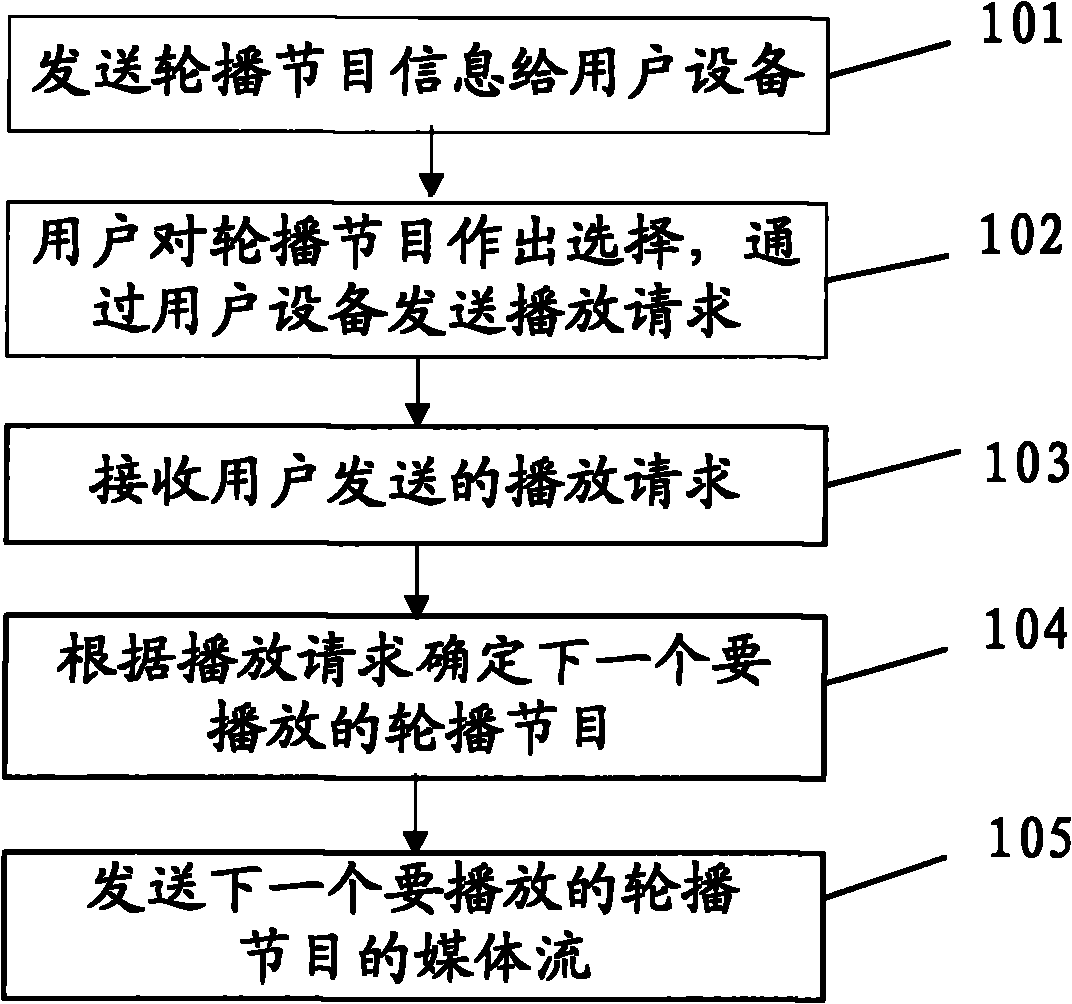
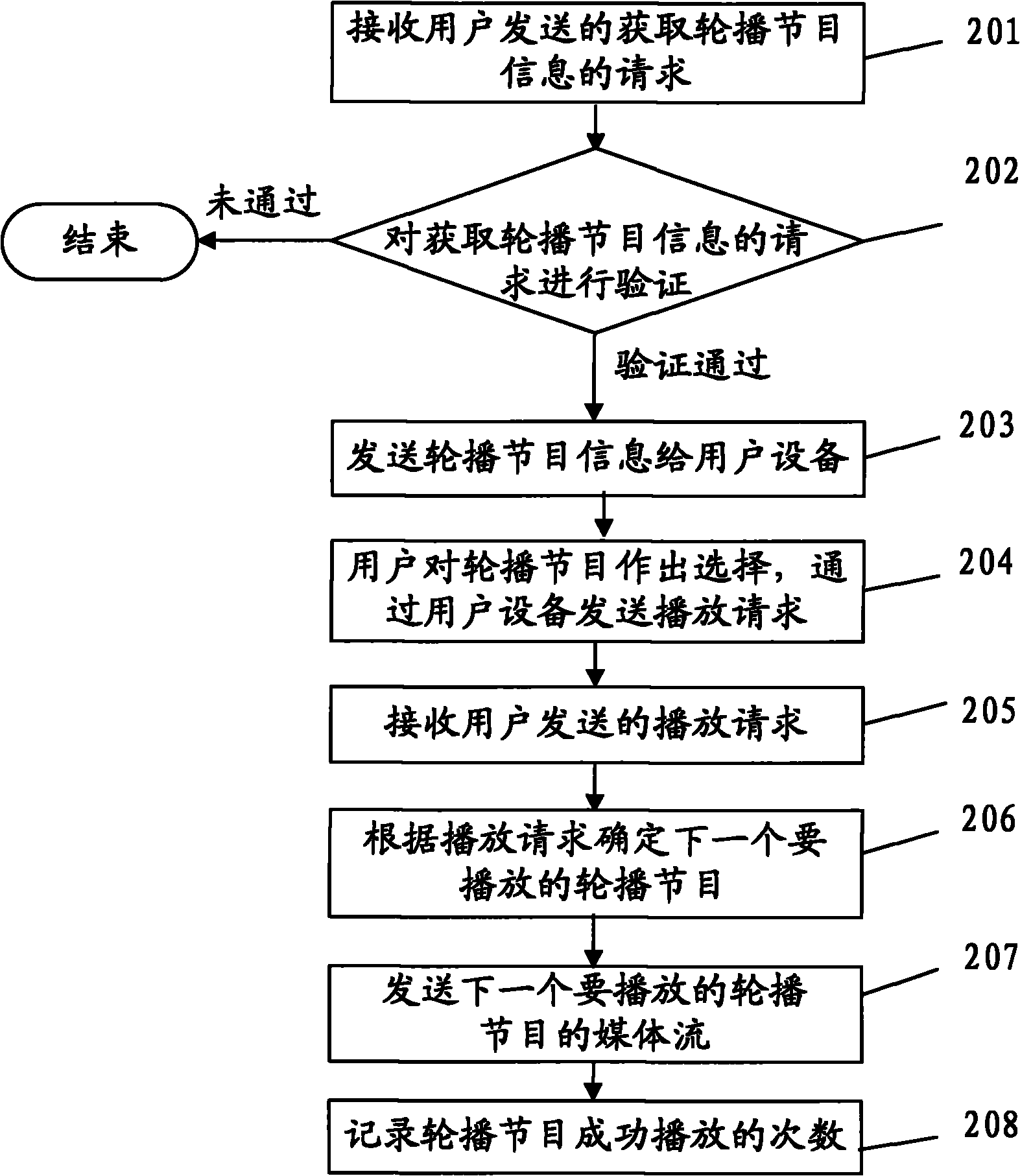
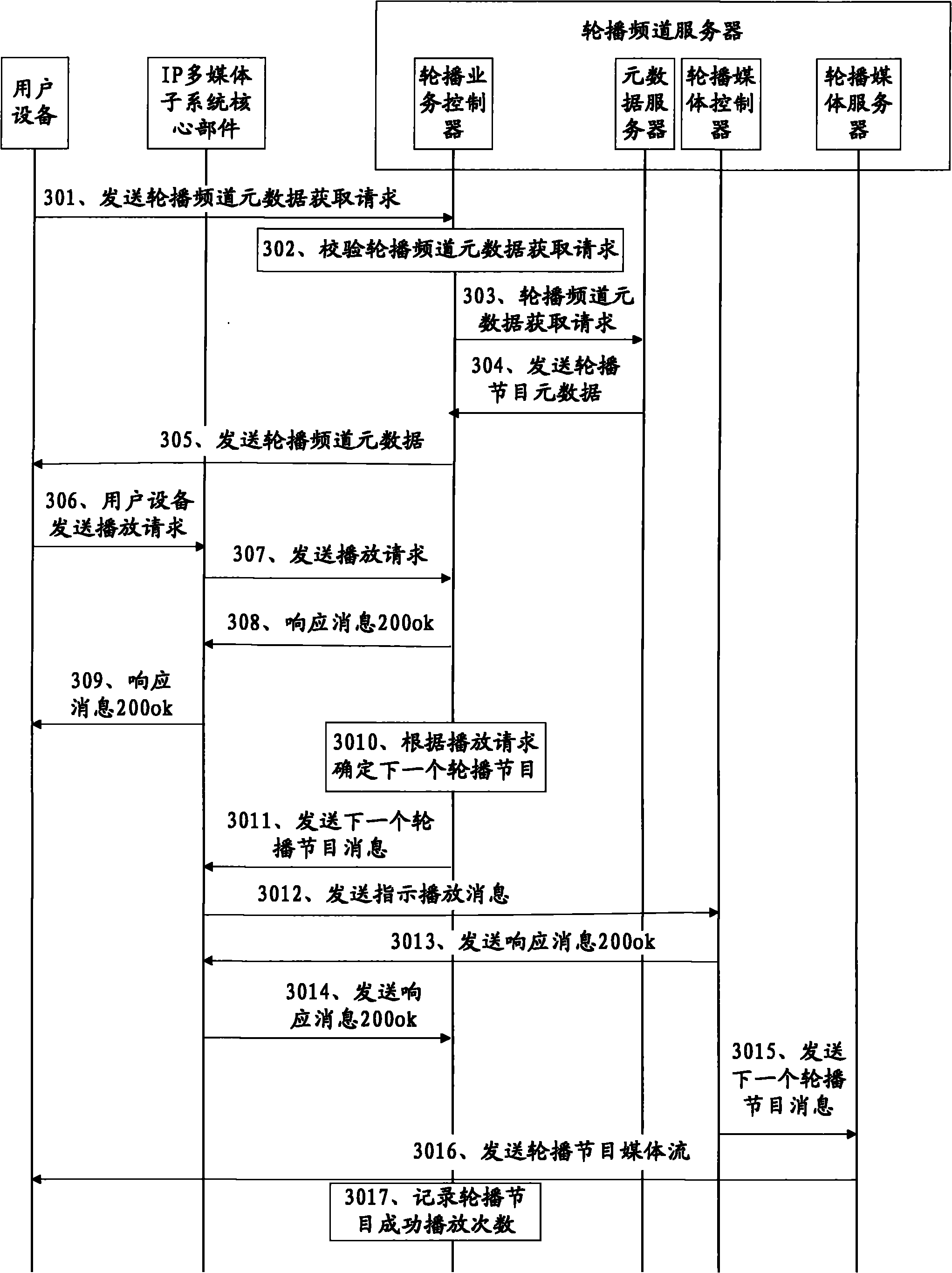
Method, device and system for realizing interactive near video-on-demand (NVOD) channels
ActiveCN102137277AReduce operating costsSelective content distributionNear video on demandOperational costs
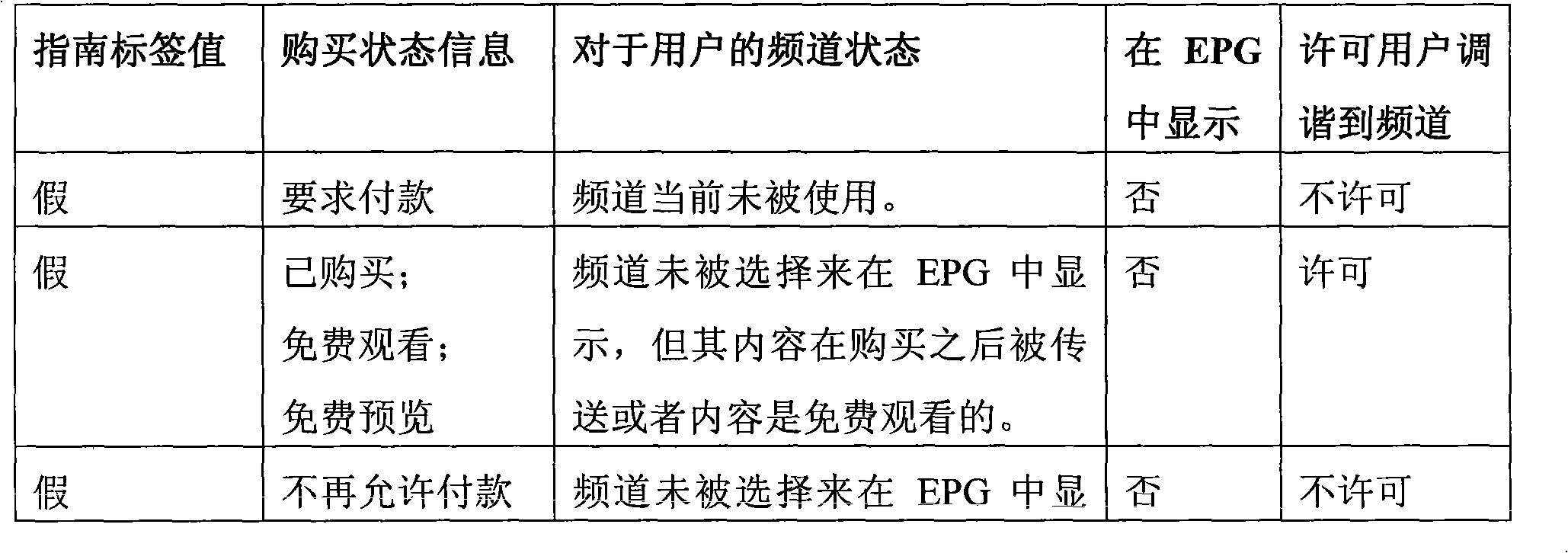
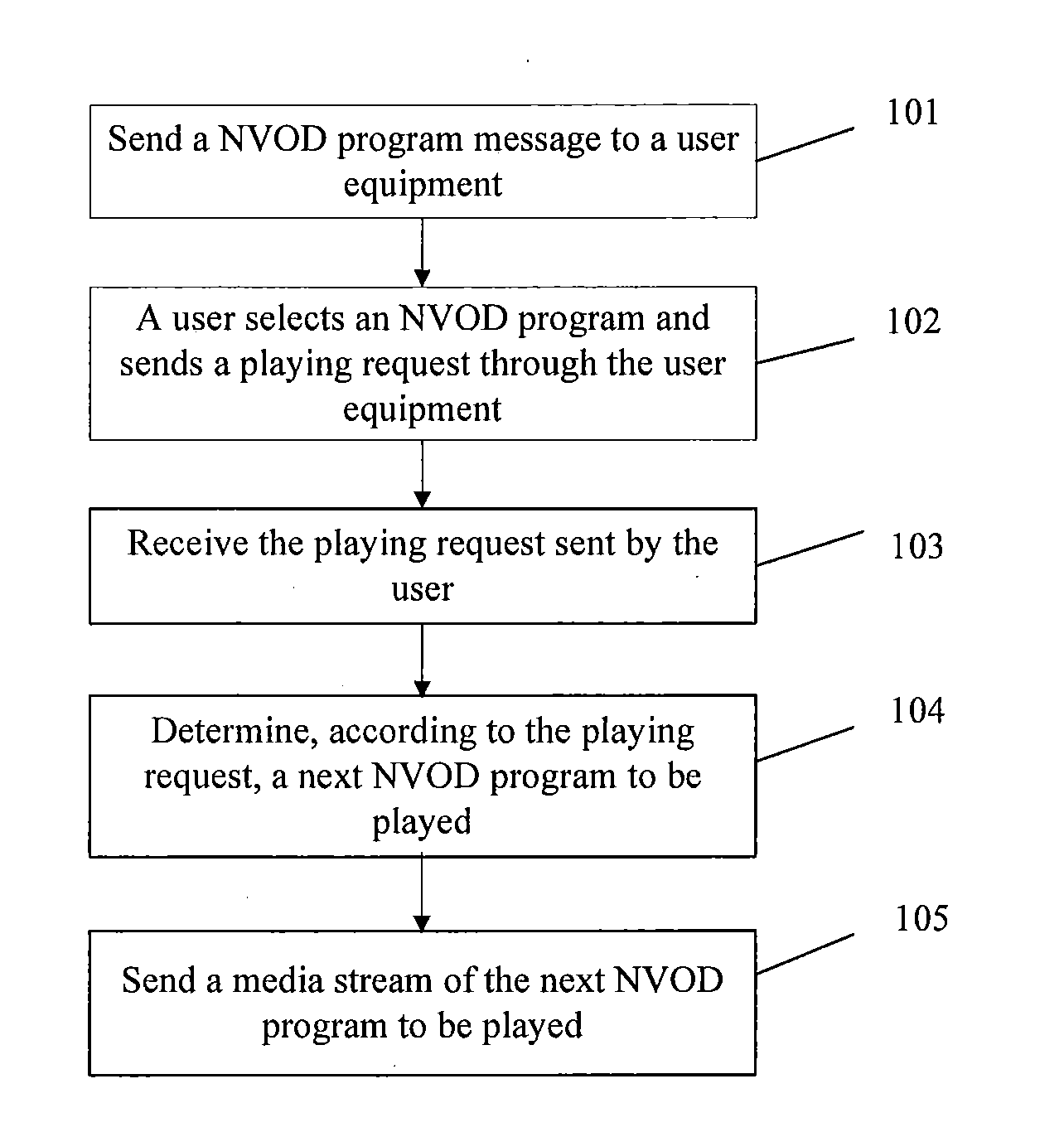
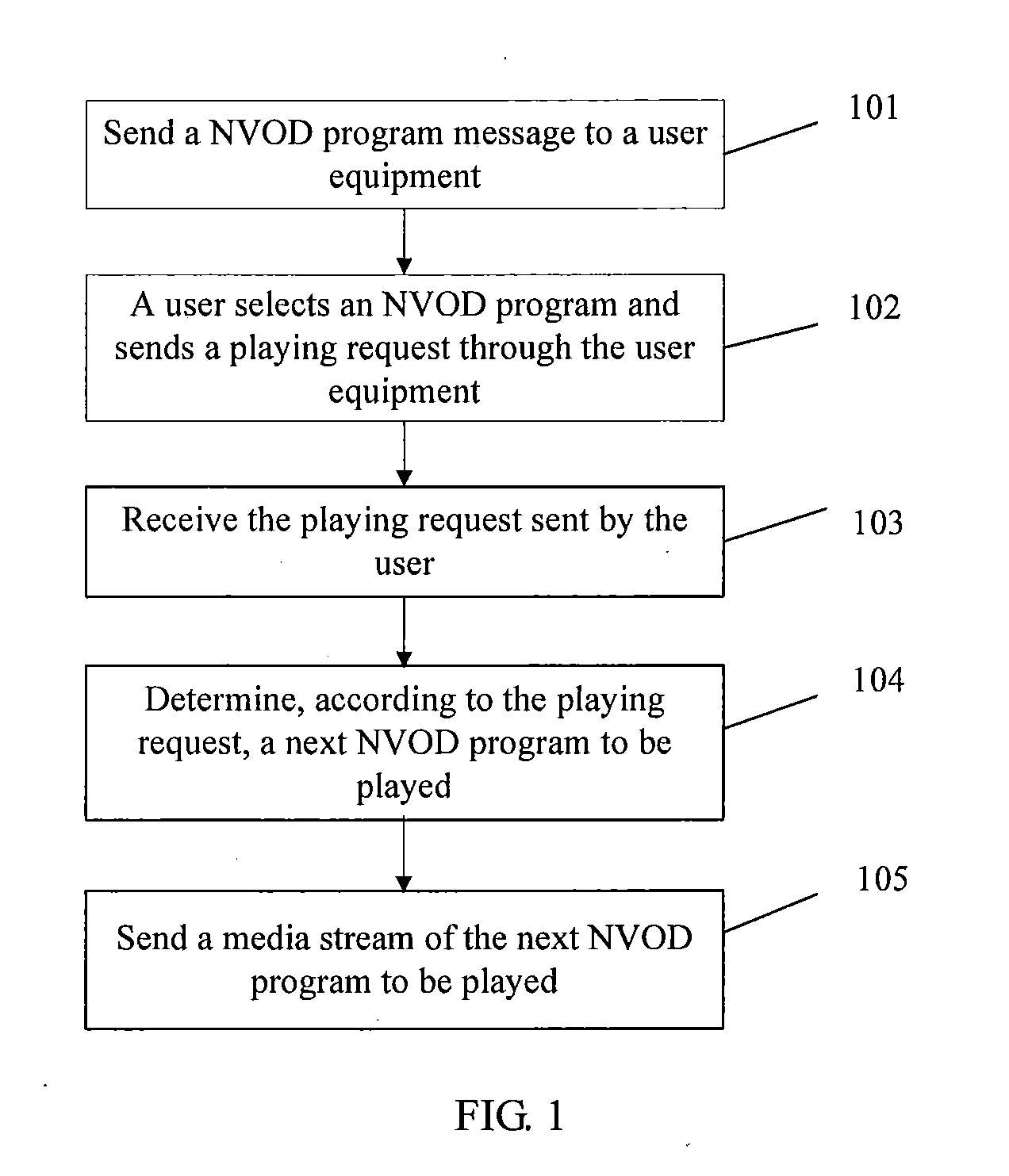
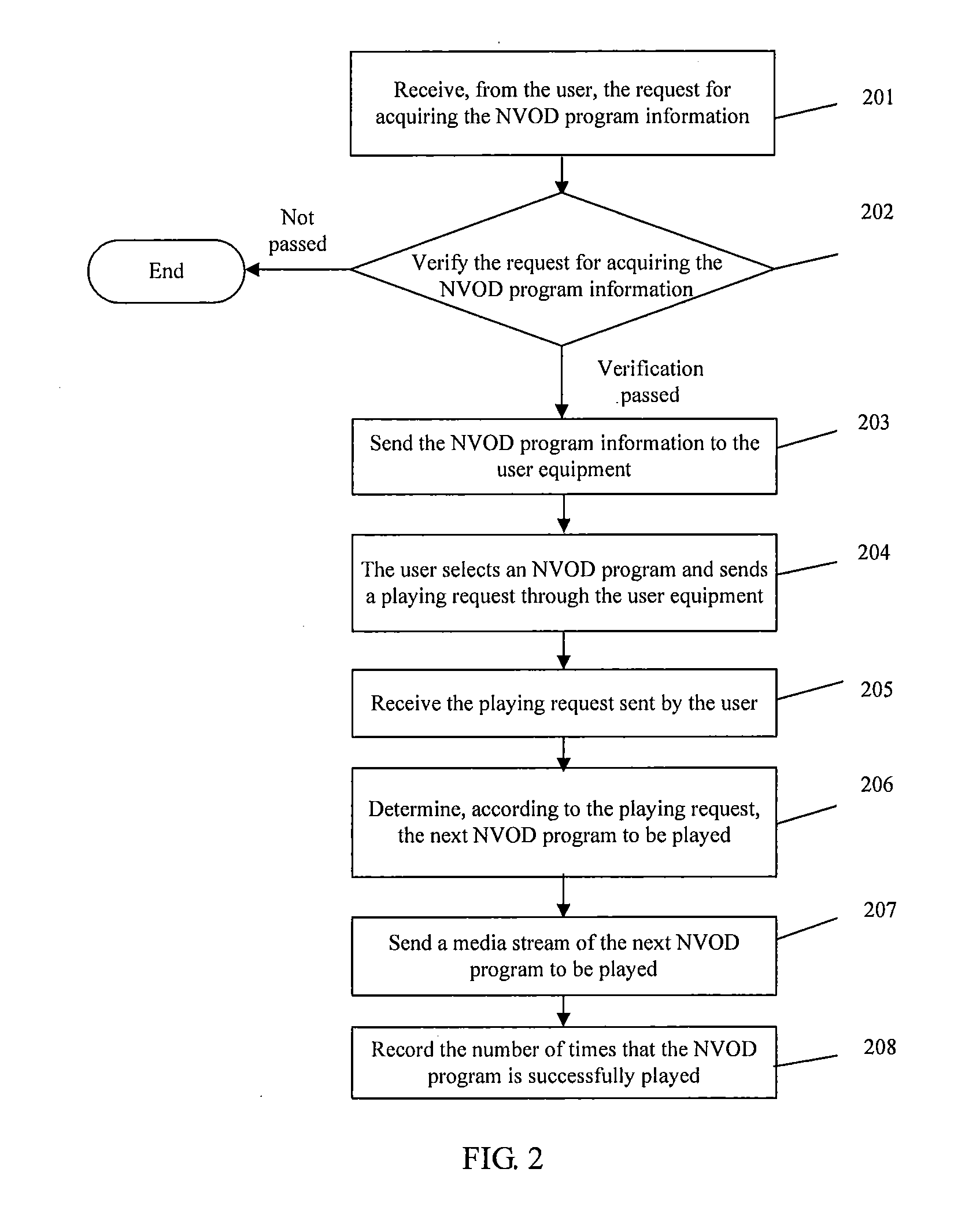
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method, a device and a system for realizing interactive near video-on-demand (NVOD) channels, which relate to the field of the NVOD channels and can realize the interactive NVOD channels at relatively low operating cost. The method comprises the following steps of: sending the metadata of an NVOD program to user equipment; receiving a playing request of the NVOD program sent by the user equipment, wherein the playing request comprises the NVOD program selected in the metadata of the NVOD program by a user through the user equipment; and determining the next NVOD program to be played according to the playing request, and sending a media stream of the determined NVOD program in a multicasting / broadcasting form. The method, the device and the system are mainly applied to the NVOD channels and can be applied to an Internet protocol television (IPTV) system based on an IP multimedia subsystem (IMS).
