Patents
Literature
130 results about "Vertex point" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Vertex is a point located in the western hemisphere of a chart (the right-hand side) that represents the intersection of the ecliptic and the prime vertical. In astrology, it is considered an auxiliary Descendant. The Anti-Vertex is the point that is exactly opposite the Vertex.
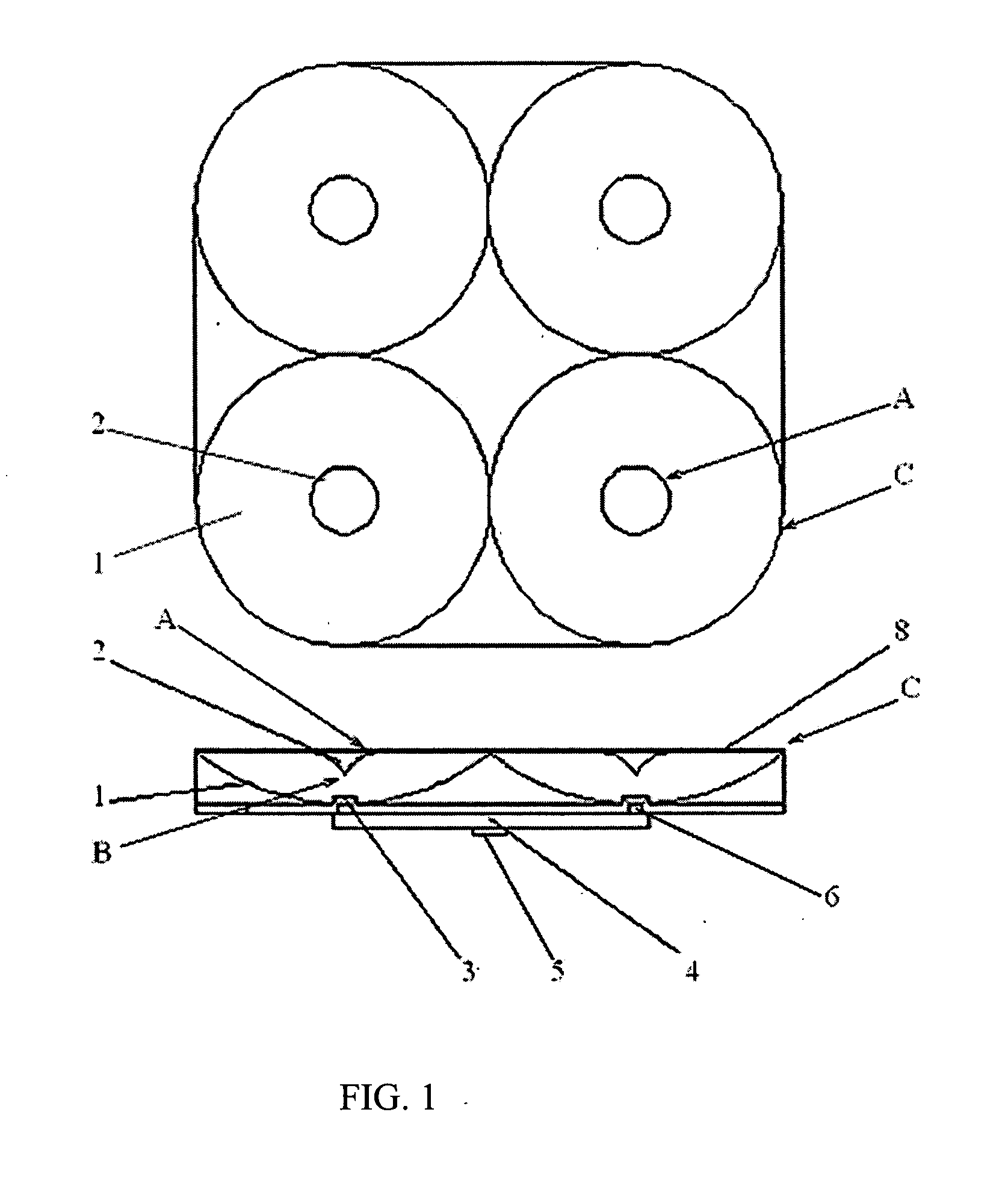
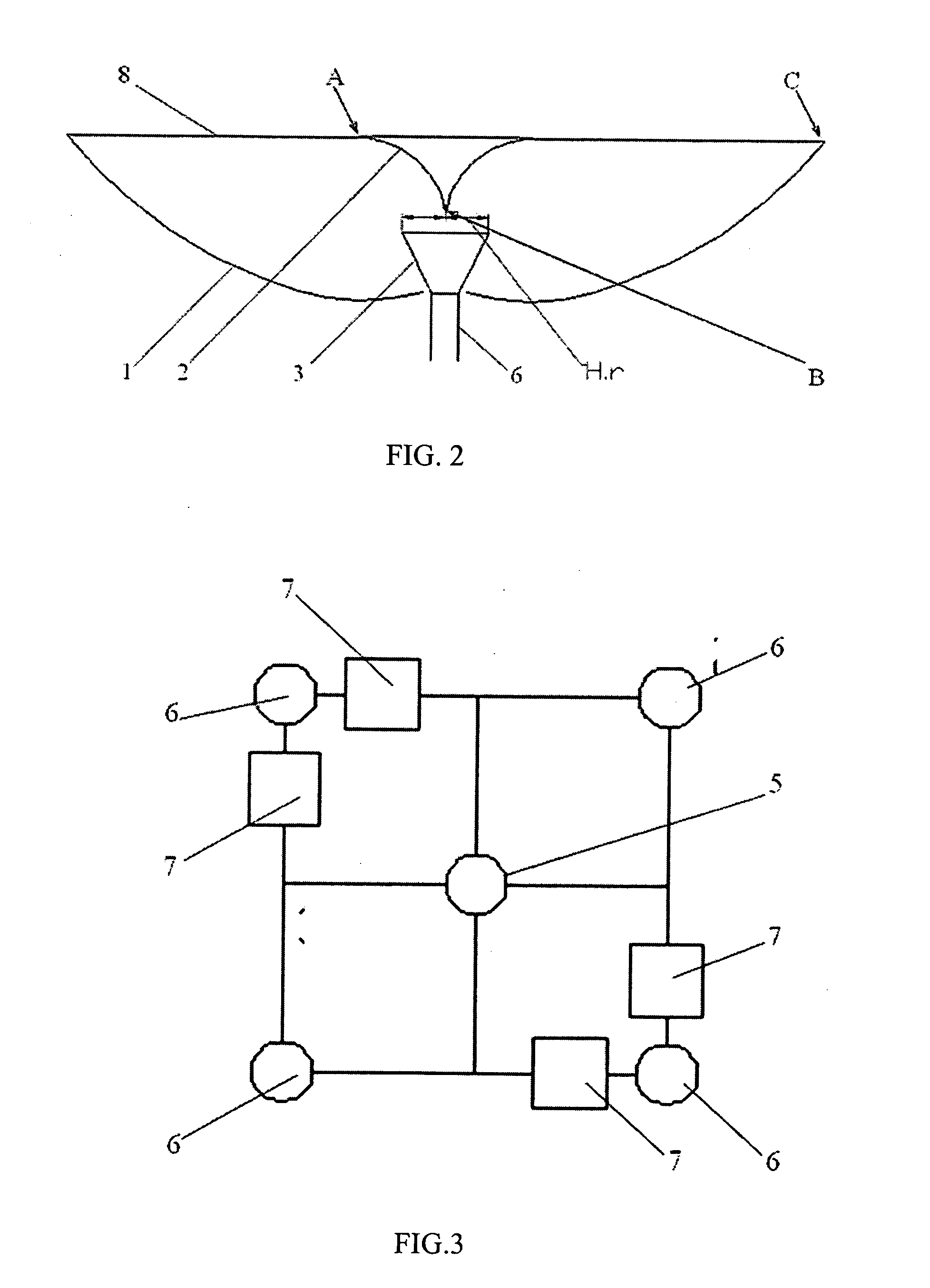
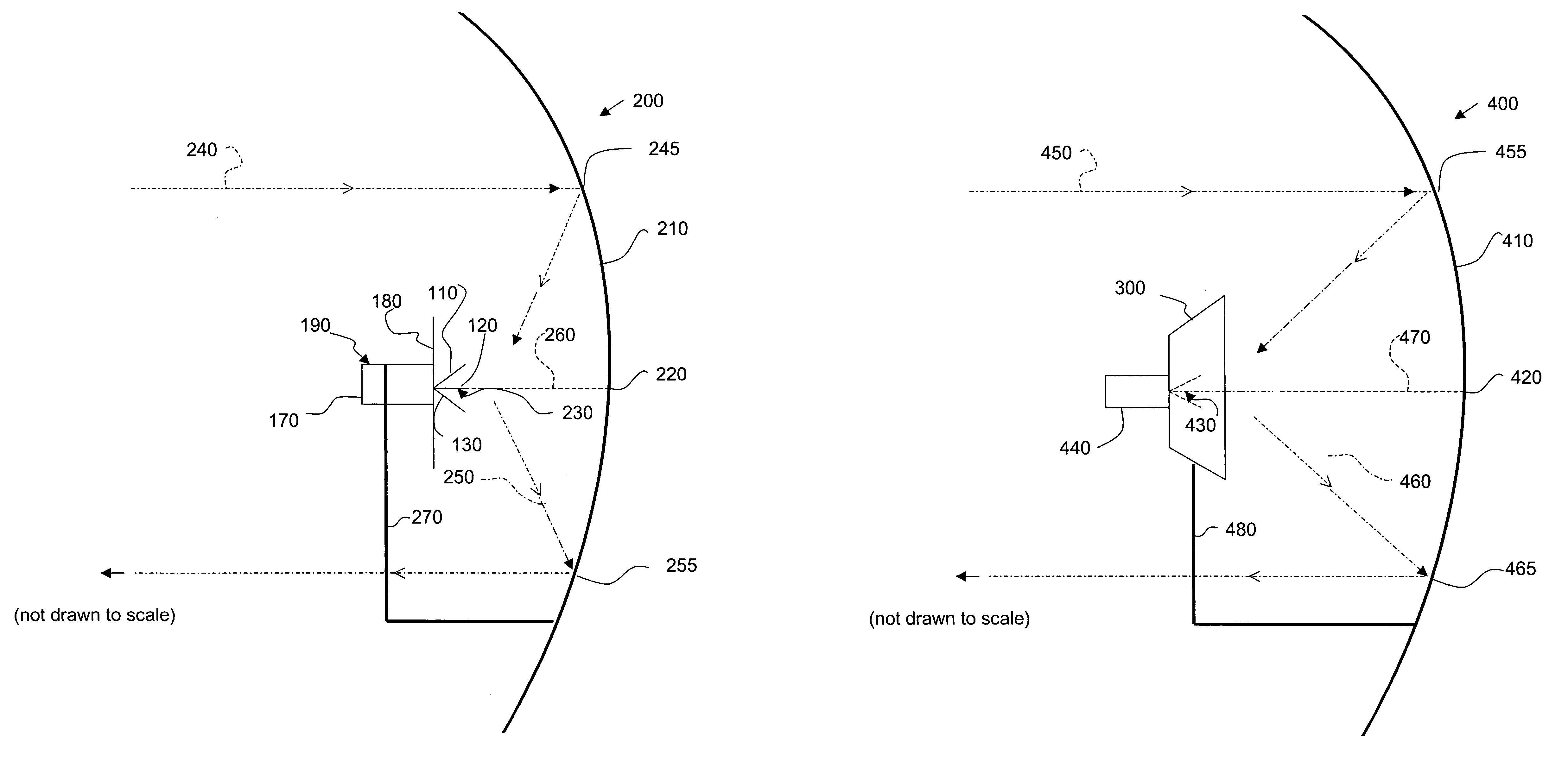
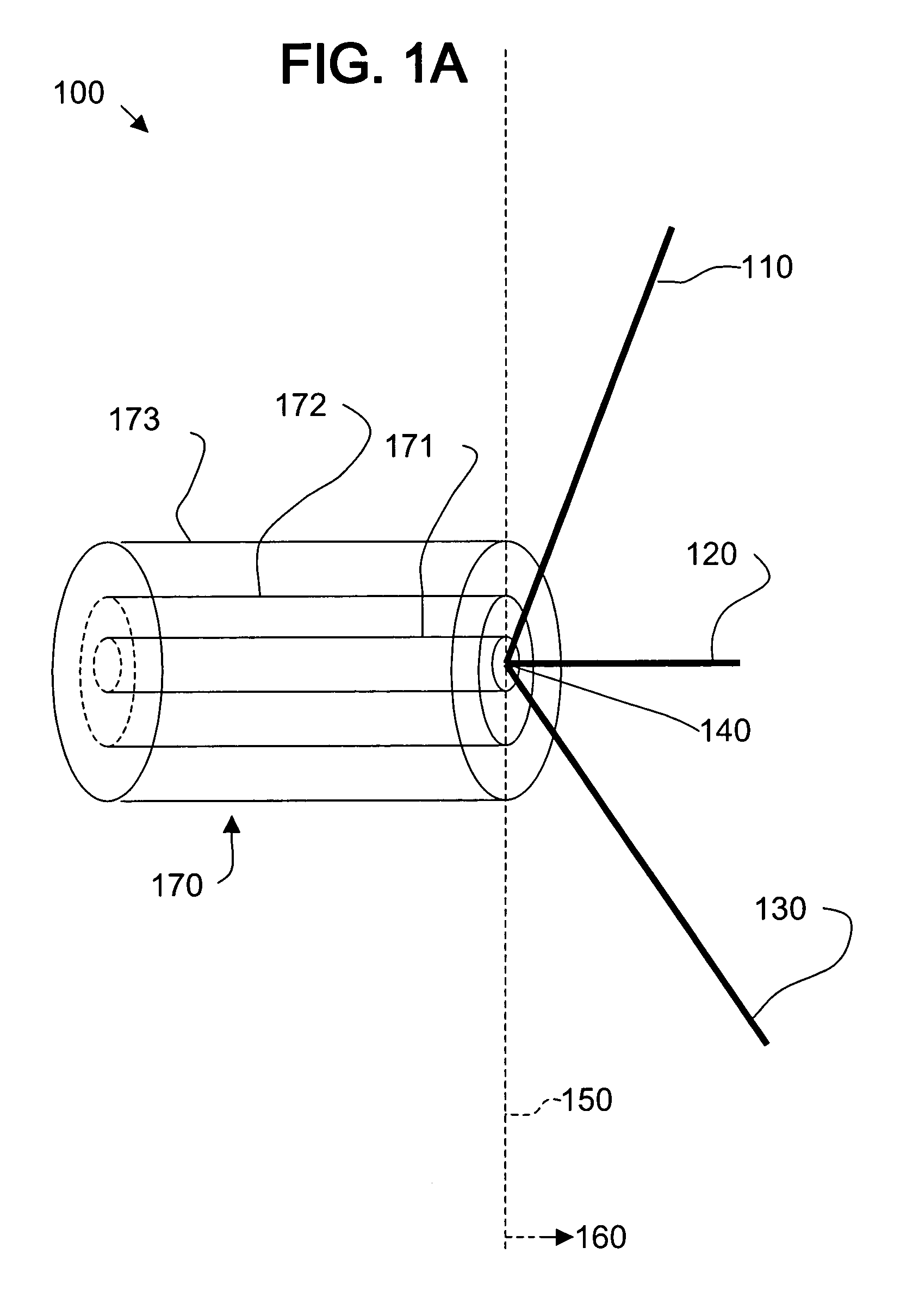
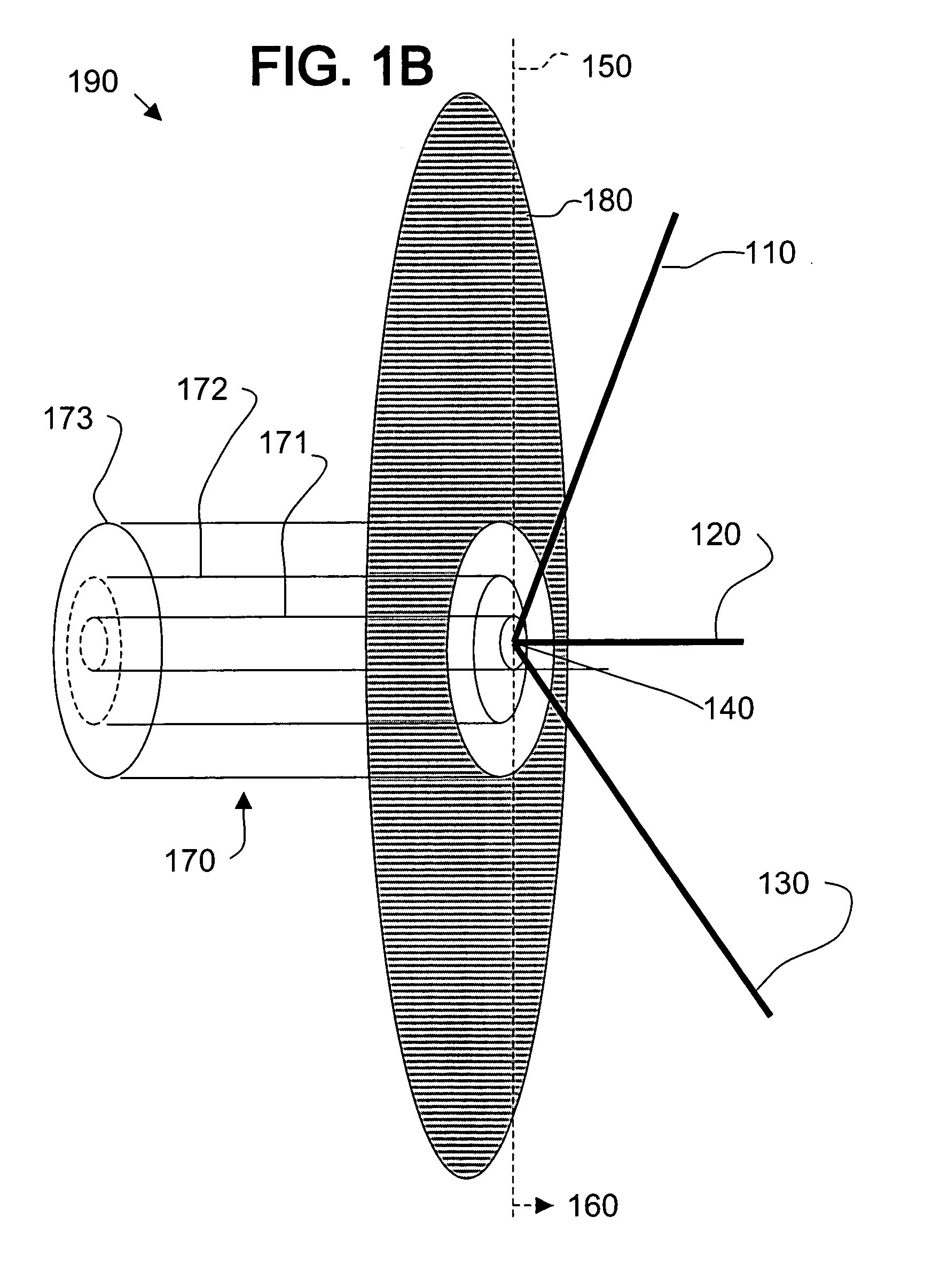
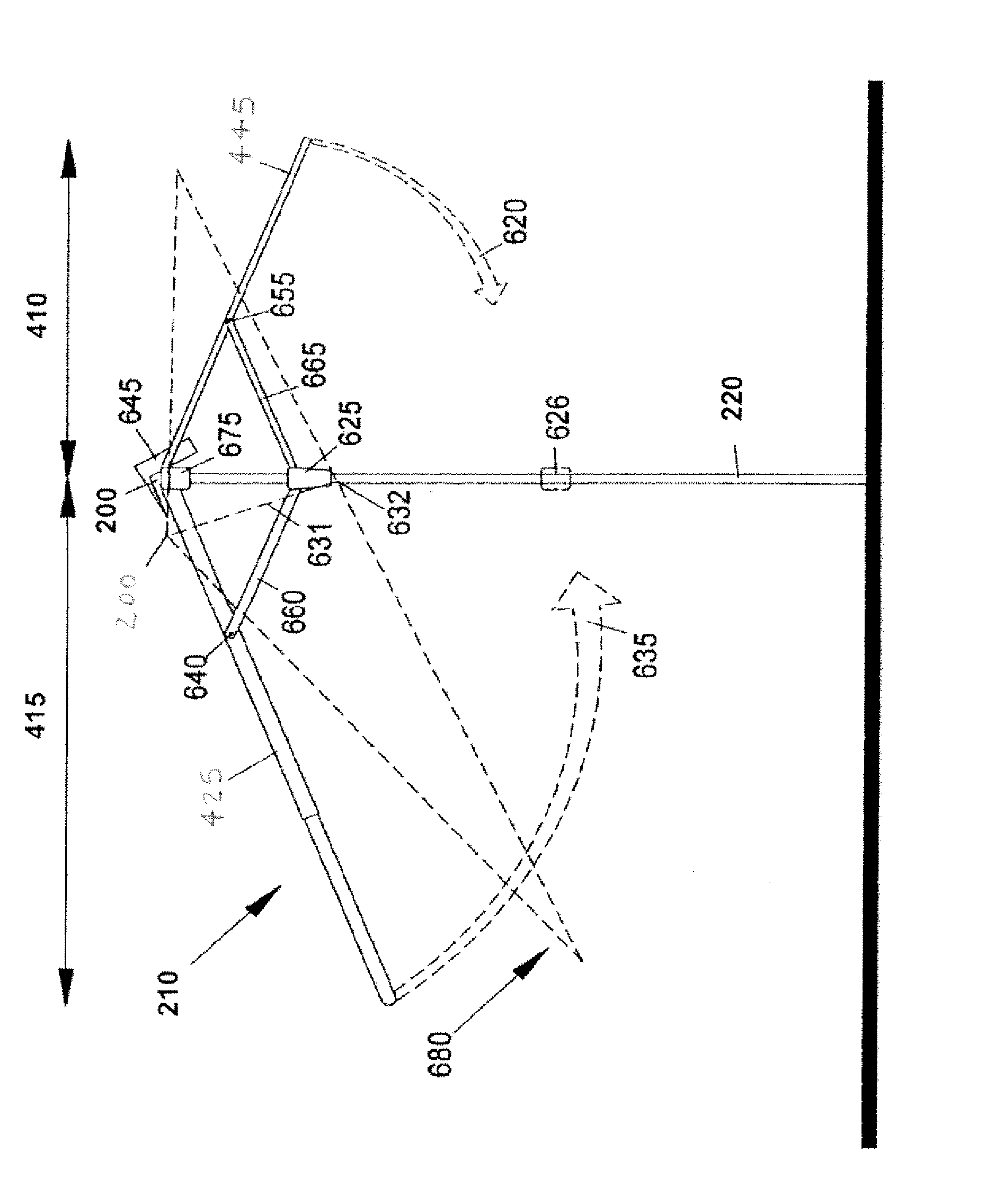
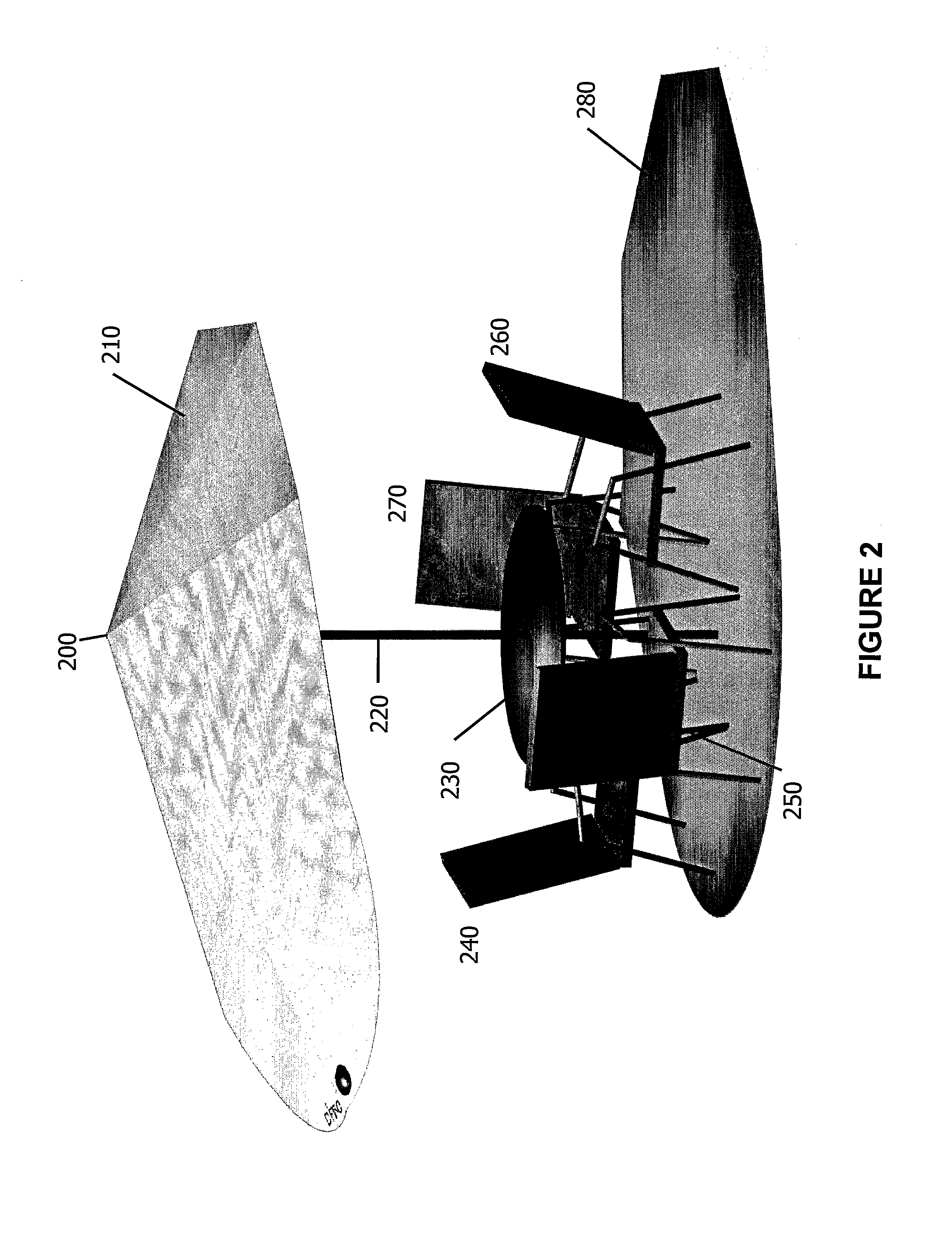
Multi-polarized feeds for dish antennas
InactiveUS20070132651A1Antenna supports/mountingsAntennas with plural divergent straight elementsVertex pointAcute angle
A multi-polarized forward feed and dish configuration for transmitting and / or receiving radio frequency (RF) signals is disclosed. The configuration comprises a conductive reflector dish, having a focal point and a vertex point, and a multi-polarized forward feed element positioned substantially at the focal point. The forward feed element comprises at least two radiative members each having a first end and a second end. The second ends of the radiative members are electrically connected at an apex point and are each disposed outwardly away from the apex point toward the vertex point at an acute angle relative to an imaginary plane intersecting the apex point.
