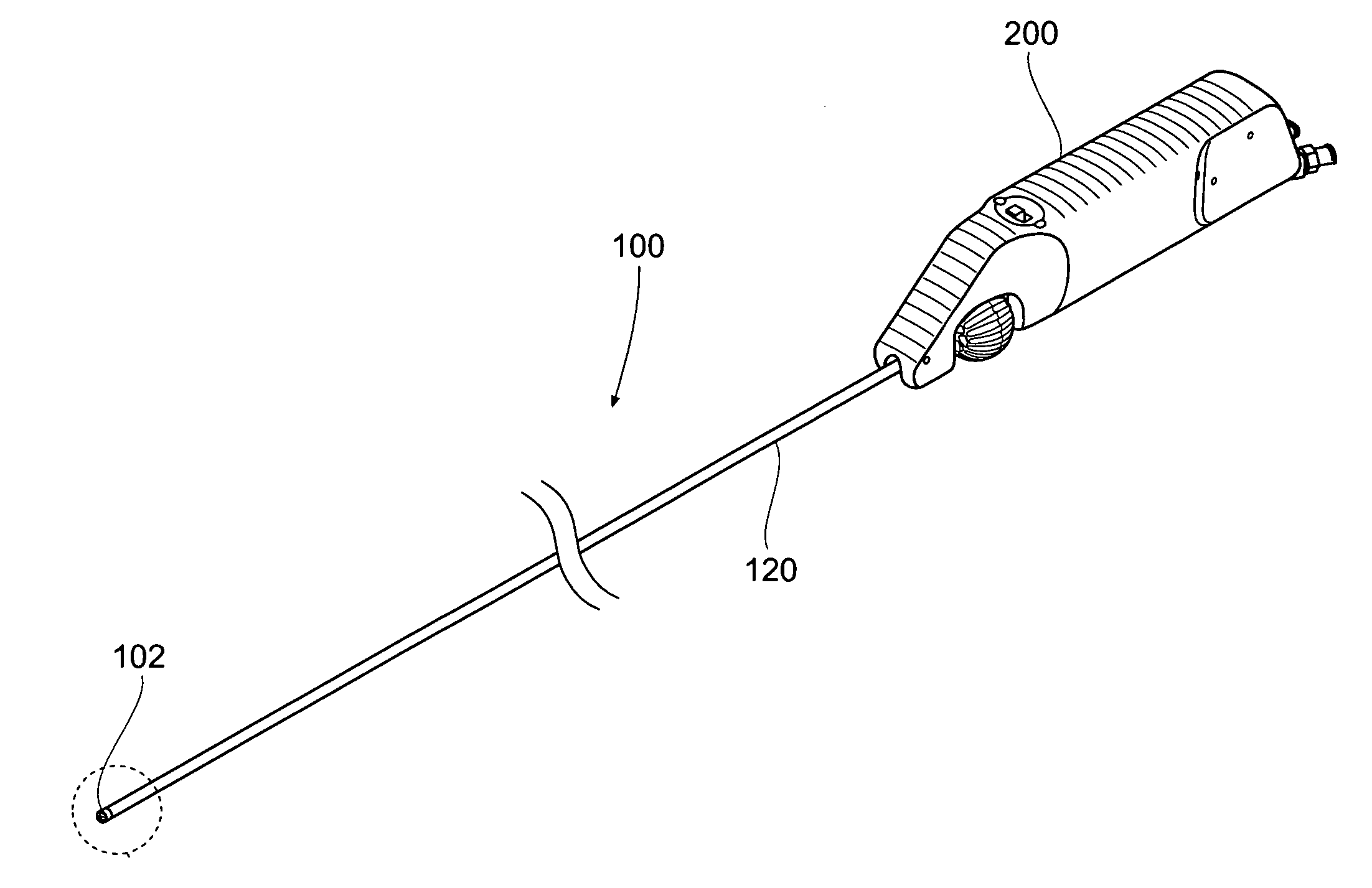
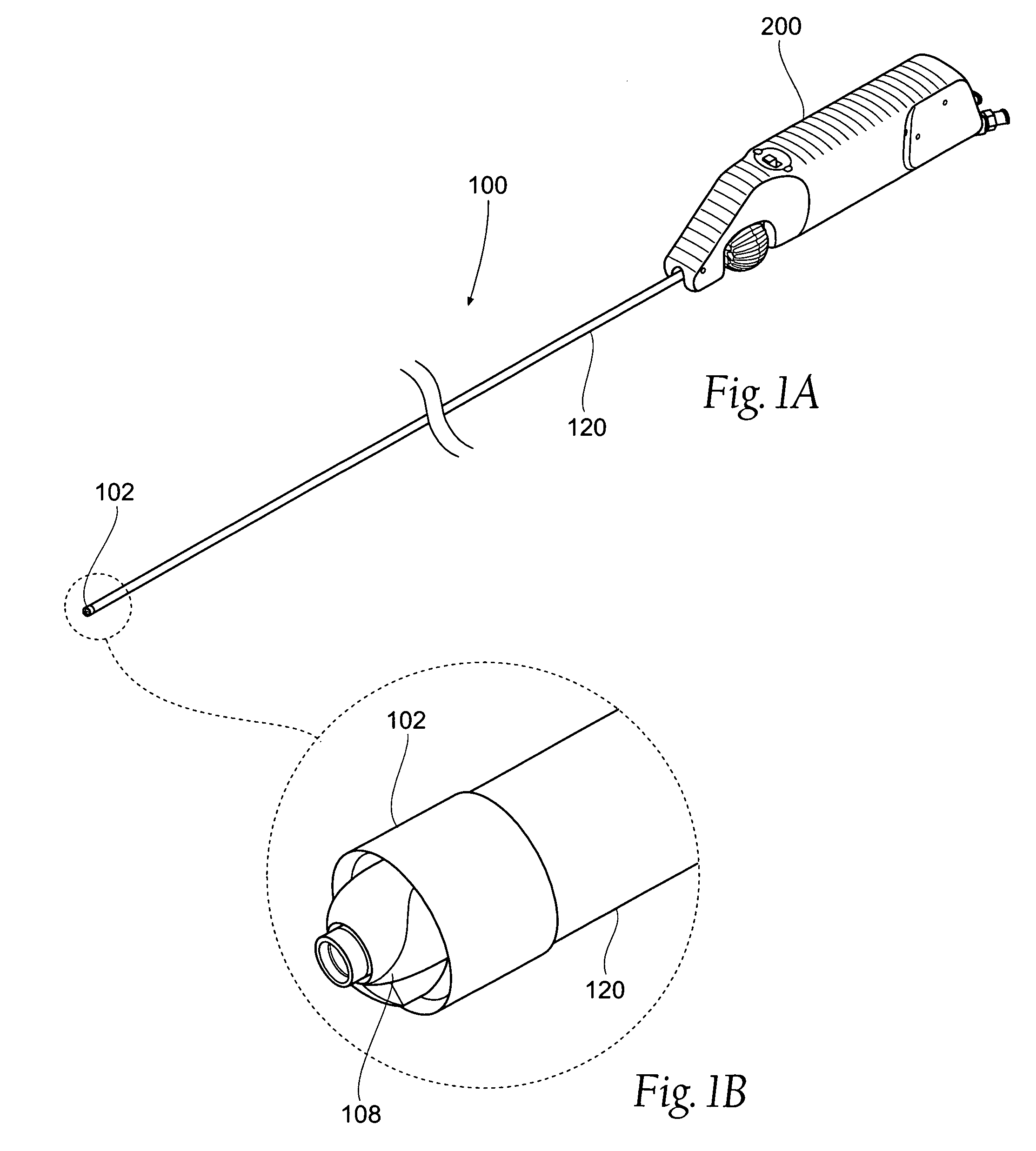
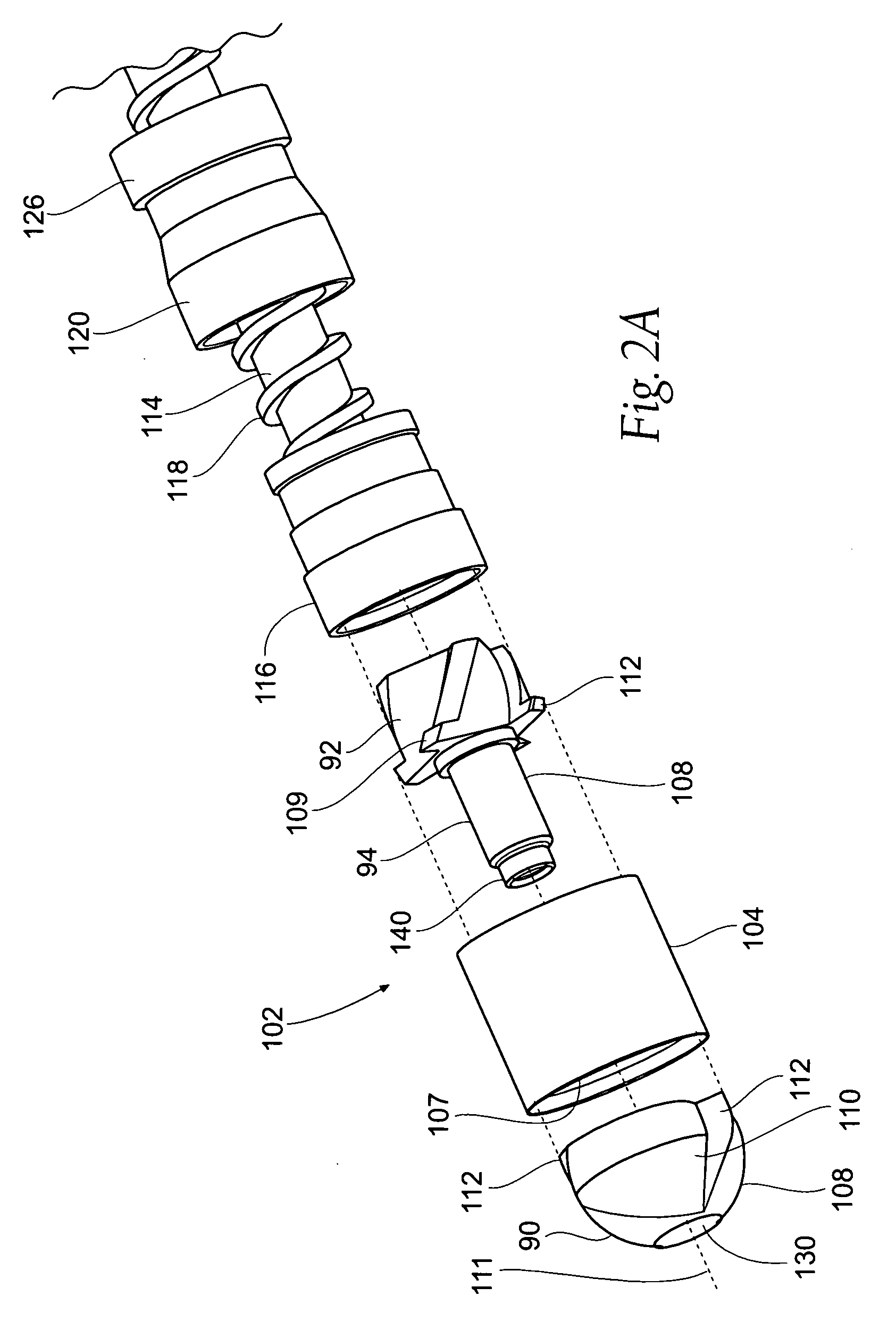
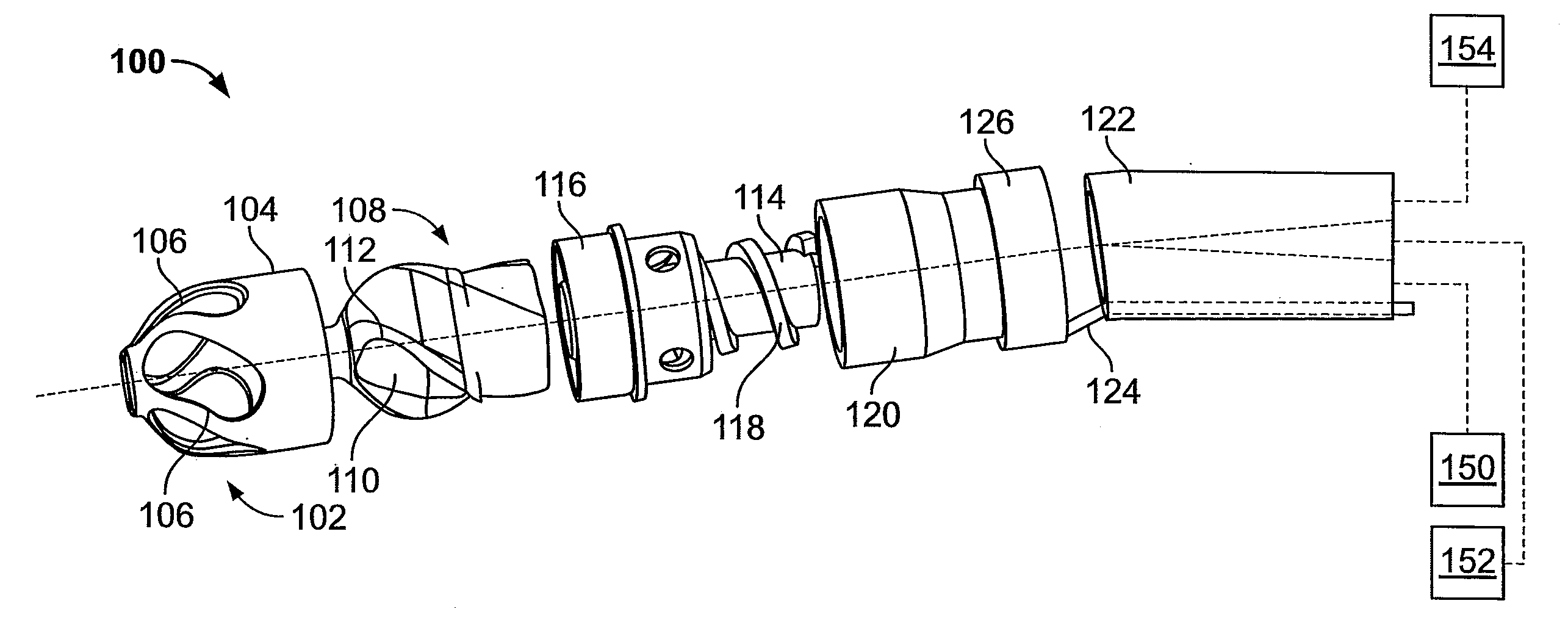
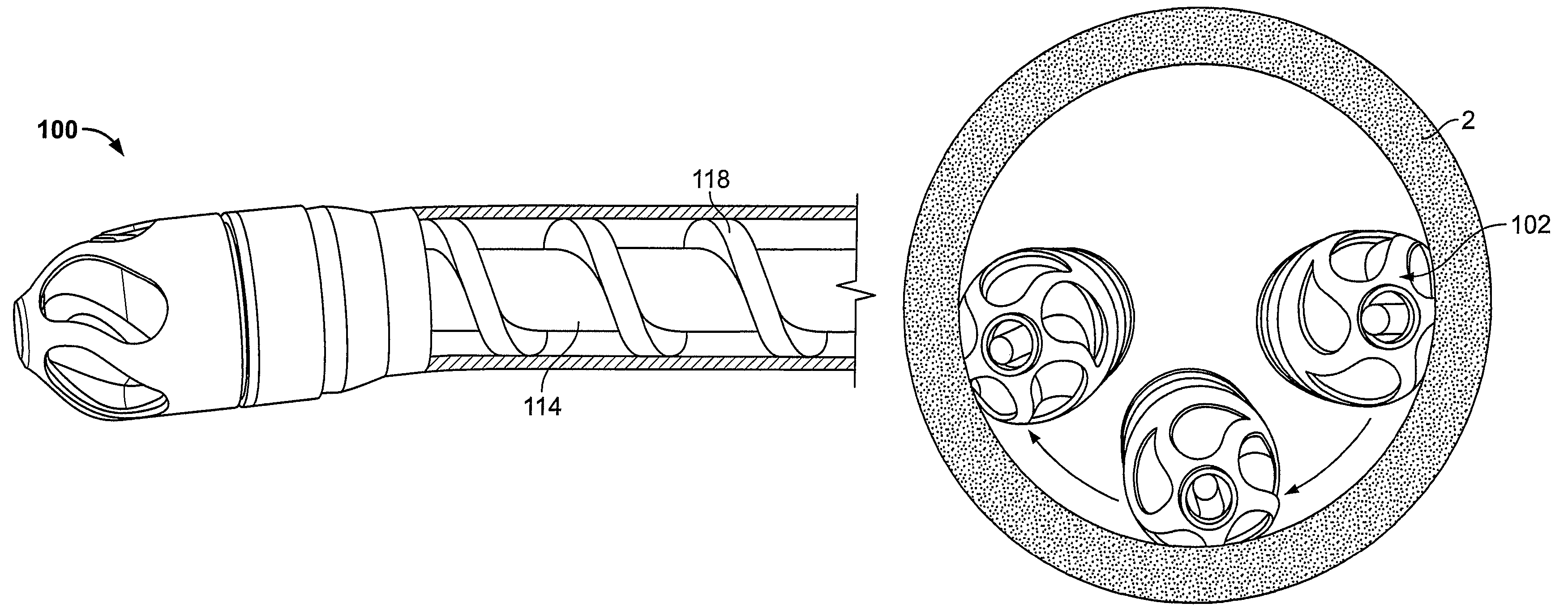
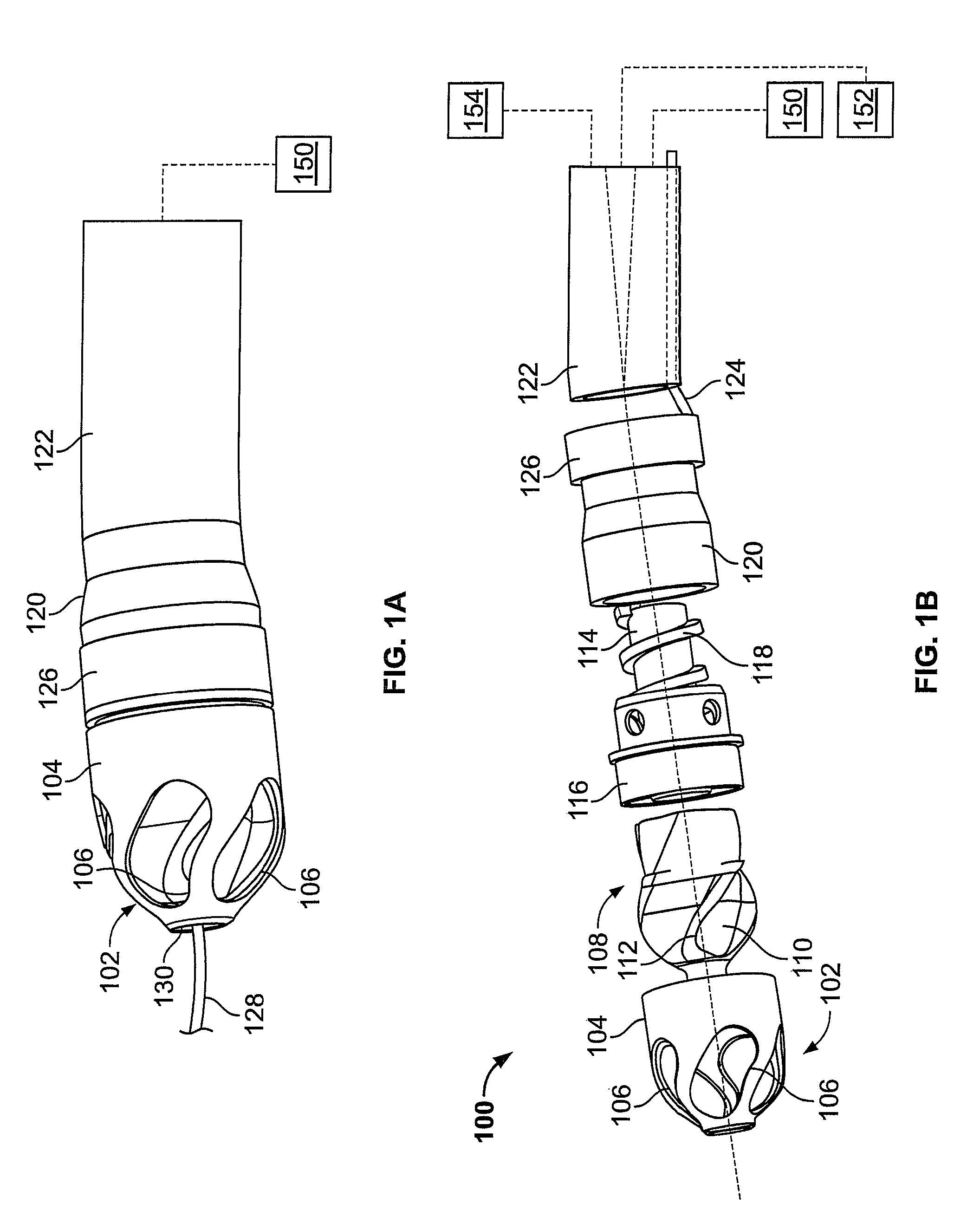
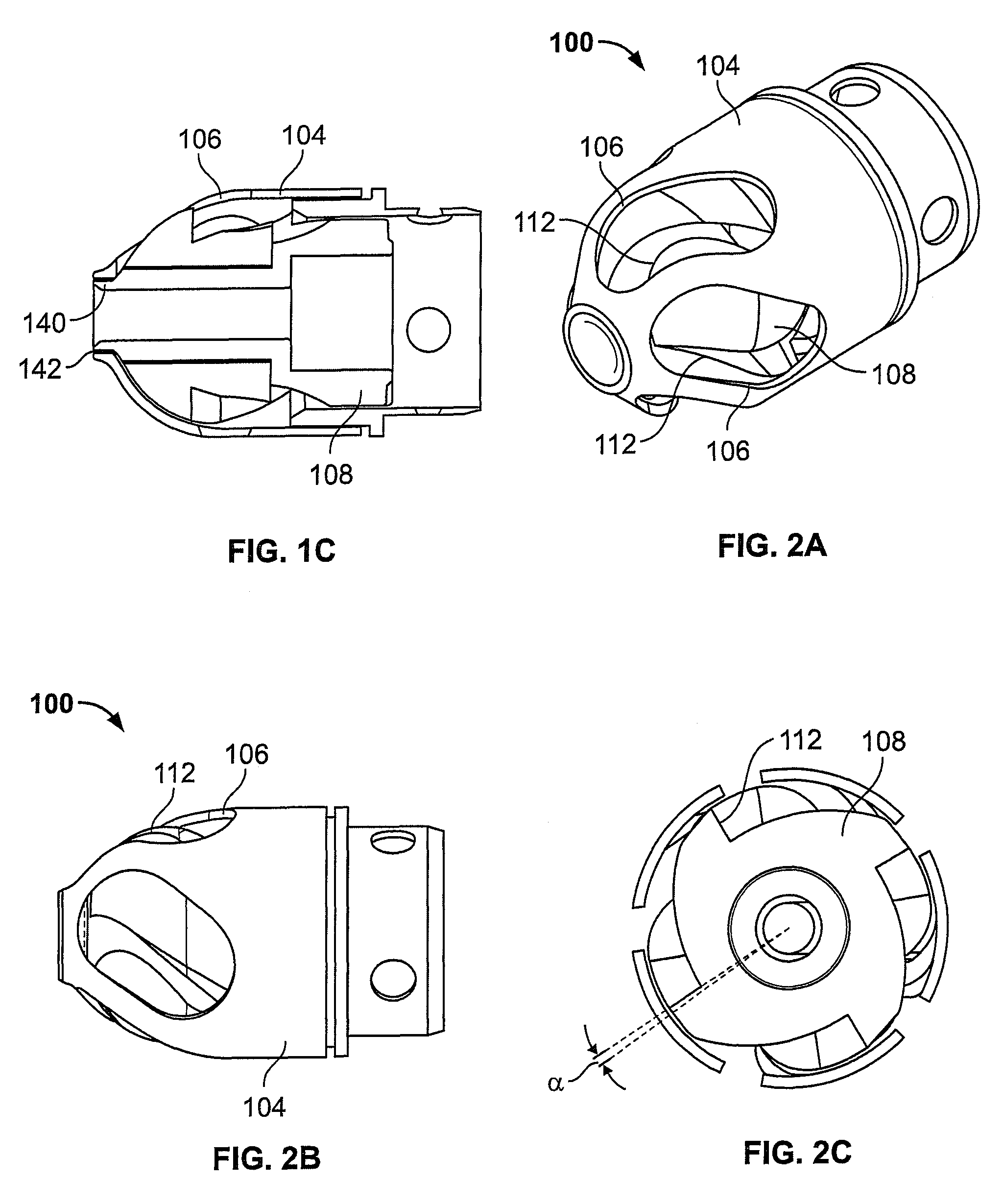
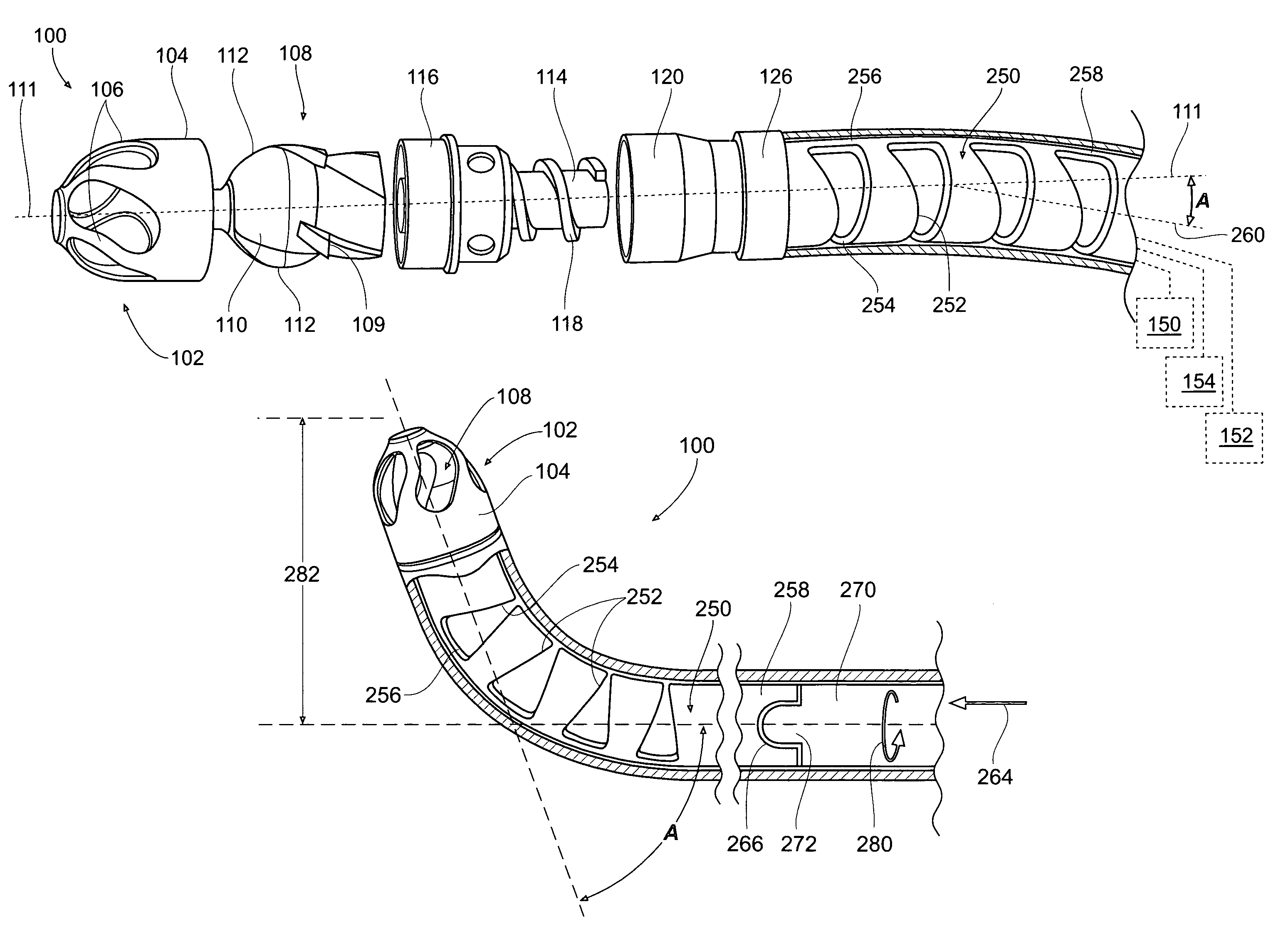
Patents
Literature
126 results about "Atherectomy device" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
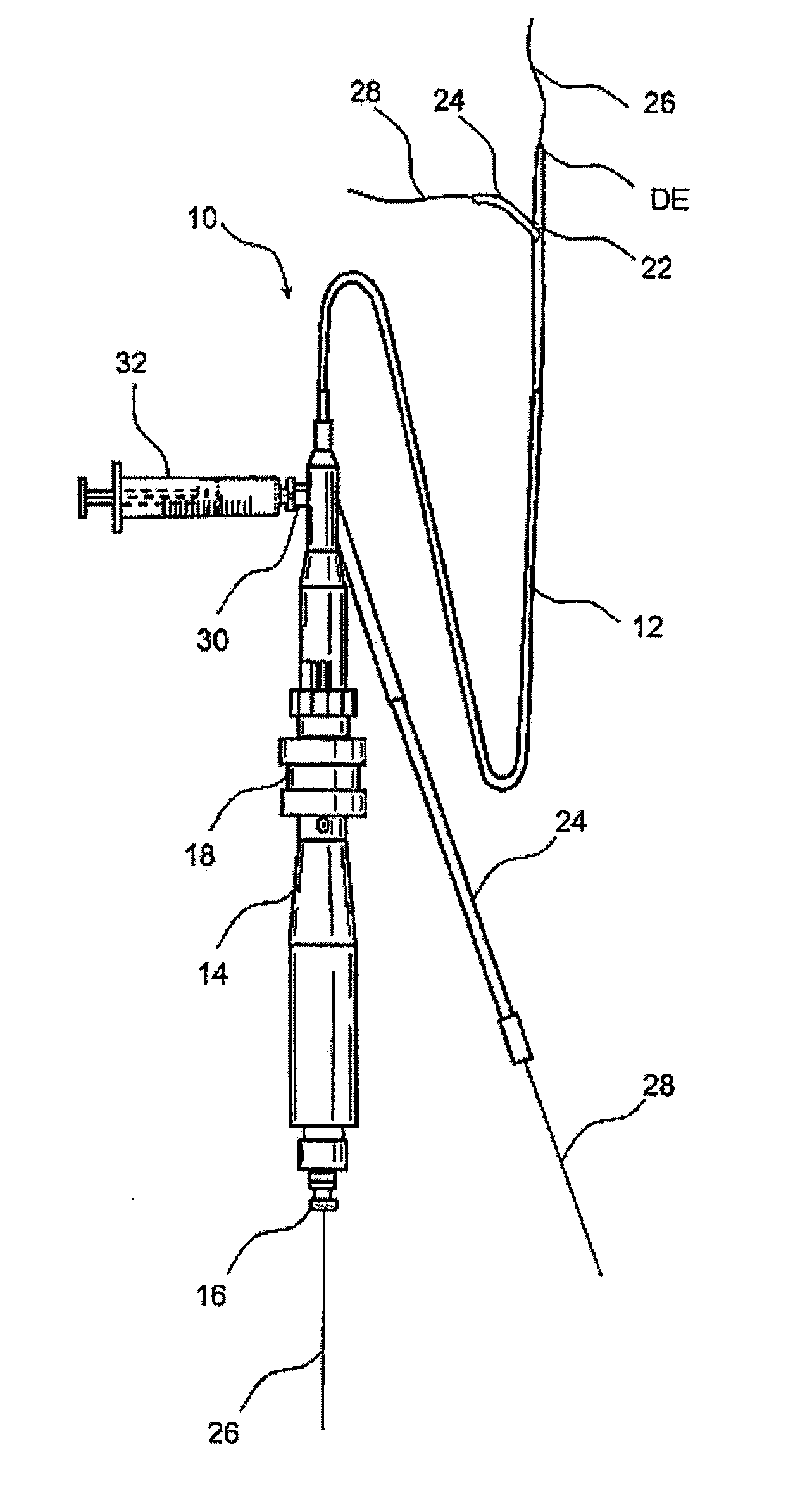
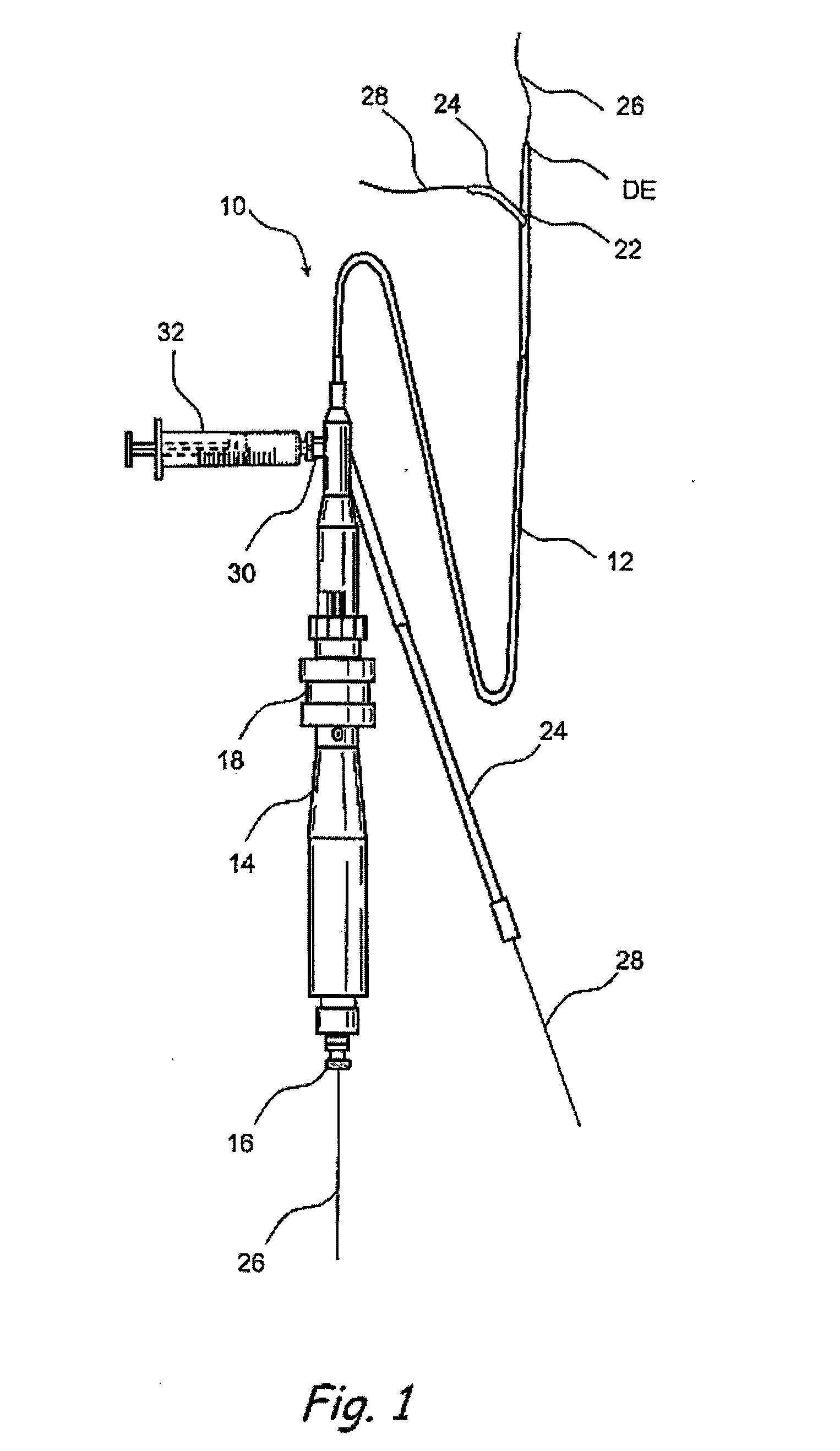
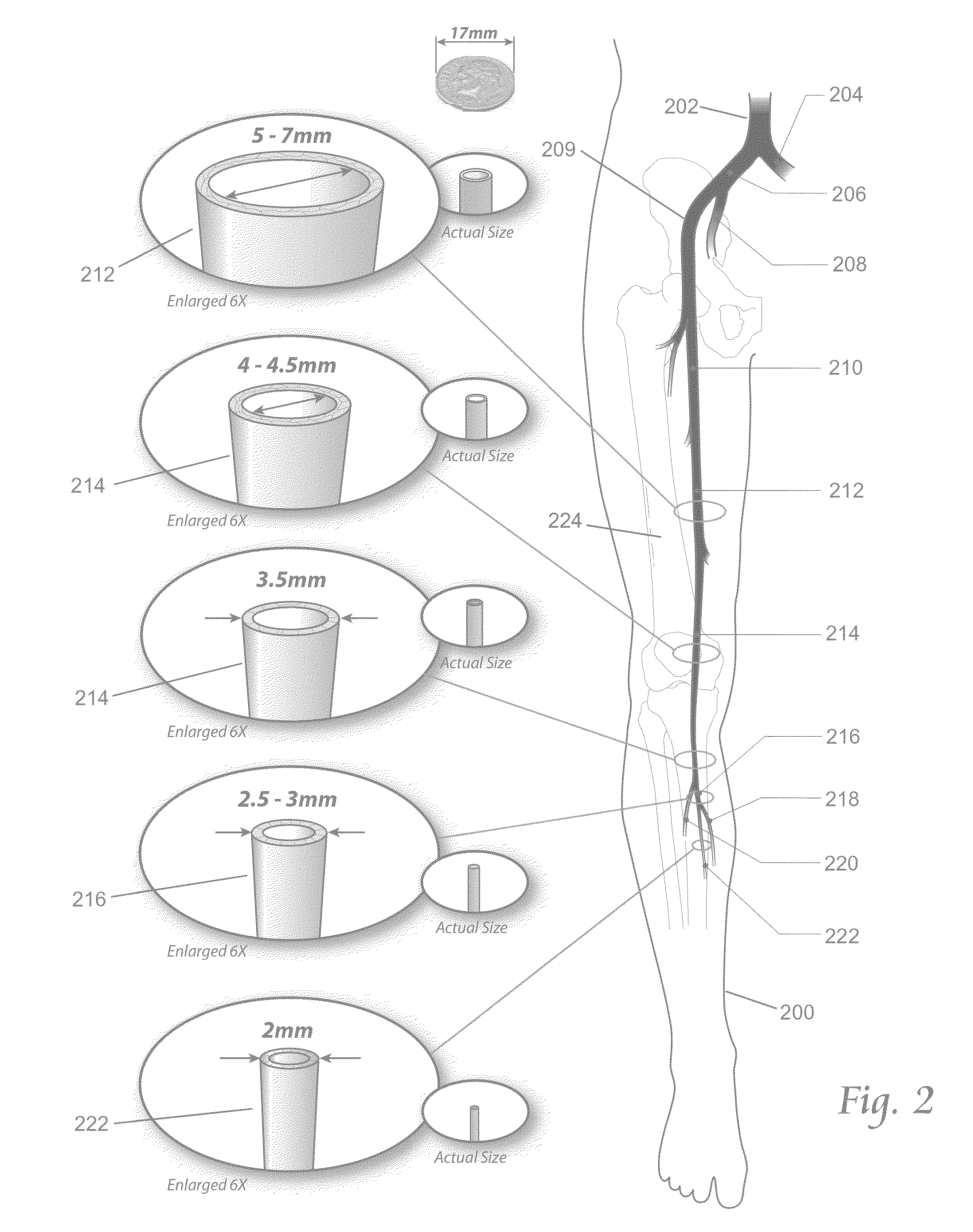
Atherectomy is a non-surgical procedure to open blocked coronary arteries or vein grafts by using a device on the end of a catheter to cut or shave away atherosclerotic plaque (a deposit of fat and other substances that accumulate in the lining of the artery wall).
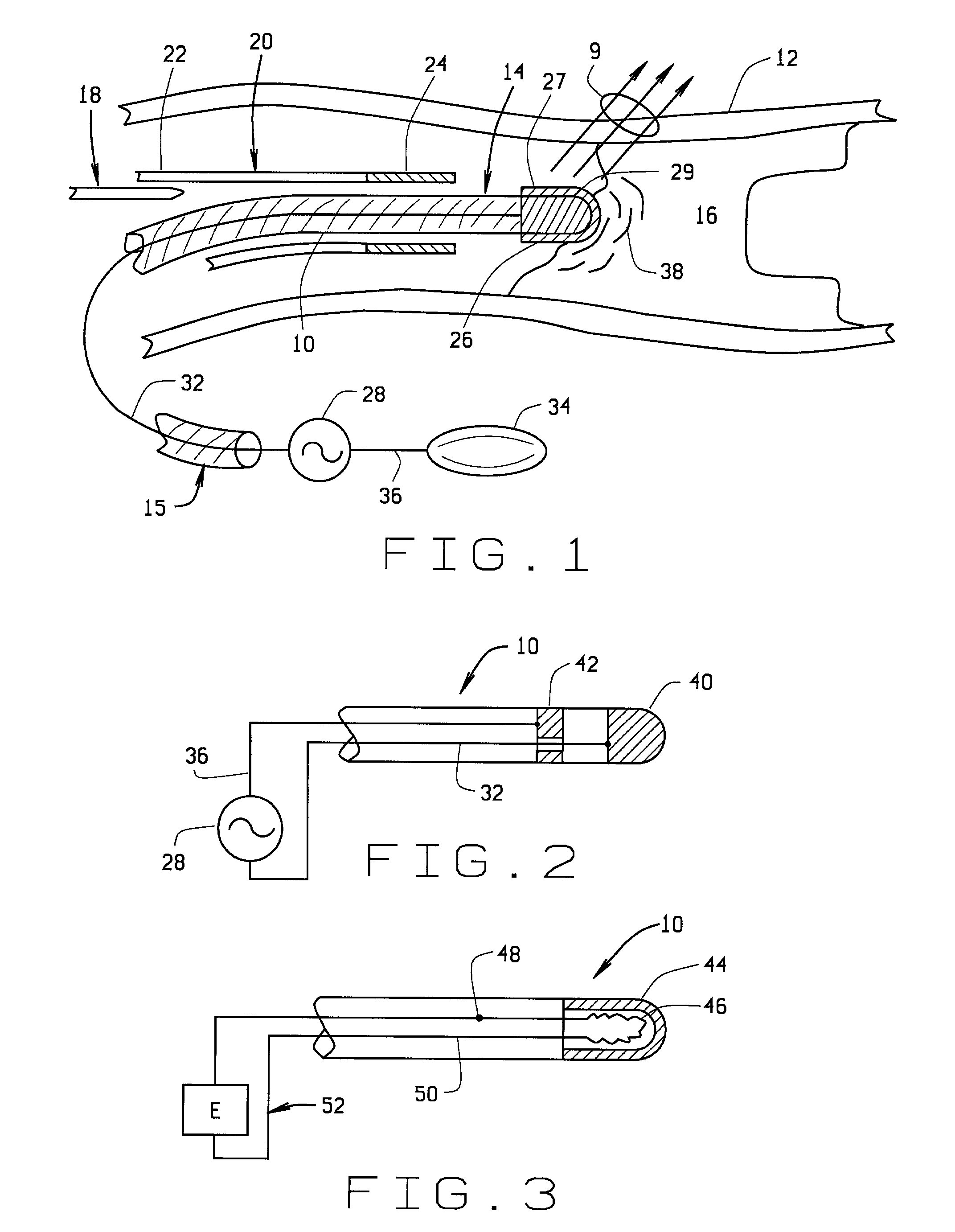
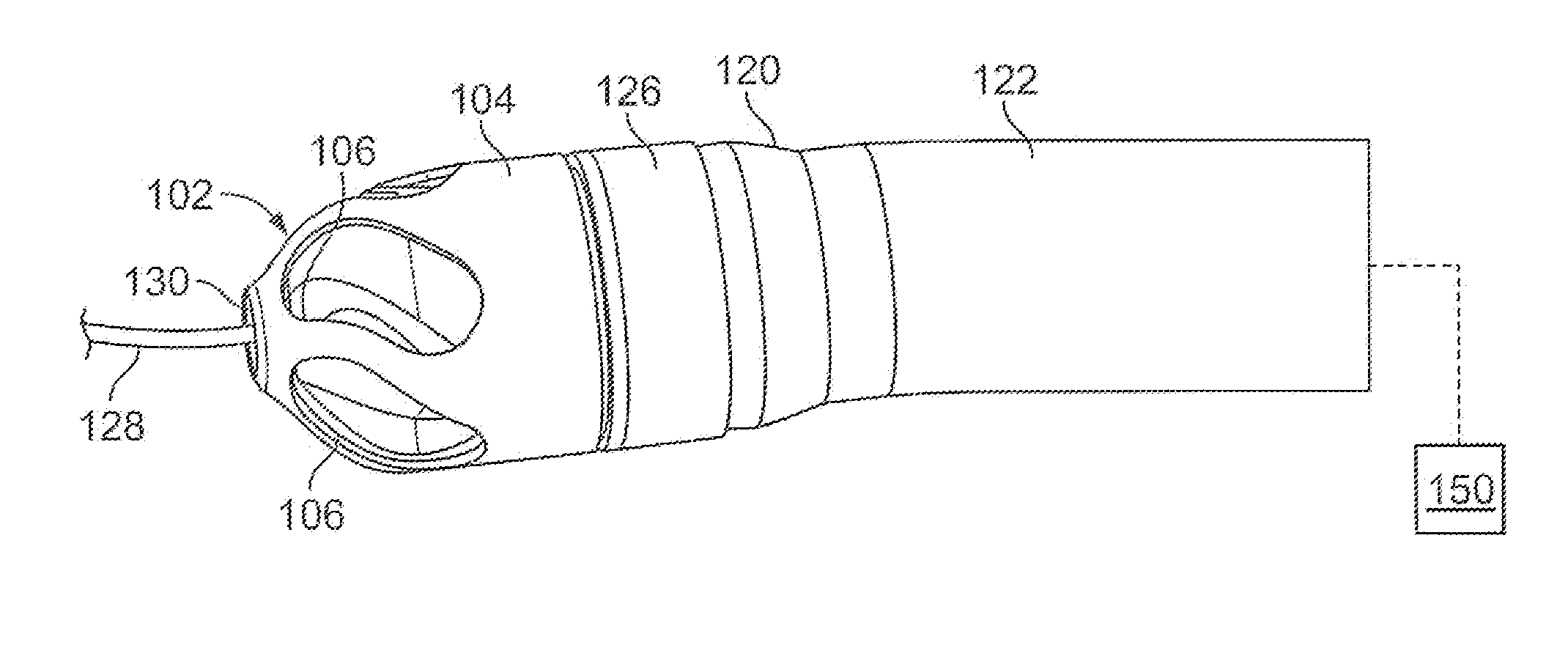
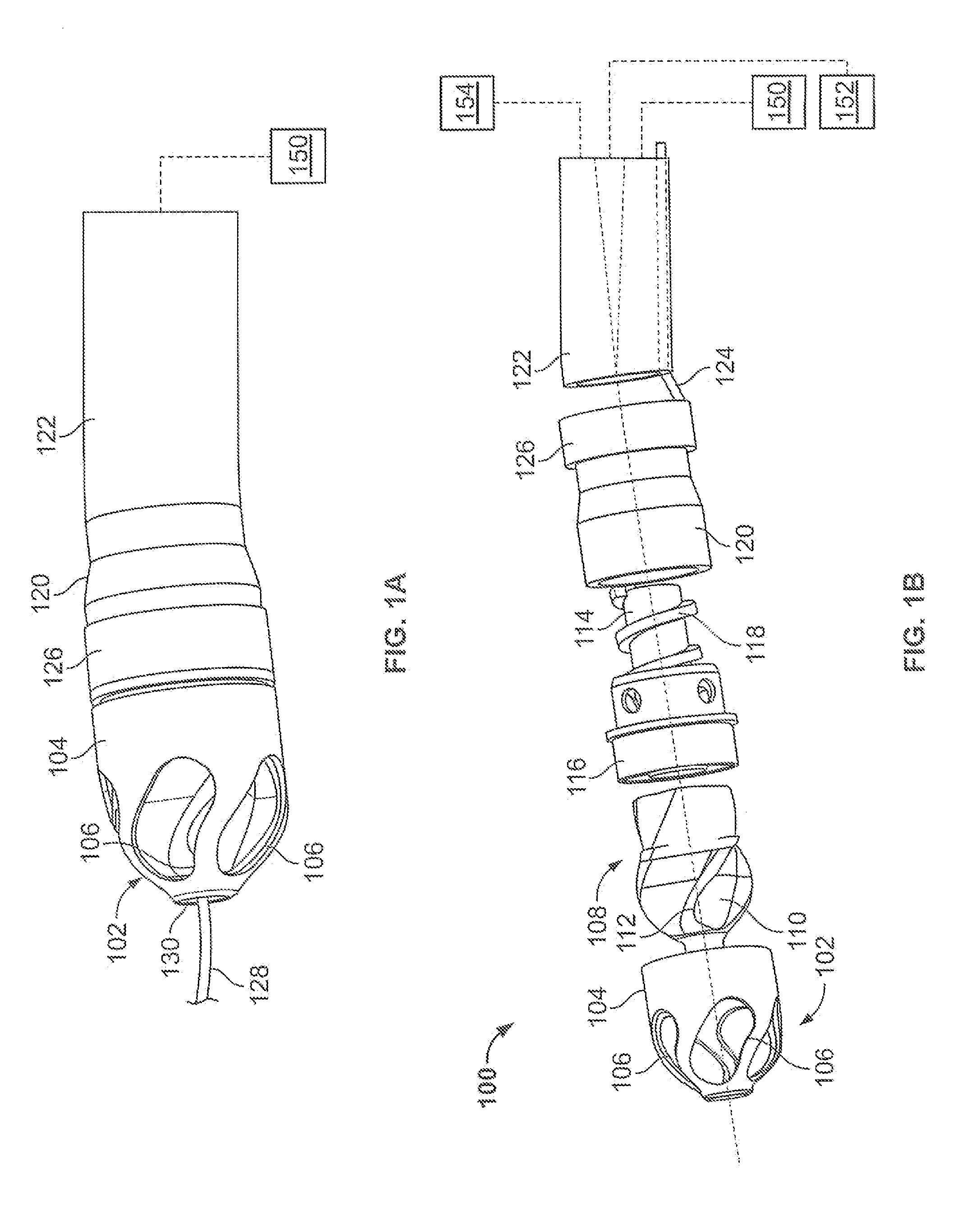
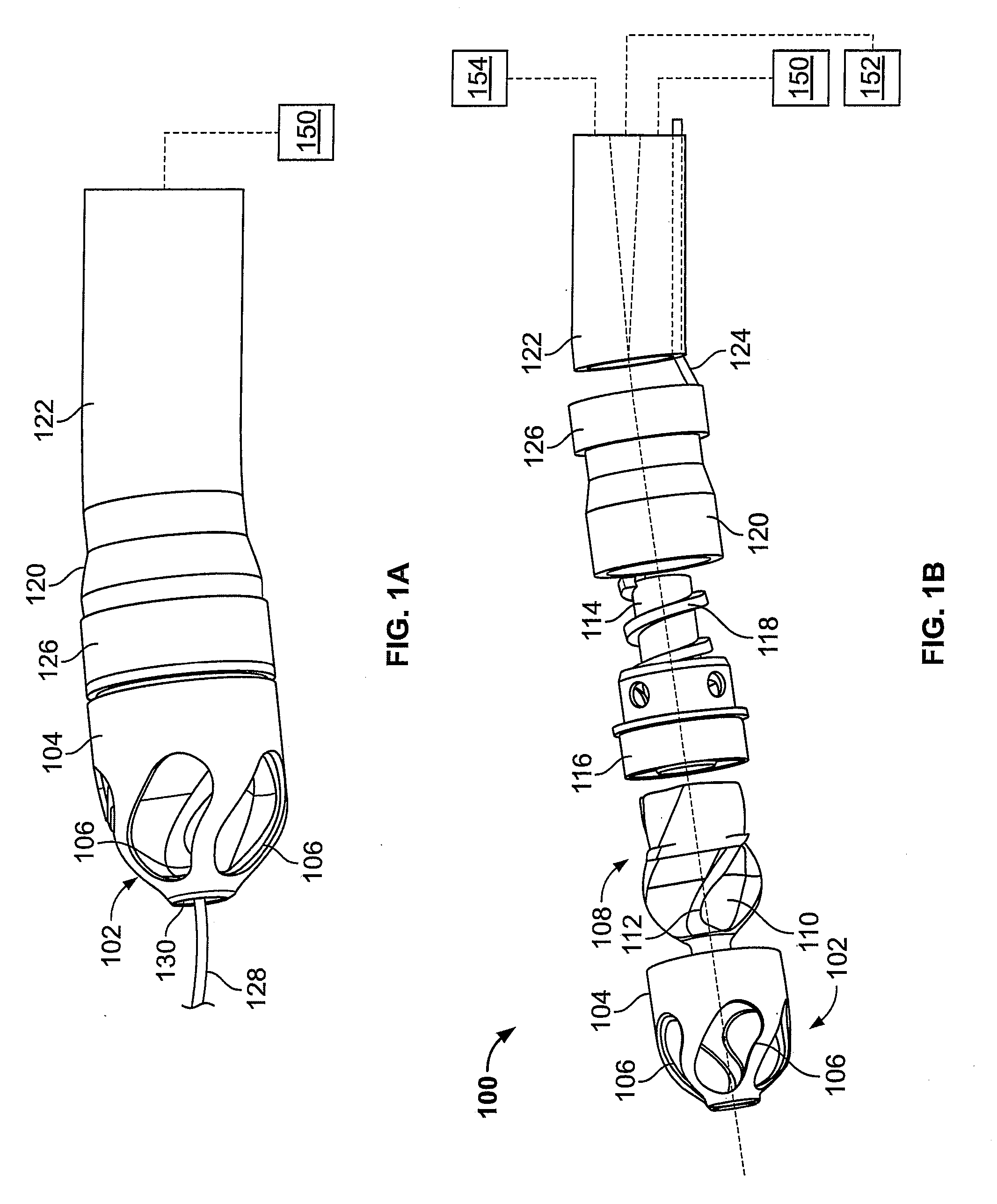
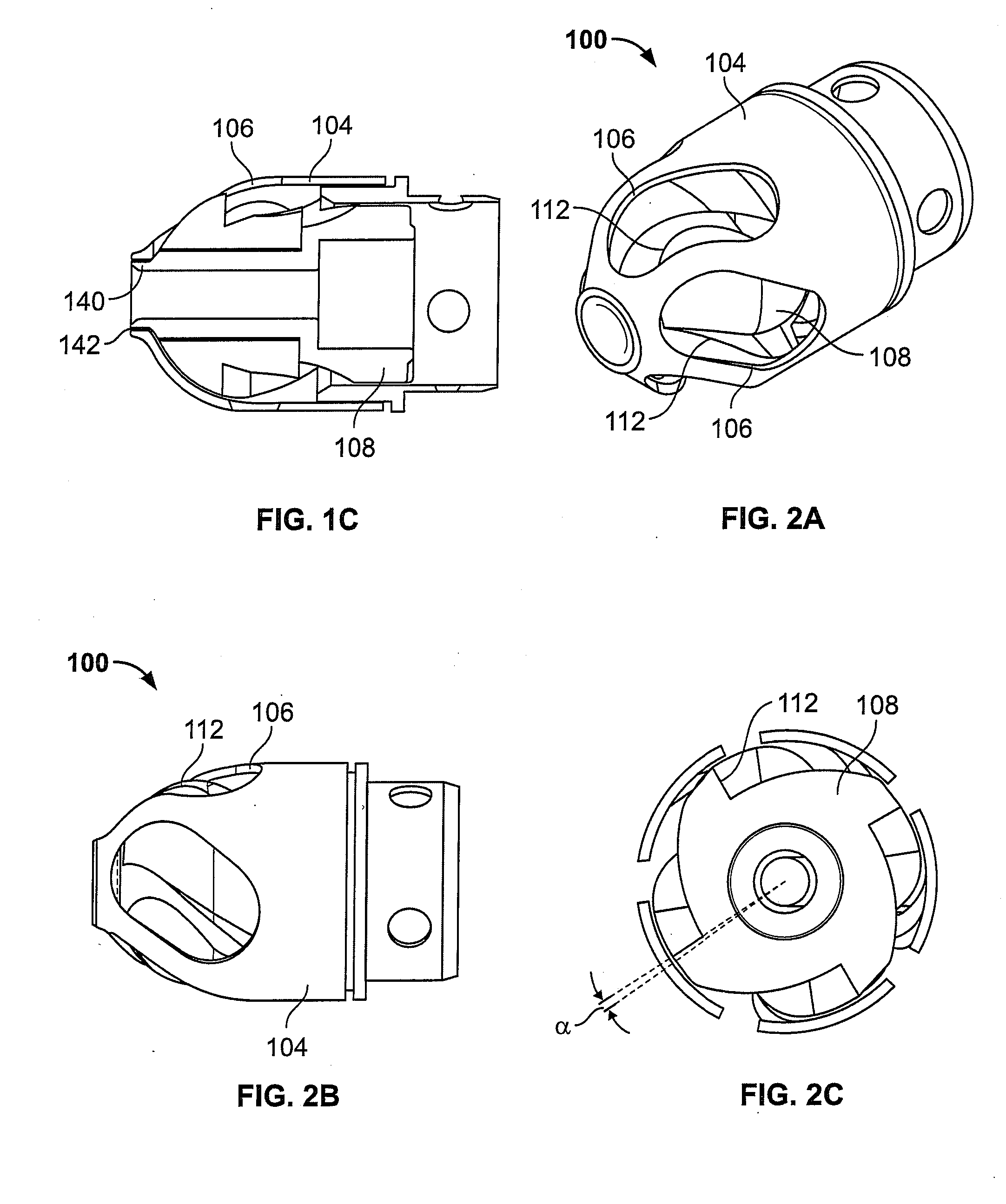
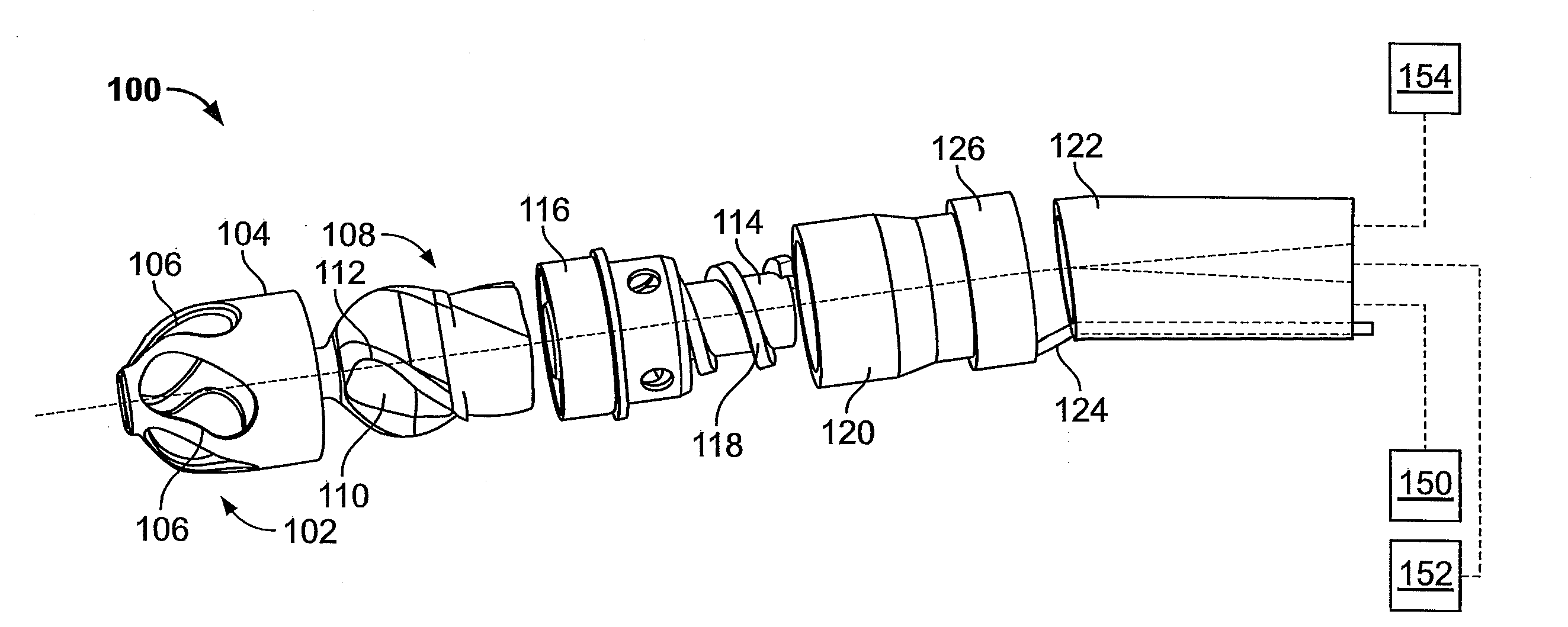
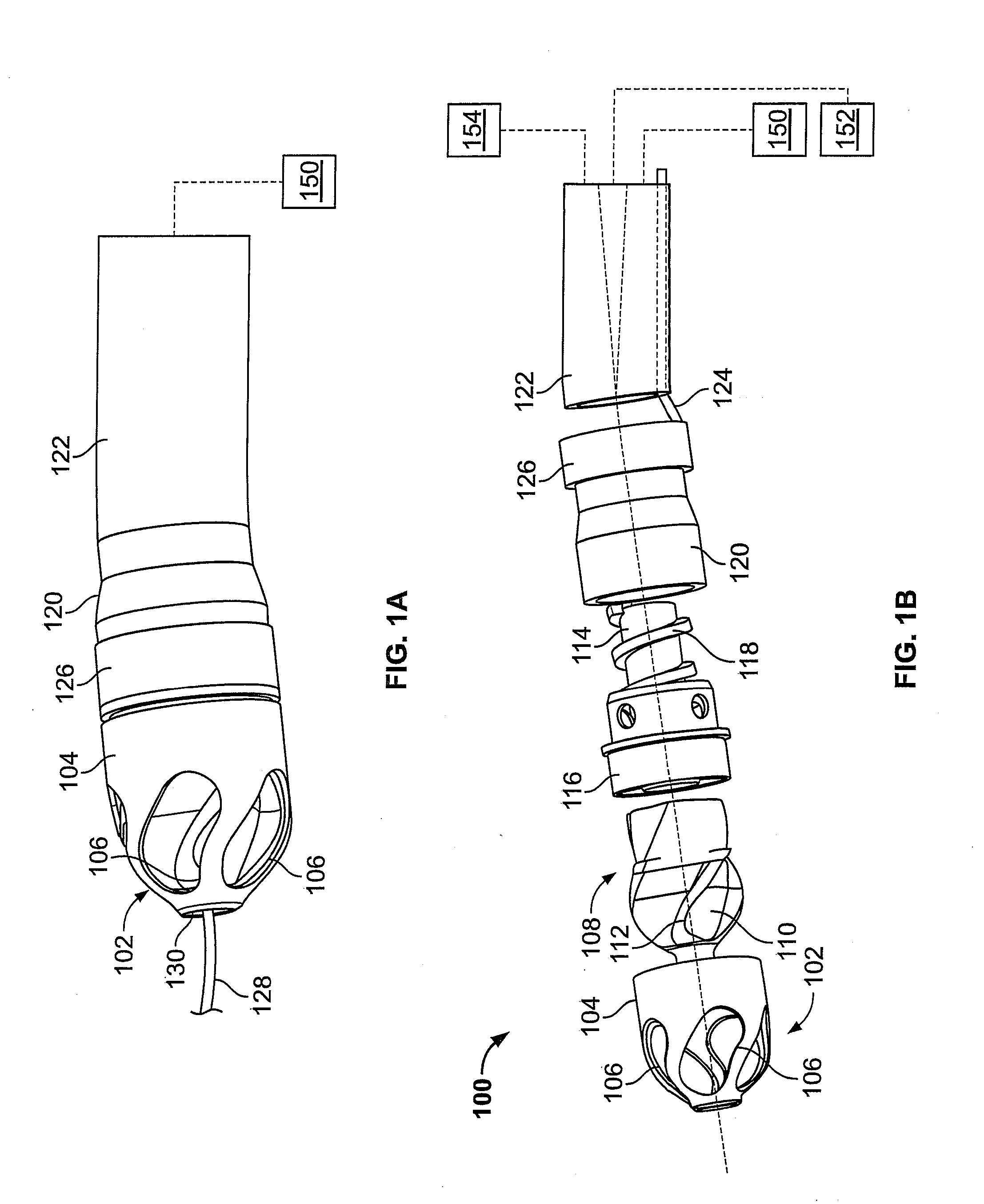