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
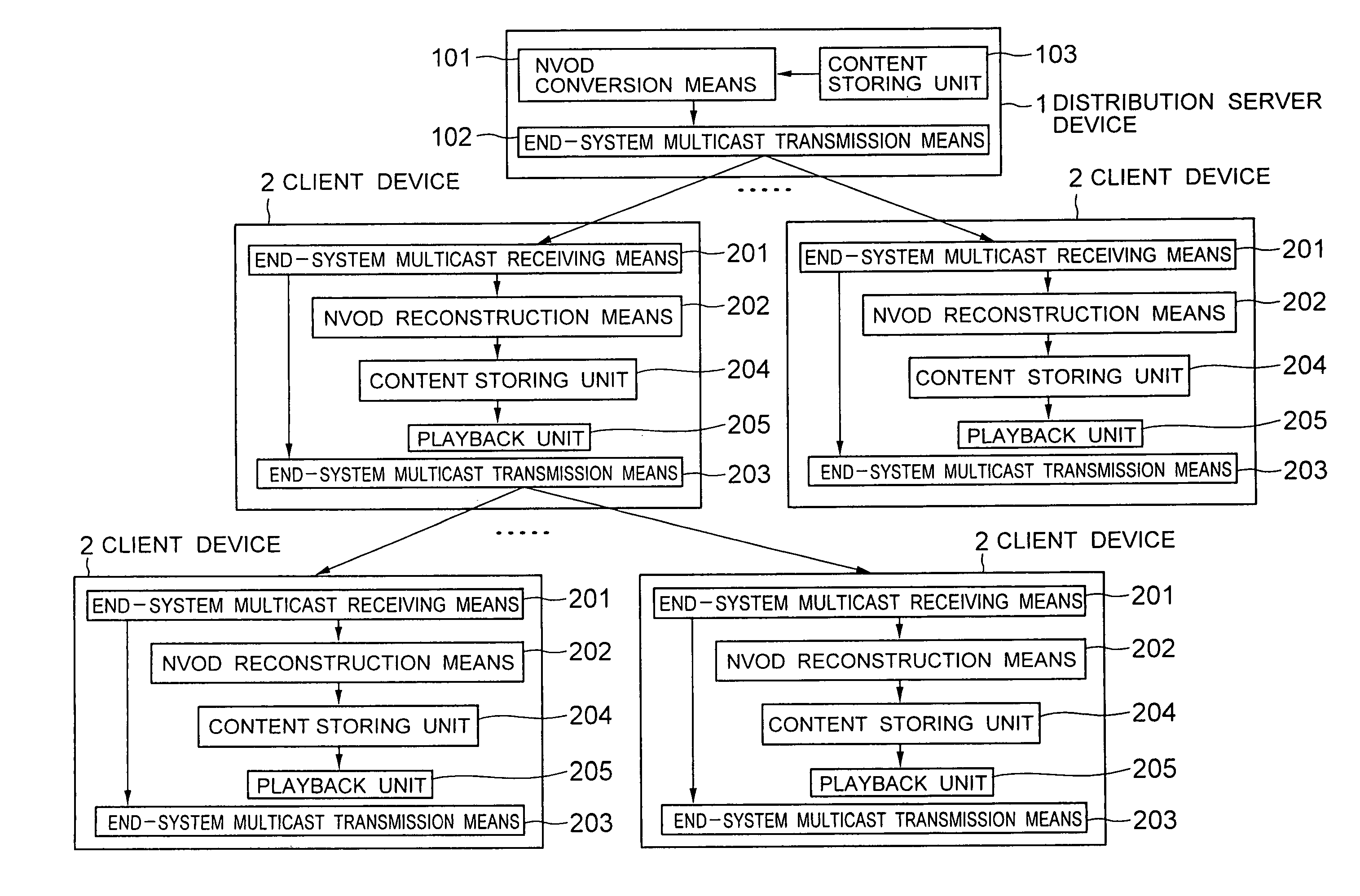
Content distribution system and content distribution method
InactiveUS20050010674A1Reduce loadSuppress waiting periodMultiple digital computer combinationsTwo-way working systemsStreaming dataContent distribution
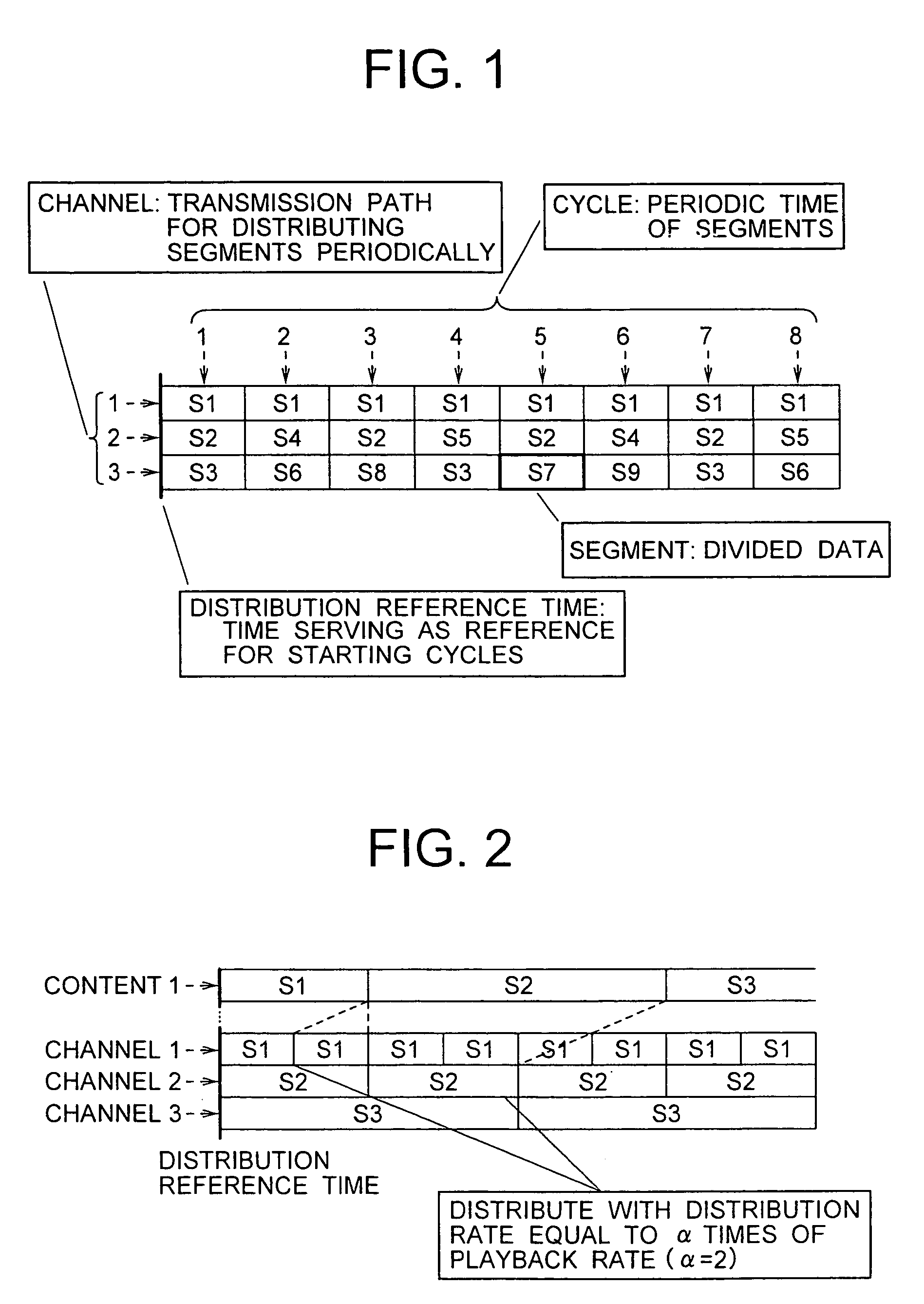
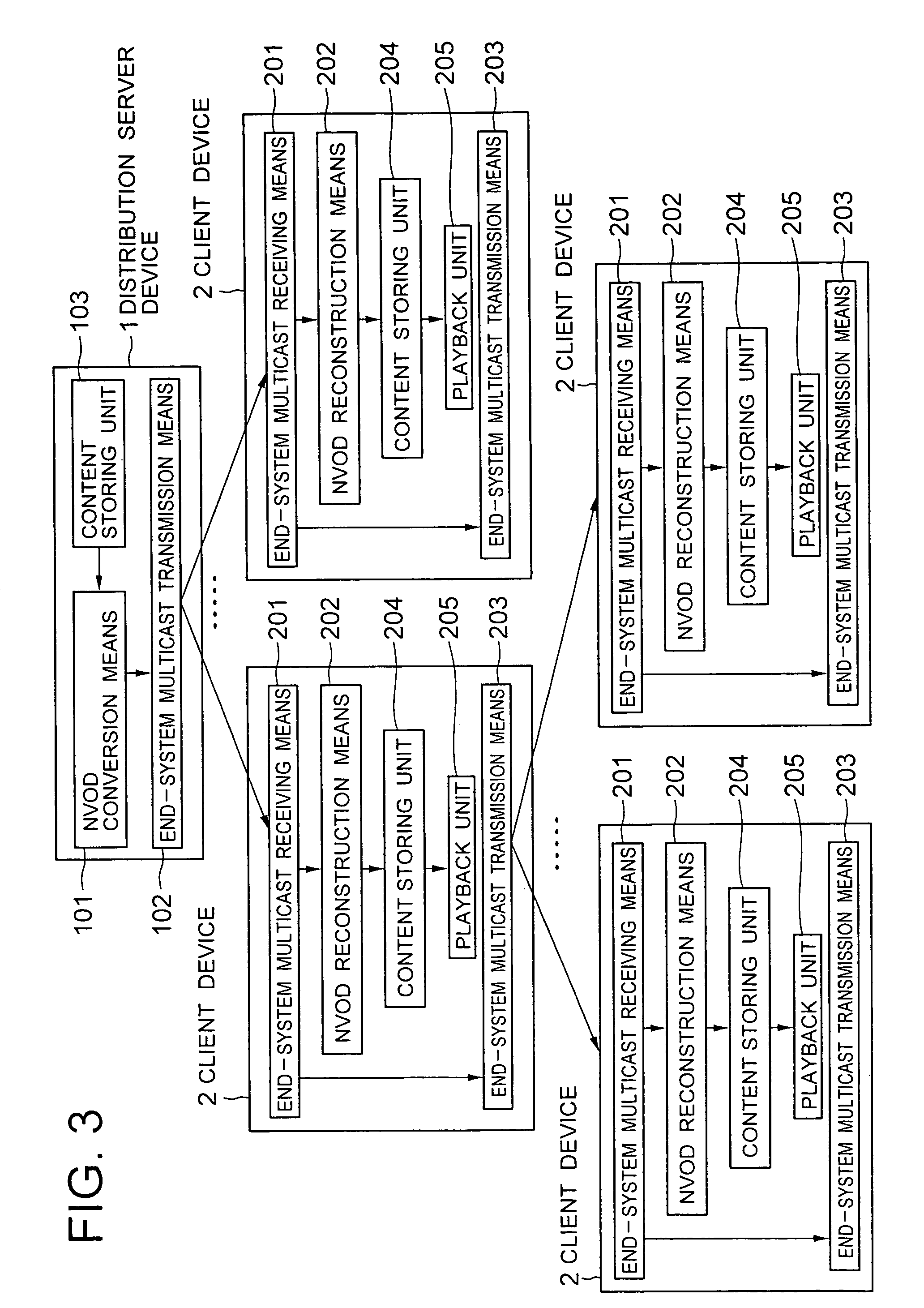
To obtain a content distribution system in which the load placed on a distribution server is reduced, the installation cost and the operational cost are reduced, introduction can be easily realized in a large area, and clients only wait short periods for playing back. A distribution server device converts a content into stream data using an algorithm of near video on demand, and transmits the stream data to an end-system multicast tree established among plural client devices requesting playback of the content. The client devices relay the received stream data of the near video on demand in accordance with the end-system multicast tree.
Owner:NEC CORP
Digital television middleware-based video-on-demand method and system
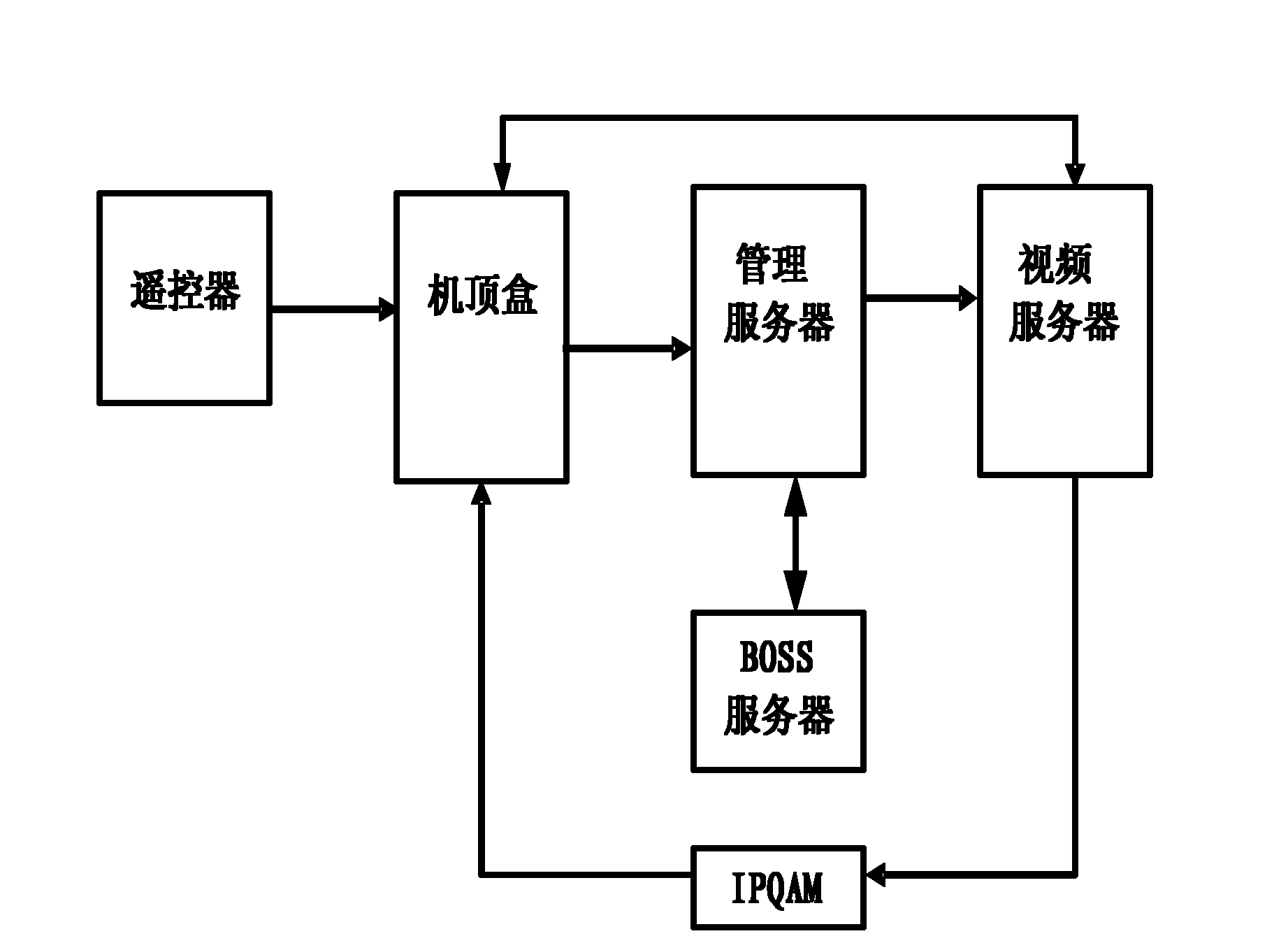
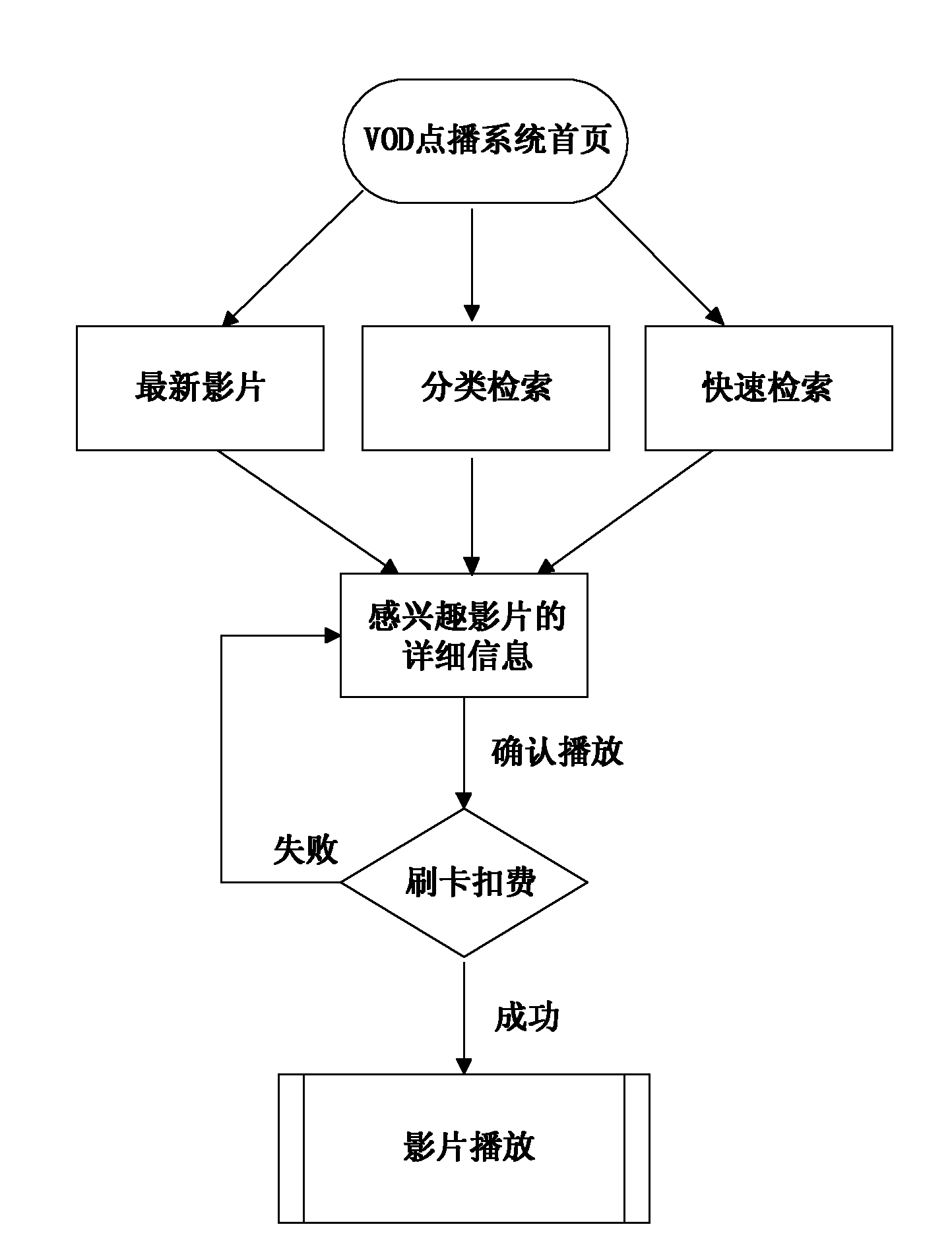
ActiveCN102196302AResolve delayControl playbackNon-electrical signal transmission systemsSelective content distributionNear video on demandIp address
The embodiment of the invention discloses a digital television middleware-based video-on-demand method and system. The video-on-demand method mainly comprises the following steps of: initiating a video-on-demand request to a management server by utilizing a set-top box according to coding of a remote controller; initiating a video playing request to a video server by utilizing the management server; creating an on-demand flow and returning data to the management server by utilizing the video server, wherein the data content comprises related information such as a server IP (Internet Protocol) address, a port and flow control word information, IPQAM (Internet Protocol-Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) frequency point information, port information and the like; sending the server IP address, port and flow control word information and the IPQAM frequency point information and port information to the set-top box by utilizing the management server; and after the information is received by the set-top box, creating an LSCP (Lightweight Stream Control Protocol) link with the video server to decode and play. Through the video-on-demand method and system which are provided by the embodiment of the invention, the delay problem in NVOD (Near Video on Demand) is solved and the real on-demand effect is realized to ensure that a person can select favorite movies and other programs from a network at any time and immediately play.