Owner:NILSSON JACK
Antenna-feeder device and antenna
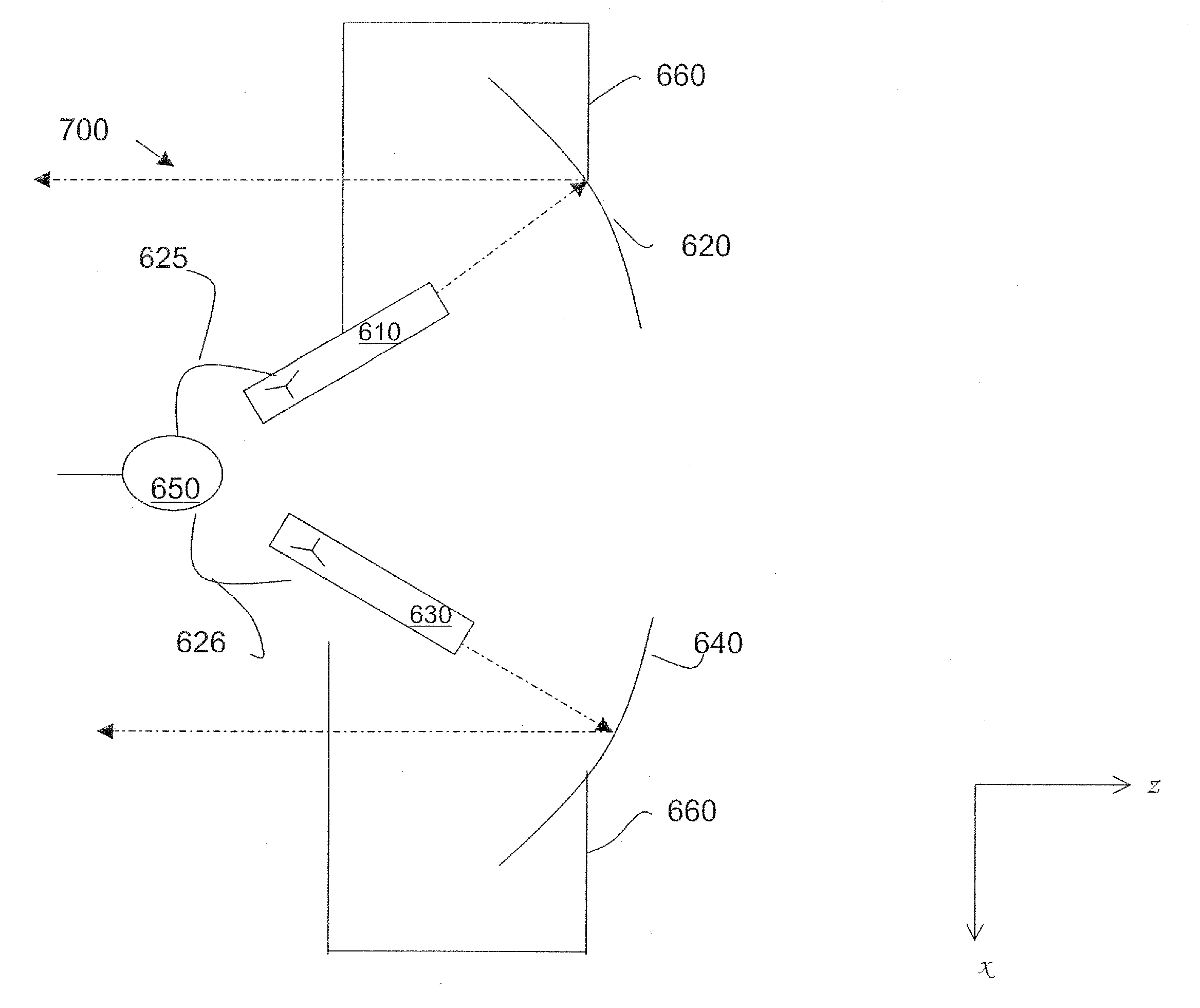
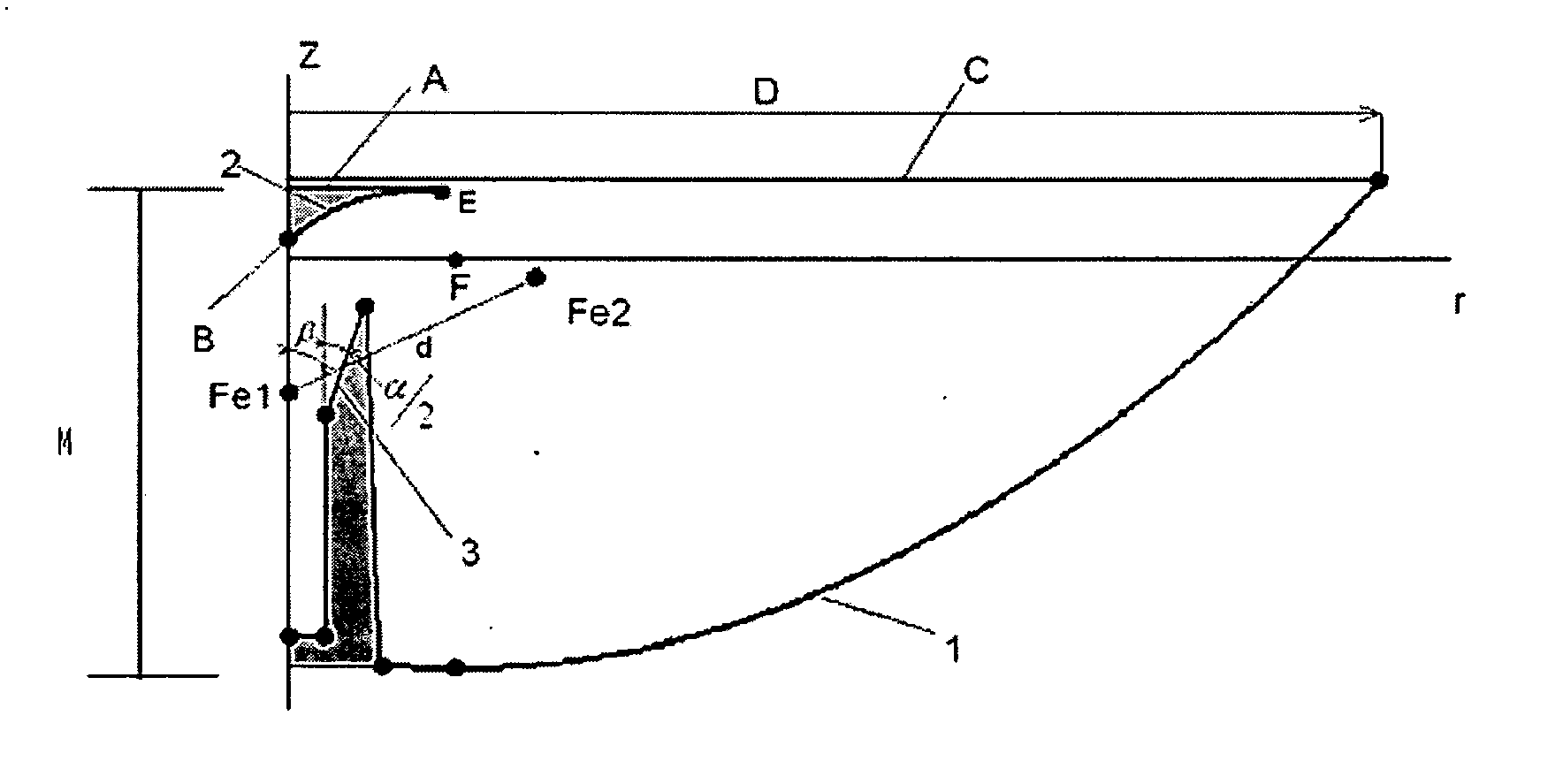
An antenna comprises: a main reflector being a body of revolution of arbitrary curve which axis diverges from axis of the revolution; a sub-reflector being a body of the revolution of arbitrary curve along the axis of revolution, having a circle and a vertex pointing to the main reflector and being placed between the circle and the main reflector; a radiator being located along the axis of revolution and being placed between the main reflector and the sub-reflector; and wherein the main reflector and the sub-reflector are: zm(r,D)=∑n=04∑m=06qmn,mDm-n+1rn,zs(r,D)=∑n=04∑m=06qsn,mDm-n+1rn,z, r are coordinates of the main reflector and the sub-reflector measured in millimeters, Index m corresponds to the main reflector, index s to the sub-reflector D is the main reflector diameter measured in millimeters.
Owner:AHN JIHO
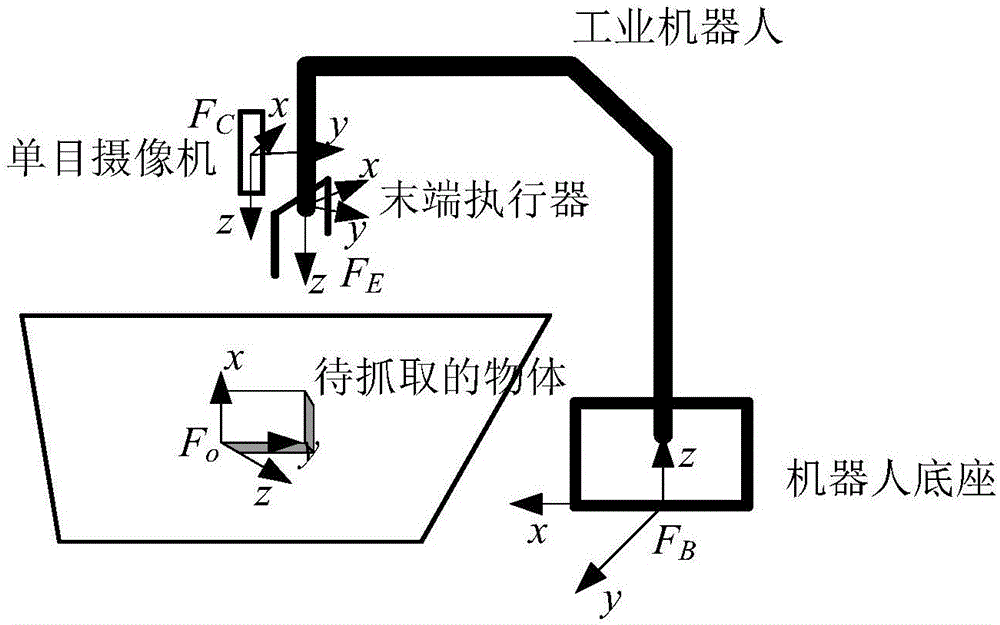
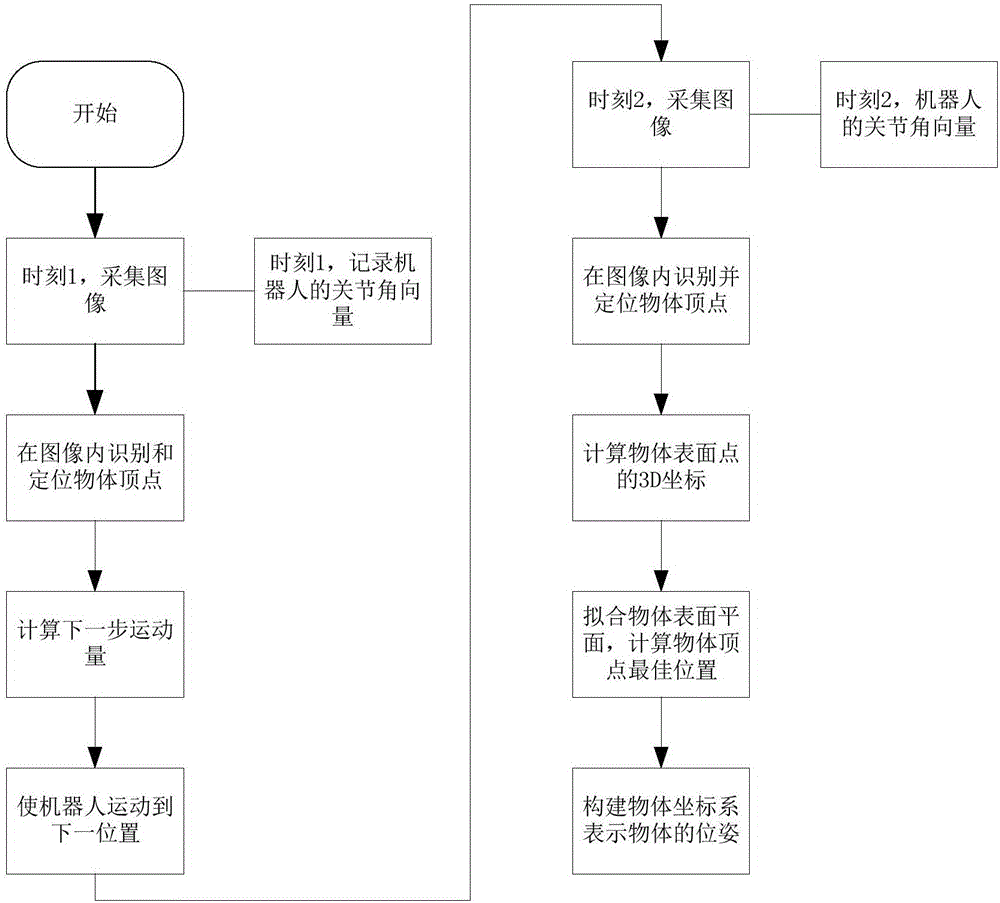
Six-freedom-degree locating method and system used in process of grabbing objects by industrial robot
ActiveCN106553195AAccurate 6-DOF poseAnti-interferenceProgramme-controlled manipulatorVertex pointComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a six-freedom-degree locating method and system used in the process of grabbing objects by an industrial robot. According to the scheme, natural features and local feature points on the surfaces of the objects to be grabbed can be extracted from images, and then recognizing and locating can be carried out through the features. According to the method, next appropriate movement of a robot can be calculated according to joint angles of the robot and a kinematic model and can be executed by the robot. Finally, according to the movement process of the robot and the recognition results of two times, 3D coordinates of vertex points on the surfaces of the objects can be calculated, a corresponding coordinate system of the objects can be established, six-freedom-degree poses of the objects can be obtained, and therefore the corresponding objects can be accurately grabbed.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
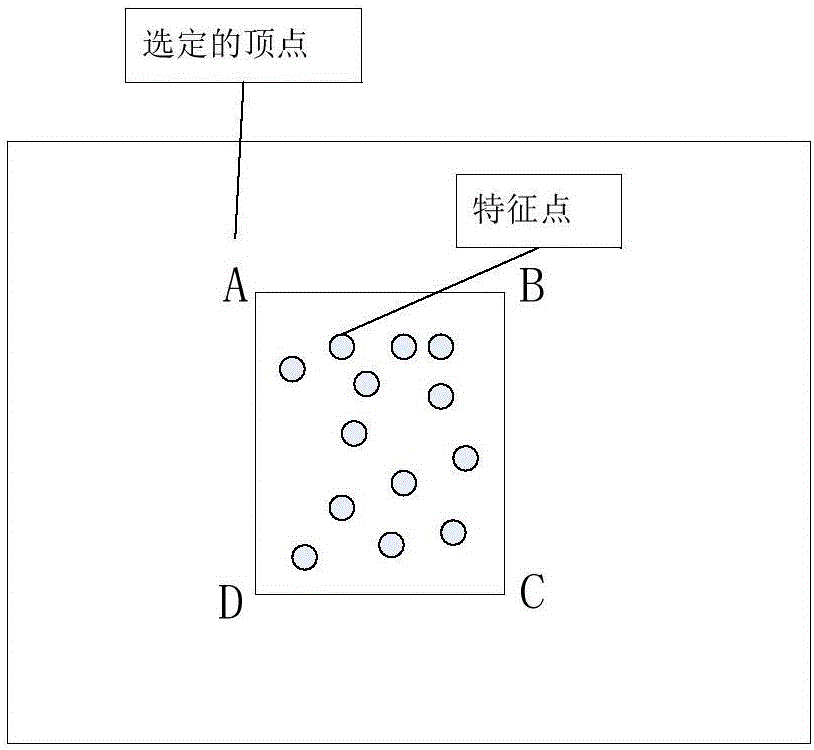
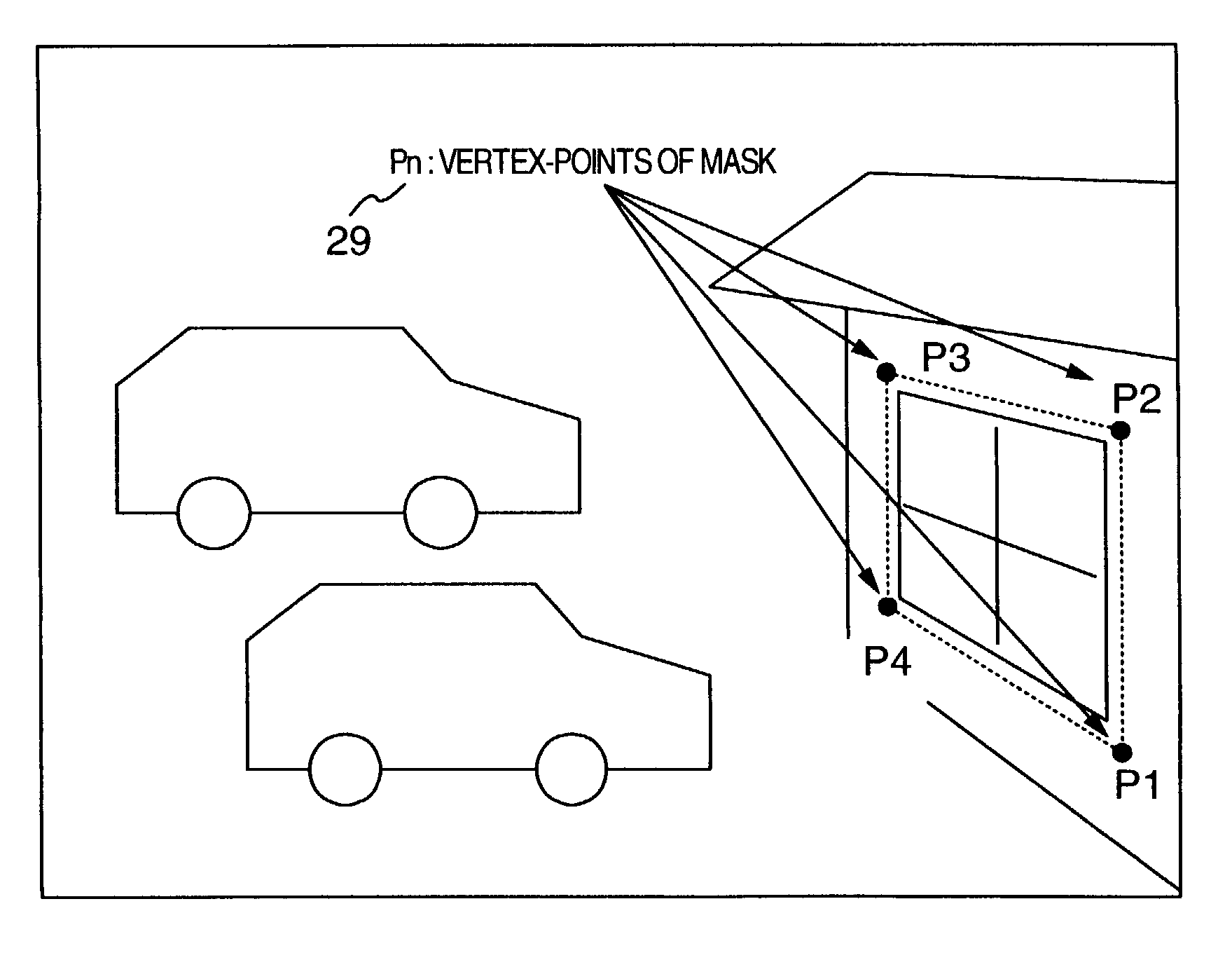
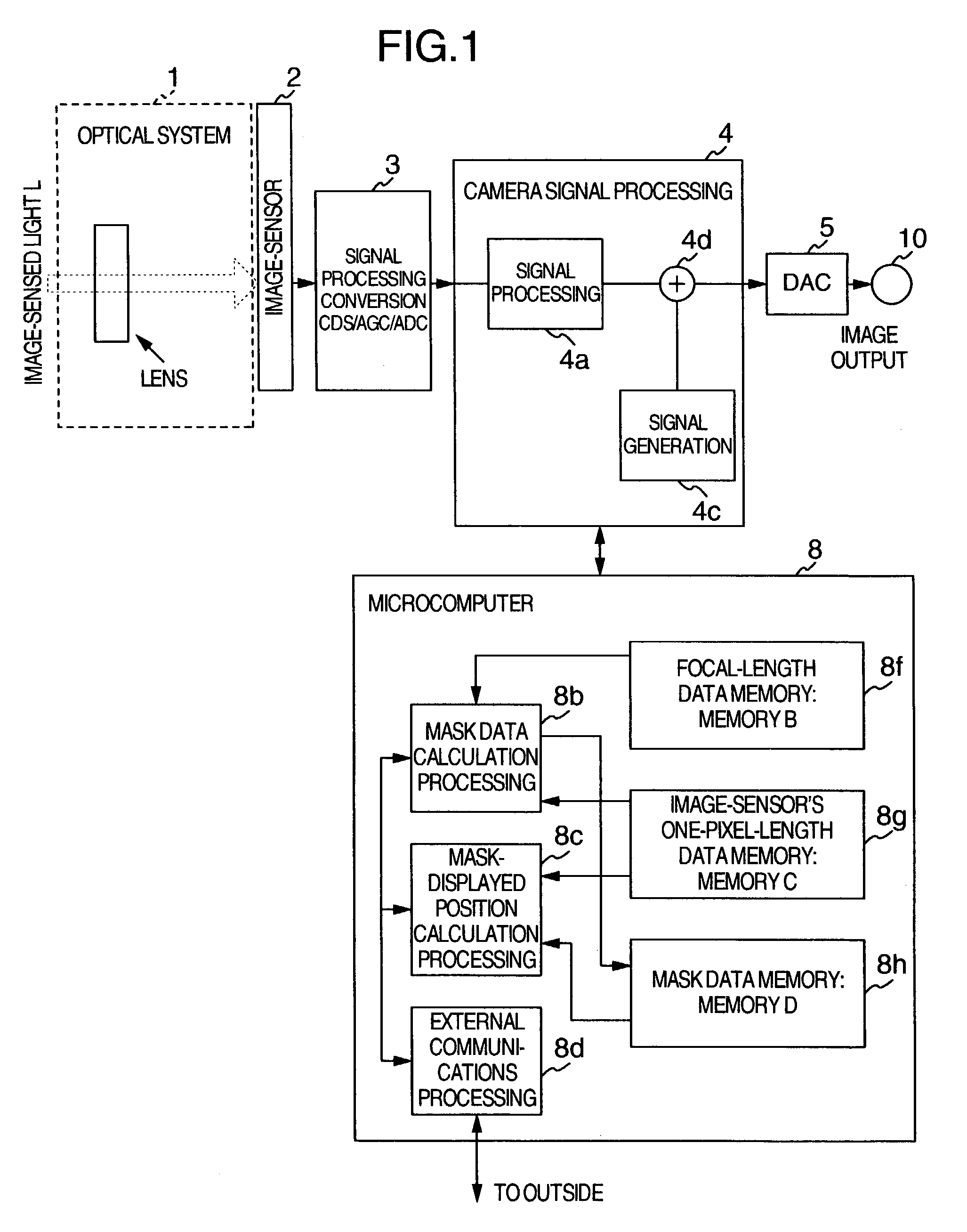
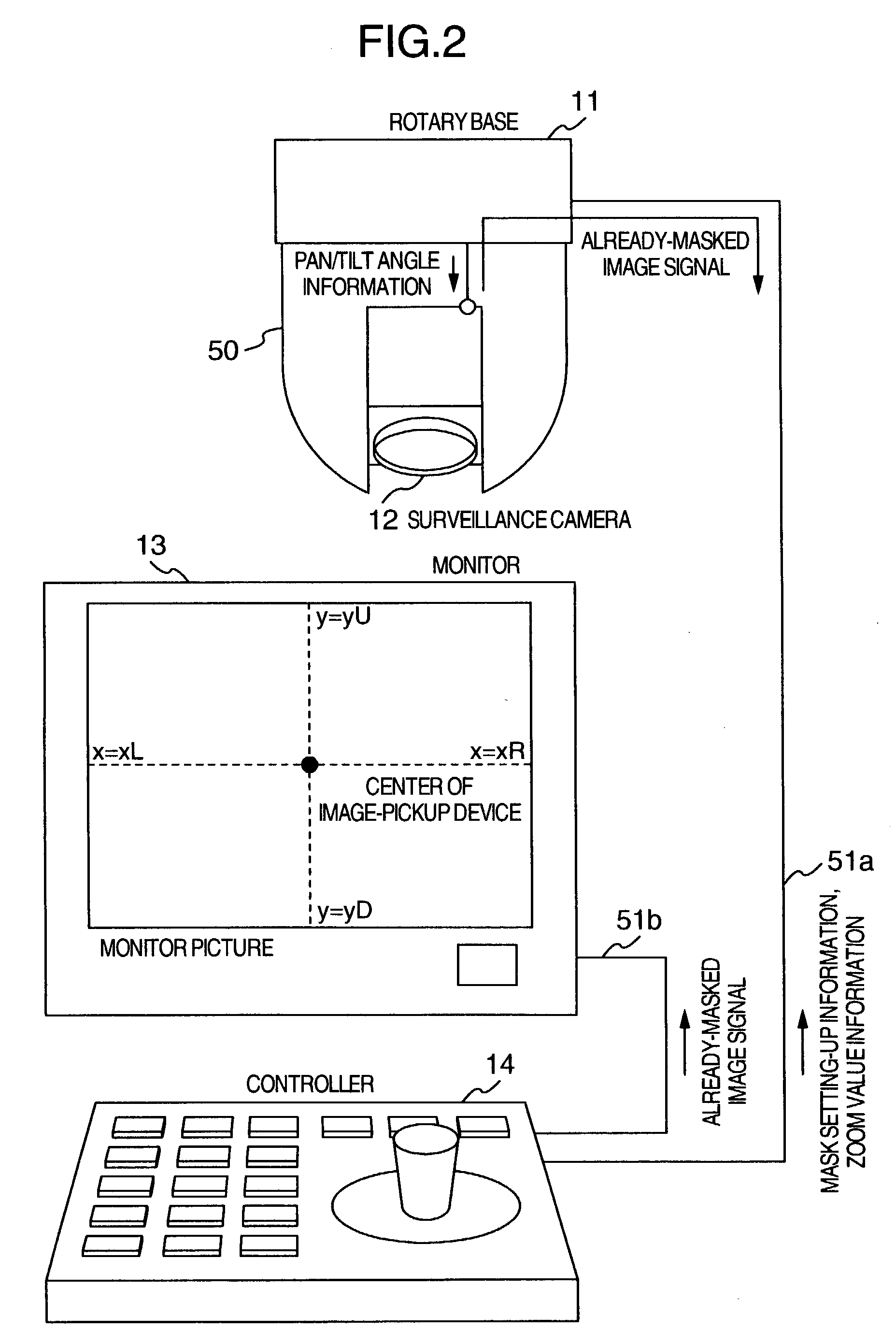
Pan/tilt/zoom surveillance system and method for dynamically adjusting a user defined image picture mask
InactiveUS7218342B2Reduce calculationImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionVertex pointOptical axis
A surveillance camera apparatus includes a first storage unit for storing a size of pixels configuring a image-sensor, a computation unit for performing a computation using first information, second information, third information, and fourth information to calculate angle information on a plurality of vertex-points, the information stored in the first storage unit being defined as the first information, a focal length of an optical lens being defined as the second information, angle information on an optical axis that passes through a rotation center of the surveillance camera apparatus as the third information, and pixel information corresponding to a plurality of vertex-points that form a region to be masked whose image has been picked up by the image-sensor being defined as the fourth information, and a second storage unit for storing the computation result by the computation unit.