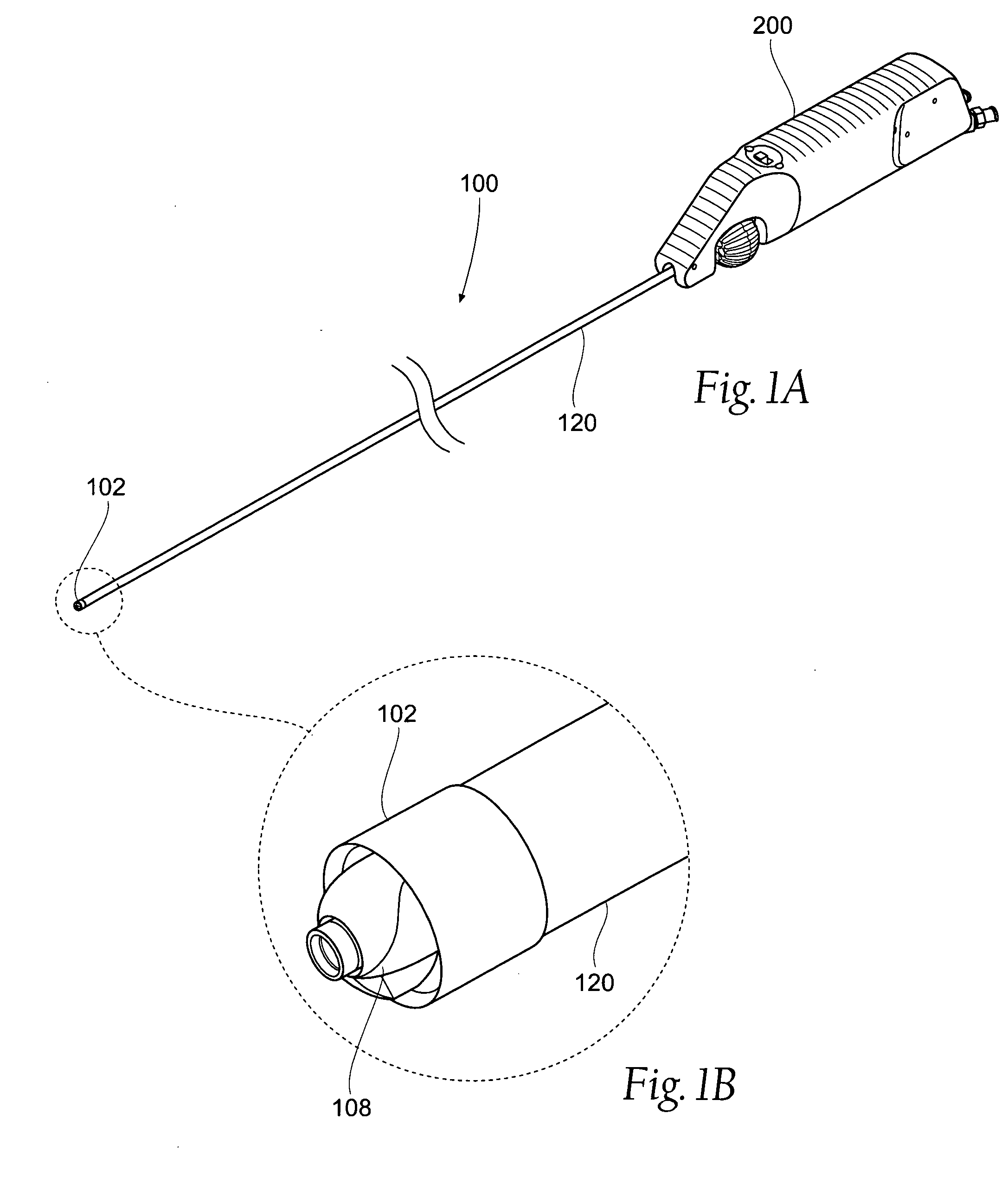
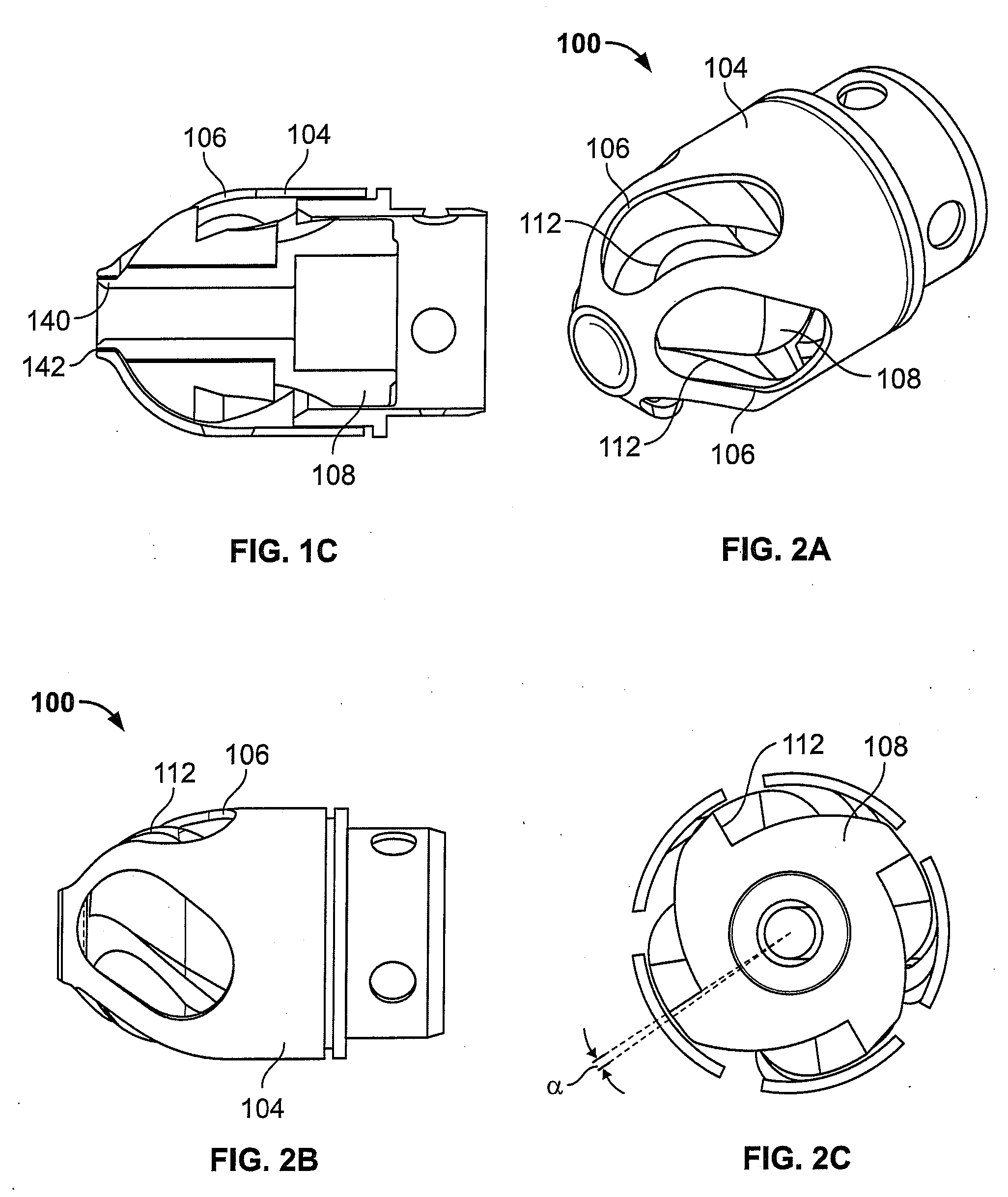
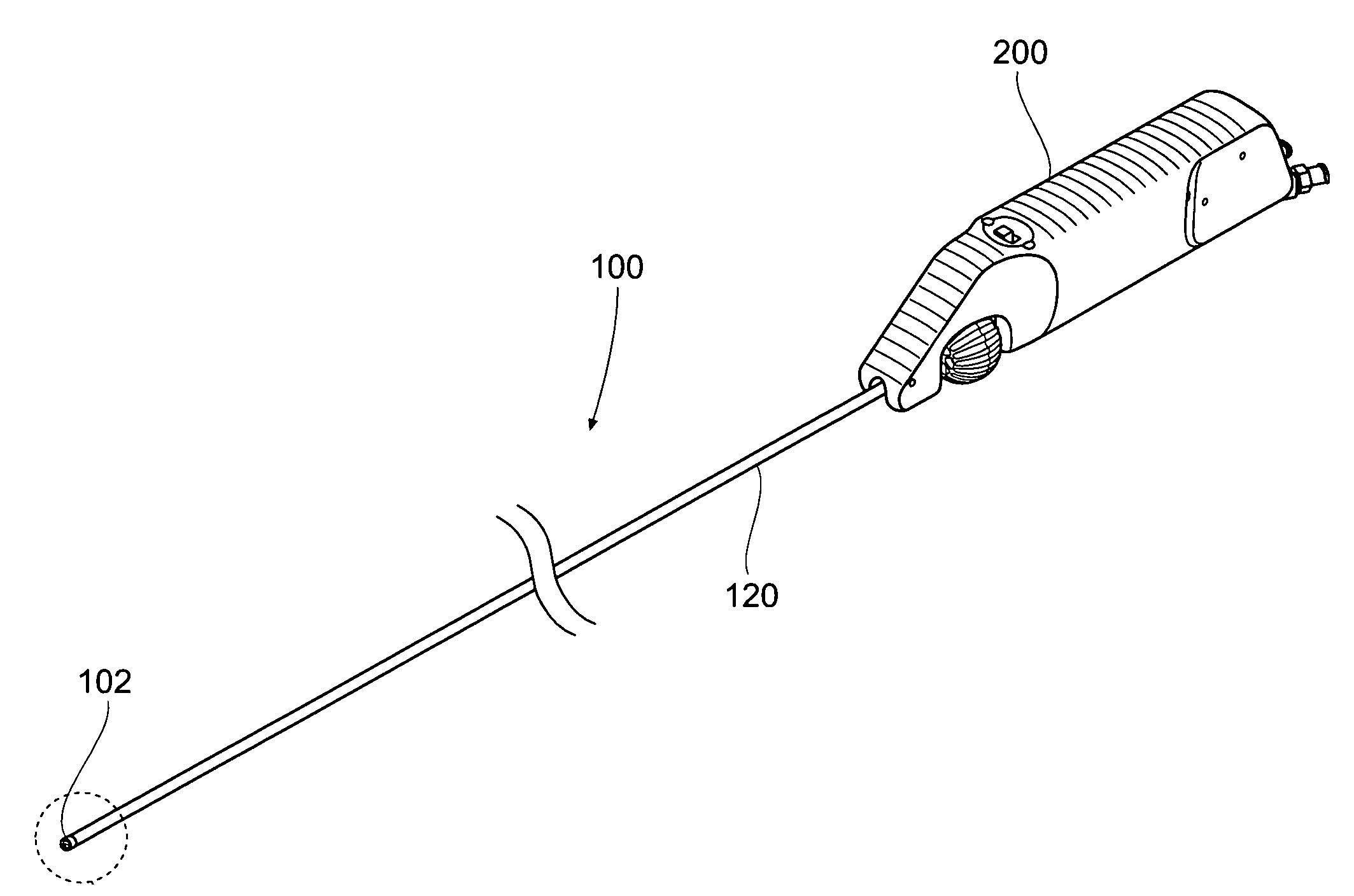
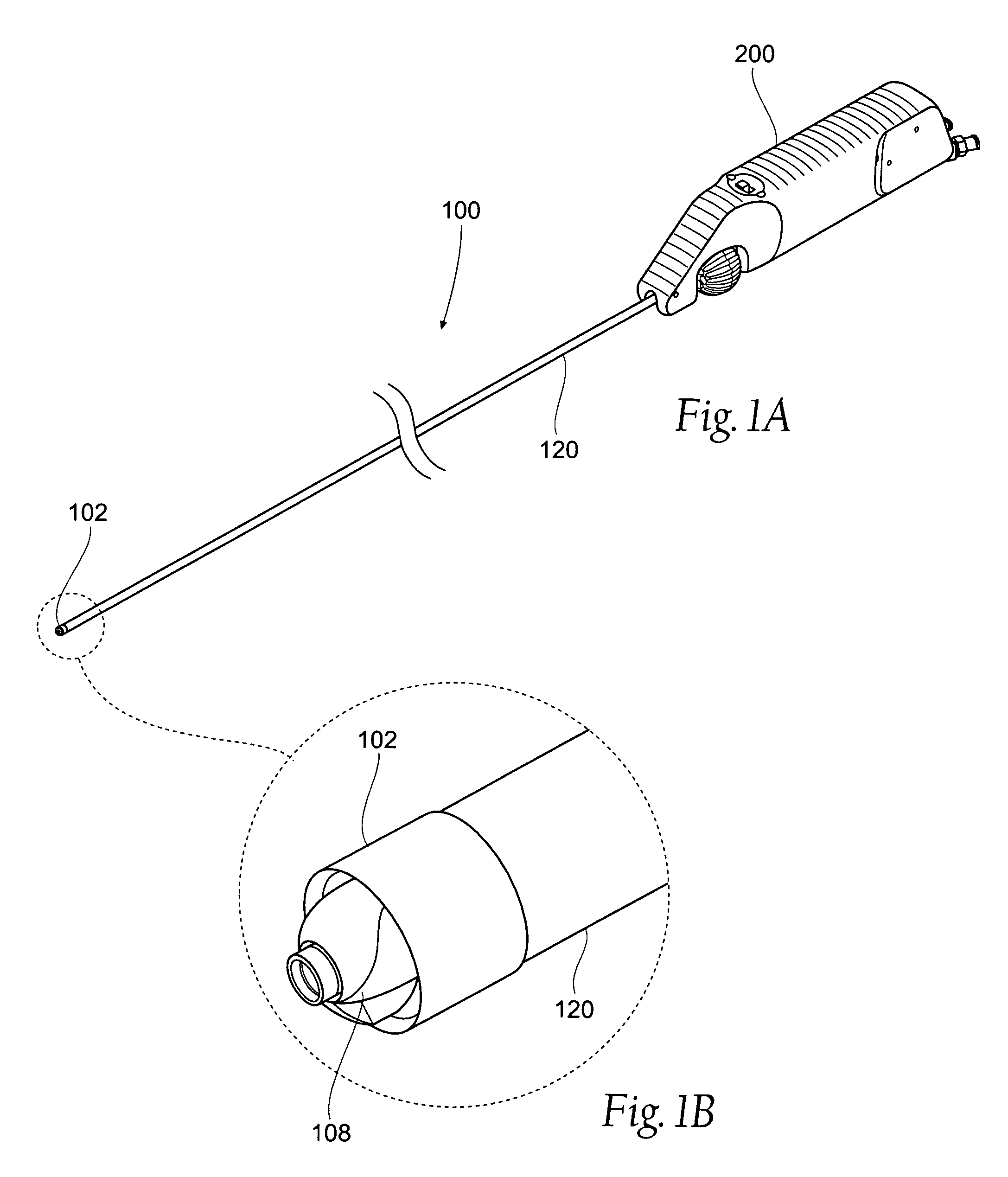
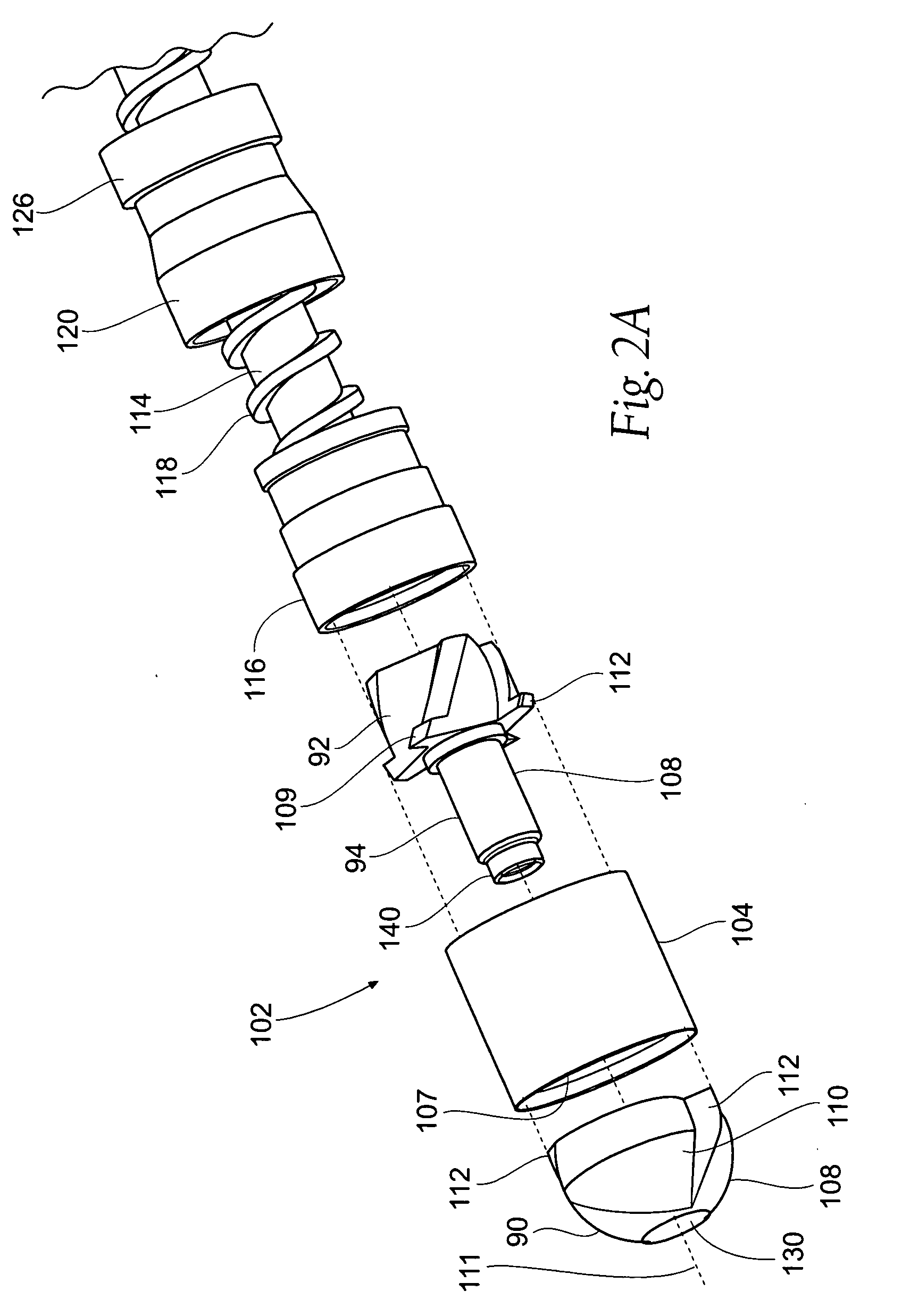
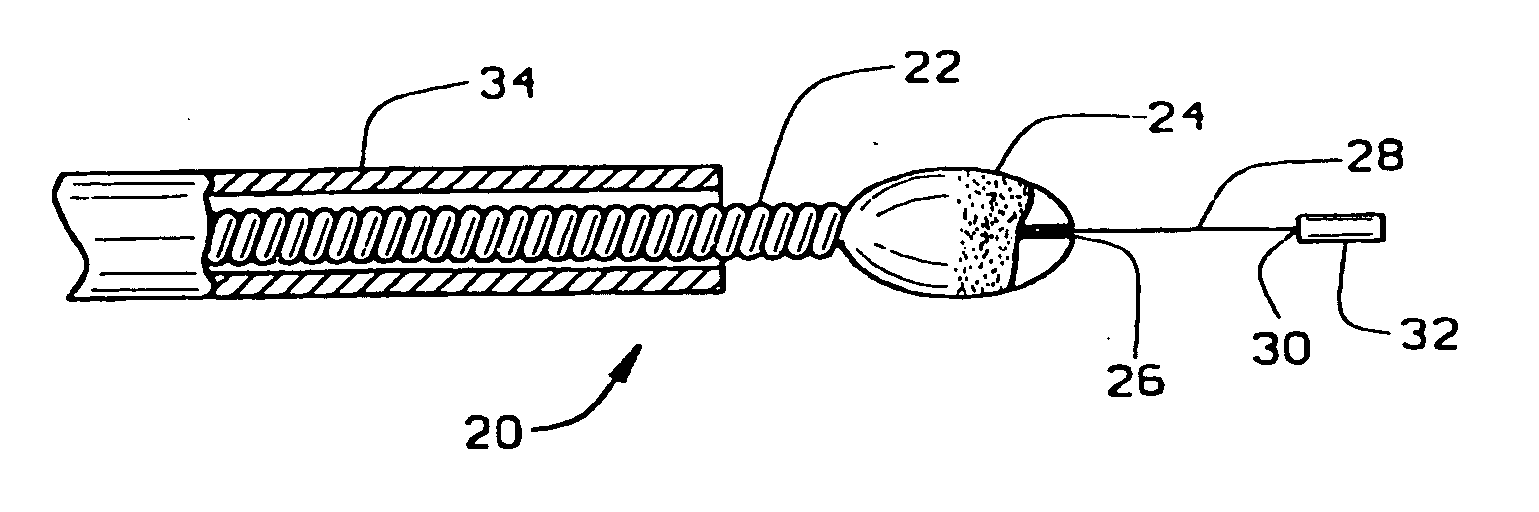
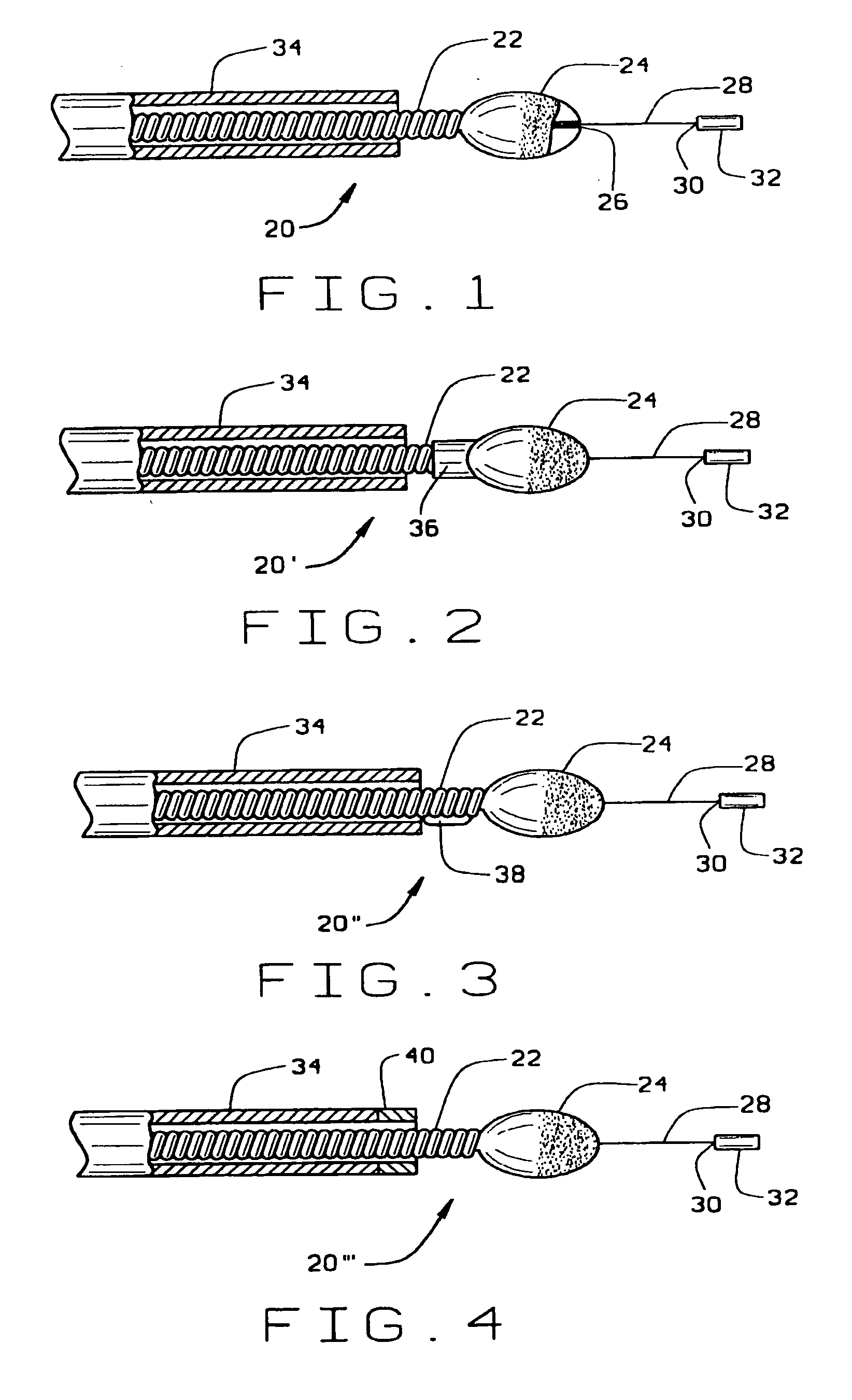
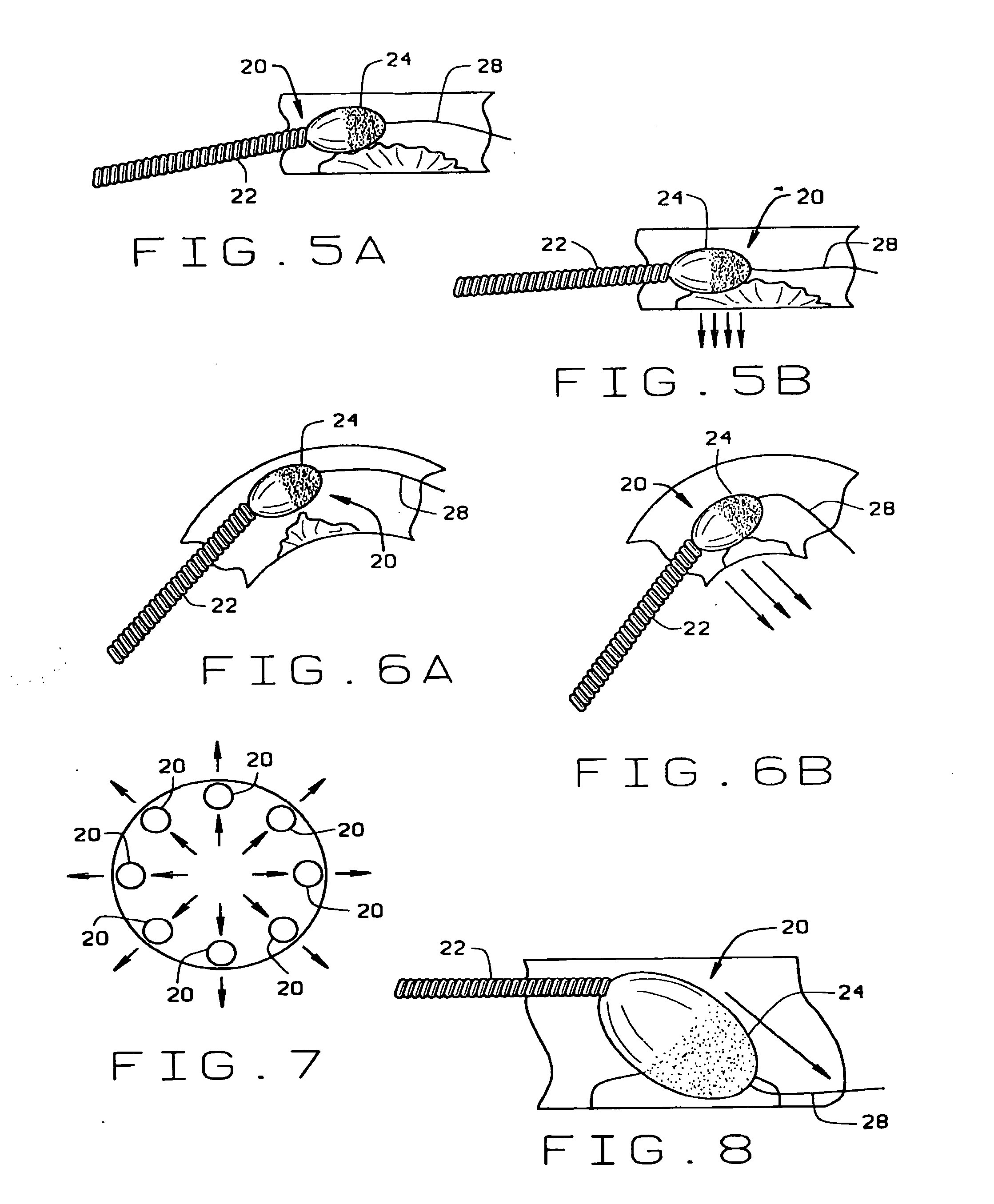
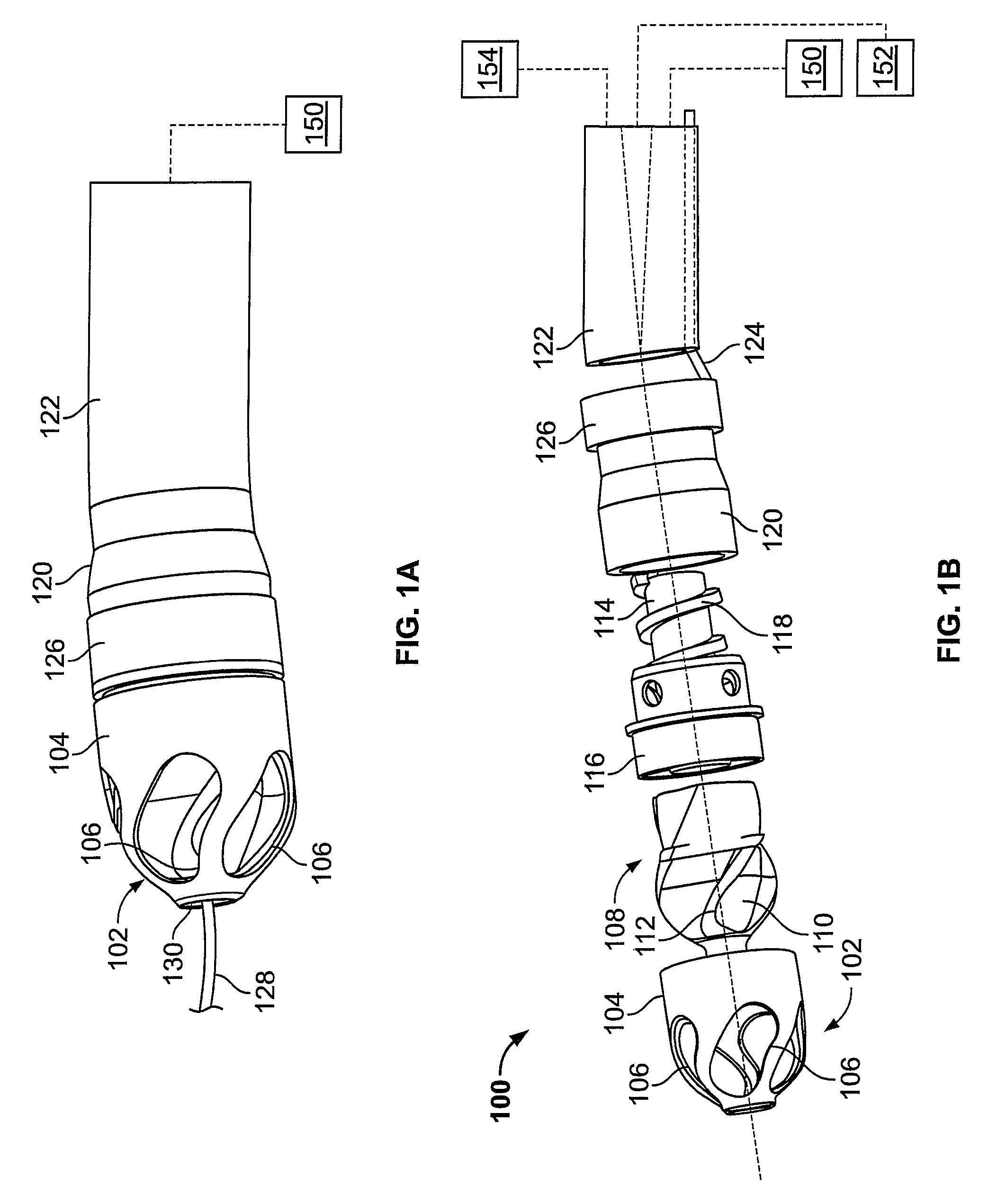
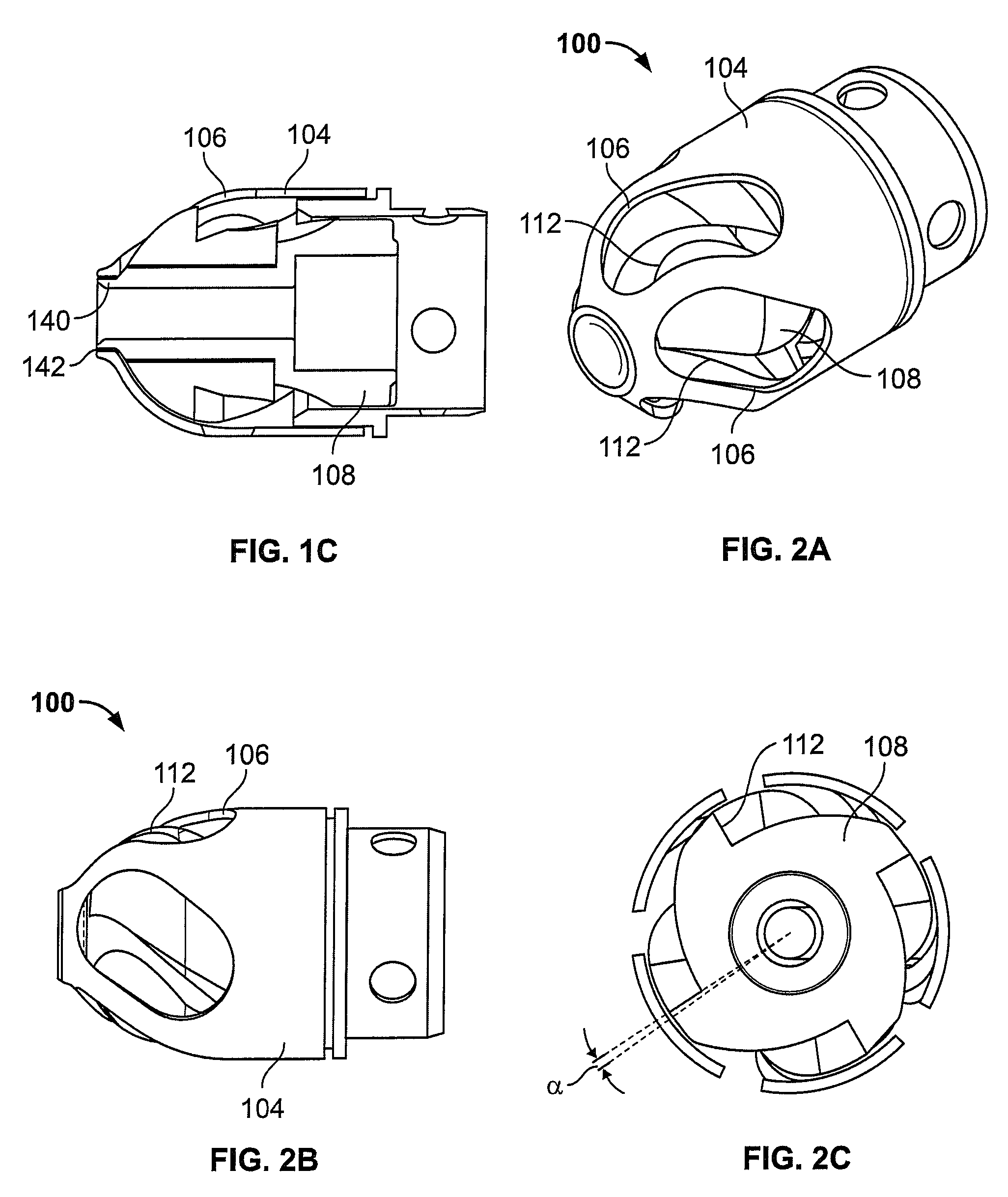
Atherectomy devices, systems, and methods
Owner:ATHEROMED
Magnetically guided atherectomy
Atherectomy device are guided by and manipulated by externally applied magnetic fields to treat total or partial occlusions of a patient's vasculature.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
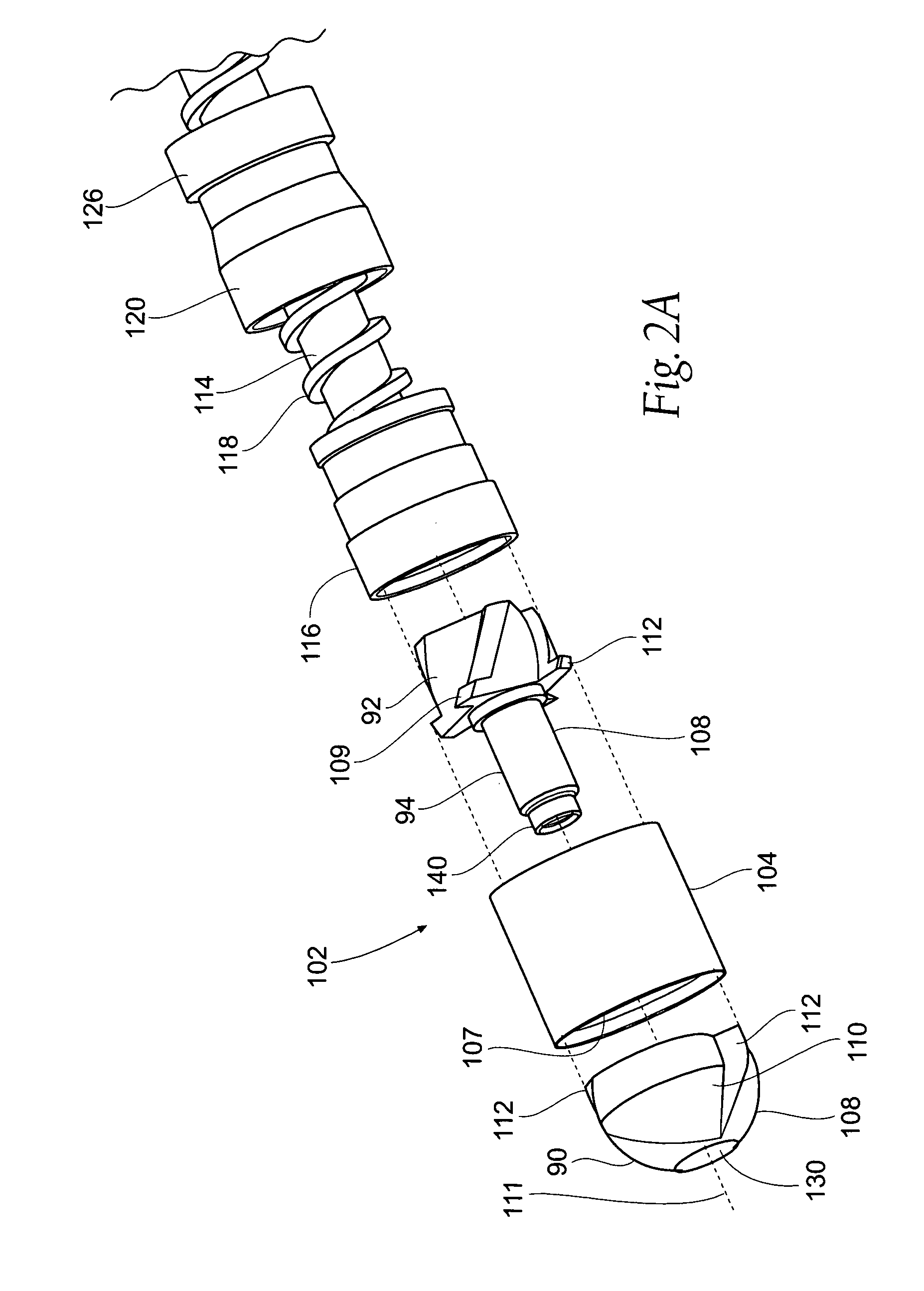
Atherectomy devices and methods
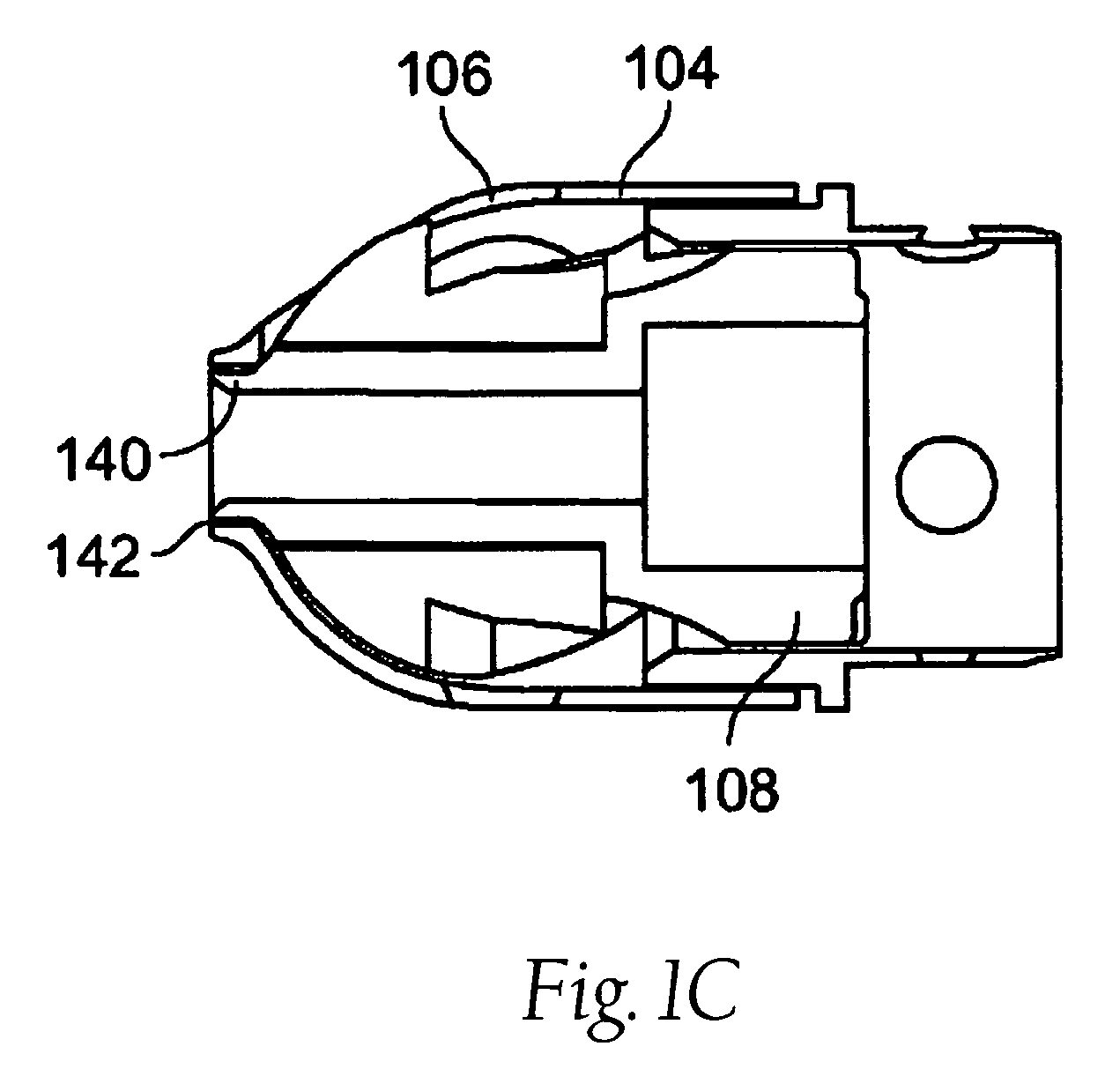
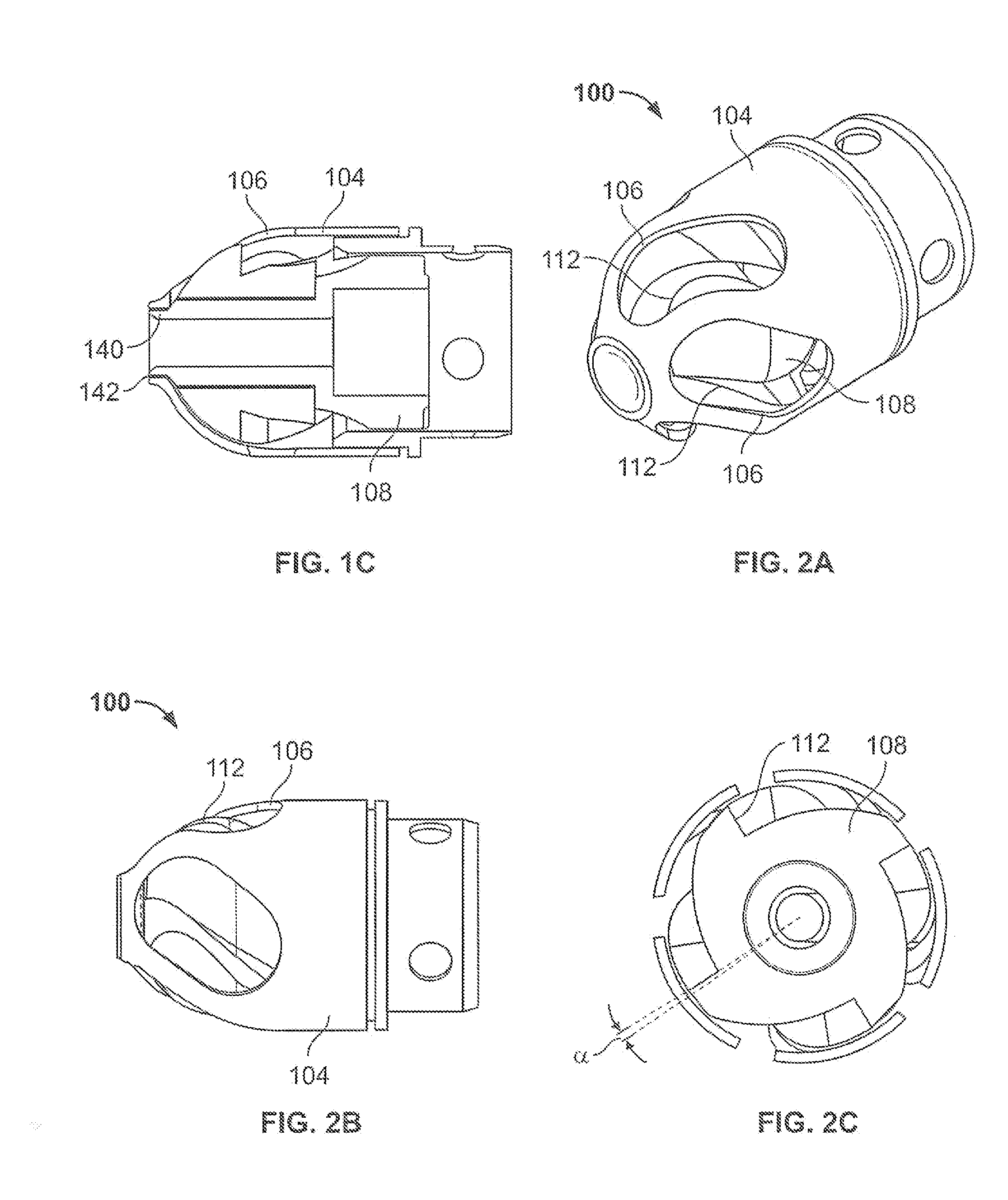
ActiveUS8070762B2Prevent accidental cuttingIncrease blockingEar treatmentCannulasBiomedical engineeringBlood vessel
Owner:ATHEROMED
Atherectomy devices and methods
InactiveUS20080045986A1Improve visualizationAvoid damageCannulasCatheterMedicineBiomedical engineering
Owner:ATHEROMED