Owner:GUANGDONG XINGHAI DIGITAL HOME IND TECH RES INST +1
Channel tapping in a near-video-on-demand system
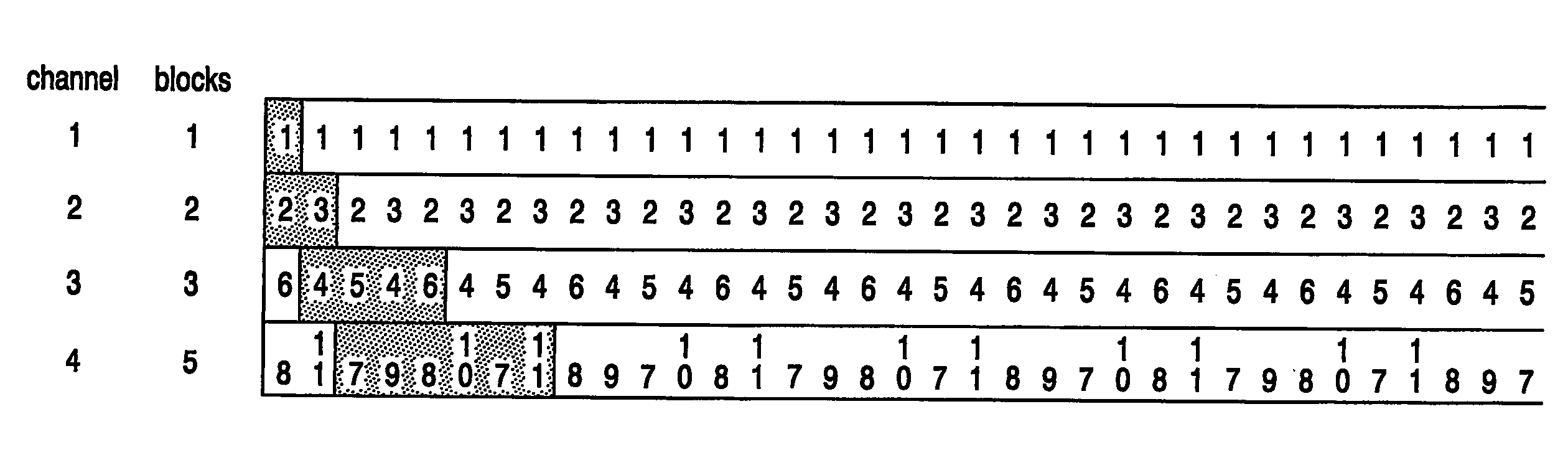
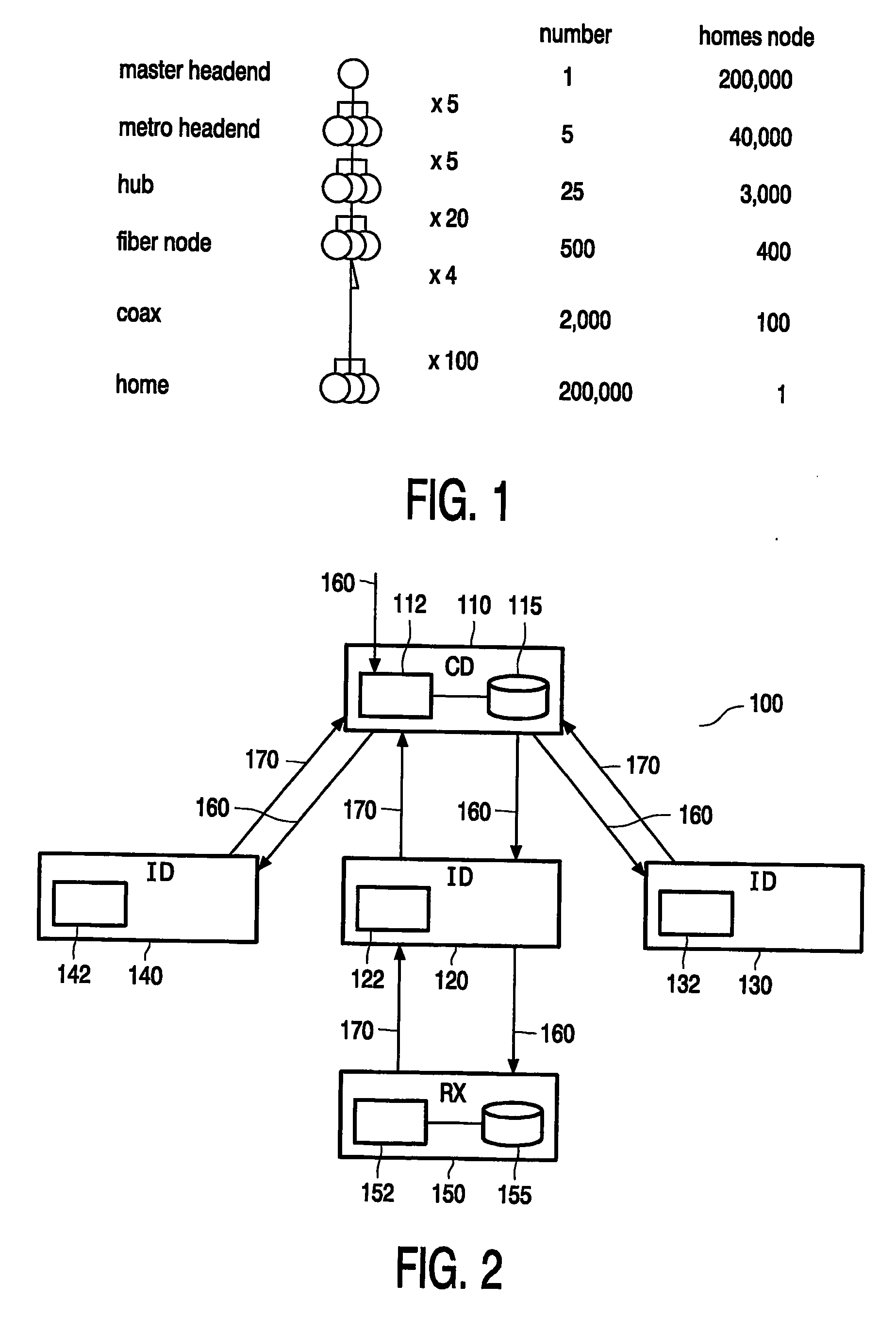
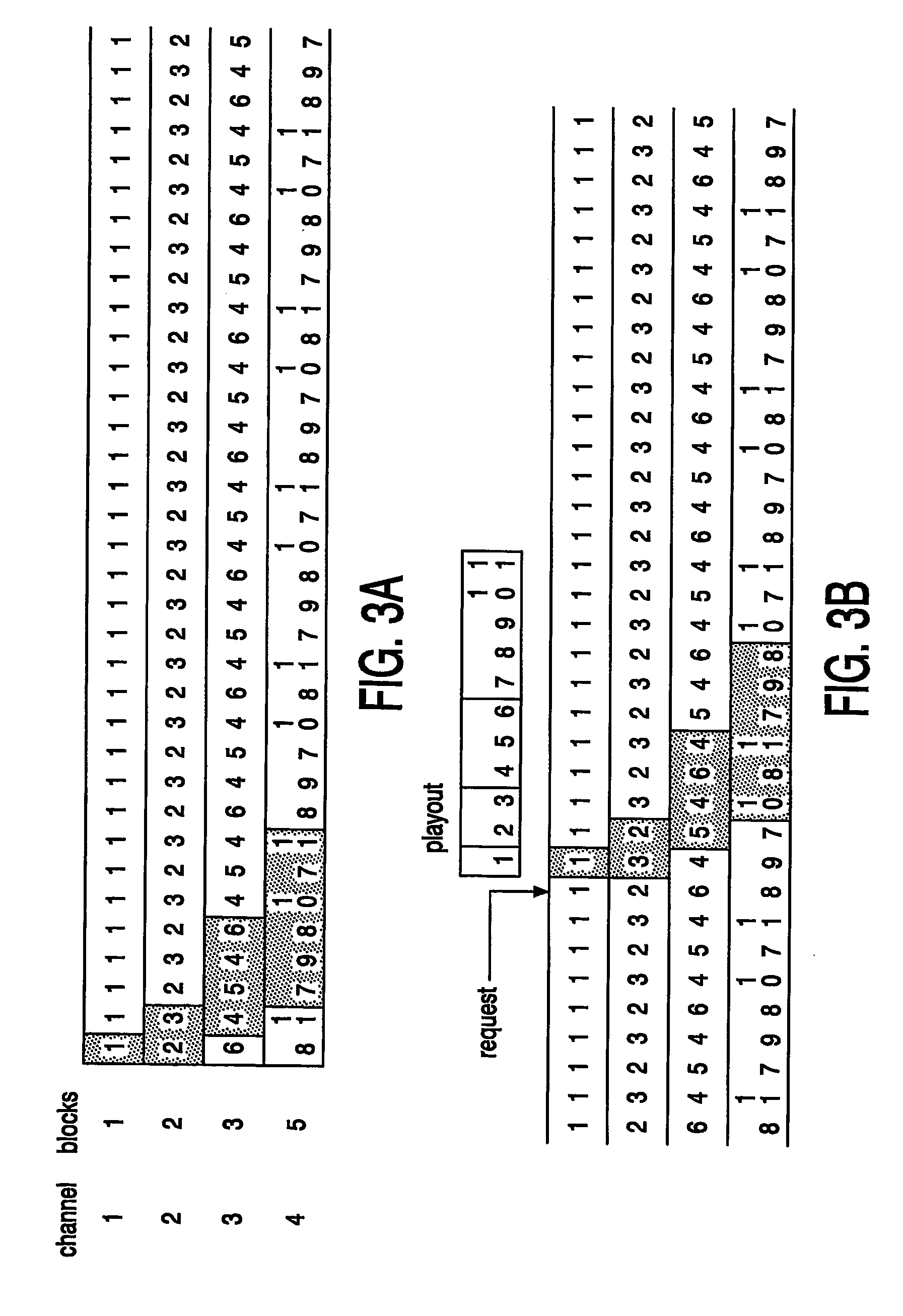
InactiveUS20060095948A1Short response timeWasted capacityTwo-way working systemsSelective content distributionBroadcast channelsNear video on demand
In a broadcast system 100 a broadcasting device broadcasts titles using a near-video-on-demand broadcasting protocol. Data blocks of a title are broadcast via c parallel equal capacity channels of the broadcast system. The broadcast channels 160 including time-sequentially interleaved sub-channel(s). The title is divided in a plurality of consecutive data block sequences. Each block sequence is assigned to one respective sub-channel. The broadcasting device repeatedly broadcasts each block sequence in the assigned sub-channel. The broadcast receiver 150 has a capacity to simultaneously receive all sub-channels of a plurality r (1i, the receiver terminates reception of the sub-channel in channel i and starts reception of at least one sub-channel of channel r+i.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Communications system and method therefor
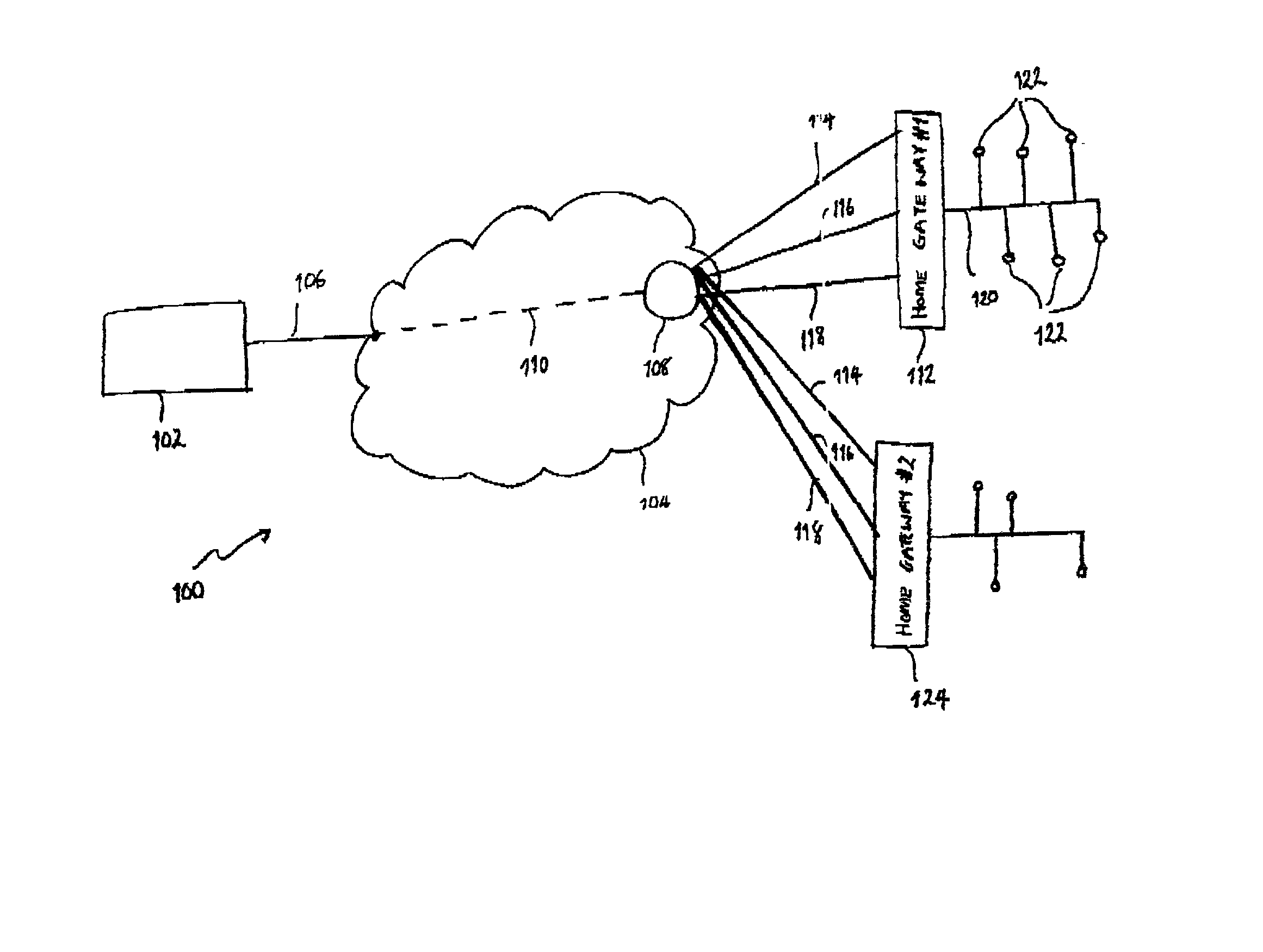
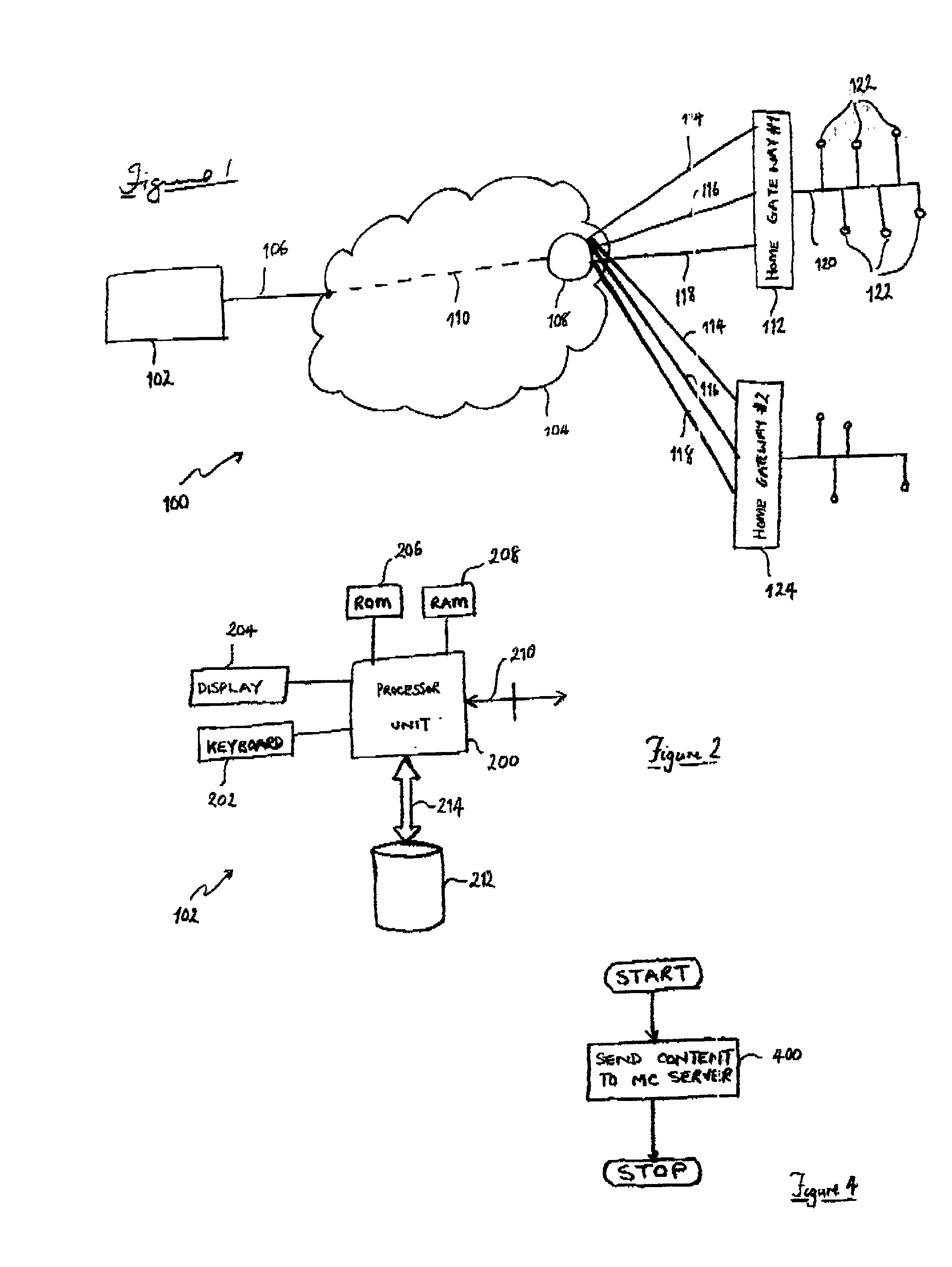
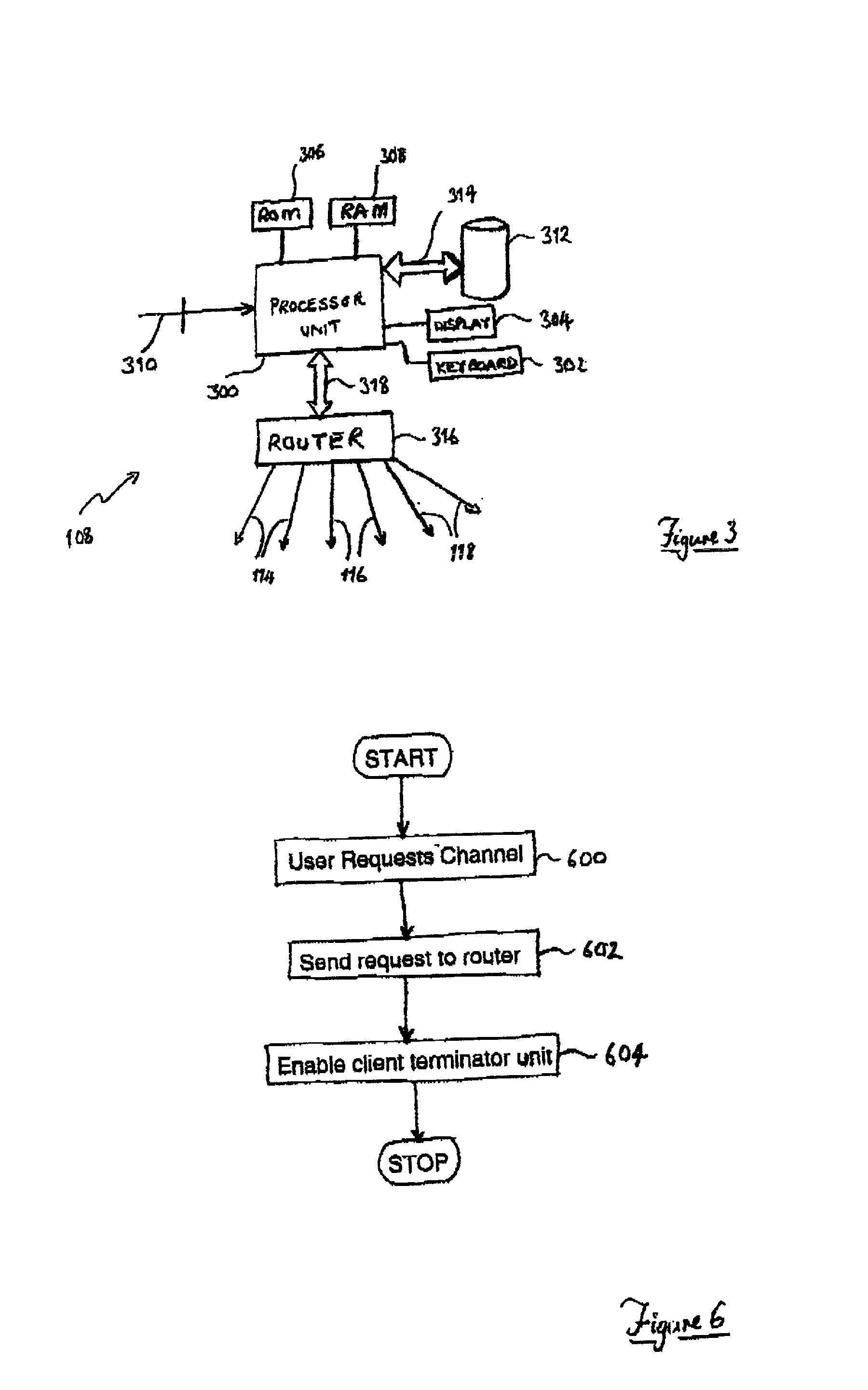
InactiveUS20020078219A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTwo-way working systemsNear video on demandData stream
