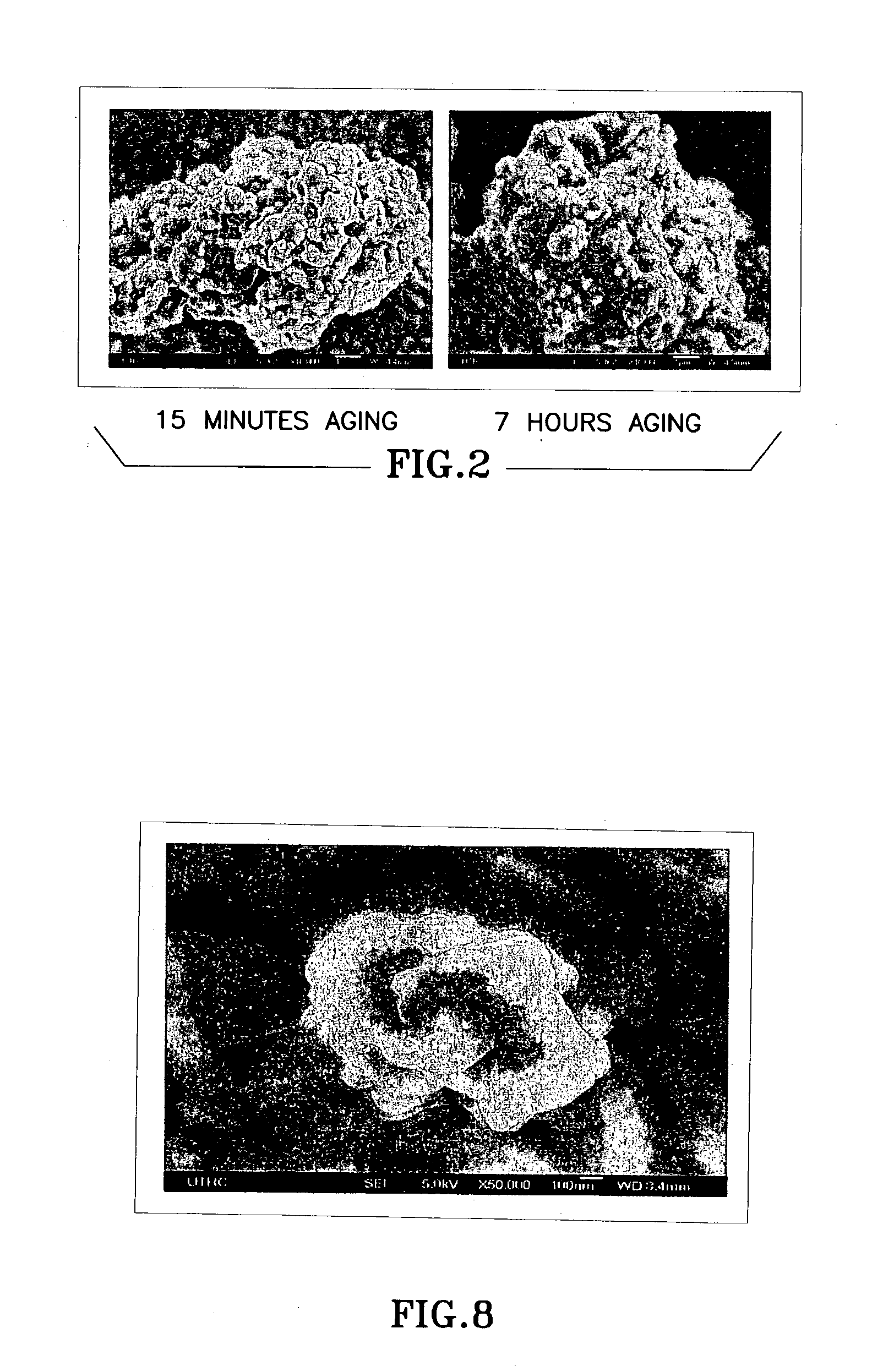
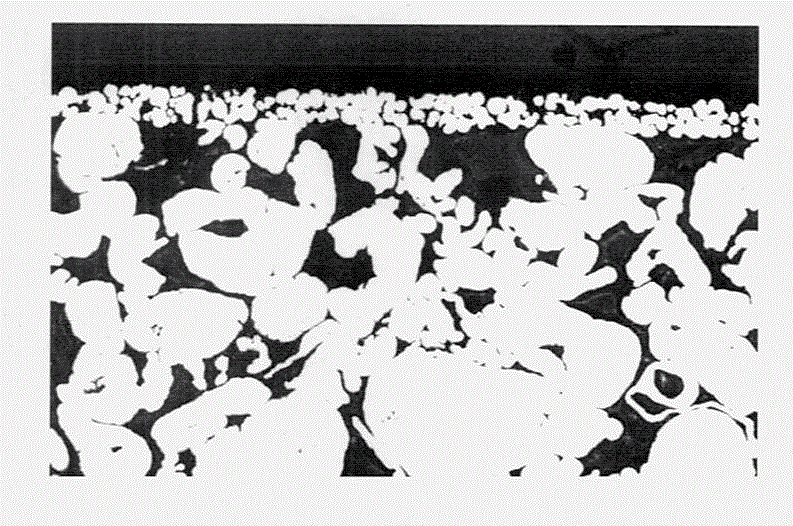
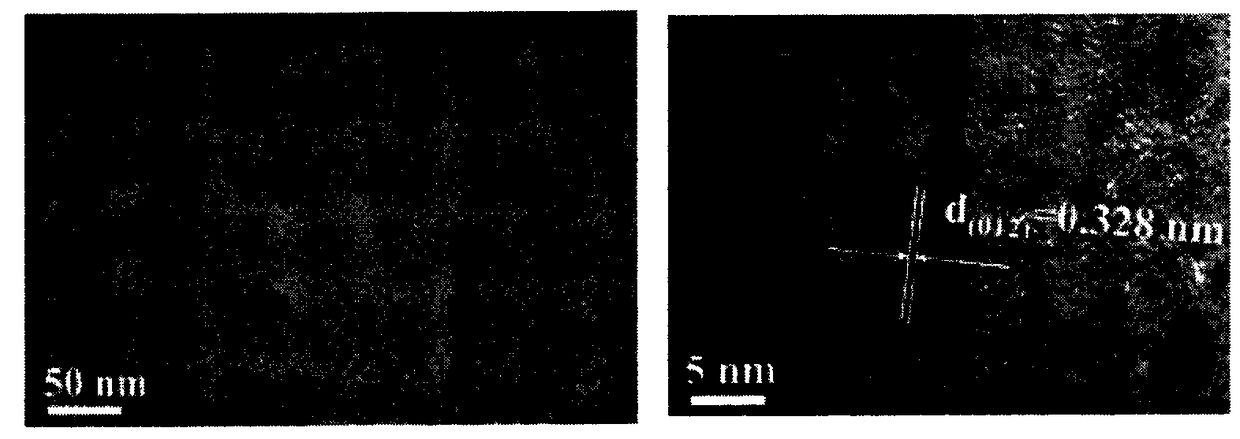
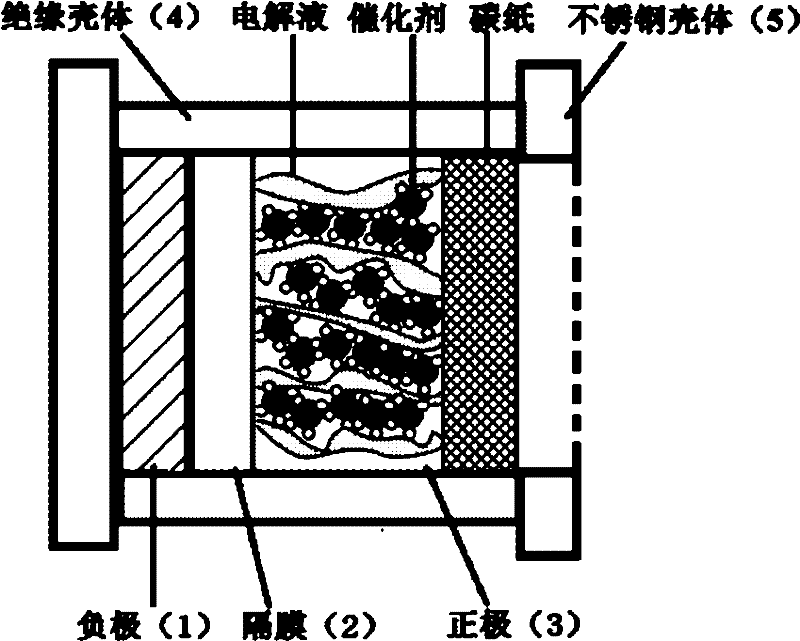
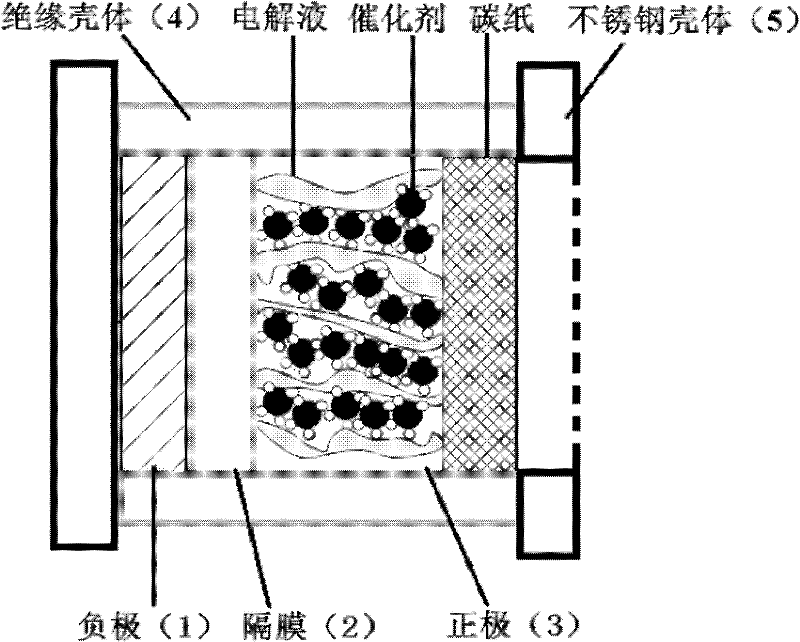
Patents
Literature
459 results about "Mass transfer resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
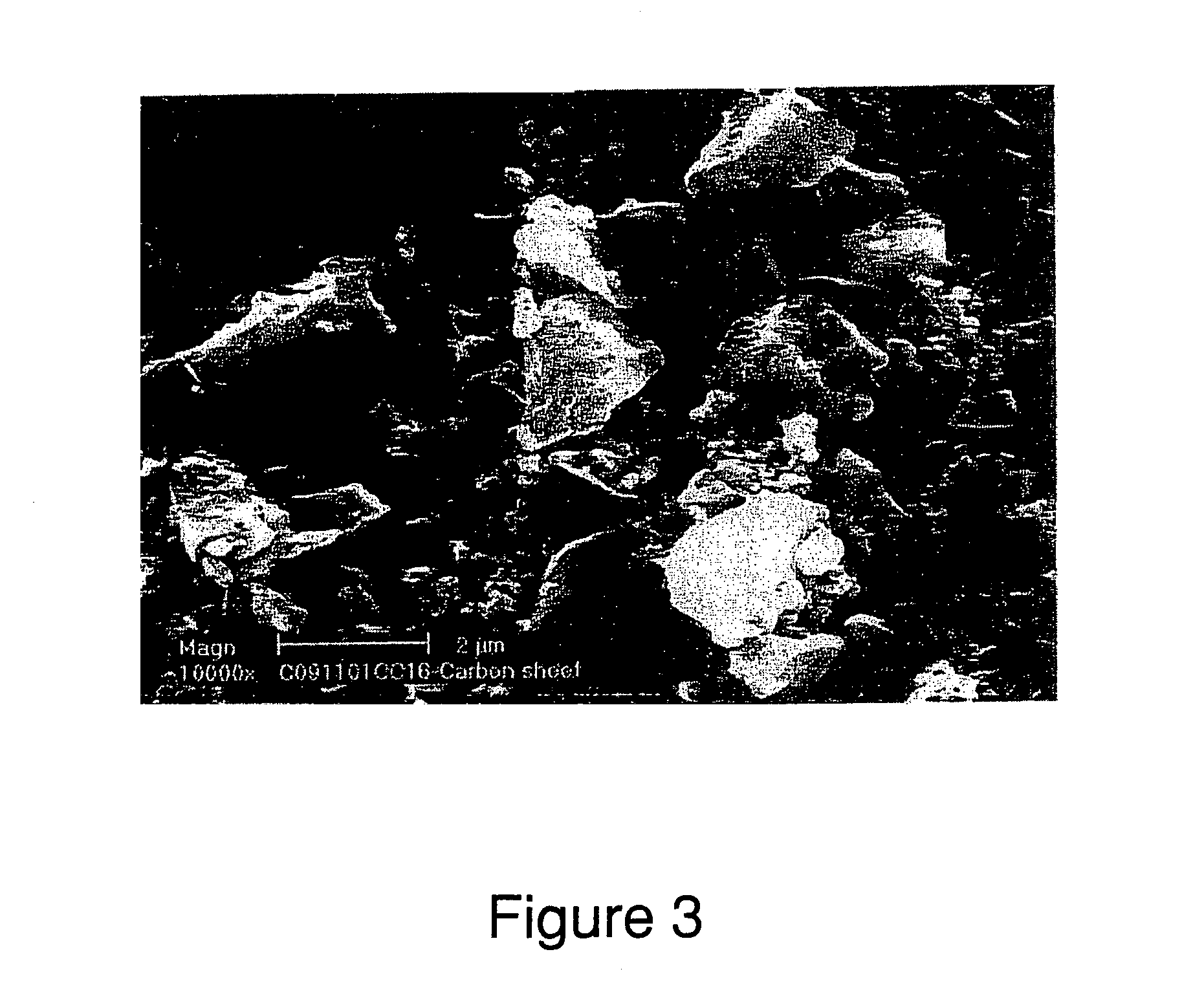
Adsorbent sheet material for parallel passage contactors
ActiveUS7077891B2Maximize capacityImprove efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesParticulatesSorbent
An adsorbent material fabricated into a reinforcement-free, self-supported coherent thin sheet and configured for use as a parallel passage contactor element in adsorption / separation applications with gases and liquids is disclosed. The adsorbent sheet material is obtained by enmeshing fine adsorbent particulates in a polymer binder. Particulates include but are not limited to carbon particles, inorganic oxides particles, or ceramic particles, or synthetic polymer resin particles. The adsorbent sheet advantageously contains a large volume percentage of active adsorbent particles. The parallel passage contactor device fabricated from the adsorbent sheet material is characterized by minimal mass transfer resistance and better separation efficiency expressed as height equivalent to a theoretical plate, while it maintains most of the adsorptive properties of the starting particulates, and can be used in gas separation applications with short adsorption cycles, such as rapid pressure swing adsorption, rotary concentrators, rapid electric swing adsorption.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
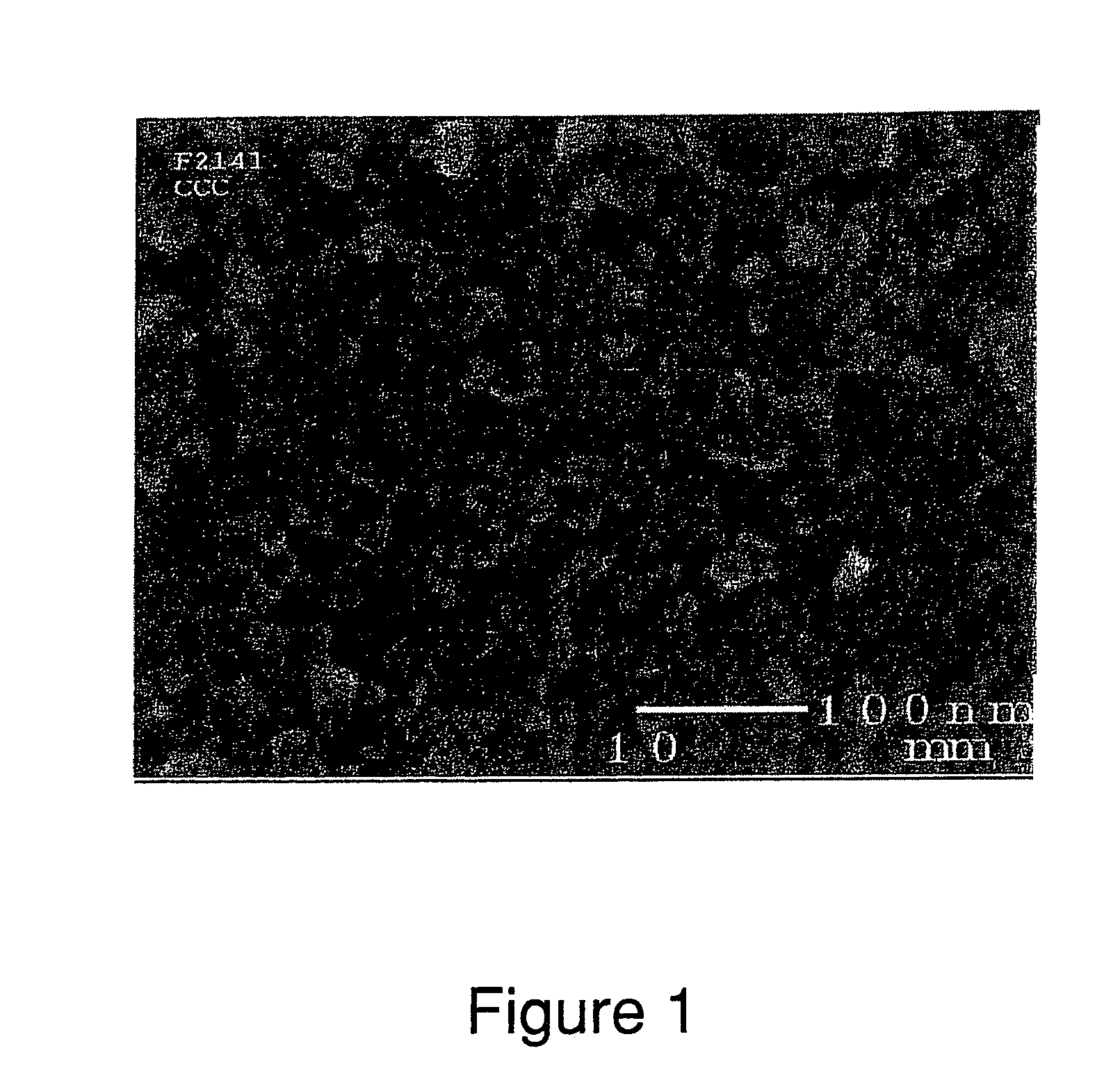
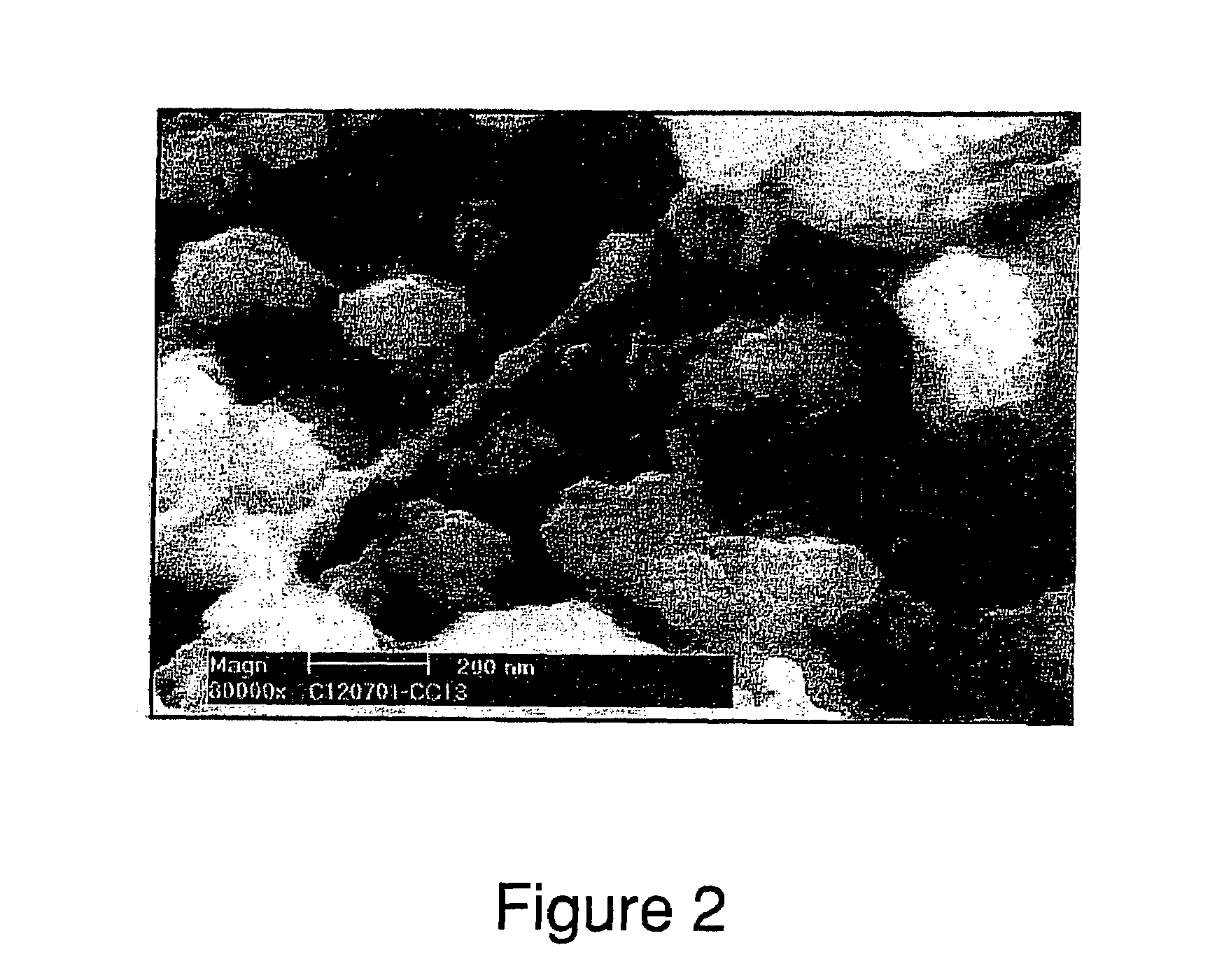
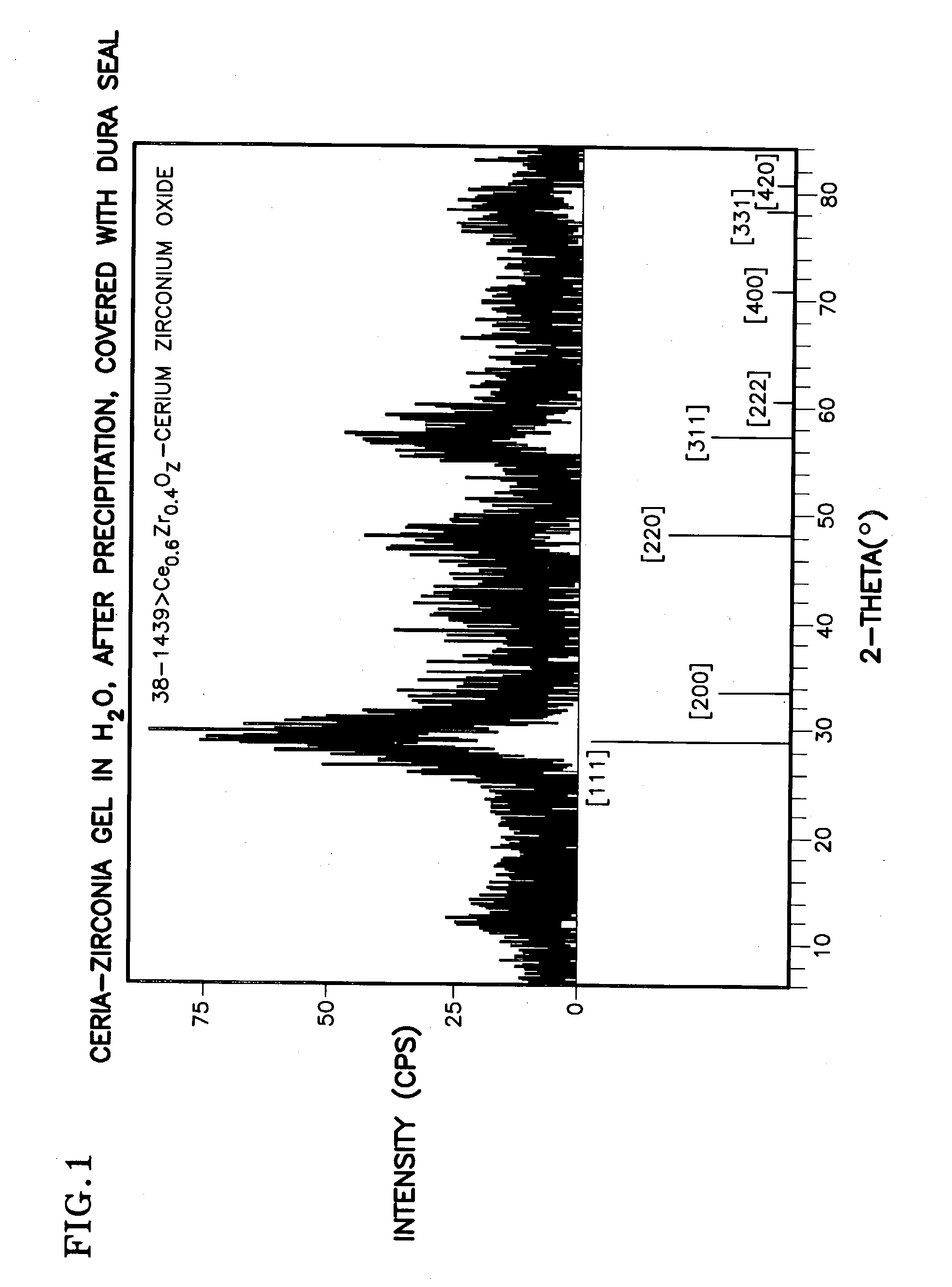
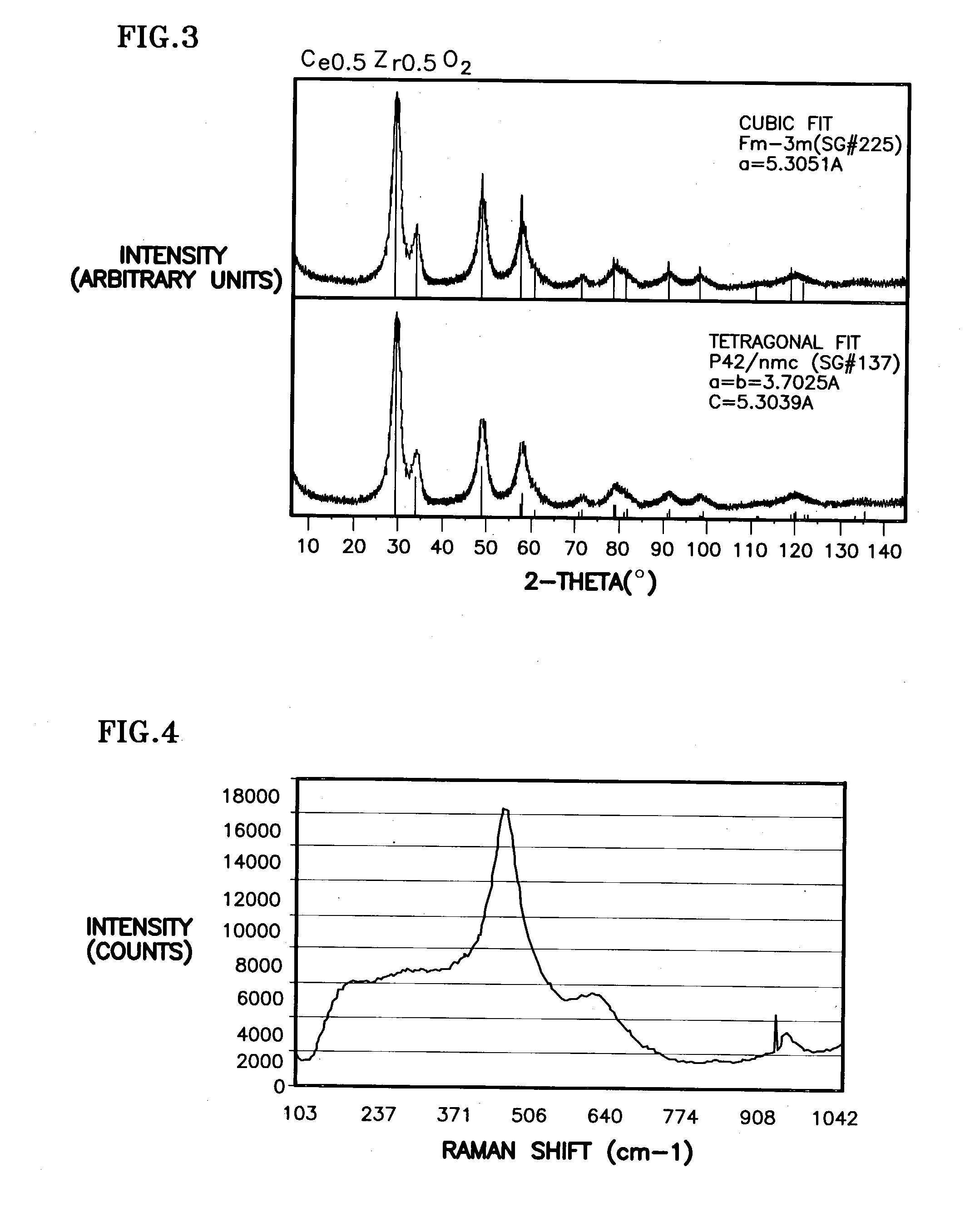