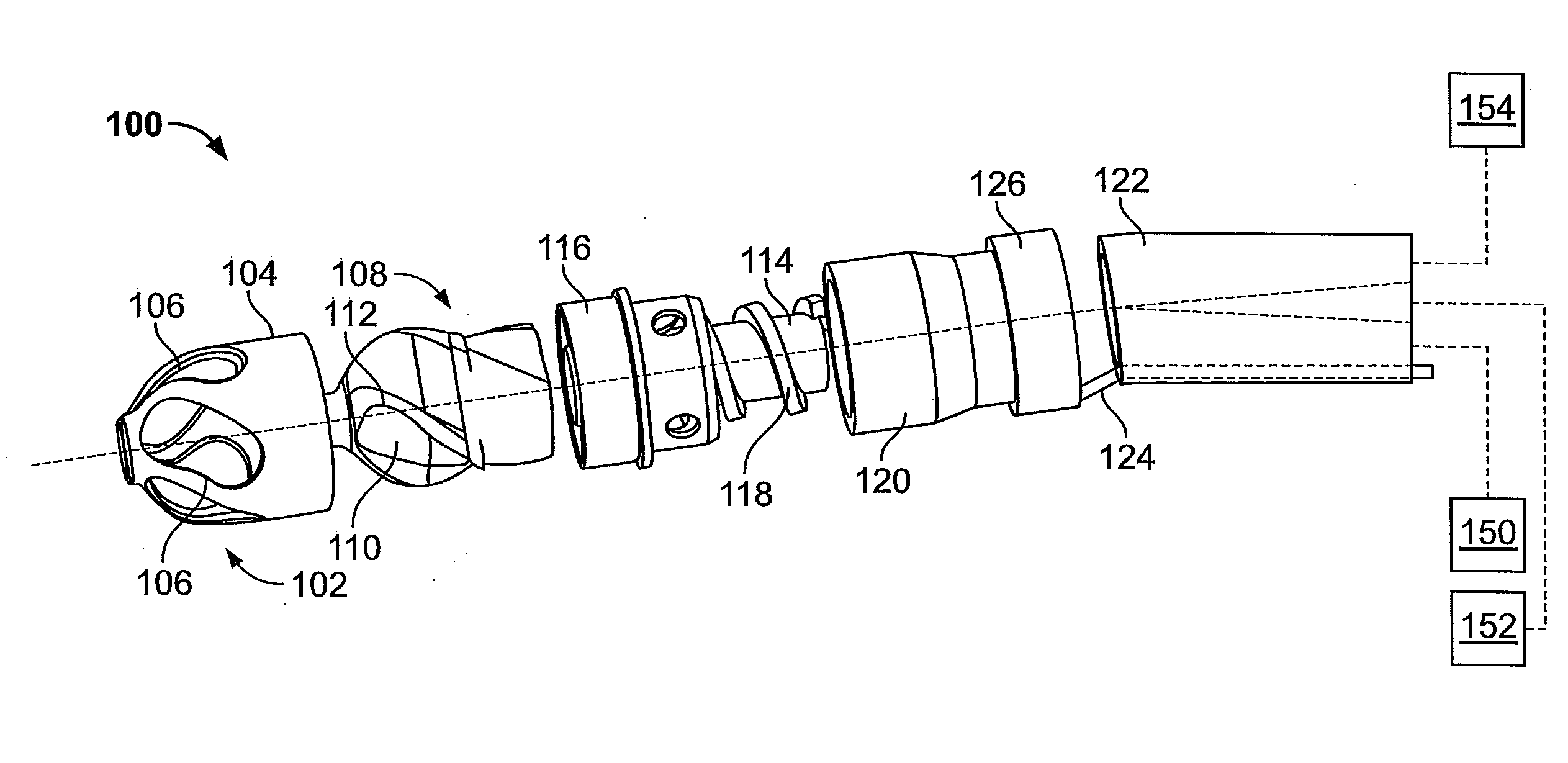
Atherectomy devices, systems, and methods
InactiveUS20090018566A1Easy to optimizeSet were undesirableCannulasCatheterBlood vesselBiomedical engineering
Owner:ATHEROMED
Atherectomy devices and methods
Owner:ATHEROMED
Atherectomy devices and methods
Owner:ATHEROMED
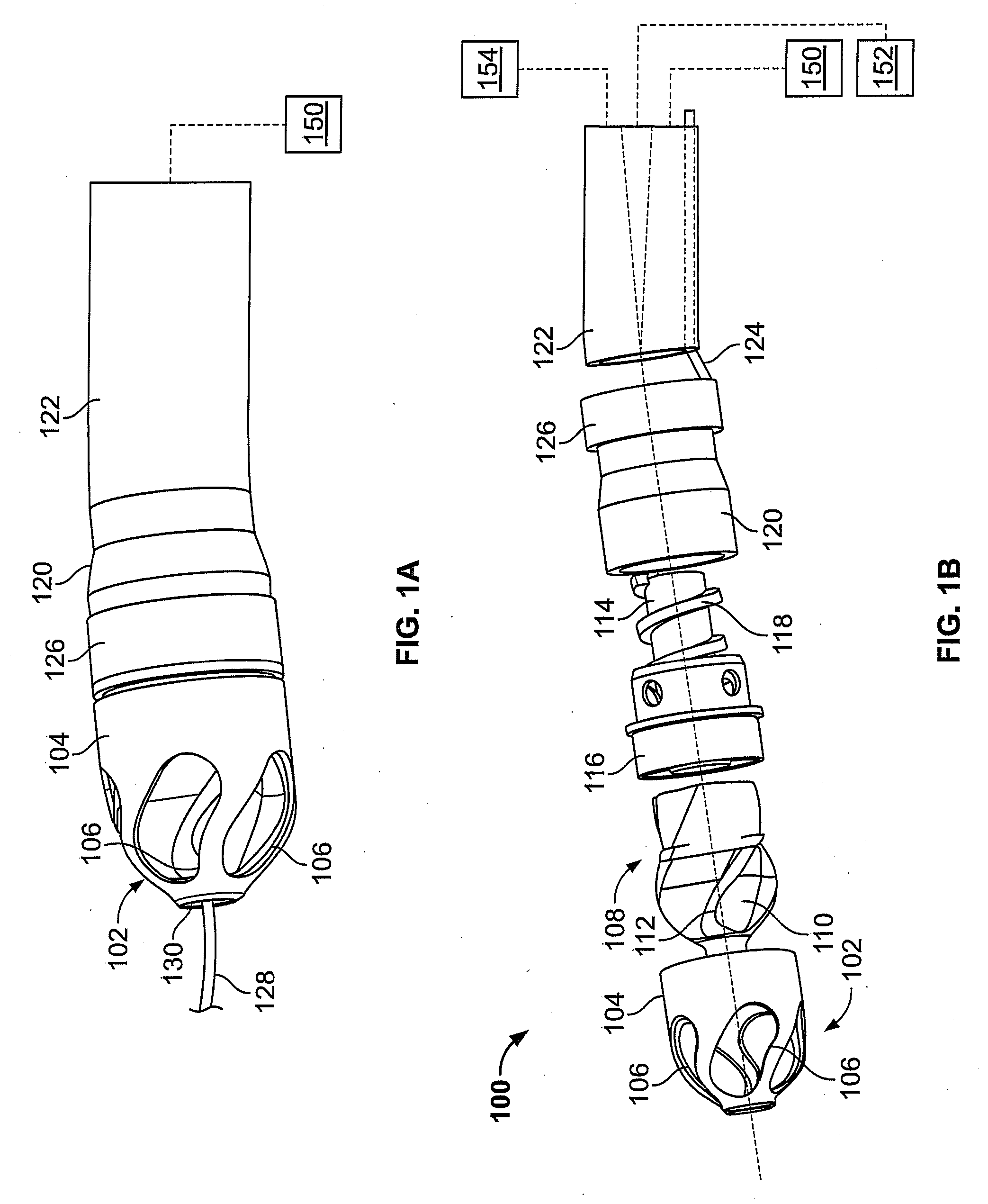
Atherectomy devices, systems, and methods
ActiveUS20090018565A1Easy to optimizeSet were undesirableBalloon catheterCannulasBlood vesselBiomedical engineering
Owner:ATHEROMED
Atherectomy devices and methods
ActiveUS20100049225A1Prevent accidental cuttingIncrease blockingCannulasCatheterMedicineBiomedical engineering
Owner:ATHEROMED
Atherectomy devices, systems, and methods
ActiveUS20090024085A1Easy to optimizeSet were undesirableMedical devicesCatheterMedicineBlood vessel
Owner:ATHEROMED
Atherectomy devices and methods
Owner:ATHEROMED
Atherectomy devices, systems, and methods
ActiveUS20090018567A1Easy to optimizeSet were undesirableCannulasExcision instrumentsBlood vesselBiomedical engineering
Owner:ATHEROMED
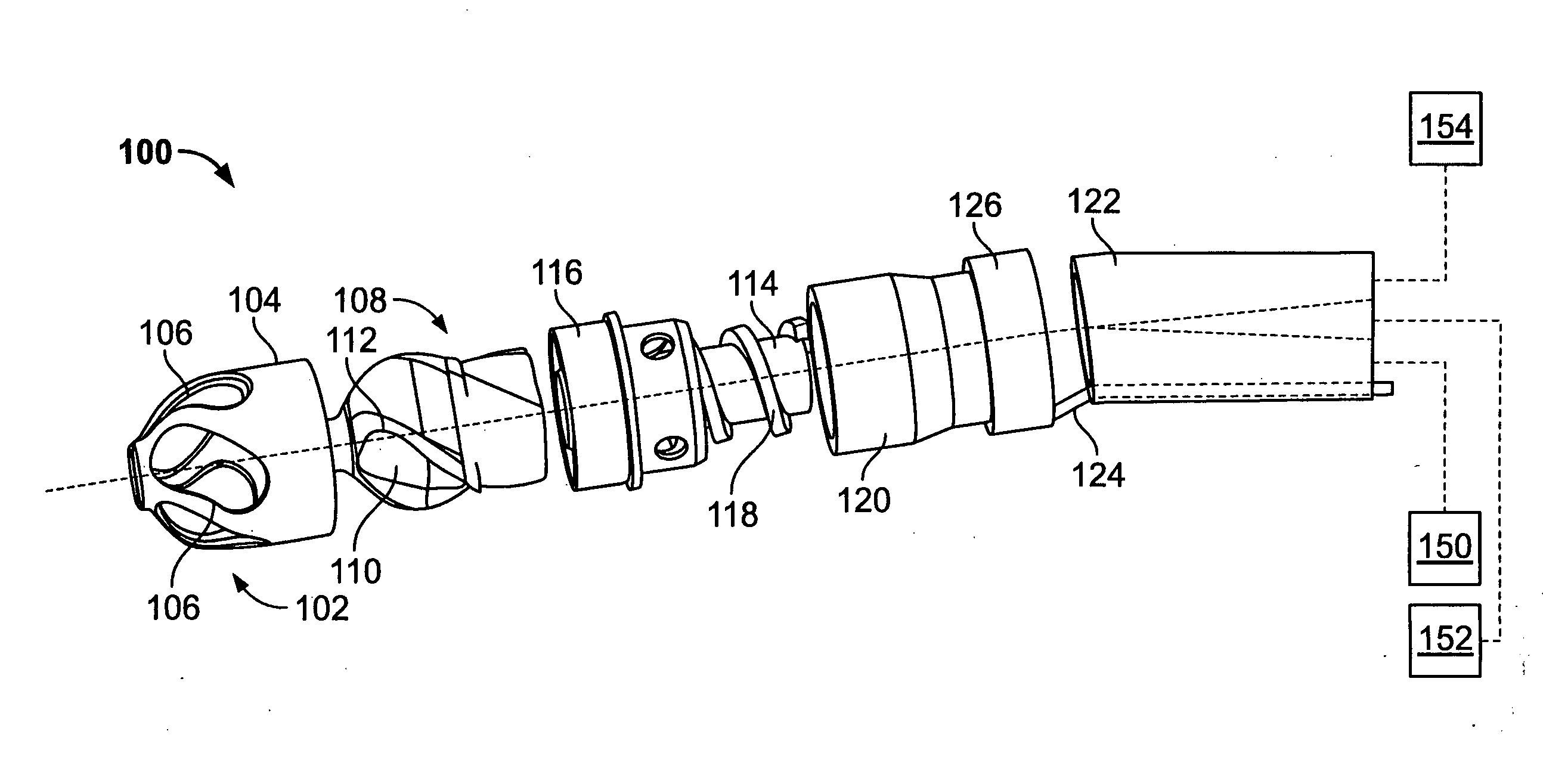
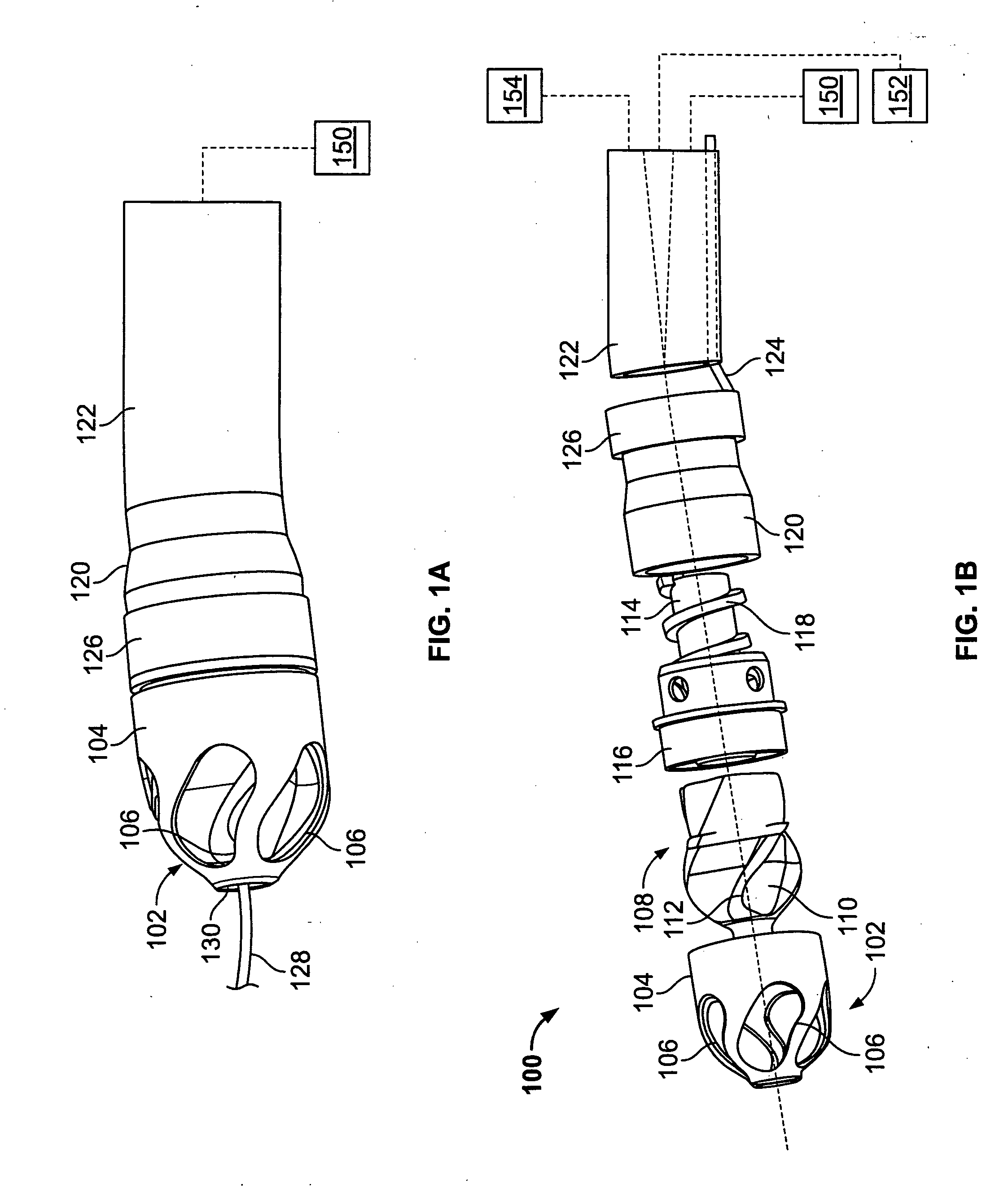
