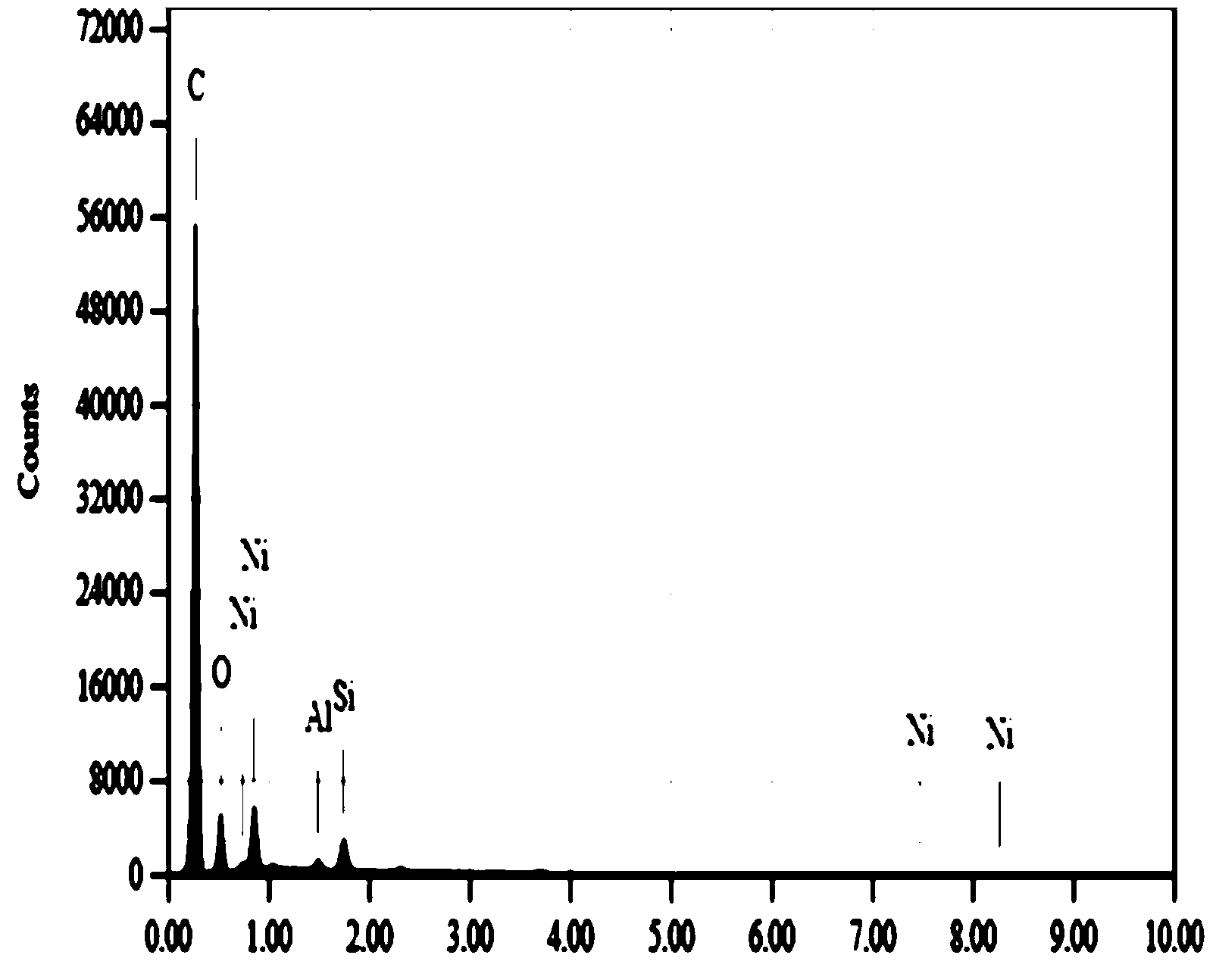
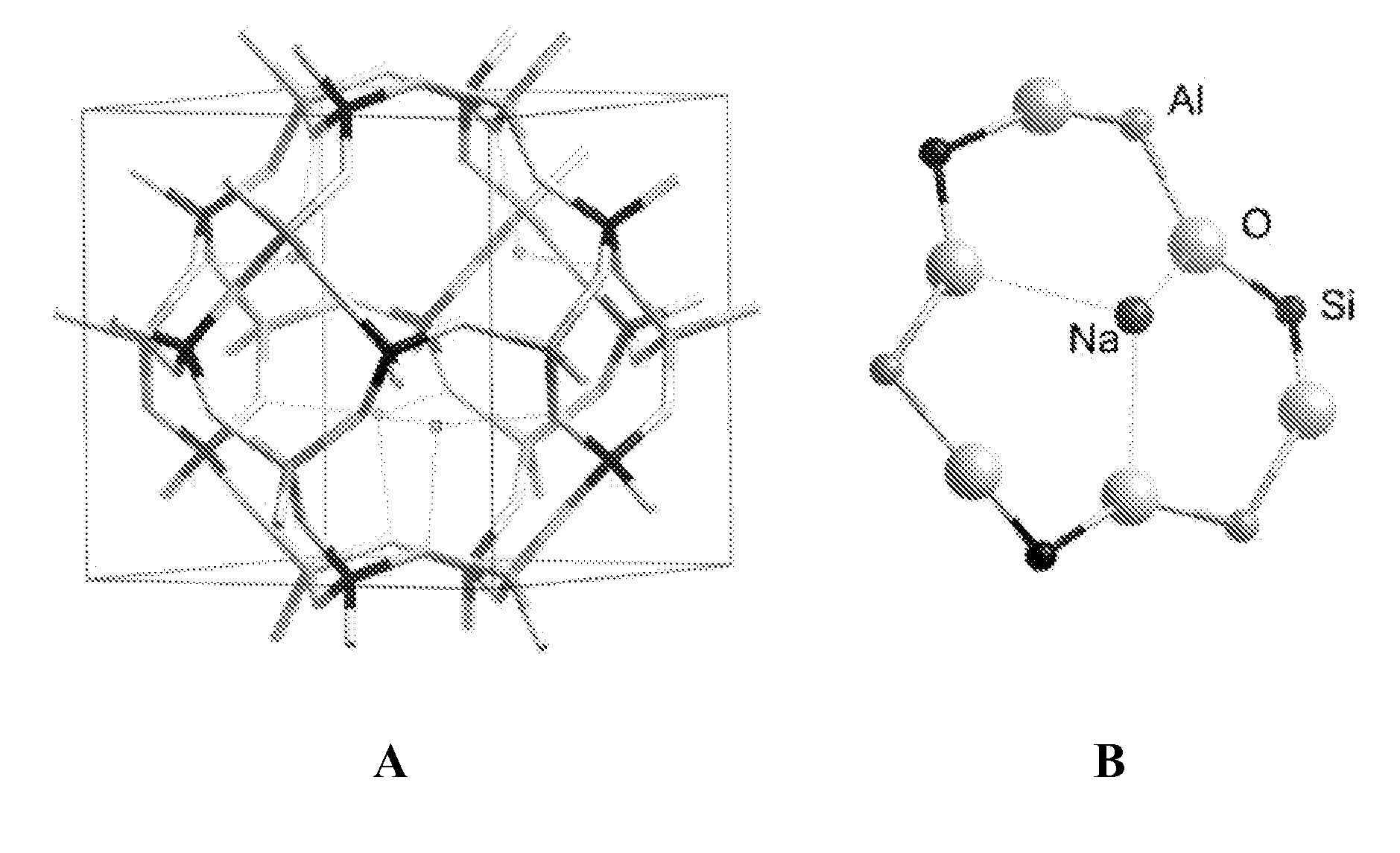
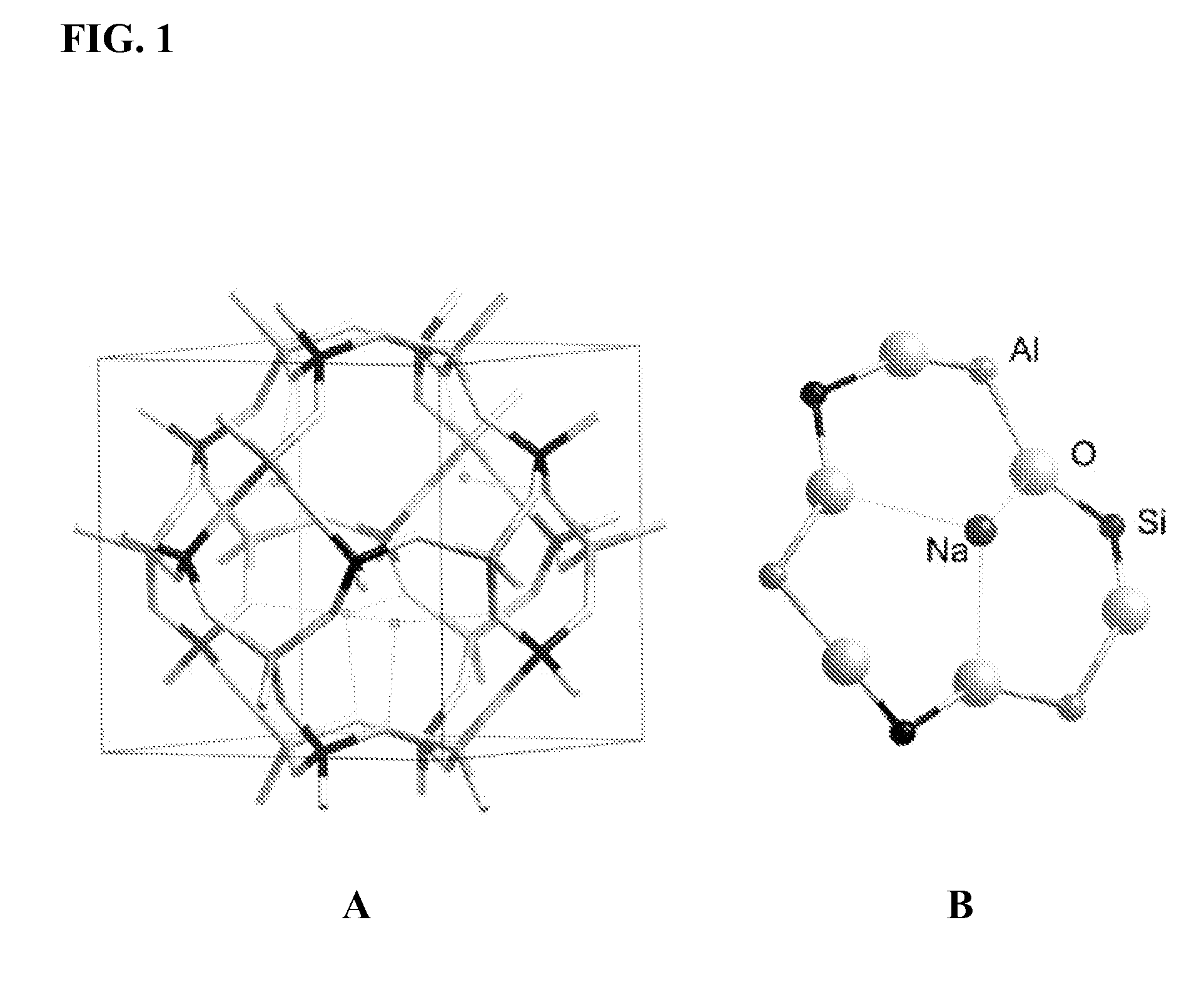
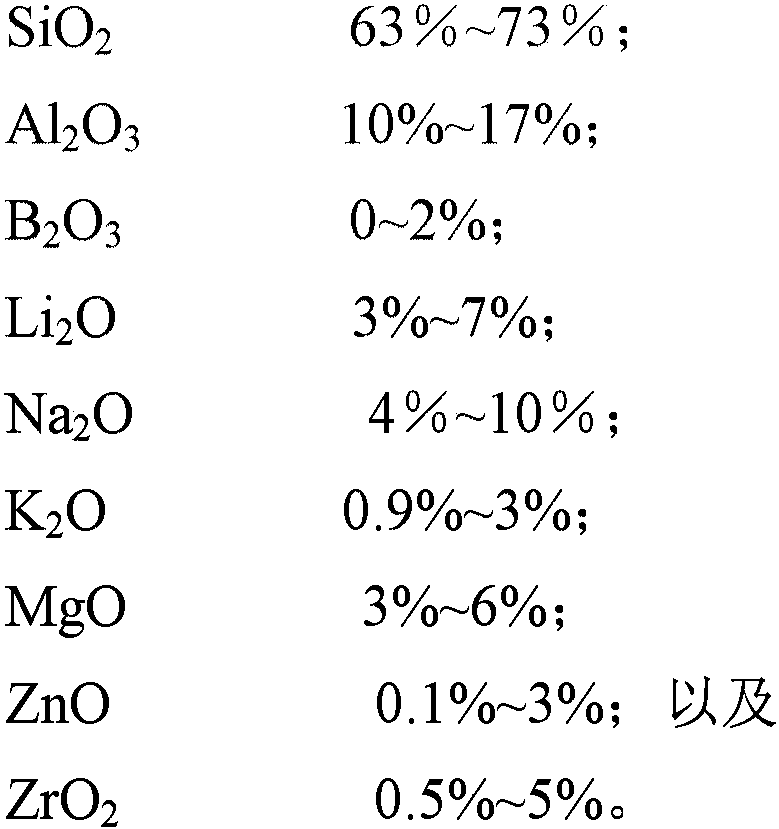Patents
Literature
91results about How to "Facilitate ion exchange" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
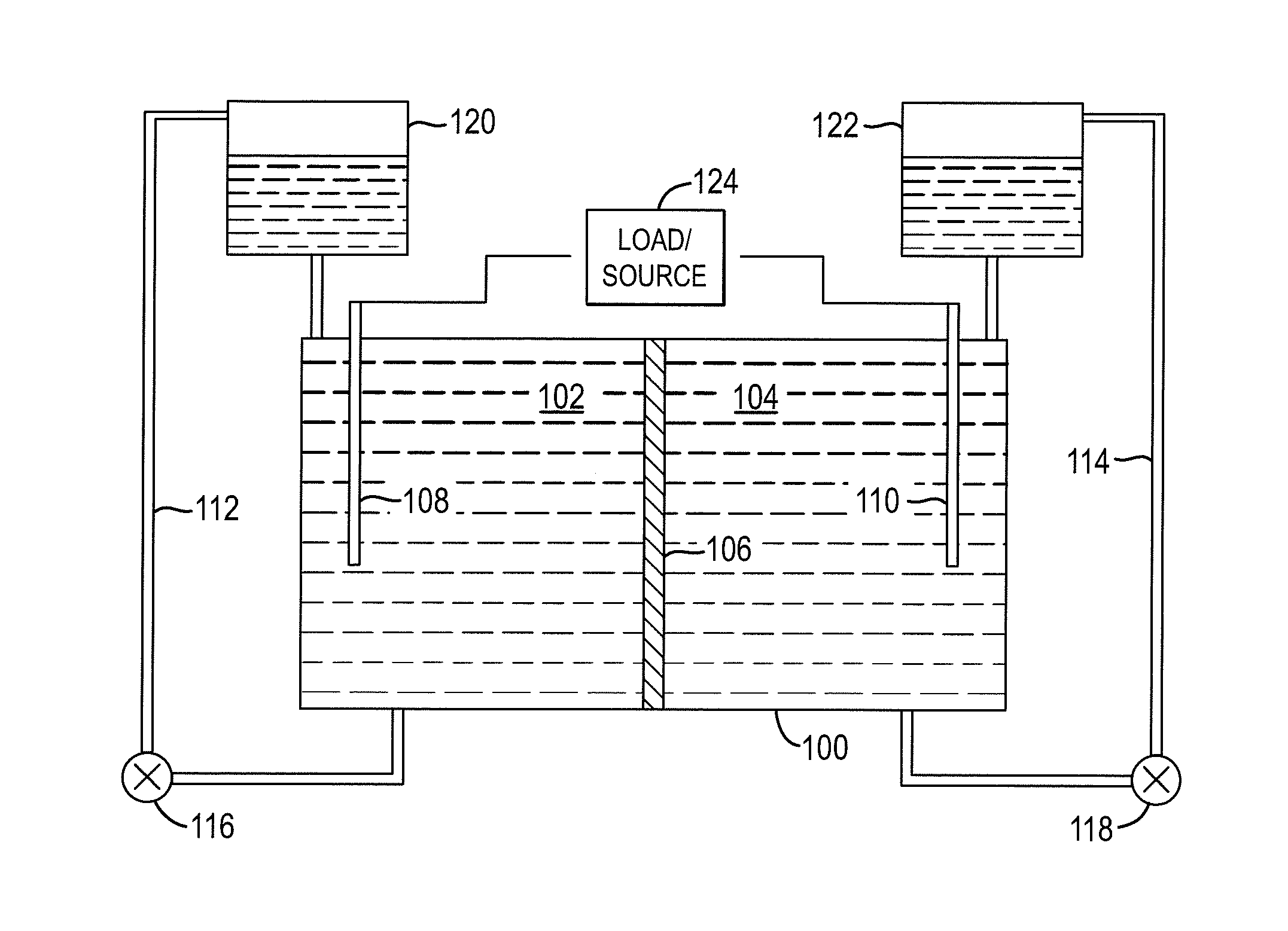
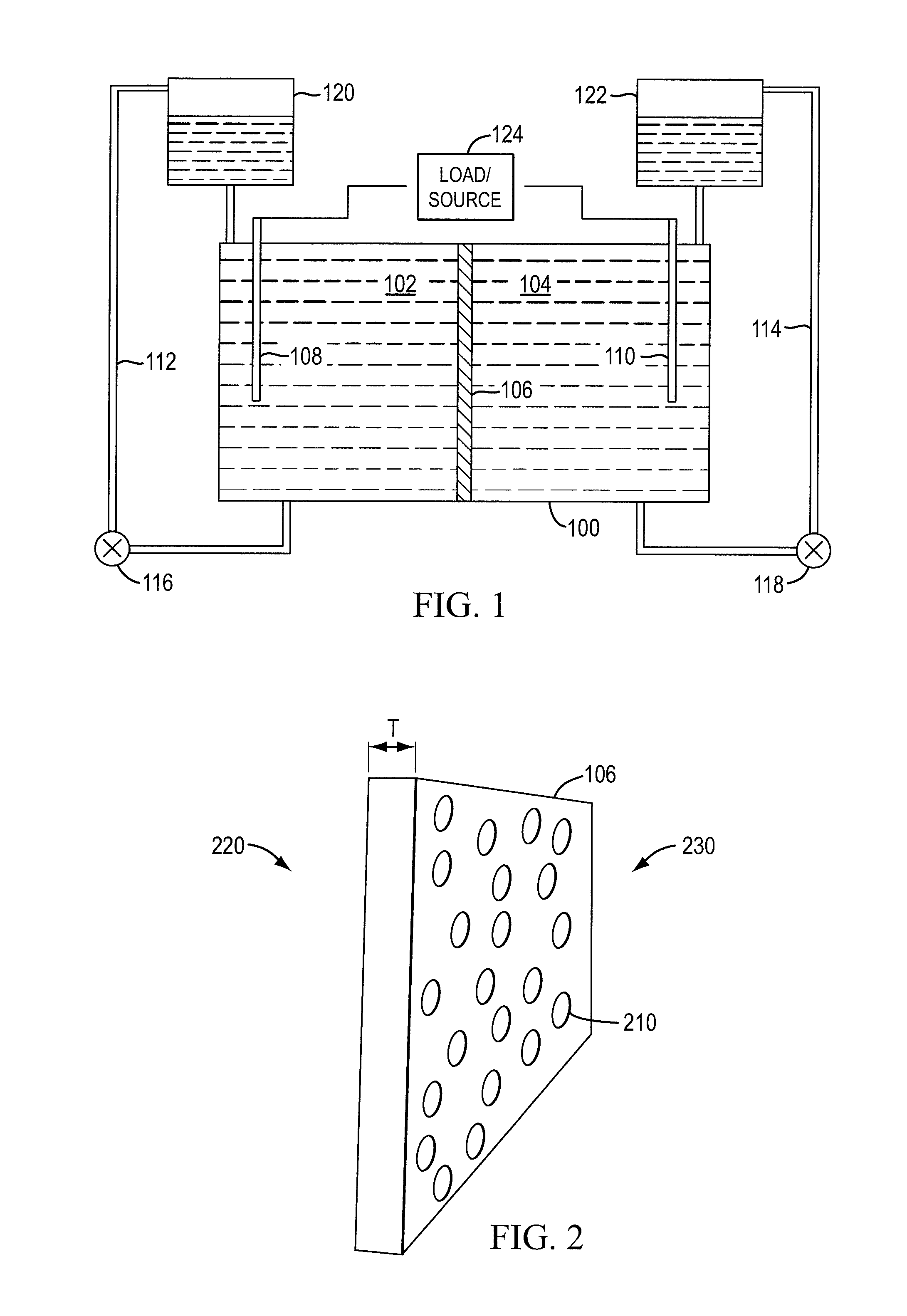
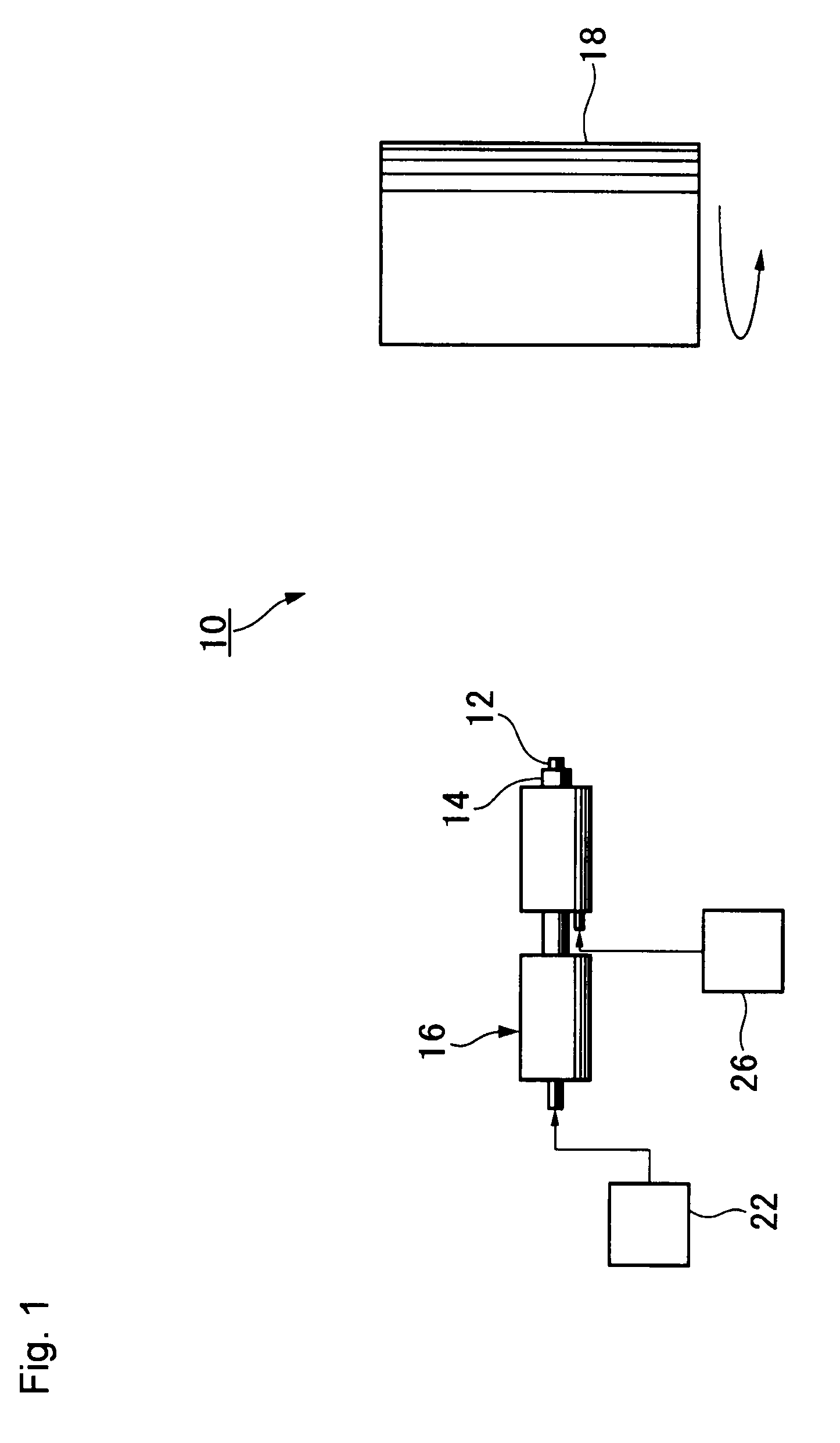
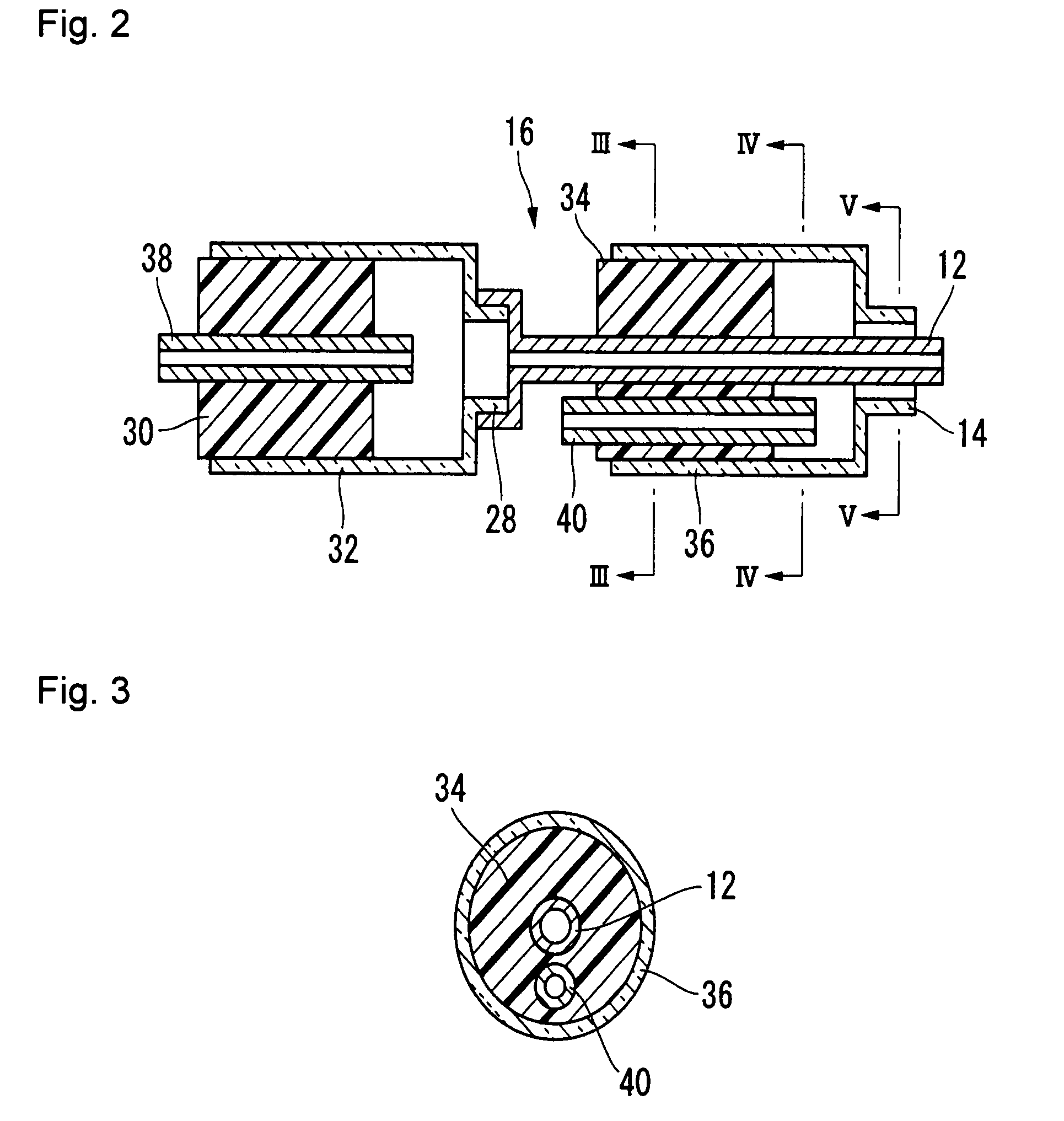
Redox flow cell
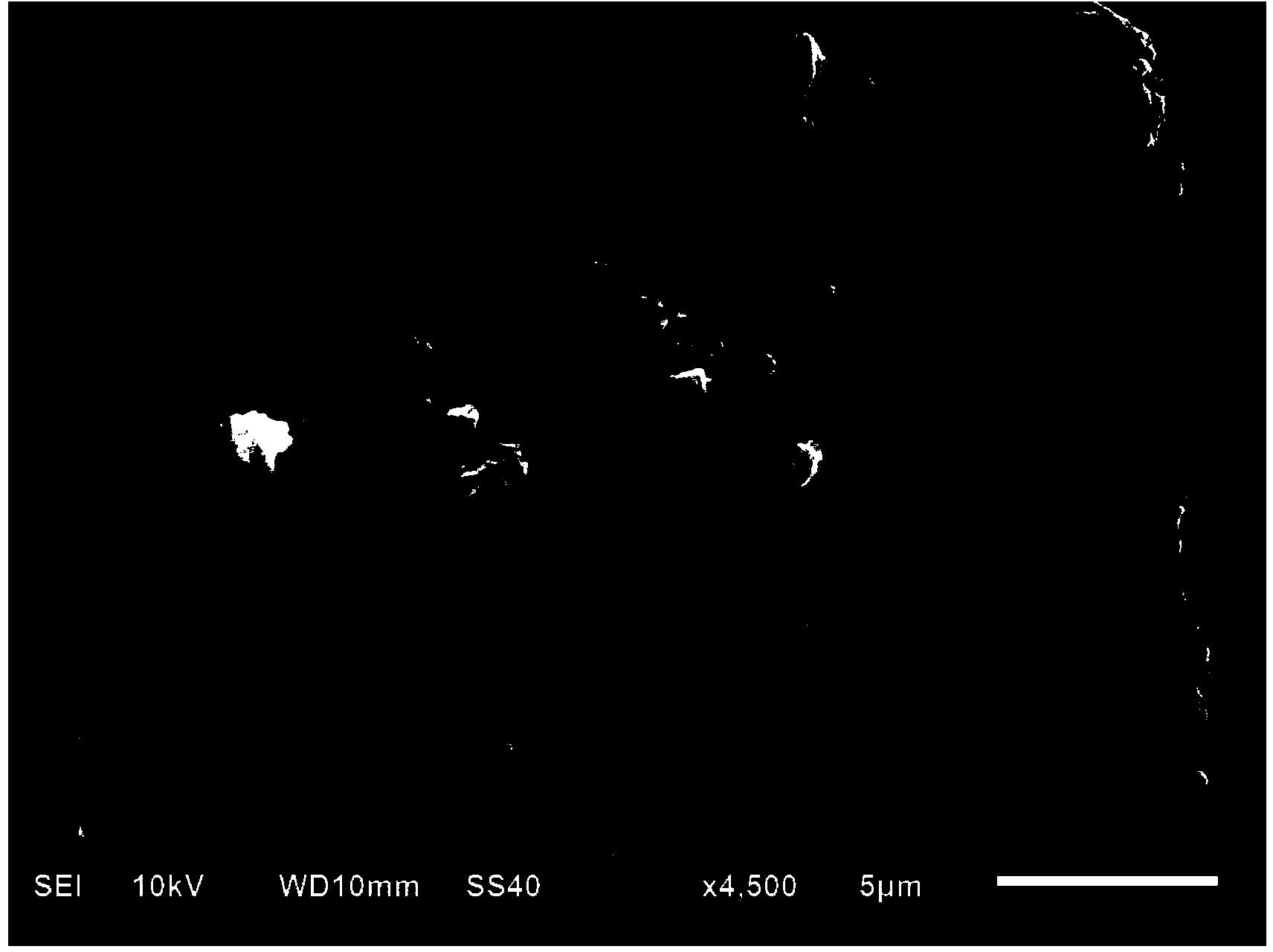
InactiveUS20100003586A1Facilitate ion exchangeCell electrodesFuel cell auxillariesFlow cellPorous membrane
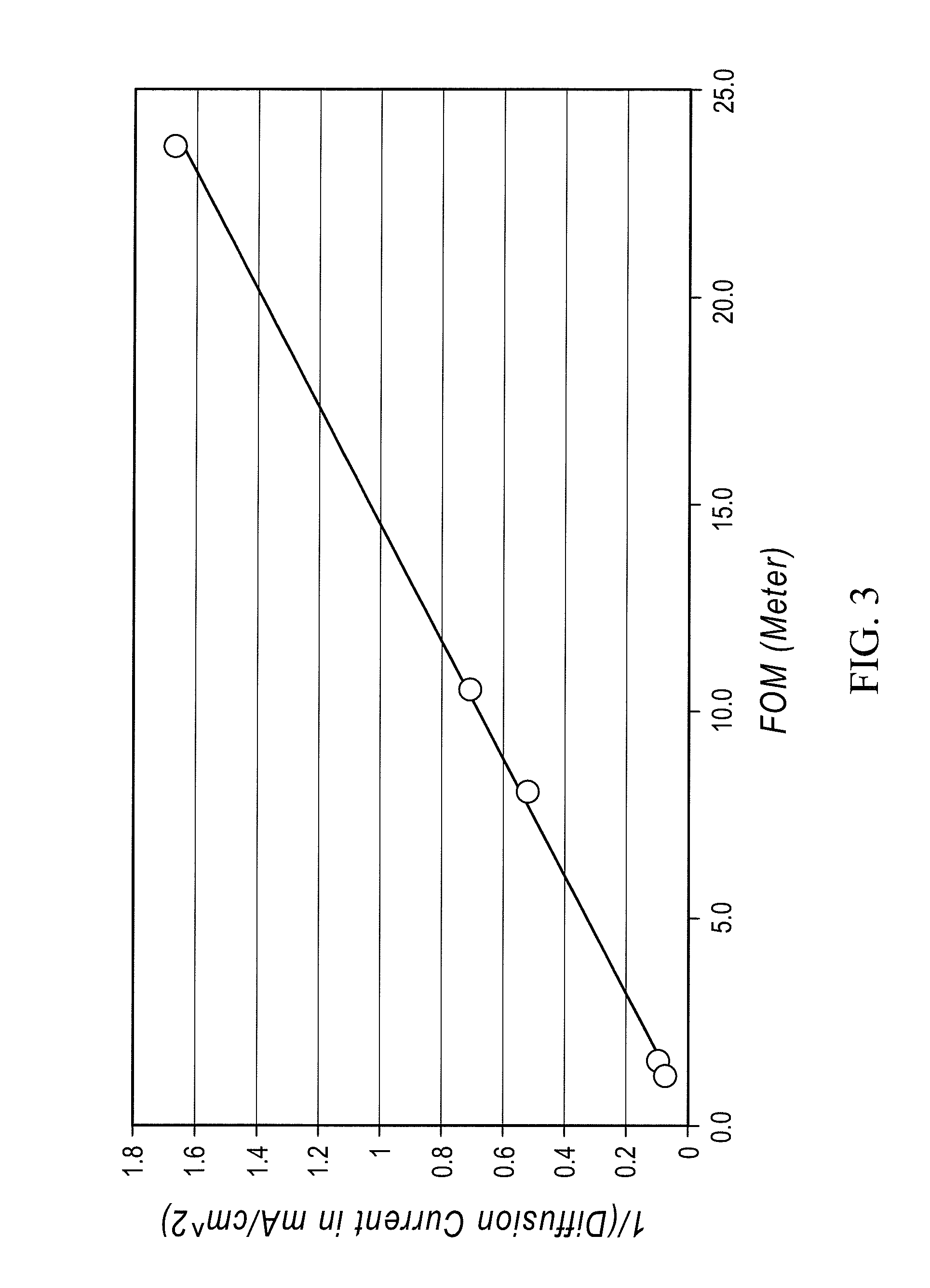
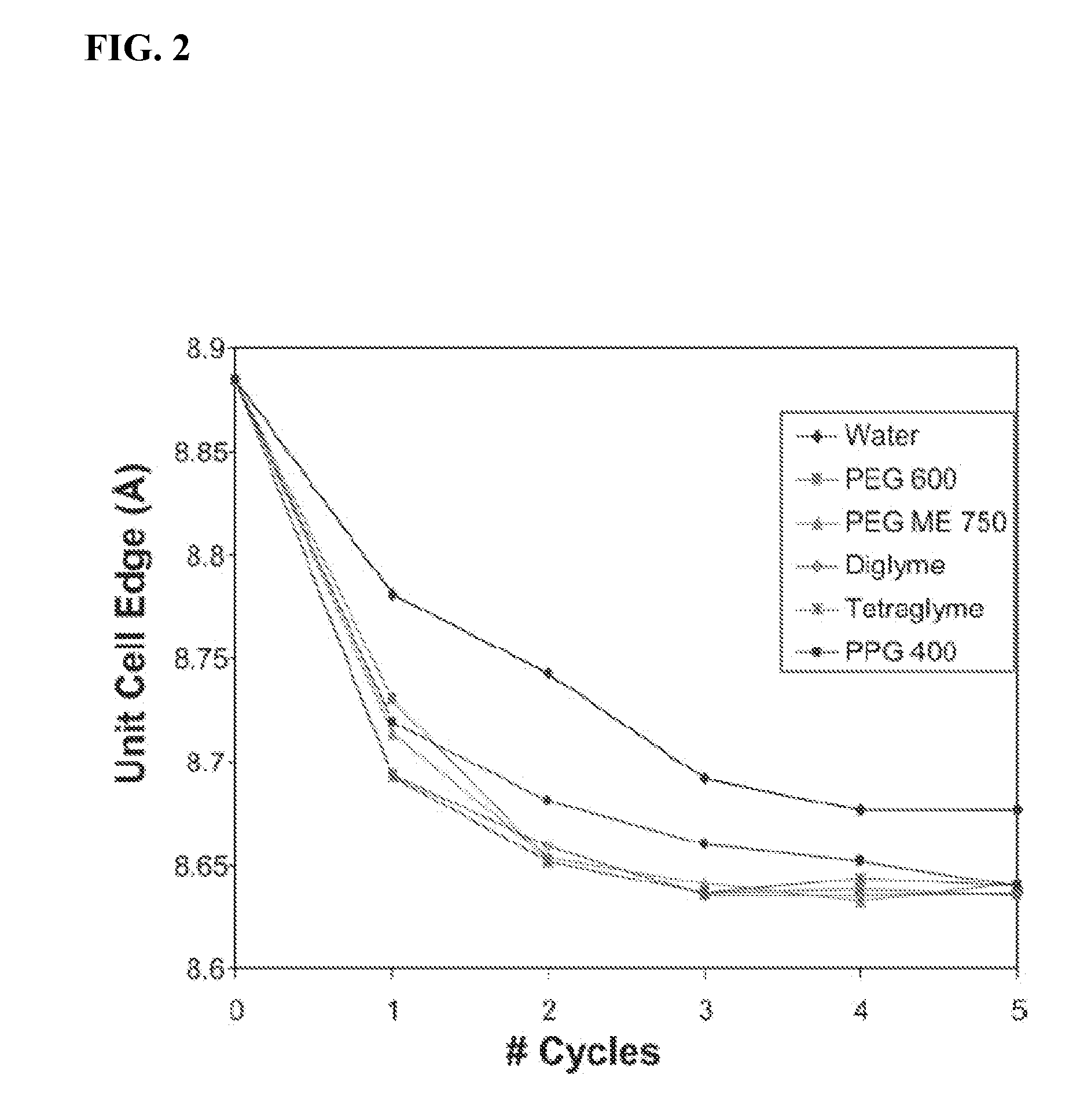
A redox flow cell is presented that utilizes a porous membrane separating a first half cell and a second half cell. The porous membrane is chosen to have a figure of merit (FOM) is at least a minimum FOM. A method of providing a porous membrane for a flow cell can include determining a figure of merit; determining a first parameter from a pore size or a thickness for the porous membrane; determining a second parameter from the pore size or the thickness that is not the first parameter for the porous membrane, based on the figure of merit; and constructing a porous membrane having the pore size and the thickness.
Owner:IMERGY POWER SYST
Heavy metal stabilizing agent and method for treating heavy metal contaminated soil by using same
ActiveCN102965116ACaptureHarmlessContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersSodium BentoniteApatite
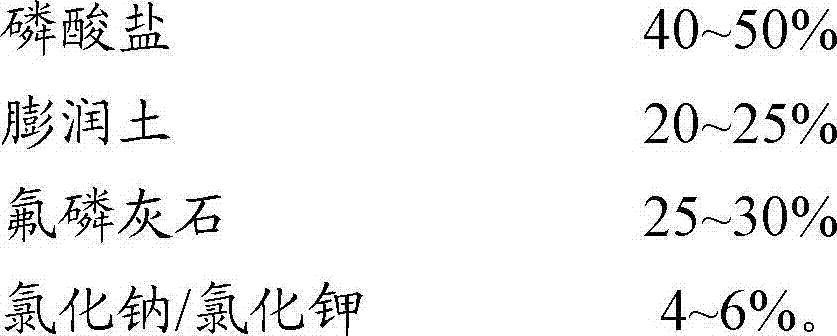
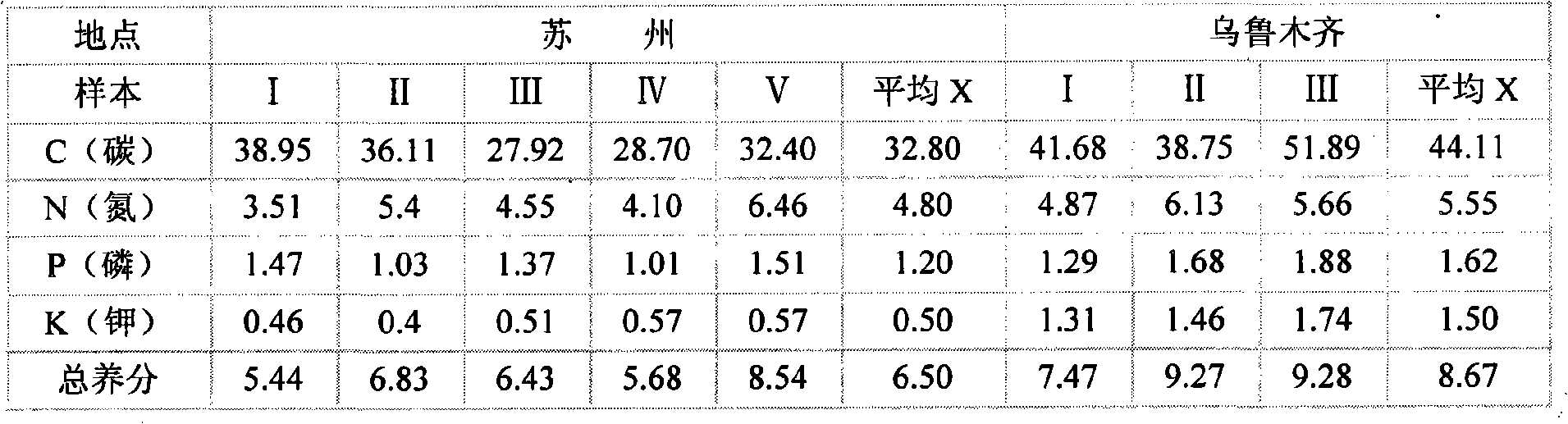
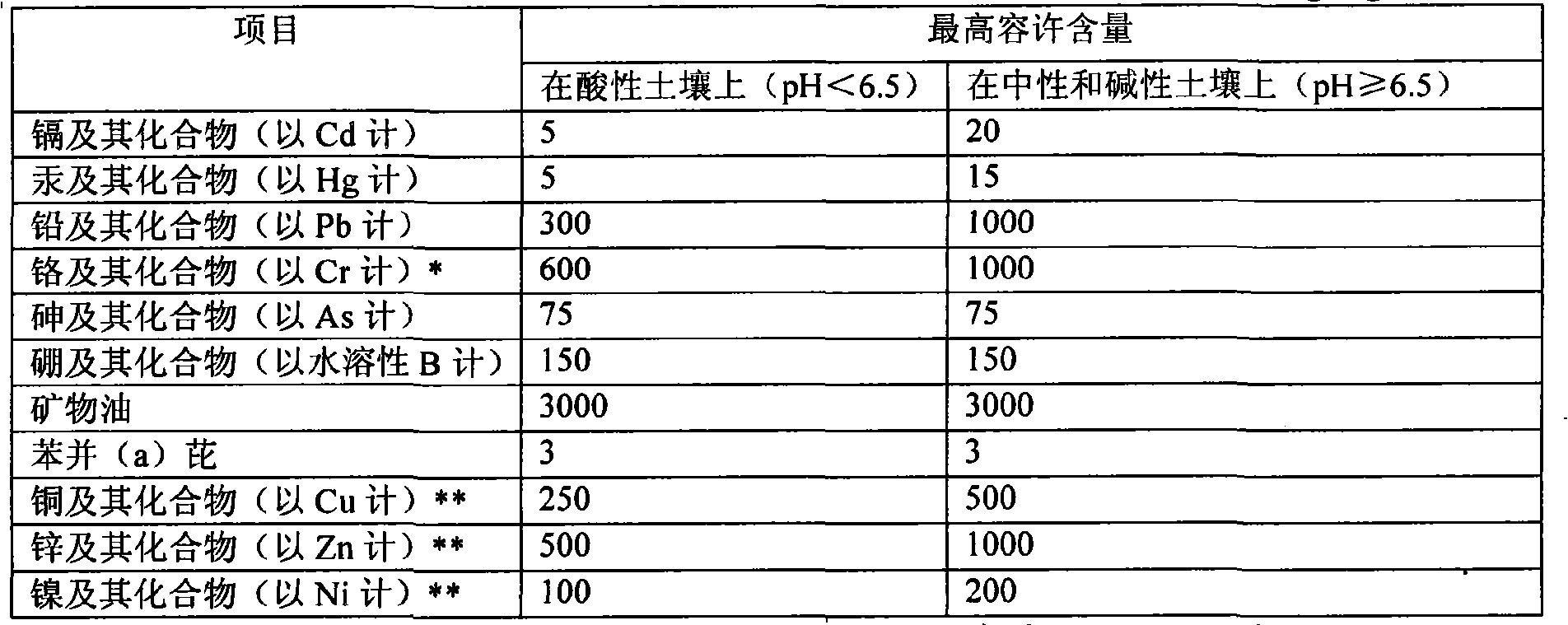
The invention discloses a heavy metal stabilizing agent and a method for treating heavy metal contaminated soil by using the heavy metal stabilizing agent. The heavy metal stabilizing agent is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 40 to 50 percent of phosphate, 20 to 25 percent of bentonite, 25 to 30 percent of fluor apatite and 4 to 6 percent of sodium chloride / potassium chloride. When