Owner:HITACHI INFORMATION & CONTROL SOLUTIONS LTD
Calculation of plane equations after determination of z-buffer visibility
ActiveUS20110080406A1Easy to processReduce memory bandwidth3D-image renderingComputational scienceVisibility
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for computing plane equations for primitive shading after non-visible pixels are removed by z culling operations and pixel coverage has been determined. The z plane equations are computed before the plane equations for non-z primitive attributes are computed. The z plane equations are then used to perform screen-space z culling of primitives during and following rasterization. Culling of primitives is also performed based on pixel sample coverage. Consequently, primitives that have visible pixels after z culling operations reach the primitive shading unit. The non-z plane equations are only computed for geometry that is visible after the z culling operations. The primitive shading unit does not need to fetch vertex attributes from memory and does not need to compute non-z plane equations for the culled primitives.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
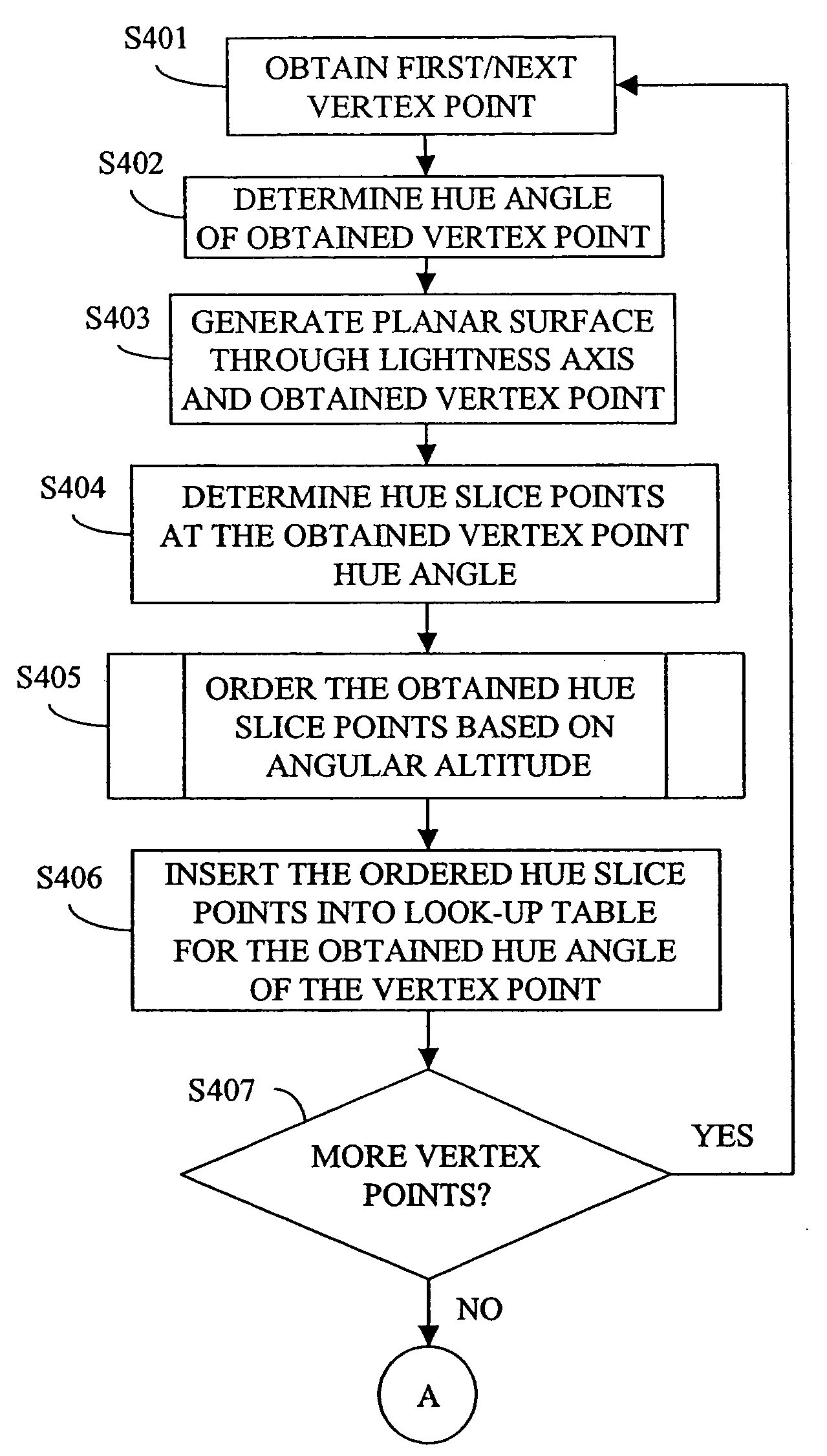
Generation of hue slice table for gamut mapping
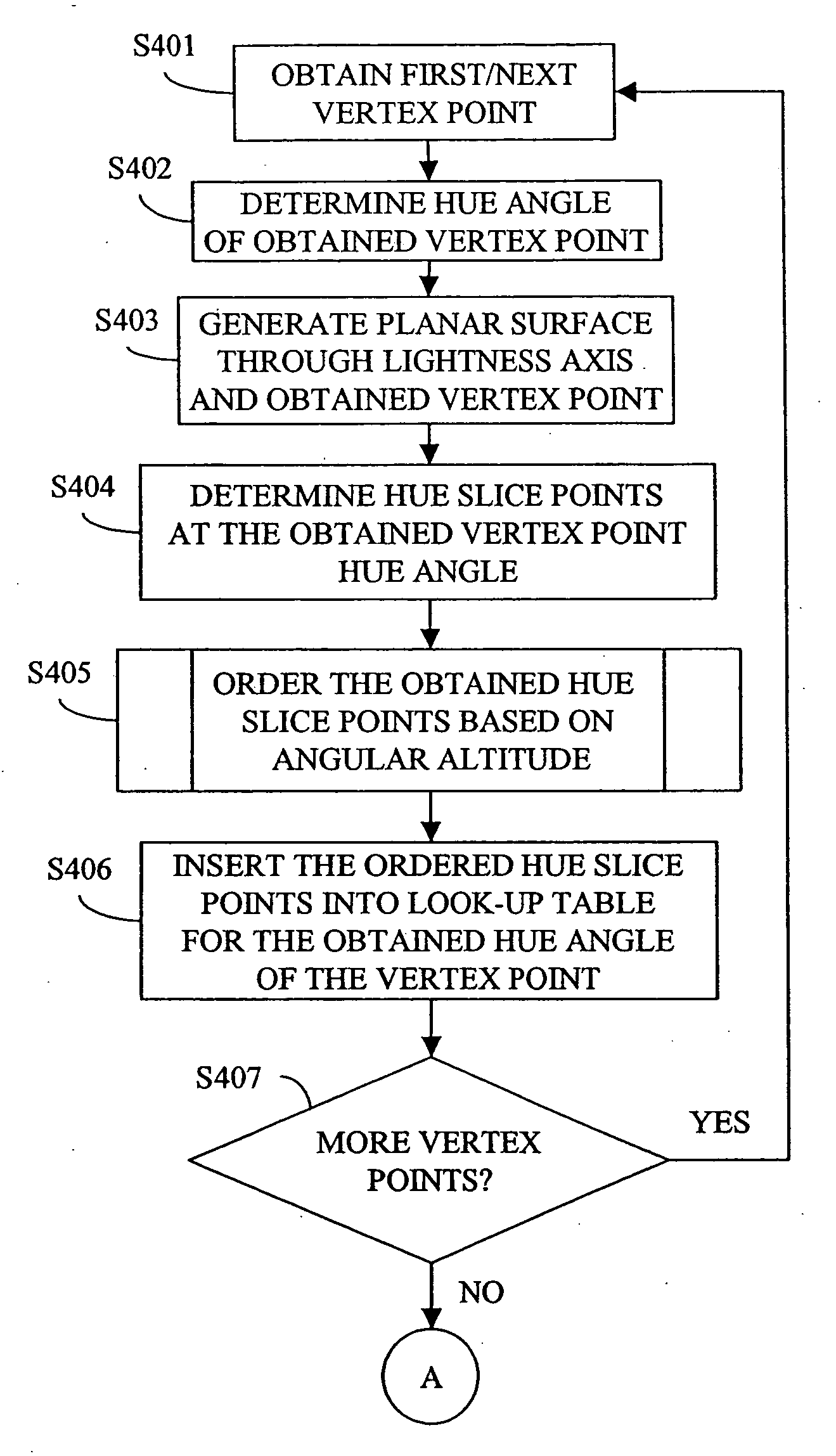
InactiveUS20060170999A1Accurate representationDigitally marking record carriersColor signal processing circuitsGamutVertex point
A table representing a color gamut for a device for use in a color management system where colors are represented in a color appearance space comprises data representing a collection of hue slices through a boundary surface of the color gamut. The collection of hue slices comprises entries for vertex point hue slices obtained at each vertex point on the boundary surface of the color gamut, and entries obtained for additional hue slices between adjoining vertex point hue slices, where a number of the additional hue slices is determined such that there is no more than a specified angular difference between each hue slice. Each hue slice is represented by a hue value and a collection of hue slice points each containing a lightness value and a chroma value. The hue slice points of each hue slice are ordered in the table based on an angular altitude of each point, the angular altitude of each point being determined between a lightness axis of the color gamut and a vector projected from a midpoint of the lightness axis to the hue slice point.
Owner:CANON KK
Automated centerline detection algorithm for colon-like 3d surfaces
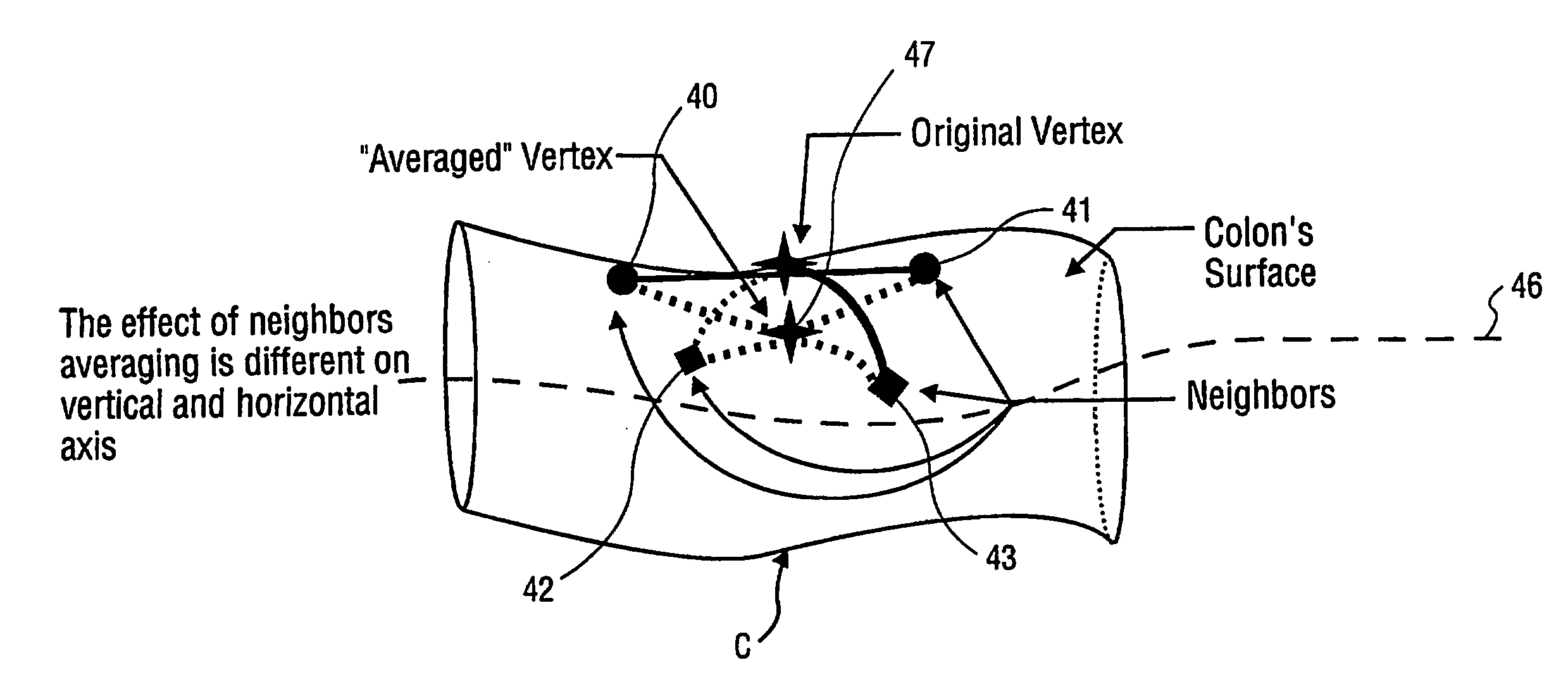
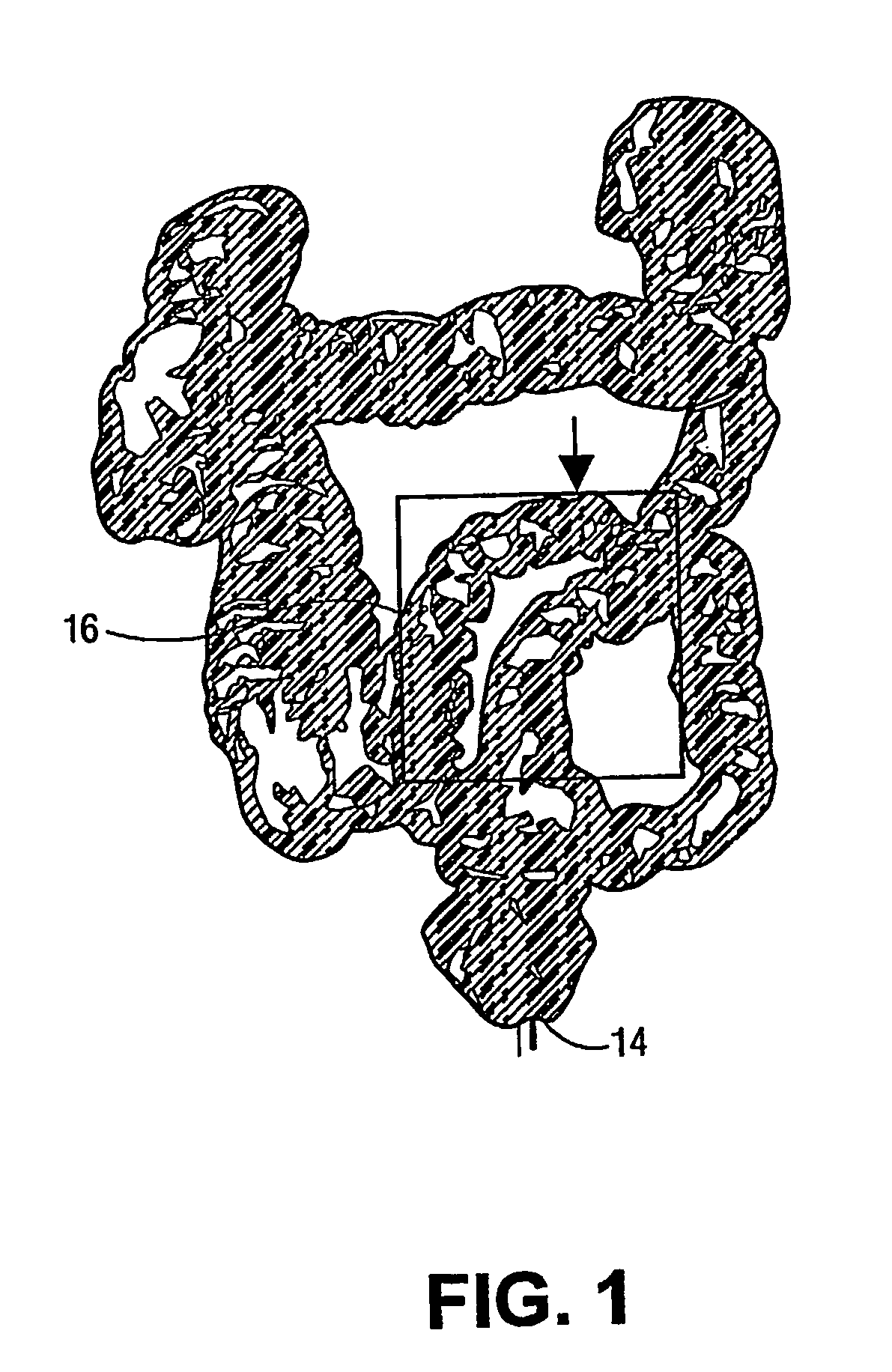
ActiveUS20050117787A1Accurate ring profileEliminate useImage enhancementImage analysisProximateVertex point
A three dimensional image of the colon like surface is processed to determine at least its ring structure. The image is composed of vertex points, each vertex point having a discrete point identifier and three dimensional position information. The three dimensional position information is averaged in a shrinking procedure to contract the three dimensional image proximate to a major axis of the colon-like surface. Evenly spaced points are taken through the shrunken colon like surface and connected to form a curve. Planes are generated at intervals normal to the curve to split the shrunken colon like surface into image segments. By mapping these image segments back to the original image through their discrete point identifiers, an accurate ring profile of the colon like surface can be generated.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Porous material pore space boundary extracting and quantization method
InactiveCN101413792AEasy to guide manufacturingEasy to guide applicationImage analysisUsing optical meansPlanar polygonVertex point
The invention discloses a method for extracting and quantizing pore boundary of porous materia, comprising the following steps: a microscopic pore structure image of a plurality of parallel sections of a porous material to be detected is taken; a plurality of the pore structure images are respectively transmitted to a computer to be pretreated; the boundary of a black image area and a white image area, namely the pore boundary, in a black and white pore structure image is extracted and marked; the marked pore boundary is a polygon consisting of a plurality of pixels as vertex points; the two-dimension coordinate value of the vertex points is determined and the vertex points are numbered continuously, thus obtaining the two-dimensional pore boundary; and all the vertex points of all plane polygons in two adjacent two-dimensional pore boundary images are connected in sequence according to the number sequence, thus forming a spatial polygon which is the three-dimensional pore boundary. The invention has the advantages of simple operation and low cost, can quantize the performance parameters of the porous material such as pore appearance, degree of cook of a pore channel, and the like; and can analyze accurately.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
Generation of hue slice table for gamut mapping
InactiveUS7397588B2Accurate representationDigitally marking record carriersColor signal processing circuitsGamutVertex point
A table representing a color gamut for a device for use in a color management system where colors are represented in a color appearance space comprises data representing a collection of hue slices through a boundary surface of the color gamut. The collection of hue slices comprises entries for vertex point hue slices obtained at each vertex point on the boundary surface of the color gamut, and entries obtained for additional hue slices between adjoining vertex point hue slices, where a number of the additional hue slices is determined such that there is no more than a specified angular difference between each hue slice. Each hue slice is represented by a hue value and a collection of hue slice points each containing a lightness value and a chroma value. The hue slice points of each hue slice are ordered in the table based on an angular altitude of each point, the angular altitude of each point being determined between a lightness axis of the color gamut and a vector projected from a midpoint of the lightness axis to the hue slice point.