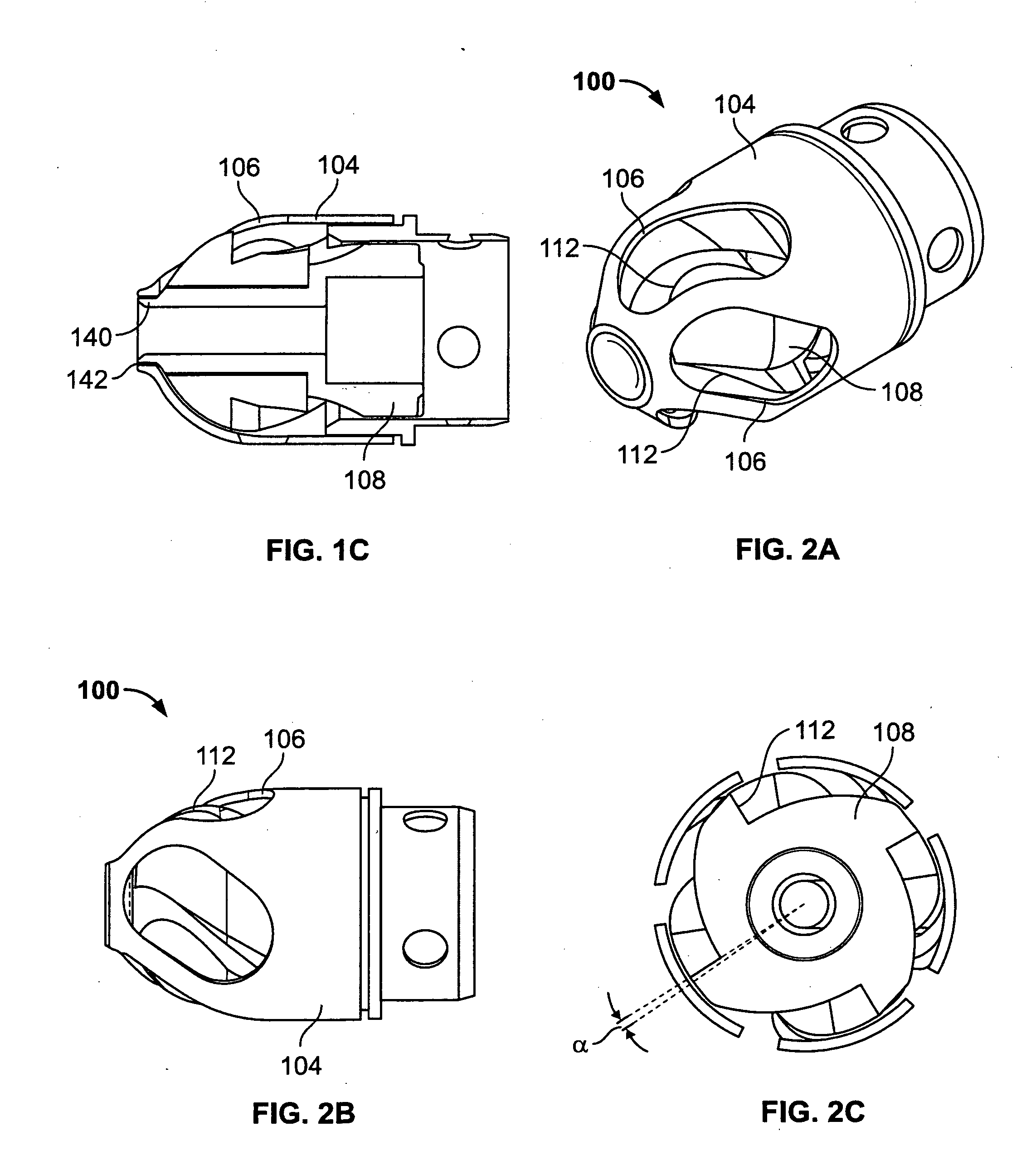
Magnetically navigable and/or controllable device for removing material from body lumens and cavities
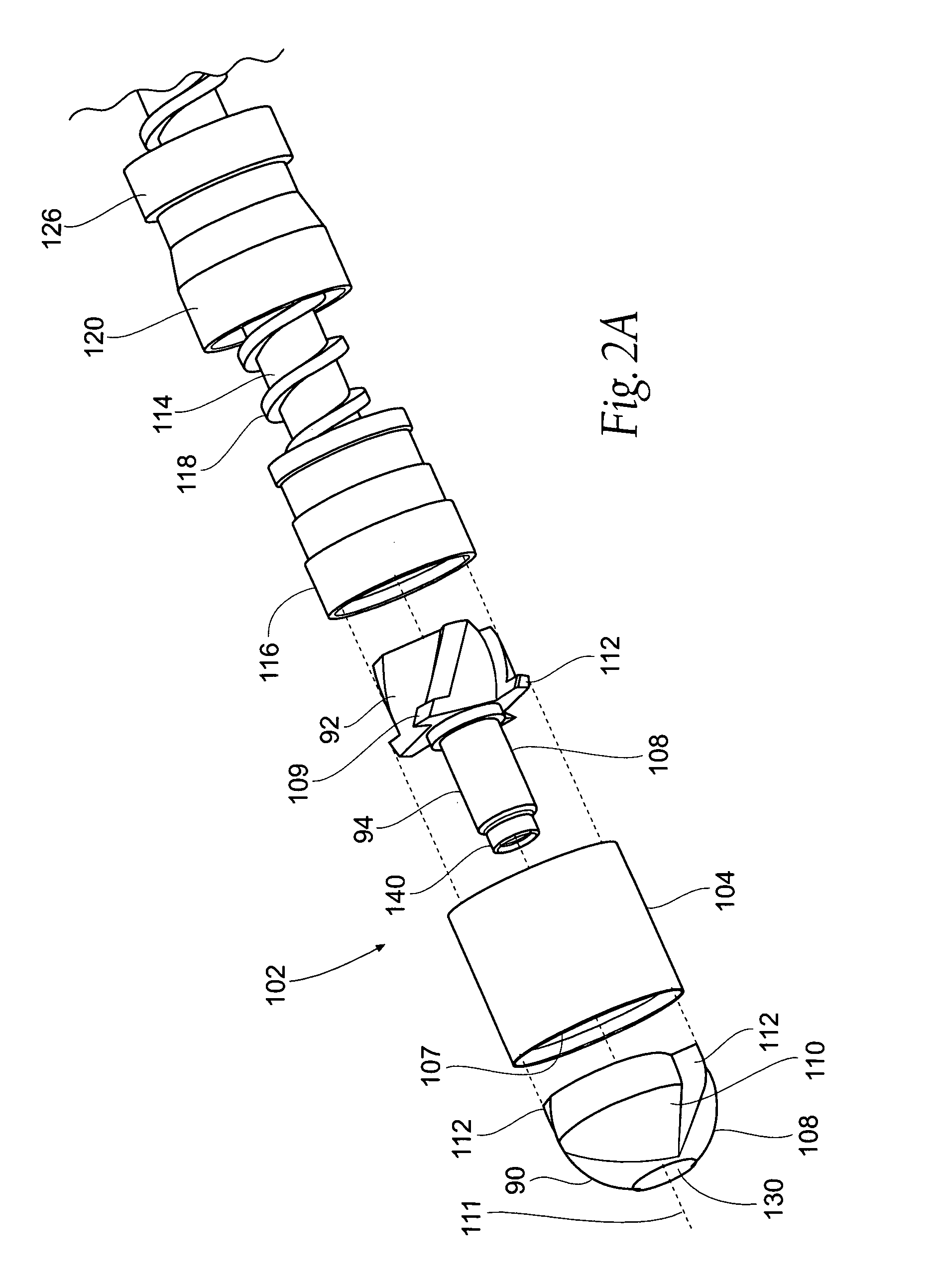
A magnetically navigable atherectomy device includes a cutting head, a flexible drive shaft having a proximal and a distal end, with the cutting device on the distal end, and a magnet associated with the cutting head, the magnet of sufficient size to allow the cutting head to be oriented by an externally applied magnetic field. The magnet may be a portion of the cutting head made from a magnetically permeable or permanent magnetic material, a portion of the drive shaft made from a magnetically permeable or permanent magnetic material; a separate magnet between the cutting head and the drive shaft, a portion a magnet on a sheath covering the drive shaft. Alternatively a guide wire can provided with a magnetic material on its distal end. Through the application of a magnetic field and / or a magnetic gradient, the artherectomy device can be guided to the location of the atheromatous material in the body. Once at