the heavy metal stabilizing agent is used for treating the contaminated soil, the heavy metal stabilizing agent and water are mixed together to form a suspension, then the suspension is added into the heavy metal contaminated soil, and the suspension and the heavy metal contaminated soil are fully mixed. The heavy metal stabilizing agent has high stability for treating soil, and the technical problem that the conventional curing agent and curing method cause reverse dissolution easily is solved.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL SCI RES & DESIGN INST OF ZHEJIANG PROVINCE
Preparation and use of a nanocomposite of elastomer and exfoliated clay platelets formed in situ within an elastomer host and articles of manufacture, including tires, having at least one component comprised thereof
InactiveUS20040054059A1Efficient intercalation flexibilityEfficient combinationNanostructure manufactureSpecial tyresElastomerPolymer science
This invention relates to preparation and use of nanocomposites comprised of an elastomer matrix which contains a dispersion therein of at least partially exfoliated platelets of an intercalated, multilayered, water swellable clay (e.g. montmorillonite clay). The exfoliated platelets are derived from such intercalated clay formed by an in situ cation exchange phenomenon between cationically exchangeable ions within the galleries between the layers of the multilayered clay with a preformed latex of cationic (positively charged) elastomer particles. Said positively charged latex elastomer particles may be prepared by free radical emulsion polymerization using: (A) a non-polymerizable cationic surfactant, and / or (B) a polymerizable cationic surfactant. Optionally, an additional cationic charge may be incorporated onto the cationic elastomer latex particles through the use and in the presence of: (C) a polymerizable comonomer bearing a cationic charge, (D) a free radical generating polymerization initiator bearing a cationic charge, and / or (E) a free radical chain transfer agent bearing a cationic