Owner:CANON KK
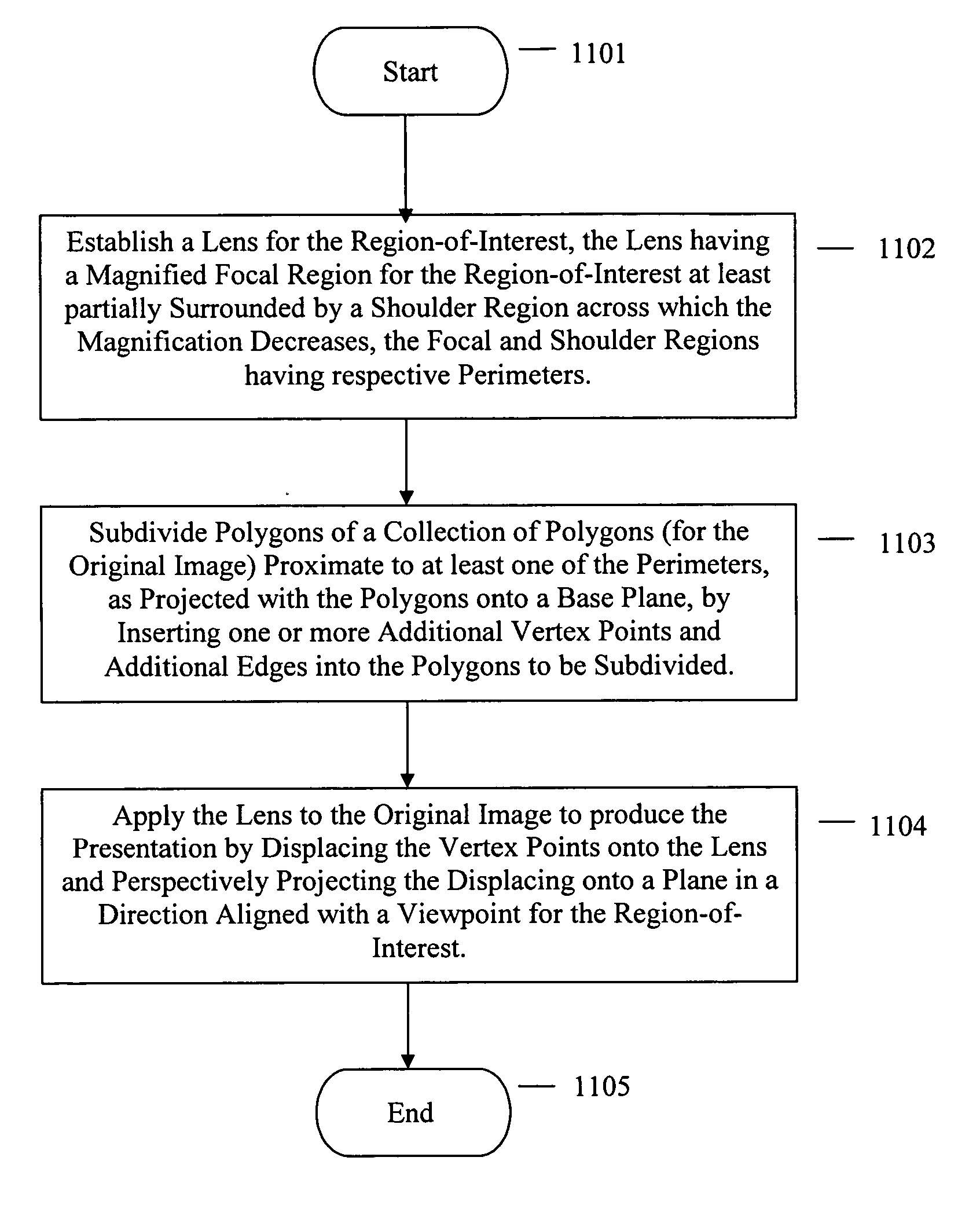
Occlusion reduction and magnification for multidimensional data presentations
ActiveUS20060050091A1Reduce magnificationCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage data processing detailsViewpointsVertex point
A method in a computer system for generating a presentation of a region-of-interest in an original image for display on a display screen, the original image being a collection of polygons having polygons defined by three or more shared edges joined at vertex points, the method comprising: establishing a lens for the region-of-interest, the lens having a magnified focal region for the region-of-interest at least partially surrounded by a shoulder region across which the magnification decreases, the focal and shoulder regions having respective perimeters; subdividing polygons in the collection of polygons proximate to at least one of the perimeters, as projected with the polygons onto a base plane, by inserting one or more additional vertex points and additional edges into the polygons to be subdivided; and, applying the lens to the original image to produce the presentation by displacing the vertex points onto the lens and perspectively projecting the displacing onto a view plane in a direction aligned with a viewpoint for the region-of-interest.
Owner:ACCESSIFY LLC
Heterogeneous Internet of Vehicles time slot allocation method
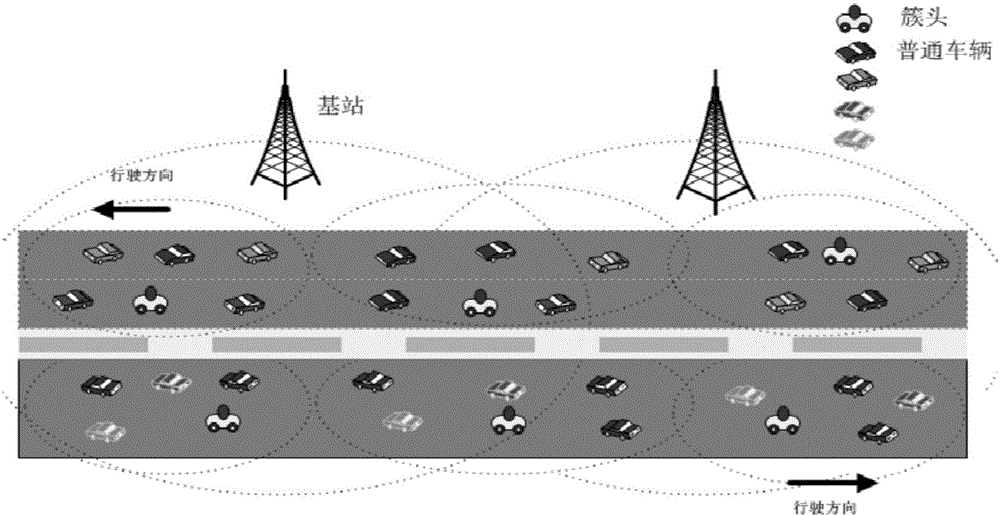
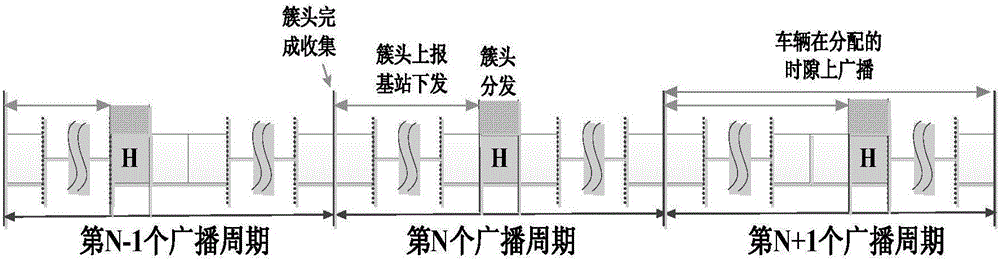
ActiveCN105848295AIncrease profitEnsure fairnessTransmissionNetwork planningVertex pointTopological graph
The invention provides a heterogeneous Internet of Vehicles time slot allocation method and relates to a heterogeneous Internet of Vehicles. The heterogeneous Internet of Vehicles comprises a base station and vehicle nodes; the vehicle nodes comprise cluster heads and general nodes; the heterogeneous Internet of Vehicles time slot allocation method comprises the following steps: in a first step, all general nodes send real time position information of the same to the cluster heads via current allocated time slots; in a second step, the base station obtains the real time position information of all the vehicle nodes from all the cluster heads, the vehicle nodes are used as vertex points when a topological graph demonstrating a vehicle position relation is constructed, time slots are allocated for all the vertex points of the topological graph based on a node coloring algorithm according to preset time slot reuse distance, and the allocated time slots are distributed to corresponding vehicle nodes. The heterogeneous Internet of Vehicles time slot allocation method does not require improvement of a heterogeneous Internet of Vehicles time slot resource utilization rate, fairness can be ensured, and an equivalent time slot quantity of a system can be improved.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polygon clipping method based on intersection point sorting
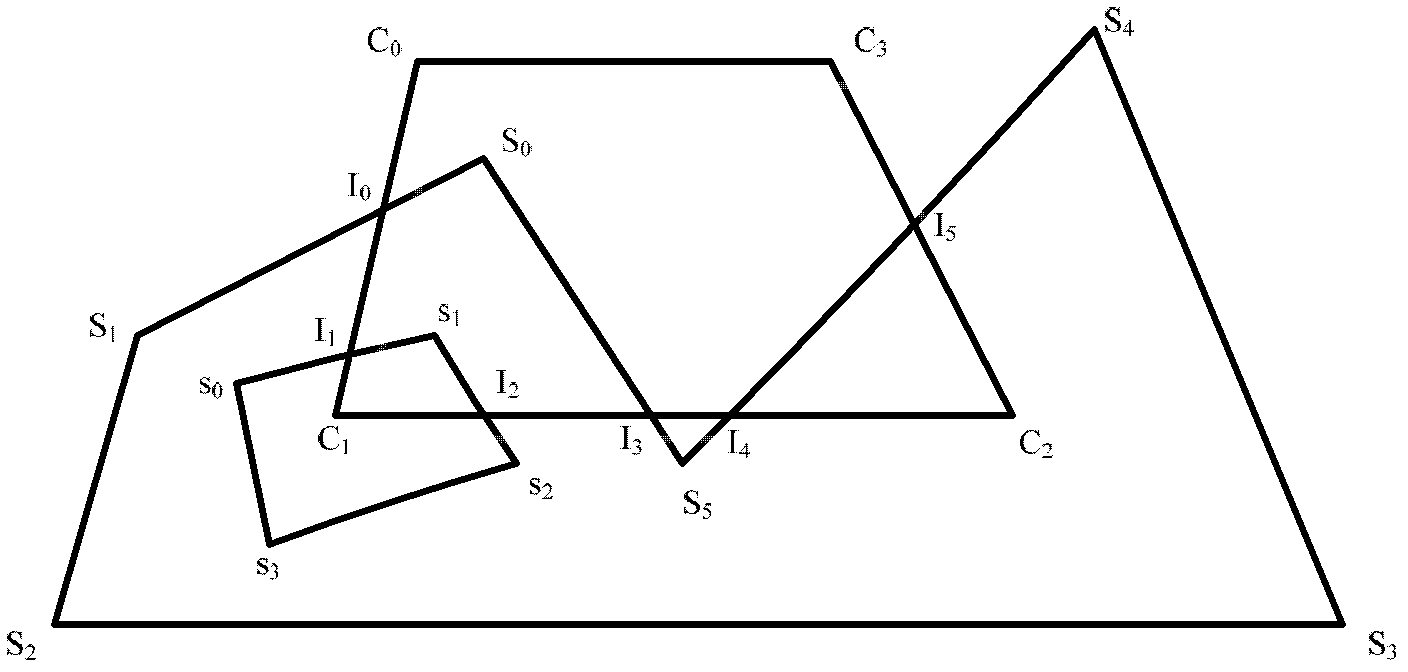
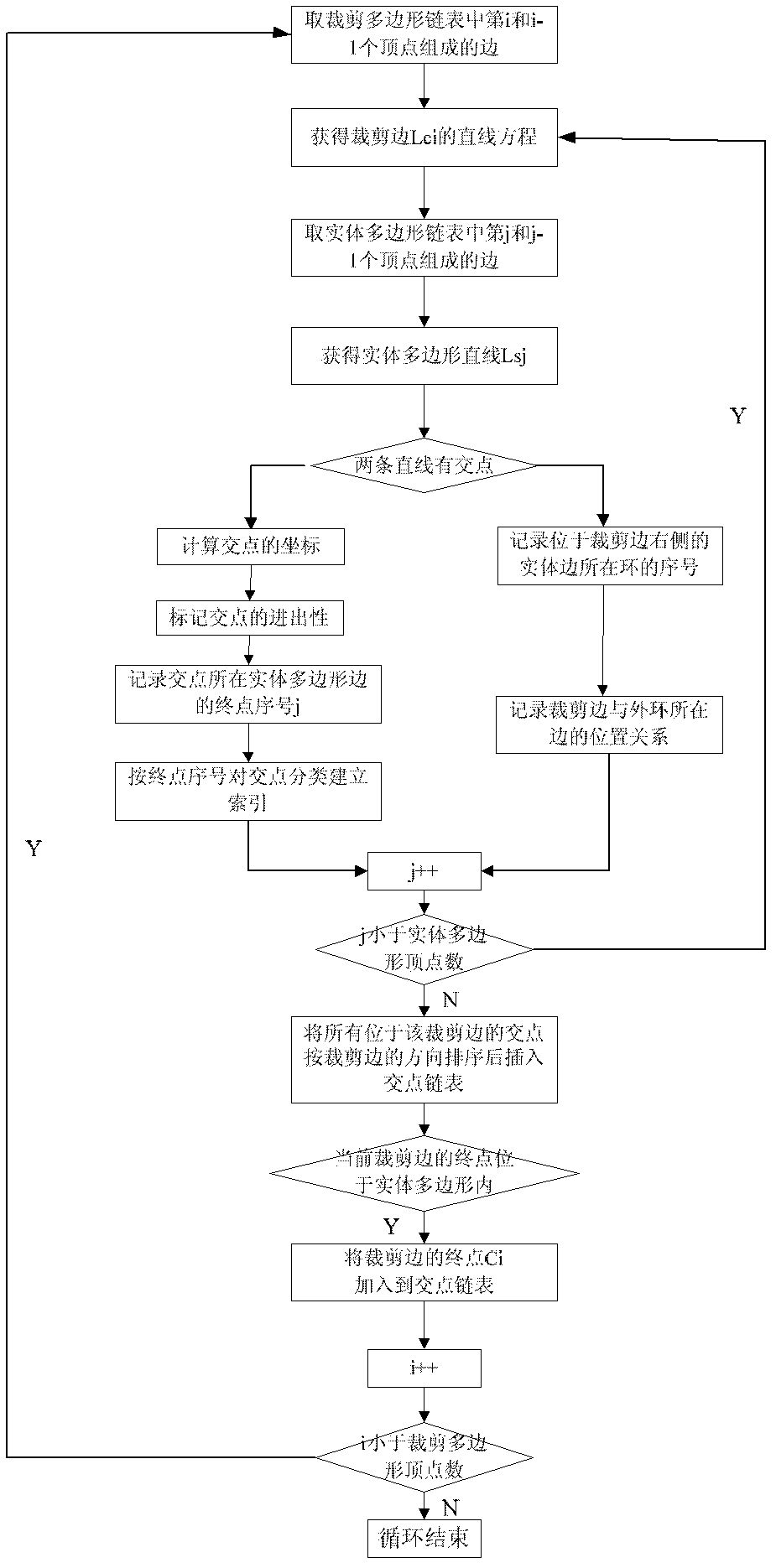
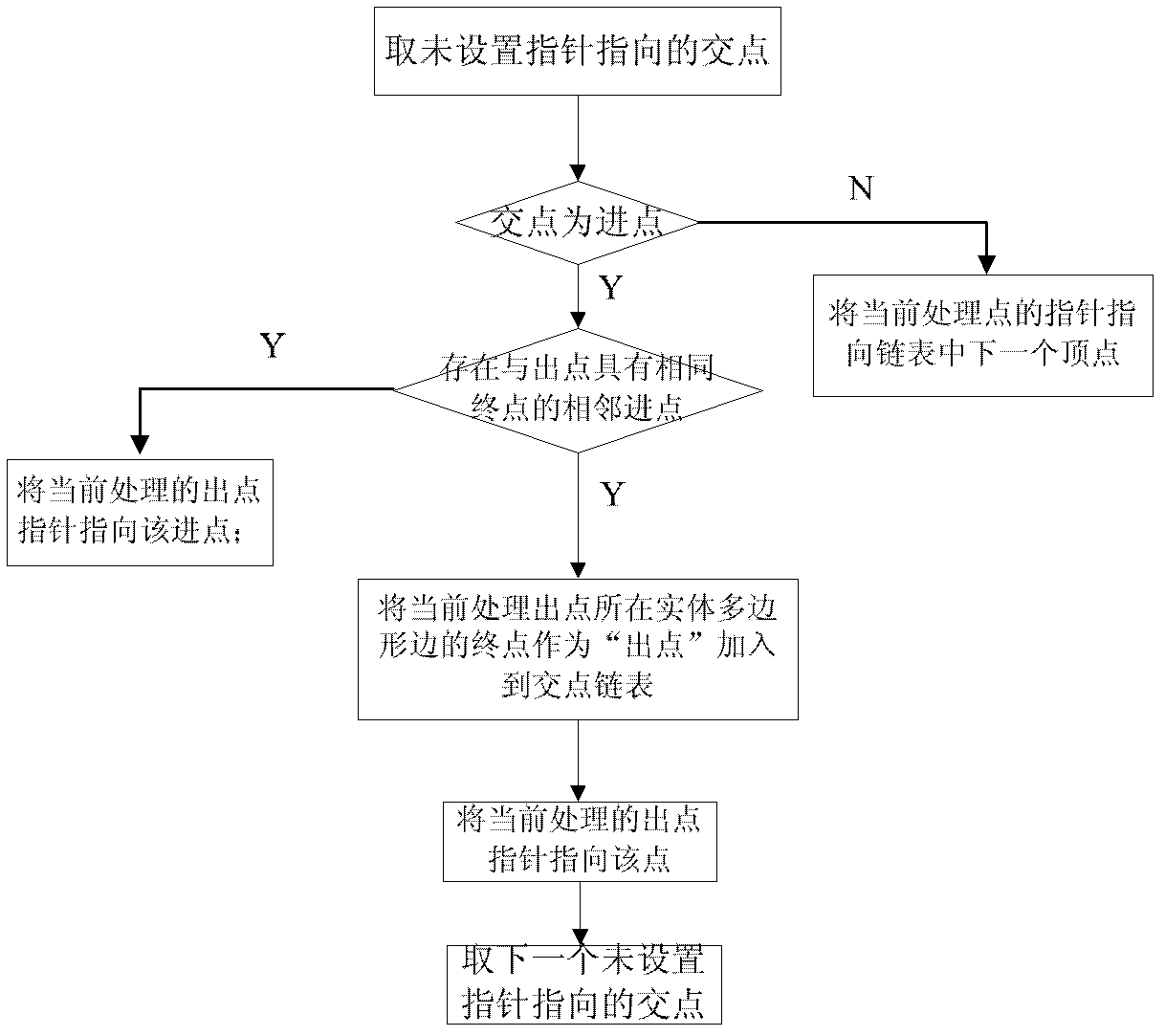
InactiveCN102360507ASimplify the separate cropping problemGuaranteed correctness2D-image generationNODALVertex point
The invention discloses a polygon clipping method based on intersection point sorting. The polygon clipping method comprises steps including that 1, whether segments are intersected or not is judged according to opposite clipping positions of four intersection points of a clipped side, and in and out properties of the intersection points are analyzed, 2, a solid polygon is subjected to intersection by means of taking sides of a clipped polygon sequentially, whether final points of the clipped sides can form a result polygon or not is judged according to sequence and the in and out properties of the intersection points on each clipped side, vertexes of the clipped polygon forming the result polygon are inserted into an intersection point linked list, and accordingly a point pair consisting of an in point and an out point is formed, 3, pointer directions of all intersection points are set according to the in and out properties of the intersection points and a sequence number of a final point of the recorded solid polygon, vertexes of the solid polygon forming the result polygon are inserted into the intersection point linked list, and secondary sorting of the intersection points is completed, and 4, a result vortex linked list is traversed, and the result polygon is outputted according to the pointer directions. The polygon clipping method has important actual application values in the field of computer graphics.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and device for implementing mobile terminal 3D (three dimensional) model
ActiveCN103617220AUtilize memory spaceImprove access efficiencySpecial data processing applications3D-image renderingVertex pointComputer graphics (images)
Owner:BEIJING ZHANGKUO MOBILE MEDIA TECH
Millable Fracture Balls Composed of Metal
A ball is used for engaging in a downhole seat and can be milled out after use. The ball has a spherical body with an outer surface. An interior of the spherical body is composed of a metallic material, such as aluminum. The spherical body has a plurality of holes formed therein. The holes extend from at least one common vertex point on the outer surface of the spherical body and extend at angles partially into the interior of the spherical body.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Adaptive Loop subdivision surface drawing method based on irregular region
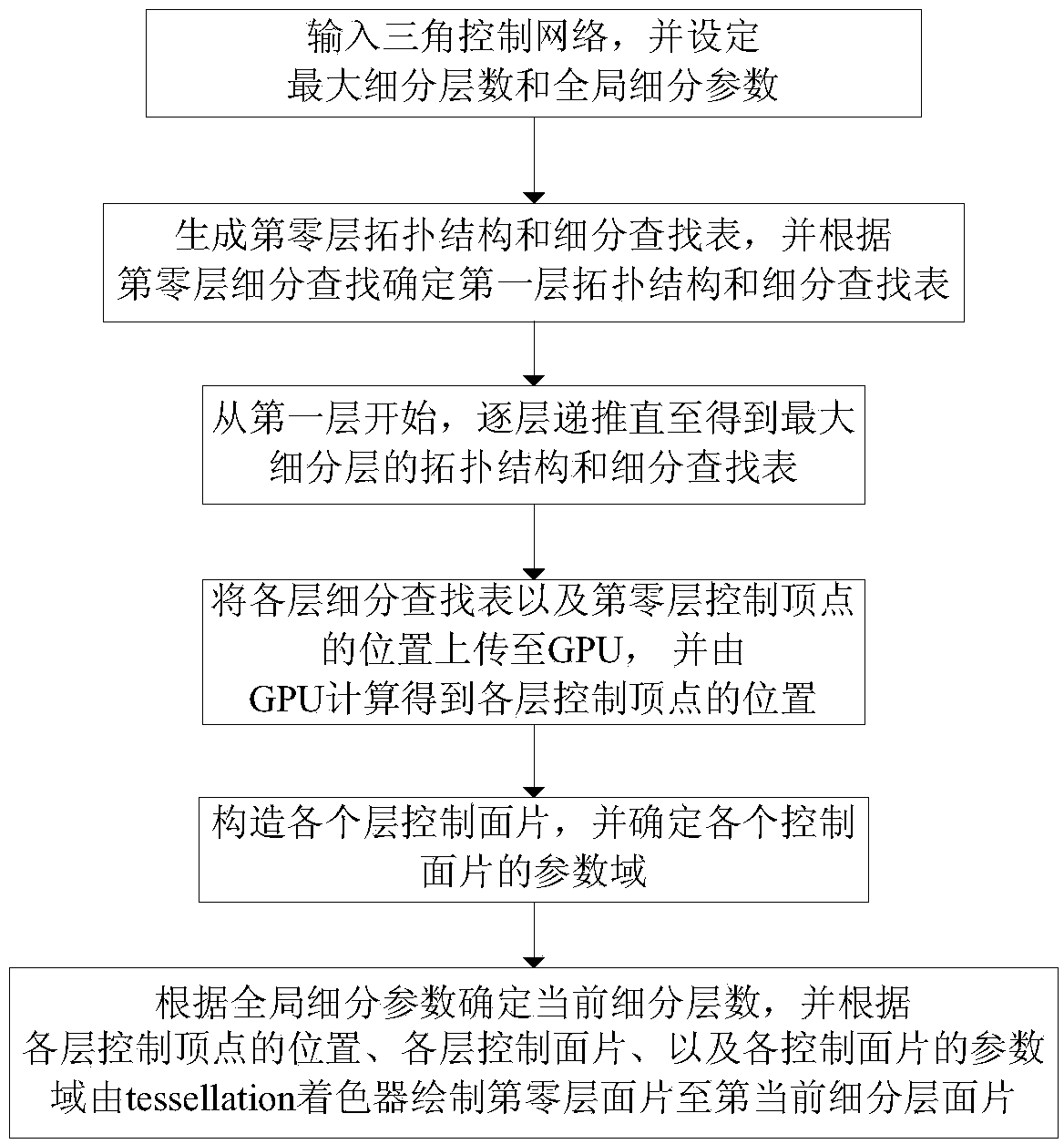
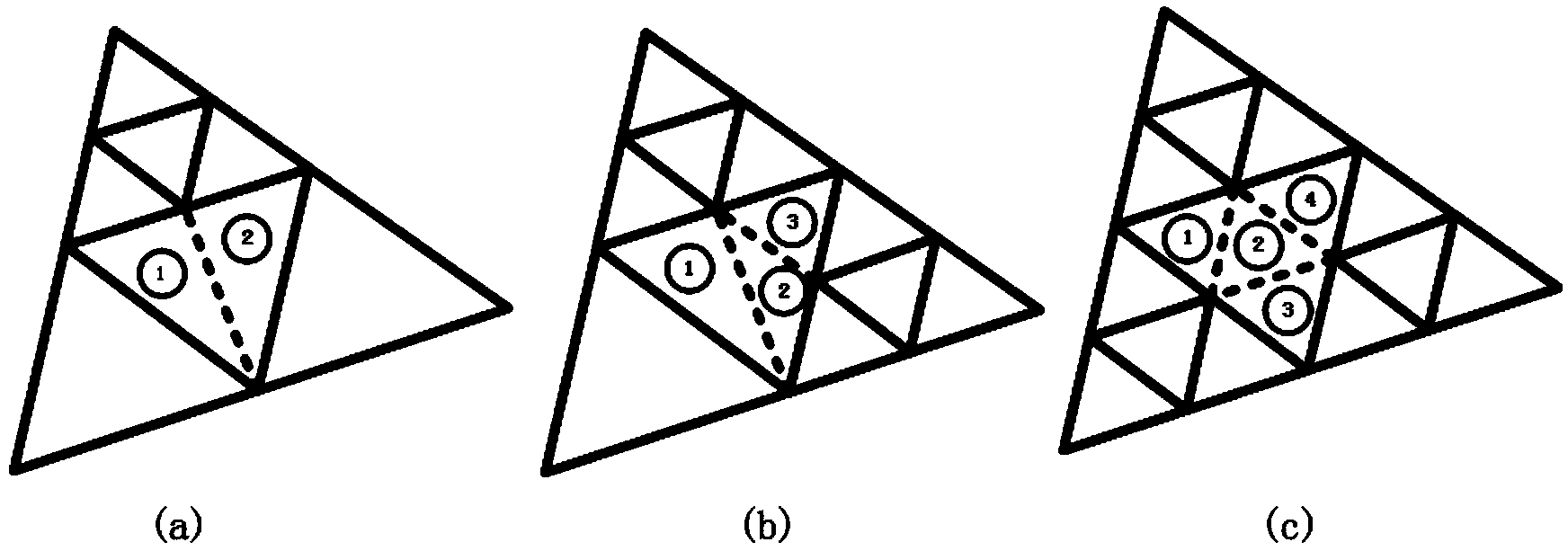
The invention provides an adaptive Loop subdivision surface drawing method based on an irregular region. According to the drawing method, based on an adaptive mode of the irregular region, the position of a control vertex is computed by a compute shader, an irregular original surface patch is divided into a plurality of regular sub surface patches according to the relationship between the current original surface patch and an adjacent original surface patch, a triangulation grid is reconstructed and drawn by a tessellation shader to obtain corresponding surface patches, and T cracks can be effectively eliminated. The position of the vertex of each layer in the triangulation grid can be accurately computed by the aid of the tessellation shader through division, so that all computed vertexes and normal vectors are as same as those of extreme Loop subdivision surfaces, hardware is drawn by the tessellation shader, the problems of huge memory and bandwidth of a global subdivision method are solved, and the Loop subdivision surfaces can be accurately drawn in real time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