Ceria-based mixed-metal oxide structure, including method of making and use
InactiveUS20030186805A1Increase surface areaSimple structureRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMaterial nanotechnologyPtru catalystCerium(IV) oxide
A homogeneous ceria-based mixed-metal oxide, useful as a catalyst support, a co-catalyst and / or a getter, is described. The mixed-metal oxide has a relatively large surface area per weight, typically exceeding 150 m<2> / g, a structure of nanocrystallites having diameters of less than 4 nm, and including pores larger than the nanocrystallites and having diameters in the range of 4 to about 9 nm. The ratio of the pore volumes, VP, to skeletal structure volumes, VS, is typically less than about 2.5, and the surface area per unit volume of the oxide material is greater than 320 m<2> / cm<3>, such that the structural morphology supports both a relatively low internal mass transfer resistance and large effective surface area for reaction activity of interest. The mixed metal oxide is made by co-precipitating a dilute metal salt solution containing the respective metals, which may include Zr, Hf, and / or other metal constituents in addition to Ce, replacing water in the co-precipitate with a water-miscible low surface-tension solvent, and relatively quickly drying and calcining the co-precipitate at moderate temperatures. A highly dispersive catalyst metal, such as Pt, may be loaded on the mixed metal oxide support from a catalyst-containing solution following a selected acid surface treatment of the oxide support. The mixed metal oxide, as catalyst support, co-catalyst or getter, is applied in various reactions, and particularly water gas shift and / or preferential oxidation reactions as associated with fuel processing systems, as for fuel cells and the like.