the site of atheromatous material, through the application of a magnetic field or magnetic gradient, the device can be manipulated into proximity to the atheromatous material to remove the material.
Owner:HALL ANDREW F +3
Occlusion-crossing devices, imaging, and atherectomy devices
ActiveUS20120253186A1Avoid damageIncrease relative motionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic markersCatheter devicePeripheral Artery Diseases
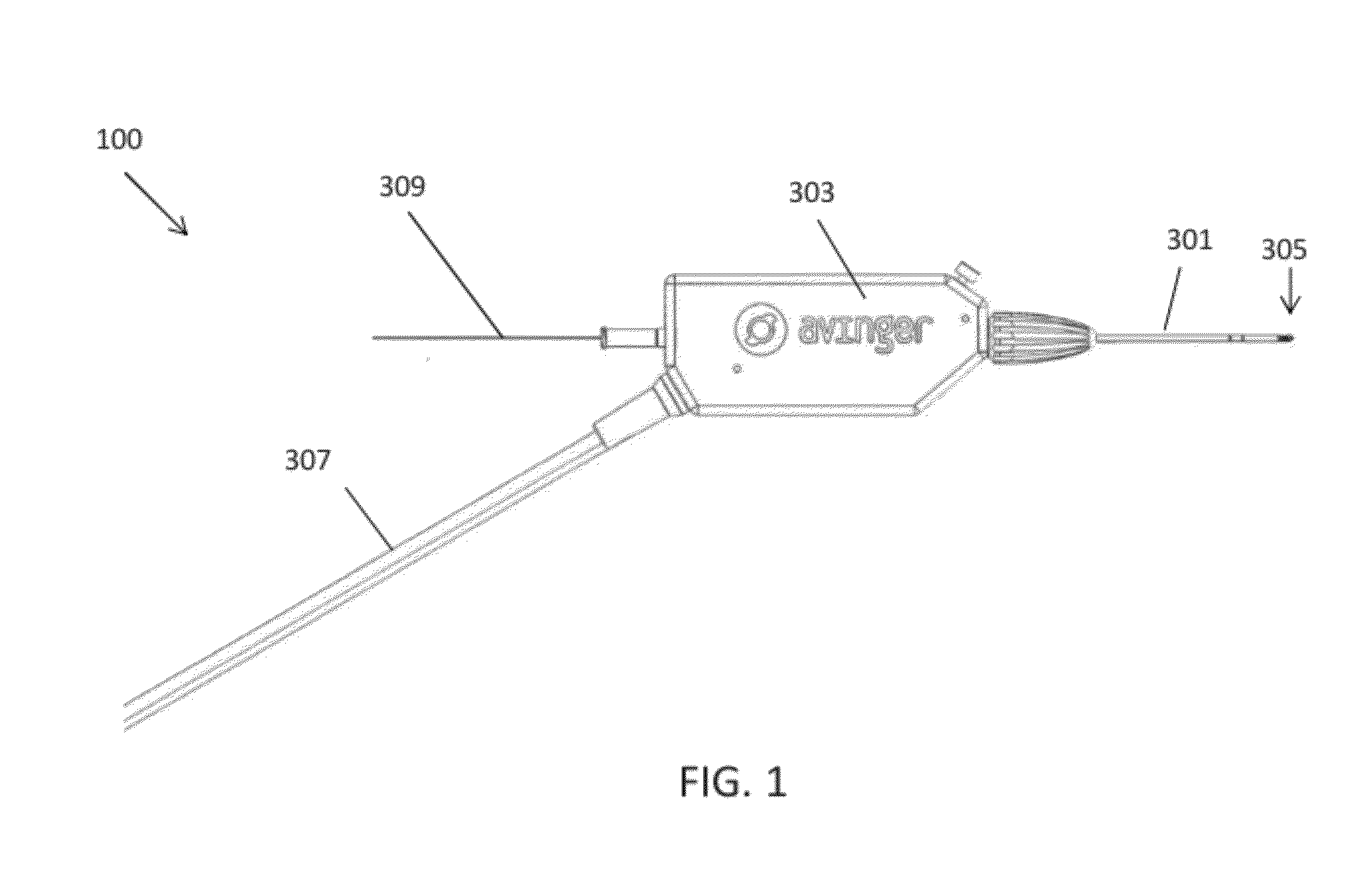
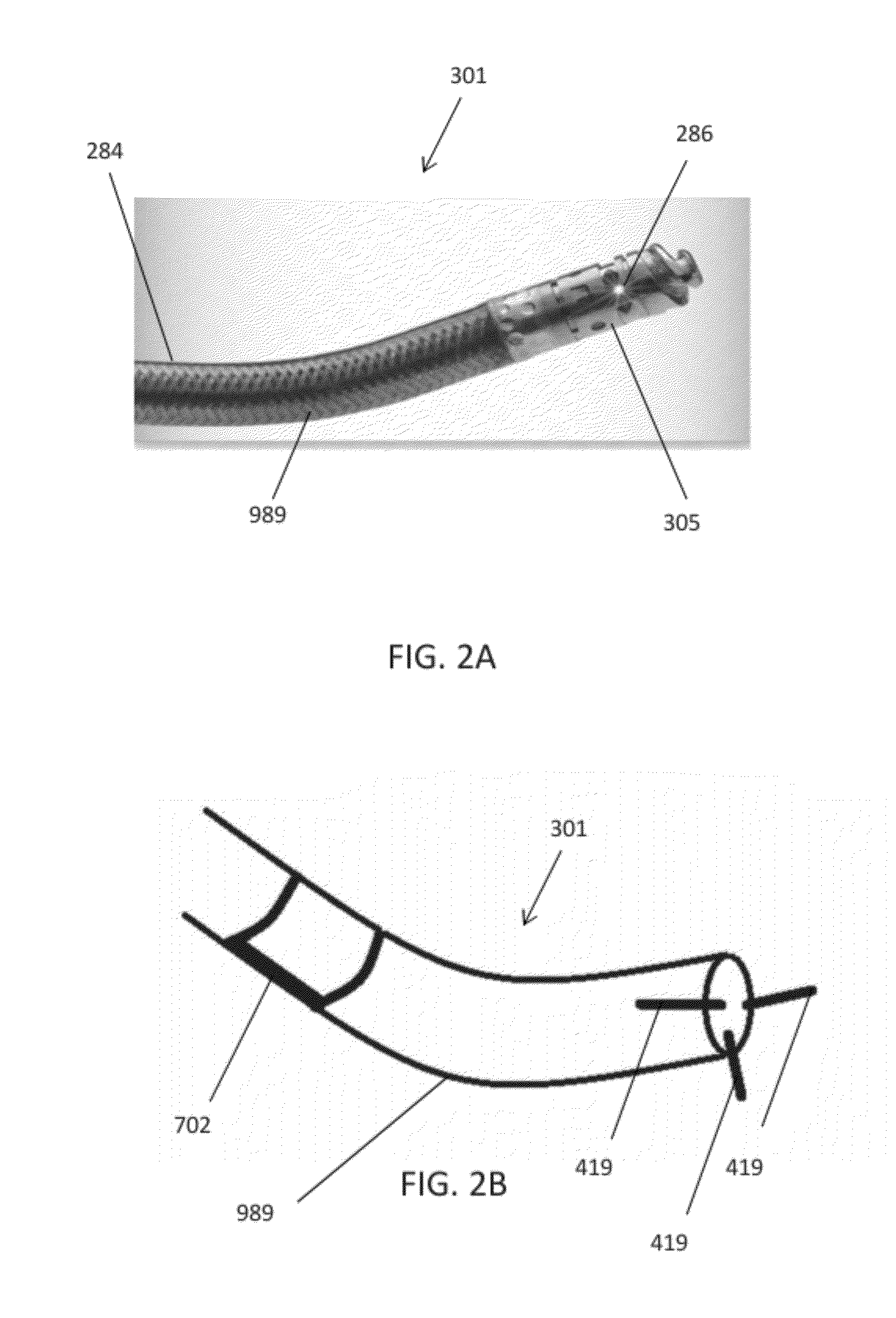
The present invention relates to: (1) guidewire support / placement catheters; (2) support / placement catheters with imaging; (3) atherectomy catheters, (4) atherectomy catheters with imaging, (5) occlusion crossing catheters, and (6) occlusion crossing catheters with imaging as well as methods for using them to treat disorders (and particularly peripheral artery disease) and systems including them.
Owner:AVINGER
Magnetically Guided Atherectomy
Atherectomy devices are guided by and manipulated by externally applied magnetic fields to treat total or partial occlusions of a patient's vasculature.