charge. Such free radical induced emulsion polymerizations are exclusive of a thermoplastic polymer latex and are exclusive of the presence of an anionic surfactant. Rubber composites can be prepared by blending such nanocomposite with additional elastomer(s), additional reinforcing filler(s) and / or a coupling agent. The invention further relates to the preparation of articles of manufacture, including tires, having at least one component comprised of said nanocomposite or said rubber composite. Such a tire component may be selected from, for example, tire tread and tire innerliner.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Preparation method for 3D Ni-Co bimetallic hydroxide hollow microsphere and application in super capacitor
InactiveCN103680993ASolve the problem that the specific surface is greatly reducedLarge capacityHybrid capacitor electrodesHybrid/EDL manufactureMass transfer resistanceMicrosphere
The invention belongs to the field of chemistry, and provides a preparation method for a 3D Ni-Co bimetallic hydroxide hollow microsphere and application in a super capacitor. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) a SiO2 microsphere is synthesized; 2) a AlOOH sol is prepared; 3) the SiO2 microsphere is added into the AlOOH sol so that a SiO2@ AlOOH microsphere is obtained; 4) the SiO2@ AlOOH microsphere, a alkali source and de-ionized water are mixed, and a nickel and cobalt salt precursor is added so that the 3D Ni-Co bimetallic hydroxide hollow microsphere is prepared; and 5) an electrode sheet is prepared. Compared with methods in the prior art, the obtained 3D Ni-Co bimetallic hydroxide hollow microsphere provides a larger specific surface, smaller mass transfer resistance and more excellent structural stability. Besides, the synthesized 3D Ni-Co bimetallic hydroxide hollow microsphere is applied to electrode material of the super capacitor so that the 3D Ni-Co bimetallic hydroxide hollow microsphere is much better than existing precious metal oxide on aspects of cost and performance.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