Owner:INT FUEL CELLS
Ceria-based mixed-metal oxide structure, including method of making and use
InactiveUS20030235526A1Increased internal surface areaHigh catalytic activityRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMaterial nanotechnologyRheniumFuel cells
A homogeneous ceria-based mixed-metal oxide, useful as a catalyst support, a co-catalyst and / or a getter has a relatively large surface area per weight, typically exceeding 150 m<2> / g, a structure of nanocrystallites having diameters of less than 4 nm, and including pores larger than the nanocrystallites and having diameters in the range of 4 to about 9 nm. The ratio of pore volumes, VP, to skeletal structure volumes, VS, is typically less than about 2.5, and the surface area per unit volume of the oxide material is greater than 320 m<2> / cm<3>, for low internal mass transfer resistance and large effective surface area for reaction activity. The mixed metal oxide is ceria-based, includes Zr and or Hf, and is made by a novel co-precipitation process. A highly dispersed catalyst metal, typically a noble metal such as Pt, may be loaded on to the mixed metal oxide support from a catalyst metal-containing solution following a selected acid surface treatment of the oxide support. Appropriate ratioing of the Ce and other metal constituents of the oxide support contribute to it retaining in a cubic phase and enhancing catalytic performance. Rhenium is preferably further loaded on to the mixed-metal oxide support and passivated, to increase the activity of the catalyst. The metal-loaded mixed-metal oxide catalyst is applied particularly in water gas shift reactions as associated with fuel processing systems, as for fuel cells.
Owner:AUDI AG
Carbon nanosphere with at least one opening, method for preparing the same, carbon nanosphere-impregnated catalyst using the carbon nanosphere, and fuel cell using the catalyst
InactiveUS20060239890A1Improve area utilizationReduce mass transfer resistanceMaterial nanotechnologySpecific nanostructure formationHigh current densityFuel cells
A carbon nanosphere has at least one opening. The carbon nanosphere is obtained by preparing a carbon nanosphere and treating it with an acid to form the opening. The carbon nanosphere with at least one opening has higher utilization of a surface area and electrical conductivity and lower mass transfer resistance than a conventional carbon nanotube, thus allowing for higher current density and cell voltage with a smaller amount of metal catalyst per unit area of a fuel cell electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Film material with ionic exchange performance and use thereof
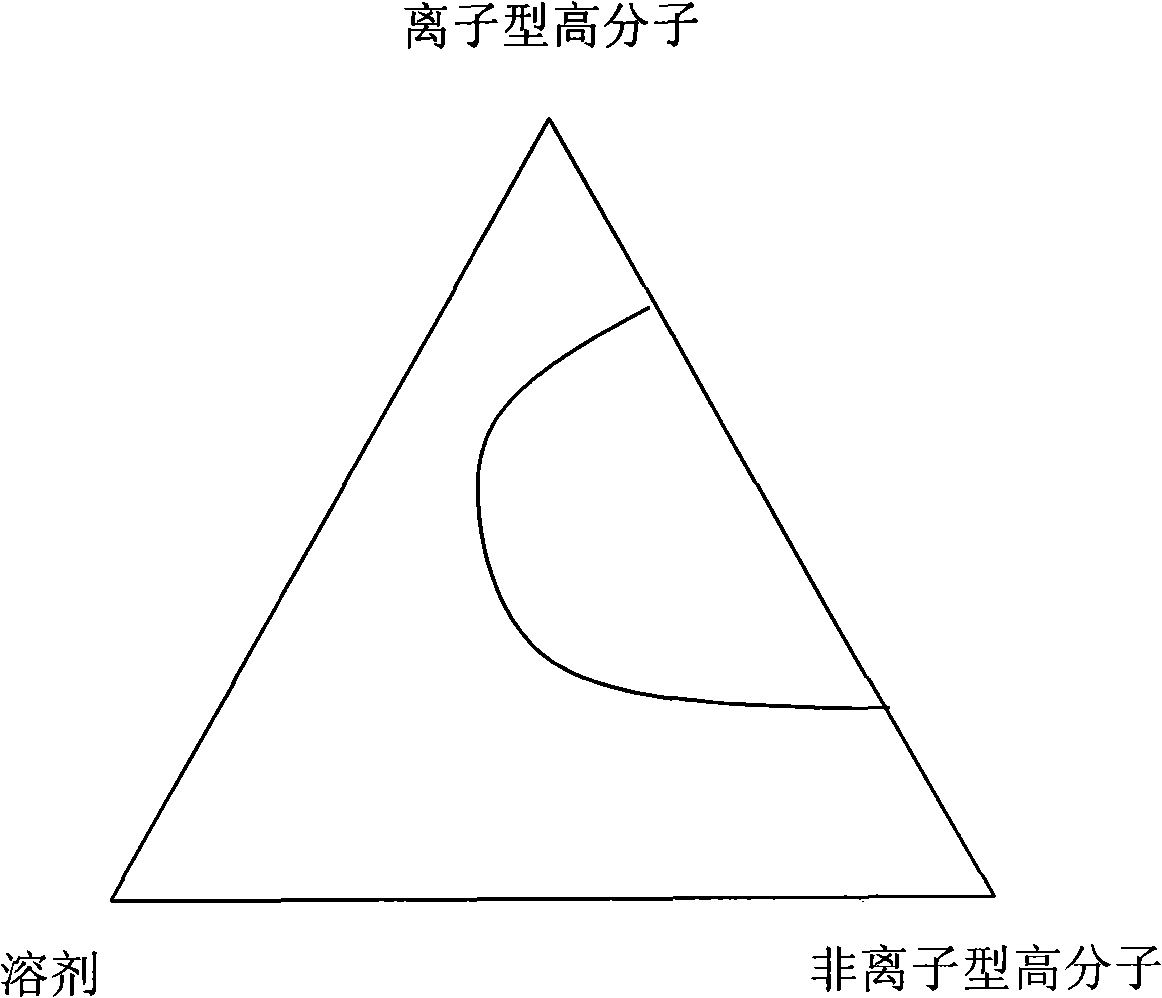
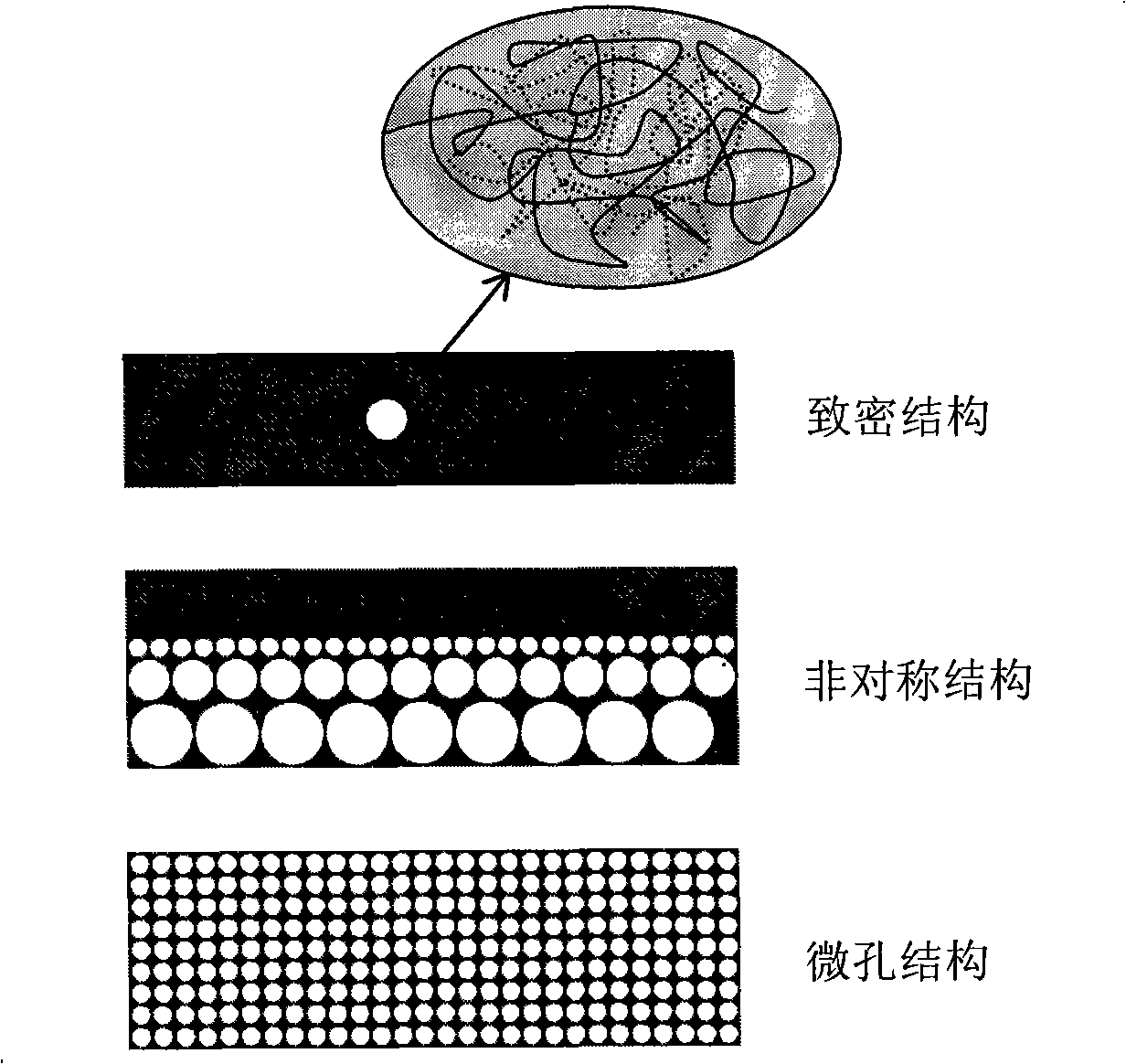
InactiveCN101264427AReduce mass transfer resistanceGood chemical stabilitySemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionChemical physicsWater vapor
The invention discloses a membrane material with ion exchange performance, which is characterized in that the membrane material is in a compact structure or a millipore structure, and is mixed by the polymer with ion exchange performance and the polymer with nonionic exchange performance; wherein, the weight ratio of the polymer with ion exchange performance to the polymer with nonionic exchange performance is 5 / 95 percent to 95 / 5 percent. The invention also discloses the application of the membrane material in the separation of anion and cation and the recovery membrane extraction, the removal of the vapor in the gas and the desalination of the water system in the process of driving the positive permeation by non-pressure. The membrane material has the advantages of getting rid of the supporting concept of supporting liquid membrane, enjoying high chemical stability, and low mass transfer resistance to ions. The membrane material not only provides a long-time stability in the separation process of the liquid membrane ions, but also finds application points in other separation fields.