Owner:HALL ANDREW F +1
Atherectomy devices and methods
Owner:ATHEROMED
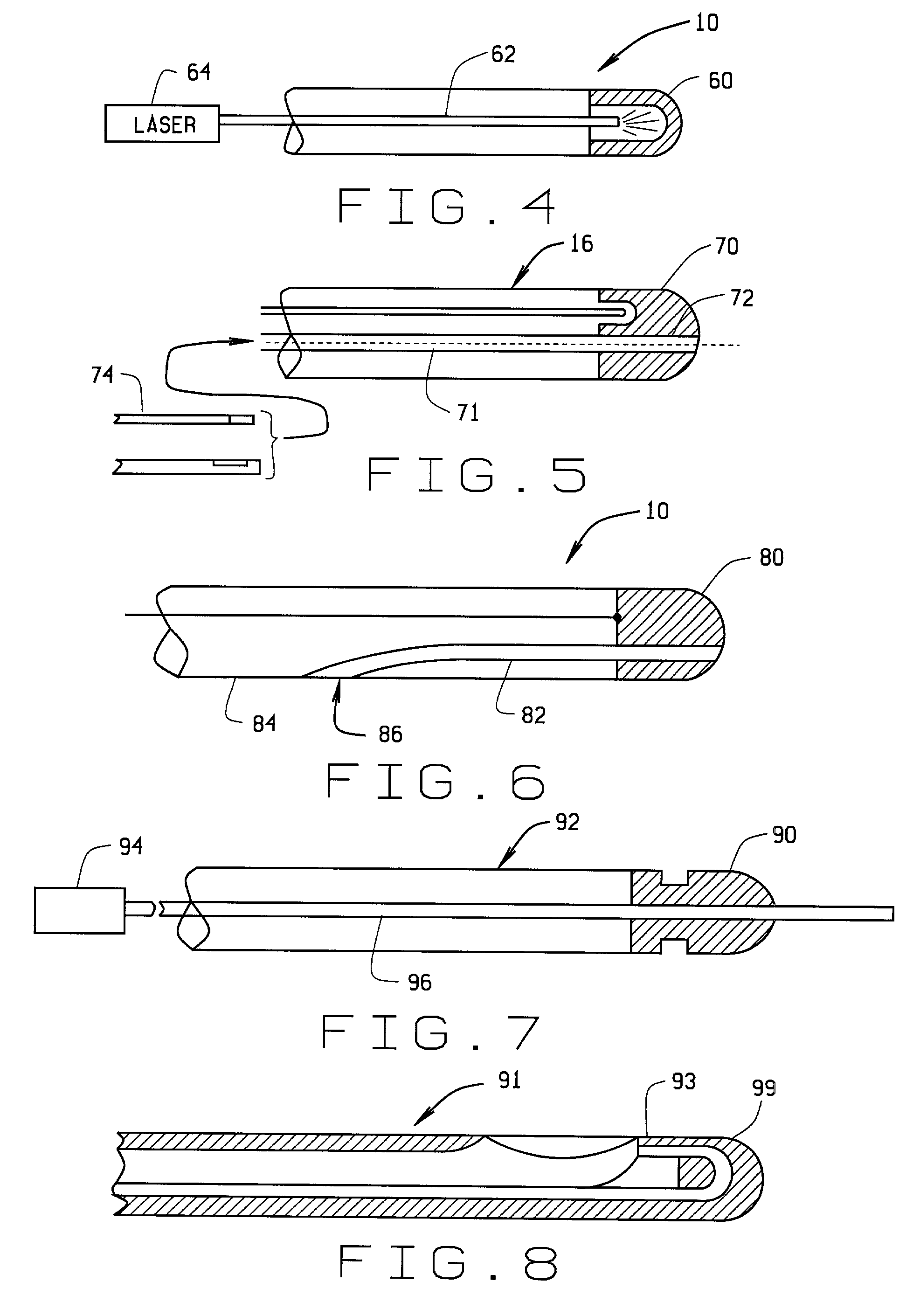
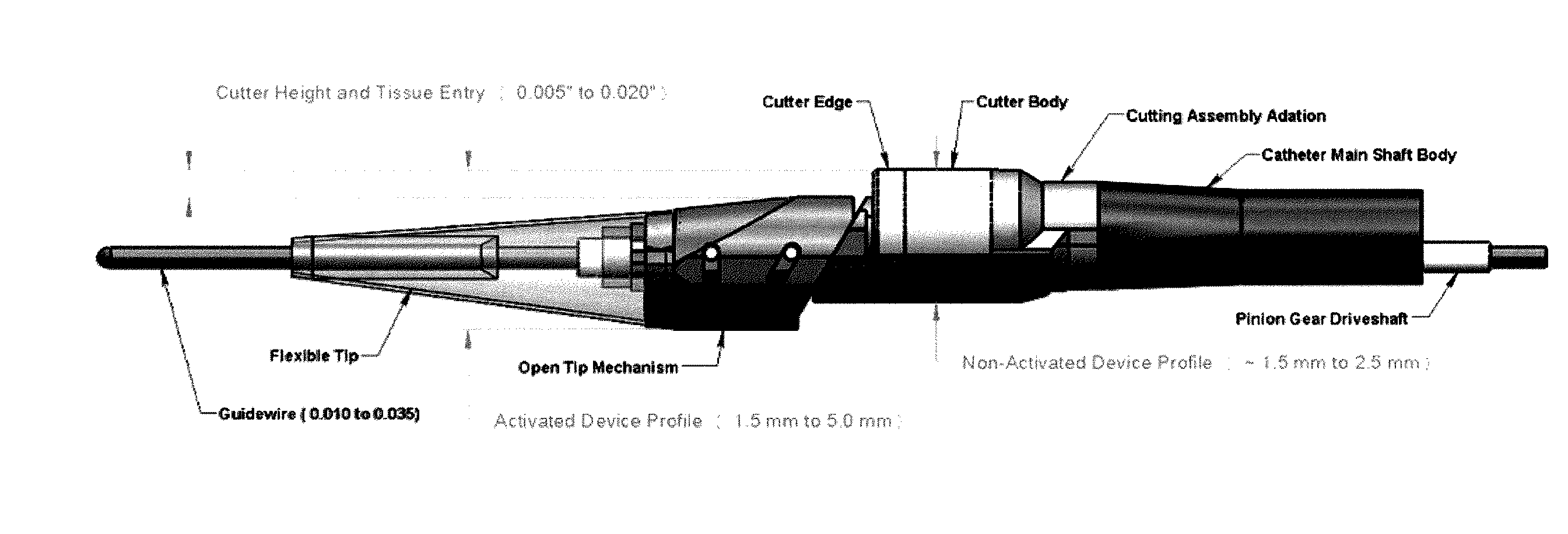
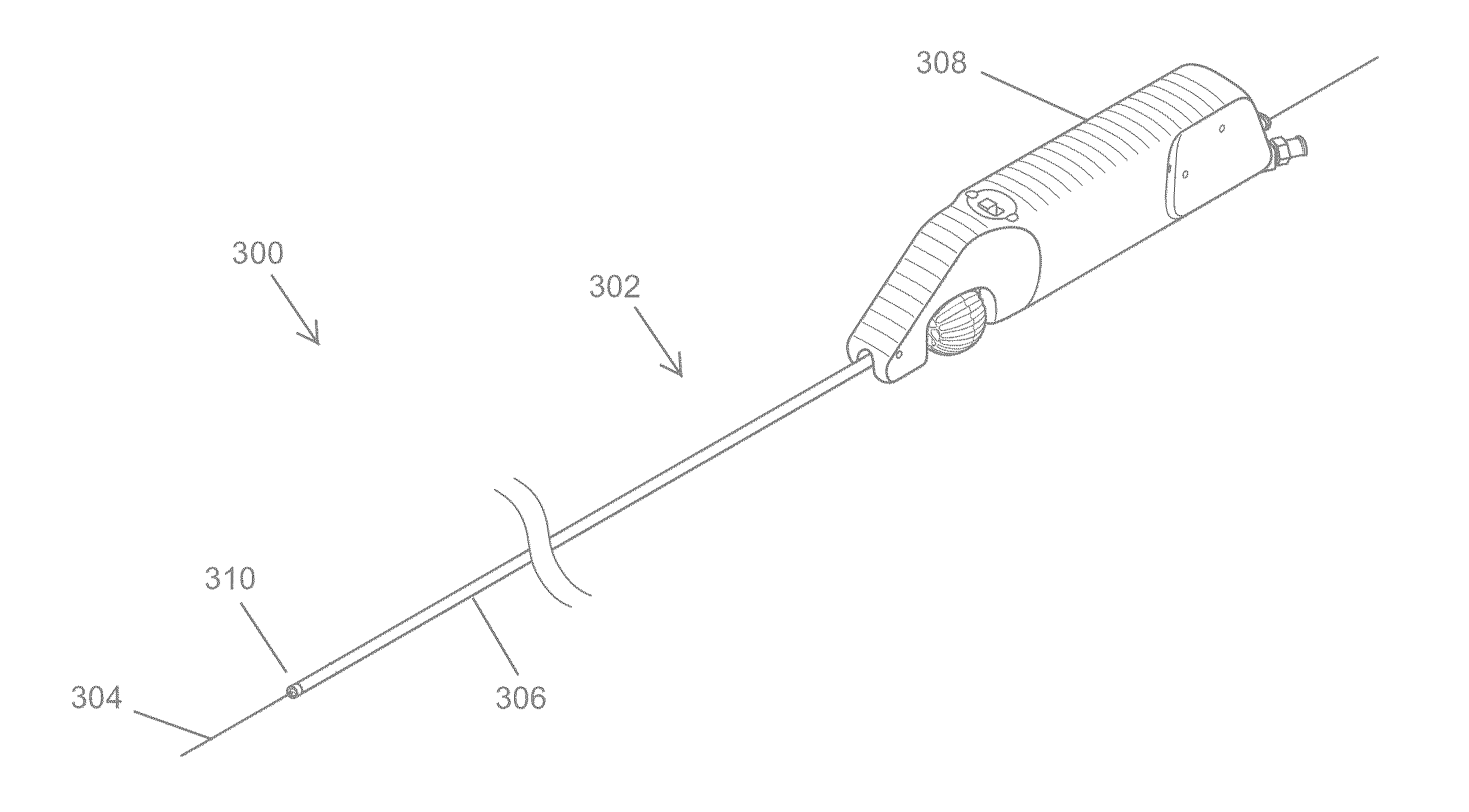
Atherectomy catheter with laterally-displaceable tip
ActiveUS20110004107A1Maximize cut tissue cross-sectional areaDepth is minimizedCannulasCatheterBody axisGear drive
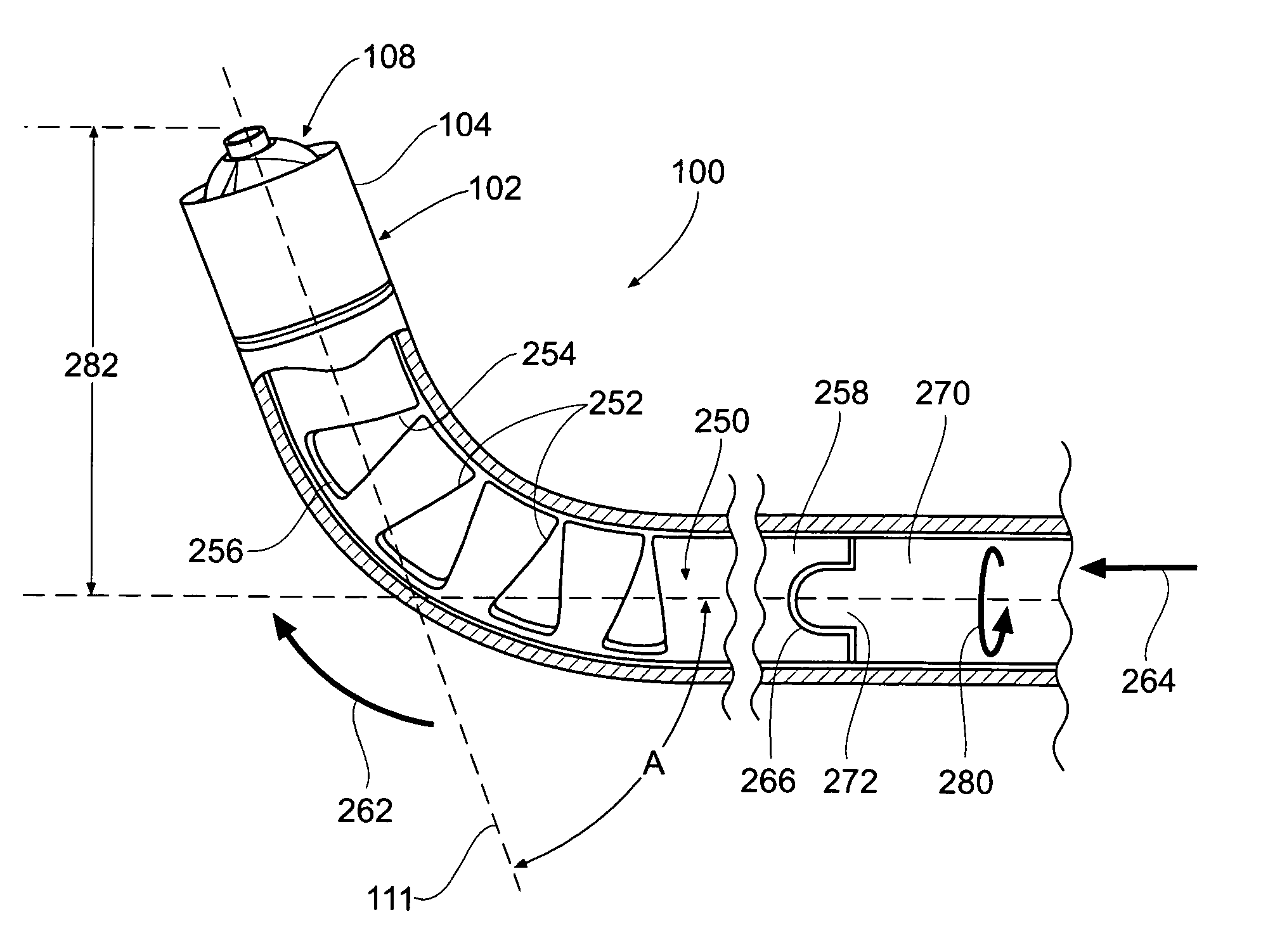
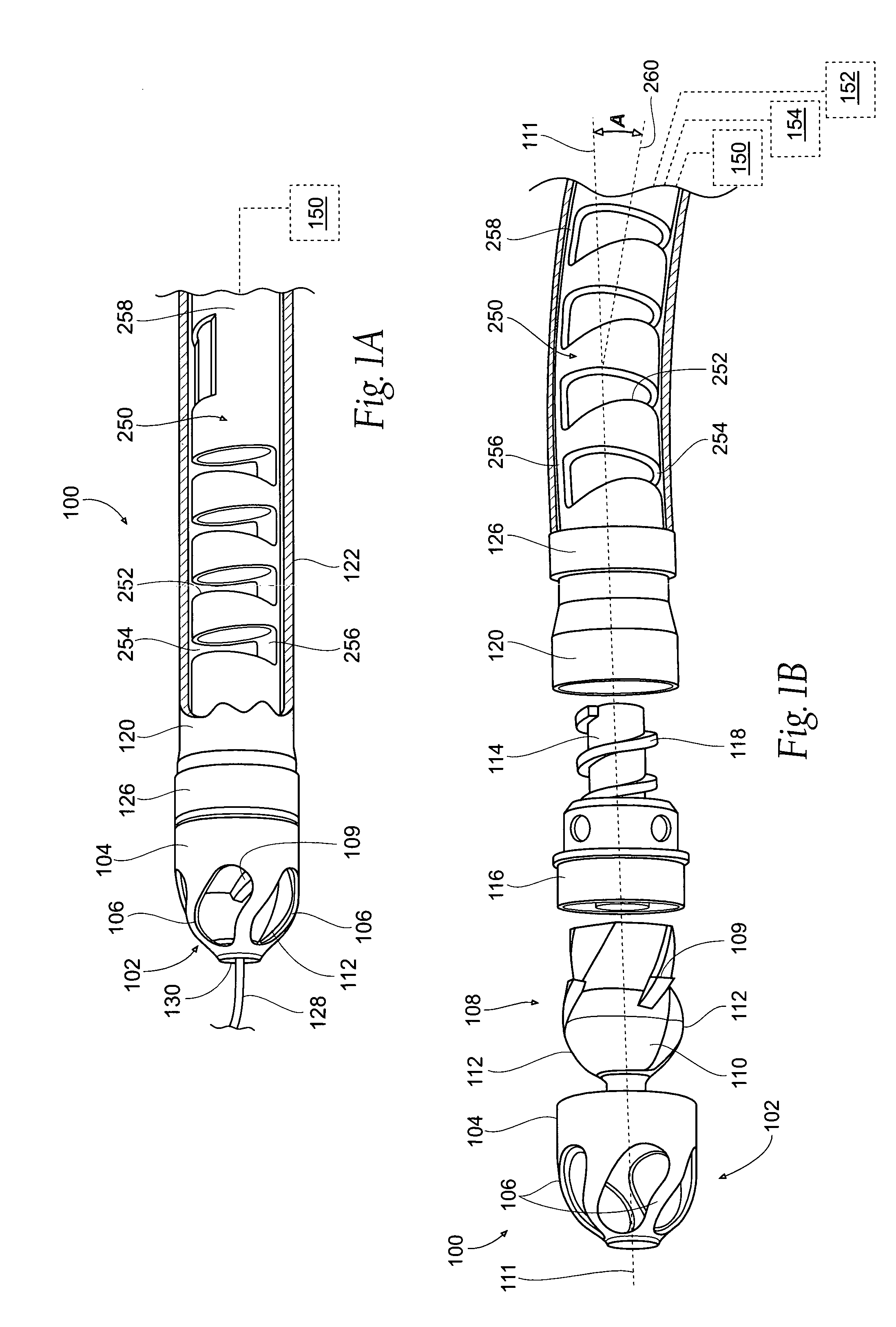
Described herein are atherectomy catheters, systems and methods that include a distal tip region that may be moved laterally so that its long axis is parallel with the long axis of the main catheter body axis. Displacing the distal tip region laterally out of the main catheter body axis exposes an annular blade and opens a passageway for cut tissue to enter a storage region within the catheter. The annular blade may be internally coupled to a drive shaft that rotates the blade, and thus the exposed blade edge may have the same crossing profile (OD) as the rest of the distal end region of the catheter. Also described herein are gear-driven atherectomy devices that may use a cable drive shaft to actuate the annular blade. Both push-to-cut and pull-to-cut variations are described, as are methods for cutting tissue and systems including these atherectomy catheters.
Owner:AVINGER
Atherectomy devices and methods
Owner:ATHEROMED
High Torque, Low Profile Catheters and Methods for Transluminal Interventions
ActiveUS20080125748A1Raise the possibilitySmall diameterGuide needlesMulti-lumen catheterBlood vessel occlusionPartial obstruction
Catheter devices having low profile shafts and laterally deployable members (e.g., cannulas, needles, etc.) that may be extended or advanced laterally from the catheter shaft. Also disclosed are methods for bypassing a vascular obstruction (e.g., a chronic total occlusion or other full or partial obstruction) wherein a guidewire is entrapped in a subintimal space adjacent to the obstruction. A catheter of the foregoing character is advanced over the entrapped guidewire and into the subintimal space. The laterally deployable member is then advanced or extended from the subintimal space back into the true lumen of the blood vessel distal to the obstruction. A second guidewire is then advanced through or along the laterally deployable member. The catheter and first guidewire are then removed and one or more working device(s) (balloons, atherectomy devices, setnts, etc.) is / are advanced over the second guidewire and used to establish a subintimal bypass channel through which blood may flow around the obstruction.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Atherectomy devices and methods
Owner:ATHEROMED
Atherectomy devices and methods
Owner:ATHEROMED
Atherectomy devices and methods
ActiveUS8236016B2Prevent radial twistingAvoid distortionCannulasCatheterBiomedical engineeringBlood vessel
Owner:ATHEROMED
Device for applying and monitoring medical atherectomy
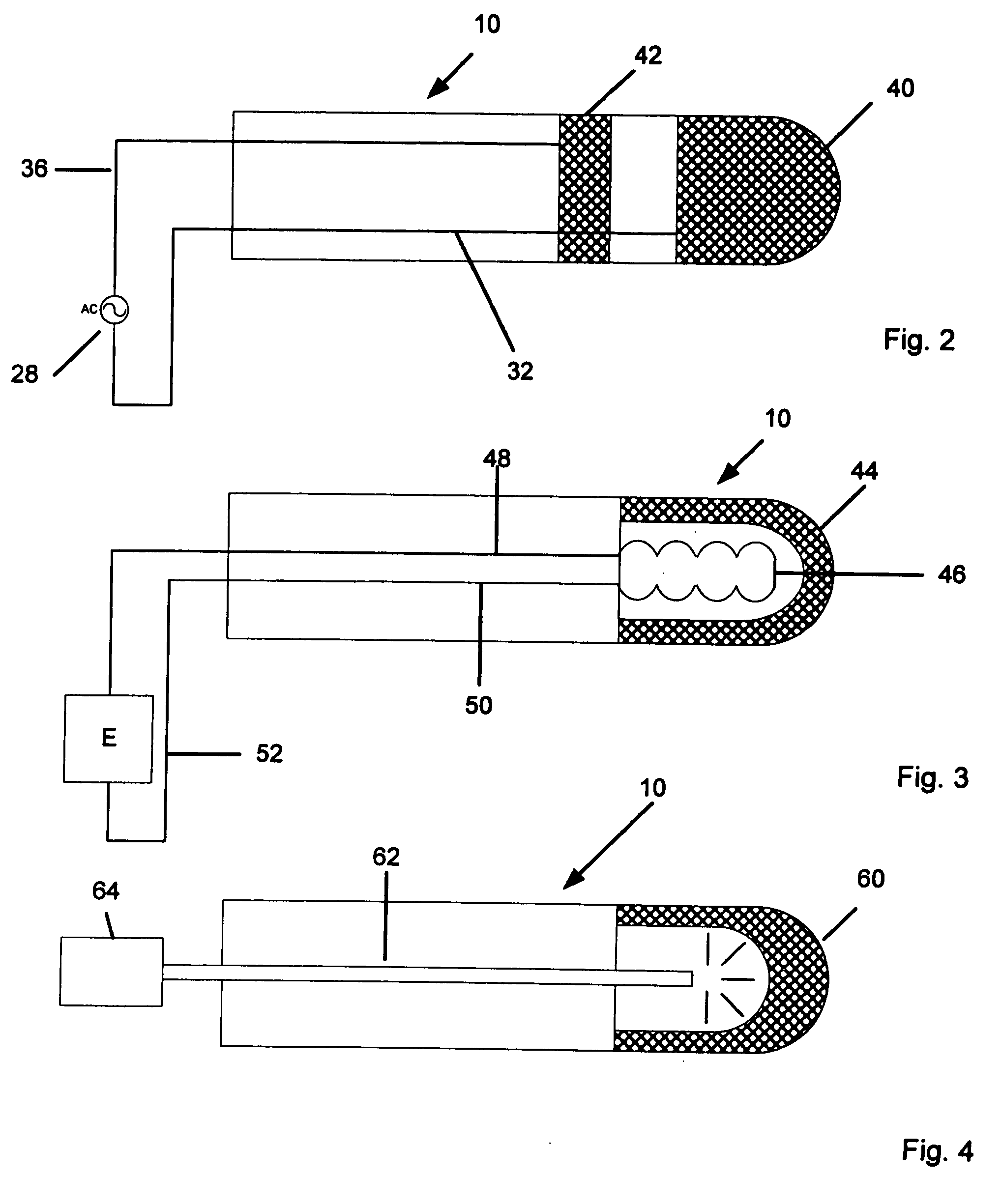
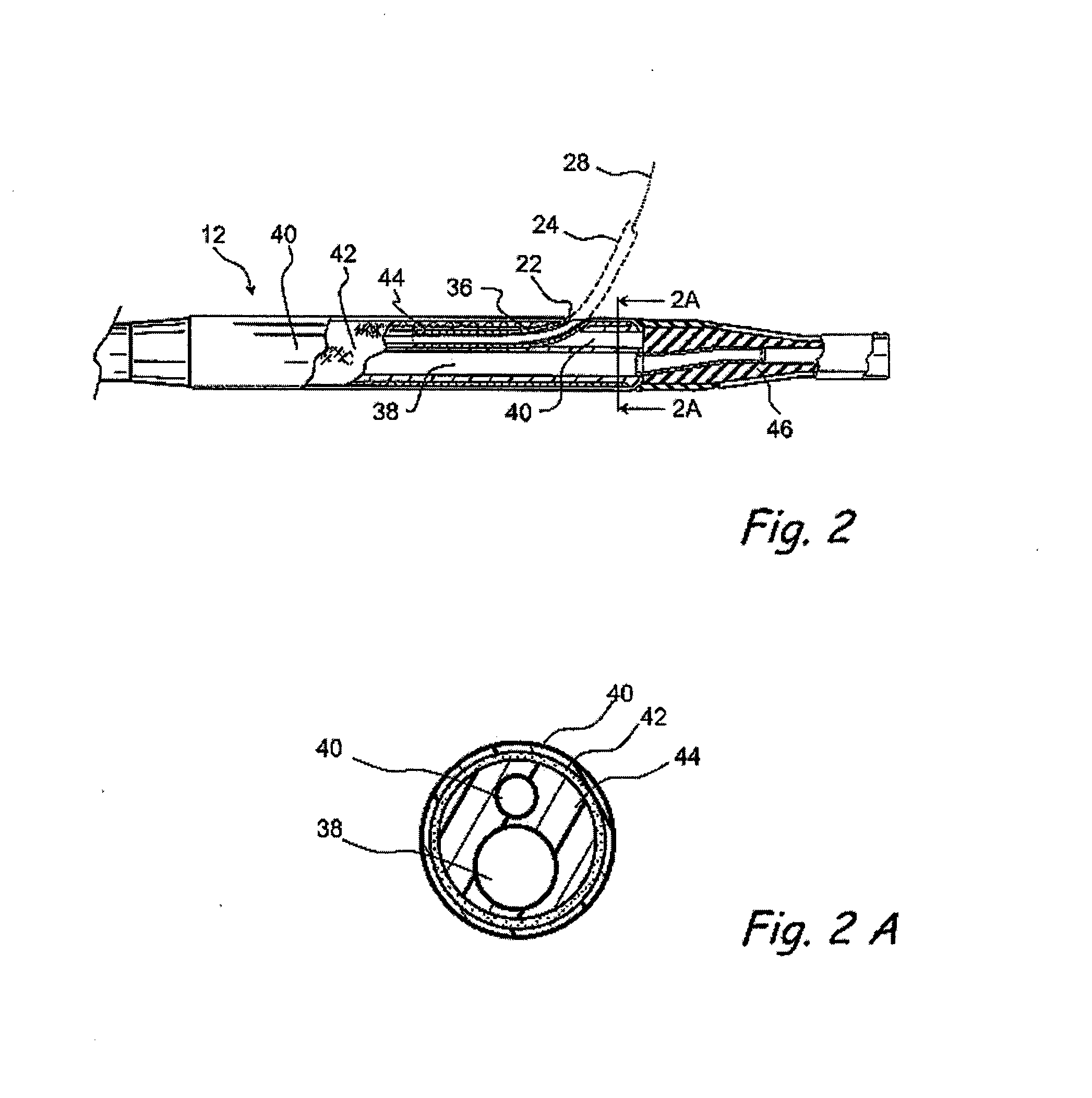
InactiveUS20050187571A1Reduce in quantityHigh detail resolution of structureCannulasSurgical navigation systemsWindow openingArtery walls