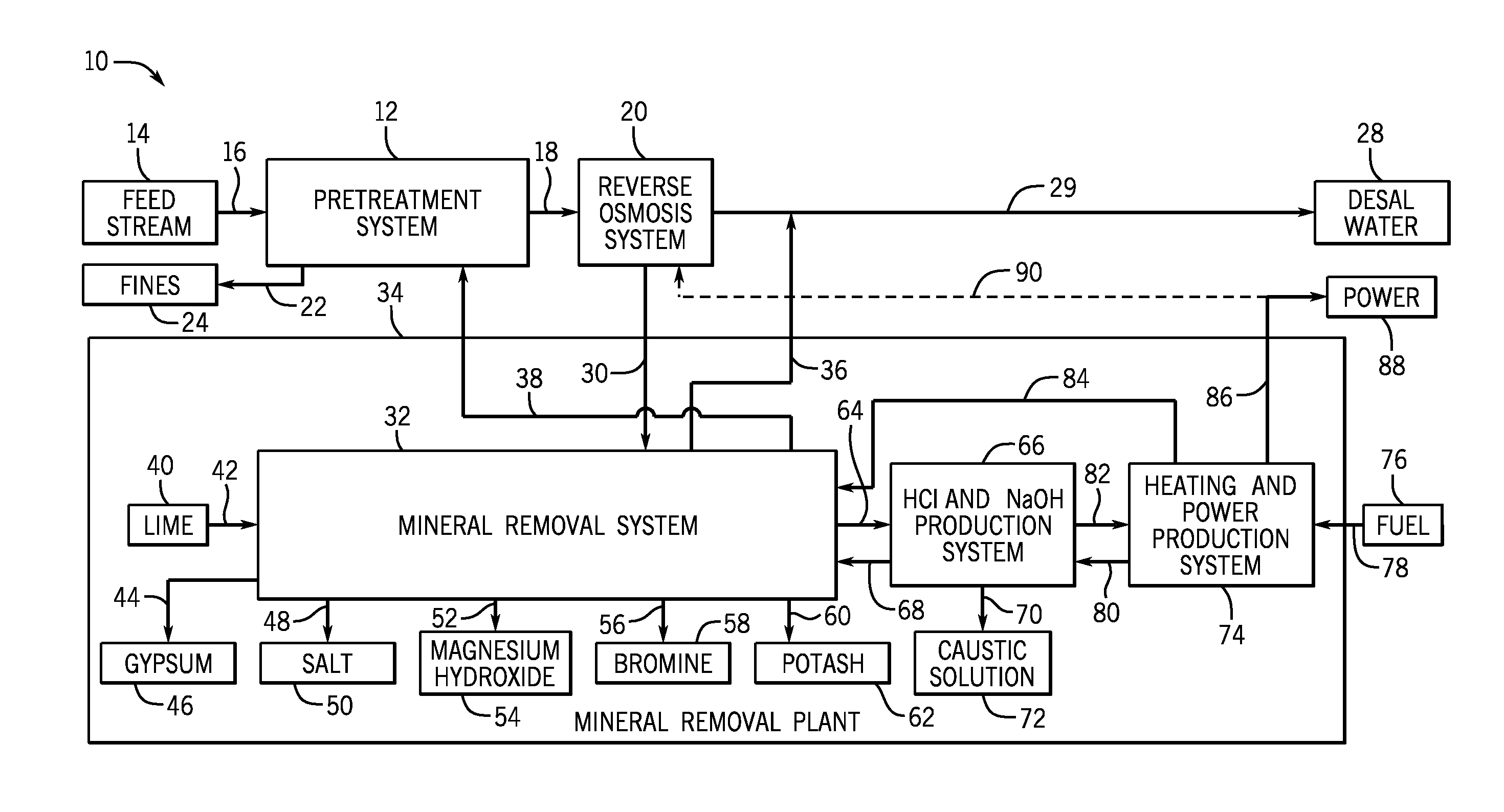
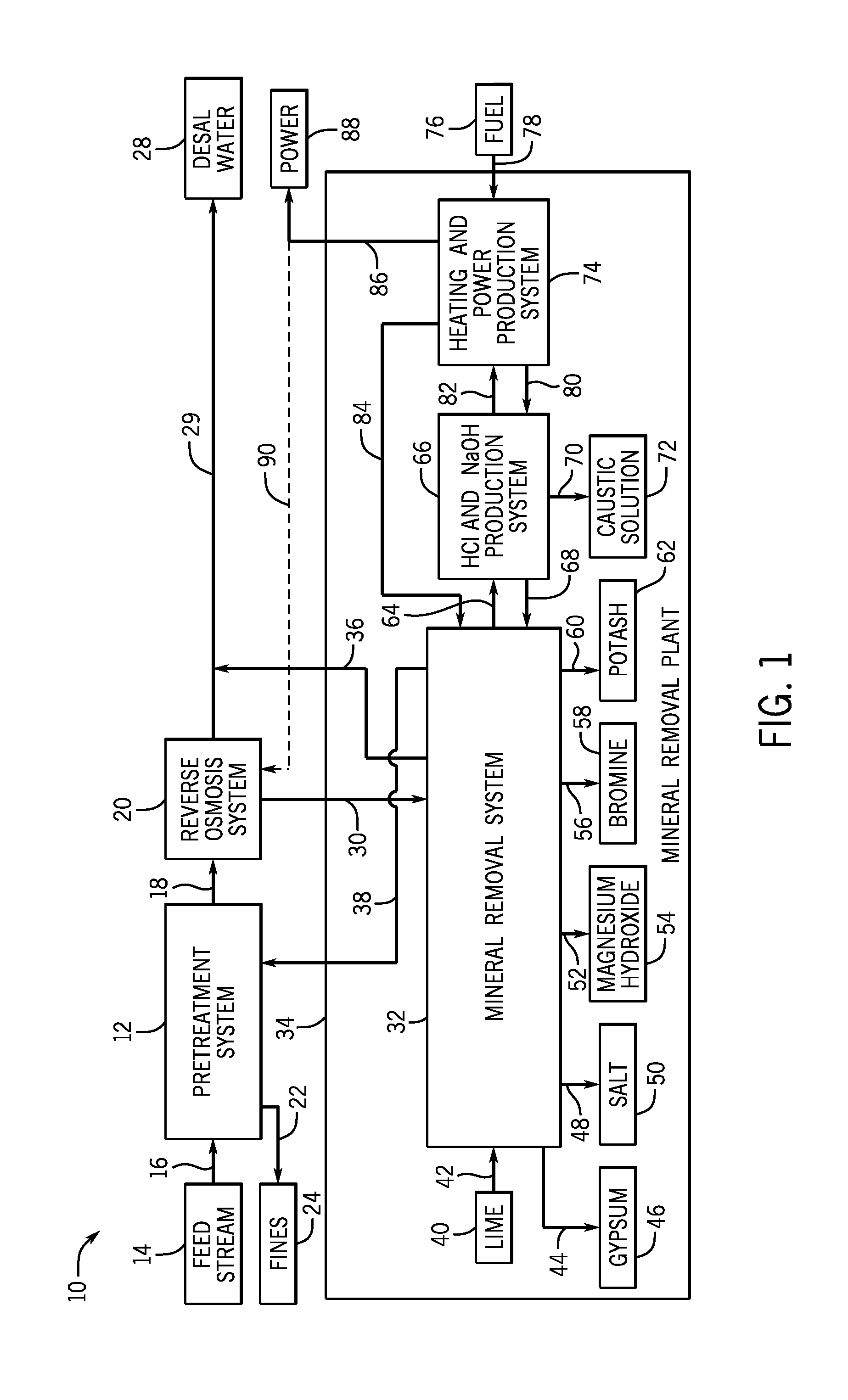
Electrical current generation system
InactiveUS20060257708A1Facilitate ion exchangeFuel cell auxillariesHydrogen/synthetic gas productionHydrogenFuel cells
An electrical generating system consists of a fuel cell, and an oxygen gas delivery. The fuel cell includes and anode channel having an anode gas inlet for receiving a supply of hydrogen gas, a cathode channel having a cathode gas inlet and a cathode gas outlet, and an electrolyte in communication with the anode and cathode channel for facilitating ion exchange between the anode and cathode channel. The oxygen gas delivery system is coupled to the cathode gas inlet and delivers oxygen gas to the cathode channel. The electrical current generating system also includes gas recirculation means couple to the cathode gas outlet for recirculating a portion of cathode exhaust gas exhausted from the cathode gas outlet to the cathode gas inlet.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
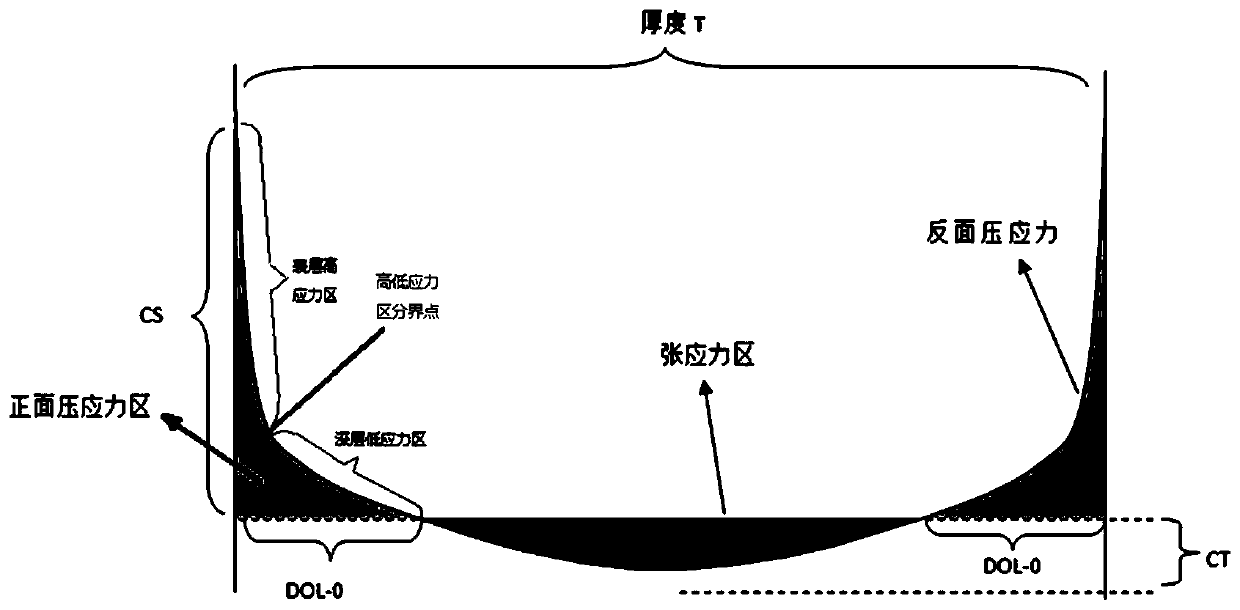
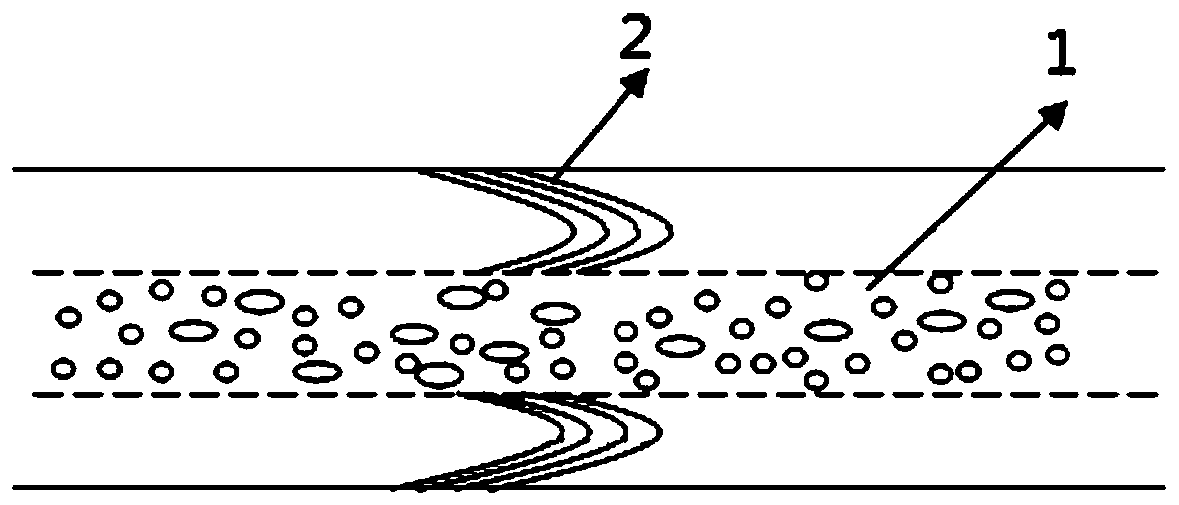
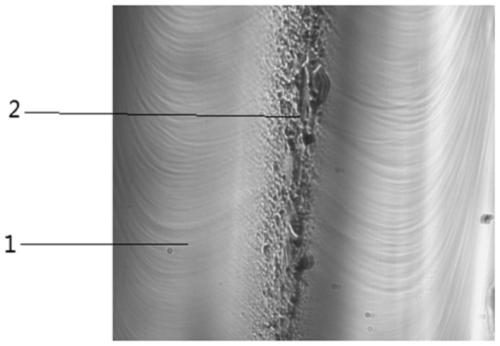
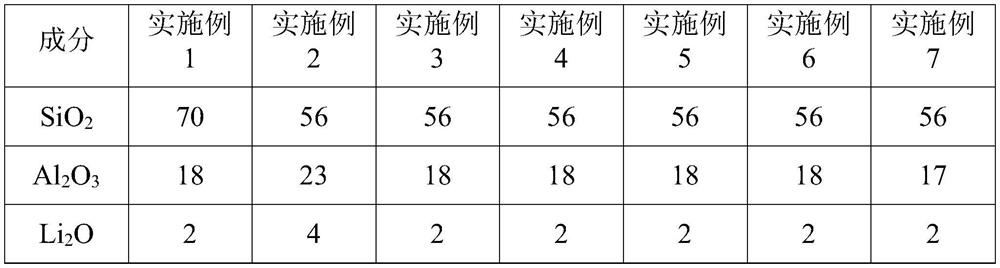
Lithium aluminum silicon glass, lithium aluminum silicon chemically strengthened glass and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses lithium aluminum silicon glass, lithium aluminum silicon chemically strengthened glass and a preparation method and application thereof. The molar content of oxide components contained in the lithium aluminum silicon glass satisfies the following relationship: the SiO2 content is at least 66.5 mol%, and the total amount of an alkali metal oxide usable for ion exchange is not more than 14 mol%; (Na2O+Li2O) / (SiO2+Al2O3) is 0.09-0.22; Na2O / Li2O is 0.4-1.2; MgO / SiO2 is 6%-18%; (Na2O+Li2O+0.3*MgO) / Al2O3 is 0.7-1.4; and 0.5%<P2O5+ZnO+SnO2+K2O+ZrO2+TiO2<7%. The lithium aluminum silicon chemically strengthened glass is formed by chemically strengthening the lithium aluminum silicon glass as basic glass.