Owner:南京奥特高科技有限公司
Preparation and application of hierarchical pore metal-organic framework loaded heteropolyacid catalyst
InactiveCN107694611AGuarantee structureImprove stabilityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsMetal-organic frameworkCatalytic oxidation
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a hierarchical pore metal-organic framework loaded heteropolyacid catalyst. The catalyst adopts hydrothermal-extraction method for preparation. The method includes: dissolving an organic ligand, a template agent, a metal salt and Keggin type heteropolyacid in a solvent, conducting hydrothermal synthesis of a crystal product, and thenperforming Soxhlet extraction to obtain a catalyst. The obtained catalyst has a meso-micro hierarchical porous structure, realizes high dispersion of the active component heteropolyacid and ultra-highloading capacity, and at the same time solves the problems of large mass transfer resistance, long diffusion path and small reaction place in microporous materials. The catalyst provided by the invention shows excellent catalytic performance in both photocatalytic degradation of dye wastewater and catalysis of oxidation-extraction desulfurization reaction, the catalysis reaction uses visible light and hydrogen peroxide respectively, the process is clean, environment-friendly and green, and after repeated use, the catalyst still maintains high activity, and has high industrial application value.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
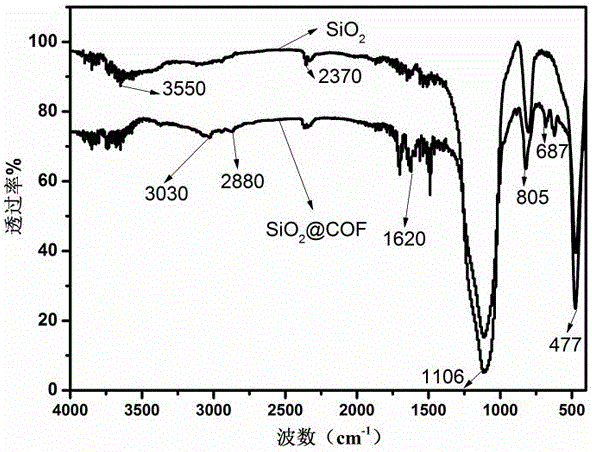
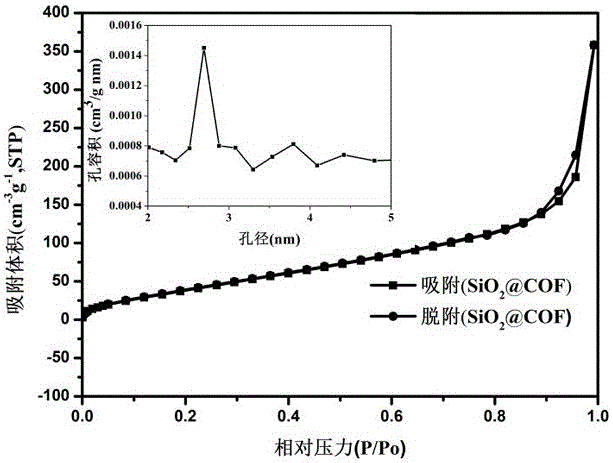
Preparation method of covalent organic framework composite microspheres with core-shell structures
InactiveCN107175053AMild preparation conditionsRaw materials are cheap and easy to getOther chemical processesDispersed particle separationMicrosphereSolid phase extraction
The invention relates to a preparation method of covalent organic framework composite microspheres with core-shell structures. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving silicon dioxide microspheres, a first construction element and a second construction element in an organic solvent; and after adding a catalyst, rapidly synthesizing into the composite microspheres with core-shell structures at a certain temperature. In a preparation process, reaction conditions are gentle, the method is simple, and the yield is high; the prepared covalent organic framework composite microspheres have the advantages of good core-shell morphology, high specific surface area, ordered pore structures, good mechanical stability, thermal stability, chemical stability and the like, if the microspheres are used as a chromatographic stationary phase, the chromatographic mass transfer resistance can be reduced effectively, the theoretical plate height is improved, and finally, column efficiency and degree of separation are improved; and if the microspheres are used as solid-phase extracting filler, the enrichment effect can be improved remarkably. The covalent organic framework composite microspheres with core-shell structures have good application prospects in the aspect of separation and enrichment of small organic molecules.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for preparing super-hydrophobic membrane for removing dissolved gas in water
InactiveCN103285746AReduce mass transfer resistanceImprove mechanical propertiesSemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment by degassingSolubilityHydrophobic polymer
The invention discloses a novel method for preparing a super-hydrophobic membrane for removing dissolved gas in water. Based on a self-cleaning bionic principle, coupling agent modified inorganic nanoparticles with low surface energy and hydrophobic polymer PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride) are blended to obtain a super-hydrophobic flat membrane with good mechanical properties by a phase inversion method. The surface of the super-hydrophobic membrane has a water contact angle of 154+ / -1 degrees and a rolling angle of 4+ / -1 degrees, so that the has super-hydrophobic membrane good super-hydrophobicity and self-cleaning properties, the mass transfer resistance of the wetted membrane can be obviously reduced, and the separation efficiency of a membrane contactor is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG ZHONGYU ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH +1
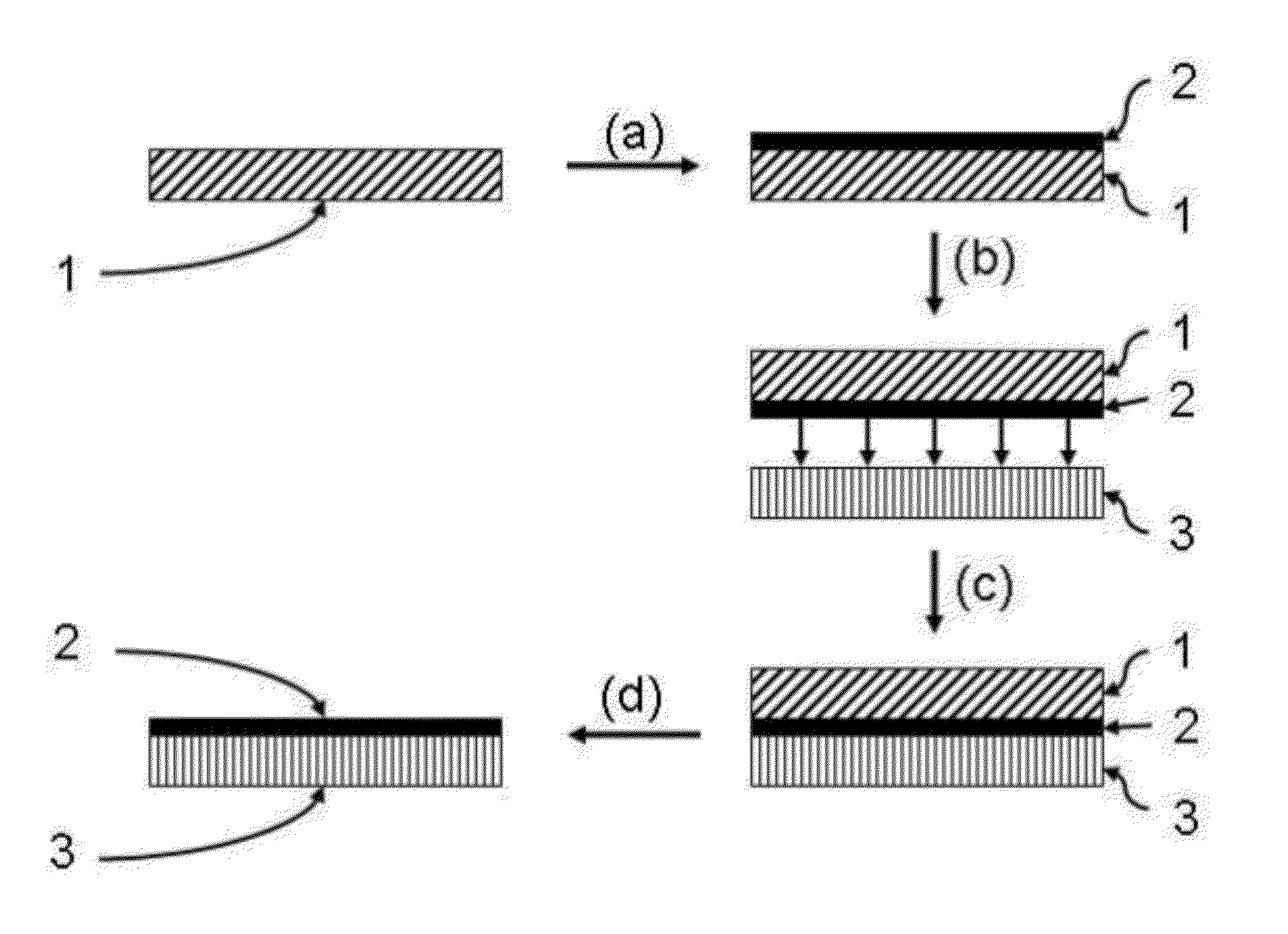
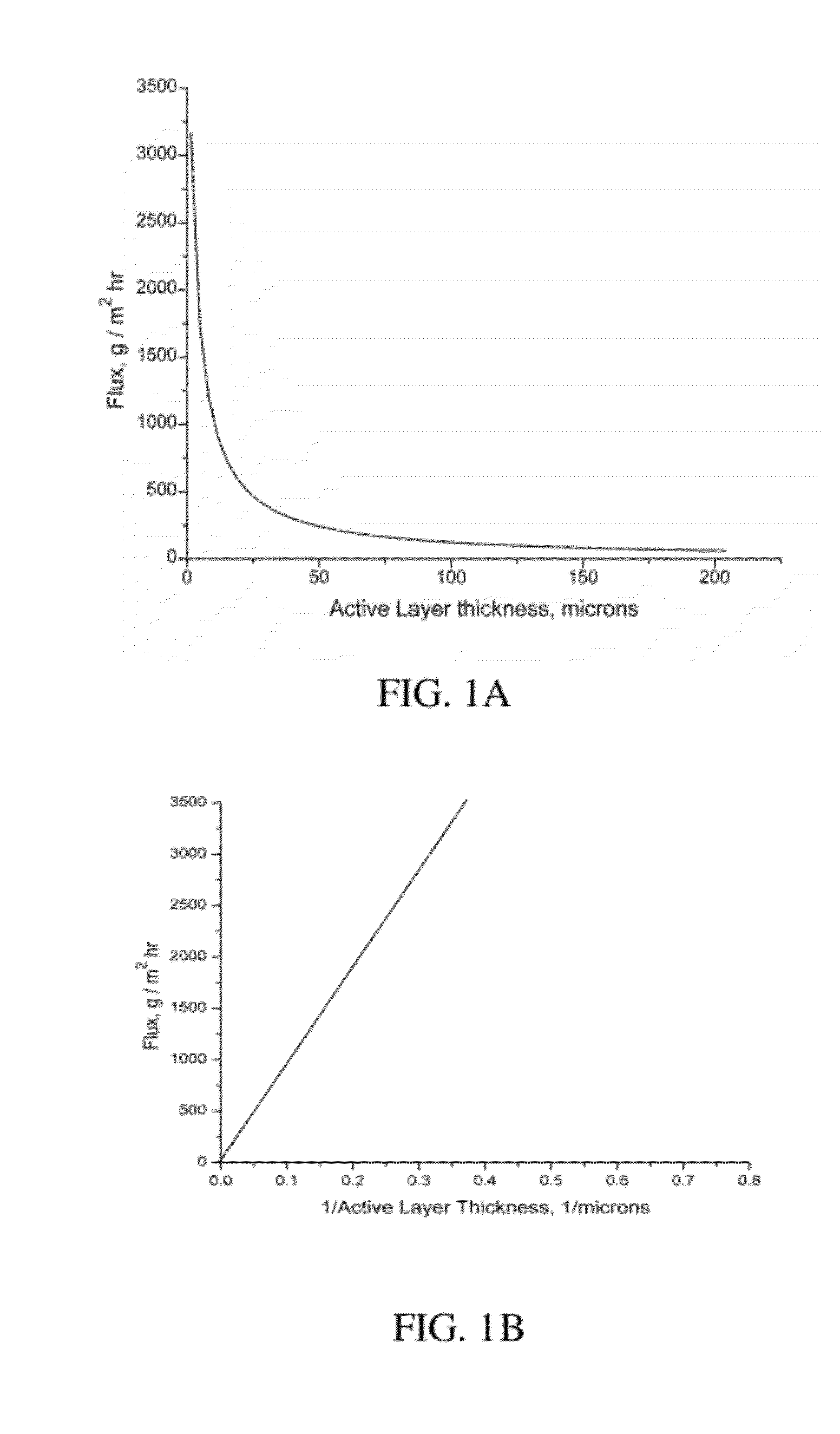
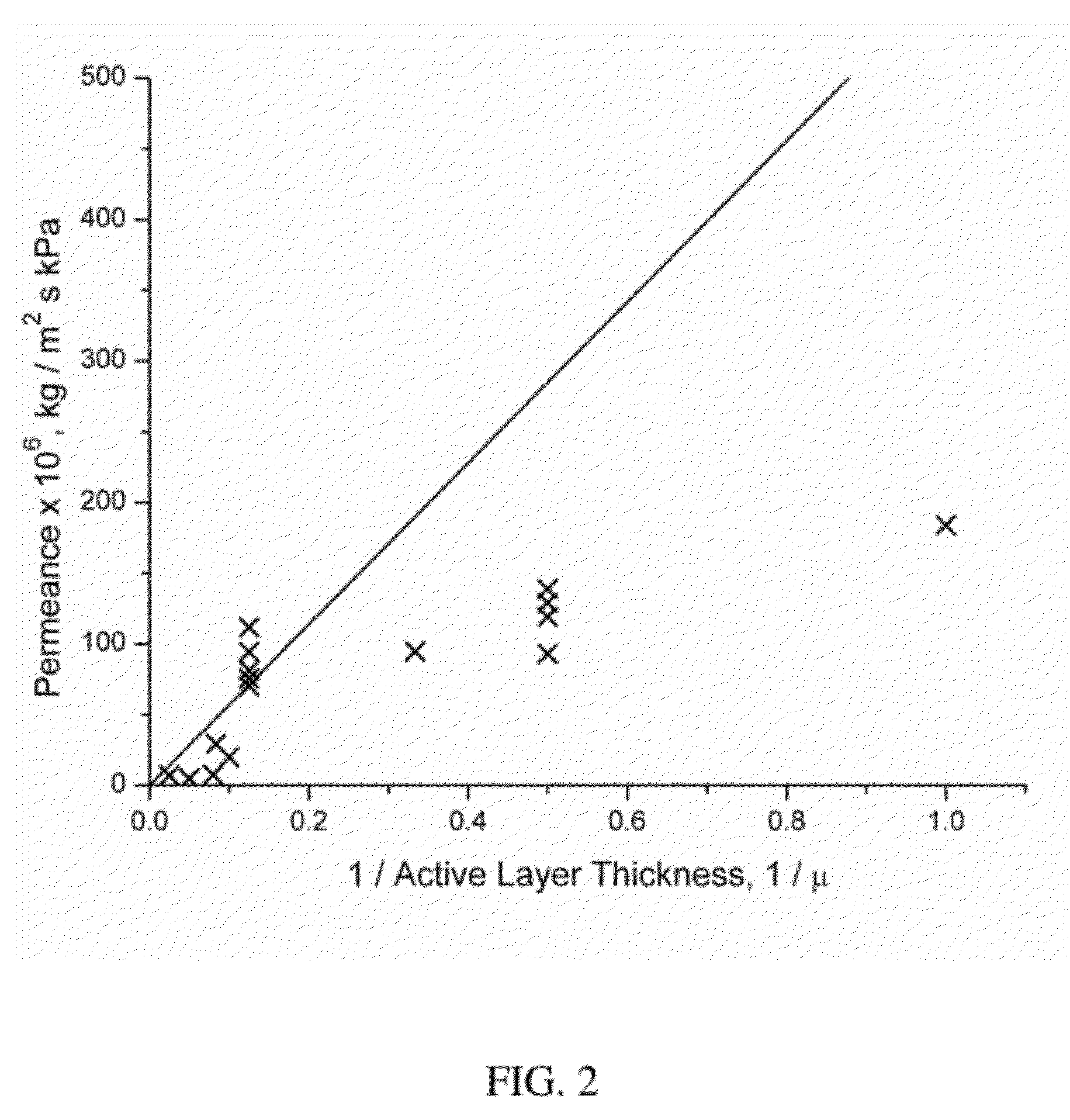
Thin film composite membranes and their method of preparation and use
InactiveUS20120080147A1Adhesive processesSolid sorbent liquid separationMass transfer resistanceThin-film composite membrane
The present invention is a technique to fabricate thin-film composite perm-selective membranes by a transfer method. The composite membranes are useful in separating liquid, vapor or gaseous mixtures by selective permeation and reduce mass transfer resistance of the support layer. Selectivity and flux are improved by reduction of the mass transfer resistance of the support layer.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Preparation method for 3D Ni-Co bimetallic hydroxide hollow microsphere and application in super capacitor
InactiveCN103680993ASolve the problem that the specific surface is greatly reducedLarge capacityHybrid capacitor electrodesHybrid/EDL manufactureMass transfer resistanceMicrosphere
The invention belongs to the field of chemistry, and provides a preparation method for a 3D Ni-Co bimetallic hydroxide hollow microsphere and application in a super capacitor. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) a SiO2 microsphere is synthesized; 2) a AlOOH sol is prepared; 3) the SiO2 microsphere is added into the AlOOH sol so that a SiO2@ AlOOH microsphere is obtained; 4) the SiO2@ AlOOH microsphere, a alkali source and de-ionized water are mixed, and a nickel and cobalt salt precursor is added so that the 3D Ni-Co bimetallic hydroxide hollow microsphere is prepared; and 5) an electrode sheet is prepared. Compared with methods in the prior art, the obtained 3D Ni-Co bimetallic hydroxide hollow microsphere provides a larger specific surface, smaller mass transfer resistance and more excellent structural stability. Besides, the synthesized 3D Ni-Co bimetallic hydroxide hollow microsphere is applied to electrode material of the super capacitor so that the 3D Ni-Co bimetallic hydroxide hollow microsphere is much better than existing precious metal oxide on aspects of cost and performance.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Micro-interface enhancement reactor reaction rate structure-activity regulation and control model modeling method
ActiveCN107561938AReduce mistakesImprove versatilityAdaptive controlActivity regulationReaction rate
The invention discloses a micro-interface enhancement reactor reaction rate structure-activity regulation and control model modeling method. Based on the Levenspiel theory, a reaction rate structure-activity model suitable for a micro-interface enhancement reactor is constructed. According to the invention, the reaction rate structure-activity regulation and control model constructed through the method can intuitively make out the effects of the bubble diameter, gas-liquid mass transfer coefficients, the mass transfer resistance and the like on the reaction rate; the bubble diameter of a reaction system, the reaction efficiency (energy efficiency and material efficiency), the physical and chemical properties of the system, micro-interface characteristics, mass transfer characteristics andthe reactor structure are correlated through a mathematic method; the energy efficiency and material efficiency of a reaction process are maximized by adjusting structural parameters and operating parameters; and alternatively, a reaction target (mission), energy consumption and material consumption are given, the efficient reactor structure is designed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Carbon nanosphere with at least one opening, method for preparing the same, carbon nanosphere-impregnated catalyst using the carbon nanosphere, and fuel cell using the catalyst
InactiveUS7837968B2Improve area utilizationReduce mass transfer resistanceSpecific nanostructure formationMaterial nanotechnologyHigh current densityFuel cells
A carbon nanosphere has at least one opening. The carbon nanosphere is obtained by preparing a carbon nanosphere and treating it with an acid to form the opening. The carbon nanosphere with at least one opening has higher utilization of a surface area and electrical conductivity and lower mass transfer resistance than a conventional carbon nanotube, thus allowing for higher current density and cell voltage with a smaller amount of metal catalyst per unit area of a fuel cell electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Catalyst carrier with run-through macropores and mesopores, catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102350374AReduce mass transfer resistanceCatalyst carriersCatalytic crackingFiberMass transfer resistance
The invention provides a method for preparing a catalyst carrier with macropores and mesopores which are in run-through. The method comprises the following steps of: adding solid cellosilk in the process of preparing or forming the catalyst carrier, so that the solid cellosilk is dispersed in the catalyst carrier; and removing the solid cellosilk by forming and roasting to obtain the catalyst carrier with the run-through macropores and mesopores. The invention also provides a method for preparing a catalyst by further supporting active ingredients by the catalyst carrier and the carrier and the catalyst which are prepared by the method. By the method, the run-through performance of a mesoporous channel of the carrier is improved greatly by adding the solid cellosilk; and the run-through macropore formed by the cellosilk provides a quickly-dispersed channel for reaction molecules, so the mass transfer resistance in the catalytic reaction process is reduced. The method is suitable for preparing various catalysts of which the reaction speed is controlled by internal diffusion, such as a petroleum distillate (particularly heavy oil distillate) hydrogenation catalyst.