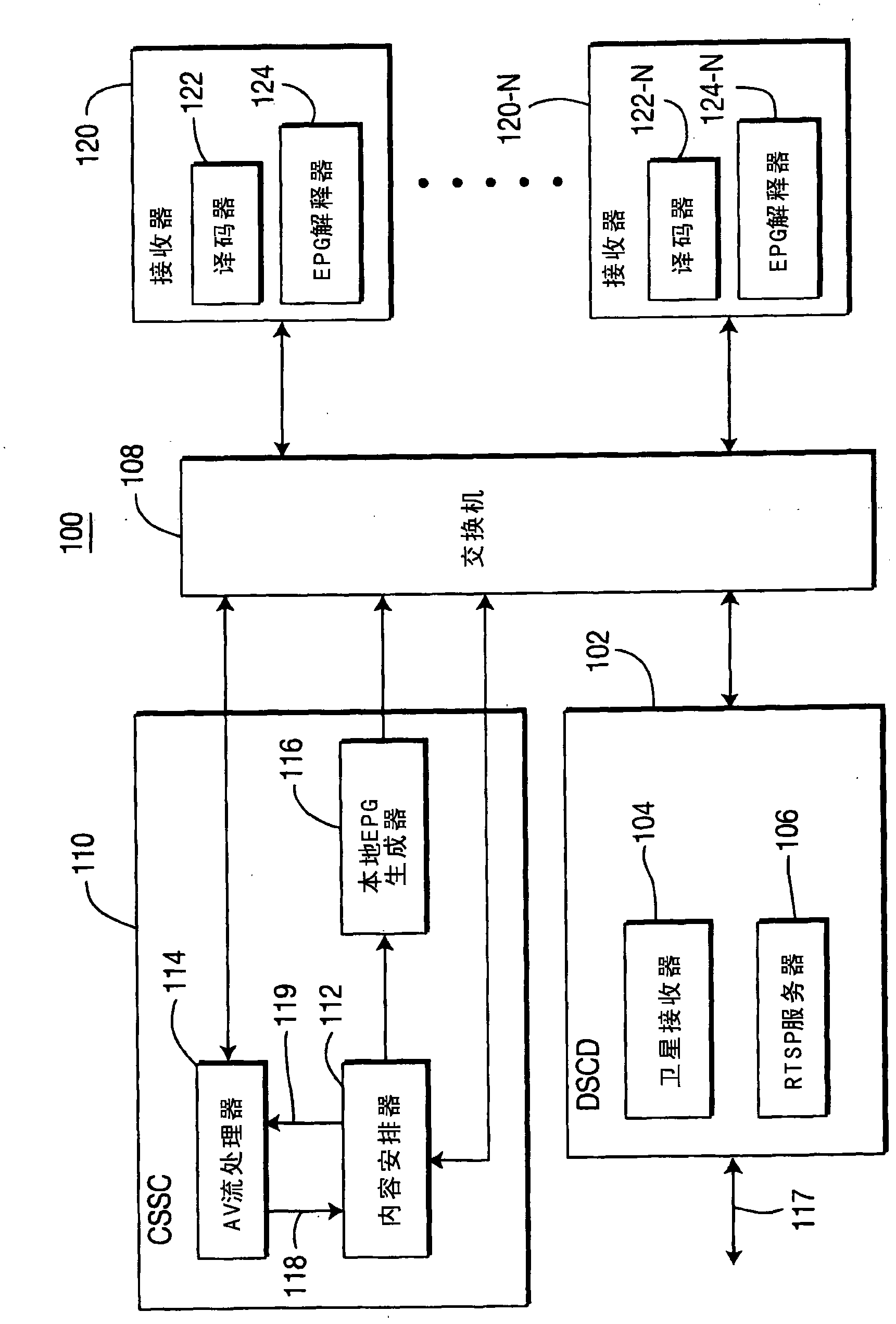
Known communications systems for providing Near Video On-Demand services require a large quantity of bandwidth in order to transfer a number of time-staggered versions of an original data stream to a set-top decoders. In order to reduce bandwidth requirements, the present invention provides a communications system (100) for providing data streaming services to a plurality of client terminator units (122) by providing a multicast server (108) capable of delivering a number of time-staggered versions of an original data stream to the plurality of client terminator units (122). (Consequently, the present invention advantageously obviates a need for a relatively large bandwidth to be provided for communications between a content providing server (102) and the multicast server (108).
Owner:CIENA
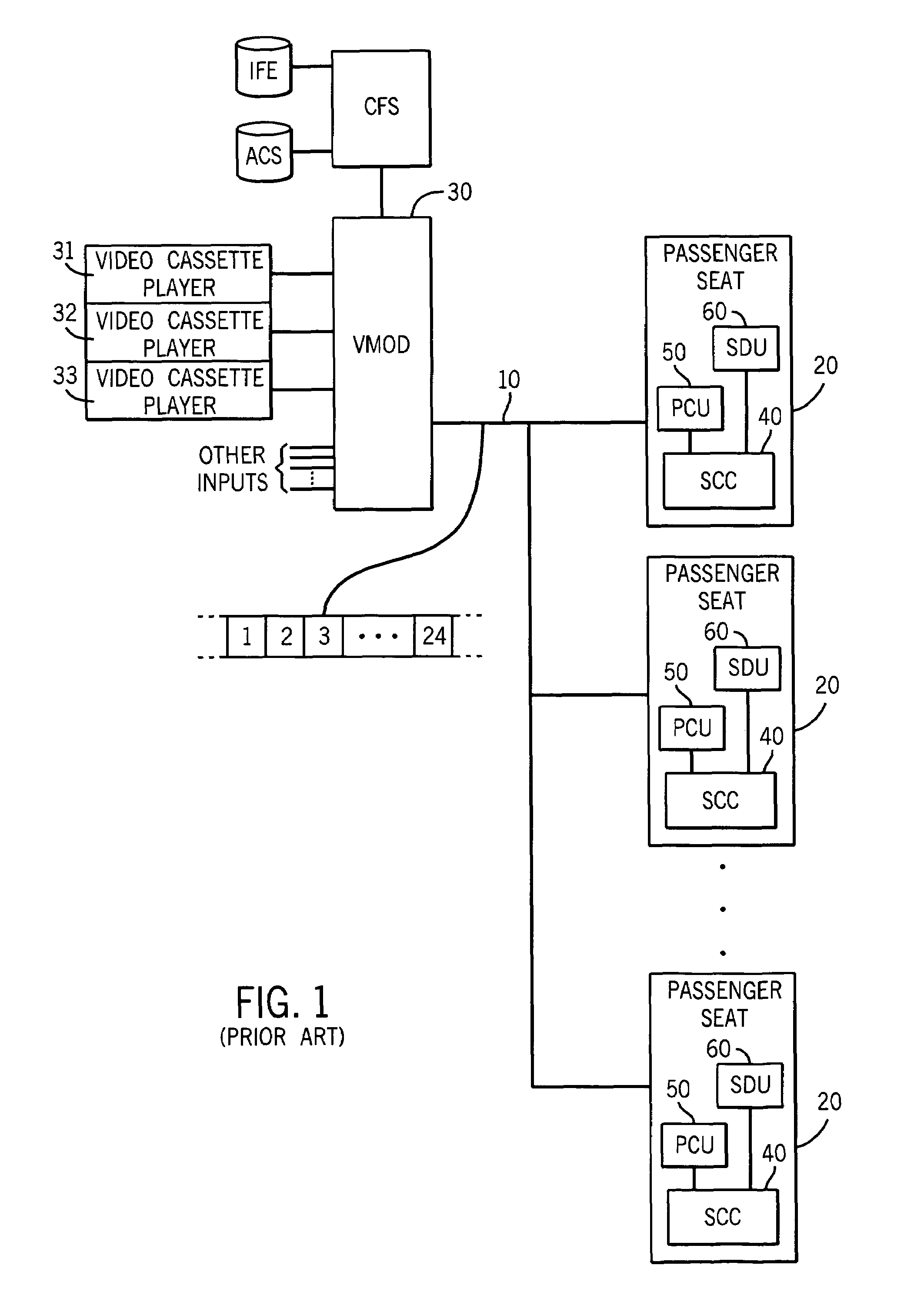
Channel identification for digital broadcasts in passenger entertainment systems
InactiveUS7600248B1Closed circuit television systemsSelective content distributionNear video on demandAudio on demand
A passenger entertainment system having video-on-demand, audio-on-demand, near video-on-demand, and digital and audio broadcast capabilities delivers multiple programming signals to the passenger seats. The system allocates an RF channel and one of multiple streams in that RF channel to a particular program channel so that channel surfing may be available to the passengers even when multiple programming signals are delivered on a single RF channel.