Owner:CHONGQING XINJING SPECIAL GLASS CO LTD
Multifunctional porous purifying ceramic granular material and preparation method
ActiveCN103172402ALarge specific surface areaEnvironmental purification performance advantagesCeramicwareSlurryMaterials science
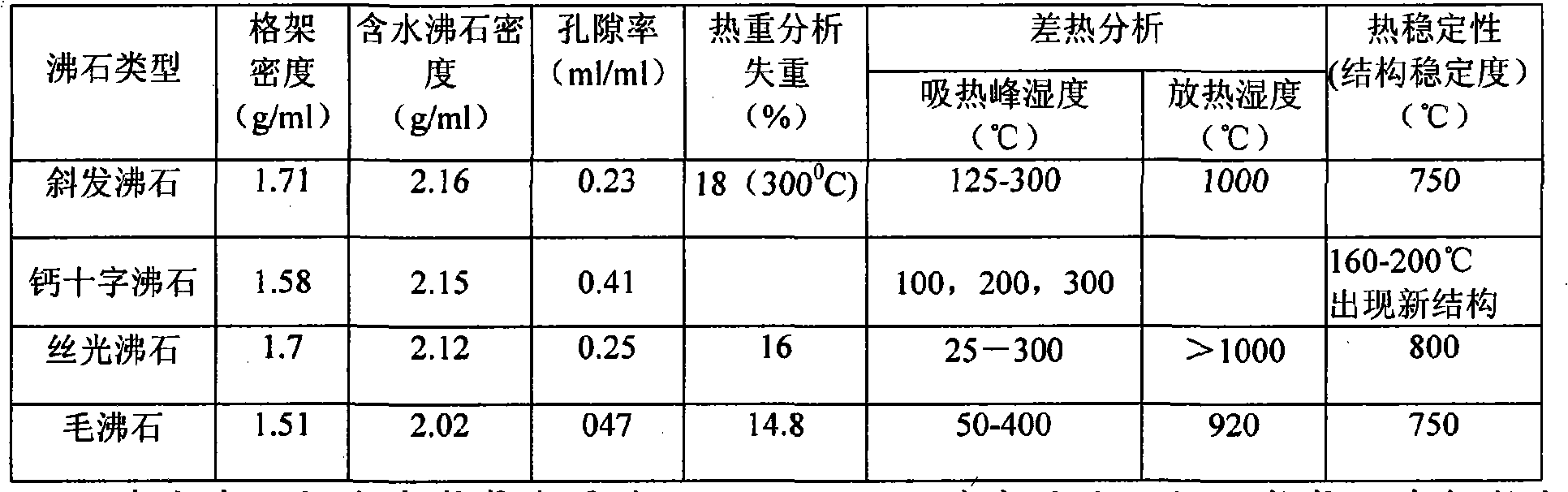
The invention relates to a multifunctional porous purifying ceramic granular material and a preparation method, the granular material comprises the following components by weight: 30-50 parts of endellite, 10-20 parts of zeolite, 20-30 parts of diatomite, 10-20 parts of alumina and 1-3 parts of nano photocatalysis composite material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing the materials, performing ball milling, sieving slurry, forming pore, drying in the shade, calcining at high temperature, dipping and calcining at low temperature. Compared with the prior art, the multifunctional porous purifying ceramic granular material has a three-dimensional structural tunnel with different aperture gradients, and has the advantages of strong adsorptivity, good sterilization and bacteriostasis effects, and cycle usage.
Owner:上海风享环保科技有限公司
Interior protectant/cleaner composition
ActiveUS20070163463A1Facilitate ion exchangeImproves UV protectionFireproof paintsAntifouling/underwater paintsWaxMedicine
The present invention provides a liquid protectant composition composed of a cationic microemulsion of a natural wax (camauba wax) nanometer sized particles and zinc oxide nanometer sized particles in combination with a quaternary siloxane compound. The protectant composition of the present invention cleans, protects preserves and enhances the appearances of leather or vinyl surfaces used for covering items in the home or in vehicles. The product is easy to apply to both smooth and textured surfaces and has a transparent appearance. The product dries quickly and does not leave an oily residue. Utilization of nano technology to select components having nano sized particles provides a uniform deposition of the product leaving a thin film having exceptional protection properties. Unlike conventional protectants, the invention of the instant composition dries quickly and leaves no oily residue behind.
Owner:ENERGIZER GRP LTD
Preparation method of graphene/xylogen-based active carbon
InactiveCN104599861AStable structureImprove conductivityHybrid capacitor electrodesHybrid/EDL manufactureCapacitanceActivated carbon
The invention belongs to the field of chemistry, and provides a preparation method of graphene / xylogen-based active carbon; the method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing xylogen-based active carbon; 2) mixing graphite oxide with active carbon to obtain graphite oxide / xylogen-based active carbon compound; 3) activating the compound by alkali, treating with pyrolysis and reduction, so as to prepare graphene / xylogen-based active carbon composite material; 4) preparing an electrode slice. Comparing to the prior art, the obtained graphene / xylogen-based active carbon provides a larger specific surface, a smaller mass transfer resistance, and a better conductivity. Additionally, applying the synthesized graphene / xylogen-based active carbon to the electrode material of a super capacitor is much better than the existing active carbon material from cost and performance.
Owner:江苏江大环保科技开发有限公司
Nickel-based steam reforming catalyst for biomass tar and preparation and application method of catalyst
ActiveCN103846088ALow priceGuaranteed stabilityHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsSteam reformingCatalytic reforming
The invention belongs to the technical field of the energy and chemical industry and particularly relates to a nickel-based steam reforming catalyst for biomass tar and a preparation and application method of the catalyst. The catalyst adopts low-cost brown coal as a carrier and comprises the following components by weight percent: 23-25% of Ni, 64.26-66.26% of C, 6.06% of O and 6% of impurity elements. The catalyst is prepared by adopting the cooperation of an ion exchange method and an impregnation method. The catalyst has the good activity and economy, the brown coal is low in cost and large in specific surface area, after being washed by sodium hydroxide, micropores of the brown coal become mesopores and macropores, so that macromolecular compounds of the tar are relatively easy to pass; simultaneously, a relatively large quantity of new through holes are also formed in the brown coal; in the process of catalytic reformation of the tar, a relatively large quantity of effective pore channels are formed, so that the efficiency for reforming the biomass tar is relatively high; the carbon deposited amount of the catalyst and the carbon consumption amount of catalyst carrier carbon can form dynamic balance, so that the service life of the catalyst is prolonged and the catalyst is not easily inactivated.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Formulation and method for improved ion exchange in zeolites and related aluminosilicates using polymer solutions
InactiveUS20100047161A1UtilityIon exchange efficiencyGas treatmentAluminium compoundsCounterionIon exchange
Among other things, this disclosure provides a method for exchanging cations in an aluminosilicate. The method includes combining, in an exchange solvent and under ion exchange conditions, an ion-exchangeable aluminosilicate having a first cation associated therewith as a counter ion and a second cation source, to provide a mixture that includes the ion-exchanged aluminosilicate which includes the second cation associated therewith as a counter ion. Suitable exchange solvents include polyalkylene oxide glycols, polyalkylene oxide glycol monoethers, polyalkylene oxide glycol diethers, or any combination thereof.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Long active organic compounded fertilizer and production method
InactiveCN101289348ASolve land occupationSolve secondary pollutionAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserClimate change adaptationResource utilizationPhosphate
The invention relates to a long-acting organic compound fertilizer and a manufacturing method thereof, which belongs to the manure field. By taking sludge in a municipal sewage treatment plant as main raw material, adding zeolite, urea, ammonium diacid phosphate, potassium chloride and sodium silicate, then being stirred and mixed with the urea, the ammonium diacid phosphate and the potassium chloride after sludge compression, zeolite drying, stirring and mixing, natural air drying or kiln drying and grinding, and spraying the sodium silicate so as to granulate, dry, disinfect and sterilize the mixture, a product is then produced. The long-acting organic compound fertilizer and the manufacturing method solve the problem of land occupation of the sludge in the sewage treatment plant and secondary pollution, and realize the harmless disposal and resource utilization of the sludge. The fertilizer ensures that crops has good growth power, high plants, more grains, stronger lodging resistance and obvious stimulation effect and ensures that the quality of agricultural products is improved. Furthermore, the fertilizer can increase the ability of reserving nutrients in soil, can modify acid or saline alkali sandy soil, can improve soil aggregate structure, can keep fertilizer efficiency and resist crop diseases.
Owner:屈智和 +1
Highly-hydrophilic adsorbent as well as preparation and application to absorption of rubidium ions or lithium ions
ActiveCN108435143AFix instabilityGood quid pro quoOther chemical processesWater contaminantsRubidiumDesorption
The invention discloses a highly-hydrophilic adsorbent as well as preparation and application to absorption of rubidium ions or lithium ions. The preparation method of the highly-hydrophilic adsorbentis characterized in that a lithium ion sieve or a rubidium ion exchanger is added in an aqueous solution of a hydrophilic polymer, is fully stirred and mixed and drops in a phase conversion agent ina form of droplets; and after a primary ecological adsorbent in a form of a sphere is formed by solution phase transformation, the chemical cross-linking reaction is performed in an oil phase solutionof diisocyanate to obtain the highly-hydrophilic adsorbent. The adsorbent disclosed by the invention has the benefits that the ion exchange conditions of a lithium ion and rubidium ion adsorbent areensured due to high hydrophilic capacity, and the problem of solution loss of the adsorbent in the repeated use is solved; the preparation method is simple, and the preparation and the regulation aremild; the adsorbent prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention is higher in absorption and desorption speed.
Owner:西安金藏膜环保科技有限公司
Process for producing fiber and method for producing catalyst layer
InactiveUS20100096769A1Low costFacilitate ion exchangeElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureCell electrodesFiberPolymer science
To provide a process whereby an ultrafine fiber of a fluorinated ion exchange resin can be produced easily at low cost, and a method whereby a catalyst layer having a high gas diffusion property can be produced easily at low cost.A process for producing a fiber by spinning a spinning solution containing a fluorinated ion exchange resin and a solvent by a dry spinning method, or producing an electrically conductive composite fiber by spinning n types (where n is an integer of at least 2) of spinning solutions, of which at least one type contains a fluorinated ion exchange resin and a solvent, and at least one type contains an electrically conductive material and a solvent, simultaneously by a dry spinning method, wherein the spinning solution which is being spun by the dry spinning method, is stretched by a gas stream; and a method for producing a catalyst layer, which comprises accumulating the fiber produced by such a process to form a non-woven fabric thereby to obtain a catalyst layer having the non-woven fabric.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
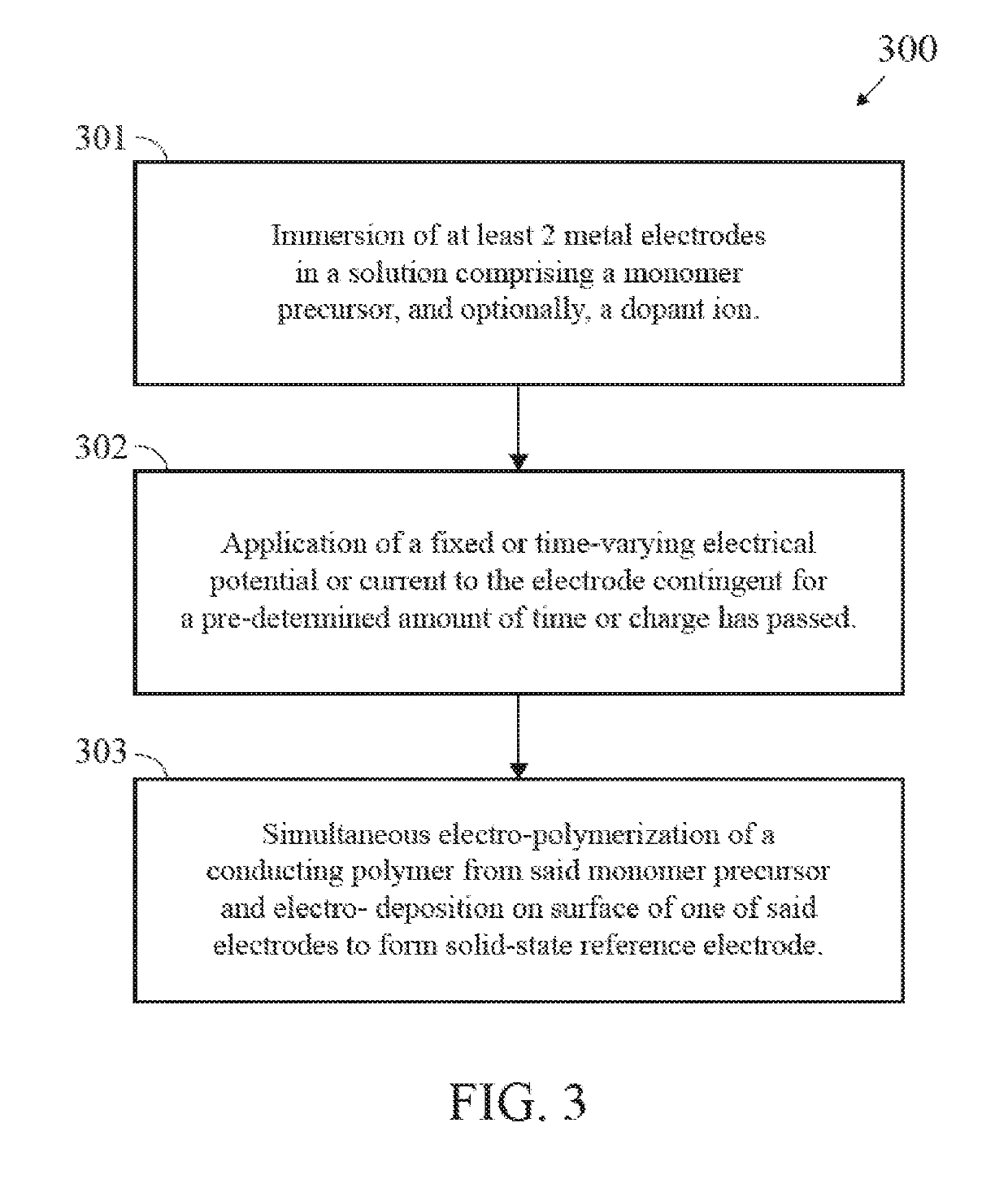
Electro-Deposited Conducting Polymers For The Realization Of Solid-State Reference Electrodes For Use In Intracutaneous And Subcutaneous Analyte-Selective Sensors
PendingUS20190309433A1Stable and controlled electrochemical reactionStability can be compromisedCellsAnodisationElectricityMetallic electrode
A method (300) for constructing a solid-state reference electrode for use in an analyte-selective intracutaneously- or subcutaneously-implanted electrochemical cell is disclosed herein. The method (300) includes immersing a metallic electrode in a solution comprising a monomer precursor. The method (300) also includes applying a fixed or time-varying electrical potential or current to the metallic electrode, thereby serving to simultaneously electro-polymerize the monomer precursor and electro-deposit a conducting polymer, synthesized from the electro-polymerization of the monomer precursor, onto the said metallic electrode surface.
Owner:BIOLINQ INC
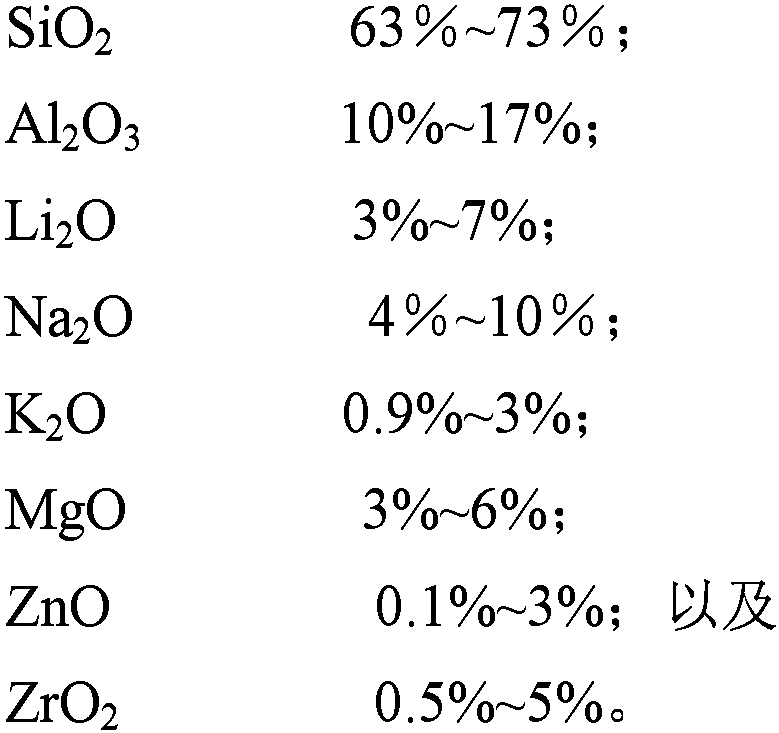
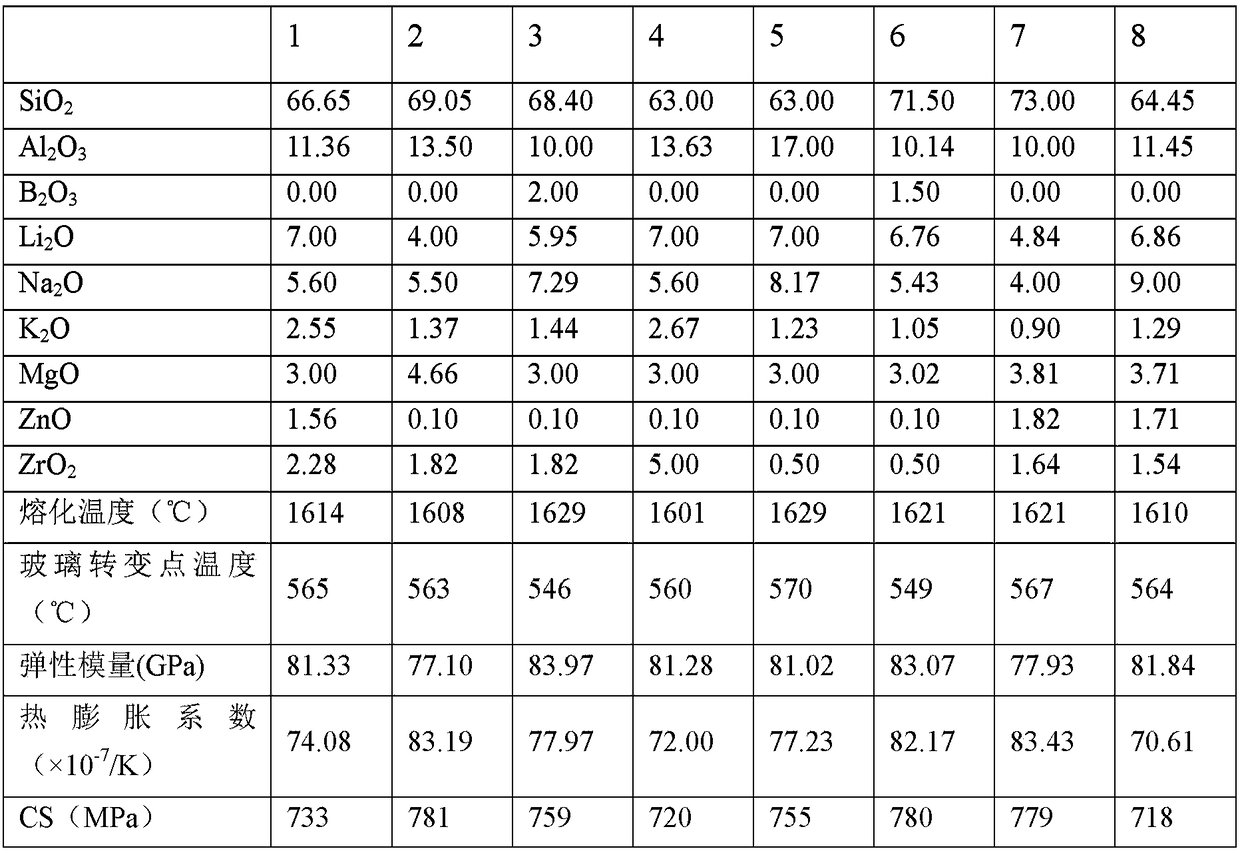
Aluminosilicate glass, preparation method thereof, electronic display screen protection glass
InactiveCN109293234AImprove thermal shock resistanceGood for hot bendingMelting temperatureAluminosilicate
The invention discloses an aluminosilicate glass, an aluminosilicate reinforced glass, a production method of aluminosilicate reinforced glass, and an electronic display screen protection glass. The aluminosilicate glass based on oxides includes, by mass, 63-73% of SiO2, 10-17% of Al2O3, 3-7% of Li2O, 4-10% of Na2O, 0.9-3% of K2O, 3-6% of MgO, 0.1-3% of ZnO and 0.5-5% of ZrO2. Li2O, ZnO and otherlow-melting point raw materials are adopted to reduce the melting temperature of ZrO2-containing glass, and proportions of other oxides are adjusted to make the glass have a high hardness and a good resistance to crack propagation.