Owner:UNISIZE TECH CHANGZHOU +1
Preparation method for high-gradient porous metal film
The invention relates to a preparation method for a high-gradient porous metal film. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the steps of firstly, carrying out hole blocking treatment on a porous metal matrix by using prepared inorganic powder; then, carrying out metal powder coating; carrying out high temperature sintering under a hydrogen or inert atmosphere to obtain an impurity-containing gradient porous metal film; finally, flushing (carrying out vacuum soaking on) residual impurities in a film matrix by using a chemical reagent or removing the residual impurities in the film matrix by using an ultrasonic technology to obtain the high-gradient porous metal film. According to the high-gradient porous metal film prepared by the preparation method, the powder coating quality is good, the operation is simple and convenient, the residual impurities in a matrix pore passage is easy to be completely removed, and the obtained metal film is good in integrality, high in gradient and low in mass transfer resistance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Microballons of laminar dual hydroxy composite metal oxide and preparation method
This invention relates to a method for preparing lamellar dihydroxyl composite metal oxide microspheres. The method comprises: preparing lamellar dihydroxyl composite metal oxide (hydrotalcite) nano- or submicro-particles by co-precipitation, nucleation / crystallization / isolation, nonequilibrium crystallization or hydrothermal synthesis, preparing into slurry with a certain solid content, adding bonding agent, spin-spraying for granulation, and drying to obtain microspheres with diameters of 5-100 mu.m. The bulk density, specific surface area, pore volume and most probable pore diameters of the microspheres are 0.4-0.8 g / cm3, 40-150 m2 / g, 0.1-0.8 cm3 / g and 2-40 nm, respectively. The microspheres can be directly used for catalysis or separation after activated, and the mass transfer resistance and carbon accumulation are minimized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
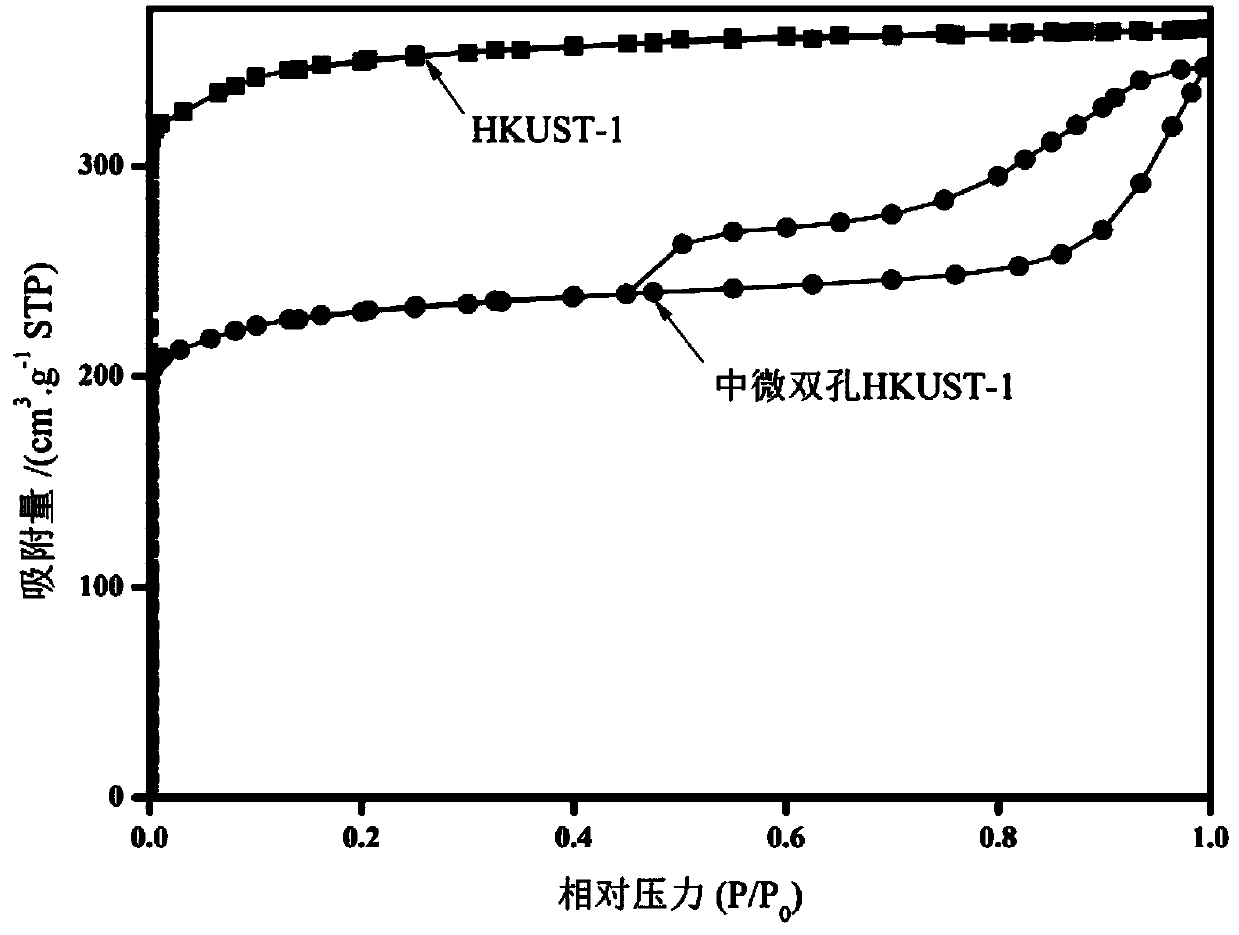
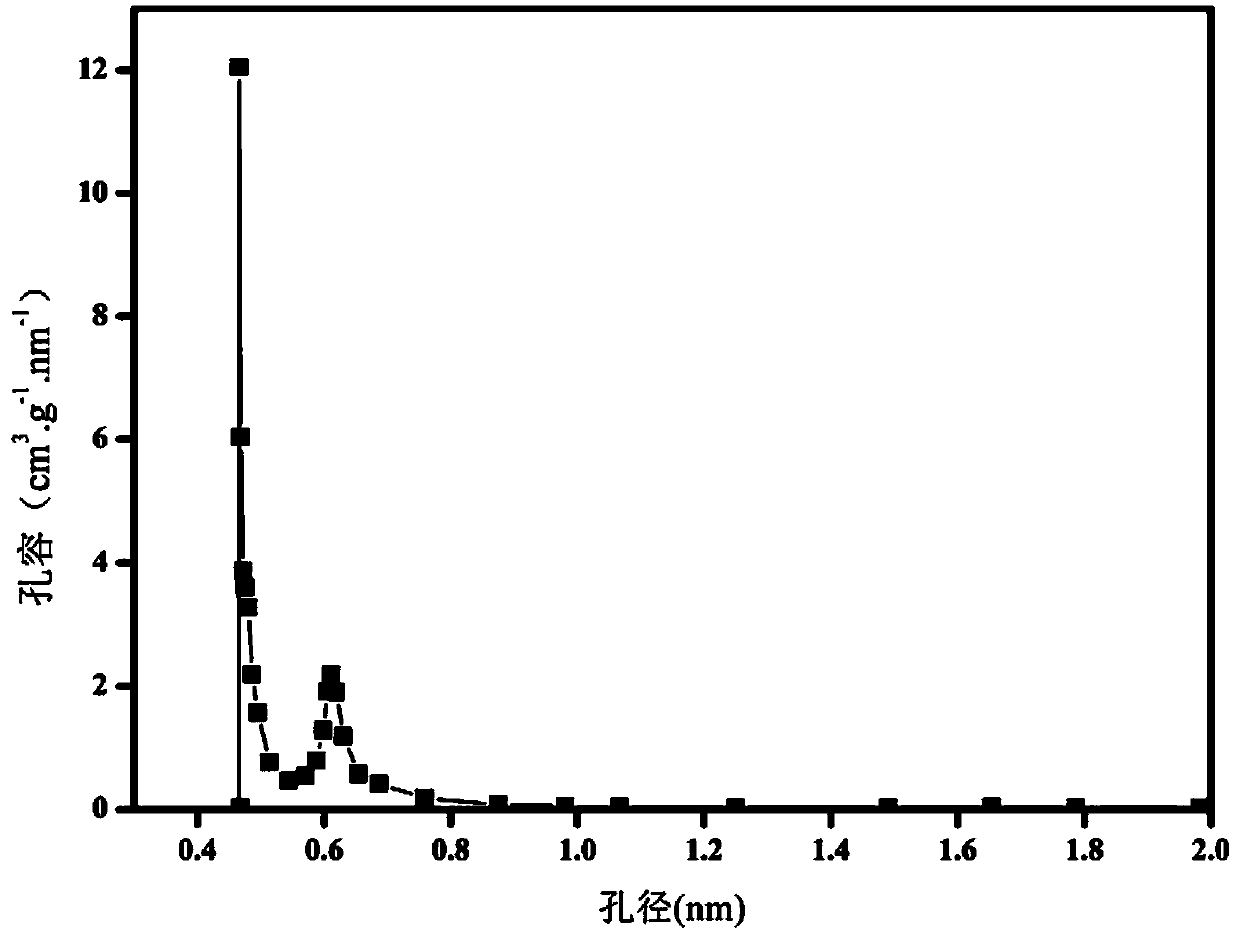
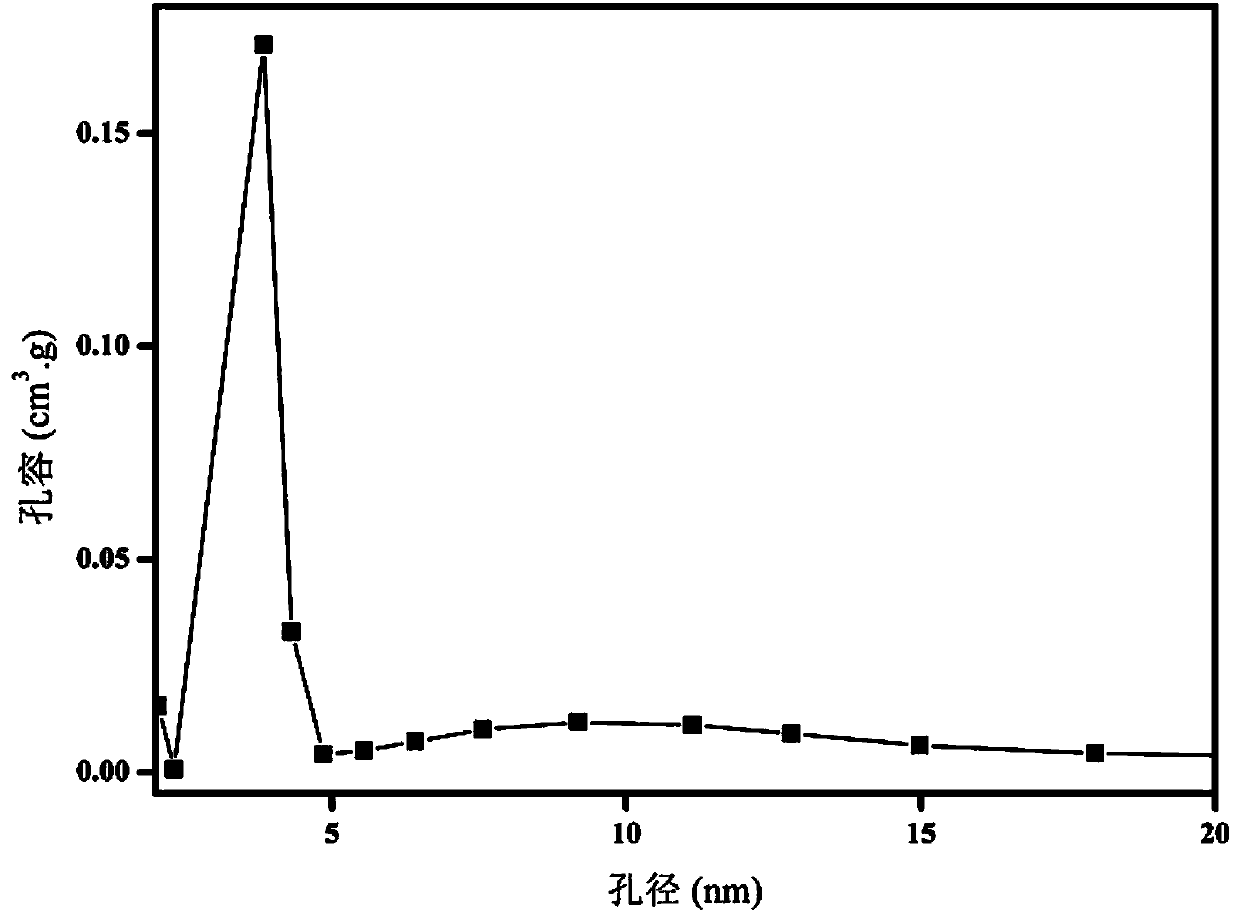
Small and medium dual-hole HKUST-1 material and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104193768ARich microporous structureRich mesostructureOther chemical processesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAlcoholMass transfer resistance
The invention belongs to the field of preparation of metal-skeleton organic matters and discloses a small and medium dual-hole HKUST-1 material and a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: respectively dissolving Cu(NO3)2.3H2O and H3BTC into a mixed solution of DMF, ethyl alcohol and water; stirring to obtain a clear solution A and a clear solution B; adding the clear solution A to the clear solution B and mixing evenly; adding 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane and stirring; transferring the obtained mixed solution to a stainless steel high-pressure reaction kettle, and carrying out temperature programming; cooling the reaction kettle to room temperature, filtering the product, and drying the product in vacuum; and washing the obtained product with ethyl alcohol for four times, thus obtaining the small and medium dual-hole HKUST-1 material. The product has a single mesoporous and microporous crystal structure, the mass transfer resistance is overcome in reaction, the mass transfer efficiency is improved, and particularly, the product has a relatively good application prospect in the fields of catalysis, adsorption, separation and the like involving macromolecules.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Graphene/ lignin-based activated carbon preparation method and application in supercapacitors
InactiveCN104576077AStable structureImprove conductivityHybrid capacitor electrodesHybrid/EDL manufactureCapacitanceActivated carbon
The invention belongs to the field of chemistry, provides a graphene / lignin-based activated carbon preparation method and application in supercapacitors. The method includes the steps that 1, lignin-based activated carbon is prepared; 2, graphite oxide and the activated carbon are mixed, and a graphite oxide / lignin-based activated carbon compound is obtained; 3, pyrolysis reduction is conducted on the compound obtained after alkaline activation is conducted, and graphene / lignin-based activated carbon composite material is prepared; 4, electrode plates are prepared. Compared with the prior art, the obtained graphene / lignin-based activated carbon has a larger specific surface, lower mass transfer resistance and more excellent electric conductivity. Furthermore, the composite graphene / lignin-based activated carbon is applied to electrode material of the supercapacitors, and the cost and performance are greatly superior to those of existing activated carbon material.