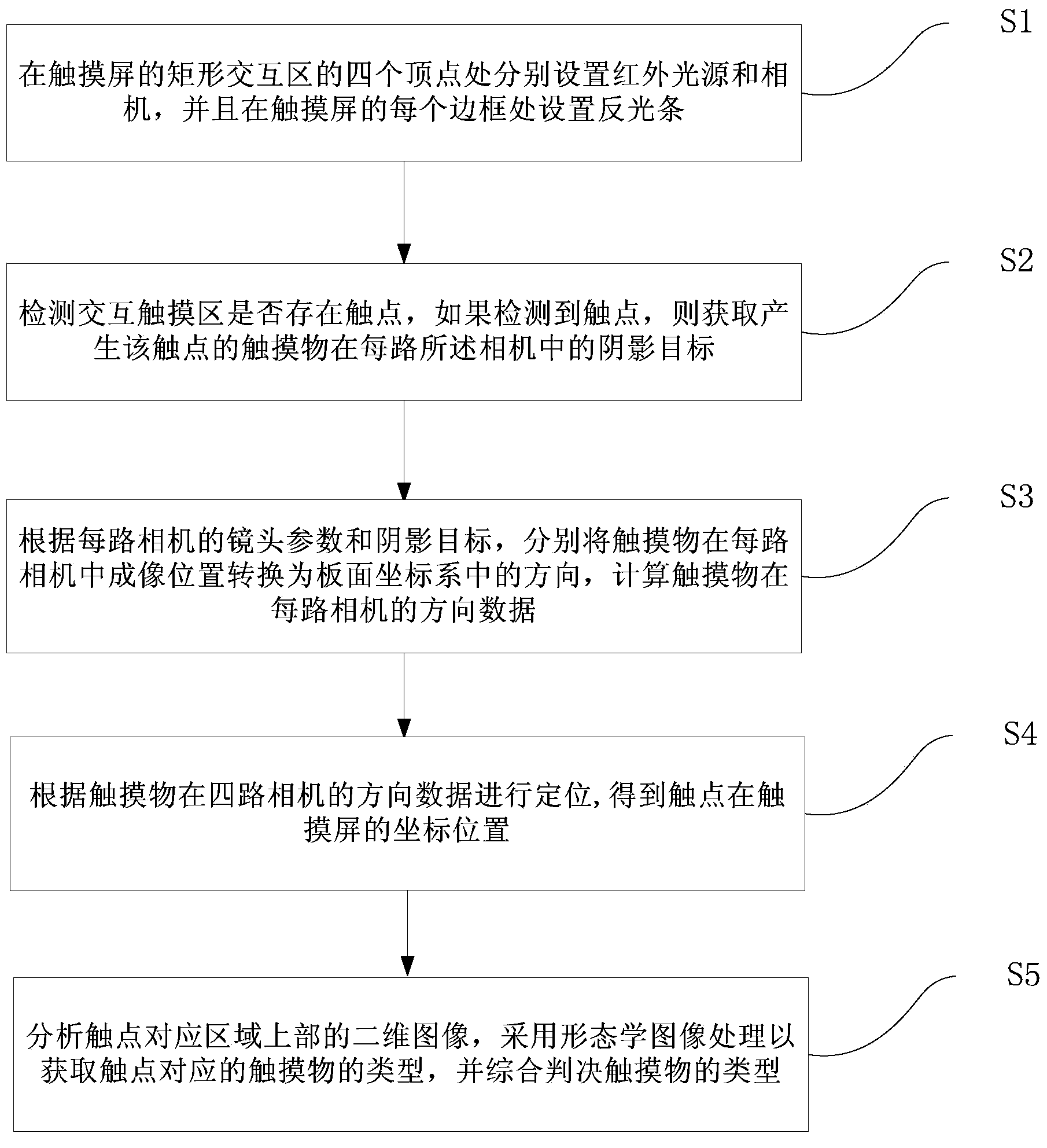
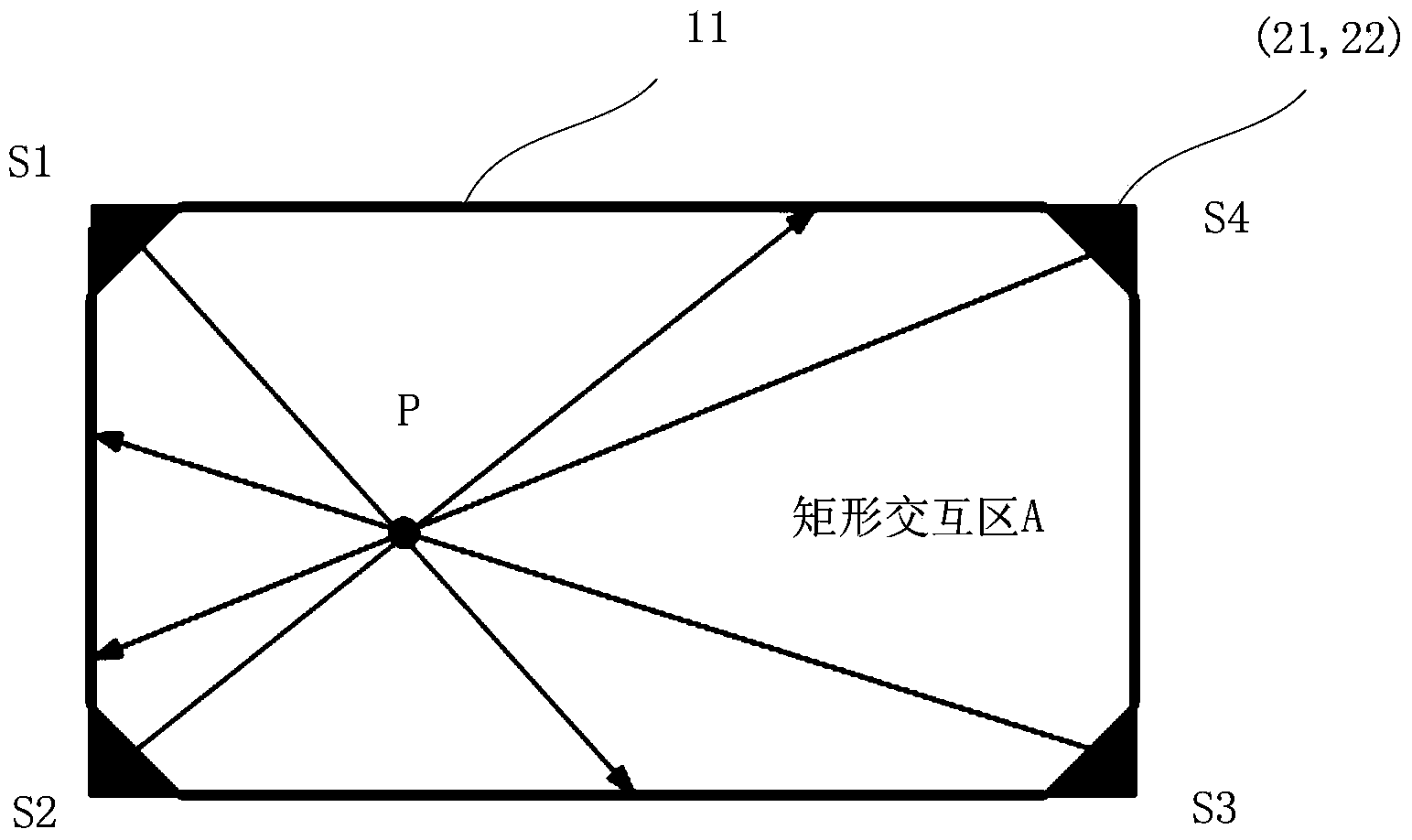
Imaging locating method of optical touch module and optical touch control equipment
ActiveCN103793113AIn line with operating habitsInput/output processes for data processingVertex pointImaging processing
The invention provides an imaging locating method of an optical touch module. The imaging locating method of the optical touch module comprises the steps that infrared light sources and cameras are arranged at the positions of four vertex points of a rectangular interaction area of a touch screen and a reflection strip is arranged at the position of each frame of the touch screen; whether a touch point exists in the interaction touch area or not is detected, and if yes, a shadow target, in each camera, of a touch object generating the touch point is obtained; an imaging position, in each camera, of the touch object is converted into a direction in a board coordinate system and direction data, in each camera, of the touch object are calculated; locating is conducted according to the direction data, in the four cameras, of the touch object to obtain the coordinate position, on the touch screen, of the touch point; a two-dimensional image of the upper portion of an area corresponding to the touch point is analyzed, and morphology imaging processing is adopted so as to obtain the type of the touch object corresponding to the touch point. The invention further provides optical touch control equipment. The imaging locating method of the optical touch module and the optical touch control equipment can realize multi-point touch control and full-screen accurate touch and can further recognize touch objects in a classifying mode.
Owner:TIANJIN XITONG ELECTRONICS EQUIP CO LTD
Printer and printing method for lenticular sheet
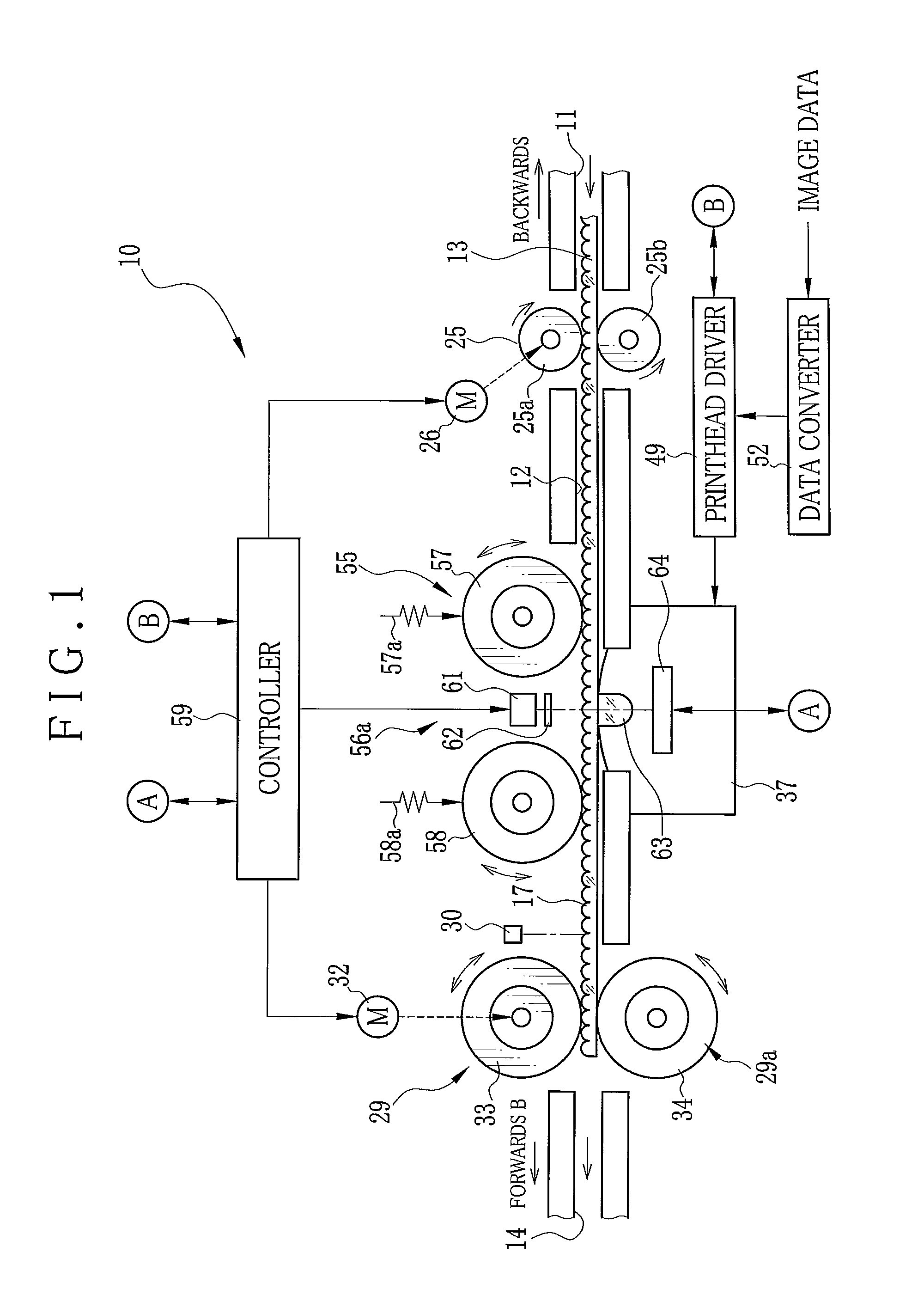
InactiveUS20110116058A1Precise positioningImprove accuracyStereoscopic photographyPhotographic printingLine sensorParallax
A lenticular sheet includes an array of lenticules and a back surface located opposite to the lenticules. In a printer, a printhead prints plural interlaced images on the back surface, the interlaced images being formed by interlacing two original images having disparity. A line sensor has plural sensor elements arranged in an array direction of the lenticules, and receives detection light condensed by a cylindrical lens, to output a detection signal for representing a vertex point of the lenticules. A transport device transports the lenticular sheet in the array direction, and adjusts an orientation of the lenticular sheet during transport to remove offset of the lenticular sheet from the array direction. A controller controls the transport device according to the detection signal, sets a longitudinal direction of the lenticules perpendicular to the array direction by adjusting the orientation, and drives the printhead for printing.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Alzheimer's disease cortex auto-classification method based on multi-scale mesh surface form features
ActiveCN104102839AAvoid detrimental effects of segmentation accuracyImprove reliabilitySpecial data processing applicationsTest performanceVertex point
The invention discloses an Alzheimer's disease cortex auto-classification method based on multi-scale mesh surface form features. The method includes the steps of determining two sample groups, namely an AD (Alzheimer's disease) group and an NC (normal control) group, and dividing the sample groups into a sample set and a test set under equal proportion; extracting multi-scale mesh surfaces from brain MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) images of samples; calculating LVPD (local vertex point distance) and average curvature for each vertex; with the smoothed LVPD and average curvature, extracting areas having a significant statistical difference and screening two seed points in index sense; extracting a feature row vector for each sample of the training set to form a feature matrix, and training a classifier with the reduced dimensionality feature matrix and corresponding sample classes; testing performance of the classifier with the samples in the test set. By the use of the Alzheimer's disease cortex auto-classification method based on multi-scale mesh surface form features, the defects the prior art is susceptible to cortex segmentation errors and certain-scale difference may be missed are overcome, and the two sample groups can be classified according to the cortex multi-scale form features.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Multi primary conversion
InactiveUS20120001963A1Improve computing efficiencyAvoiding impositionColor signal processing circuitsCathode-ray tube indicatorsVertex pointComputer graphics (images)
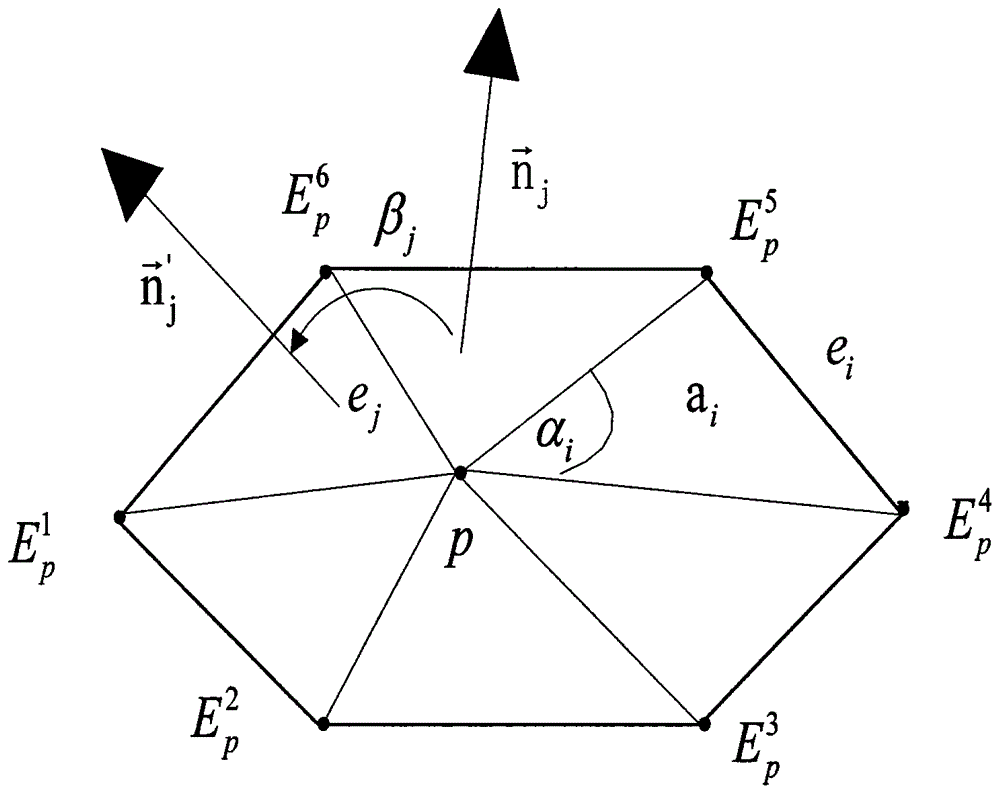
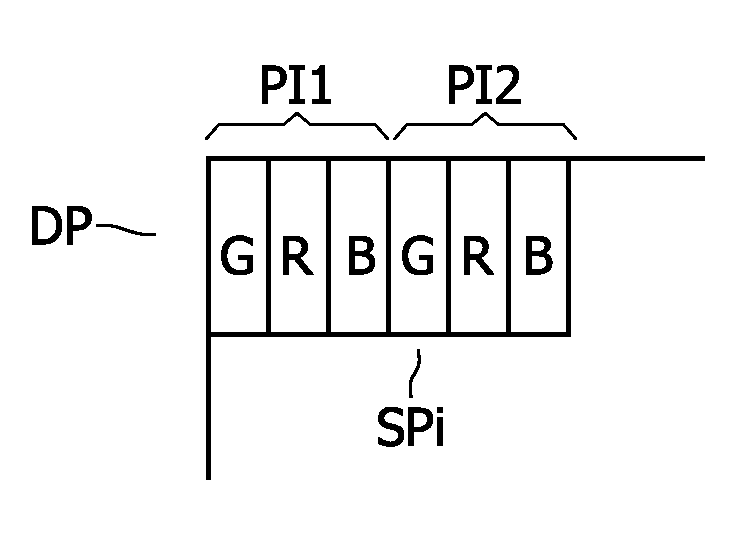
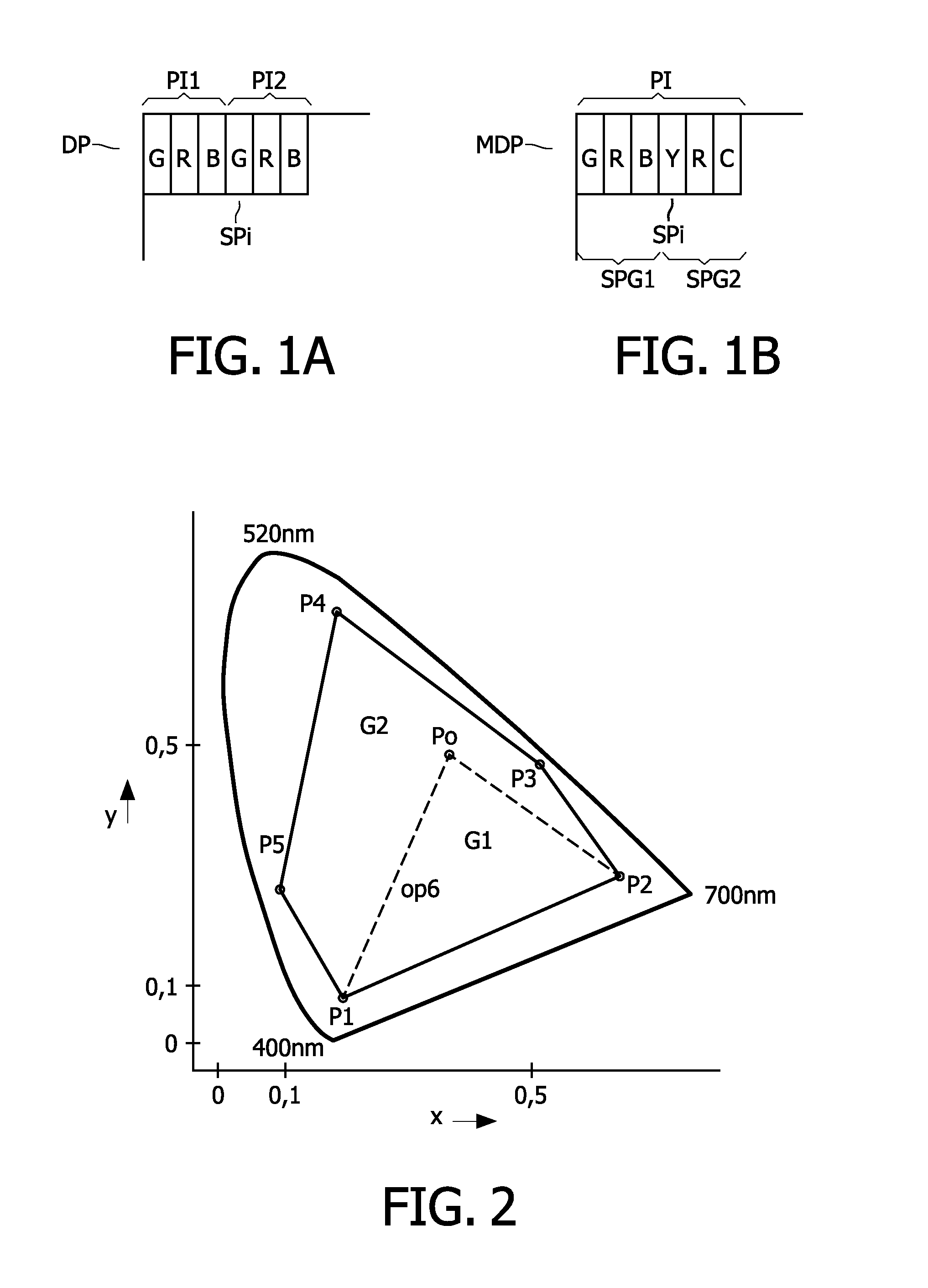
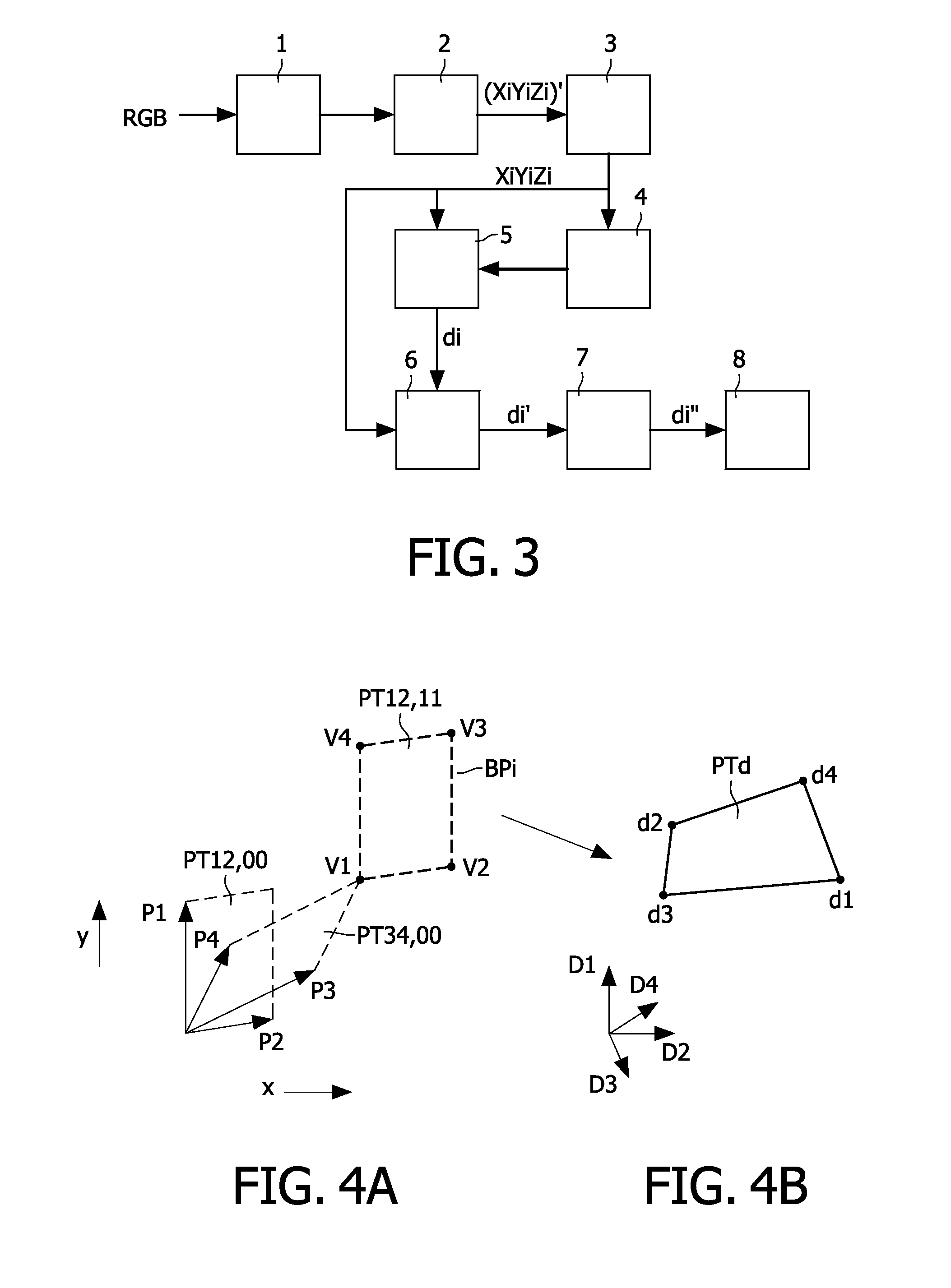
A multi-primary conversion (5) of input drive values (RGB) defines a color of a pixel (PI) of a multi-primary display(DP) in an M dimensional color space (XYZ) into N>M output drive values (di) in an N dimensional drive space. The N output drive values (di) drive N sub-pixels (SPi) of the pixel (PI). The color of the pixel (PI) in the color space (XYZ) is defined by linear combinations of N color primaries of the respective N sub-pixels (SPi). The multi-primary conversion(5) comprises: defining a constraint in the color space (XYZ) thereby causing in the color space (XYZ) a convex polytope (U0; L0; V50) defined by vertex points (V10, V11, V12; V20, V21; V50), wherein only colors in the color space (XYZ) belonging to the convex polytope fulfill the constraint, determining exemplary solutions of the output drive values (di) for at least a subset of the vertex points (V10, V11, V12; V20, V21; V50), and constructing the output drive values (di) fulfilling the constraint as a convex combination of the exemplary solutions.