Owner:BURRANA IP & ASSETS LLC
Interactive media system and method for presenting pause-time content
InactiveUS20110243534A1Inhibition featureTelevision system detailsRecording carrier detailsNear video on demandVideo Media
Interactive media systems and methods are provided for substituting pause-time content in place of media that has been paused. The user may pause media such as real-time media, video-on-demand media, near video-on-demand, or recorded media. If the user pauses real-time media or near video-on-demand media, the interactive media application may store the media. The interactive media application may also provide the user with the ability to rewind, resume play of, and fast-forward the media. The pause-time content may be audio or video media and may be an advertisement, trivia, program summaries or any other suitable pause-time content. The interactive media application may provide customized pause-time content specific to the user or specific to the media paused by using media data associated with the media. The interactive media application may also prevent the user from accessing features (e.g., fast-forward) of the system.
Owner:ROVI GUIDES INC
Interactive media system and method for presenting pause-time content
InactiveUS20100192177A1Inhibition featureTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsNear video on demandVideo Media
Interactive media systems and methods are provided for substituting pause-time content in place of media that has been paused. The user may pause media such as real-time media, video-on-demand media, near video-on-demand, or recorded media. If the user pauses real-time media or near video-on-demand media, the interactive media application may store the media. The interactive media application may also provide the user with the ability to rewind, resume play of, and fast-forward the media. The pause-time content may be audio or video media and may be an advertisement, trivia, program summaries or any other suitable pause-time content. The interactive media application may provide customized pause-time content specific to the user or specific to the media paused by using media data associated with the media. The interactive media application may also prevent the user from accessing features (e.g., fast-forward) of the system.
Owner:UNITED VIDEO PROPERTIES
Near video-on-demand signal receiver
InactiveUS20090049503A1Television system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsNear video on demandDisplay device
A video signal receiver receives a plurality of video channels simultaneously carrying, offset by a transmission interval, a single video program, selects one channel from which to obtain the program for display to a user, and achieves a pause function in the display of the transmitted video program by temporarily storing a segment of the video program equal to the length of the transmission interval and obtaining the remainder of the program at a later time from the same or another channel.