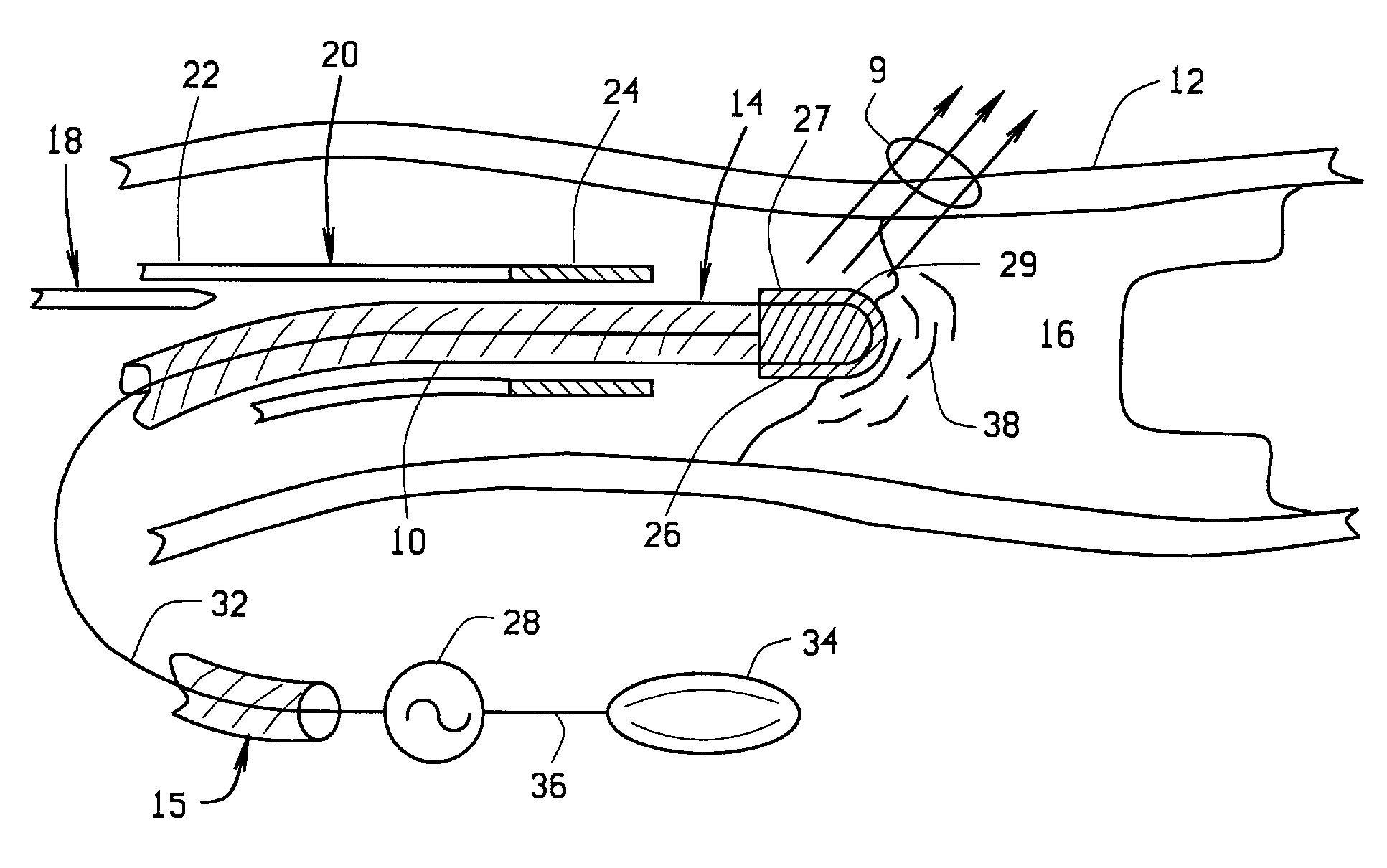
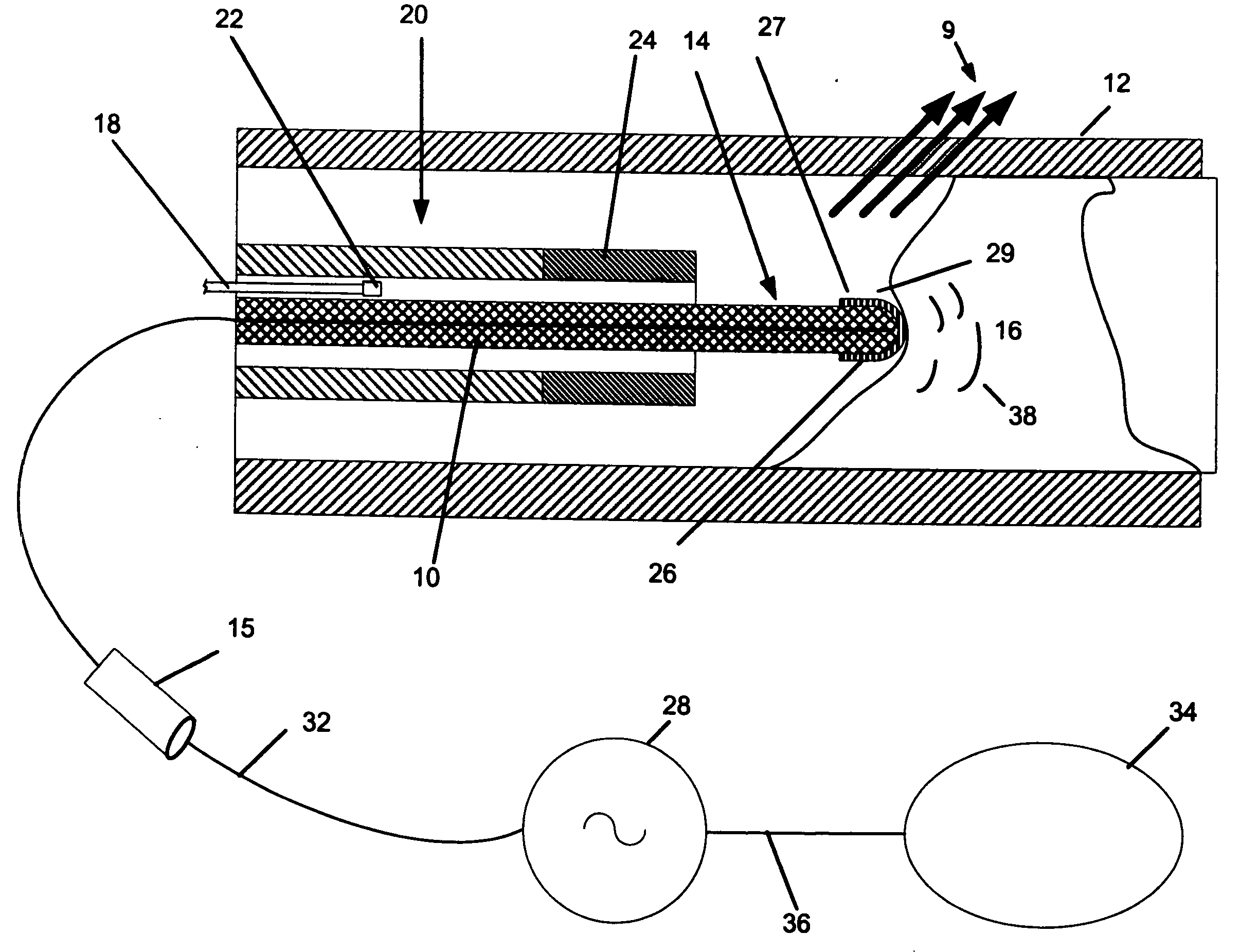
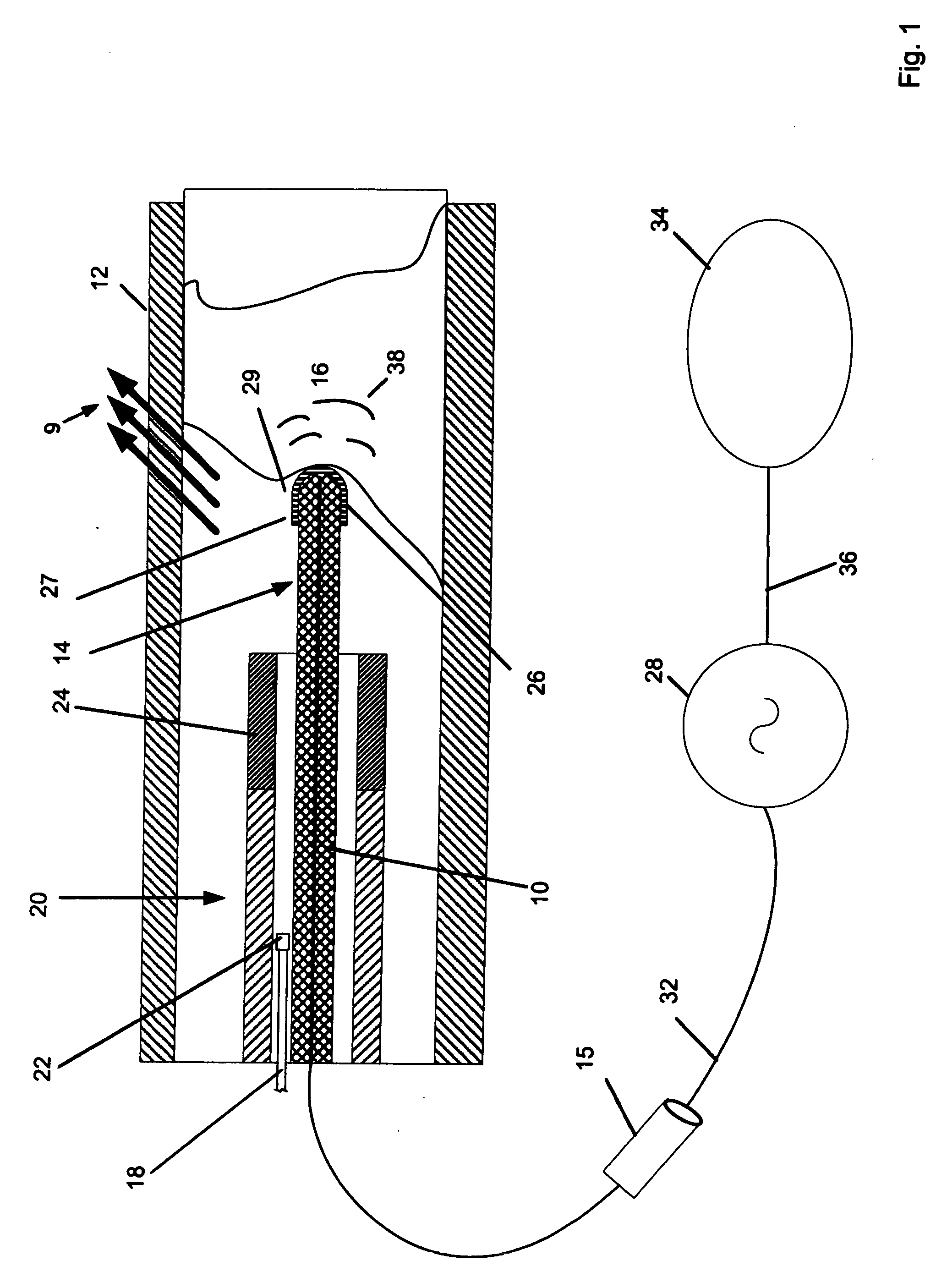
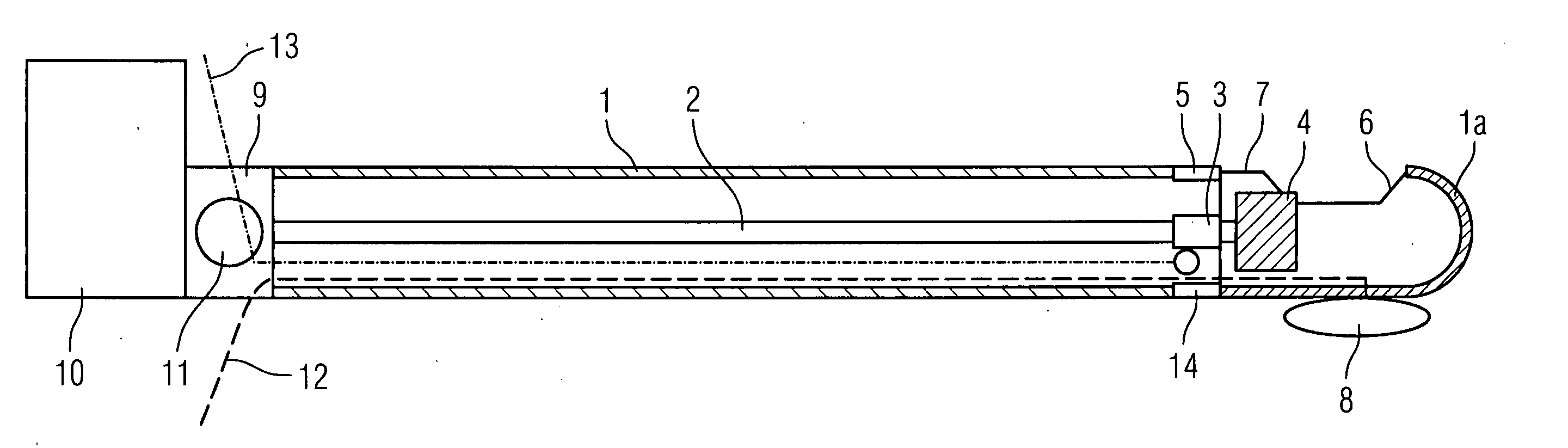
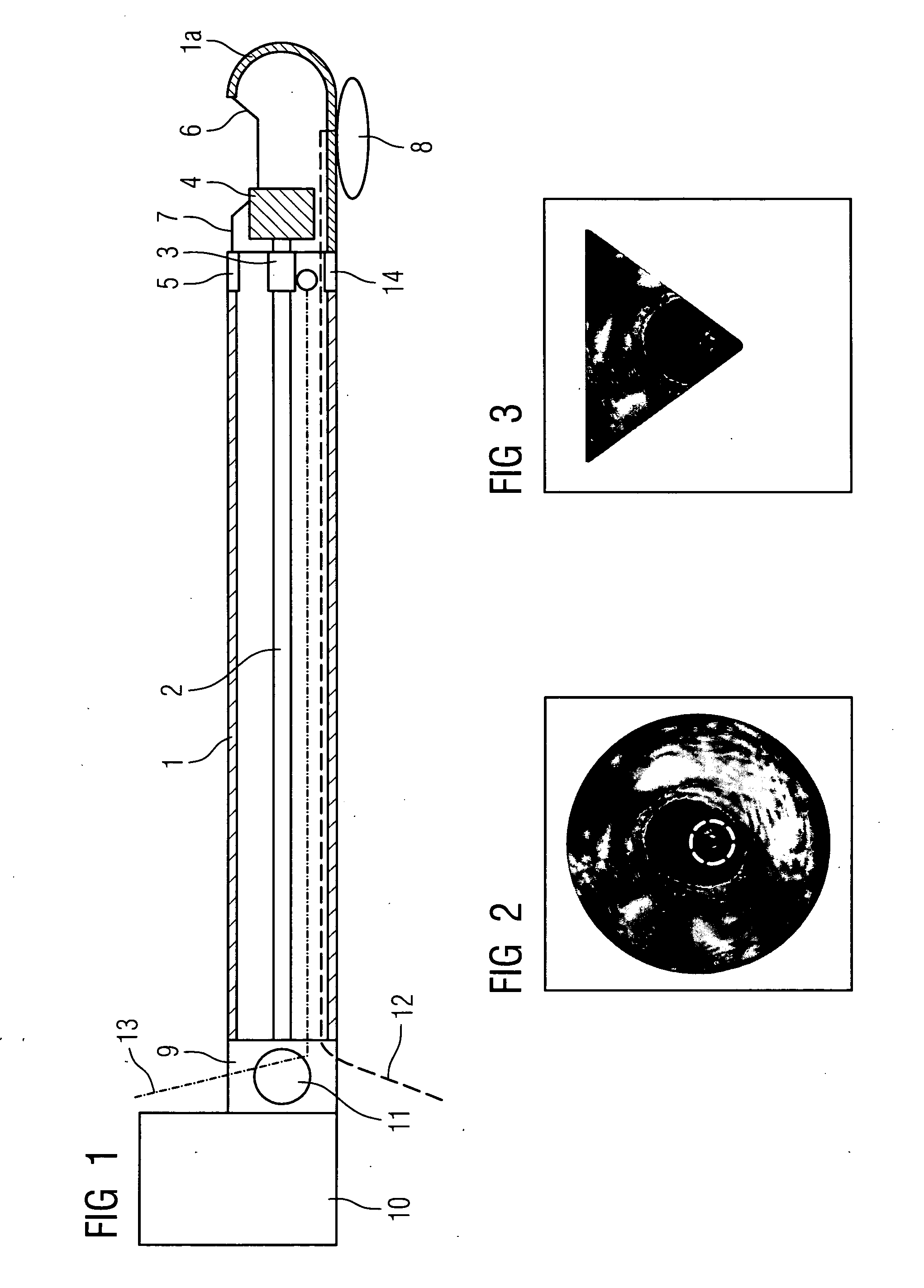
Device for carrying out and monitoring an atherectomy, with which a cutting knife driven in a rotating manner by an external unit and set back to project into an opening in the tip of the catheter can be pressed onto the artery wall by means of an inflatable balloon arranged on the side of the catheter casing opposite the window opening, an atherectomy catheter being connected to an OCT catheter to form an integrated unit.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
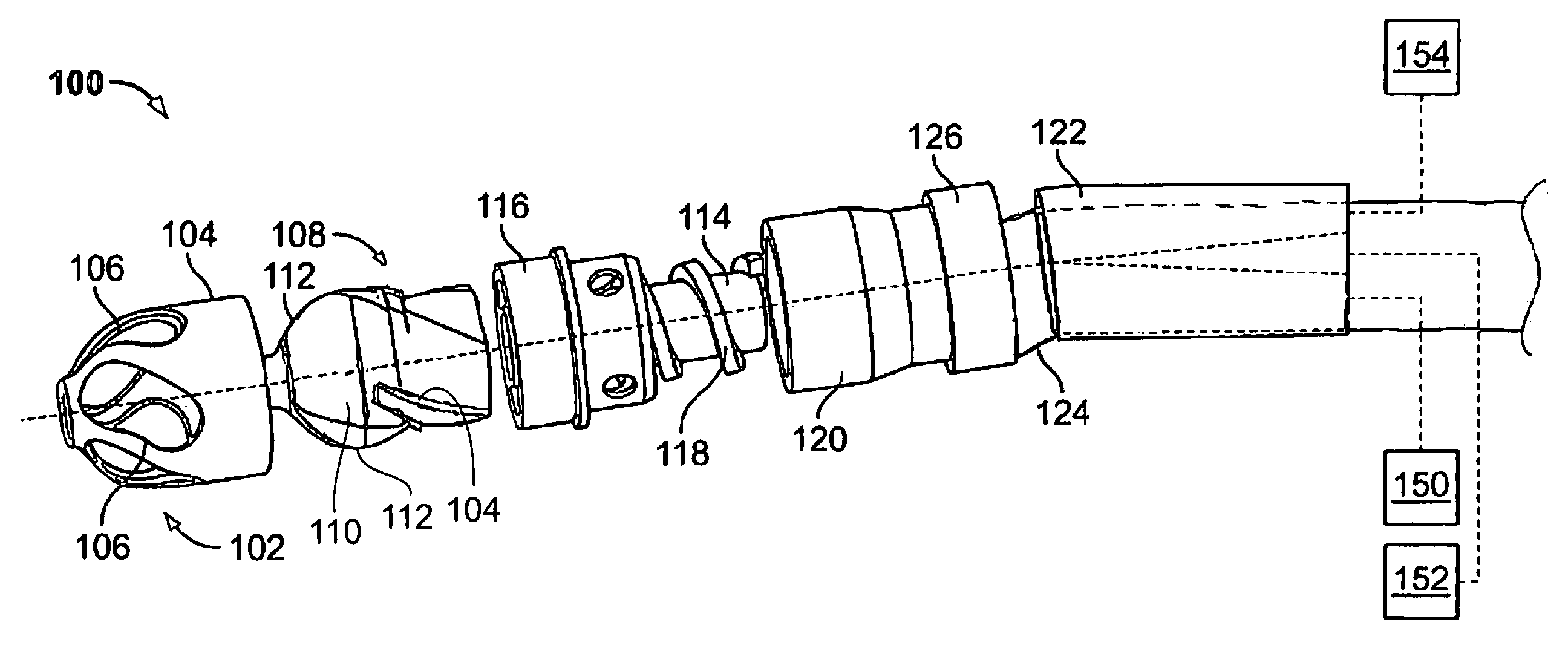
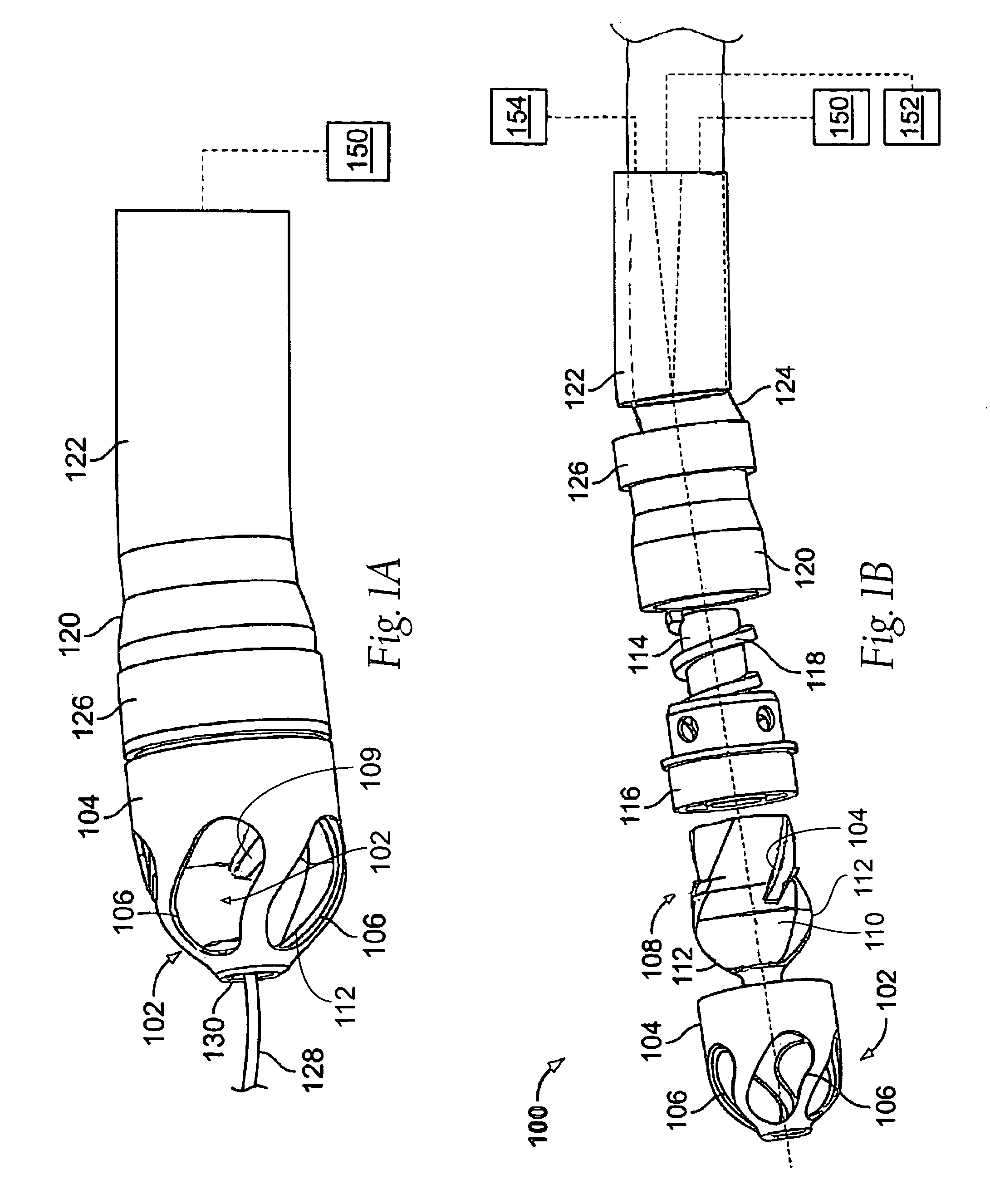
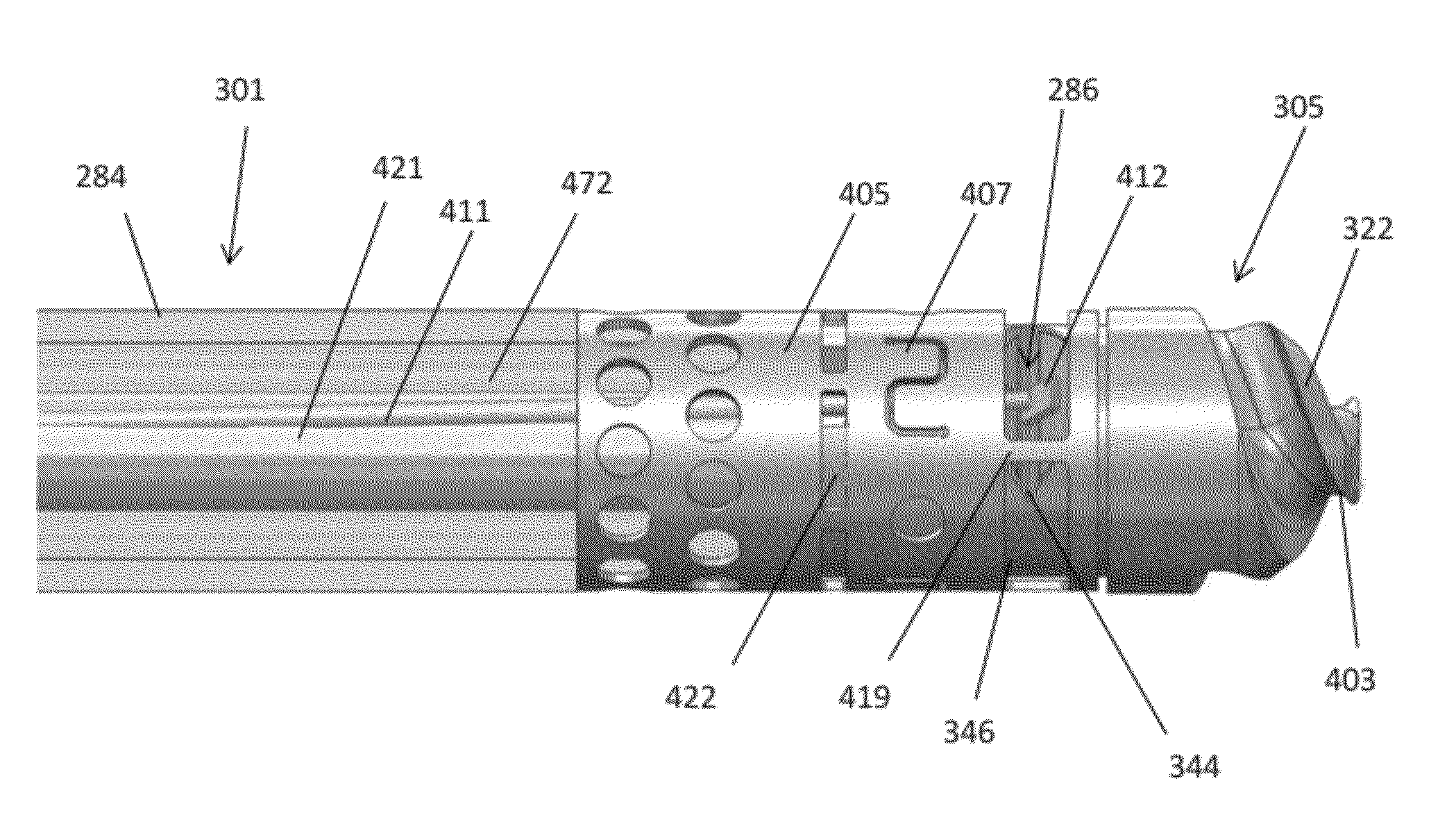
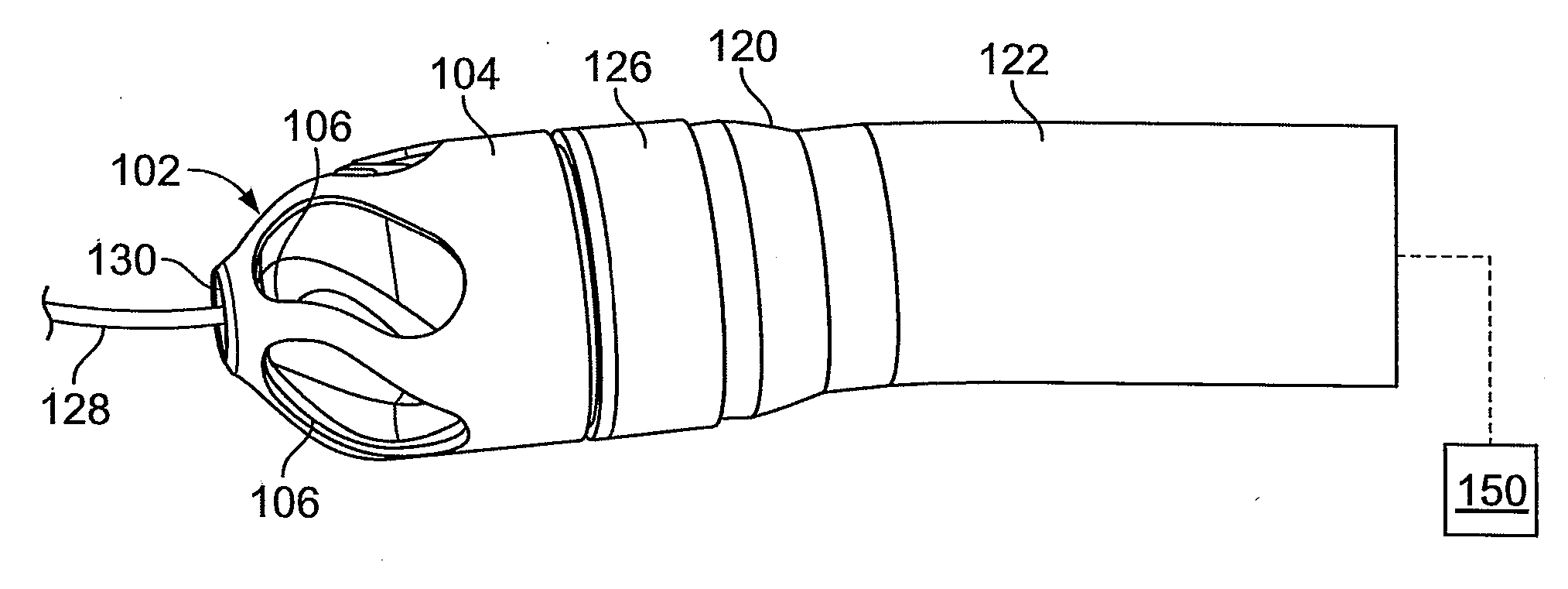
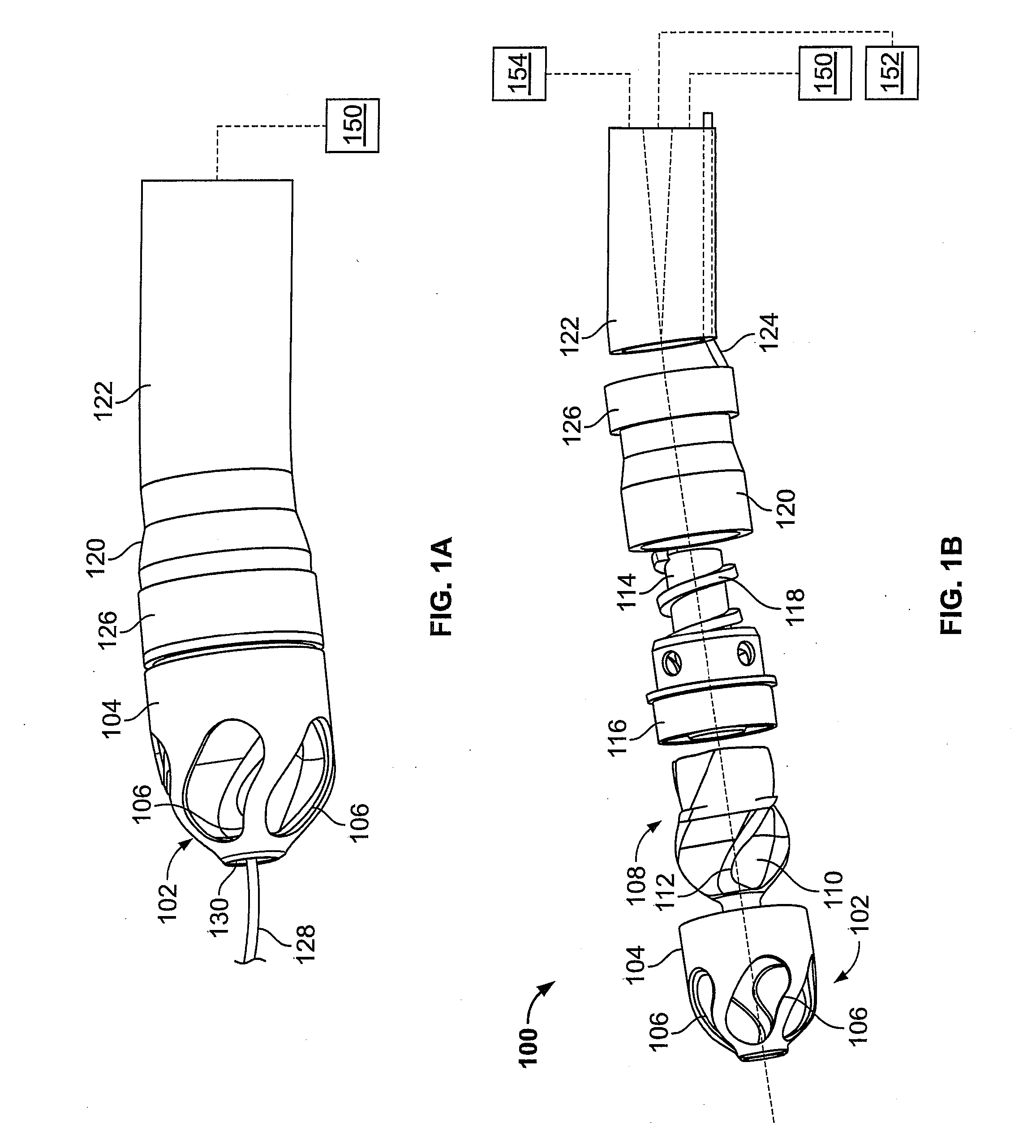
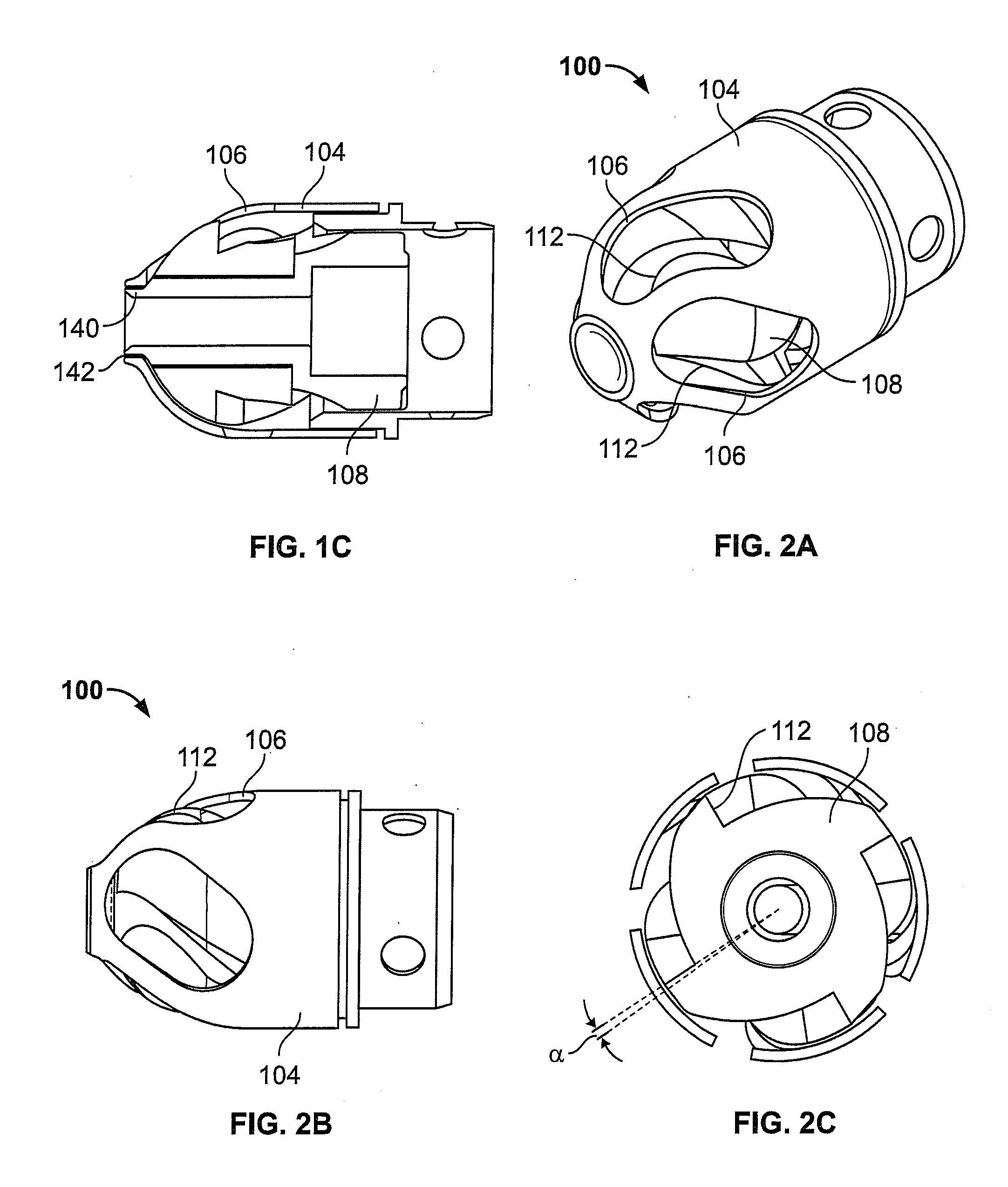
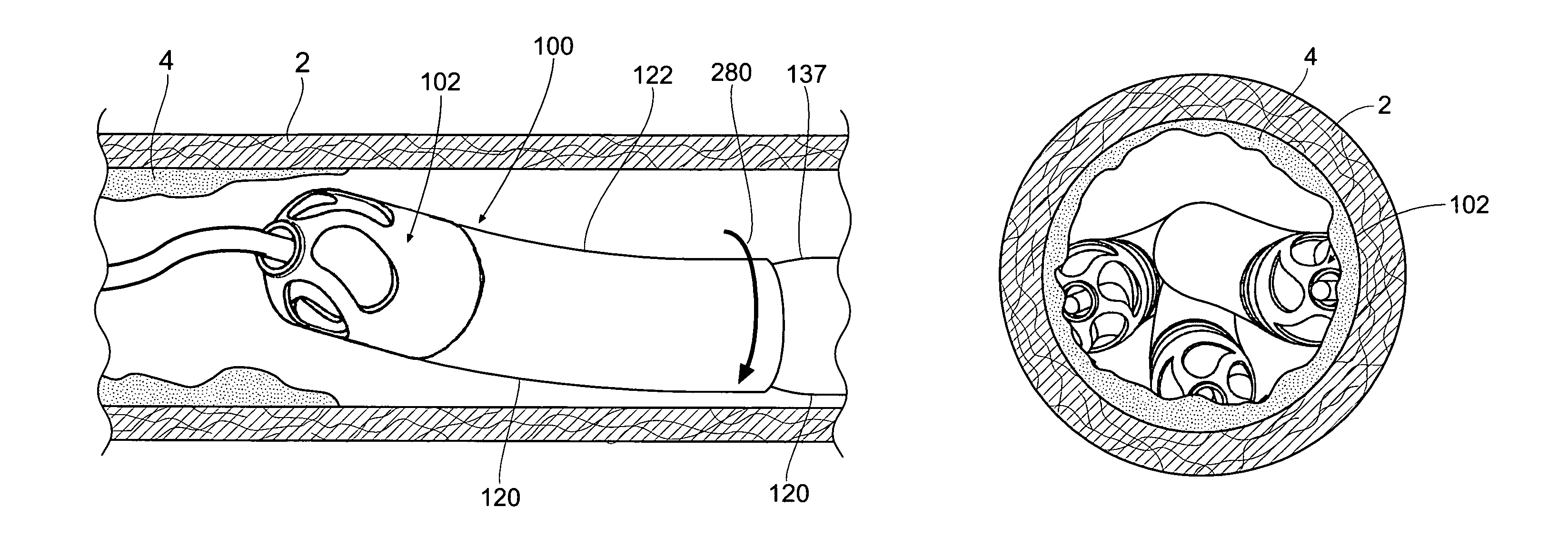
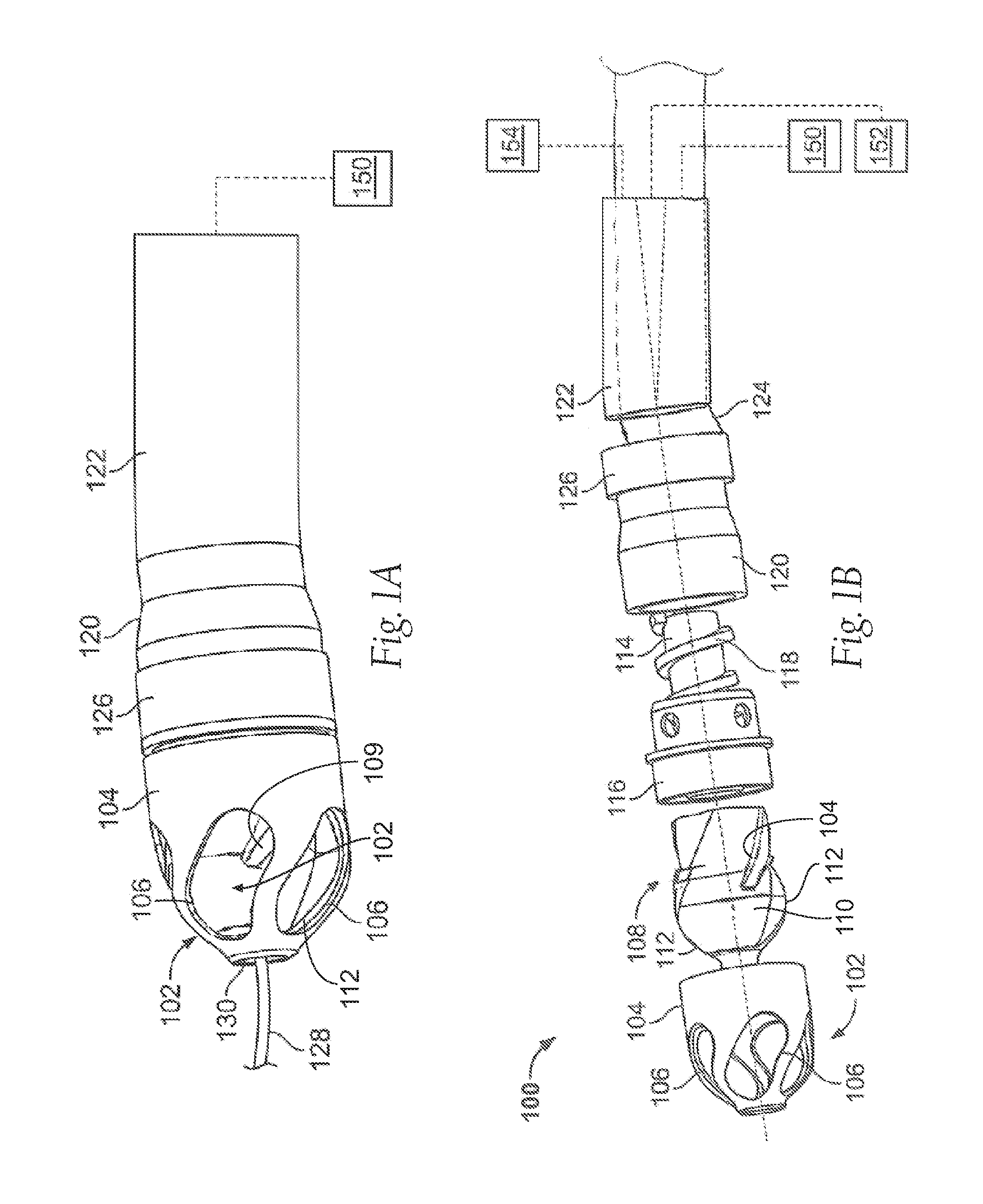
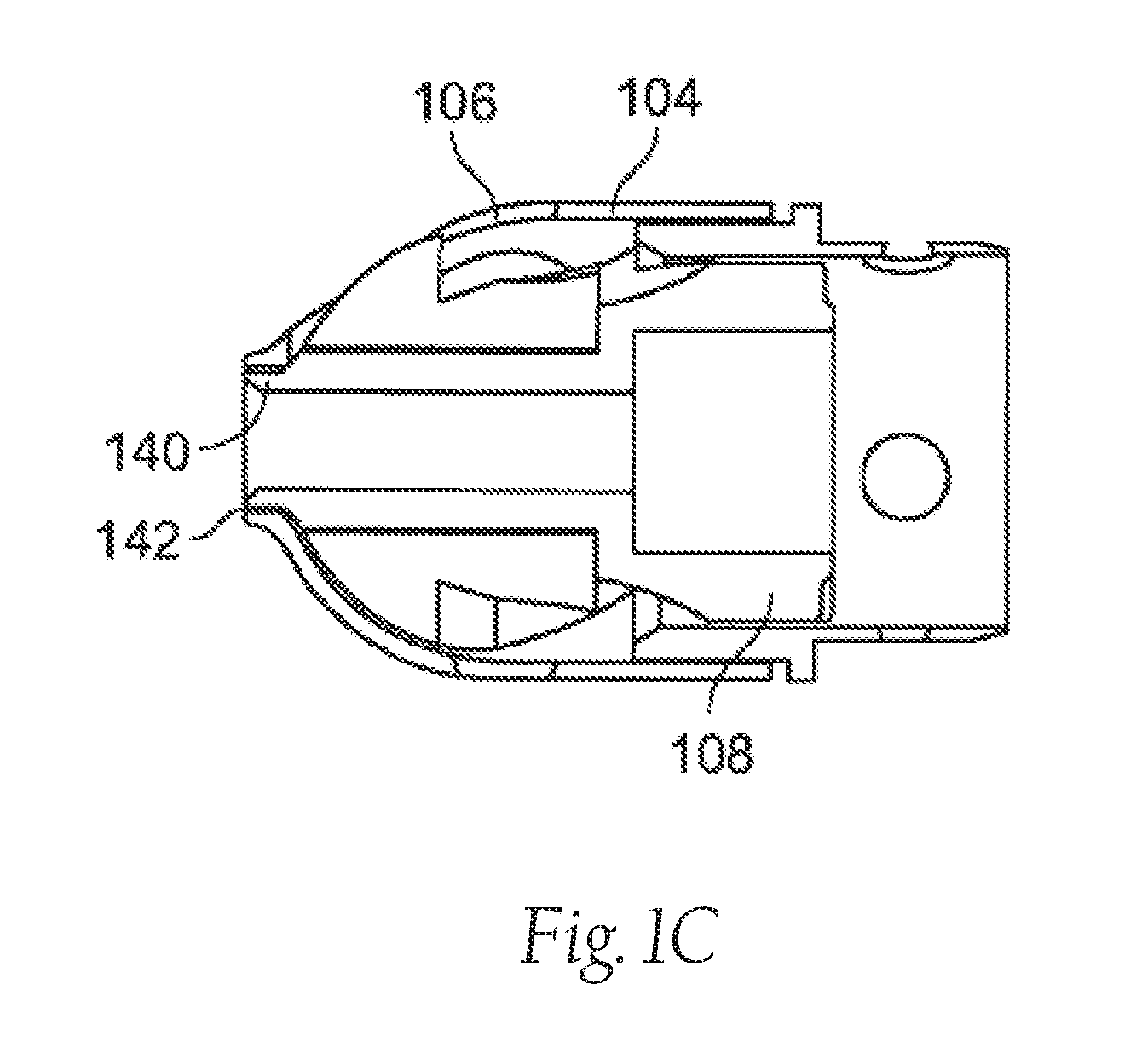
Atherectomy apparatus, systems and methods
Described here are devices and methods for performing atherectomies. Generally, the atherectomy devices may comprise a handle, a cutter assembly, and a catheter or catheter assembly therebetween. The cutter assembly may include a cutter housing and a cutter comprising a first cutting element and a second cutting element, each of which may be rotated relative to the atherectomy device to cut occlusive material.
Owner:ATHEROMED
Atherectomy devices, systems, and methods
ActiveUS8628549B2Prevent radial twistingAvoid distortionBalloon catheterEar treatmentVascular deviceBlood vessel
The devices and methods generally relate to treatment of occluded body lumens. In particular, the present devices and methods relate to removal of the occluding material from the blood vessels as well as other body lumens. In some variations, the methods comprise providing a vascular device comprising a catheter body, a cutter assembly, a drive mechanism, a torque shaft, and a deflecting mechanism. The methods may further comprise operating the drive mechanism to cut occlusive material, operating the deflecting mechanism to deflect the cutter assembly, and rotating the distal end of the catheter body to sweep the cutter assembly.
Owner:ATHEROMED
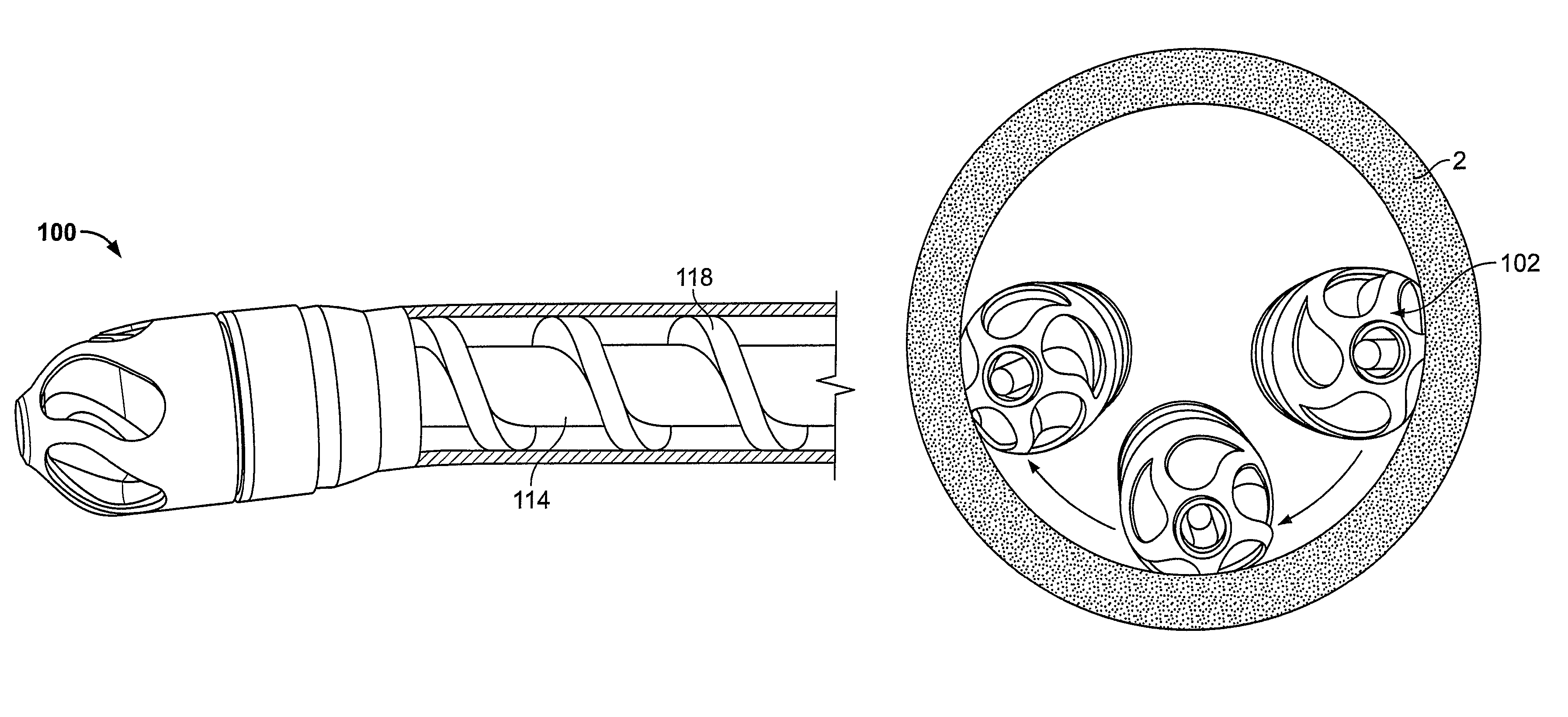
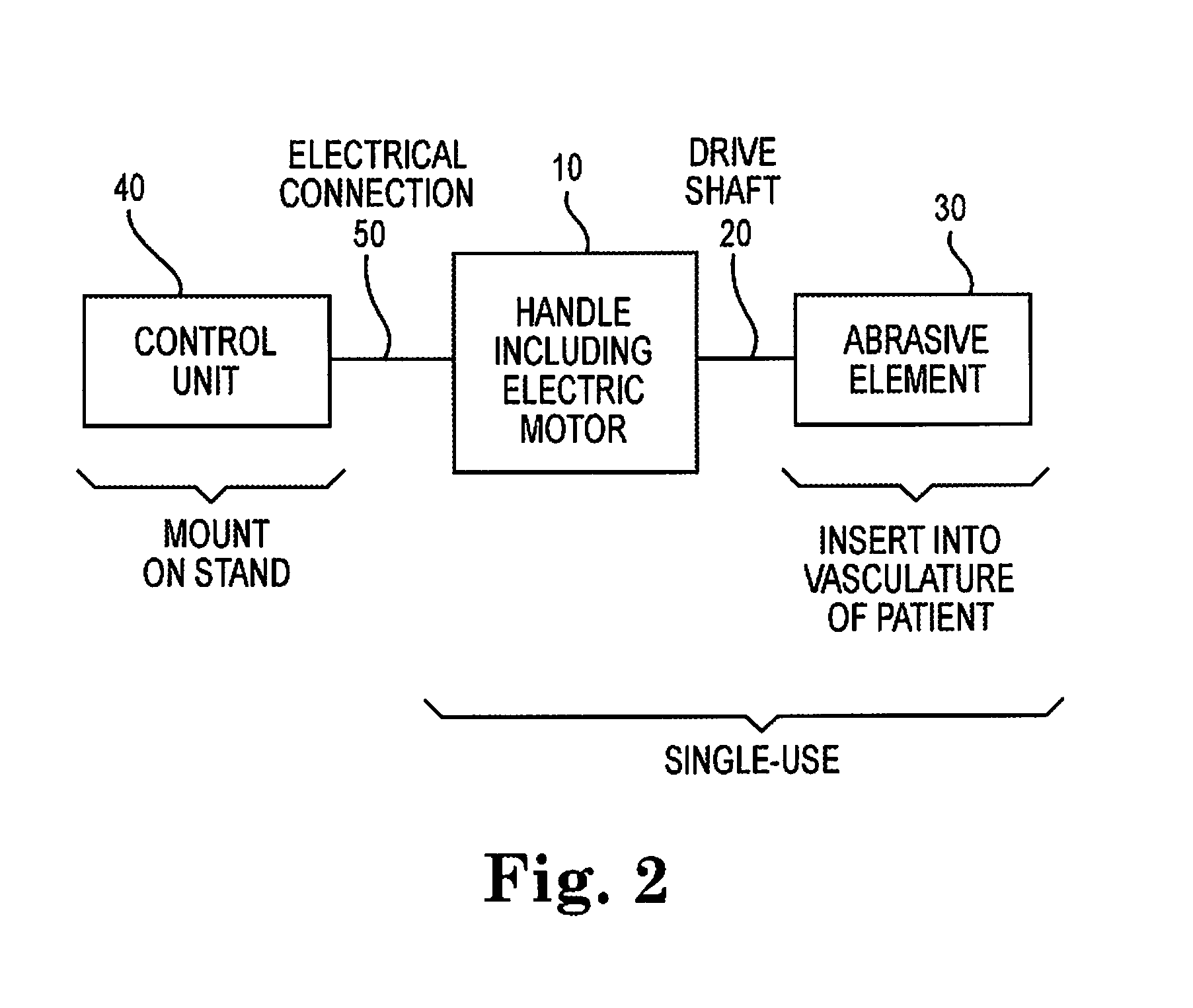
Rotational atherectomy device with electric motor
An atherectomy device is disclosed, which is rotationally driven by an electric motor. In some designs, the device includes features unavailable on gas turbine-driven systems, such as the storing in memory of low / medium / high preset rotation speeds for particular models of handle, calculations of the amount of saline left in the IV and associated warnings when it gets sufficiently low, and automatic adjustment of the IV pump rate to a predetermined or calculated level when the rotational speed of the motor is changed. The electric motor has far more rotational inertia than a comparable gas turbine, so the system includes a control mechanism that helps prevent damage from excessive torque being applied to the distal end of the drive shaft. When an obstruction at the distal end is detected, by a drop in the motor rotational speed, the motor is released and is allowed to spin freely as a flywheel. The freely-spinning motor allows the large angular momentum of the system to dissipate rapidly and safely, without excessive torque to the drive shaft.