Owner:TP VISION HLDG
SPH fluid surface reconstruction method based on second-layer regular grid
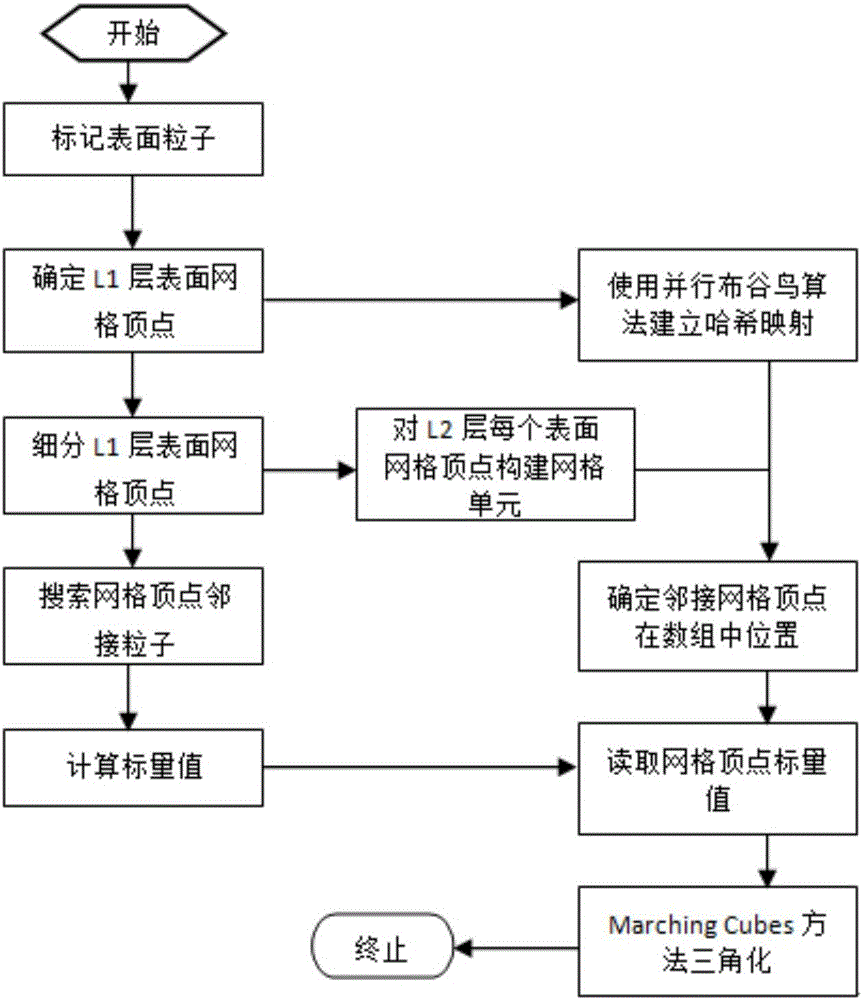
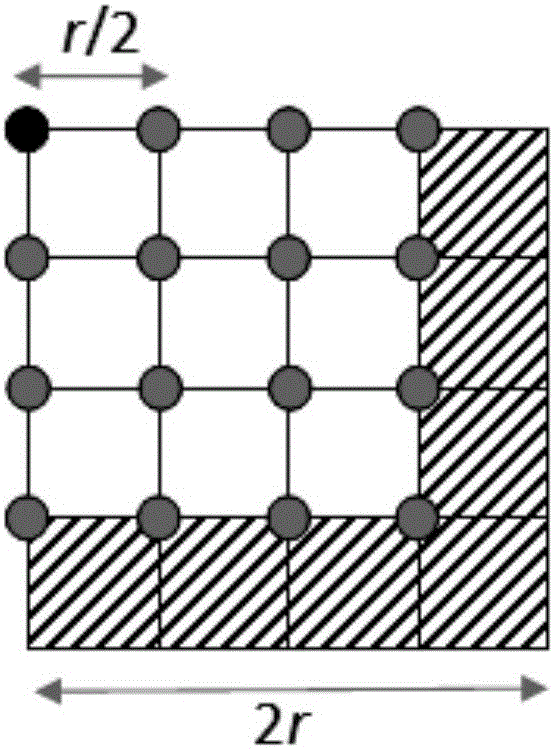
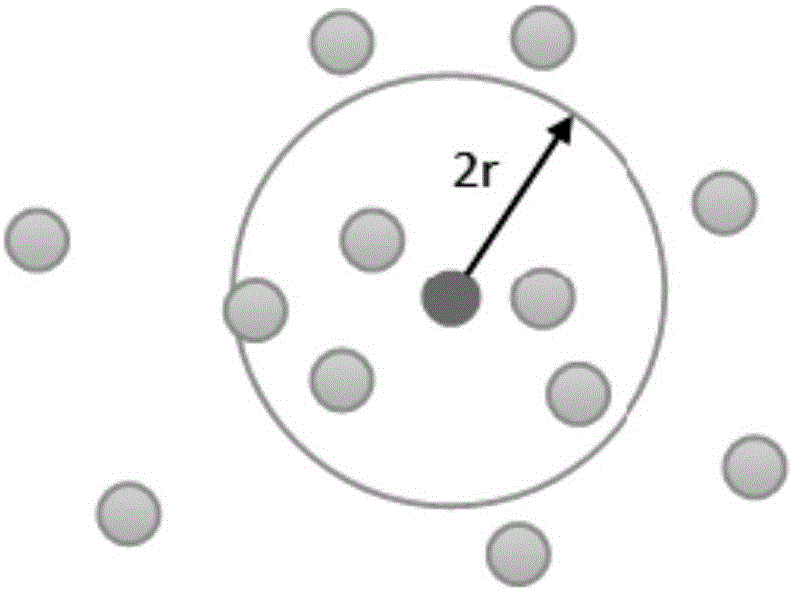
ActiveCN105760588AReduce the number of transfersImprove computing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsVideo memoryRegular grid
The invention provides an SPH fluid surface reconstruction method based on a second-layer regular grid. The method is achieved in parallel on the basis of a CUDA platform, L1-layer coarse-grained grid dividing with the grid side length of 2r is performed on a whole simulating area, and after grids of an area nearby the surface of fluid in the L1 layer are determined, the area is further divided into L2-layer fine grids. The method particularly comprises the following steps that 1, the grid vertex points of the surface of the simulating area are determined; 2, scalar values are calculated; 3, grid triangulation is performed. According to the method, through the second-layer regular grid spatial data structure, the spatial locality of the grid vertex points stored in a video memory is improved, the overall calculation efficiency of the surface reconstruction algorithm is greatly improved by decreasing the transmission frequency of data in the video memory and a calculating unit, and the purpose of real-time and efficient rendering is achieved.
Owner:THE FIRST INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY SOA
Multi-polarized feeds for dish antennas
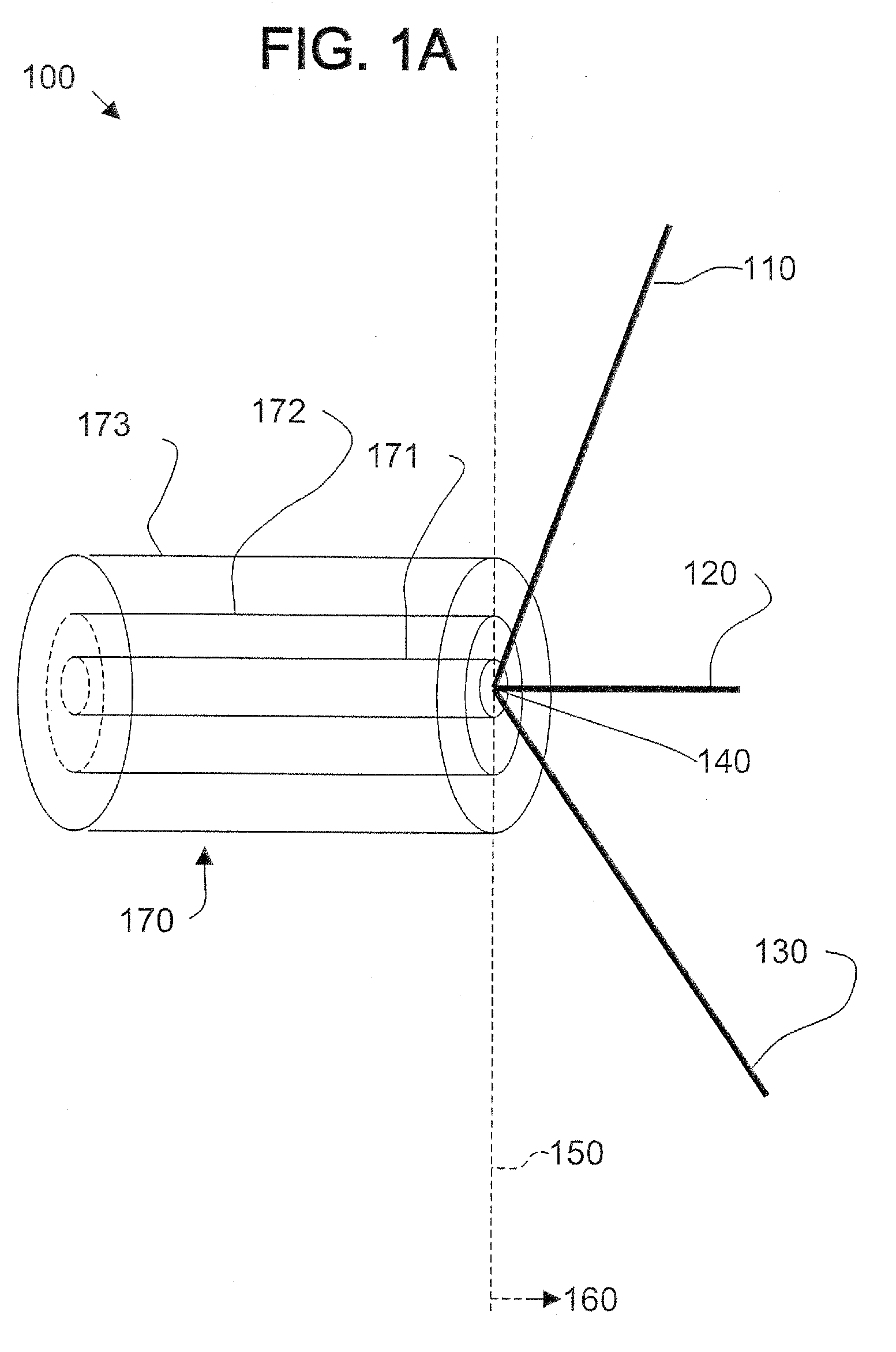
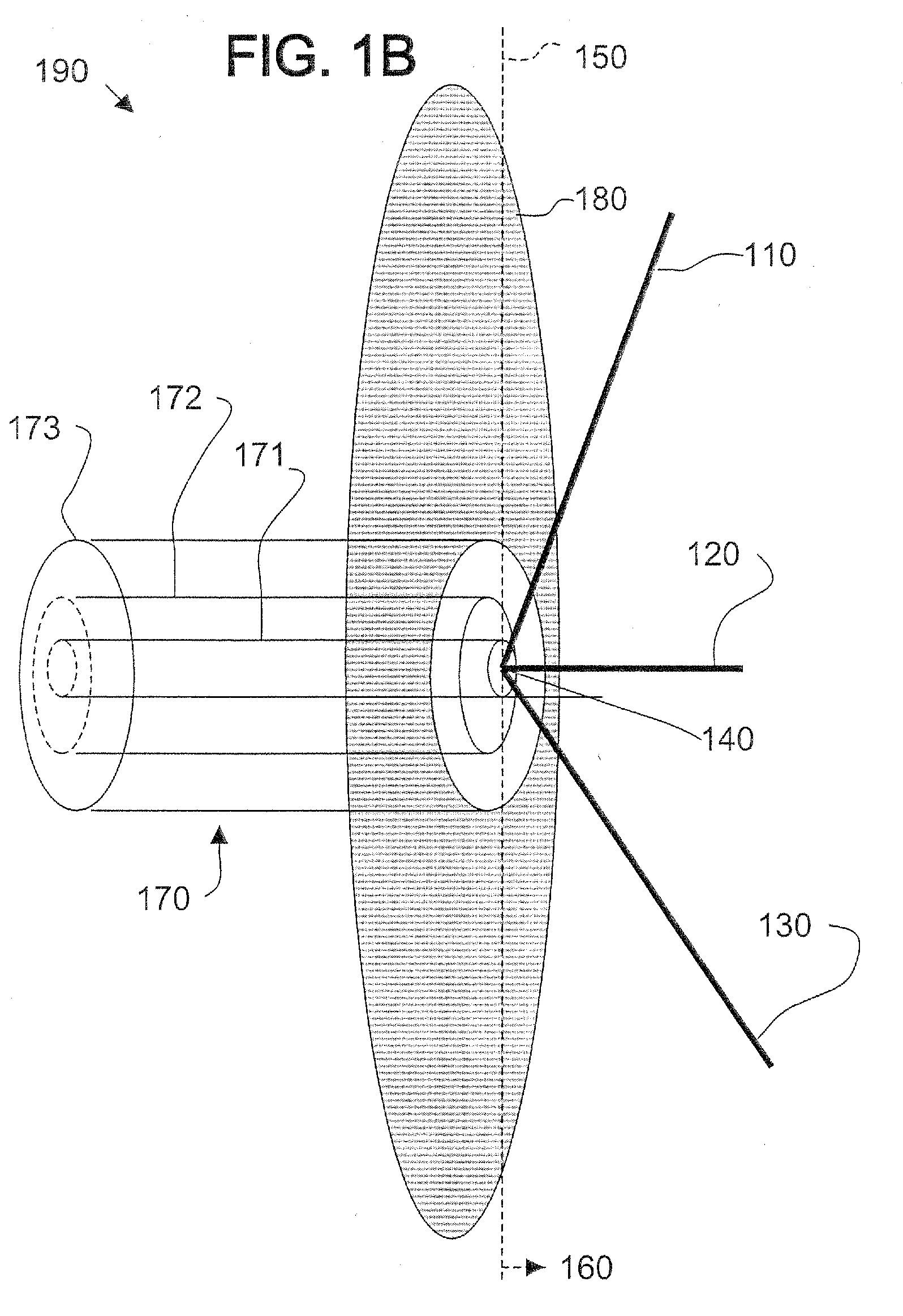
InactiveUS7030831B2Antenna supports/mountingsAntennas with plural divergent straight elementsVertex pointAcute angle
A multi-polarized forward feed and dish configuration for transmitting and / or receiving radio frequency (RF) signals is disclosed. The configuration comprises a conductive reflector dish, having a focal point and a vertex point, and a multi-polarized forward feed element positioned substantially at the focal point. The forward feed element comprises at least two radiative members each having a first end and a second end. The second ends of the radiative members are electrically connected at an apex point and are each disposed outwardly away from the apex point toward the vertex point at an acute angle relative to an imaginary plane intersecting the apex point.