Owner:江苏江大环保科技开发有限公司
Preparation method of 3D coralline graphene/NiCo2O4 composite material and application of same in super capacitor
InactiveCN104576075AGood dispersionLarger than surfaceHybrid capacitor electrodesHybrid/EDL manufactureCapacitanceMass transfer resistance
The invention belongs to the chemistry field, and provides a preparation method of a 3D coralline graphene / NiCo2O4 composite material and the application of the 3D coralline graphene / NiCo2O4 composite material in a super capacitor. The preparation method comprises the steps that (1) GO is synthesized; (2) Ni-Co salt and an alkali source are added into suspension liquid of the GO, and microwave heating is carried out to assist in preparing a GO / Ni-Co layered double metal hydroxide composite material; (3) high-temperature calcination is carried out on the prepared GO / Ni-Co layered double metal hydroxide composite material to manufacture the 3D coralline graphene / NiCo2O4 composite material; (4) an electrode plate is manufactured, the simulation super capacitor is assembled, and the performance of the simulation super capacitor is evaluated. Compared with the prior art, the 3D coralline graphene / NiCo2O4 composite material prepared through the preparation method is more excellent in electrical conductivity, larger in specific area, smaller in mass transfer resistance and longer in cycle life. Furthermore, when applied to the electrode material of the super capacitor, the synthetic 3D coralline graphene / NiCo2O4 composite material is much superior than existing precious metal oxide in cost and performance.
Owner:江苏江大环保科技开发有限公司
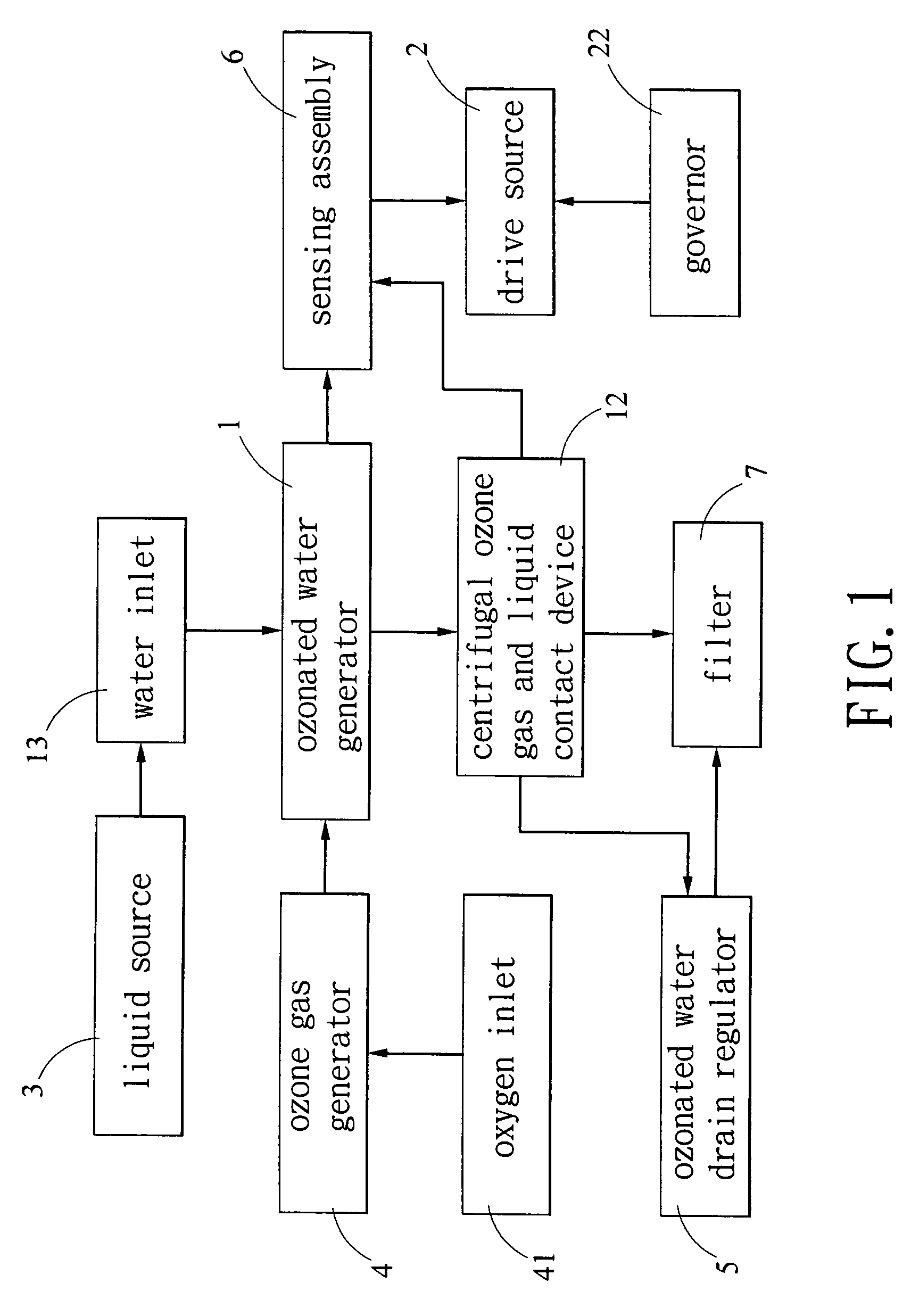
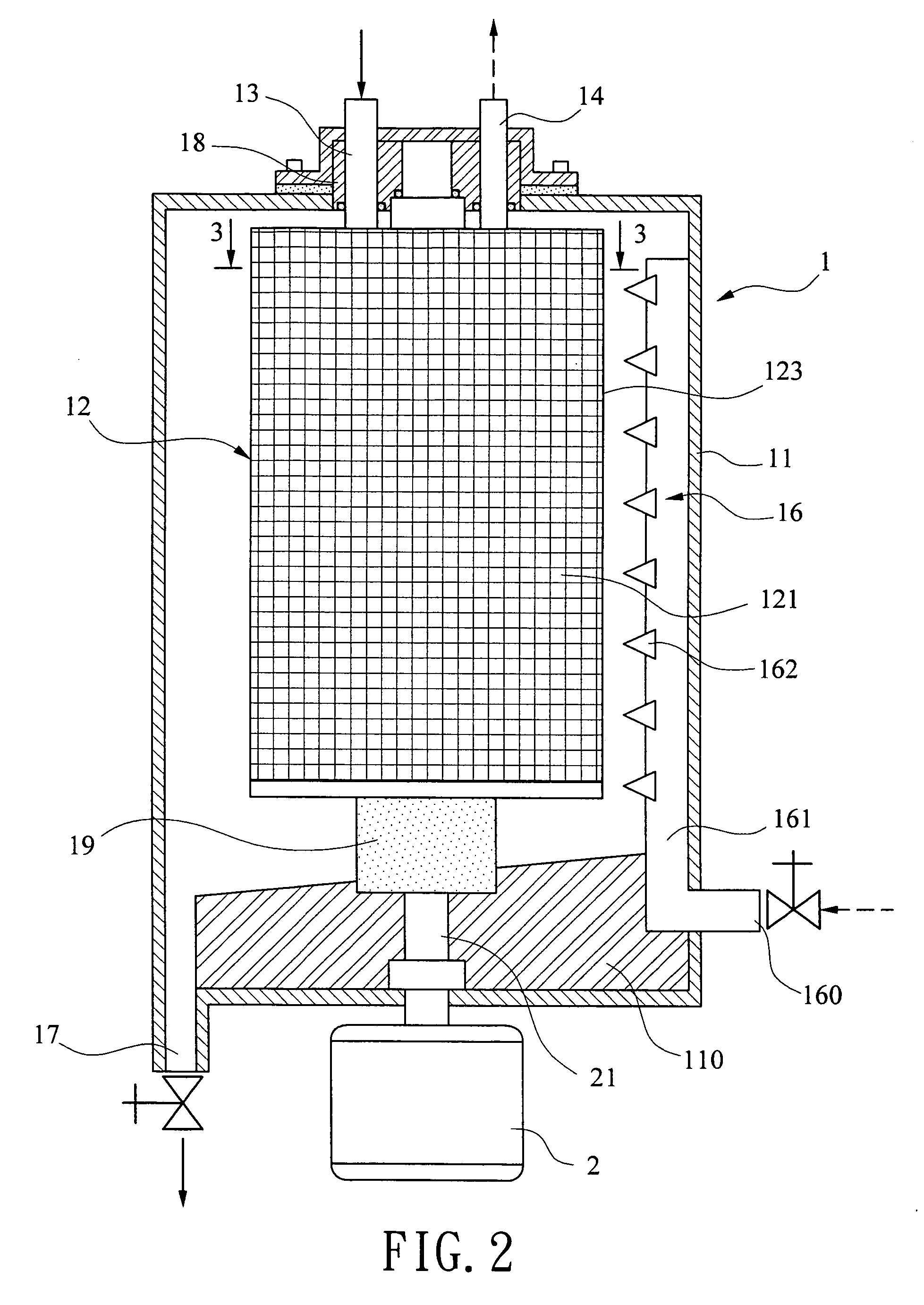
Method of centrifugally generating ozonated water and system thereof
InactiveUS20060151896A1Increase contact areaReduce mass transfer resistanceFlow mixersLighting and heating apparatusEnvironmental engineeringDissolution
In a system including a centrifugal ozonated water generator, a centrifugal drive source for rotating the ozonated water generator, a liquid source for supplying water to the ozonated water generator, an ozone gas generator fluidly connected to the ozonated water generator, an ozonated water drain regulator, and a sensing assembly for monitoring ozone gas concentration, a method comprises supplying water to an ozonated water generator, supplying ozone gas to the ozonated water generator, activating a drive source to rotate a centrifugal ozone gas and liquid contact device in the ozonated water generator, causing water to contact ozone gas in the ozonated water generator for generating ozonated water, and withdrawing ozonated water from the ozonated water generator. The invention can provide a high contacting area and low mass transfer resistance between ozone gas and water, thereby facilitating the dissolution of ozone gas in water.