Owner:INOUE HAJIME +4
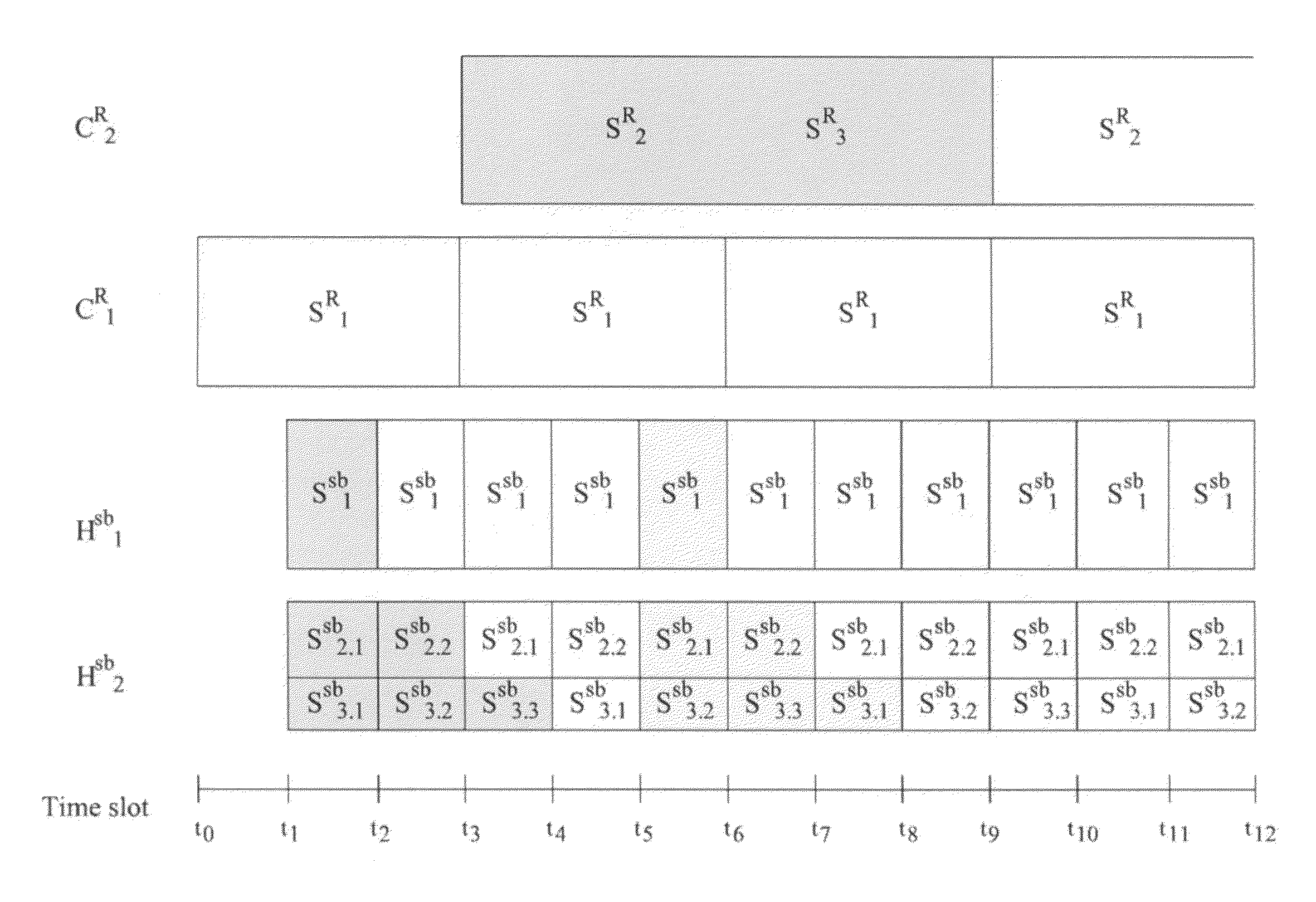
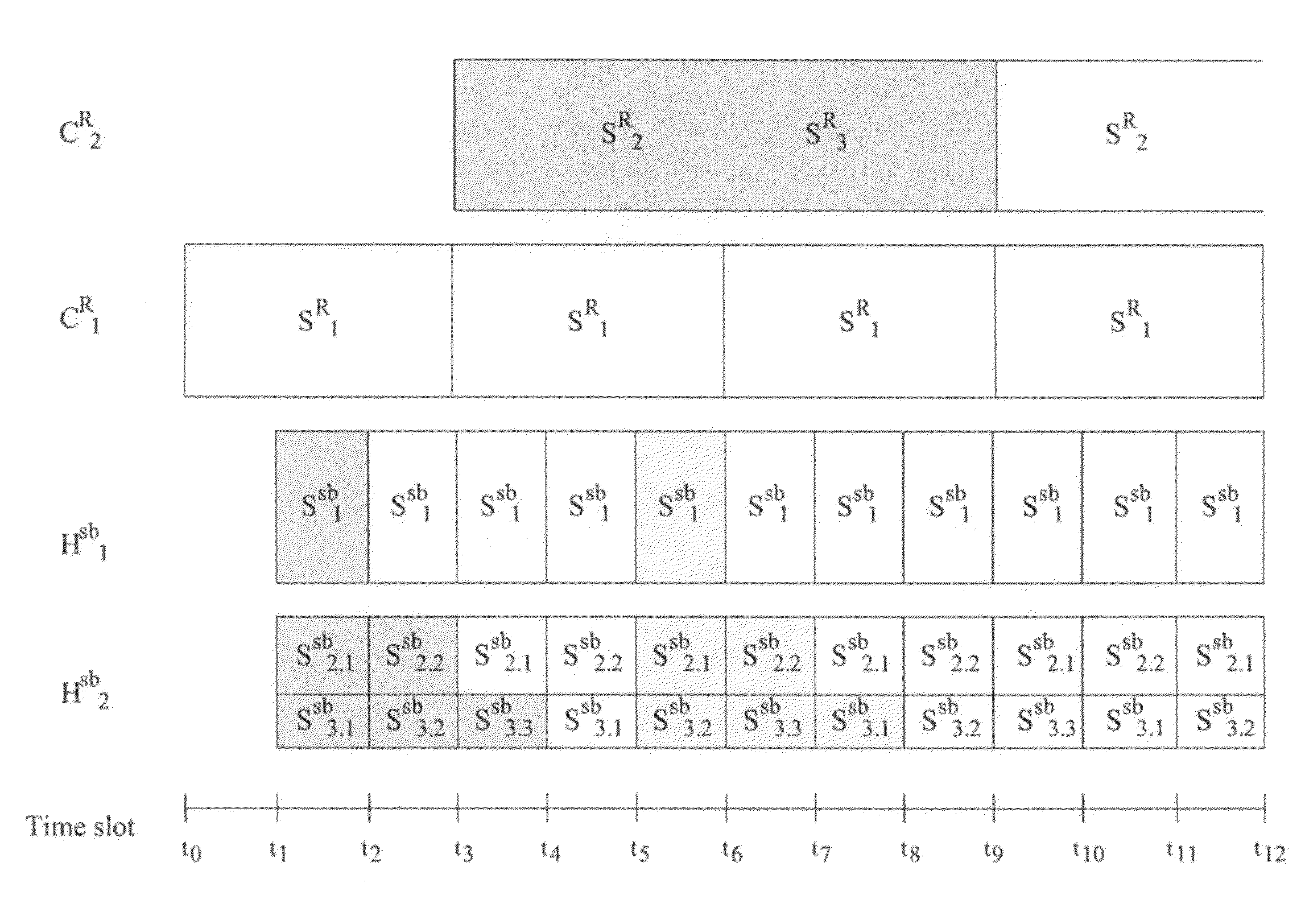
METHOD FOR TRANSMITTING NEAR VIDEO ON DEMAND (NVoD) USING CATCH AND REST (CAR) AND SUB-CHANNELS
InactiveUS20100186054A1Reduce service latencyTwo-way working systemsSelective content distributionNear video on demand
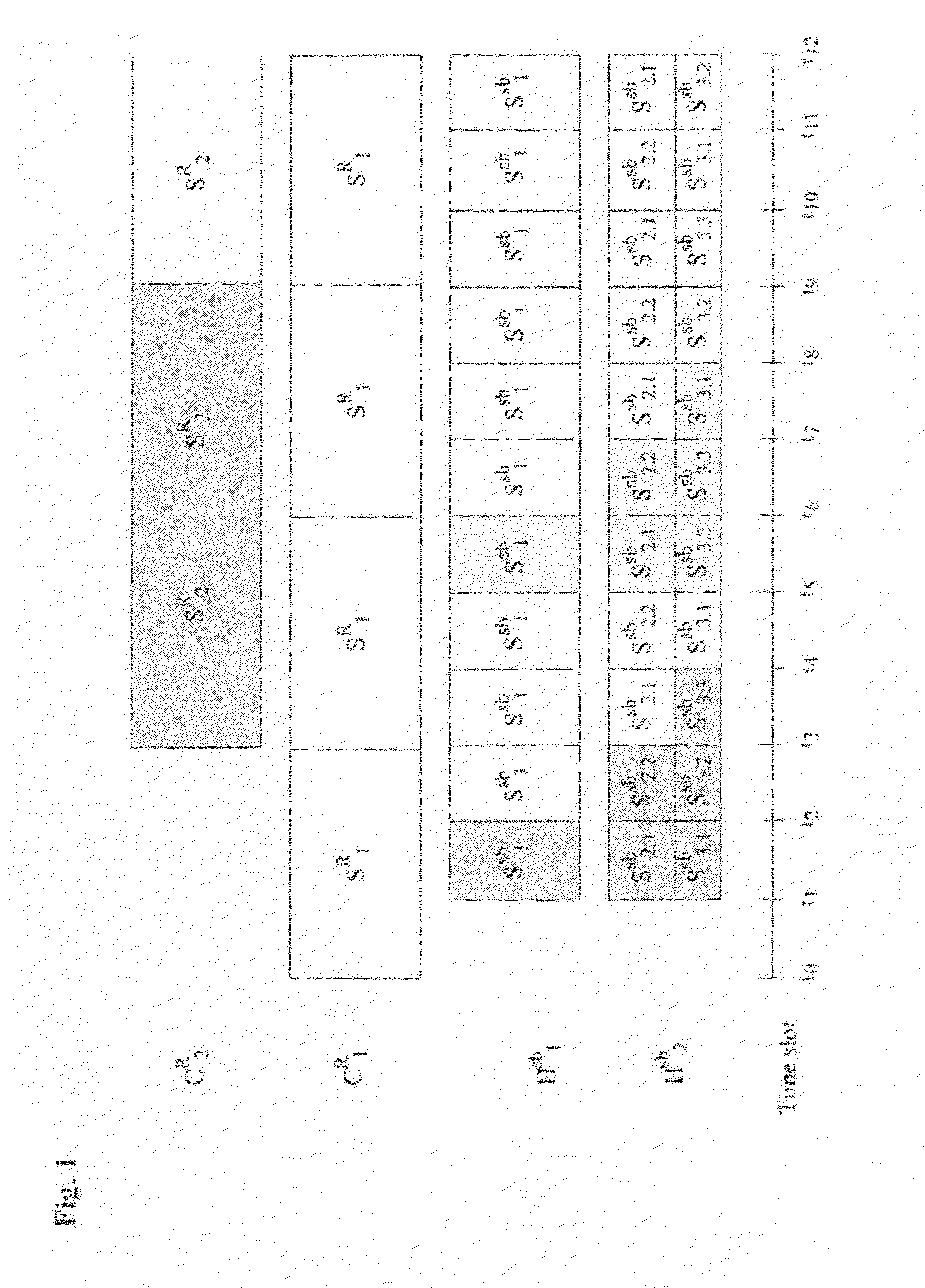
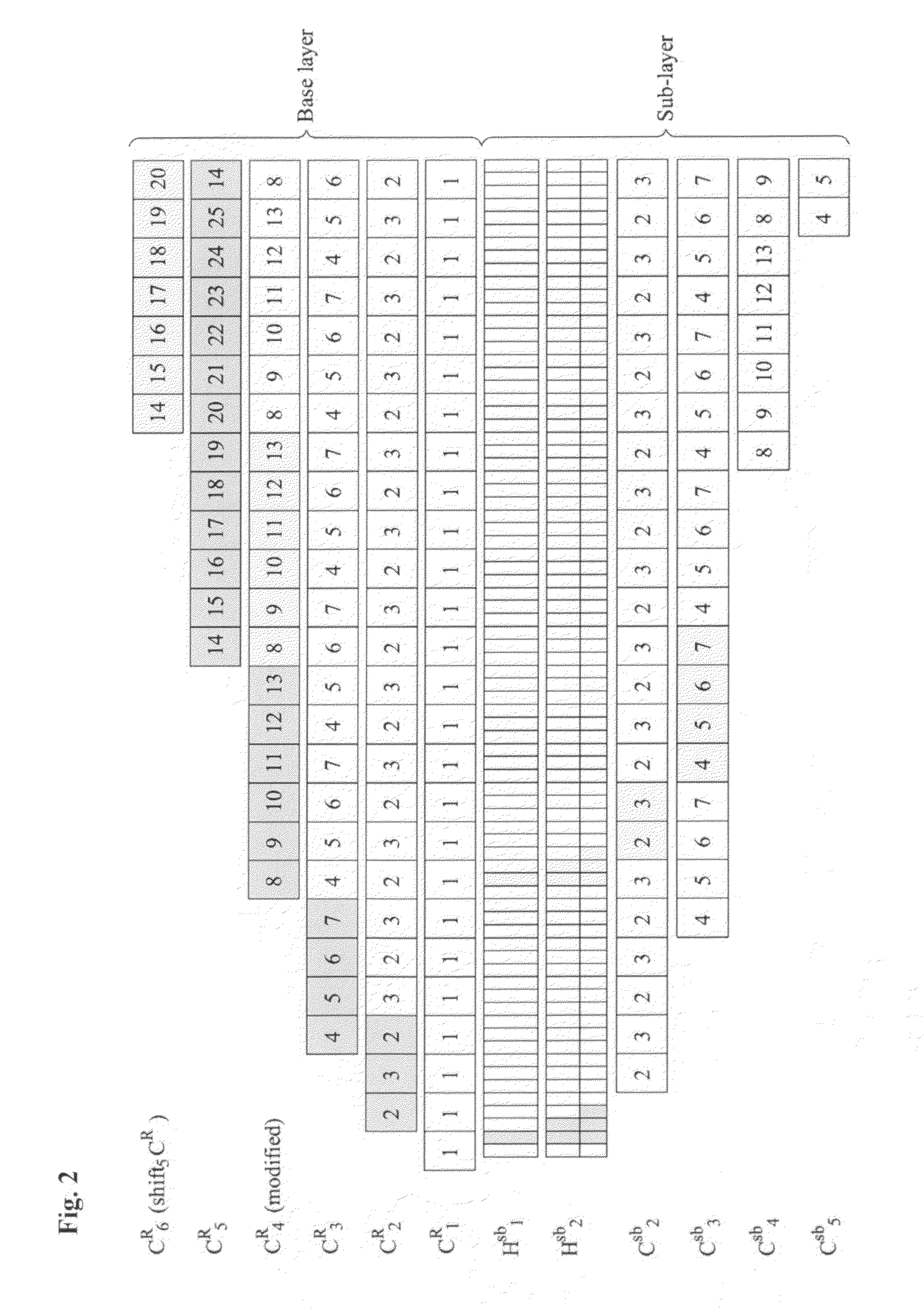
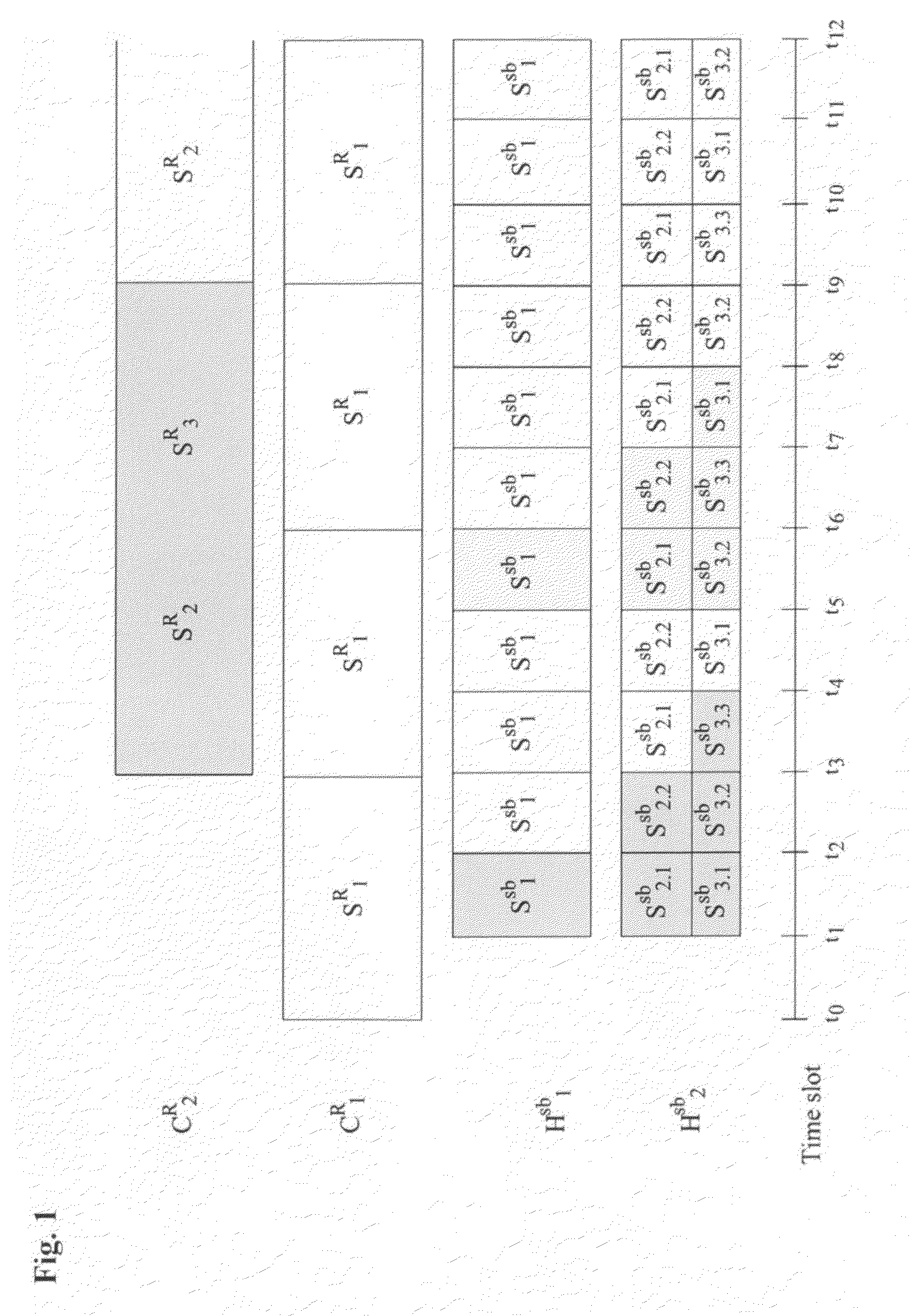
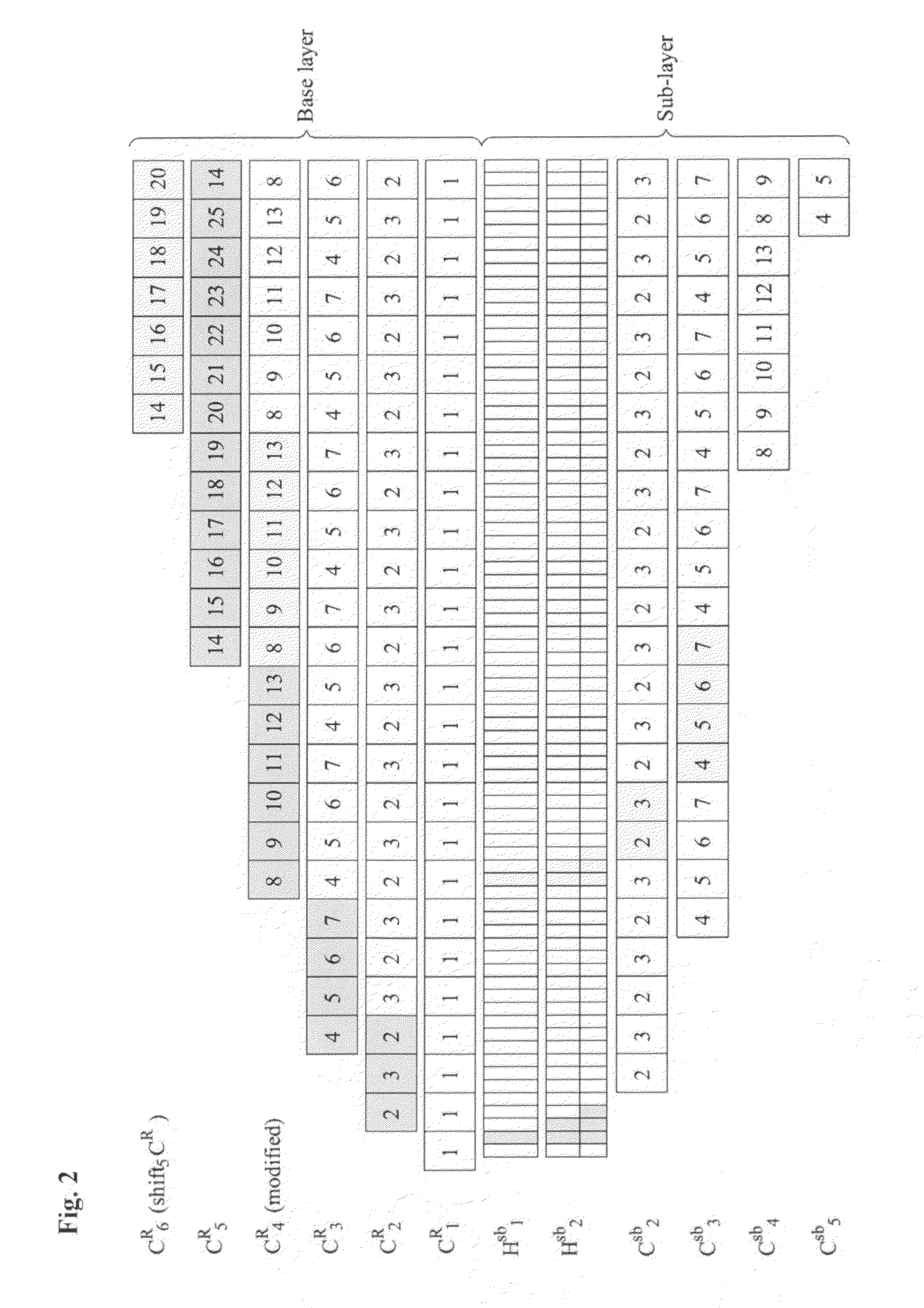
The present invention discloses a method for transmitting Near Video on Demand (NVoD) using Catch and Rest (CAR) and sub-channels which includes: dividing an L-sized content into N segments using the CAR broadcasting scheme, allocating the segments to K channels including a replicate channel, and broadcasting the segments; dividing a first segment S1R (SiR represents an i-th segment of a regular channel) into Nsb sub-segments again at given bandwidth using the harmonic broadcasting scheme, and dividing an i-th sub-segment Sisb into i segments again; broadcasting the sub-segments {Si.1sb, . . . , Si.isb} in n sub-channels; and adding the segments {S2R, . . . , SNR} to a sub-layer and broadcasting the segments, the first segment broadcast in the first channel being divided and allocated to a few sub-channels, the succeeding segments broadcast in the other channels being just shifted and broadcast.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY CO LTD
Methods and systems for providing a program guide for near video on demand systems
InactiveCN102057685ASimple browsingShow suppressionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsNear video on demandDuplicate content
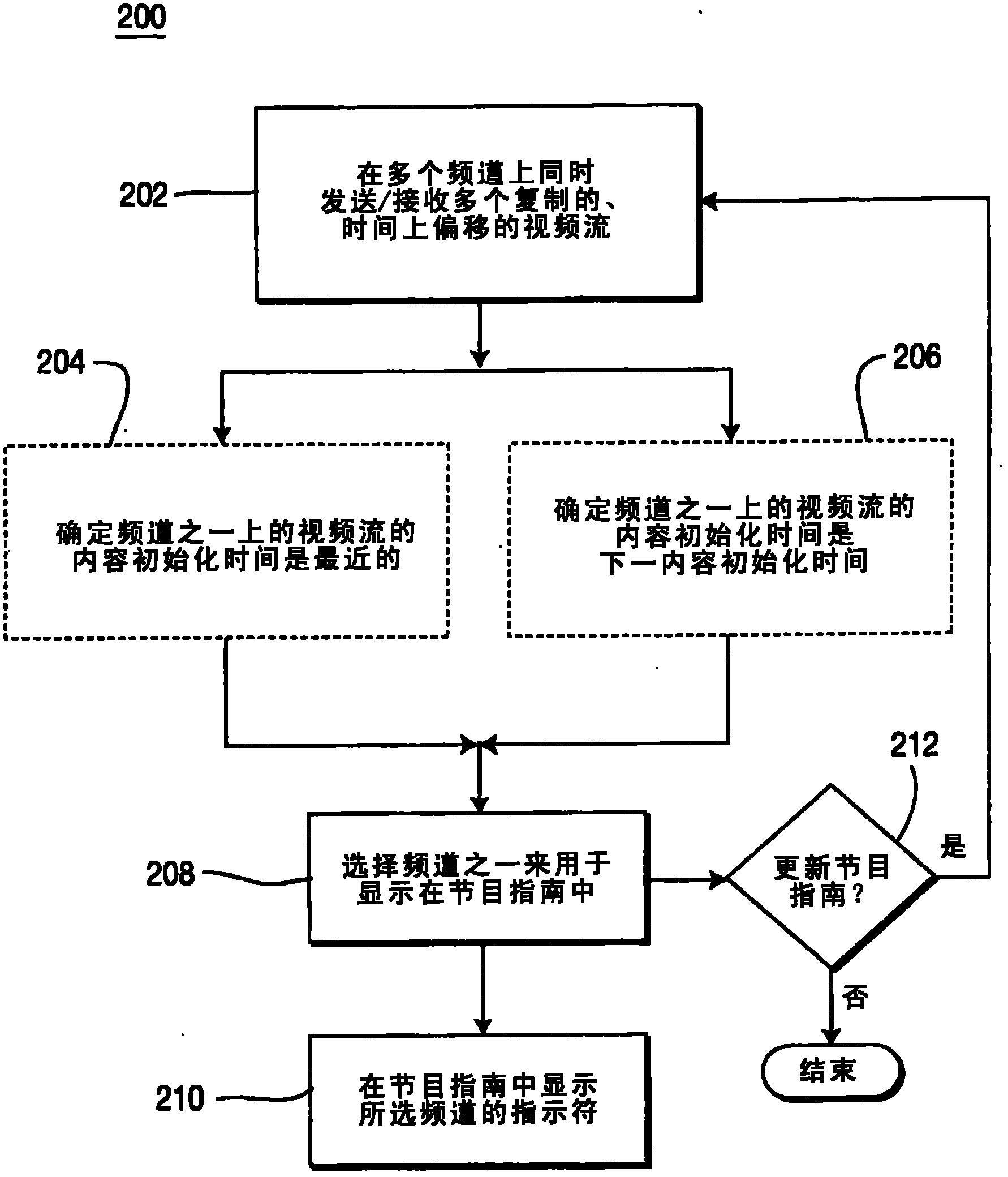
In accordance with aspects of the present principles, a program guide display for a near video on demand system can be provided. The NVOD system can transmit and / or receive (202) a plurality of duplicate, temporally offset video streams on separate channels to enable viewing of video content at practically any time from its beginning. According to one aspect of the present principles, a channel carrying a program having a start time that coincides with a current time can be selected (208) for display in the program guide while suppressing other NVOD channels carrying duplicate content with offset start times.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Method, apparatus, and system for implementing interactive near video on demand channel
InactiveUS20130097628A1Reduce operating costsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTwo-way working systemsNear video on demandOperational costs
