Method for solving mirror surface parameter of conical mirror surface refraction and reflection camera by utilizing straight line
A camera and straight line technology, applied in the field of computer vision, can solve the problems of combining conical and mirror viewpoints for analysis and discussion, and no method for finding the distance between the mirror vertex and the optical center of the camera is provided, so as to simplify the calculation difficulty.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
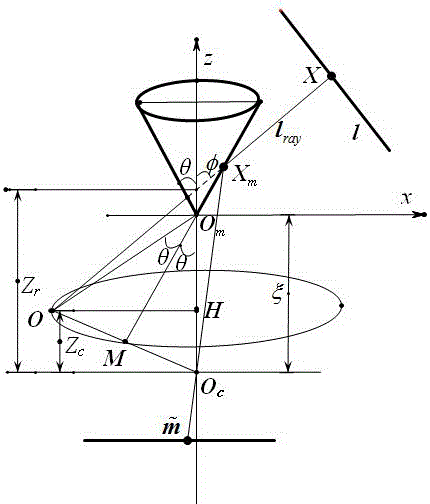
[0072] The present invention proposes a method that utilizes space straight lines A method for solving the mirror parameters of a cone-mirror catadioptric camera for a target. The schematic diagram of the target structure used in the present invention is as follows figure 1 shown. The embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail below with an example.
[0073] A cone-mirror catadioptric camera based on a straight line in space calculates mirror parameters using a straight line in space ,Such as figure 1 shown. Utilize the method in the present invention to solve the conical mirror surface parameter for the conical mirror surface catadioptric camera used for experiment, concrete steps are as follows:
[0074] 1. Extract the image points on the line image
[0075] In the present invention, the internal parameters of the known camera are . Use a conical mirror catadioptric camera to take an image containing a straight line in space, read the image, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com