Owner:WANG WEN
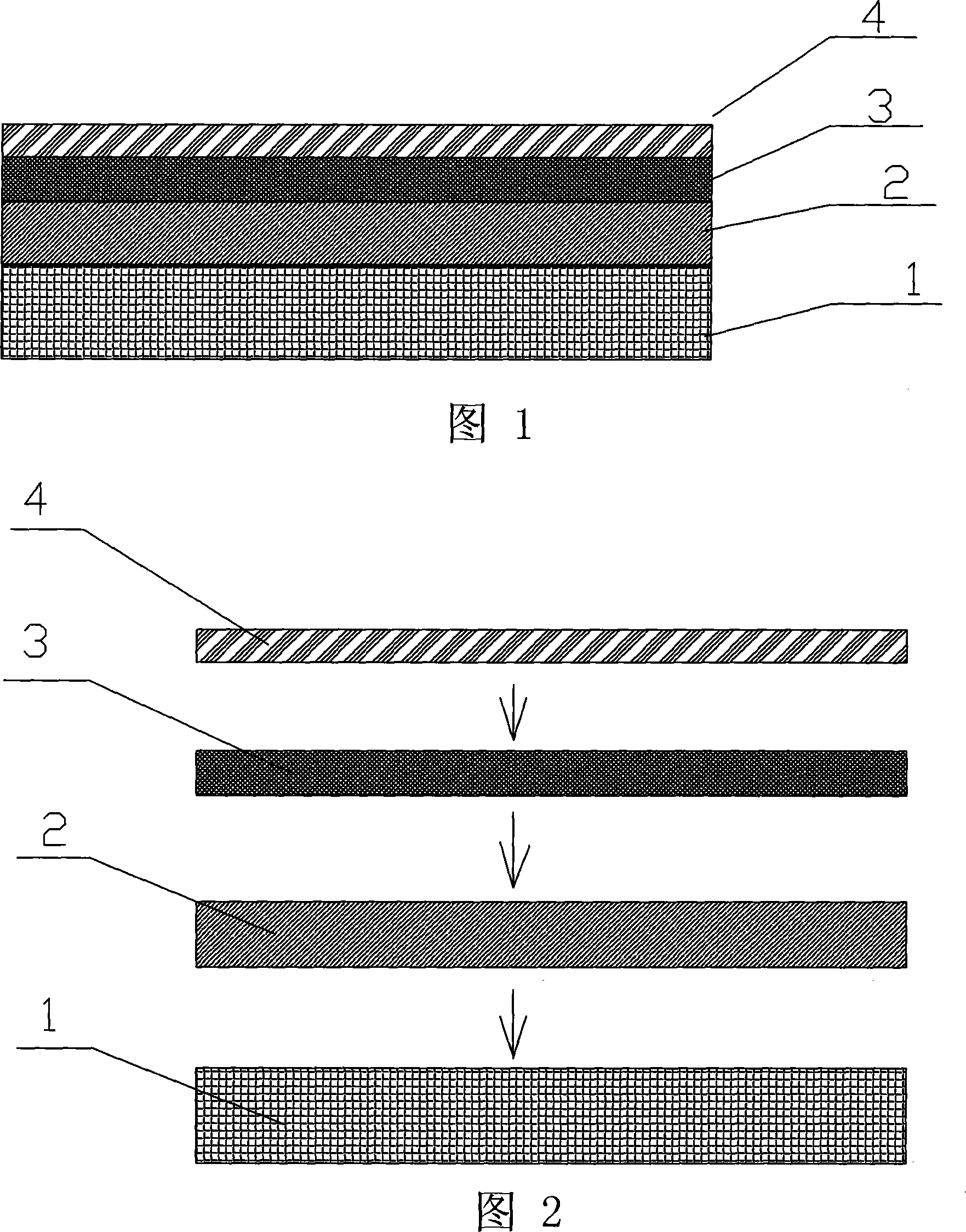
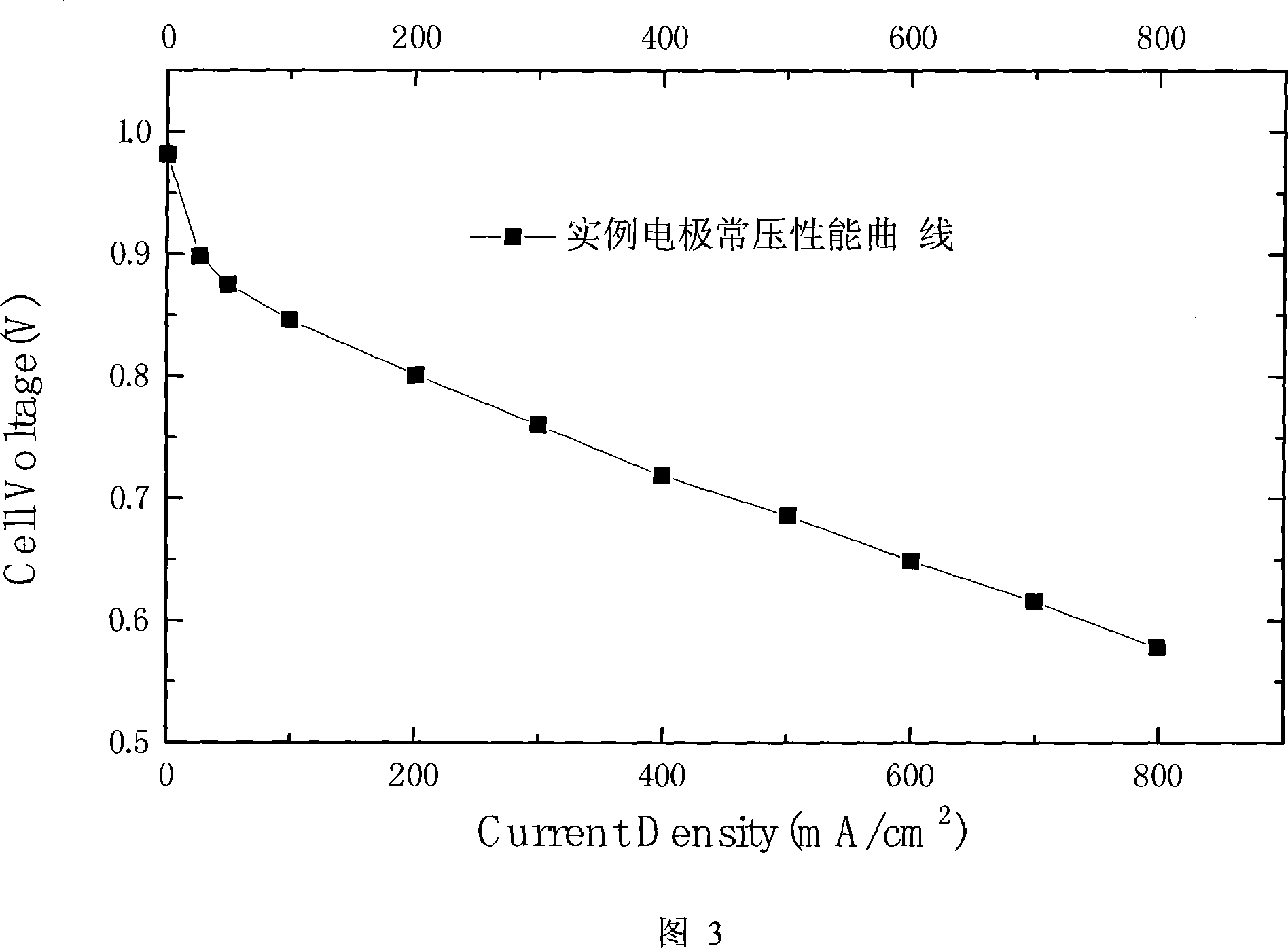
Electrode with progressive structure of proton exchanging film fuel battery and method for making the same
ActiveCN101202349AOvercoming the disadvantage of low utilizationRaise the reactive gasCell electrodesSolid electrolyte fuel cellsMass transfer resistanceHydrophile
The invention provides an electrode with a progressive structure of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell and a preparation method. The electrode consists of a supporting layer, a leveling layer and a catalyzing layer; a strong-hydrophobic macropore layer is the supporting layer; a weak-hydrophobic mesopore layer is above the strong-hydrophobic macropore layer; a weak-hydrophobic mesopore catalyzing layer is above the weak-hydrophobic mesopore layer; a hydrophile micropore catalyzing layer is above the weak-hydrophobic mesopore catalyzing layer; wherein, the weak-hydrophobic mesopore layer comprises the weak-hydrophobic mesopore catalyzing layer in the leveling layer and the catalyzing layer. The invention has the advantages that the electrode catalyzing layer consists of progressive multilayer structure of hydrophile and hydrophobe, the shortage is overcome of low utilization ratio of catalyst in the hydrophobic catalyzing layer, and the transmission effect of reaction gas, especially an air oxidant in the catalyzing layer is improved; a pore-forming agent which is introduced in the electrode improves the porous structure of the levelling layer and the catalyzing layer of the electrode, forms an progressive structure of pore, reduces the mass transfer resistance in the reaction process, and improves the performance of the electrode.
Owner:SUNRISE POWER CO LTD
Forward osmosis composite membrane and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112023732AReduce mass transfer resistanceIncrease water fluxSemi-permeable membranesGeneral water supply conservationPolymer scienceConcentration polarization
The invention belongs to the technical field of membrane separation, and particularly relates to a forward osmosis composite membrane based on a two-dimensional nano material and a macroporous substrate and a preparation method and application of the forward osmosis composite membrane. According to the composite membrane, a two-dimensional nano material is deposited on the surface of a macroporoussubstrate to serve as a middle layer, a polyamide separation layer is formed on the surface of the middle layer, and the composite membrane is obtained. The two-dimensional nano material middle layerin the composite membrane prevents polyamide from permeating into the macroporous substrate to damage the original macroporous and mutually communicated pore structure, reduces the mass transfer resistance, and effectively relieves the internal concentration polarization phenomenon in the forward osmosis process, thereby greatly enhancing the separation performance of the polyamide composite membrane and prolonging the service life of the composite membrane. The forward osmosis composite membrane can be widely applied to seawater desalination, juice concentration and other fields.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Active carbon-silicon aerogel complex for removing volatile organic pollutants
ActiveCN102125821AImprove adsorption capacityImprove desorption efficiencyOther chemical processesDispersed particle separationActivated carbonMass transfer resistance
The invention relates to an active carbon-silicon aerogel complex and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of removal of volatile organic pollutants. The active carbon-silicon aerogel complex is prepared from active carbon granules serving as a skeleton structure and water glass serving as a silicon aerogel precursor by sol-gel reaction and normal-pressure drying. The active carbon-silicon aerogel complex is prepared from cheap raw materials, has a multistage pore structure, and is favorable for improving the adsorption quantity of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), reducingthe mass transfer resistance and improving the desorption efficiency.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method and application of carbon loaded bismuth nanoparticle catalyst
ActiveCN108745340AGood dispersionIncrease current densityElectrolytic organic productionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHigh current densityFormate
The invention discloses a preparation method of a carbon loaded bismuth nanoparticle catalyst, and application of the prepared carbon loaded bismuth nanoparticle catalyst to a CO2 electrochemical reduction catalyst. The preparation method uses a water solution chemical reduction method for synthesis. The carbon loaded bismuth nanoparticle catalyst is prepared by the simple water solution chemicalreduction method; by effectively regulating and controlling the addition quantity of a stabilizing agent and the carbon material variety, metal Bi particles of a nanometer structure are obtained; relatively good dispersibility is realized; in the CO2 reduction process, the selectivity on formate is high; the current density can be improved; the electrochemical surface area of the catalyst can be greatly improved; the exposure of CO2 reduction active sites is improved; the electron mass transfer resistance is reduced; the current density of CO2 reduction is increased; the utilization rate and the conversion rate of CO2 are effectively improved; the preparation method is simple; the yield is great; the preparation method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of immobilized enzyme by applying amphiphilic porous hollow carbon microspheres
InactiveCN102443579ALarge specific surface areaLarge internal cavityOn/in inorganic carrierMass transfer resistanceCarrying capacity
The invention discloses a preparation method of an immobilized enzyme by applying amphiphilic porous hollow carbon microspheres. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: mixing amphiphilic porous hollow carbon microspheres and a solution of an enzyme to be immobilized, and reacting for 0.5 to 24 hours at a temperature of between 4 and 45 DEG C to obtain the immobilized enzyme, wherein the amphiphilic porous hollow carbon microspheres are prepared by the following way: carbonizing yeast in an aqueous solution or water at a temperature of between 180 and 240 DEG C to obtain the amphiphilic porous hollow carbon microspheres. The method has the advantages that: (1) enzyme package embedding and carrier preparation are separately carried out to avoid inactivation of the enzyme; (2) non-covalent effect exists between the enzyme and the carrier, the surface group of the carrier is not required to be modified, and the method is simple; (3) damage of strong stirring and other external factors to the enzyme can be effectively avoided, and the operation stability of the immobilized enzyme is improved; (4) the mass transfer resistance is small; (5) the amphiphilic property of the hollow carbon microspheres provides possibility for the application of the hollow carbon microspheres in an organic medium system; (6) the method has universality; and (7) the enzyme carrying capacity is high, and the stability is strong.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Self-dehydration hydrophobic separation membrane and preparation method
InactiveCN104307388AHigh mechanical strengthWith the function of self-dehydrationSemi-permeable membranesMicro nanoFiltration
The invention discloses a self-dehydration hydrophobic separation membrane and a preparation method. The surface of a hydrophilic membrane is coated with polyvinylidene fluoride particles so as to form the self-dehydration hydrophobic separation membrane with a micro nano grade convex-concave structure. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing the polyvinylidene fluoride particles into turbid liquid; performing ultra-filtration so as to enable the the surface of the hydrophilic polyvinylidene fluoride porous membrane-based membrane to be coated with the polyvinylidene fluoride turbid liquid; drying the hydrophilic polyvinylidene fluoride porous membrane-based membrane coated with the polyvinylidene fluoride turbid liquid so as to obtain the self-dehydration hydrophobic separation membrane. The self-dehydration hydrophobic separation membrane is sufficient in mechanical strength and has a self-dehydration function, once being dissociated from an aqueous solution, the surface of the hydrophobic separation membrane can be automatically dried, so that the purpose of drying the hydrophobic separation membrane pores is realized; the hydrophobic layer of the hydrophobic separation membrane is thin, the surface pure water contact angle of the hydrophobic separation membrane is large, the separation mass transfer resistance can be effectively alleviated, the separation efficiency is improved, and the large-scale industrialization application of a membrane separation technique is facilitated.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