Embodiments of the present invention disclose a method, an apparatus, and a system for implementing an interactive near video on demand (NVOD) channel. The present invention relates to the field of NVOD channels and can implement an interactive NVOD channel at a low operation cost. The method includes: sending NVOD program metadata to a user equipment; receiving a request for playing an NVOD program, where the playing request is sent by the user equipment and includes the NVOD program that a user selects from the NVOD program metadata through the user equipment; determining, according to the playing request, a next NVOD program to be played, and sending a media stream of the determined NVOD program in multicast / broadcast mode. The present invention is mainly applied to NVOD channels and may be applied to IMS-based IPTV systems.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Efficient NVOD service method for various client environments and apparatus there-for
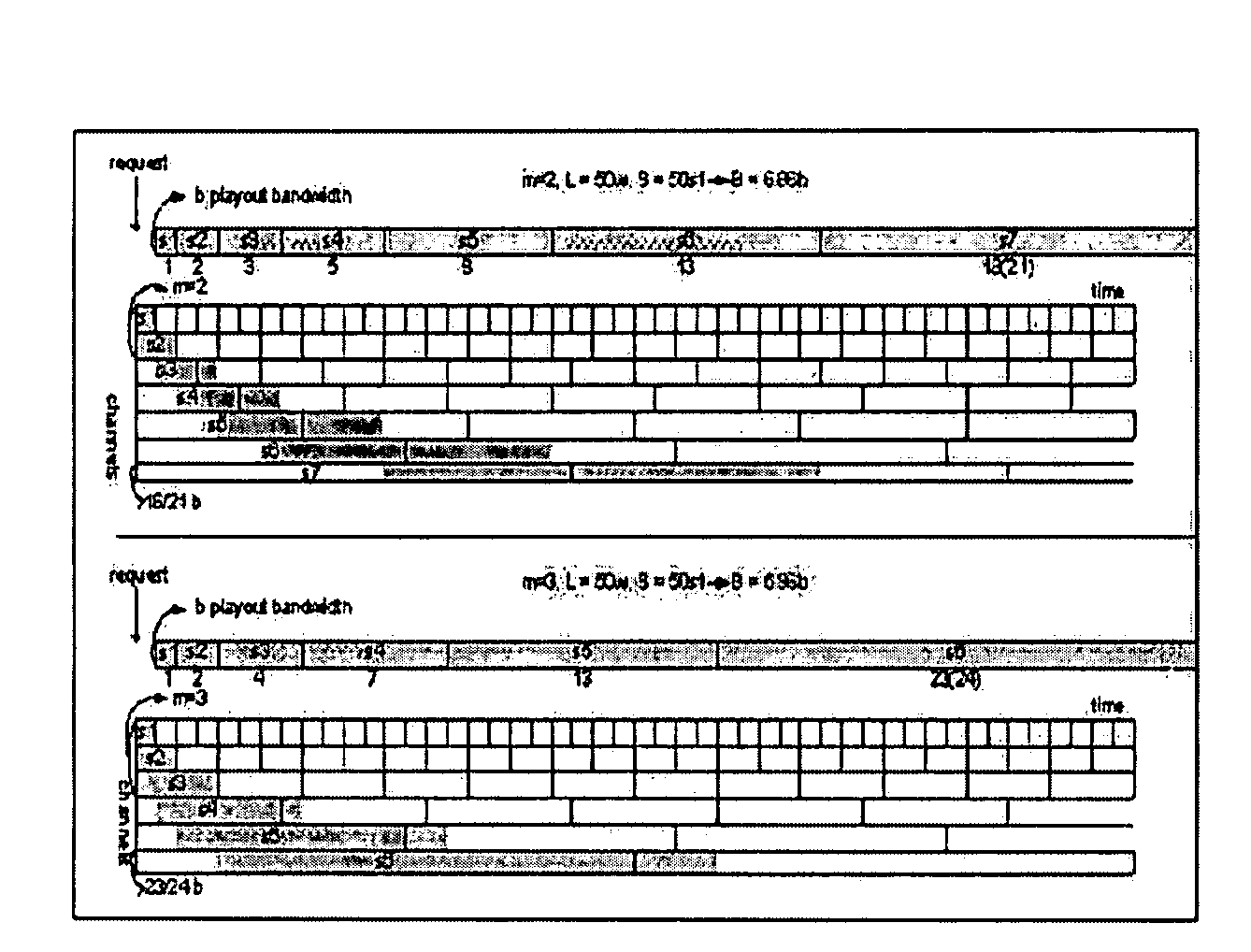
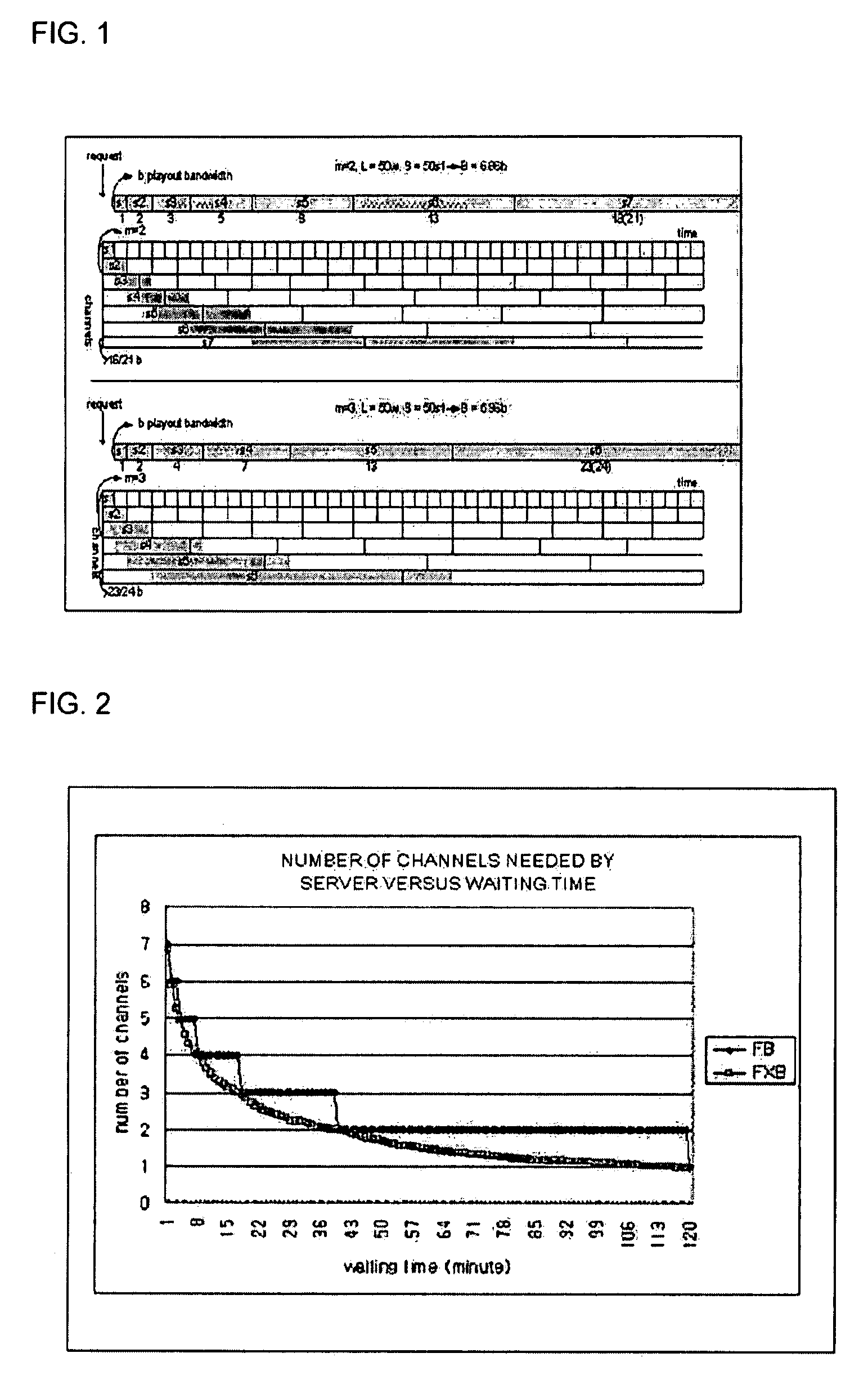
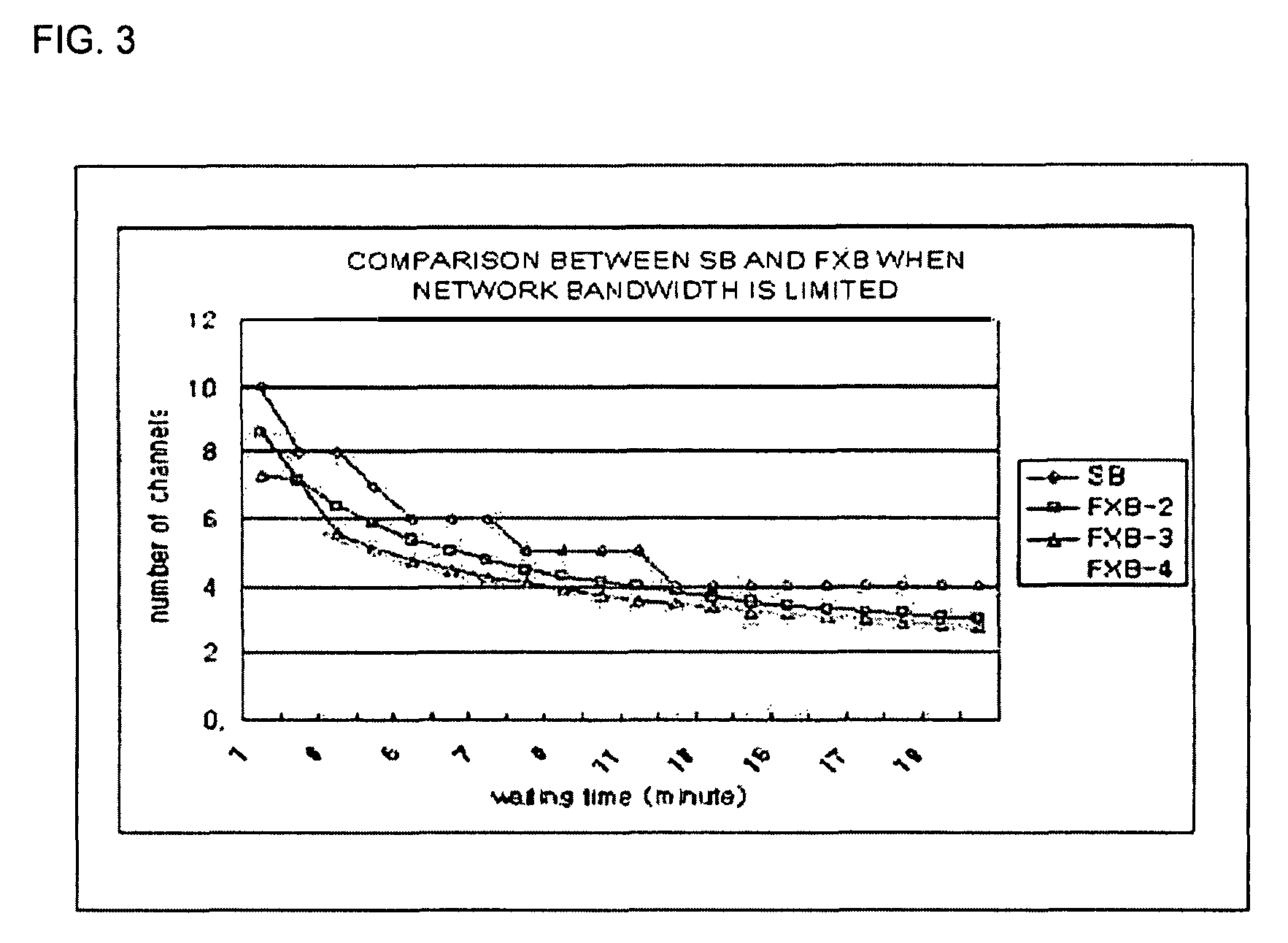
InactiveUS7941825B2Efficient receptionGuaranteed normal transmissionNetwork traffic/resource managementTwo-way working systemsNear video on demandData segment
An efficient near video on demand (NVOD) service for various client environments is provided. The NVOD service method for transmitting video data including moving pictures to a plurality of clients in a network includes identifying a relative network bandwidth “m” of a client with respect to a video playout bandwidth, dividing the video data into data segments having different sizes according to the relative network bandwidth “m” and transmitting the data segments to the client through a plurality of channels.
Owner:CHUNG ANG UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Method for transmitting near video on demand (NVoD) using catch and rest (CAR) and sub-channels
InactiveUS8272021B2Reduce service latencyTwo-way working systemsSelective content distributionNear video on demand
The present invention discloses a method for transmitting Near Video on Demand (NVoD) using Catch and Rest (CAR) and sub-channels which includes: dividing an L-sized content into N segments using the CAR broadcasting scheme, allocating the segments to K channels including a replicate channel, and broadcasting the segments; dividing a first segment S1R (SiR represents an i-th segment of a regular channel) into Nsb sub-segments again at given bandwidth using the harmonic broadcasting scheme, and dividing an i-th sub-segment Sisb into i segments again; broadcasting the sub-segments {Si.1sb, . . . , Si.isb} in n sub-channels; and adding the segments {S2R, . . . , SNR} to a sub-layer and broadcasting the segments, the first segment broadcast in the first channel being divided and allocated to a few sub-channels, the succeeding segments broadcast in the other channels being just shifted and broadcast.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com