Owner:MP ANTENNA
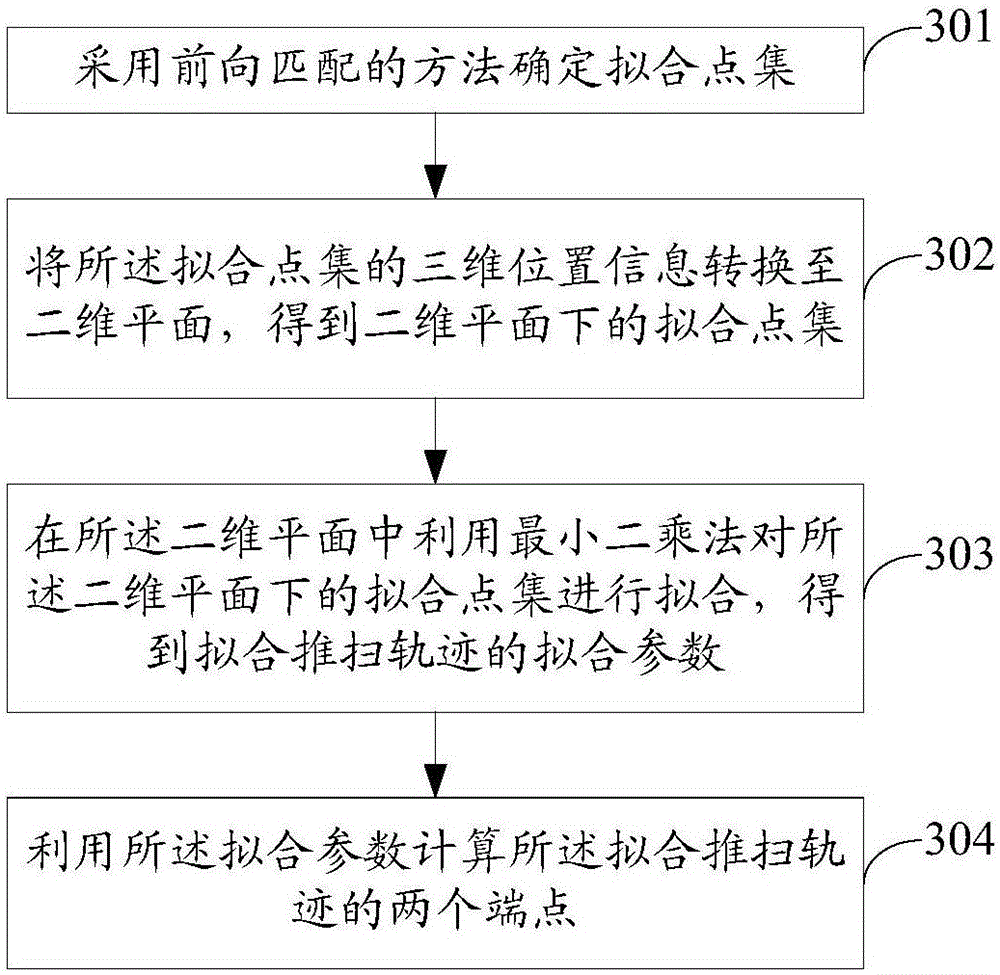
Agile satellite target decomposition method and system based on push-scan trajectories
ActiveCN106597434AIncrease profitFull Coverage GuaranteedCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsVertex pointQuaternion
The invention discloses a satellite target decomposition method and system based on a push-scan trajectories. The method includes obtaining vertex-crossing side sway of a satellite when crossing each vertex of a satellite target, and calculating breadth corresponding minimum side sway of the vertex-crossing side sway as strip width; utilizing the strip width to solve two endpoints of each push-scan trajectory; calculating boundary feature points of a corresponding strip according to the two endpoints of each push-scan trajectory; utilizing the boundary feature points to extend the push-scan trajectory, thereby obtaining a push-scan trajectory vector; substituting the push-scan trajectory vector and the strip width into a strip four-vertex calculation model, thereby obtaining strip four-vertex coordinates; and the strip four-vertex calculation model is a model established by use of a method for coordinate conversion based on conjugate quaternion and is used for calculating the strip four-vertex coordinates. The method and system provided by the invention selects the width corresponding to the minimum side sway at a vertex-crossing moment of the satellite as the strip width, so that the strip can be guaranteed to be fully covered, and the utilization rate of the width of the satellite is improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
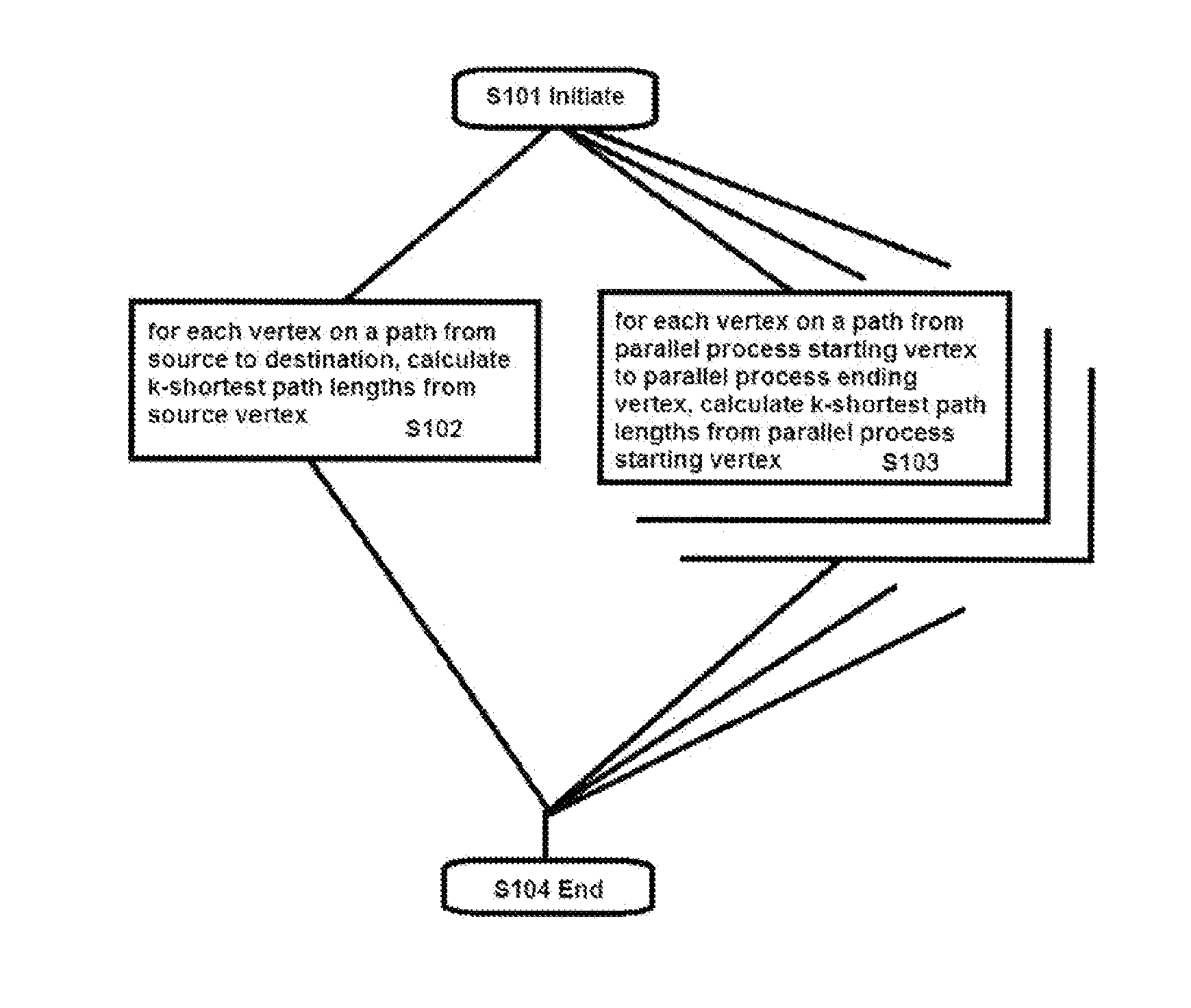
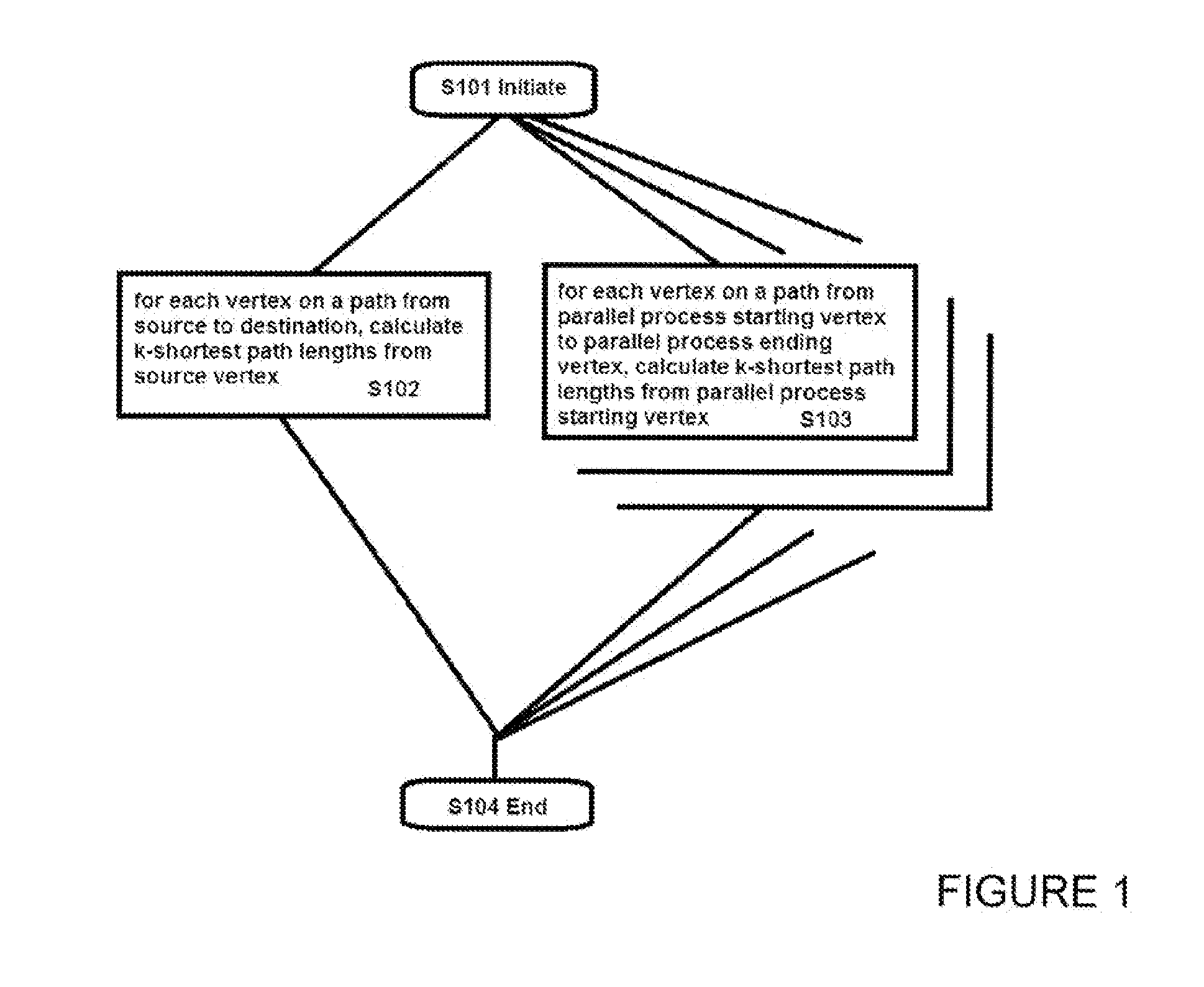
Computer-implemented k-shortest path finding method
InactiveUS20150256442A1Quick searchEasy to compareForecastingData switching by path configurationComputational scienceVertex point
A computer-implemented method includes a principal process including performing a computational procedure in which the or each vertex preceding a particular vertex receives a notification that a computational procedure has been completed for the preceding vertex; and calculates new path lengths for the particular vertex by adding the length value attributed to the edge from the preceding vertex to the particular vertex to each of the recorded k shortest path lengths from the first vertex to the preceding vertex. A record of the k shortest path lengths calculated for the particular vertex is maintained. After the new path lengths have been calculated for the or each of the preceding vertices, a notification that the computational procedure has been completed for the particular vertex is issued. The computational procedure is performed with the source vertex as the first vertex and each vertex on a path from the source vertex to the destination vertex as the particular vertex.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Reflective laser differential confocal curvature radius measuring method and device
ActiveCN105758336ARealize high-precision measurementShorten the lengthUsing optical meansVertex pointOptical measurements
The invention belongs to the technical field of precise optical measurement, and relates to a reflective laser differential confocal curvature radius measuring method and device.The method comprises the steps that by utilizing the characteristic that a laser differential confocal light intensity response curve zero crossing point precisely corresponds to a system focal point, focusing measurement is performed on the focal point of an objective lens and the vertex point of the back surface of the objective lens by moving a measured mirror to obtain a position difference value L1 of the measured mirror, then focusing measurement is performed on the focal point of the objective lens and the vertex point of the back surface of the objective lens by moving a reflecting mirror to obtain the position difference value L2 of the reflecting mirror, a curvature radius value of the measured mirror is solved through the measured position difference value L1 of the measured mirror and the measured position difference value L2 of the reflecting mirror, and high-precision measurement on the curvature radius is achieved.Compared with an existing measurement method, not only can curvature radius measurement on a concave mirror be achieved through the method, but also the method can be applied to curvature radius measurement on a convex mirror, and the method has the advantages of being high in measurement precision, short in measurement optical path, high in environment interference resisting capacity and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
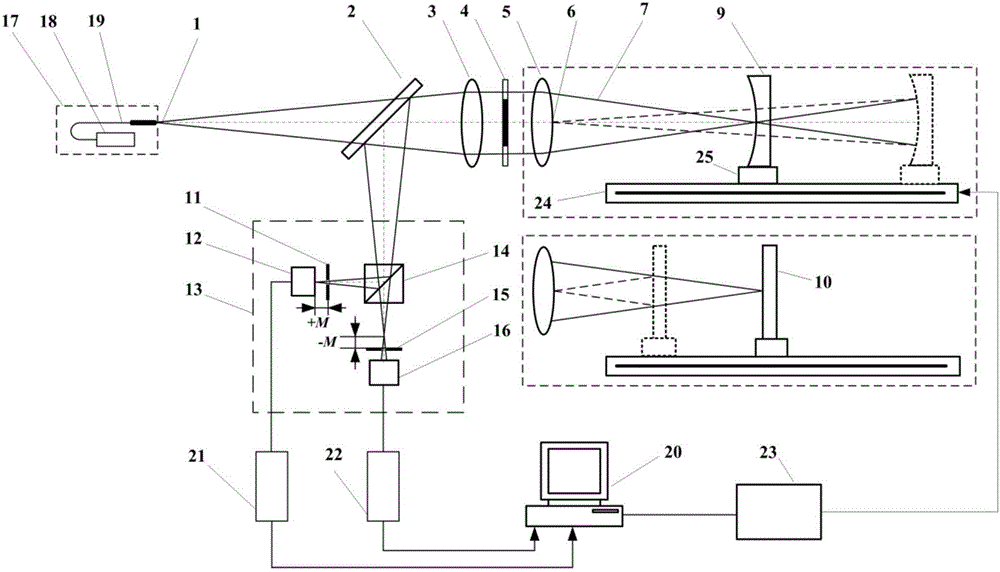
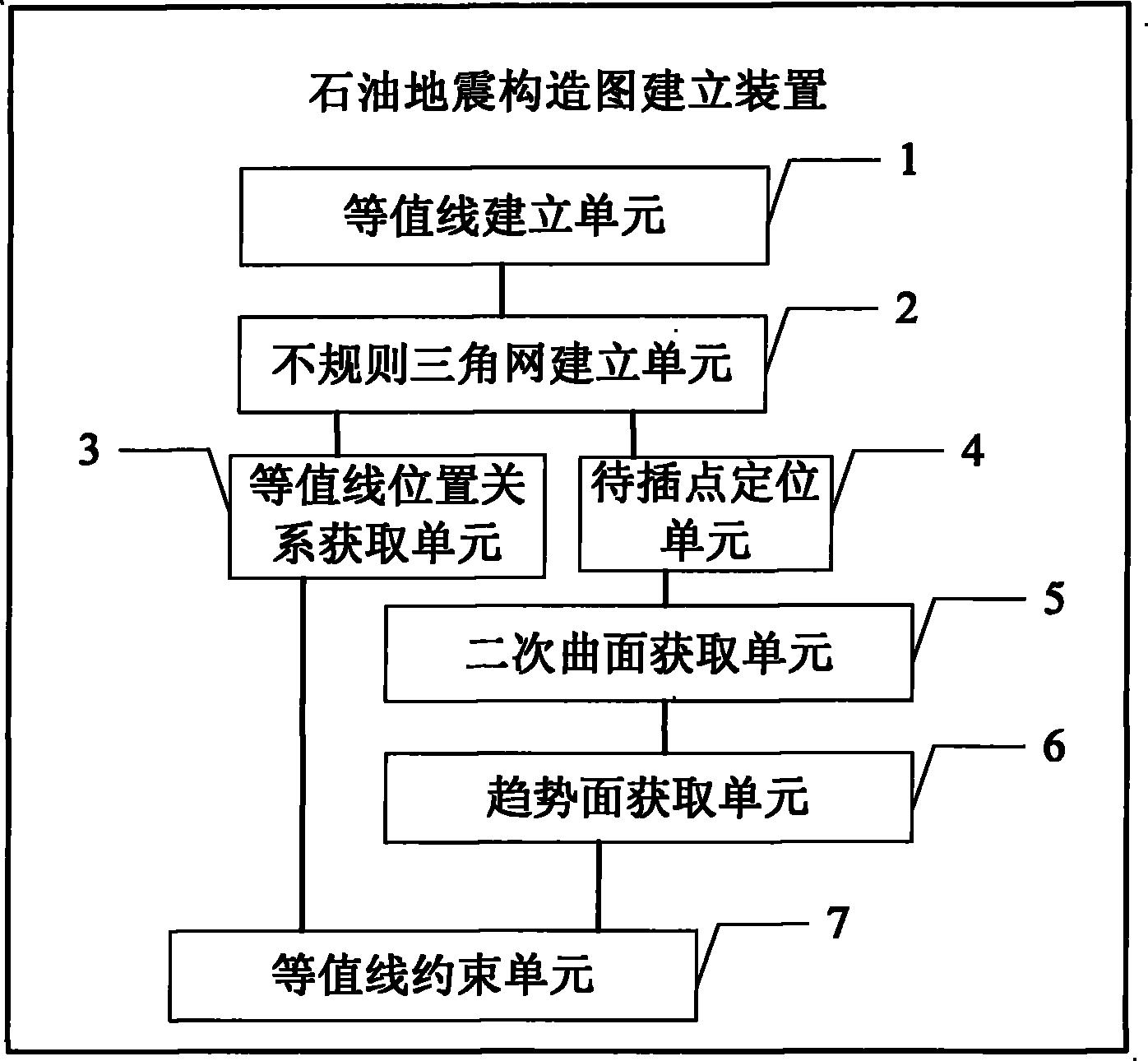
Creating device of petroleum seismic structural map
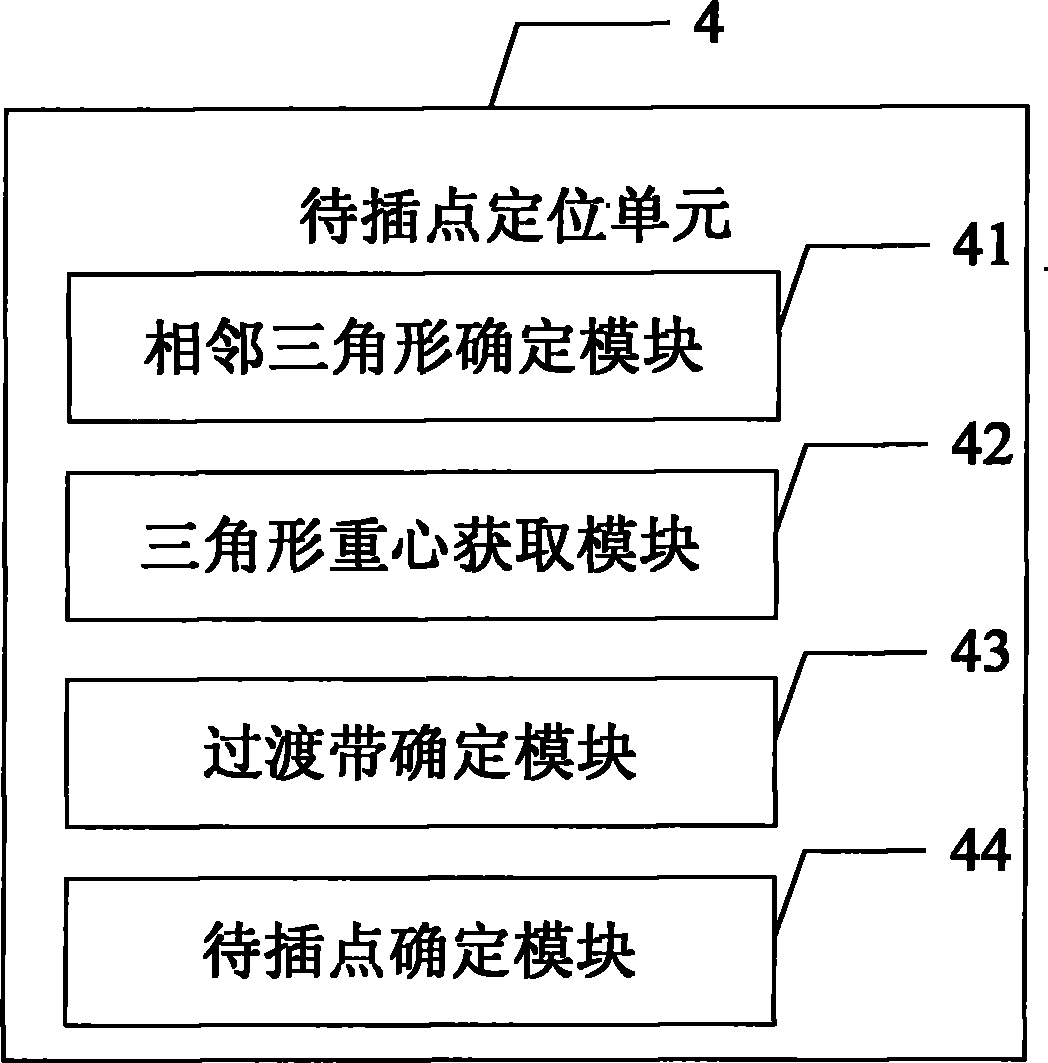
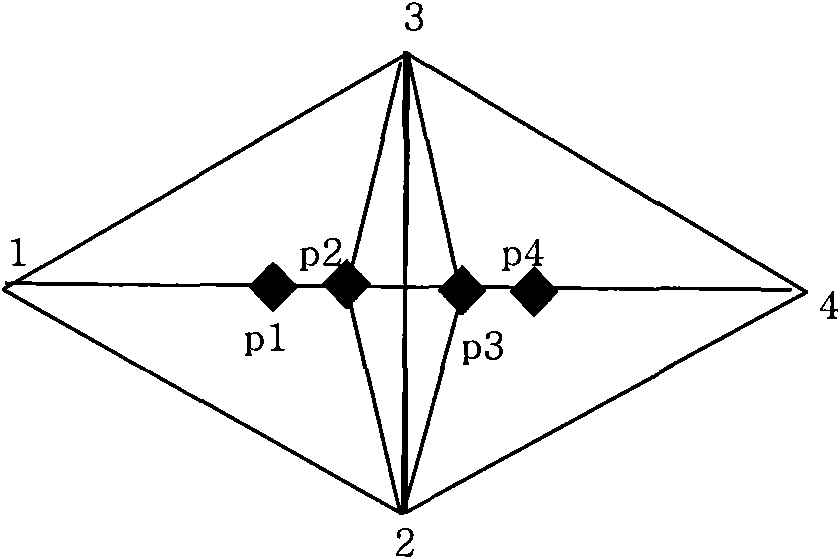
ActiveCN101866015ASolve the problem of intersectionReduce mistakesSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingVertex pointTriangulated irregular network
The invention provides a creating device of a petroleum seismic structural map. The device creates isolines of the petroleum seismic structural map according to the profile data of seismic information, a triangulated irregular network is established according to the discrete data of the isolines, the position relation between adjacent isolines of the isolines is acquired and a point to be inserted is positioned in a triangle of the triangulated irregular network according to the topological structure of the triangulated irregular network; any two of three peaks beside the common point of three adjacent triangles of the triangle in which the point to be inserted is positioned are selected to be combined with the common point, and a quadric surface passing by the common point is acquired by the following formula: f (x, y) = a + bx + cy + dx2 + ey2, wherein a, b, c, d and e are natural numbers, and (x, y) is the coordinate of the common point; then accumulation average operation is carried out on the plurality of acquired quadric surfaces so as to obtain a quadric surface trend surface passing by the common point; and then the change of the area between adjacent isolines is restrained according to the quadric surface trend surface and the empty circumcircle property and the maximum and minimum angle properties of the triangulated irregular network.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Canopy for a stationary covering device having an asymmetrical shape
A canopy for a stationary covering device in accordance with the present invention comprises a cover that has a vertex point. The vertex point can be characterized by a fixed uppermost point or tip, at the highest culminating point of the canopy from which the cover projects. According to the invention, the cover includes unequal extensions from the vertex point. As such, the vertex point comprises an asymmetrically positioned vertex point. More specifically, the canopy of the invention is rotatable around a fixed longitudinal axis that is elevated from the ground. In this way, the canopy provides an adjustable coverage zone for a pre-determined stationary area beneath it when it is either rotated or tilted, and located at a suitable elevated level relative to the ground, from a first canopy position to a second canopy position.