Owner:CSG HOLDING +1
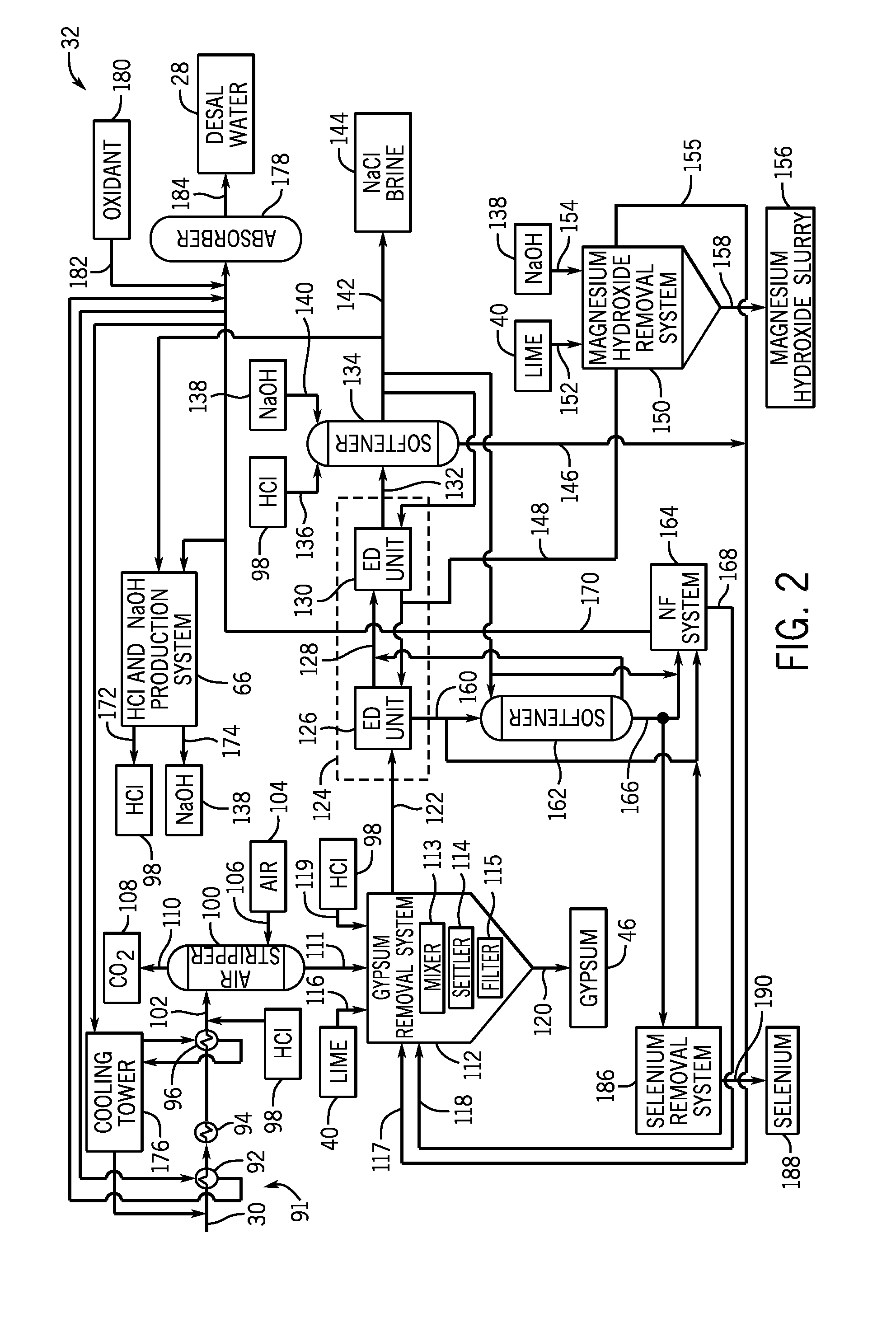
System for rinsing electrodialysis electrodes
ActiveUS20140042029A1Facilitate ion exchangeMaintain conductivitySludge treatmentReverse osmosisEngineeringElectrodialysis
A system for rinsing electrodialysis electrodes includes an anode input coupled to an anode of an electrodialysis (ED) system for receiving a first fluid from the anode. The first fluid is for removing ions from the anode. The system also includes an anode output coupled to the anode of the ED system for providing the first fluid to the anode. The system includes a cathode input coupled to a cathode of the ED system for receiving a second fluid from the cathode. The second fluid is for removing ions from the cathode of the ED system. The system also includes a cathode output coupled to the cathode of the ED system for providing the second fluid to the cathode. The system includes an air stripper for receiving the first and / or second fluid, and for removing oxygen and / or a chlorine gas from the first and / or second fluid.
Owner:ENVIRO WATER MINERALS COMPANY
Anti-blue-light high-strength lithium-aluminum-silicon cover plate glass and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN113121109AIncrease intrinsic strengthFacilitate ion exchangeGlass shaping apparatusGlass tempering apparatusPhysical chemistrySilicon
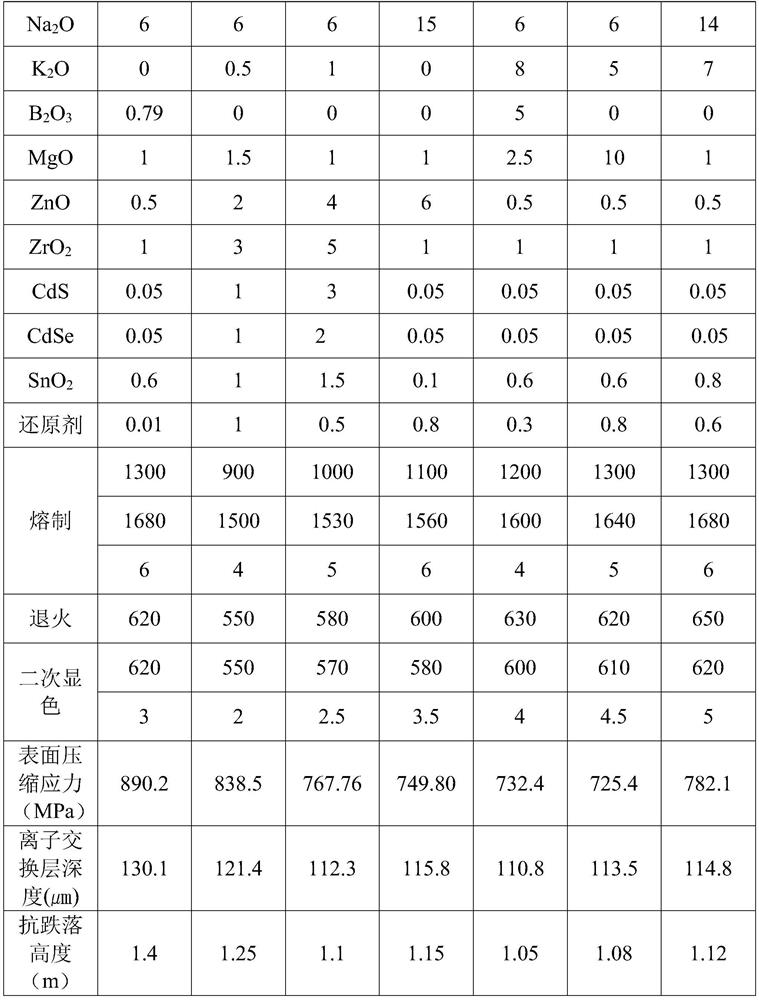
The invention relates to the technical field of cover plate glass, in particular to anti-blue-light high-strength lithium-aluminum-silicon cover plate glass which is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 56%-70% of SiO2, 18%-23% of Al2O3, 2%-4% of Li2O, 6%-15% of Na2O, 1%-10% of MgO, 0.5%-6% of ZnO, 1%-5% of ZrO2, 0.05%-3% of CdS, 0.05%-2% of CdSe, 0.6%-1.5% of SnO2, 0-8% of K2O, 0-5% of B2O3 and 0.01%-1% of a reducing agent. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the anti-blue-light high-strength lithium-aluminum-silicon glass, the anti-blue-light high-strength lithium-aluminum-silicon glass is prepared through mixing, founding, annealing, secondary developing treatment and then composite chemical strengthening, and the anti-blue-light high-strength lithium-aluminum-silicon glass has an anti-blue-light effect, is suitable for being used as a screen protection material of electronic equipment such as a mobile phone and can effectively prevent the surface of a panel display product from being impacted or scratched and damaged.
Owner:CAIHONG GRP SHAOYANG SPECIAL GLASS CO LTD
Method of preparing hierarchical pore ceramsite from red mud and coal ash
PendingCN109942274ALarge specific surface areaImprove removal efficiencyCeramic materials productionCeramicwareRed mudIon exchange
The invention discloses a method of preparing hierarchical pore ceramsite from red mud and coal ash and belongs to the technical field of solid waste reclamation and environment. The method comprisesthe following steps: uniformly mixing the coal ash, the red mud and agriculture and forestry waste residues, and adding water and uniformly stirring the mixture to obtain mixed mud B; granulating themixed mud B to obtain a ceramsite blank sample C; putting the ceramsite blank sample C at 90-120 DEG C to be treated for 60-180 min and then putting the ceramsite blank sample at 350-450 DEG C to be treated for 30-60 min at a constant temperature to obtain pre-ceramsite; putting the pre-ceramsite at 950-1150 DEG C to be roasted for 20-70 min and then carrying out furnace cooling to obtain hierarchical pore ceramsite D; and adding the hierarchical pore ceramsite D into an alkaline solution, then adding sodium metaaluminate to be uniformly mixed to obtain a ceramsite treatment system, heating the same at a uniform speed till the temperature of the ceramsite treatment system is 80-140 DEG C and treating the same for 6-24 hours, extracting the ceramsite, washing the same to be neutral and drying the ceramsite to obtain the hierarchical pore ceramsite. The hierarchical pore ceramsite has two duct structures: macropores and micropores and has good water absorption, water retaining property and ion exchange function.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Soil conditioner used for alkaline earth
ActiveCN107163950ALower pHFacilitate ion exchangeAgriculture tools and machinesOther chemical processesIon exchangeGypsum
The invention discloses a soil conditioner used for alkaline earth. The soil conditioner used for alkaline earth is prepared from, by weight, 16 to 90 parts of desulfurized gypsum, 1 to 20 parts of ferrous sulphate, and 1 part of citric acid. The soil conditioner used for alkaline earth is capable of reducing pH value of alkaline earth, promoting ion exchange, improving soil structure, improving soil permeability, and improving soil fertility; action speed and efficiency of the soil conditioner in improving alkaline earth are improved; cost is low; the soil conditioner is safe for the ecological environment; large area application can be realized; the dosage of desulfurized gypsum can be reduced, and the dosage of desulfurized gypsum can be reduced by 40% at most; and improvement effect is improved.