System for deep treatment of coking wastewater by means of catalytic ozonation-ceramic membrane filtration
InactiveCN102849875AStrong upward impactInhibition falls intoMultistage water/sewage treatmentParticulatesChemical oxygen demand
The invention discloses a system for deep treatment of coking wastewater by means of catalytic ozonation-ceramic membrane filtration, mainly consisting of an ozone generator, an ozone oxidation reactor, a booster pump, a ceramic membrane component, a gas-liquid separator, a tail gas absorbing device, a wastewater reflowing pump, a catalyst reflowing pump, a catalyst adding pump, a catalyst outflowing groove, a catalyst adding groove and corresponding pipe fittings, valves and instruments. According to the system, the application of a powder catalyst in a dynamic reactor can be realized due tothe combination of the catalytic ozonation and the ceramic membrane separation; the ozonation and the catalytic ozonation can be guaranteed to be carried out in a single reactor in a segmental way due to the convection current of the reflowing wastewater and the catalyst slurry and the impact of upcurrent; the mass transfer resistance when the ozonation and the catalytic ozonation are independently used can be reduced; the use ratio of hydroxyl free radical and the removal rate of organic matters can be improved; the aims, such as the COD (chemical oxygen demand), the chroma and the turbidityof the deeply-treated coking wastewater, can be achieved; and the problems that the activity is suddenly reduced when the powder catalyst is formed into particulates, the running needs to be suspended when the mass transfer resistance is increased due to the use of the particulate catalyst and the particulate catalyst is changed and the like can be solved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Surface self-cleaning carbon nitride Fenton-photocatalytic nanofiltration membrane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109569311AEfficient degradationEffective combinationMembranesSemi-permeable membranesFenton reagentWater quality
The invention discloses a surface self-cleaning carbon nitride Fenton-photocatalytic nanofiltration membrane and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the fields of water treatment membrane materials and preparation processes of the water treatment membrane materials. The method comprises selecting carbon nitride photocatalysts which integrate plasticity of polymer molecules and chemical stability of carbon materials and performing surface modification, chemical modification, Fenton-like agent compounding and the like to prepare a multifunctional water treatment membrane. On the one hand, inter-element triangular nanopores formed by carbon nitride can provide stable natural channels for rapid passage of water molecules; on the other hand, through irradiated catalytic degradation andiron-containing agent Fenton-like oxidation, in-situ degradation of nanofiltration retained pollutants can be achieved. The surface self-cleaning carbon nitride Fenton-photocatalytic nanofiltration membrane provides a new way for solving the problem of membrane contamination difficult for traditional nanofiltration membrane materials and has the advantages of being simple in preparation method, low in cost, resistant to pollution, low in water mass transfer resistance and the like, thereby being applicable to application to the field of water purification.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Hydrophobic ceramic hollow fiber membrane applied to membrane distillation and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102172478AControl sintering temperatureImprove high temperature resistanceSemi-permeable membranesPhase conversionMass transfer resistance
The invention provides a preparation method of a hydrophobic ceramic hollow fiber membrane applied to membrane distillation. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: a) mixing ceramic powder, polyether sulfone, N-methyl-1-ketopyrrolidine and a dispersant and grinding to obtain slurry; b) extruding the slurry out by using a spinning jet and performing phase conversion molding to obtain a hollow fiber blank; c) sintering the hollow fiber blank to obtain a ceramic hollow fiber membrane; and d) modifying the ceramic hollow fiber membrane by taking silane as a modifier to obtain the hydrophobic ceramic hollow fiber membrane. The hydrophobic ceramic hollow fiber membrane has a hollow fiber structure, a thinner membrane wall and small mass transfer resistance, so that a higher membrane flux is achieved, the filling density of a membrane component is high and the separating effect is good during membrane distillation. Moreover, the ceramic hollow fiber membrane is taken as a substrate of the hydrophobic hollow fiber membrane, so that the hydrophobic hollow fiber membrane has high high-temperature resistance, high structural stability and high restoration and regeneration performance, is easy to clean and has a long service life.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Bipolar-structured lithium-air battery
InactiveCN102263311ASimple structureReduce volatilityFuel and primary cellsMass transfer resistanceLithium–air battery
The invention discloses a bipolar-structured lithium-air battery, which belongs to the technical field of preparation of lithium-air batteries. The bipolar-structured lithium-air battery mainly comprises a cathode, a diaphragm, an anode and a housing, wherein lithium metal as the cathode is arranged inside the housing, and the diaphragm and the anode are sequentially arranged at the upper part of the lithium metal; and the battery does not contain the traditional electrolytic solution layer, and the anode is obtained by preparing a non-volatile electrolytic solution with stable chemical property on a perforated electrode. The bipolar-structured lithium-air battery disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple structure, small mass transfer resistance, and capabilities of reducing the volatilization of electrolytic solution, decelerating the cathode corrosion, increasing the specific discharge energy capacity and prolonging the cycle life.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
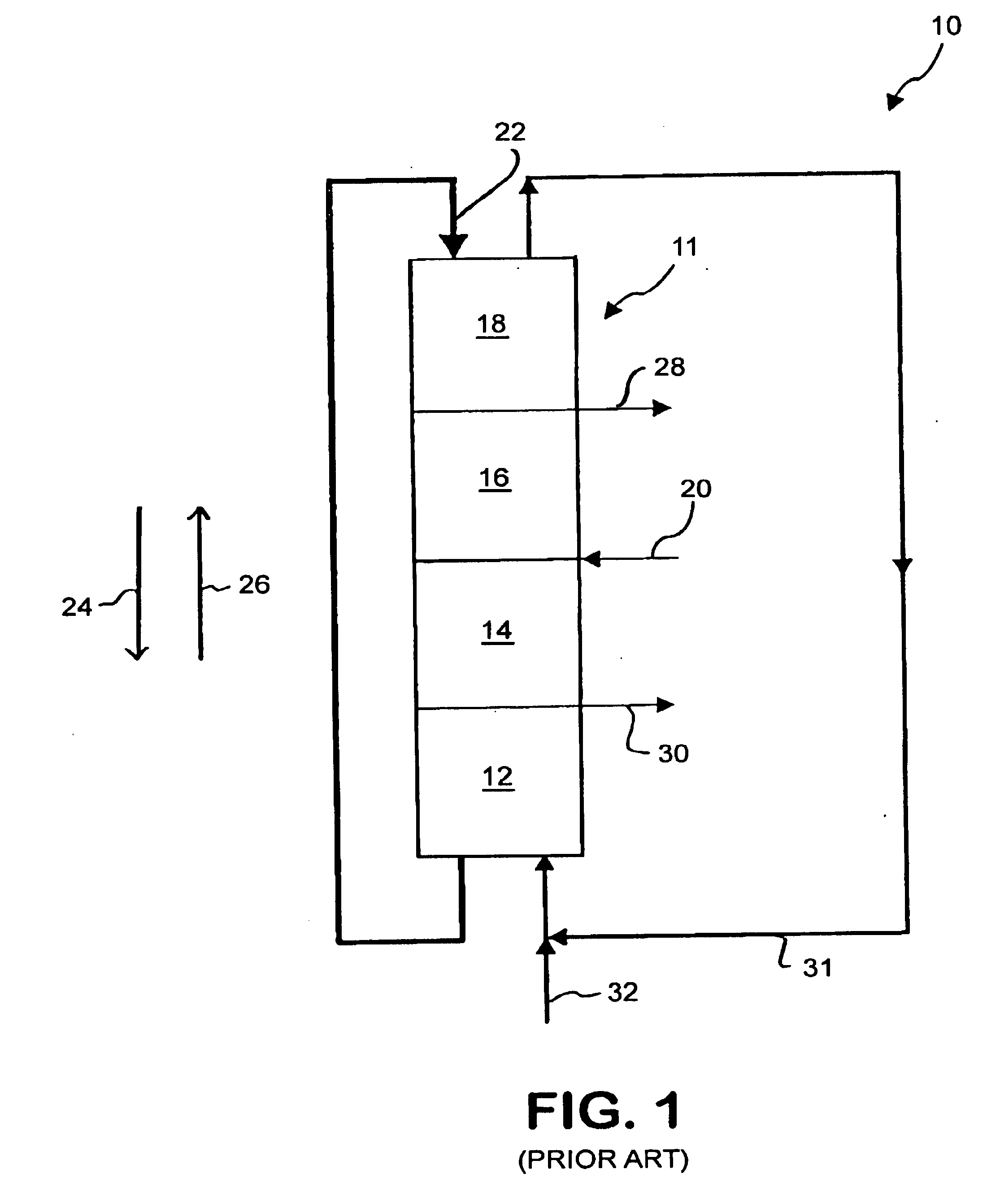
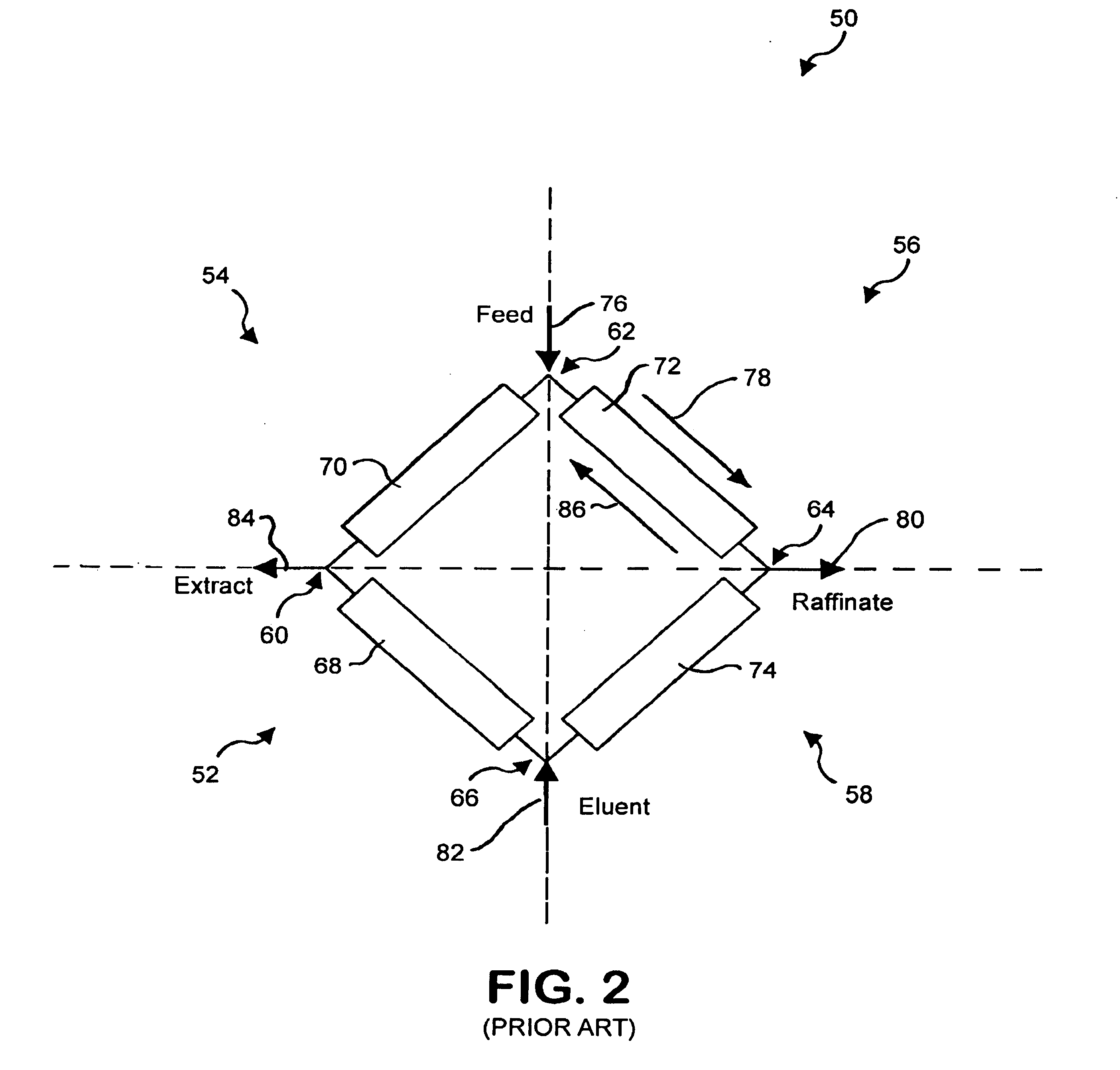
Method and apparatus for separating a component from a mixture
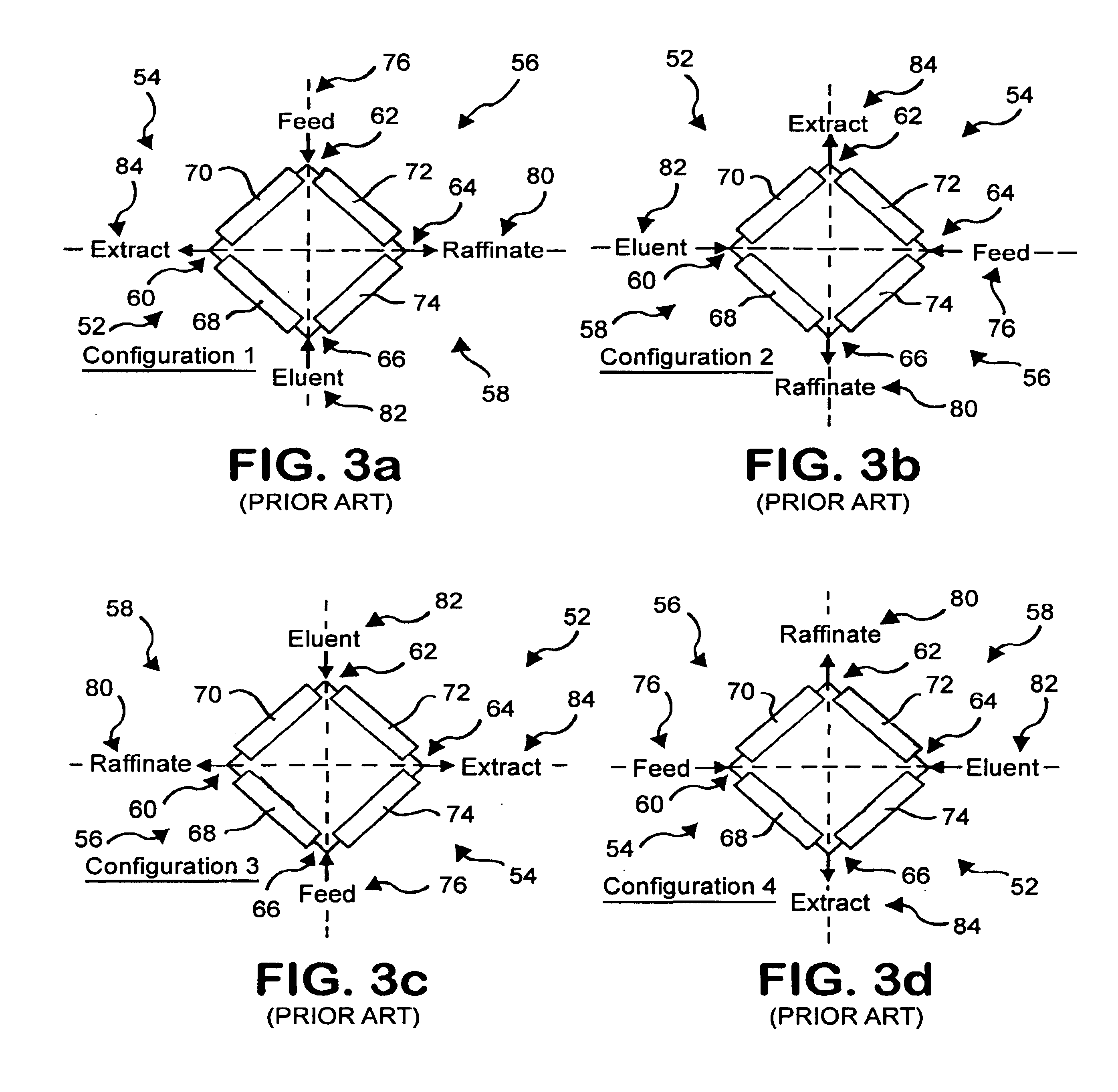
InactiveUS6843854B2Ion-exchange process apparatusJuice extractionMass transfer resistanceSimulated moving bed
The present invention comprises the optimization of a four zone simulated moving bed system configured to separate a first component from a mixture containing the first component and a second component wherein the first component exhibits non-linear adsorption and non-negligible mass transfer resistances. In one example, the four zone simulated moving bed is optimized to separate Clarithromycin from a mixture containing Clarithromycin and 6,11-O-methyl erythromycin A. The present invention further comprises a four zone or a five zone apparatus having a first portion and a second portion and the optimization of the four zone or five zone apparatus to separate a first component from a mixture containing the first component and a second component and the method of using the same. In one example, the four zone and five zone simulated moving beds are optimized to separate Clarithromycin from a mixture containing Clarithromycin and 6,11-O-methyl erythromycin A. The present invention further comprises a batch elution system configured to separate Clarithromycin from a mixture containing Clarithromycin and 6,11-O-methyl erythromycin A.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com