Owner:DFIRO DESIGN
Determining the position of a mobile device in a geographical area
ActiveUS20170074665A1High positioning accuracyLess energyInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsGraphicsVertex point
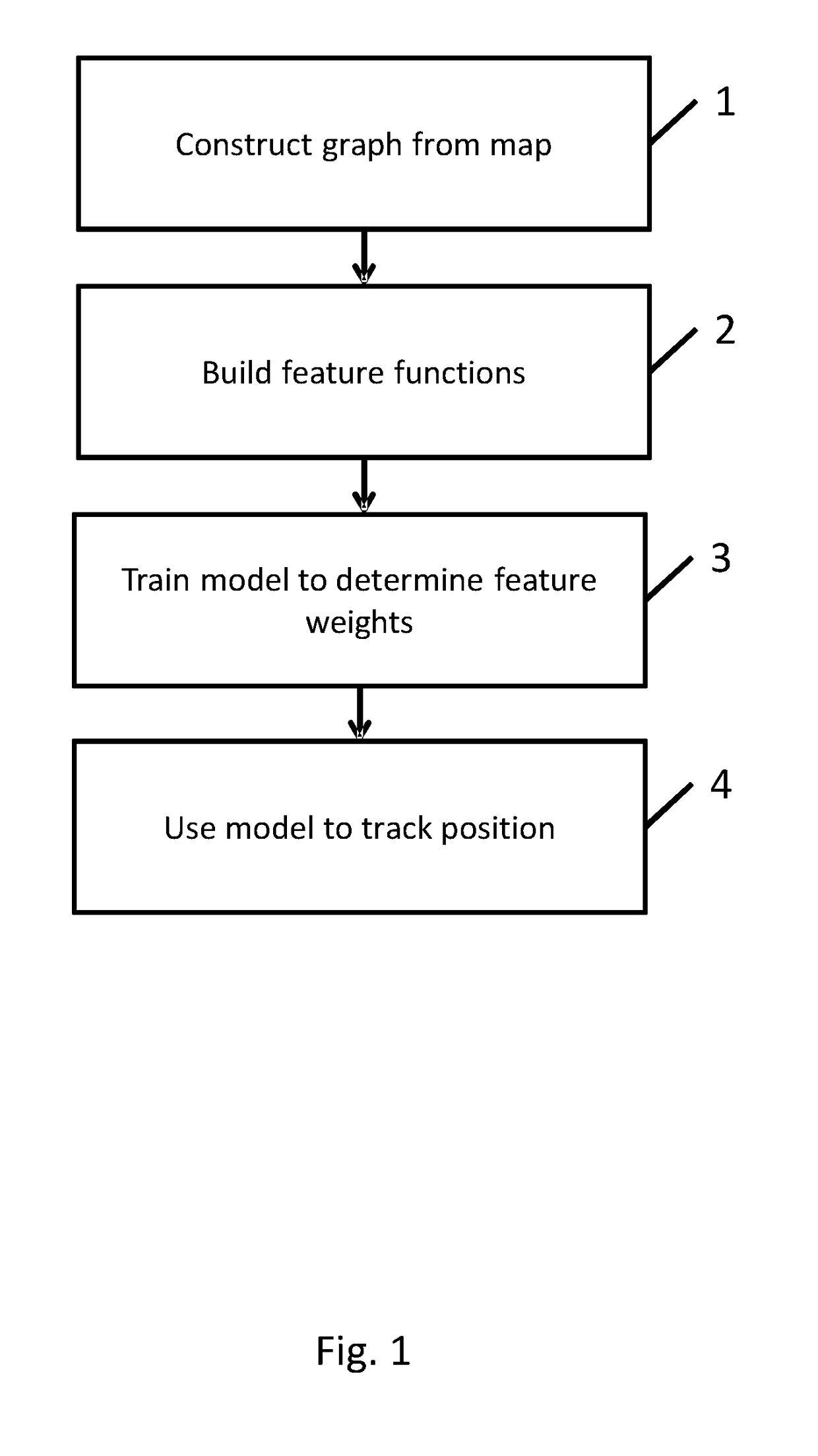
A method of determining the position of a mobile device using a model. The model comprises a graph comprising a set of vertices and a set of edges between the vertices, and one or more feature functions that take as input one or more vertices of the graph and a set of observations for the device, and return a feature value. The model is constructed by obtaining a map of the geographical area, constructing the graph using the map, wherein the vertices of the graph correspond to areas of the map, and two vertices are joined by an edge when the areas corresponding to the vertices are adjacent and can be travelled between by a device, and building the one or more feature functions using the graph, wherein the feature value of the one or more feature functions indicates the extent to which the observations support the device being positioned in the areas corresponding to the one or more vertices of the graph. The method then comprises the steps of: obtaining a set of observations from the sensors of the device; determining the trajectory for the device that optimises the values given by the feature functions given for the set of observations; and determining the position of the device to be the end point of the trajectory.
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
Method for developing an x-ray diffraction imaging system
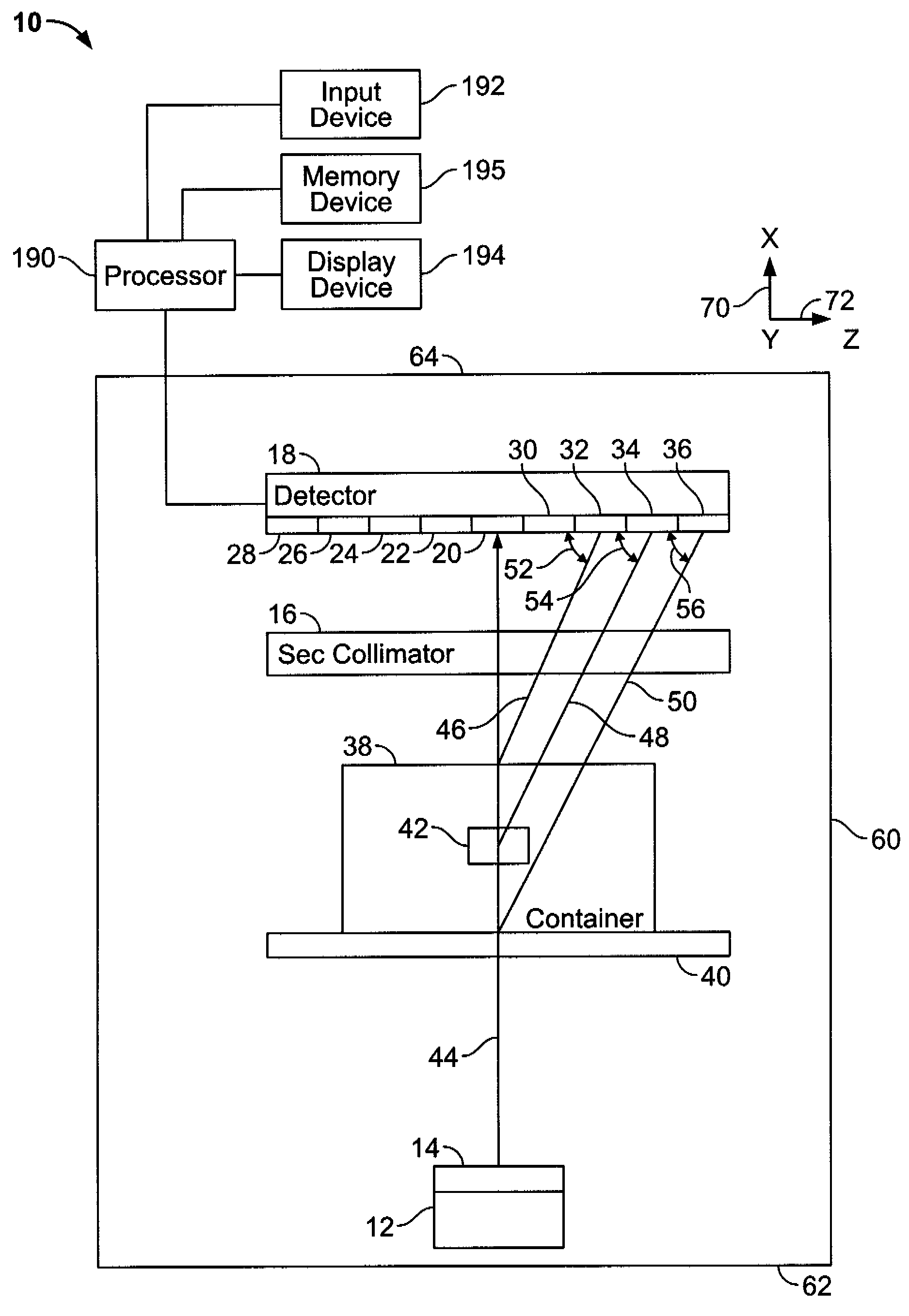
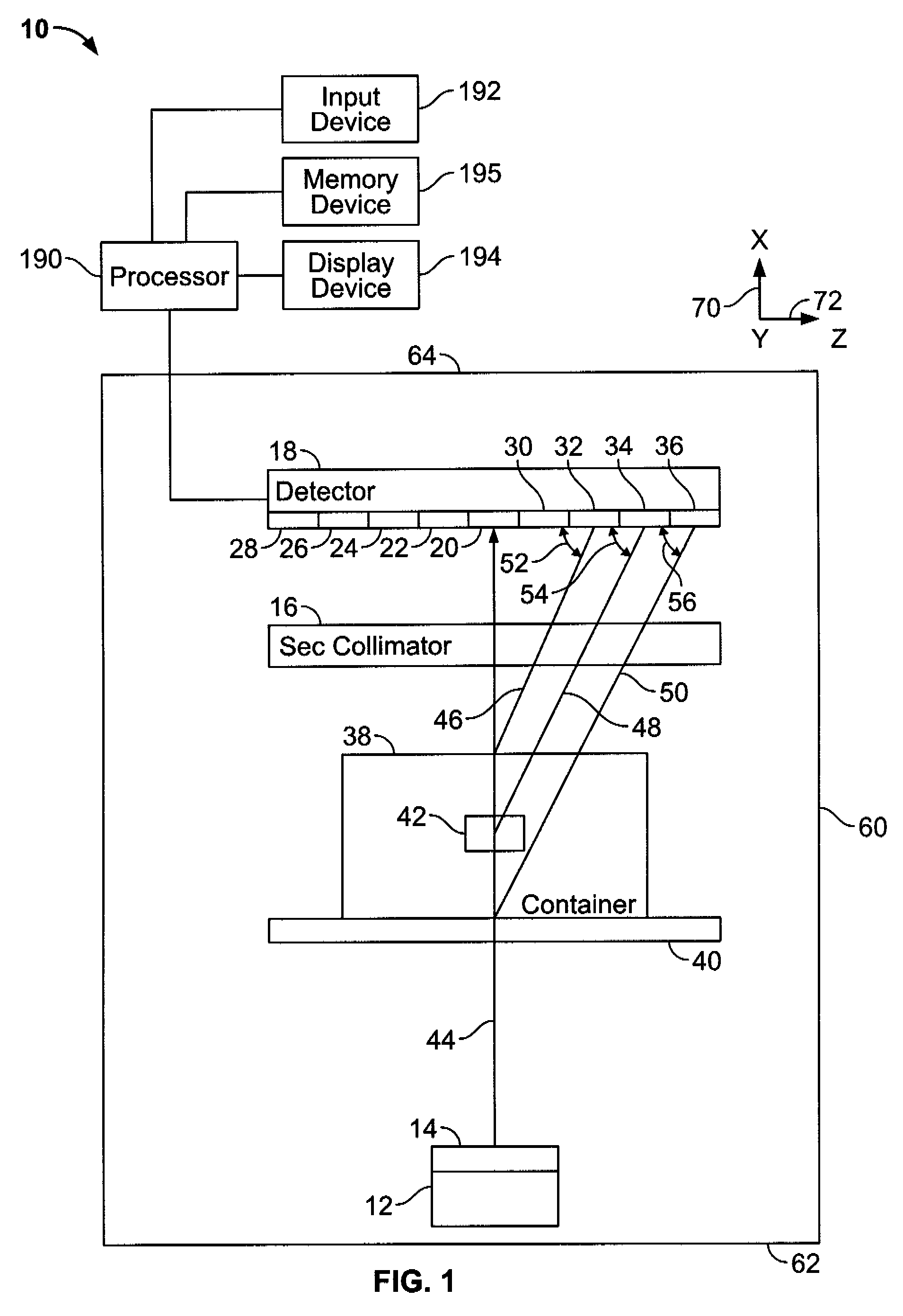
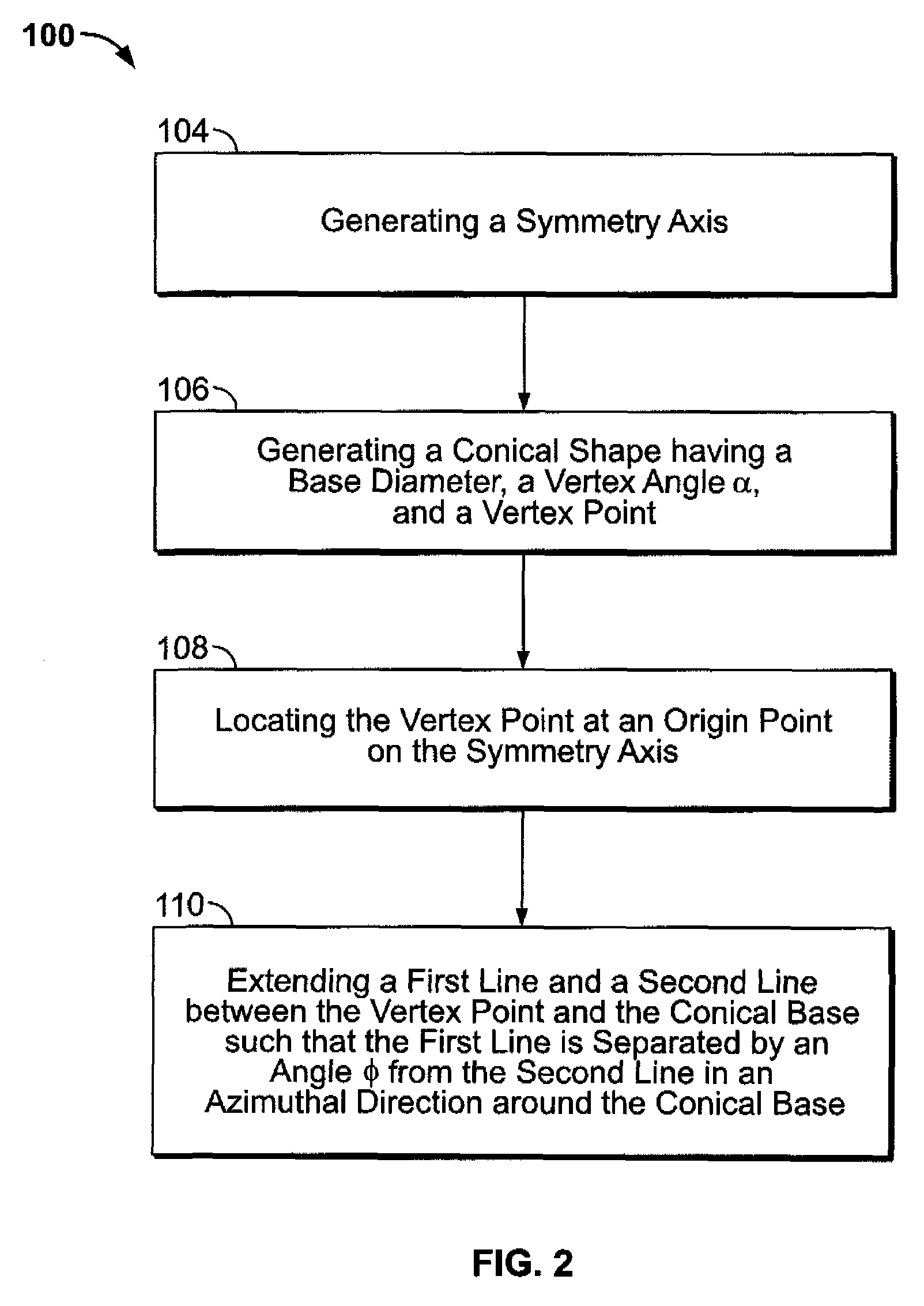
A method for developing a virtual representation of an x-ray diffraction imaging system includes generating a symmetry axis, generating a conical shape having a base diameter, a vertex angle α, and a vertex point, locating the vertex point at an origin point on the symmetry axis, and extending a first line and a second line between the vertex point and the conical base such that the first line is separated an angle dφ from the second line in an azimuthal direction around the conical base.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
Method for solving mirror surface parameter of conical mirror surface refraction and reflection camera by utilizing straight line
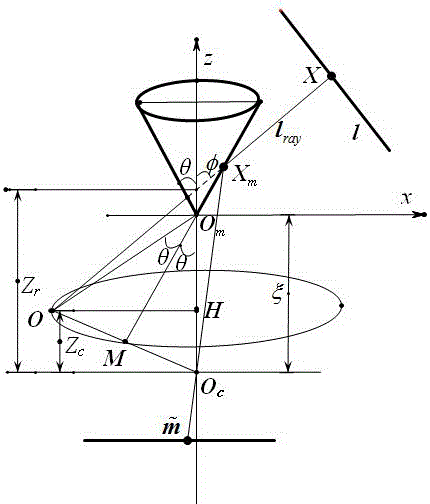
InactiveCN106780621APhysical scale is not requiredSimplify calculation difficultyImage analysisVertex pointPlücker coordinates
The invention relates to a method for solving a mirror surface parameter of a conical mirror surface refraction and reflection camera by utilizing a straight line. The method comprises the steps of firstly, extracting pixel coordinates of image points from an image by utilizing a function in Matlab; secondly, calculating a coefficient and a cone apex angle 2 theta of a line image according to the pixel coordinates of the image points, wherein theta is an included angle between any generatrix of a conical mirror surface and a rotational symmetric axis of the conical mirror surface; and finally, calculating Plucker coordinates of the spatial straight line and a distance from a vertex of the conical mirror surface to an optical center of the camera, namely, the mirror surface parameter xi. The method does not have a requirement on the physical size of the spatial straight line, so that coordinates of the spatial straight line in a world coordinate system do not need to be known.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Fan impeller and fan adopting same
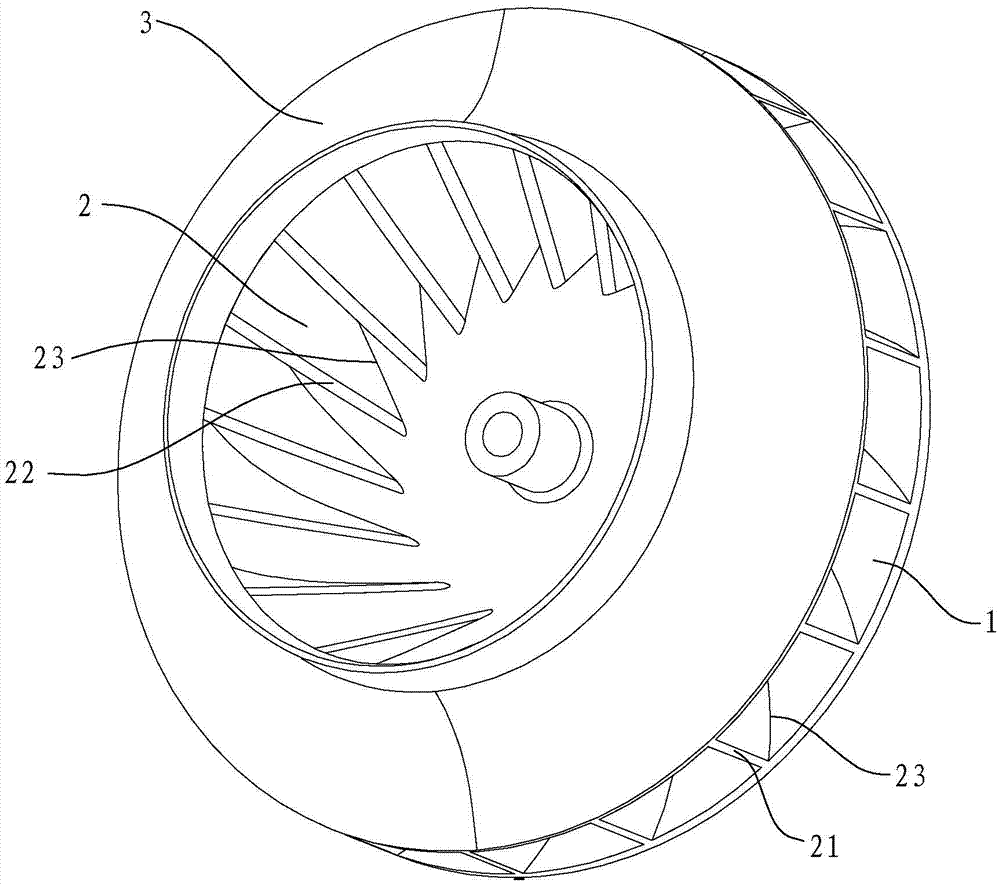
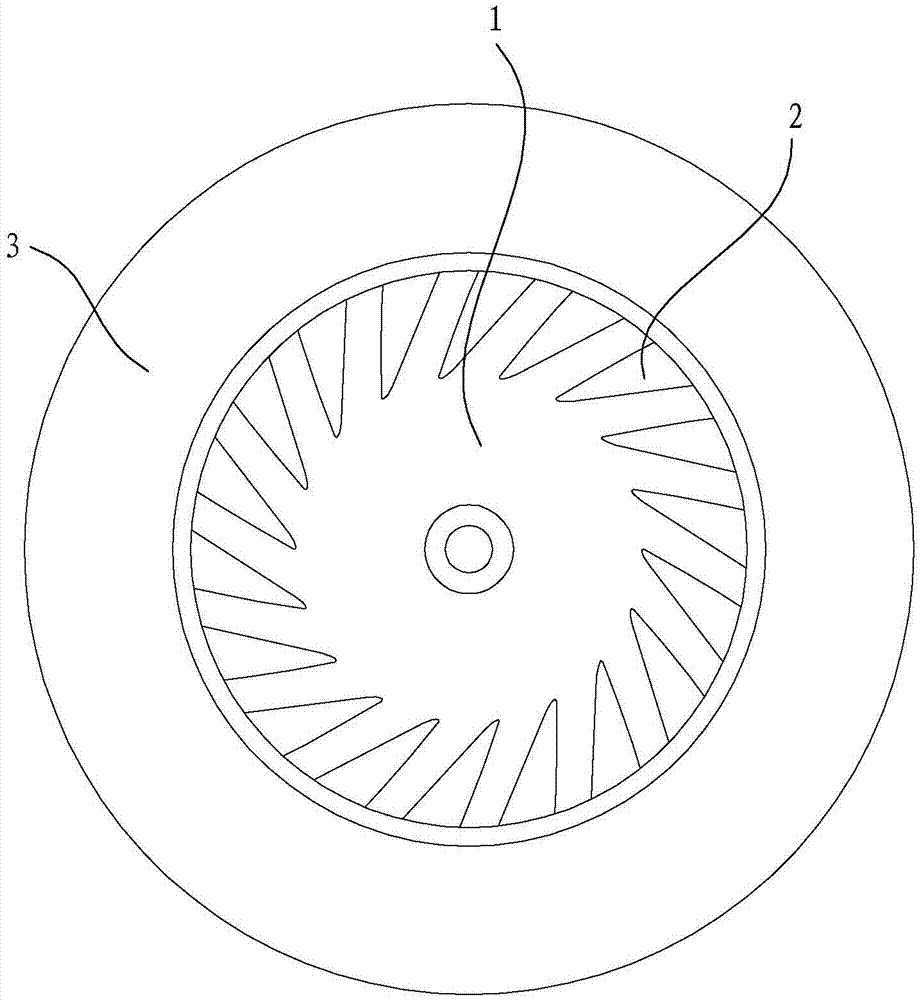
ActiveCN107023509ANovel structureCompact structurePump componentsPump installationsImpellerVertex point
The invention discloses a fan impeller. The fan impeller comprises a rear impeller disc and blades, the bottoms of the blades are installed on the disc surface of the rear impeller disc, and the blades are sequentially arranged in the circumferential direction of the rear impeller disc; the outer side edge of each blade serves as an air outlet edge, wherein an included angle alpha formed between the projection of the outer side edge on the outer circumference face of the rear impeller disc and the normal line of the rear impeller disc is larger than or equal to minus 60 degrees and smaller than or equal to 60 degrees; the inner side edge of each blade serves as an air inlet edge, wherein an included angle beta formed between the projection of the inner side edge on the outer circumference face of the rear impeller disc and the normal line of the rear impeller disc is larger than or equal to 20 degrees and smaller than or equal to 70 degrees; an included angle theta formed between a connecting line between the bottom end of each outer side edge and the circle center of the rear impeller disc and a connecting line between the bottom end of each inner side edge and the circle center of the rear impeller disc is larger than or equal to 10 degrees and smaller than or equal to 65 degrees, and the vertical height h1 of the vertex point of each outer side edge relative to the rear impeller disc is smaller than the vertical height h2 of the vertex point of each inner side edge relative to the rear impeller disc. The invention further discloses a fan adopting the fan impeller. The fan impeller has the advantages of being novel in structure and good in pneumatic performance; the fan adopting the impeller has the advantages of being compact in structure, high in fan efficiency and air pressure and large in generated negative pressure gradient.
Owner:NINGBO FOTILE KITCHEN WARE CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com