Owner:华清农业开发有限公司
Preparation of core type greening brick
InactiveCN101497520AStrong water absorptionImprove water retentionClimate change adaptationCeramic shaping apparatusBrickSodium Bentonite
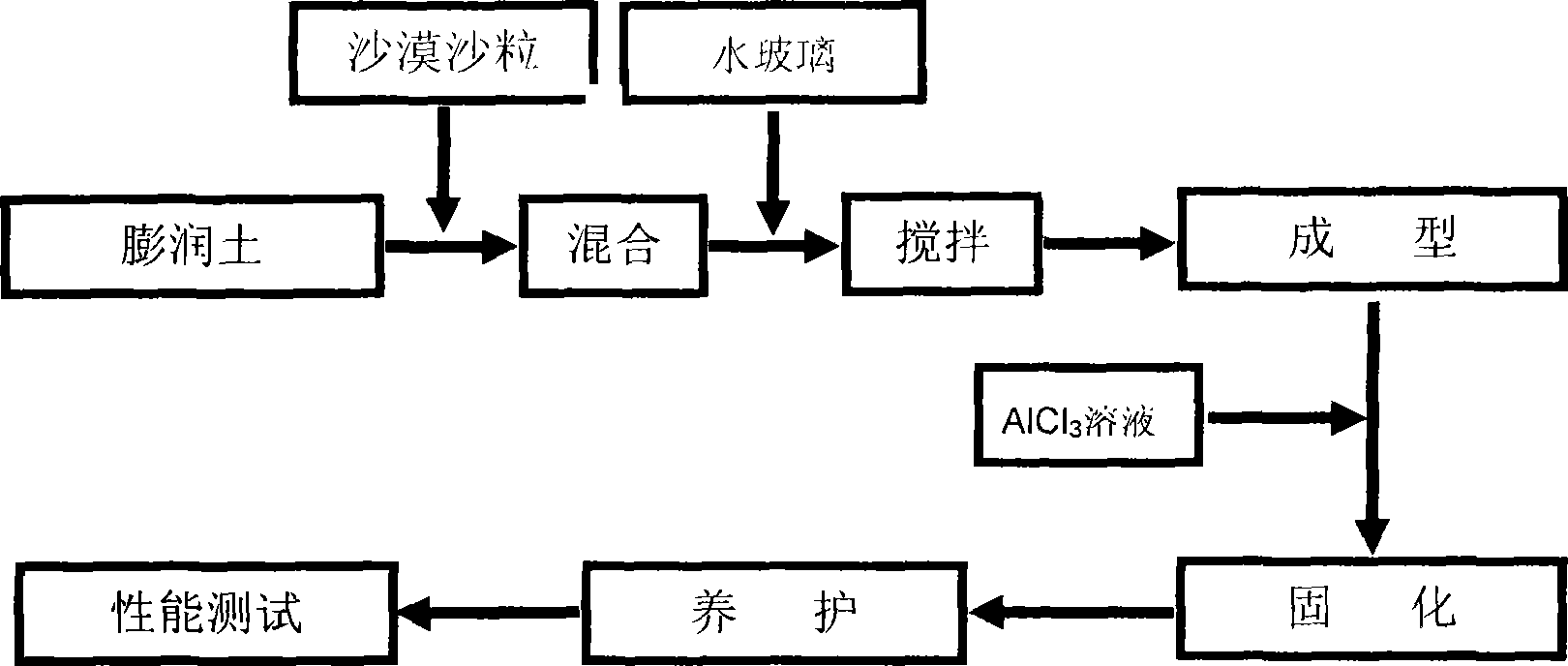
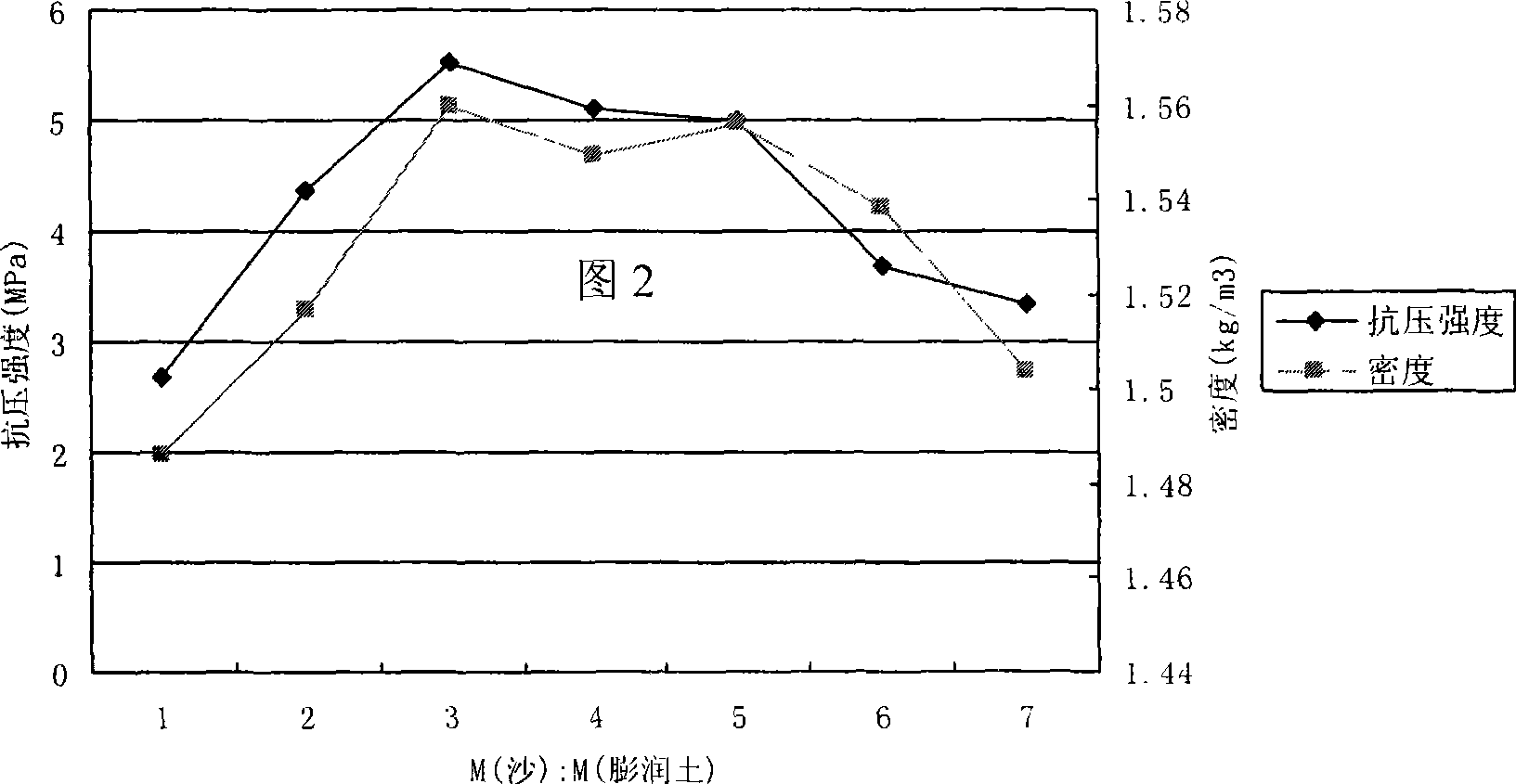
The invention discloses a method for preparing a green core brick with the advantages of simplicity, low cost and short curing time. The green core brick consists of 0.5 to 5 portions of gelling agent, 2 to 10 portions of curing agent, 3 to 45 portions of desert sand grains, and 1 to 15 portions of bentonite, wherein the gelling agent is water glass, and the curing agent is AlCl3 solution. The penetration depth and the cementing strength of the green core brick are set according to the grain size of the sand grains, and simultaneously, a little amount of the bentonite is added in the formulation to obtain a chemical sand fixing brick with good moisture and fertility preserving properties. A curing layer of the green core brick is suitable for Tibet plateau with large wind sand and more drift sand in particular.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Co/hydroxyapatite catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109453797AReduce contentGood dispersionNitrous oxide captureGas treatmentFiltrationIon exchange
The invention discloses a Co / hydroxyapatite catalyst as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The catalyst takes hydroxyapatite as a carrier and cobalt as an active component, whereinthe mole ratio of Ca to P is 1.35-1.67, and cobalt accounts for 0.5-2.6% of the total mass of the catalyst. (NH4)2HPO4 serves as a phosphorus source, Ca(NO3)2.4H2O serves as a calcium source, ammoniumhydroxide is added to condition the pH value of the system after the phosphorus source and the calcium source are dissolved and mixed uniformly, the mixture is treated with operations such as filtration, drying and calcination, and the carrier is prepared; and cobalt salt is dissolved in a PBS (phosphate buffer saline) dispersant solution and subjected to ultrasonic treatment, then the carrier powder is added, ion exchange is conducted at the room temperature, the product is treated with steps such as filtration, drying and calcination, and the catalyst is prepared. The preparation technologyof the catalyst is simple, the raw materials sources are wide, the cost is low, and the catalyst is harmless to the human body and the environment. The catalyst can catalyze and decompose N2O withina wide temperature range, and has the excellent oxygen resistant, waterproof and NO resistant properties.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Method for producing decolorizer of edible oil
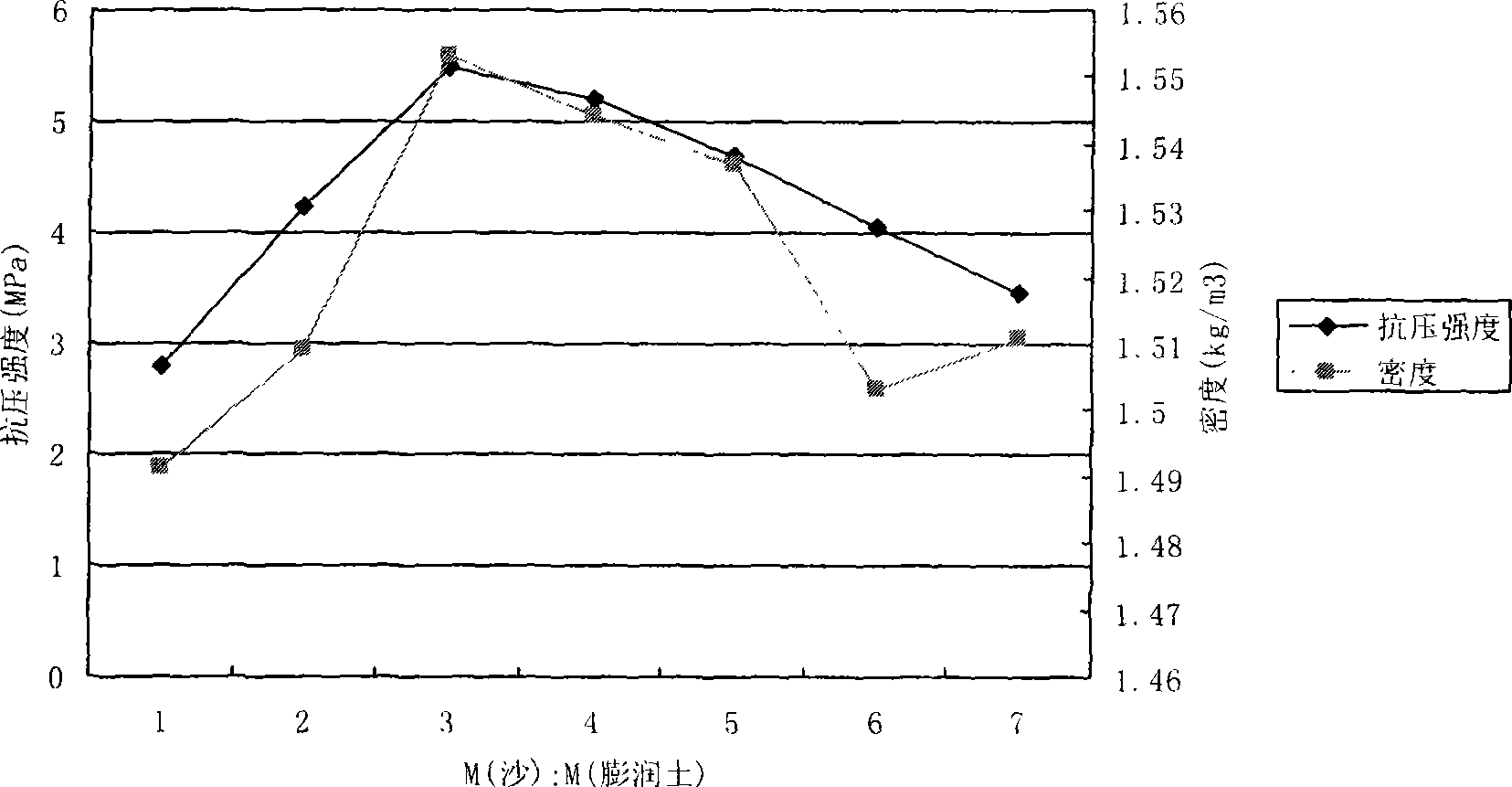
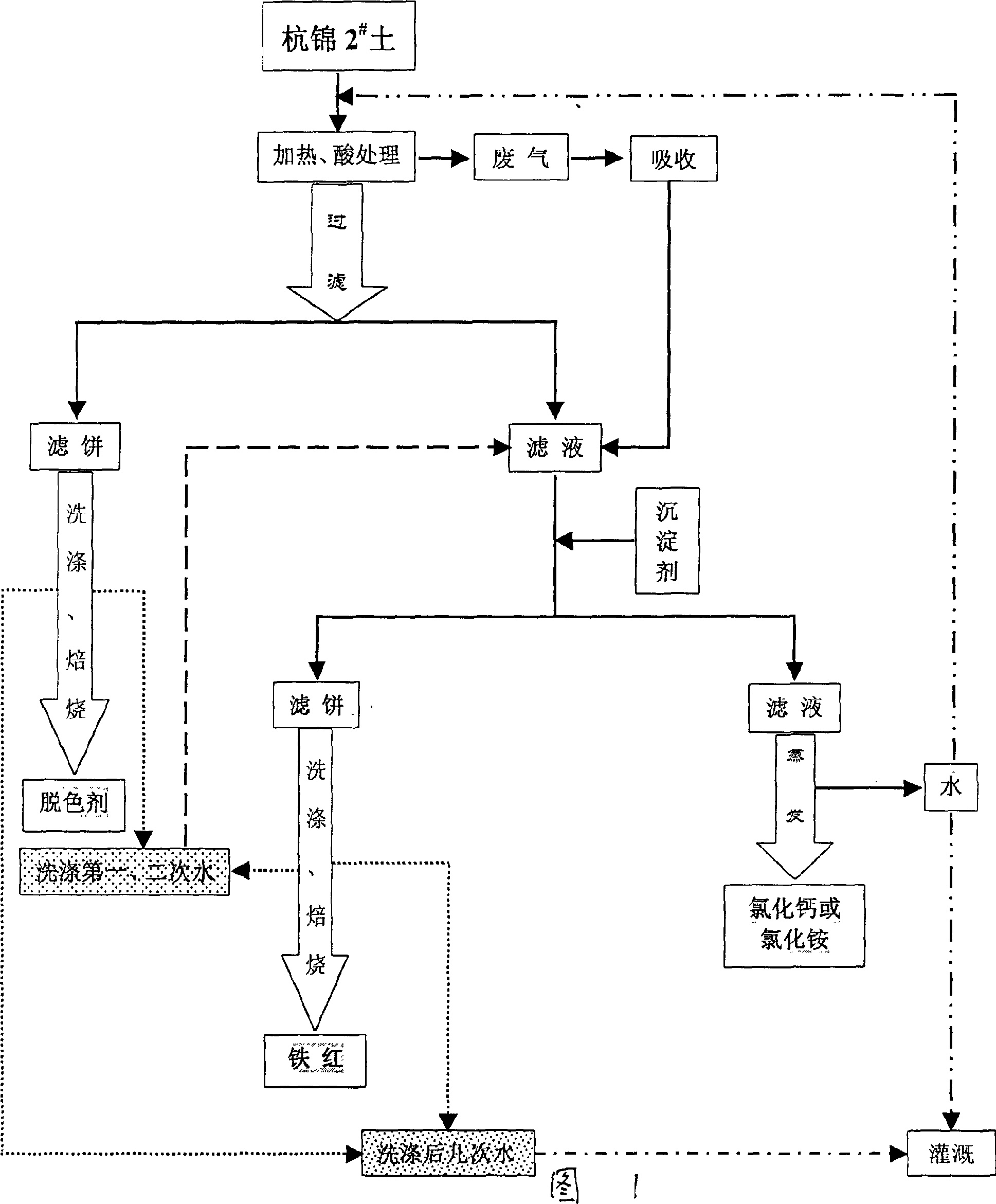
The present invention discloses a production method of decolouring agent for edible oil. Said method is characterized by that it adopts the following steps: pulverizing Hangjin No.2 soil, adding hydrochloric acid and slightly boiling, filtering to obtain filter cake, collecting filtrate, washing filter cake with water to neutrality, natural drying cleaned filter care, roasting in high-temp. furnace, cooling and pulverizing to above 250 meshes so as to obtain the invented decolouring agent for edible oil.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Preparation method of positive electrode post of lithium battery
InactiveCN101567435AImprove discharge capacityImprove performanceCell component detailsElectricityIon exchange
The invention relates to a preparation method of a positive electrode post of a lithium battery, which comprises: step (1) mixing and stirring solid raw materials and liquid materials according to a certain ratio to prepare the raw material of a positive electrode, wherein the solid raw material is powder; step (2) preparing the raw material of the positive electrode into granules, wherein the diameter of the granules is 1 mm to 3 mm; step (3) firing the granules; and step (4) molding and forming the product. The method adopts granulation technique to process the raw material of the positive electrode, and then molds the granules for formation to prepare the positive electrode post of the lithium battery. The method can enlarge and increase the space inside the positive electrode post, thus the products inside the lithium battery do not block the space inside the positive electrode post easily. The method is more beneficial for electrolyte absorption, ion exchange and utilization rate of the positive electrode of the lithium battery, and guarantees the electricity conduction effect of the positive electrode of the lithium battery. Therefore, with the adoption of the positive electrode post, prepared by the method, of the lithium battery, the discharging capacity and the overall performance of the lithium battery can be effectively increased.
Owner:武汉中原长江科技发展有限公司
Method for treating nuclear power plant radioactive waste liquid based on birnessite in-situ reaction
ActiveCN105355250AEfficient removalReduce volumeRadioactive decontaminationLiquid wasteRadioactive waste
The invention relates to a method for treating nuclear power plant radioactive waste liquid based on the birnessite in-situ reaction. The method comprises following steps: (1) adding potassium permanganate into the nuclear power plant waste liquid containing radioactive elements and uniformly mixing the liquid; (2) adding manganous salt into the liquid on the basis that the molar ratio of manganous ions (Mn2+) in the potassium permanganate to manganous ions (Mn2+) in the manganous salt is 3:2, and uniformly mixing the liquid to obtain the mixed solution; (3) adding an alkaline solution into the mixed solution drop by drop so as to adjust the pH of the mixed solution to be 8-13, enabling the potassium permanganate to react with the manganous salt to generate birnessite MnO2, then adding magnetic Fe3O4 powder into the solution, and stirring the solution at a constant temperature of 20-80 DEG C for 15-300 minutes; and (4) allowing the solution to stand, performing magnetic separation and removing the precipitate, thereby completing the purification treatment of the nuclear power plant radioactive waste liquid. Compared with the prior art, the method is advantageous in that the steps are simple, conditions are easy to control, the method is economical and practical, the radioactive ion removing efficiency is high, the using range of the method is wide, and no secondary pollution is formed.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Synthetic method of sepiolite/nano TiO2 composite material
InactiveCN103521206ALow priceLarge specific surface areaPhysical/chemical process catalystsOther chemical processesIn situ polymerizationNano tio2
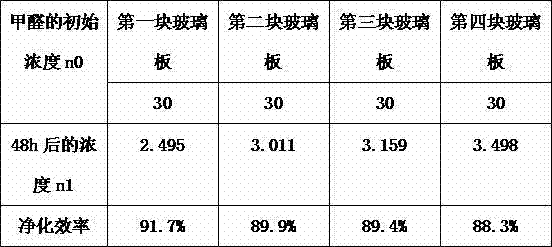
The invention discloses a synthetic method of a sepiolite / nano TiO2 composite material. According to the method, sepiolite and tetrabutyl titanate are taken as raw materials, and the sepiolite / nano TiO2 composite material is synthesized with an in-situ polymerization method. The method comprises the steps as follows: 1), the sepiolite, the tetrabutyl titanate and ethyl alcohol are mixed, stirred, dissolved and subjected to ultrasonic dispersion; 2), the temperature is raised gradually until the ethyl alcohol is volatilized thoroughly, hydrochloric acid and water are added, heating is performed continuously, and the water is volatilized, so that a dried solid is obtained; and 3), the dried solid is washed for a plurality of times and then heated and dried, a dried component is obtained, then the dried component is calcined, and powder, namely, the sepiolite / nano TiO2 composite material, is obtained. With the adoption of the method, the composite material which has a good formaldehyde-removing function can be prepared.