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Atherectomy devices and methods
ActiveUS20120083810A1Prevent accidental cuttingIncrease blockingCannulasGuide wiresBiomedical engineeringBlood vessel
Owner:ATHEROMED
Orbital atherectomy device guide wire design
InactiveUS20050209615A1Minimize traumaReduce traumaCannulasDiagnosticsDrive shaftOrbital atherectomy
A guide wire for assisting in implantation and balancing of an orbital atherectomy device is disclosed. The guide wire is generally configured to be received within a driveshaft and cutting region of the orbital atherectomy device. The guide wire is sufficiently flexible to minimize trauma to the vessel walls is positioned within a patient. The distal end of the guide wire can include on or more weighted elements movable along the distal region of the guide wire to permit the balancing of an a rotating drive shaft and cutting region of an orbital atherectomy device. The guide wire can also include an atraumatic tip located on the end of the guide wire to reduce trauma to the vessels during implantation. Lubricious coatings are also provided to reduce friction between the driveshaft and cutting region of the atherectomy device and guide wire.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Atherectomy devices, systems, and methods
Owner:ATHEROMED
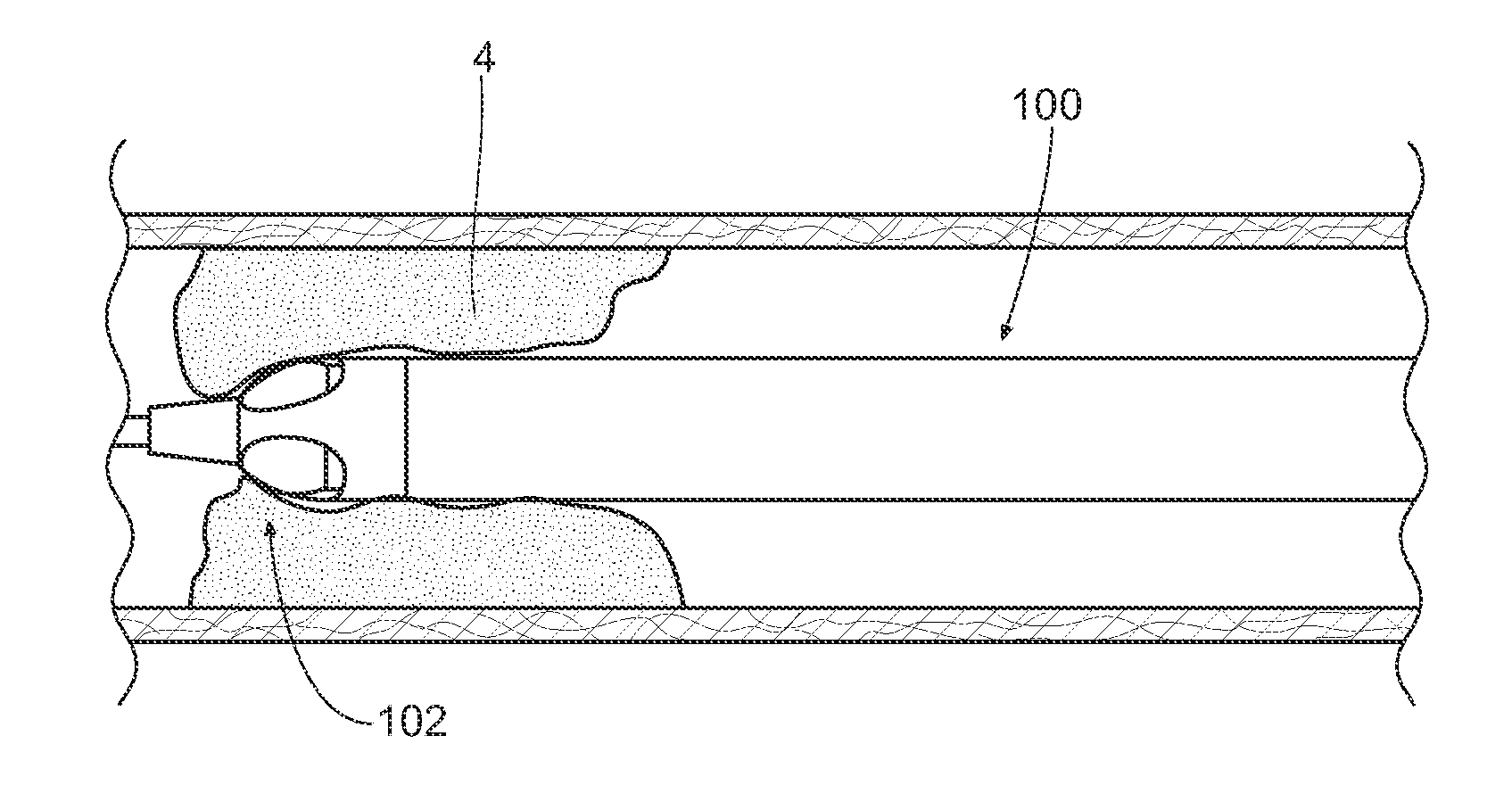
Method and apparatus for increasing rotational amplitude of abrasive element on high-speed rotational atherectomy device
A high-speed atherectomy device is disclosed, for abrading a blockage (stenosis) in the interior of a lumen (artery). The device uses a rapidly rotating drive shaft that includes an eccentric abrasive element that has its center of mass laterally offset from the rotational axis of the drive shaft. As the drive shaft rotates, centrifugal force drives the eccentric abrasive element outward, so that it traces an abrading diameter at high rotational speeds that is larger than its rest diameter. The drive shaft includes counterweights on both sides of the abrasive element, which may stabilize operation at high rotational speeds. In some cases, the counterweights are also eccentric, with their centers of mass laterally offset from the rotational axis in the opposite direction as that of the abrasive element. The counterweights are longitudinally separated from the abrasive element, and in some cases, the separations are adjustable and / or controllable. In some cases, the guide wire may be retracted prior to or during the high-speed rotation of the drive shaft, with the retraction being to the distal counterweight, the abrasive element, the proximal counterweight, or beyond the proximal counterweight.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com