Owner:四川嘉宝莉涂料有限公司
Composition substrate
InactiveCN103626554AFacilitate ion exchangeImprove adsorption capacityFertilizer mixturesIon exchangeAdsorption effect
The invention discloses a composition substrate. The composition substrate comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 100 to 500 parts of cattle dung, 500 to 1000 parts of corn straw, 50 to 100 parts of zeolite powder, 100 to 500 parts of grass carbon and 10 to 200 parts of urea. The cattle dung which is an organic fertilizer and the grass carbon which is an organic matter are fermented, and then the urea is added, so that rich nutrient elements can be provided; the zeolite powder, which contains major elements and trace elements required by the growth of sprouts, is included in the composition, and meanwhile, the zeolite powder has excellent ion exchange and adsorption effects, is good in stability, biotoxicity resistance, oxidation resistance and the like, and has the benefits of being capable of absorbing heavy metal ions. The composition substrate is used for both seedling culture and cultivation of vegetables in greenhouses, is not harmful to the soil; the organic matter is used instead of a chemical fertilizer, so that a crop is hardly influenced.
Owner:李春娣
Desulfation method for scr catalyst
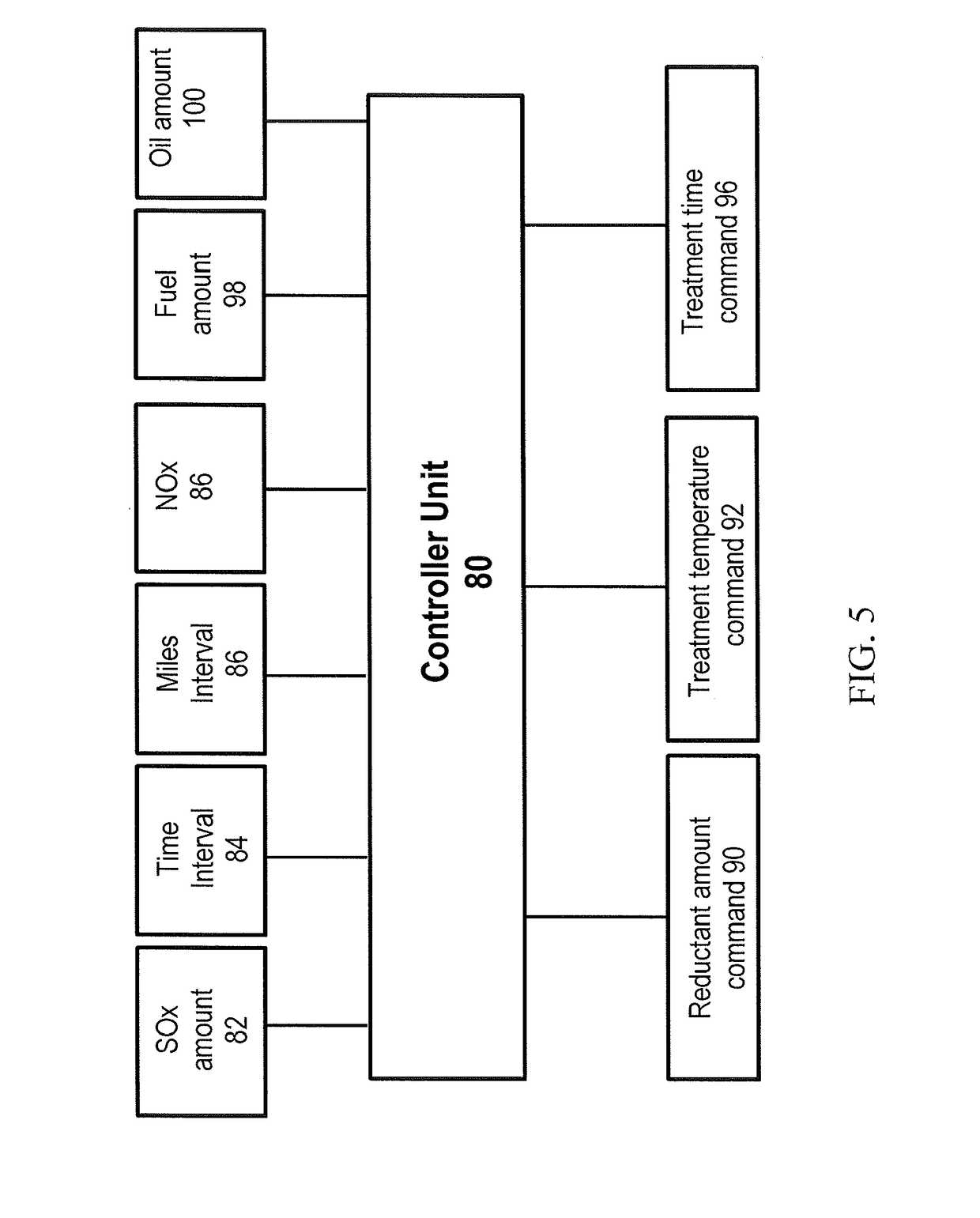
ActiveUS20190083967A1Increase temperatureNOx conversion activityGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesSulfurControl system
The present invention provides methods for low temperature desulfating sulfur-poisoned SCR catalysts, and emission control systems adapted to apply such desulfating methods, in order to regenerate catalytic NOx conversion activity. The methods are adapted for treating an SCR catalyst to desorb sulfur from the surface of the SCR catalyst and increase NOx conversion activity of the SCR catalyst, the treating step including treating the SCR catalyst with a gaseous stream comprising a reductant for a first treatment time period and at a first treatment temperature, wherein the first treatment temperature is about 350° C. or less, followed by a second treatment time period and a second treatment temperature higher than the first treatment temperature, wherein the molar ratio of reductant to NOx during the treating step is about 1.05:1 or higher.
Owner:BASF CORP
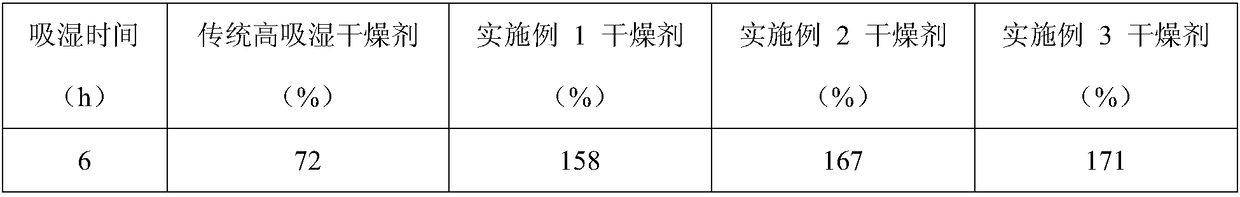
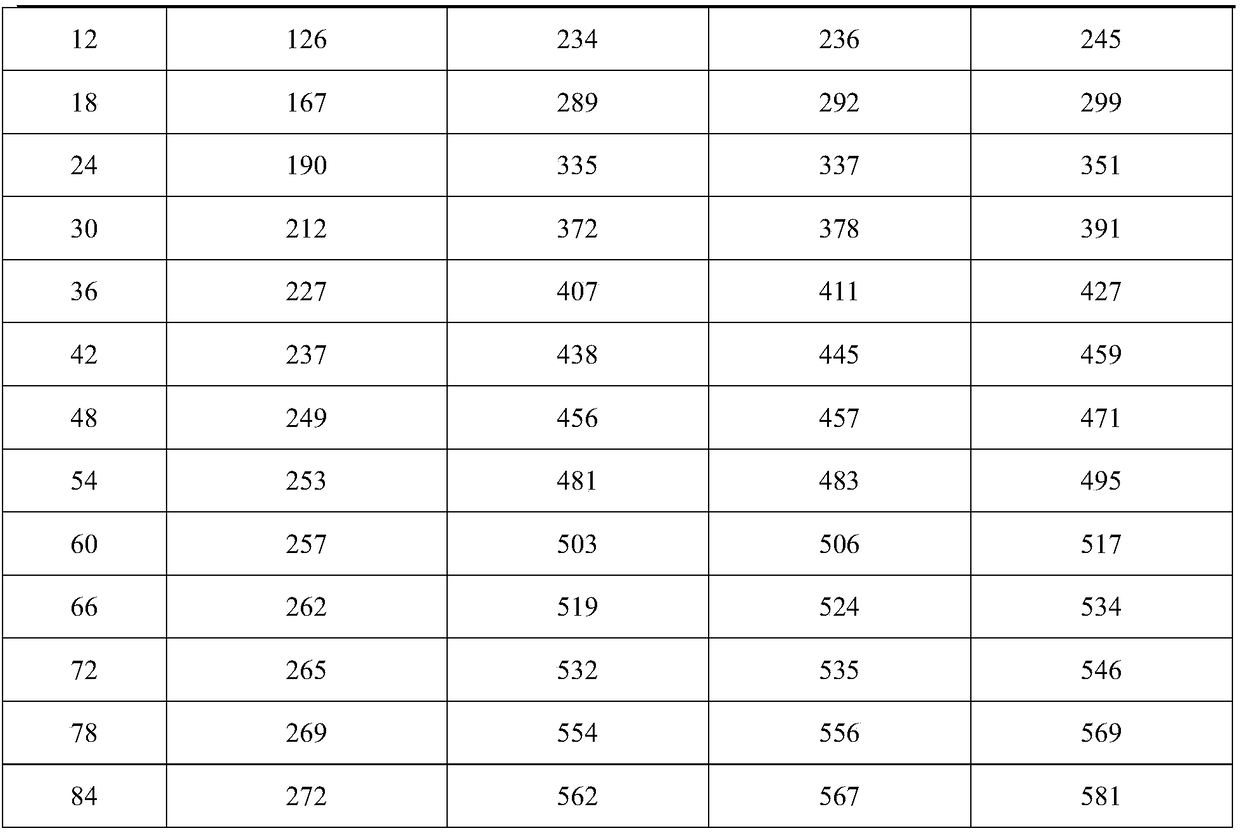
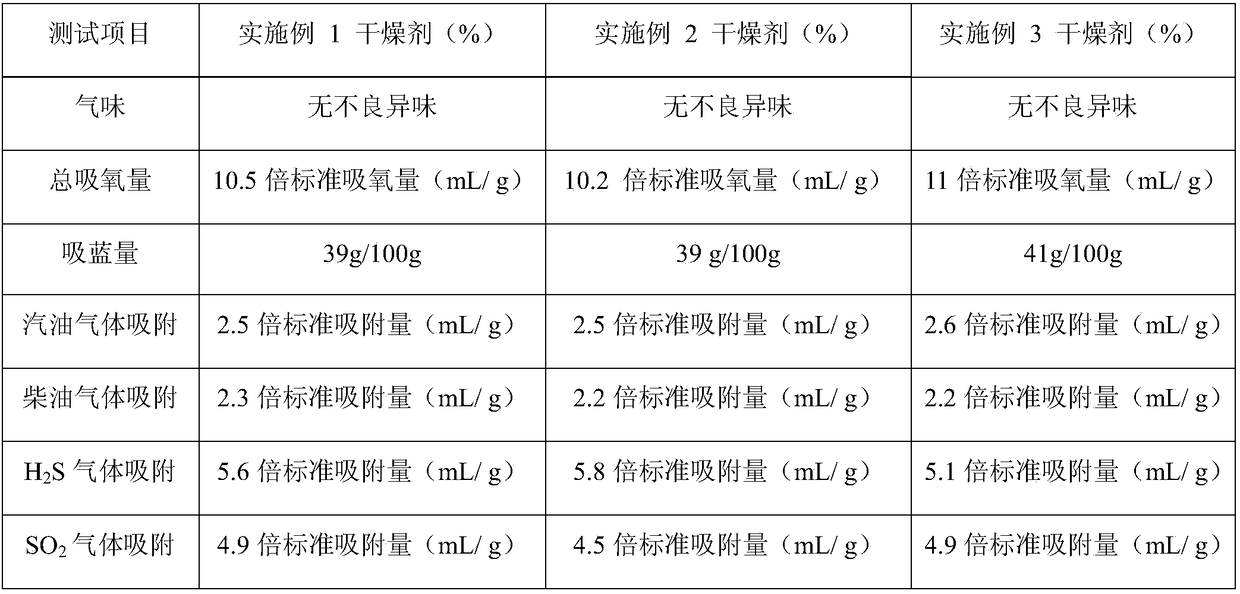
Military mildew-proof and anti-oxidation high moisture absorption desiccant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108927115AImprove water locking abilityInhibition of spit phenomenonOther chemical processesDispersed particle separationMicrosphereMoisture absorption
The invention discloses a military mildew-proof and anti-oxidation high moisture absorption desiccant, which comprises the following components by weight: 20-30 parts of montmorillonite; 20-30 parts of attapulgite; 5-10 parts of microsphere silica gel; 3-5 parts of lemon peel powder; 0.5-1 part of chitosan; 5-8 parts of pomelo peel powder; 10-15 parts of calcium chloride; and 5-8 parts of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose. The desiccant provided by the invention has the characteristics of fast drying speed, good moisture absorption effect, strong moisture absorption capacity and difficult re-damping, excellent oxidation resistance and mildew-proof and bacteriostatic functions, and is suitable for use on warships in high humidity and high salt sea surface environment.
Owner:中国人民解放军海军航空大学青岛校区
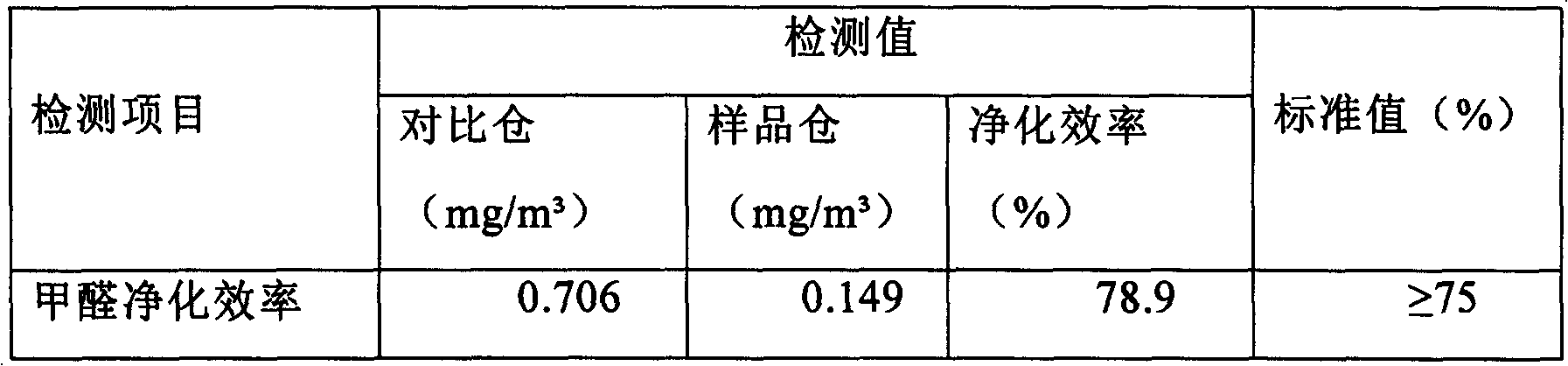
Formaldehyde eliminating coating with dual functions of adsorption and decomposition and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a formaldehyde eliminating coating with dual functions of adsorption and decomposition, which solves the problem that the existing coatings release harmful substances such as formaldehyde into air and have no function in eliminating formaldehyde. The formaldehyde eliminating coating comprises the following components by weight percent: 25-30% of coarse whiting, 10-15% of emulsion, 4-10% of calcined kaolin, 4-10% of washed kaolin, 4-10% of titanium dioxide, 4-10% of sepiolite or nanometer TiO2 composite material, 0.1-0.6% of dispersing agent, 0.1-0.6% of wetting agent, 0.1-0.6% of antifoaming agent, 0.1-0.6% of multifunctional assistant, 0.1-0.6% of mildew preventive, 0.1-0.6% of coalescing agent, 0.1-0.6% of antifreezing agent, 0.1-0.6% of bactericide, 0.1-0.6% of thickener, and 25-30% of water. The invention also provides a preparation method of the coating. The coating has very strong function in eliminating formaldehyde, and is safe and reliable.
Owner:四川嘉宝莉涂料有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com